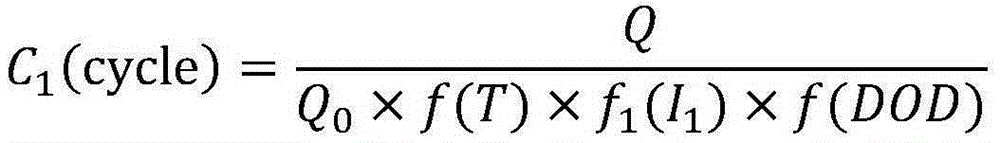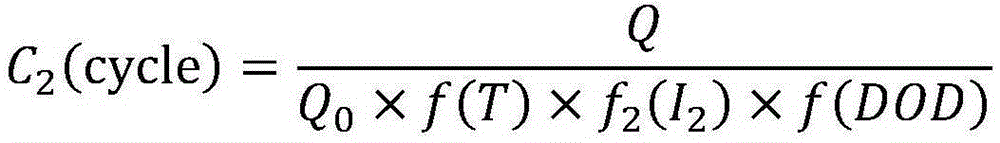Patents
Literature
258 results about "Depth of discharge" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Depth of discharge is an alternative method to indicate a battery's state of charge. The depth of discharge is the complement of state of charge: as one increases, the other decreases. While the state of charge is usually expressed using percentage points (0 % = empty; 100 % = full), depth of discharge is usually expressed using units of A h (e.g, 0 is full and 50 A h is empty) or percentage points (100 % is empty and 0 % is full). The capacity of a battery may be higher than its nominal rating. Thus it is possible for the depth of discharge value to exceed the nominal value (e.g., 55 A h for a 50 A h battery, or 110 %).
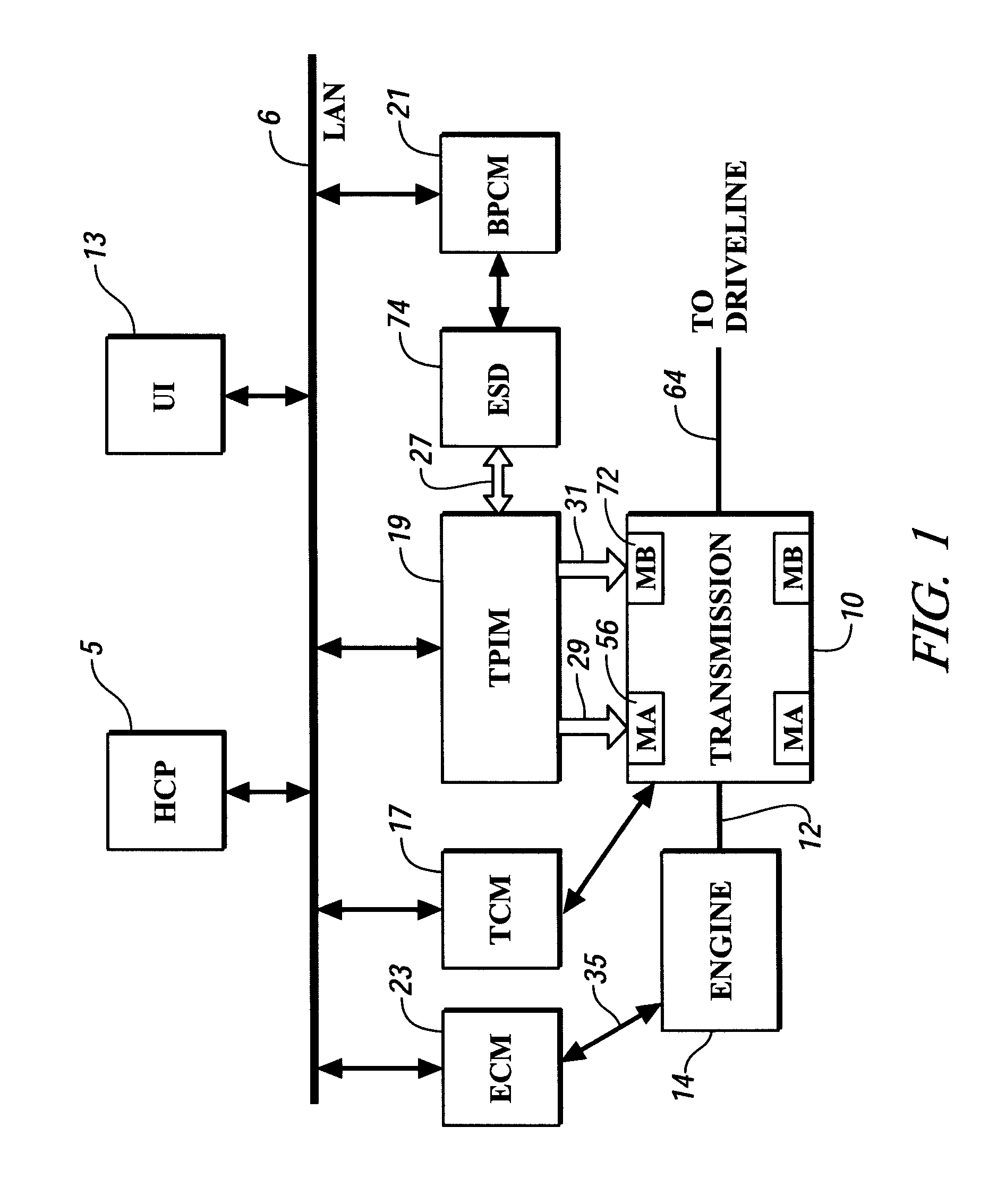
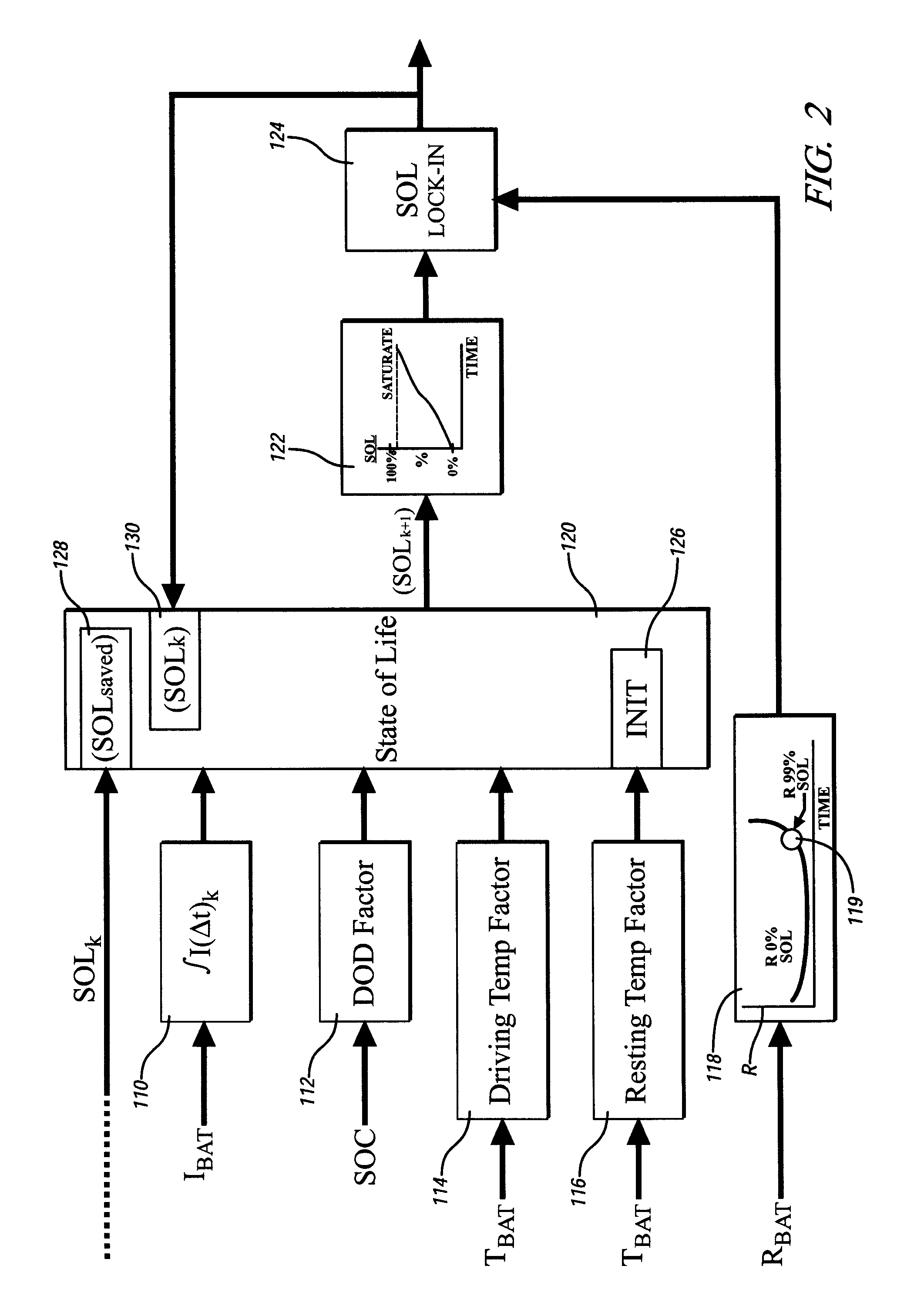
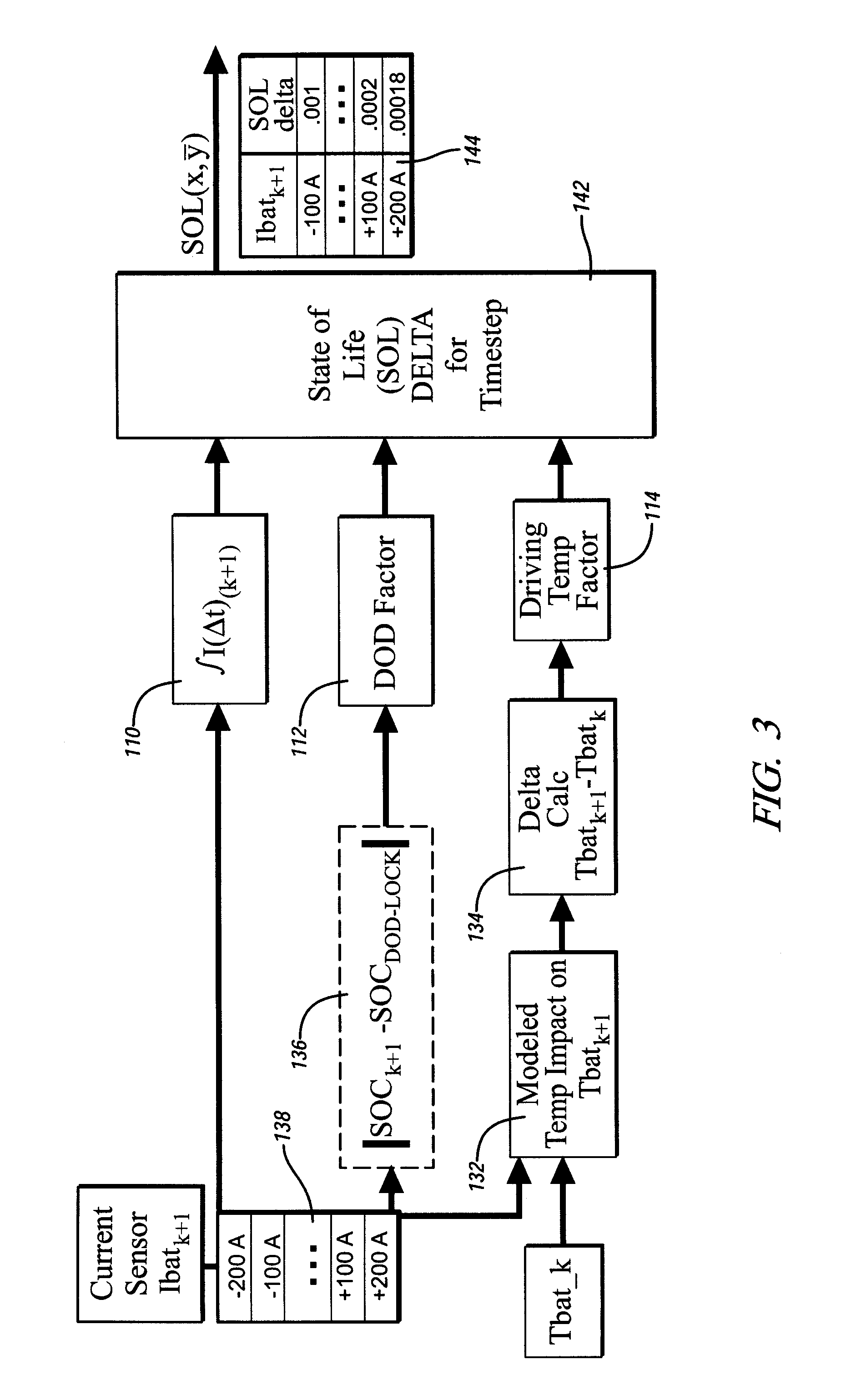
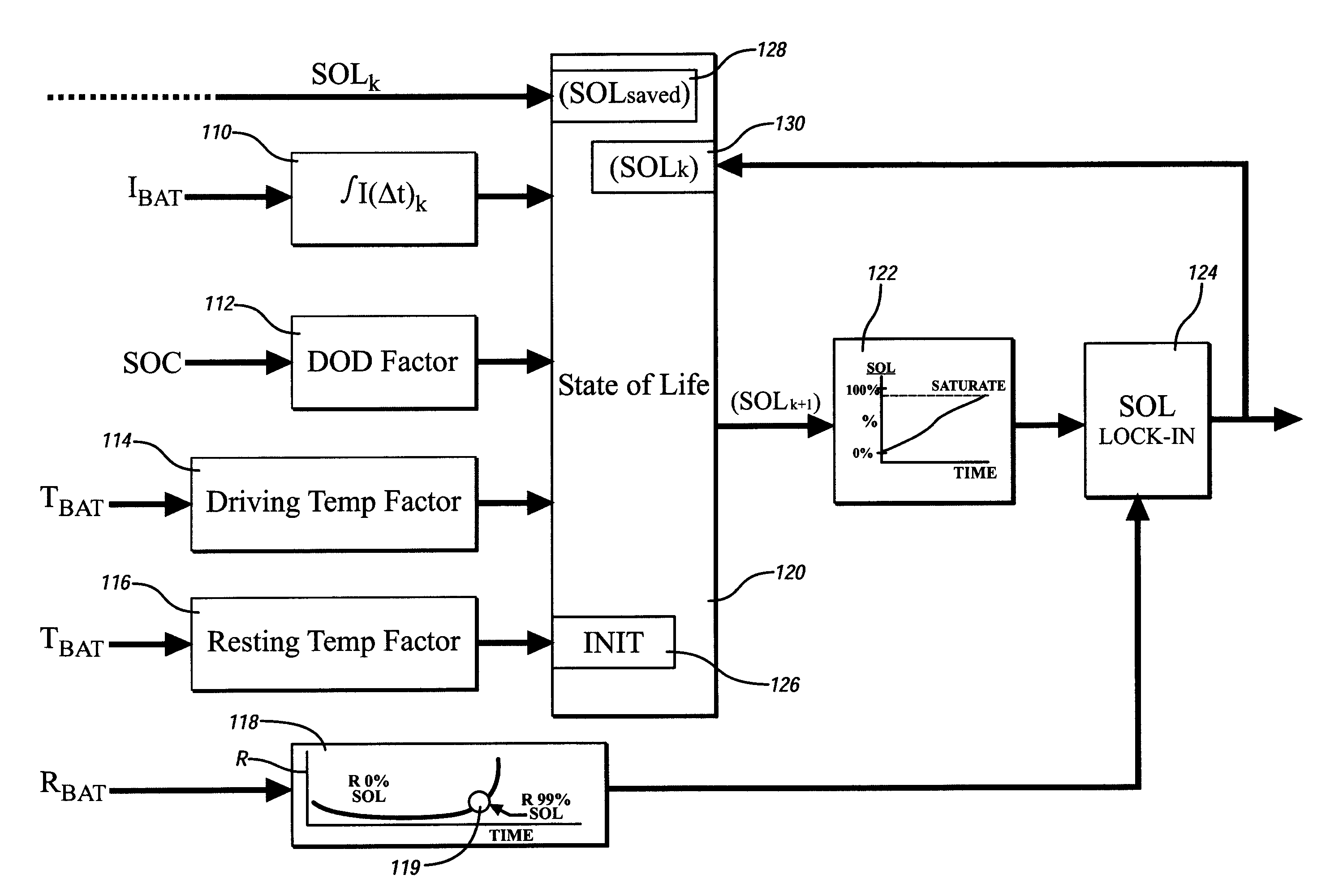
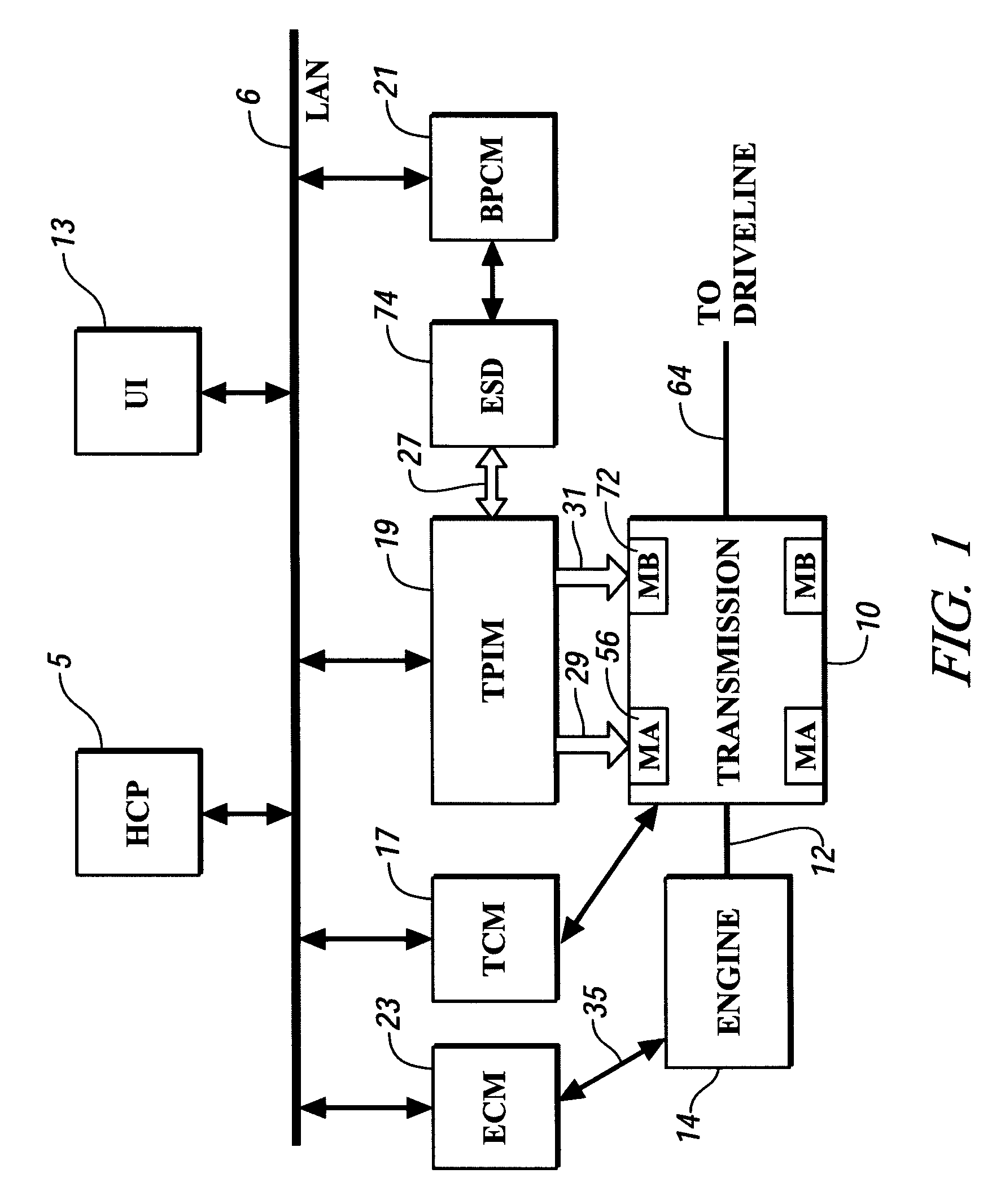
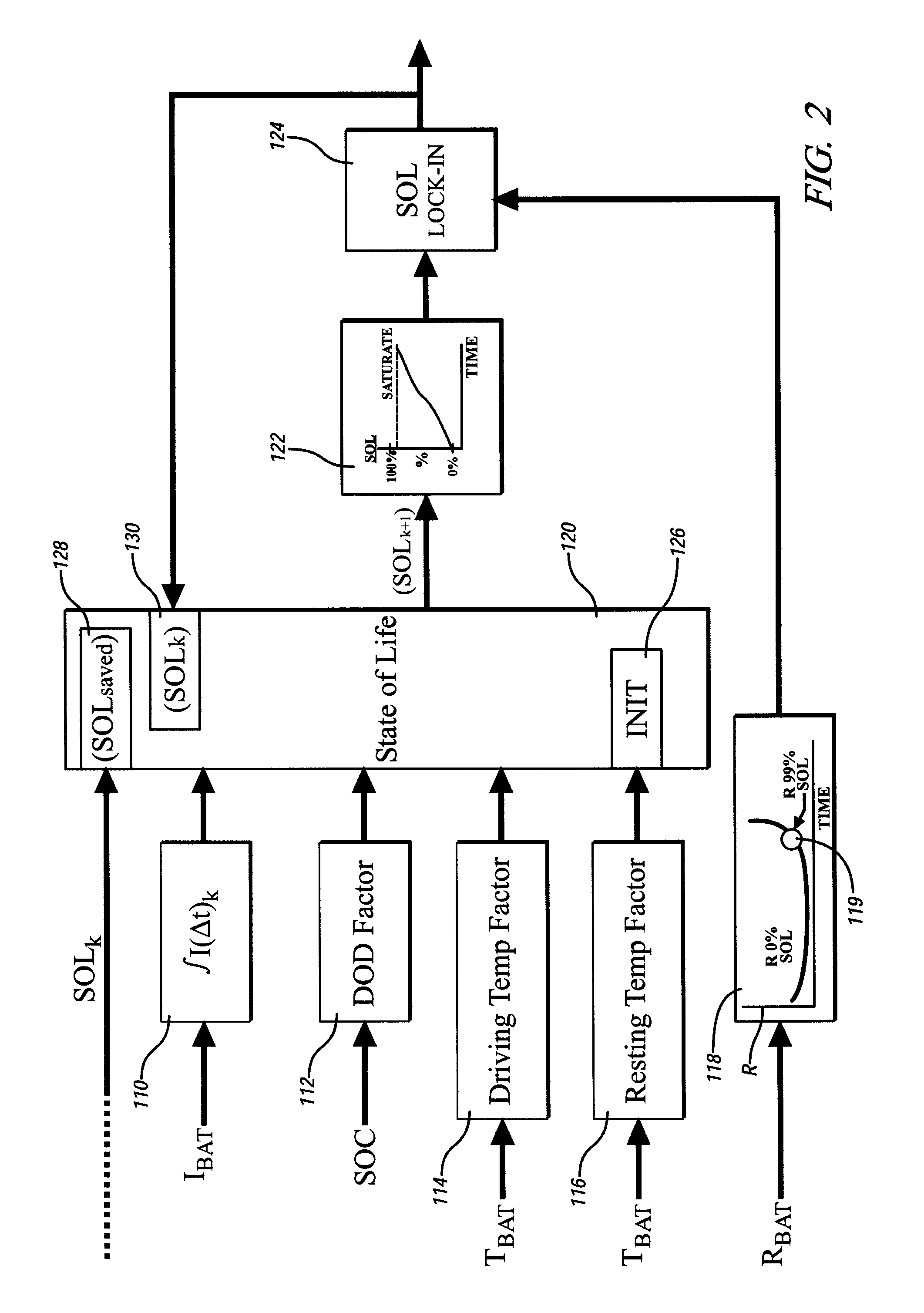
Method and apparatus for predicting change in an operating state of an electric energy storage device
A method for predicting change in an operating state, e.g. state of life, for an electrical energy storage device includes establishing a plurality of values for an operating parameter, e.g. current, of the electrical energy storage device and, for each respective value, determining a corresponding change in the operating state for the energy storage device based upon the respective value. Preferably, change in the state of life is determined based upon an integration of electrical current, a depth of discharge of the energy storage device, and an operating temperature factor of the electrical energy storage device.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
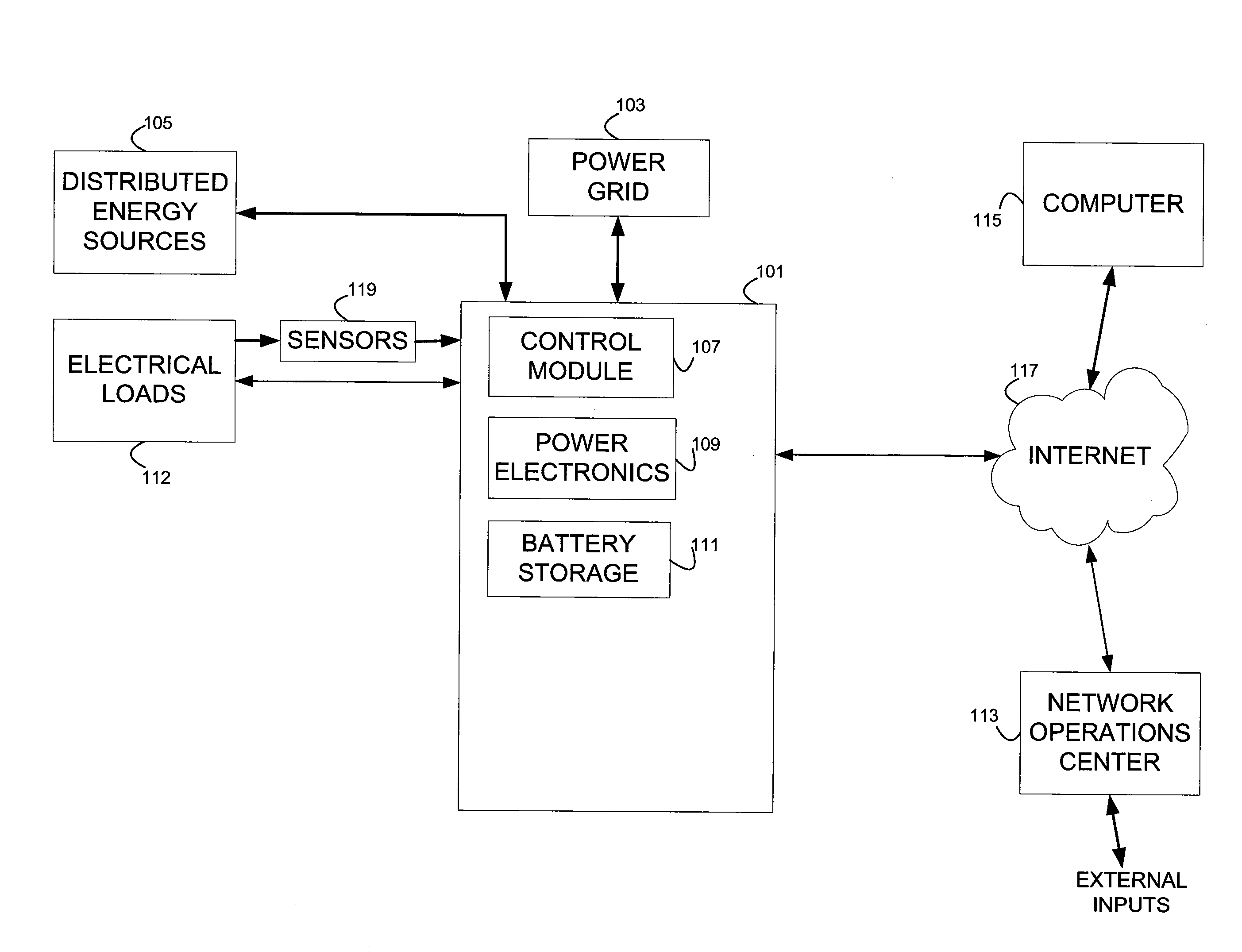
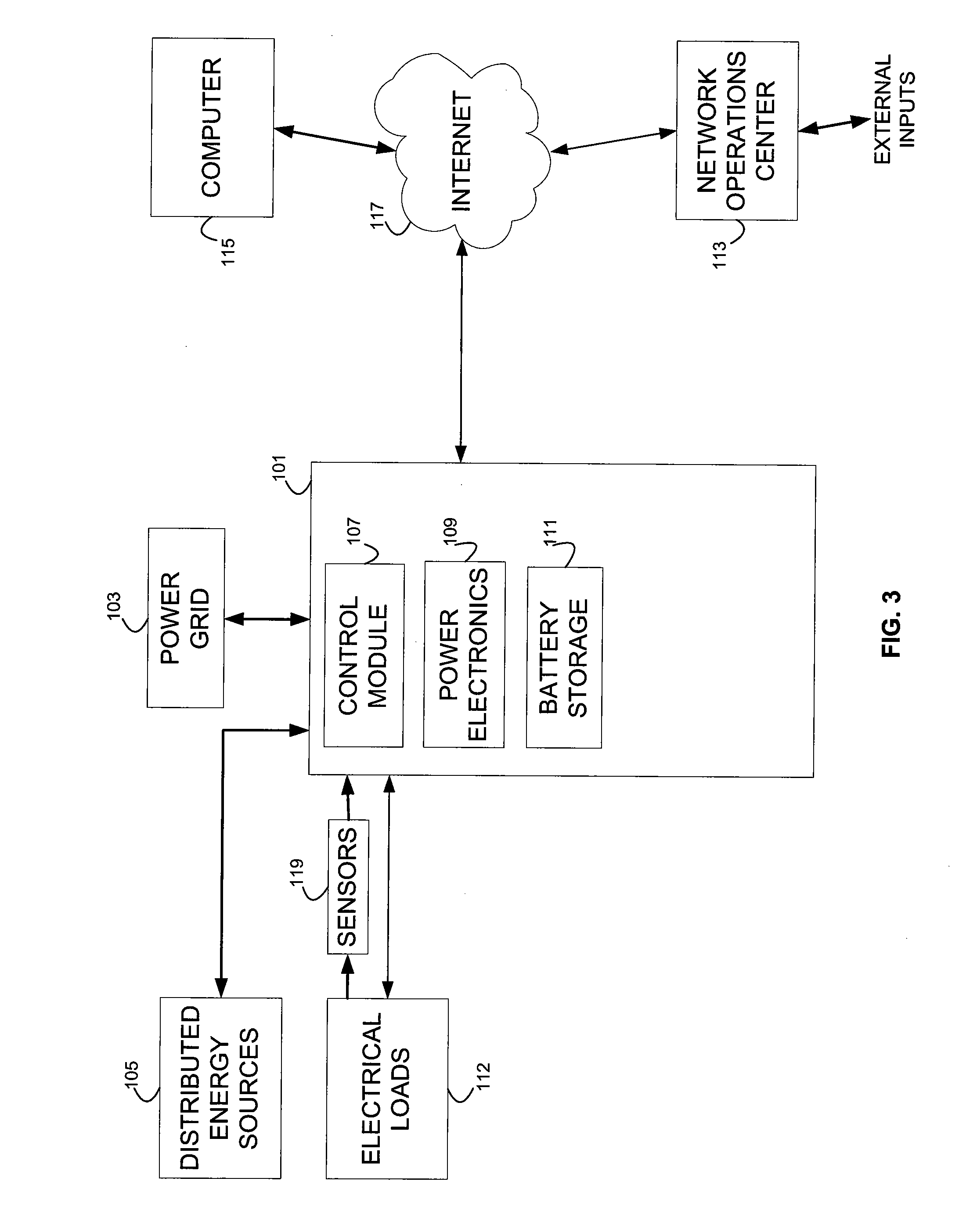
Energy arbitrage by load shifting
Methods and systems are provided for realizing energy cost savings through load shifting utilizing a battery bank that may serve as a battery back-up on a premises for providing power in the event of a grid power outage or curtailment. A budget of unreserved cycles of battery charging and discharging is determined, taking into account the rated battery life in terms of both time (e.g., years) and number of cycles. That cycle budget is allocated to days of the year identified as days on which the greatest savings can be realized through load shifting. These days are identified by taking into account the peak and off-peak usage rates applicable on those days, any rate tiers that may be entered as a result of the additional energy expended to load shift, and the round trip efficiency of the charge / discharge cycles. Load shifting is executed in accordance with an established schedule of the identified days, by discharging the batteries during peak usage hours and charging the batteries during off-peak periods. In the event the budget of unreserved cycles exceeds the number of profitable days for load shifting, the depth of discharge on each cycle may be increased to realize greater savings on the scheduled days, at the tolerable cost of losing cycles not expected to be used in any event.
