Patents
Literature
126results about How to "Suitable for welding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Flux-cored wire for stainless steel welding
ActiveCN103521951ASuitable for weldingWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaManganeseRare earth
The invention relates to a flux-cored wire for stainless steel welding, and particularly discloses the flux-cored wire for stainless steel welding. The flux-cored wire is composed of flux-cored powder and a stainless steel belt, wherein the flux-cored powder is wrapped by the stainless steel belt. The flux-cored wire for stainless steel welding is characterized in that the flux-cored powder accounts for15-25% of the total weight of the flux-cored wire, the flux-cored powder comprises, by weight, 30-38 parts of metal chromium powder, 6-15 parts of metal nickel powder, 3-10 parts of metal manganese powder, 20-35 parts of rutile, 1-6 parts of silicon iron, 1-7 parts of ferrotitanium, 2-10 parts of feldspar, 5-10 parts of quartz, 1-5 parts of rare earth fluoride, 1-5 parts of metal nitride powder and appropriate iron powder, and the total flux-cored powder is, by weight, 100 parts. A reduction jar of the flux-cored wire for welding is long in service cycle, and deposited metal formed by the flux-cored wire has the excellent effects of high temperature oxidation resistant capacity and high temperature sulphur corrosion resistant capacity.
Owner:BEIJING JINWEI WELDING MATERIAL +1
Electromagnetic inductive welding method of steel-plastic compound pipe
InactiveCN101852323AEasy to implementSuitable for weldingPipe connection arrangementsPipe fittingWater leak
The invention discloses an electromagnetic inductive welding method of a steel-plastic compound pipe, which belongs to a pipeline connecting method. The traditional methods can not realize welding of steel-plastic compound pipes of all specifications. In the method, firstly, the steel-plastic compound pipe is inserted into a connecting port of a pipe fitting; secondly, a steel pipe layer of the steel-plastic compound pipe in the inserting position is heated by an electromagnetic inductive heater to fuse plastics on both sides of the steel pipe layer; and finally, the plastics are cooled to realize welding of the steel-plastic compound pipe and the pipe fitting. Because the steel-plastic compound pipe is inserted into the connecting port of the pipe fitting at first, and then the inserting position is heated for welding, the method is easy. The structures of the pipe fitting and the pipe are not changed, and thus the pipe is easy to be manufactured. The method is suitable for welding of steel-plastic compound pipes of all specifications and the pipe fitting, and is easy to realize double-face seal. In case of water leak or water seepage caused by bad welding quality, the inserting part can be heated again for improvement.
Owner:中科华飞管业(东莞)有限公司
900MPa-level high-performance gas shielded welding wire
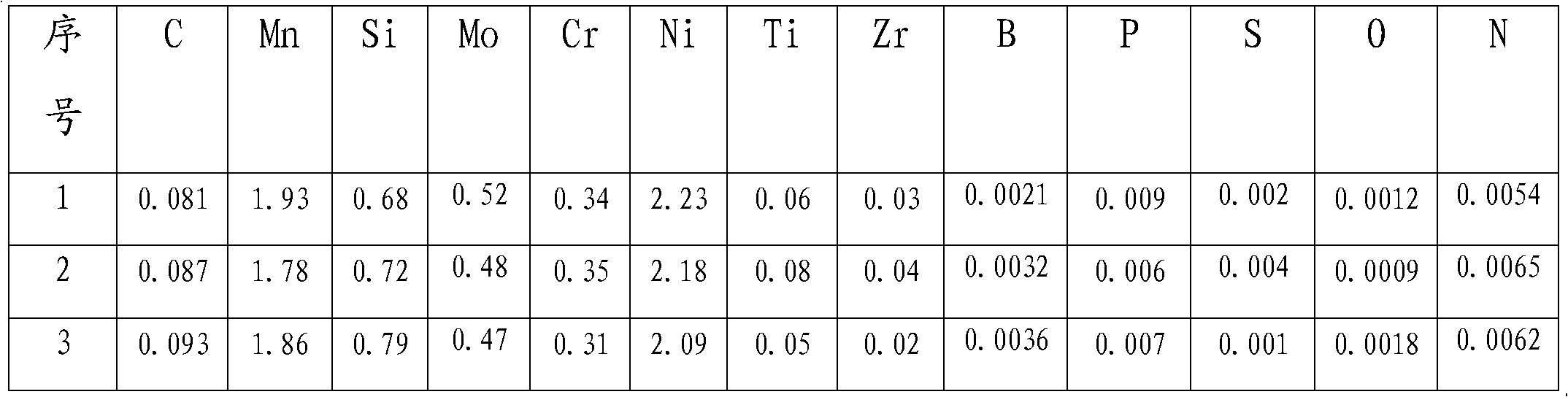
InactiveCN101987403AImprove crack resistanceImprove low temperature toughnessWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaCrack resistanceAlloy
The invention provides a 900MPa-level high-performance gas shielded welding wire, which is suitable for welding large-sized important structural members in the heavy load fields of engineering machinery, coal mine machinery, railroad bridges, automobile cranes, high pressure vessels and the like. The gas metal arc welding welding wire comprises the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 0.05 to 0.10 percent of C, 0.40 to 0.80 percent of Si, 1.60 to 2.00 percent of Mn, 2.0 to 2.6 percent of Ni, 0.3 to 0.7 percent of Mo, 0.20 to 0.60 percent of Cr, 0.02 to 0.08 percent of Ti, 0.002 to 0.006 percent of B, 0.02 to 0.08 percent of Zr, less than or equal to 0.010 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.010 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.003 percent of O, less than or equal to 0.007 percent of N, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The welding wire adopts Ar+20 percent CO2 gas shielded welding rich in argon, can be used for welding high-strength low ally steel of which the tensile strength Rm is more than or equal to 900MPa, and a weld metal has high obdurability and cracking resistance under a welding condition and a post-welding hardening and tempering condition.
Owner:SHENYANG AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY
Buried arc stud welding machine and operation method thereof
InactiveCN101138804ASuitable for weldingEffective protectionWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesSlagEngineering
This present invention discloses an arc stud welding machine, comprising a welding device, a controller, a welding power supply, a ground clamp connected to welded workpiece and a welding cable. The present invention is characterized in that the welding power supply is direct current supply of instant output maximum current with declined and static characteristics, which also comprises a welding fluid box and a conveying and recovery mechanism of welding fluid. The welding fluid conveying and recovery mechanism is provided with a conveying pipe and a recovery pipe of welding. The conveying pipe and the recovery pipe are respectively connected with the welding fluid box. The welding fluid box is installed in the welded device and positioned in the contacting point of a weldment and a welder. An operation method of a hidden arc stud welding machine is: the power supply is switched on, the welder is held on, and welding, cooling and slag clearing are practiced. The hidden arc stud welding machine has features of effective protection for a molten pool and a welding line, sufficient reflection for metallurgy, large penetration, and a high-strength welding line. The welder is inserted into the molten pool and the welding joint is firm. The high-ridged welding line enhances mechanical strength of the welding joint.
Owner:黄贤聪
High-strength high-toughness high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel welding wire and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108526750AIncrease contentImprove solid solubilityArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsManganeseAustenite
The invention relates to a high-strength high-toughness high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel welding wire and a preparation method thereof. The welding wire is prepared from the alloy components in percentage by weight: less than 0.1 percent of C, less than 0.02 percent of S, less than 0.03 percent of P, 0.1 to 0.9 percent of Si, 5 to 21 percent of Mn, 15 to 23 percent of Cr, 0 to 8 percent ofNi, 0 to 5 percent of Mo, 0.2 to 0.95 percent of N, the balance Fe, and less than 0.1 percent of other impurities. The preparation process comprises the steps of smelting through an induction furnace, electro slags remelting, hot forging, hot rolling, heat treating, and drawing of the welding wire. According to the welding wire provided by the invention, the component proportion is scientific andreasonable, the content of nitrogen elements is increased, the content of manganese elements is adjusted, and the solid solubility of the nitrogen is increased, so that the prepared welding wire is stable in welding process, less in escape amount of hydrogen elements, less in blowhole defects, good in welding processability, high in deposited metal strength, excellent in impact toughness at the temperature of minus 40 DEG C, suitable for welding high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel, particularly suitable for welding the austenitic stainless steel with the requirement on low-temperature impact toughness, and capable of being surfacing-welded so as to be used as anti-corrosion layers for other steel and iron materials.
Owner:CHINA WEAPON SCI ACADEMY NINGBO BRANCH
Automatic welding device
ActiveCN102489911AReduce adverse effectsImprove welding positioning accuracyWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesNumerical control systemThermal deformation
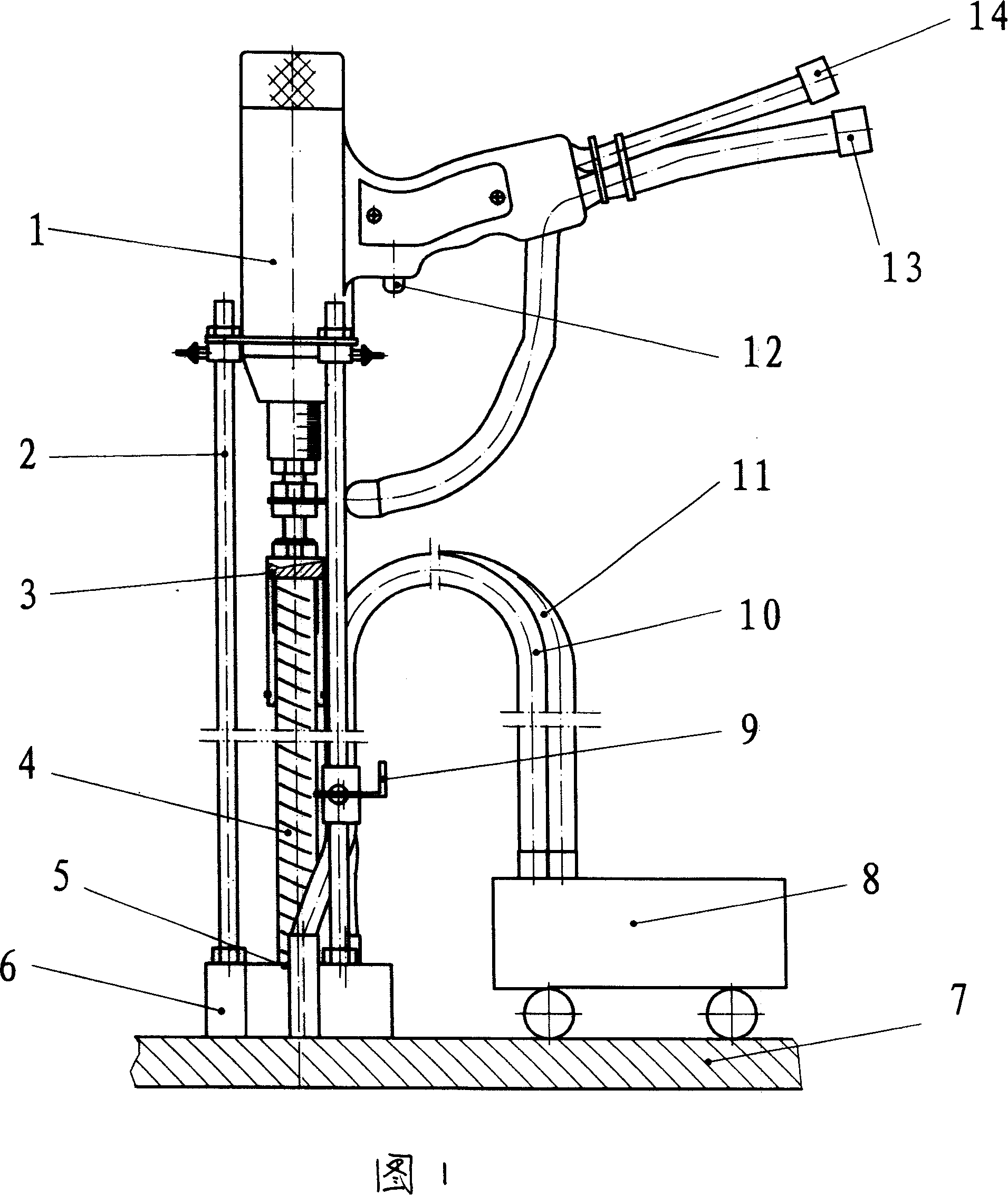
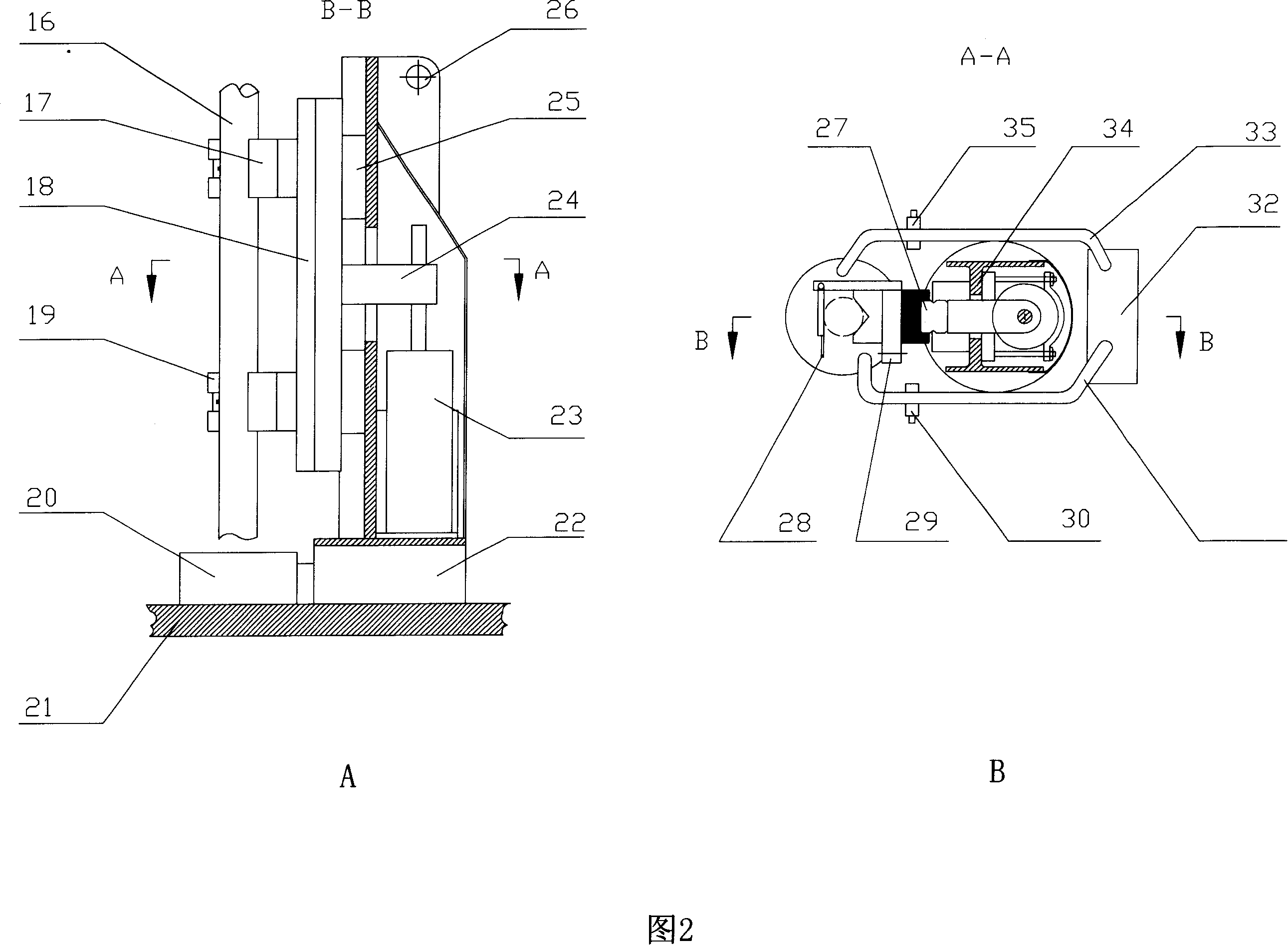
The invention discloses an automatic welding device, which belongs to the field of metal processing and comprises a frame, a displacement sensor, a traveling mechanism, a clamping mechanism, a position sensor, an adaptive tool, a welding mechanism and a numeral control system, wherein mechanisms, a main part and auxiliary parts are installed on the frame, one end of the main part is fixed on the frame, and the other end of the main part is arranged along the direction of welding thermal deformation and is in the free state. The adaptive tool comprises an elastic body and a deformation servo mechanism, wherein the elastic body is arranged along the direction of the main part, and the elastic deformation curve of the elastic body and an actual thermal deformation characteristic curve of the main part are consistent. The numeral control system is connected with each mechanism and controls the motions of the mechanisms. The automatic welding device can effectively overcome adverse influences of the thermal deformation on welding effects, improve welding position accuracy, get rid of manual operation, achieve automatic welding, improve production efficiency, reduce production cost and achieve low carbon and environmental protection.
