Patents
Literature
343 results about "Leadscrew" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
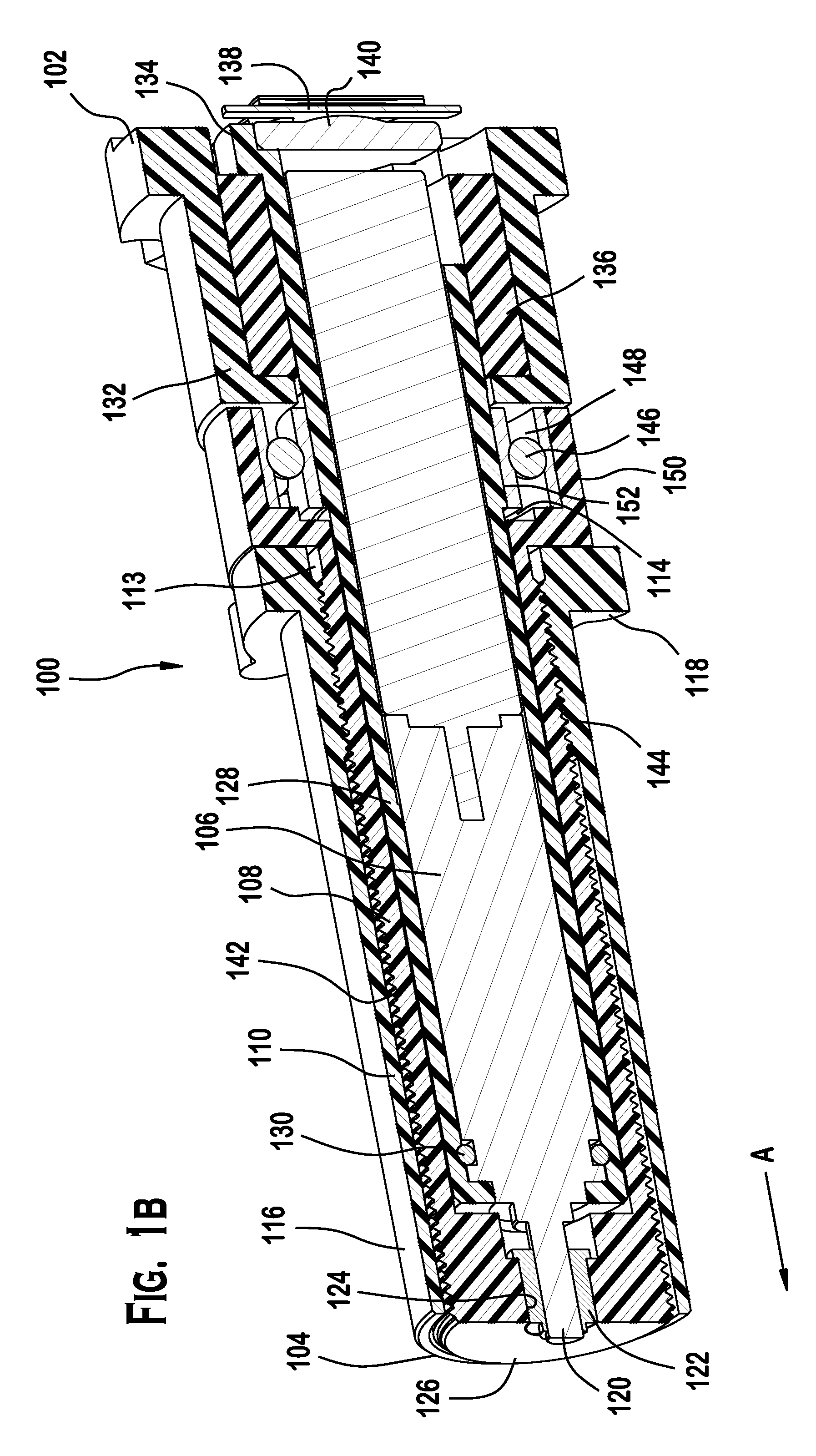
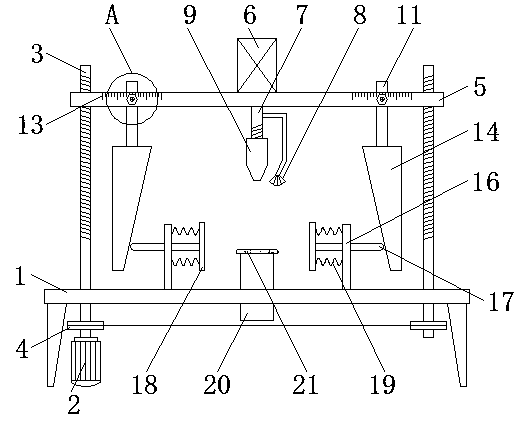
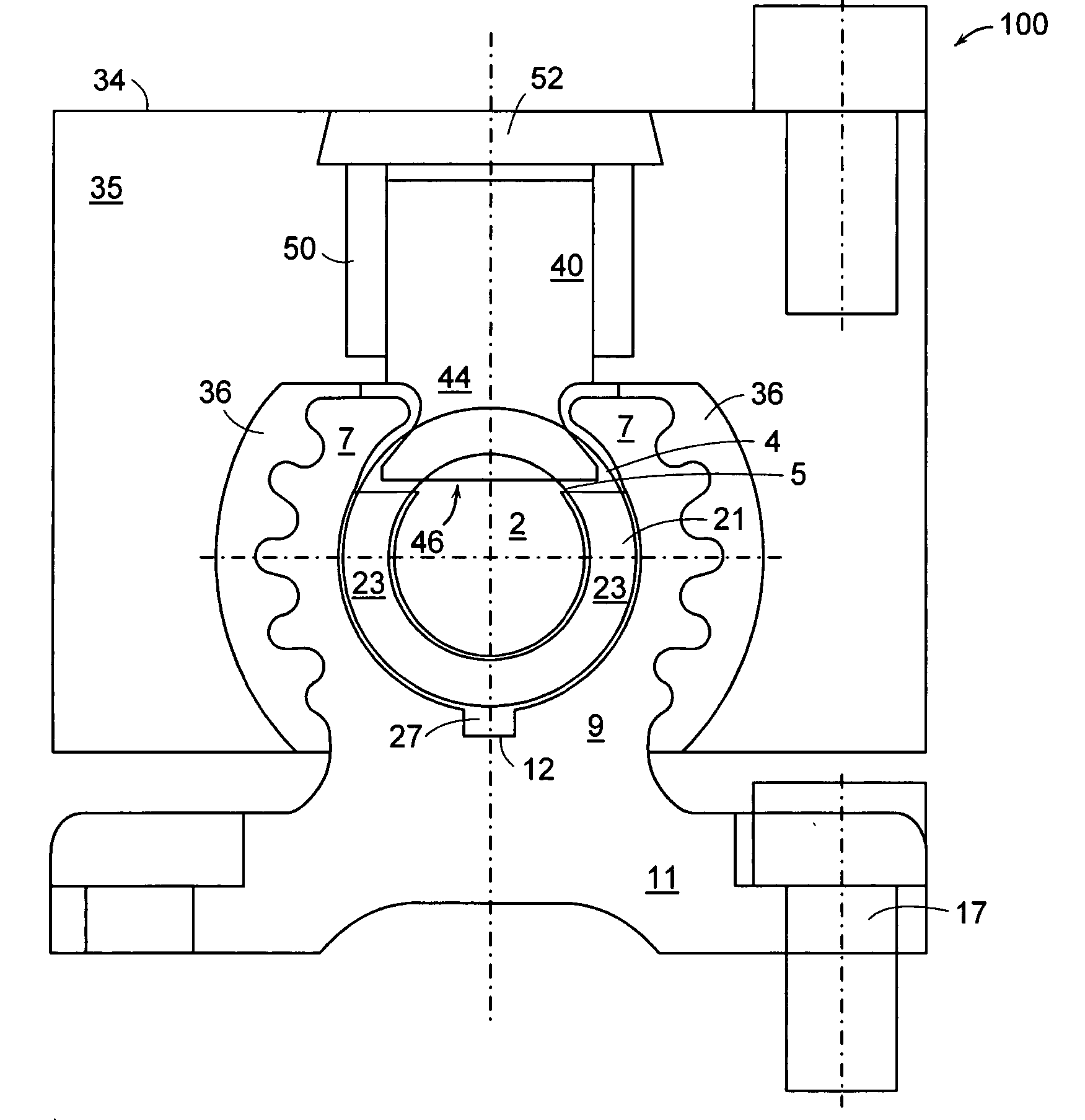
A leadscrew (or lead screw), also known as a power screw or translation screw, is a screw used as a linkage in a machine, to translate turning motion into linear motion. Because of the large area of sliding contact between their male and female members, screw threads have larger frictional energy losses compared to other linkages. They are not typically used to carry high power, but more for intermittent use in low power actuator and positioner mechanisms. Common applications are linear actuators, machine slides (such as in machine tools), vises, presses, and jacks.
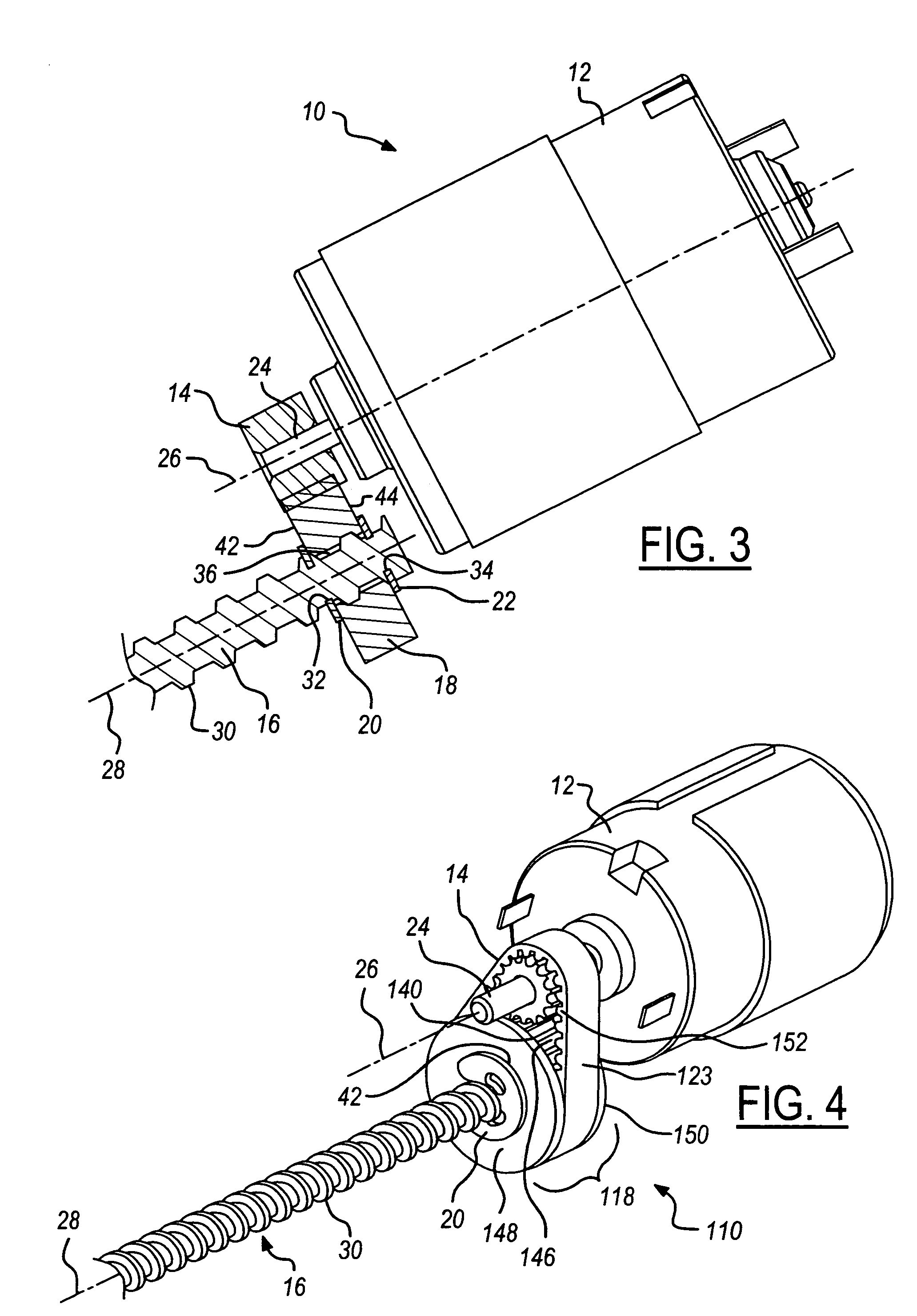
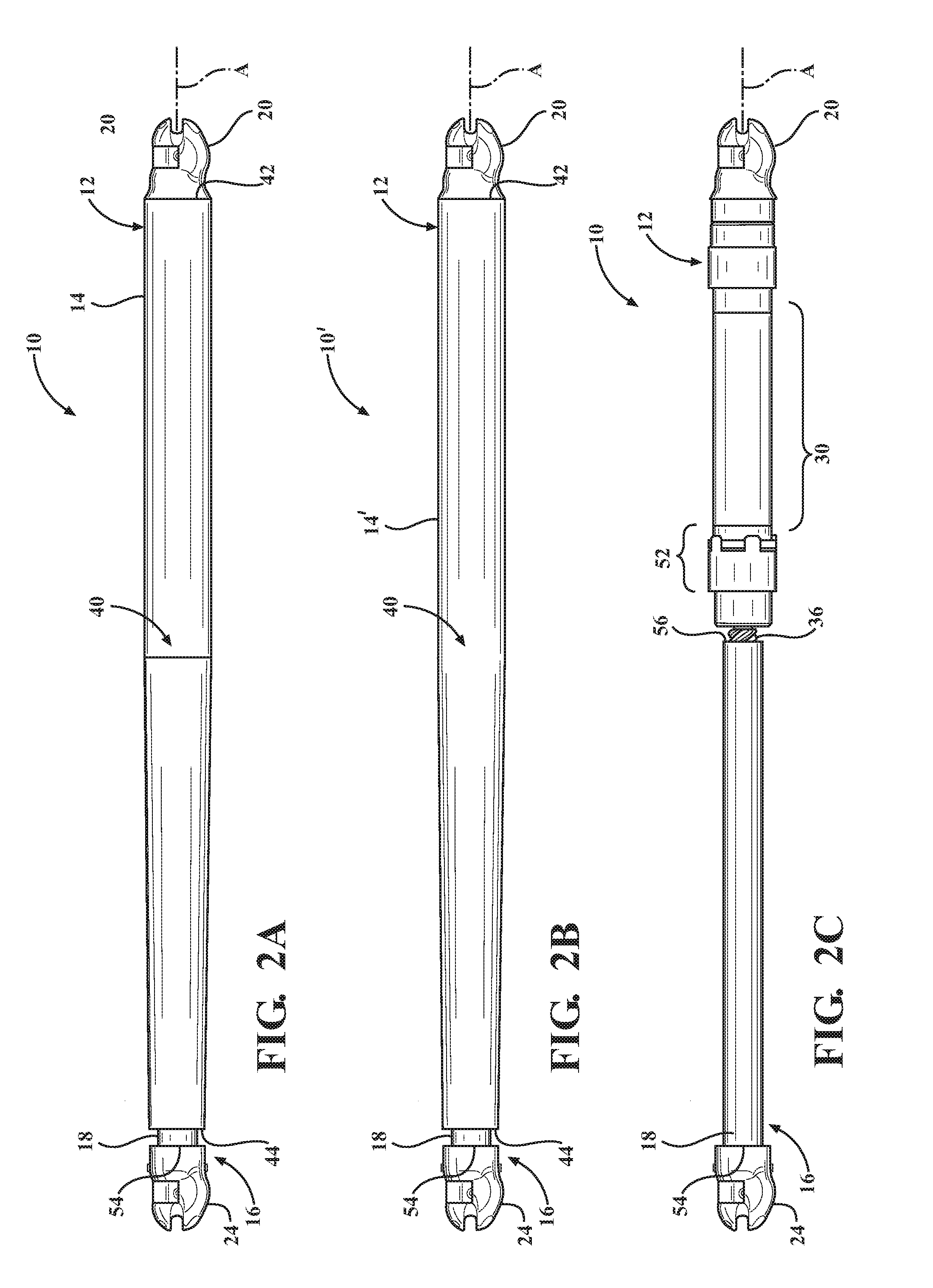
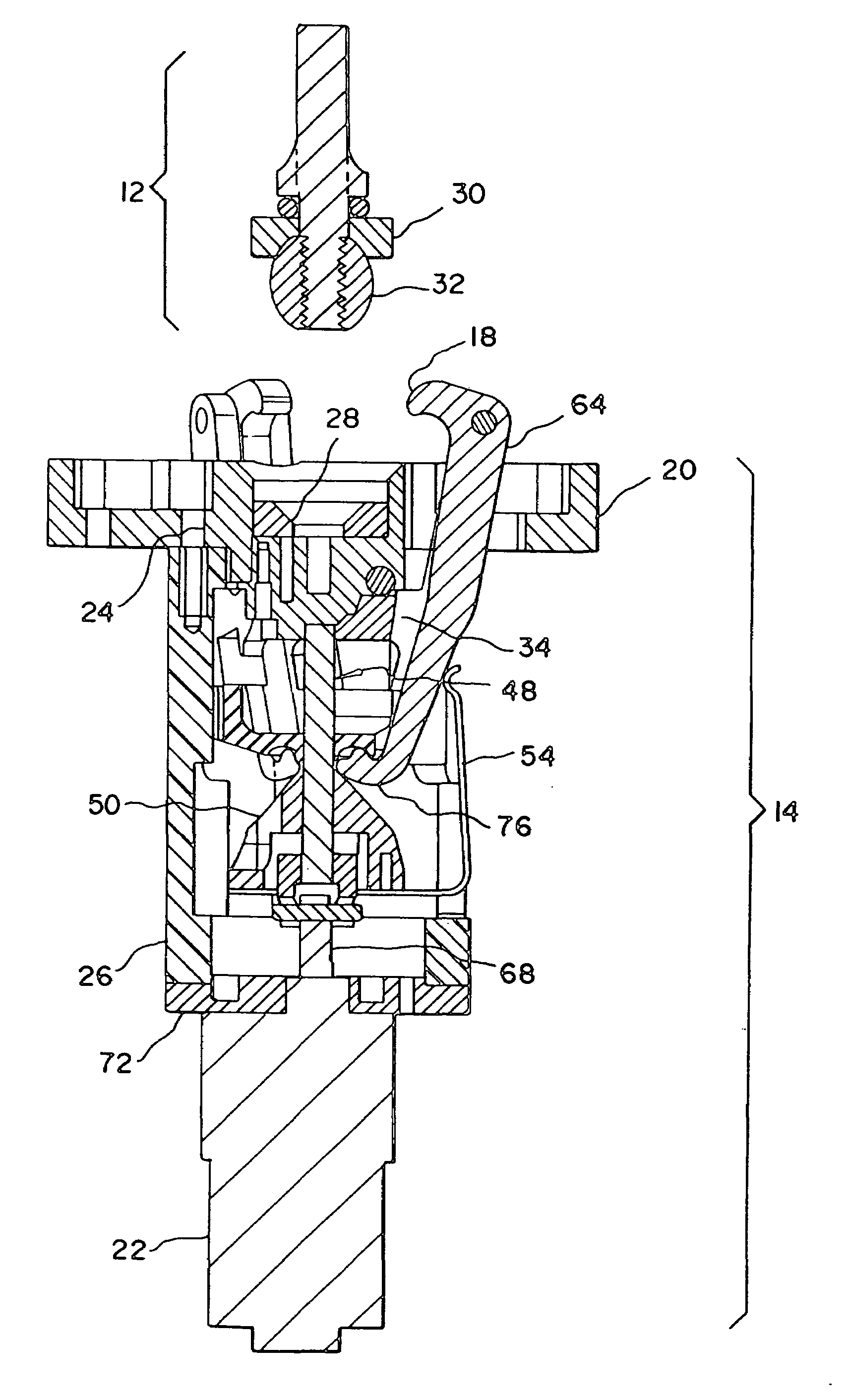
Powered end effector assembly with pivotable channel
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
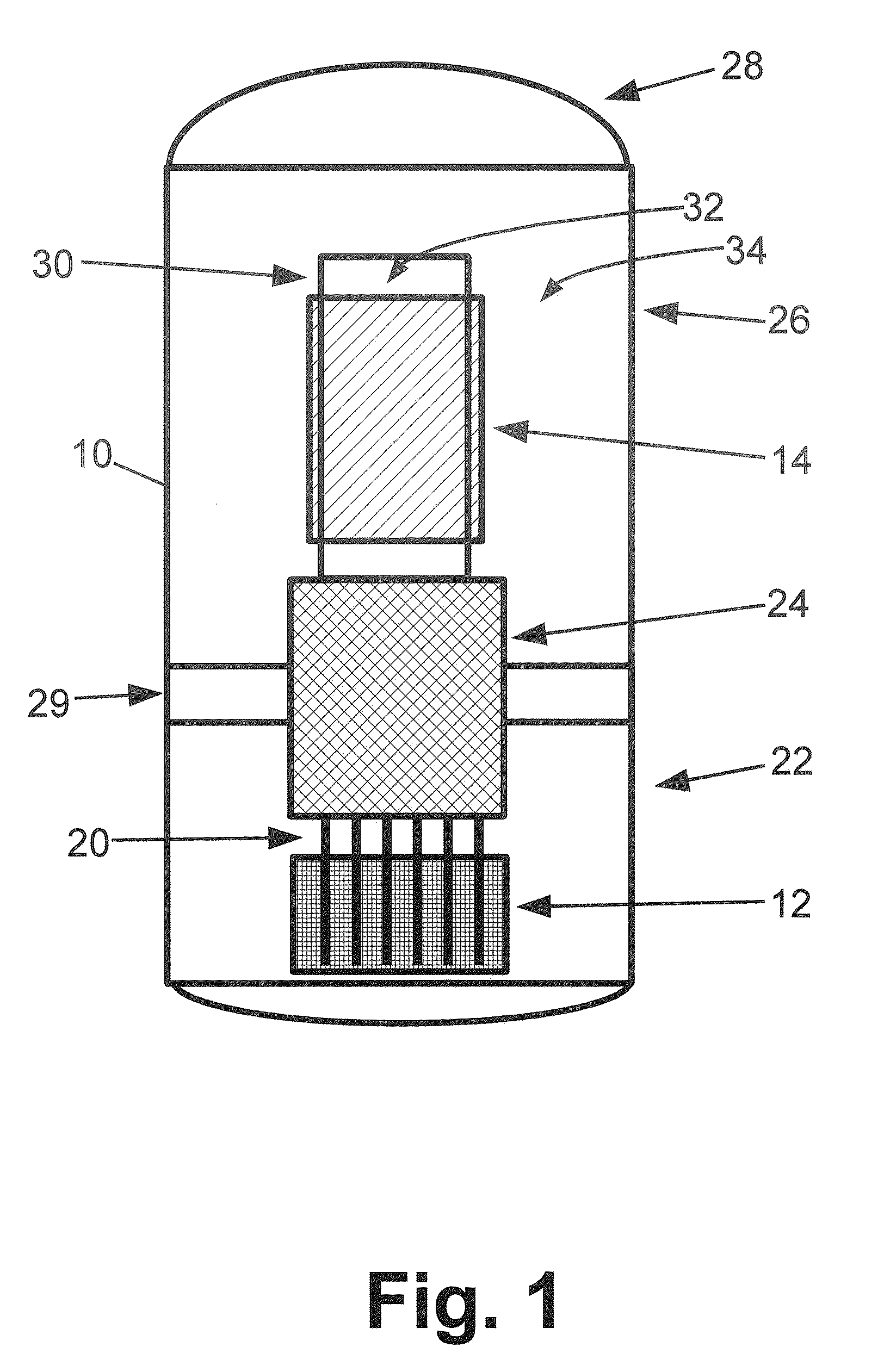
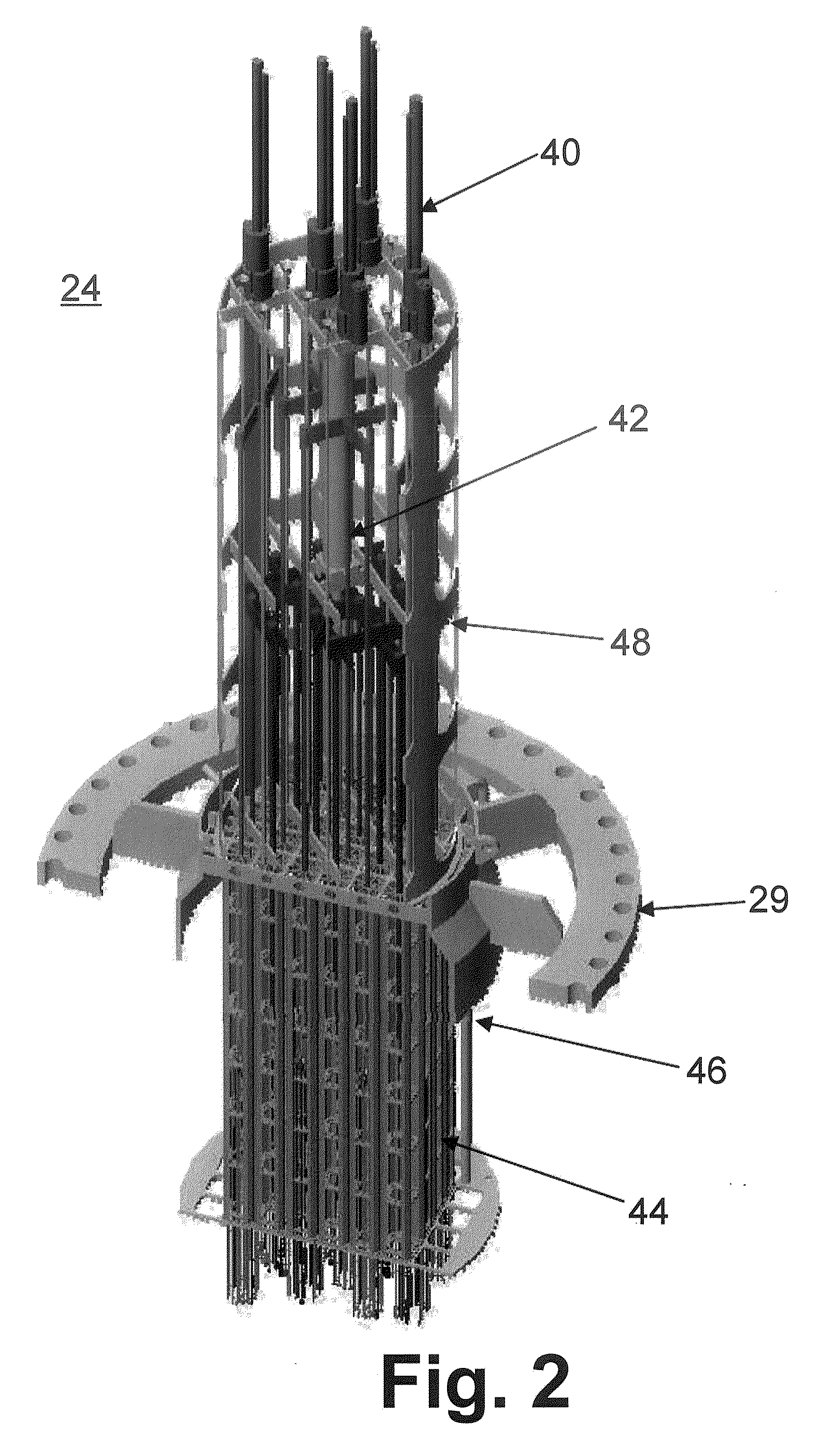