Owner:GRIDPOINT
Battery designs with high capacity anode materials and cathode materials
ActiveUS20140065464A1Primary cell to battery groupingMaterial nanotechnologyHigh energyDischarge rate
Improved high energy capacity designs for lithium ion batteries are described that take advantage of the properties of high specific capacity anode active compositions and high specific capacity cathode active compositions. In particular, specific electrode designs provide for achieving very high energy densities. Furthermore, the complex behavior of the active materials is used advantageously in a radical electrode balancing design that significantly reduced wasted electrode capacity in either electrode when cycling under realistic conditions of moderate to high discharge rates and / or over a reduced depth of discharge.
Owner:IONBLOX INC
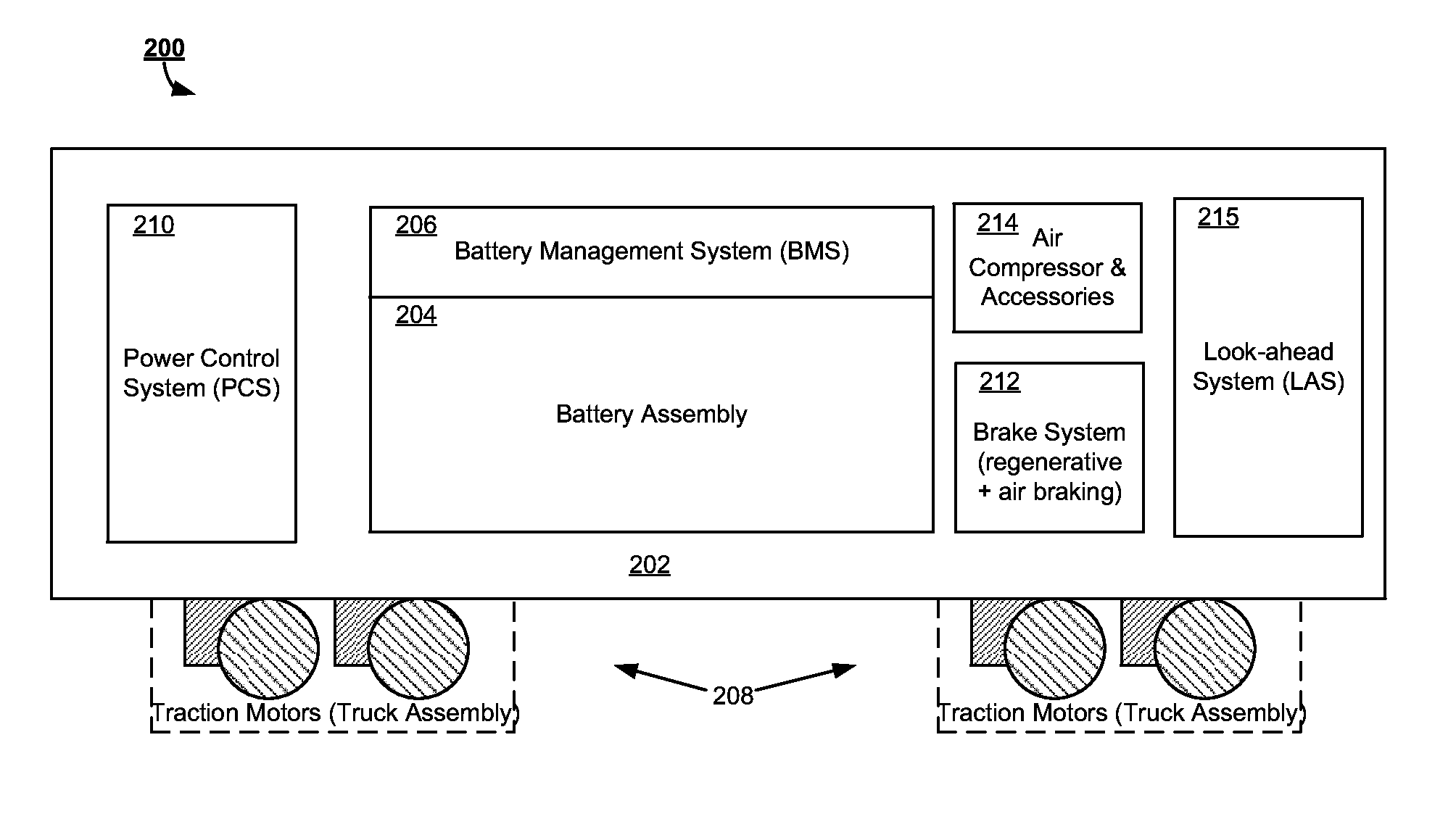
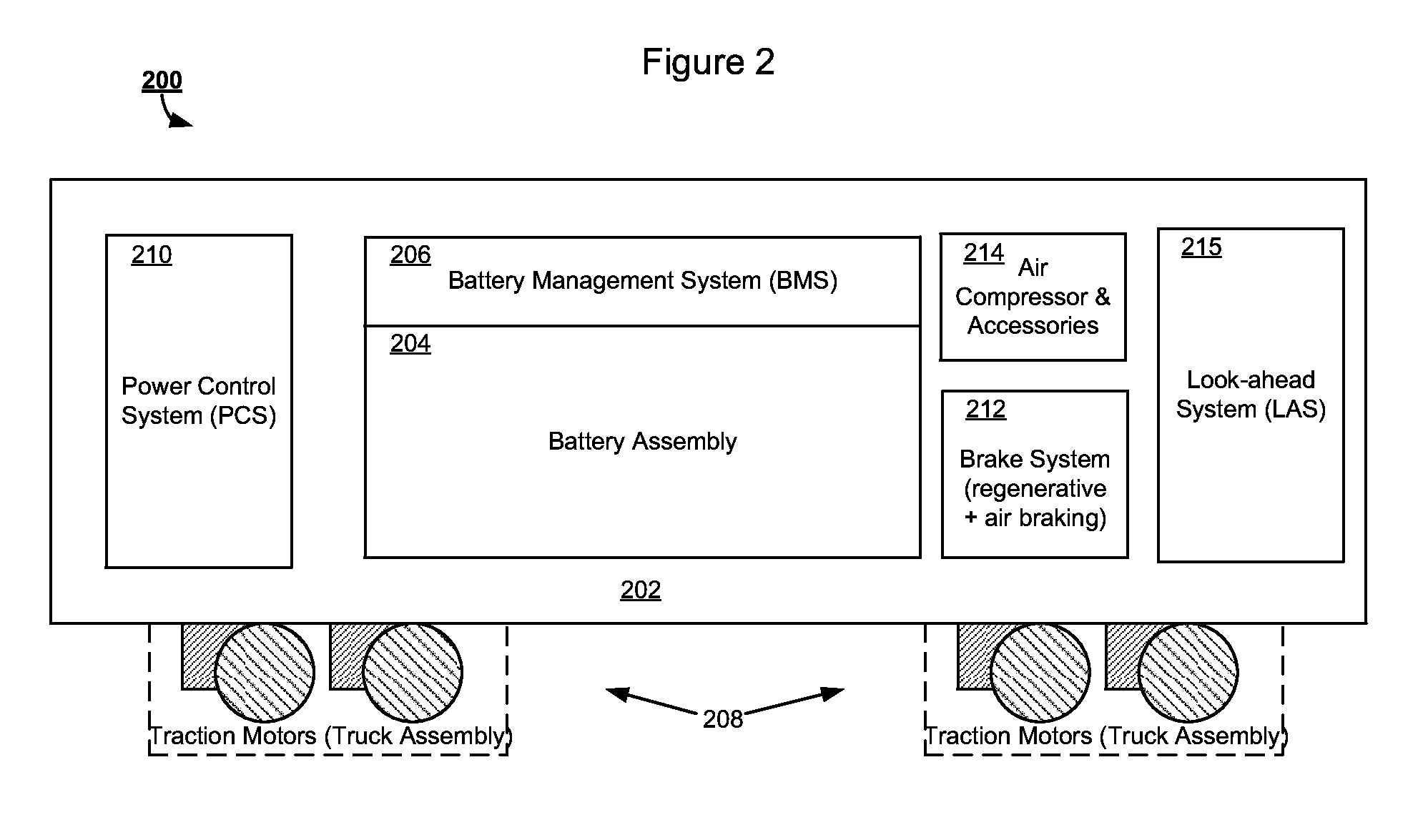
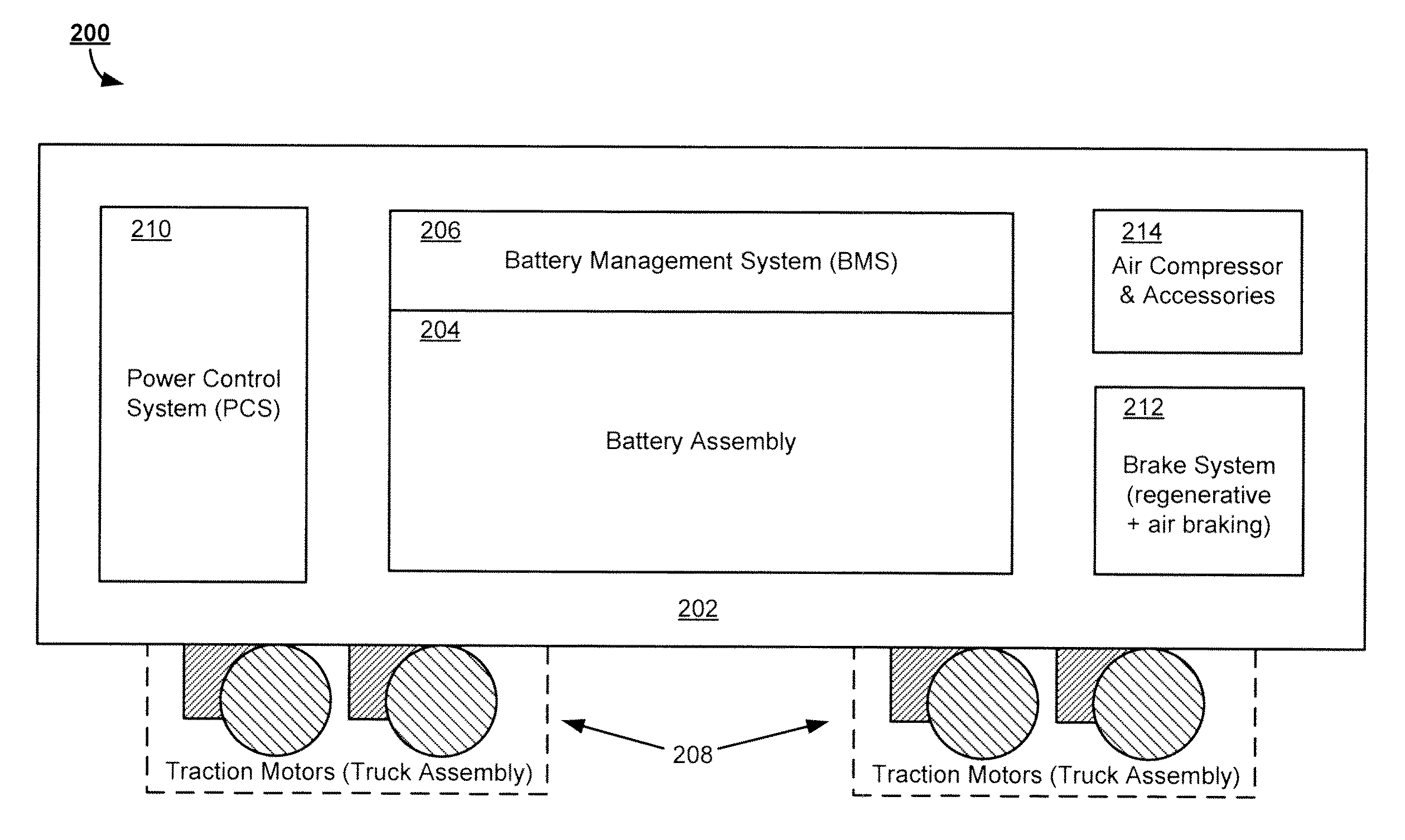
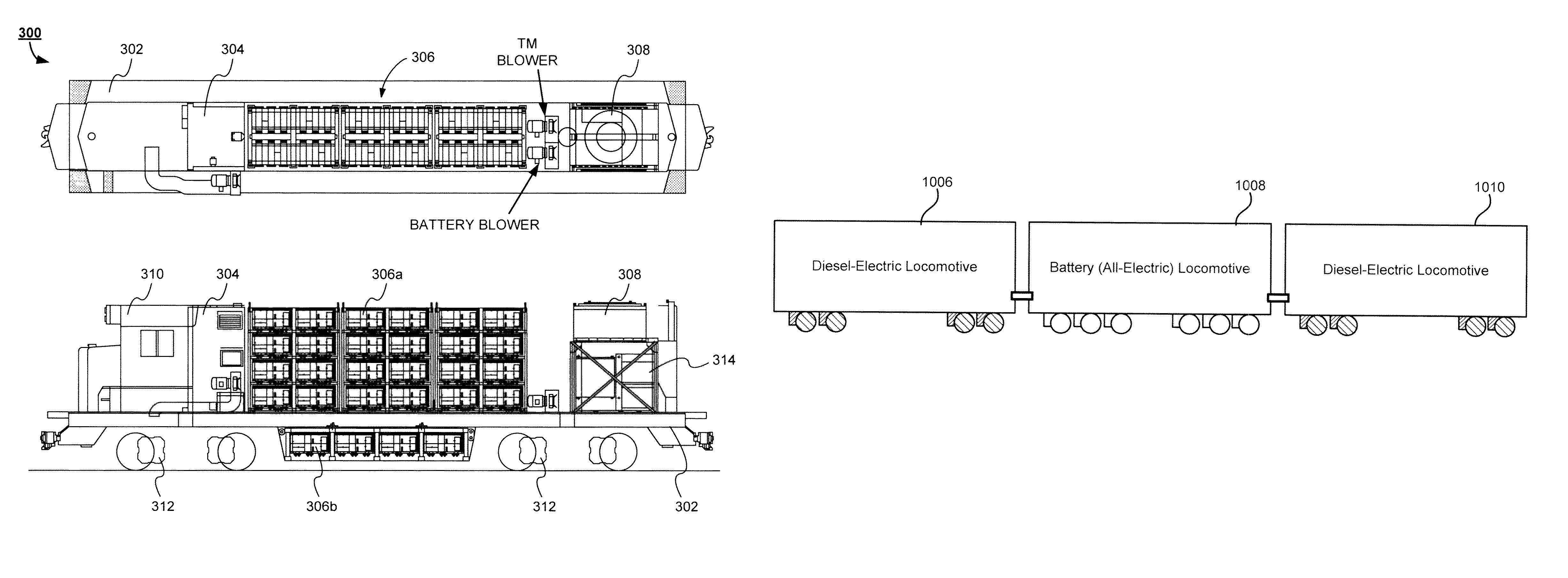
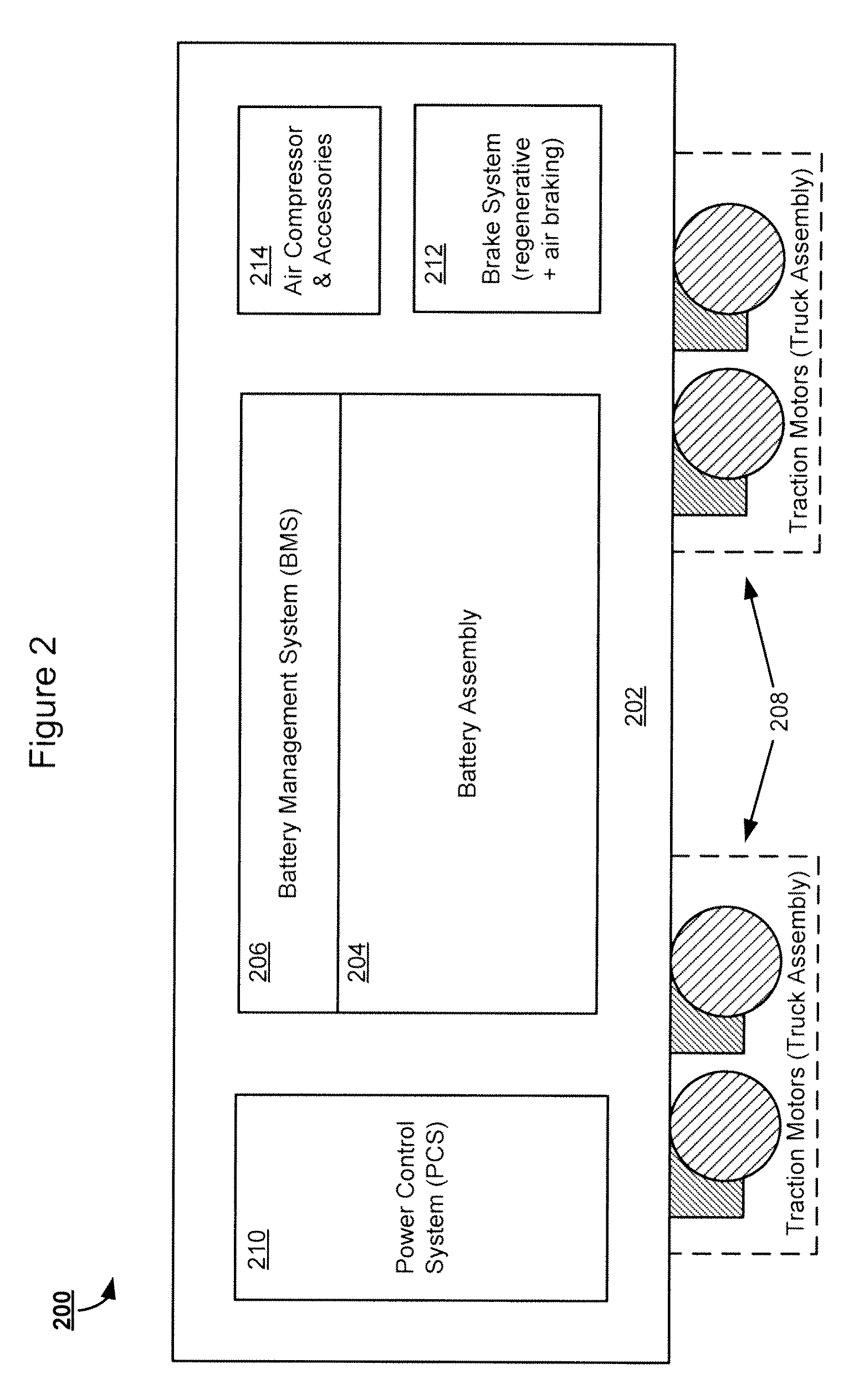
Battery-Powered All-Electric and/or Hybrid Locomotive and Related Locomotive and Train Configurations
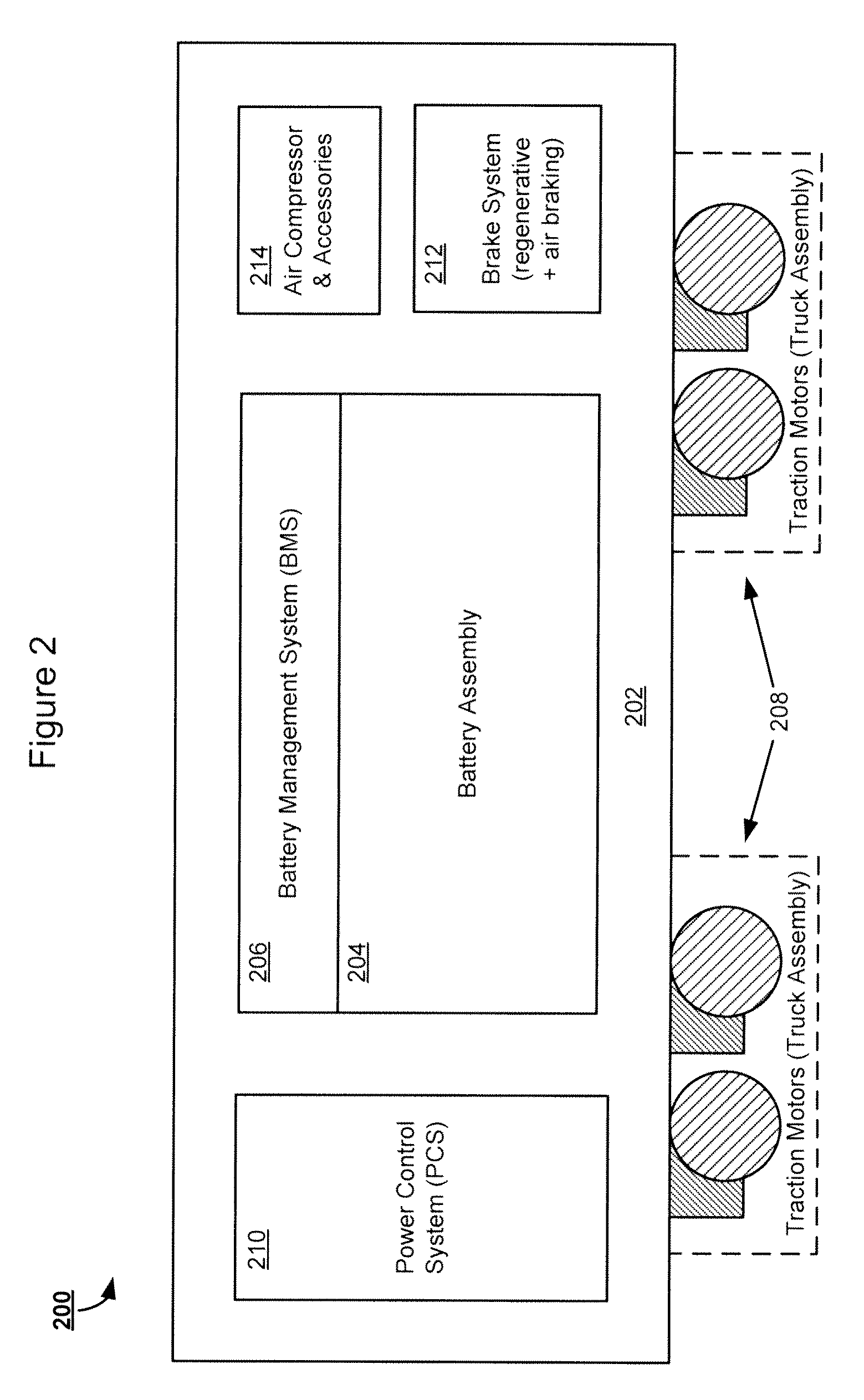
InactiveUS20130167752A1Guaranteed maximum utilizationAxle-box lubricationVehicular energy storageConfiguration designElectrical battery
Designs for a battery-powered, all-electric locomotive and related locomotive and train configurations are disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, a locomotive may be driven by a plurality of traction motors powered exclusively by a battery assembly which preferably comprises rechargeable batteries or other energy storage means. The locomotive carries no internal combustion engine on board and receives no power during operation from any power source external to the locomotive. A battery management system monitors and equalizes the batteries to maintain a desired state of charge (SOC) and depth of discharge (DOD) for each battery. A brake system may be configured to prioritize a regenerative braking mechanism over an air braking mechanism so that substantial brake energy can be recovered to recharge the battery assembly. Many locomotive or train configurations involving battery-powered or battery-toting locomotive(s) may be implemented. In one embodiment, a battery-toting locomotive is directly coupled with and positioned between two diesel-electric locomotives, wherein the batteries recover energy from regenerative braking and / or supply power to drive traction motors.
