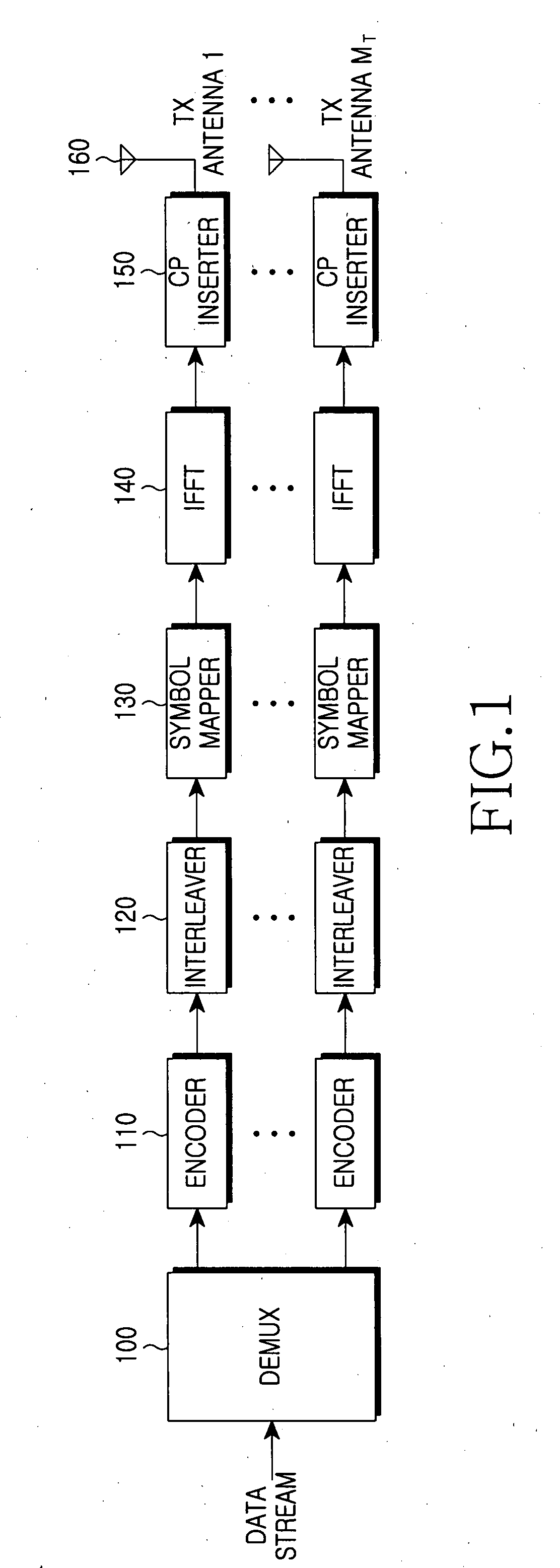
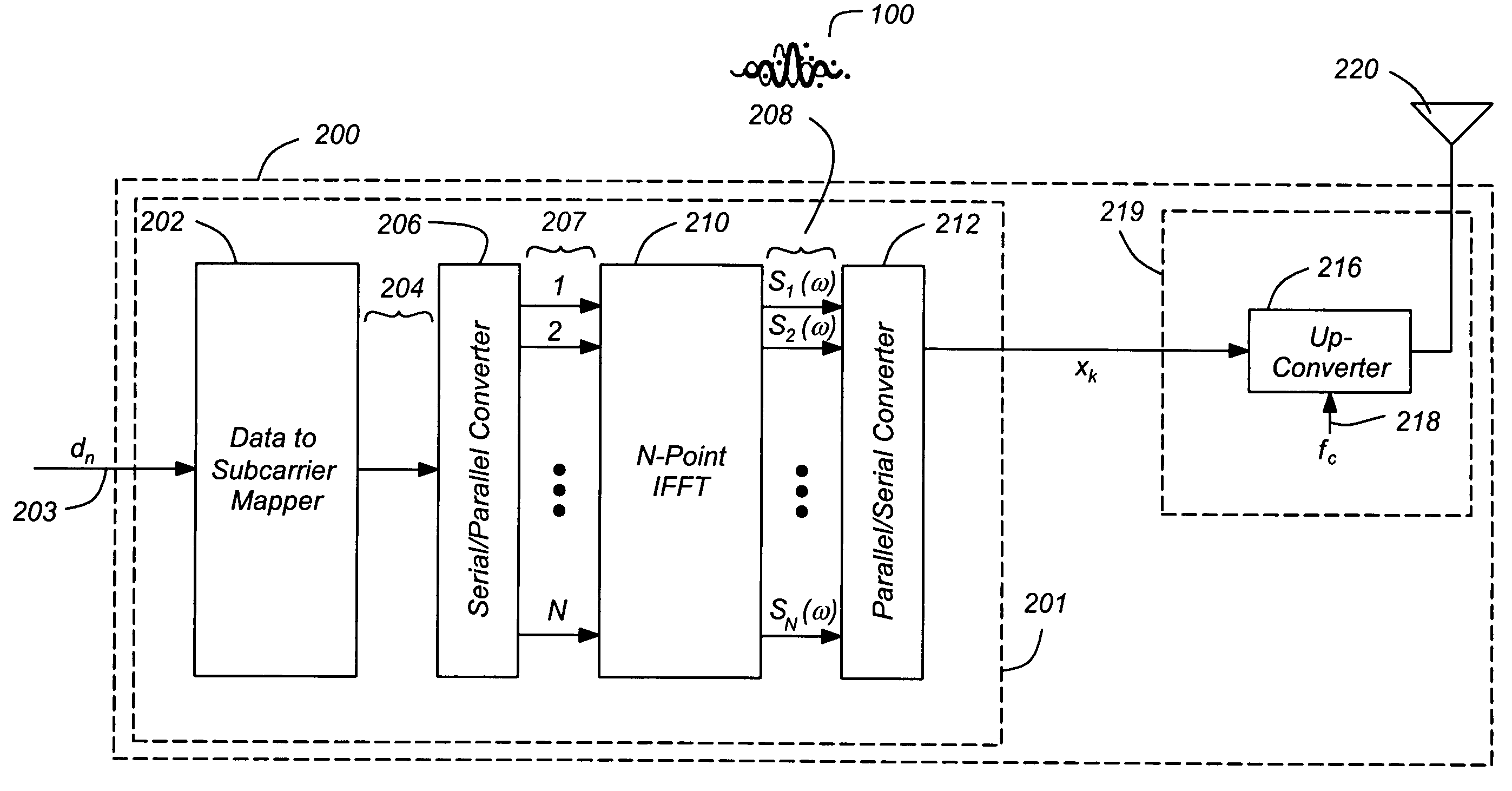
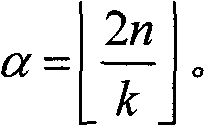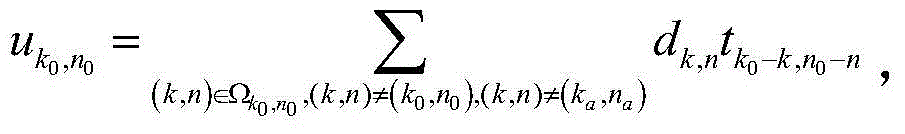Patents
Literature
235 results about "Intercarrier interference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
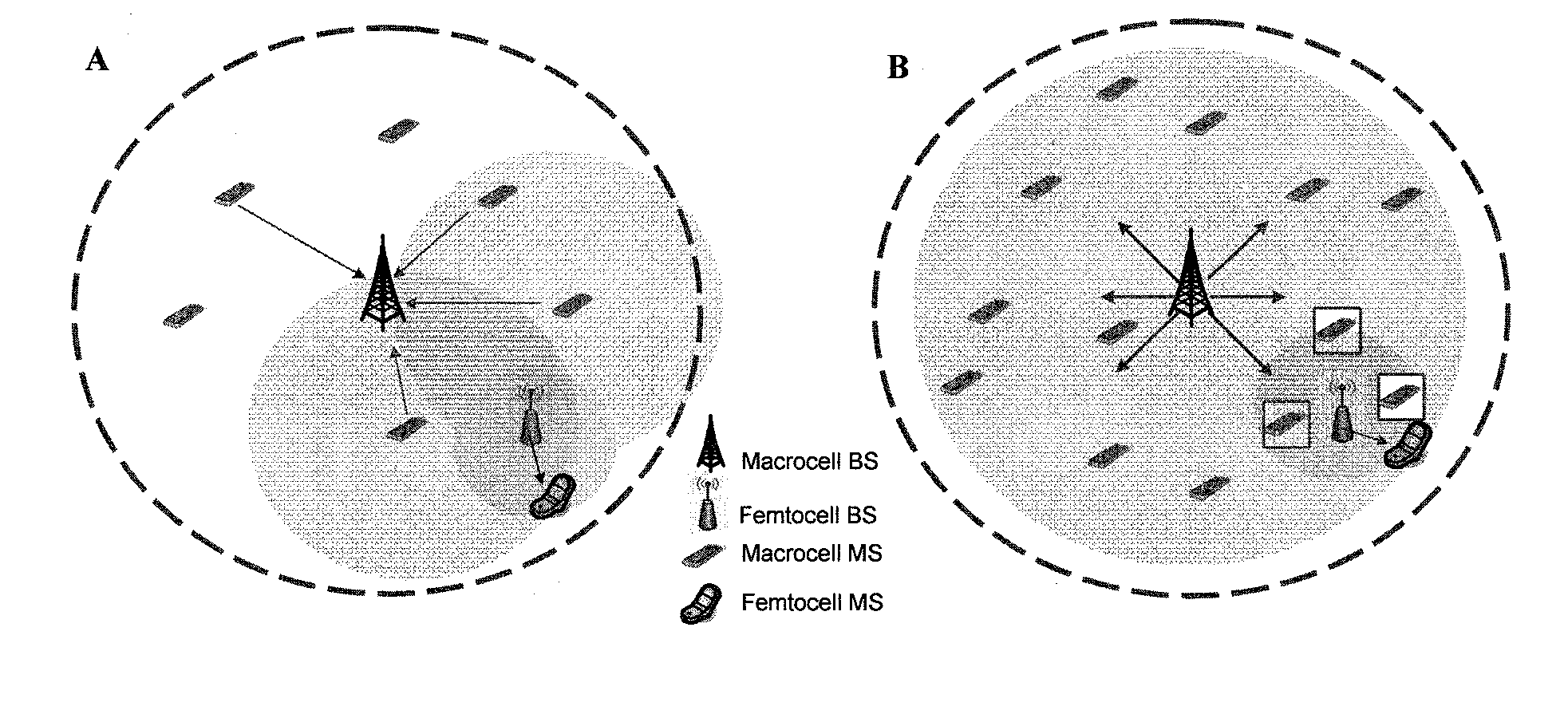
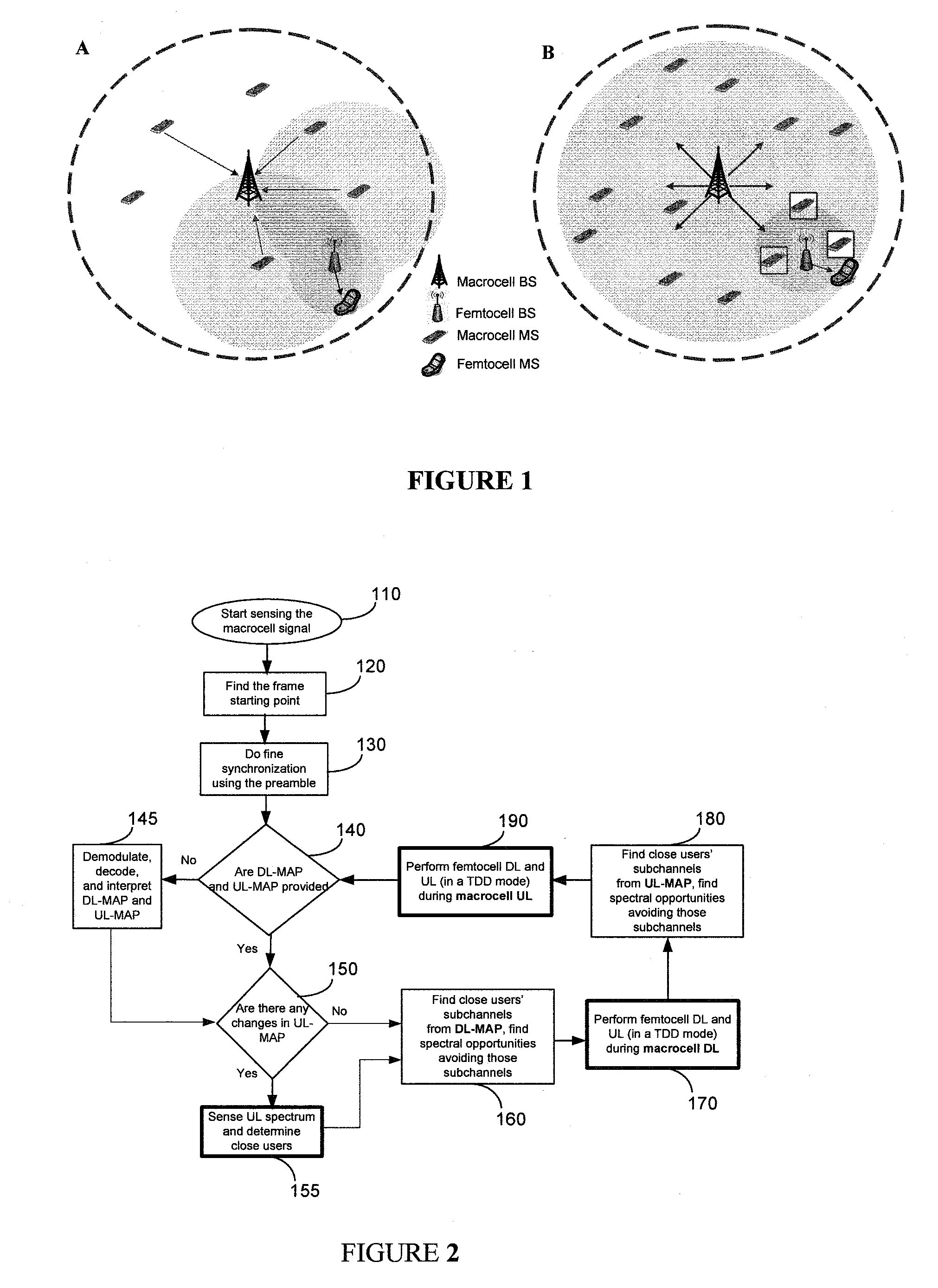
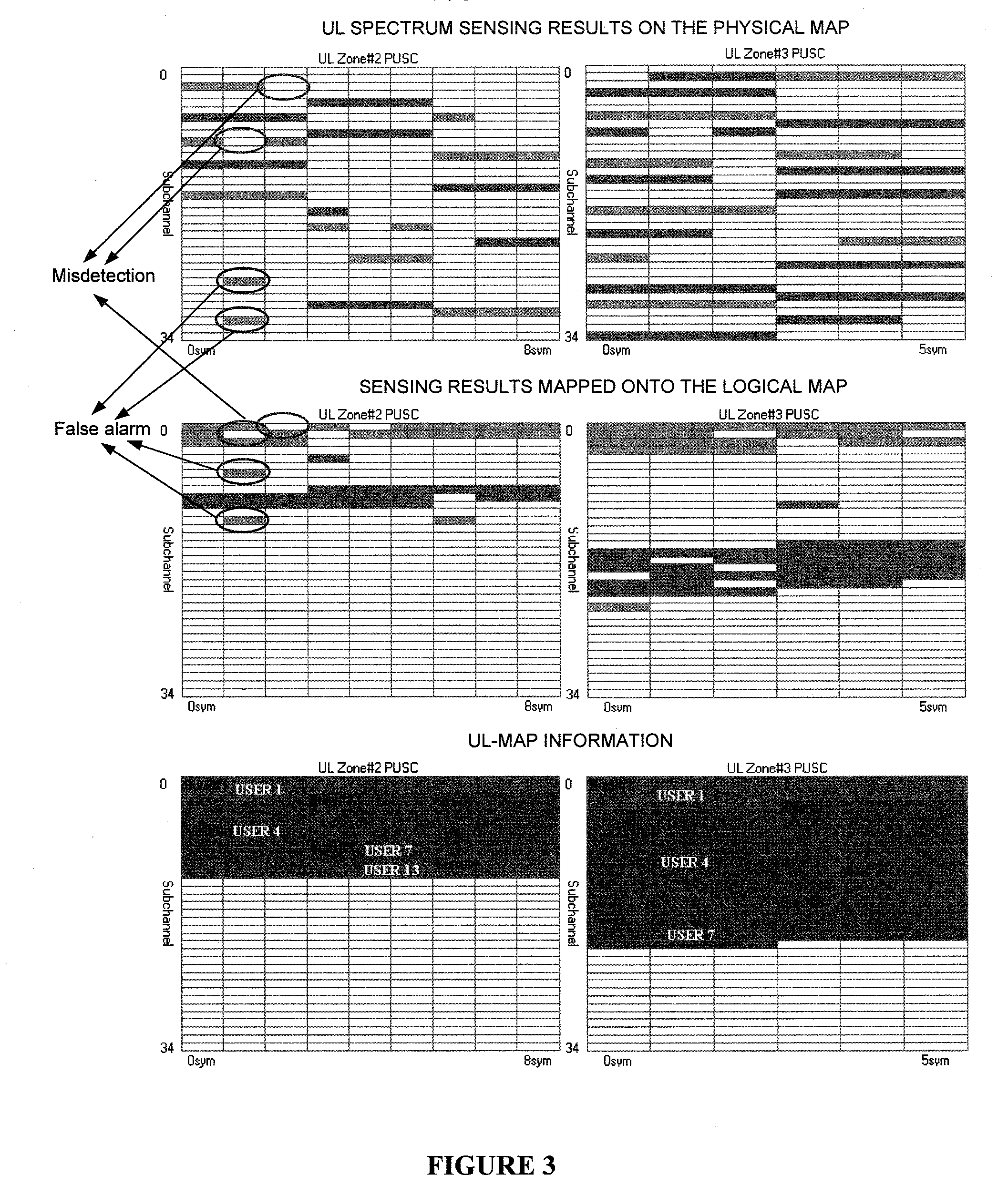
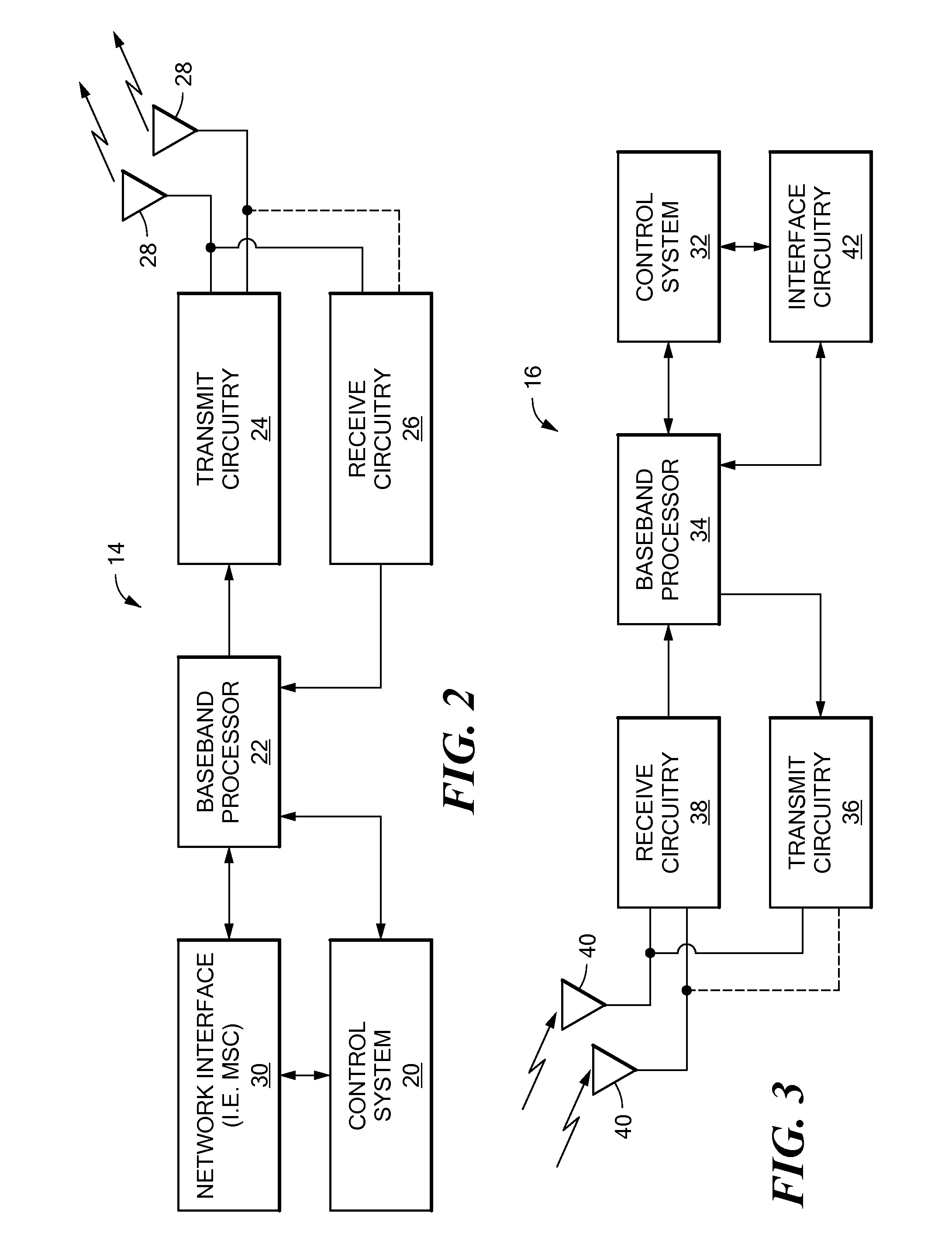
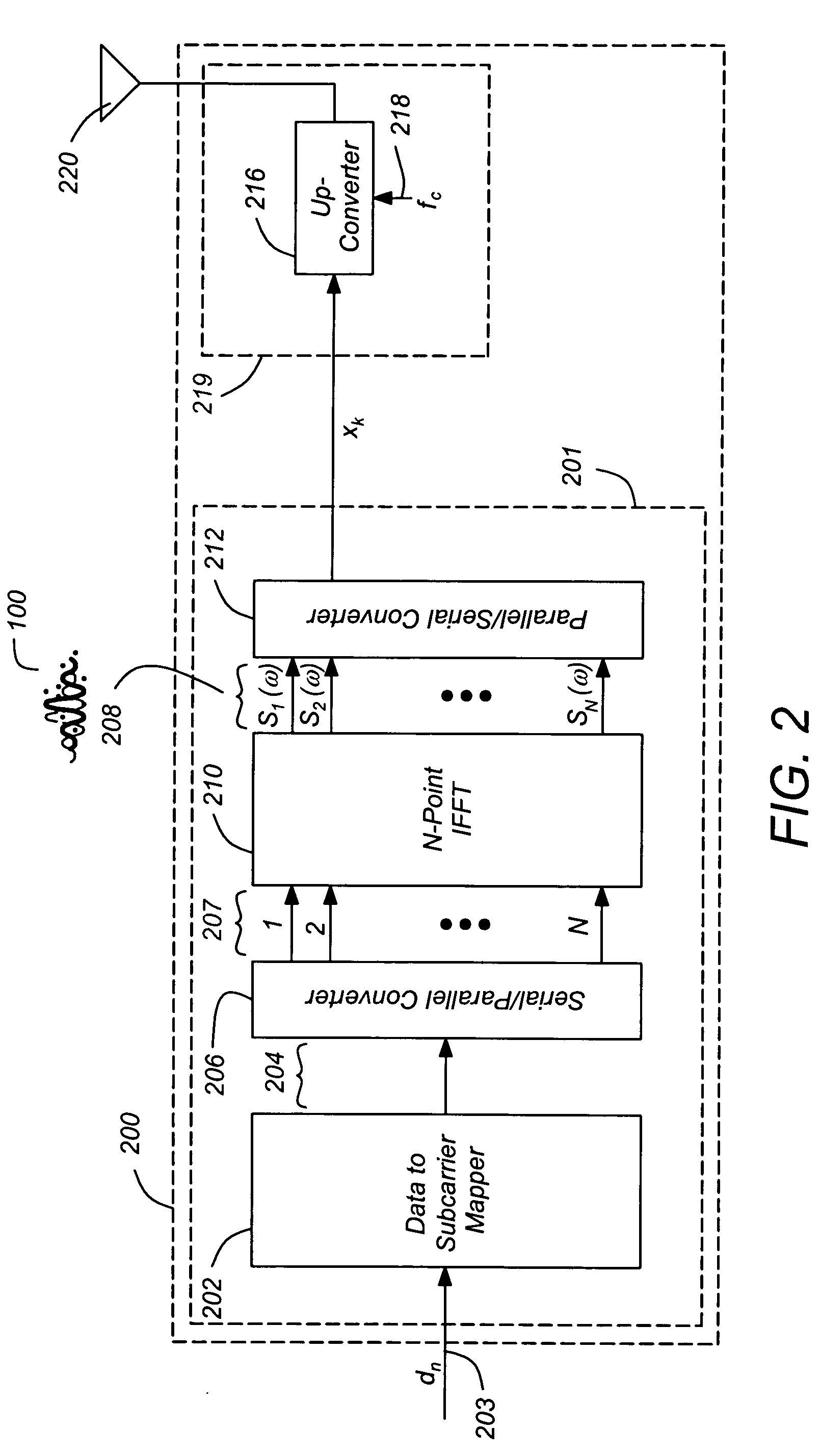
OFDMA-based co-channel femtocell
ActiveUS20090221295A1Improve efficiencyExpand coverageTransmission path divisionNetwork topologiesFrequency spectrumCarrier signal
A femtocell increases efficiency and coverage of a macrocellular network operating in a co-channel manner within the macrocell spectrum by selecting subcarriers for its mobile station using both the subcarrier allocation map received from the macrocell and a spectrum sensing operation. Interference is avoided by selecting only subcarriers not allocated by the macrocell and subcarriers allocated to users not nearby to the femtocell. Interference is eliminated from the received signals using co-channel interference avoidance techniques. Selection of subcarriers for femtocell use may take into consideration inter-carrier interference detected.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
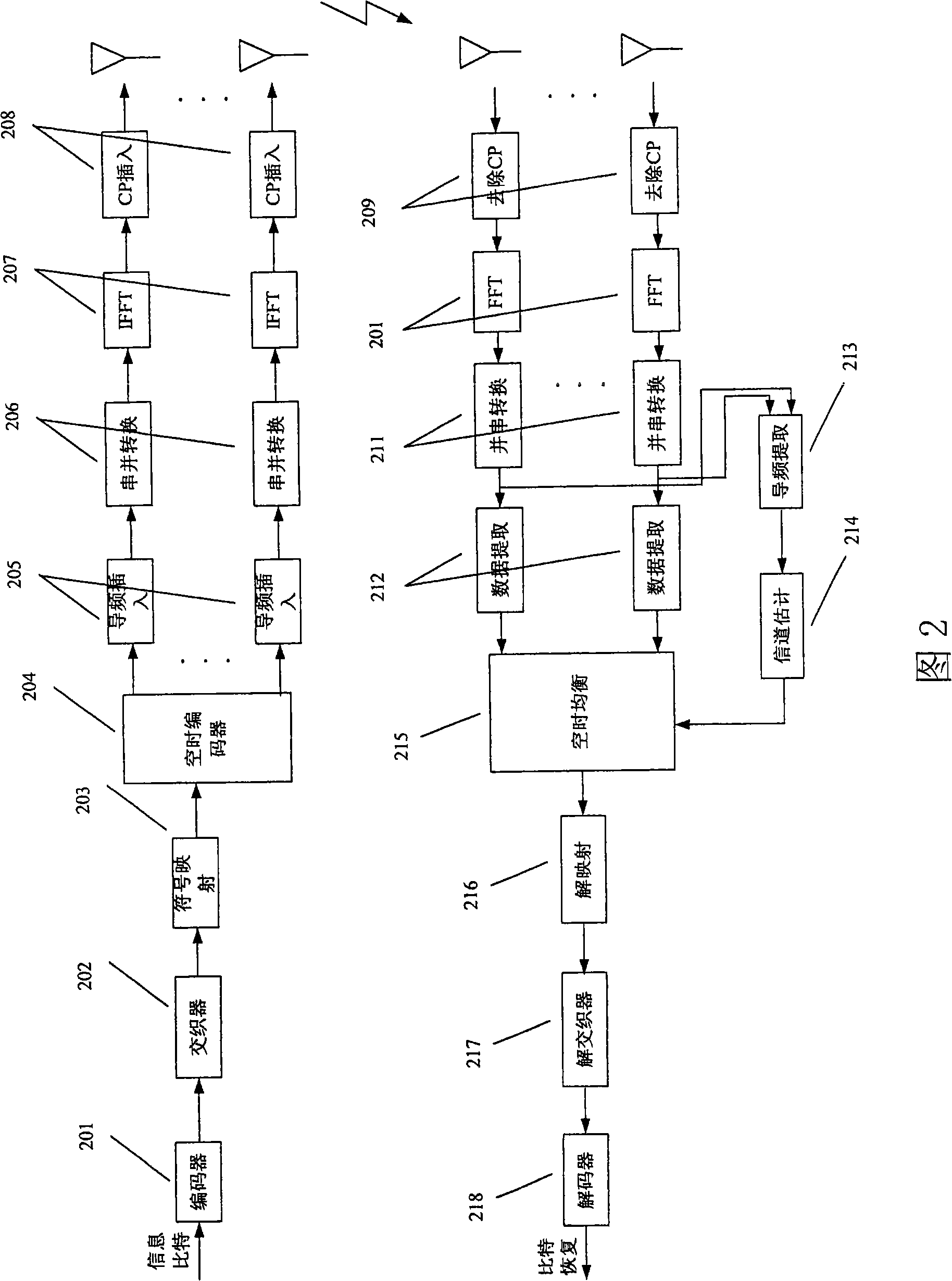
Method and system for reducing inter carrier interference for OFDM
According to one embodiment, a method of encoding a plurality of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) signals is disclosed. The method includes: modulating the plurality of OFDM signals according to a modulation scheme, wherein the modulated OFDM signals are mapped to a first axis