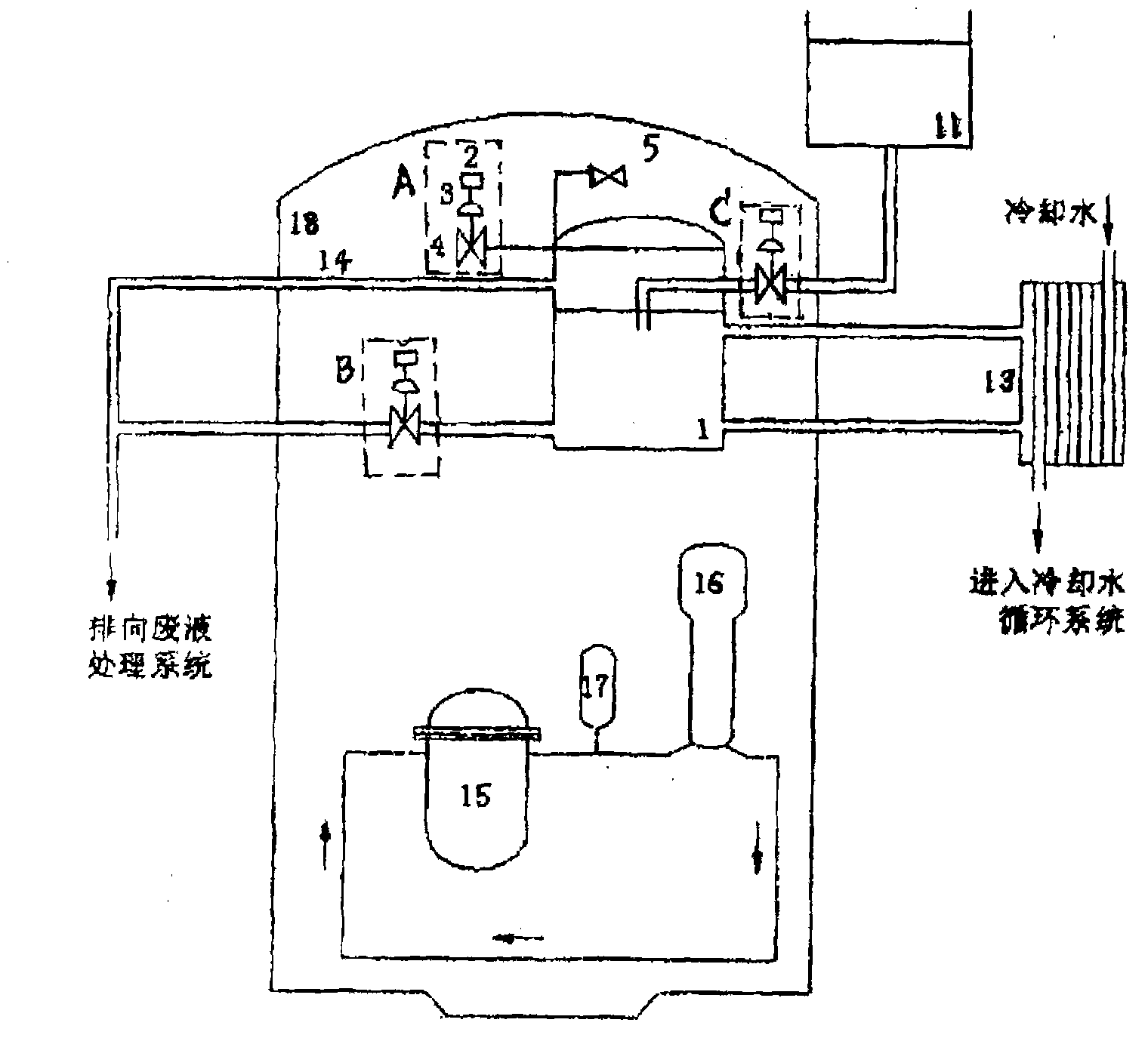
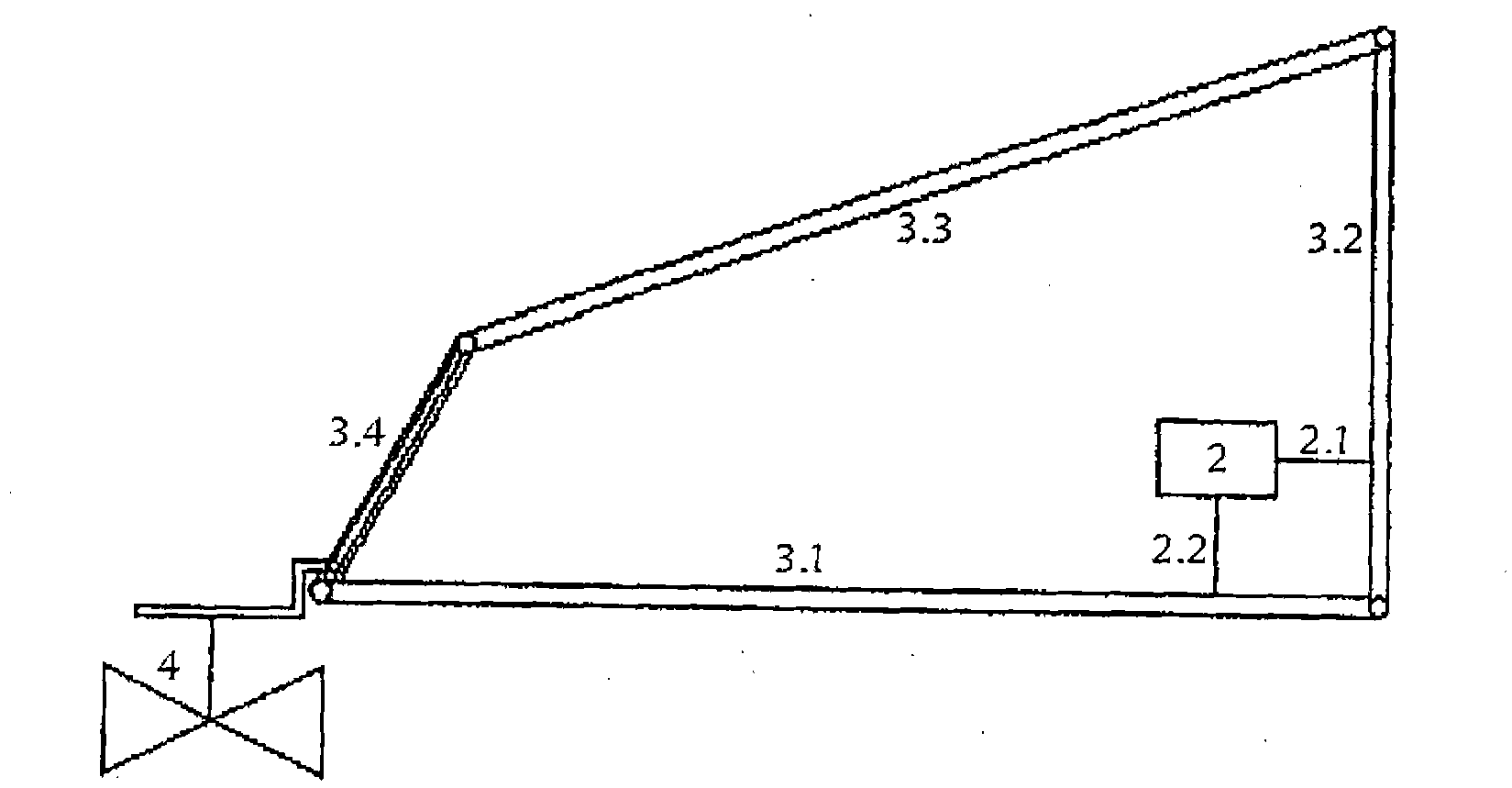
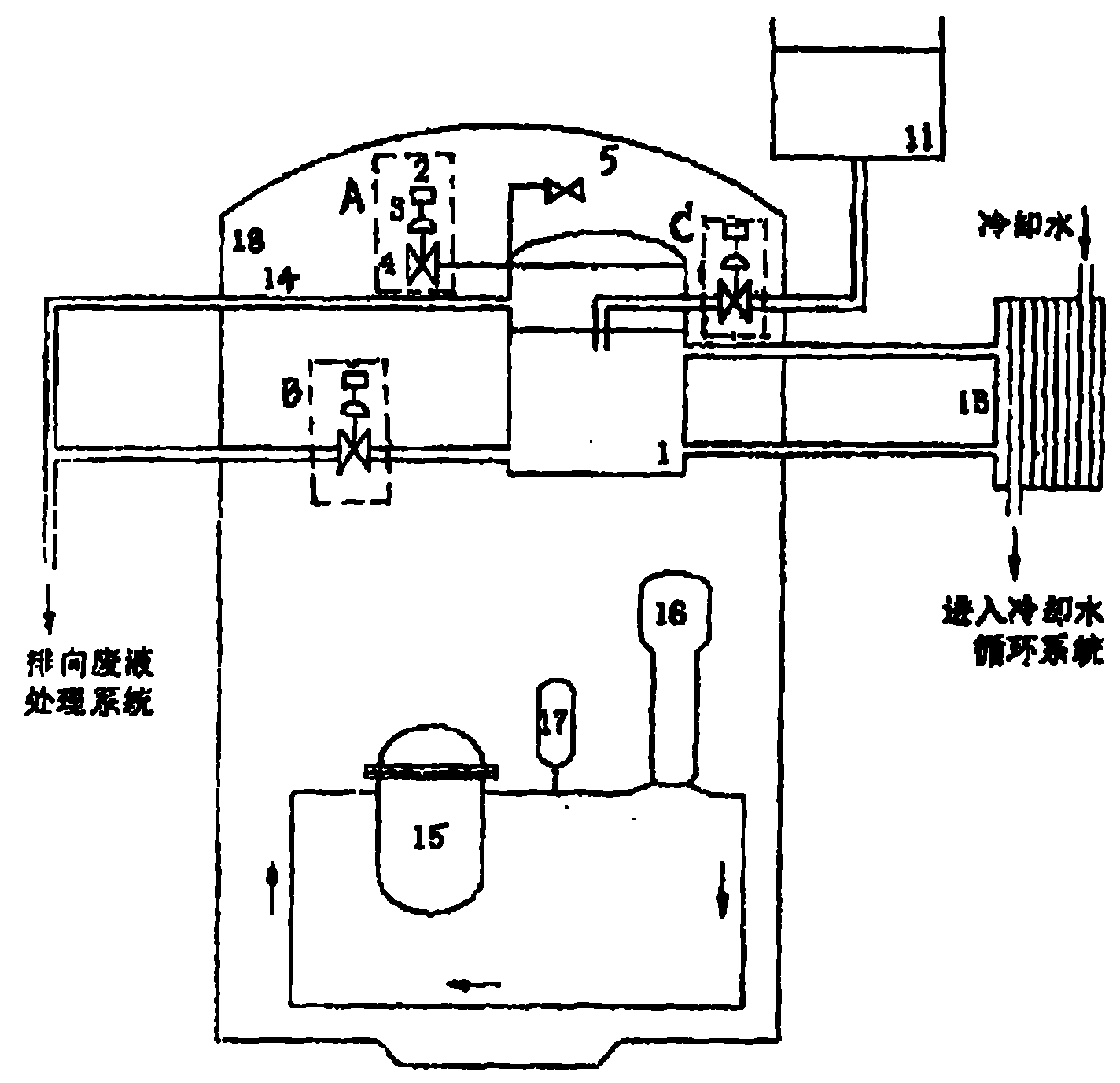
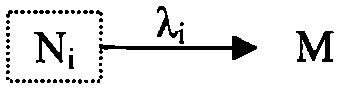Patents
Literature
88 results about "Loss-of-coolant accident" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A loss-of-coolant accident (LOCA) is a mode of failure for a nuclear reactor; if not managed effectively, the results of a LOCA could result in reactor core damage. Each nuclear plant's emergency core cooling system (ECCS) exists specifically to deal with a LOCA.
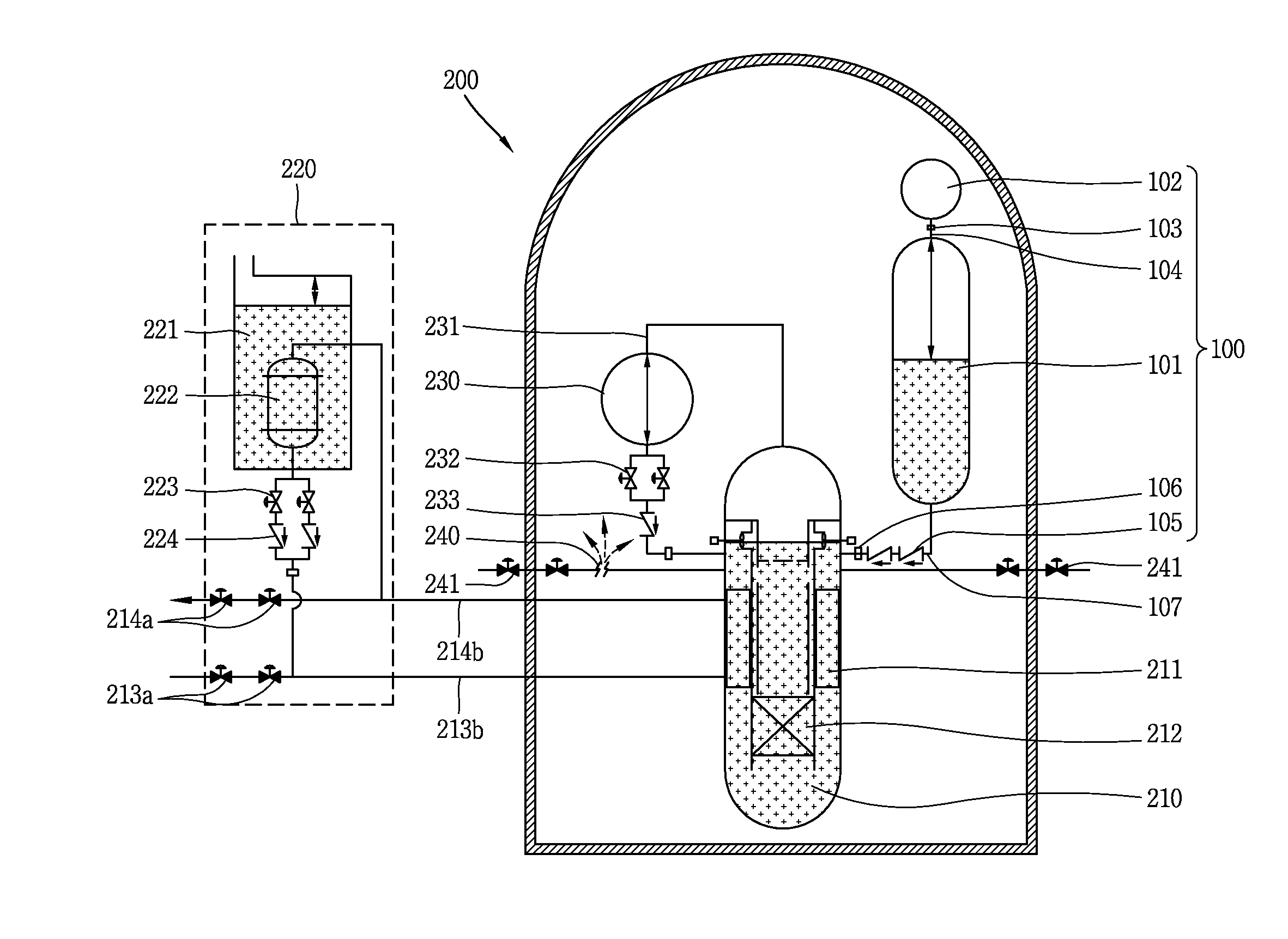
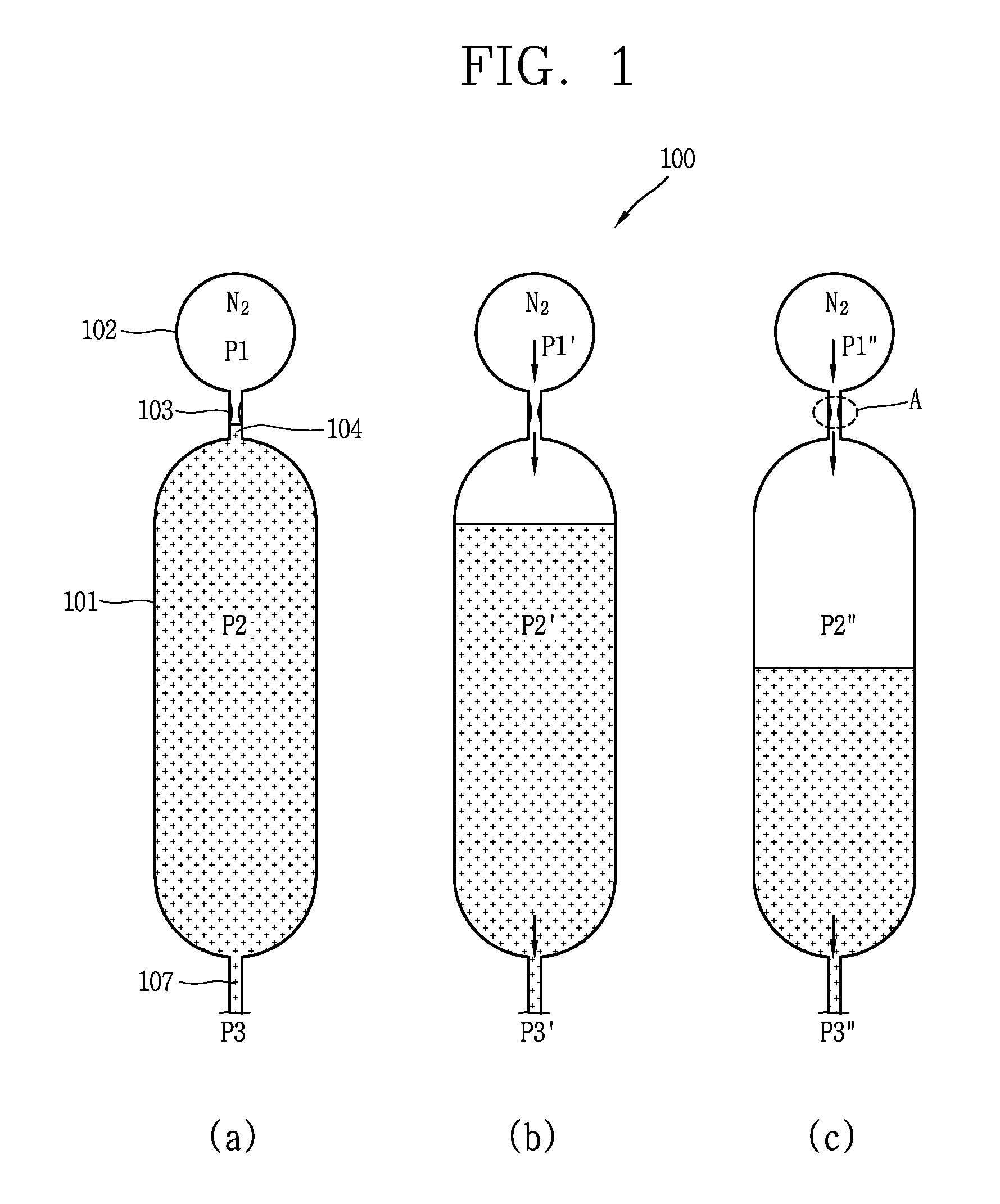
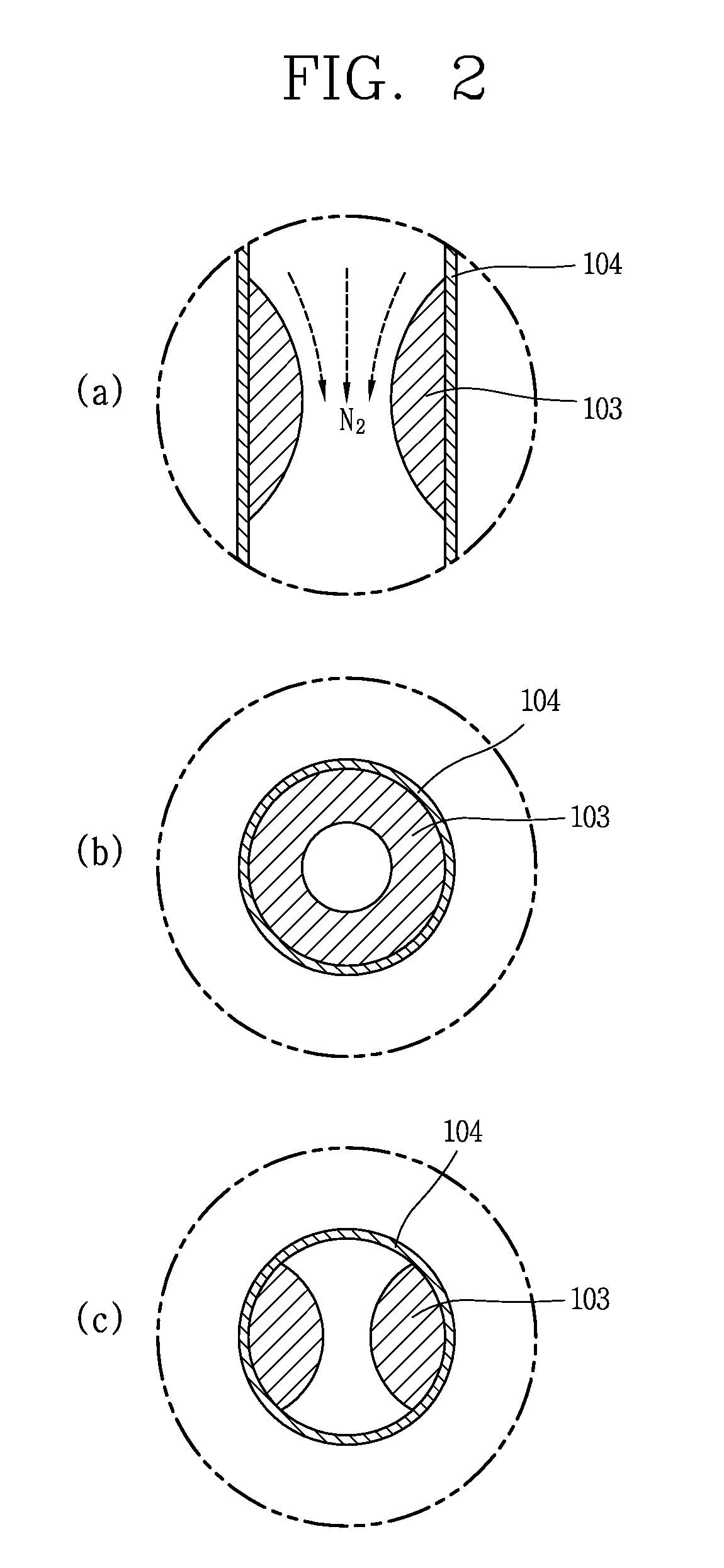
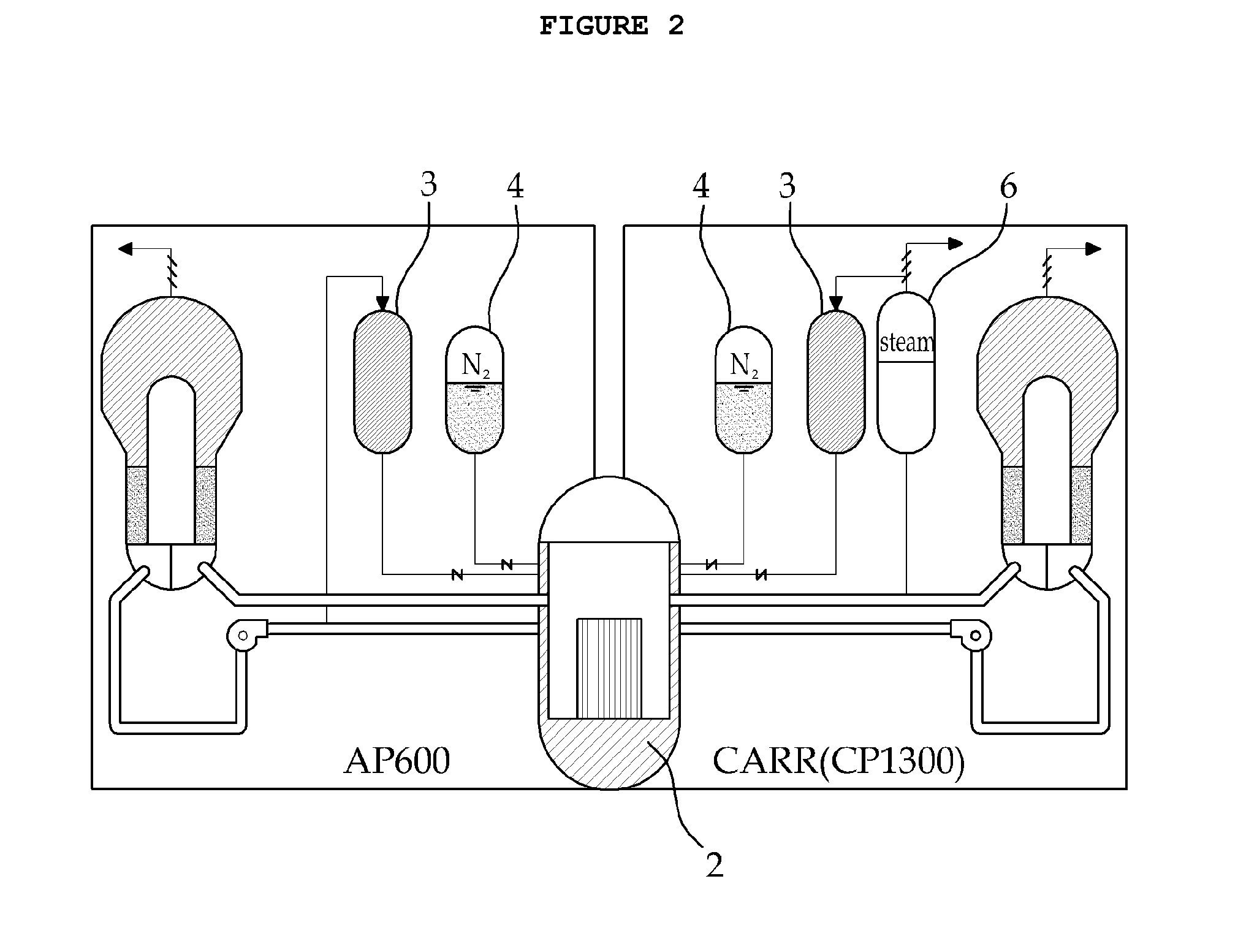
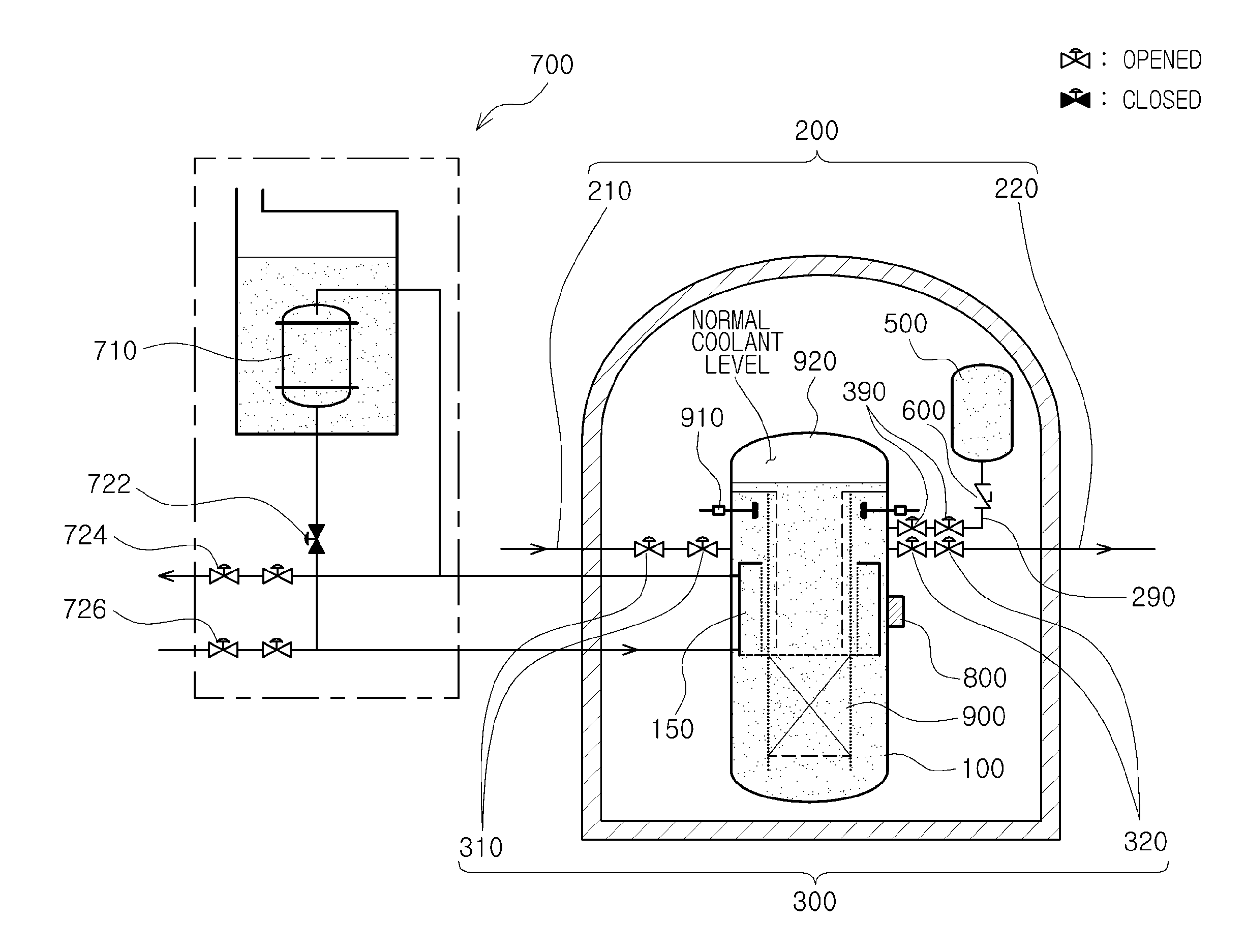
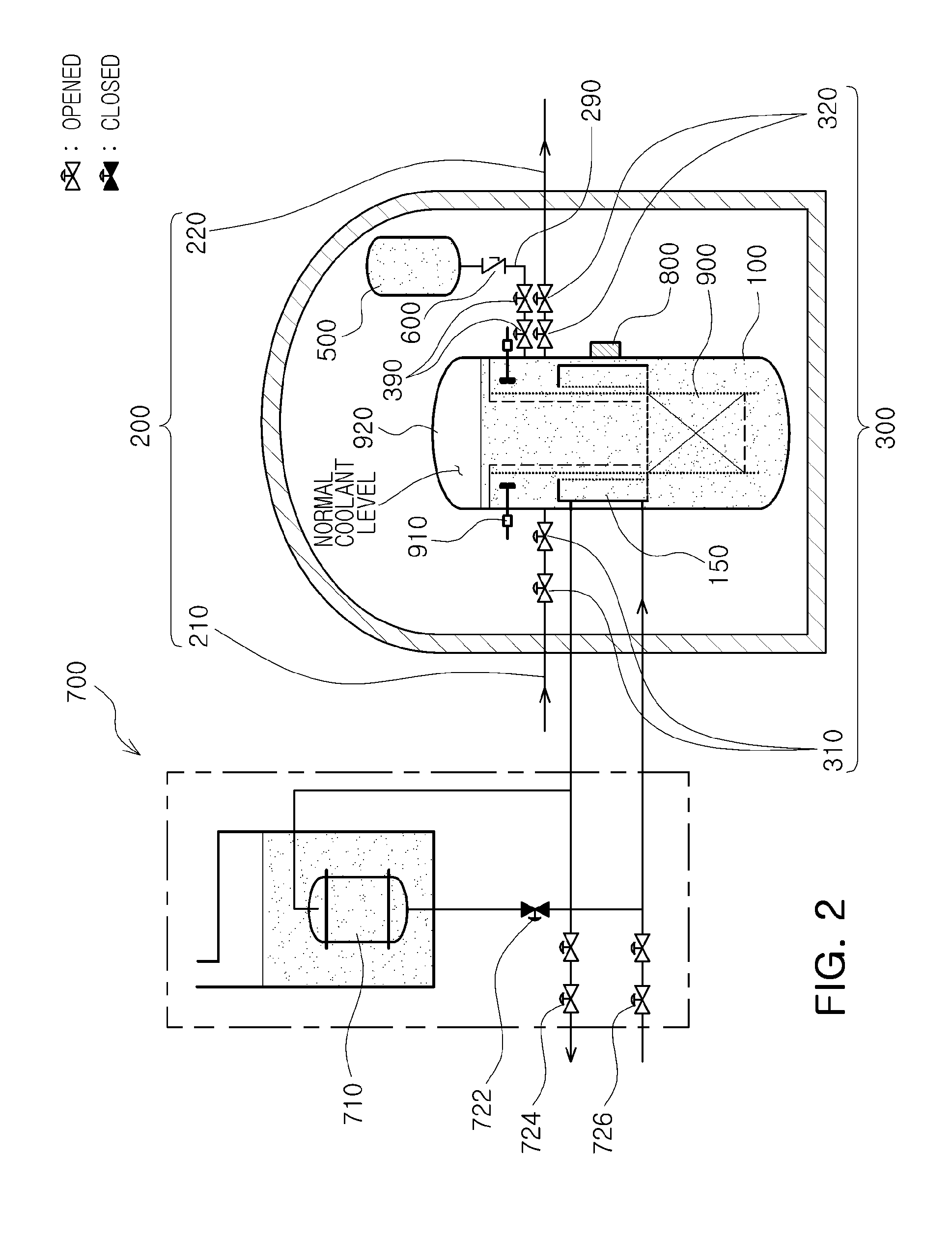
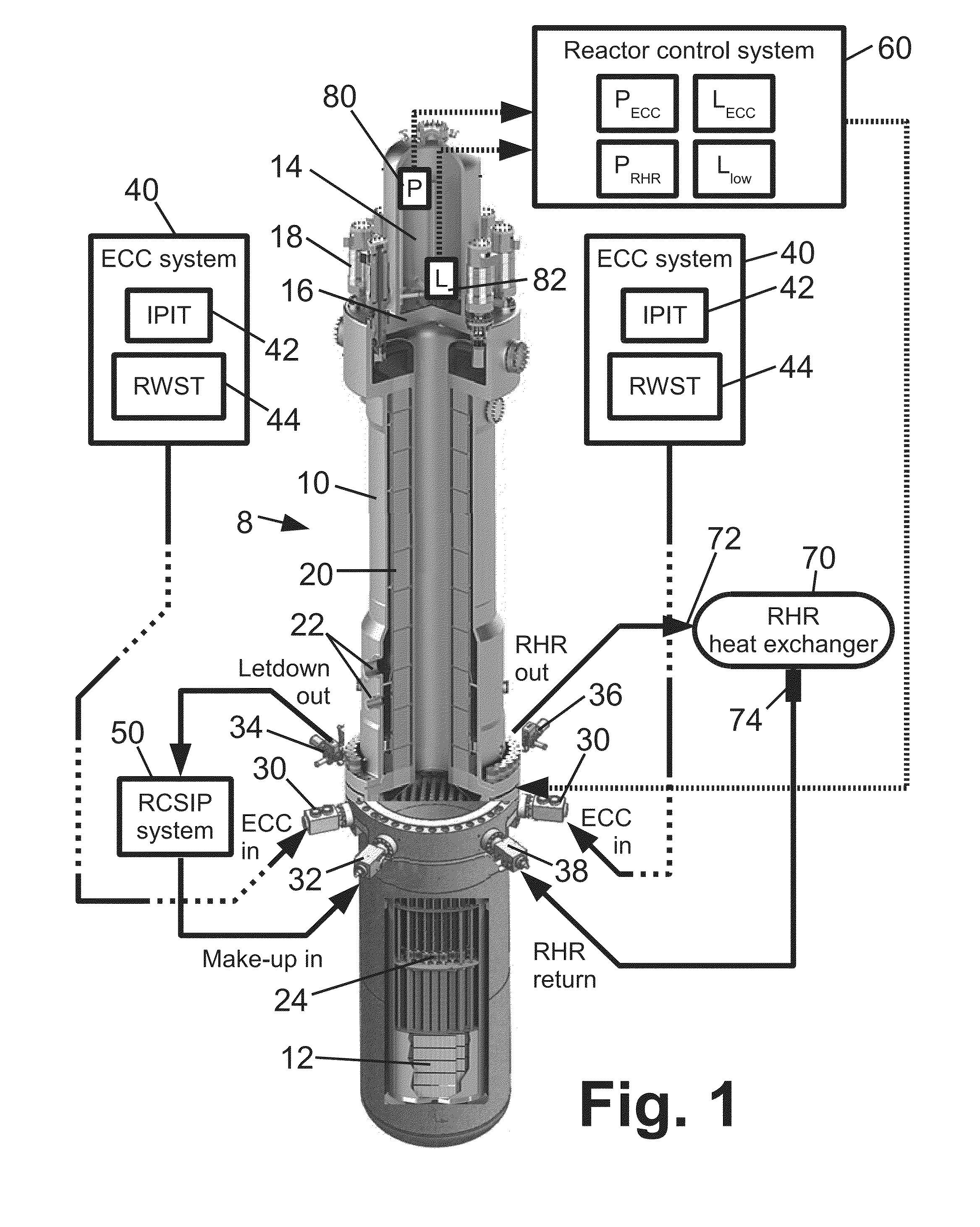
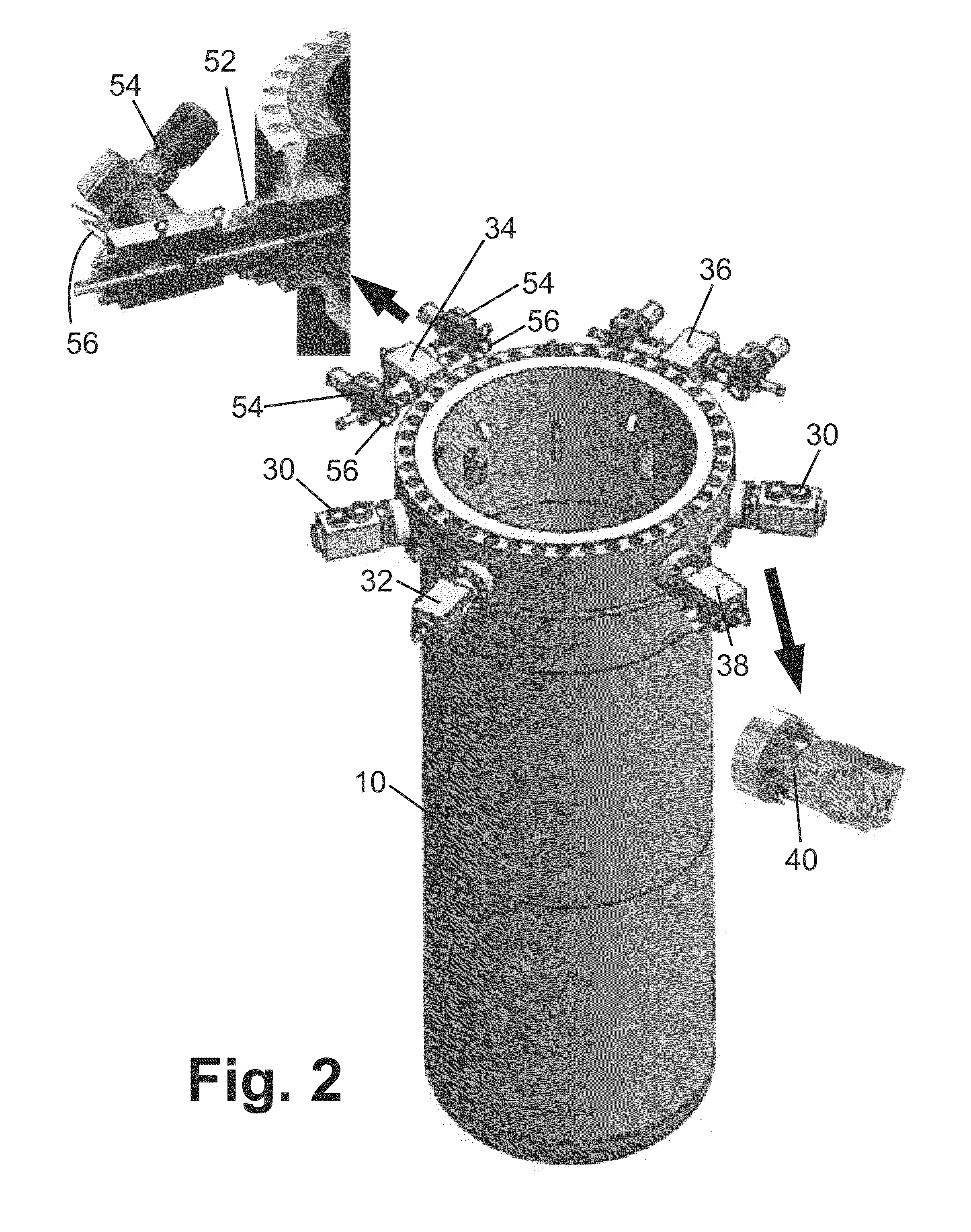
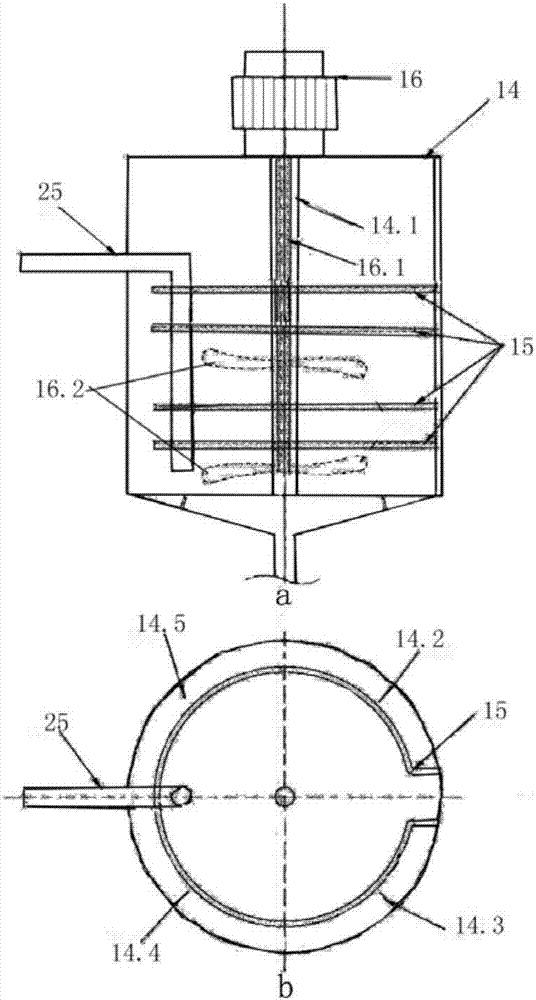