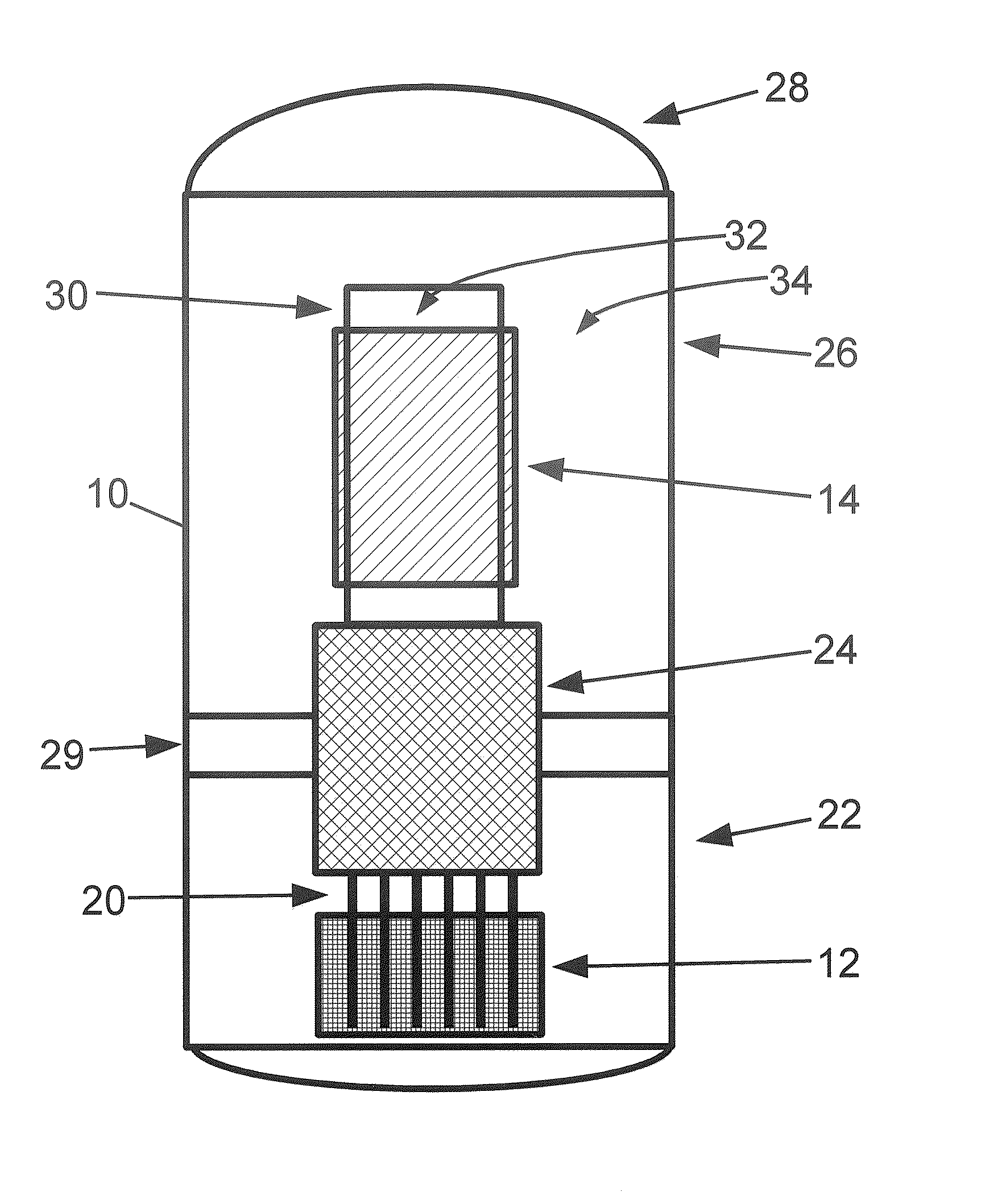
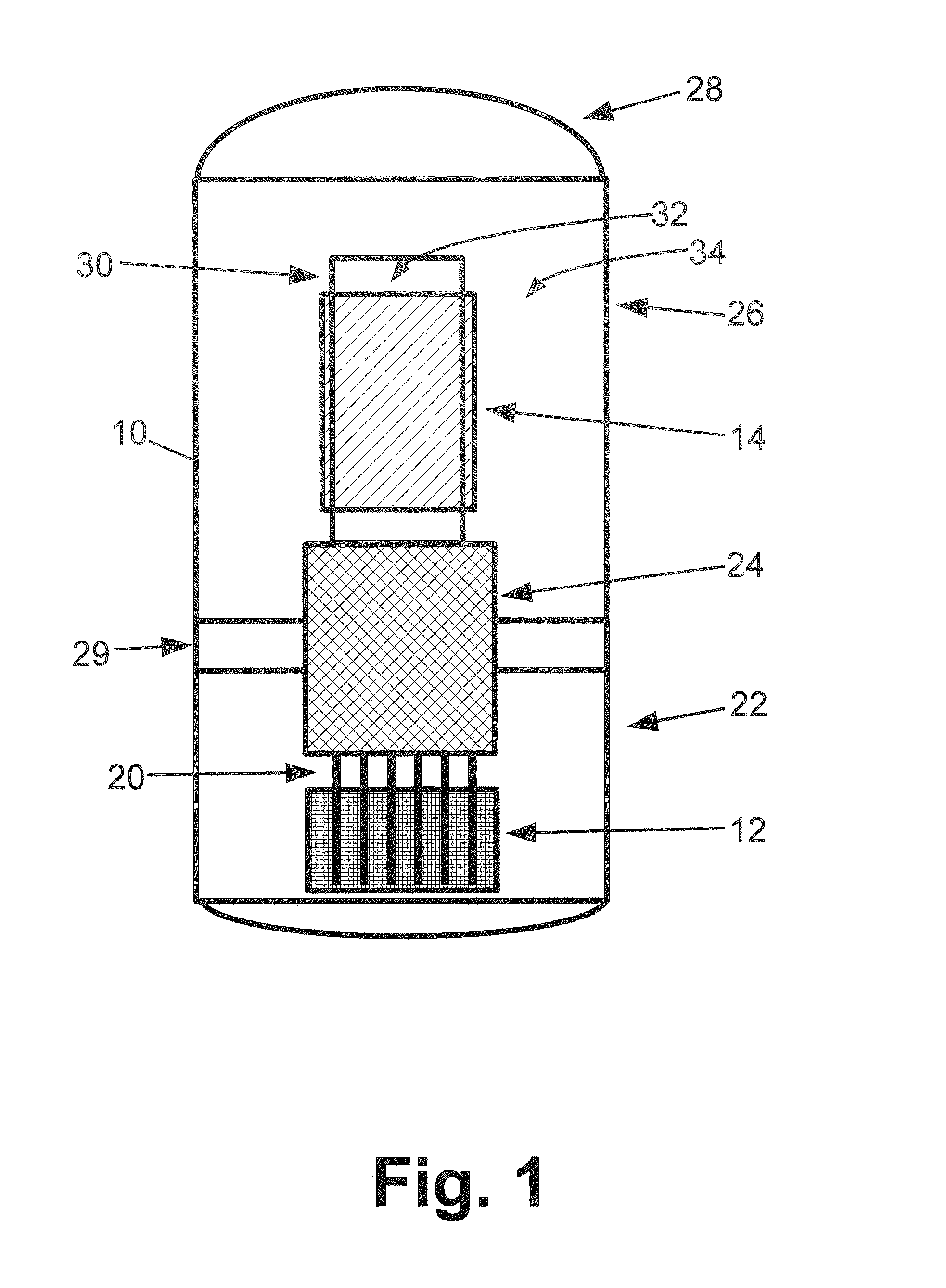
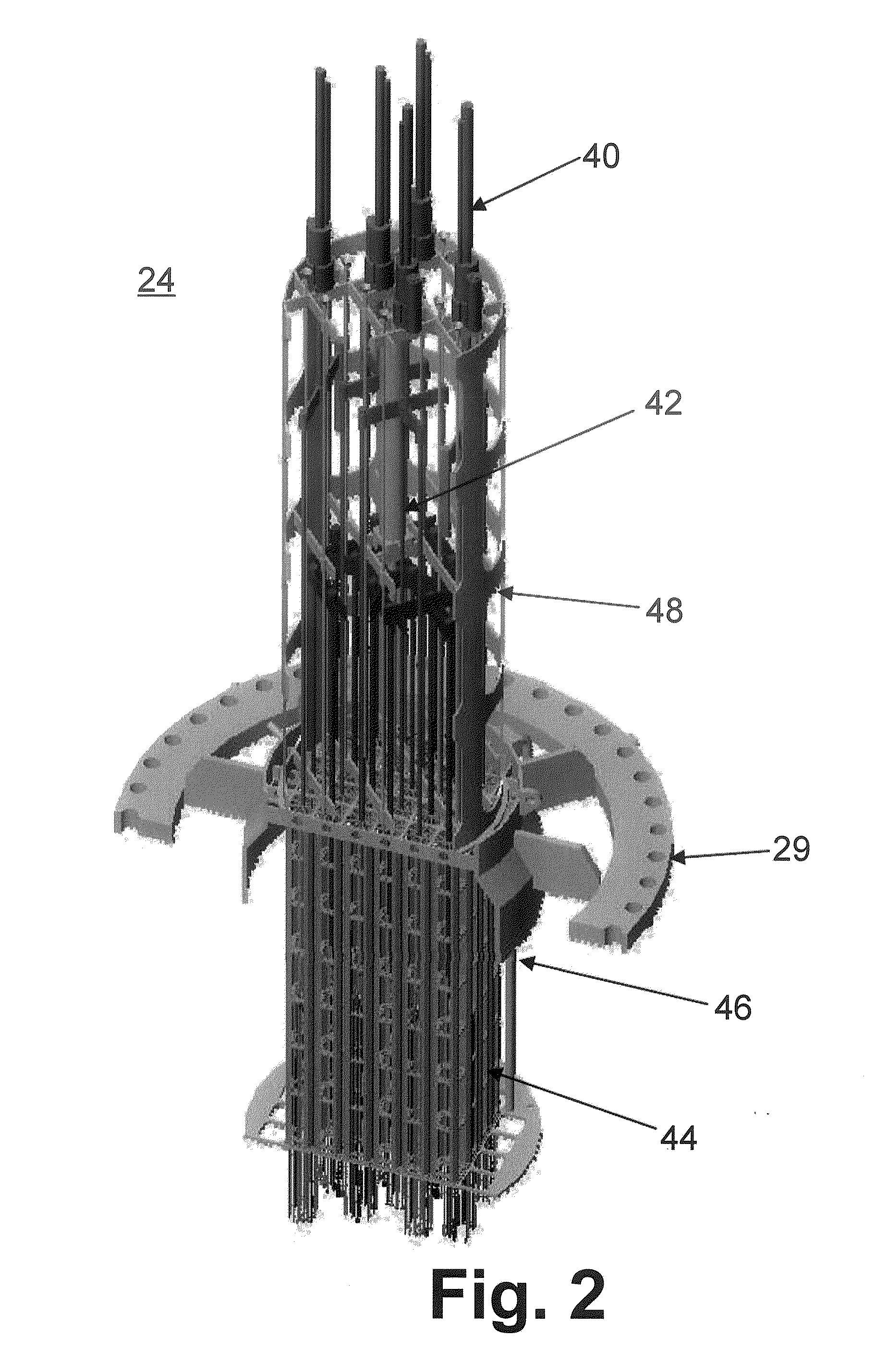
Control rod drive mechanism for nuclear reactor
ActiveUS20100316177A1Nuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
A control rod drive mechanism (CRDM) for use in a nuclear reactor, the CRDM comprising: a connecting rod connected with at least one control rod; a lead screw; a drive mechanism configured to linearly translate the lead screw; an electromagnet coil assembly; and a latching assembly that latches the connecting rod to the lead screw responsive to energizing the electromagnet coil assembly and unlatches the connecting rod from the lead screw responsive to deenergizing the electromagnet coil assembly. The latching assembly is secured with and linearly translates with the lead screw, while the electromagnet coil assembly does not move with the lead screw. The electromagnet coil assembly is at least coextensive with a linear translation stroke over which the drive mechanism is configured to linearly translate the lead screw.
