Patents
Literature
57results about How to "High quality welding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Squeezing detection control method for consumable electrode arc welding
ActiveUS20080223840A1Reduce generationHigh quality weldingArc welding apparatusElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
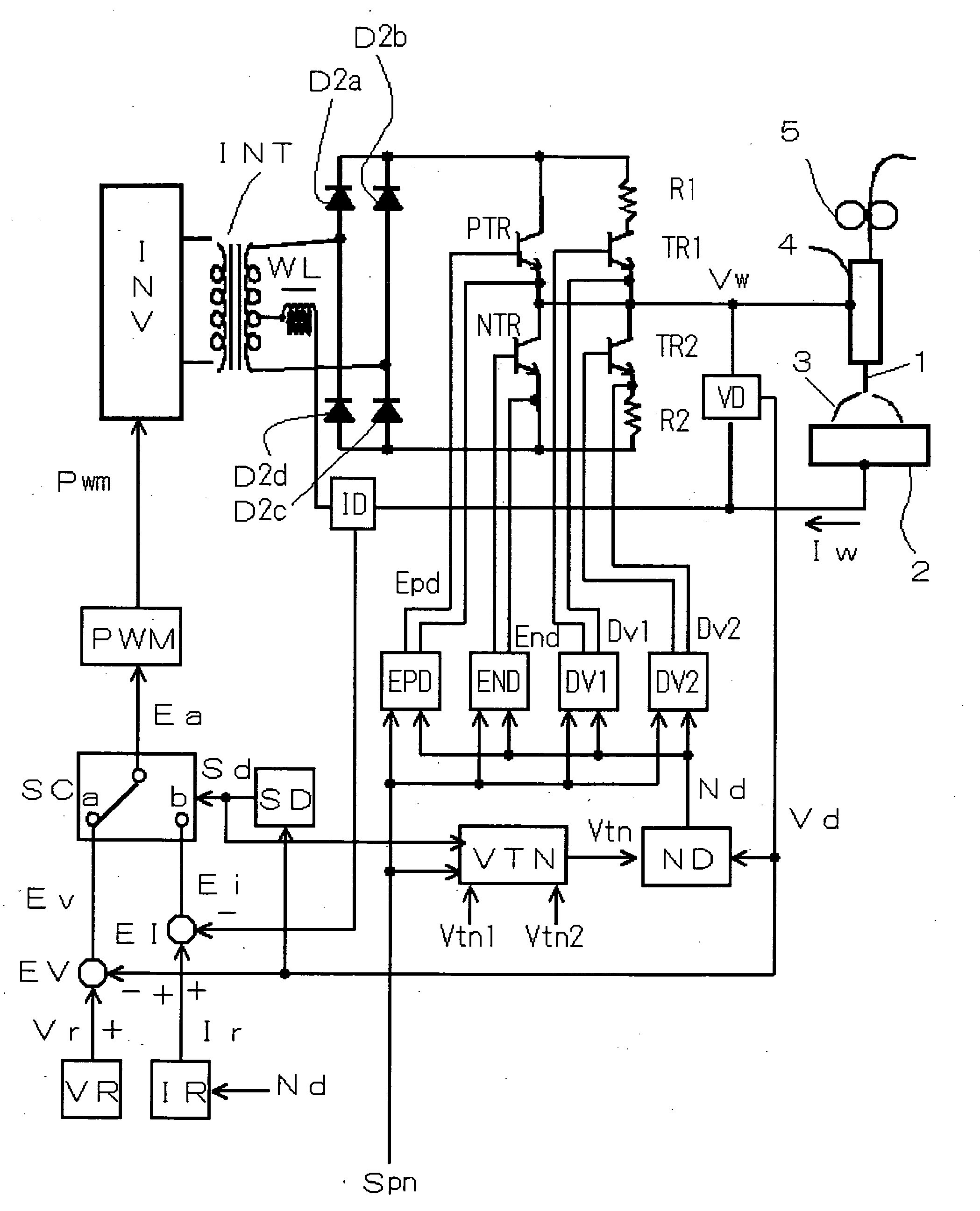
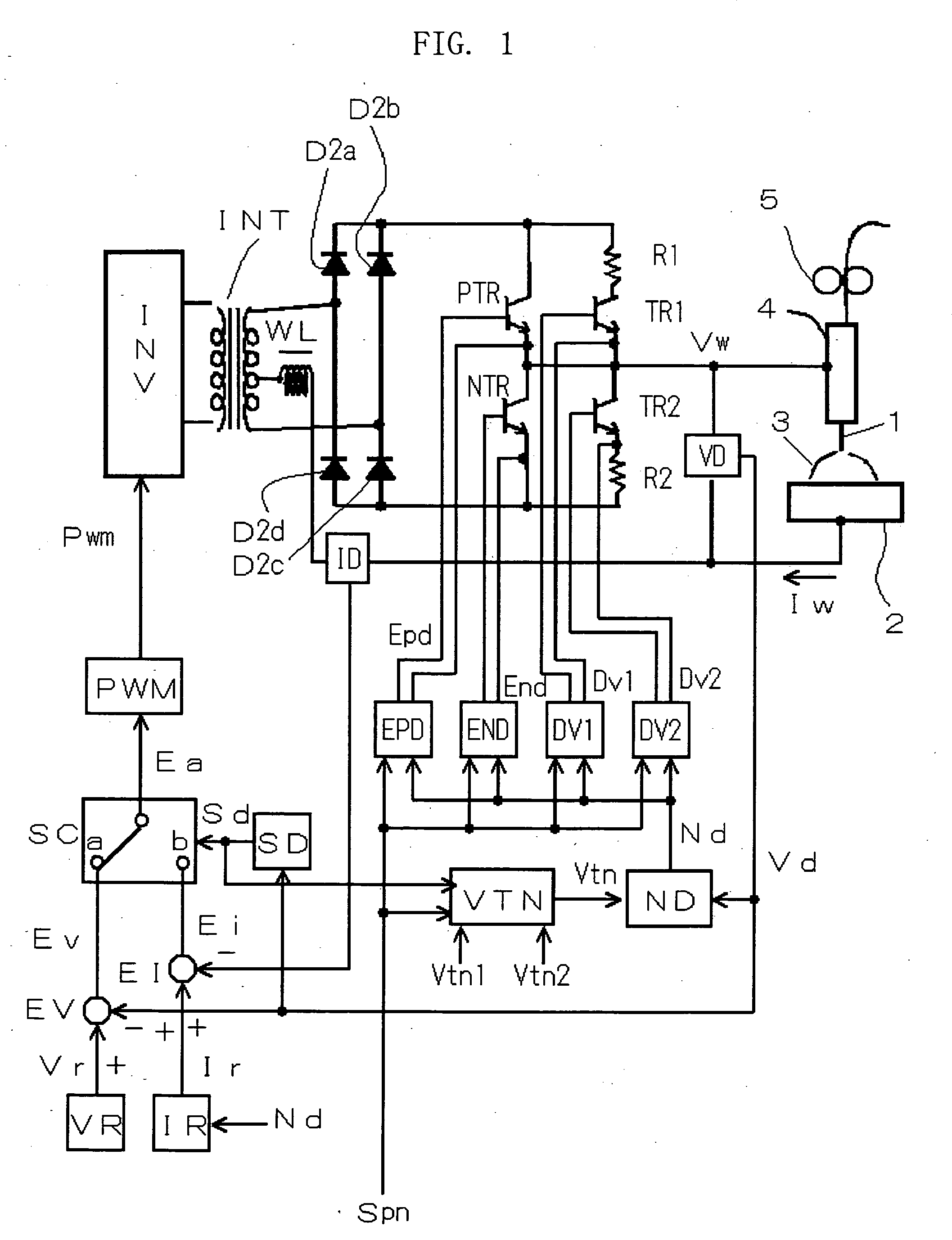
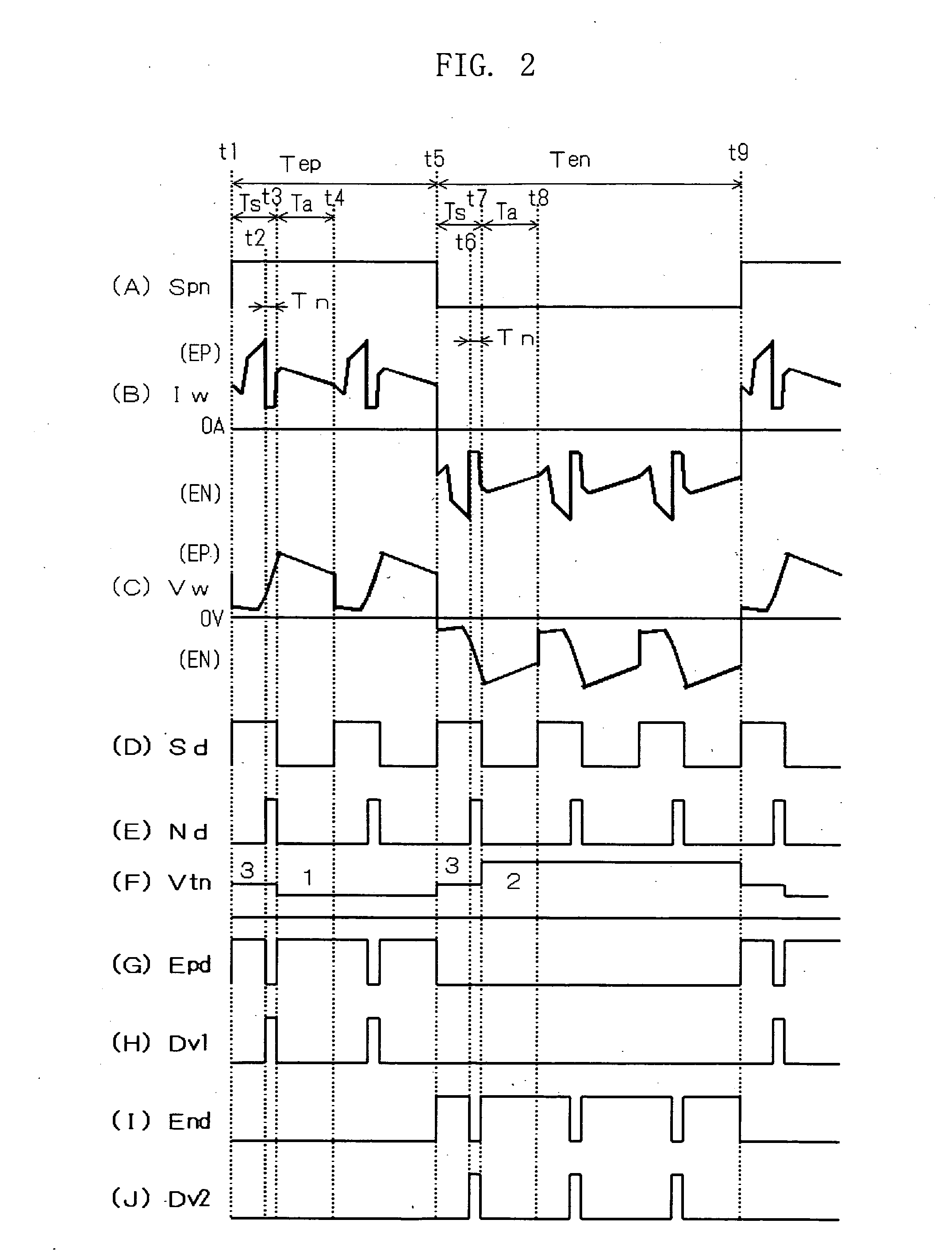
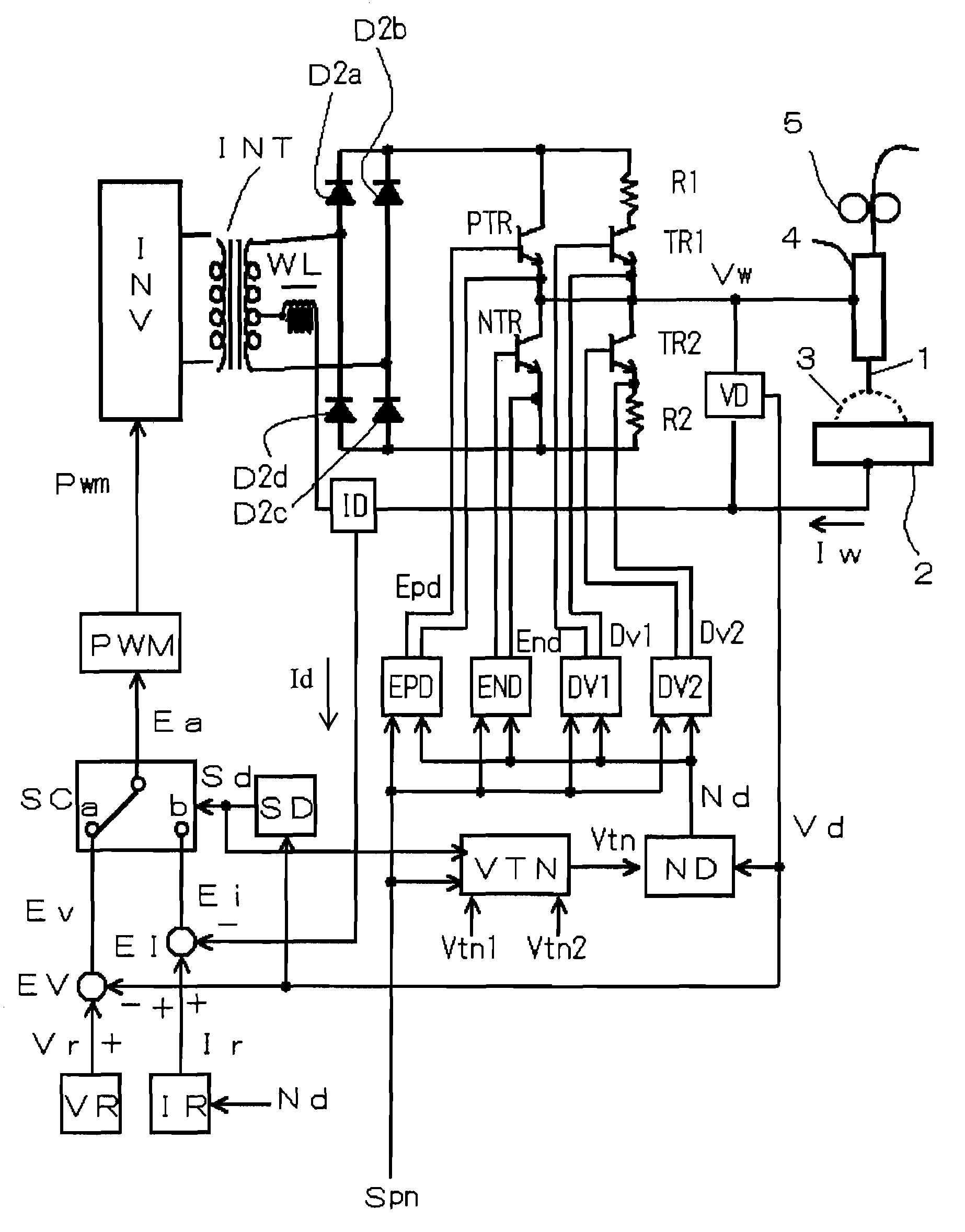
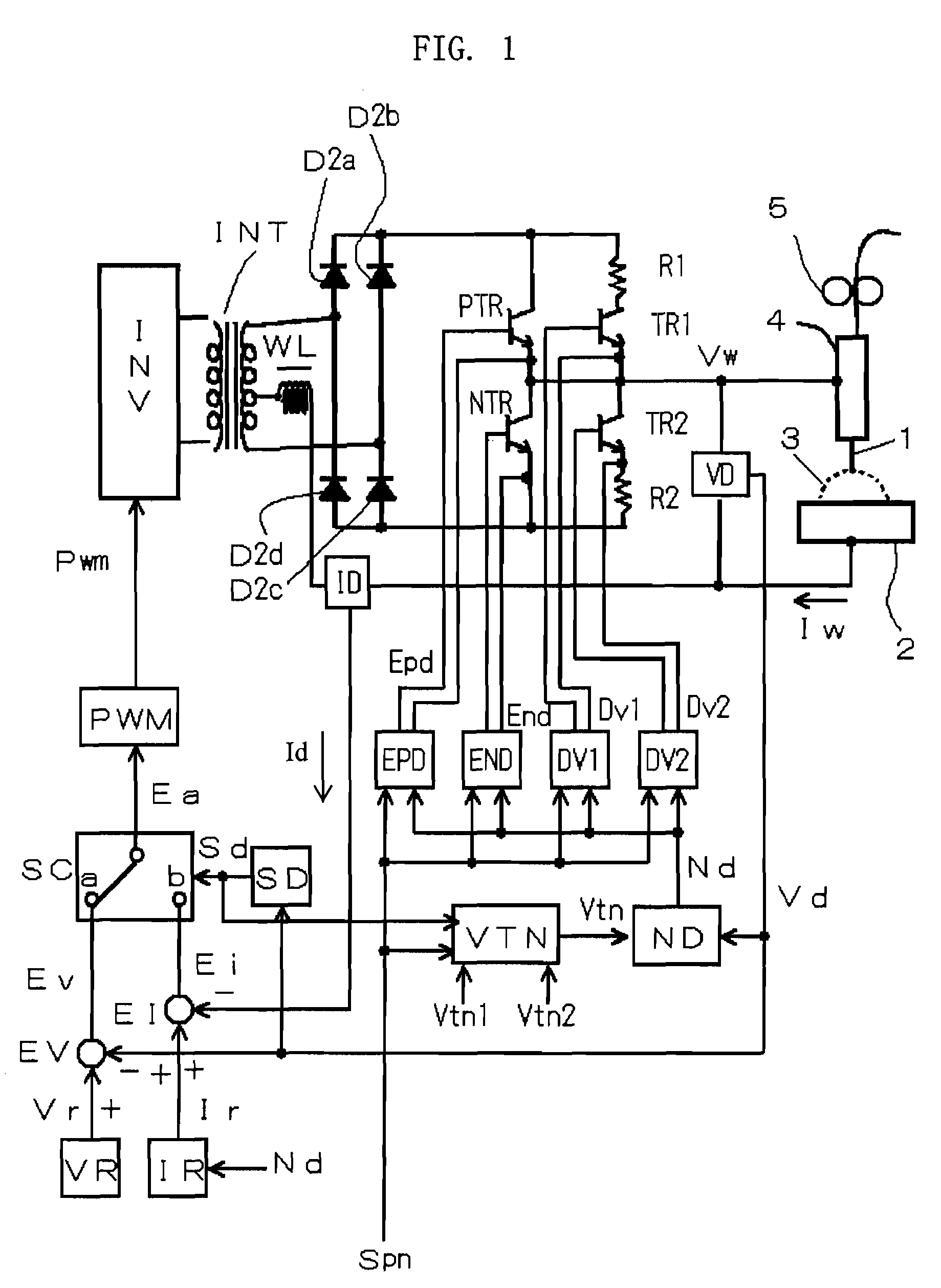
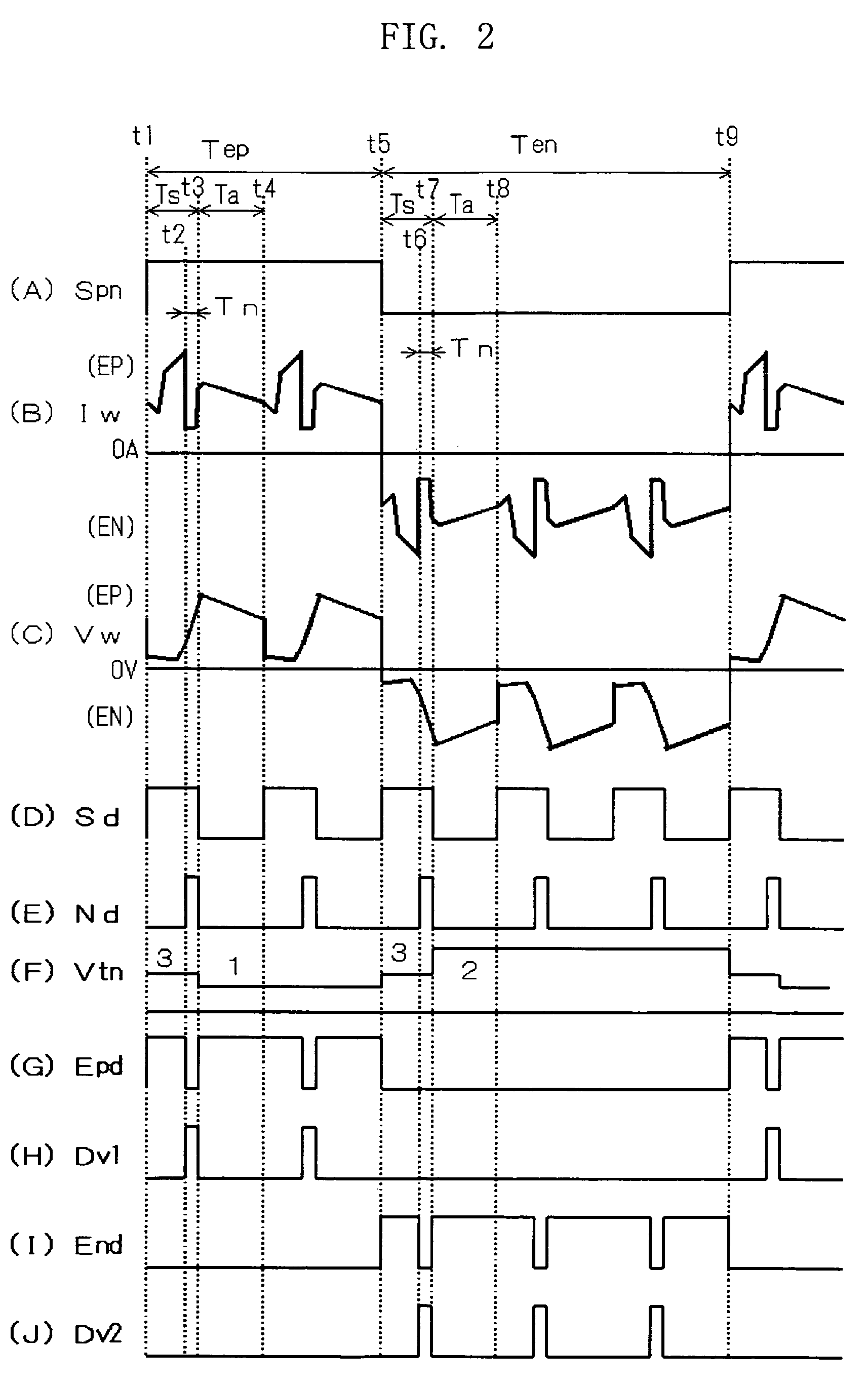
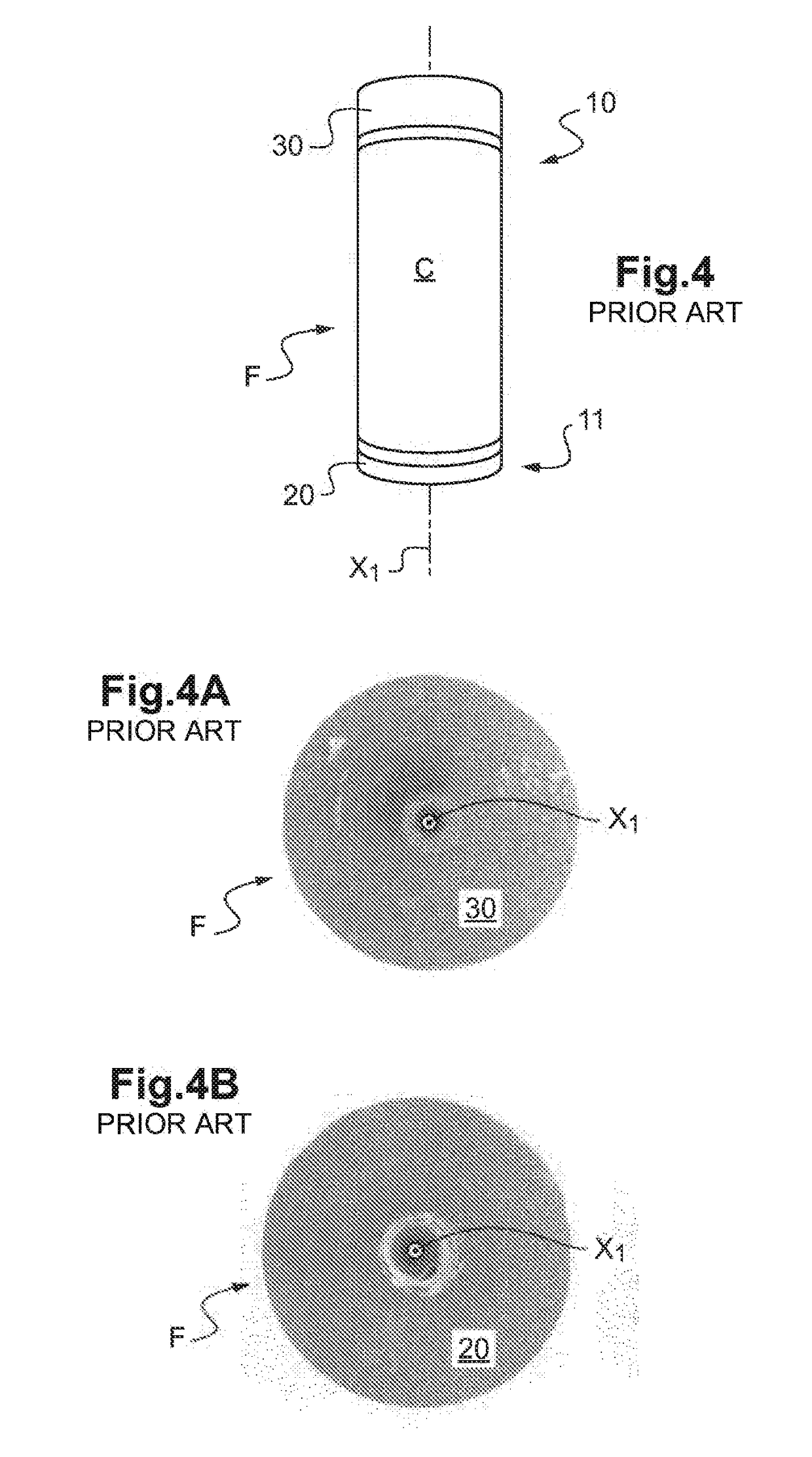
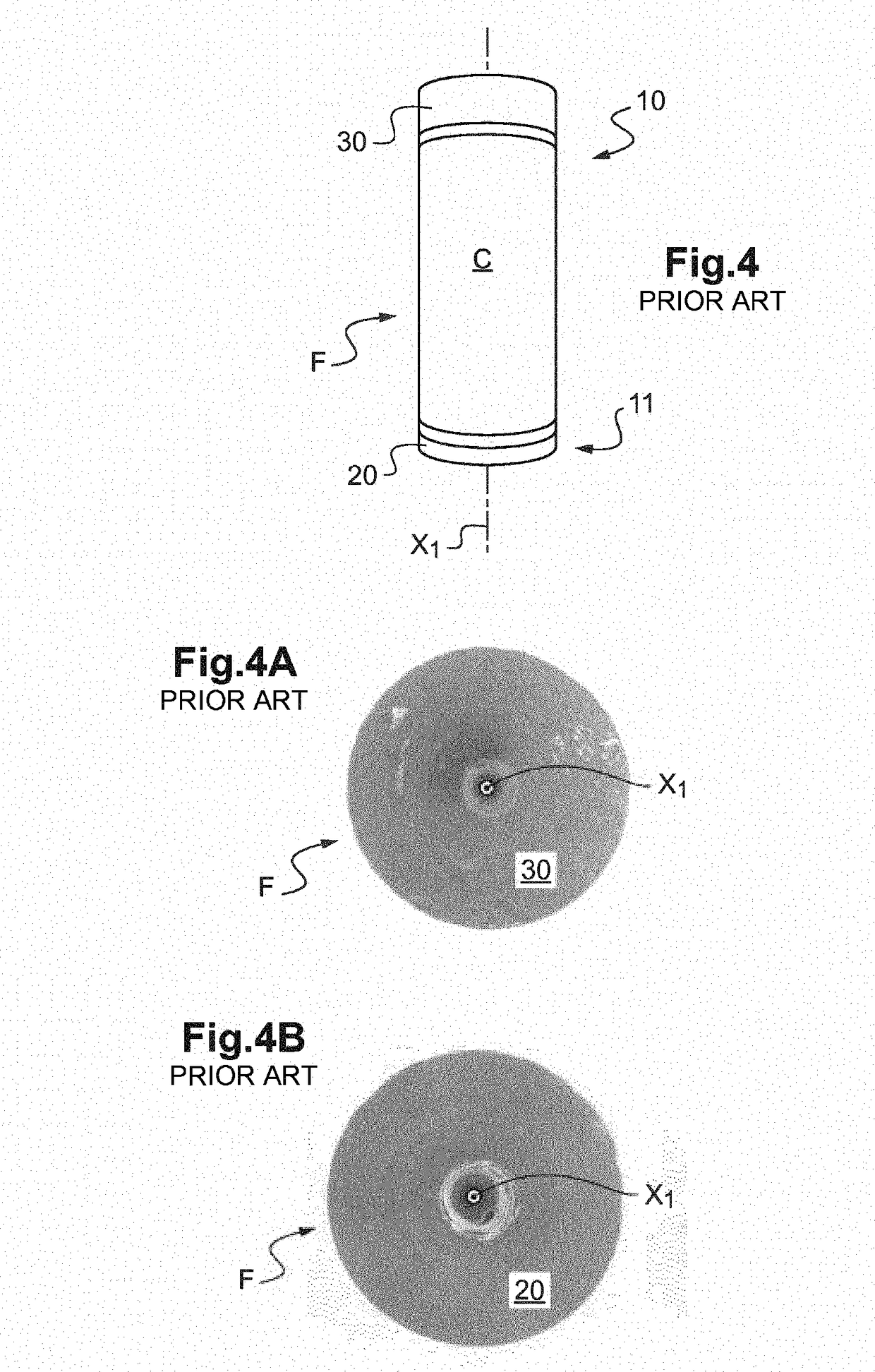
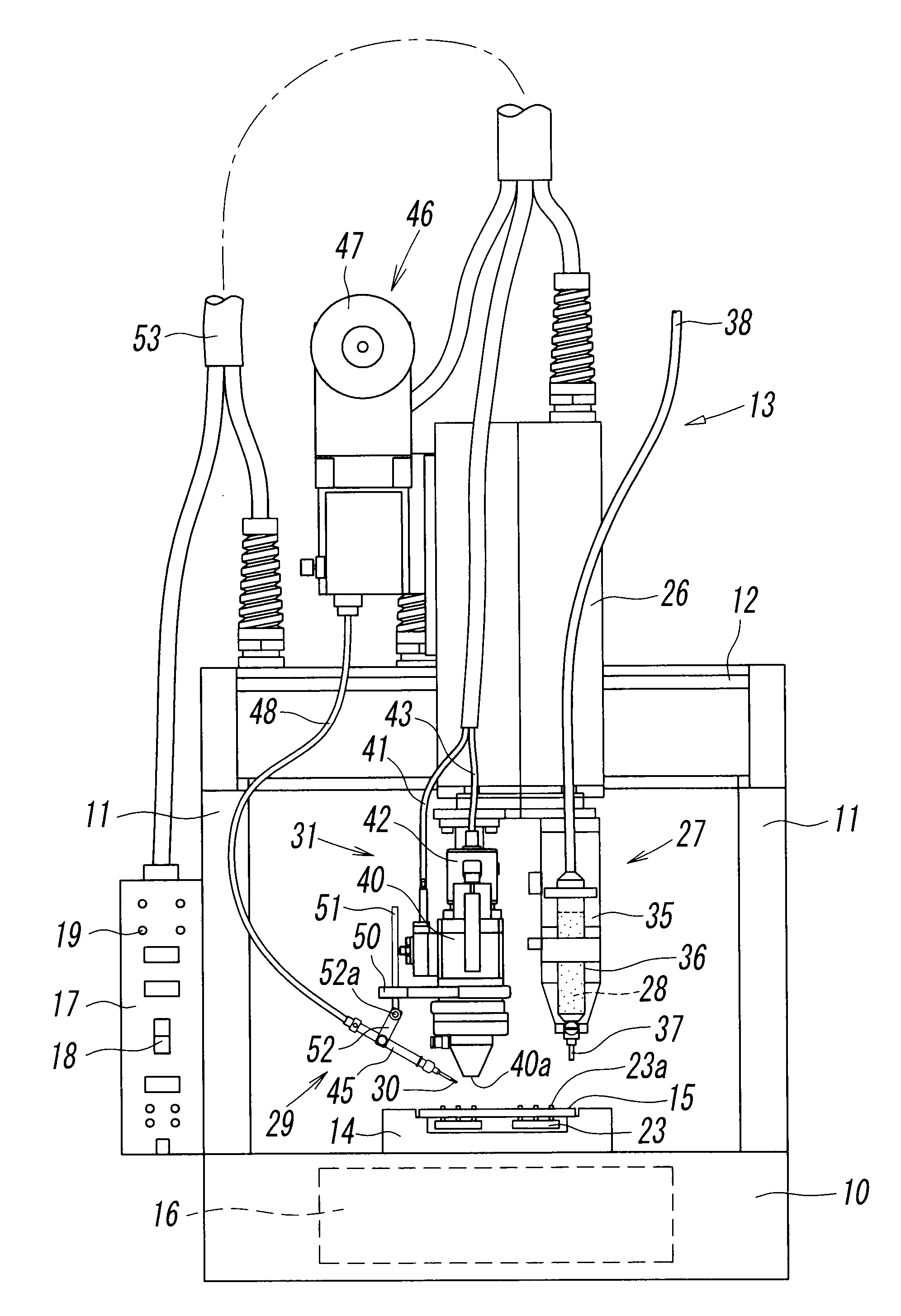
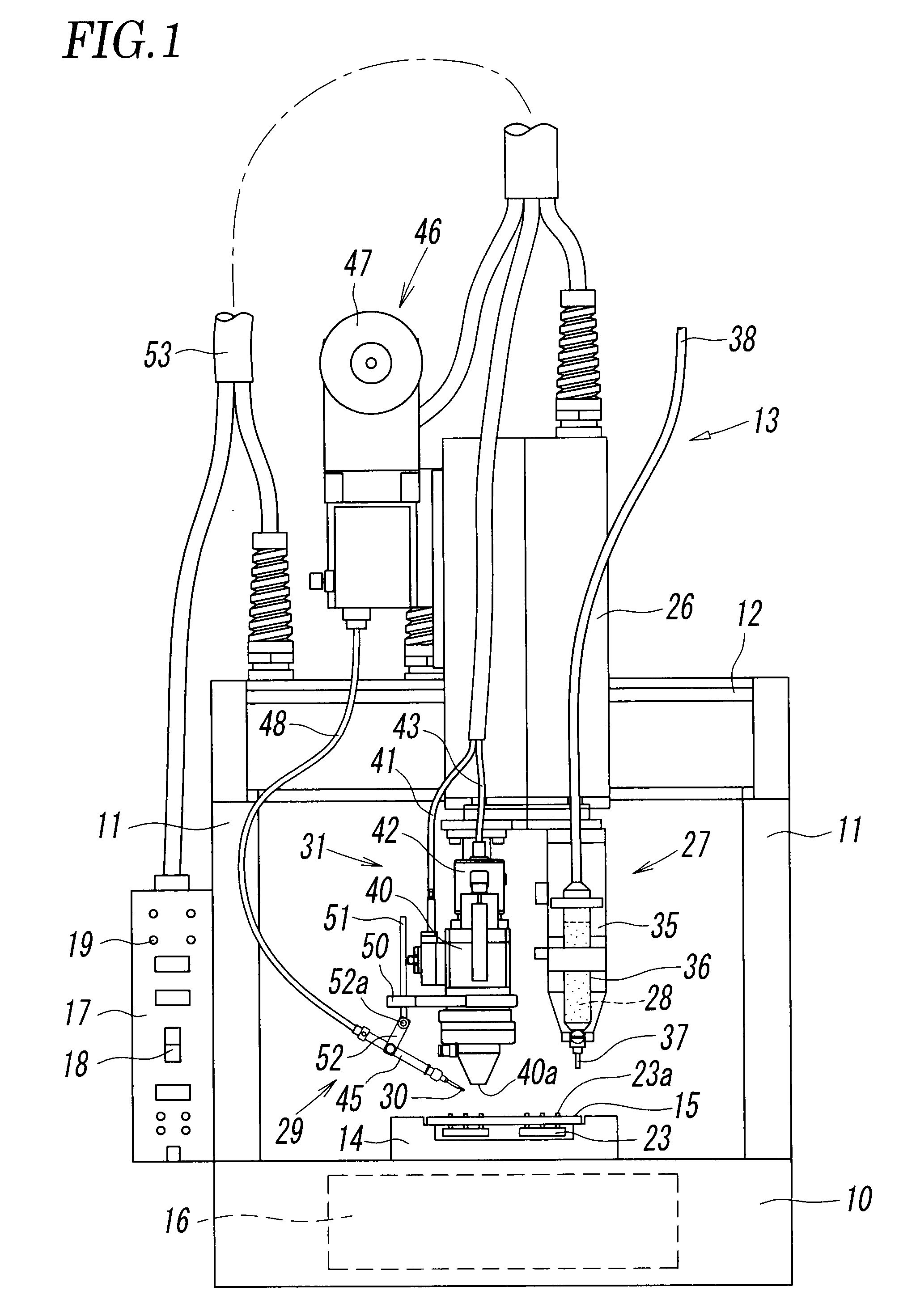
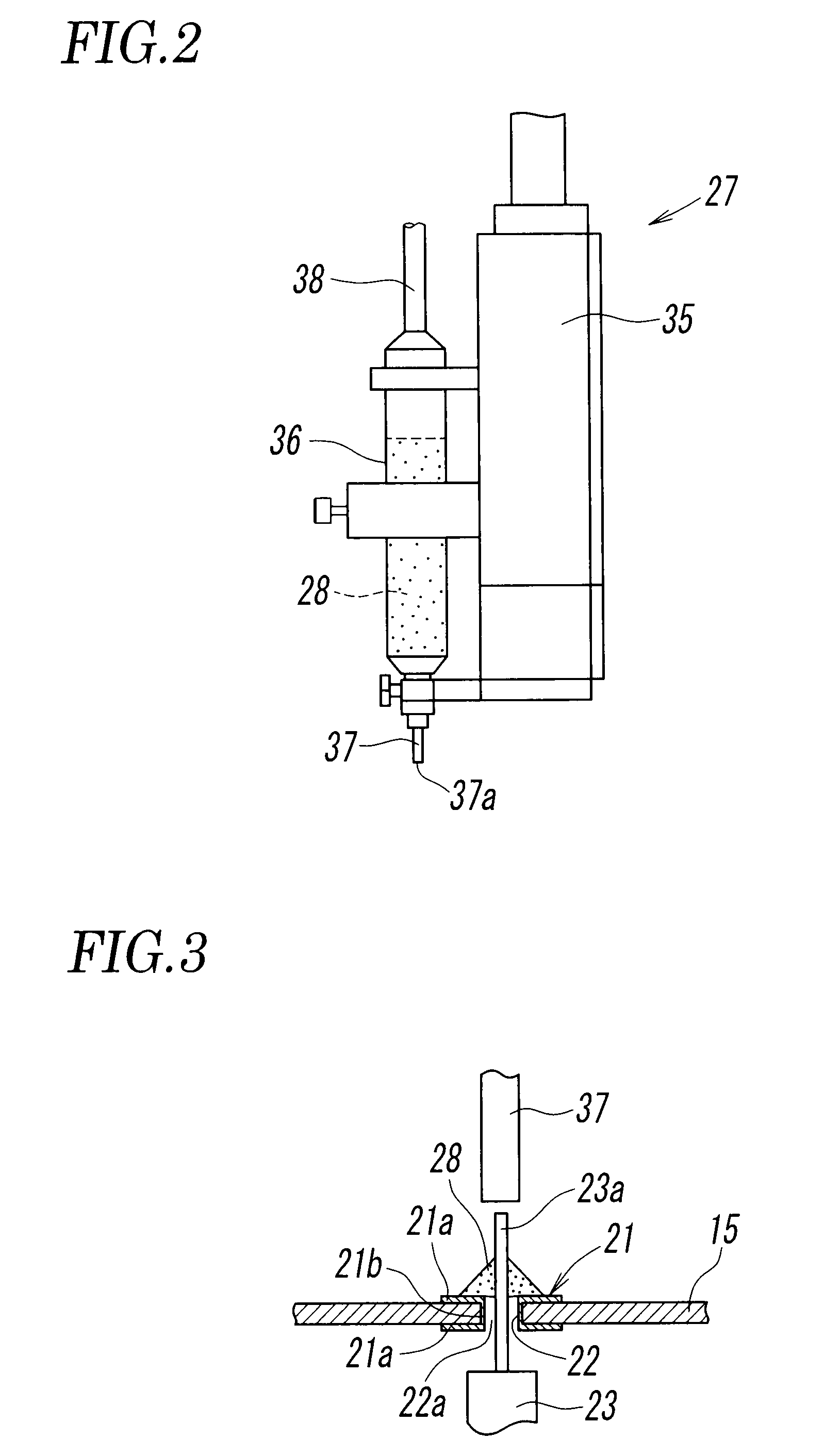
A squeezing detection control method is provided for consumable electrode arc welding. The method includes a step of detecting a droplet squeezing phenomenon by checking that a change in a voltage or resistance between the consumable electrode and base material reaches a squeezing detection reference value, and a step of executing output control for rapidly decreasing a welding current passing through a short-circuited load when the squeezing phenomenon is detected, so that arc re-striking occurs in a state of low current. The squeezing detection reference value is set to a first value during the electrode positive polarity, and set to a second value during the electrode negative polarity. The second value is different from the absolute value of the first value, and each of the first and the second values is set such that the resultant welding state is satisfactory. (FIG .2)