Owner:张旭
Digitally-controlled multifunctional inverted arc welding machine
ActiveCN102922091AFast dynamic responseAccurate static performanceArc welding apparatusSignal conditioning circuitsControl system
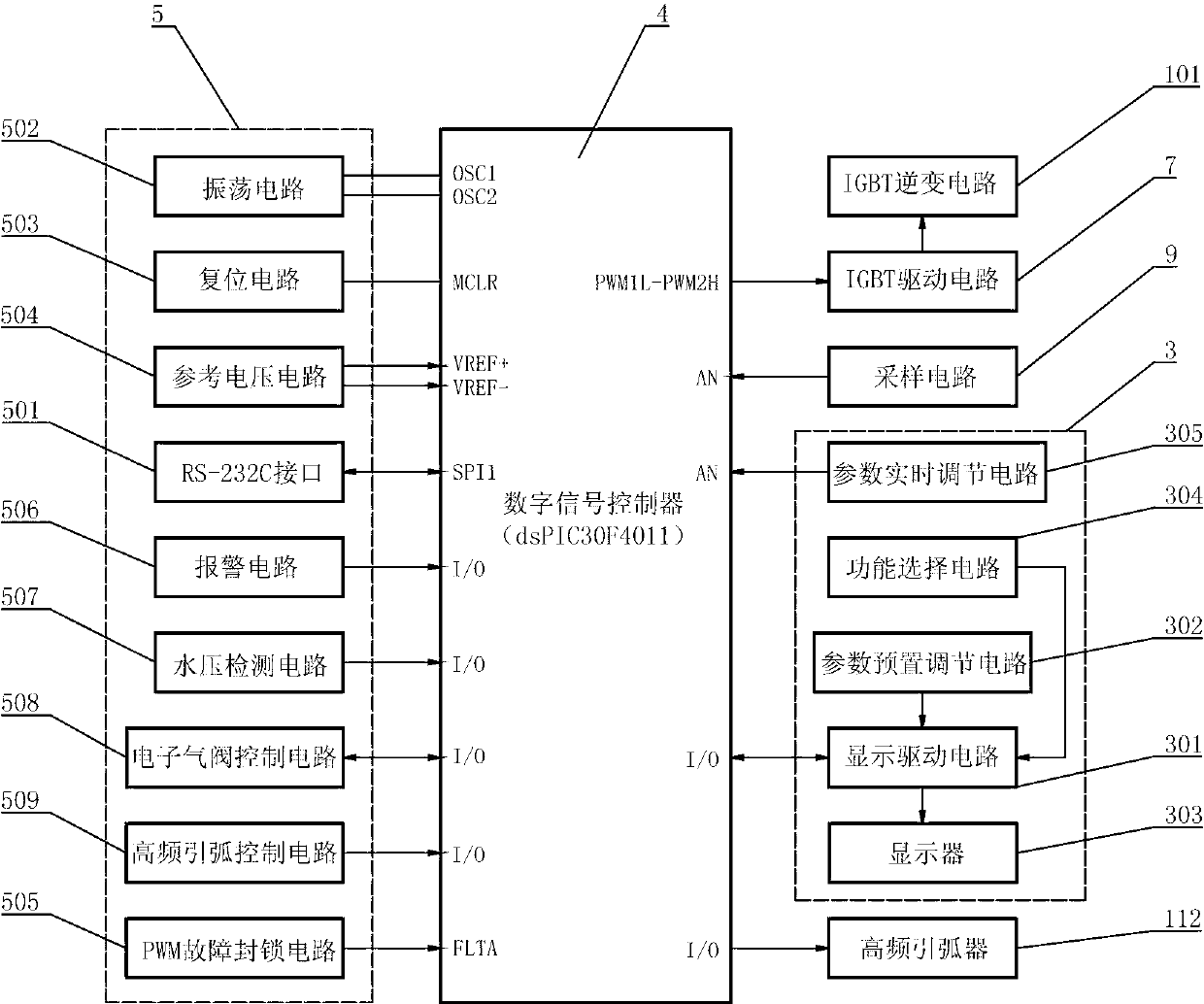
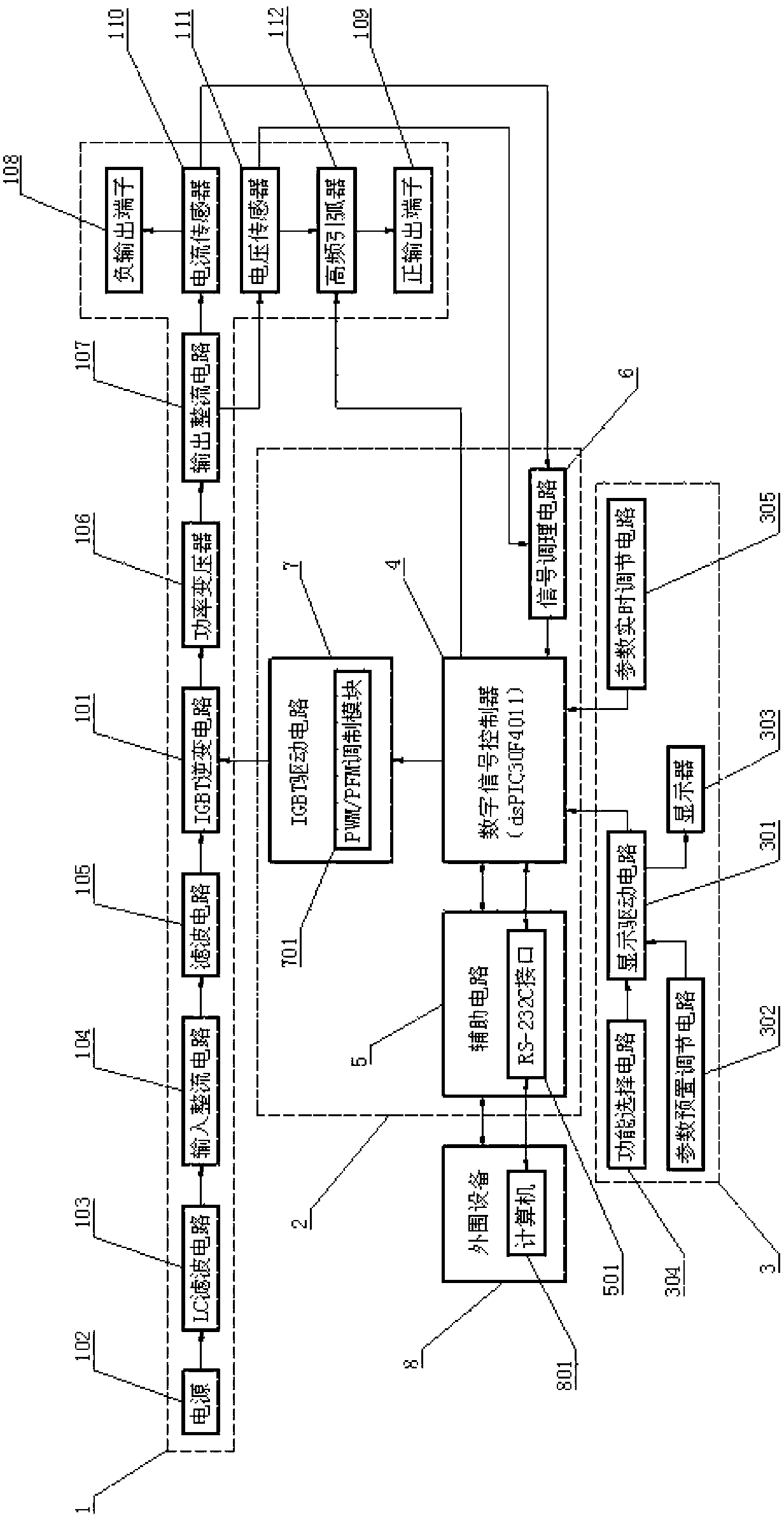
The invention relates to an inverted arc welding machine and particularly relates to a digitally-controlled multifunctional inverted arc welding machine which has high working efficiency and fast dynamic response. The digitally-controlled multifunctional inverted arc welding machine comprises a main circuit system (1) of an IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Translator) inverting circuit (101), a digital control system (2) and a man-machine switching system (3), wherein the digital control system (2) adopts a digital signal controller (4) as a core control unit and further comprises an auxiliary circuit (5) connected with the digital signal controller (4), a signal conditioning circuit (6) for processing collected data of the main circuit system (1), and an IGBT driving circuit (7) for carrying out driving control on the IGBT inverting circuit (101); the type of the digital signal controller (4) is dsPIC30F4011 and the digital signal controller (4) is connected with the IGBT inverting circuit (101) through the IGBT driving circuit (7); and the digital signal controller (4) is used for adjusting and controlling the main circuit system (1).
Owner:甘肃居立门业有限责任公司
Miniature drainage cover for local dry welding underwater robot of double-airflow structure
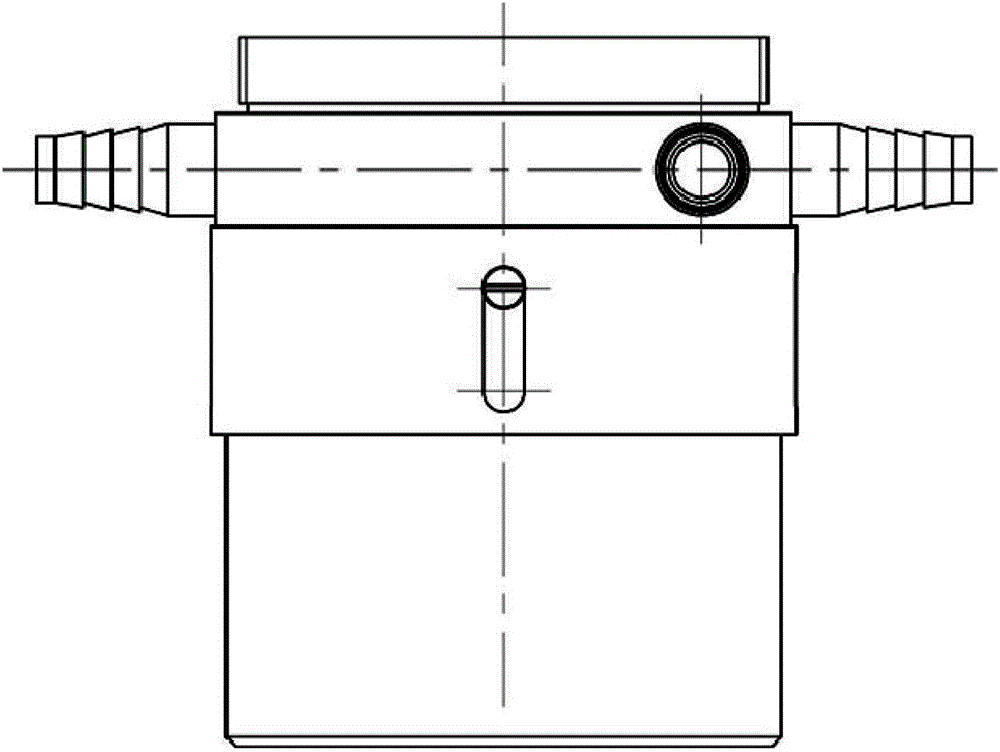
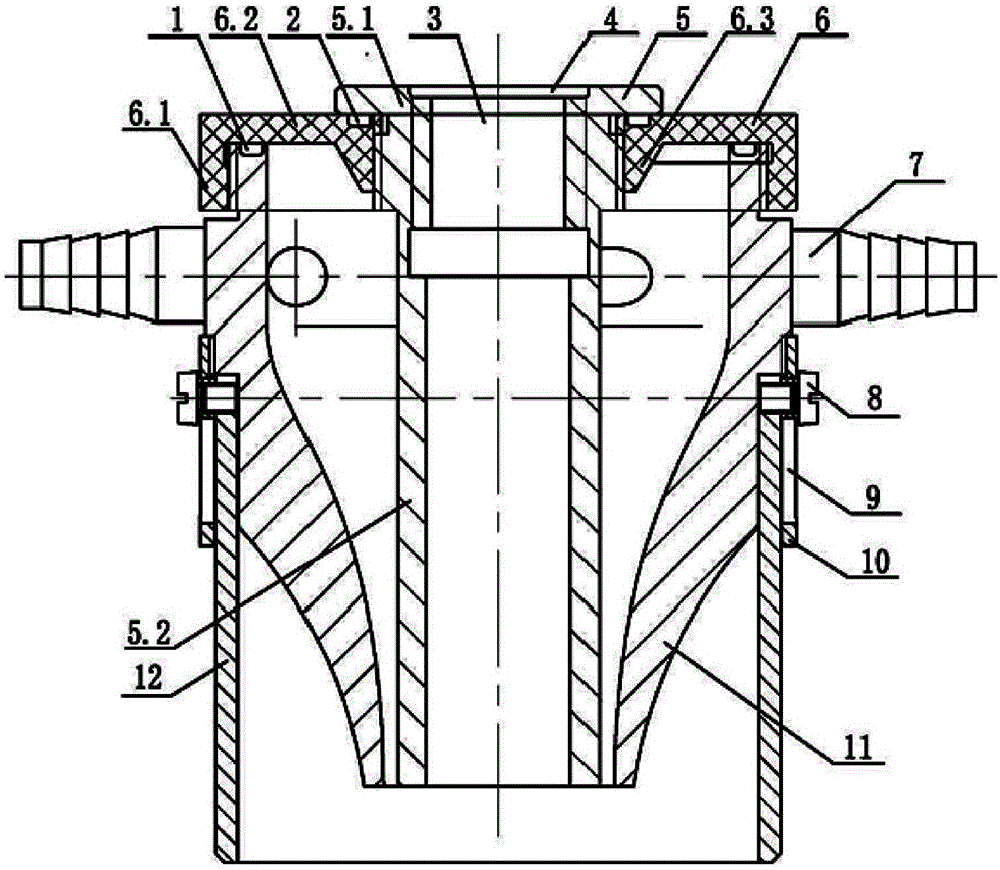
ActiveCN106624258AReasonable structureImprove drainage capacityGas flame welding apparatusSlagEngineering
The invention provides a miniature drainage cover for a local dry welding underwater robot of a double-airflow structure. The miniature drainage cover is characterized by comprising an inner air cover, an outer air cover and a water retaining sleeve, wherein the inner air cover, the outer air cover and the water retaining sleeve are arranged in sequence from inside to outside; a welding torch mounting hole which is used for arranging a welding torch is formed in the inner air cover; a convergent nozzle cavity is formed between the outer air cover and the inner air cover; a sealing cover covers the top of the convergent nozzle cavity; at least one air inlet pipe is connected with the outer air cover; a pipe cavity of the at least one air inlet pipe communicates with the convergent nozzle cavity so as to input compressed gas; the water retaining sleeve is connected with the outer air cover so as to form a slag discharge cavity; and the lower part of the welding torch mounting hole and the lower part of the convergent nozzle cavity respectively communicate with the slag discharge cavity. The drainage cover has the advantages of reasonable structure, small size and flexibility in use and has a good drainage effect and a preventive effect on a welding area, and the underwater welding quality can be increased.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
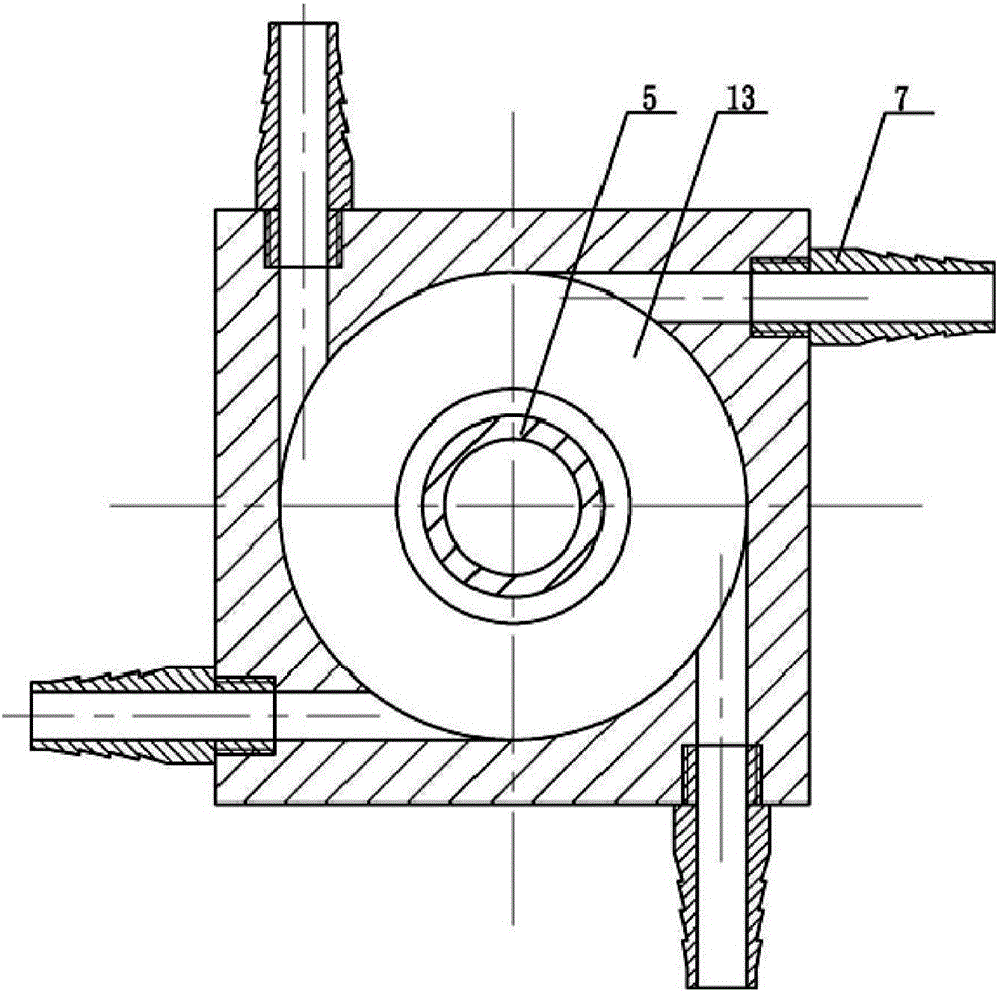
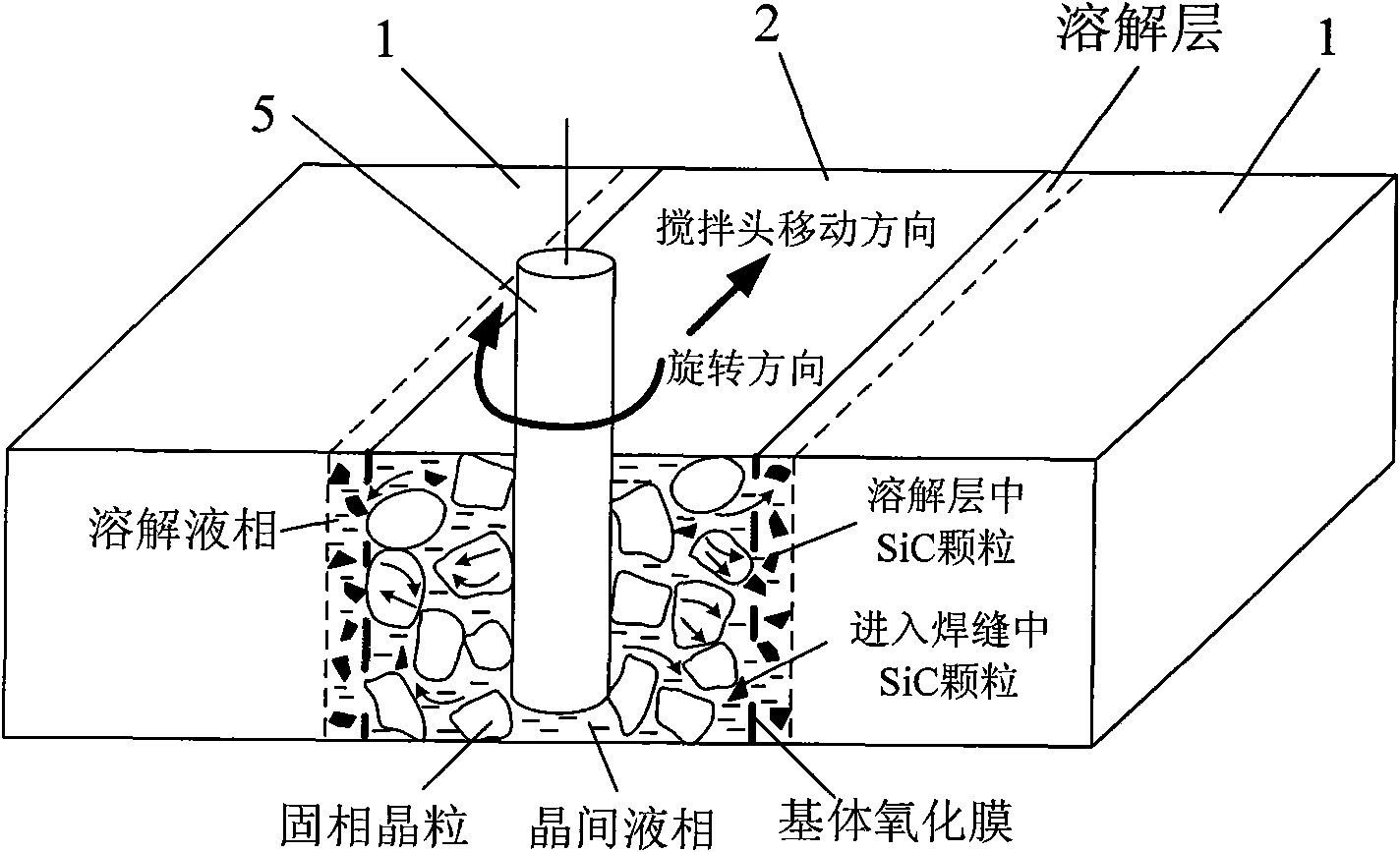
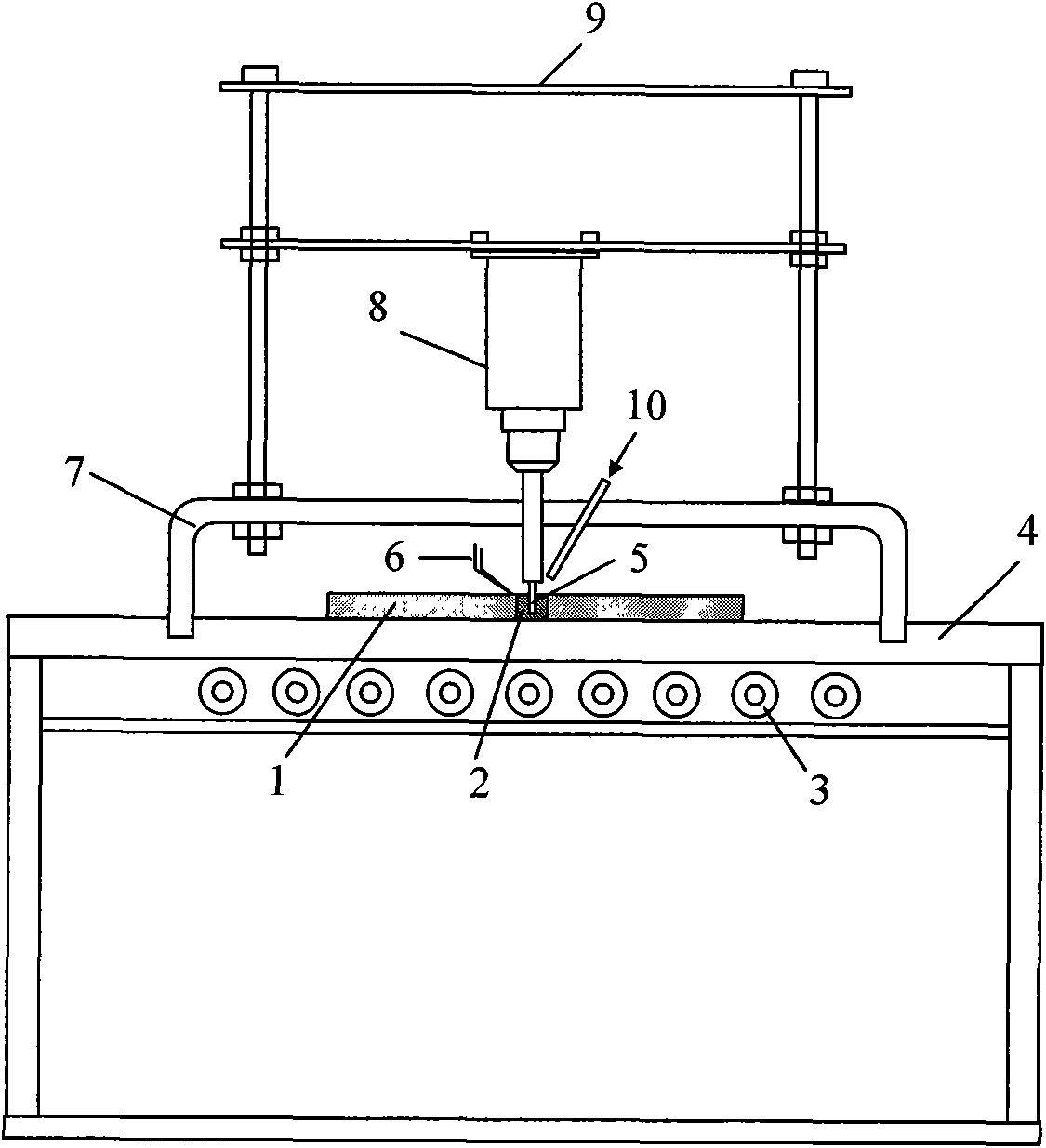
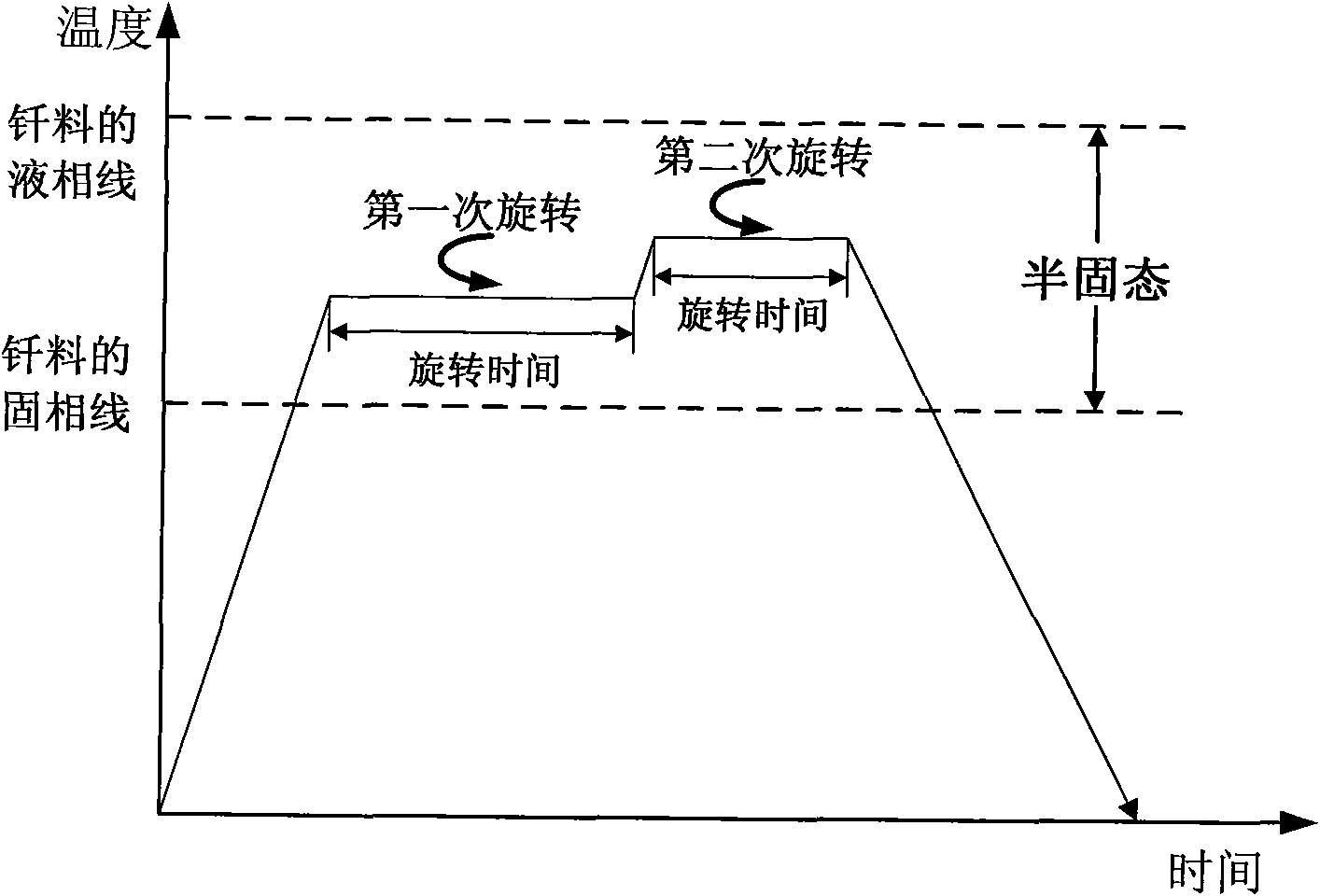
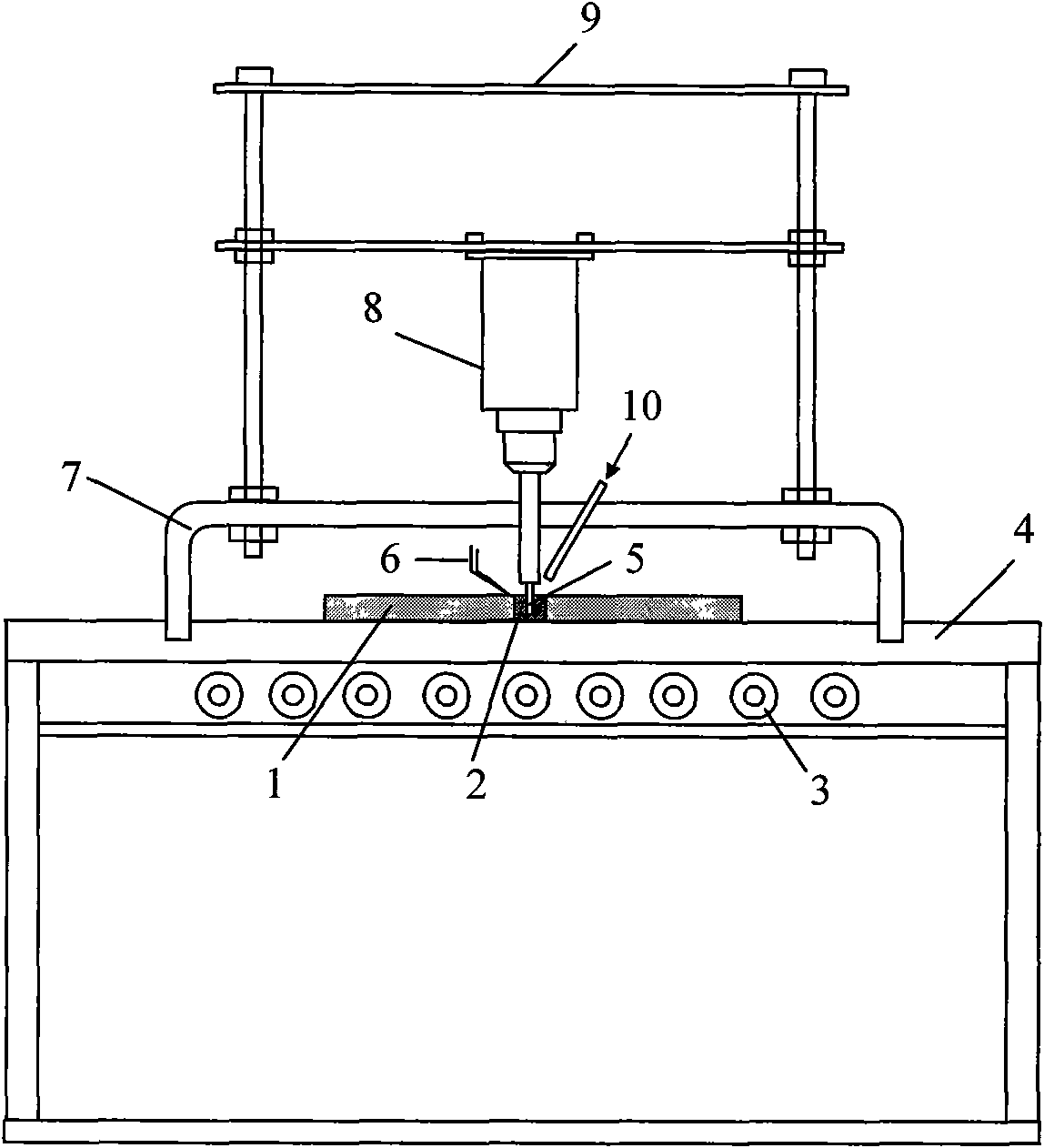
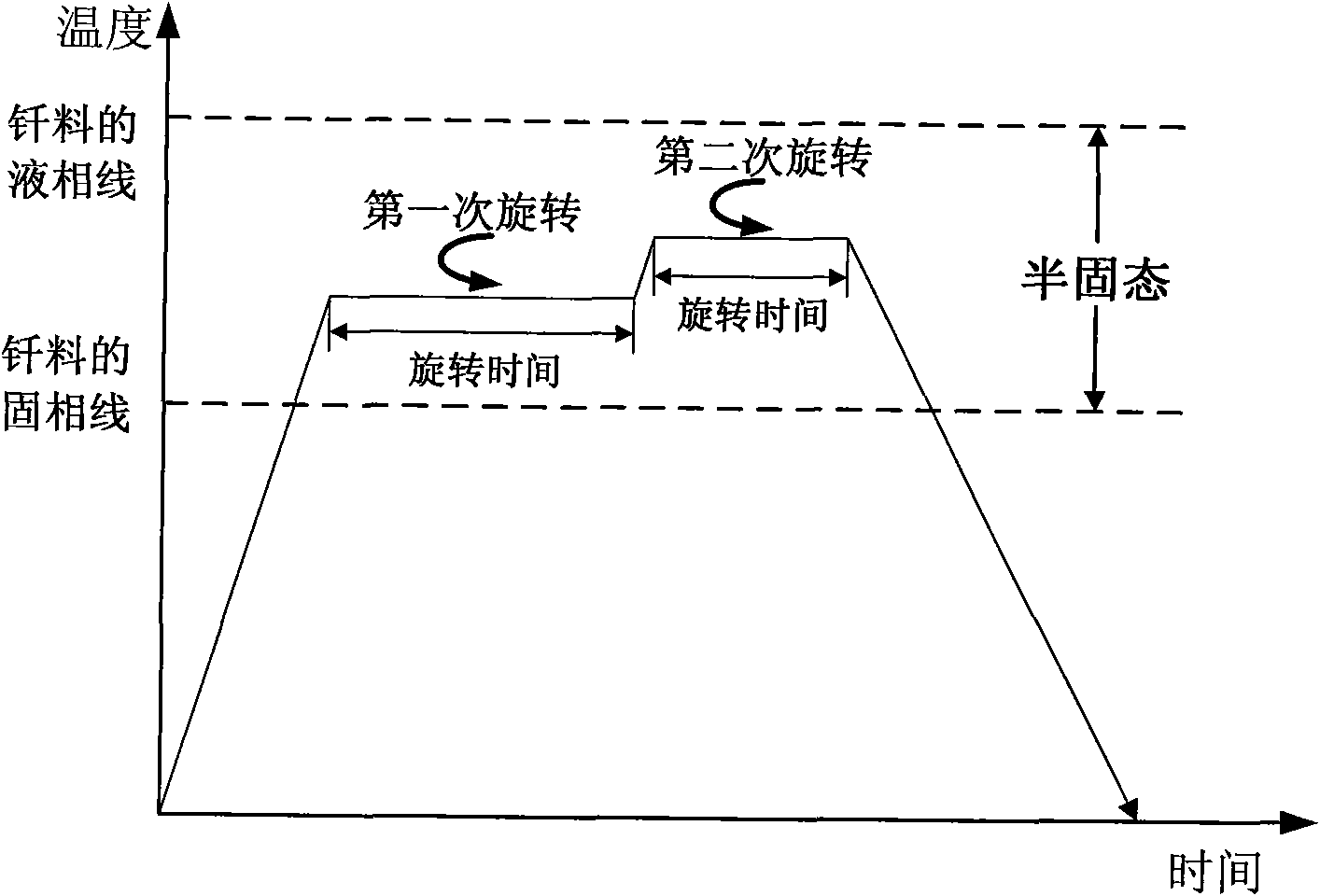
Non-vacuum semi-solid stirring brazing method for aluminum alloy and composite material thereof
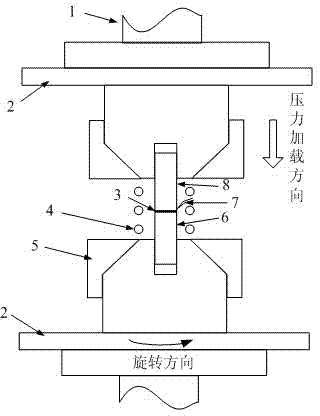
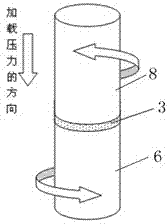
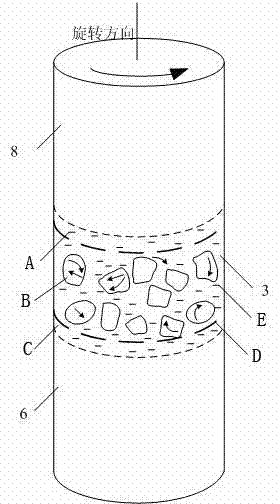
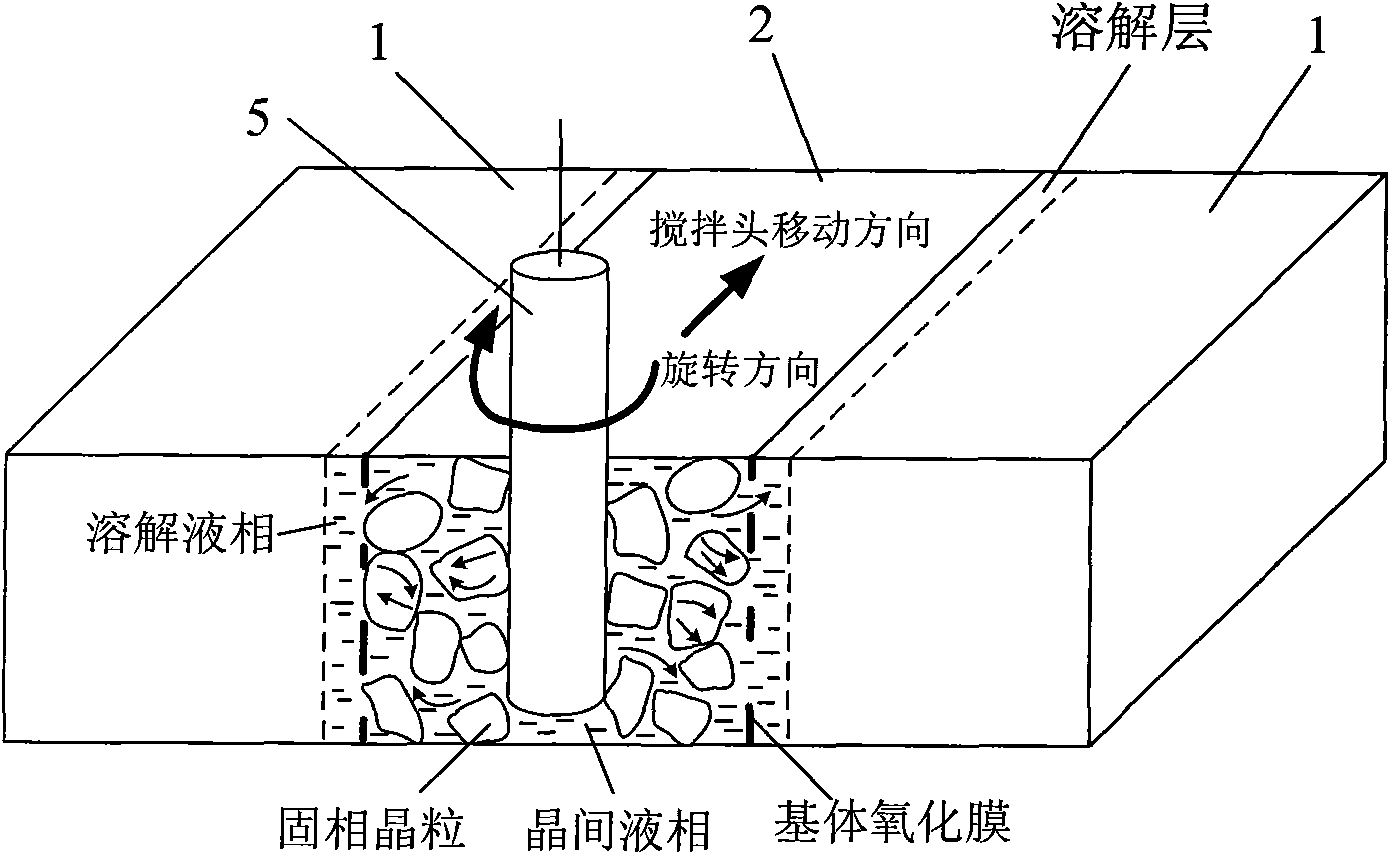
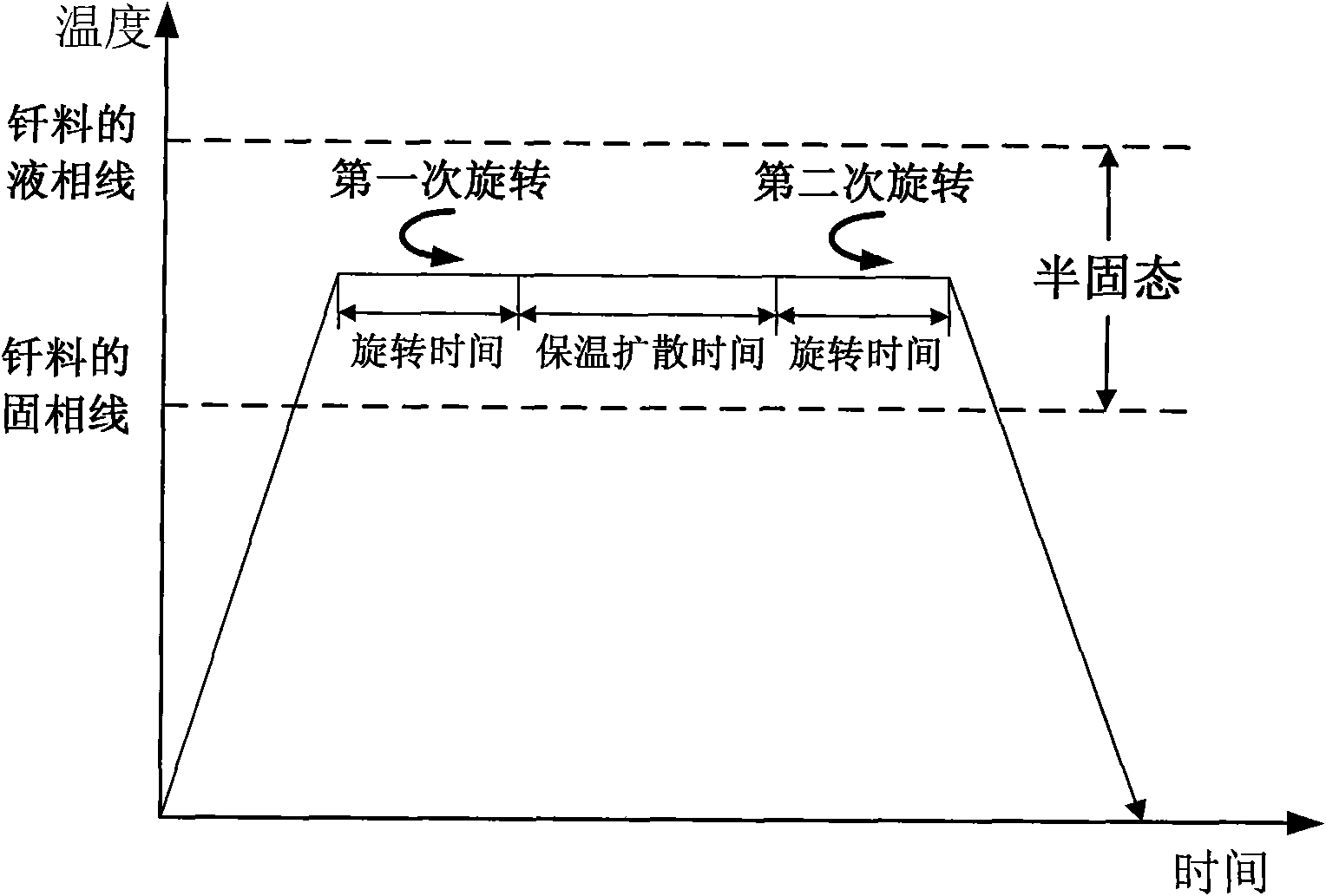