Owner:BWXT NUCLEAR OPERATIONS GRP
Control rod drive mechanism for nuclear reactor
ActiveUS20110222640A1Nuclear energy generationNuclear reaction controlNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
A control rod drive mechanism (CRDM) comprises a lead screw, a motor threadedly coupled with the lead screw to linearly drive the lead screw in an insertion direction or an opposite withdrawal direction, a latch assembly secured with the lead screw and configured to (i) latch to a connecting rod and to (ii) unlatch from the connecting rod, the connecting rod being free to move in the insertion direction when unlatched, and a release mechanism configured to selectively unlatch the latch assembly from the connecting rod.
Owner:BWXT NUCLEAR OPERATIONS GRP
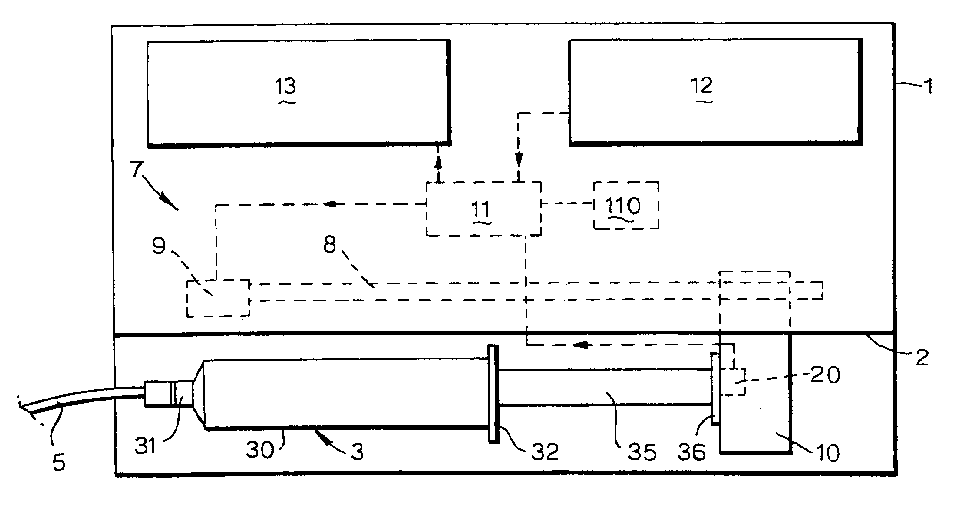
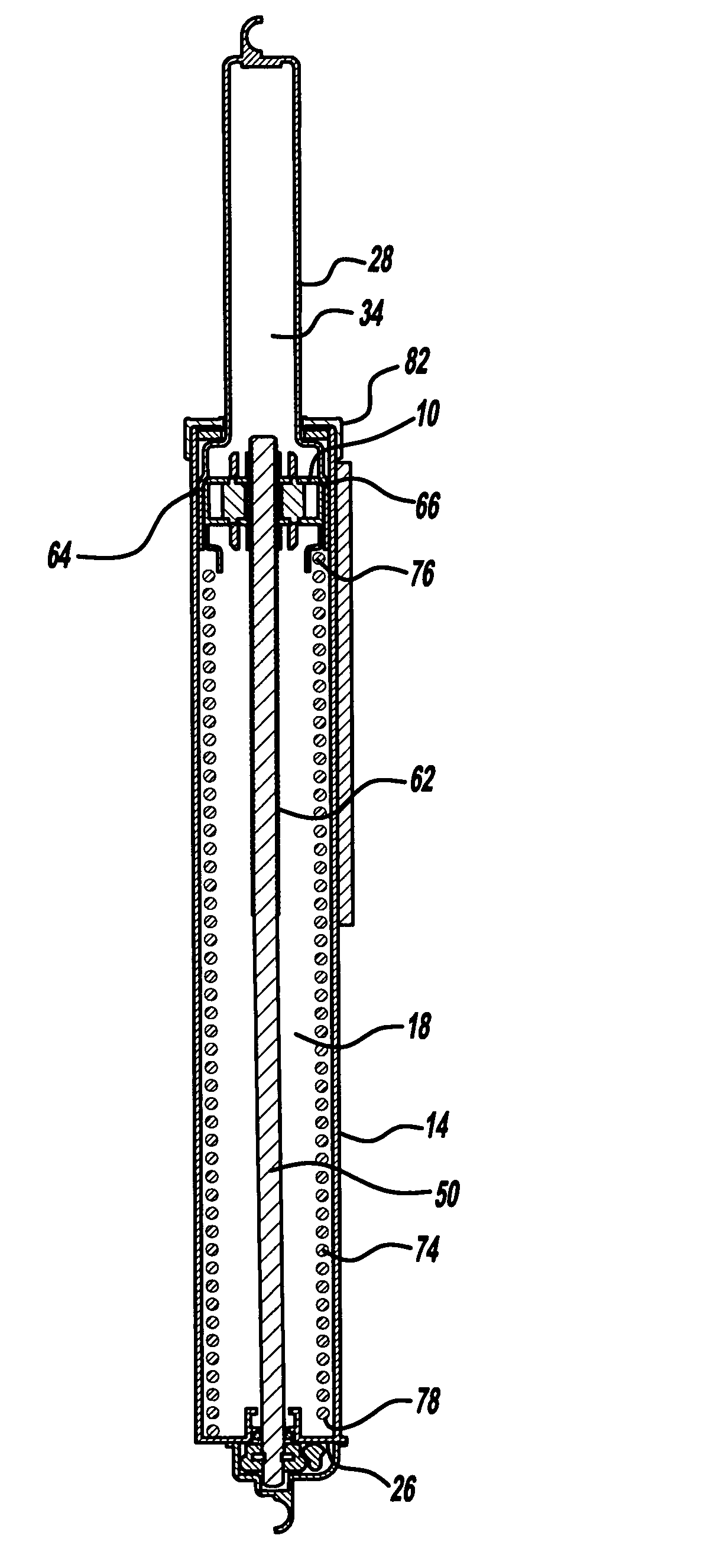
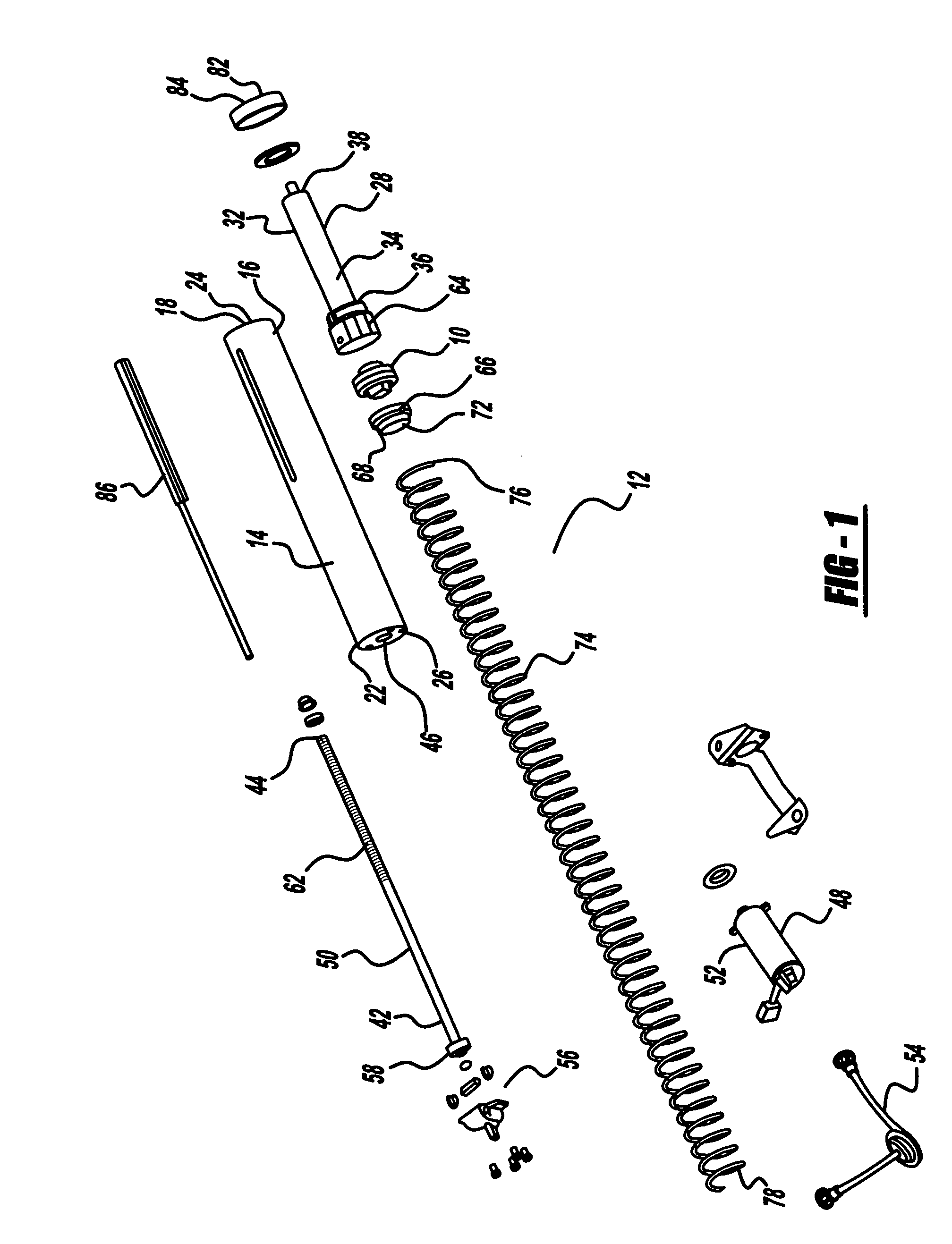
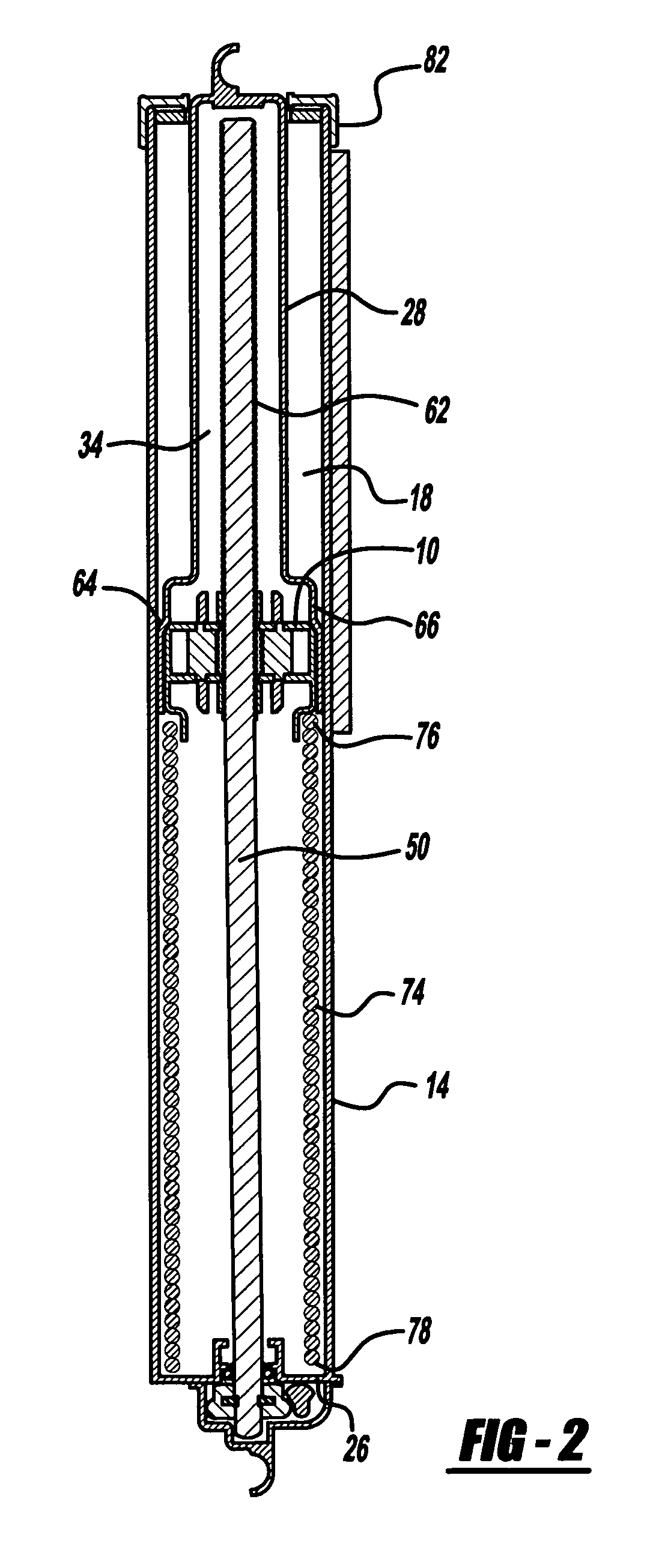
Lead screw delivery device using reusable shape memory actuator device
ActiveUS20090143730A1More compact and less complicated designInfusion devicesMedical devicesRatchetRotational axis
A drug delivery device drive that includes a single shape memory alloy wire actuator to advance a lead screw via a ratcheting mechanism and method thereof are disclosed. In one embodiment, a shape memory alloy wire is operably connected to one of a pair of ratchet wheels and configured to drive incrementally the rotation of the connected ratchet wheel via a contraction, which in turn drives the rotation of the other ratchet wheel about a rotational axis which moves a lead screw and advances a plunger to dispense a liquid drug from a drug container. A drug delivery device using the shape memory alloy wire actuator in combination with the ratcheting mechanism to incrementally rotate a shaft, a lead screw or a sleeve provides for a more compact an less complicated design.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC +1
Drive Mechanism and Method of Use
Described is a drive mechanism for a drug infusion pump. In one embodiment, an in-line drive mechanism is provided that includes a motor operatively coupled to a lead screw, which is configured to engage a piston. The piston includes a cavity to receive the motor and the lead screw such that the lead screw and at least a portion of the motor are substantially contained within the piston cavity when the piston is in a retracted position. In one embodiment, at least a portion of the motor is also substantially contained within a cavity of the lead screw regardless of whether the piston is in the retracted or extended position. The configuration of the piston, the lead screw and the motor results in a more compact drug delivery device.
Owner:ANIMAS CORP
Interspinous process device and method
ActiveUS20100280551A1Increase distanceReduce distanceInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnLeadscrew
An interspinous process device is configured for placement between adjacent spinous processes on a subject's spine. The device includes a housing configured for mounting to a first spinal process, the housing having a lead screw fixedly secured at one end thereof. A magnetic assembly is at least partially disposed within the housing and configured for mounting to a second spinal process. The magnetic assembly includes a hollow magnet configured for rotation within the magnetic assembly, the hollow magnet comprising a threaded insert configured to engage with the lead screw. An externally applied magnetic field rotates the hollow magnet in a first direction or a second, opposite direction. Rotation of the hollow magnet in the first direction causes telescopic movement of the magnetic assembly out of the housing (i.e., elongation) and rotation in the second direction causes telescopic movement of the magnetic assembly into the housing (i.e., shortening).