and a second axis perpendicular to the first axis, and correspond to a first constellation having a plurality of points symmetric with respect to the first axis and the second axis; and differentially encoding the plurality of OFDM signals according to a second constellation plurality of points defined by shifting a position of one of the first constellation plurality of points toward an origin located at an intersection of the first axis and the second axis.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
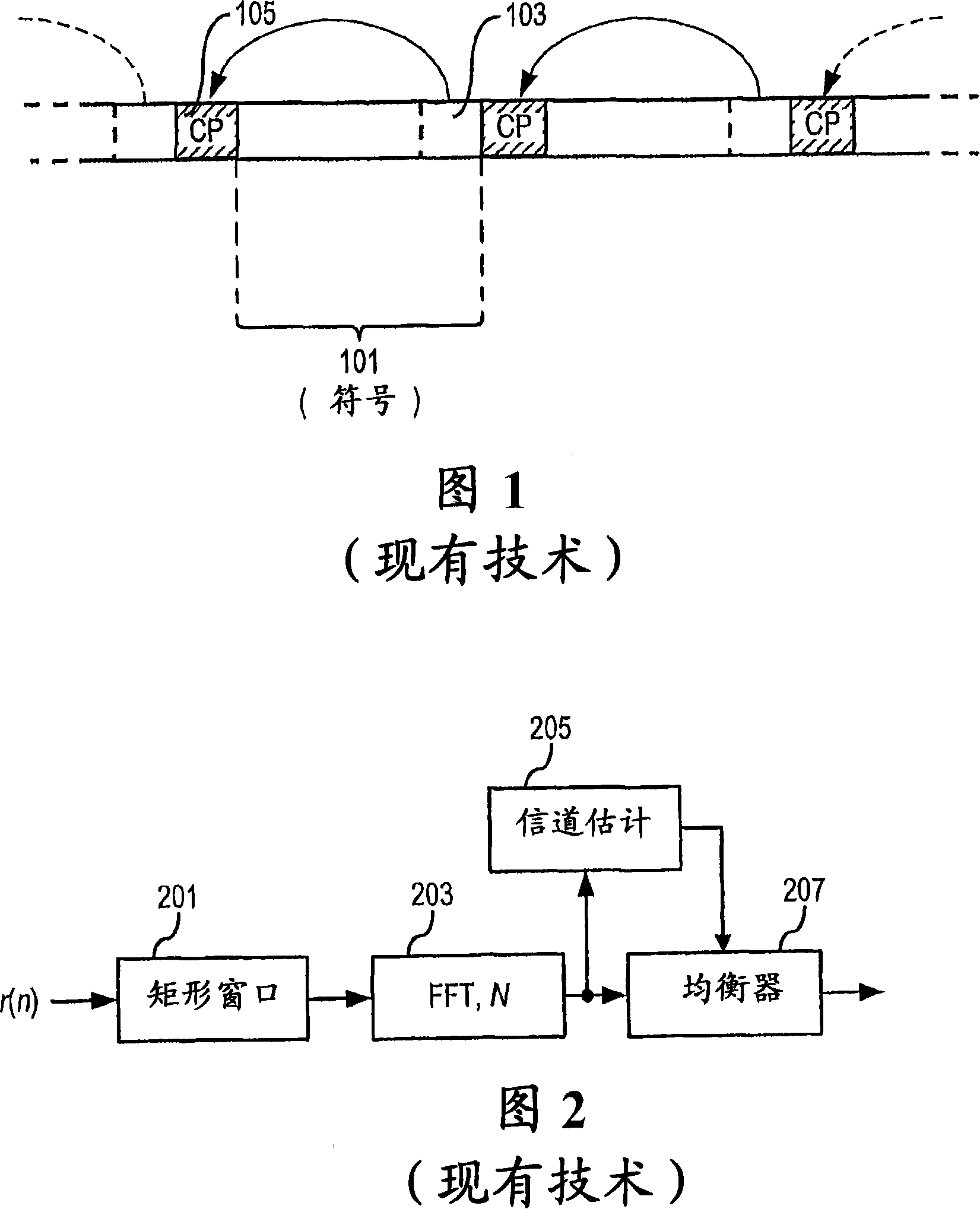
Channel estimation method and system for inter-carrier interference-limited wireless communication network
A method and system for wireless communication channel estimation. A frequency offset hypothesis is determined. An interchannel interference (“ICI”) matrix based on the frequency offset hypothesis is generated. Pilot channel estimates based on the ICI matrix are obtained. A correlation error of the pilot channel estimates to the frequency offset hypothesis is calculated. The correlation error is compared with a predetermined correlation error value. The frequency offset hypothesis is updated and the aforementioned steps are iteratively repeated if the correlation error is greater than the predetermined correlation error value. The pilot channel estimates are used to estimate the wireless communication channel.
Owner:APPLE INC
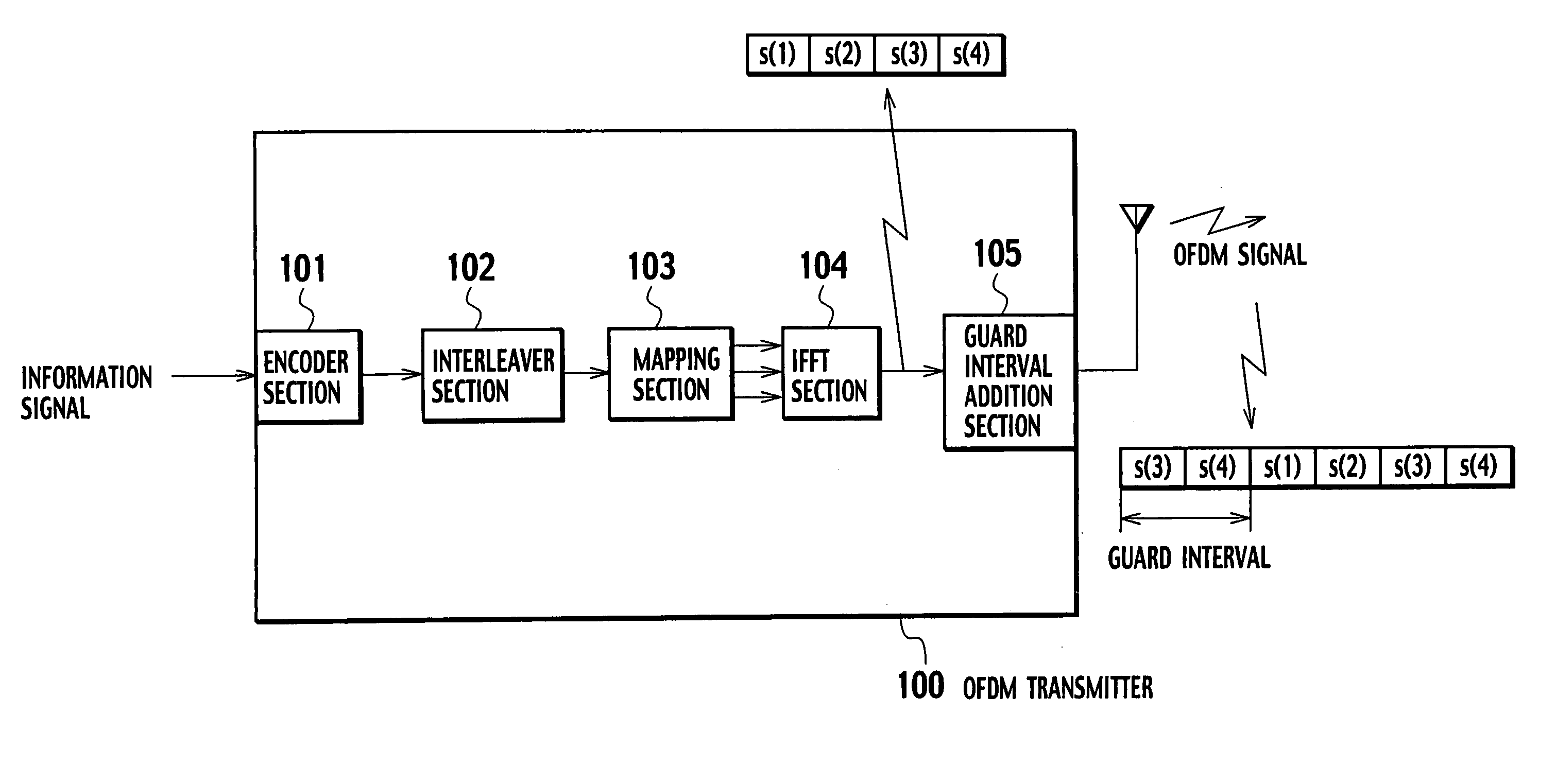
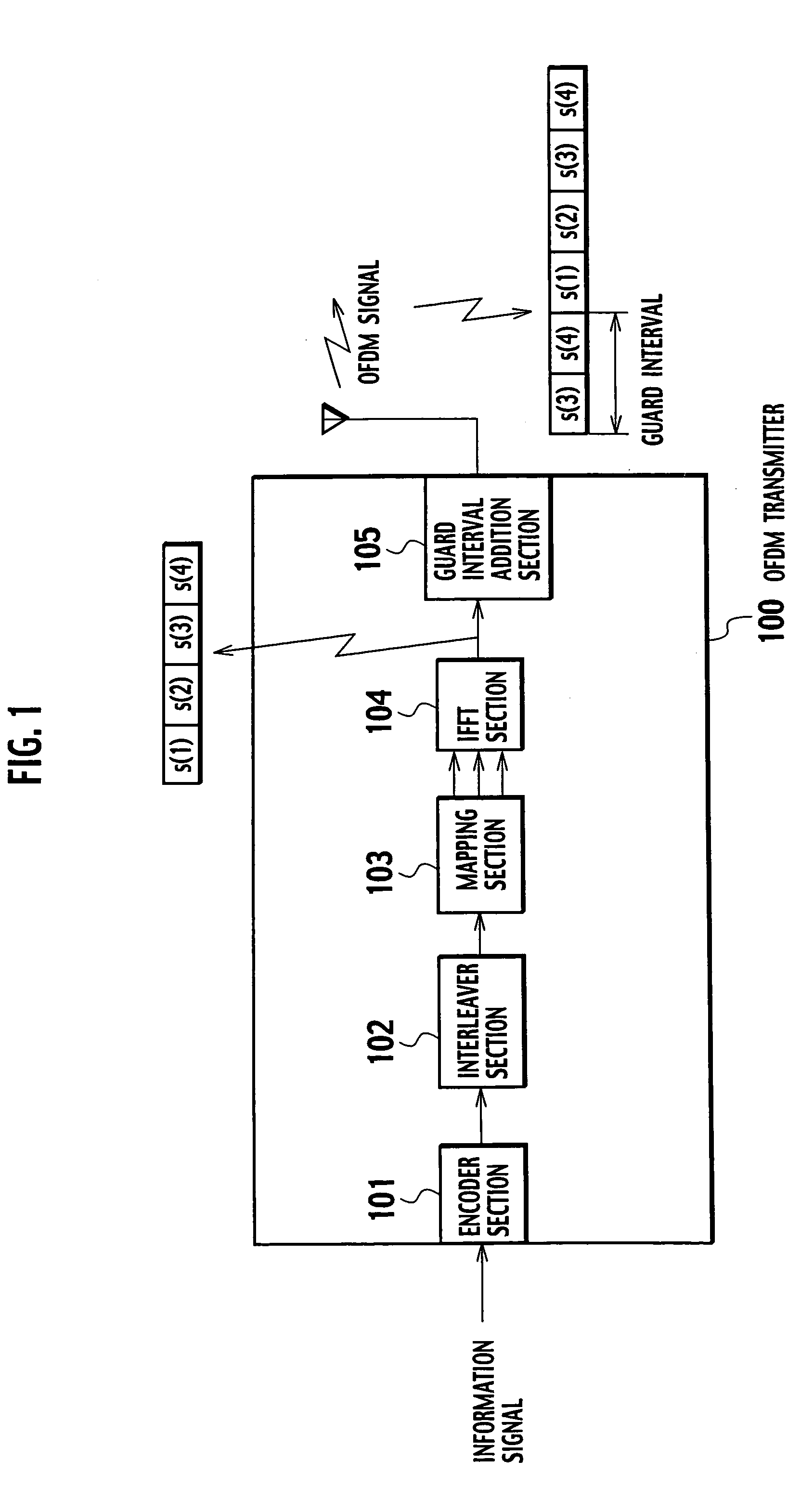
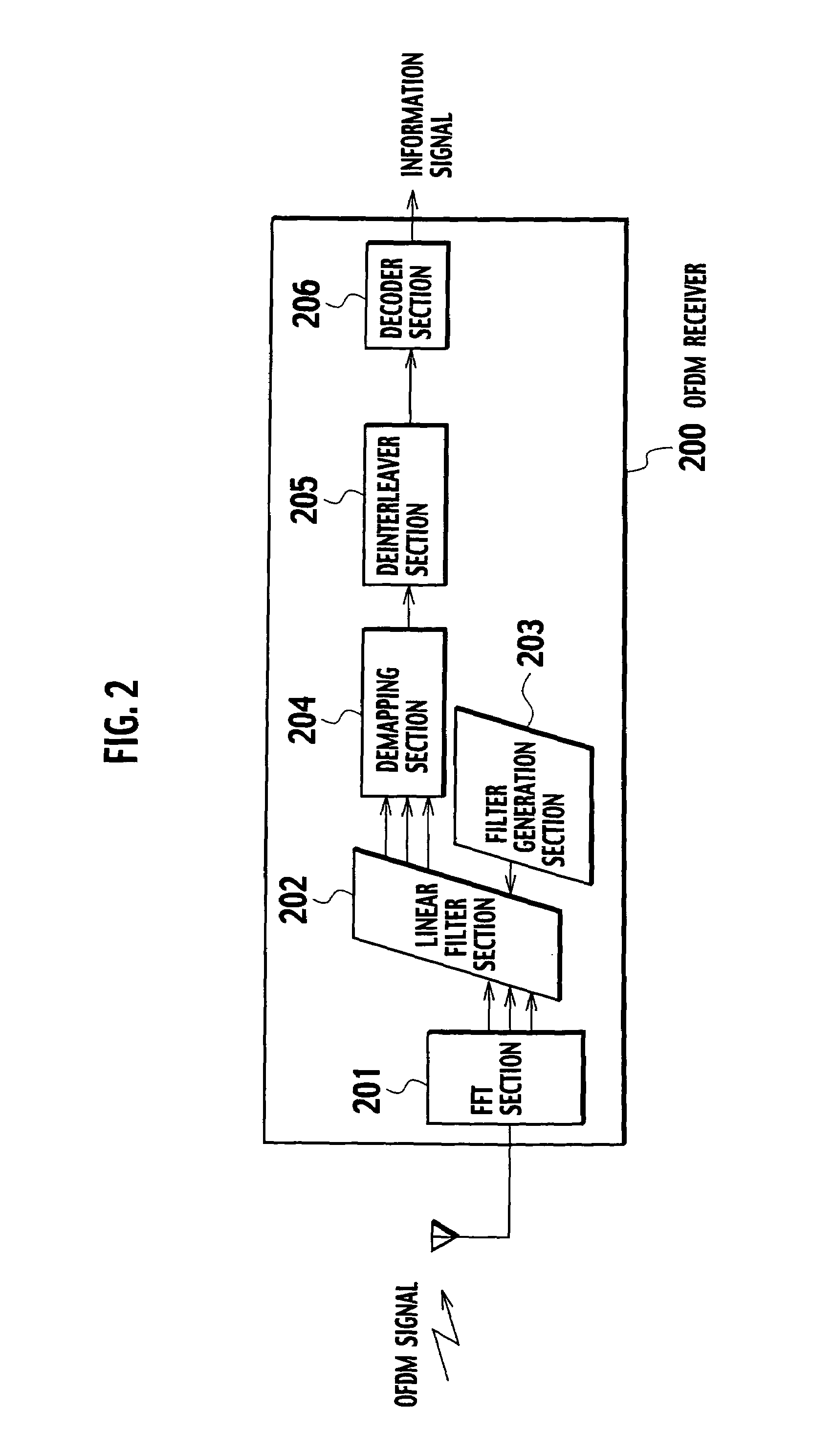
OFDM receiver
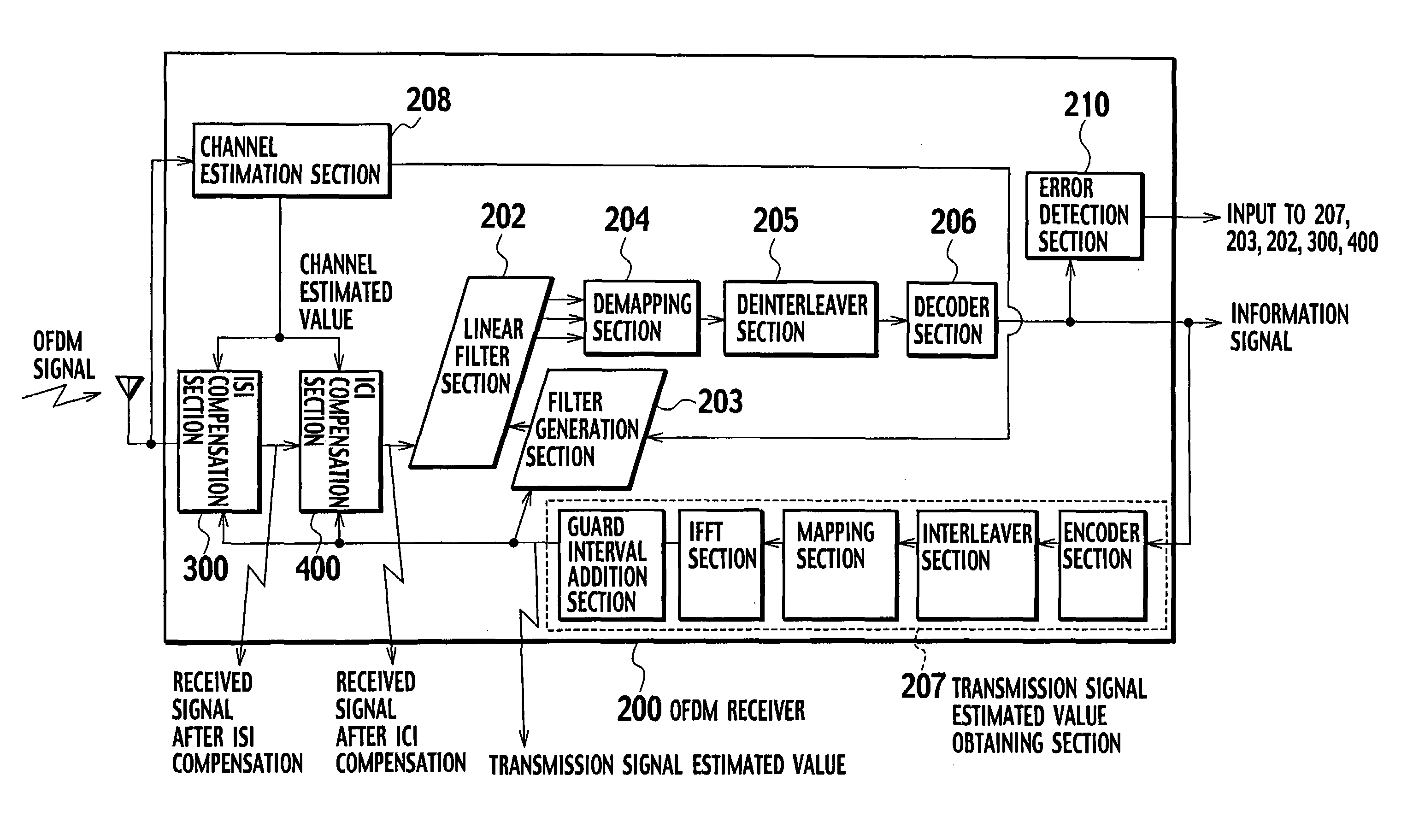
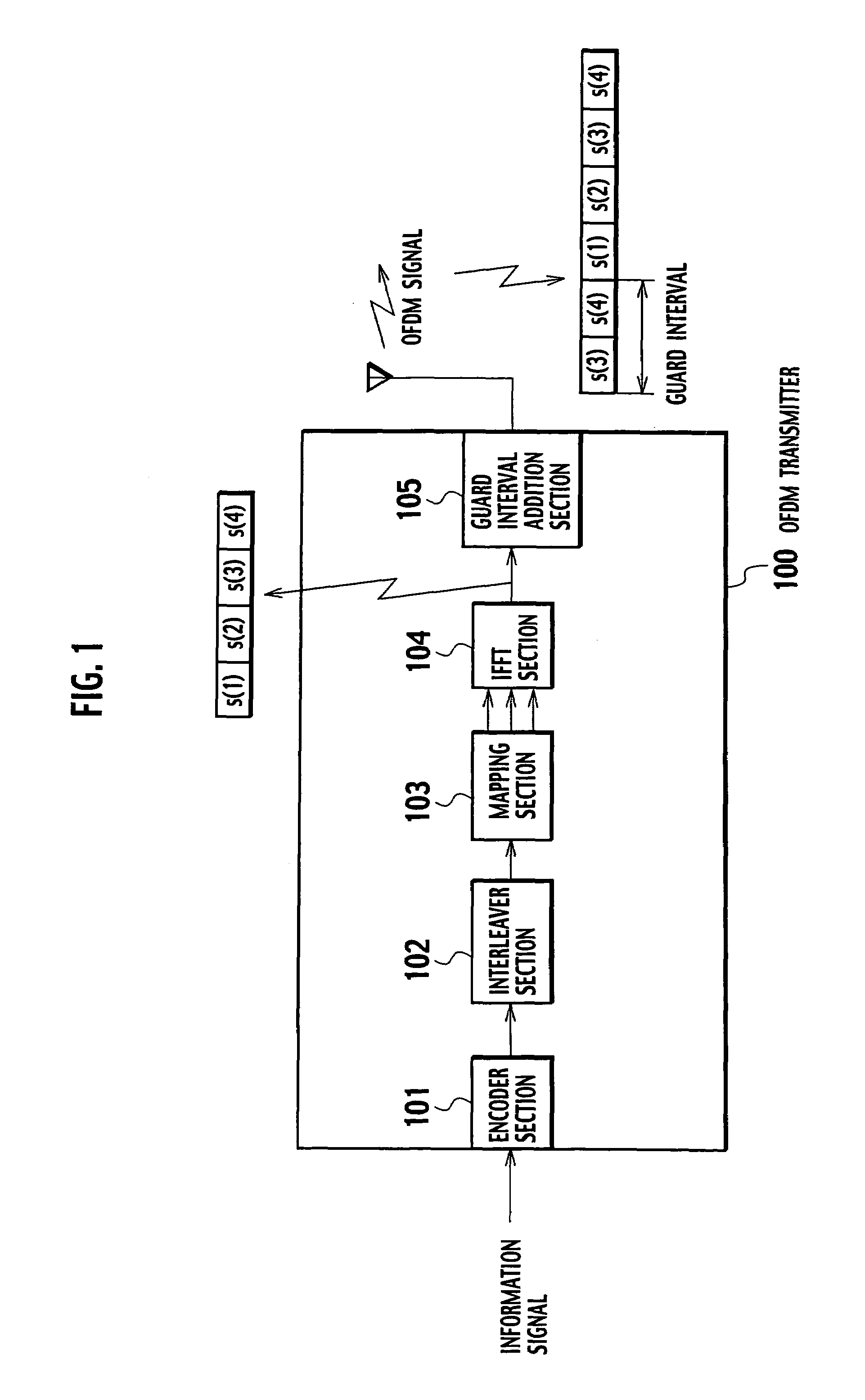
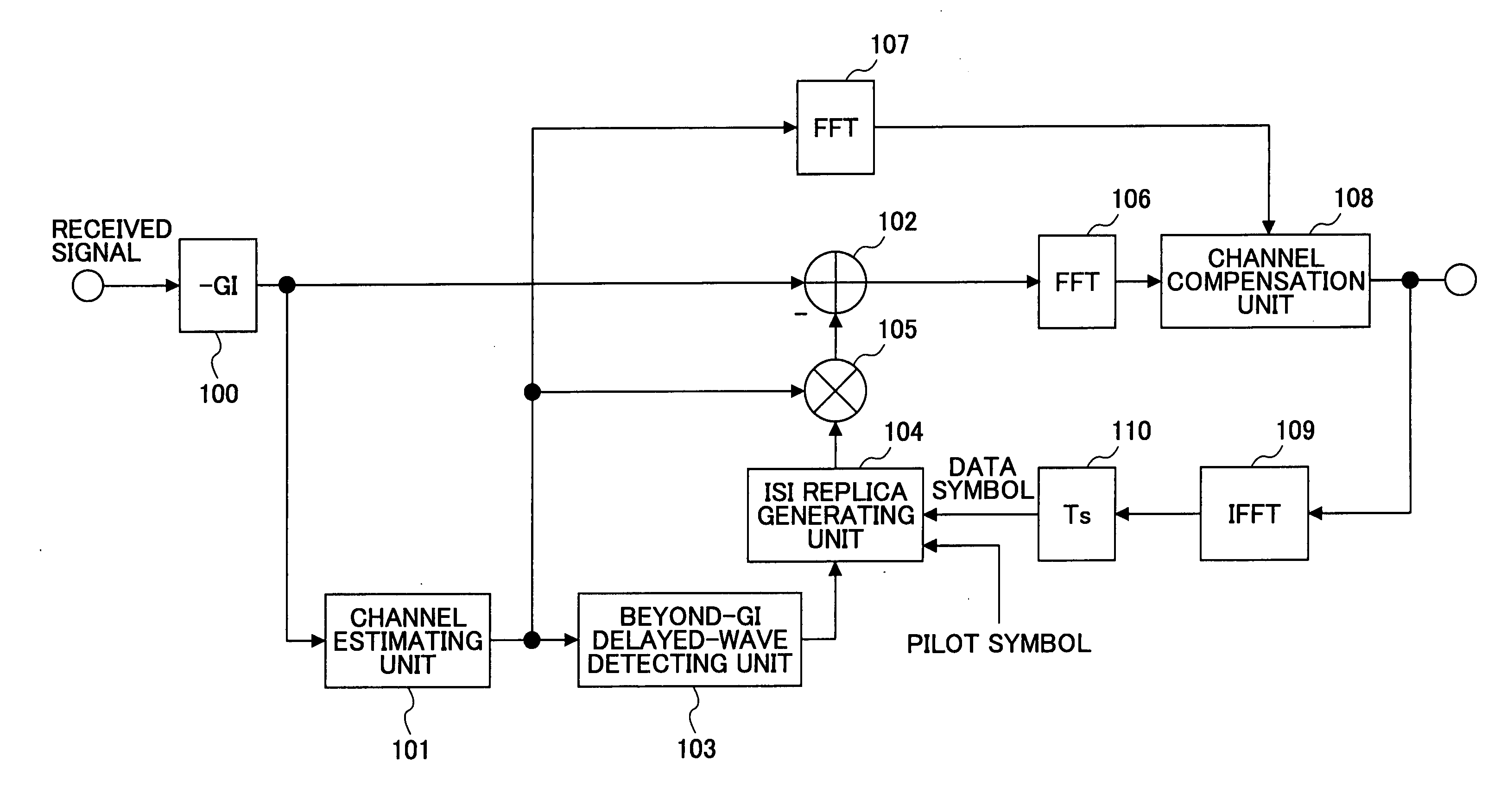
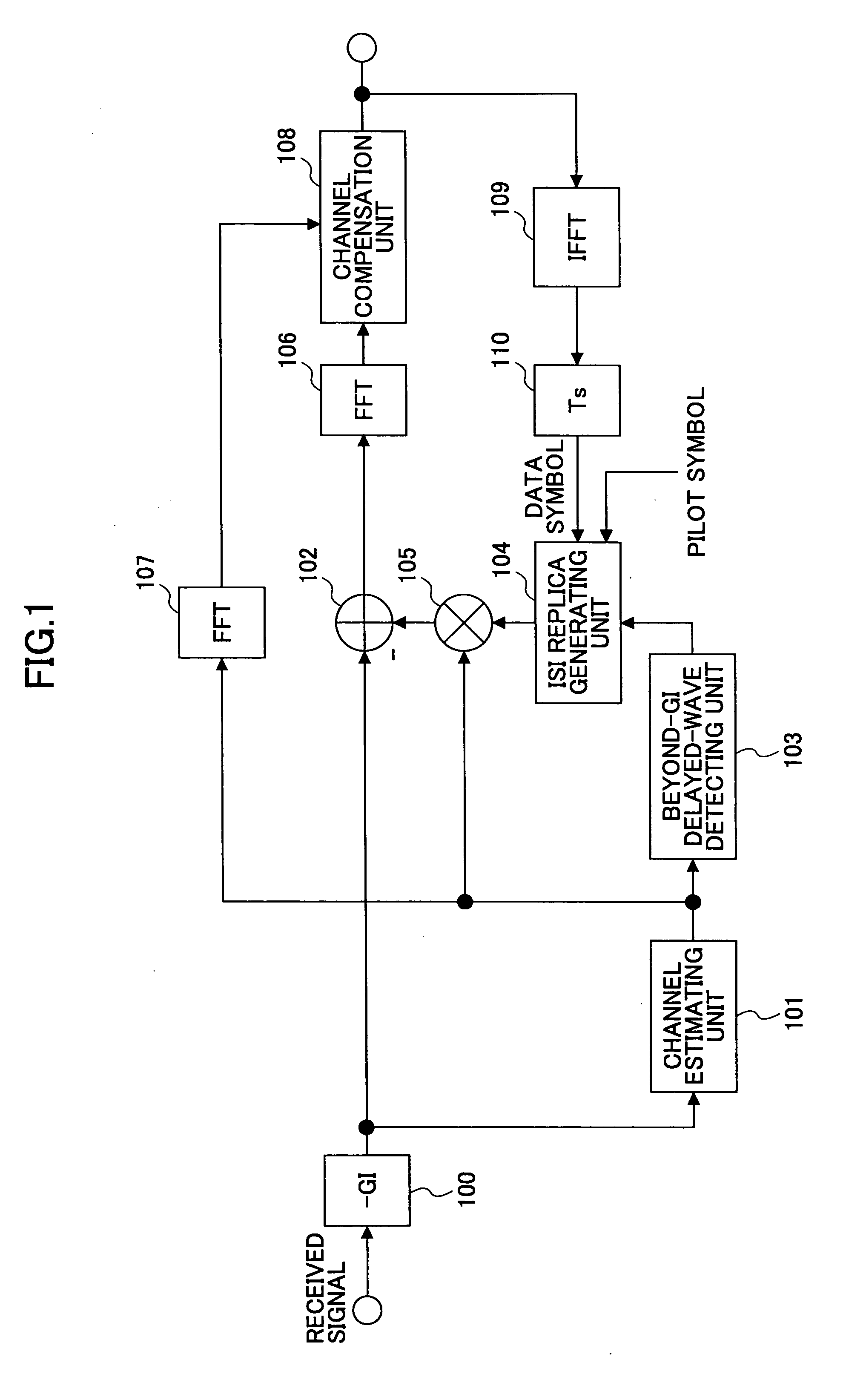