Owner:NORFOLK SOUTHERN
Battery cell engineering and design to reach high energy
Improved high energy capacity designs for lithium ion batteries are described that take advantage of the properties of high specific capacity anode active compositions and high specific capacity cathode active compositions. In particular, specific electrode designs provide for achieving very high energy densities. Furthermore, the complex behavior of the active materials is used advantageously in a radical electrode balancing design that significantly reduced wasted electrode capacity in either electrode when cycling under realistic conditions of moderate to high discharge rates and / or over a reduced depth of discharge.
Owner:IONBLOX INC
Energy arbitrage by load shifting
Methods and systems are provided for realizing energy cost savings through load shifting utilizing a battery bank that may serve as a battery back-up on a premises for providing power in the event of a grid power outage or curtailment. A budget of unreserved cycles of battery charging and discharging is determined, taking into account the rated battery life in terms of both time (e.g., years) and number of cycles. That cycle budget is allocated to days of the year identified as days on which the greatest savings can be realized through load shifting. These days are identified by taking into account the peak and off-peak usage rates applicable on those days, any rate tiers that may be entered as a result of the additional energy expended to load shift, and the round trip efficiency of the charge / discharge cycles. Load shifting is executed in accordance with an established schedule of the identified days, by discharging the batteries during peak usage hours and charging the batteries during off-peak periods. In the event the budget of unreserved cycles exceeds the number of profitable days for load shifting, the depth of discharge on each cycle may be increased to realize greater savings on the scheduled days, at the tolerable cost of losing cycles not expected to be used in any event.
Owner:GRIDPOINT
Battery-powered all-electric locomotive and related locomotive and train configurations
InactiveUS20100275810A1Guaranteed maximum utilizationAC motor controlDc motor stoppersConfiguration designOn board
Designs for a battery-powered, all-electric locomotive and related locomotive and train configurations are disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, a locomotive may be driven by a plurality of traction motors powered exclusively by a battery assembly which preferably comprises rechargeable batteries or other energy storage means. The locomotive carries no internal combustion engine on board and receives no power during operation from any power source external to the locomotive. A battery management system monitors and equalizes the batteries to maintain a desired state of charge (SOC) and depth of discharge (DOD) for each battery. A brake system may be configured to prioritize a regenerative braking mechanism over an air braking mechanism so that substantial brake energy can be recovered to recharge the battery assembly. Many locomotive or train configurations involving battery-powered or battery-toting locomotive(s) may be implemented. In one embodiment, a battery-toting locomotive is directly coupled with and positioned between two diesel-electric locomotives, wherein the batteries recover energy from regenerative braking and / or supply power to drive traction motors.
Owner:NORFOLK SOUTHERN
Energy arbitrage by load shifting
Methods and systems are provided for realizing energy cost savings through load shifting utilizing a battery bank that may serve as a battery back-up on a premises for providing power in the event of a grid power outage or curtailment. A budget of unreserved cycles of battery charging and discharging is determined, taking into account the rated battery life in terms of both time (e.g., years) and number of cycles. That cycle budget is allocated to days of the year identified as days on which the greatest savings can be realized through load shifting. These days are identified by taking into account the peak and off-peak usage rates applicable on those days, any rate tiers that may be entered as a result of the additional energy expended to load shift, and the round trip efficiency of the charge / discharge cycles. Load shifting is executed in accordance with an established schedule of the identified days, by discharging the batteries during peak usage hours and charging the batteries during off-peak periods. In the event the budget of unreserved cycles exceeds the number of profitable days for load shifting, the depth of discharge on each cycle may be increased to realize greater savings on the scheduled days, at the tolerable cost of losing cycles not expected to be used in any event.
Owner:GRIDPOINT
Method for estimating aging rate and testing fault of battery and apparatus for managing and monitoring battery
InactiveCN1862279ANo error accumulationImprove accuracyElectrical testingFloating chargeEstimation methods
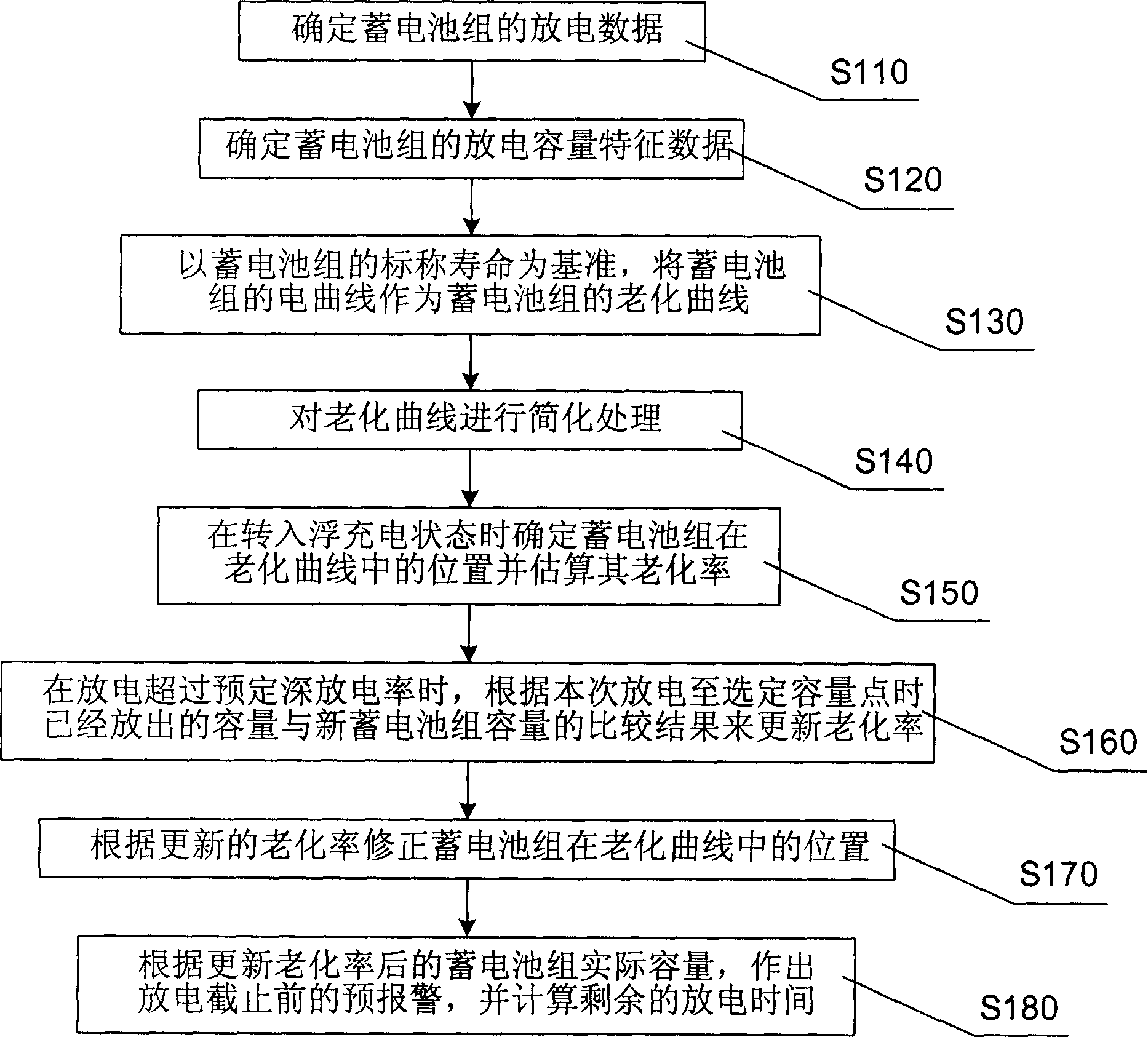
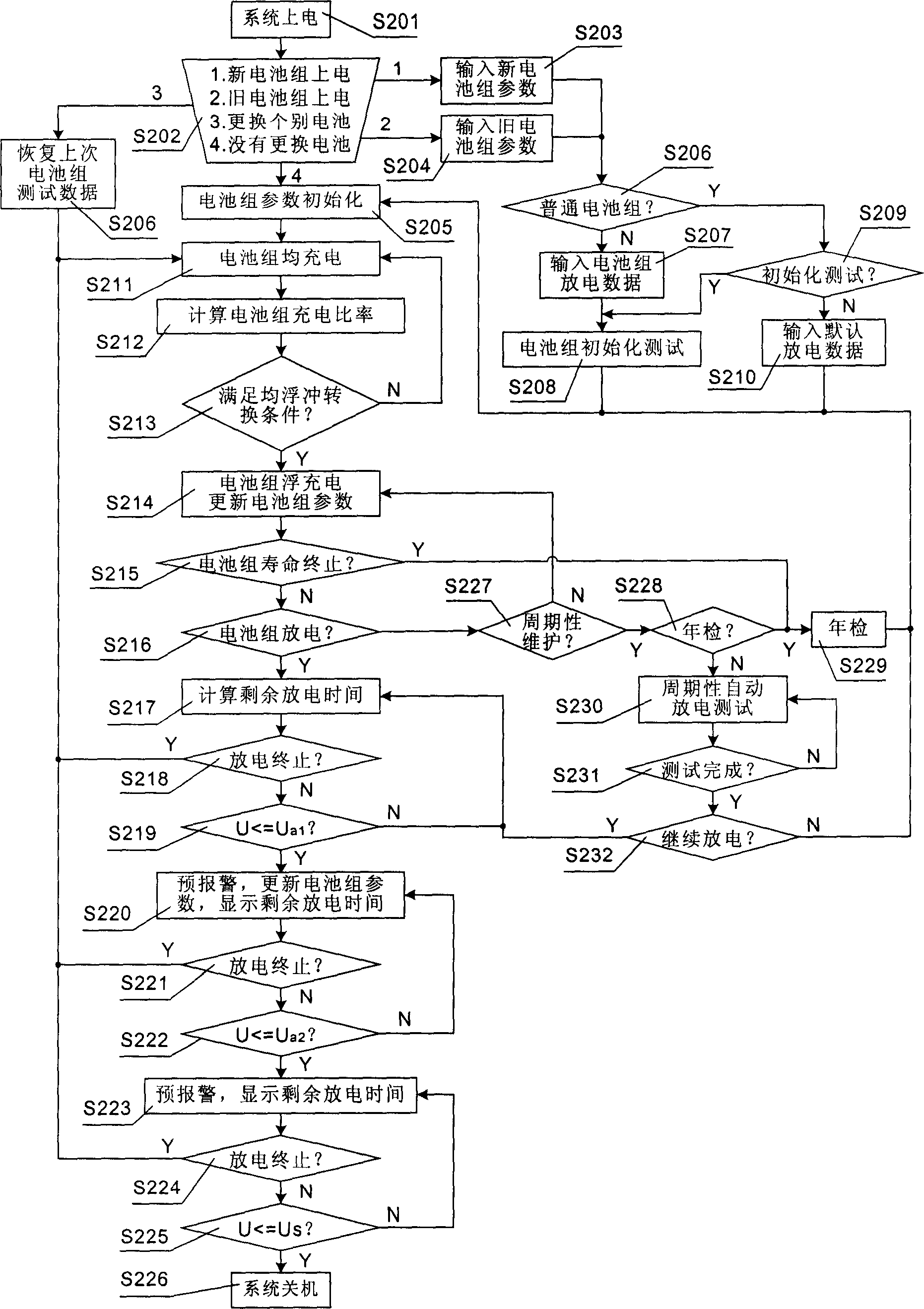
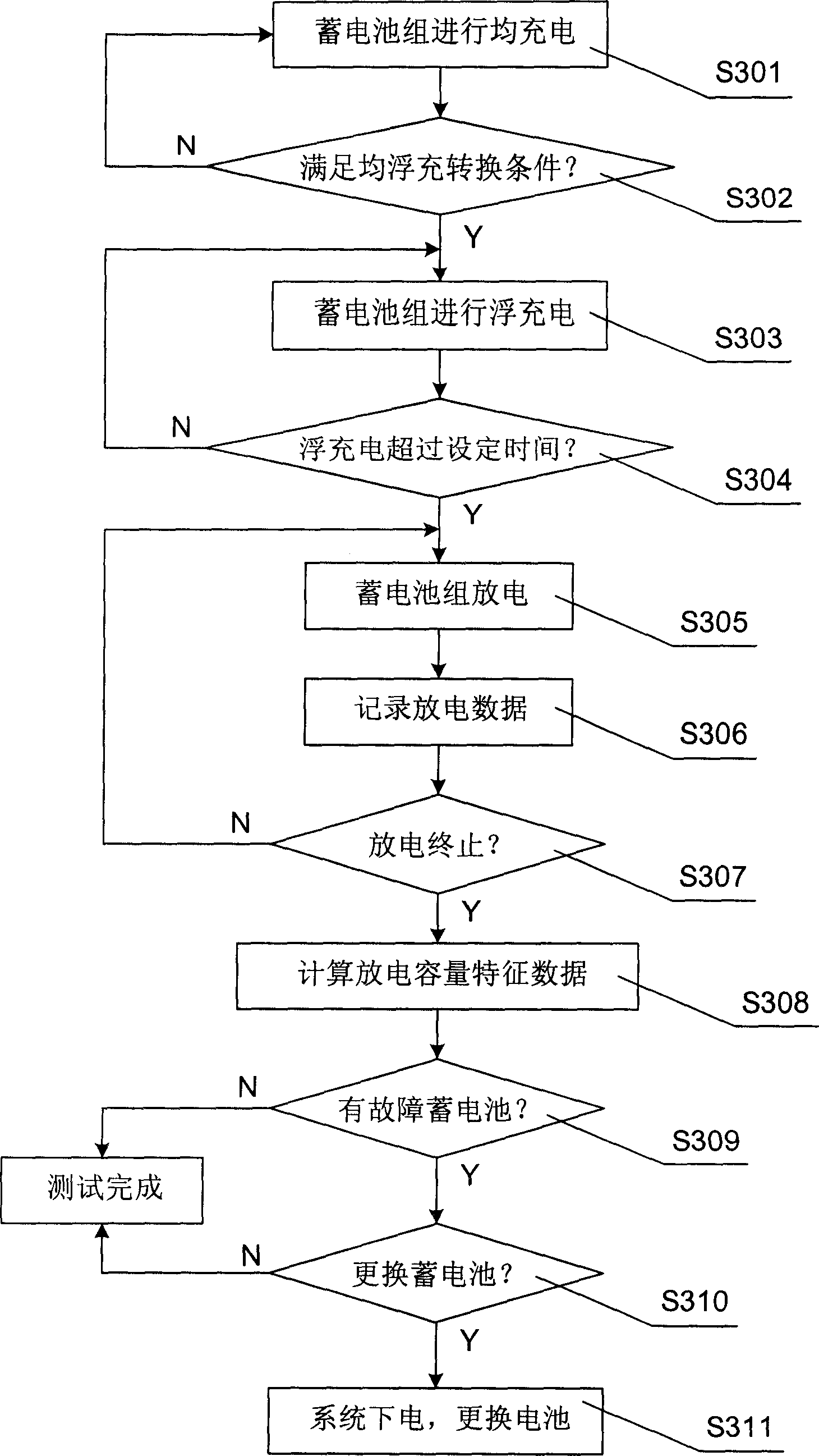