Owner:NUVASIVE SPECIALIZED ORTHOPEDICS INC
Actuator structure and method for attaching a gear or pulley to lead screw
An improved lead screw actuator for use in applications including power vehicle windows is provided that significantly reduces the amount of machining that must be performed on the lead screw to enable secure attachment of a gear or pulley. The lead screw has a plurality of threads on its outer annular surface and a first and second axially spaced circumferential groove. A gear or pulley disposed about the lead screw has a female thread formed into an inner annular surface that is configured to engage at least one of the plurality of threads of the lead screw between the first and second grooves. A pair of rings are disposed within the first and second grooves in order to restrict axial movement of the gear or pulley on the lead screw.
Owner:DANA AUTOMOTIVE SYST GRP LLC
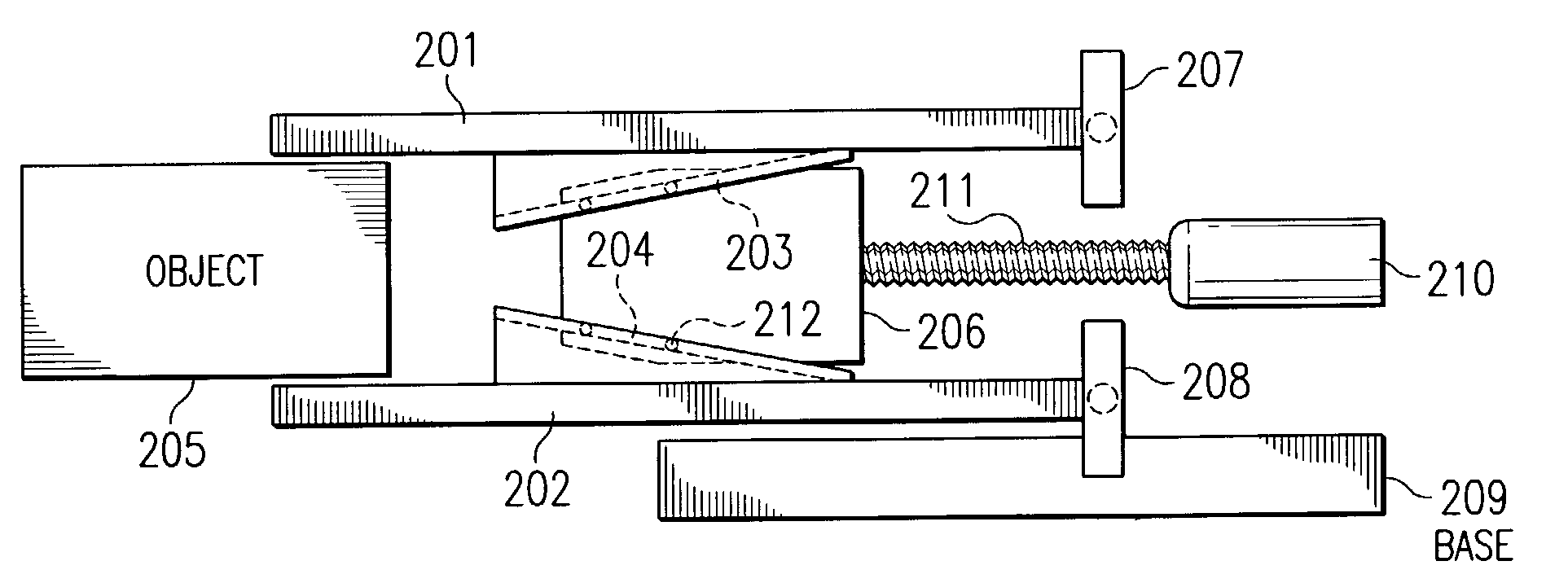
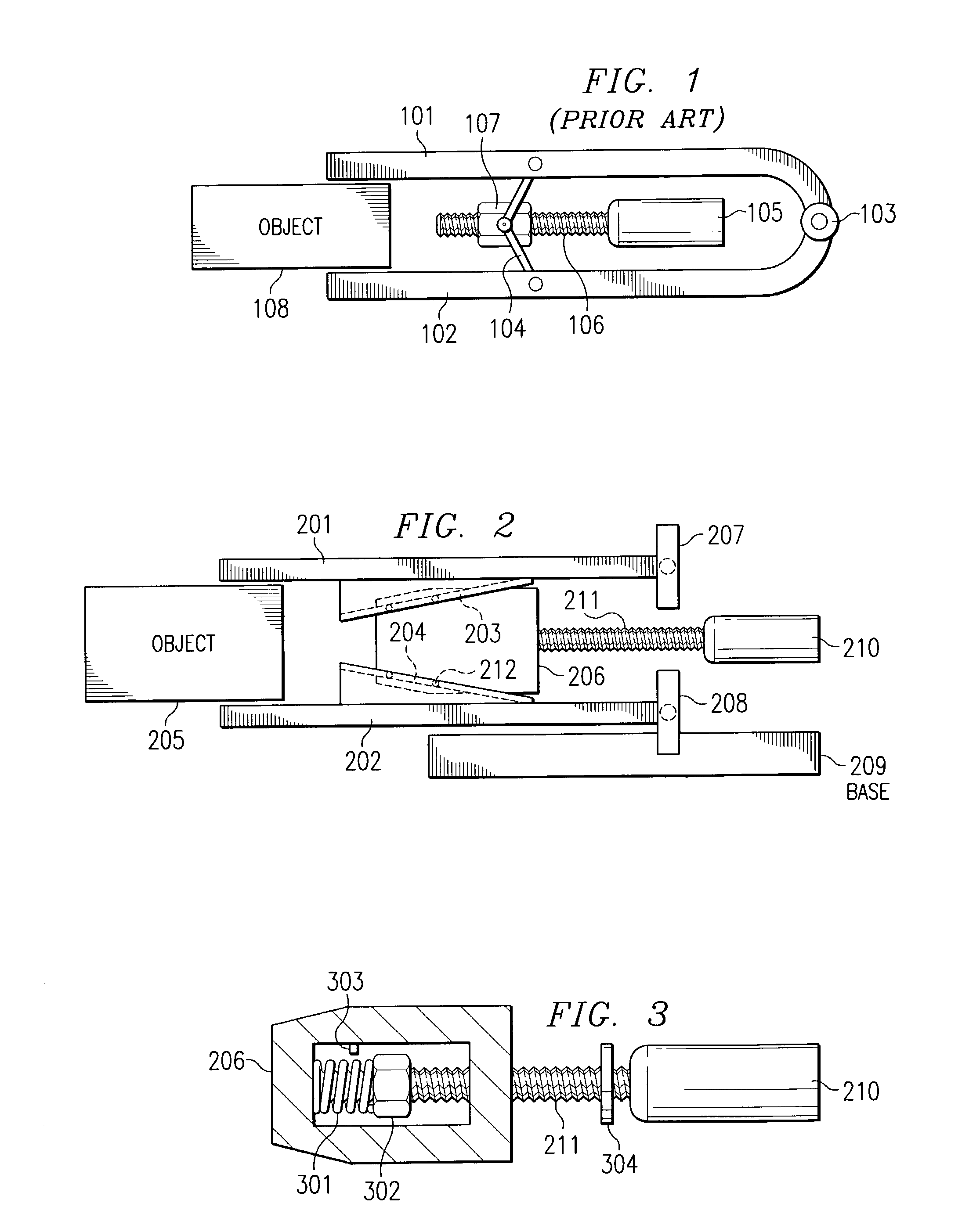
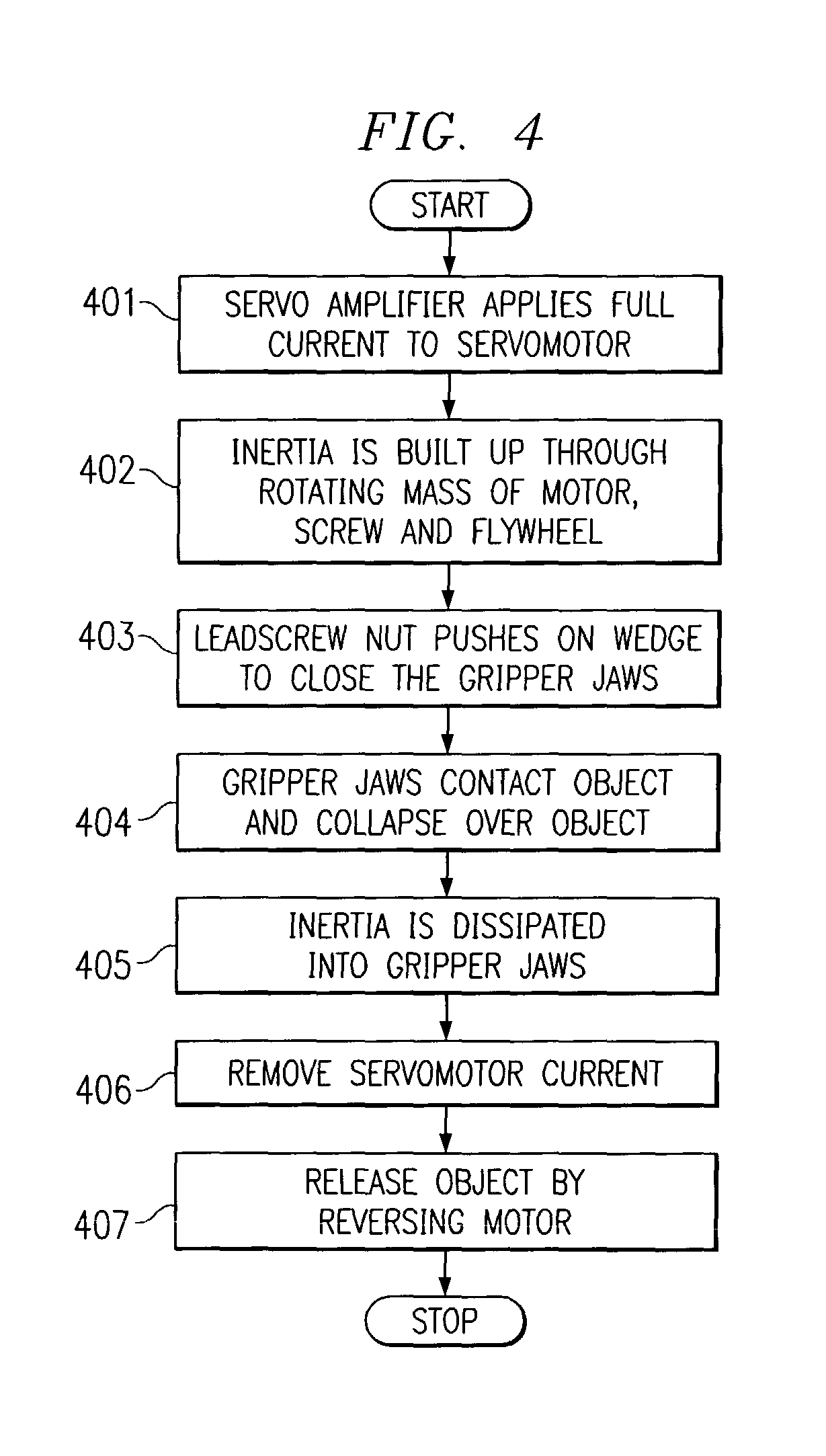
Inertia actuation for robotic gripper mechanism
InactiveUS7014235B1Increase forceIncrease speedProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsPower flowEngineering
A method for gripping objects by means of a robotic gripper mechanism is provided, wherein the gripping mechanism comprises gripping jaws, a wedge actuator between the gripping jaws, wherein the wedge actuator moves the gripping jaws together and apart as it slides backward and forward, and a motor that moves the wedge actuator by means of a connecting leadscrew. The method comprises applying current to the motor so that the motor reaches maximum operating speed before the gripper mechanism comes into contact with any object. When the gripping jaws contact an object, e.g., media cartridge, they collapse over the object, gripping it. The inertia from the rotating mass of the motor increases the force and speed of the gripping action. In another embodiment, a flywheel may be added to the leadscrew to provide additional rotating mass and increase the inertia before contact.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Power swing door actuator with articulating linkage mechanism
ActiveUS20170292310A1Efficient packagingWing fastenersPower-operated mechanismActuatorControl theory
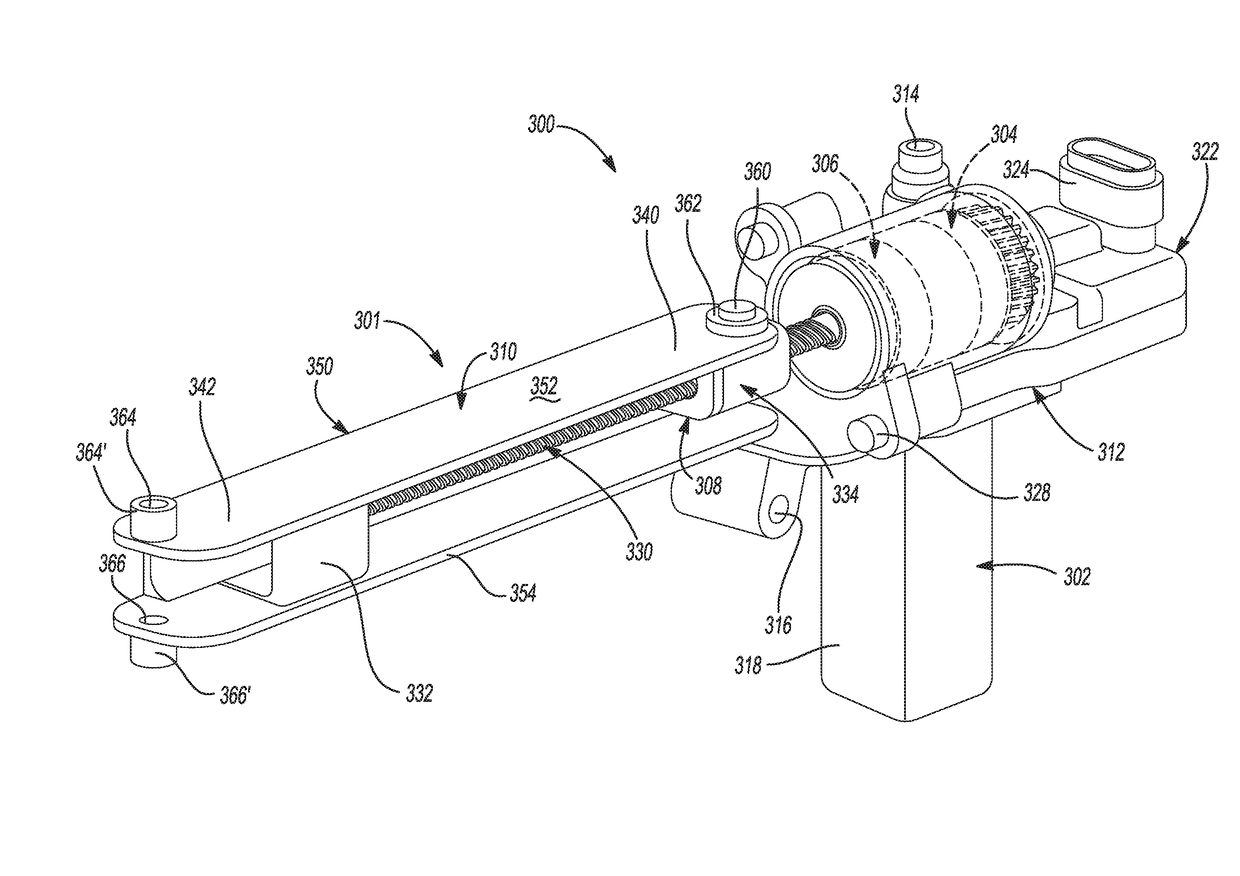
A power swing door actuator for moving a passenger swing door relative to a body portion of a motor vehicle. The power swing door actuator includes a housing rigidly fixed to the swing door, a motor mounted to the housing, a connector link having a first end pivotably coupled to the vehicle body portion and a second end pivotably coupled to a drive nut of a spindle drive mechanism. A leadscrew of the spindle drive mechanism is rotatably driven by the motor for causing relative translational movement between the drive nut and the leadscrew which, in turn, results in pivoting movement of the connector link while the vehicle door swings between open and closed positions in response to selective actuation of the motor.
Owner:MAGNA CLOSURES INC
Portable electric driven compressed air gun
InactiveUS20050188974A1Robust and simple designFiring/trigger mechanismsCompressed gas gunsElectric machineryElectric drive
A portable electric motor driven air gun powered by a power source. The motor is coupled to a lead screw, which drives a piston. The piston compresses air in a chamber producing high-pressure air. When sufficient energy is stored within the air stream by the piston a valve opens which releases the air to act on the projectile. The compressed air is used to push a projectile such as a paintball, an airsoft ball, a “bb”, or a pellet through a barrel. The lead screw is then reversed and the piston is reset for the next shot. The piston is preferably coupled to a feeding mechanism to facilitate positioning of the projectile for firing. The direction speed and operative modes of the gun are preferably controlled with an electric circuit. The power source is preferably rechargeable and allows the air gun to be operated completely independent from either a wall outlet or a compressed air supply.