Passive safety system of integral reactor
ActiveUS20140016734A1Maintain water levelSimple facilitiesPower plant safety arrangementIntegral reactorsNuclear engineeringNitrogen gas
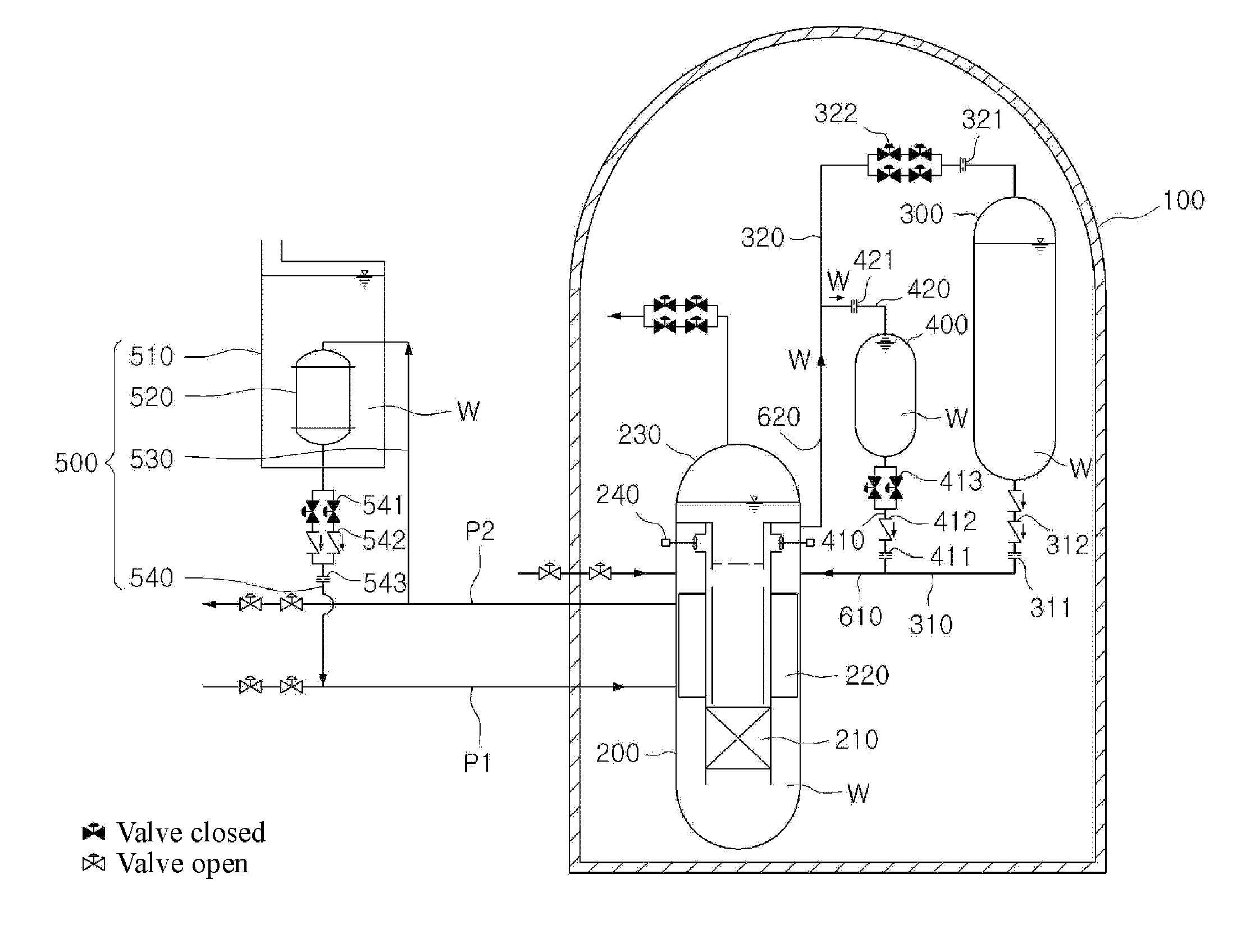
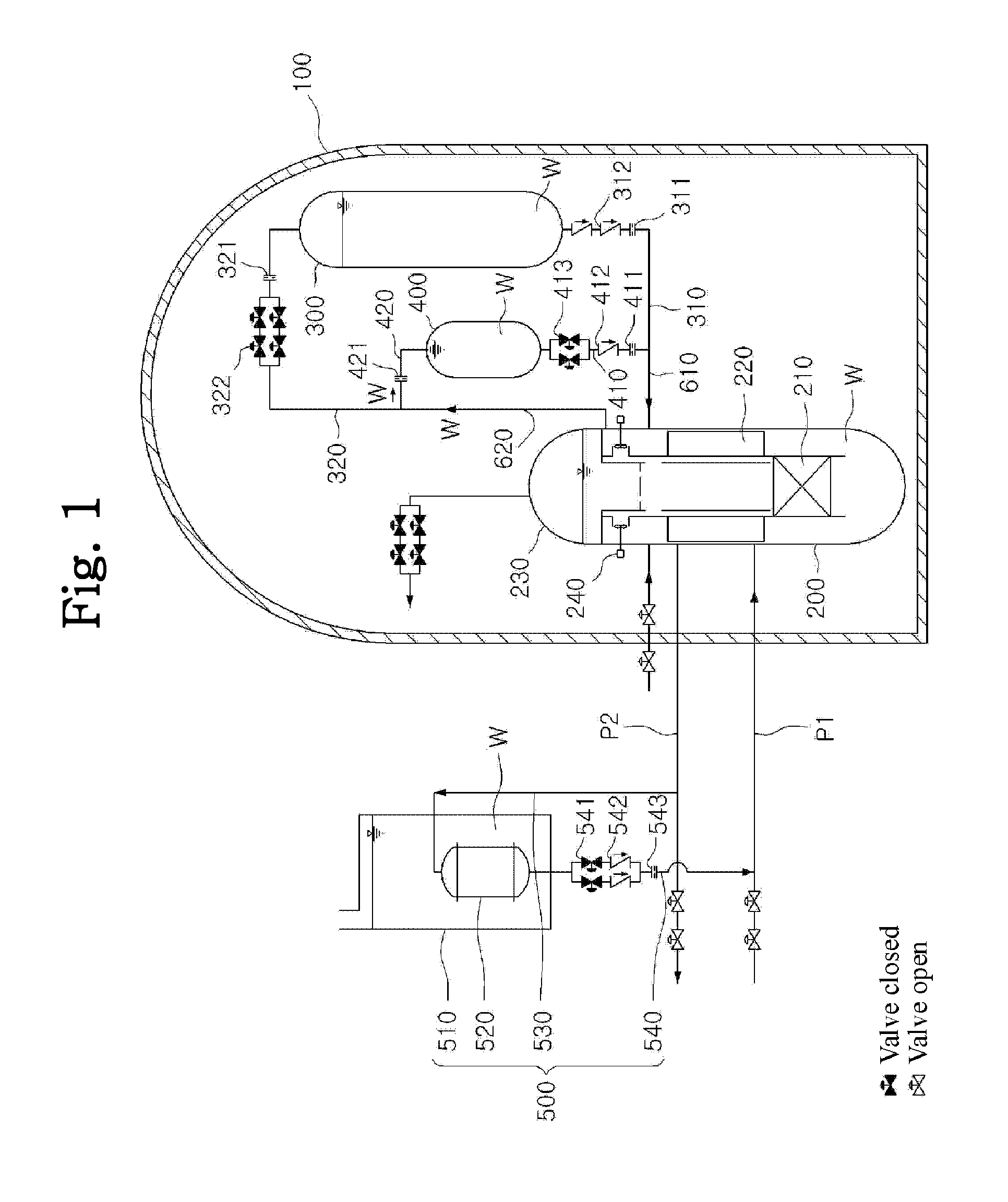
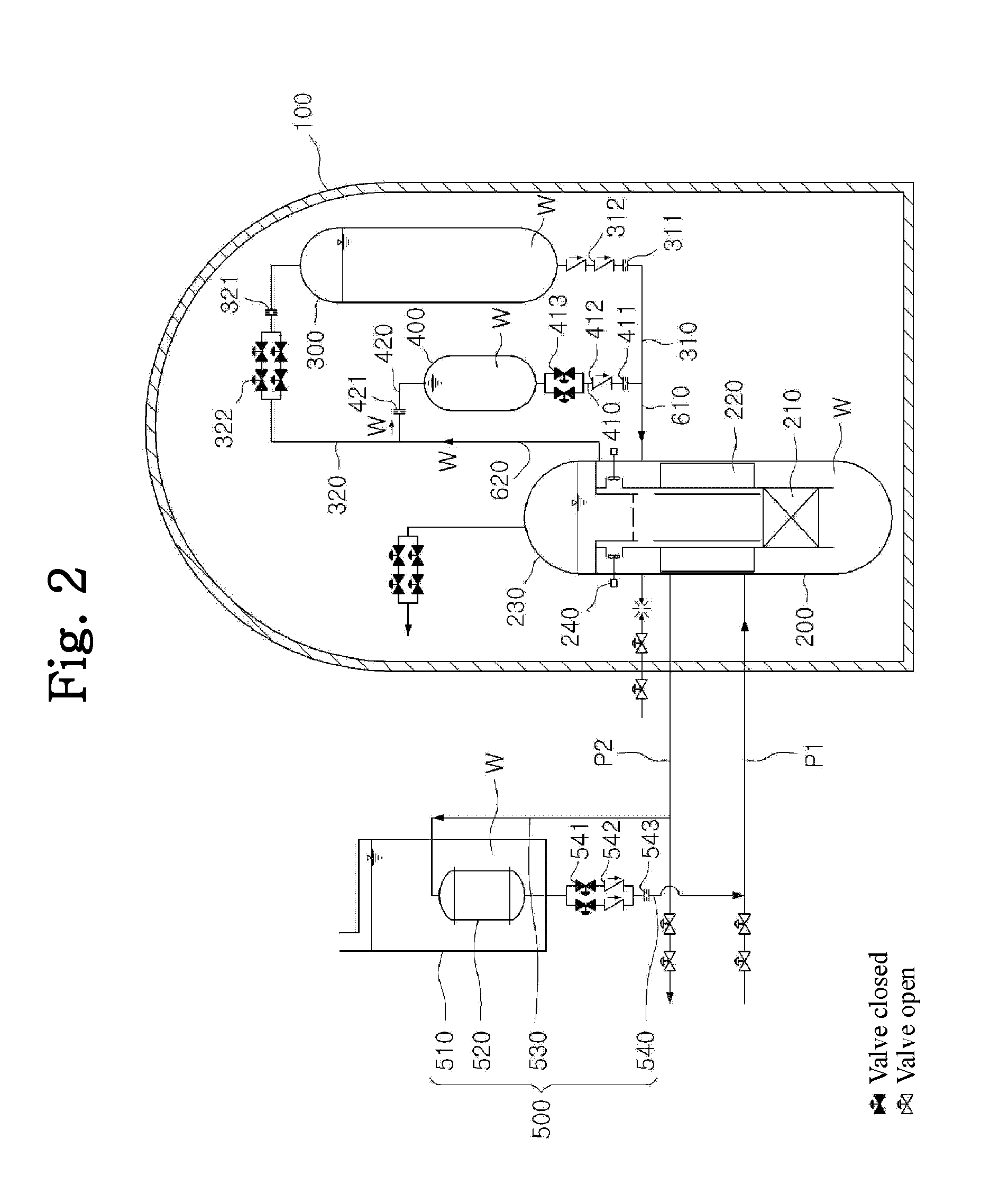
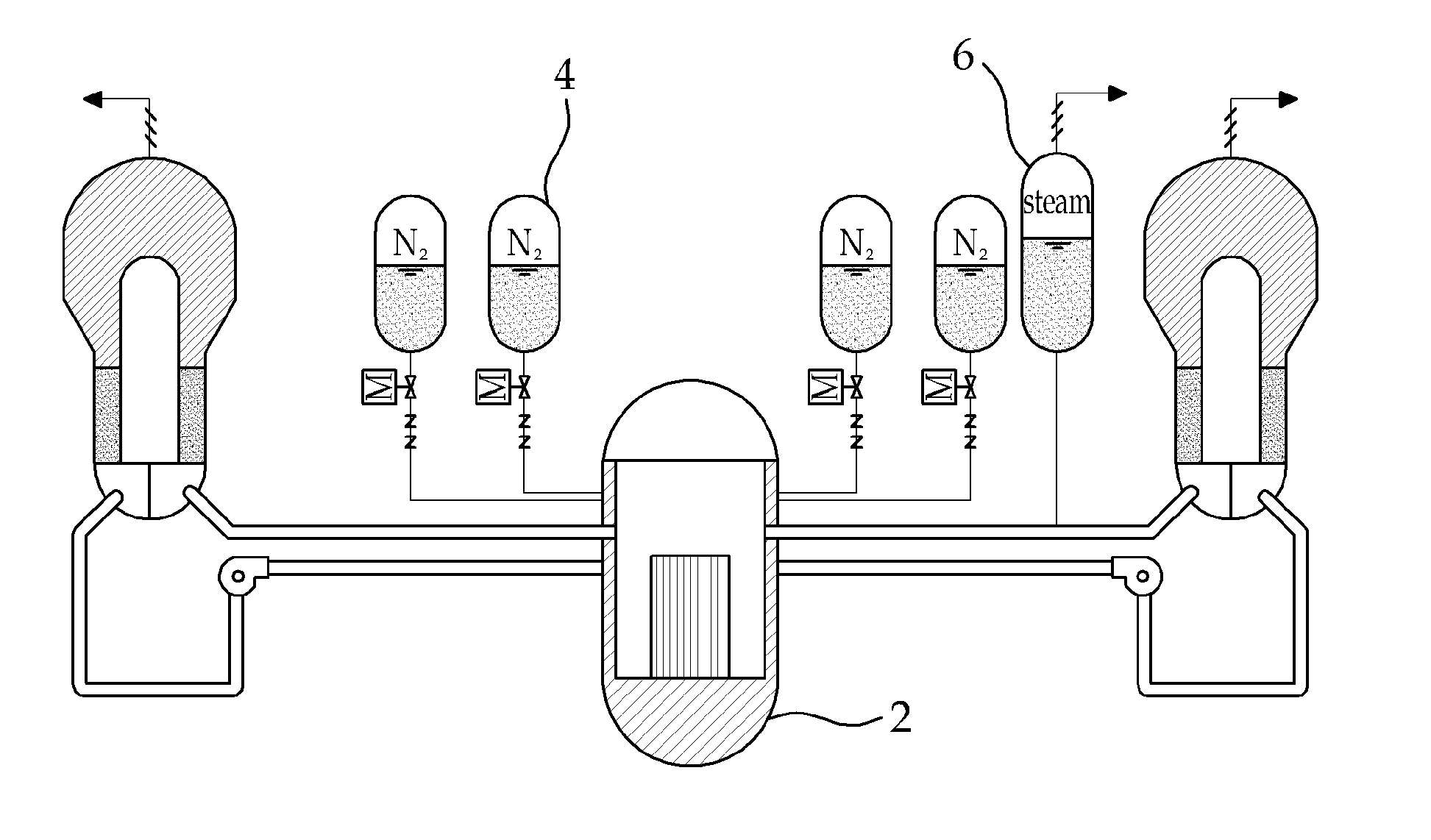
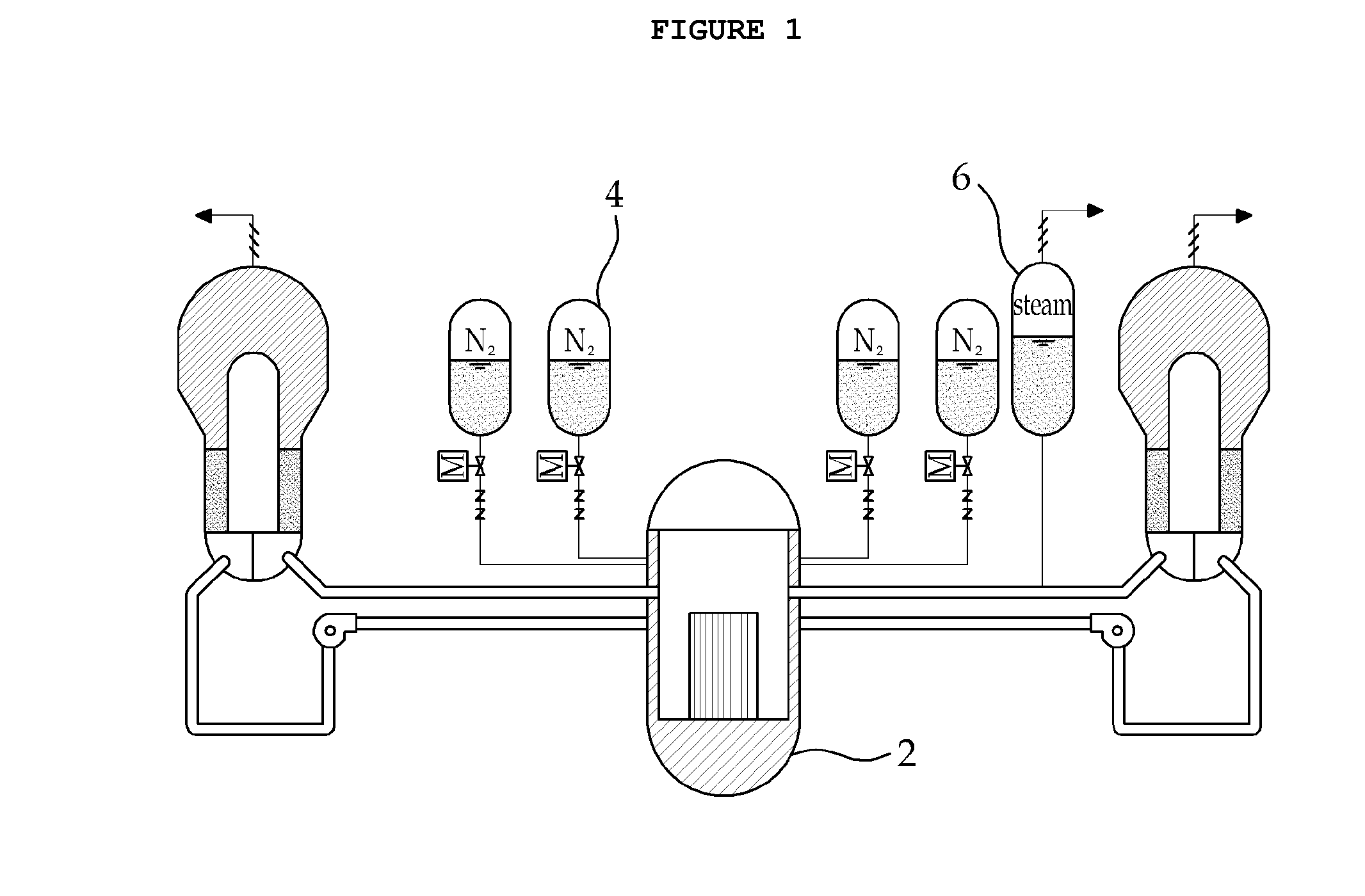
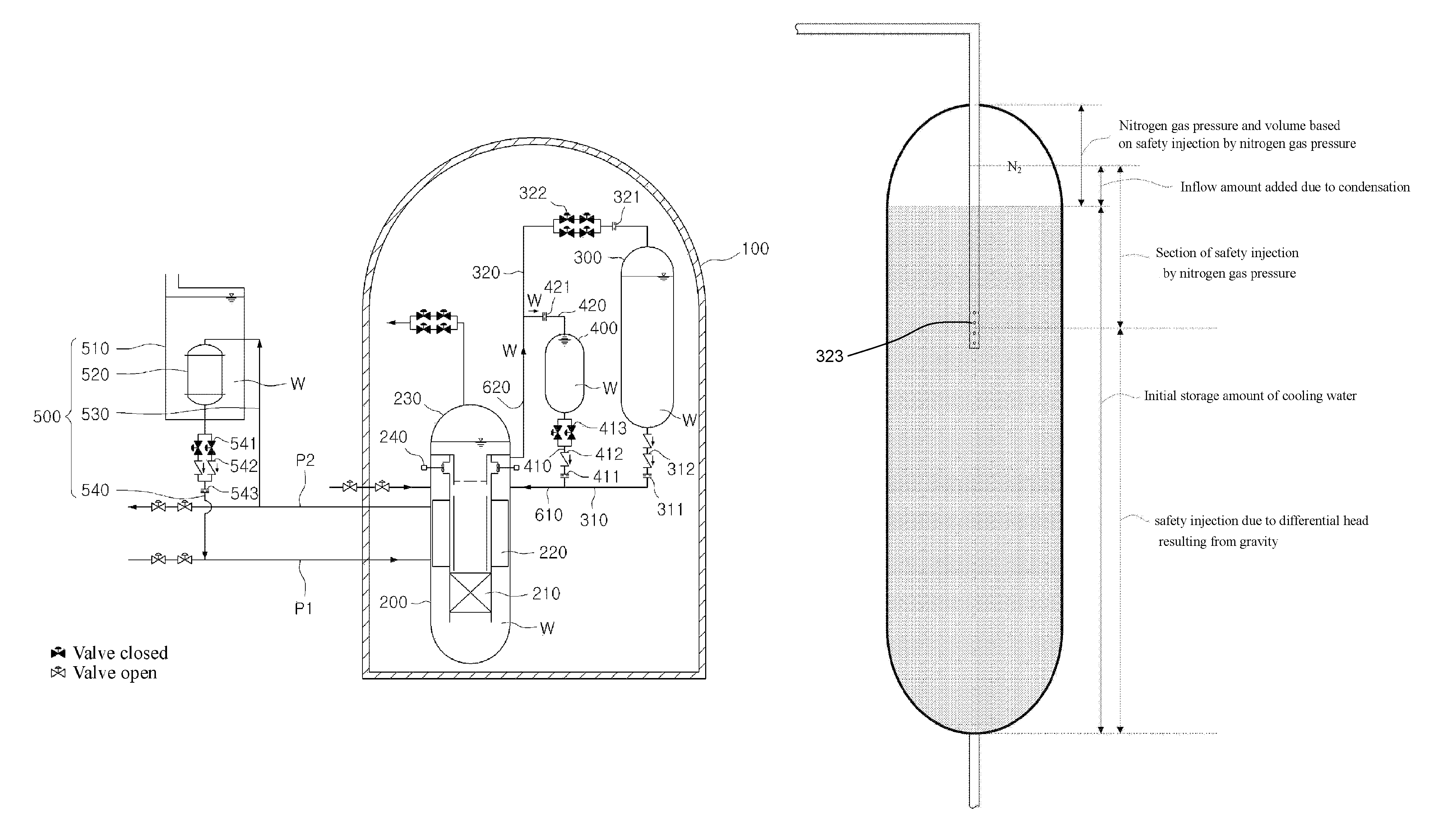
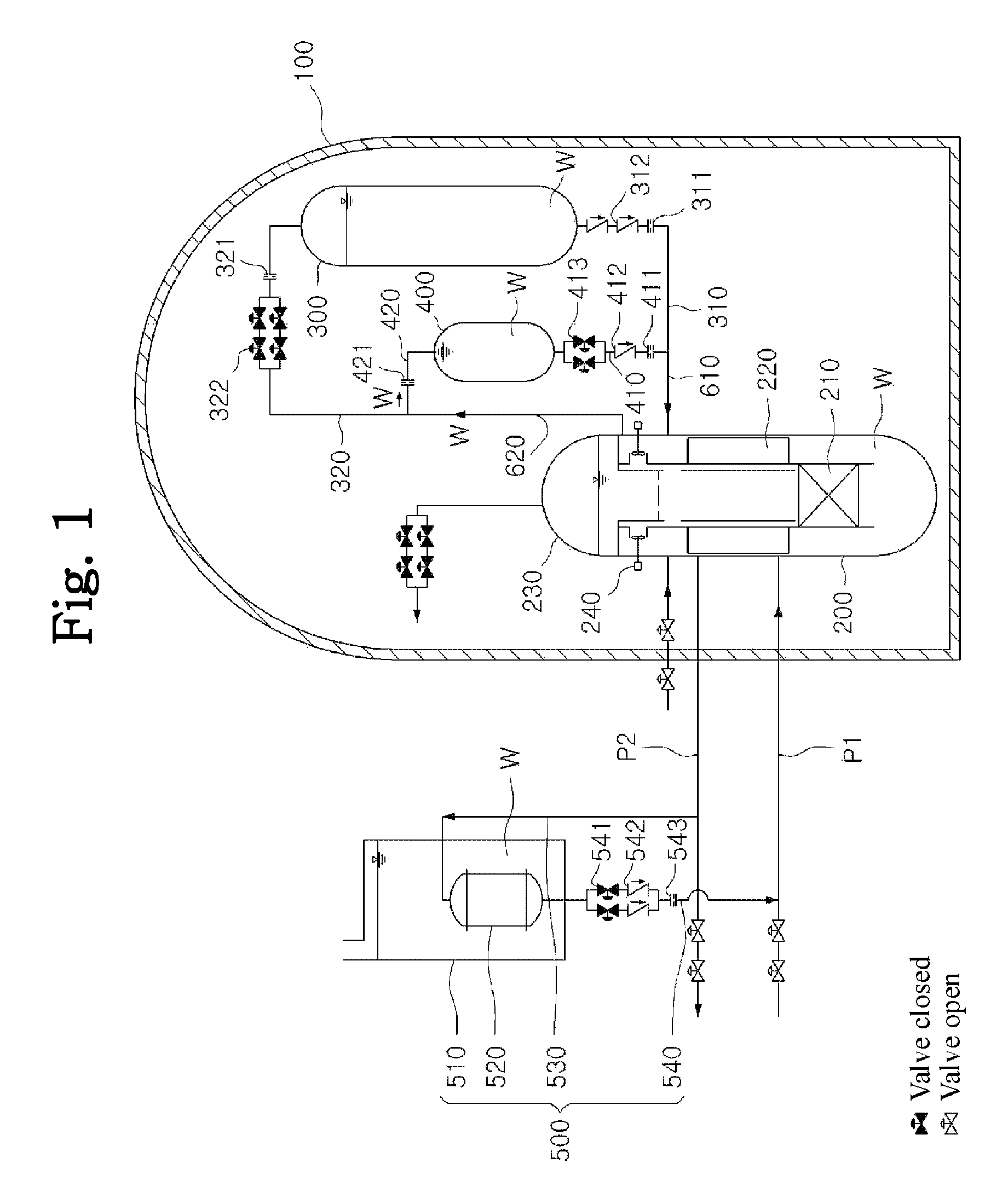
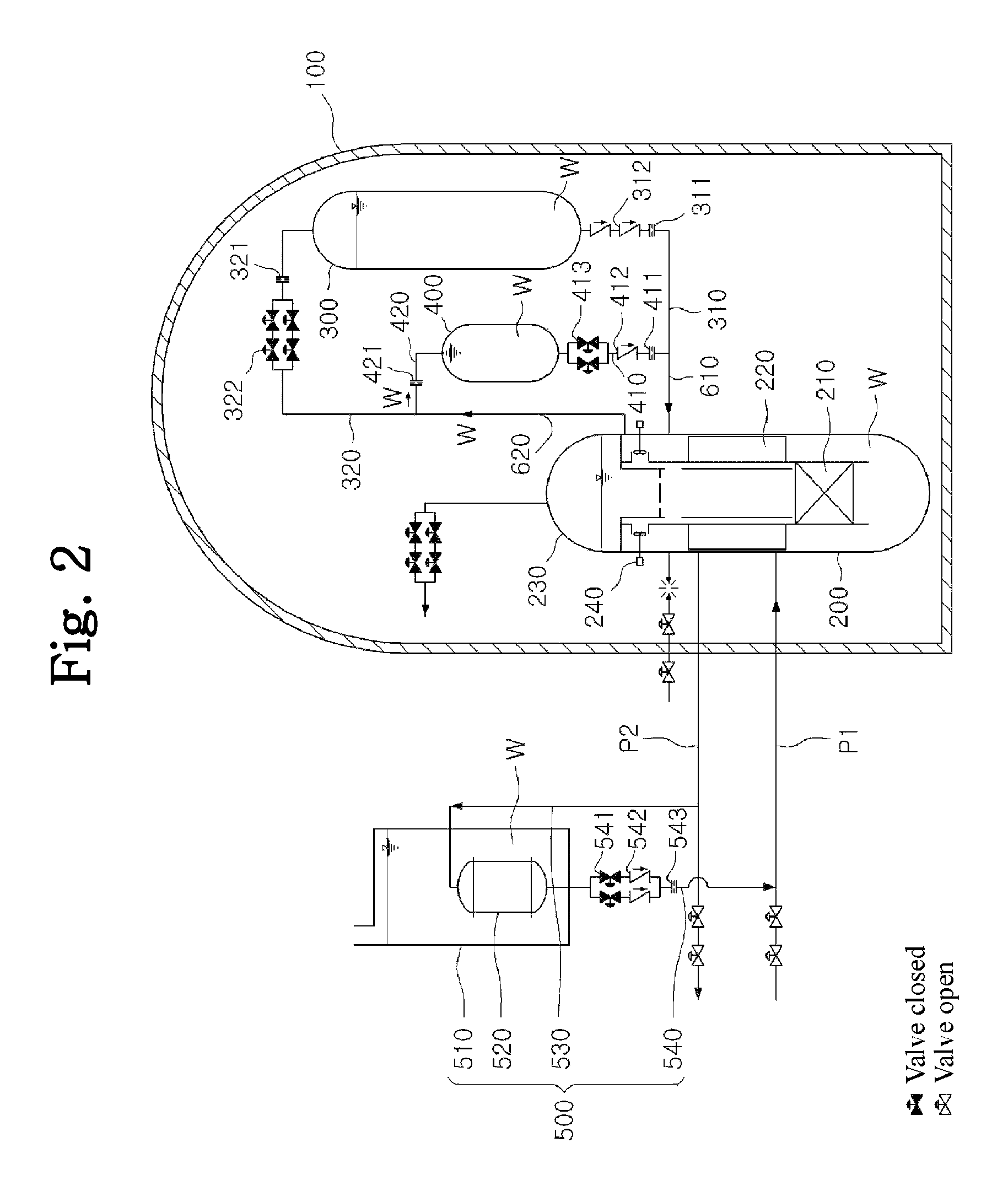
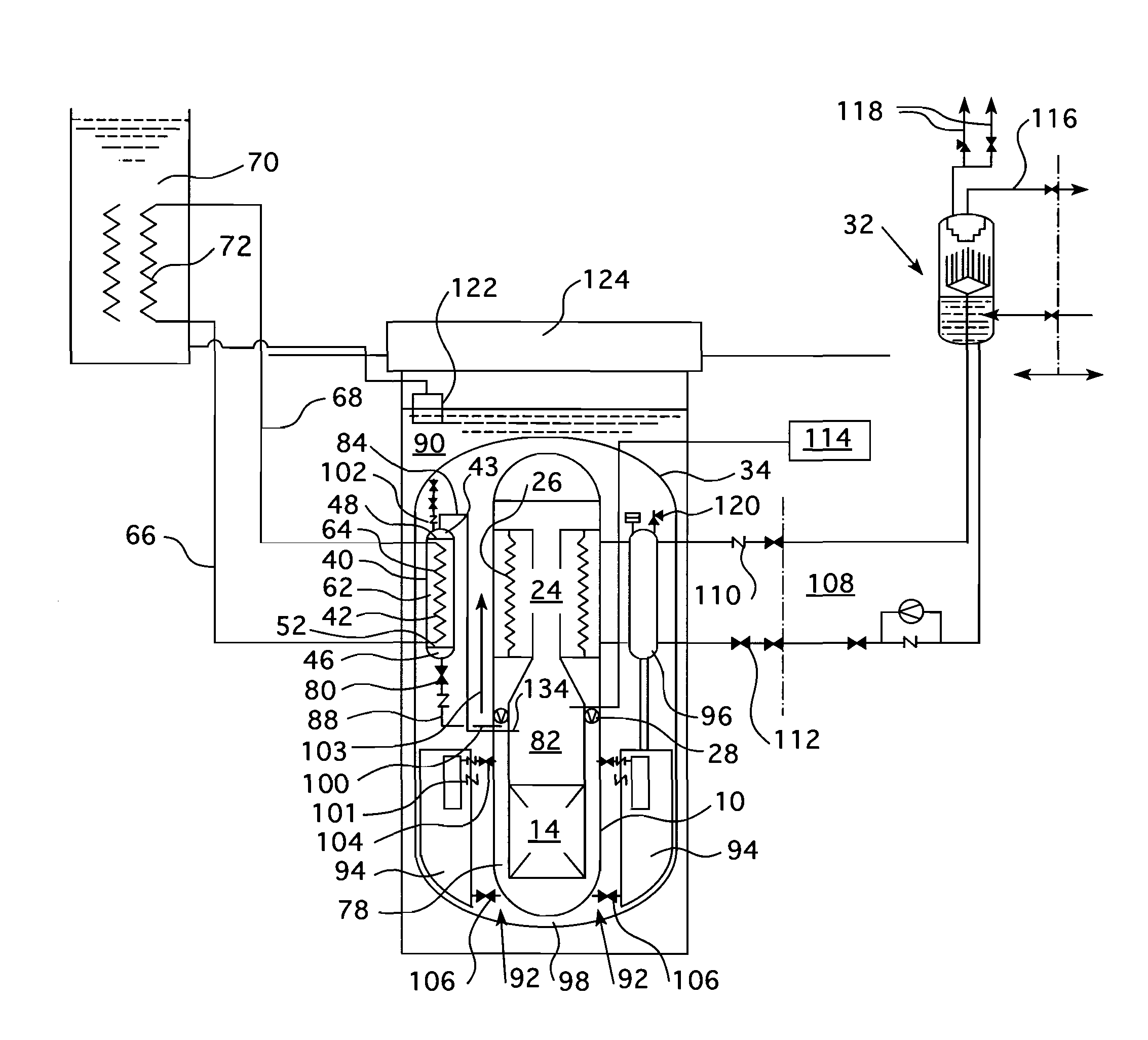
A passive safety system includes a containment, a reactor in the containment, a plurality of safety injection tanks connected with the reactor and having water and nitrogen gas to supply water thereof into the reactor through a safety injection line communicating to the first safety injection line upon a loss of coolant