InactiveUS20050129136A1Reduce the amount of processingSpatial transmit diversityLine-faulsts/interference reductionOfdm transmitterMulti path
An OFDM receiver receives an OFDM signal transmitted from an OFDM transmitter by using a sub-carrier. The OFDM receiver includes a channel estimator configured to obtain a channel estimated value of each multi-path based on OFDM signals received through a plurality of multi-paths; a transmission signal estimated value calculator configured to calculate a transmission signal estimated value as an estimated value of the OFDM signal; and an inter-carrier interference compensator configured to extract a multi-path not becoming a form to contain a signal component only of a target symbol in an FFT window based on the transmission signal estimated value and the channel estimated value of each multi-path, and to compensate for inter-carrier interference in the OFDM signal based on signal components corresponding to all sub-carriers of the multi-paths.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Synchronization of a pilot assisted channel estimation orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system
ActiveUS7023928B2Minimize estimated channel errorSensitive to frequencyBaseband system detailsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase differenceCarrier signal
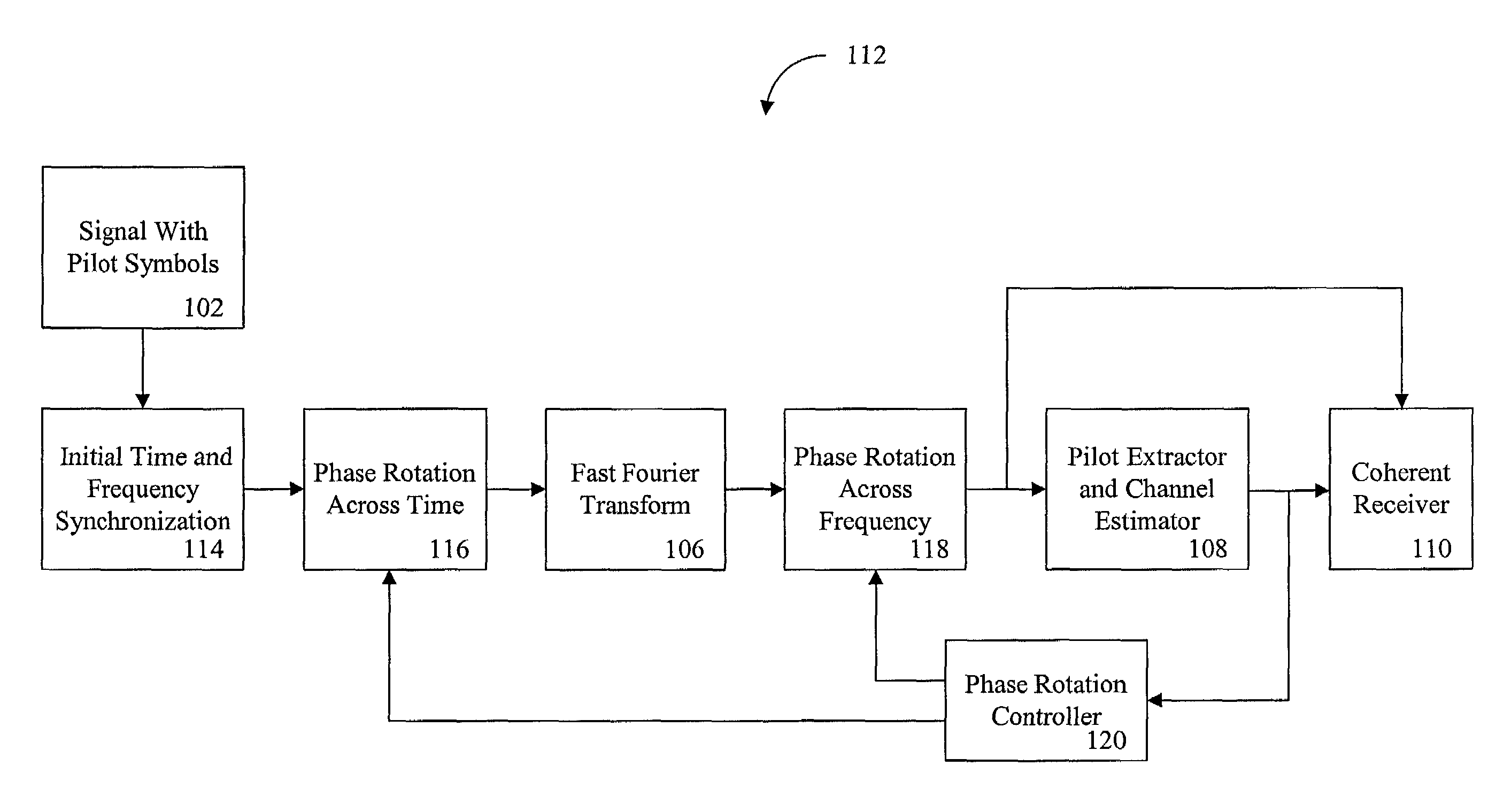
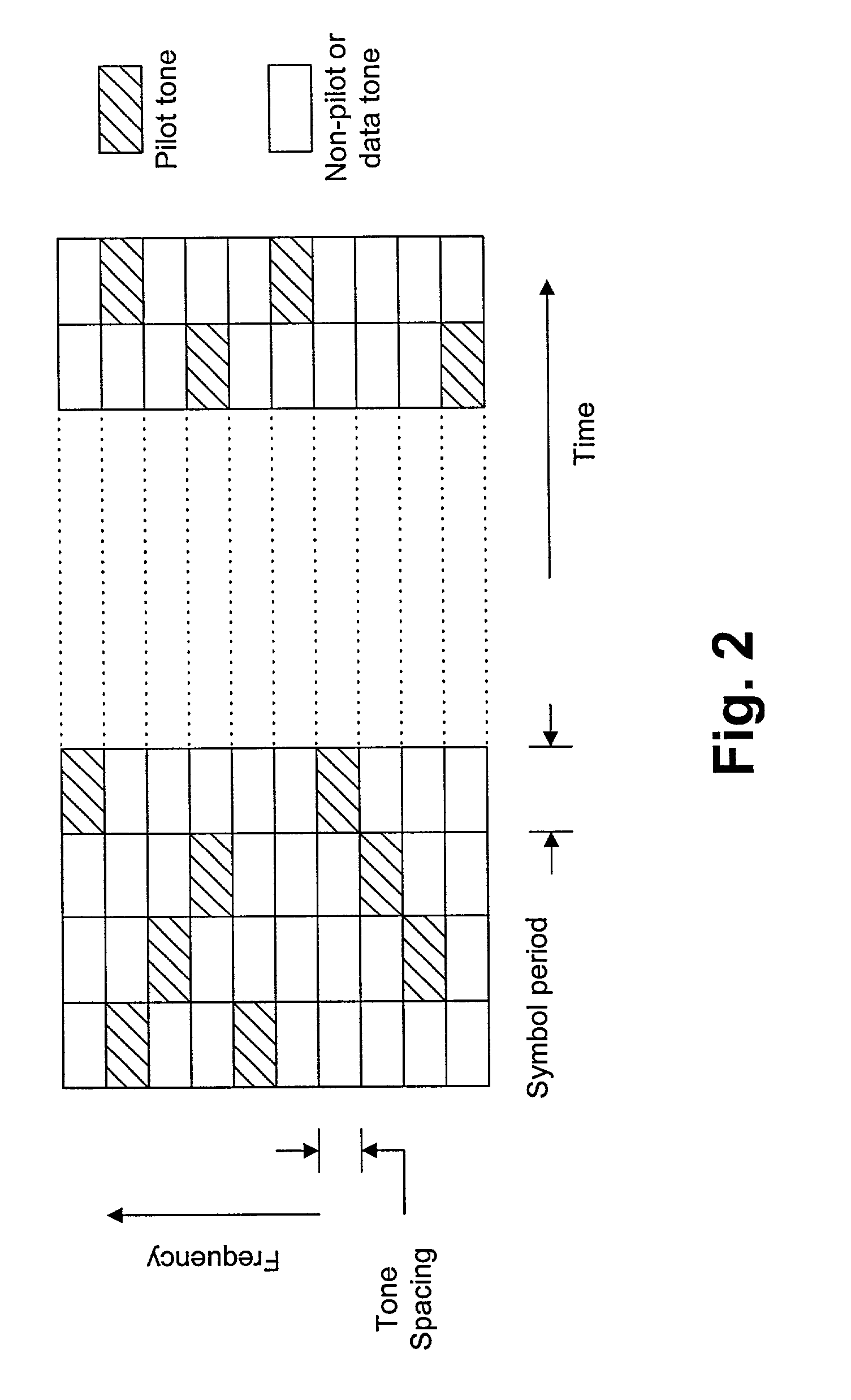
A synchronization of a pilot assisted channel estimation orthogonal frequency division multiplexing can be achieved by receiving a signal containing pilot symbols, providing an initial time and frequency synchronization to the signal, phase rotating the signal across time, transforming the signal with a fast Fourier transformation, phase rotating the signal across frequency, extracting