The invention provides a semi-solid brazing method for aluminum alloy and a composite material thereof under the assistance of non-vacuum mechanical stirring, which comprises the steps of: mounting a weldment taking the aluminum alloy or the composite material thereof as a base material on a welding platform first; placing intermediate-temperature solder on two surfaces to be welded, heating the weldment to between 390 and 420 DEG C, and ensuring that the solid fraction of the solder is between 50 and 80 percent; staring a rotary sliding device, wherein the rotating speed is between 150 and 300 r / m, the temperature is constant, and the longitudinal movement rate, which is parallel to a welding seam, of a stirring head is between 0.5 and 2 cm / min; stopping the rotary sliding when the stirring head moves to the terminal of the welding seam; increasing the temperature to between 430 and 450 DEG C, performing thermal insulation for 1 to 5 minutes, and ensuring that the solid fraction of the solder is between 10 and 40 percent; restarting the rotary device again, wherein the rotating speed is between 20 and 150 r / m; sliding the stirring head in a reverse direction, wherein the movement speed is between 1 and 2 cm / m; stopping the rotation, when the stirring head moves to the initial end of the welding seam, and lifting the stirring head; and cooling the solder along with a furnace after thermal insulation for 5 to 30 minutes. The method can realize the low-cost, high-efficiency and high-quality welding of the aluminum alloy or the composite material thereof.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Magnesium alloy and aluminum alloy heterogeneous non-vacuum mechanical forced rotation semi-solid brazing method
InactiveCN102284758ALow costHigh quality weldingSoldering apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesSemi solidMagnesium alloy
The invention relates to a magnesium alloy and aluminum alloy heterogeneous non-vacuum machinery forced rotation semi-solid brazing method; a magnesium alloy weldment and an aluminum alloy weldment are clamped on a clamp, Zn-Sn or Zn-Al-Sn system other brazing materials are arranged on two surfaces to be brazed, the weldments are heated, the heating temperature is between 350DEG C to 450DEG C, simultaneously pressure is increased, the pressure range is 0.1MPa to 1MPa, so that the brazing materials on a middle layer are in a semi-solid state, a rotary device is started, the rotating speed is 65r / min to 1500r / min, the temperature is constant during a rotation process, and the rotation time is 10s to 300s. After the rotation, the temperature rises by a certain rate, the heat is insulated at preset temperature, so that the brazing materials dissolve parent materials with a certain thicknesses, the heat insulating temperature is between 400DEG C to 480DEG C, and the heat insulating time is1min to 5min. Afterwards, pressure is increased, the pressure range is 0.1MPa to 1MPa, the rotary device is started again (secondary rotation), the rotating speed is 65r / min to 600r / min, rotation is stopped after 3s to 60s, and cooling is carried out with a furnace after the heat is insulated for 5 min to 30min. The magnesium alloy and aluminum alloy heterogeneous non-vacuum machinery forced rotation semi-solid brazing method can realize the high-efficiency, high-quality and economic connection of a magnesium alloy and an aluminum alloy.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Anti-vacuum semi-solid states stirring soldering method of magnesium alloy and composite material thereof
The invention provides an anti-vacuum semi-solid states stirring soldering method of magnesium alloy and composite material thereof, which comprises the following steps of: a weldment taking the magnesium alloy or the composite material thereof as a parent metal is arranged and blocked on a welding platform and medium temperature brazing filler metal is put on two surfaces to be welded; the weldment is heated in the temperature of 380 to 430 DEG C to cause that the solid phase ratio of the brazing filler metal is between 50 to 80%; hereupon, a rotational sliding device is started; the rotary speed is 150 to 300 r / m; the temperature is constant; a stirring head is parallel to the longitudinal movement speed of 0.5-2cm / min of a welding line; when the stirring head moves to the terminal of the welding line, the rotational sliding stops; the holding time is 1 to 5 minutes so that the weldment is further dissolved; the rotational device is started again; the rotary speed is 20 to 150 r / m; the stirring head slides in a negative direction; the movement speed is 1 to 2 cm / min. When the stirring head moves to the initial end of the welding line, the rotary stops; the stirring head is lifted; the holding temperature is 5-30 minutes, and a furnace cools. The method can realize the low cost, high efficient, high quality welding of the magnesium alloy and the composite material thereof.