accident, a plurality of core makeup tanks connected with the reactor to supply water thereof into the reactor through a second safety injection line communicating to a safety injection line upon the loss of coolant accident, and a plurality of passive residual heat removal systems to remove residual heat from the reactor upon the loss of coolant accident or a non-loss of coolant accident. The water in each of the safety injection tank is stably supplied to the reactor for many hours by a differential head resulting from gravity or gas pressure.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
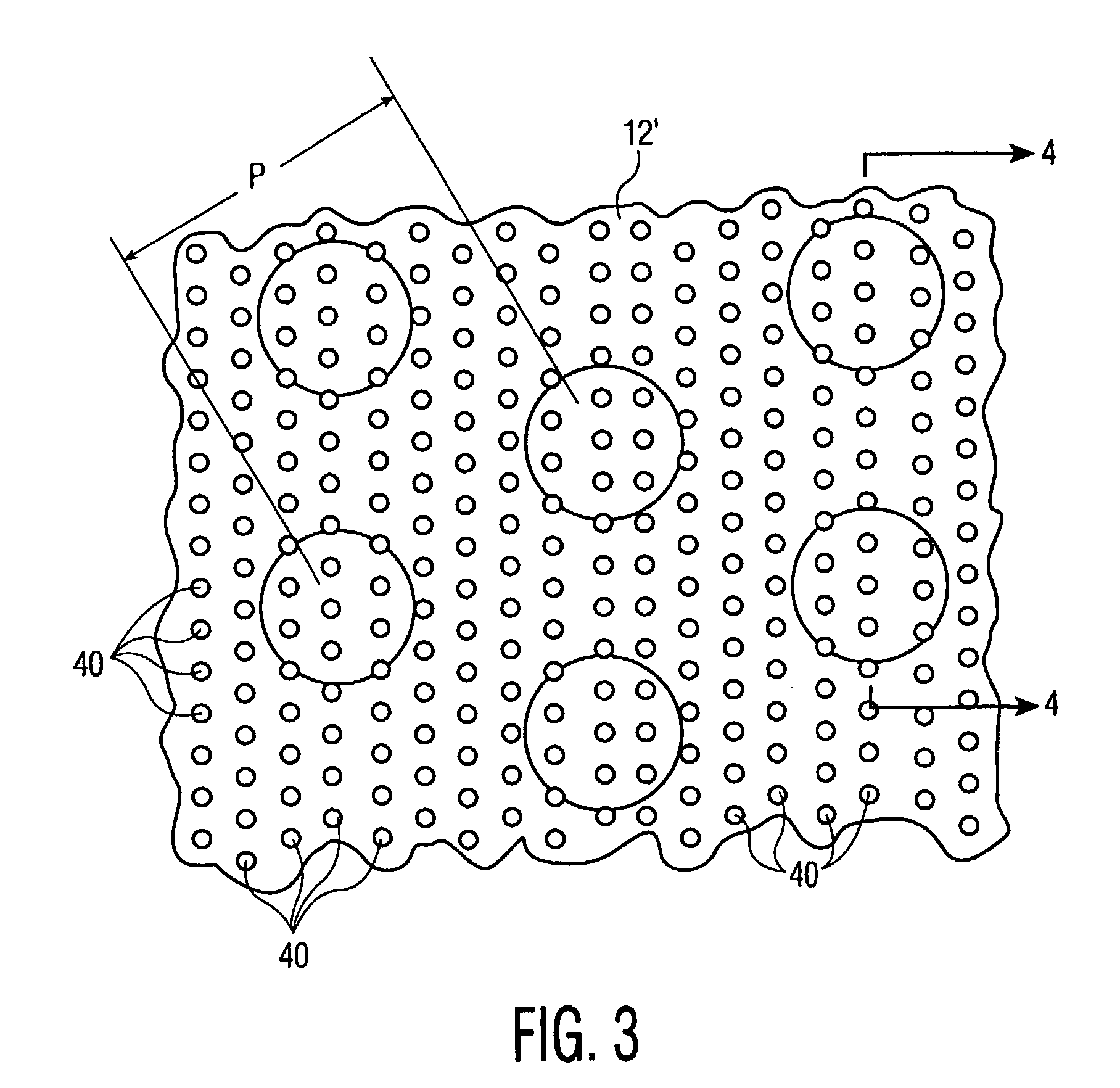
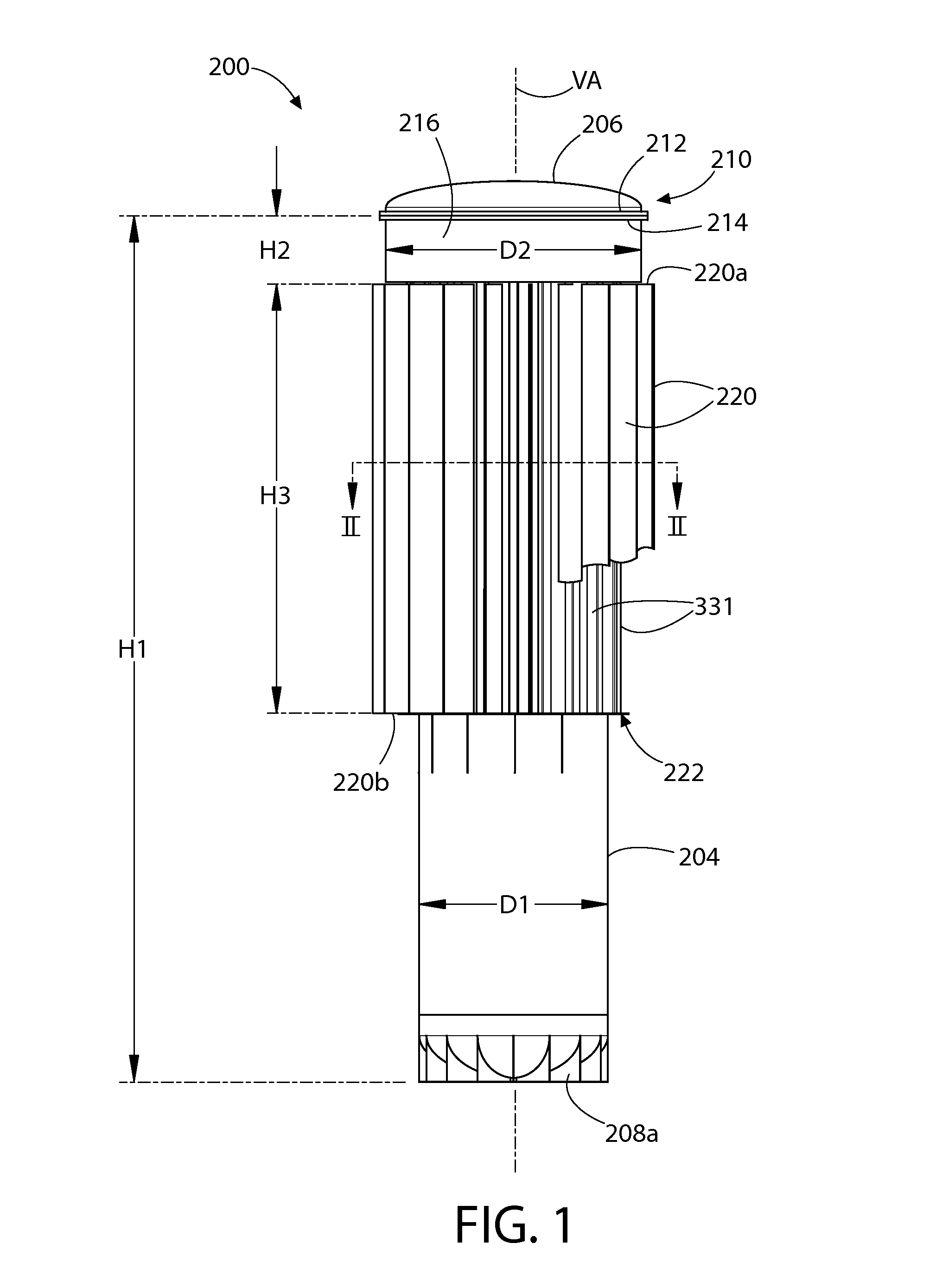
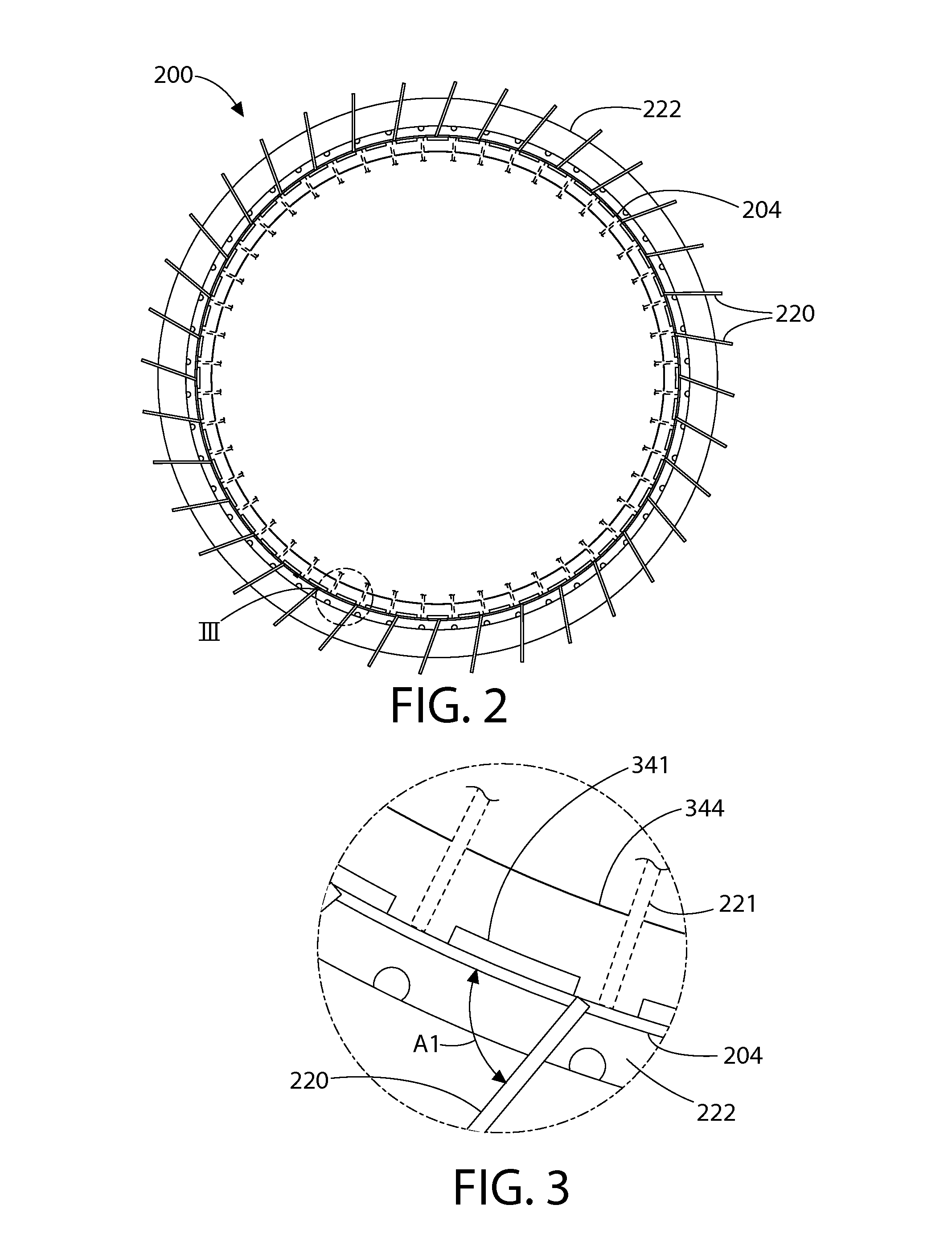
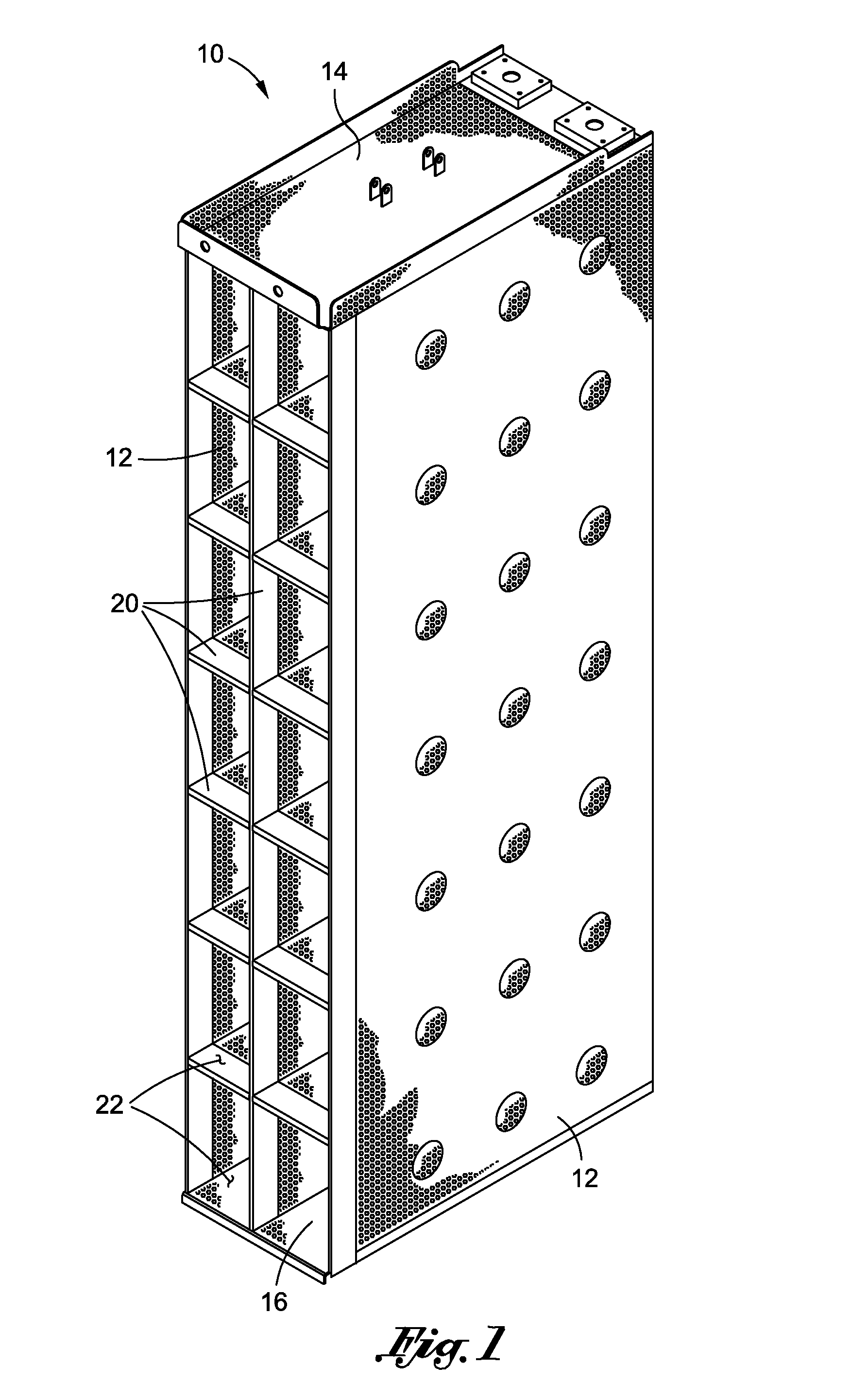
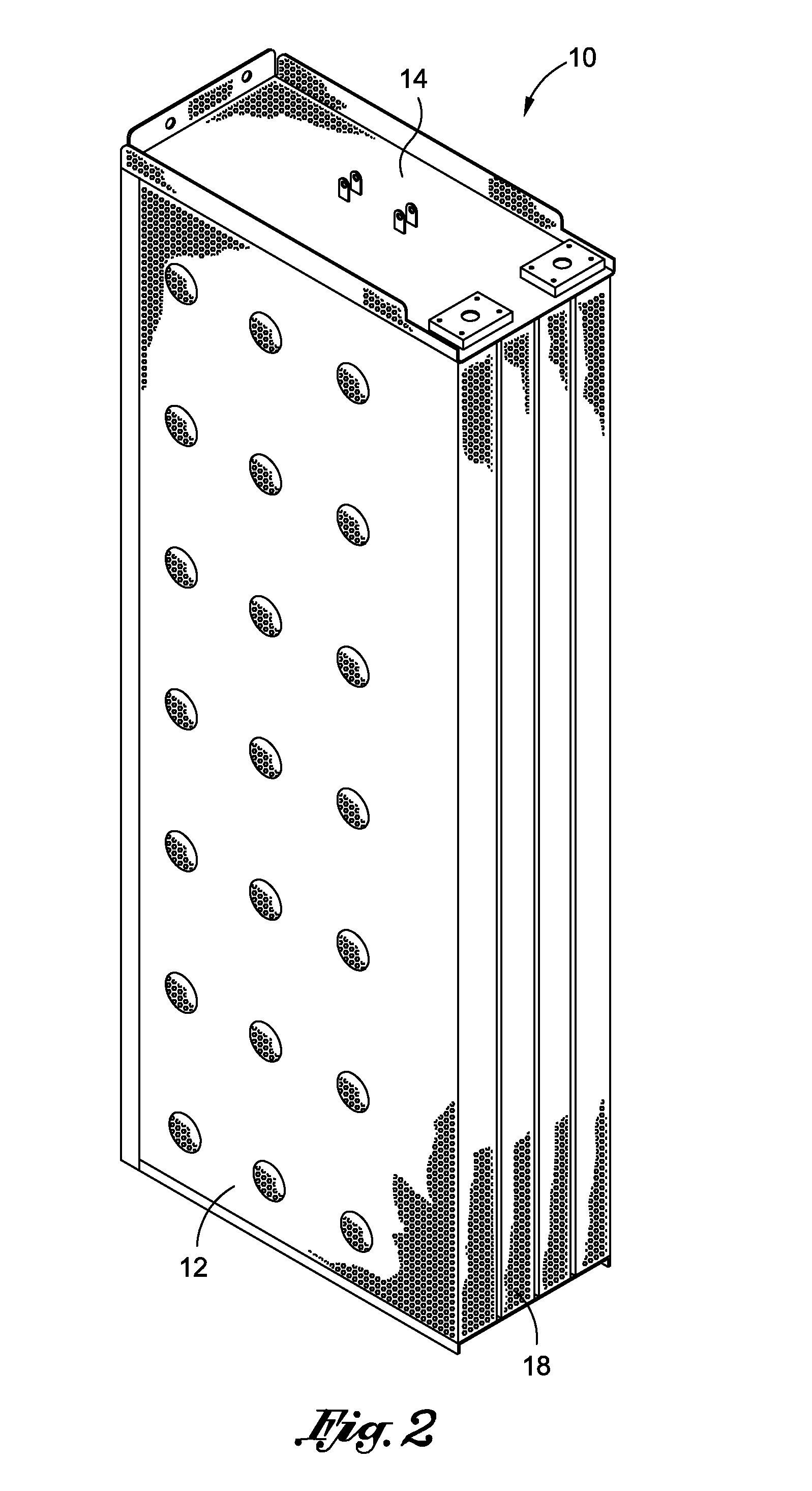
Finned Strainer
ActiveUS20080156712A1Uniform fluid flowNuclear energy generationSedimentation separationNuclear powerNuclear engineering