The present invention discloses an ageing rate estimation method of storage battery. Said method includes the following steps: defining discharge data and discharge capacity characteristic data of storage battery; using nominal life of storage battery as reference, using its discharge curve as ageing curve; when the storage battery is come into floating charge state from equalizing charge state, defining its position in ageing curve and estimating its ageing rate; when the discharge exceeds predefined discharge depth, according to the comparison result of capacity discharged from the present discharge to described selected capacitor point and new storage battery capacity renewing ageing rate; then utilizing said renewed ageing rate to correct the position of storage battery in ageing curve. Said invention also discloses a fault detection method of storage battery and a storage battery management monitoring device.
Owner:西安金泽电气技术有限公司
Lithium iron phosphate battery modeling and SOC estimating method in account of capacity loss
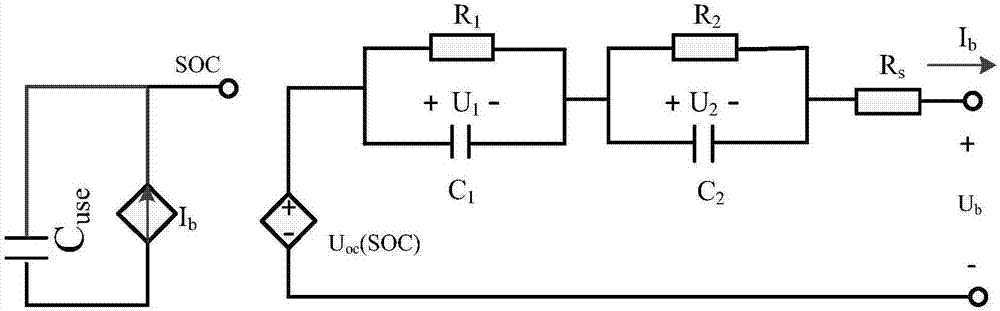
ActiveCN106909716AImprove output accuracyHigh applicable valueElectrical testingDesign optimisation/simulationCapacitanceMathematical model
The invention provides a lithium iron phosphate battery modeling and SOC estimating method in account of capacity loss. The method is provided based on the facts that the working state of the existing lithium iron phosphate battery is influenced by many factors of temperature, current, cycle times, depth of discharge and the like, and thus the modeling process is very complicated. According to the method, based on the Thevenin equivalent circuit, the modeling work is conducted on the lithium iron phosphate battery; the model open-circuit voltage, resistance and capacitance value identification method are given; and the capacity loss of the lithium iron phosphate battery in the life cycle is taken into account; a capacity estimation mathematical model is established; the output precision of a lithium iron phosphate battery model is improved; and the lithium iron phosphate battery SOC estimating problem brought by uncertainty noise is solved with extended Kalman filtering (EKF) algorithm. The method has the advantages of being simple, scientific and reasonable, high in application value, good in effect and the like.
Owner:NORTHEAST DIANLI UNIVERSITY +1
Method and system for testing consistency of performances of batteries
ActiveCN103513190AAccurate and convenient assessmentComprehensive test dataElectrical testingConsistency testBattery charge
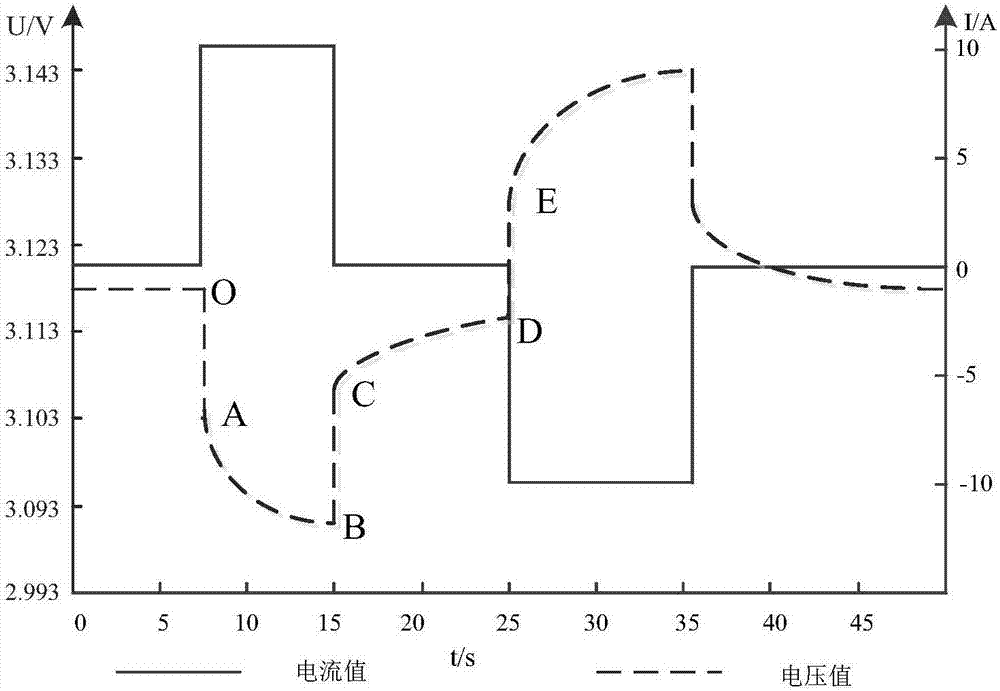
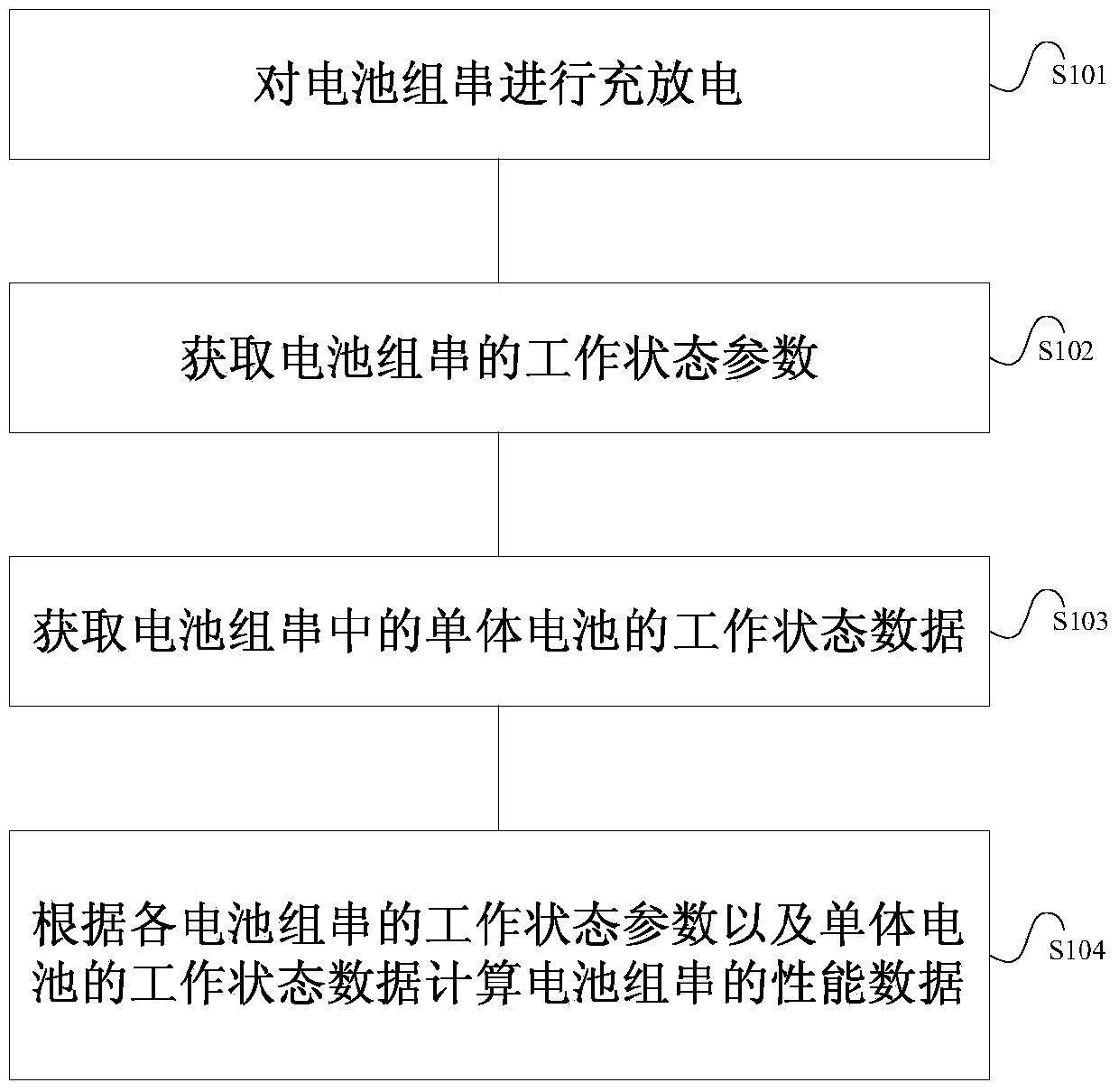
The invention discloses a method and system for testing consistency of performances of batteries. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out charging and discharging on battery pack strings; acquiring working state parameters of the battery pack strings; acquiring working state data of single batteries in the battery pack strings; according to the working state parameters of each battery pack string and the working state data of the single batteries, generating a battery performance consistency testing result. By the method and system for testing consistency of the performances of the batteries, which is disclosed by the invention, performance testing of the energy storage battery pack strings on various aspects, such as battery dynamic voltage consistency testing, battery voltage curve consistency testing, battery dynamic temperature consistency testing, and battery charge-discharge depth consistency testing, is implemented; testing data is rich; acquisition accuracy is high; the method and the system are flexible and convenient to implement; a user can accurately, conveniently and rapidly evaluate the performances of the energy storage batteries.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
Assembled battery, power-supply system and production method of assembled battery
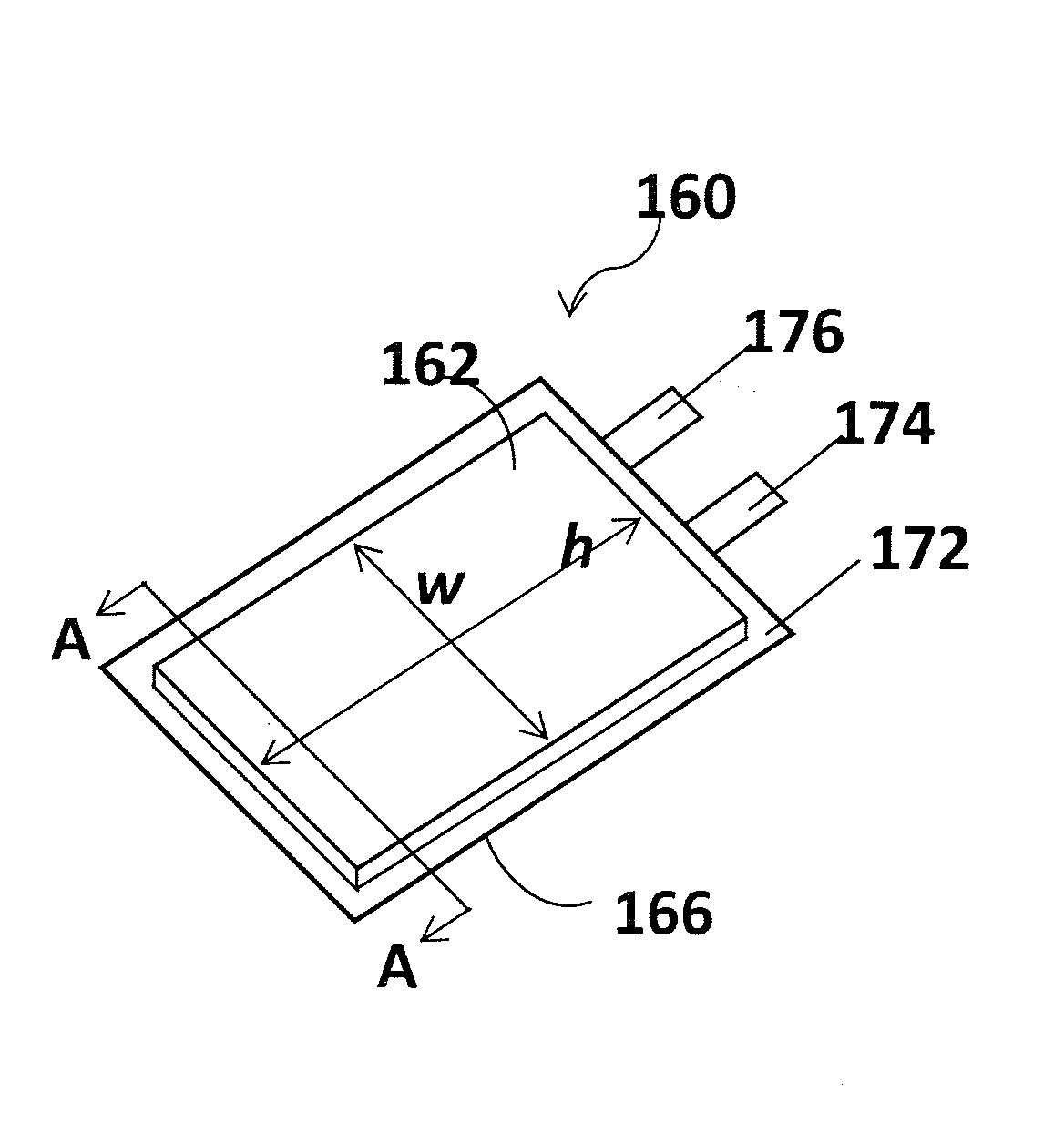
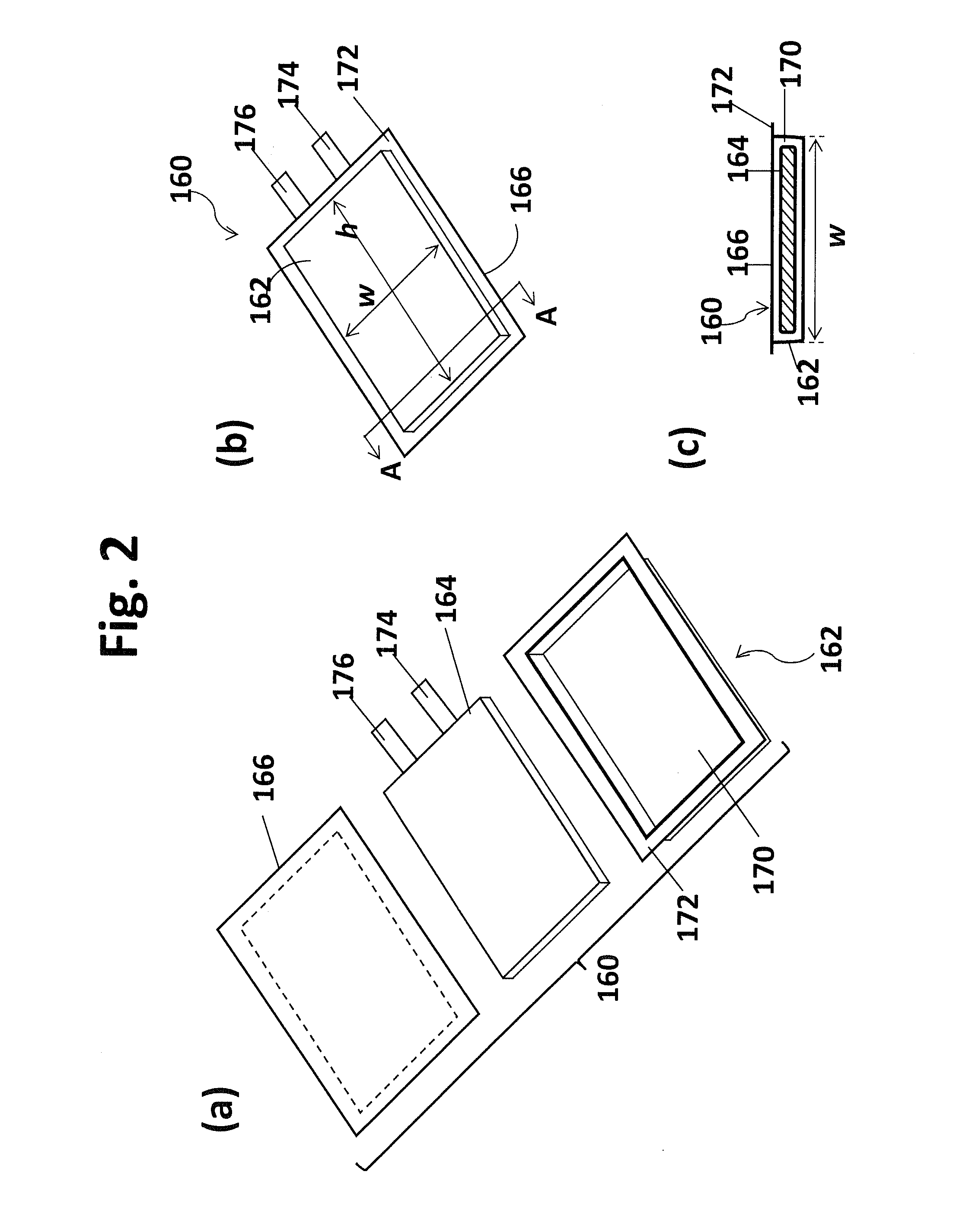
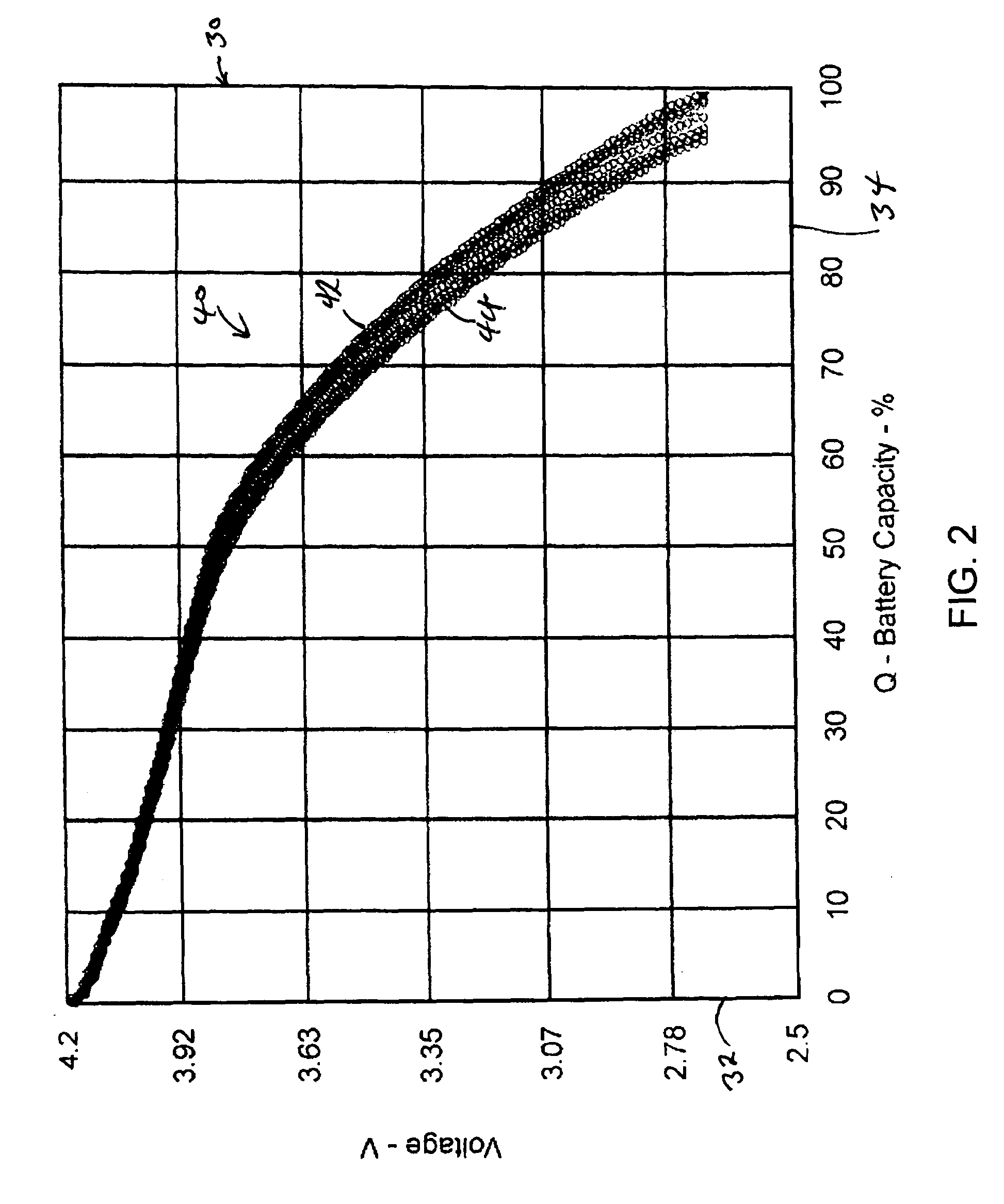
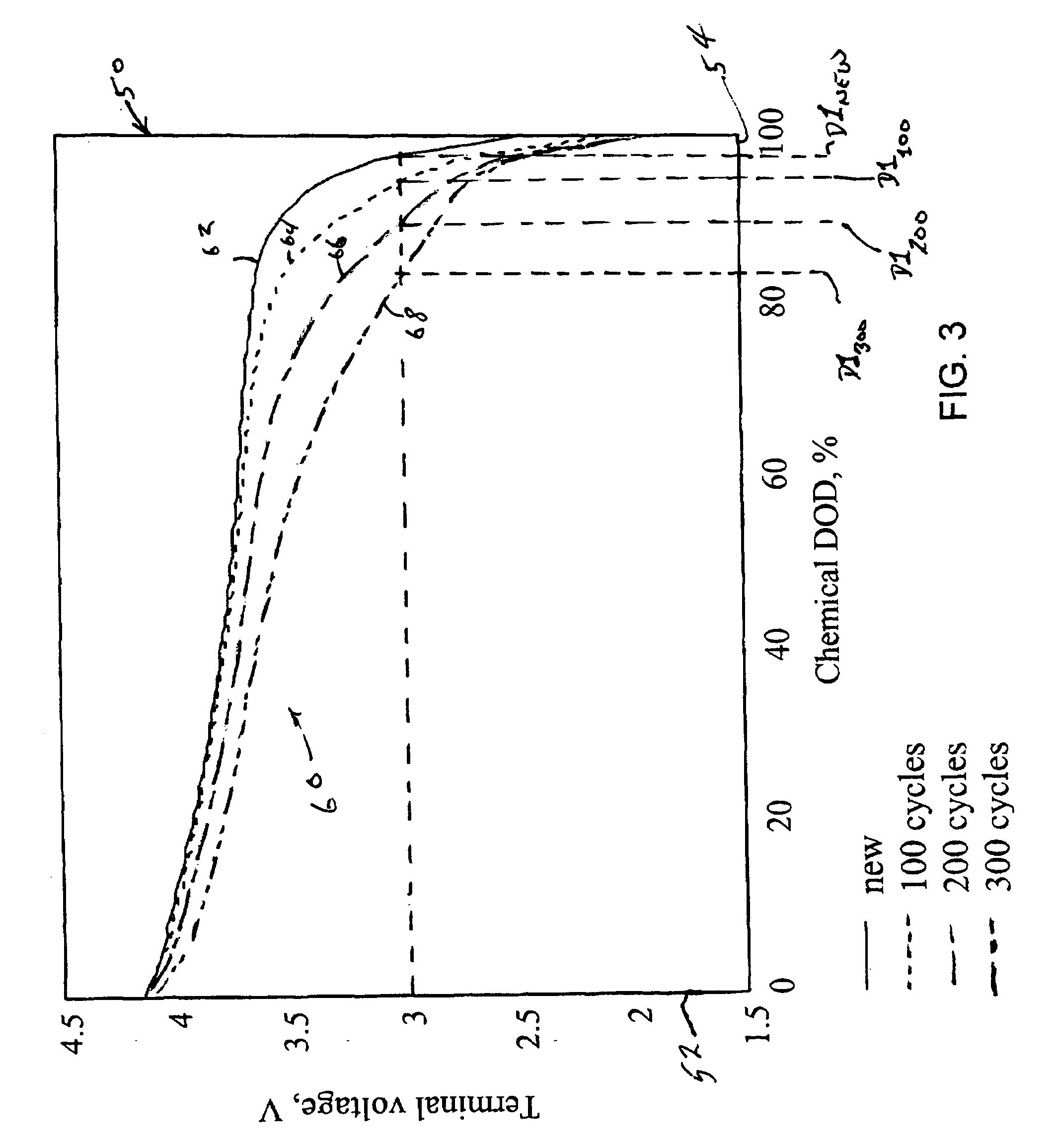
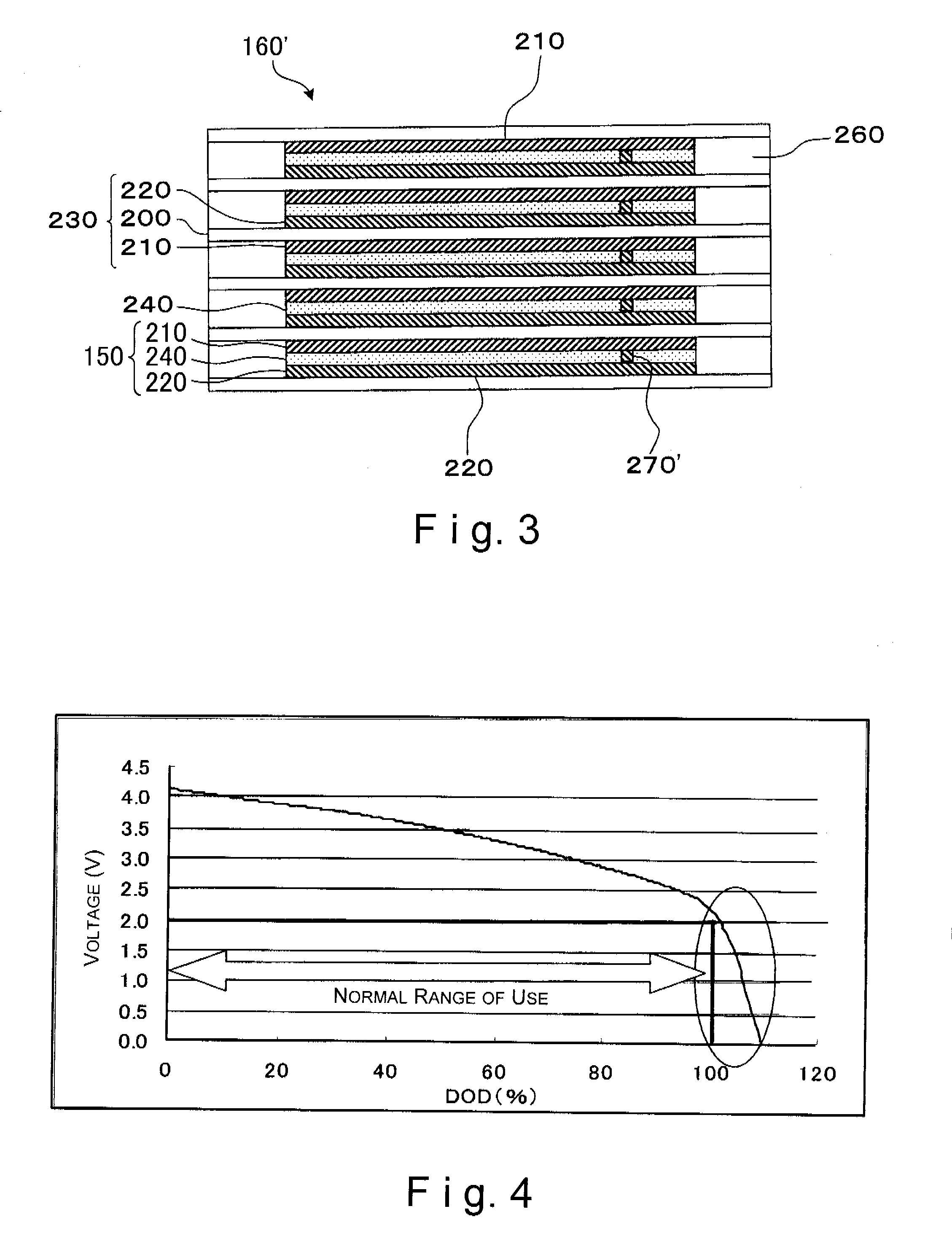
InactiveUS20070166607A1Increase powerPrevent overcharge and overdischarge effectivelyPrimary cell to battery groupingElectrode carriers/collectorsEngineeringDepth of discharge
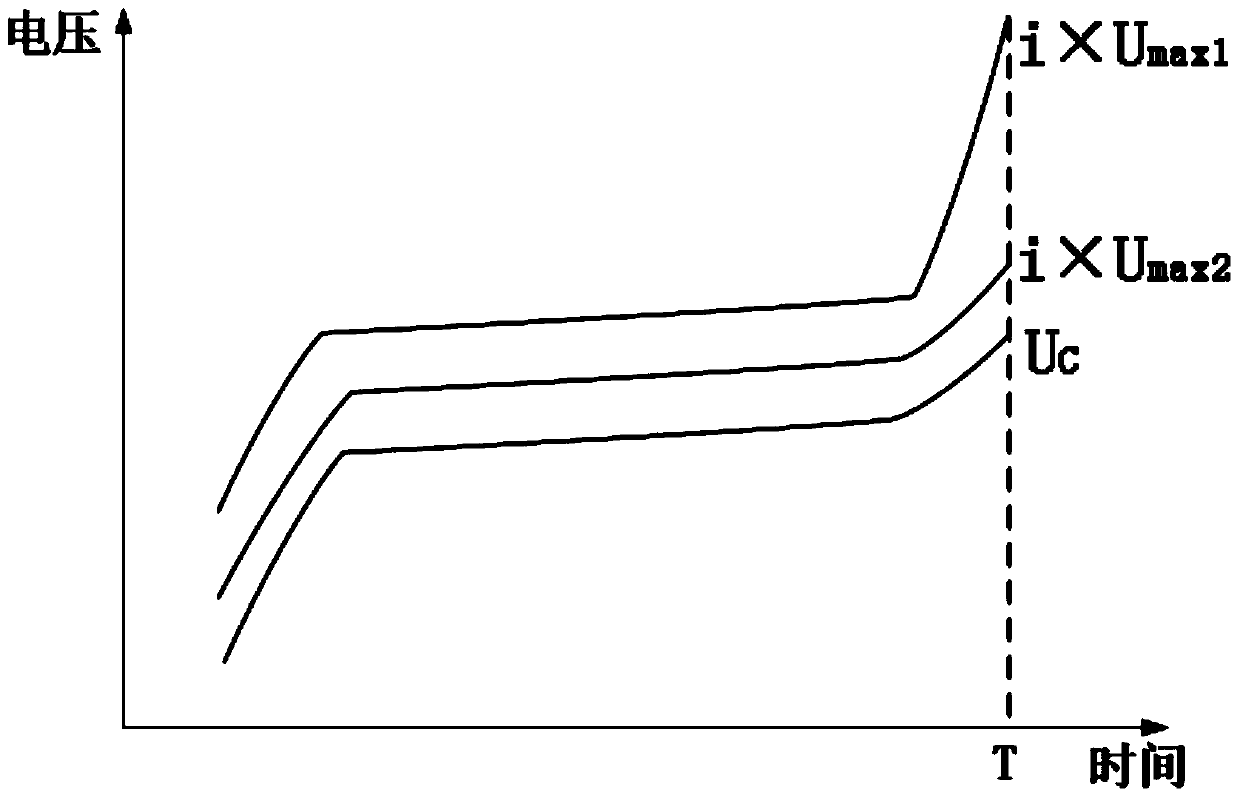
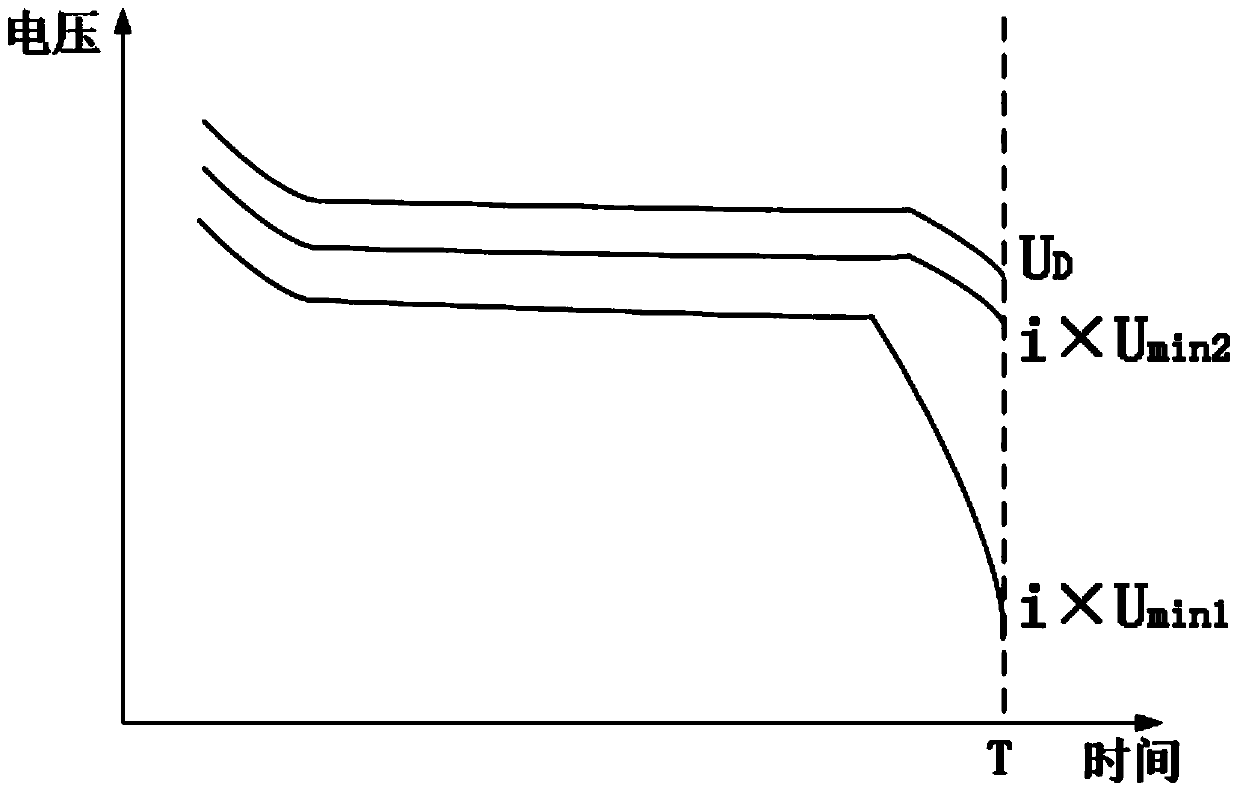
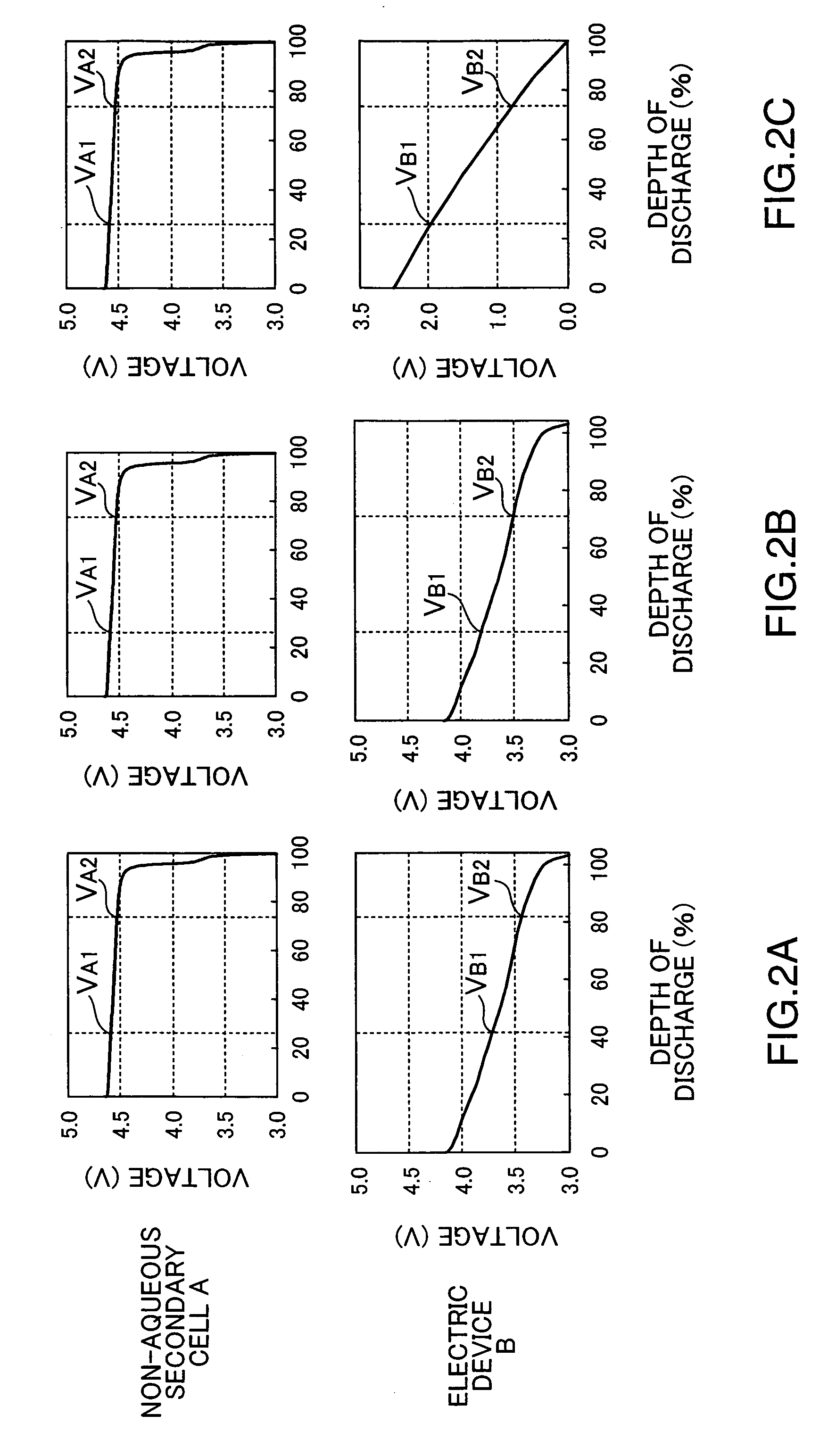
An assembled battery comprises mainly multiple non-aqueous secondary cells A and at least one electric device B for voltage detection containing a non-aqueous electrolyte connected to the multiple non-aqueous secondary cells A in series. When a difference in the non-aqueous secondary cell A between a voltage per cell (VA1) at a depth of discharge of 25% and a voltage per cell (VA2) at a depth of discharge of 75% is designated as ΔVA, and a difference in the electric device B between a voltage per cell (VB1) at a depth of discharge equivalent to the depth of discharge of 25% of the non-aqueous secondary cell A and a voltage per cell (VB2) at a depth of discharge equivalent to the depth of discharge of 75% of the non-aqueous secondary cell A is designated as ΔVB, the ΔVB of electric device B is greater than the ΔVA of non-aqueous secondary cell A.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for evaluating life of space hydrogen-nickel storage batteries
InactiveCN102520367AConvenient researchImprove developmentElectrical testingMathematical modelProcess engineering
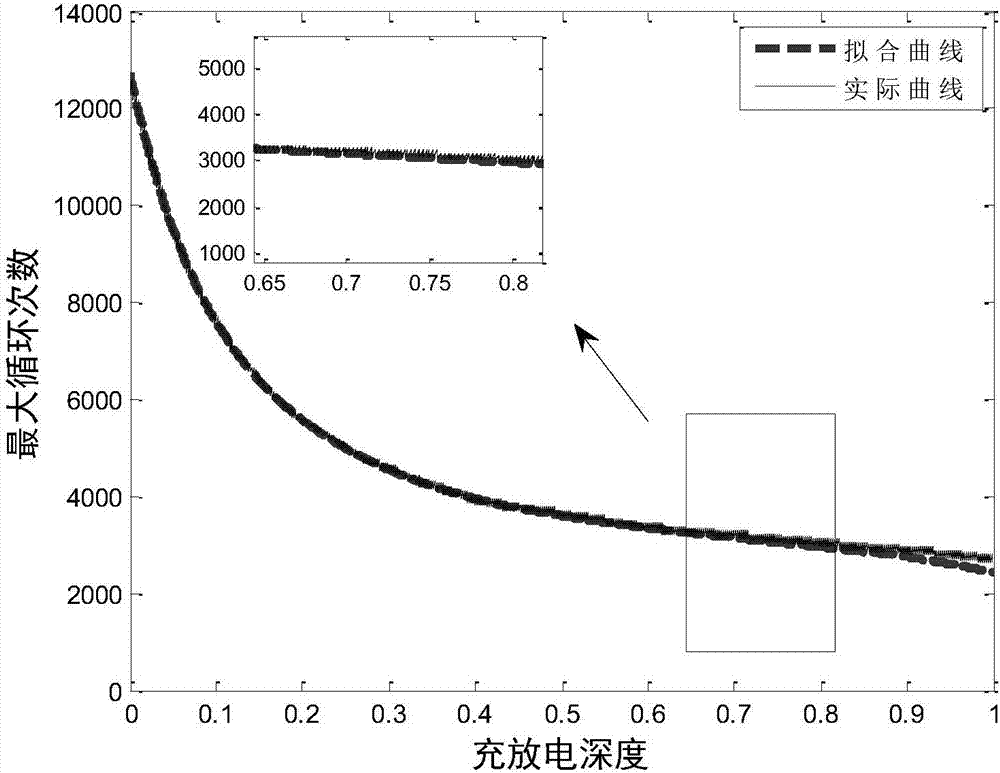
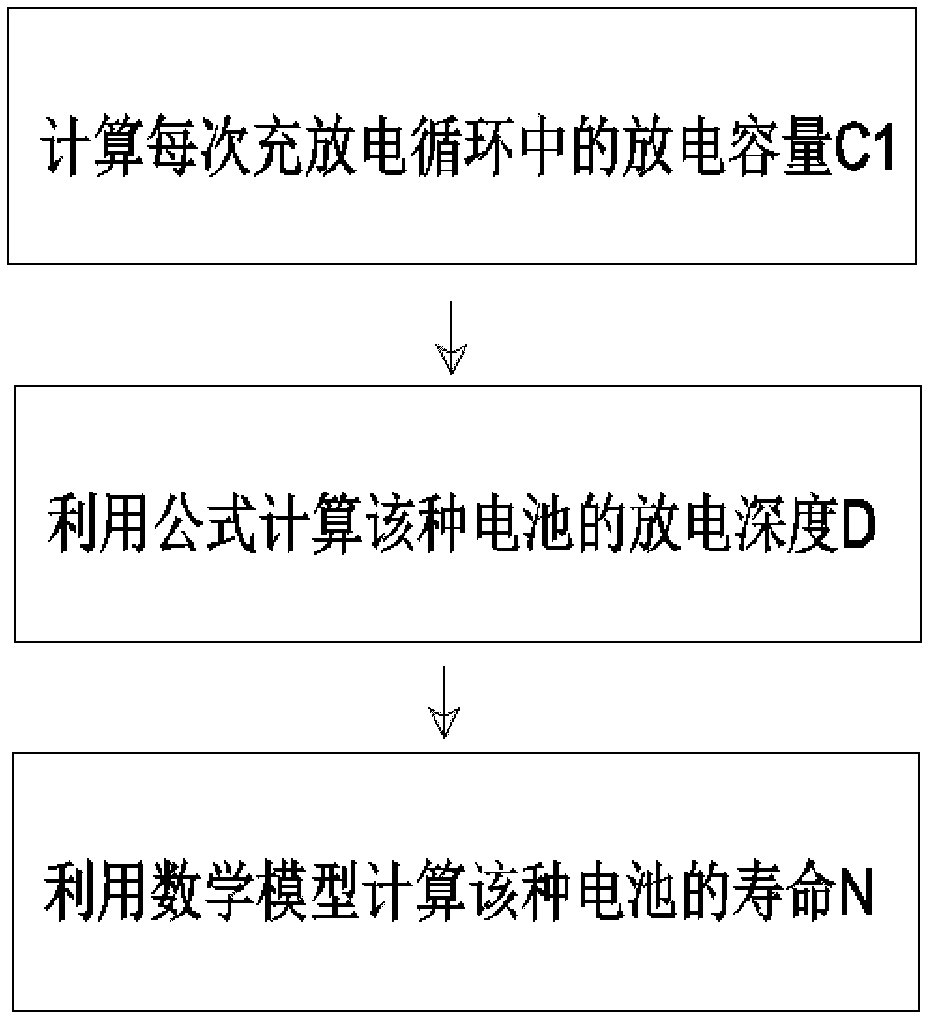
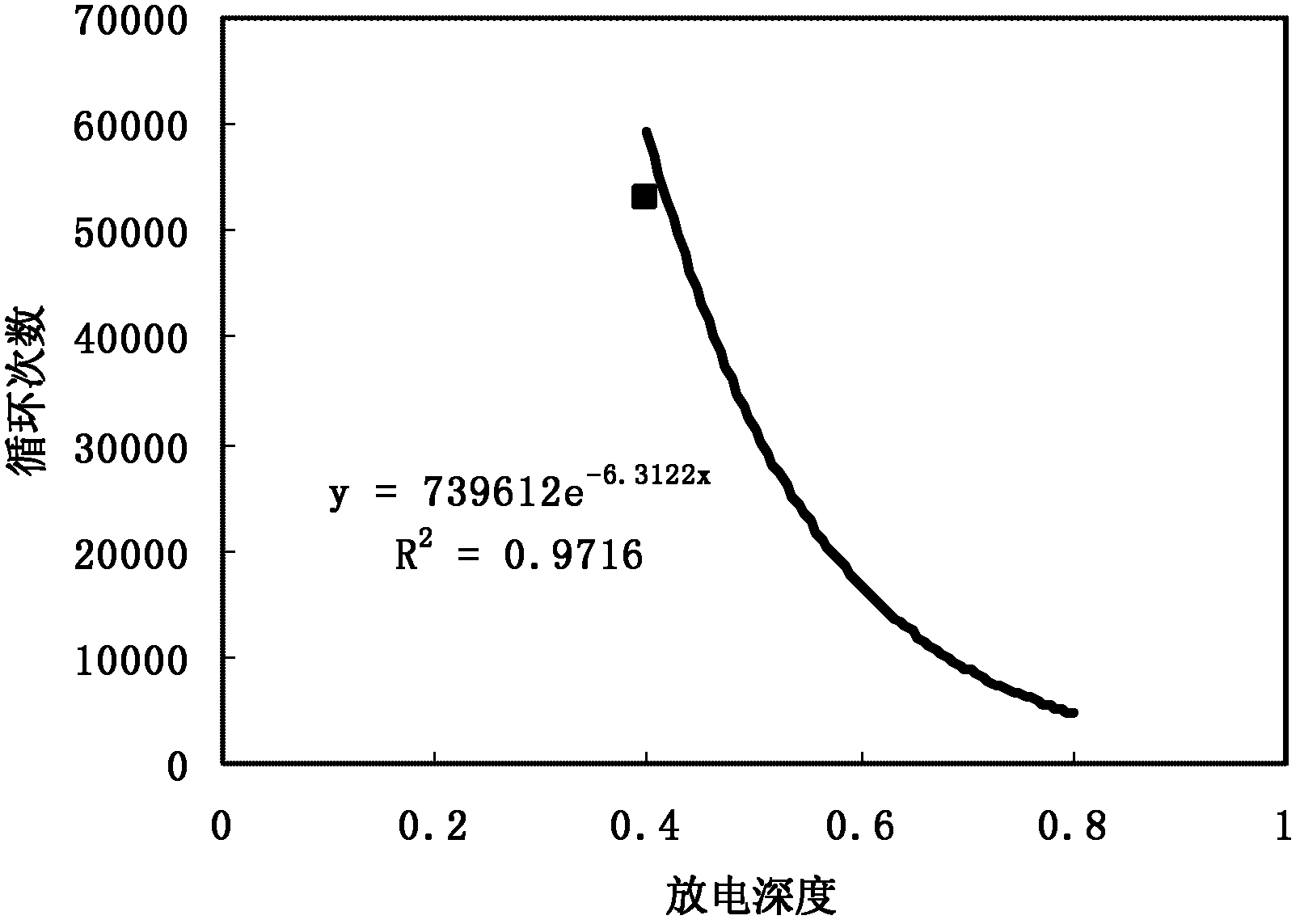
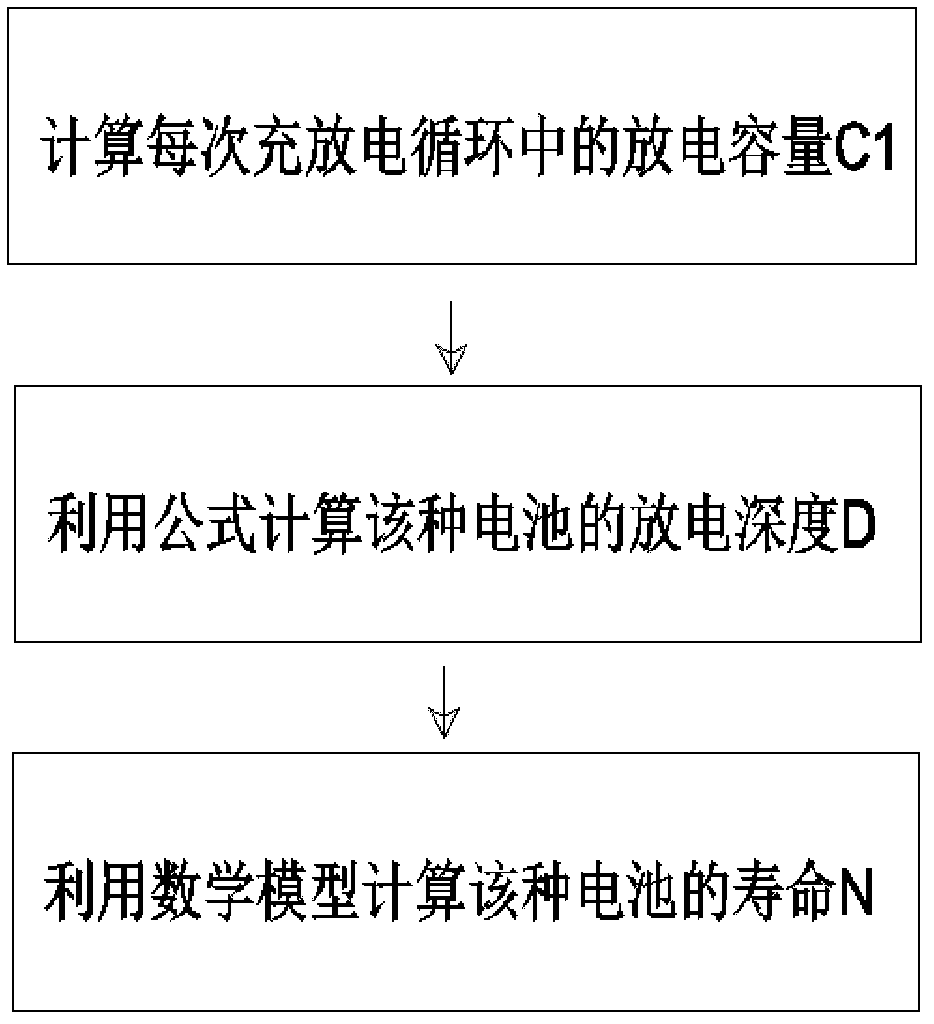