Owner:DAIHEN CORP
Squeezing detection control method for consumable electrode arc welding
ActiveUS8067714B2Reduce generationHigh quality weldingArc welding apparatusElectrical resistance and conductancePower flow
A squeezing detection control method is provided for consumable electrode arc welding. The method includes a step of detecting a droplet squeezing phenomenon by checking that a change in a voltage or resistance between the consumable electrode and base material reaches a squeezing detection reference value, and a step of executing output control for rapidly decreasing a welding current passing through a short-circuited load when the squeezing phenomenon is detected, so that arc re-striking occurs in a state of low current. The squeezing detection reference value is set to a first value during the electrode positive polarity, and set to a second value during the electrode negative polarity. The second value is different from the absolute value of the first value, and each of the first and second values is set such that the resultant welding state is satisfactory.
Owner:DAIHEN CORP
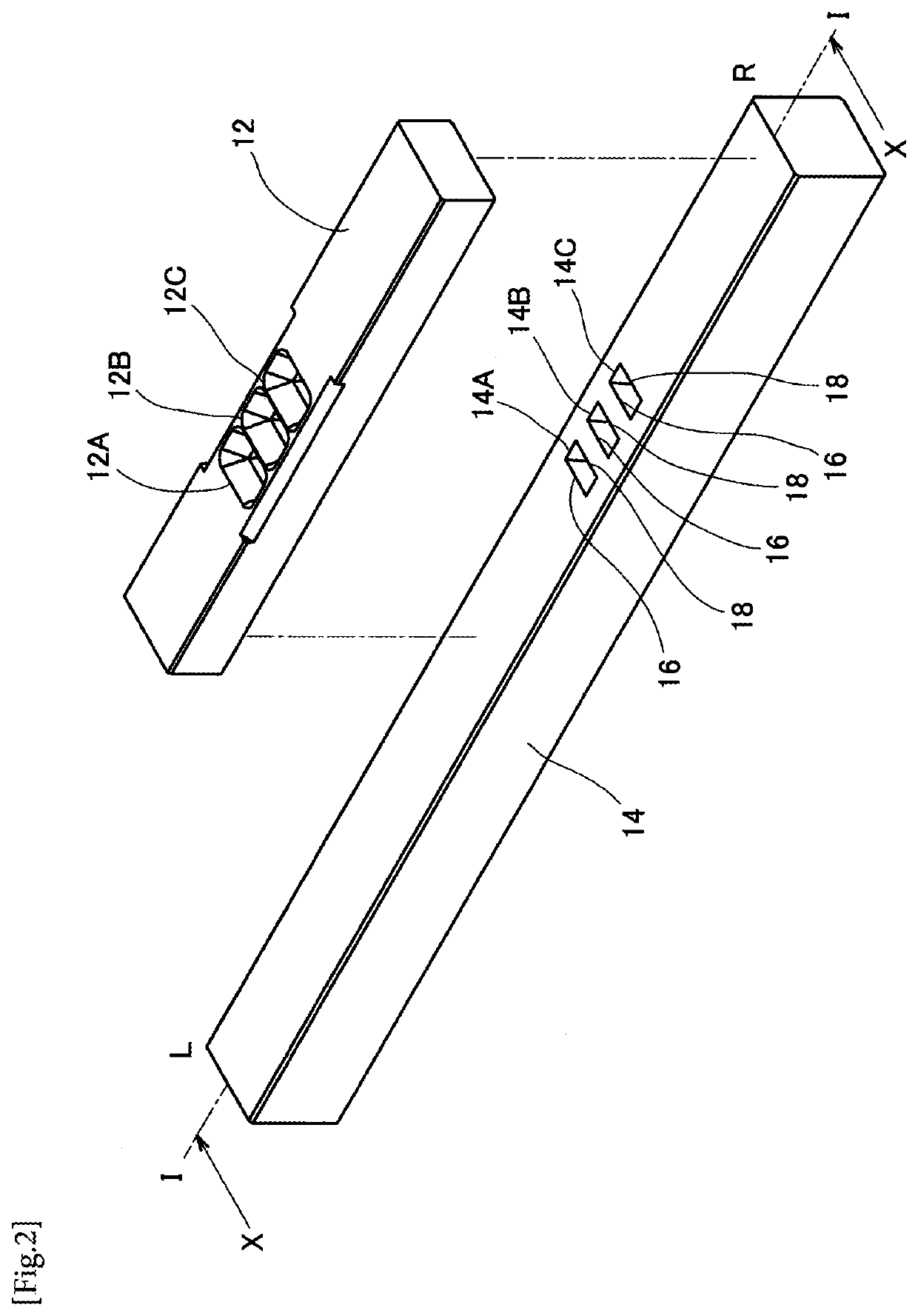
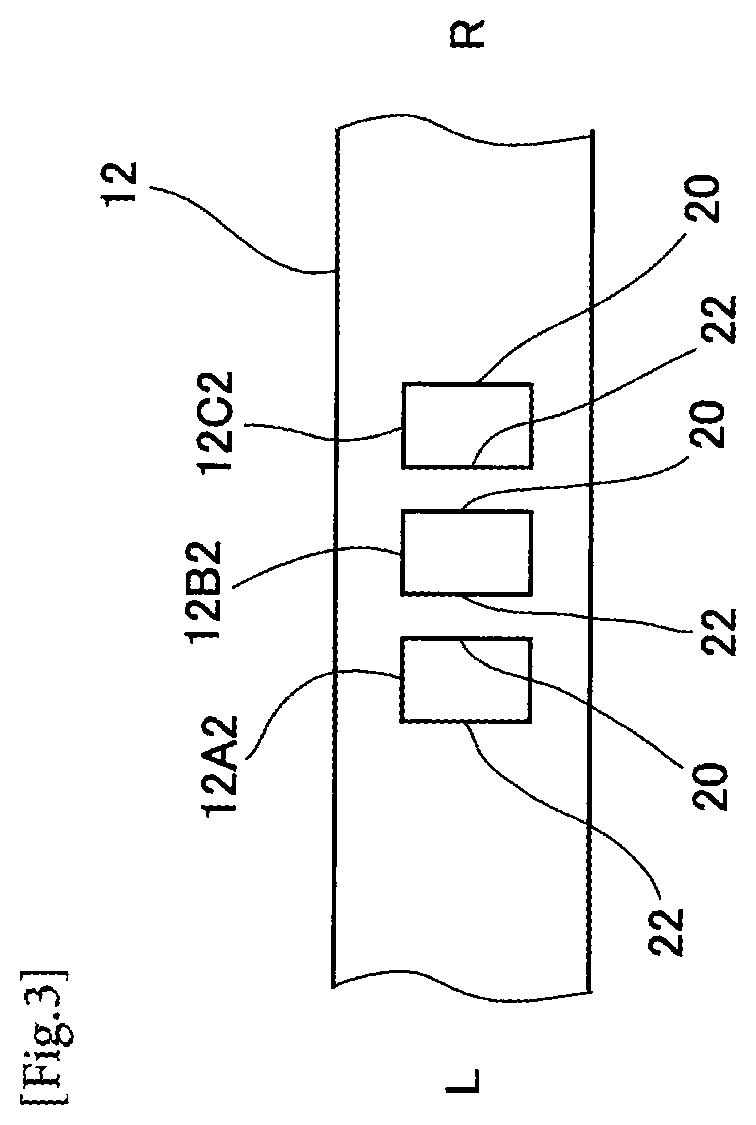
Method for connecting poles of battery cells