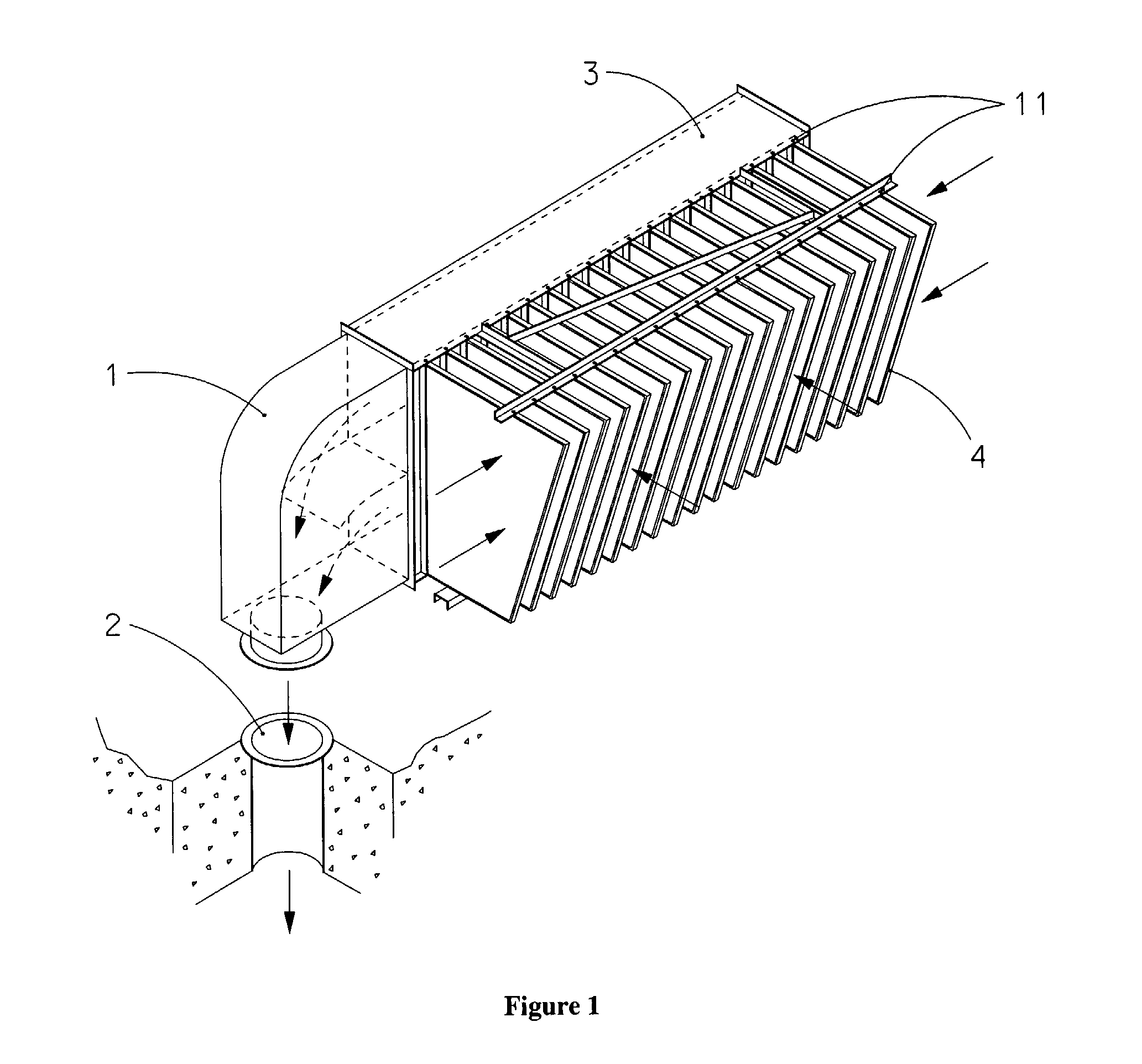
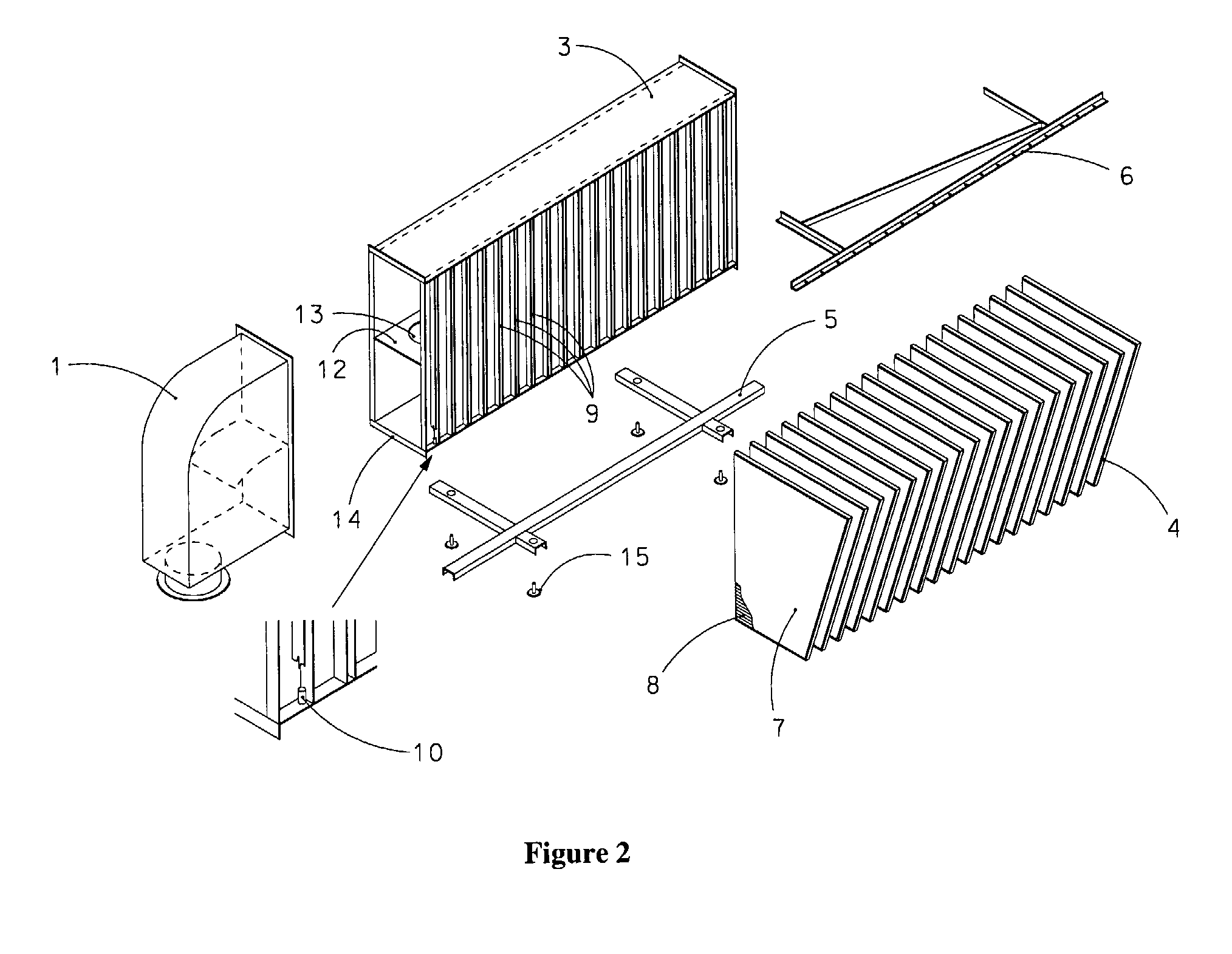
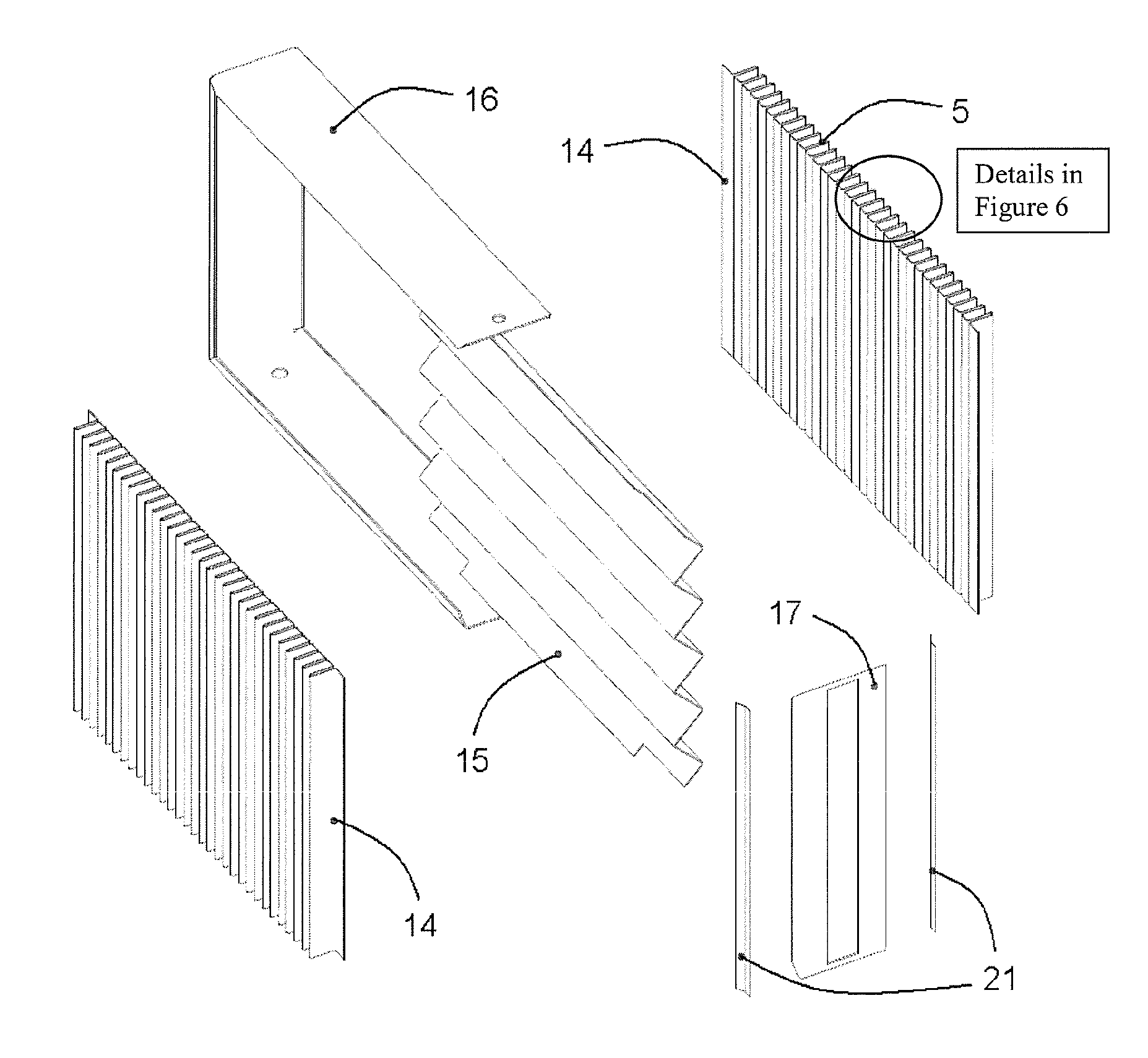
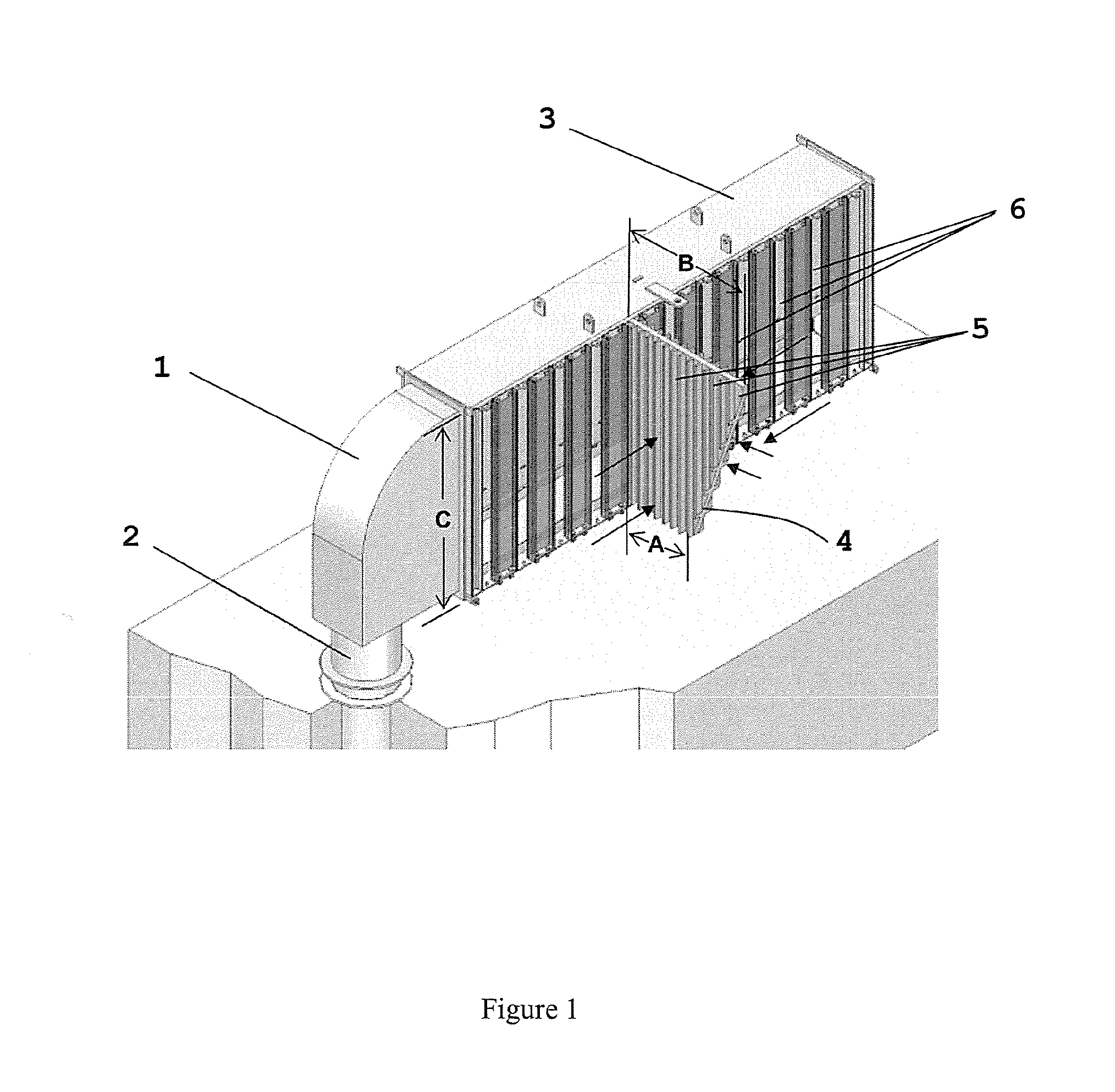
The present invention relates to filters used to remove debris from water being sucked into a piping system. It has particular application use in nuclear power plants, which, after a loss of coolant accident, must pump cooling water back into the reactor core from a collection sump. This water may contain various types of debris that must be removed before the water is sent back into the reactor cooling system. There are restrictions on the allowable pressure drop across the strainer and the space available for installing this equipment. The finned strainer of the present invention addresses these issues while maximizing the quantity of debris filtered from the water.