the pilot symbols and generating a channel estimator. The phase rotating across time and the phase rotating across frequency are controlled by a phase rotation controller in accordance with the channel estimator. The initial time and frequency synchronization synchronizes the signal such that intercarrier interference effects and intersymbol interference effects are negligible. The signal may include plural carrier frequencies each having an arrival timing offset and a frequency offset. The signal may also include delay spread or Doppler spread. The phase rotation controller measures a phase different between the channel estimator at times k and k+Δk, where k is time and Δk is a symbol period and measures a phase difference between the channel estimator at frequencies n and n+Δn, where n is tone frequency and Δn is a frequency spacing between adjacent tones.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Method and device for generating pilot frequency sequence
ActiveCN102202027ALower estimated impactHigh precisionTransmission path divisionMulti-frequency code systemsMultiplexingCarrier signal
The invention discloses a method for generating a pilot frequency sequence. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting OCCs (Orthogonal Cover Code) from an OCC set according to different rules in each code division and frequency division and / or time division hybrid multiplexing demodulation reference signal (DMRS) port by using different code division multiplexing groups and / or generating scrambling sequences of the DMRS according to different rules by using different code division multiplexing groups; and multiplying the selected OCCs with the scrambling sequences to generate a final pilot frequency sequence of each DMRS port. The invention further discloses a device for generating a pilot frequency sequence. By adopting the method and the device, corresponding layers among different code division multiplexing port groups can be lowered, the influence of inter-carrier interference caused by the problems of Doppler frequency shift and timing error on channel estimation is reduced, and the channel estimation accuracy is increased.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Improving receiver performance in a communication network
ActiveUS20100091920A1Improving error correction capability of systemError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemCarrier signal
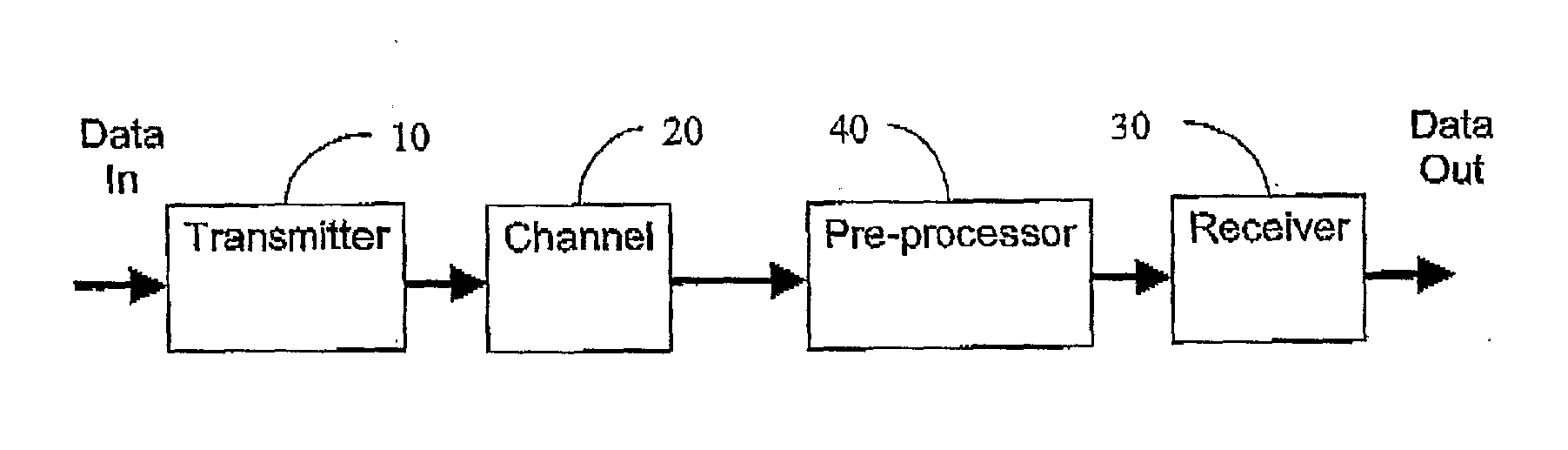
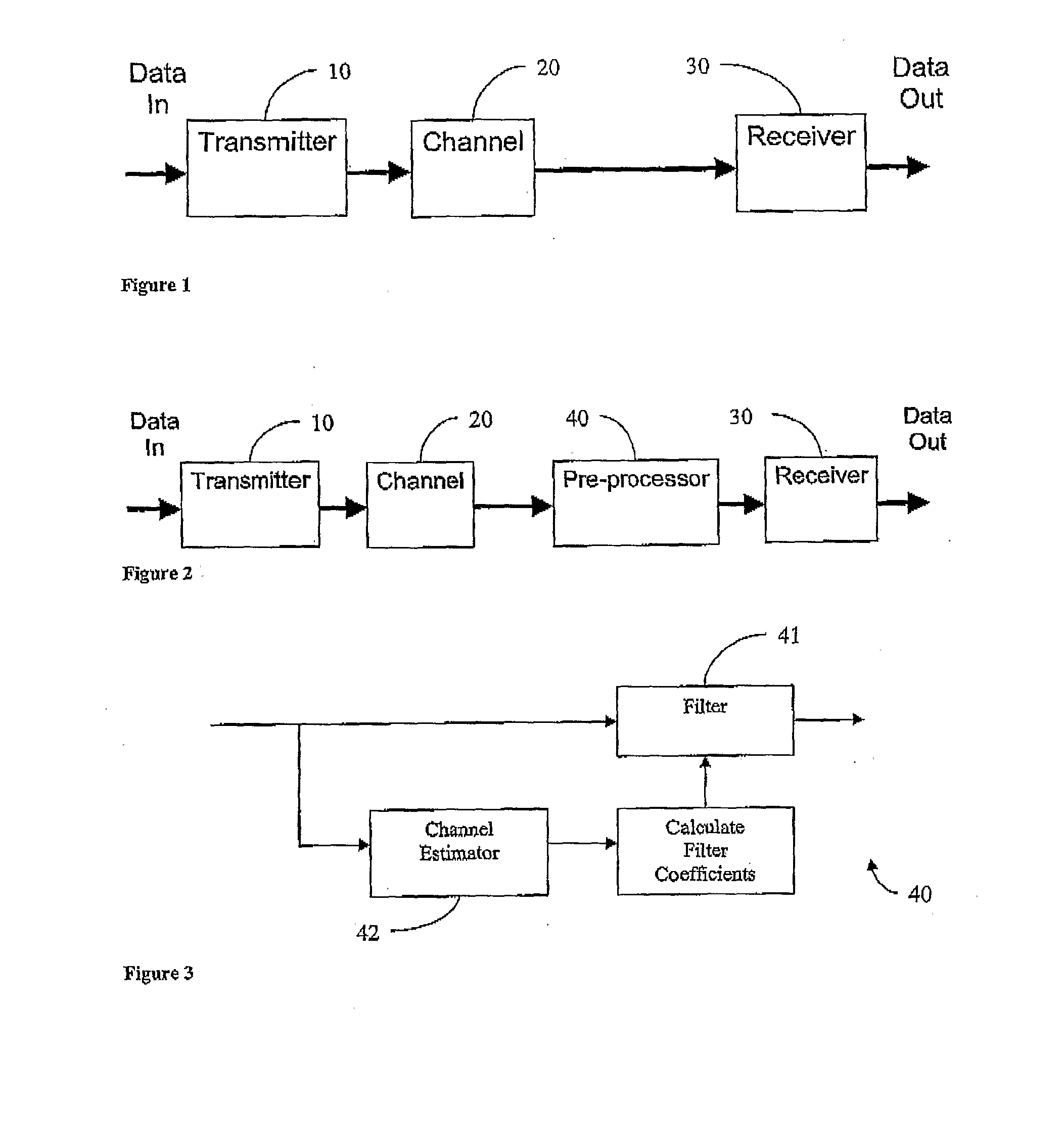
Methods and apparatus are described for improving receiver performance in a multicarrier communication network in which an encoded symbol (250) is transmitted over a transmission channel (20) in the communications system. A model of the transmission channel (20) is estimated (718, 760), said model characterising an effect of intercarrier interference on at least one carrier in the multicarrier system. The received symbol (250) is decoded (720, 762) using the estimated model to remove a predicted effect of intercarrier interference. A pre-processor (40) is also described for operation in conjunction with a communications receiver (30) in the network. The pre-processor (40) includes a channel estimator (42) operable to estimate at least one feature of the communication channel based on a received signal. The pre-processor (40) modifies the received signal dependent on the at least one estimated feature and provides the modified signal to the communications receiver (30).