InactiveUS20150099152A1Simple and cost-effective connectionCost-effective connectionLine/current collector detailsElectric connection structural associationsElectrical batteryLaser beams
A method for connecting poles of two battery cells includes using a connecting element, which is configured as a stranded wire and connects the poles of the battery cells to one another. The stranded wire is connected directly to a pole of a battery cell in a welding area with a laser beam for forming a laser beam weld.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Automatic welding method of loop-weld structured but joints
InactiveCN104551344AHigh quality weldingHigh quality welding requirementsArc welding apparatusHeat treatingSoldering gun
Owner:SHANGHAI SPACE PRECISION MACHINERY RES INST
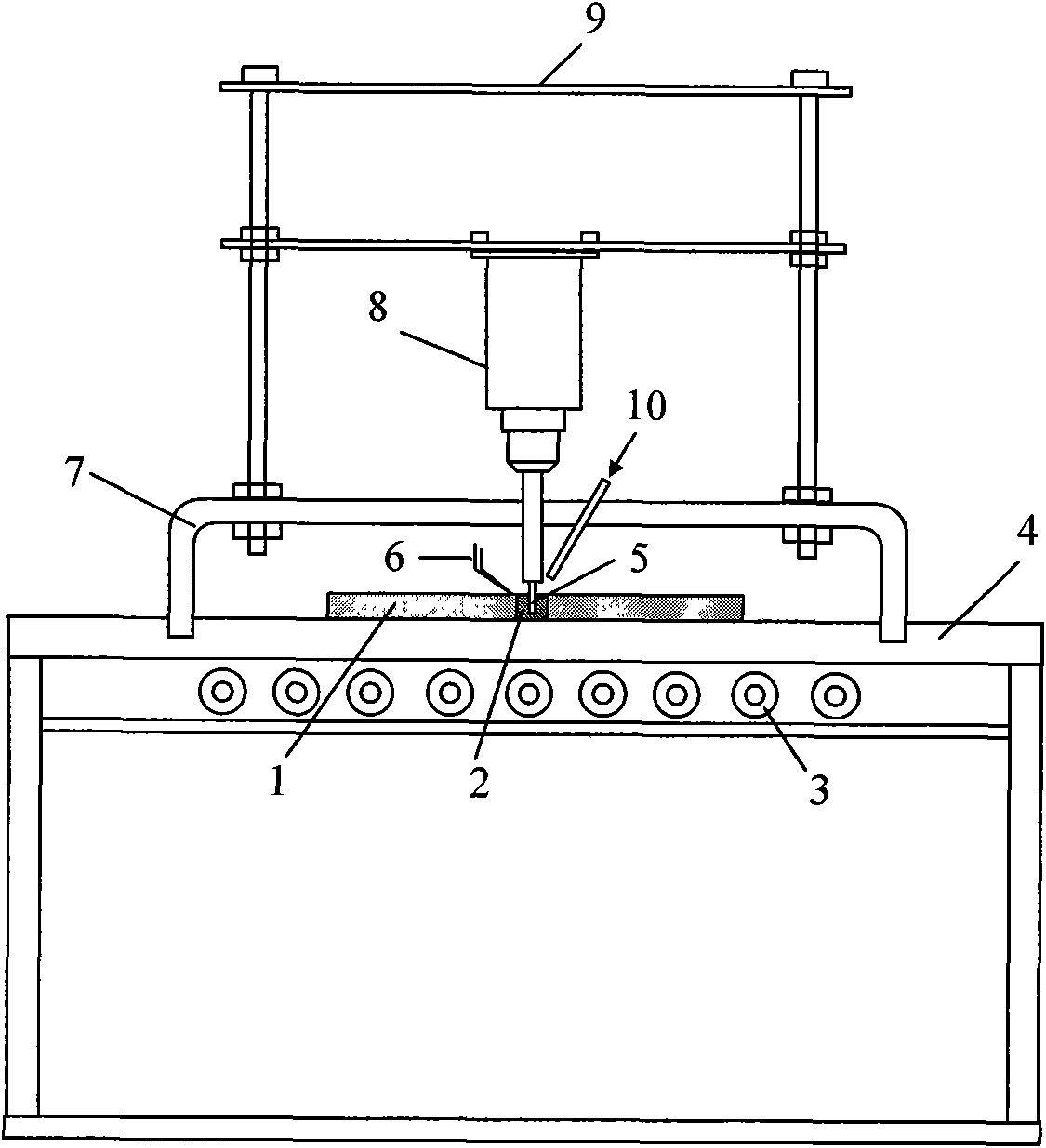
Non-vacuum semi-solid stirring brazing method for aluminum alloy and composite material thereof
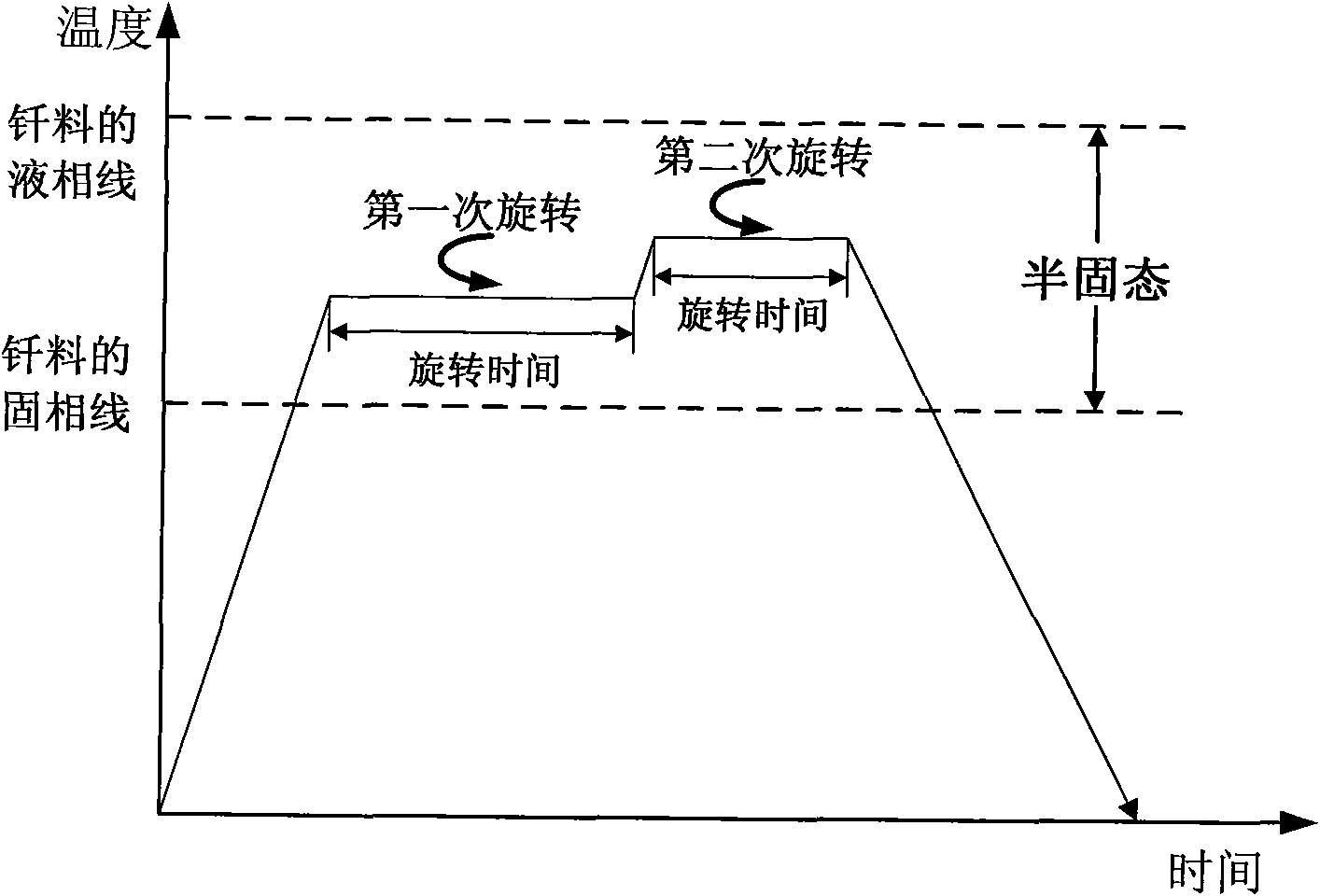
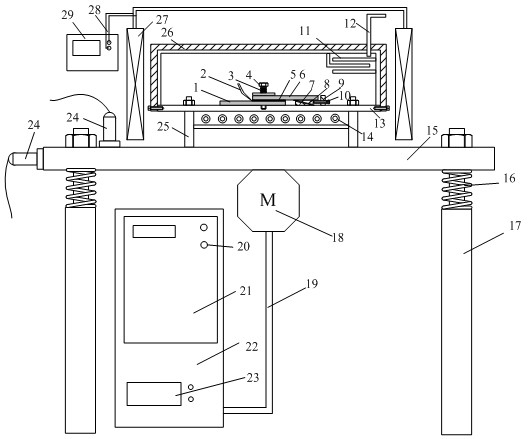
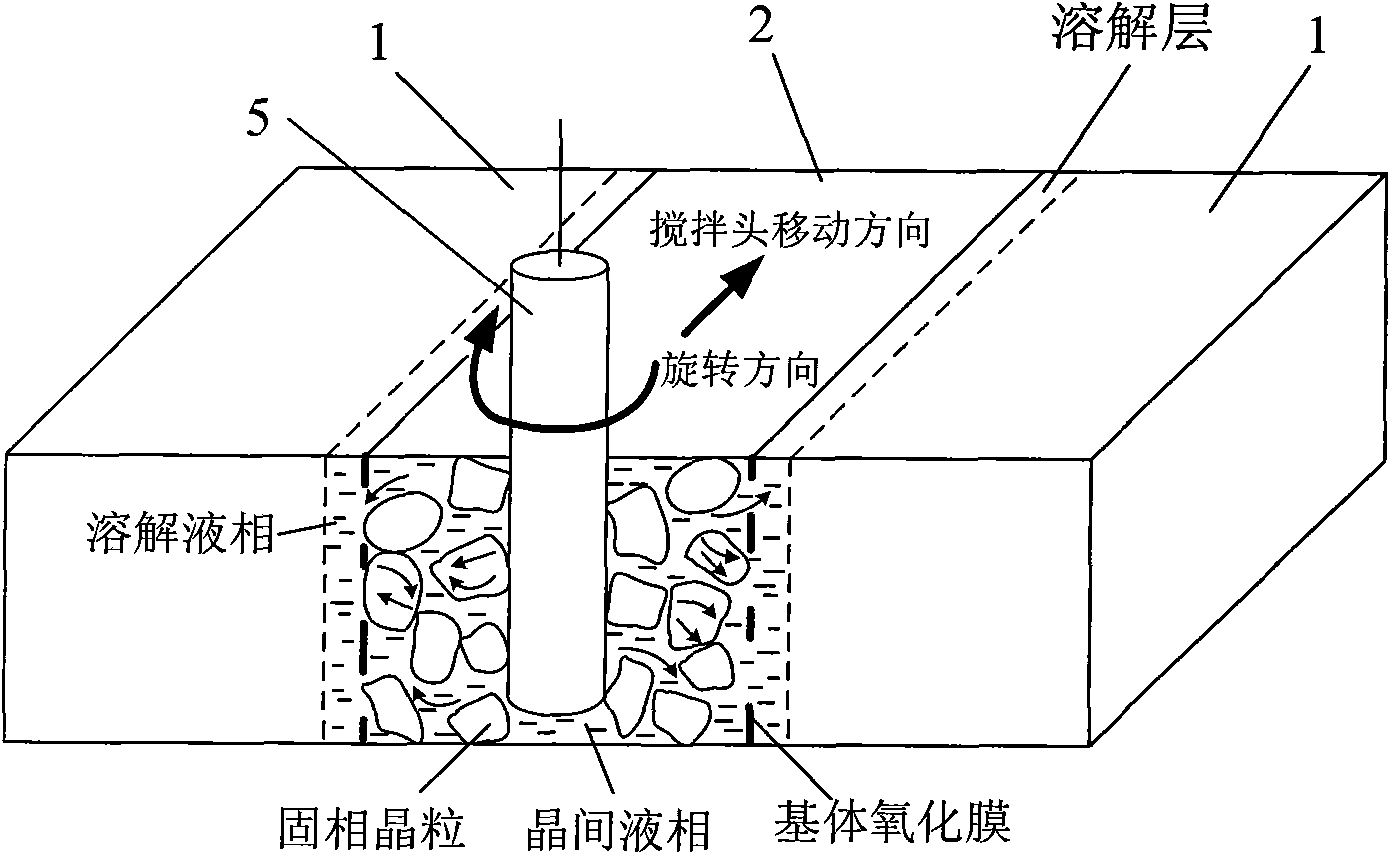
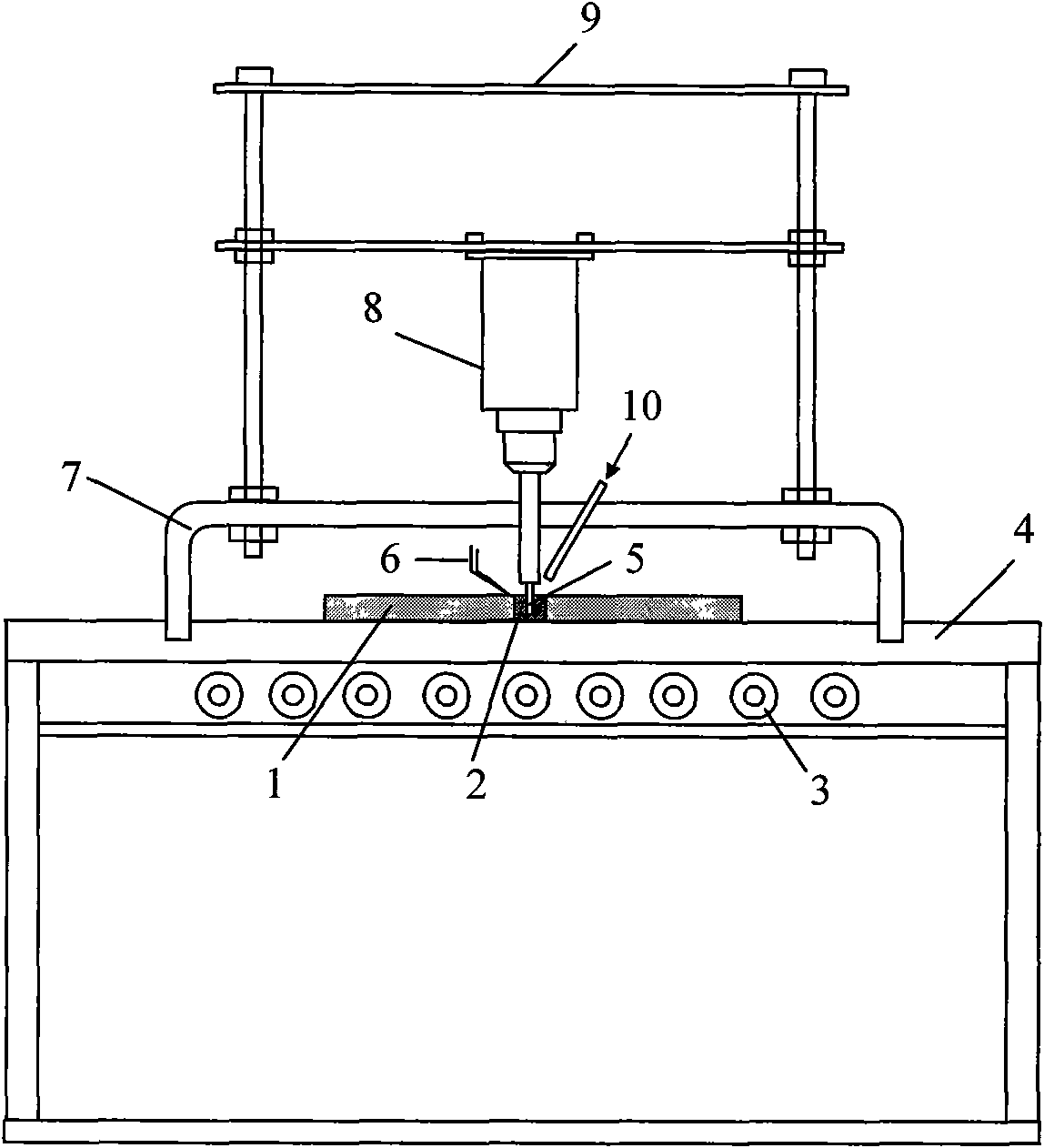
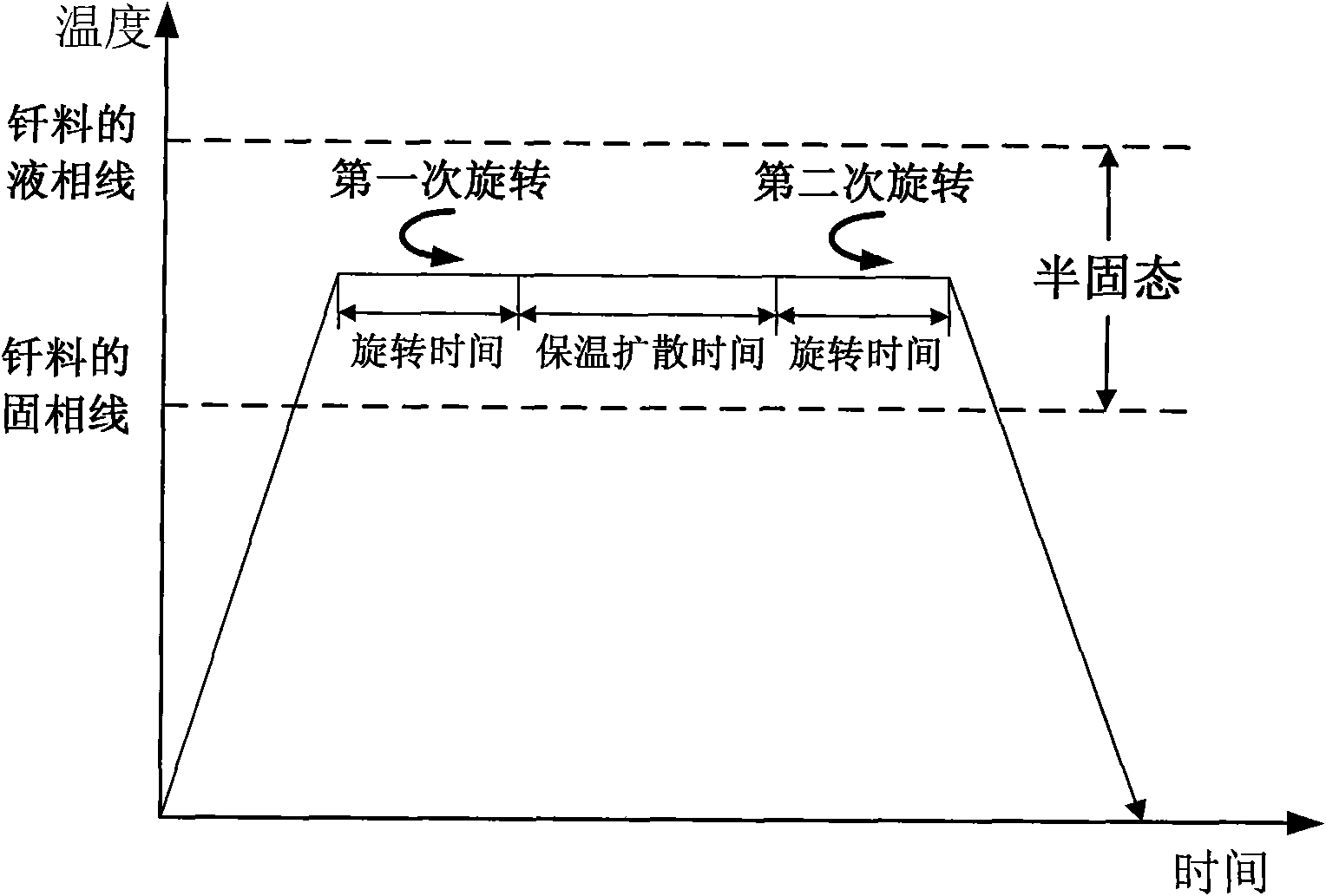
The invention provides a semi-solid brazing method for aluminum alloy and a composite material thereof under the assistance of non-vacuum mechanical stirring, which comprises the steps of: mounting a weldment taking the aluminum alloy or the composite material thereof as a base material on a welding platform first; placing intermediate-temperature solder on two surfaces to be