Owner:ATOMIC ENERGY OF CANADA LIMITED
Vaned filtering element
ActiveUS20120273407A1More compact designReduce thin-bed effectNuclear energy generationMembrane filtersNuclear powerEngineering
The present invention relates to filters used to remove debris from water being sucked into a piping system. It has particular application for use in nuclear power plants, which, after a loss of coolant accident, must pump cooling water back into the reactor core from a collection sump. This water may contain various types of debris that must be removed before the water is sent back into the reactor cooling system. Filtering of the debris is realized with the component known as “strainers”. There are restrictions on the space available for installing strainers. The vaned filtering element, for example a vaned fin, of the present invention is designed to reduce the space required for strainer installation by increasing strainer surface area per unit volume, while maximizing the quantity of debris that can be filtered from the water.
Owner:ATOMIC ENERGY OF CANADA LIMITED
Experimentally runnable dynamic simulation model for pressurized water reactor and steam generator thereof
InactiveCN102324205AImprove sensibilityEnhance rational understandingEducational modelsPressurized water reactorNuclear power
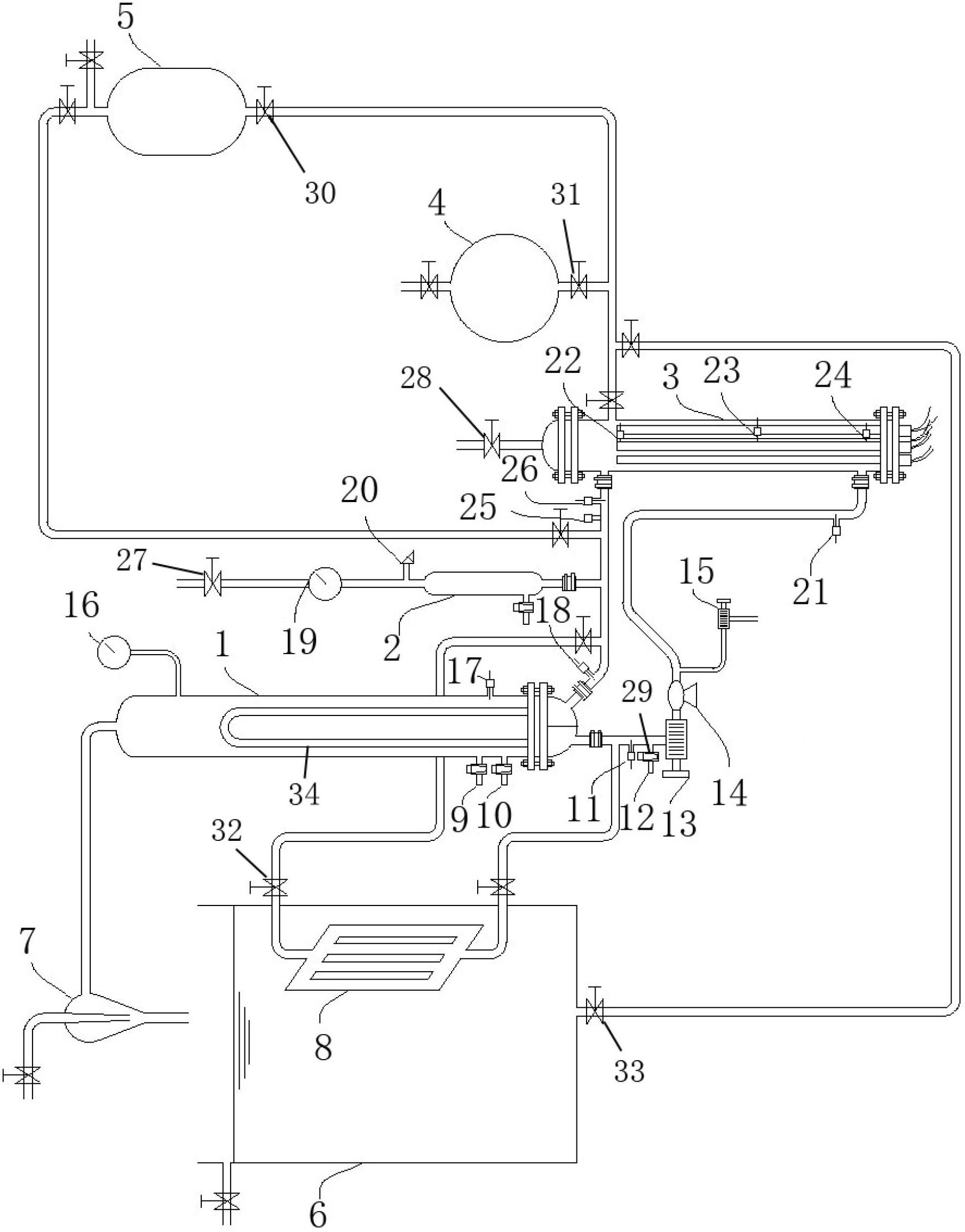
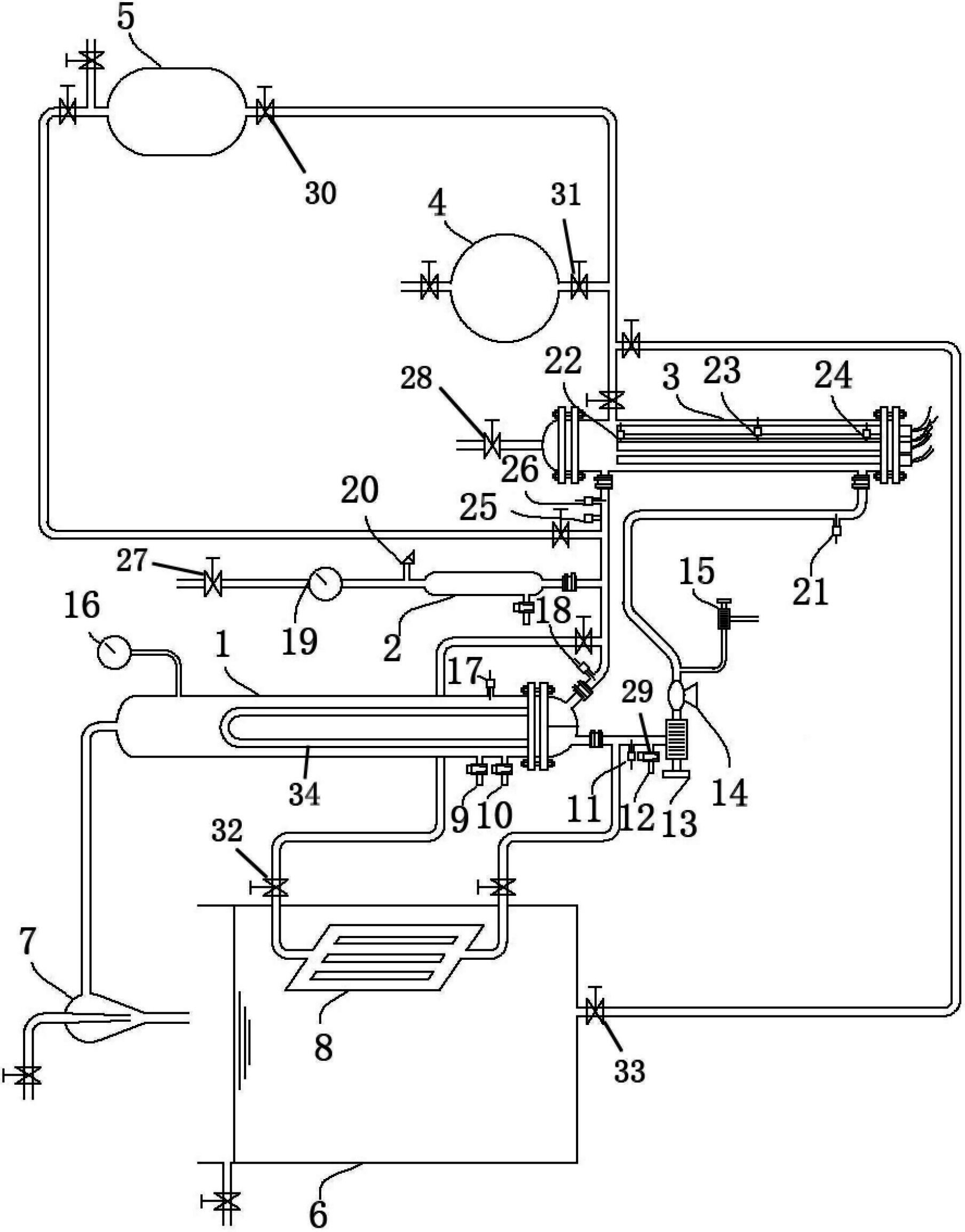
The invention belongs to the technical field of nuclear power and particularly relates to a dynamic simulation model for a pressurized water reactor and a steam generator thereof, which can be used for conducting teaching experiments and simulating the normal operation and the loss-of-coolant accident of the pressurized water reactor. The dynamic simulation model consists of the steam generator, a pressure vessel, a pressure stabilizer, pipelines, a measurement system and a heating element. The lower head of the steam generator is divided into a water inlet chamber and a water outlet chamber through a baffle, wherein the water inlet chamber is connected with the upper part of the pressure vessel through a water inlet pipeline and the water outlet chamber is connected with the lower part of the pressure vessel through a water outlet pipeline. The water inlet pipeline is connected with the pressure stabilizer by arranging a bypass on the water inlet pipeline. The top of the pressure stabilizer is respectively connected with the tops of four liquid column manometers through the pipelines. The bottoms of the four liquid column manometers are respectively connected with four outlets which are evenly distributed on the side wall of the pressure vessel along the height direction. The model has the advantages that the structure is simple, the implementation is easy, the model not onlyis safe and reliable, but also can be operated by students in person, the perceptual and rational knowledge of the students to a nuclear reactor is improved and the goals of teaching and conducting scientific researches are achieved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Passive containment vessel spraying device
InactiveCN103489490ASpray evenlyImprove securityNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementNuclear reactorActive component
The invention belongs to a device for spraying and cooling of the outer surface of a containment vessel in a passive mode, and particularly relates to the nuclear reactor containment vessel spraying and cooling device. The passive containment vessel spraying device comprises a safe spraying box, the safe spraying box is connected with an annular spraying header through a water transmission pipeline, the annular spraying header is arranged above a containment vessel dome, and a normally closed valve assembly is arranged between the water transmission pipeline and the annular spray header. The passive containment vessel spraying device has the advantages that the passive containment vessel spraying device is different from an active containment vessel interior spraying system of a conventional nuclear power plant and adopts an external spraying mode, does not need a safety-level emergency power supply and active components, and can realize short-term and long-term cooling of the containment vessel during superposition of a reactor loss-of-coolant accident or a main steam pipeline fracture accident with a station blackout accident and other superposition of multiple extreme accidents.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Low Head Loss Modular Suction Strainer with Contoured Surfaces
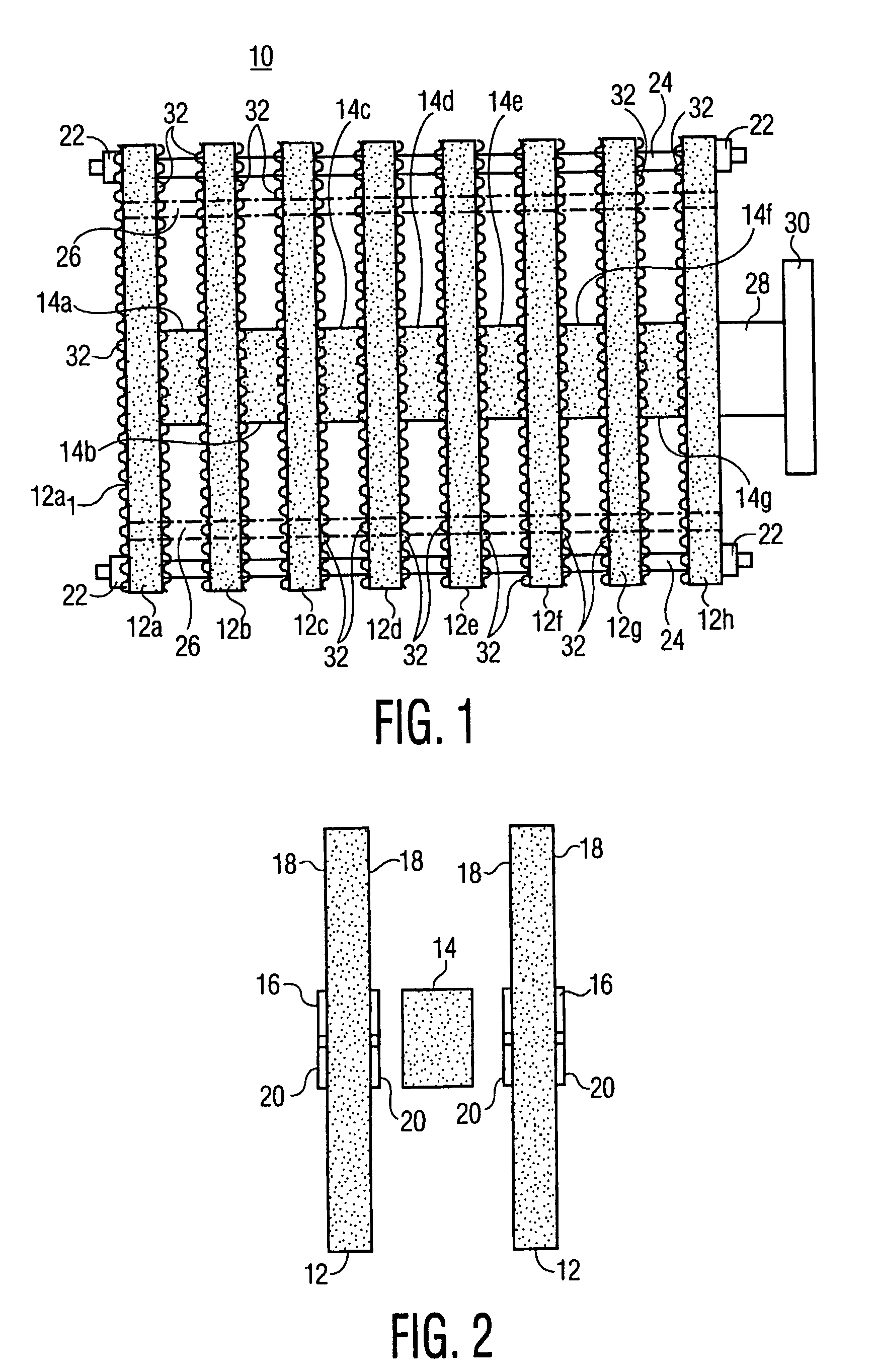
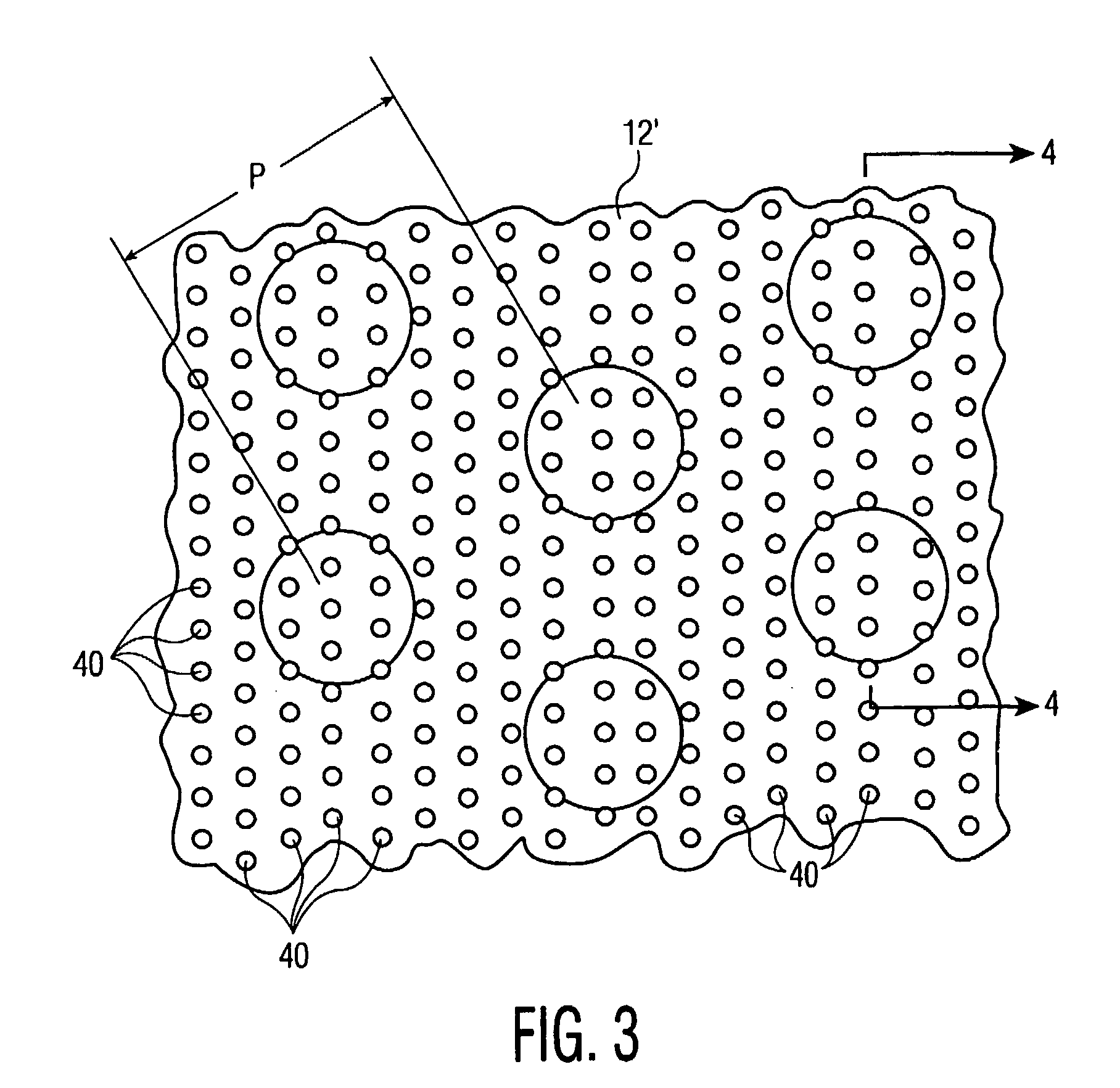
A strainer for an emergency core cooling system (ECCS) in a nuclear power plant comprises a perforated strainer element that is immersed in a reservoir of cooling water, which is drawn through the strainer element into the emergency core cooling system. The side of the strainer element in contact with the cooling water has a contoured configuration for disrupting the formation of a flat bed of fibrous material that can trap small particulate material intended to pass through the strainer element. Incorporating this strainer element into an ECCS strainer enables the strainer to be made more compact, because the debris bed need not be spread over an unduly large area to prevent excessive head loss from the debris load in the event of a reactor loss of coolant accident. The strainer also incorporates a modular construction that uses individual strainer disc modules. Each disc module includes a perforated first disc part having a central opening and a perforated second disc part also having a central opening. The first and second disc parts fit together to form an interior space with facing perforated major surfaces and an axial opening, and connecting tubes between the discs place the axial openings in fluid communication. The entire assembly is secured together by tie rods that hold the discs together with the connecting tubes compressed between them.
Owner:CONTINUUM DYNAMICS
Separate type safety injection tank and integral type reactor having the same
ActiveUS20140050292A1Prevent backflowPower plant safety arrangementIntegral reactorsNuclear engineeringProduct gas
A separate type safety injection tank comprises: a coolant injection unit connected to a reactor coolant system by a safety injection pipe such that coolant stored therein is injected into the reactor coolant system by a pressure difference from the reactor coolant system when a loss-of-coolant-accident (LOCA) occurs; a gas injection unit connected to the coolant injection unit, and configured to pressurize the coolant injected into the reactor coolant system, by introducing gas stored therein to an upper part of the coolant injection unit in the loss-of-coolant-accident; and a choking device disposed between the coolant injection unit and the gas injection unit, and configured to contract a flow cross-sectional area of the gas introduced to the coolant injection unit, and configured to maintain a flow velocity and a flow rate of the gas introduced to the coolant injection unit as a critical flow velocity and a critical flow rate when a pressure difference between the coolant injection unit and the gas injection unit is more than a critical value.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Risk-informed nuclear power plant LLOCA (large break loss of coolant accident) analysis method
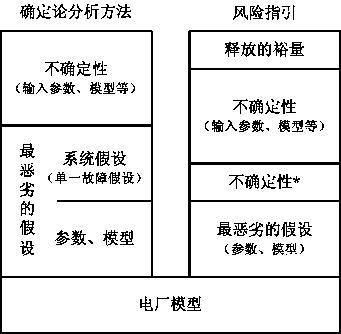
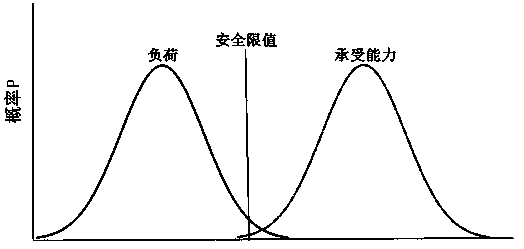
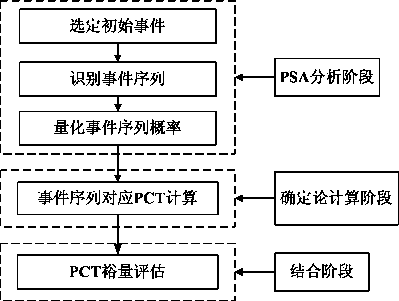
The invention discloses a risk-informed nuclear power plant LBLOCA (large break loss-of-coolant accident) analysis method. The method mainly comprises the following steps: 1) selecting an initial event as a nuclear power plant LLOCA; 2) according to a risk system evaluation method, establishing an event tree under the initial event, and indentifying all possible response sequences of a safety system for mitigation measures of a nuclear power plant after occurrence of the LLOCA; 3) for the event tree analysis results, combining with fault tree analysis and taking various failure data into overall consideration, quantizing occurrence possibility of all event sequences; 4) calculating peak cladding temperature corresponding to each event sequence; and 5) estimating peak cladding temperature margin of the LLOCA. By introducing a probability risk evaluation technique to a conventional deterministic analysis method, a purpose of taking overall consideration of cognitive uncertainty and accidental uncertainty of the nuclear power plant is achieved, and analysis result is closer to actual situations of the nuclear power plant.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER TECH RES INST CO LTD +3
Low head loss modular suction strainer with contoured surfaces
A strainer for an emergency core cooling system (ECCS) in a nuclear power plant comprises a perforated strainer element that is immersed in a reservoir of cooling water, which is drawn through the strainer element into the emergency core cooling system. The side of the strainer element in contact with the cooling water has a contoured configuration for disrupting the formation of a flat bed of fibrous material that can trap small particulate material intended to pass through the strainer element. Incorporating this strainer element into an ECCS strainer enables the strainer to be made more compact, because the debris bed need not be spread over an unduly large area to prevent excessive head loss from the debris load in the event of a reactor loss of coolant accident. The strainer also incorporates a modular construction that uses individual strainer disc modules. Each disc module includes a perforated first disc part having a central opening and a perforated second disc part also having a central opening. The first and second disc parts fit together to form an interior space with facing perforated major surfaces and an axial opening, and connecting tubes between the discs place the axial openings in fluid communication. The entire assembly is secured together by tie rods that hold the discs together with the connecting tubes compressed between them.
Owner:CONTINUUM DYNAMICS
Passive high pressure safety injection tank system (HPSIT) for responding to station blackout (SBO) and loss-of-coolant accidents (LOCA)
ActiveUS20120263268A1Simplify System DesignSimplified mitigationPower plant safety arrangementNuclear energy generationReactor systemOperation mode
A high pressure safety injection tank (HPSIT) system includes one safety injection tank (HIT) which replaces a core makeup tank (CMT) and a low pressure (approximately 4.3 Mpa or below) safety injection tank (SIT) and which can shift to and operate on a high pressure (approximately 17 Mpa) operation mode, to enable injection of emergency core coolant into a reactor system both under low pressure (approximately 4.3 Mpa or below) and high pressure (approximately 17 Mpa).