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Method for light alloy welding and multi-pass system
InactiveCN102500922ARealize flexible outputIt has the effect of "preheating and slow cooling"Laser beam welding apparatusWeld seamOutput device
The invention discloses a method for light alloy welding and a multi-pass system. The method is characterized in that energy of a solid laser used for welding is divided into three paths through a main optical path and two auxiliary optical paths, the three paths of dividing laser are coupled respectively and enter a three-path optical fiber, and the three paths of laser that are coupled and enter the optical fiber are connected with three output heads of a three-optical-path output device to realize flexible output. According to the multi-pass system, a 45-degree total reflective mirror, a 45-degree semi reflective mirror for the main optical path, a 45-degree semi reflective mirror for one auxiliary optical path, and a 45-degree total reflective mirror for the other auxiliary optical path divide the energy of the laser into three paths; when the three beams of laser are arranged serially along the welding direction, an effect of preheating and slow-cooling light alloy (such as aluminium alloy) can be achieved, the absorptivity is increased, and hot cracks of welding seams and air holes are reduced; and when the three beams of laser are arranged in a parallel or cross manner along the welding direction, the weld width of a welding seam can be enlarged, the phenomenon that a focus point diverges from the welding seam can be avoided, and the clearance adaptiveness of laser to the welding seam can be improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Working device and working method, and production equipment using it
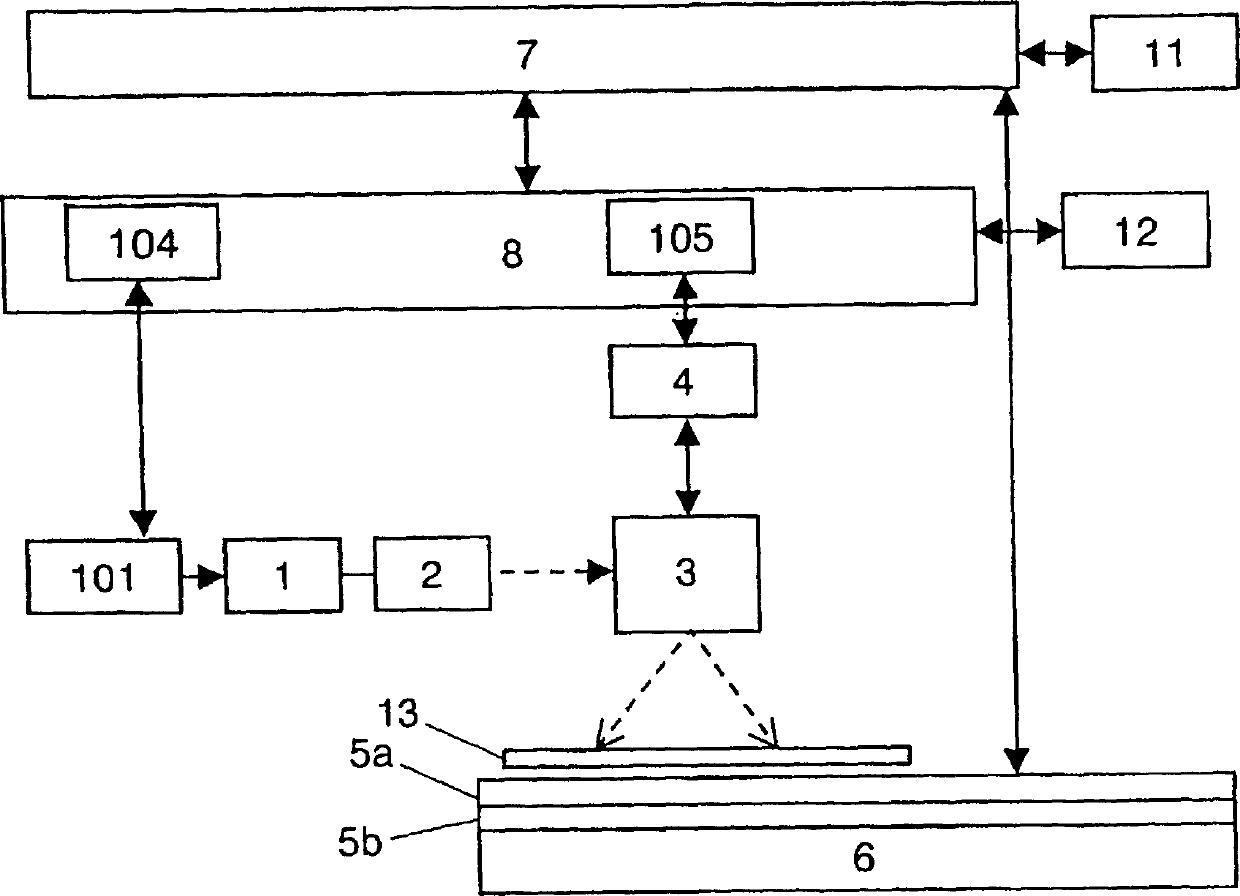
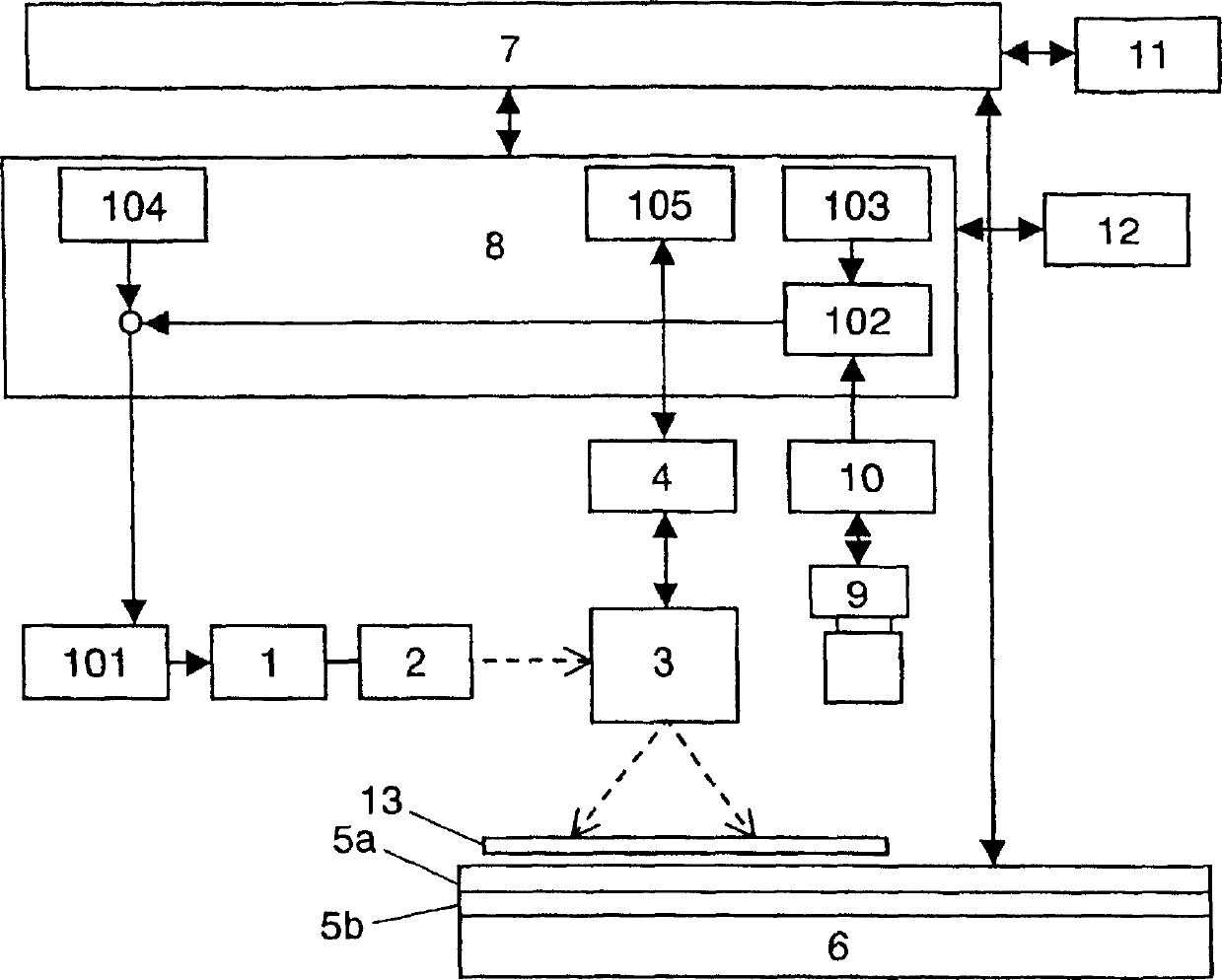
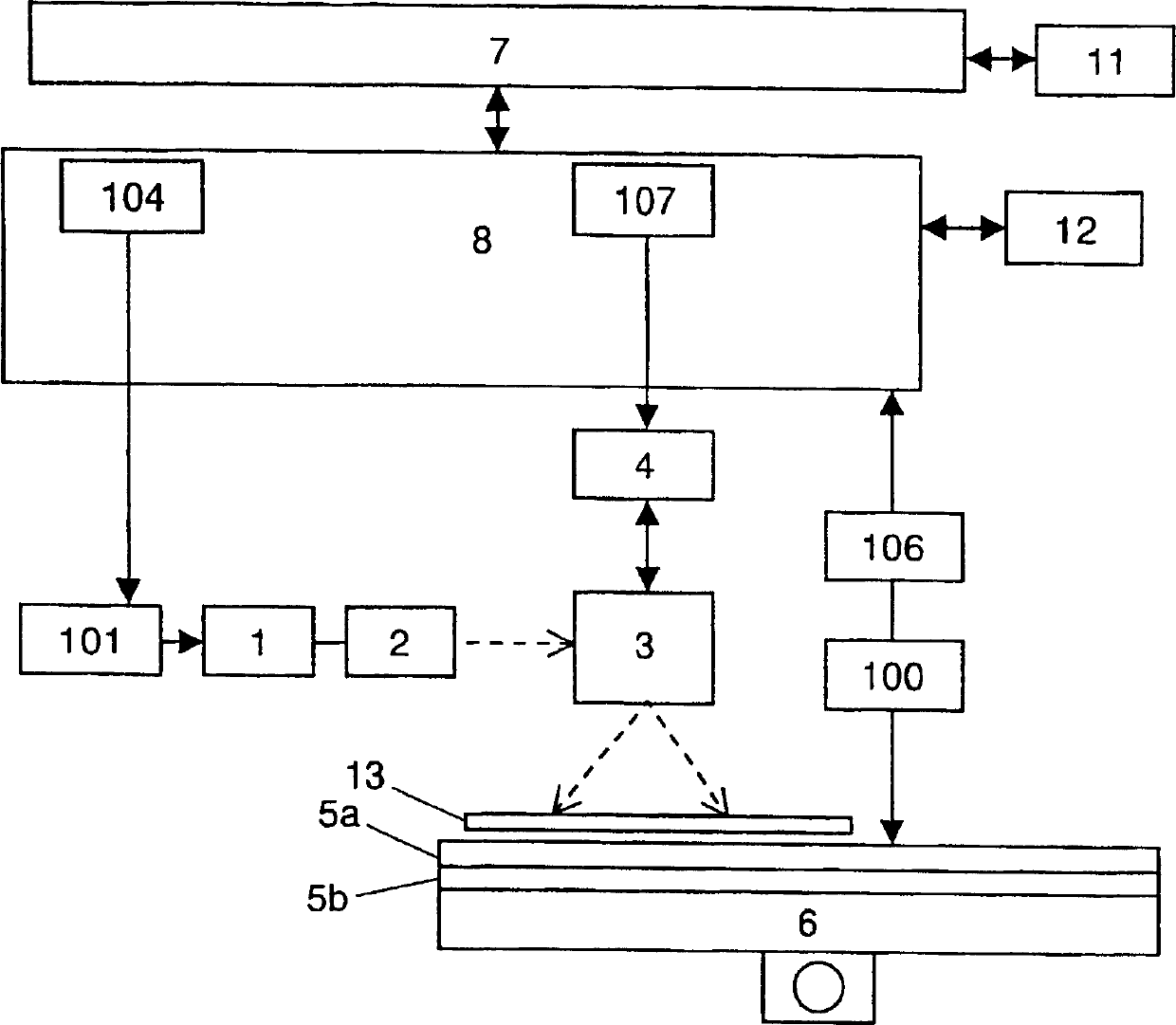
InactiveCN1479661AHigh speed localized heatingSuitable for weldingPrinted circuit assemblingHeating appliancesLight energySoldering
A machining apparatus includes a light source (1) for generating light energy, an optical system (2, 3) for guiding the generated light energy to a joint position of a workpiece, a table (5a) on which the workpiece is mounted, and a heating device (5b) provided at the table for heating the workpiece. The machining apparatus, a machining method and production equipment using the machining apparatus allow the workpiece to be locally heated fast, which is applicable to soldering or the like.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for welding eccentric circumferential seams by using electron beam scanning
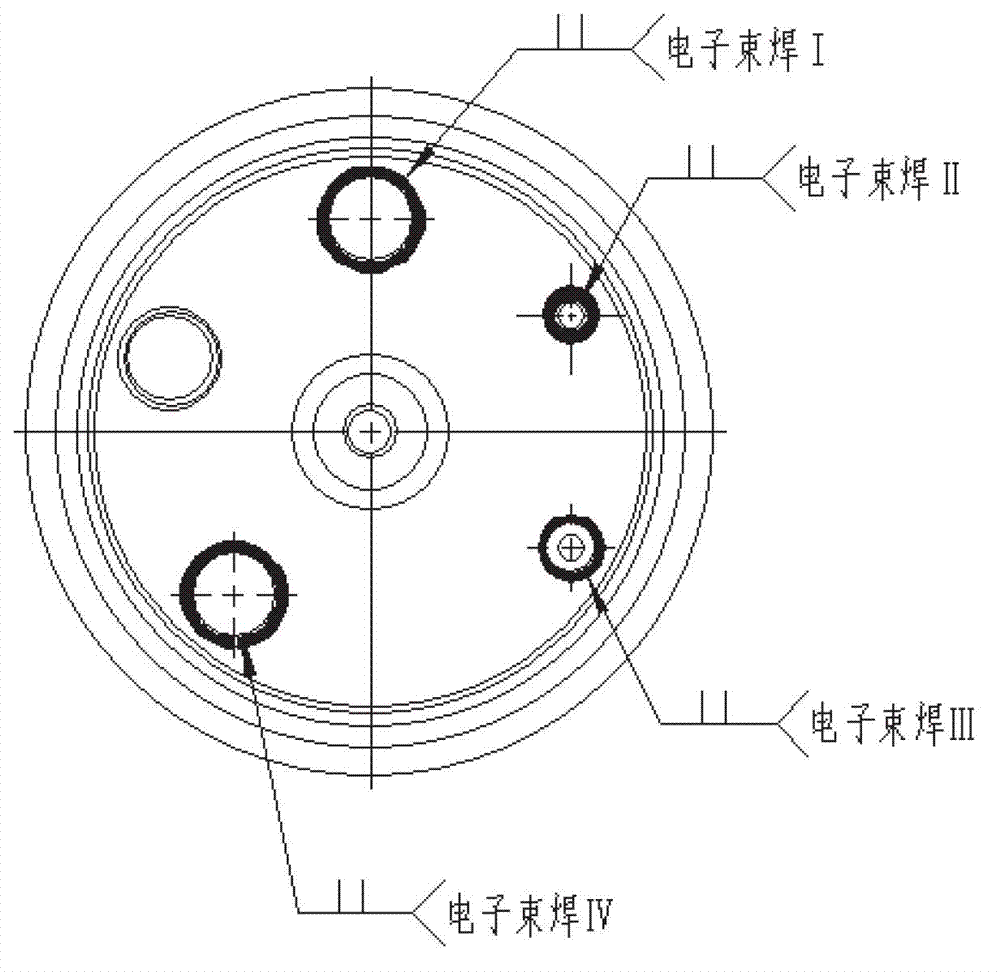
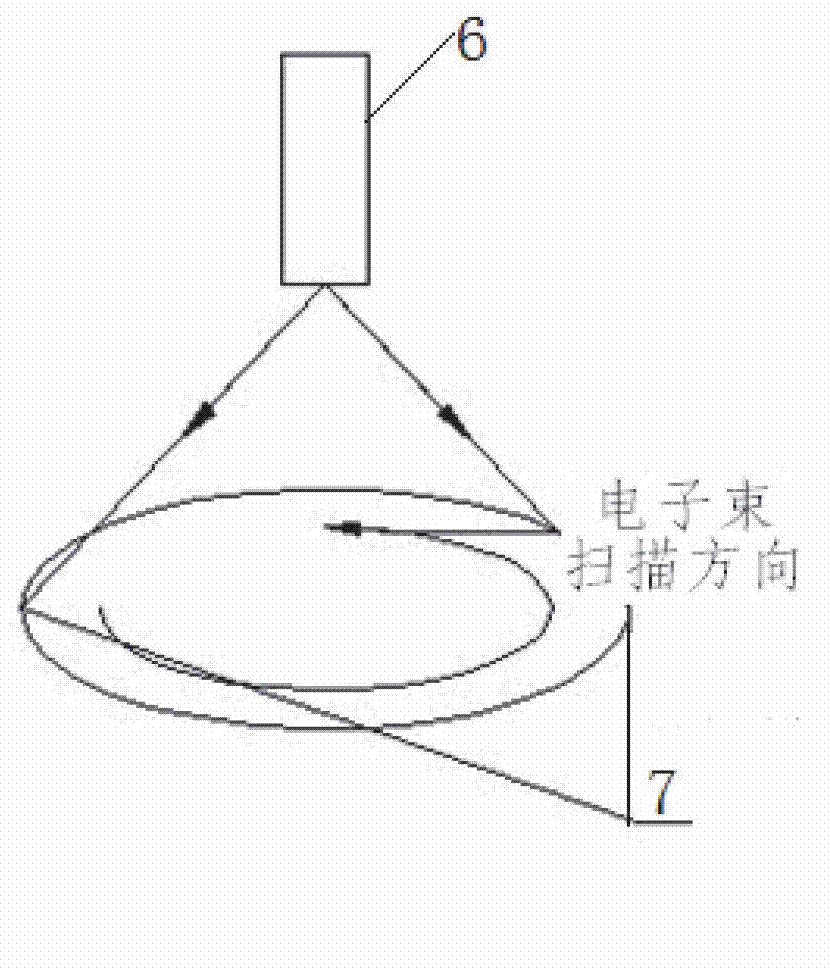
ActiveCN102962578ADesensitizationQuality improvementElectron beam welding apparatusPeak valueBeam scanning
The invention discloses a method for welding eccentric circumferential seams by using electron beam scanning. The purpose of the invention is to provide the method for welding eccentric circumferential seams, which is easy to control and has stable quality and high efficiency. The method is implemented by the following technical scheme: the oxide of the surfaces of the workpiecesparts to be welded on workpieces is first removed, and organic cleaning agent is used for cleaning the parts of the an eccentric circumferential seams; the workpieces to be welded, which have the eccentric circumferential seams, are assembled together and clamped on a three-jaw chuck; the scanning program of an electron