Owner:PEDICINI CHRISTOPHER S +1
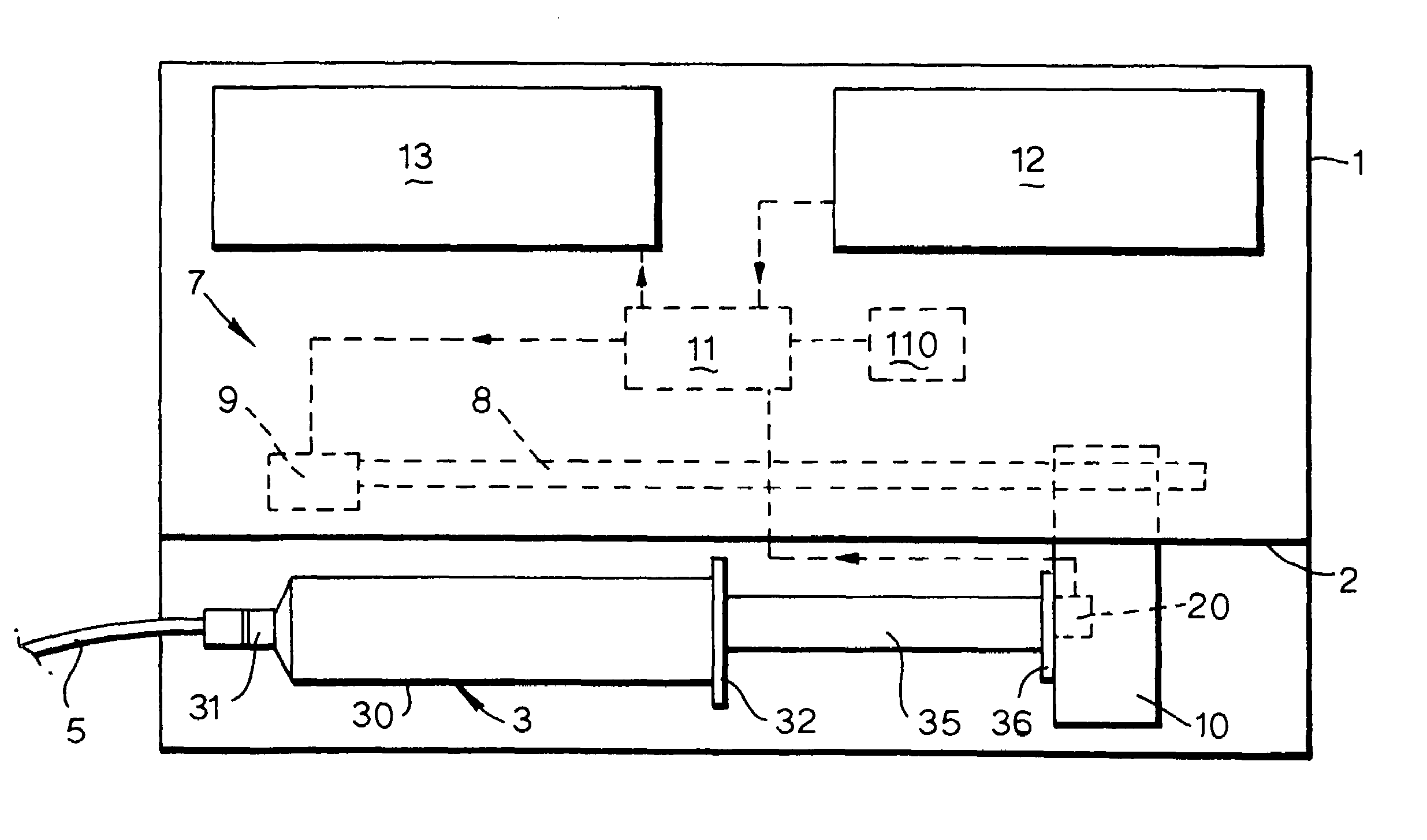
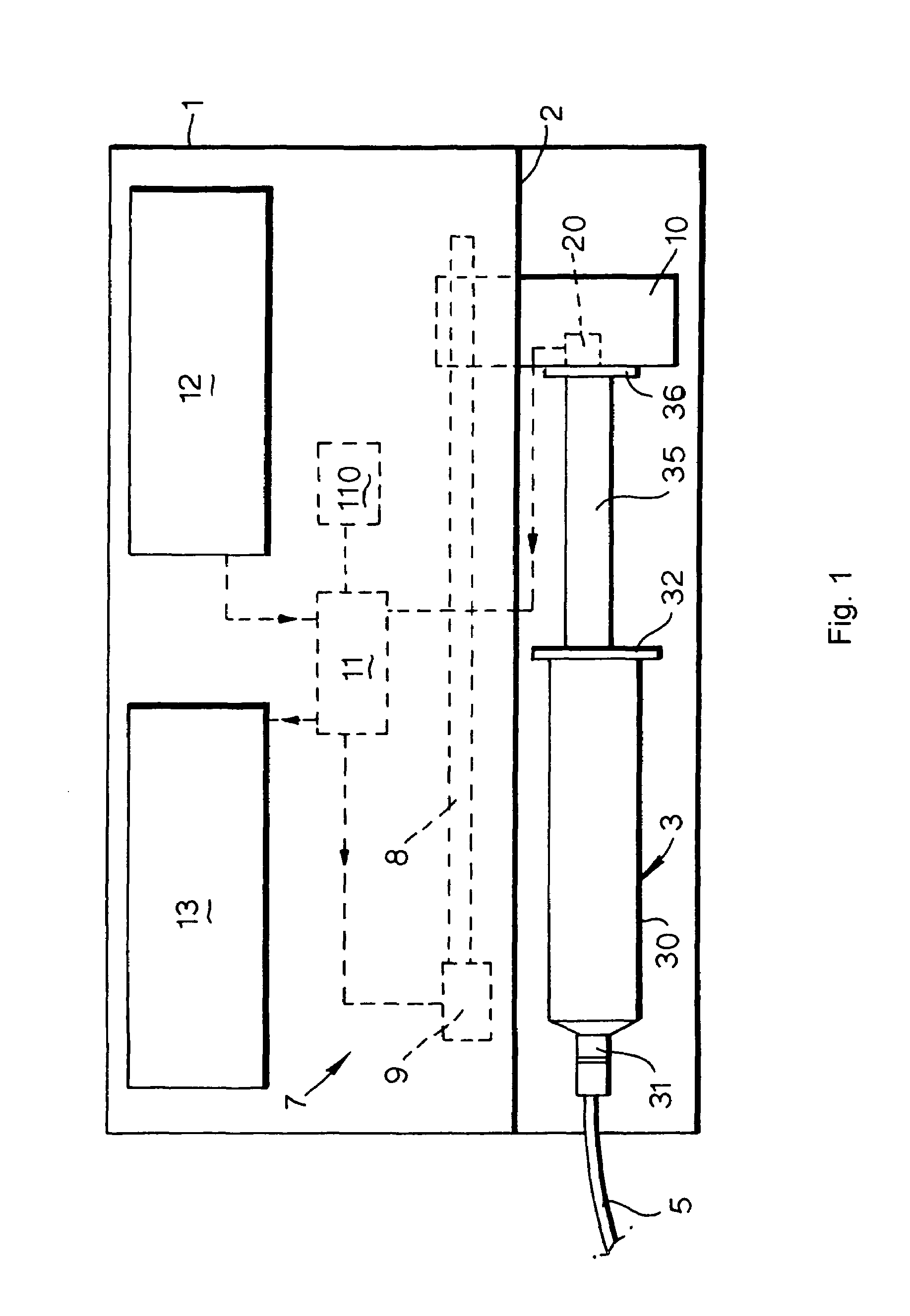
Syringe pumps
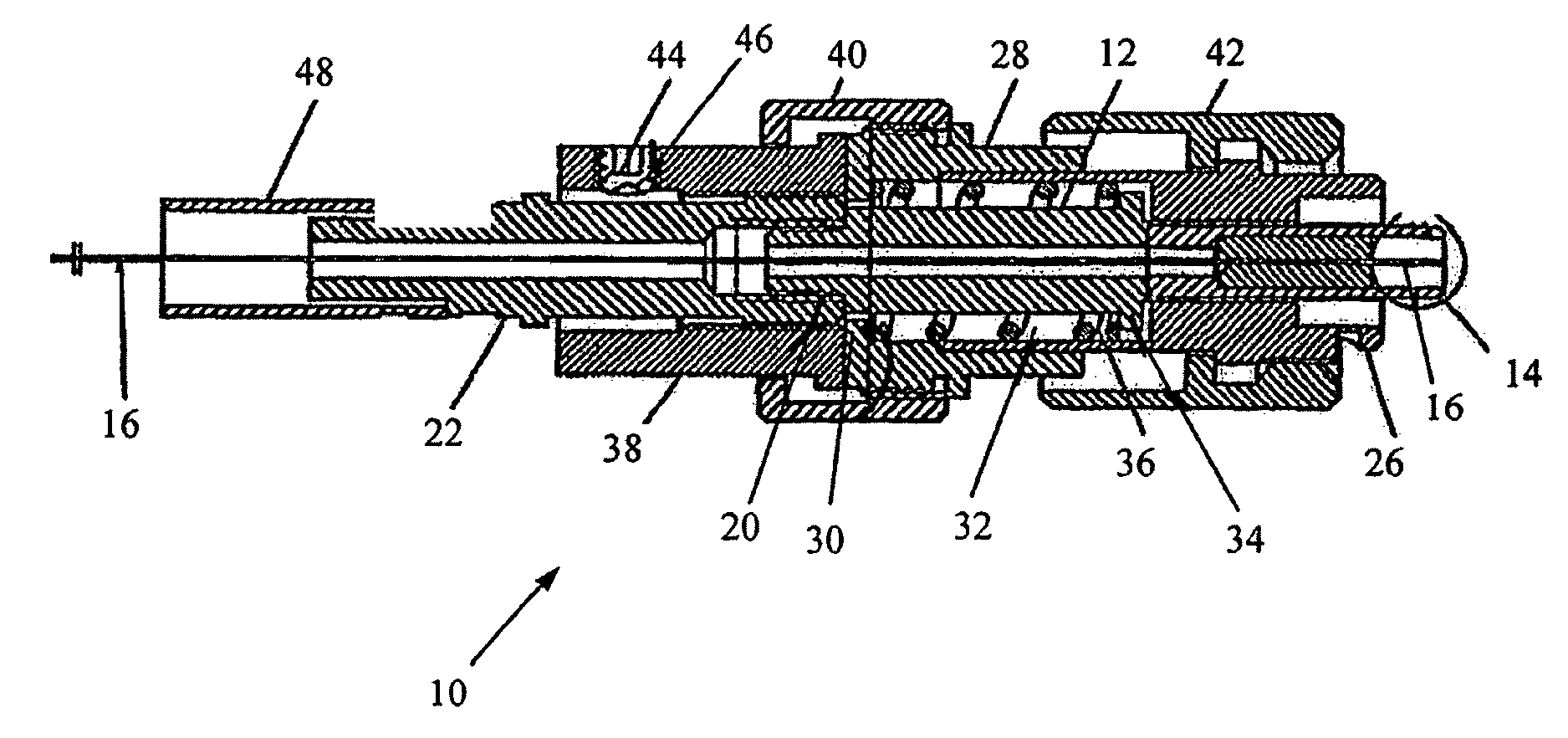
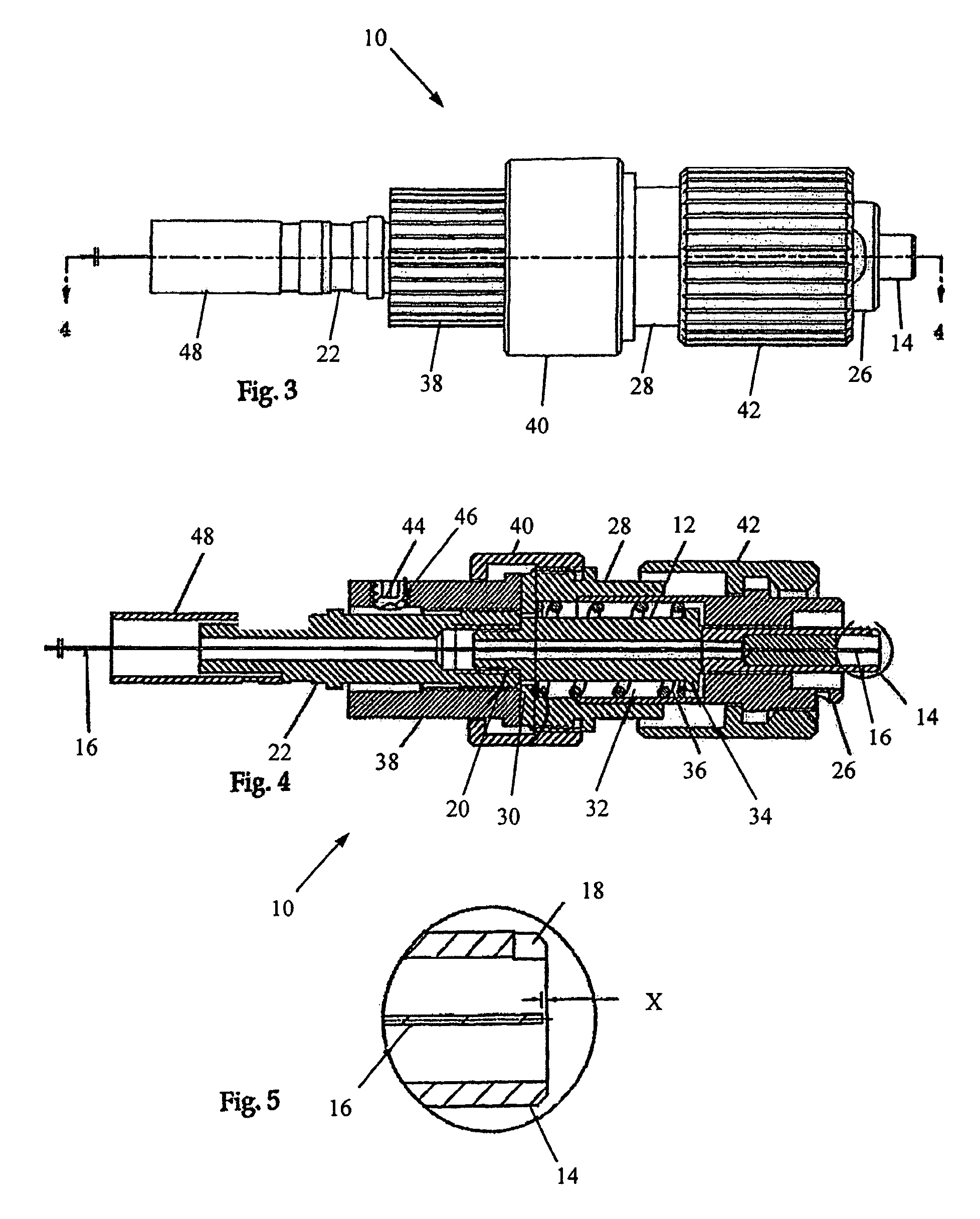
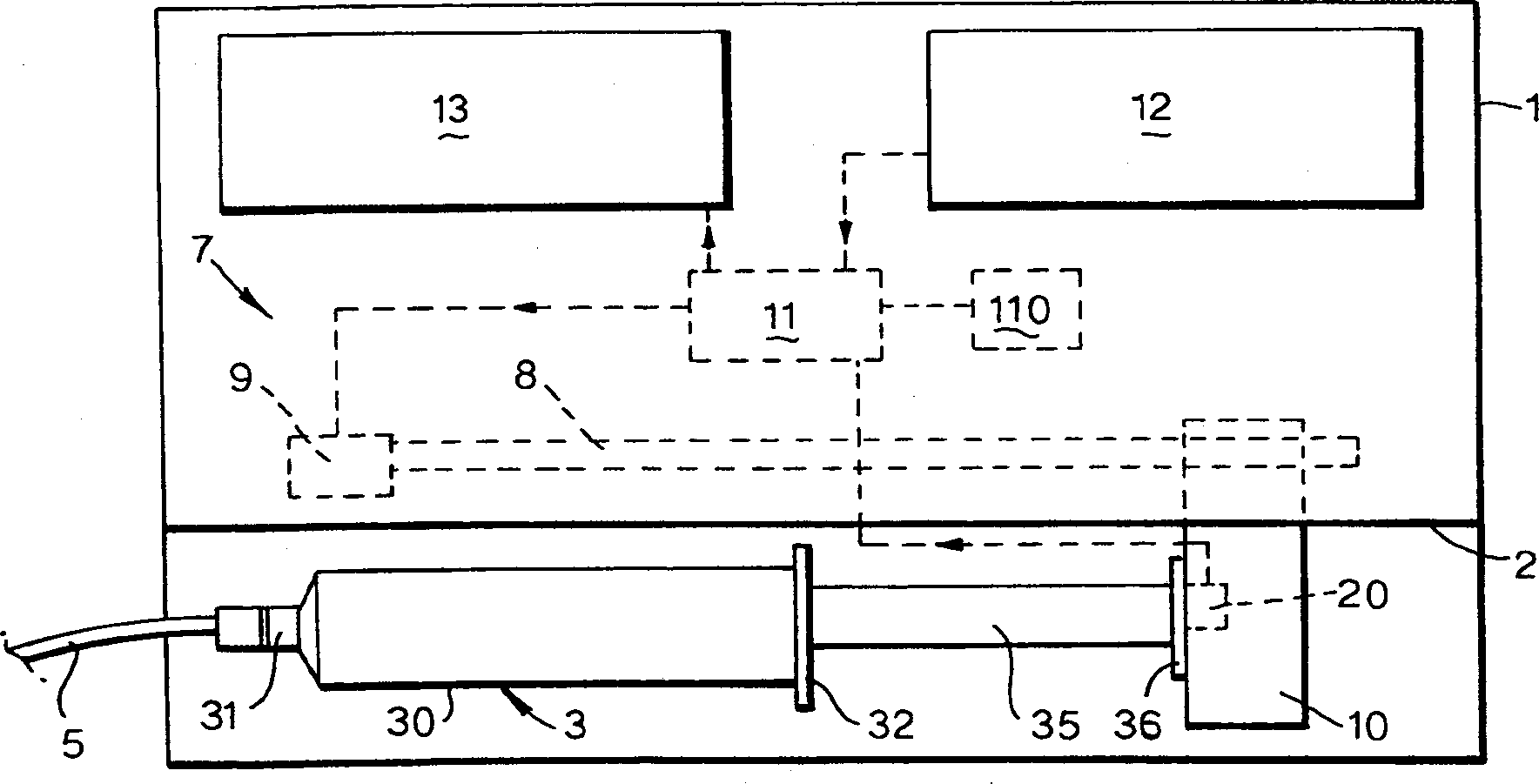
A syringe pump has a motor rotating a leadscrew to drive a plunger head actuator along it. The head actuator engages the plunger of a syringe and moves the plunger along the syringe barrel to dispense medication. An optical encoder mounted on the leadscrew is rotated by the motor to produce a pulse output. A control unit times the interval between the pulses and compares these timings with a stored value representative of a predetermined multiple of the minimum time. If the head actuator is obstructed, the speed of rotation of the motor is slowed and the time interval between pulses rises. When this exceeds the stored value, the control unit stops the drive to the head actuator and generates an alarm.