welded, heating the weldment to between 390 and 420 DEG C, and ensuring that the solid fraction of the solder is between 50 and 80 percent; staring a rotary sliding device, wherein the rotating speed is between 150 and 300 r / m, the temperature is constant, and the longitudinal movement rate, which is parallel to a welding seam, of a stirring head is between 0.5 and 2 cm / min; stopping the rotary sliding when the stirring head moves to the terminal of the welding seam; increasing the temperature to between 430 and 450 DEG C, performing thermal insulation for 1 to 5 minutes, and ensuring that the solid fraction of the solder is between 10 and 40 percent; restarting the rotary device again, wherein the rotating speed is between 20 and 150 r / m; sliding the stirring head in a reverse direction, wherein the movement speed is between 1 and 2 cm / m; stopping the rotation, when the stirring head moves to the initial end of the welding seam, and lifting the stirring head; and cooling the solder along with a furnace after thermal insulation for 5 to 30 minutes. The method can realize the low-cost, high-efficiency and high-quality welding of the aluminum alloy or the composite material thereof.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
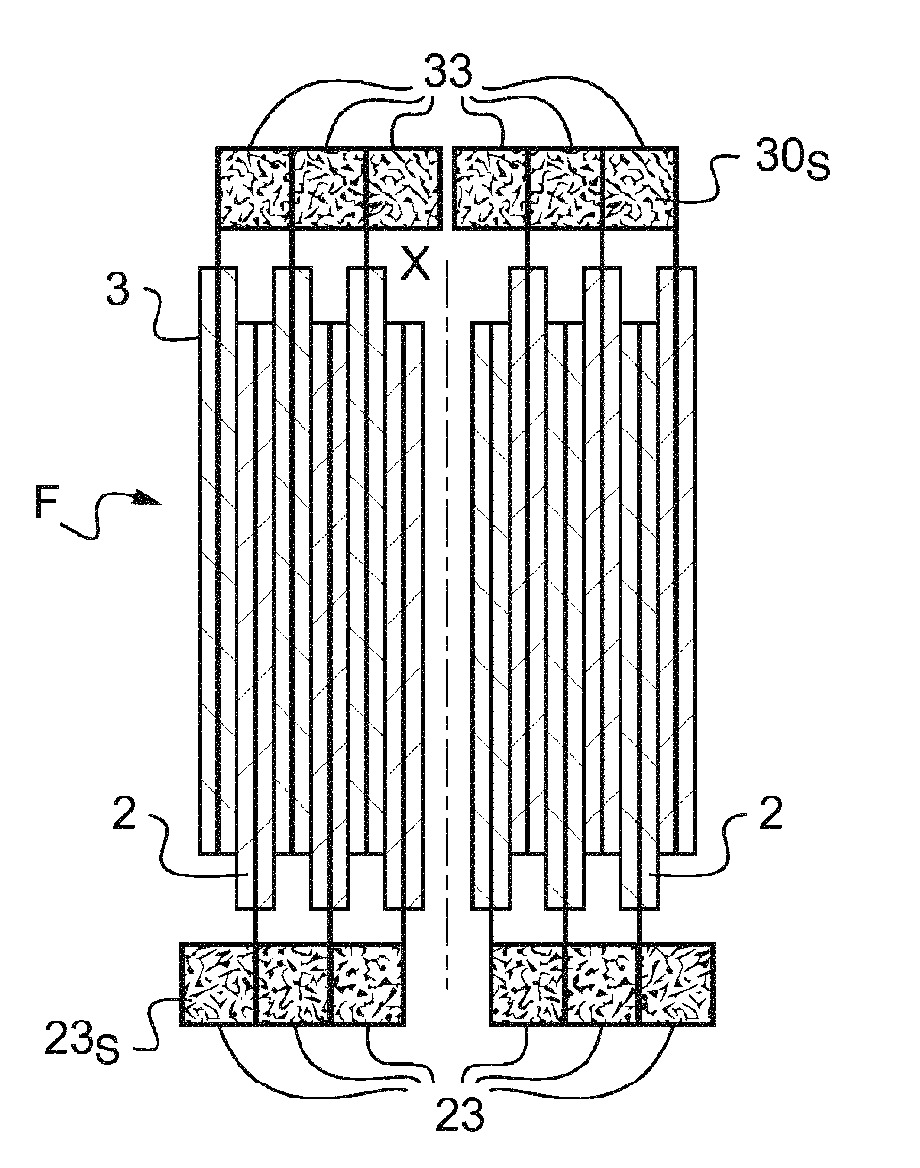
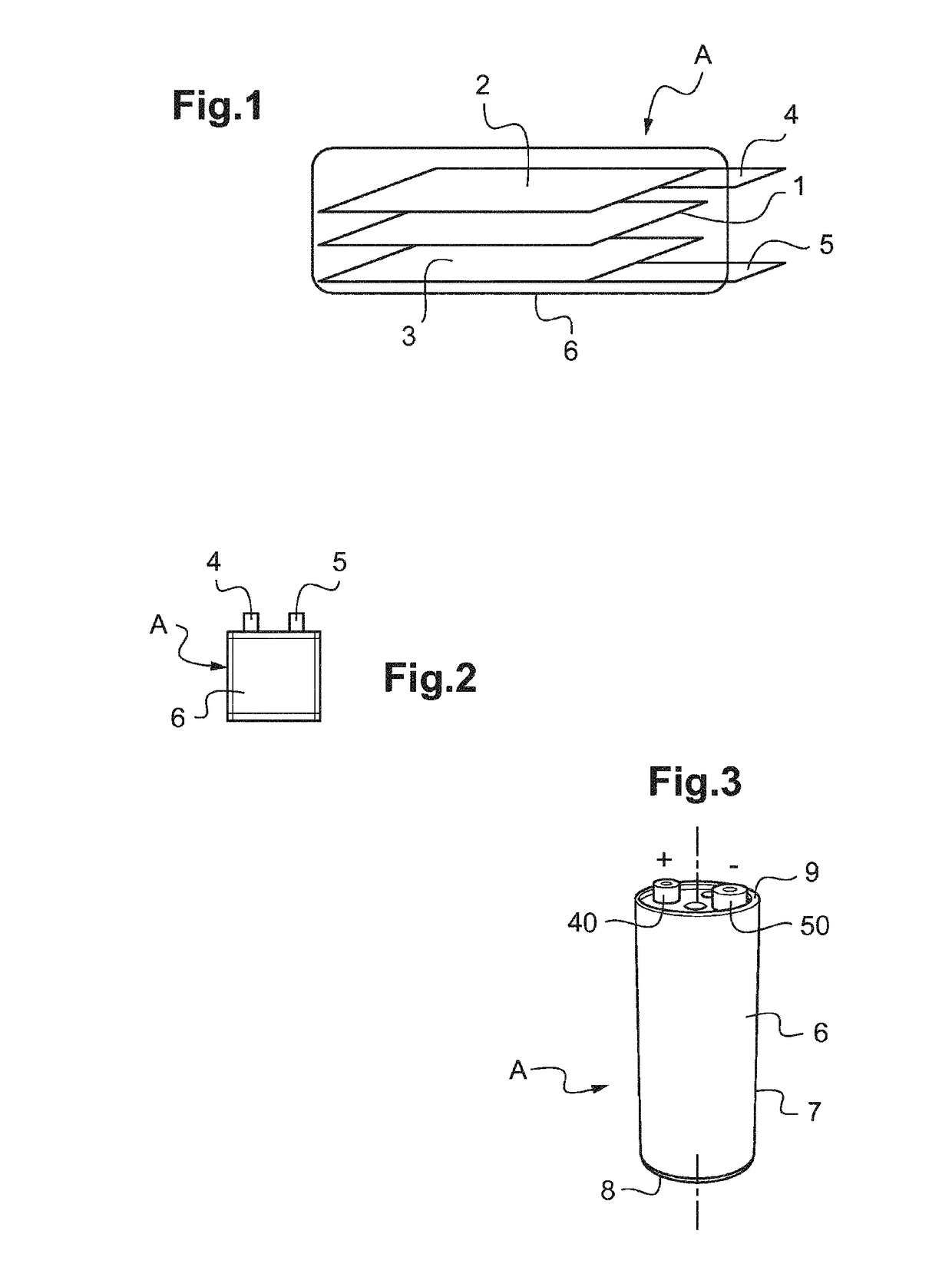
Method for producing an electrochemical bundle for a metal-ion accumulator comprising folding or coiling the foil ends around themselves