beam welder is set to drive an electron beam in an electron gun to oscillate and revolve within a certain deflection angle range, so that a surface heat source is generated, electron scanning process parameters are set, i.e., the energy of the electron beam is rapidly increased to a peak value, the beam rise time is set as 1s to 2s, the beam welding and scanning time for keeping heating is set as 25s to 30s, the fall time is set as 10s to 12s, the scanning frequency is 400Hz to 600Hz, and under the process parameters, the scanning track of the electron beam is controlled and the workpieces scanned by the electron beam are heated, melted and welded at the seams.
Owner:四川泛华航空仪表电器有限公司
End socket assembly welding machine for low-temperature heat-insulating gas cylinder
InactiveCN103317212AImprove welding efficiencySimple structureWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesGas cylinderEngineering
The invention discloses an end socket assembly welding machine for a low-temperature heat-insulating gas cylinder. The end socket assembly welding machine for the low-temperature heat-insulating gas cylinder comprises a rack, a rotating shaft is arranged on the rack, one end of the rotating shaft is connected with a driving device arranged on the rack, and a fixed end rotating chuck is arranged at the other end of the rotating shaft. A moving end rotating chuck capable of moving along the gas cylinder axially is further arranged on the rack, and two cylinder supporting devices are oppositely arranged on the rack. Each cylinder supporting device comprises a support arranged on the rack, a mounting plate perpendicular to the axis of the gas cylinder is arranged on each support, carrier rollers are arranged at the two ends of each mounting plate respectively, and a welding trolley is movably arranged on the rack.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG FREE TRADE ZONE CHANGJIANG NEW ENERGY EQUIP
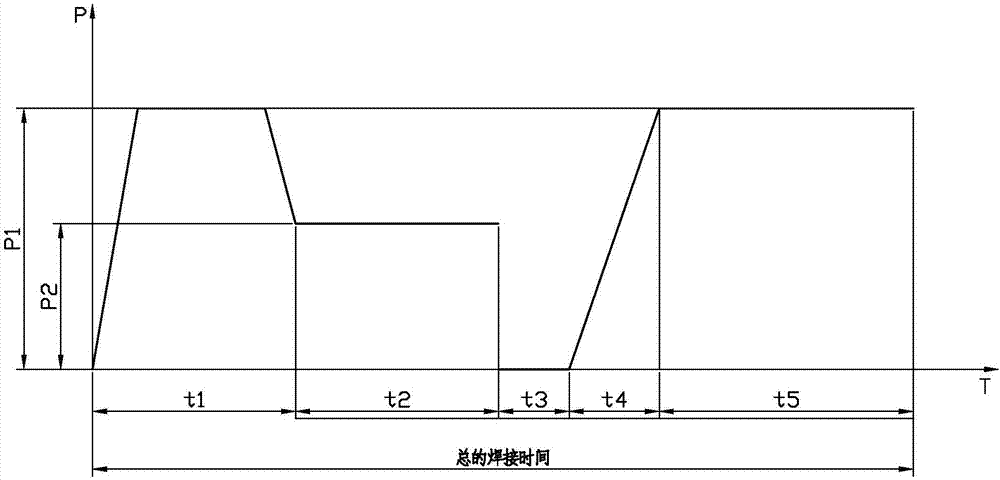
Manufacturing method for sweat soldering PVC pipe fitting
ActiveCN107498883AIncreasing the thicknessHigh strengthPipe connection arrangementsSiphonsPipe fittingFree cooling
The invention relates to a manufacturing method for a sweat soldering PVC pipe fitting. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps that a multi-angle pipe cutter is used for cutting a tubular object into required lengths and angles; the cut tubular objects are put on a fixture of a soldering machine and fixed well; the end faces to be soldered of the two tubular objects are treated to be smooth; the end faces are gathered, the centring situation is checked, misalignment edges of the two end faces to be soldered do not exceed 10% of the wall thickness, or otherwise the clamping force of the fixture is used for carrying out adjustment, and the two end faces to be soldered are treated again to be smooth; a heating plate of the soldering machine is arranged between the two pipe ends, pressure P1 is gradually exerted within t1 so that the pipe ends can be heated on the heating pipe, and after uniform soldering beads are formed, the pressure is gradually reduced to P2, P2 is kept, heat absorbing is carried out; the pipe ends are loosened, the heating plate is taken out, and the pipe ends are gathered again; the pressure is gradually increased to P1 from 0, soldering portions of the pipes form uniform flanges inwards and outwards; and the pressure P1 is kept, and the soldering portions are naturally cooled.
Owner:JIANGSU HUASHENG PLASTIC
Non-vacuum semi-solid mechanically assisted rotary brazing method for magnesium alloy and its composite materials
InactiveCN102284760ALow costHigh quality weldingSoldering apparatusNon-electric welding apparatusVacuum assistedSemi solid
