Loss expenditure calculating method for electric vehicle battery participating in power grid dispatching
A technology of electric vehicles and calculation methods, which is applied in the directions of calculation, measurement of electricity, and measurement of electrical variables, etc. It can solve the problems of not discussing the battery capacity decay of the battery cycle life in detail, the calculation is not accurate enough, and the impact of the battery is not considered.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
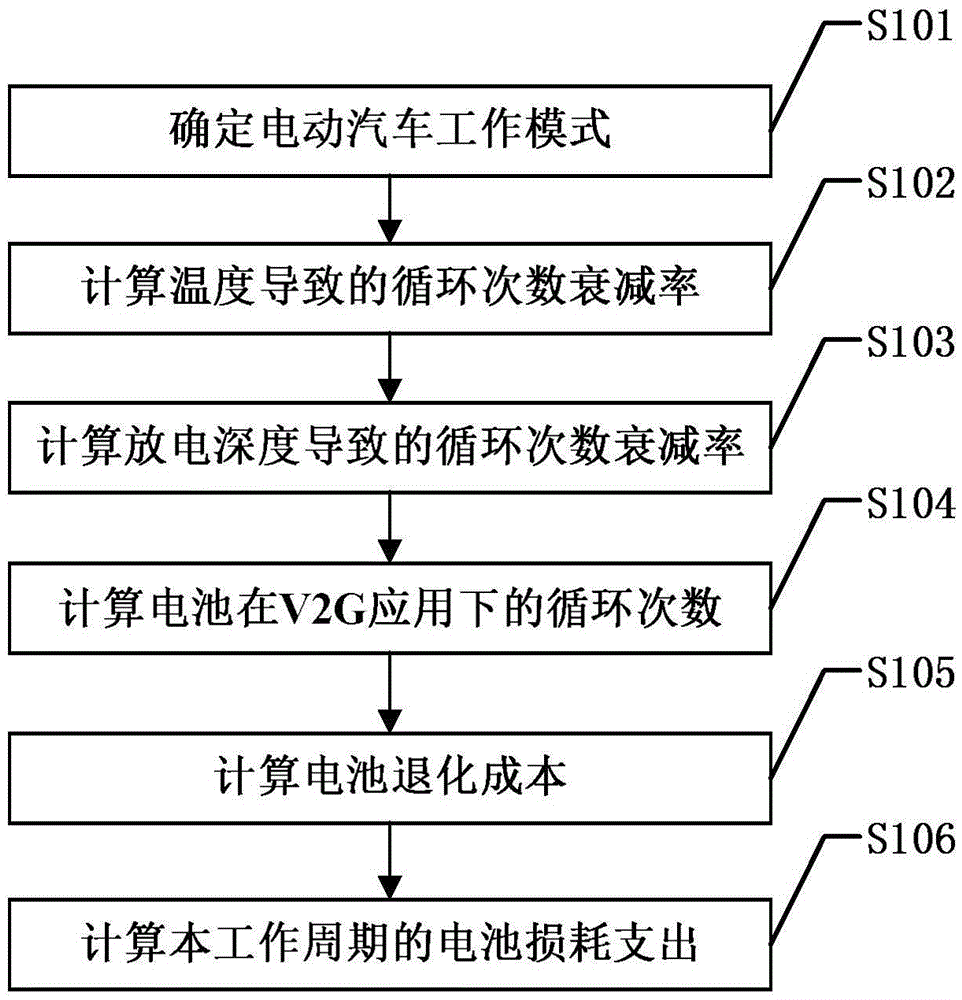
[0055] figure 1 It is a flow chart of the calculation method for battery loss expenditure of electric vehicles participating in power grid dispatching in the present invention. Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention participates in the electric vehicle battery loss calculation method of power grid dispatching comprising the following steps:
[0056] S101: Determine the working mode of the electric vehicle:
[0057] The aggregator uses an intelligent control algorithm to determine the working mode of the electric vehicle in real time in this working cycle. The working mode in this embodiment includes charging, discharging, and frequency modulation to obtain the charging and discharging rate C of the battery of the electric vehicle. The charging and discharging rates of electric vehicles are generally set when they are connected to the grid.
[0058] Since the discharge depth D also has a great impact on battery loss, it is also necessary to obtain the current disch...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com