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST +1
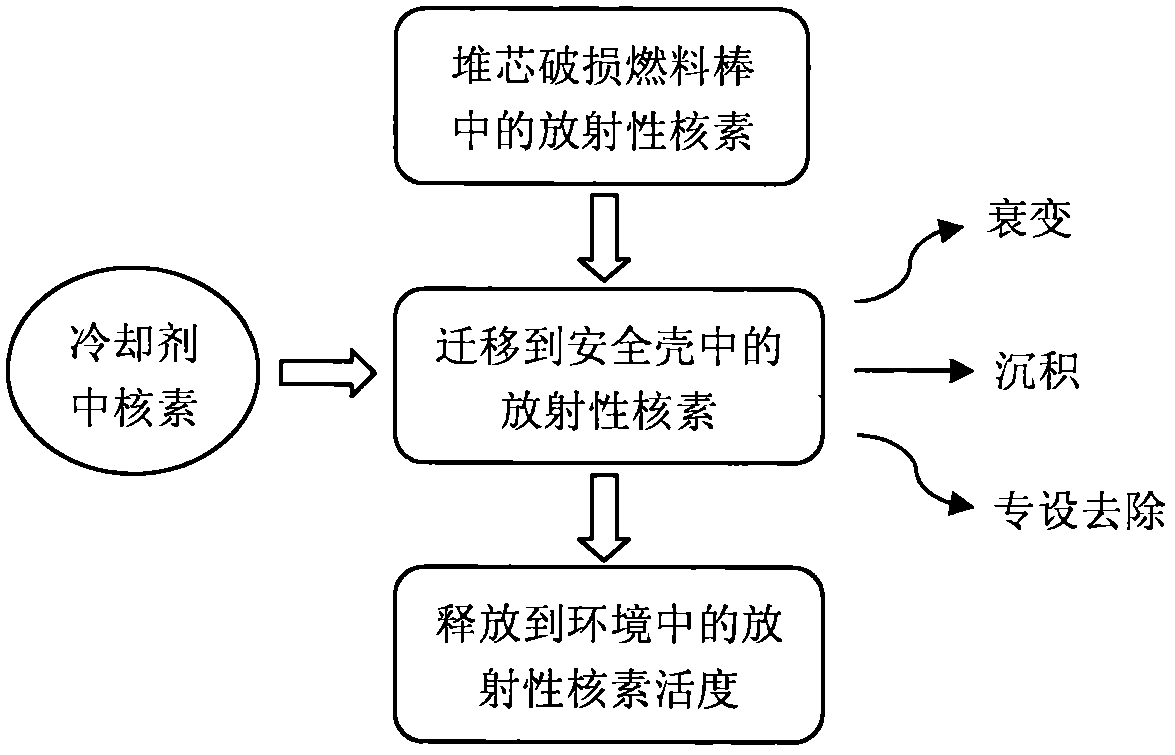
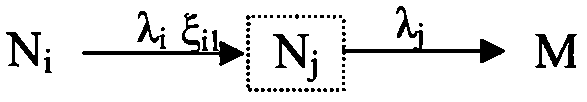
Pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant loss of coolant accident radioactive source term evaluation method
InactiveCN108537424AActivity classification calculationCalculations are reasonableResourcesNuclear engineeringPressurized water reactor
The invention relates to the field of nuclear radiation safety and particularly relates to a pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant loss of coolant accident radioactive source term evaluation method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) based on reactor equilibrium cycle life end core burden and the release share of radionuclides from the core to a containment atmosphere, the initial radioactivity of radionuclides released to the containment atmosphere by the reactor core is calculated; (2) the radionuclides are divided to three types according to decay types, and according tothe initial value of radionuclides in the containment atmosphere and a generation term and a subduction term during migration and release processes of the radionuclides in the containment, the radioactivity of each radionuclide in the containment atmosphere at different time is classified and calculated; and (3) according to the leakage rate of the containment and the radioactivity of the radionuclides in the containment atmosphere obtain in the second step, the radioactivity of the radionuclides released to the environment is subjected to integral calculation. The calculation method providedin the invention considers a complete nuclide decay chain, and the method is scientific and reasonable and strong in generality.
Owner:NUCLEAR & RADIATION SAFETY CENT
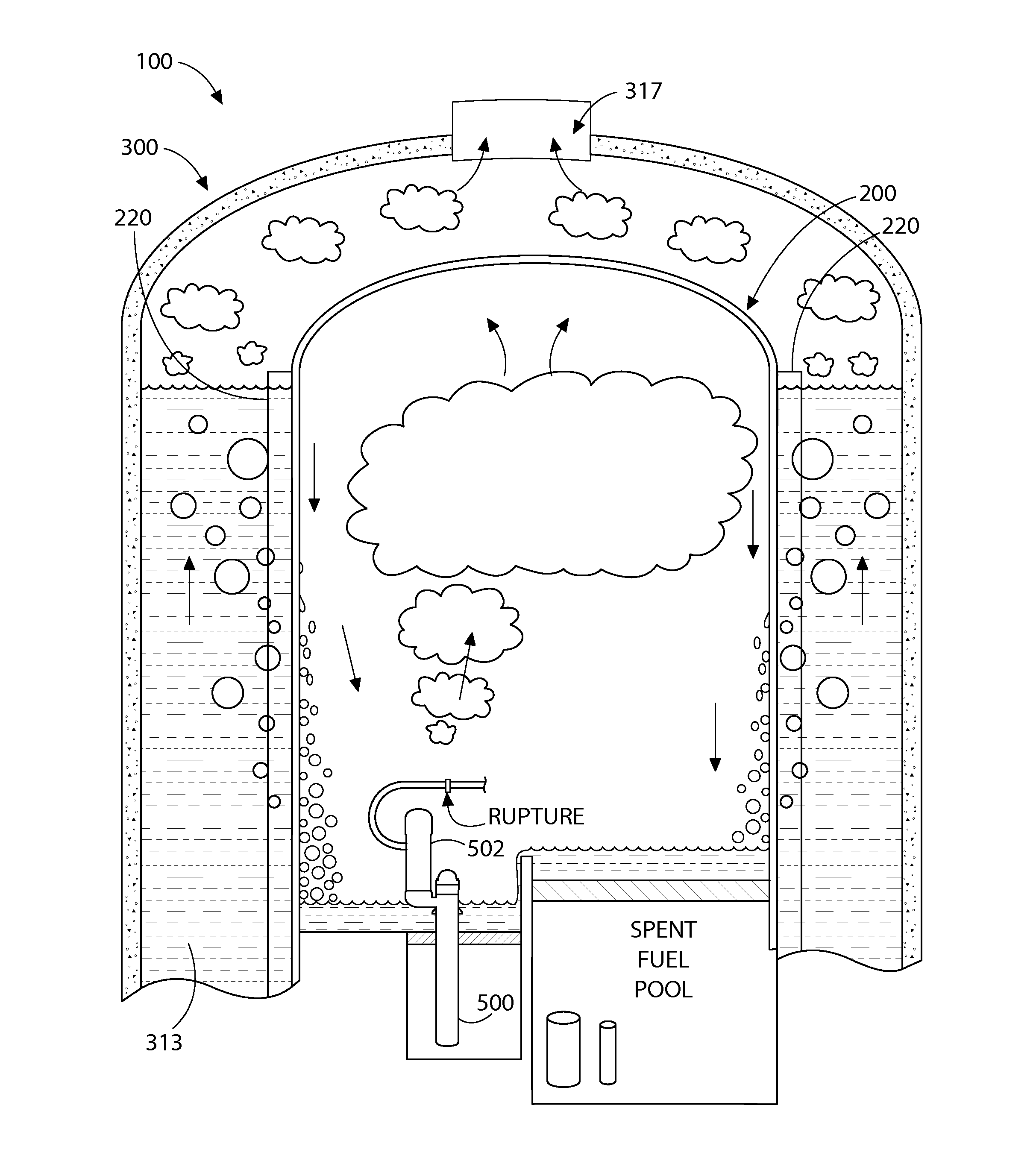
Loss-of-coolant accident reactor cooling system
ActiveUS20140321597A1Avoid warpingNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear reactorWater storage tank
A nuclear reactor cooling system with passive cooling capabilities operable during a loss-of-coolant accident (LOCA) without available electric power. The system includes a reactor vessel with nuclear fuel core located in a reactor well. An in-containment water storage tank is fluidly coupled to the reactor well and holds an inventory of cooling water. During a LOCA event, the tank floods the reactor well with water. Eventually, the water heated by decay heat from the reactor vaporizes producing steam. The steam flows to an in-containment heat exchanger and condenses. The condensate is returned to the reactor well in a closed flow loop system in which flow may circulate solely via gravity from changes in phase and density of the water. In one embodiment, the heat exchanger may be an array of heat dissipater ducts mounted on the wall of the inner containment vessel surrounded by a heat sink.
Owner:SMR INVENTEC +1
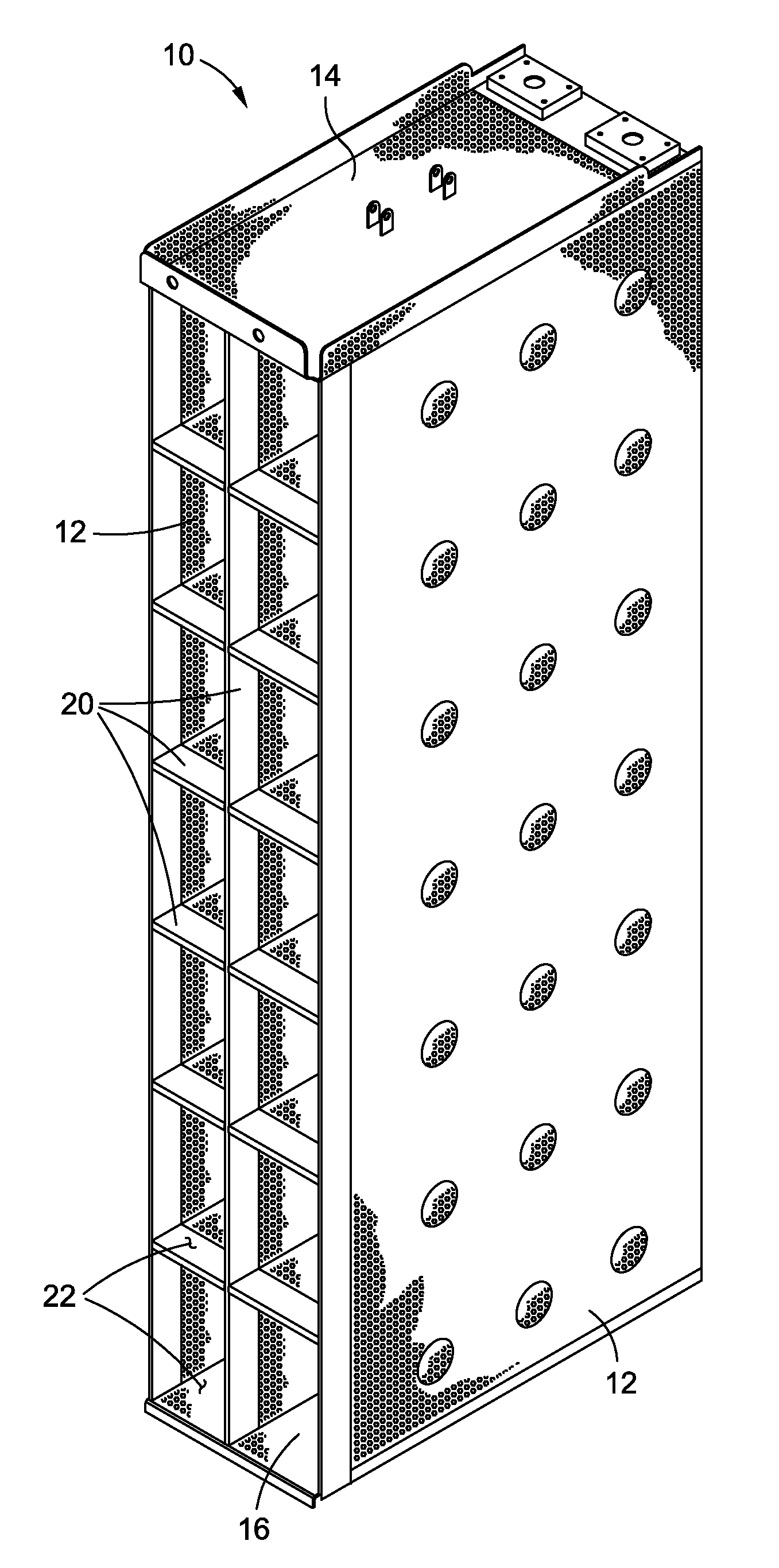
Enhanced nuclear sump strainer system
ActiveUS20130208847A1Easy to createEfficient trappingNuclear energy generationReactor fuel elementsFiberNuclear power
In accordance with the present invention, there is provided a strainer system for use in a nuclear sump. The strainer system of the present invention includes at least one primary strainer module which defines a primary strainer / filter surface. In the strainer system, the primary strainer surface of the primary strainer module has a debris interceptor which is cooperatively engaged thereto, and may be outfitted with one or more pressure released or activated membranes. In a loss of coolant accident, the debris interceptor, alone or in combination with the pressure activated membrane(s), is adapted to reduce the differential pressure experienced across the strainer system in nuclear power plants with medium to high fiber loads.
Owner:CONTROL COMPONENTS INC
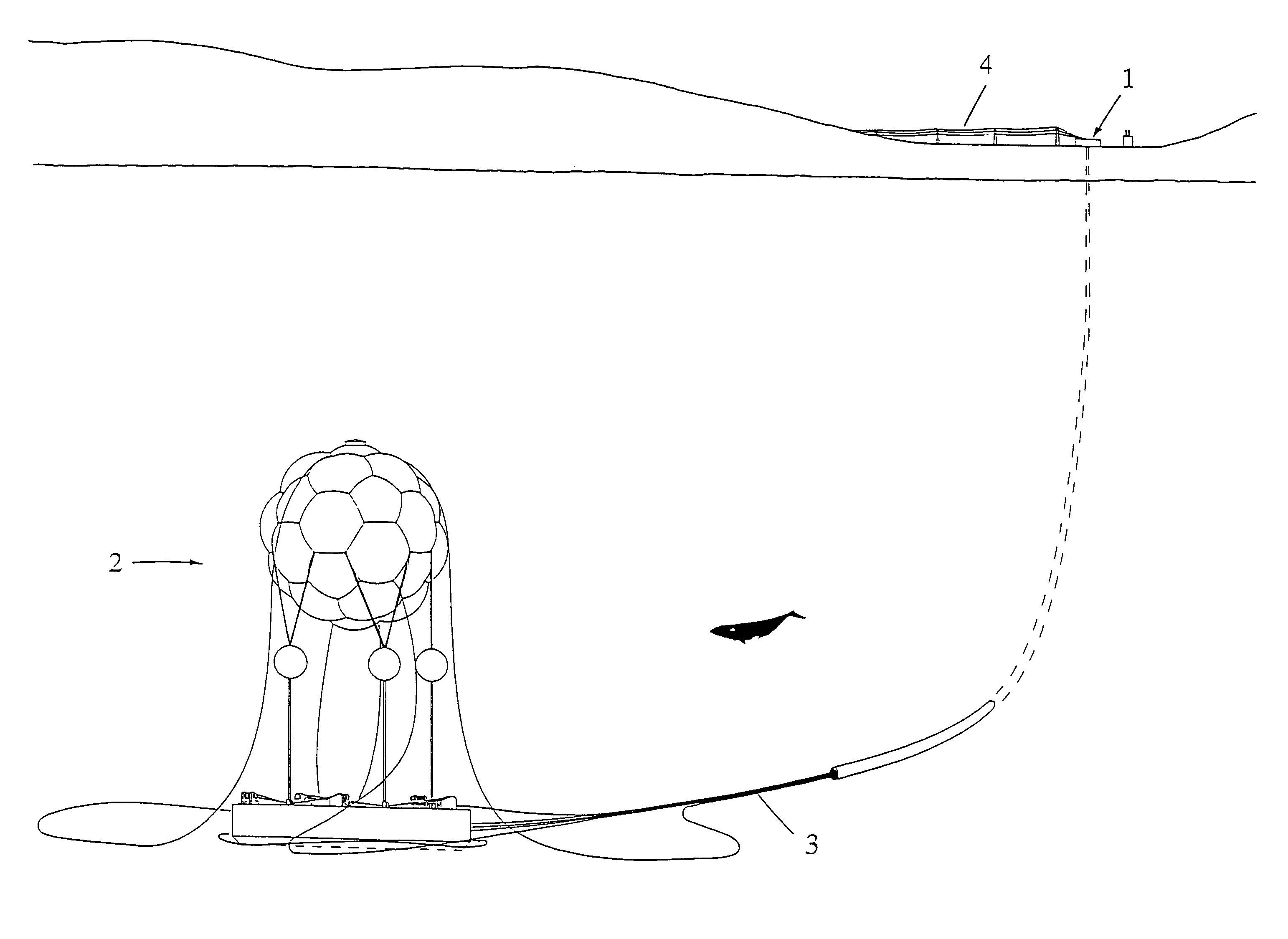
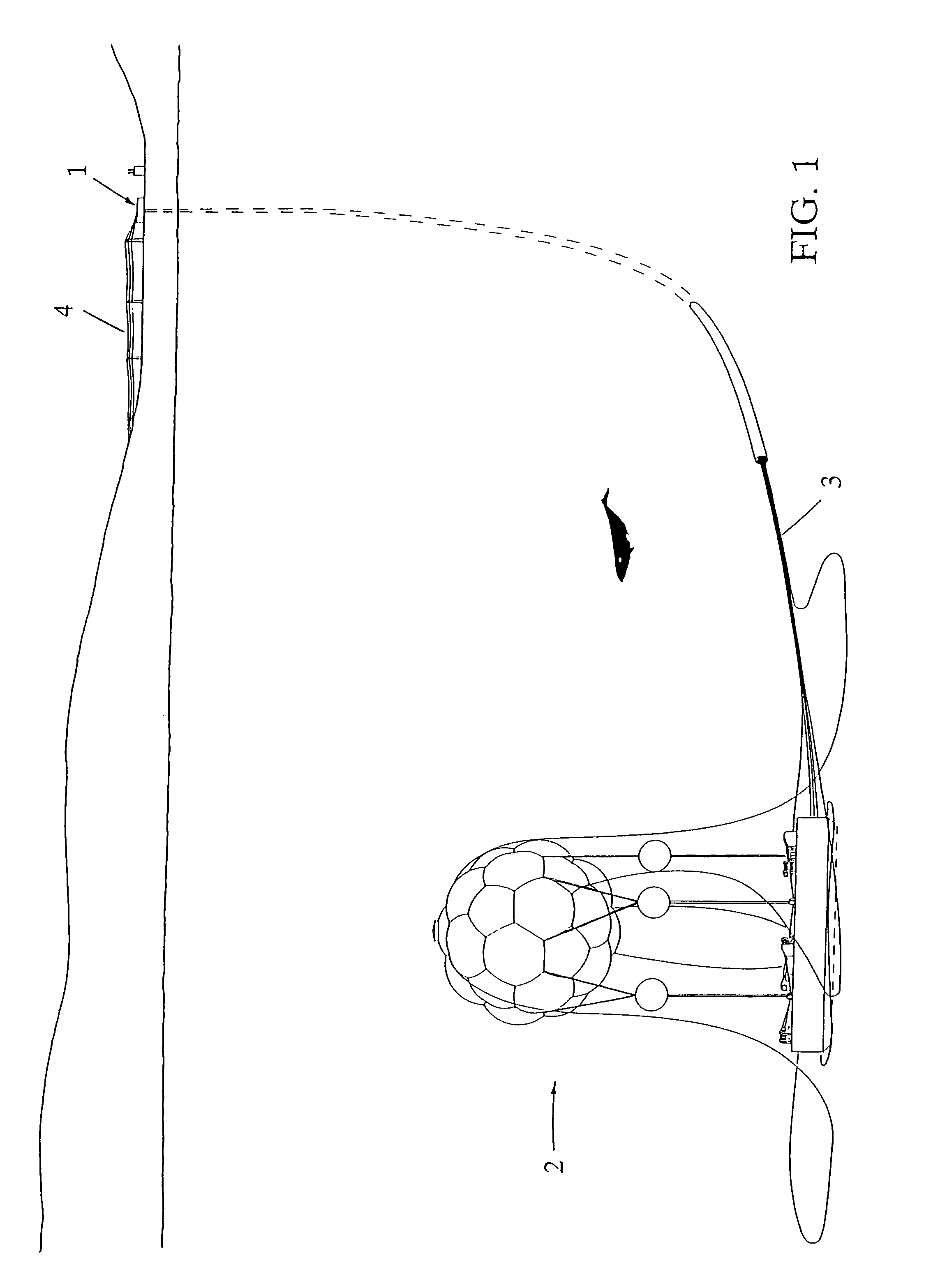
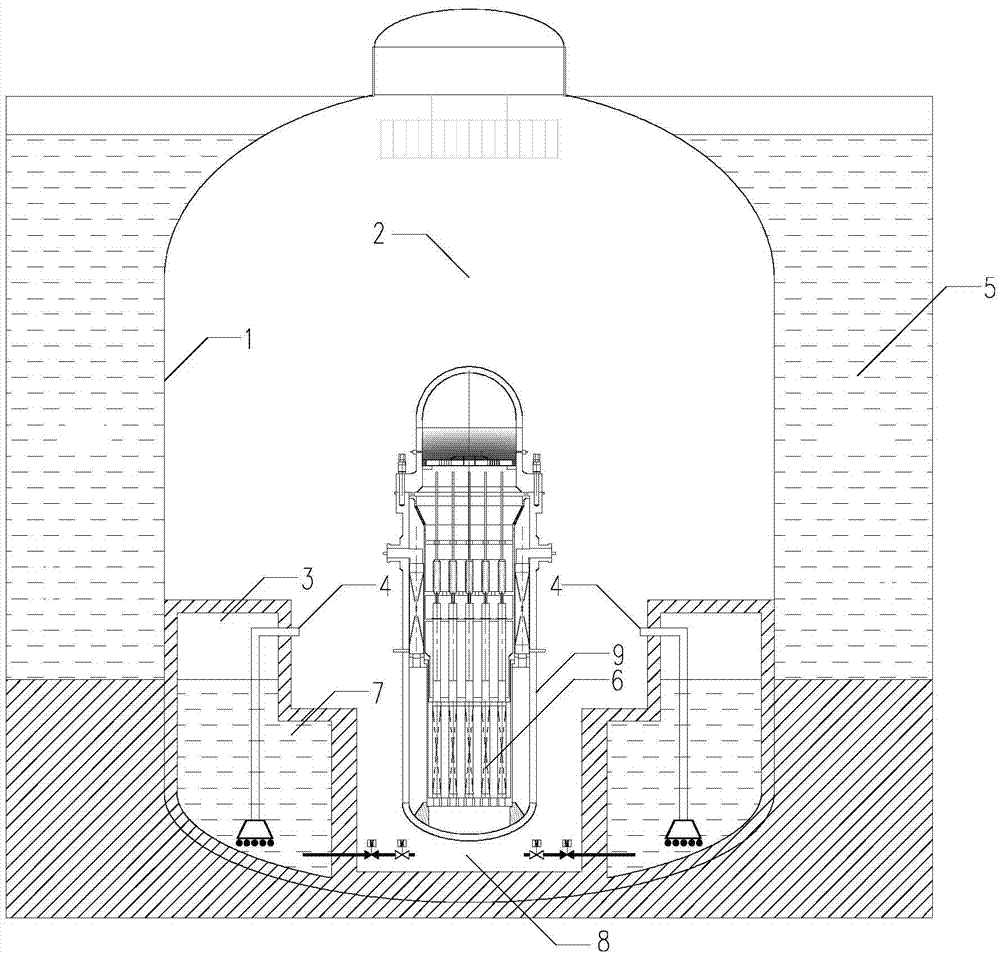
Seafloor power station
ActiveUS7978806B1Eliminates convection coolingReduce oxidationWaterborne vesselsNuclear energy generationElectricityOcean bottom
The Seafloor Power Station is one or more unmanned electric power generating Units (2) sending power to and operated from existing coastal sites by a manned facility (1) by connecting lines and hoses (3) delivering power to a grid by lines (4). Each Unit's hull (11) maintained in a vacuum, contains both nuclear steam and electricity generating systems. The hull functions as overpressure containment and as condenser in the event of a loss of coolant accident or other steam release. The Units operate submerged in very cold water, with depth set by remotely controlled vertical mooring systems, mounted on gravity mats (27). A Unit must be surfaced by its mooring system to refuel the reactor, an action both conspicuous and public, enabling international oversight of the fuel disposition.