The invention relates to a non-vacuum semi-solid machine-assisted rotary soldering method for a magnesium alloy and a composite material thereof, which comprises the following steps of: clamping the magnesium alloy and a composite material weldment thereof on a fixture, putting Zn-Sn or Zn-Al-Sn solders and the like on two surfaces to be welded, heating the weldment at the temperature of between 350 and 450 DEG C, and applying pressure of 0.1 to 1MPa to make the solder in an intermediate layer positioned in a semi-solid state; starting a rotating device, rotating at a speed of 65 to 1,500r / min for 10 to 300 seconds, and keeping the temperature constant in the rotating process; raising the temperature at a certain heating rate after rotation is stopped, and preserving heat at the predetermined temperature of between 400 and 480 DEG C for 1 to 5 minutes to make the solder dissolve parent metal with certain thickness; and applying pressure of 0.1 to 1MPa, starting the rotating device again, rotating for the second time at a speed of 65 to 600r / min for 3 to 60 seconds, stopping rotation, preserving heat for 5 to 30 minutes, and cooling with a furnace. By the method, the magnesium alloy and the composite material thereof can be efficiently and economically connected at high quality.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
High-strength flux-cored wire capable of increasing penetration as well as preparation method and application of flux-cored wire
ActiveCN105345313AImprove securityReduced amount of filler metalWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaFerrosiliconRare earth
The invention discloses a high-strength flux-cored wire capable of increasing penetration as well as a preparation method and an application of the flux-cored wire. The flux-cored wire comprises powder and a tube wall for packing the powder, wherein the powder comprises components in percentage by mass as follows: 1%-5% of 75# ferrosilicon, 8%-15% of mid-carbon ferromanganese, 12%-18% of ferromolybdenum, 4%-9% of micro-carbon ferrochrome, 2%-5% of nickel metal powder, 1%-3% of ferrovanadium, 3%-6% of ferrotitanium, 1%-2% of a rare earth ferrosilicon alloy, 0-2.0% of K2CO3 powder, 0.5%-1.5% of potassium permanganate powder and the balance of Fe powder and inevitable impurities having no influence on the performance of the flux-cored wire. The high-strength flux-cored wire has the deeper penetration, so that a base material is not required to be grooved, or only a small groove is required to be formed and a large truncated edge is required to be reserved, the filler metal quantity is reduced, and the welding productivity is greatly improved. Meanwhile, the welding defect of incomplete fusion cannot be produced easily, and the safety of a welded structure is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Laser welding method for thin-walled tantalum tube and thin-walled iron-nickel alloy pipe
ActiveCN106271060AHigh strengthFirmly connectedLaser beam welding apparatusEvaporationHigh intensity
The invention provides a laser welding method for a thin-walled tantalum tube and a thin-walled iron-nickel alloy pipe. The laser welding method comprises the following steps of: 1, microscopically, removing burrs of the thin-walled tantalum tube and the thin-walled iron-nickel alloy pipe, and after grinding and polishing, carrying out ultrasonic washing; 2, assembling before welding to obtain an assembly part; 3, placing the assembly part in a welding chamber of laser equipment, aligning a laser generator with a welding hole to enable a laser beam emitted by the laser generator to be irradiated to to-be-welded positions of the thin-walled tantalum tube and the thin-walled iron-nickel alloy pipe, installing a chuck on a lathe, then closing the welding chamber, filling inert protection gas by a gas inlet pipe, rotating a rotating shaft by the lathe, and simultaneously emitting the laser beam to obtain a welded structure of the thin-walled tantalum tube and the thin-walled iron-nickel alloy pipe. The laser welding method can overcome the deficiencies and the defects of part deformation, burning loss of an iron-nickel alloy part, runoff and evaporation in the process of welding tantalum and iron-nickle alloy thin-walled parts in the prior art, and is particularly suitable for high-strength connection of the tantalum and iron-nickle alloy thin-walled parts.