Owner:COHDA WIRELESS
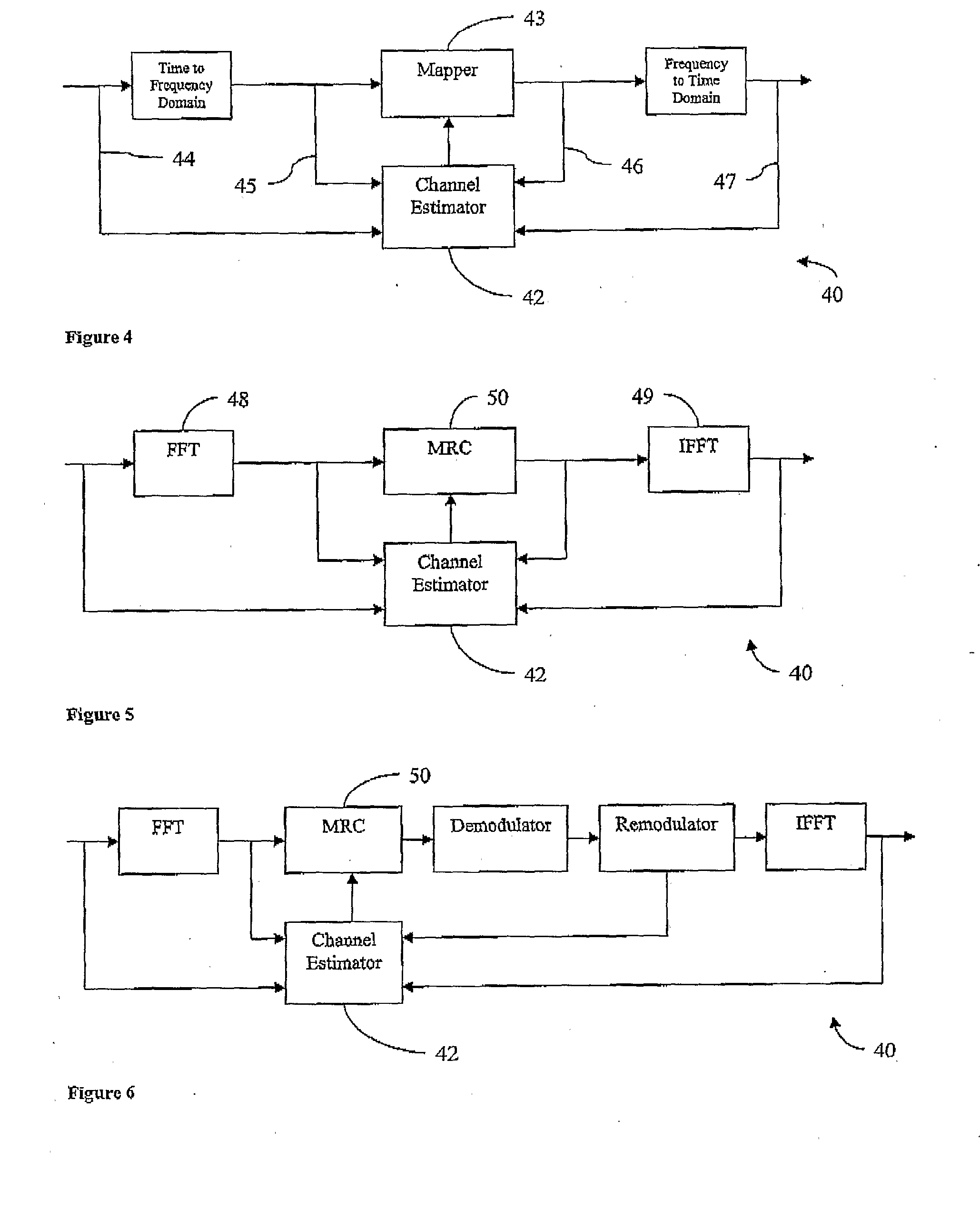
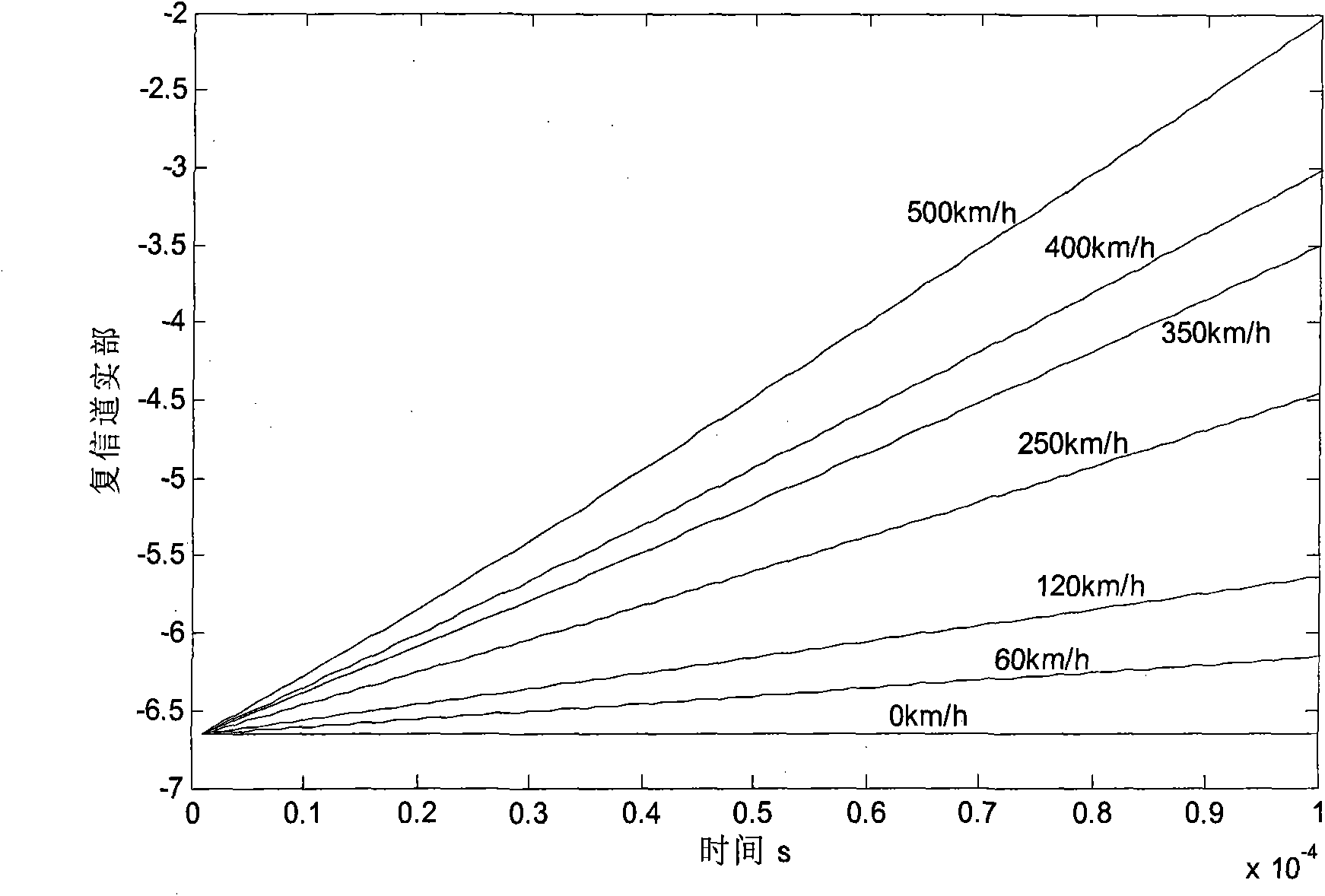
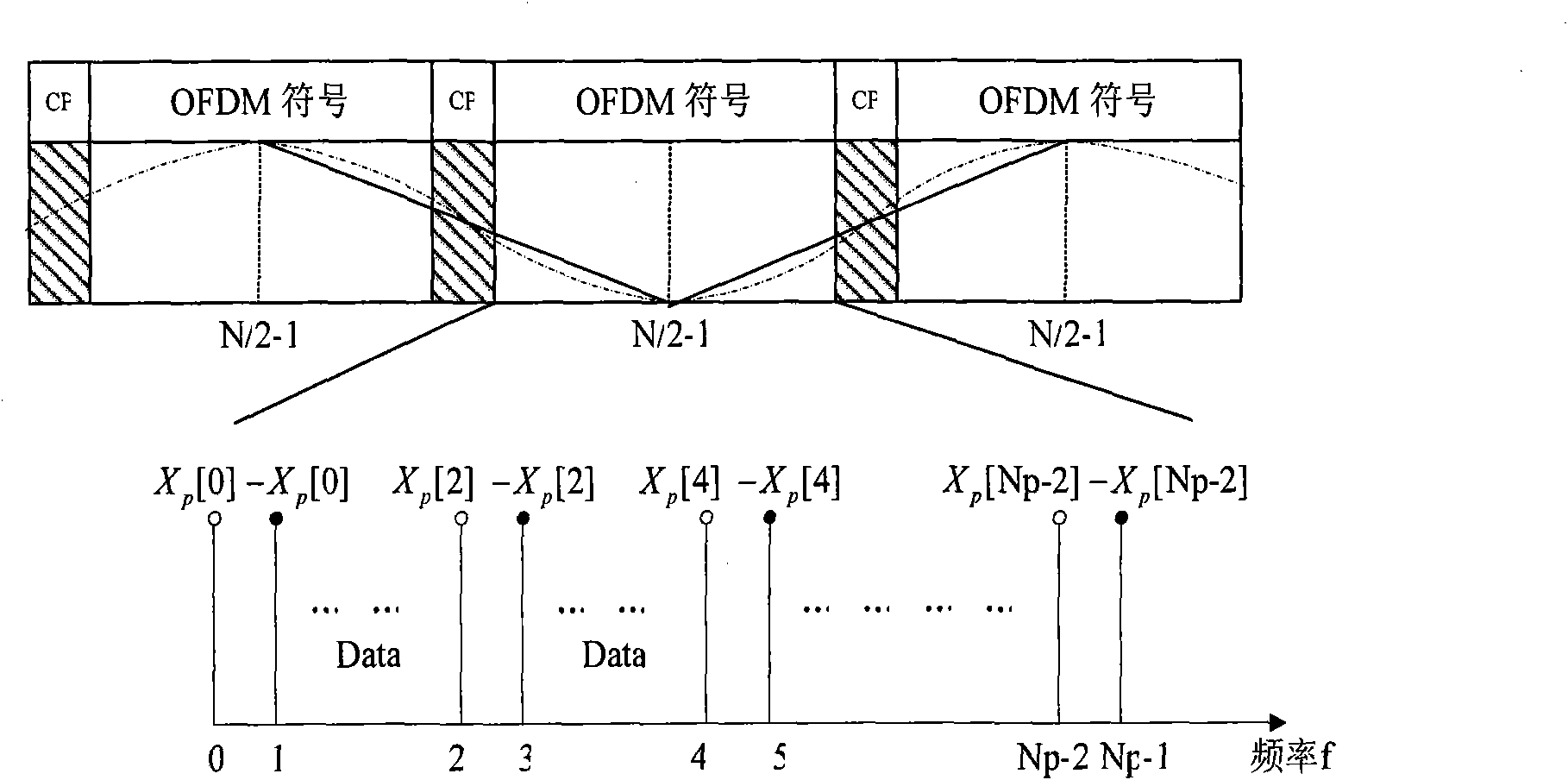
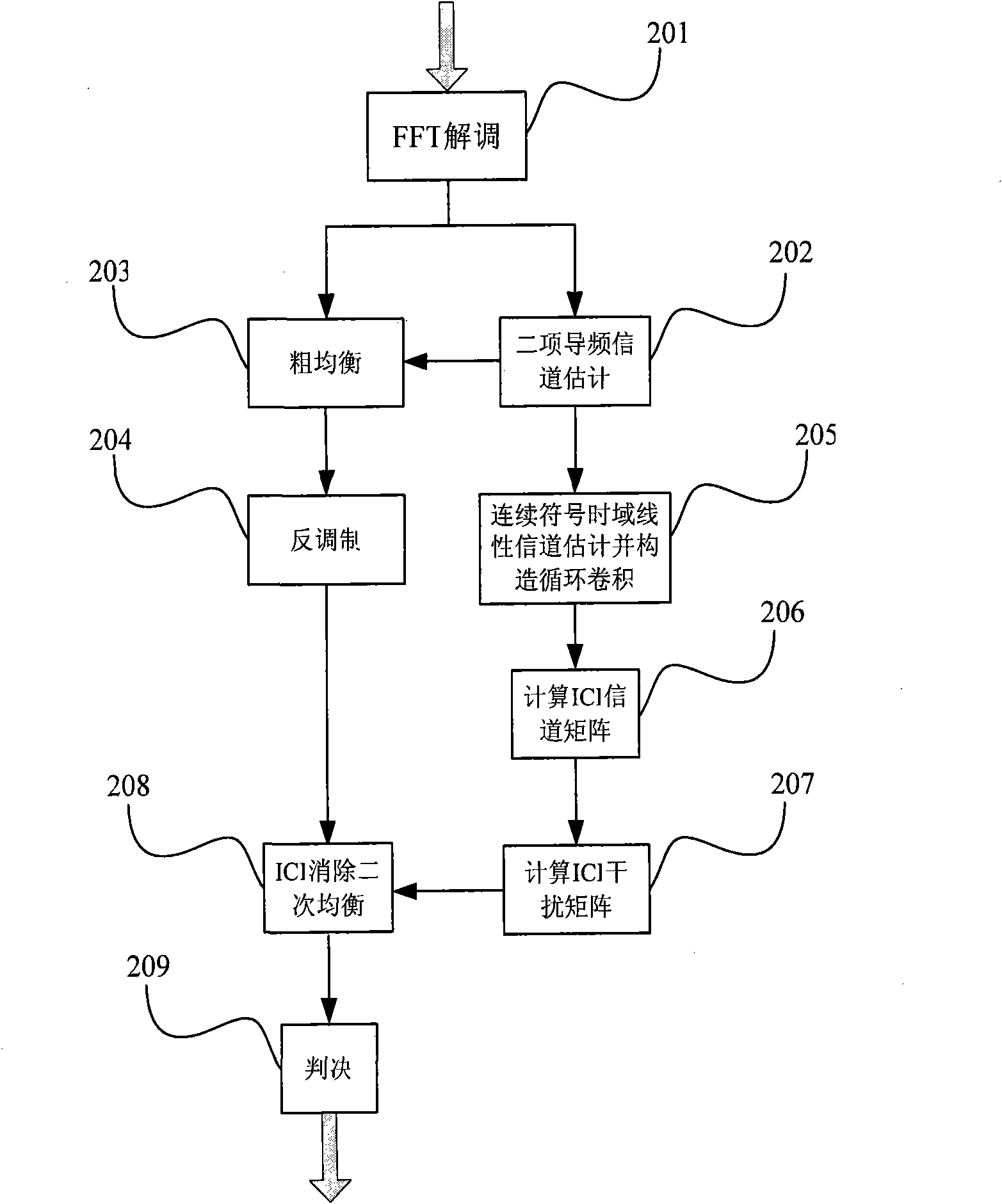
Novel OFDM signal channel estimation combination ICI self elimination method
InactiveCN101778069AImprove spectrum utilizationImprove performanceMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTime domainFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a novel OFDM signal channel estimation combination ICI self elimination method. The sending end pilot frequency design adopts a cluster type pilot frequency OFDM structure with the ICI estimation function. The receiving end is processed according to the following steps: a, converting proceeding FFT of an OFDM sign to a frequency domain, taking out the pilot frequency, and carrying out ICI elimination signal channel estimation; b, carrying out counter modulation after using the signal channel estimation in the first step for coarse balancing; c, using the signal channelestimation in the first step for time domain linear continuous sign signal channel estimation; d, calculating ICI signal channel matrixes through cyclic convolution by using a time domain pulse response structure in the third step, and obtaining ICI interference matrixes; and e, carrying out ICI elimination through combining counter modulation signals in the second step and ICI interference matrixes in the fourth step, and making the judgment after the secondary balancing. The invention solves the problem of influence on OFDM by interference between carrier waves under the condition of lineartime change signal channels, and improves the frequency spectrum utilization rate and the system performance.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
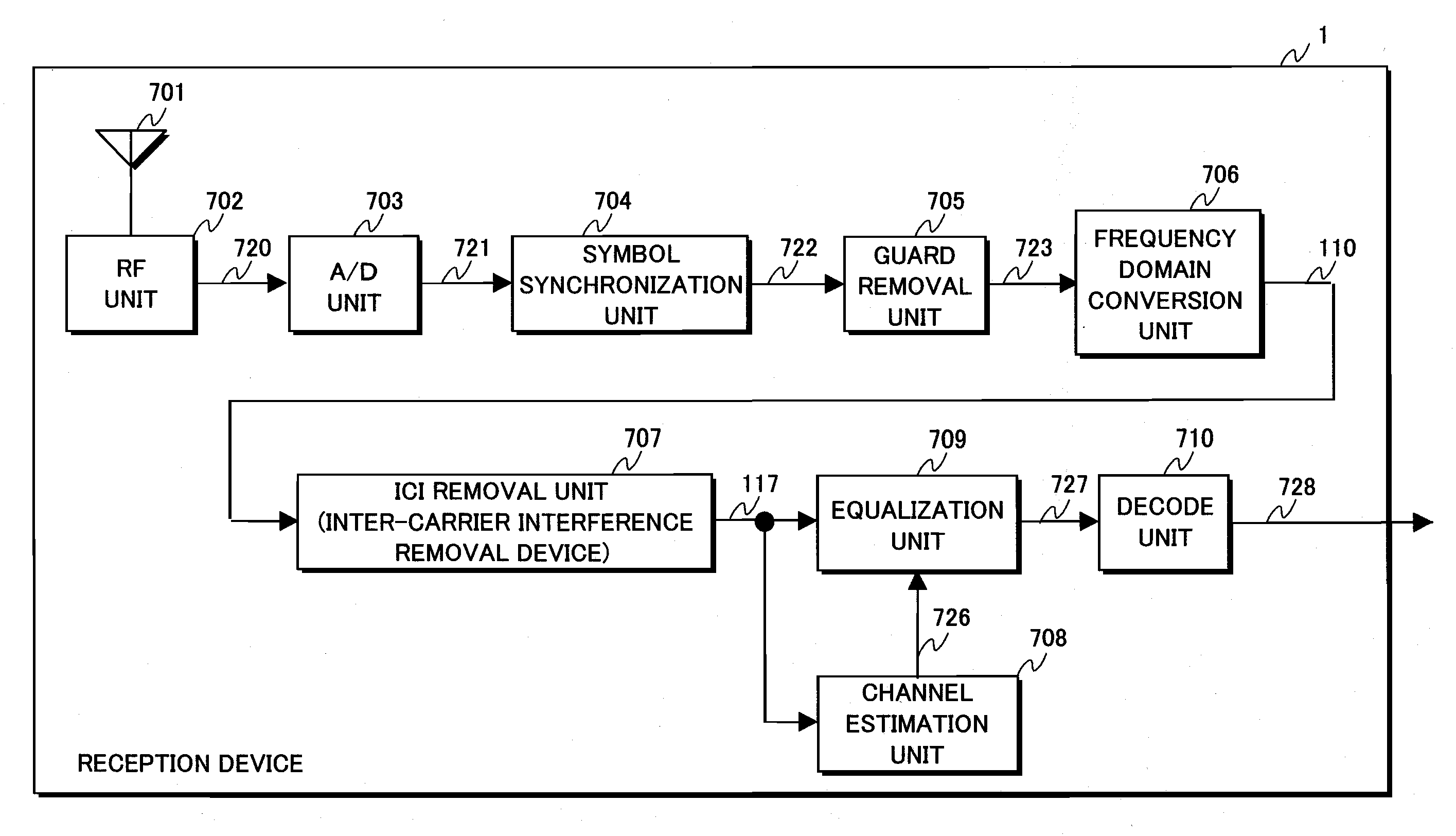
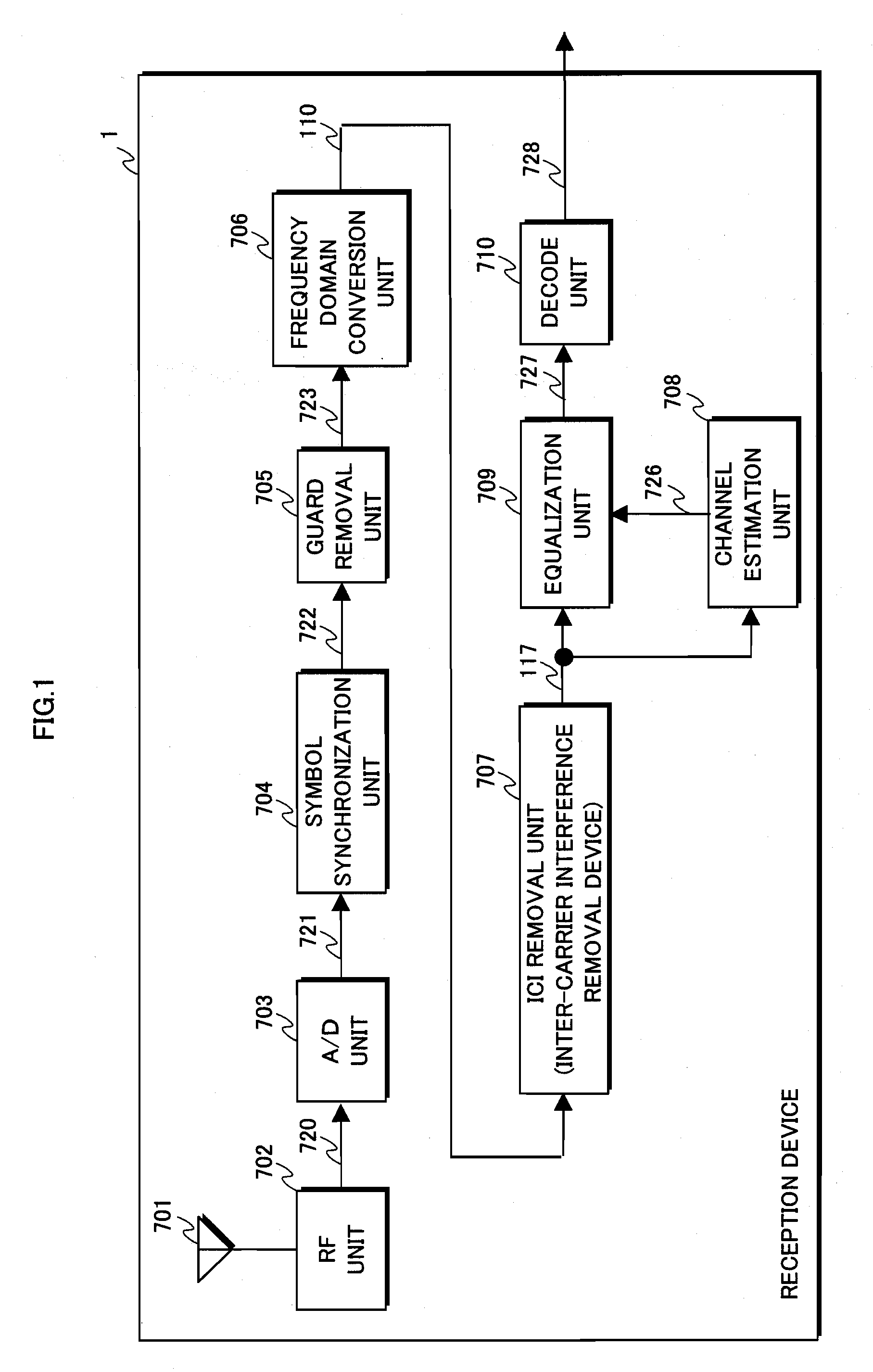
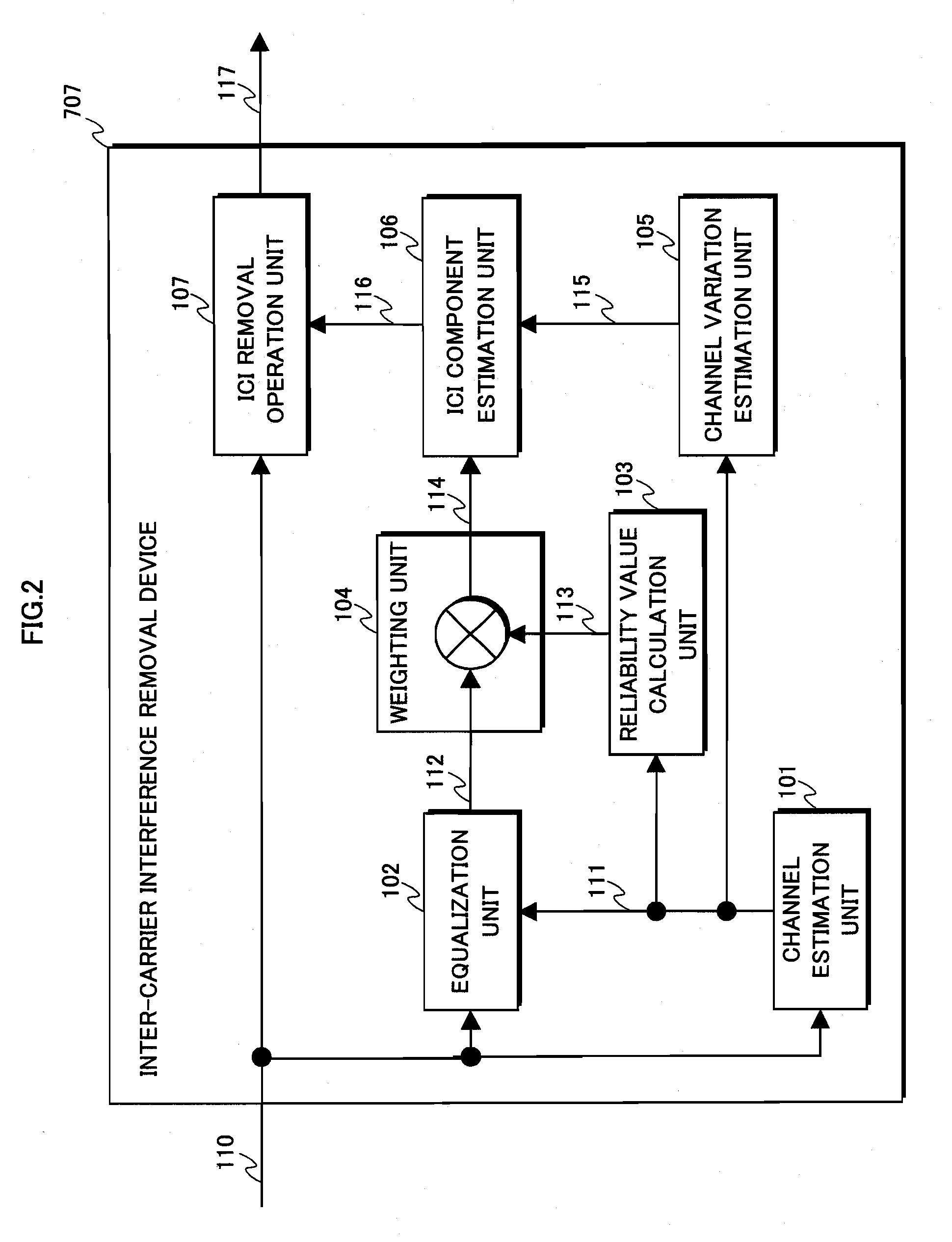
Inter-carrier interference removal device and reception device using the same
ActiveUS20090225913A1Spatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityCarrier signalEngineering