Owner:SMITHS GRP PLC
Ball screw actuator for aircraft control surfaces
InactiveUS6851648B2Guarantee capacityOvercomes drawbackAircraft navigation controlAircraft stabilisationBall screwActuator
A ball screw actuator for aircraft control surfaces includes a lead screw, a motor to set the screw in rotation about its longitudinal axis and a primary body connected to a control surface and engaged on the control screw via a plurality of balls movable on the thread of the screw. A secondary body is connected to the primary body and has an auxiliary portion provided with an engagement surface facing the thread of the lead screw at a predetermined distance; the engagement surface is shaped to engage on the thread of the lead screw. The actuator also includes a device for uncoupling the secondary body from the auxiliary portion in the rotation motion about the longitudinal axis.
Owner:UMBRA CUSCINETTI
Syringe pumps
InactiveUS7635349B2Relieve excessive stressReduce excessive forceClosuresMedical devicesDispensing medicationsSurgery
A syringe pump has a motor rotating a leadscrew, which drives a plunger head retainer to push a plunger along the barrel of a syringe so as to dispense medication to a patient. A force sensor in the head retainer measures the force on the plunger to detect when there is an occlusion restricting flow of medication. When an excess force is detected an alarm is generated and the motor is reversed to reduce the force to about 10% of that at which the occlusion is detected. The occlusion can be removed with a reduced risk of a bolus of medication being dispensed after which the user restarts the pump so that the plunger is driven normally.
Owner:SMITHS MEDICAL INT
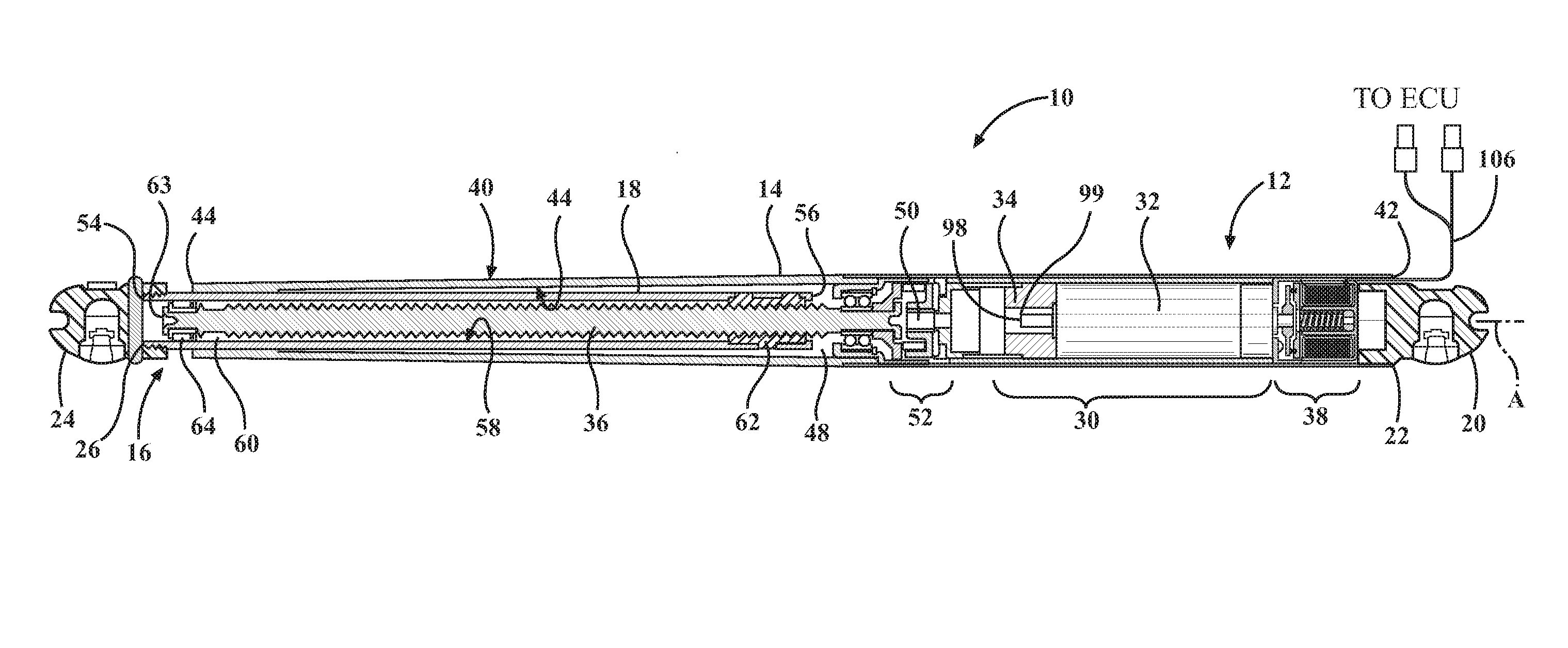
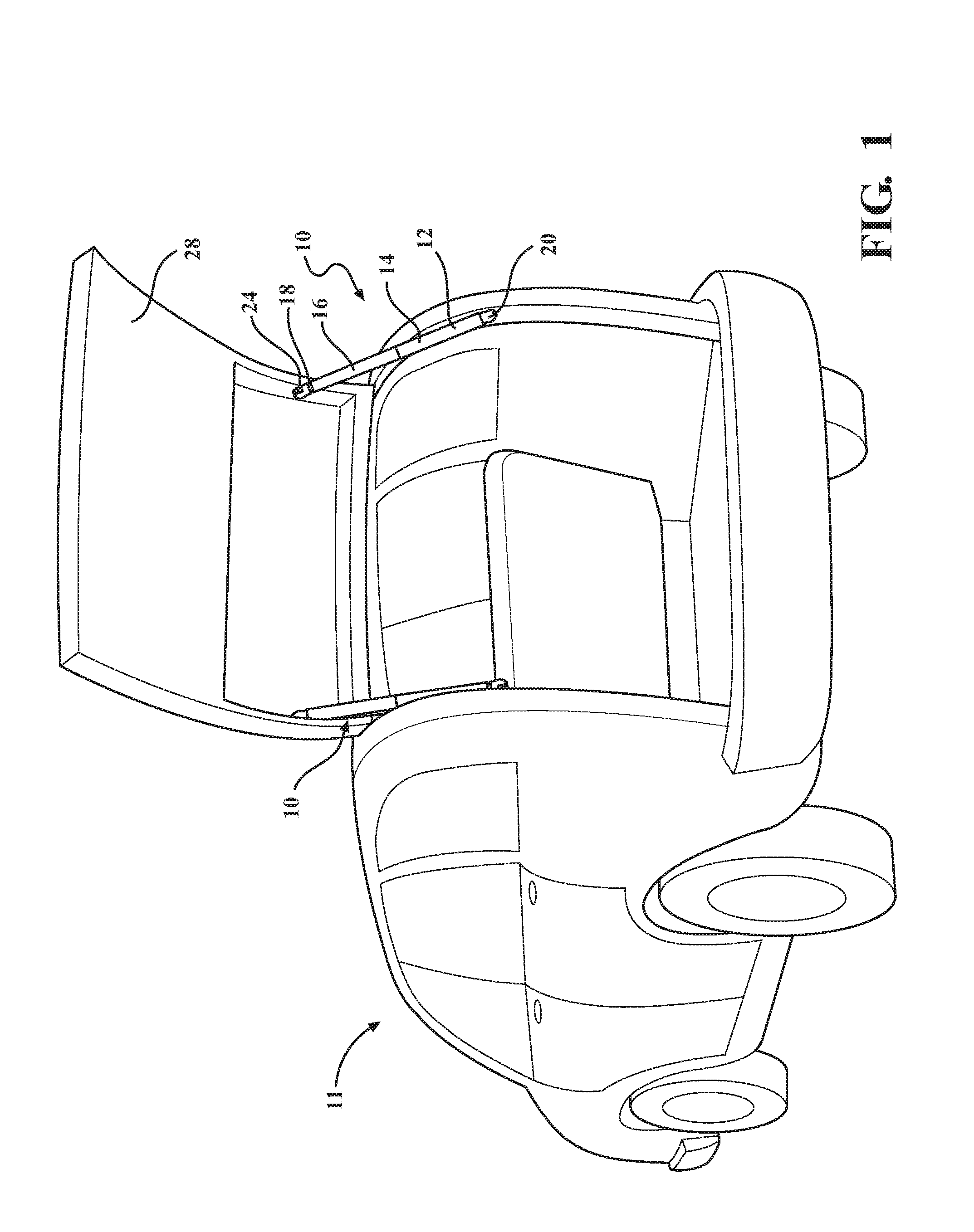
Electromechanical strut with electromechanical brake and method of allowing and preventing movement of a closure member of a vehicle
ActiveUS20160312514A1Easy to operateImprove retentionBuilding braking devicesGearingLinear motionEngineering
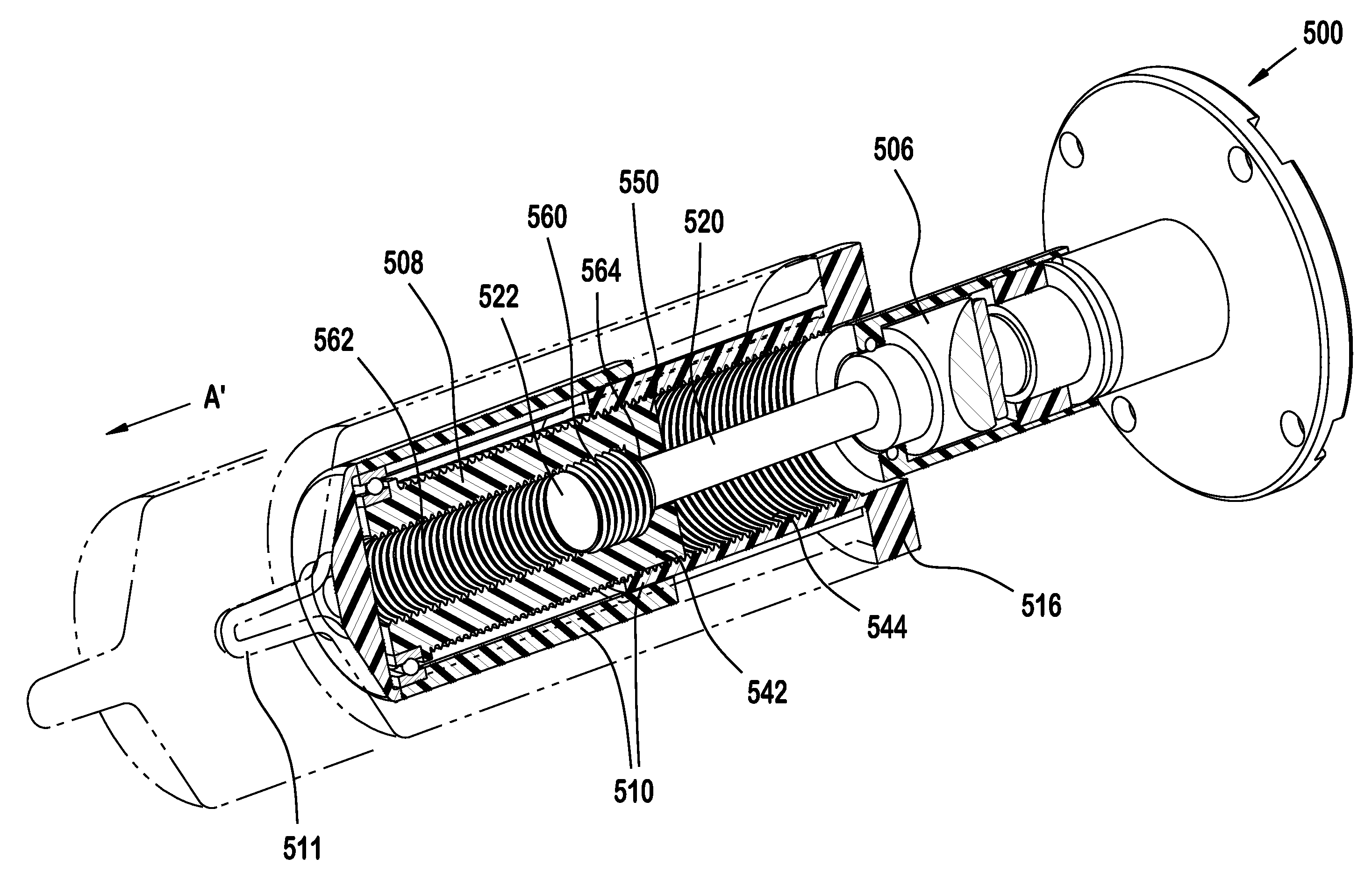
An electromechanical strut and method of moving a closure member of a vehicle between an open position and a closed position is provided. The electromechanical strut includes a power drive unit including a motor, a leadscrew, a planetary gearset operably connecting the motor to the leadscrew, and an electromechanical brake assembly. The electromechanical strut further includes a telescoping unit including an extensible tube and a drive nut for converting rotary motion of the leadscrew into linear motion of the telescoping unit. The electromechanical brake assembly is selectively moveable between an engaged state, wherein the leadscrew is prevented from rotating to prevent relative axial movement between the power drive unit and the telescoping unit, and a disengaged state, wherein the leadscrew is permitted to rotate to allow relative axial movement between the power drive unit and the telescoping unit.
Owner:MAGNA CLOSURES INC
High reliability precision latch
InactiveUS6935805B2Good repeatabilityImprove stabilityTravelling carriersCosmonautic vehiclesEngineeringCam
A reusable self-aligning precision latch, including a latch body for mounting a latch assembly, and an interface cone. A lead screw, coupled to the latch body on one end, pivots at an interface on the latch body allowing for self-alignment. A drive cam having a plurality of surfaces and positioned on the lead screw engages a plurality of linkage assemblies such that at least two links are driven. A flexure ball assembly clamped by the plurality of linkage assemblies to the latch body with a pivoting clamp plate such that all clamping forces between the pivoting clamp plate and the latch body are equalized. A motor for closing and opening the self-aligning precision latch by turning the lead screw to apply and release, respectively, the clamping forces between the pivoting clamp plate and the latch body.