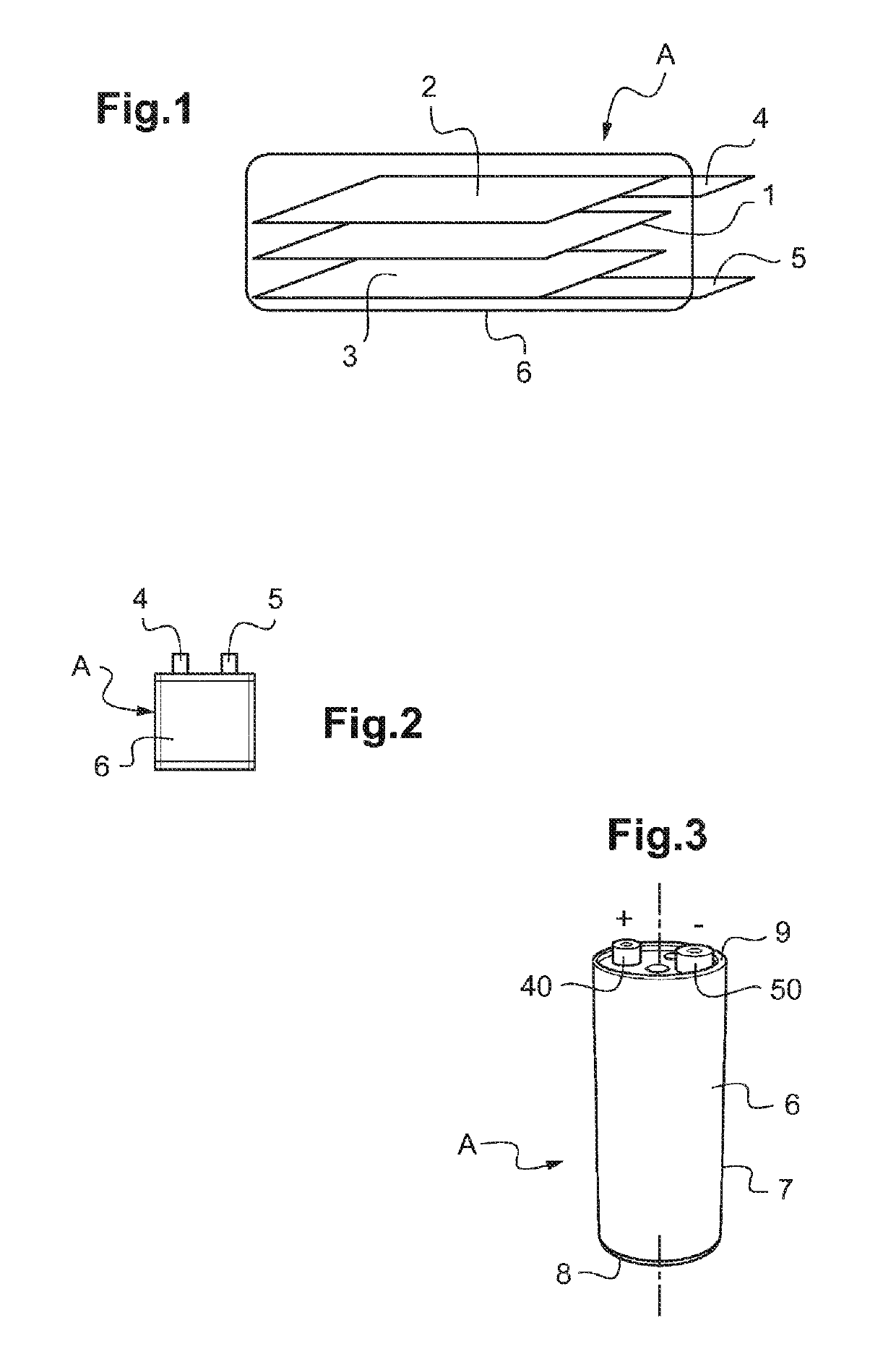
ActiveUS20180190962A1High densityRemove heatCell electrodesFinal product manufactureElectrical batteryElectrical connection
The invention relates to a method for producing an electromechanical bundle for a metal-ion battery, for electrical connection thereof to the output terminals of the battery, characterised by coiling or folding the sides of at least one of the two electrodes on itself, then compacting by packing in order to further increase the density of the coiled sides in order to weld the electrode to a current collector.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Method and apparatus for laser soldering
ActiveUS20090321394A1High quality weldingEliminate the problemPrinted circuit assemblingMetal working apparatusMetallurgyIrradiation
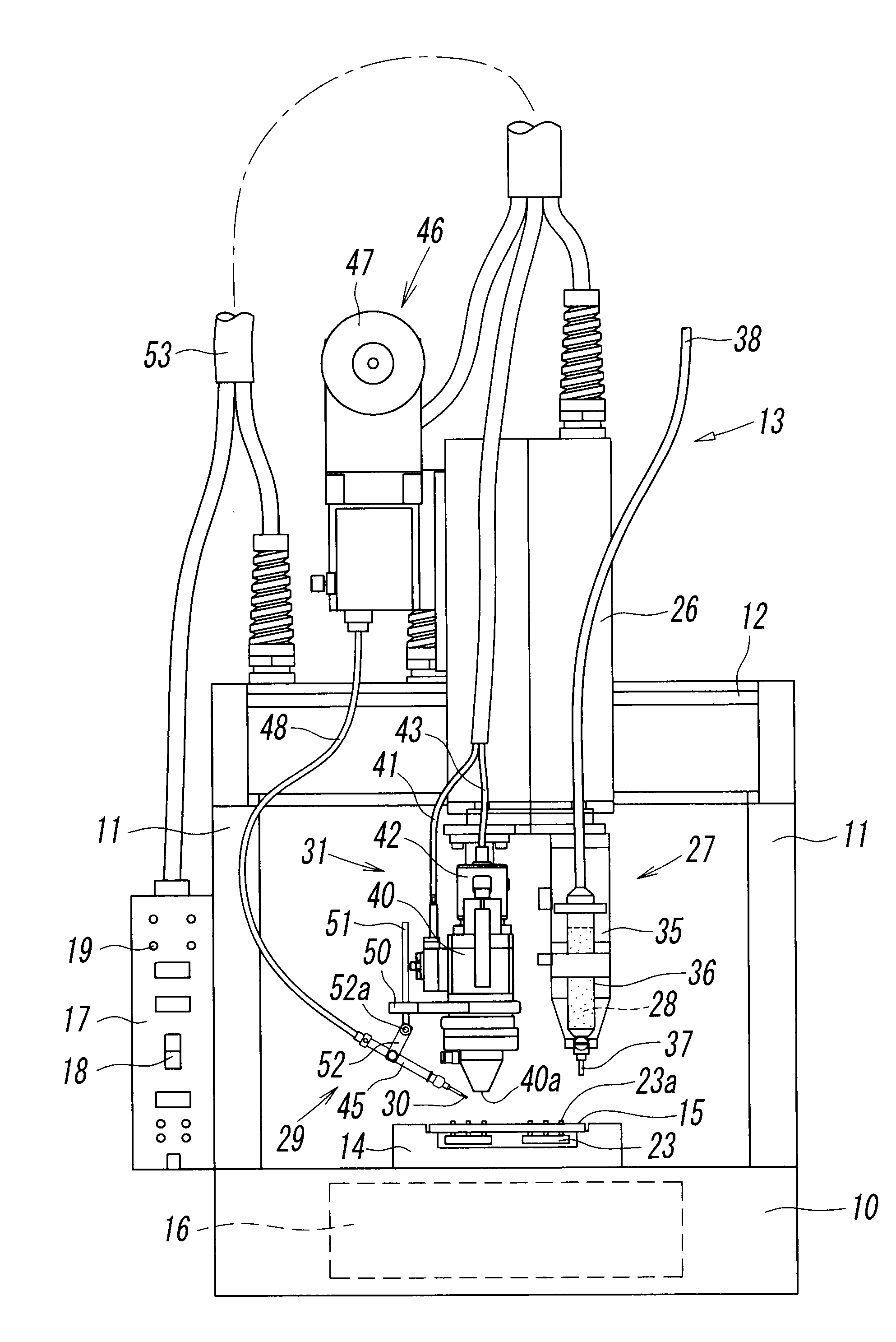
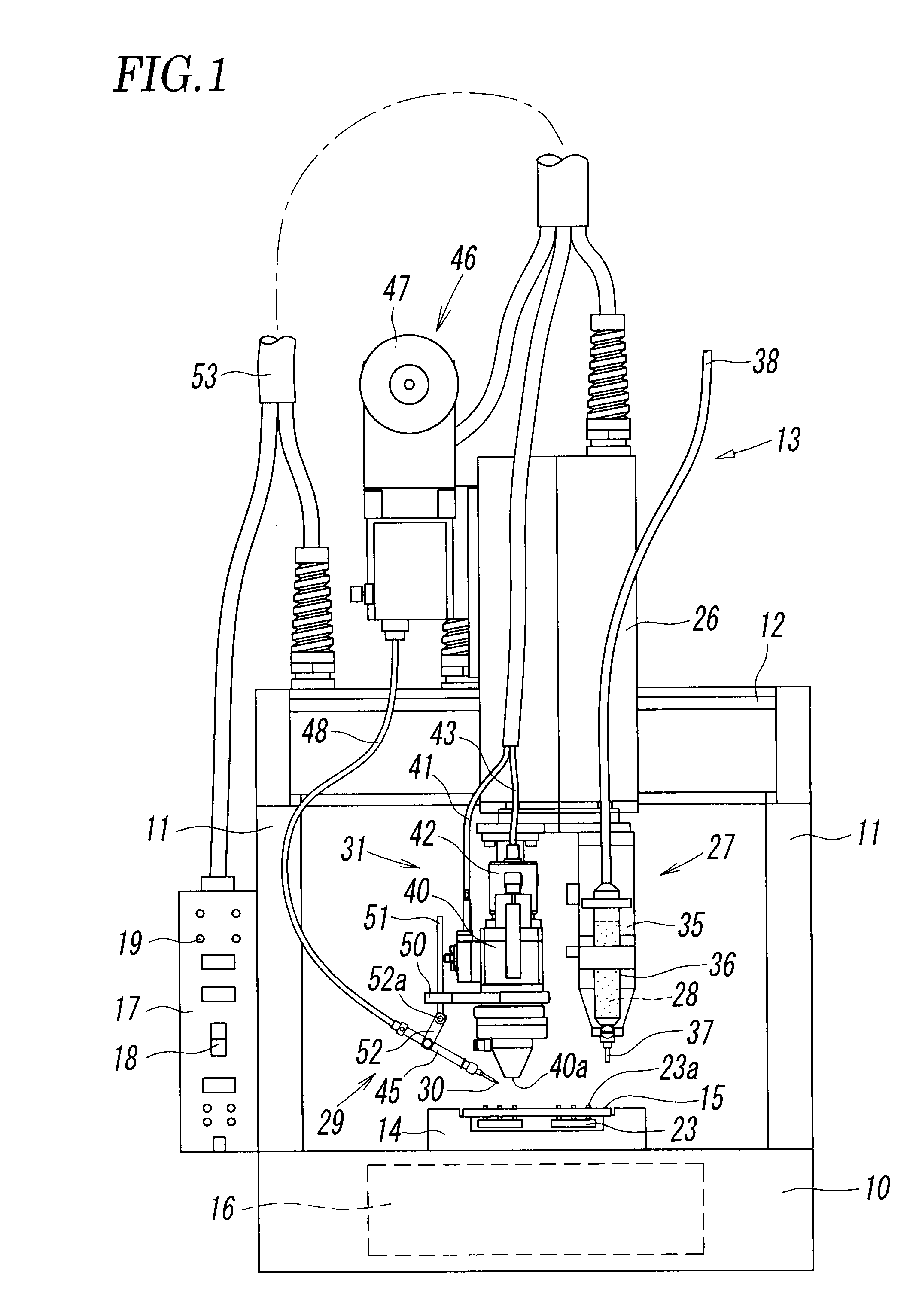
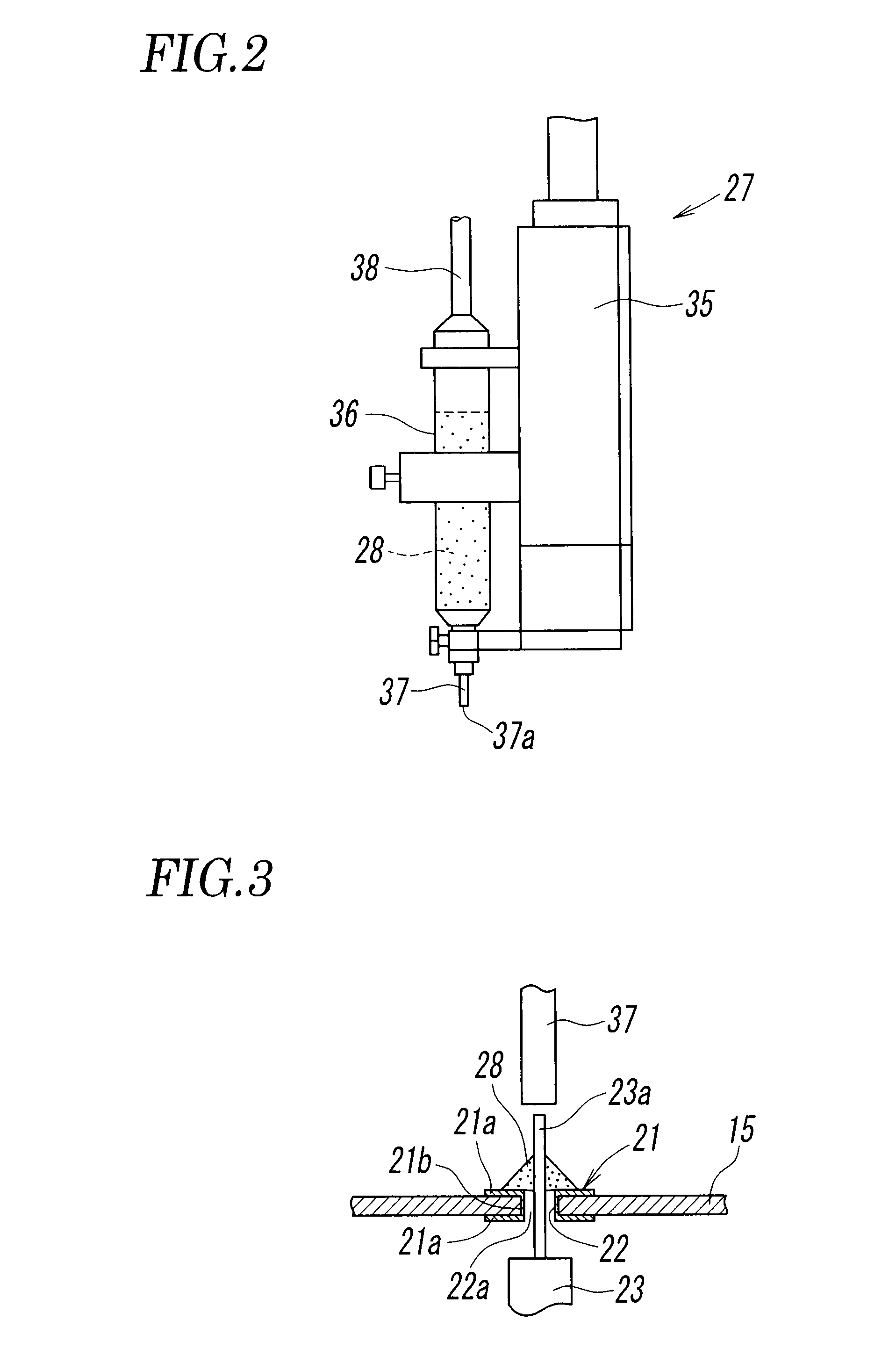
In accordance with an aspect of the invention, a solder paste feeding device feeds solder paste to a ring-like terminal surrounding a through-hole and a rod terminal fitted in the through-hole so as to fill in the through-hole, the laser beam irradiation device irradiates the solder past with a laser beam, and wire solder is further fed from above the solder past at the same time as melting of the solder paste is started, thereby fusing the wire solder and the solder paste to solder the ring-like terminal and the rod terminal.