An inter-carrier interface removal device can improve estimation accuracy of inter-carrier interference caused by Doppler shift in a received multi-carrier signal moving at a high speed, and a reception characteristic of the multi-carrier signal after removing the inter-carrier interference. The inter-carrier interference removal device includes: a channel estimation unit (101) estimating a channel frequency characteristic according to a carrier signal; an equalization unit (102) equalizing the carrier signal with the channel frequency characteristic and outputs tentative carrier data; a reliability value calculation unit (103) calculating a reliability value according to the channel frequency characteristic; a weighting unit (104) weighting the tentative carrier data with the reliability value; and an ICI component estimation unit (106) estimating an ICI component according to the weighted tentative carrier data and the estimated channel frequency characteristic; and an ICI removal calculation unit (107) removing the ICI component from the carrier signal.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
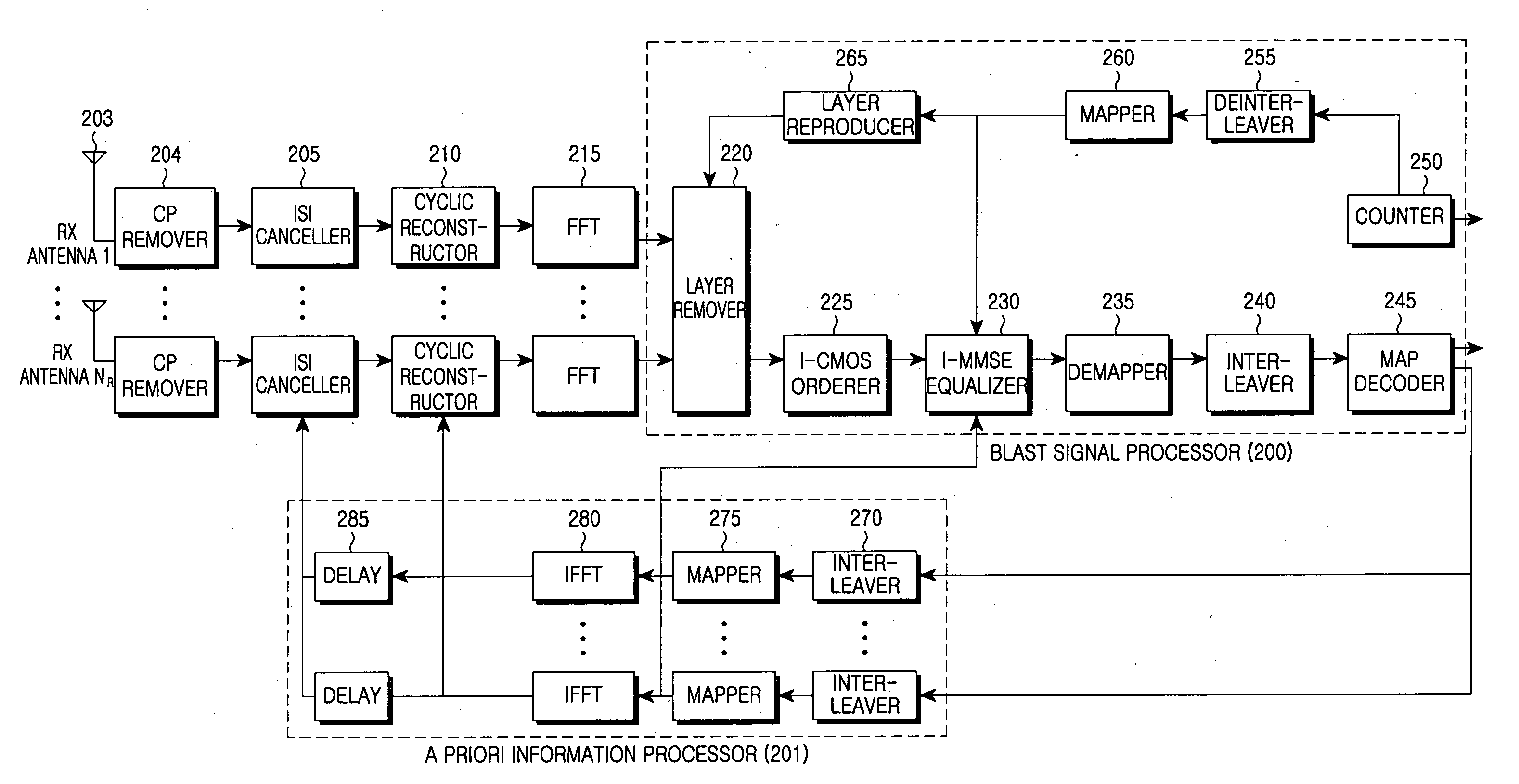
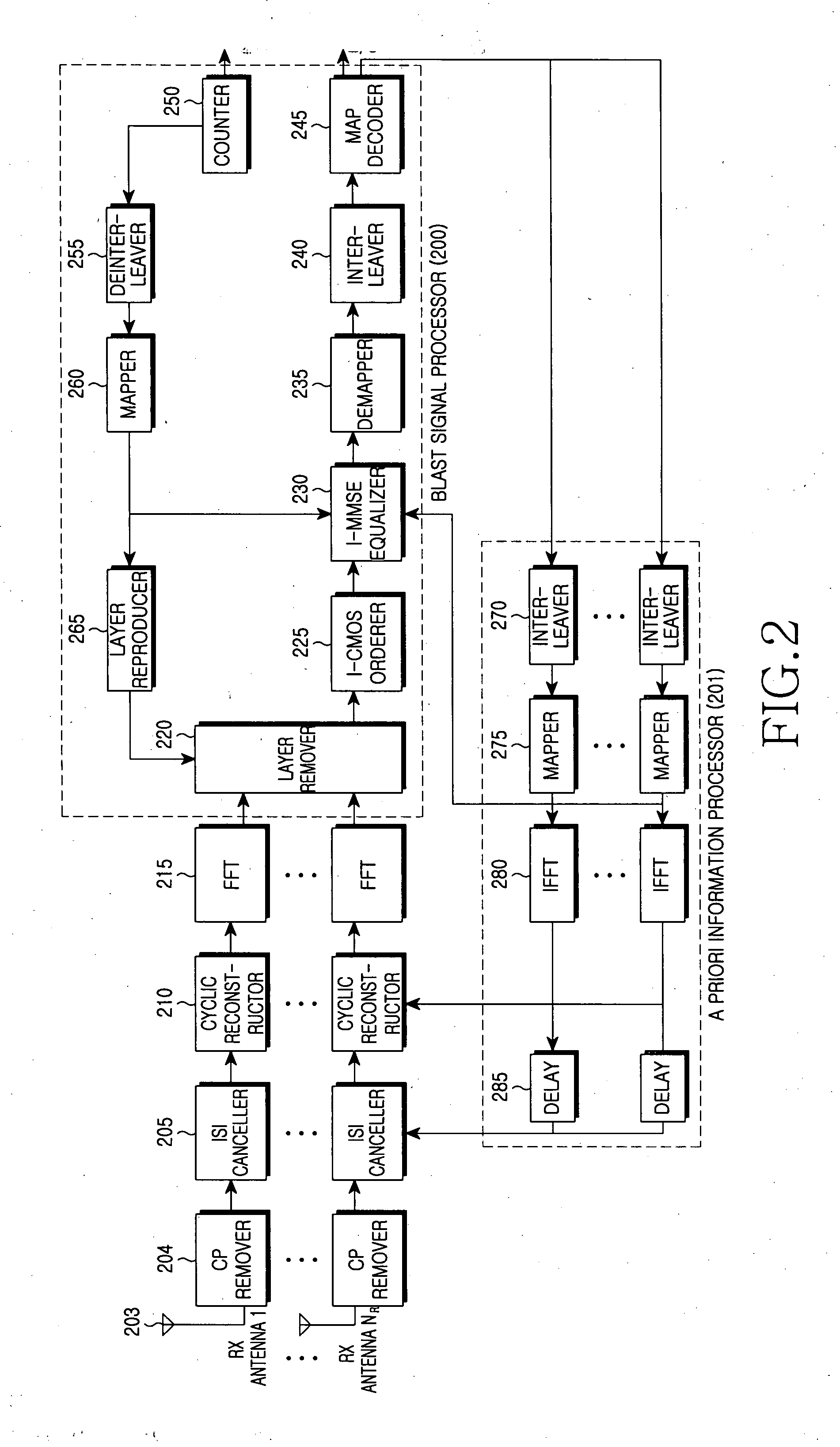
Inter-carrier interference cancellation method and receiver using the same in a MIMO-OFDM system
ActiveUS20070248151A1Effectively cancellingError minimizationLine-faulsts/interference reductionAmplitude demodulation detailsCMOSCarrier signal
A receiver for ICI cancellation in a MIMO system is provided, in which a detection orderer determines a subcarrier detection order according to SINRs of subcarriers in an I-CMOS, a detector receives a vector on the subcarriers and a priori information from a decoder according to the subcarrier detection order and iteratively estimates the received vector using the a priori information, and the decoder decodes an ICI-cancelled signal according to the estimate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Method and apparatus for canceling intercarrier interference through conjugate transmission for multicarrier communication systems
InactiveUS20050259568A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexMultiplexingCommunications system