Owner:EXCELIS INC
Electric parking brake
InactiveUS20020066626A1Quality improvementLight weightBraking action transmissionMechanically actuated brakesLinear motionElectric parking brake
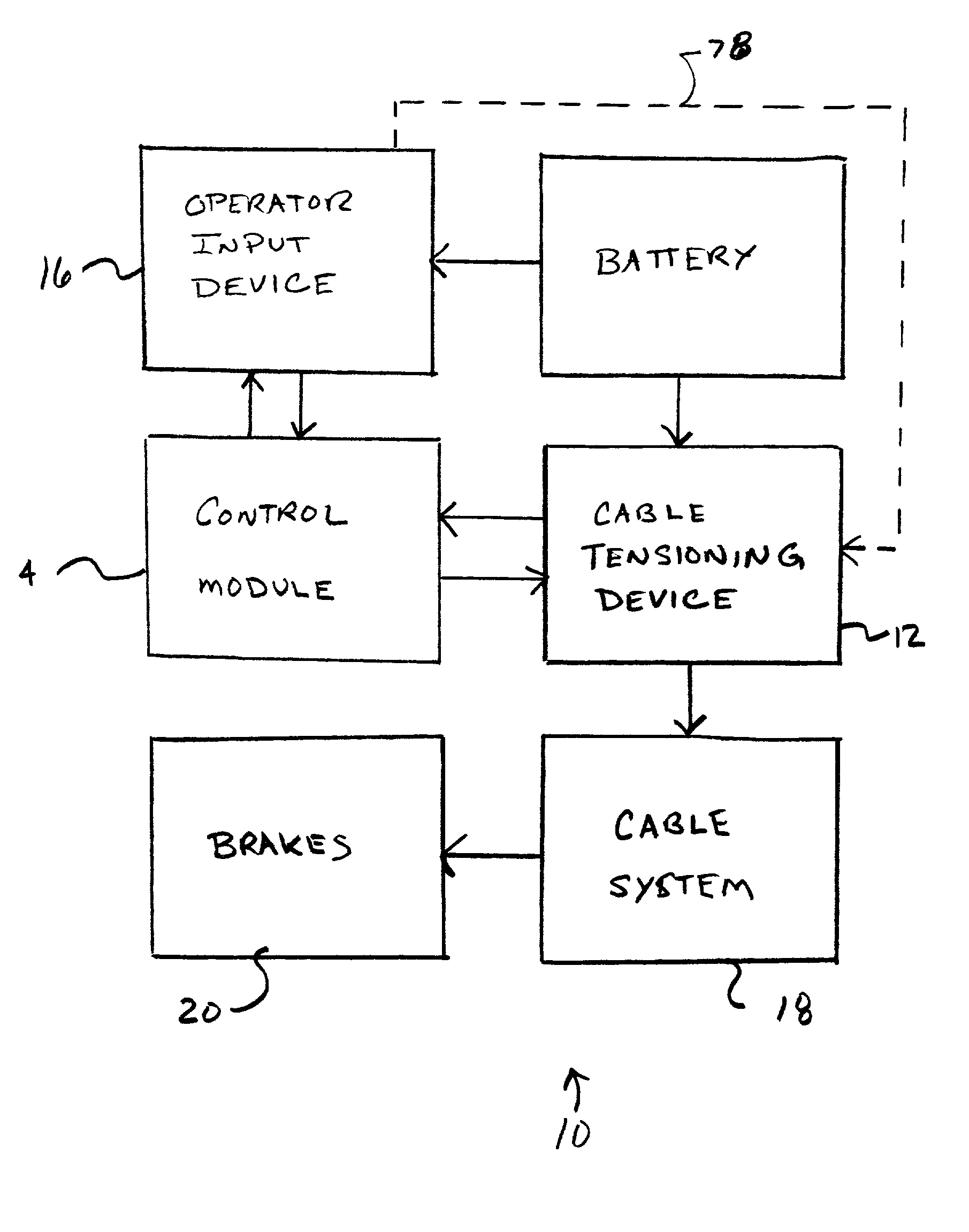
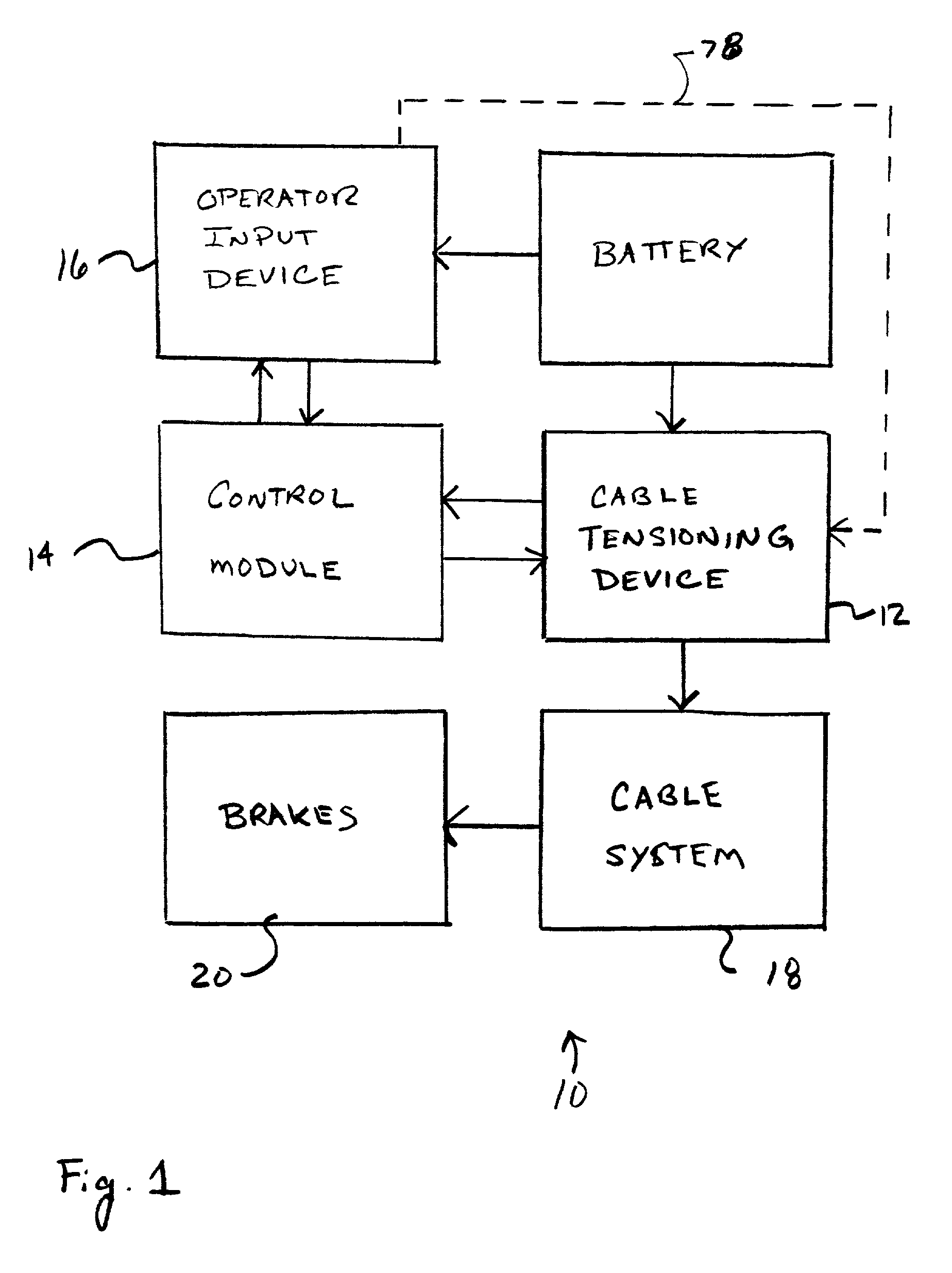
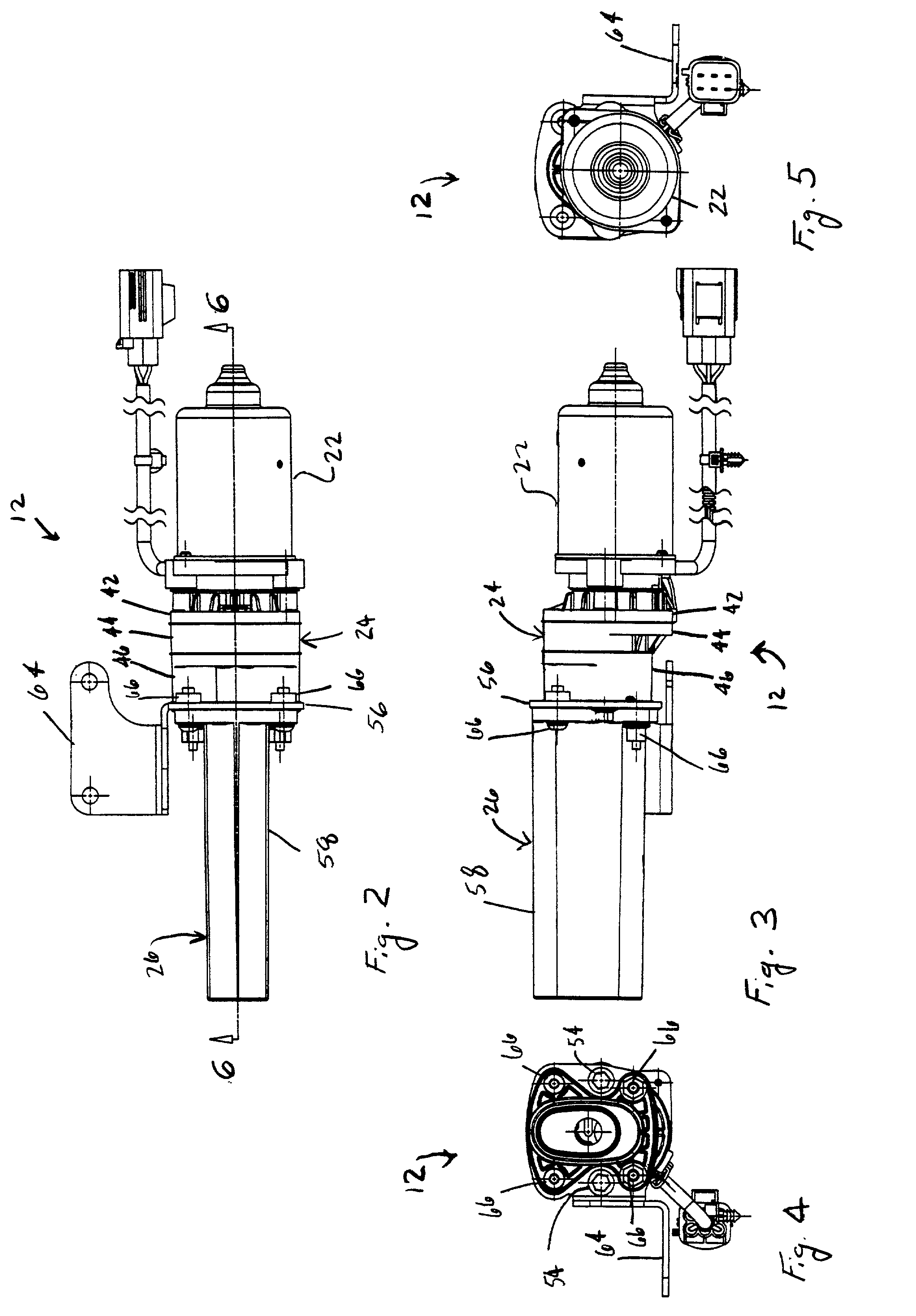
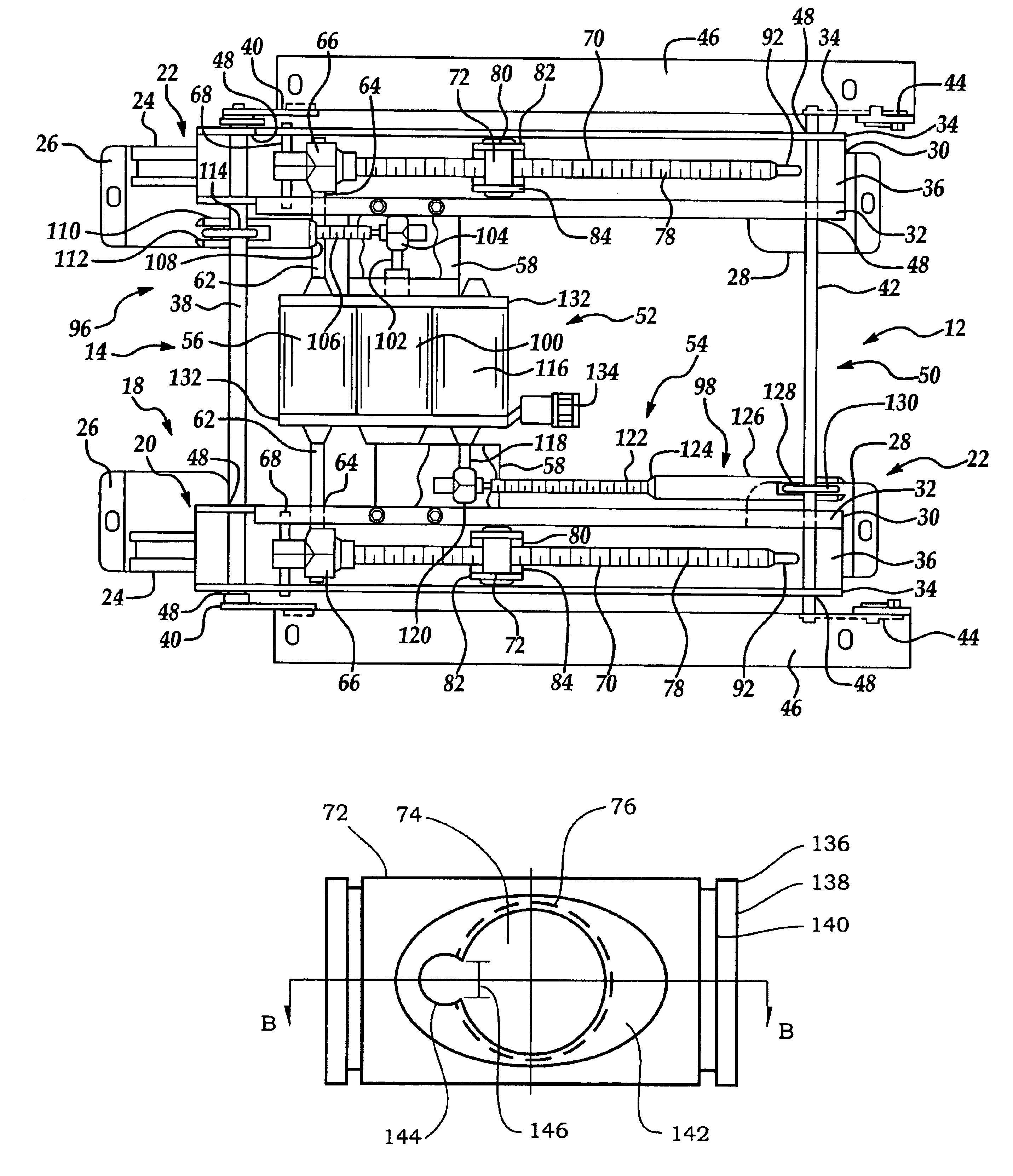
An electric parking brake assembly includes an electric motor having an output shaft, a control module coupled to the electric motor for controlling the electric motor and a transmission coupling a threaded lead screw to the output shaft of the electric motor. The transmission preferably includes a gear train having a plurality of helical gears and the lead screw and the output shaft are preferably coaxial. A stationary elongate guide shaft extends substantially parallel to and spaced apart from the lead screw. A drive nut has a lead screw bore threadably receiving the lead screw therein and a guide shaft bore slidingly receiving the elongate guide shaft therein. The drive nut also has a cable attachment for attaching a brake cable to the drive nut. The cable attachment has a central axis offset from a central axis of the lead screw and is preferably located midway between the lead screw bore and the guide shaft bore. The control module controls the electric motor such that rotation of the output shaft causes motion of the transmission and rotation of the lead screw, rotation of the lead screw causes linear motion of the drive nut along the lead screw and the guide shaft, and linear motion of the drive nut causes tensioning and untensioning of the brake cable. The assembly preferably includes a manual override device operatively connected to the lead screw. The manual override device selectively causes manual rotation of the lead screw, rotation of the lead screw causes linear motion of the drive nut, and linear motion of the drive nut causes tensioning and untensioning of the brake cable.
Owner:DURA GLOBAL TECH
Automotive seat assembly having a self-clearing drive nut
An automotive seat assembly including a seat frame having a main portion fixedly mounted to the bottom of a vehicle seat and a riser portion fixedly mounted to the floor pan of a vehicle. A seat drive mechanism is included having at least one drive motor and a threaded lead screw. A drive nut having a through-bore with internal threads that cooperate with the threads of the lead screw is adapted to cause the seat assembly to move relative to the vehicle floor pan in response to the drive motor. The drive nut also includes a second bore formed adjacent to, and extending in the general direction of, the through-bore such that the internal threads of the through-bore are interrupted by the second bore and act to clear the threads of the lead screw and prevent foreign matter that collects on the lead screw from entering the threaded interface between the drive nut and the lead screw.
Owner:LEAR CORP
Multi-leaf collimators
InactiveUS20090262901A1Drive great amountReduced shieldingHandling using diaphragms/collimetersRadiation therapyMulti leaf collimatorEngineering
A multi-leaf collimator for a radiotherapy apparatus comprises at least one array of laterally-spaced elongate leaves, each leaf being driven by an associated motor connected to the leaf via a drive means so as to extend or retract the leaf in its longitudinal direction, the drive means comprising a sub-frame on which at least a subset of the motors are mounted, the sub-frame being mounted at a location spaced from the leaf array in a direction transverse to the lateral and longitudinal directions, and including a plurality of leadscrews disposed longitudinally, each being driven by a motor and being operatively connected to a leaf thereby to drive that leaf.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Locking system having an electronic deadbolt
A motor with a shaft and a shaft axis is disposed within a housing. A lead screw has an axis and is rotatably mounted in the housing. A deadbolt linearly extends from the housing based on rotation of the lead screw. A gear set with a plurality of gears, each having an axis, is disposed in the housing and operably connects the motor and the lead screw. A circuit board is disposed within the housing and has a plurality of portions communicatively connected by a ribbon. Each portion is disposed substantially orthogonal to the motor shaft axis, the lead screw axis, and the plurality of gear axes.
Owner:AMESBURY GROUP
Gear machining punching device capable of preventing punching offset and adjusting pore diameter and punching method
PendingCN110653392AImprove practicalityAvoid position shiftFeeding apparatusPositioning apparatusPunchingGear wheel
The invention discloses a gear machining punching device capable of preventing punching offset and adjusting the pore diameter and a punching method. The gear machining punching device comprises a base plate, belt pulley mechanisms, a rotary motor and a storage platform; a servo motor is installed at the bottom of the base plate, the belt pulley mechanisms are installed at the outer sides of leadscrews, the rotary motor is installed on the upper end face of a top plate, movable grooves are reserved in the two ends of the top plate, and locking bolts are arranged at the outer sides of adjusting rods; guide blocks are connected to the bottoms of the adjusting rods, fixed plates are fixed to the upper end face of the base plate, movable rods penetrate through the interiors of the fixed plates, clamping plates are connected to the ends of the movable rods, and connected with the fixed plates through springs, and the storage platform penetrates through the middle of the base plate. According to the gear machining punching device capable of preventing offset and adjusting the pore diameter, by replacing punching heads with different diameters, pores with different sizes can be obtainedthrough punching, besides, the phenomenon of positional offset in the punching process can be avoided, and the practicability of the punching device is improved.