Owner:西安西材三川智能制造有限公司
Plastic film welding device
InactiveCN101407111ASuitable for weldingEvenly balanced weldingFlat articlesTetrafluoroethyleneWeld seam
The invention discloses a plastic film welding device. The device comprises a heating plate driven by a driver, a heating electrode matched with the heating plate and two working platforms for loading plastic films, wherein the heating electrode is arranged between two working platforms, the heating plate is arranged above the heating electrode. The device can be used for welding common plastic films and particularly for welding ethylene-tetrafluoroethylene copolymer films, increase the strength of welding seams of the welded ethylene-tetrafluoroethylene copolymer films to bigger than that of the ethylene-tetrafluoroethylene copolymer films and increase the connection firmness and safety.
Owner:四川蒙特工程建设有限公司
Special rotary horizontal pipe welding machine
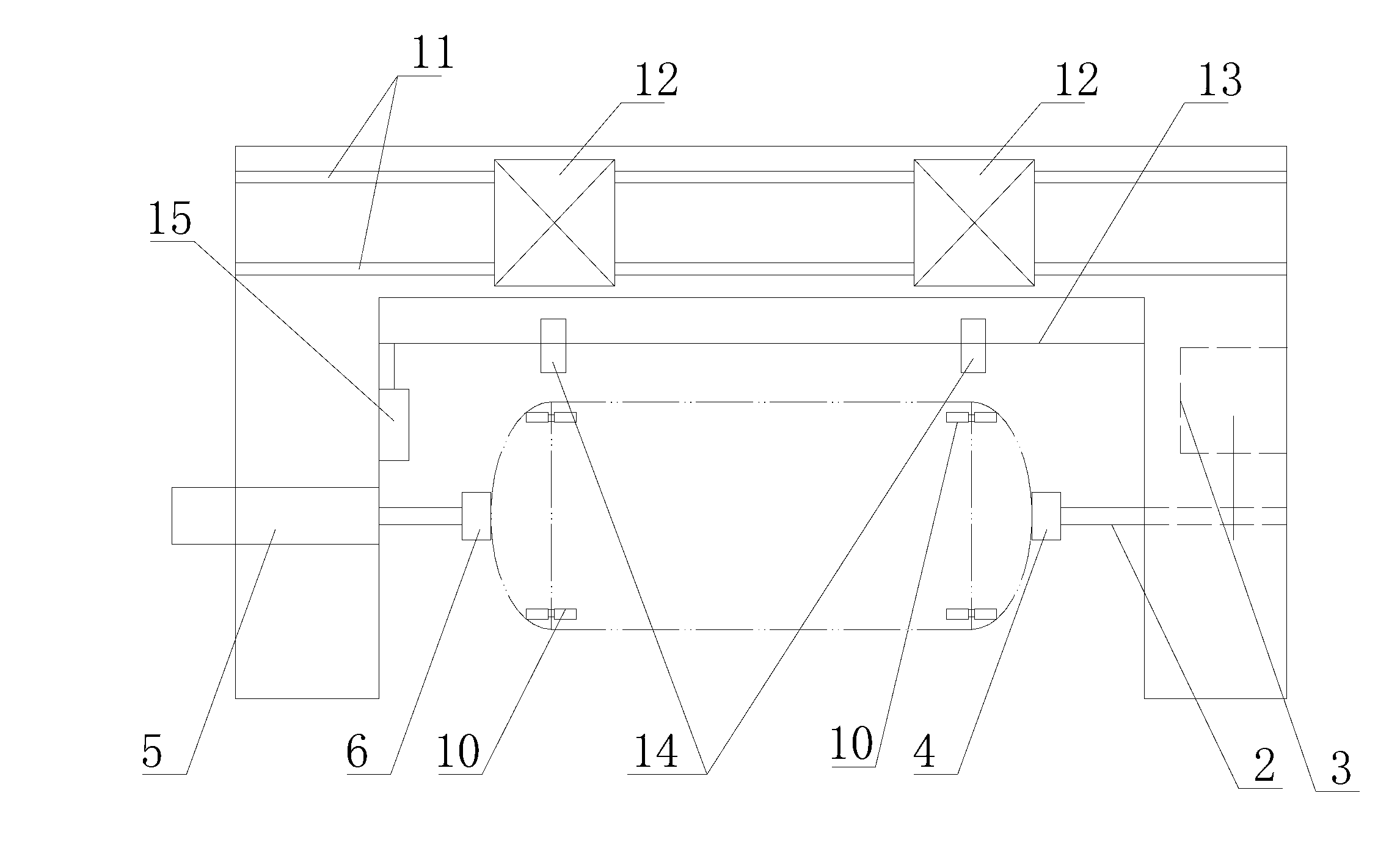
ActiveCN104476049AReduce operating intensitySimple and fast operationWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesVertical cylinderPipe welding
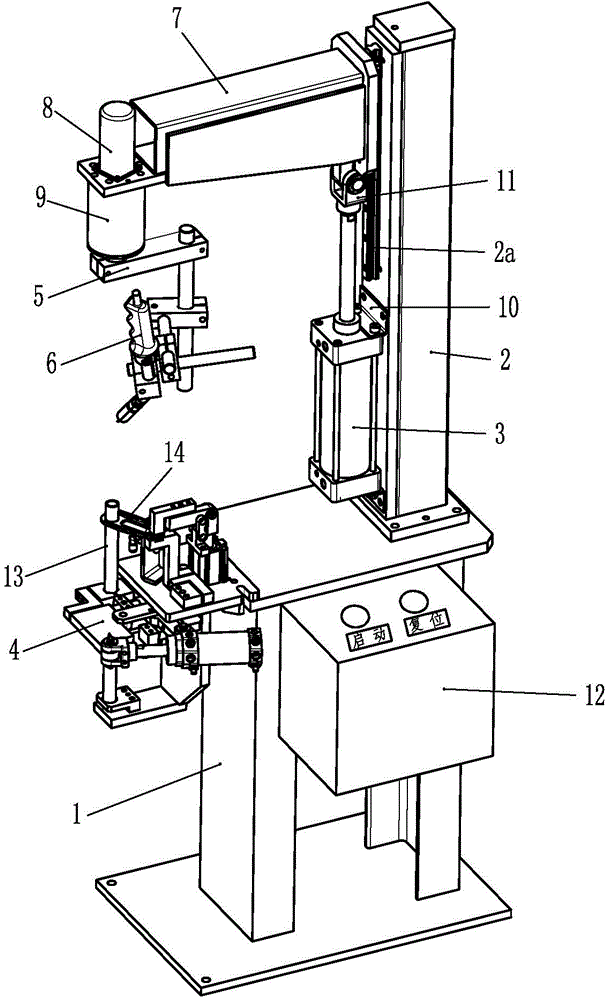
The invention discloses a special rotary horizontal pipe welding machine. The special rotary horizontal pipe welding machine comprises a base (1), a support arm (2), a vertical cylinder (3), a welding clamp (4), a welding gun adjusting mechanism (5), a welding gun (6) and a horizontal support (7), wherein the lower end of the support arm (2) is fixed on the base (1); the support arm (2) is provided with a sliding rail (2a) which extends up and down; one end of the horizontal support (7) is mounted on the sliding rail (2a); the horizontal support (7) is driven by the vertical cylinder (3) to move up and down along with the sliding rail (2a); a rotary motor (8) and the welding gun adjusting mechanism (5) are mounted on the other end of the horizontal support (7); the welding gun adjusting mechanism (5) is driven to rotate by the rotary motor (8); the welding clamp (4) is mounted on the base (1). By virtue of the special rotary horizontal pipe welding machine, the conversion from manual welding to automatic welding is realized; the problems of low production efficiency, high operation strength and poor quality stability in the manual welding process can be solved.
Owner:CHONGQING ZONGSHEN HONGLI CUSHION MFG
Long-shaft roller carrier
InactiveCN102756234AApplicable pairSuitable for weldingWelding/cutting auxillary devicesWork holdersReducerWelding
The invention discloses a long-shaft roller carrier, which comprises a driving support and a driven support. A pair of rolling shafts is arranged in parallel between the driving support and the driven support. One end of each rolling shaft is connected with a speed reducer to rotate. The long-shaft roller carrier is simple in structure and rational in design; a plurality of barrels can be arranged on the roller carrier for pairing and welding; the lengths of the rolling shafts can be designed according to the lengths of the paired barrels; and the roller carrier is also applicable to the pairing and welding of short barrels.
Owner:成都佳士科技有限公司
Swinging laser-ultrasonic hybrid welding method
ActiveCN111673272AReduce volumeEasy to implementLaser beam welding apparatusShielding gasUltrasonic vibration
The invention provides a swinging laser-ultrasonic hybrid welding method, and relates to the field of material processing engineering. The swinging laser-ultrasonic hybrid welding method aims to solvethe problems of forming defects and pores in welded parts after swinging laser welding. Ultrasound is used for assisting in changing the melt flow condition, and the undercut defects on two sides areavoided. After the use of ultrasonic wave assistance, crystal grains are further refined, the pores are suppressed, the shape of a keyhole is improved by ultrasound, the plasma and splash eruption are suppressed, and the effective utilization of energy is increased. The use of coaxial shielding gas for welding protection has a better protection effect on a molten pool, and the method is more suitable for welding titanium alloys, aluminum alloys and other easily oxidized materials. Compared with contact ultrasonic wave assistance, non-contact ultrasonic wave vibration can be applied to weldingof various complex structures and tracks, and application obstacles caused by poor contact and space limiting are avoided. The swinging laser-ultrasonic hybrid welding method is applied to the fieldof material processing.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Non-vacuum semi-solid stirring brazing method for aluminum alloy and composite material thereof
InactiveCN101596630BAchieve weldingShort welding cycleSoldering apparatusThermal insulationSemi solid
The invention provides a semi-solid brazing method for aluminum alloy and a composite material thereof under the assistance of non-vacuum mechanical stirring, which comprises the steps of: mounting a weldment taking the aluminum alloy or the composite material thereof as a base material on a welding platform first; placing intermediate-temperature solder on two surfaces to be welded, heating the weldment to between 390 and 420 DEG C, and ensuring that the solid fraction of the solder is between 50 and 80 percent; staring a rotary sliding device, wherein the rotating speed is between 150 and 300 r / m, the temperature is constant, and the longitudinal movement rate, which is parallel to a welding seam, of a stirring head is between 0.5 and 2 cm / min; stopping the rotary sliding when the stirring head moves to the terminal of the welding seam; increasing the temperature to between 430 and 450 DEG C, performing thermal insulation for 1 to 5 minutes, and ensuring that the solid fraction of the solder is between 10 and 40 percent; restarting the rotary device again, wherein the rotating speed is between 20 and 150 r / m; sliding the stirring head in a reverse direction, wherein the movementspeed is between 1 and 2 cm / m; stopping the rotation, when the stirring head moves to the initial end of the welding seam, and lifting the stirring head; and cooling the solder along with a furnace after thermal insulation for 5 to 30 minutes. The method can realize the low-cost, high-efficiency and high-quality welding of the aluminum alloy or the composite material thereof.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Flux cored wire for stainless steel welding
ActiveCN103521951BSuitable for weldingWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaRare earthManganese
The invention relates to a flux-cored wire for stainless steel welding, and particularly discloses the flux-cored wire for stainless steel welding. The flux-cored wire is composed of flux-cored powder and a stainless steel belt, wherein the flux-cored powder is wrapped by the stainless steel belt. The flux-cored wire for stainless steel welding is characterized in that the flux-cored powder accounts for15-25% of the total weight of the flux-cored wire, the flux-cored powder comprises, by weight, 30-38 parts of metal chromium powder, 6-15 parts of metal nickel powder, 3-10 parts of metal manganese powder, 20-35 parts of rutile, 1-6 parts of silicon iron, 1-7 parts of ferrotitanium, 2-10 parts of feldspar, 5-10 parts of quartz, 1-5 parts of rare earth fluoride, 1-5 parts of metal nitride powder and appropriate iron powder, and the total flux-cored powder is, by weight, 100 parts. A reduction jar of the flux-cored wire for welding is long in service cycle, and deposited metal formed by the flux-cored wire has the excellent effects of high temperature oxidation resistant capacity and high temperature sulphur corrosion resistant capacity.