Owner:HAYMAN III W Z ZACK
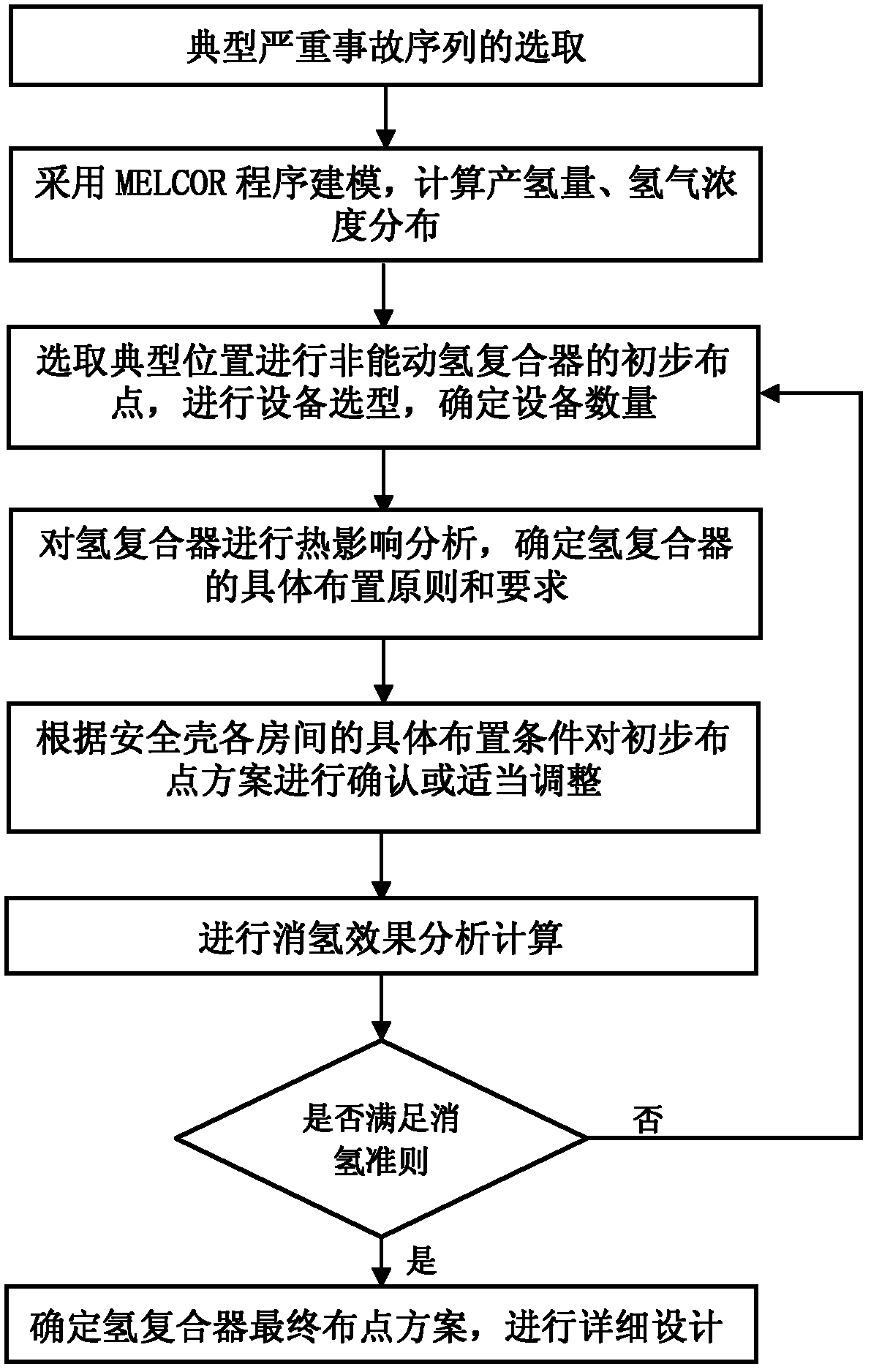
Design method for dehydrogenating containment of nuclear power station under serious accident
InactiveCN102306509AControlling Hydrogen RisksIntegrity guaranteedPower plant safety arrangementNuclear energy generationHydrogen concentrationSystems design
The invention belongs to a nuclear power station system design technology, and in particular relates to a design method for dehydrogenating a containment of a nuclear power station under a serious accident. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting large break loss of coolant accident (LBLOCA), small break loss of coolant accident (SBLOCA) and station blackout (SBO) as a typical serious accident sequence; according to the serious accident sequence, modeling by using an MELCOR program, and calculating hydrogen generation amount and hydrogen concentration distribution; according to the hydrogen generation amount and the hydrogen concentration distribution, selecting a typical position for initial point distribution of a non-kinetic hydrogen recombiner; performing thermal impact analysis on the hydrogen recombiner to determine specific arrangement principles and requirements of the hydrogen recombiner; and analyzing and calculating a dehydrogenation effect of an initial point distribution scheme of the hydrogen recombiner to determine a final power distribution scheme. In the invention, a containment non-kinetic hydrogen recombiner system can be arranged reasonably, and the method is used for controlling a hydrogen risk of the containment under the serious accident, so that the integrity of the containment serving as a third protective screen is ensured.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER ENG CO LTD
Reactor adapted for mitigating loss-of-coolant accident and mitigation method thereof
InactiveUS20130070887A1Mitigating a loss-of-coolant accidentReduce construction costsNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
Disclosed are a nuclear reactor adapted for mitigating a loss-of-coolant accident and a mitigation method thereof. The nuclear reactor includes a nuclear reactor vessel, a first pipe part connected to the nuclear reactor vessel to supply or drain fluid, and a first opening / closing part connected to the first pipe part. When the first pipe part is broken, the first opening / closing part closes the first pipe part to stop discharge of coolant. A supplementary coolant injection part is connected to the nuclear reactor vessel through a second pipe part. When the second pipe part is broken, a second opening / closing part closes the second pipe part to stop discharge of coolant.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Nuclear reactor direct safety injection system
ActiveCN104658621AInhibit expansionGood drainageNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
The invention discloses a nuclear reactor direct safety injection system which is used for directly offering cooling liquid to a pressure container in a nuclear reactor, wherein a hanging basket is arranged inside the pressure container; a nuclear reactor core is arranged inside the hanging basket; an annular cavity is formed between the pressure container and the hanging basket; the safety injection system comprises a safety injection cold source and a direct safety injection tube; the direct safety injection tube has an inlet and an outlet; the inlet is communicated with the safety injection cold source; the direct safety injection tube penetrates into the pressure container and extends into the annular cavity, and the outlet is formed below the nuclear reactor core. Since the direct safety injection tube penetrates into the pressure container and extends into the annular cavity, and the outlet is formed just below the nuclear reactor core, when loss of coolant accident occurs, the cooling liquid can be directly conveyed into the nuclear reactor core by virtue of the direct safety injection tube, so as to cool and boronize the nuclear reactor core timely and effectively, greatly improve the capacity of controlling and relieving accidents and effectively prevent the loss of coolant accident from developing to a hyper design basis accident.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER TECH RES INST CO LTD +2
Performance evaluation system for integrity of zirconium alloy fuel cladding for nuclear power station under LOCA (Loss-Of-Coolant Accident) working condition
The invention relates to a performance evaluation system for integrity of a zirconium alloy fuel cladding for a nuclear power station under an LOCA (Loss-Of-Coolant Accident) working condition. The performance evaluation system comprises a reaction device, a working gas distribution system, a mixed gas supply device, a steam-gas separator, a hydrogen gas analyzer, a water quenching system, a pressure measuring device and a vacuum system, wherein the reaction device comprises a sample chamber, a heating electrode for heating the cladding, and a temperature measurement device for measuring temperatures of the inner wall and the outer wall of the cladding; the sample chamber comprises a quartz tube, an upper end cover, a lower end cover, a mixed gas feeding pipe and an exhaust pipe; the working gas distribution system comprises a first gas tank for storing helium gas and a second gas tank for storing argon gas. The performance evaluation system provided by the invention can be used for evaluating loss-of-coolant of a reactor; after a safety injection system is started, water is injected into the reactor; after the cladding is quenched, the integrity of the cladding is evaluated; and the amount of hydrogen gas released by the zirconium alloy cladding in a high-temperature steam reaction process can also be measured, and equipment support is provided for out-of-pile performance evaluation in a zirconium alloy research and development process.
Owner:SUZHOU NUCLEAR POWER RES INST +2
Simulation running apparatus for passive safety master system of pressurized water reactor nuclear island
InactiveCN102693673AUnderstand the running processEducational modelsNuclear engineeringPressurized water reactor
The invention discloses a simulation running apparatus for a passive safety master system of a pressurized water reactor nuclear island, and belongs to the technical field of nuclear energy. The structure of the simulation running apparatus is that: a reactor core makeup water tank, a first electromagnetic valve, a second electromagnetic valve, an accumulator, a pressure vessel, an eighth thermal couple, an ink injector and a valve are assembled together through a pipeline, wherein the ink injector, a voltage regulator, a safety valve, a second pressure meter, a relief valve and a valve are assembled together through a pipeline; and the ink injector, a third thermal couple, a vapor generator, an injection pump and a valve are assembled together through a pipeline. The simulation running apparatus has the advantages that circulating processes of a first loop and a second loop under a normal working condition in a containment vessel of a nuclear island of a nuclear plant and running processes of a safe injection system and a passive residual heat removal exchanger under a loss of coolant accident (LOCA) working condition can be directly known.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
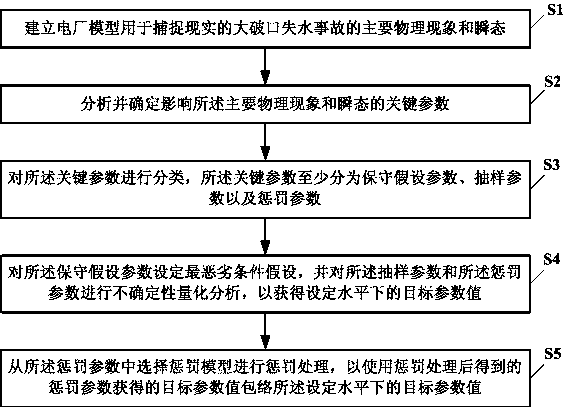
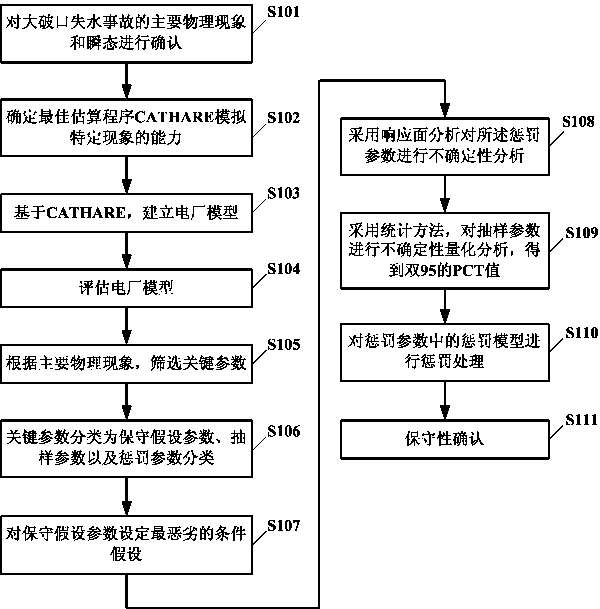
Method for analyzing large break accident of nuclear power plant
ActiveCN107644694AAvoid sampling calculationsAvoid being overly conservativeNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringTransient stateNuclear power
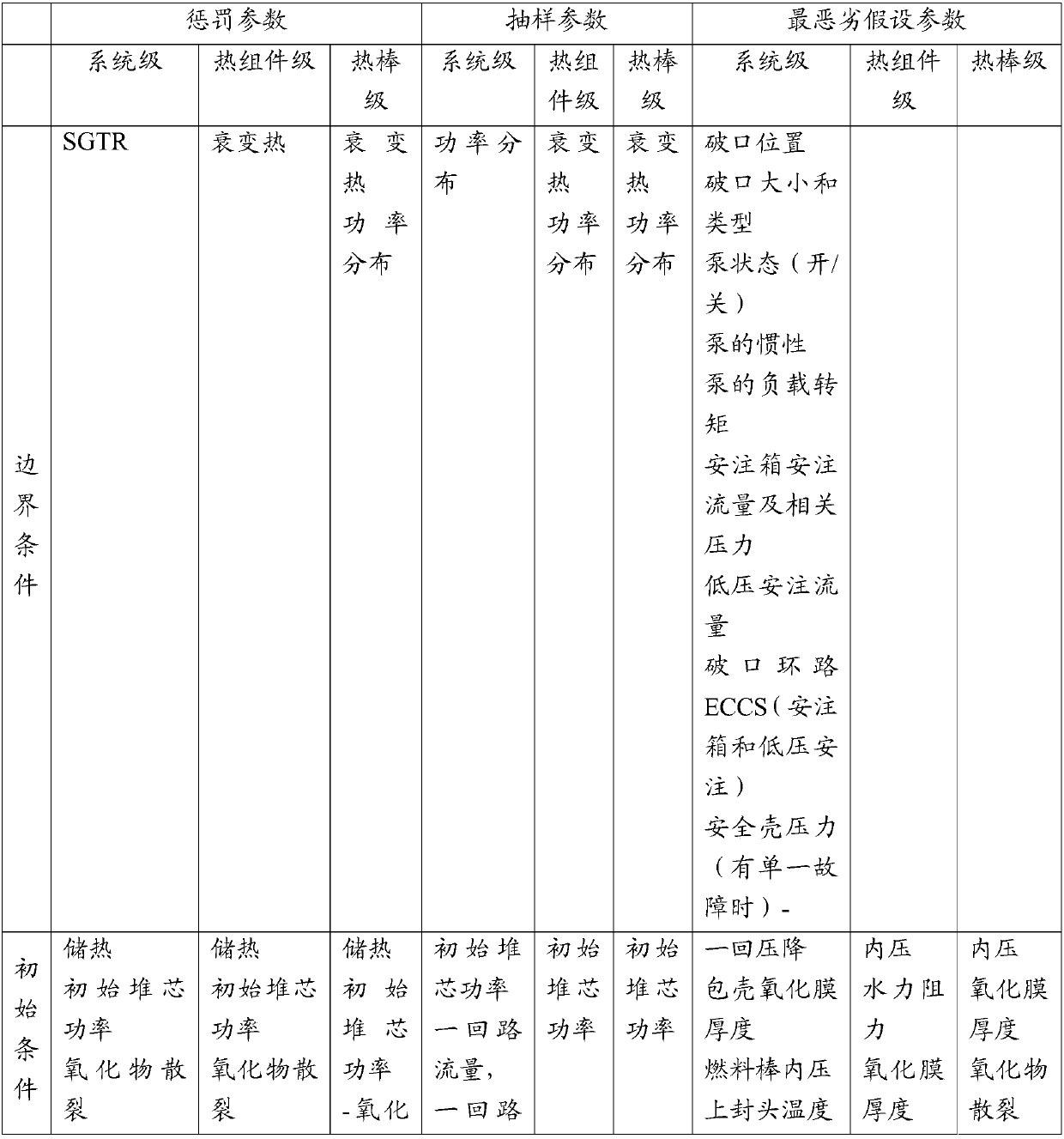
The invention provides a method for analyzing large break accident of a nuclear power plant. The method comprises the following steps: S1, building a power plant model for catching major physical phenomenon and transient state of real large break loss of coolant accident; S2, analyzing and determining key parameters of the major physical phenomenon and the transient state; S3, classifying the keyparameters, wherein the key parameters are classified into at least conservative assumption parameters, sampling parameters and penalty parameters; S4, setting the most severe condition assumption forthe conservative assumption parameters, and quantitatively analyzing uncertainty of the sampling parameters and the penalty parameters so as to obtain the target parameter value at the set level; S5,selecting a penalty model from the penalty parameters, and performing penalty, so as to realize that the target parameter value obtained through the penalty parameters obtained by penalty treatment includes the target parameter value at the set level. With the adoption of the method in the embodiment, the sampling calculation of a method combining the best estimation and the uncertainty analyzingis reduced, and the conservation margin of deterministic realistic method is decreased.
Owner:LINGDONG NUCLEAR POWER +3
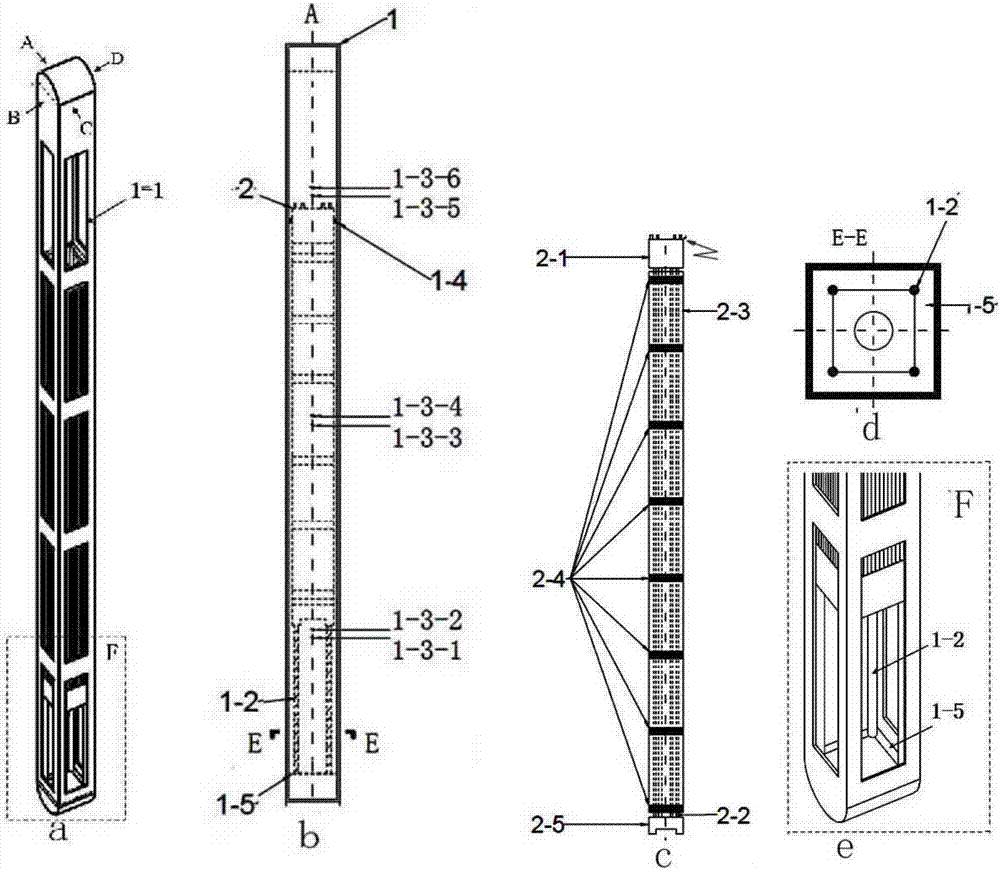
Migration transfer characteristic test system of fragments of reactor containment and test method thereof
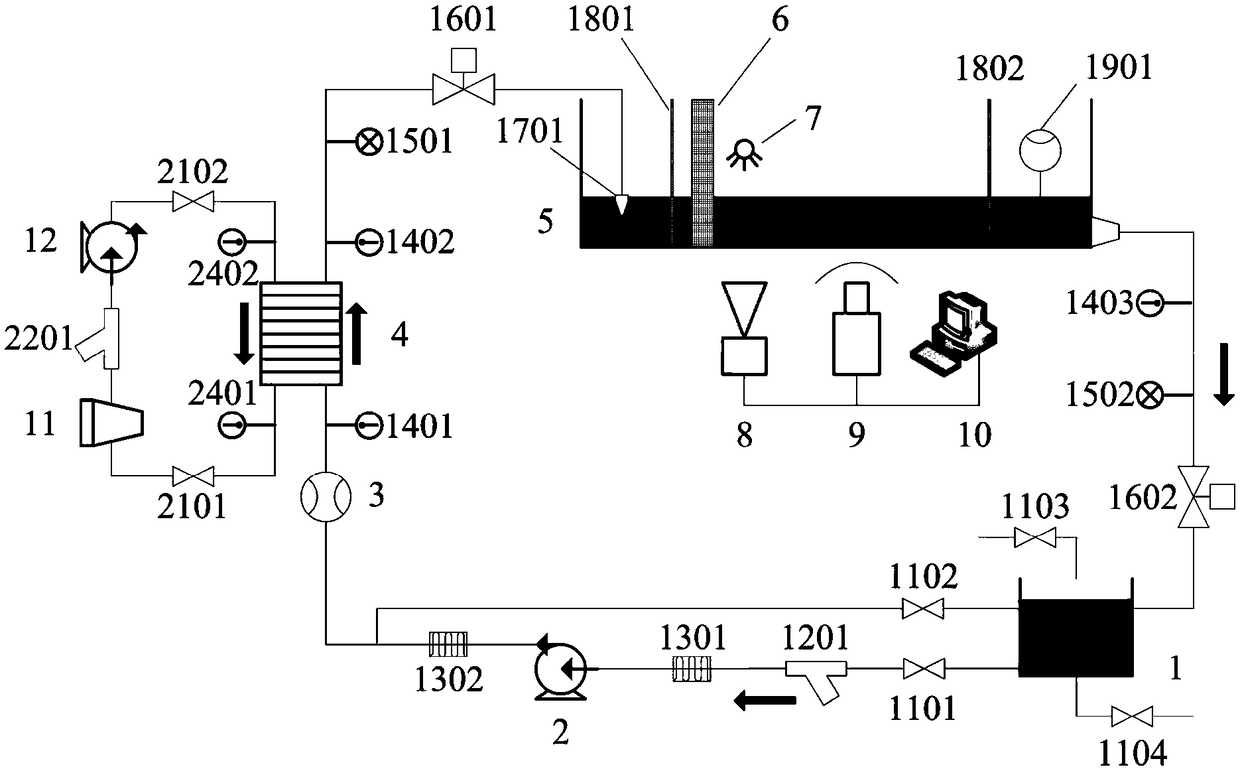
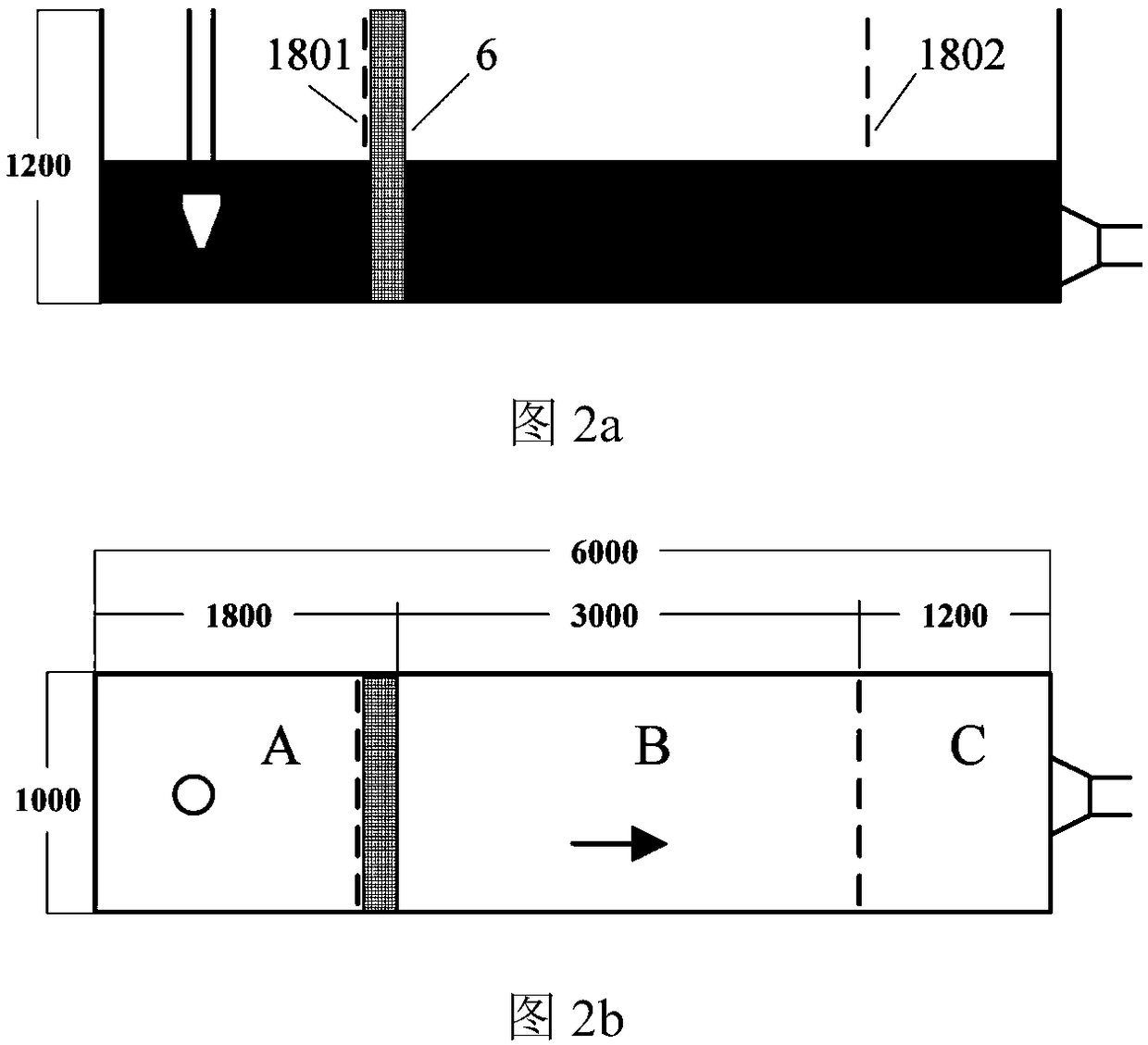
ActiveCN109243638AGet sportyMeet the test strength requirementsNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringCooling towerTest segment
The invention relates to a migration transfer characteristic test system of fragments of a reactor containment and a test method thereof. The system comprises a test segment module composed of a waterchannel, a rectifying grid, a filter screen and related equipment, a flow rate adjusting module composed of a water tank, a main water pump, an electric valve and related pipelines and instruments, acooling module composed of a cooling water pump, a heat exchanger, a cooling tower and related pipelines and instruments, a thermotechnical hydraulic parameter measuring module composed of a flowmeter, a temperature sensor, a pressure sensor and a liquidometer, an image collecting module composed of a high-speed camera, a local area network computer and related image processing software, a flow field information collection module composed of PIV equipment, a local area network computer and related flow field processing software and a remote control module composed of a programmable logic controller, a water pump, an electric valve and related equipment. The system simulates a ground water flow velocity field of the containment accurately after loss of coolant accident and acquires characteristic parameters of different fragments migrating in water.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
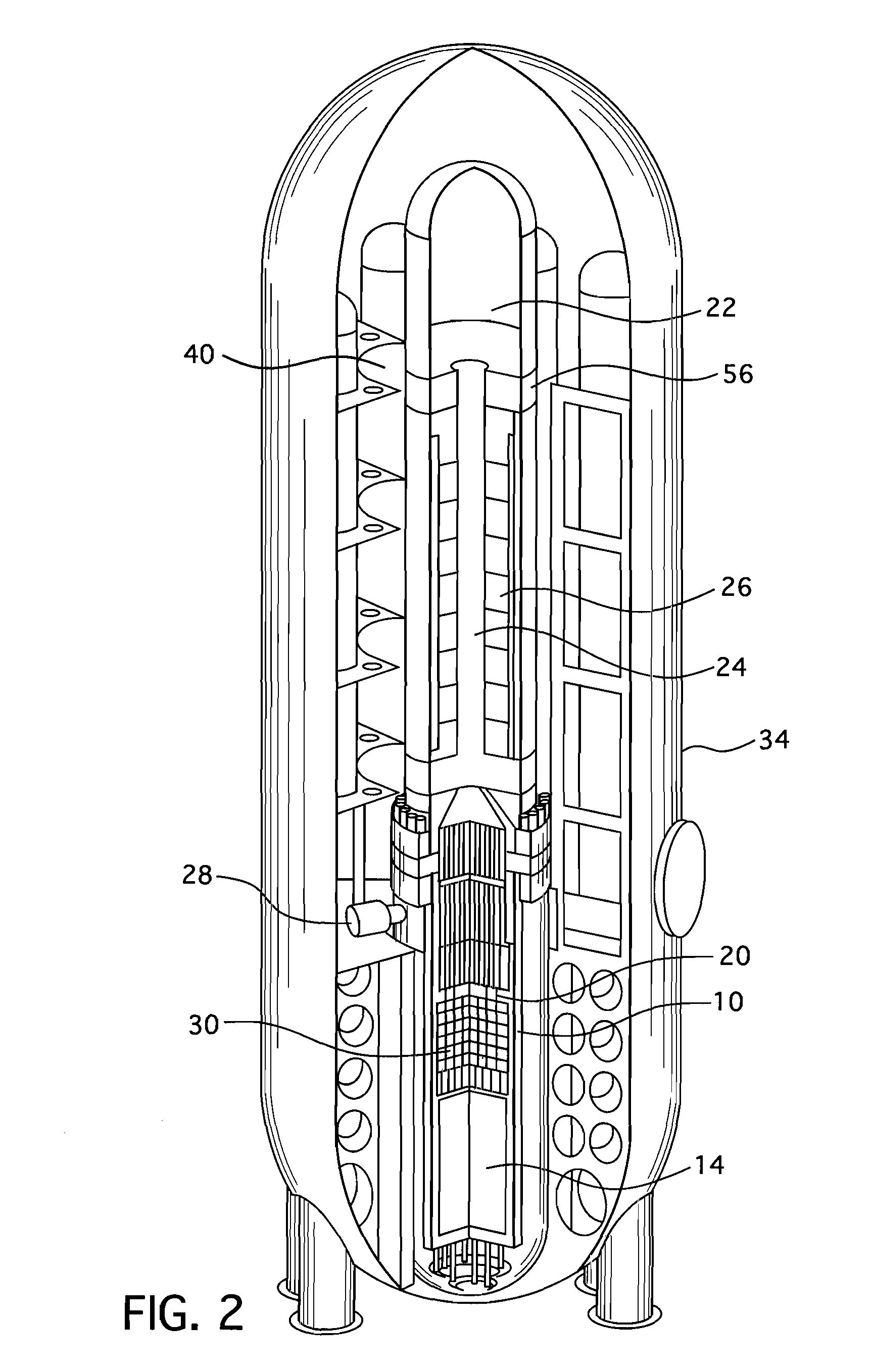
Integral isolation valve systems and methods of operating same for loss of coolant accident (LOCA) protection
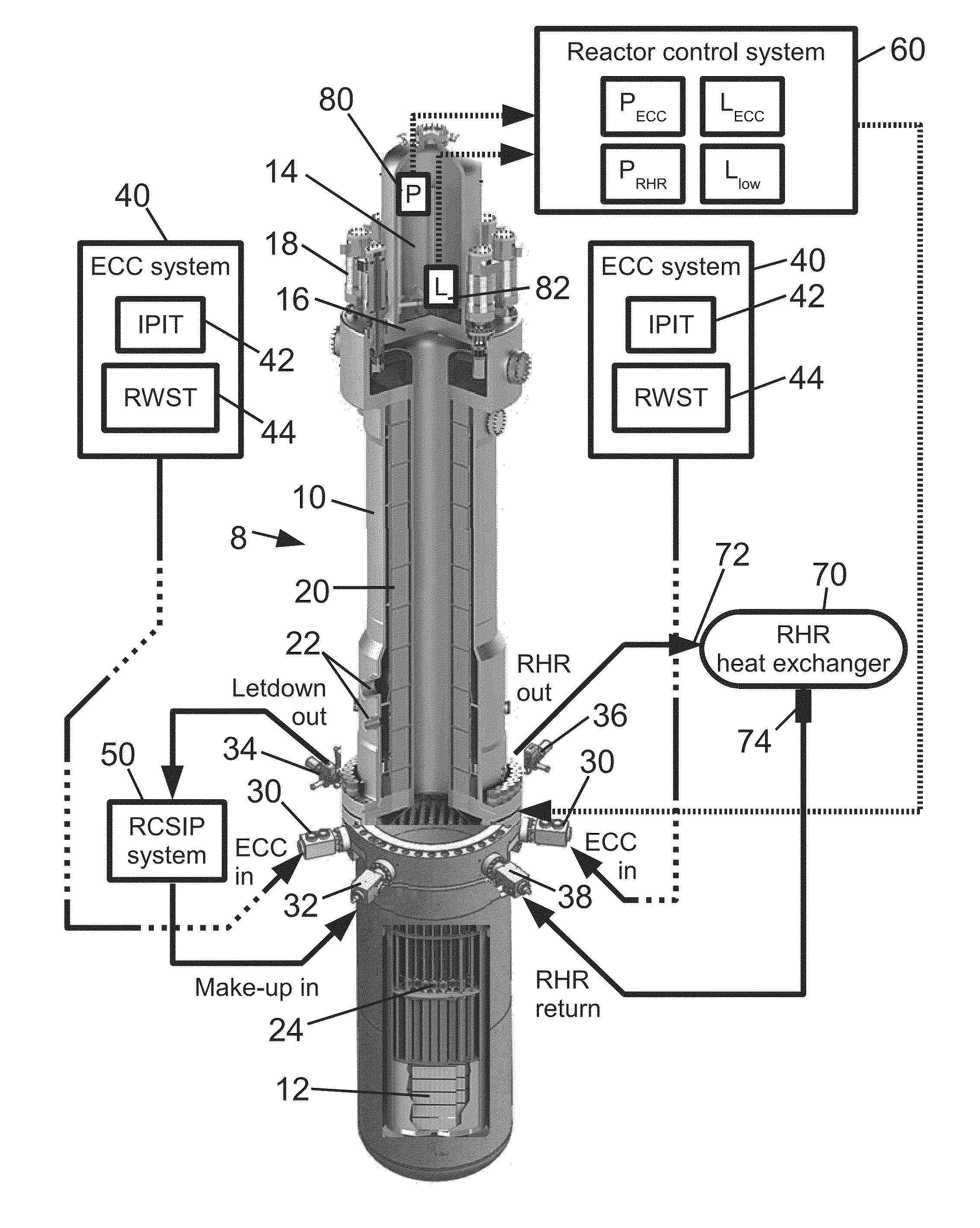
ActiveUS20160027535A1Nuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear reactor coreIsolation valve
A nuclear reactor includes a nuclear reactor core comprising fissile material disposed in a reactor pressure vessel having vessel penetrations that exclusively carry flow into the nuclear reactor and at least one vessel penetration that carries flow out of the nuclear reactor. An integral isolation valve (IIV) system includes passive IIVs each comprising a check valve built into a forged flange and not including an actuator, and one or more active IIVs each comprising an active valve built into a forged flange and including an actuator. Each vessel penetration exclusively carrying flow into the nuclear reactor is protected by a passive IIV whose forged flange is directly connected to the vessel penetration. Each vessel penetration carrying flow out of the nuclear reactor is protected by an active IIV whose forged flange is directly connected to the vessel penetration. Each active valve may be a normally closed valve.