The invention relates to a method for evaluating the life of space hydrogen-nickel storage batteries, and belongs to the technical field of hydrogen-nickel storage batteries. The method for evaluating the life of the space hydrogen-nickel storage batteries is characterized by comprising the following steps of: selecting similar hydrogen-nickel storage batteries, performing a charge-discharge cycle life test at the ambient temperature of between -5 and +5 DEG C, detecting the discharge capacity of the hydrogen-nickel storage batteries in each charge-discharge cycle, calculating the discharge depth of the hydrogen-nickel storage batteries, fitting to obtain a hydrogen-nickel storage battery life prediction mathematical model, and predicting and evaluating the life of the hydrogen-nickel storage batteries by using the mathematical model. The method has the advantages that: the method is simple, is convenient to operate, and is high-efficiency and quick, data is accurate, the life is easy to detect, and the like, the cycle life of the hydrogen-nickel storage batteries under the design discharge depth can be quickly predicted, design efficiency is improved, and the research and development of track hydrogen-nickel storage batteries are facilitated.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 18 RES INST
Cycle life testing method for power battery
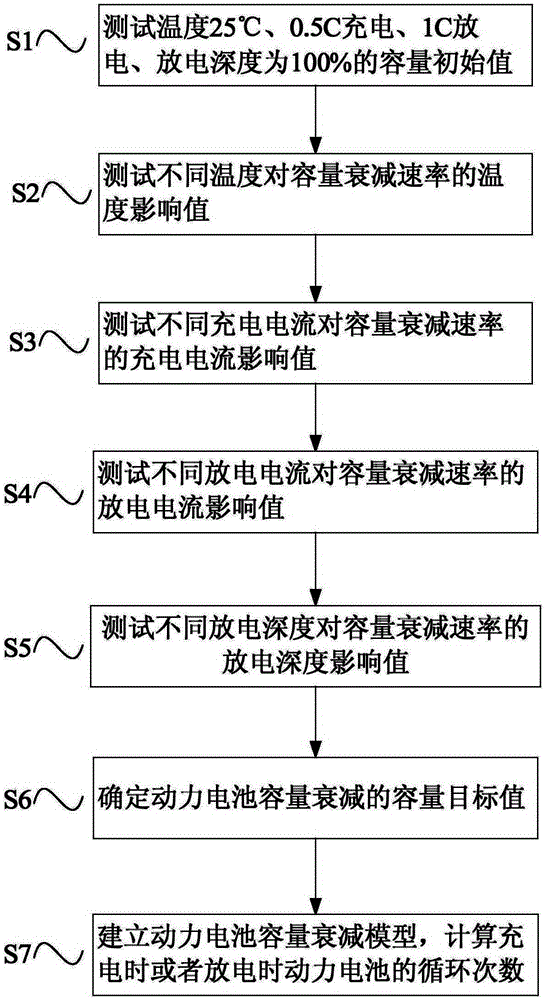
The invention belongs to the technical field of automobile testing, and provides a cycle testing method for a power battery. The method comprises the steps: testing capacity initial values Q0 during the temperature 25 DEG C, 0.5C charging, 1C discharge and the discharge depth of 100%; testing a temperature impact value on a capacity attenuation rate from different temperatures, the charging current impact value on the capacity attenuation rate from different charging currents, the discharge current impact on the capacity attenuation rate from different discharging currents, and the discharge depth impact value on the capacity attenuation rate from different discharge depths; determining the capacity target value of the capacity attenuation of the power battery; building a model of the capacity attenuation of the power battery; and calculating the cycle number of the power battery during charging and the cycle number of the power battery during discharging. The method can accurately calculate the cycle life of the power battery of an electric car during operation through building power battery capacity attenuation rate models of different temperatures, charging currents, discharge currents, and discharge depths, and is high in testing effectiveness.
Owner:ANHUI JIANGHUAI AUTOMOBILE GRP CORP LTD
Coulomb efficiency measuring method used for SOC (system-on-chip) evaluation of power battery
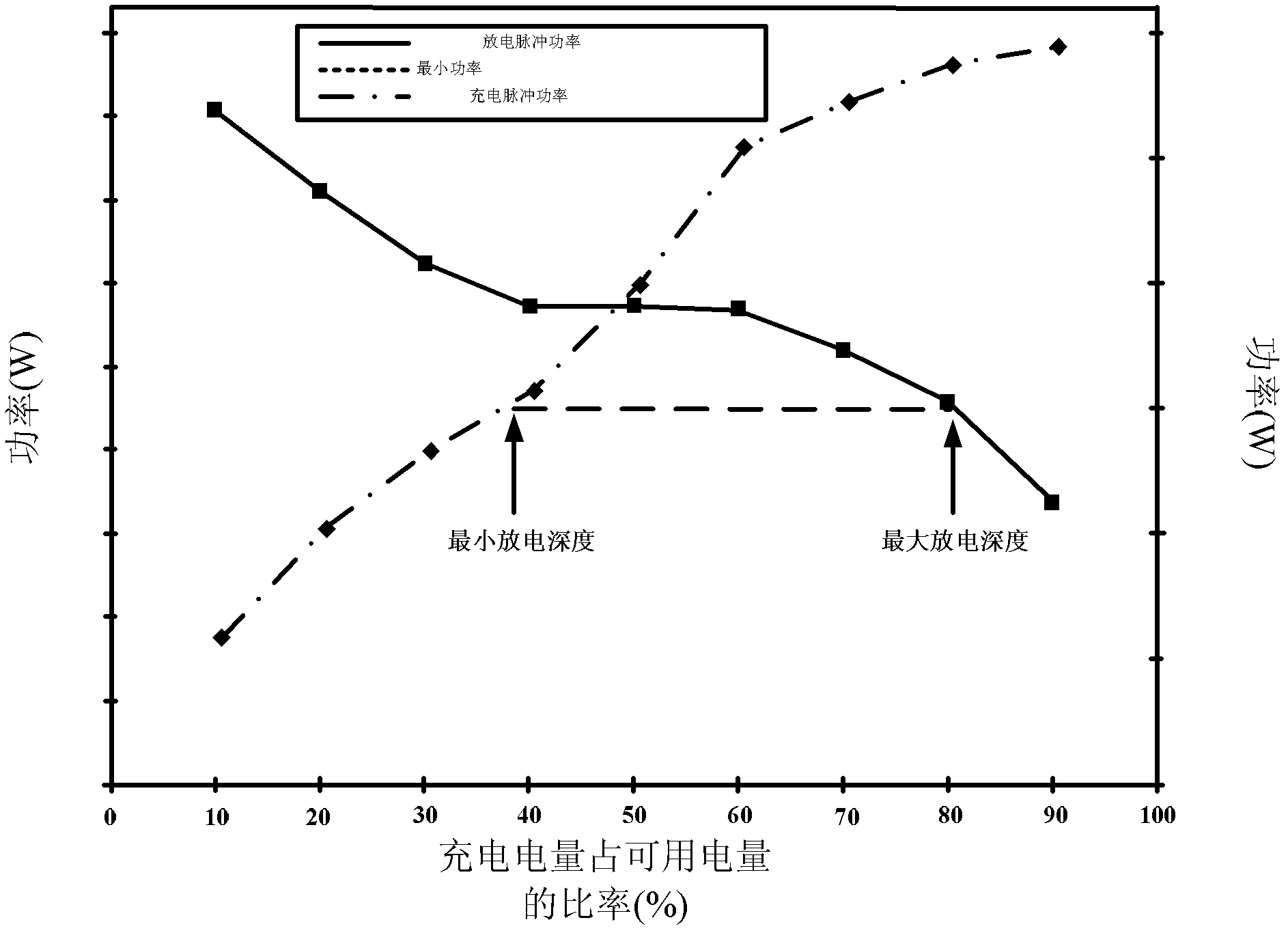
InactiveCN102608540AGuaranteed Coulombic efficiencyMeet the actual vehicle requirementsElectrical testingCapacitanceDepth of discharge
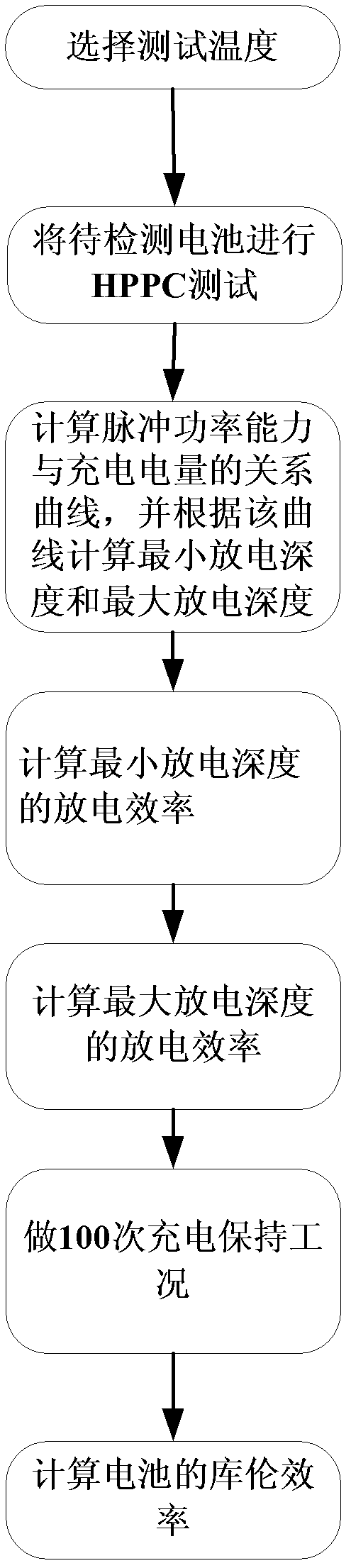
The invention discloses a coulomb efficiency measuring method used for SOC (system-on-chip) evaluation of a power battery, relates to the technical field of power batteries or power battery pack management and aims at solving the problems that in the prior art, when the coulomb efficiency is calculated, the capacitance range of the battery in the practical use is not considered, and the coulomb efficiency is not accurate caused by the self temperature change of the battery in charging and discharging process and the like. The method comprises the following specific steps: conducting HPPC (hybrid pulse-power capability) test on a battery to be detected, and recording a voltage time curve and a current time curve in the HPPC test; calculating the relation curve of pulse power capacity and charging electric quantity according to the obtained voltage time curve and current time curve, and calculating the minimum discharging depth and the maximum discharging depth according to the curve; calculating the coulomb efficiency of middle discharging depth; charging the battery to the middle discharging depth, charging for n times to keep the work condition, discharging the battery completely, and calculating the coulomb efficiency of the battery to be detected. The method disclosed by the invention is used for measuring the coulomb efficiency of batteries in the fields of electric automobiles, renewable energy sources, and large-scale energy storage.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +1
A method for acidification formation a long-life lead storage battery
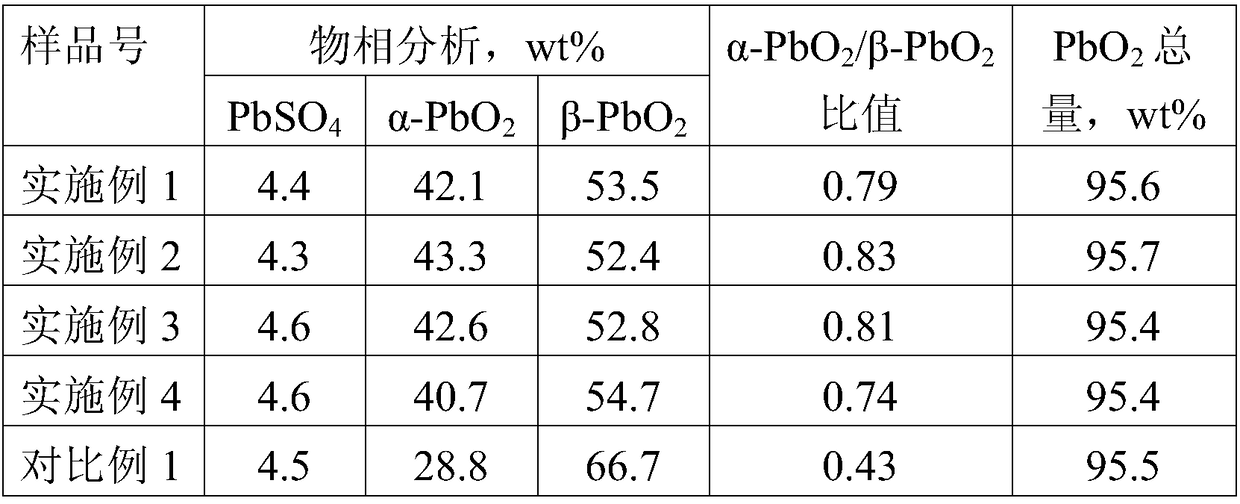
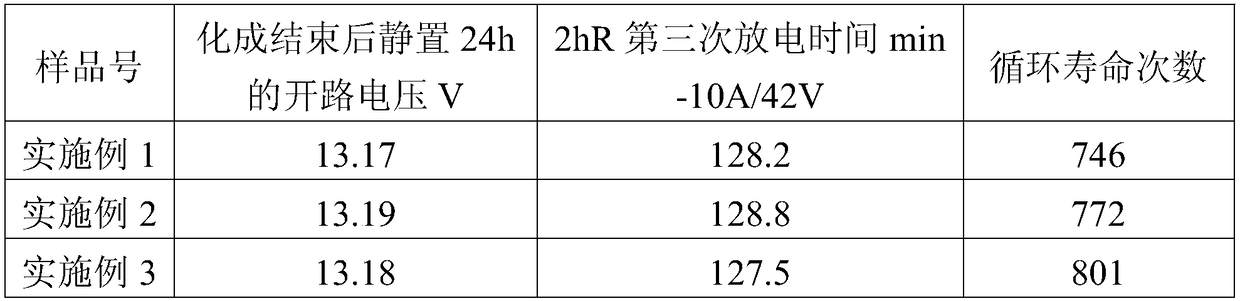
ActiveCN109148815AExtended service lifeUniform responseFinal product manufactureSecondary cells charging/dischargingAbsorption capacityEngineering
A method for acidification formation of a long-life lead storage battery is disclosed, the method includes the following steps: 1, adding acid to a lead storage battery for the first time, adding lowspecific gravity sulfuric acid solution with density of 1.05-1.25 g / cm3 to lead storage battery to be acidified, the adding volume being 90-105% of saturated acid absorption capacity of the lead storage battery; 2, formation in the first stage, charging, wherein the total char electric quantity is 3.5 C - 5.0 C; (3) adding acid for the second time, adding high specific gravity sulfuric acid solution with density of 1.25-1.65 g / cm3, and filling; (4) forming in the second stage, first discharging and then charging, the depth of discharging is 25% - 80%, the total charge quantity is 3.5 C - 5.0 C; (5) Extraction of residual acid. As the acid is added in two times, the specific value of the positive electrode active material alpha-PbO2 / beta-PbO2 can be effectively improved, the service life ofthe battery is prolonged, the polarization can be effectively reduced, the formation efficiency can be improved and the formation period can be shortened.