Owner:盐城永安科技有限公司
Long-span lead screw assembly with anti-backlash nut
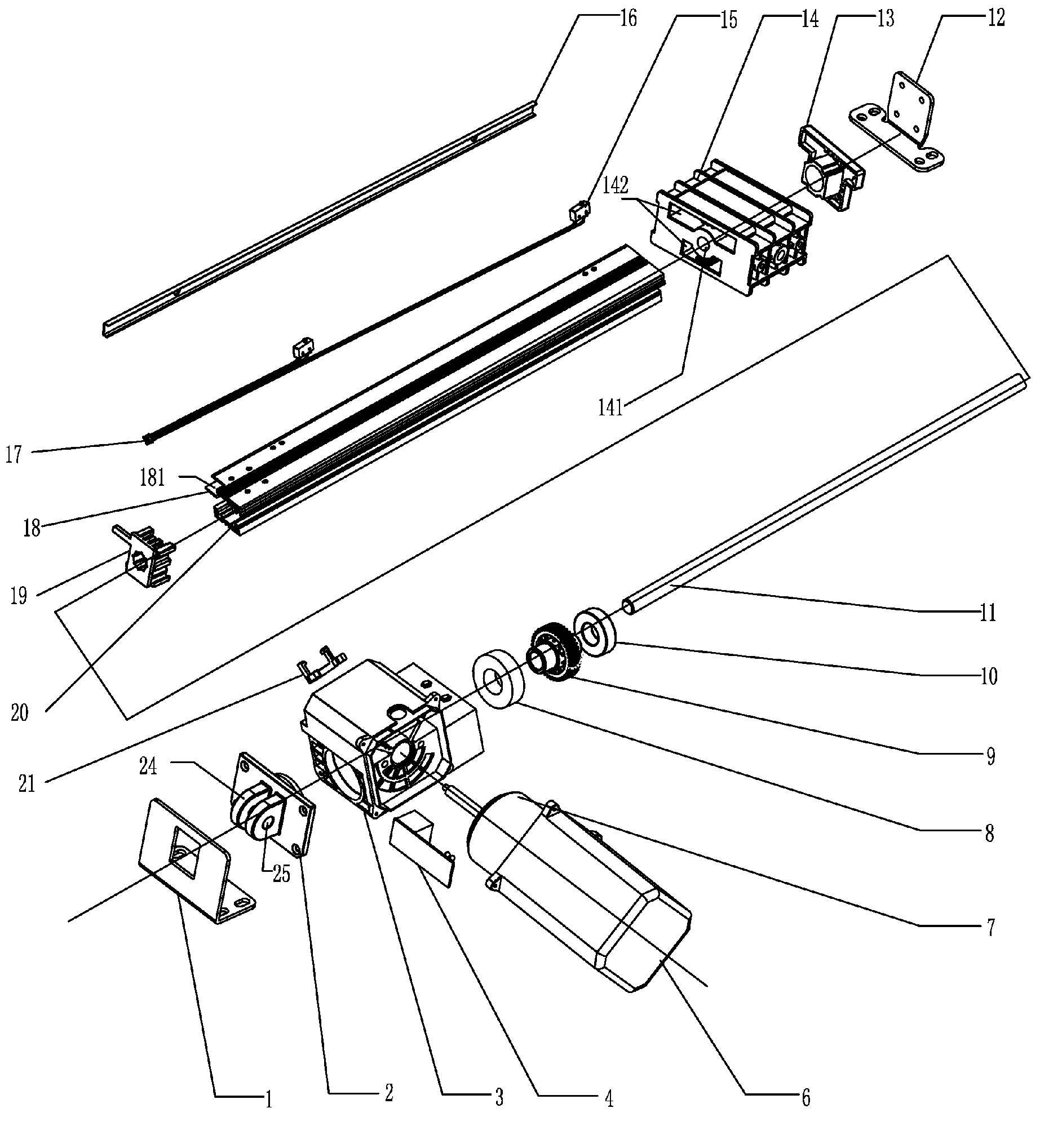
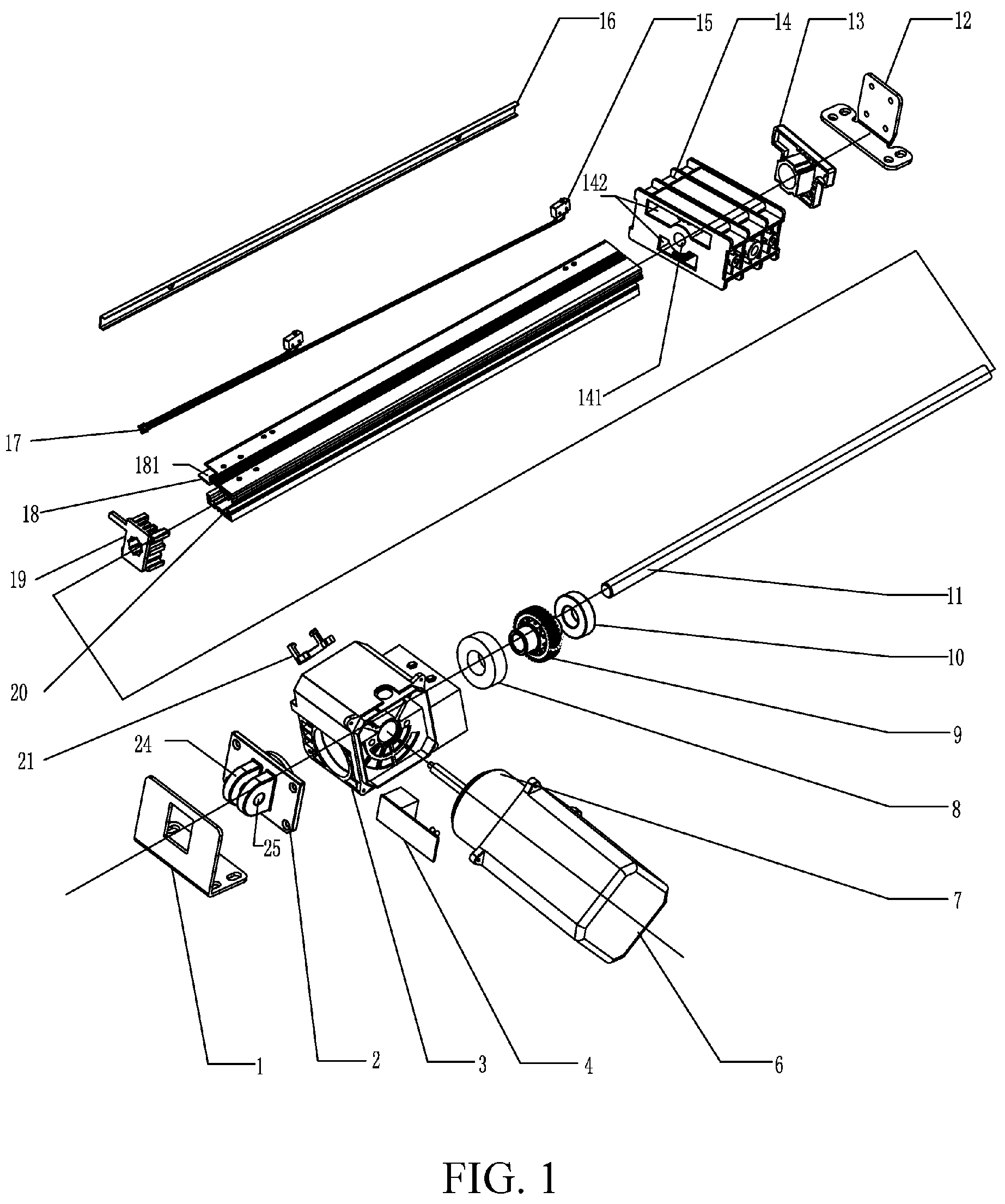
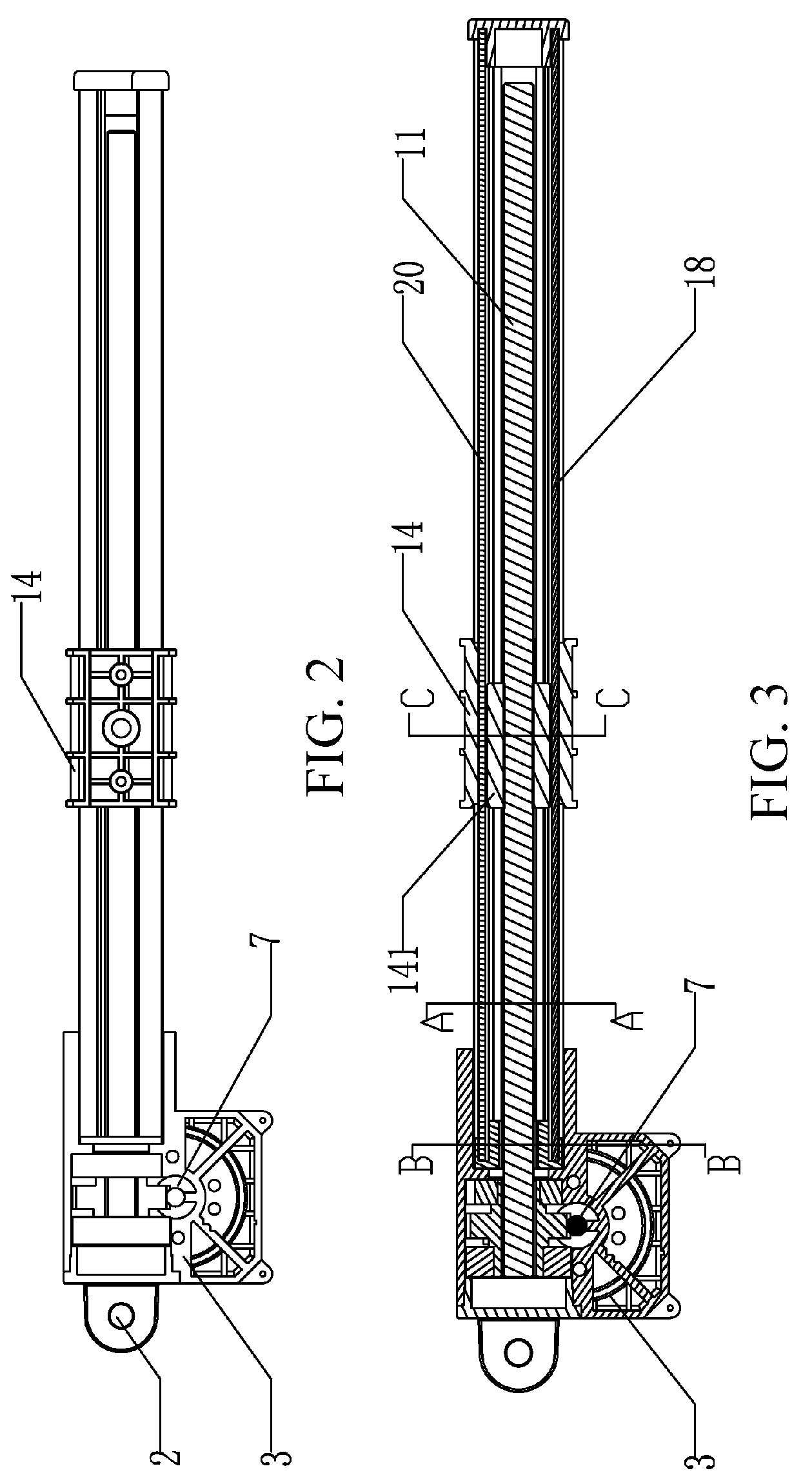
ActiveUS20050178225A1Operational securityMinimizing whippingPortable liftingToothed gearingsEngineeringLong span
A lead screw assembly having a lead screw rotatable within a hollow tubular portion of a reinforcing rail. A nut engages with threads of the lead screw and is movable along the reinforcing rail. The lead screw includes plurality of first threaded portions having an outer diameter and extending lengthwise of the lead screw; and at least one second gap portion having an outer diameter that is less than the outer diameter of the first threaded portions. The second gap portion is positioned between adjacent first threaded portions of the lead screw. At least one generally U-shaped bearing is secured within the reinforcing rail and contacts the lead screw at a second gap portion. Each U-shaped bearing supports the lead screw along its length as the screw rotates within the rail, so that the lead screw assembly can be safely operated at high speeds over comparatively long distances while minimizing whipping and vibration of the lead screw. The reinforcing rail can include a base portion which permits the assembly to be securely mounted to a support structure at any convenient location along its length. An anti-backlash nut assembly includes a threaded follower for engagement with the threads of a lead screw. A pair of wedges bias the follower in a radial direction so that the threads of the follower are brought into forcible engagement with the mating threads of the screw. In a preferred embodiment, the nut assembly is adjustable to provide variable levels of backlash resistance and wear-compensation.
Owner:KERK MOTION PROD
Detection device and method for improving layer-to-layer transition of steel wire ropes
InactiveUS20190094127A1Conveniently changedUsing mechanical meansTension measurementRelative displacementThreaded rod
Systems and methods for detecting a layer-to-layer transition of a lifting steel wire rope on a reel are described. The system includes a reel assembly for winding a steel wire rope on a reel and a tensioning assembly for tensioning a segment of said steel wire rope. The system further includes a loading assembly and a lead screw sliding assembly. The loading assembly provides a vertical loading to the tensioning assembly so as to generate a loading force between the tensioned steel wire rope and the steel wire rope wound around the reel. The lead screw sliding assembly drives the tensioning assembly so as to move on a horizontal guide rail to generate a relative displacement between the tensioned steel wire rope and the steel wire rope wound around the reel. The tensioning assembly is connected to the loading assembly via a first threaded rod and a static torque sensor.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Apparatus for aspirating liquids from sealed containers
ActiveUS7481978B2Easy constructionLess componentsWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringLinear actuator
Apparatus for aspirating liquid from a container, e.g., a test tube, having a puncturable stopper includes a pair of stepper motors that share a common linear actuator or drive member. One motor operates to axially advance the linear drive member (preferably a lead screw) to a position in which it serves to position a rigidly connected tube-detector / stripper member in engagement with the top of a stopper on a tube. Thereafter, the second motor operates to move along the surface of the same drive member to advance an aspiration probe through the engaged stopper and into a liquid aspirating position within the tube. Preferably, a linear guide rail, slidably-mounted on a frame that supports the liquid-aspirating apparatus, serves to guide both the movement of the aspiration probe and the linear drive member. As a result of the shared components, the apparatus is highly precise and reliable.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Drive for adjusting parts of seating and reclining furniture
InactiveUS20100064830A1Improve adjustabilityReduce manufacturing costLinear bearingsSofasInterior spaceGear wheel
A drive for adjusting parts of seating and reclining furniture is provided, which includes: an electric motor, disposed within a motor cover of a cabinet and engaged with a gear connected to a lead screw via one end of a drive shaft of the electric motor, and a slider, for moving rectilinearly back and forth in cooperation with the lead screw. The slider is provided with a drive nut therein, which is screwed onto the lead screw to enable the slider to move rectilinearly. One or more positioning grooves are disposed on the slider in parallel with the nut. Guide rails are correspondingly disposed in the positioning grooves. One end of each guide rail is fixed to the cabinet and the other end of each guide rail is fixed to a top stopper. Therefore, a better adjustability is achieved within a limited inner space of the furniture. Moreover, the drive does not need to move, and the stroke length of the drive is independent from the cabinet size thereof, so that the drive has a low manufacturing cost and is easily assembled.
Owner:REMACRO MASCH & TECH (WUJIANG) CO LTD
Long-span lead screw assembly with anti-backlash nut
ActiveUS7219570B2Operational securityMinimizing whipping and vibrationToothed gearingsPortable liftingEngineeringLong span
A lead screw assembly having a lead screw rotatable within a hollow tubular portion of a reinforcing rail. A nut engages with threads of the lead screw and is movable along the reinforcing rail. The lead screw includes plurality of first threaded portions having an outer diameter and extending lengthwise of the lead screw; and at least one second gap portion having an outer diameter that is less than the outer diameter of the first threaded portions. The second gap portion is positioned between adjacent first threaded portions of the lead screw. At least one generally U-shaped bearing is secured within the reinforcing rail and contacts the lead screw at a second gap portion. Each U-shaped bearing supports the lead screw along its length as the screw rotates within the rail, so that the lead screw assembly can be safely operated at high speeds over comparatively long distances while minimizing whipping and vibration of the lead screw. The reinforcing rail can include a base portion which permits the assembly to be securely mounted to a support structure at any convenient location along its length.An anti-backlash nut assembly includes a threaded follower for engagement with the threads of a lead screw. A pair of wedges bias the follower in a radial direction so that the threads of the follower are brought into forcible engagement with the mating threads of the screw. In a preferred embodiment, the nut assembly is adjustable to provide variable levels of backlash resistance and wear-compensation.
Owner:KERK MOTION PROD
Electrical cabinet protection base
InactiveCN107565402AEasy to useImprove protectionSubstation/switching arrangement casingsArchitectural engineeringLeadscrew
The invention discloses an electrical cabinet protection base, and relates to the technical field of electronic products. The electrical cabinet protection base comprises a base. Bottom grooves are fixedly connected on the two sides of the top part of the base. A flexible block is slidably connected on the right side of the internal part of each bottom groove. A first spring is fixedly connected between the left side of the flexible block and the left side of the internal wall of each bottom groove. A support rod is rotatably connected on the surface of the flexible block. A lead screw grooveis rotatably connected on one end, which is away from the flexible block, of the support rod. A lead screw is rotatably connected in the lead screw groove. According to the electrical cabinet protection base, the bottom grooves are fixedly connected on the two sides of the top part of the base, the flexible block is slidably connected on the right side of the internal part of each bottom groove, the support rod is rotatably connected on the surface of the flexible block, the lead screw groove is rotatably connected on one end, which is away from the flexible block, of the support rod, the leadscrew is rotatably connected in the lead screw groove, vertical rods are rotatably connected on the two sides of the surface of the lead screw, and clamping devices are fixedly connected on the opposite sides of the two vertical rods to clamp and fix the electrical cabinet so that the stability is high and the use effect is great.
Owner:合肥慕智信息技术有限公司
Electromechanical strut with electromechanical brake and method of allowing and preventing movement of a closure member of a vehicle
ActiveUS10280674B2Prevent movementEasy to operateBuilding braking devicesGearingLinear motionEngineering
An electromechanical strut and method of moving a closure member of a vehicle between an open position and a closed position is provided. The electromechanical strut includes a power drive unit including a motor, a leadscrew, a planetary gearset operably connecting the motor to the leadscrew, and an electromechanical brake assembly. The electromechanical strut further includes a telescoping unit including an extensible tube and a drive nut for converting rotary motion of the leadscrew into linear motion of the telescoping unit. The electromechanical brake assembly is selectively moveable between an engaged state, wherein the leadscrew is prevented from rotating to prevent relative axial movement between the power drive unit and the telescoping unit, and a disengaged state, wherein the leadscrew is permitted to rotate to allow relative axial movement between the power drive unit and the telescoping unit.
Owner:MAGNA CLOSURES INC
Adjustable focus connector with spring action
An adjustable focus connector with spring action is especially adapted for use with common FC or SAM fiber optic receptacles. The connector includes a ferrule holder which mounts a fiber-carrying ferrule at a distal end thereof. At its proximal end the ferrule holder is threadedly connected to a lead screw member. A thrust collar surrounds the ferrule holder and traps a compression spring in the cavity between the thrust collar and the ferrule holder. Because of appropriate interengagement between the components the ferrule holder cannot rotate relative to the trust collar. A traveler is threadedly connected to the lead screw and abuts against the thrust collar. A connection nut is provided at the distal end of the connector to connect it to the fiber optic receptacle. The spring action of the connector prevents damage to the fiber end during connection of the connector to the fiber optic receptacle.
Owner:OZ OPTICS
Syringe pump
A syringe pump has a motor rotating a leadscrew, which drives a plunger head retainer to push a plunger along the barrel of a syringe so as to dispense medication to a patient. A force sensor in the head retainer measures the force on the plunger to detect when there is an occlusion restricting flow of medication. When an excess force is detected an alarm is generated and the motor is reversed to reduce the force to about 10% of that at which the occlusion is detected. The occlusion can be removed with a reduced risk of a bolus of medication being dispensed after which the user restarts the pump so that the plunger is driven normally.
Owner:SMITHS GRP PLC
Power strut assembly
A power strut assembly for a vehicle includes a first strut member having joined outer walls that define an interior cavity. The first strut member extends from a first end to a second end. The first end includes a base wall joined to the outer walls. A second strut member also having joined outer walls defining an inner cavity extends from a first end to a second end. The second strut member is telescopically disposed within the interior cavity of the first strut member. A lead screw extends from a first end to a second end and is rotatively retained at the first end of the first strut member. The lead screw extends into the interior cavities of the first and second strut members. A clutch is retained by the second strut member and the lead screw is positioned to interact with the clutch. The clutch is movable between a disengaged position relative to the lead screw where the clutch is free to travel longitudinally relative to the lead screw and an engaged position wherein rotation of the lead screw translates to longitudinal motion of the second strut member relative to the first strut member.
Owner:DURA GLOBAL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com