Owner:BWXT MPOWER INC
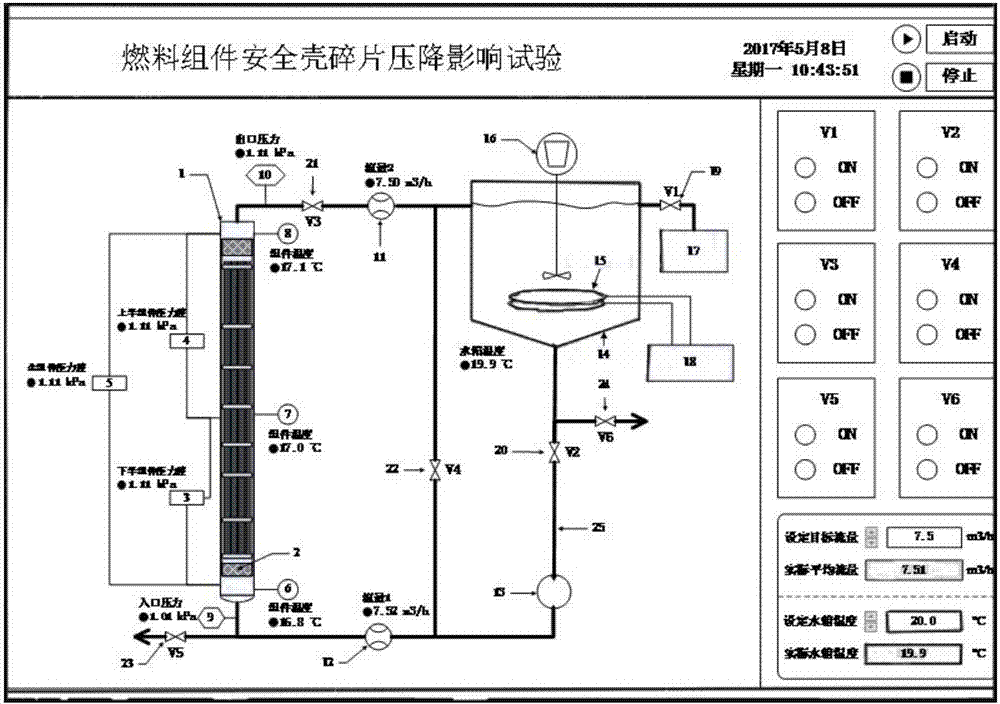
Online monitoring apparatus for monitoring influence of nuclear power plant containment fragments upon pressure drop of fuel assembly
InactiveCN107195341APrevent precipitationAvoid cloggingNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringDifferential pressurePressurized water reactor
The invention discloses an online monitoring apparatus for monitoring influence of nuclear power plant containment fragments upon pressure drop of a fuel assembly and belongs to the technical field of nuclear safety. The online monitoring apparatus comprises a test segment, a full-size fuel assembly, an armored thermocouple, a differential pressure gauge, a pressure meter electric V-shaped ball valve, a flow meter, and a stirring water tank. By simulating the fact that fragments from an accident in a pressurized water reactor nuclear power station penetrate a containment pit strainer and comprehensively utilizing the measuring instruments such as a temperature sensor, a pressure sensor, a differential pressure sensor and a flow meter, the pressure drop of the fuel assembly corresponding to different conditions and fragment quantities is monitored online; by monitoring operation of the apparatus in test, it is possible to study the distribution, attachment and blockage of fragments in the fuel assembly and quantitatively evaluate the influence of fragments in the containment after LOCA (loss of coolant accident) of the pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant, and support is provided to ensure reliable execution of safety functionality of an emergency core cooling system of the pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Passive safety system of integral reactor
ActiveUS9583224B2Improve securityMaintain water levelPower plant safety arrangementIntegral reactorsNuclear reactorNitrogen gas
A passive safety system includes a containment, a reactor in the containment, a plurality of safety injection tanks connected with the reactor and having water and nitrogen gas to supply water thereof into the reactor through a safety injection line communicating to the first safety injection line upon a loss of coolant accident, a plurality of core makeup tanks connected with the reactor to supply water thereof into the reactor through a second safety injection line communicating to a safety injection line upon the loss of coolant accident, and a plurality of passive residual heat removal systems to remove residual heat from the reactor upon the loss of coolant accident or a non-loss of coolant accident. The water in each of the safety injection tank is stably supplied to the reactor for many hours by a differential head resulting from gravity or gas pressure.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Pressurized water reactor depressurization system
InactiveUS20140241484A1Reduce pressureReduce openingIntegral reactorsNuclear energy generationPressurized water reactorDecay heat
A passive cooling system of a pressurized water reactor that relies on a depressurization system to reduce the pressure in the reactor vessel in the event of a loss of coolant accident and vent the steam generated by the decay heat of the reactor core in a post loss of coolant accident stage. The depressurization results in a low pressure difference between the reactor vessel and the containment and enables gravity driven cooling system injection into the reactor vessel. The depressurization system includes a flow restrictor within an orifice in the reactor vessel wall that connects to a vent pipe which forms a flow path between the interior of the reactor vessel and the containment atmosphere when a valve within the vent pipe is in an open position. Preferably, the flow restrictor is a venturi that has a gradual contraction and a gradual expansion in the flow path area.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
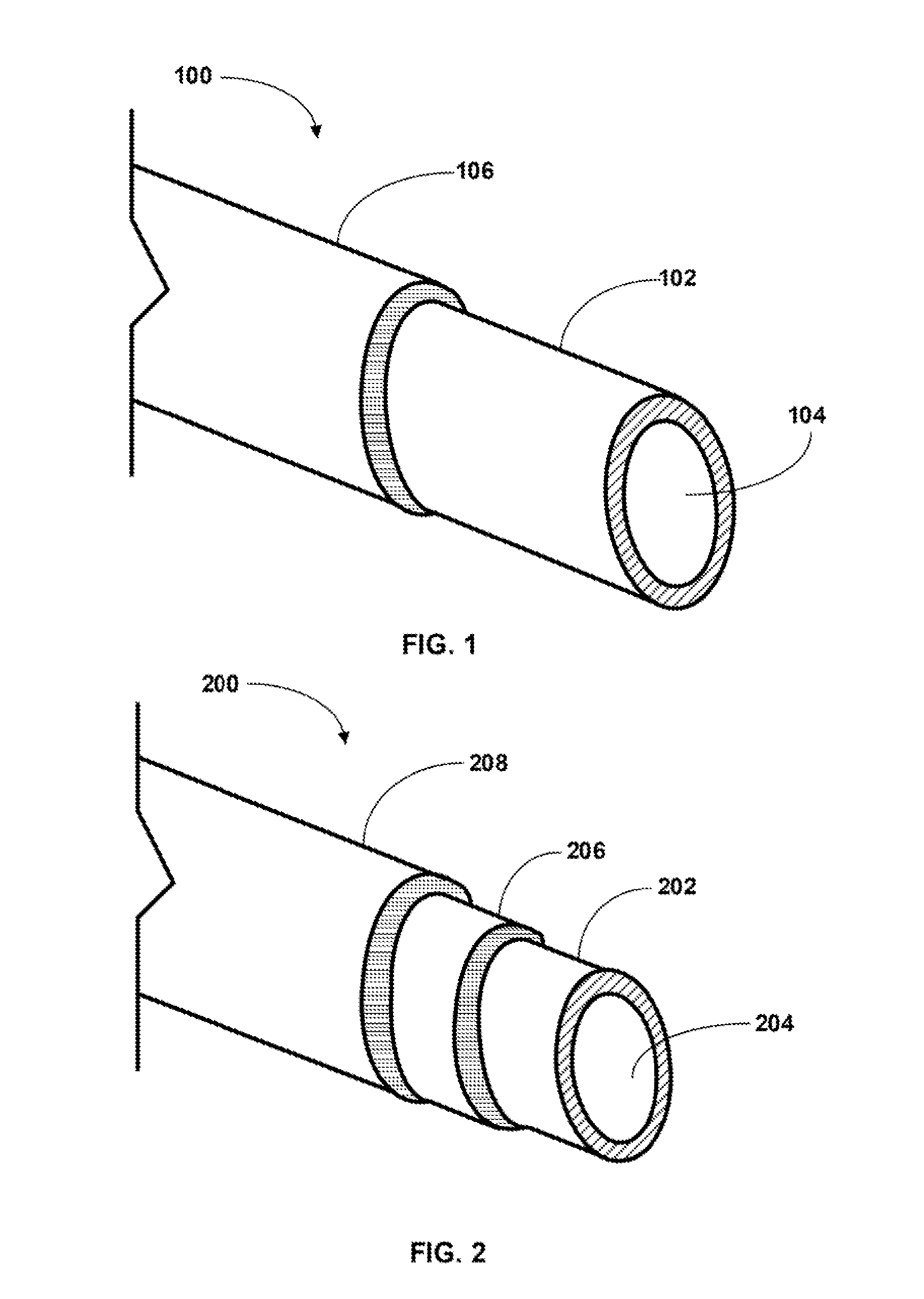
Fuel Rod Cladding and Methods for Making and Using Same
ActiveUS20150063522A1High strengthImprove antioxidant capacityOptical rangefindersFuel elementsAlloyEngineering
In general, the present invention is directed to novel nuclear fuel rod claddings that have better performance characteristics compared to current claddings, particularly during a severe accident, such as a loss of coolant accident. The present invention provides a duplex cladding having two layers, an inner Mo or Mo-alloy layer and a protective layer disposed on the outside of the Mo or Mo-alloy layer. Optionally, the Mo or Mo-alloy layer may have a coating disposed on its inner surface to provide additional capability with the fuel pellets, thereby creating a triplex cladding.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST INC
Containment pressure suppression and cooling system having inherent safety
InactiveCN106898389AEliminate the risk of failureReduce thicknessNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsInherent safetyReinforced concrete
The invention belongs to the technical field of containment pressure suppression and cooling systems, and particularly relates to a containment pressure suppression and cooling system having inherent safety. The containment pressure suppression and cooling system can perform pressure suppression and cooling on a containment after a loss of coolant accident and a steam pipe rupture accident happen to a reactor. A reactor pressure vessel is positioned in a steel containment, a reactor is positioned in the reactor pressure vessel, the lower part of the reactor pressure vessel is arranged in a round reactor cavity at the lowest elevation position in the steel containment, and the upper part of the steel containment is immersed in a shielding pond; the upper space in the steel containment is a dry well, the lower space of the steel containment is a wet well, the dry well and the wet well are separated by a reinforced concrete wall and a floor slab to form respectively independent spaces, and a communicating pipe is the only connection channel for the dry well and the wet well; and the lower part of the wet well is a pressure suppression pond, and the upper part of the wet well is a gas space. The containment pressure suppression and cooling system provided by the invention can perform pressure suppression and cooling on the containment after a loss of coolant accident and a steam pipe rupture accident happen to the reactor.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Containment pressure suppression system for marine nuclear power station
ActiveCN107293336AOptimize layoutCompact layoutNuclear energy generationShieldingPressure riseNuclear power
The invention discloses a containment pressure suppression system for a marine nuclear power station. The containment pressure suppression system comprises a pressure suppression pool arranged in a containment, wherein the pressure suppression pool comprises a water space and an air space; the water space is arranged at the bottom of the containment and surrounds a reactor core; the water space communicates with a containment dry well; the air space is arranged above the water space and surrounds main equipment; an air space cavity directly communicates with the water space. When the nuclear power station generates LOCA (Loss Of Coolant Accidents), a mixture of air, steam and water in the containment dry well is introduced into the water space and is fast condensed by cooling water in the water space, so that the pressure rise effect of the containment can be relieved; the containment pressure suppression system is favorable for the realization of the radiation shielding function; the layout is compact; the space utilization rate is high; the miniaturization design of the containment of the marine nuclear power station is also facilitated.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER TECH RES INST CO LTD +2
Method and system for dealing with loss of coolant accident (LOCA) of nuclear power station
ActiveCN103700411AAutomatic outage implementationAvoid damageNuclear energy generationNuclear reaction controlNuclear engineeringNuclear power
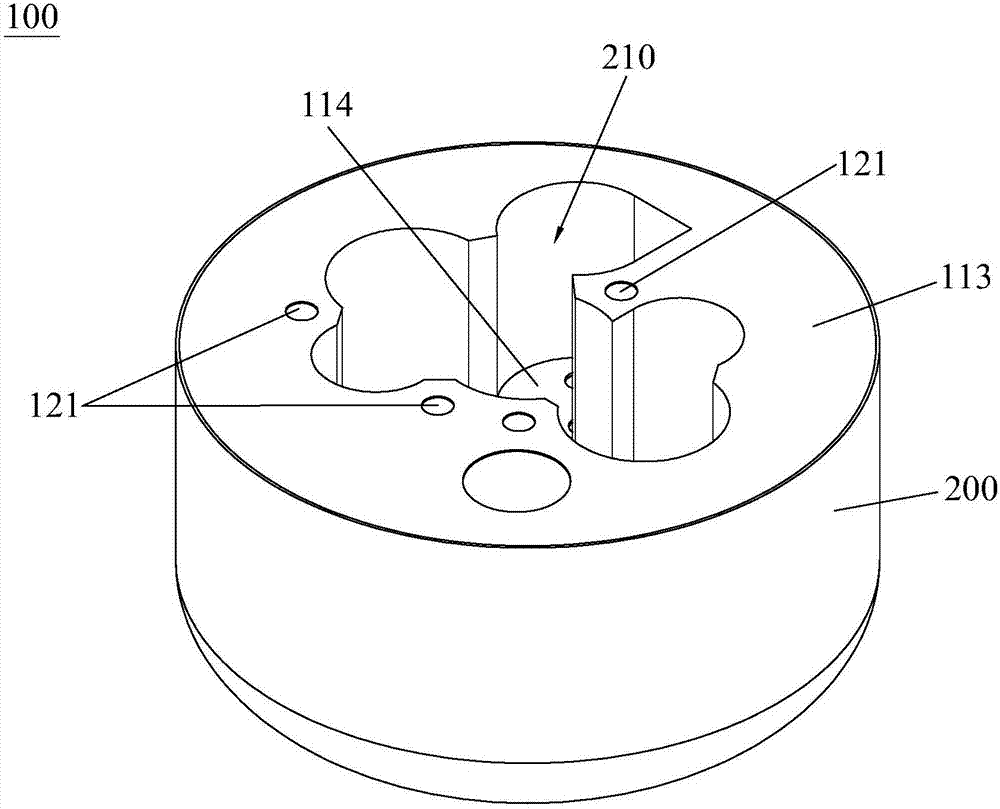
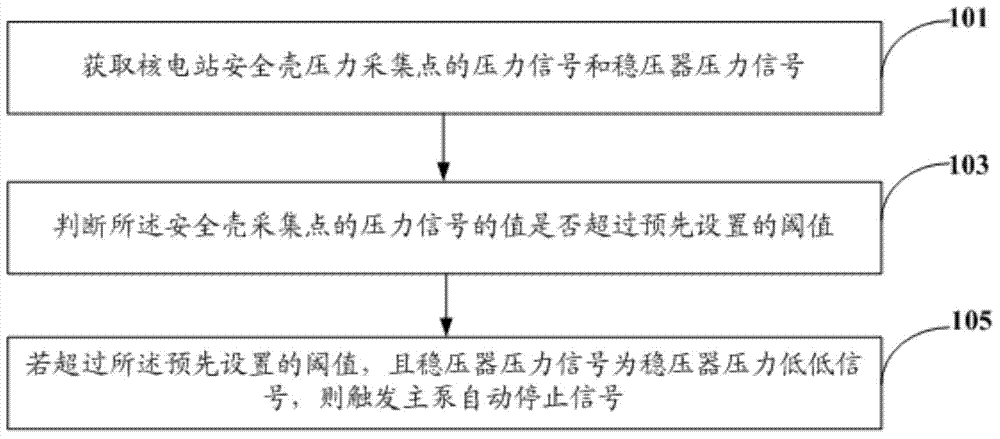
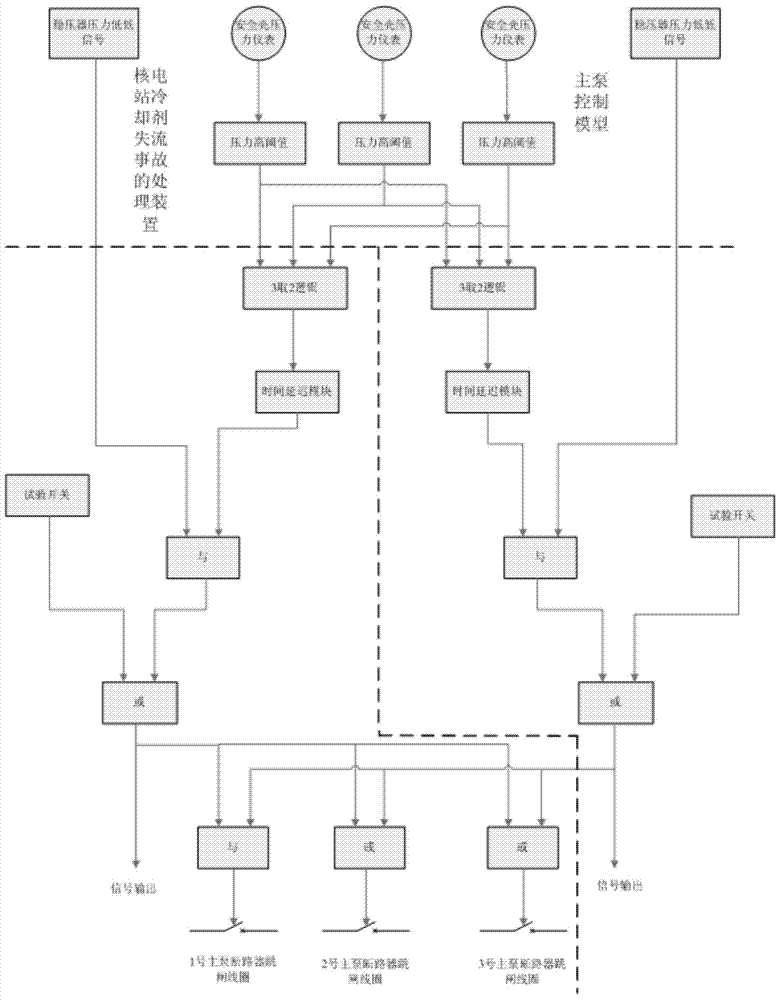
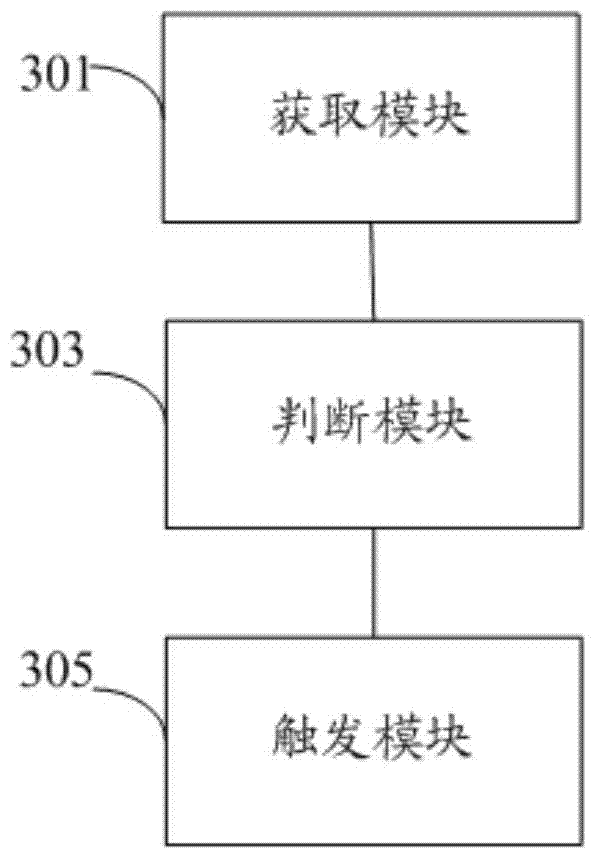
The invention discloses a method for dealing with a loss of coolant accident (LOCA) of a nuclear power station. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a pressure signal of a pressure collection point of a containment vessel of the nuclear power station and a pressure signal of a pressure stabilizer; judging whether the value of the pressure signal of the pressure collection point of the containment vessel exceeds a preset threshold value or not; and if yes, judging that the pressure signal of the pressure stabilizer indicates the pressure of the pressure stabilizer is low, and triggering a main pump to automatically shut down. After the method for dealing with the LOCA of the nuclear power station is adopted, the main pump can automatically and intelligently shut down after the medium / small LOCA happens. Furthermore, the invention also discloses a system for dealing with the LOCA of the nuclear power station.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
Passive nuclear power station LOCA (Loss of Coolant Accident) accident mitigating system
InactiveCN101916594ALarge openingAvoid dischargeNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear engineeringWater vapor
The invention discloses a passive nuclear power station LOCA (Loss of Coolant Accident) accident mitigating system belonging to the technical field of nuclear power station safety. Memory alloy is connected with a four-bar mechanism and a valve in series to form a corresponding memory alloy intelligent switching device by utilizing the characteristic that the memory alloy generates contraction deformation at certain temperature, and the memory alloy intelligent switching device is installed at a proper position in a containment and executes a corresponding brake action under the condition that high-temperature and high-pressure steam is filled in the LOCA accident containment. The strong moisture absorption characteristic of lithium bromide solution is utilized to absorb the high-temperature and high-pressure steam in the containment, thereby achieving the goal of mitigating the accident. Lots of passive modes of natural circulation, four-bar mechanism power transmission, pressure action and the like exist in the system. The system mainly adopts the passive automatic operation and has the advantages of convenient implementation, simple control and high reliability, safety and stability.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com