Owner:TIANNENG BATTERY GROUP
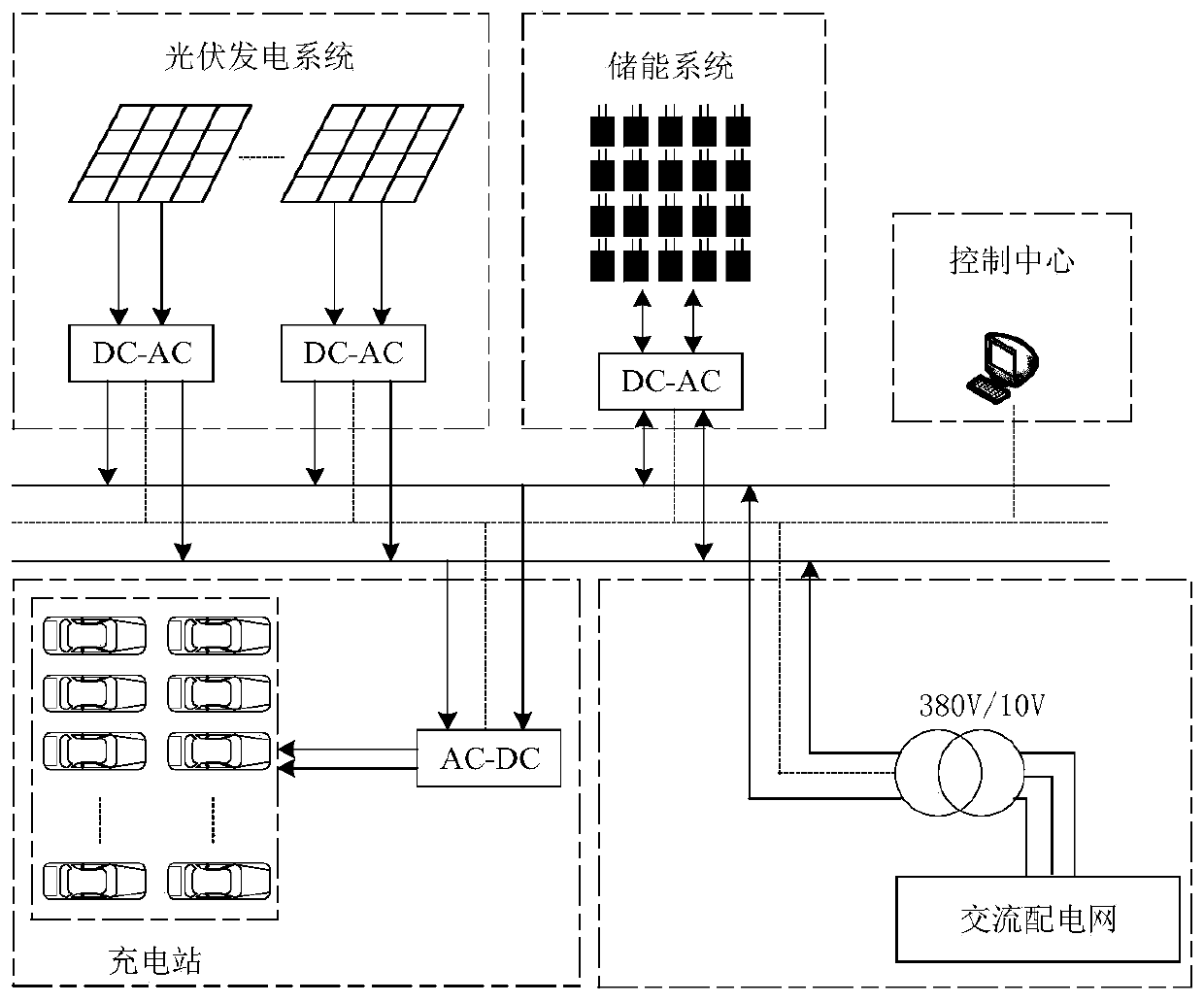
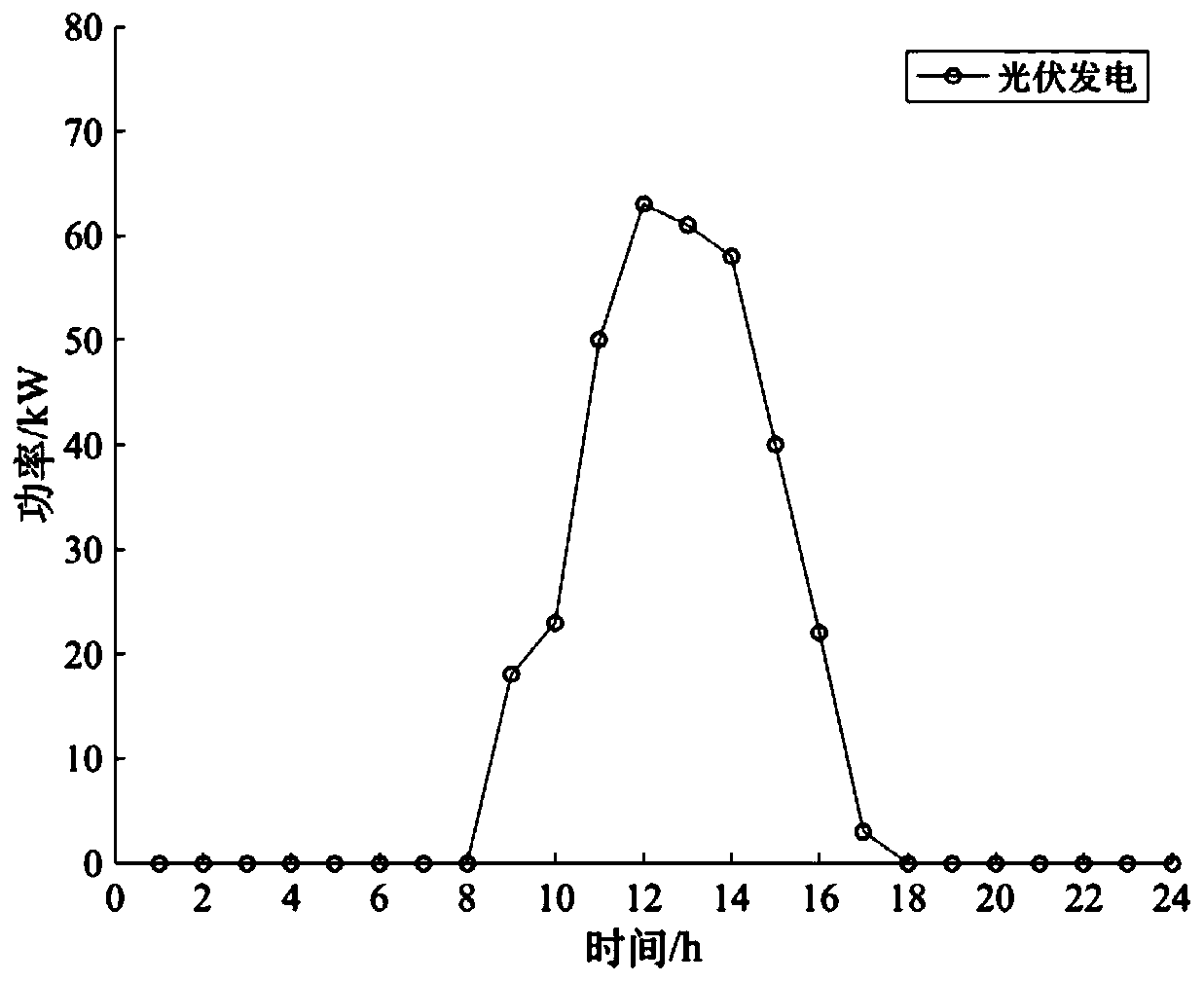
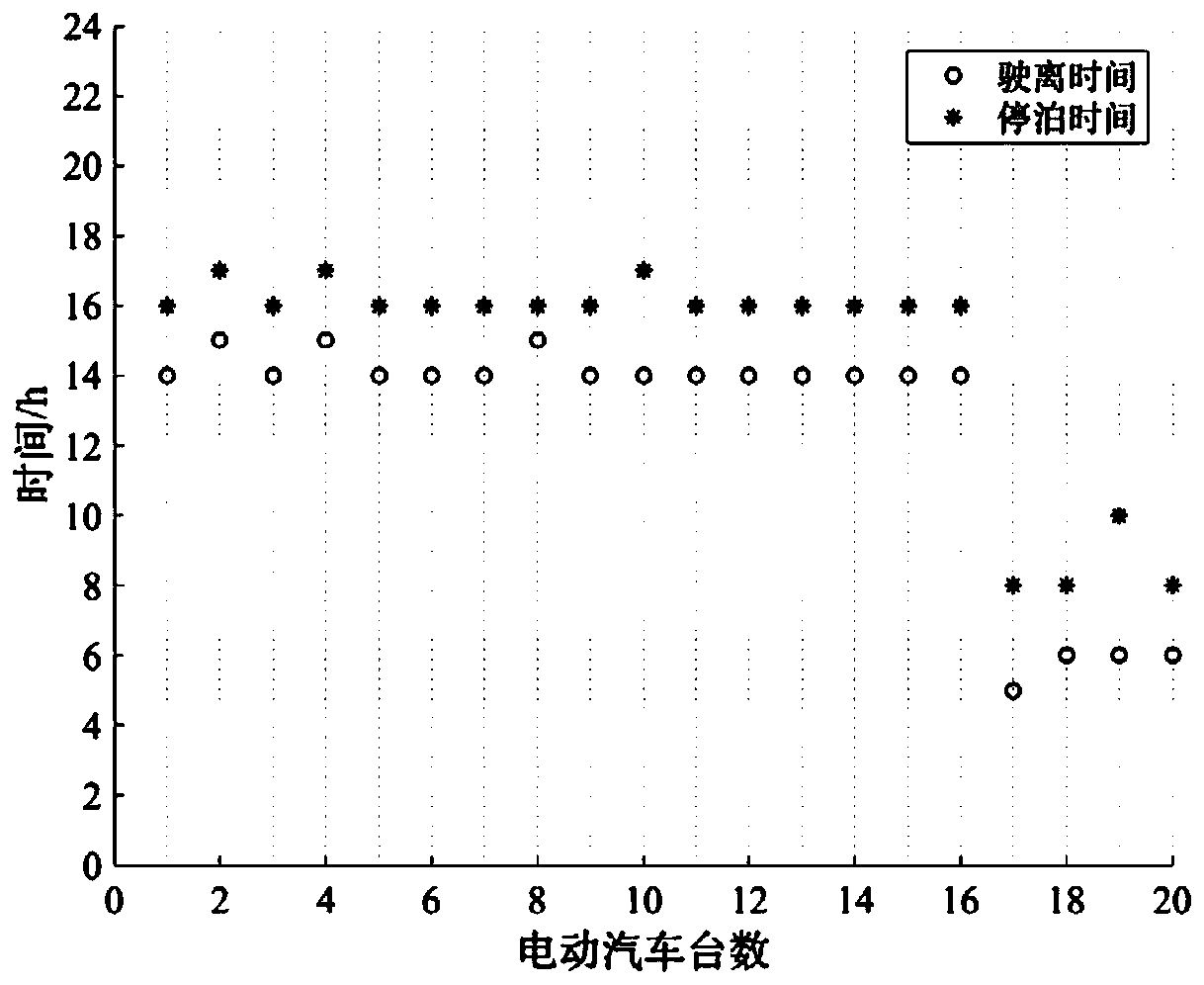
Electric vehicle photovoltaic charging station optimization scheduling method considering user behavior
ActiveCN109713696AMeet the needs of useImprove benefitsInternal combustion piston enginesSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsMathematical modelCharging station
The invention discloses an electric vehicle photovoltaic charging station optimization scheduling method considering a user behavior, that is, an electric vehicle supplies power to a power grid only when an electricity price is higher than the discharge loss of a vehicle-borne storage battery. Therefore, according to measured data, a B-spline curve is used to establish mathematical models of the influence of a discharge depth and an ambient temperature on the cycle life of a storage battery through the two steps of preliminary fitting and partial correction, the influences of a discharge depthfactor and a temperature factor on the cycle life of the storage battery are comprehensively considered, and the discharge loss corresponding to each discharge behavior of the vehicle-borne battery is obtained. On the basis, with the output of an energy storage system and the interaction power with a large power grid as the optimization variables, with minimum operating cost of the system as an optimization goal, the day-to-day optimal scheduling model of the system is established, and the model is solved by using an adaptive genetic optimization algorithm. The invention has a certain significance for extending the service life of the electric vehicle storage battery and promoting the development of renewable energy.
Owner:杭州东华电力设备有限公司
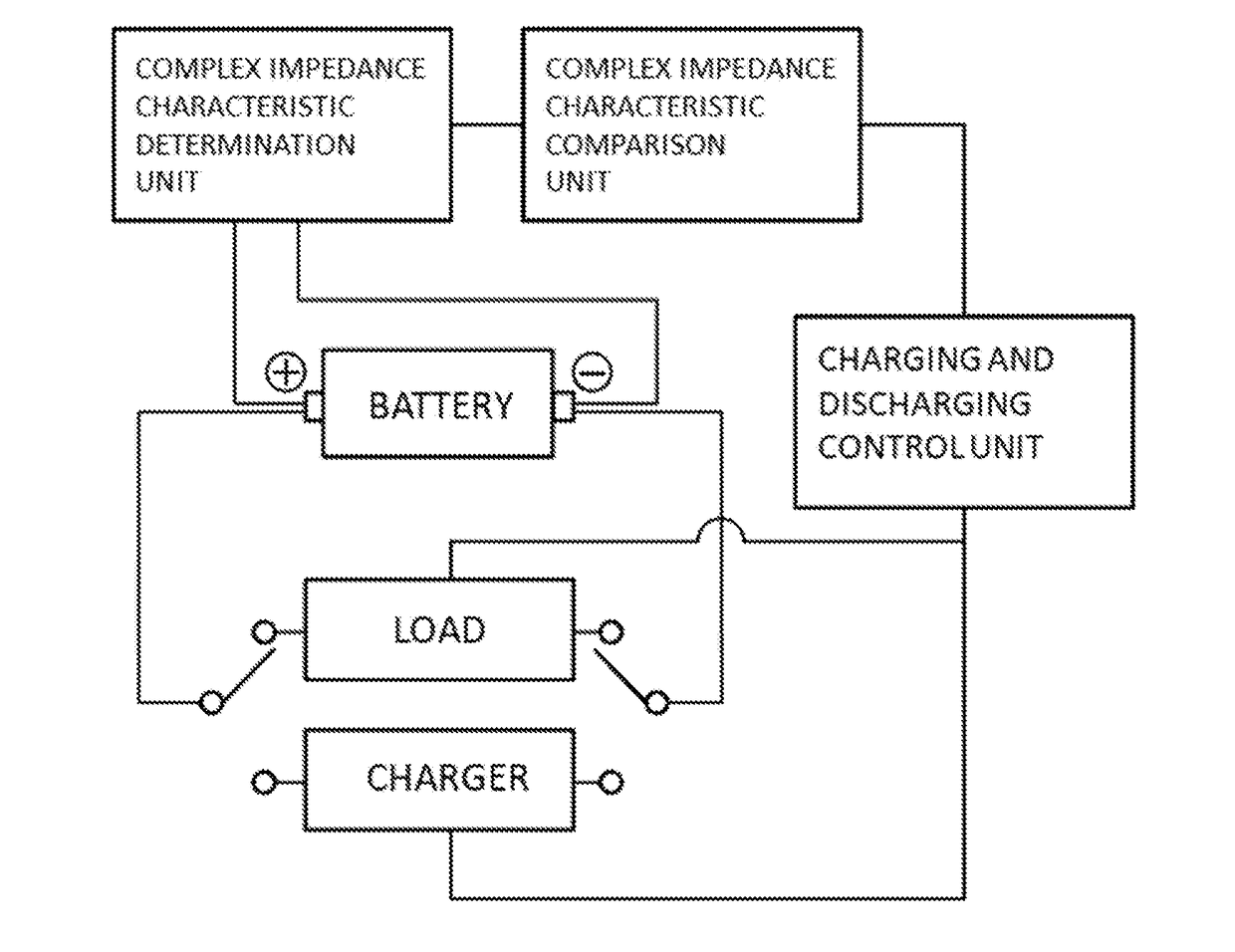
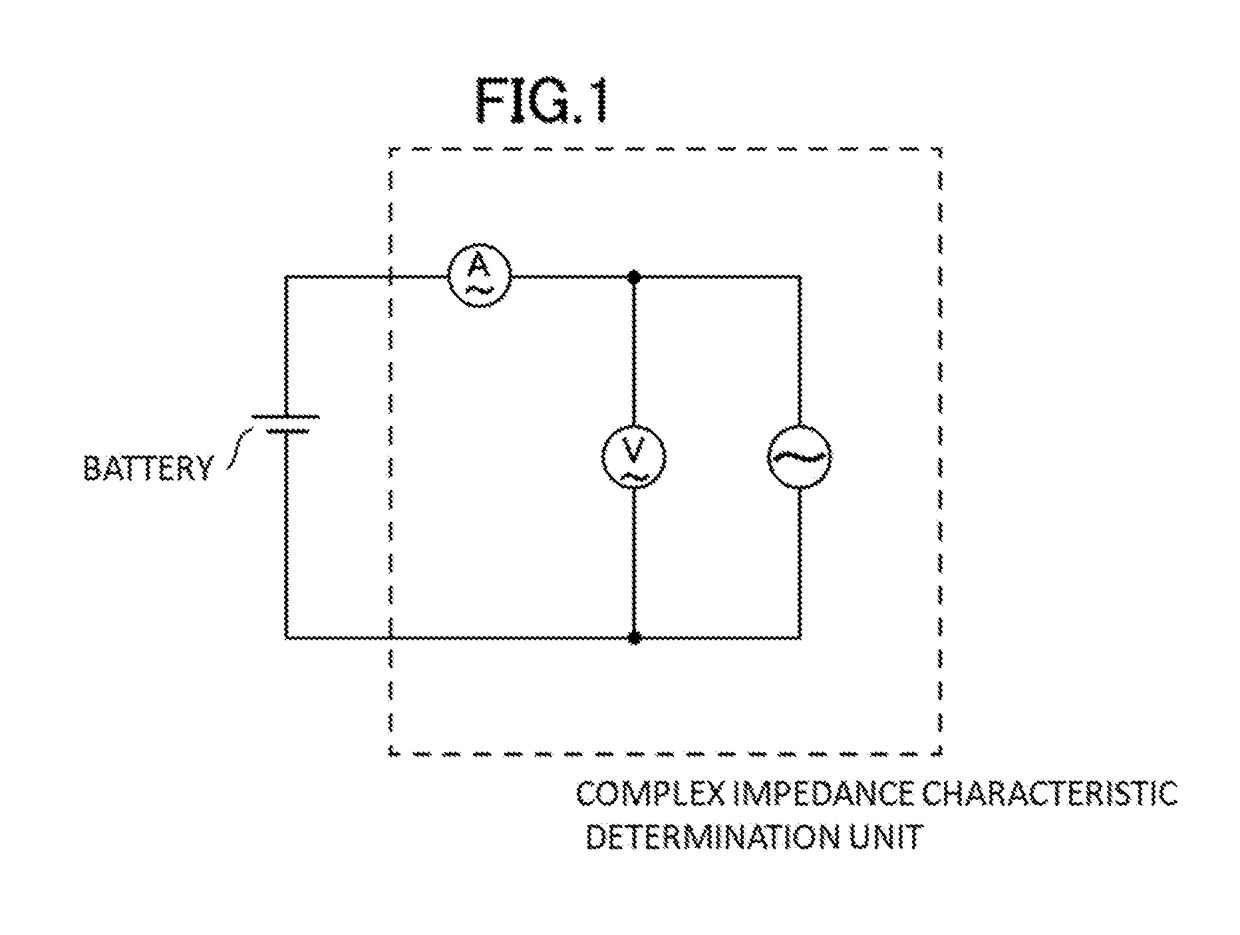
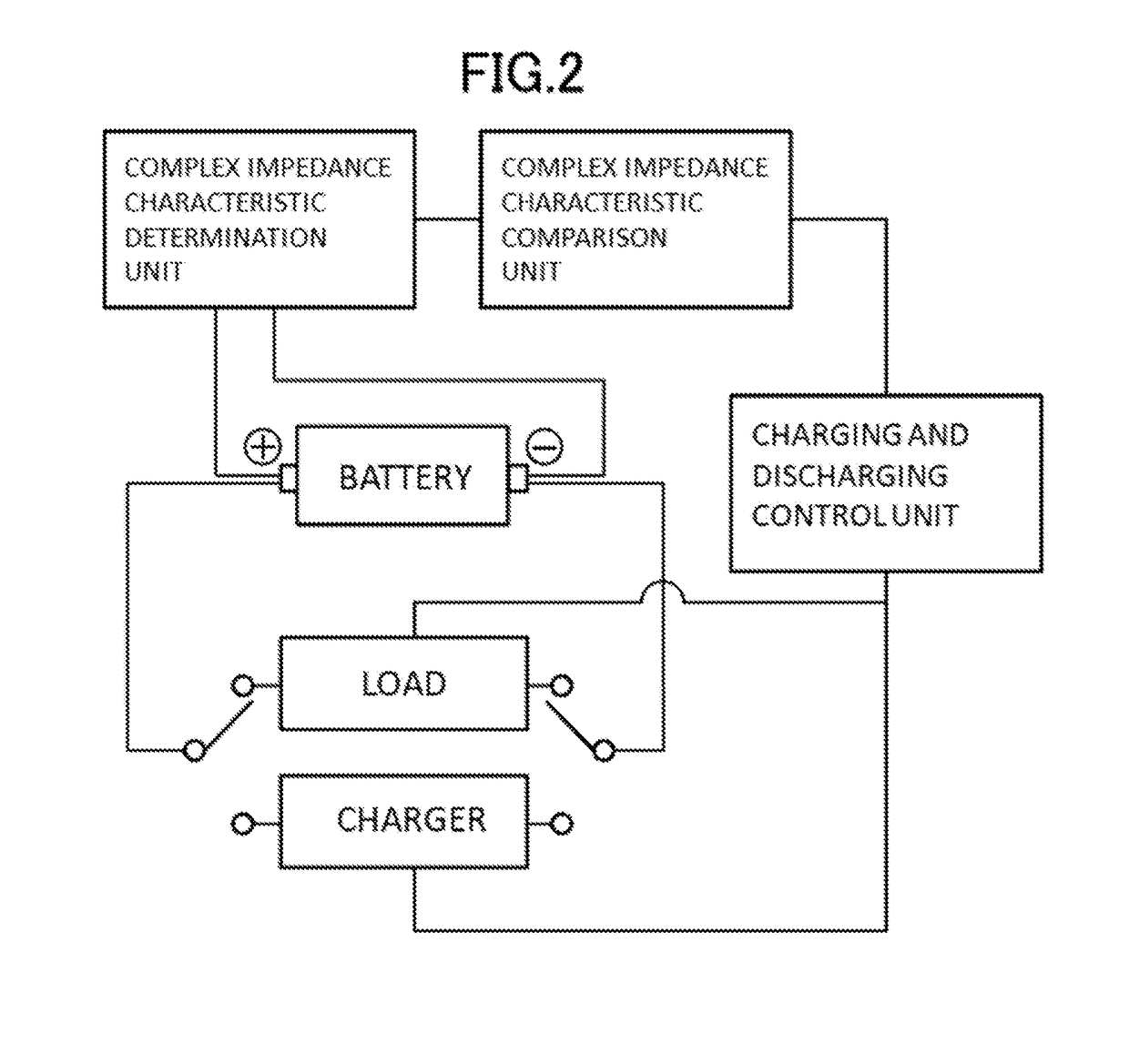
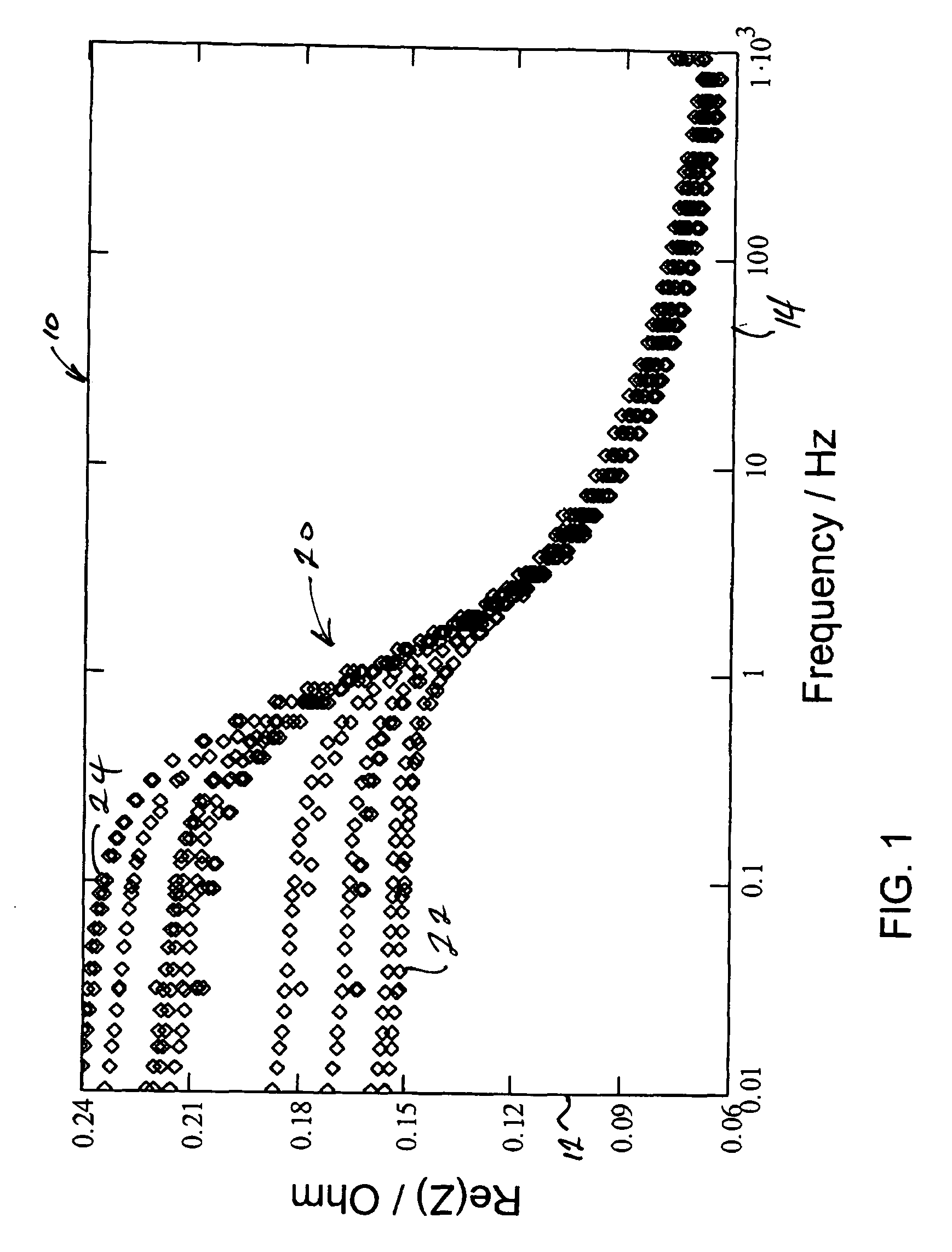
Method and system for estimating state of charge or depth of discharge of battery, and method and system for evaluating health of battery
ActiveUS20180321326A1Wide marketabilityIncrease heightCircuit monitoring/indicationElectrical testingState of chargeEngineering
It is intended to recognize the state of charge or depth of discharge of the battery more accurately than conventional technologies and to recognize health of a battery appropriately. Complex impedance between positive and negative electrodes of the battery is determined at a plurality of frequencies, and the state of charge or depth of discharge of the battery is estimated by comparing frequency dependency of Warburg impedance of the determined complex impedances with frequency dependency of Warburg impedance corresponding to a known state of charge or depth of discharge of the battery. Similarly, complex impedance is determined, and the health of the battery is evaluated by using the real part of the complex impedance at a point where the imaginary part of the complex impedance is zero on a line obtained by extending a part, which indicates frequency dependency of Warburg impedance, of a complex impedance characteristic curve representing a correlation relationship between the real and imaginary parts of the determined complex impedance.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
Lithium ion secondary cell
InactiveCN1830114AHigh outputIncrease capacityPrimary cell to battery groupingFinal product manufactureLithiumPositive current
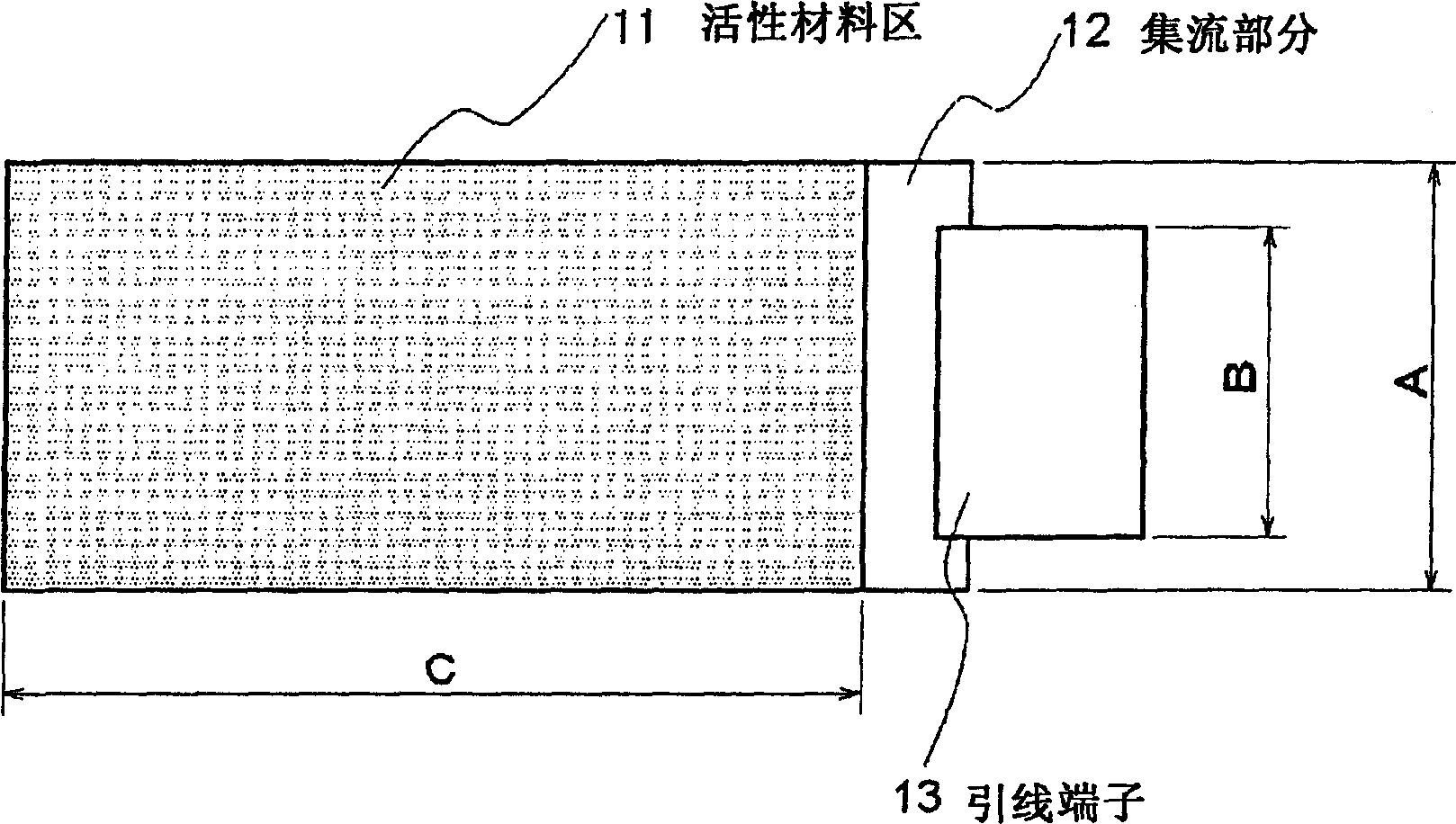
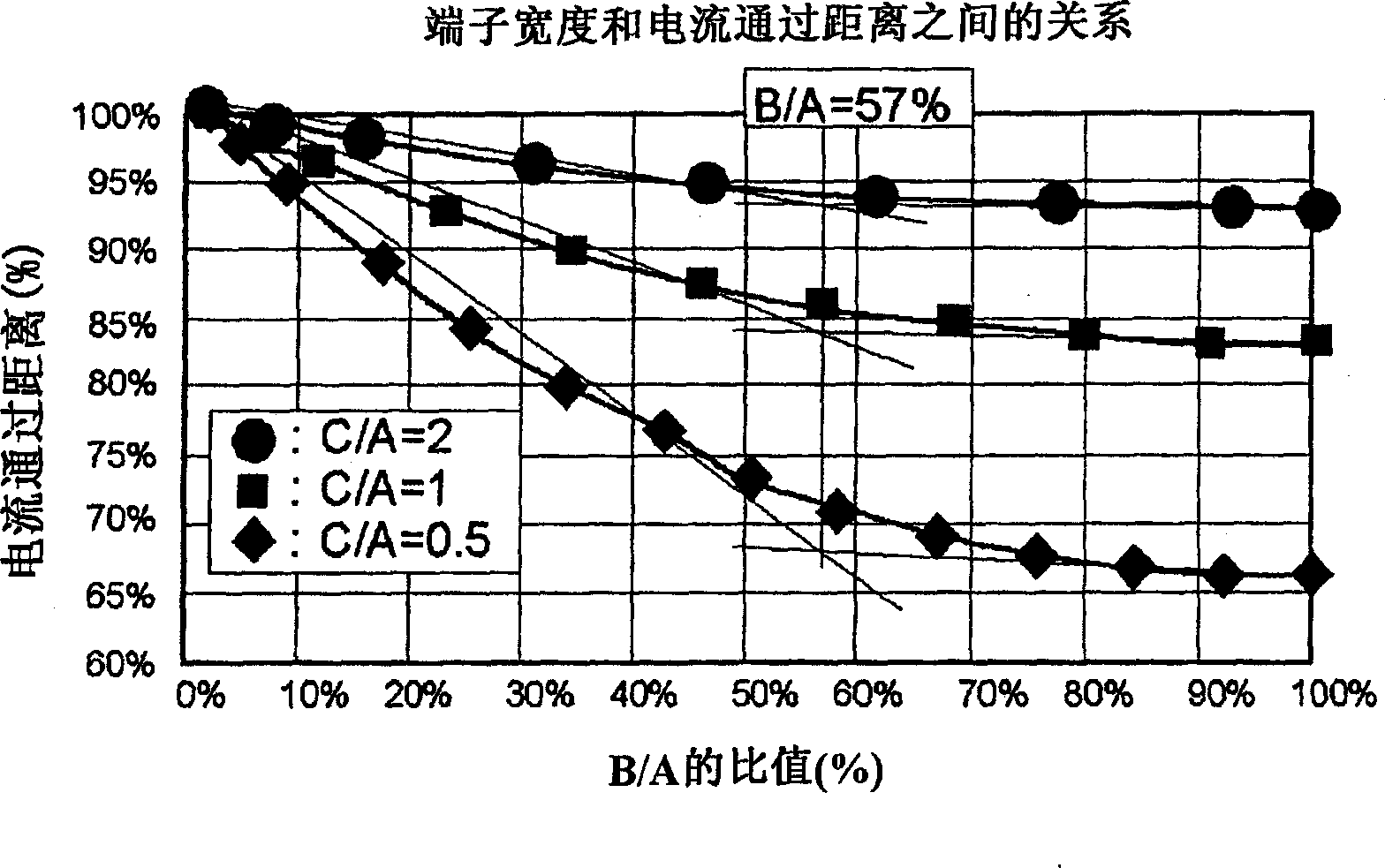
A lithium ion secondary battery comprising a battery element obtained by alternately stacking a plurality of positive electrodes having layers of a positive electrode active material formed on both sides of positive current collectors and a plurality of negative electrodes having layers of a negative electrode active material formed on both sides of negative current collectors through separators in such a way that the positive electrode active material layers face the negative electrode active material layers, the battery element impregnated with liquid electrolyte and held by a laminate case, the lithium ion secondary battery having a 10-second output value of 3000 W / kg or above at a depth of discharge capacity of 50% and 25 DEG C and having the following configuration in which: (1) the positive electrode active material has an average particle size of 3 to 10 m and the positive electrode excluding the current collector has a thickness of 30 to 110 m, (2) the negative electrode active material has an average particle size of 5 to 10 m and the negative electrode excluding the current collector has a thickness of 30 to 110 m, and (3) terminals of the positive electrode and the negative electrode are led out to the outer edge part with the terminals separated from each other and the positive electrode terminal and the negative electrode terminal respectively satisfy B / A 0.57: where A is a width of a region of the active material region perpendicular to the direction of current and B is a width of the electrode terminal perpendicular to the direction of current.
Owner:NEC CORP
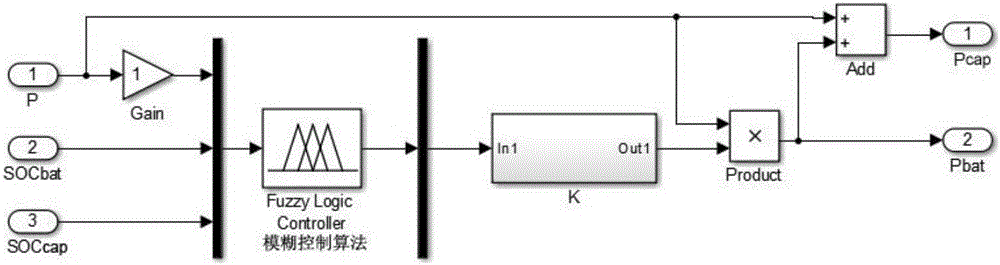
Lithium battery and super capacitor dual-energy power distribution control system and method
InactiveCN106080223AReduce depth of dischargeIncrease usagePropulsion by capacitorsVehicular energy storageCapacitanceDistribution control