Owner:JAPAN UNIX
Magnesium alloy and aluminum alloy heterogeneous non-vacuum mechanical forced rotation semi-solid brazing method
InactiveCN102284758ALow costHigh quality weldingSoldering apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesSemi solidMagnesium alloy
The invention relates to a magnesium alloy and aluminum alloy heterogeneous non-vacuum machinery forced rotation semi-solid brazing method; a magnesium alloy weldment and an aluminum alloy weldment are clamped on a clamp, Zn-Sn or Zn-Al-Sn system other brazing materials are arranged on two surfaces to be brazed, the weldments are heated, the heating temperature is between 350DEG C to 450DEG C, simultaneously pressure is increased, the pressure range is 0.1MPa to 1MPa, so that the brazing materials on a middle layer are in a semi-solid state, a rotary device is started, the rotating speed is 65r / min to 1500r / min, the temperature is constant during a rotation process, and the rotation time is 10s to 300s. After the rotation, the temperature rises by a certain rate, the heat is insulated at preset temperature, so that the brazing materials dissolve parent materials with a certain thicknesses, the heat insulating temperature is between 400DEG C to 480DEG C, and the heat insulating time is1min to 5min. Afterwards, pressure is increased, the pressure range is 0.1MPa to 1MPa, the rotary device is started again (secondary rotation), the rotating speed is 65r / min to 600r / min, rotation is stopped after 3s to 60s, and cooling is carried out with a furnace after the heat is insulated for 5 min to 30min. The magnesium alloy and aluminum alloy heterogeneous non-vacuum machinery forced rotation semi-solid brazing method can realize the high-efficiency, high-quality and economic connection of a magnesium alloy and an aluminum alloy.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
A semi-solid vibration assisted brazing equipment
InactiveCN102275023AHigh quality weldingReduce generationSoldering apparatusMetal working apparatusPhysicsHeat transfer process
The invention provides a semisolid vibrating auxiliary brazing device which comprises a brazing part, a mechanical vibrating part, an electromagnetic vibrating part and a control part, wherein a vibration exciter is mounted under the middle position of a vibrating platform; a brazing platform is mounted above the middle position of the vibrating platform; an electromagnetic coil is arranged around the brazing platform; the electromagnetic coil, the vibrating platform and the brazing platform are free from being contacted with each other; the vibration exciter is used for driving the vibratingplatform and the brazing platform on the vibrating platform to vibrate; and the electromagnetic coil is used for generating electromagnetic stirring and vibration. Under the effect of the electromagnetic stirring and vibration, the mass transfer and heat transfer processes in a molten-pool molten metal crystallizing process are changed, thereby changing the crystallizing direction of a crystal grain, refining primary tissue, reducing segregation, promoting mechanical property of brazing joint, reducing the sensibility of the brazing defects, such as pore, crack, and the like, and realizing the high-efficient high-quality brazing between aluminum alloy and magnesium alloy as well as realizing the homogeneous brazing of the magnesium alloy and the aluminum alloy.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Anti-vacuum semi-solid states stirring soldering method of magnesium alloy and composite material thereof
The invention provides an anti-vacuum semi-solid states stirring soldering method of magnesium alloy and composite material thereof, which comprises the following steps of: a weldment taking the magnesium alloy or the composite material thereof as a parent metal is arranged and blocked on a welding platform and medium temperature brazing filler metal is put on two surfaces to be welded; the weldment is heated in the temperature of 380 to 430 DEG C to cause that the solid phase ratio of the brazing filler metal is between 50 to 80%; hereupon, a rotational sliding device is started; the rotary speed is 150 to 300 r / m; the temperature is constant; a stirring head is parallel to the longitudinal movement speed of 0.5-2cm / min of a welding line; when the stirring head moves to the terminal of the welding line, the rotational sliding stops; the holding time is 1 to 5 minutes so that the weldment is further dissolved; the rotational device is started again; the rotary speed is 20 to 150 r / m; the stirring head slides in a negative direction; the movement speed is 1 to 2 cm / min. When the stirring head moves to the initial end of the welding line, the rotary stops; the stirring head is lifted; the holding temperature is 5-30 minutes, and a furnace cools. The method can realize the low cost, high efficient, high quality welding of the magnesium alloy and the composite material thereof.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Laser multi-beam compound temperature field welding device
ActiveCN108890128AHigh quality weldingGood reference valueLaser beam welding apparatusFusion weldingOptoelectronics
The invention relates to a laser multi-beam compound temperature field welding device. The device at least comprises a deep penetration welding laser head, a preheating laser head, a slow cooling laser head and an infrared temperature field measuring device, wherein the deep penetration welding laser head is arranged on a spindle and used for emitting main welding laser beam for fusion welding onwelding parts; the preheating laser head is used for emitting preheating laser beam in the fusion welding process of the welding parts and is adjustably arranged on the periphery of the spindle through the position of a first movement mechanism; the slow cooling laser head is used for emitting slow cooling laser beam in the fusion welding process of the welding parts and is adjustably arranged onthe periphery of the spindle through the position of a second movement mechanism; the infrared temperature field measuring device is arranged in a preset range of the deep penetration welding laser head, and used for measuring the temperature in a compound temperature field formed by the main welding laser beam, the preheating laser beam and the slow cooling laser beam through fusion welding during welding in real time.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING AERONAUTICAL MFG TECH RES INST
Non-vacuum semi-solid mechanically assisted rotary brazing method for magnesium alloy and its composite materials
InactiveCN102284760ALow costHigh quality weldingSoldering apparatusNon-electric welding apparatusVacuum assistedSemi solid
The invention relates to a non-vacuum semi-solid machine-assisted rotary soldering method for a magnesium alloy and a composite material thereof, which comprises the following steps of: clamping the magnesium alloy and a composite material weldment thereof on a fixture, putting Zn-Sn or Zn-Al-Sn solders and the like on two surfaces to be welded, heating the weldment at the temperature of between 350 and 450 DEG C, and applying pressure of 0.1 to 1MPa to make the solder in an intermediate layer positioned in a semi-solid state; starting a rotating device, rotating at a speed of 65 to 1,500r / min for 10 to 300 seconds, and keeping the temperature constant in the rotating process; raising the temperature at a certain heating rate after rotation is stopped, and preserving heat at the predetermined temperature of between 400 and 480 DEG C for 1 to 5 minutes to make the solder dissolve parent metal with certain thickness; and applying pressure of 0.1 to 1MPa, starting the rotating device again, rotating for the second time at a speed of 65 to 600r / min for 3 to 60 seconds, stopping rotation, preserving heat for 5 to 30 minutes, and cooling with a furnace. By the method, the magnesium alloy and the composite material thereof can be efficiently and economically connected at high quality.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Welding device used for copper craft production
InactiveCN111375979AReduce weldingHigh quality weldingWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesWelding defectPhysics
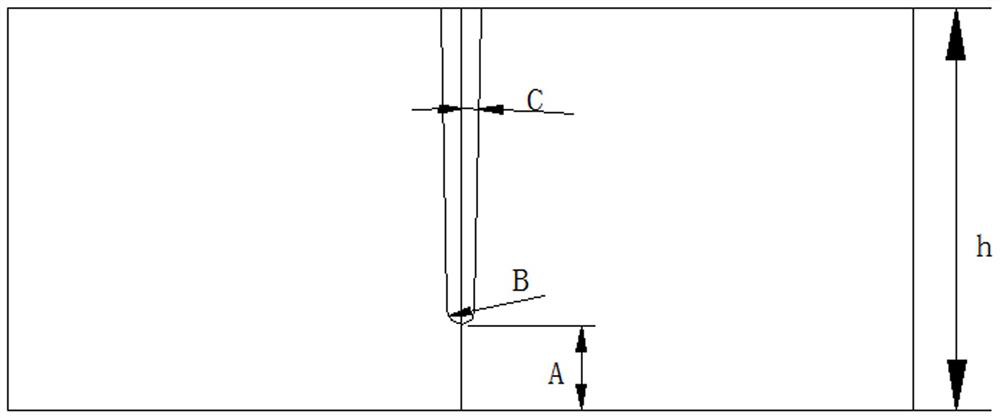
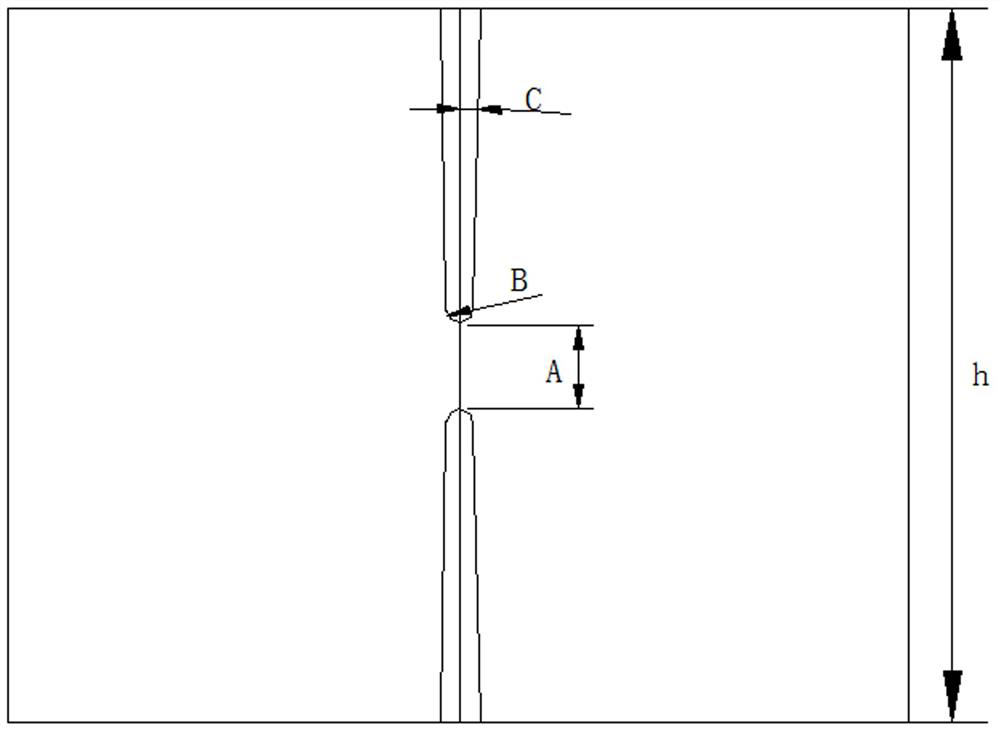
The invention belongs to the technical field of copper craft production, and particularly relates to a welding device used for copper craft production. According to the solution adopted to solve the problem of welding defects caused by mismatching of the connected portions of two parts during vertical welding of sleeve parts with the same inner diameter and different outer diameters, the welding device comprises a base which is open upwards and is of groove-shaped structure, wherein a C-shaped steel sliding rail which is open upwards is fixed to the middle of the bottom of the base, a baffle is fixed to the middle of the groove bottom of the C-shaped steel sliding rail, a bidirectional screw rod is rotatably connected to the middle of the baffle, and the two ends of the bidirectional screwrod are sleeved with sliding blocks respectively. When the welding device used for copper craft production is used for welding a vertical weld tube, extension rods of hydraulic ejection rods can be controlled to extend to enable two arc clamping plates to move towards the middle to generate an oblique downward thrust, and at this moment, a downward force component is generated to tightly press the vertical weld tube on a tube holder, so that welds are minimized, and the welding quality is improved.
Owner:宁波鄞州区景行远望科技服务有限公司
Laser welding apparatus
ActiveUS20120080413A1Uniform flow rateUniform welding qualityLaser beam welding apparatusOptical axisEngineering
Together with a scanner device, an air blower is provided above a workpiece, and the air blower exhausts air in the shape of a ring toward the workpiece, the air in a ring shape surrounding an optical axis of a laser beam emitted from the scanner device. A housing of the air blower is formed in a ring shape, a ring-shaped cavity is formed in the housing, an inner ring member is attached to an undersurface of the housing, an outer ring member is attached to an outer peripheral side of the inner ring member, and a ring-shaped exhaust port is formed between the inner ring member and the outer ring member. An exhaust direction of the air is defined by inclination of an outer-peripheral-side end surface of the inner ring member and inclination of an inner-peripheral-side end surface of the outer ring member (FIG. 2).
