Near-surface tomographic velocity analysis method
A velocity analysis and surface technology, applied in the field of seismic physical exploration, can solve problems such as the difficulty of iterative inversion of initial velocity modeling, and achieve the effect of real and reliable calculation results, strong stability, and obvious geophysical significance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
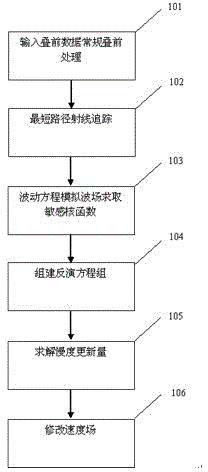
[0039] Example 1. Such as figure 1 Shown, a kind of near-surface tomographic velocity analysis method is characterized in that, the method comprises the steps:
[0040] In step 101, input parameter data into conventional processing software, including original running records, observation system and other information, and obtain the real first arrival travel time. The process goes to step 102.
[0041] In step 102, according to the initial velocity model obtained in step 101, the shortest path ray tracing is performed to obtain the travel time of the model, and the travel time residual is obtained. The process goes to step 103.
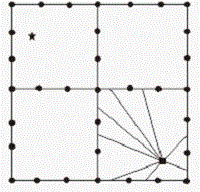
[0042] In step 103, according to the initial velocity model obtained in step 101, the wave field is simulated by the wave equation to obtain the kernel function. The wave equation is a frequency domain wave equation, and the sensitive kernel function obtained is as follows Figure 4 shown. The flow goes to step 104 .
[0043] In step 104, accor...
Embodiment 2
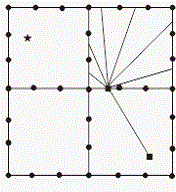
[0047]Example 2. The difference between this embodiment and Implementation 1 is that: in step 101, the input parameter data in the conventional processing software also includes relevant information such as the excitation point and the elevation of the receiving point; in step 102, when performing shortest path ray tracing, the Calculate the range of the first Fresnel zone when the forward and reverse travel is calculated with the shot point and the receiver point as the excitation point. In step 103, the sensitive kernel function is the Frechet kernel function defined by the first Fresnel band (results such as image 3 a to image 3 As shown in c) the specific expression for calculating the kernel function through the frequency wave equation is:
[0048] F T ( r , ω ) = - 2 ω ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com