The invention provides a lithium battery and super capacitor dual-energy power distribution control system and method. The lithium battery and super capacitor dual-energy power distribution control system comprises a motor needed power collection module, an energy management center, a battery pack and the super capacitor. The motor needed power collection module is connected with the signal input end of an energy management center. The signal output end of the energy management center is connected with the battery pack and the super capacitor. The lithium battery and super capacitor dual-energy power distribution control system and method have the advantages that the structure is simple, using is convenient, the depth of discharge of the battery pack is reduced by means of the rapid charging characteristic of the super capacitor, the number of service times of the battery pack is improved, the service life is prolonged, the driving mileage is increased by 50%, and energy is saved by 30% or over in the starting and stopping processes.
Owner:天津中科先进技术产业有限公司
Method and apparatus for operating a battery to avoid damage and maximize use of battery capacity
ActiveUS20070029970A1Avoid damageMaximizing battery usageCircuit monitoring/indicationDifferent batteries chargingMaximum depthEngineering
A method for terminating battery discharge to avoid battery damage and maximize battery usage includes the steps of: (a) determining battery capacity; (b) storing a capacity result of the capacity determining; (c) determining battery voltage; (d) during a monitored battery operation, integrating battery current flow over a time interval to determine an integrated charge value at an end-of-interval-time; (e) determining an extant depth of discharge at the end-of-interval-time; (f) if the extant depth of discharge is neither within a first range of a maximum depth of discharge nor the battery voltage is within a second range of a minimum battery voltage, carrying out steps (d) through (f); (h) if the extant depth of discharge is within the first range of the maximum depth of discharge or if the battery voltage is within the second range of the minimum battery voltage, terminating the monitored battery operation.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Valve control seal type lead-acid storage battery health condition monitoring method
InactiveCN104569844AHigh accuracy of health status monitoringElectrical testingMathematical modelEngineering
The invention discloses a valve control seal type lead-acid storage battery health condition monitoring method. According to a storage battery terminal voltage (V) and depth of discharge (DOD) changing curve fitting mathematic model, only after parameters in the model are identified, can the depth of discharge (DOD*) of a battery under the full-capacity discharge condition be solved with a bisection method; then, temperature variables are used for converting the depth of discharge (DOD*) into the depth of discharge (DOD*[25]) at the standard temperature of 25 DEG C; finally an SOH value of the battery can be calculated according to the definition of the storage battery health condition (SOH). The valve control seal type lead-acid storage battery health condition monitoring method has the advantages that the lead-acid storage battery health condition monitoring is high in accuracy, and on-line forecasting can be carried out.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Screening method for lithium iron phosphate battery cell
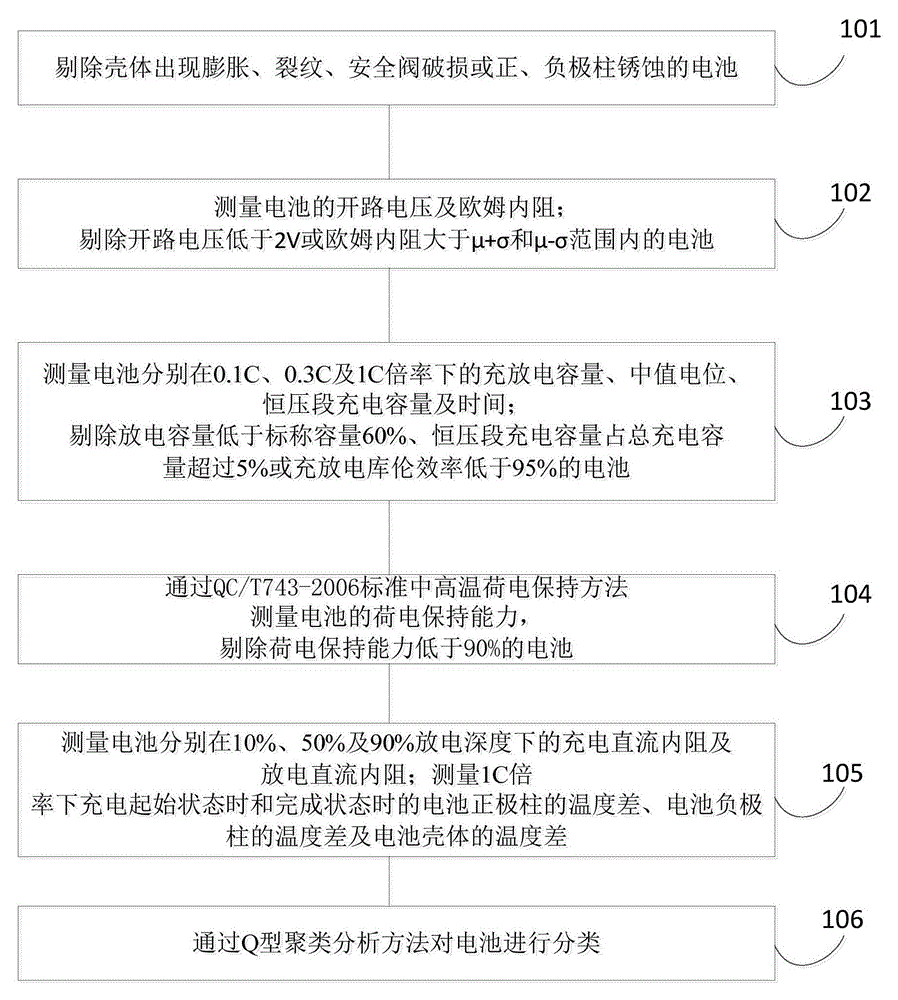
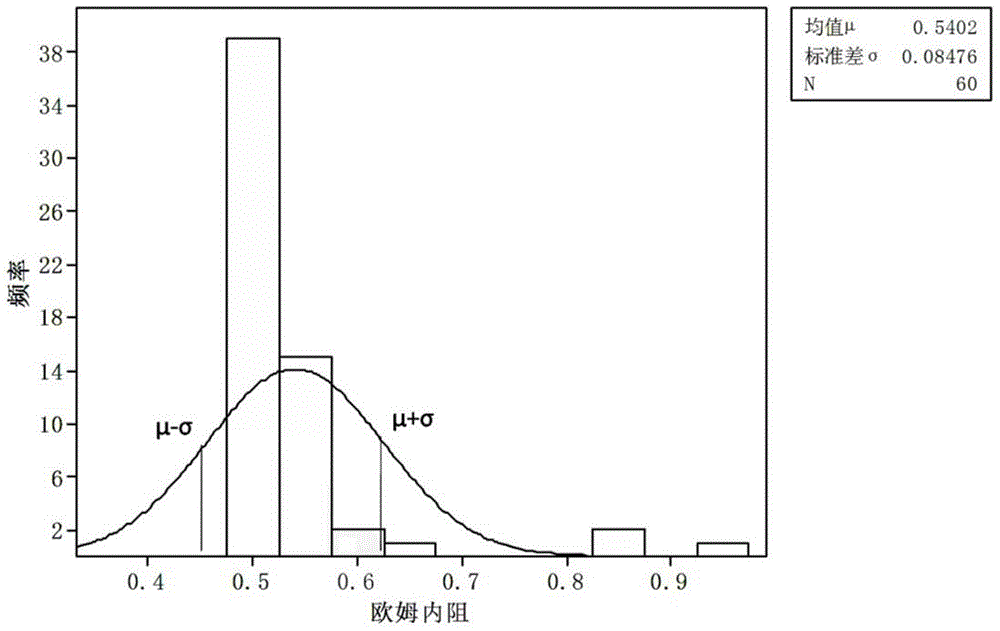
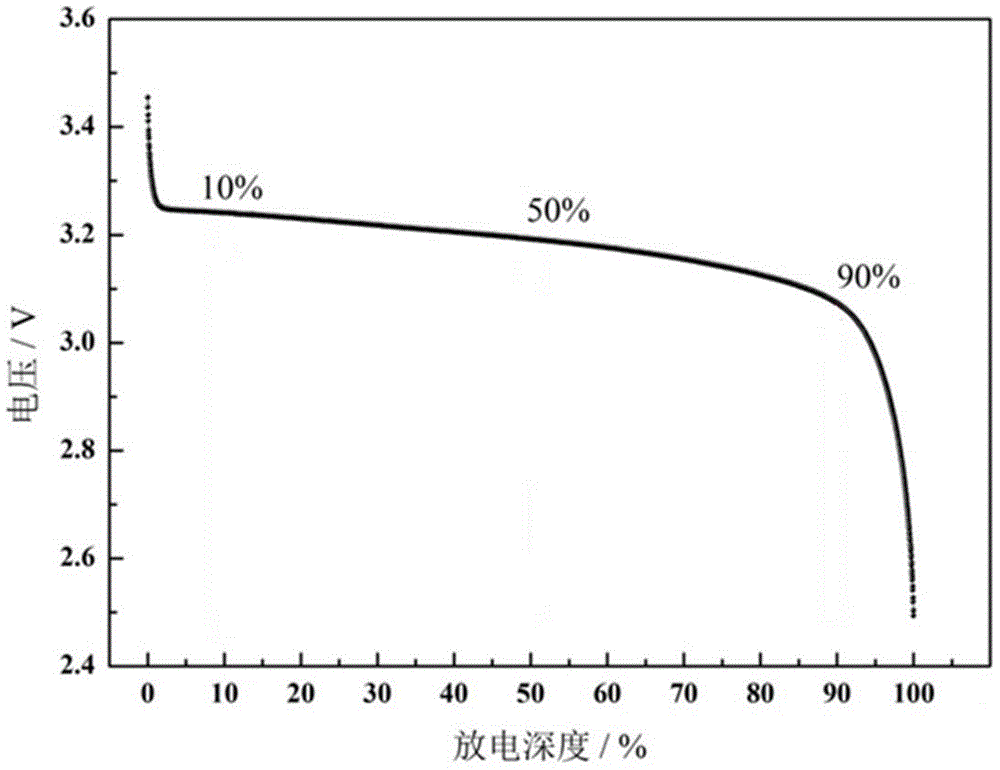
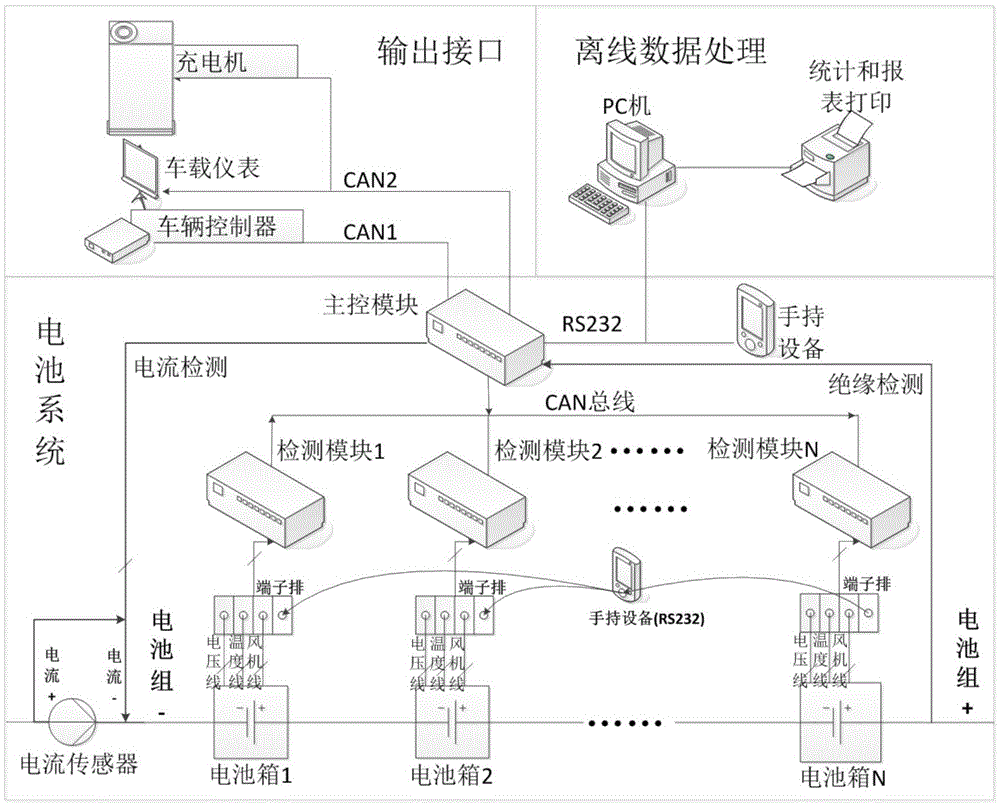
The invention discloses a screening method for a lithium iron phosphate battery cell. The screening method comprises the following steps: measuring the open-circuit voltage and Ohmic internal resistance of cells and rejecting cells with open-circuit voltage lower than 2 V or Ohmic internal resistance beyond a range from mu+sigma to mu-sigma; measuring the charge and discharge capacity, median potential and constant-voltage-section charge capacity and time of cells under at least two different rates, and rejecting cells with discharge capacity 60% lower than nominal capacity, constant-voltage-section charge capacity accounting for more than 5% of the total charge capacity or charge and discharge coulombic efficiency of lower than 95%; measuring the charge and discharge direct-current internal resistance of cells at different discharge depth; measuring the positive pole temperature difference, negative pole temperature difference and shell temperature difference of cells from time point when charging begins to time point when charging ends; and classifying the cells by using a cluster analysis method. The method provided by the invention can screen out cells with good security and excellent consistency, which facilitates subsequent assembling of a battery pack and is beneficial for improving the use security and energy utilization rate of the battery pack.
Owner:SHANGHAI SINOPOLY JIAHUA BATTERY TECH
Power lithium ion battery cycle life equivalent test method
InactiveCN105548902AEfficiently model and quantify aging mechanismsElectrical testingWorking temperatureEngineering
The invention discloses a power lithium ion battery cycle life equivalent test method, and brings forward an equivalent cycle life test method realized by simulating an actual running environment for a pure electric vehicle running environment. The method comprises erecting a pure electric vehicle test platform, acquiring pure electric vehicle real-vehicle running data, and analyzing and extracting a vehicle running condition reflecting a pure electric vehicle running feature; extracting vehicle driving working condition test stress; extracting discharge depth test stress of a power lithium ion battery; extracting working temperature test stress of the power lithium ion battery; and according to the extracted test stress, selecting a scope of different test stress reflecting actual conditions, and designing a complete cycle life equivalent test scheme simulating the working state of the power lithium ion battery in an actual pure electric vehicle running environment through combination. According to the method, the test result has certain guidance significance for actual application.