Owner:SUZUKI MOTOR CORP
Electrode unit and resistance welding device
InactiveUS20110127239A1Simple and compact arrangementOvercome deficienciesResistance electrode holdersOhmic-resistance electrodesElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
An electrode unit configuring a resistance welding device is provided with a first chassis section and a second chassis section. A plurality of stepped hole sections are formed in the first chassis section, and an electrode pin is slidably provided in each stepped hole section. On the head section of the electrode pin, a resin ball configuring a welding pressure adjusting mechanism is disposed. In the second chassis section, a screw hole is formed coaxially with each stepped hole section, and a setscrew configuring an extrusion output adjusting mechanism for adjusting an extrusion output of the electrode pin is screwed into each screw hole.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Conveyor for sheet-shaped thin plate and method of conveying same
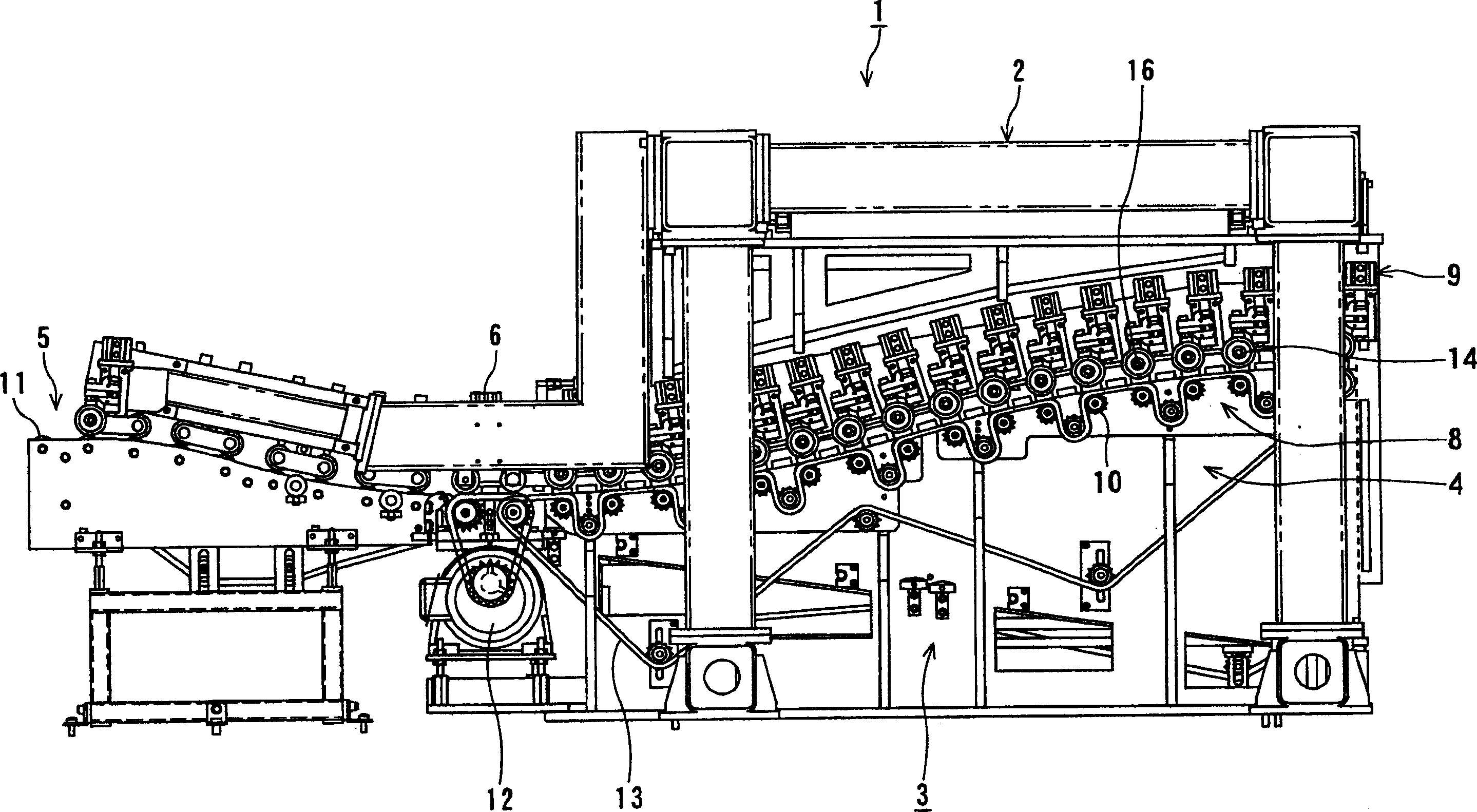
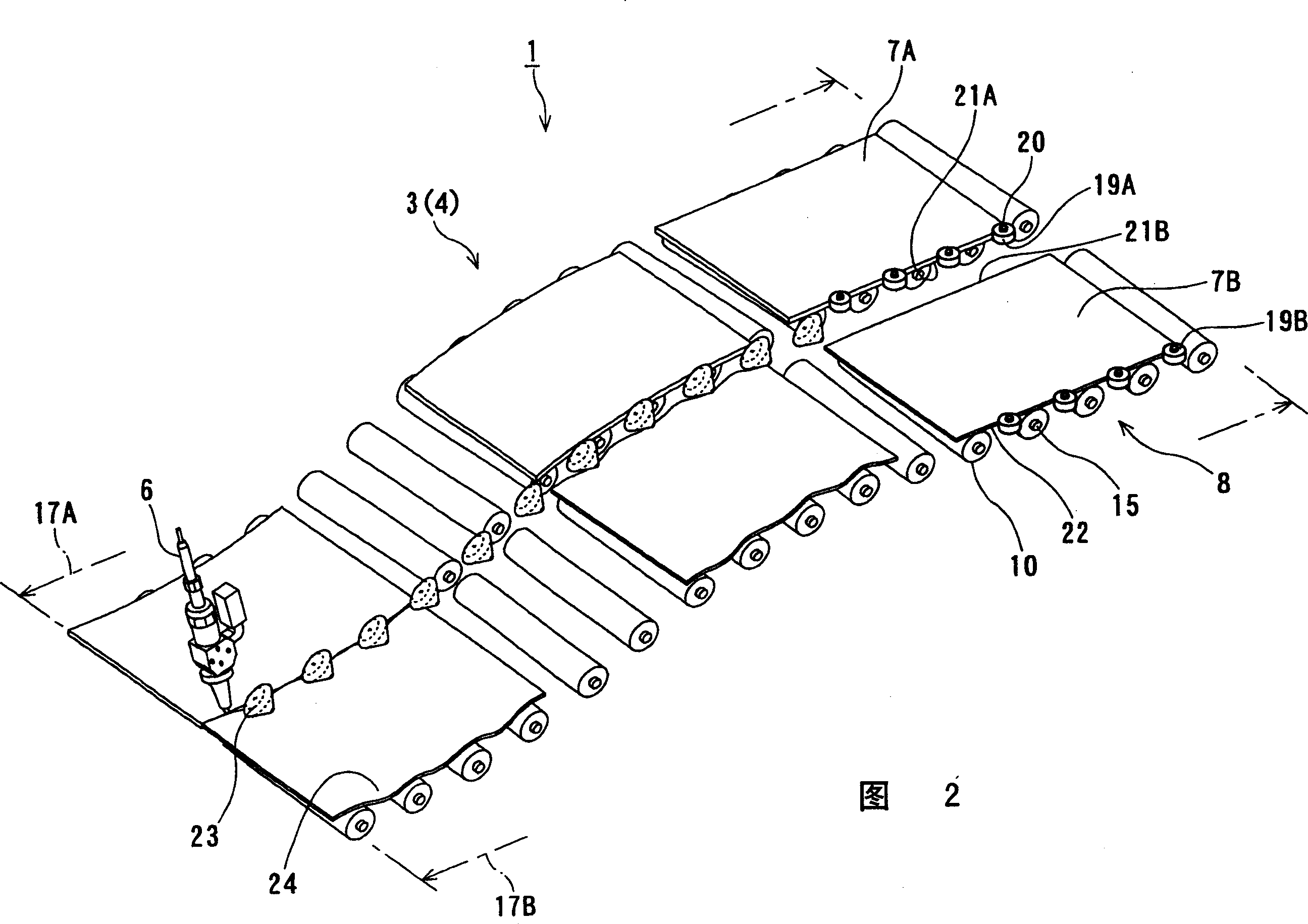
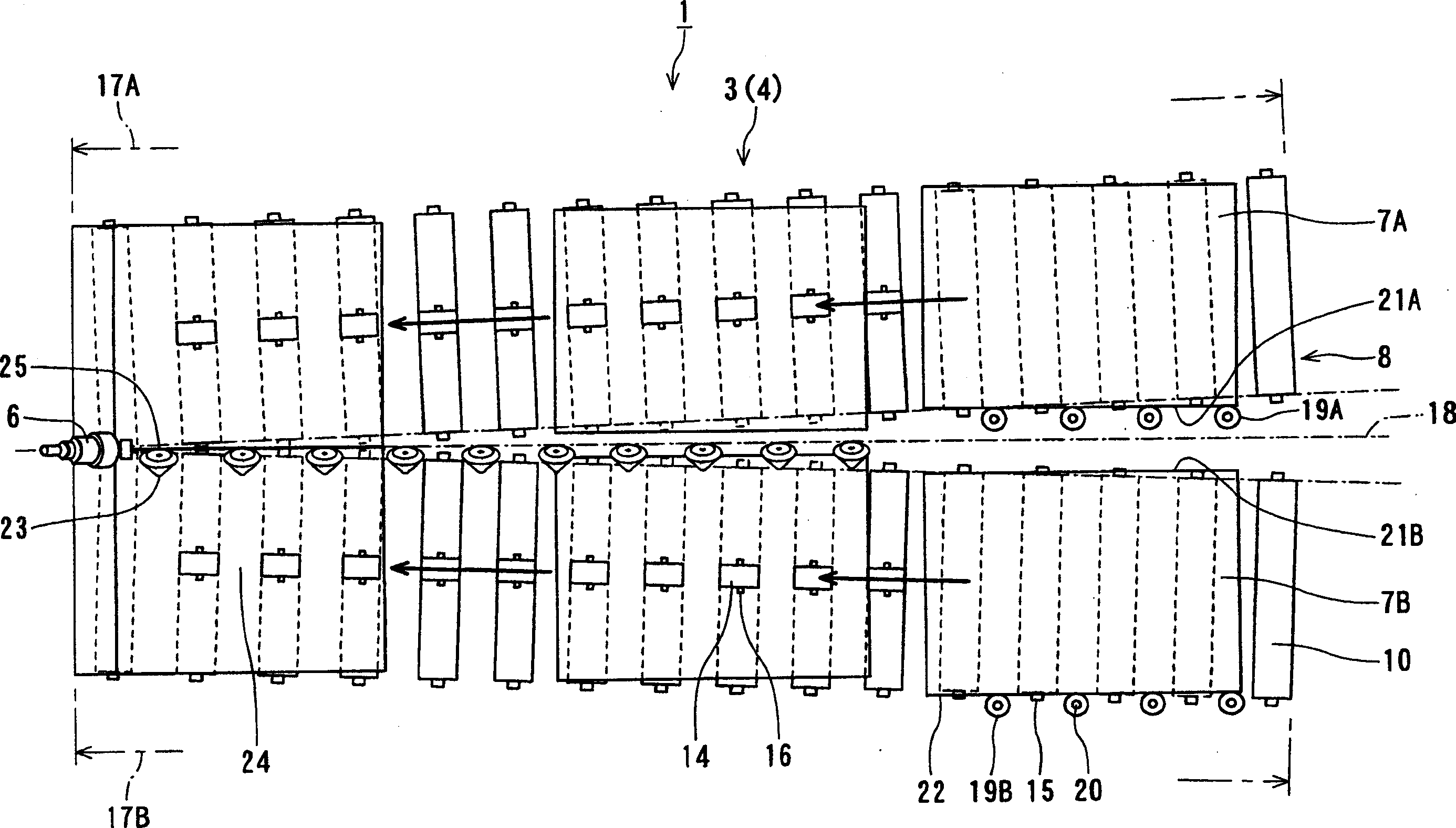
InactiveCN101357427ALess adjustment workImproved butt weld performanceWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A conveyor for guiding and conveying a plurality of sheet-shaped thin plates in rows arranged side by side to a welding position at which ends of the adjacent thin plates are butted and welded to each other, includes a plurality of conveying paths, which are adjacent to each other, having different conveying surfaces which are placed on a same horizontal plane, and a guide unit disposed between the adjacent two conveying paths for guiding the thin plates on one of the conveying paths with respect to another one thereof toward the welding position. Each of the conveying paths is composed of a plurality conveying rollers, and the guide unit includes guide rollers each having a guide surface for guiding the thin plate on the one of the conveying paths in a state that the thin plate on the one conveying path is partially depressed with respect to the another one of the conveying path.
Owner:SUZUKI MOTOR CORP
Self-guide welding machine
ActiveCN103934546ASimple structureLow manufacturing costWelding/cutting auxillary devicesArc welding apparatusSelf guidedPulley
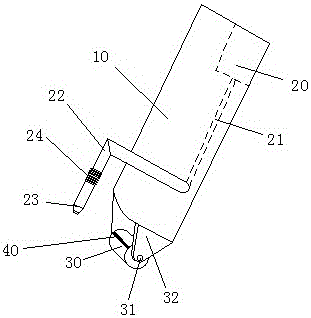
A self-guide welding machine comprises a machine frame and a welding gun, wherein the welding gun is arranged on the machine frame, the machine frame comprises a sliding rail which is transversely arranged, the sliding rail is provided with a sliding block which can transversely move along the sliding rail, and the welding gun is fixedly arranged on the sliding block; the sliding block is fixedly provided with a detecting device which can drive the sliding block to transversely move along the sliding rail; the detecting device comprises a detecting pulley made of hard materials, and the pulley is fixed opposite to the welding gun; the gun tip of the welding gun is located on the pulley circumferential surface of the detecting pulley. The self-guide welding machine is simple in structure and low in manufacturing cost, the welding gun can be aligned with a joint constantly, and high-quality welding is formed.
Owner:HUZHOU XINXING AUTOMOBILE PARTS
Welding method and device for large-area ferromagnetic target material
ActiveCN109590560AImprove welding rateImprove flatnessWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesMagnetic effectFerromagnetism
The invention discloses a welding method and device for a ferromagnetic sputtering target material. According the welding method, through the magnetic effect of a permanent magnet chuck platform on the ferromagnetic sputtering target material, the target material, a solder and a backing plate are uniformly combined to improve the welding quality of the large-area ferromagnetic sputtering target material, so that the welded rate of the target material is high and the thickness uniformity of the target material is good. The welding method is easy to operate and has strong repeatability; the high-quality welding of the large-area ferromagnetic sputtering target material can be achieved by using a magnetic platform welding device; and the sputtering performance of the target material is significantly improved.
Owner:GRIKIN ADVANCED MATERIALS
Welding device
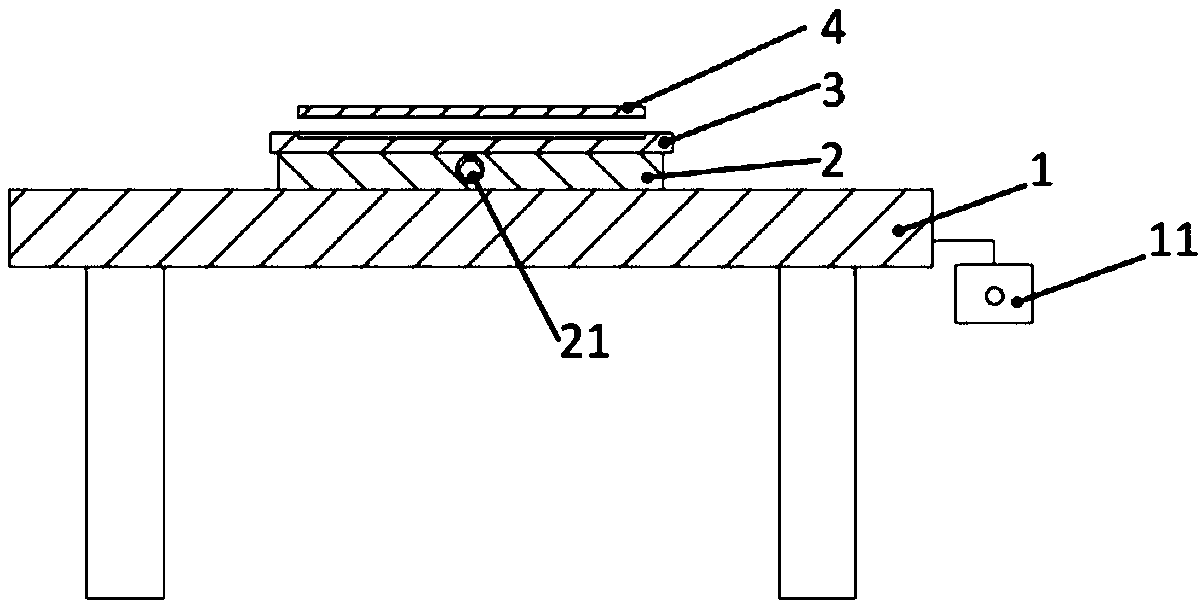
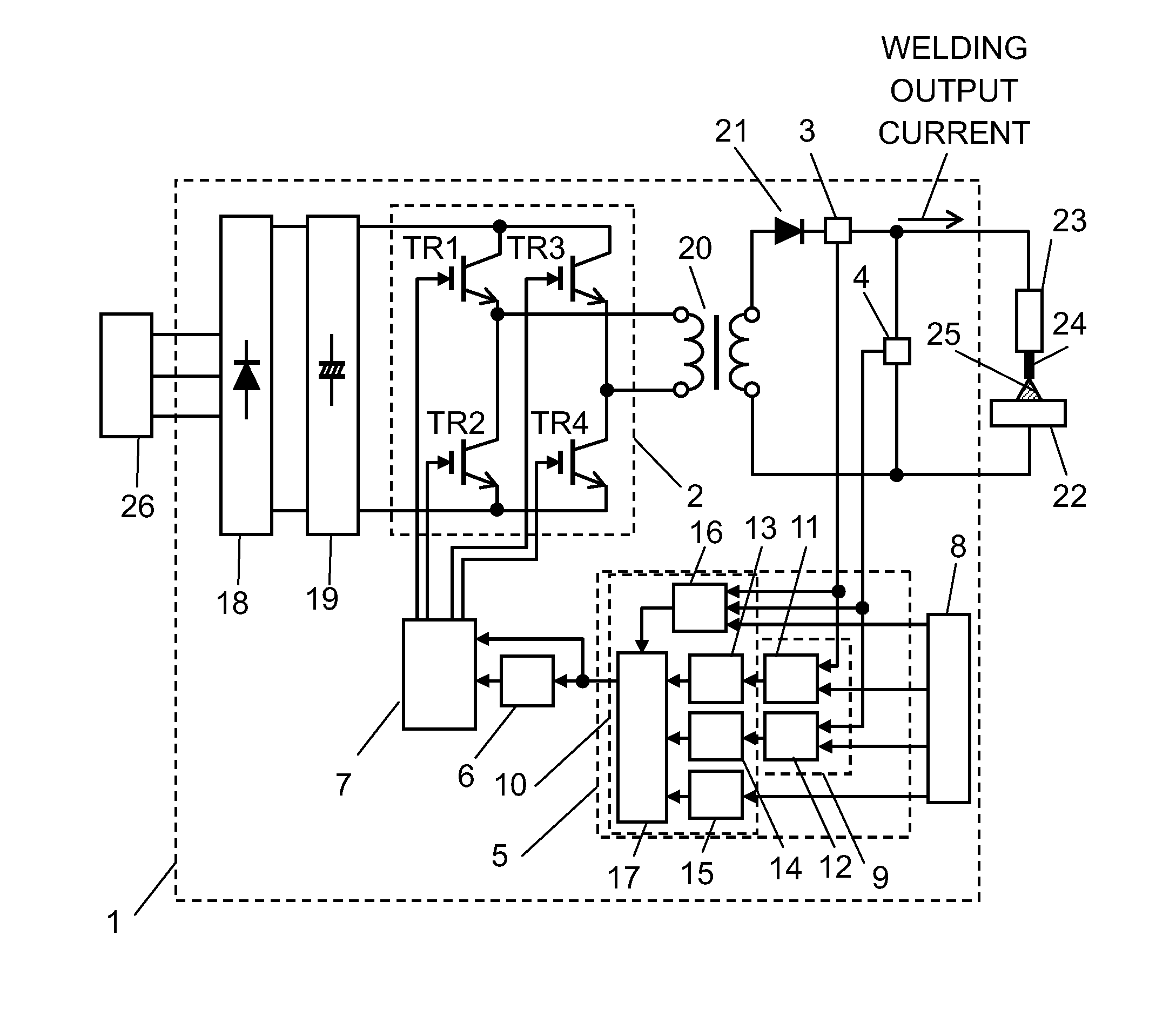
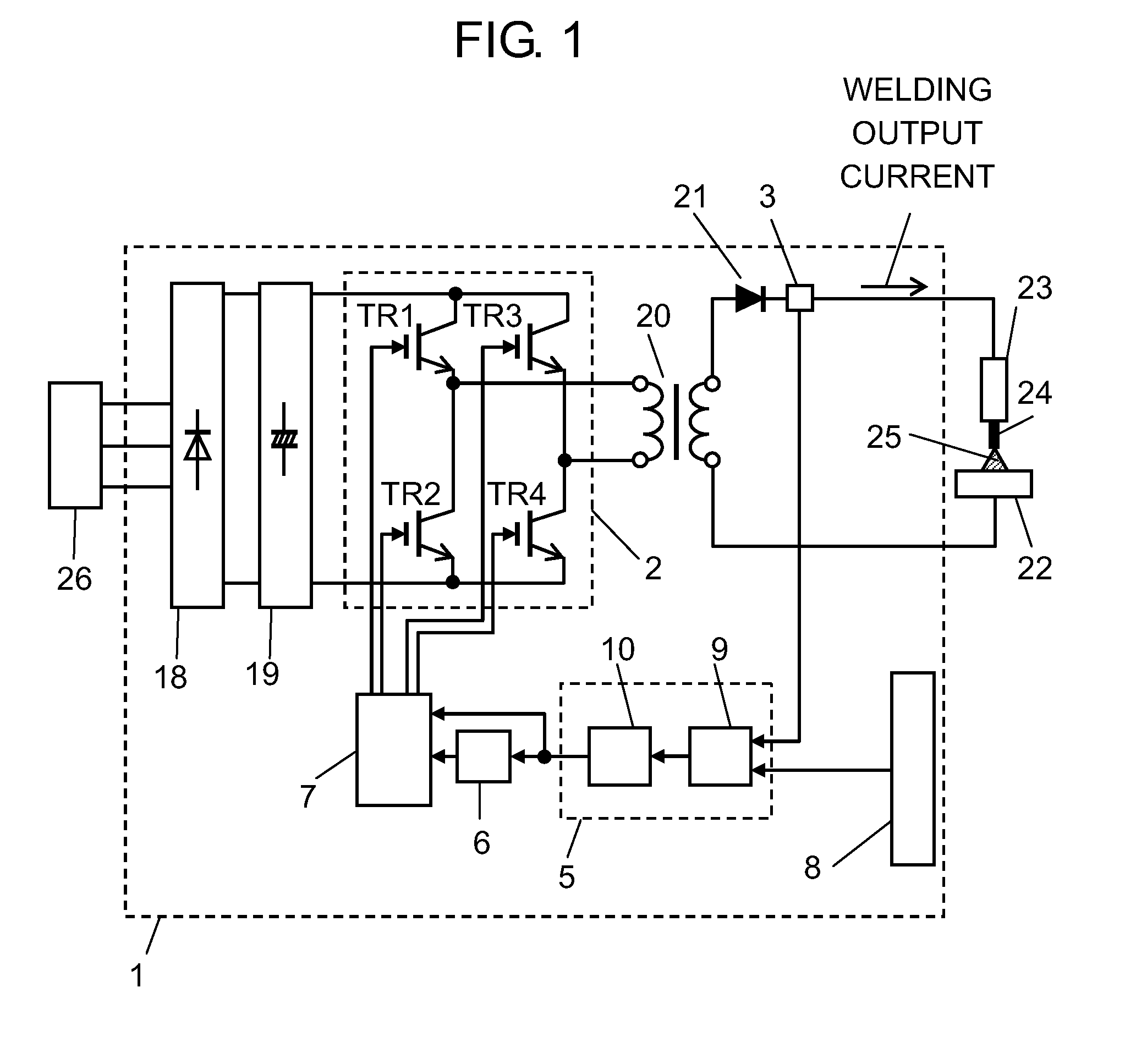
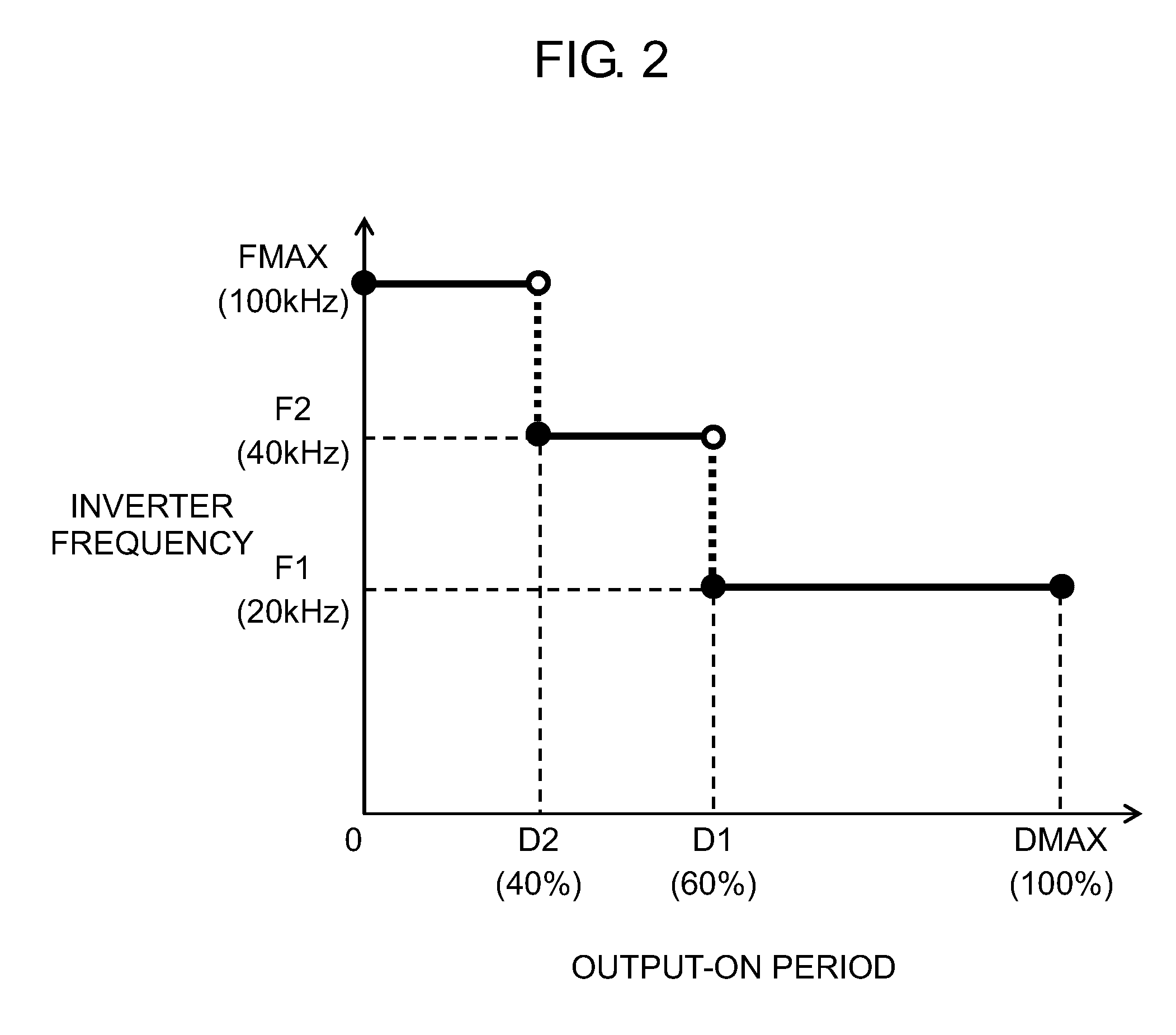
ActiveUS20160144442A1Quality improvementHigh quality weldingDc network circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversionControl switchDevice Sensor
The welding device of the present disclosure has a switching section, a setting section, an output detector, a controller, a frequency controller, and a driver. The switching section is formed of a switching element. The setting section determines setting output. The output detector detects welding output. The controller calculates an output-on period of the switching section according to the setting output and the welding output. The frequency controller determines an inverter frequency based on the output-on period. The driver controls on / off operation of a switching element of the switching section based on the inverter frequency and the output-on period. When the output-on period is calculated using a first ratio, the inverter frequency is determined to a first frequency, and when the output-on period is calculated using a second ratio smaller than the first ratio, the inverter frequency is determined to a second frequency higher than the first frequency.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Conveyor for sheet-shaped thin plate and method of conveying same
InactiveCN1803384AAvoid vertical overlapAvoid overlappingWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A conveyor for guiding and conveying a plurality of sheet-shaped thin plates in rows arranged side by side to a welding position at which ends of the adjacent thin plates are butted and welded to each other, includes a plurality of conveying paths, which are adjacent to each other, having different conveying surfaces which are placed on a same horizontal plane, and a guide unit disposed between the adjacent two conveying paths for guiding the thin plates on one of the conveying paths with respect to another one thereof toward the welding position. Each of the conveying paths is composed of a plurality conveying rollers, and the guide unit includes guide rollers each having a guide surface for guiding the thin plate on the one of the conveying paths in a state that the thin plate on the one conveying path is partially depressed with respect to the another one of the conveying path.
Owner:SUZUKI MOTOR CORP
Coil segment cutting method and coil segment cutting apparatus
ActiveUS20200303999A1High quality weldingUniform lengthManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesWindings conductor shape/form/constructionEngineeringStructural engineering
A cutting unit has a support member having insertion holes, and a movable member having through holes connected thereto. The respective left sides of upper surfaces of the square through holes are first movable blades, and the respective right sides thereof are second movable blades. Firstly, the movable member 14 is moved to the right by a predetermined amount to cut peeled-off portions of segment end portions only, and then the movable member is moved to the left by a predetermined amount to cut peeled-off portions of the segment end portions only. Distal ends of the coil segments can be cut into a uniform length to enable high quality welding, through this process.
Owner:ODAWARA ENG
Method for producing an electrochemical bundle for a metal-ion accumulator comprising metal foam at the ends of foils
InactiveUS20180175359A1High quality weldingAvoid burnsFinal product manufactureCell electrodesElectricityElectrical connection