Owner:BEIJING JINWEI WELDING MATERIAL +1
Aluminum alloy seal structure local flame heating ultrasonic braze welding method
ActiveCN104625289AReduce heatFlexible heating methodHeating appliancesWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLiquid stateFree cooling
The invention discloses an aluminum alloy seal structure local flame heating ultrasonic braze welding method which is used for conducting sealing and braze welding encapsulation on aluminum alloy cavities of built-in electronic components. The aluminum alloy seal structure local flame heating ultrasonic braze welding method comprises the first step of polishing and clearing an aluminum alloy surface of a joint to be brazed through abrasive paper; the second step of placing low-temperature Sn-based brazing filler metal on one side of the lap joint end of an aluminum alloy sealing surface; the third step of conducting local reciprocating heating on the brazing filler metal through gas flame flow to make the brazing filler metal melt and maintain a liquid state, and no heating on parent metal; the fourth step of applying ultrasonic vibration on a cavity of the aluminum alloy to be welded; the fifth step of finishing sealing the test piece through natural cooing after the ultrasonic vibration is finished. According to the aluminum alloy seal structure local flame heating ultrasonic braze welding method, overall heating is not conducted when the aluminum alloy seal structure is welded, local heating is conducted only on the brazing filler metal area, heating on a sealing element is extremely small, and the electronic components in the sealing element are not affected by heat. The aluminum alloy seal structure local flame heating ultrasonic braze welding method has the advantages of being simple in technology, high in welding efficiency, and suitable for the engineering application.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
High-frequency inverting DC resistance welding power supply based aluminum spot welding system and method
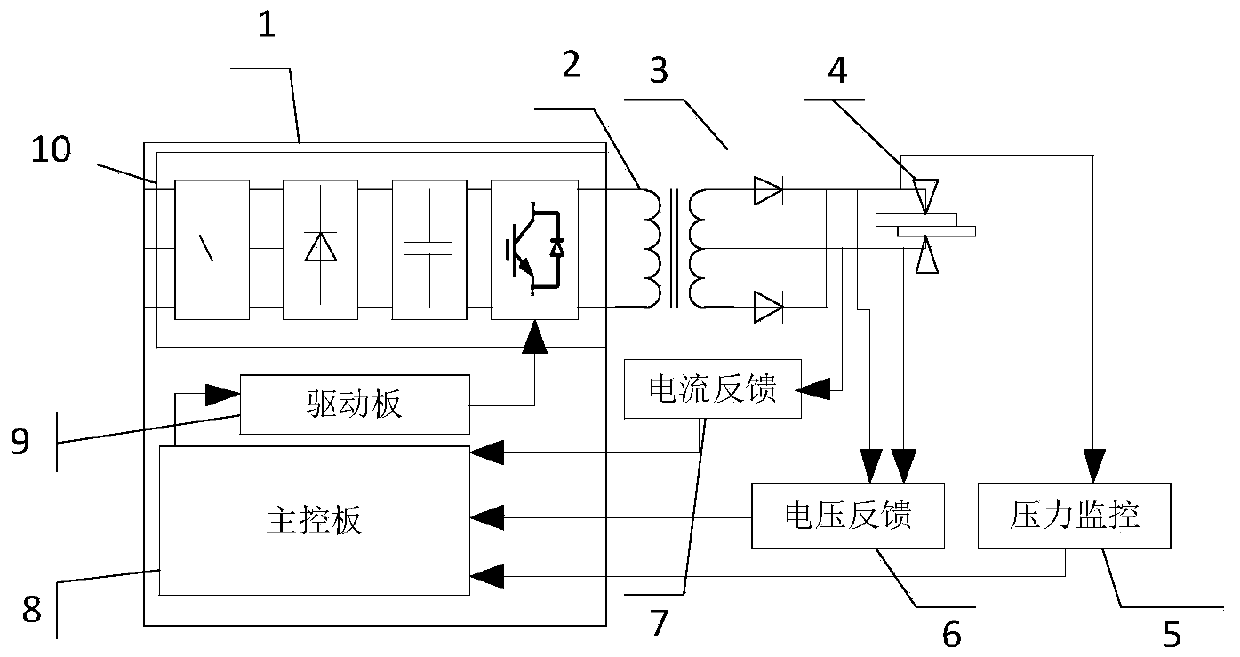
PendingCN110253129AFast adjustment frequencyEasy to adjustWelding monitoring devicesTransformerWelding power supply
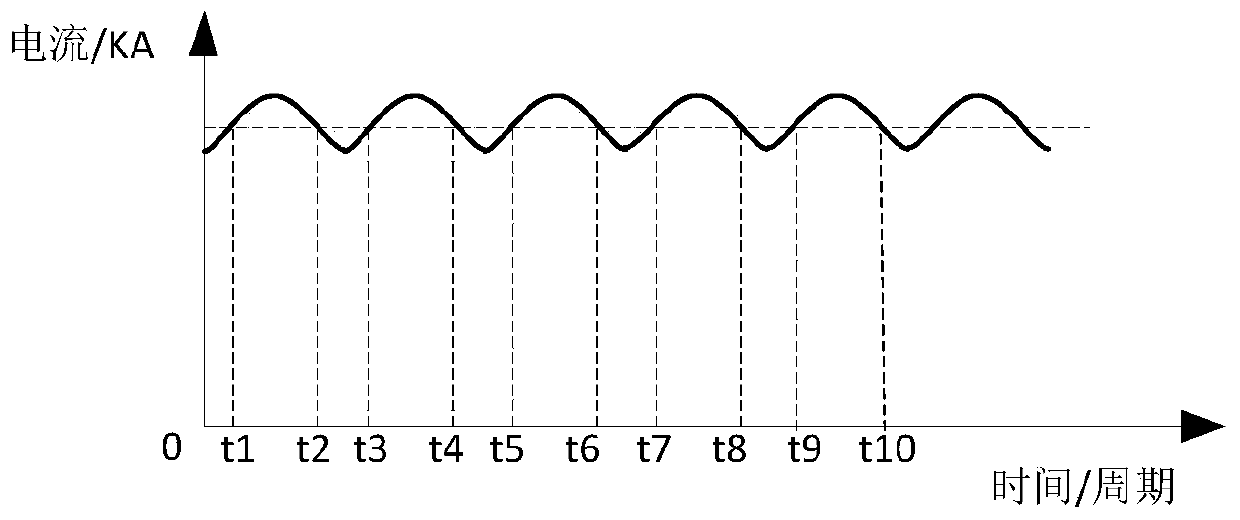
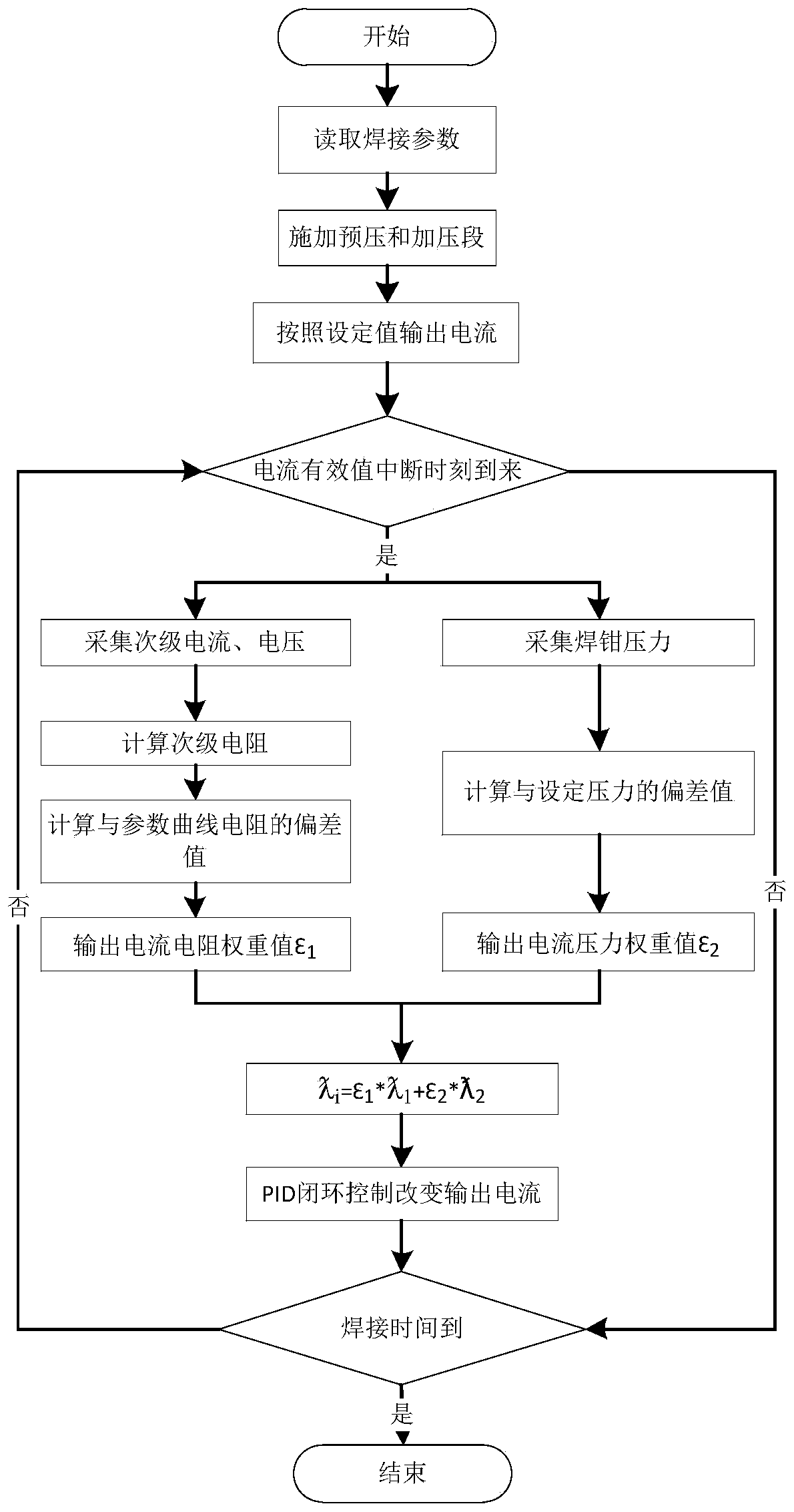
The invention provides a high-frequency inverting DC resistance welding power supply based aluminum spot welding system and method. The system is characterized by comprising a resistance welding power supply, a high-frequency transformer, a high-frequency secondary rectifying unit, an electrode unit, a voltage monitoring unit, a voltage feedback unit and a current feedback unit, wherein the voltage monitoring unit is connected to a main control panel and is used for performing pressure detection feedback and controlling an electrode holder servo motor to pressurize a workpiece based on the set pressure; the main control panel is connected to the voltage monitoring unit, the voltage feedback unit and the current feedback unit so as to acquire welding pressure, secondary voltage and secondary current. According to the system, the inverting frequency is 10KHz; 20000 groups of data points can be acquired per second based on the output waveform of the acquired secondary current, so that the system acquiring rate is increased, and the welding process can be accurately controlled.
Owner:天津七所高科技有限公司
Methods for connecting double-surface printed circuit board and welding electronic components by employing ultrasonic waves
InactiveCN105050335ASatisfy space design utilizationNot fragile metal propertiesPrinted circuit assemblingHigh densityUltrasonic welding
The invention provides methods for connecting a double-surface printed circuit board and welding electronic components by employing ultrasonic waves. The method for connecting the double-surface printed circuit board includes: during conduction connection of the double-surface printed circuit board via the ultrasonic waves, an ultrasonic machine drives a welding fixture to perform parallel ultrasonic vibration on the surfaces of metal layers of the double-surface printed circuit board, when high-frequency vibration waves are transmitted to the metal surfaces at two sides of the double-surface printed circuit board via the welding fixture, the generated high-density energy gradually catalyzes a resin layer in the middle of the printed circuit board, the metal layers at two sides are inwardly recessed to be welded together, and the connecting effect is achieved. The method for welding the electronic components by employing the ultrasonic waves includes: the high-density energy generated by ultrasonic vibration waves of an ultrasonic welding fixture enables metal surfaces of two components to perform mutual friction so that the fusion between metal layers is formed, a firm combination is formed between the components, and the welding effect is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI AMPHENOL AIRWAVE COMM ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Gas welding method for ultra-thin stainless steel workpieces
InactiveCN101602131AOvercome the shortcomings of large expansion coefficient and large deformation tendencyEasy to operateGas flame welding apparatusSlagSpot welding
The invention relates to a gas welding method for ultra-thin stainless steel workpieces. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) cleaning a welded area; (2) adopting ultra-low carbon stainless steel wires as welding wires; (3) using spot welding to align two weldments, preventing dislocation, adopting a bulk welding method or a rigid fixation method and using slight carburizing flame for welding; and (4) cleaning / clearing welding powder or slag. The method is easy to control welding temperature, can guarantee welding quality, and has the advantages of simple equipment, low cost and no need for power supply.
Owner:CHONGQING JIANSHE MOTORCYCLE CO LTD
Austenitic stainless steel welding wire having antibacterial function
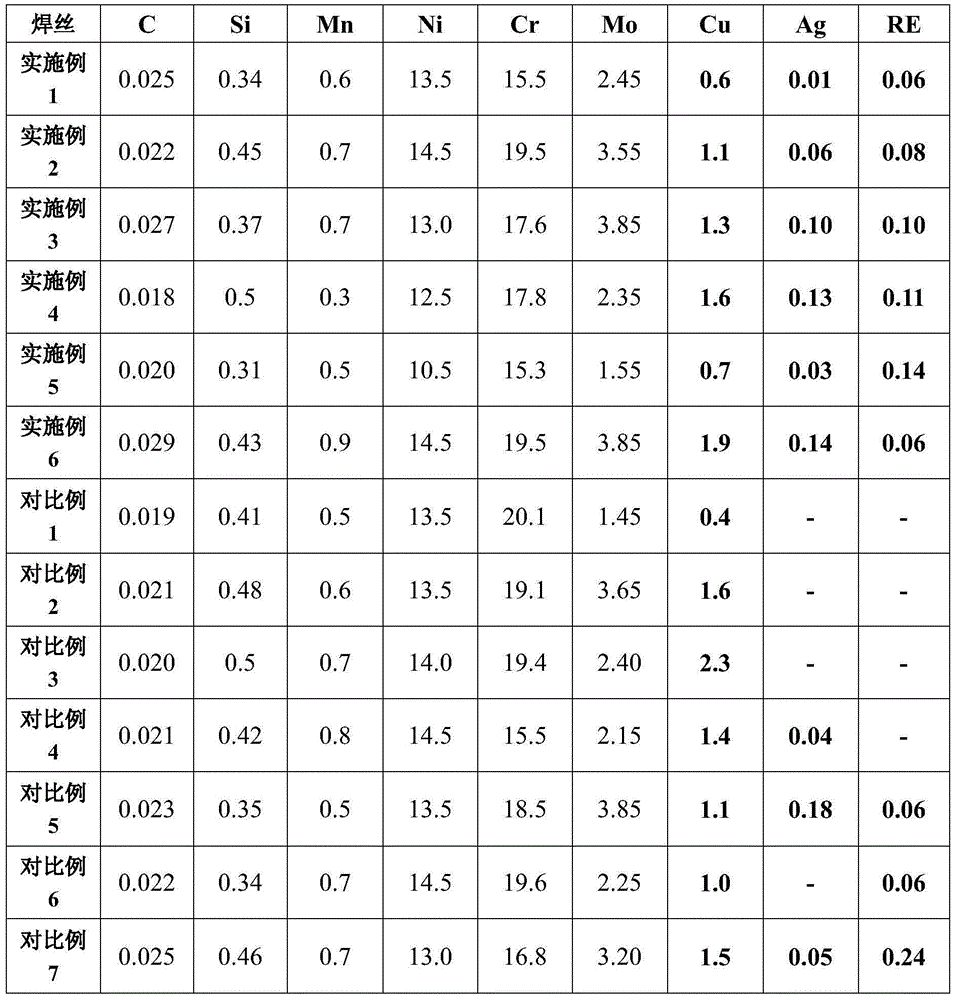
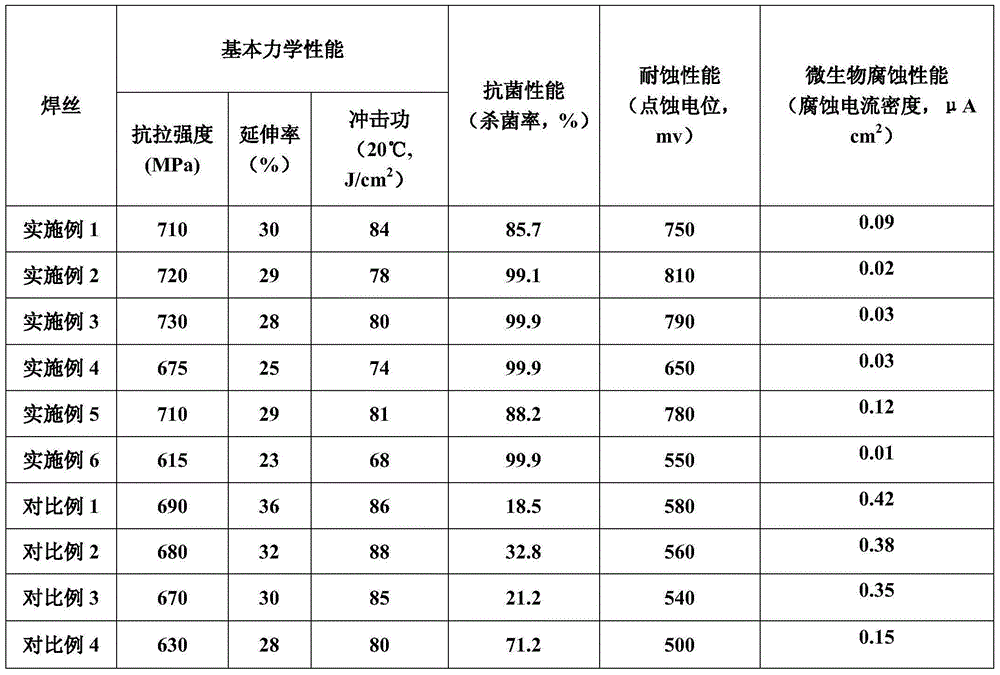
InactiveCN105057917AGood antibacterial functionGood mechanical properties at room temperatureWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaChemical compositionMicrobial corrosion
The invention aims to provide an austenitic stainless steel welding wire having an antibacterial function. The welding wire has the following chemical components in percentage by weight: C not more than 0.03, 0.3-0.5 of Si, 0.3-1.0% of Mn, S not more than 0.01, P not more than 0.01, 10.5-15 of Ni, 15-20 of Cr, 0.5-2.0% of Cu, 1.5-4.0 of Mo, 0.01-0.15 of Ag, 0.06-0.15 of RE, and the balance of Fe. On the basis of satisfying the basic requirements of room-temperature mechanical performance and corrosion resistance, the welding wire can enable a welding line connecting place to have excellent antibacterial performance without needing the after-welding heat treatment, and can prominently reduce the microbiological corrosion in the welding line place.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com