Owner:BEIJING BEIJIAO NEW ENERGY TECH CO LTD
Battery, assembled battery unit, vehicle equipped with battery, and battery voltage adjusting method
ActiveUS20070210760A1Improve battery performanceImprove performanceBatteries circuit arrangementsFinal product manufactureElectricityEngineering
A battery is basically provided with an electricity generating element and a discharging section. The electricity generating element has a plurality of electric cells connected in series. The discharging section constantly discharges electricity from each of the electric cells at a prescribed discharge rate so that a voltage in each of the electric cells is lower than a voltage corresponding to a prescribed depth of discharge. The battery is especially useful in a power supply component of a vehicle.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Battery-powered all-electric locomotive and related locomotive and train configurations
Owner:NORFOLK SOUTHERN
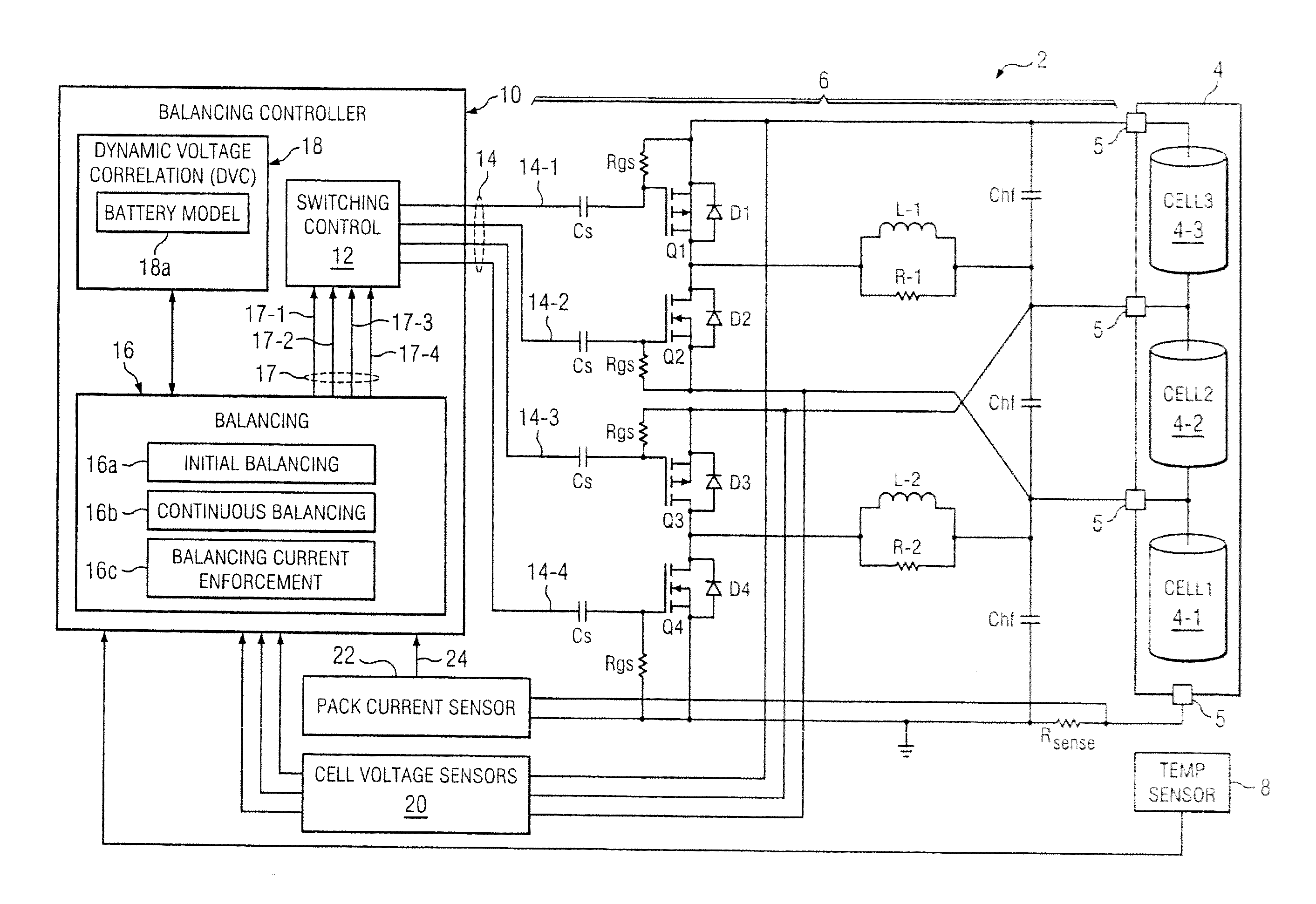
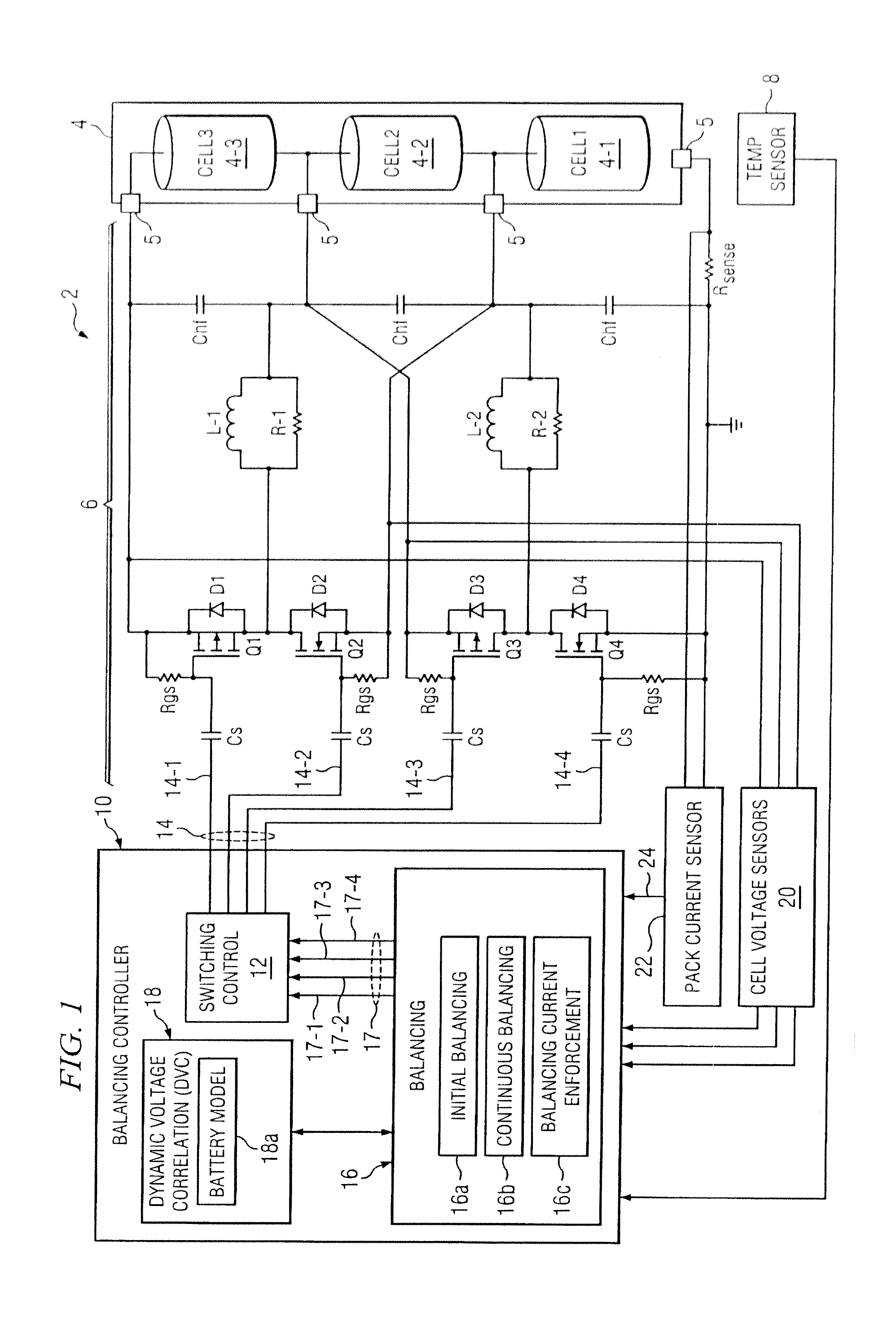
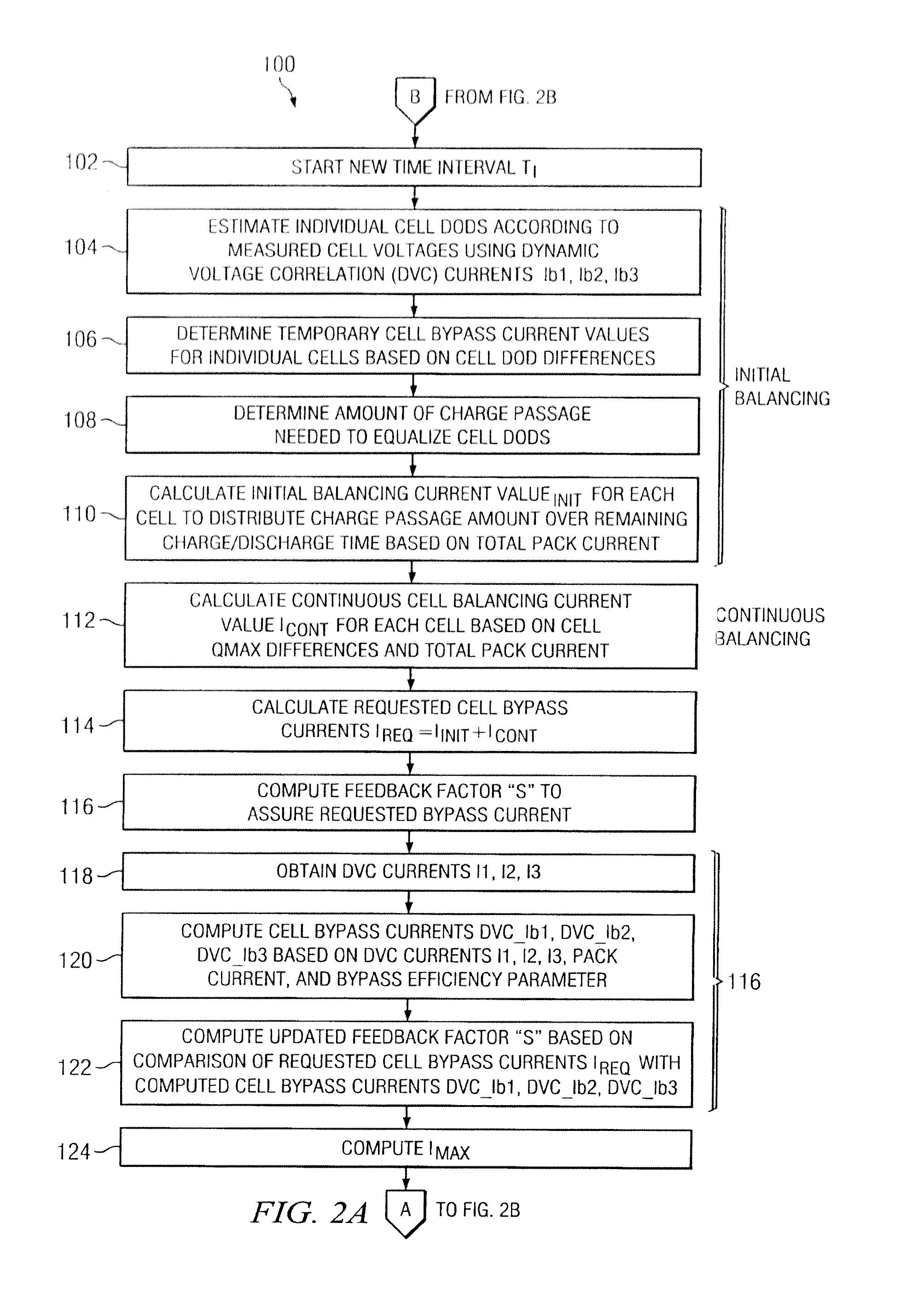
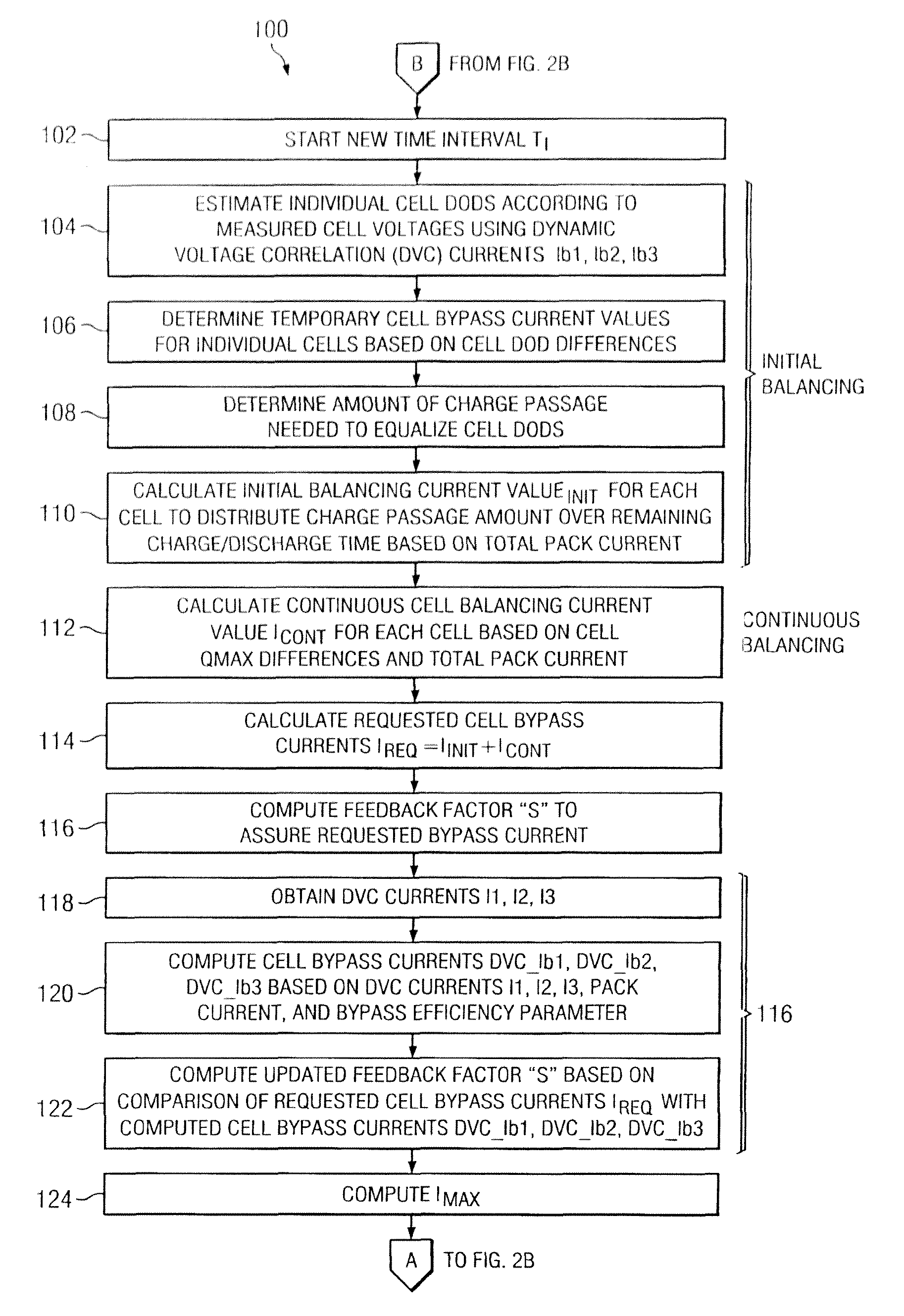
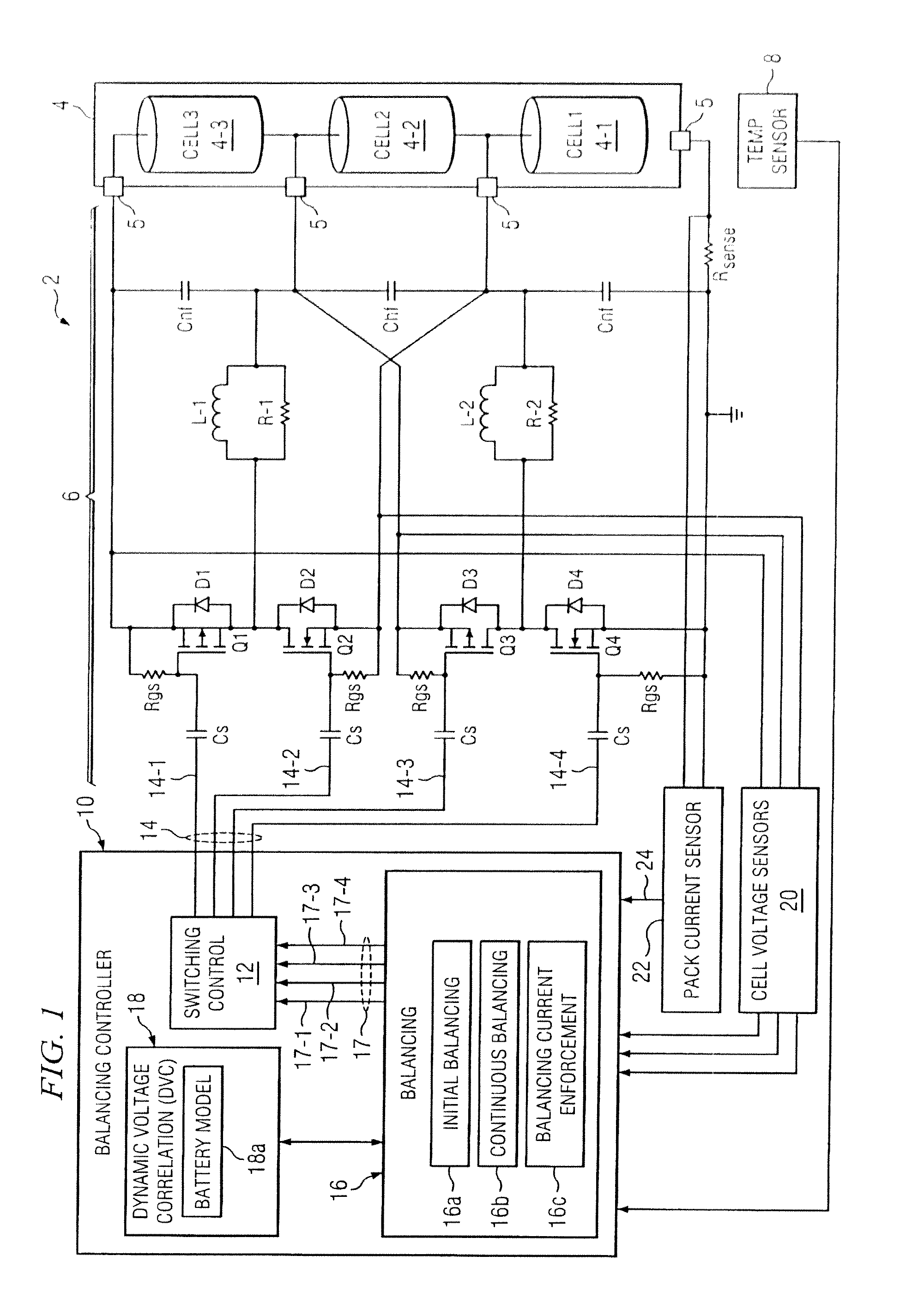
System and method for battery pack managment using predictive balancing
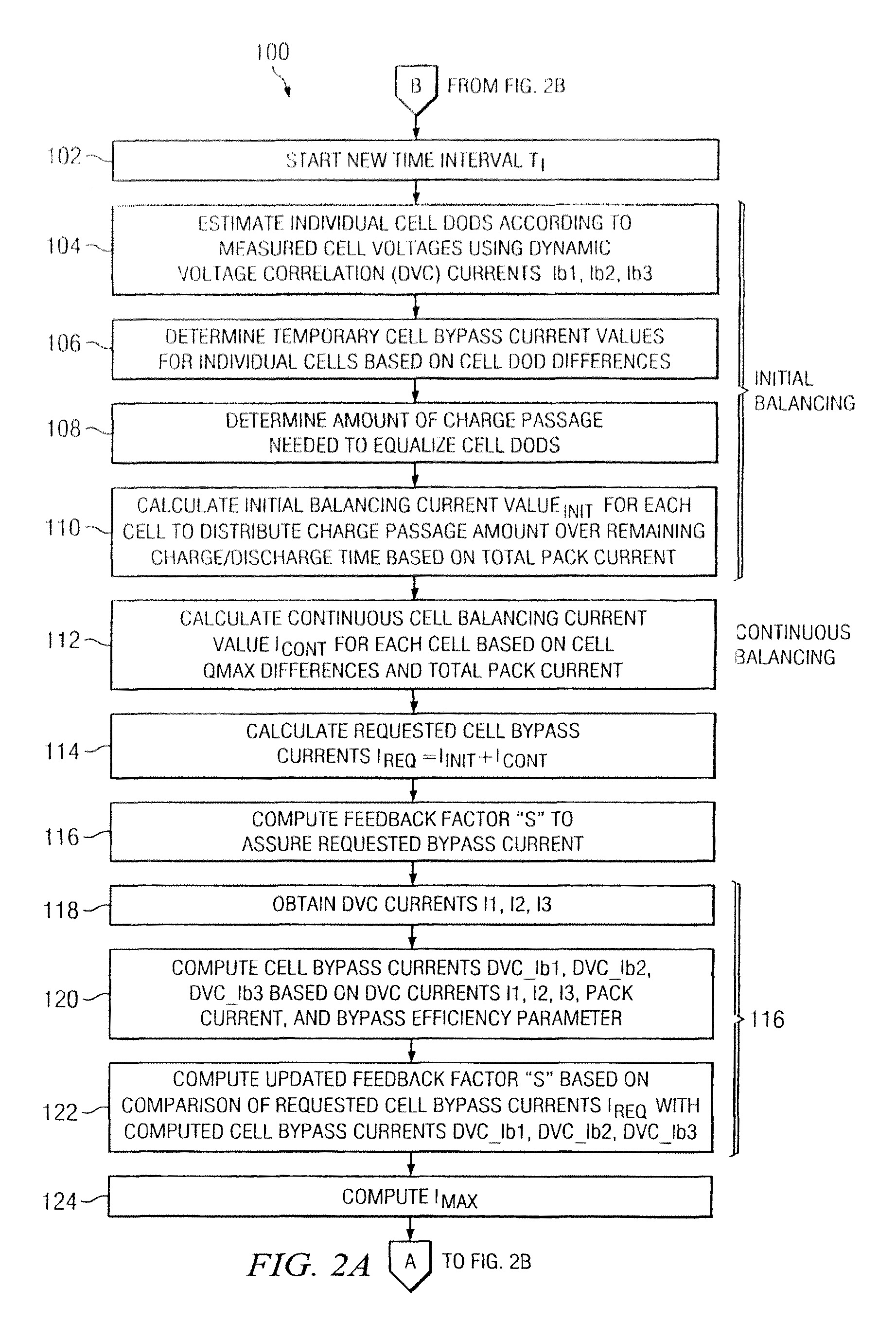
ActiveUS20140077752A1Reduce switching frequencyCharge equalisation circuitCircuit monitoring/indicationTime segmentDepth of discharge
Predictive battery pack cell balancing apparatus and methods are presented in which active bypass current switching is controlled according to initial balancing bypass current values to balance the cell depth of discharge (DOD) values by the end of a charging / discharging time period, and according to continuous balancing bypass current values representing an amount of bypass current needed to maintain a present relationship of the cell DOD values.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and apparatus for predicting change in an operating state of an electric energy storage device
A method for predicting change in an operating state, e.g. state of life, for an electrical energy storage device includes establishing a plurality of values for an operating parameter, e.g. current, of the electrical energy storage device and, for each respective value, determining a corresponding change in the operating state for the energy storage device based upon the respective value. Preferably, change in the state of life is determined based upon an integration of electrical current, a depth of discharge of the energy storage device, and an operating temperature factor of the electrical energy storage device.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
System and method for battery pack management using predictive balancing
ActiveUS9130377B2Reduce switching frequencyCharge equalisation circuitCircuit monitoring/indicationTime segmentEngineering
Predictive battery pack cell balancing apparatus and methods are presented in which active bypass current switching is controlled according to initial balancing bypass current values to balance the cell depth of discharge (DOD) values by the end of a charging / discharging time period, and according to continuous balancing bypass current values representing an amount of bypass current needed to maintain a present relationship of the cell DOD values.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
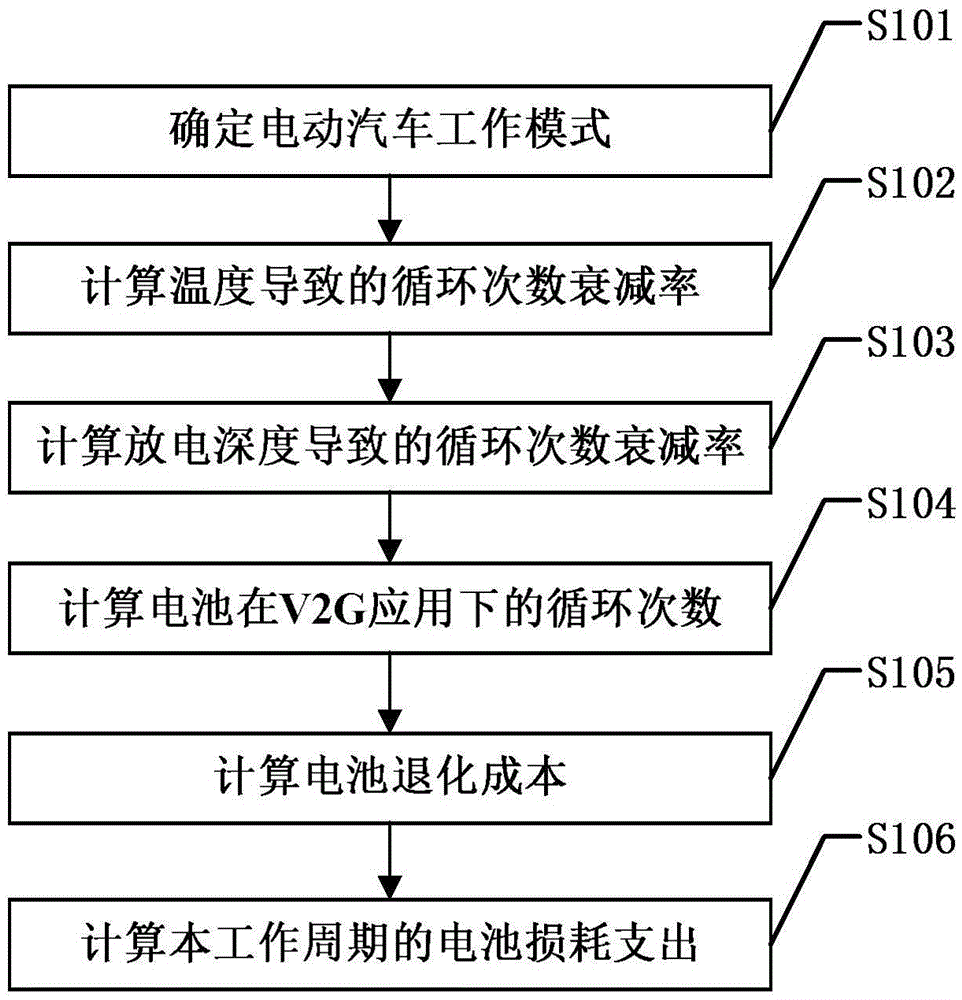
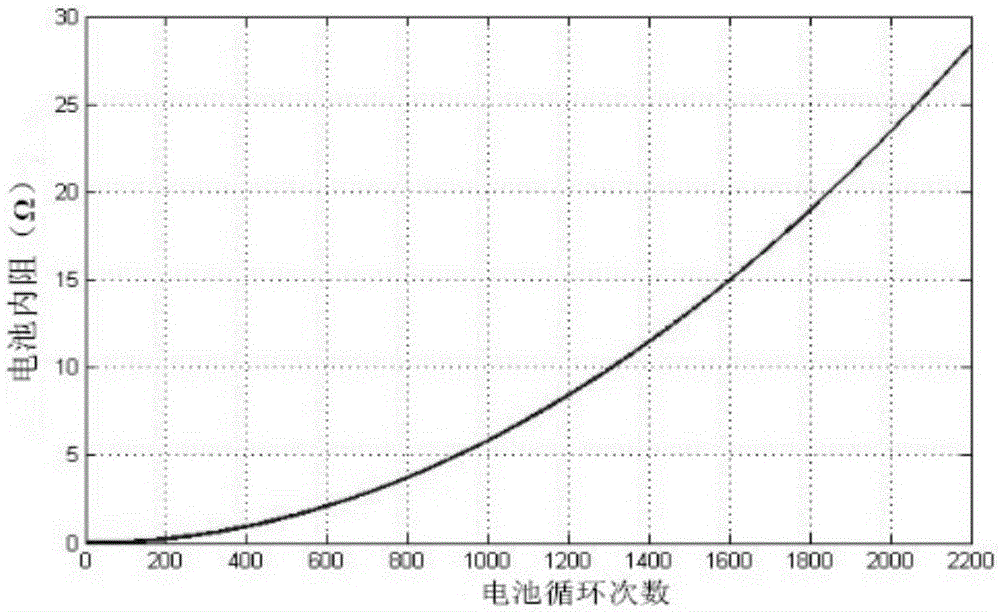
Loss expenditure calculating method for electric vehicle battery participating in power grid dispatching
InactiveCN105512475AImprove accuracyUsable capacity decayElectrical testingSpecial data processing applicationsRate numberRate parameter
The invention discloses a loss expenditure calculating method for an electric vehicle battery participating in power grid dispatching. An aggregator determines a work mode of an electronic vehicle in a current work period in real time through an intelligent control algorithm; the charge and discharge rate, discharge depth and the number of circulation times of the electronic vehicle battery are obtained; the attenuation rate of the number of battery circulation times and the attenuation rate of battery capacity generated due to temperature and the attenuation rate of the number of battery circulation times generated due to discharge depth are calculated; according to the rated number of circulation times of the battery, the number of circulation under V2G application is calculated; degradation cost of the battery is calculated according to the number of circulation times; finally, loss expenditure of the battery in the current work period is calculated according to attenuation rate parameters of the current work period. Influences of temperature and discharge depth on the number of circulation times of the battery are combined, battery temperature rise caused by changes of internal impedance of the battery is introduced, and loss estimation of the battery is more precise and accords with actual situations better.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com