One subject of the invention is a process for producing an electrochemical bundle of a metal-ion accumulator, with a view to its electrical connection to the output terminals of the accumulator, which is characterized by the addition of a strip of metal foam to the margins with a view to welding with a current collector.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Welding method for light alloy thick plate
InactiveCN107617817AHigh quality weldingEfficient weldingNon-electric welding apparatusElectrical resistance and conductanceThick plate
The invention provides a welding method for a light alloy thick plate. Compared with an existing light alloy thick plate friction-stir welding method, the welding method has the following beneficial effects that on one hand, heat in the light alloy thick plate can be promoted to be more uniform and more sufficient in the friction-stir welding process, and therefore high-quality and efficient welding of the light alloy thick plate is achieved; on the second hand, processes such as preheating before welding and heat treatment after welding do not need to be added, the technological processes aresimplified, the welding time is saved, and the work efficiency is improved; and on the third hand, a welding tool does not need to be specially improved, a common welding tool is used, resistance materials do not need to be purchased either, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:广东柳泰焊接科技有限公司
Pre-filled wire laser ultra-narrow gap welding method for titanium alloy thick plate
PendingCN113770522AResolve interferenceAchieve laser weldingLaser beam welding apparatusThick plateEnergy control
The invention discloses a pre-filled wire laser ultra-narrow gap welding method for a titanium alloy thick plate. The welding method comprises the following steps of: processing a single-side or double-side groove of a titanium alloy thick plate to be welded into a U-shaped groove with a truncated edge, wherein the groove gap does not exceed 10 mm, the thickness of the truncated edge is 1-10 mm, the fillet diameter is 0-1 mm greater than the diameter of a pre-filled thick wire, and the groove angle is 0-1.5 degrees; then carrying out welding under gas protection, in the welding process, firstly carrying out truncated edge laser welding, and then carrying out filling welding after wire laying is conducted till filling welding is completed; and finally, carrying out capping laser welding. According to the welding method, the problems that the wire filling welding efficiency of the titanium alloy thick plate is relatively low, and the stability of a key hole is interfered by a wire in the welding process are solved, the welding efficiency is greatly improved, and the stability of the welding process is guaranteed; and meanwhile, the welding gap of the titanium alloy thick plate can be guaranteed to be within 10 mm, and welding deformation and welding stress are reduced to the minimum through layer-by-layer accurate energy control, so that high-precision and high-quality welding is achieved.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Soldering iron for soldering strip of photovoltaic cell
InactiveCN106064263AReduce damageHigh quality weldingSoldering ironSoldering auxillary devicesForeign matterEngineering
The invention provides a soldering iron for a soldering strip of a photovoltaic cell. The soldering iron comprises a soldering iron body and a soldering iron head, wherein the soldering iron head is a cylinder; the soldering iron head is connected with a side plate through a rotary shaft; the soldering iron head can rotate through the rotary shaft; and the side plate is fixed at the bottom of the soldering iron body. Compared with the prior art, slide friction is changed into rolling friction, thus damage to a welding surface is reduced; and meanwhile, self-cleaning for the surface of a welding body can also be realized, thus influence of dust and foreign matters on a welding effect is prevented, and high-quality welding is realized.
Owner:TIANJIN YINGLI NEW ENERGY RESOURCES
Conveyor for sheet-shaped thin plate
InactiveCN100471614CLess adjustment workImproved butt weld performanceWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesMechanical engineeringThin sheet
A conveyor for guiding and conveying a plurality of sheet-shaped thin plates in rows arranged side by side to a welding position at which ends of the adjacent thin plates are butted and welded to each other, includes a plurality of conveying paths, which are adjacent to each other, having different conveying surfaces which are placed on a same horizontal plane, and a guide unit disposed between the adjacent two conveying paths for guiding the thin plates on one of the conveying paths with respect to another one thereof toward the welding position. Each of the conveying paths is composed of a plurality conveying rollers, and the guide unit includes guide rollers each having a guide surface for guiding the thin plate on the one of the conveying paths in a state that the thin plate on the one conveying path is partially depressed with respect to the another one of the conveying path.
Owner:SUZUKI MOTOR CORP
Method and apparatus for laser soldering
ActiveUS8269140B2Eliminate the problemHigh quality weldingPrinted circuit assemblingMetal working apparatusMetallurgyIrradiation
Owner:JAPAN UNIX
Method for producing an electrochemical bundle for a metal-ion accumulator comprising folding or coiling the foil ends around themselves
ActiveUS10516150B2Quality improvementHigh quality weldingFinal product manufactureCell electrodesElectrical batteryElectrical connection
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Argon arc preheating wire welding method
InactiveCN100335223CHigh quality weldingWide temperature rangeArc welding apparatusEngineeringCopper
A method for preheating the welding wire used for TIG welding in order to increase the speed and quality of welding features that the argon arc is used as the heat source, the output current controllable TIG power supply is electrically connected across the weld gun and the feeding mouth of welding wire, and the argon arc is triggered to preheat the welding wire.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Laser welding system, laser welding control method and device and storage medium
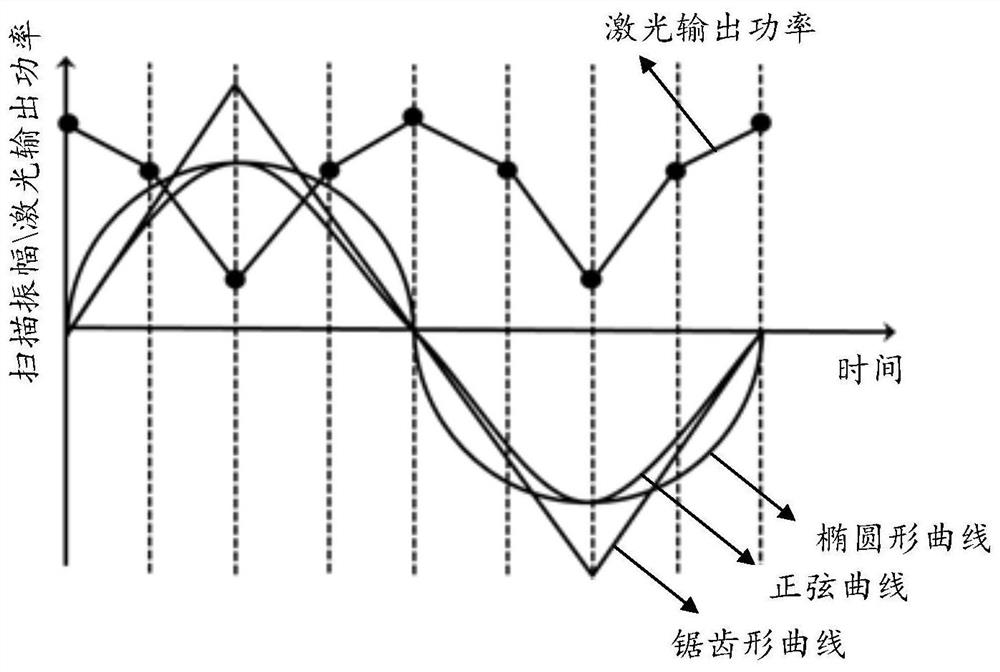
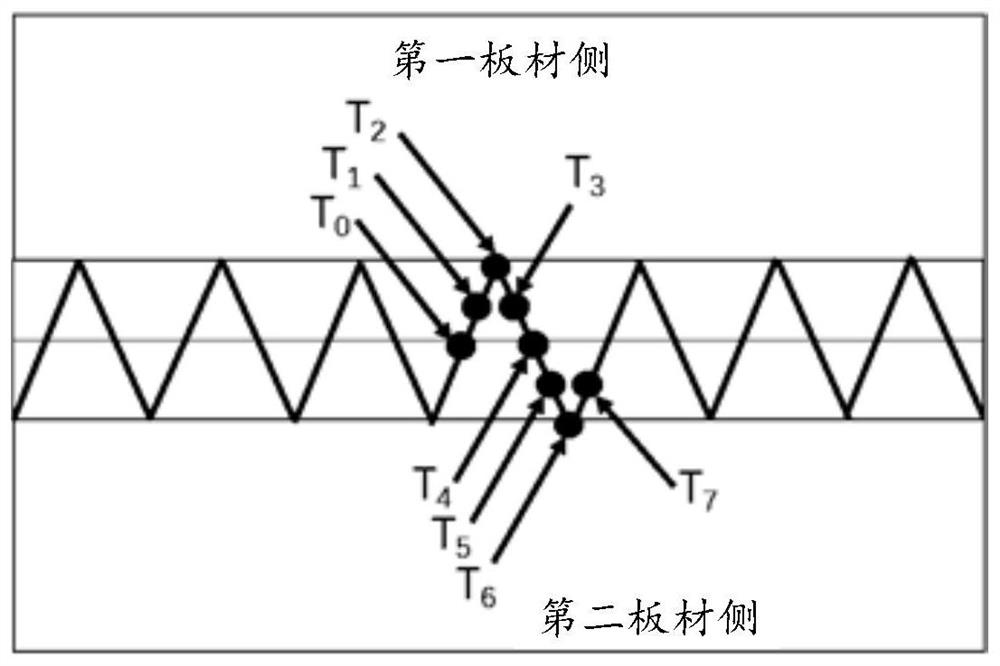
PendingCN112935553AHigh quality weldingIncrease flexibilityWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesDual beamWelding defect
The invention relates to a laser welding system, a laser welding control method and device and a storage medium, and belongs to the technical field of welding. The laser welding system comprises a workbench and a base plate placed on the workbench, the base plate is used for placing at least a first plate and a second plate which are in butt joint with each other, and the first plate and the second plate are not equal in thickness. The laser welding system further comprises a laser welding device with a scanning function, and the laser welding device is used for carrying out laser scanning in the direction perpendicular to the welding direction in the welding process so as to weld the butt joint interface of the first plate and the second plate. The laser welding device corresponds to different laser output powers at at least two different laser scanning positions. The problems that when double-beam laser is used for conducting laser welding on plates with different thicknesses, due to the fact that laser energy distribution is not flexible enough, welding defects such as incomplete fusion and air holes exist can be solved. The laser output power of different laser scanning positions can be controlled during scanning, so that high-quality welding of butt joint of plates with different thicknesses can be realized.
Owner:HUAHENG WELDING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com