A system and method for reducing ICI in multicarrier systems is disclosed. The system uses a primary transmission path to transmit a first signal using the same techniques as conventional OFDM and a second transmission path to transmit a conjugate of the first signal. The differing transmission paths can be implemented on separate channels via a variety of multiplexing and / or diversity techniques.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
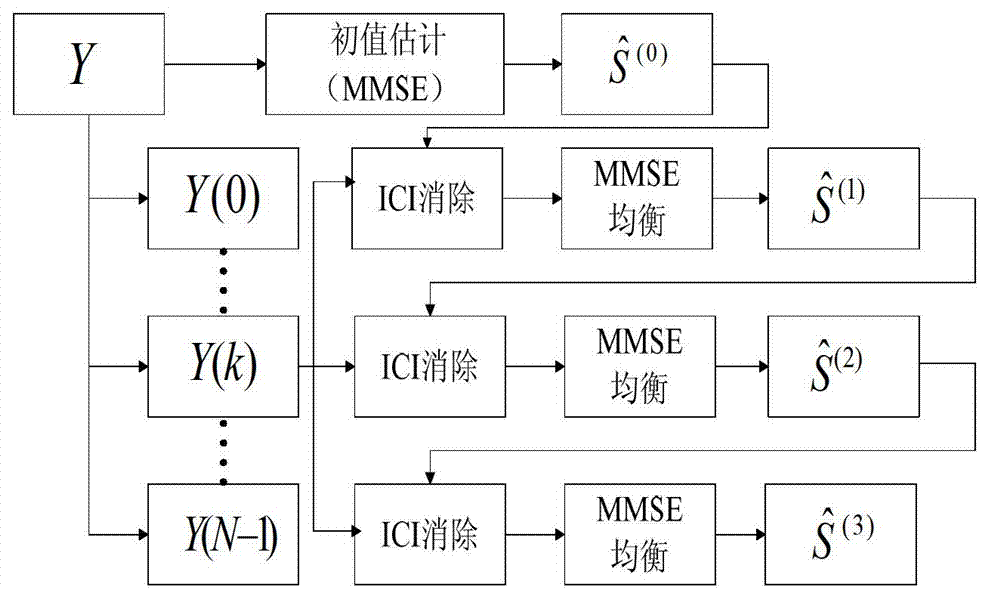
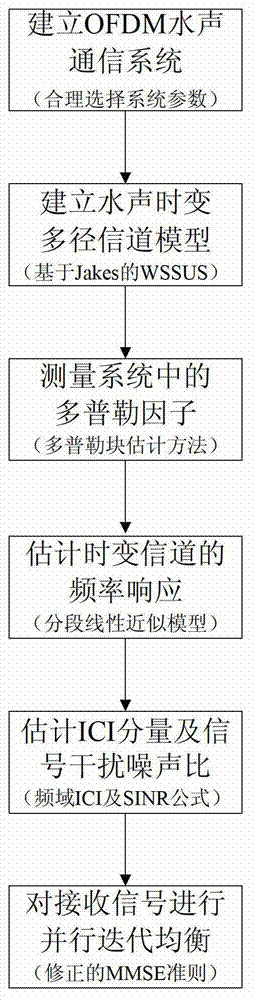
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) underwater acoustic communication parallel iterative inter-carrier interference (ICI) elimination method
InactiveCN103095639ARobust response to time-varying speed changesPrevent inversionMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksCarrier signalEngineering
The invention aims at providing an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) underwater acoustic communication parallel iterative inter-carrier interference (ICI) elimination method. The method includes the steps of building an OFDM underwater acoustic communication system, building an acoustic time varying multipath channel model, measuring Doppler factors in the system, estimating frequency response of a time varying channel, estimating an ICI component and a signal interference noise ratio (SINR), and carrying out parallel iterative minimum mean square error (MMSE) equilibrium to received signals. Through combination of a linear approximation method and the MMSE method, and through iteration to improve performance, the parallel iterative ICI elimination method is inducted into the OFDM underwater acoustic communication system, and the method can effectively resist the ICI generated under the underwater acoustic time varying channel, and the OFDM underwater acoustic communication system is steady in response to the change of channel time varying speed. Therefore, inverse operation of a high order matrix is avoided, complexity of the method is reduced, and arithmetic speed is improved.
Owner:三亚哈尔滨工程大学南海创新发展基地
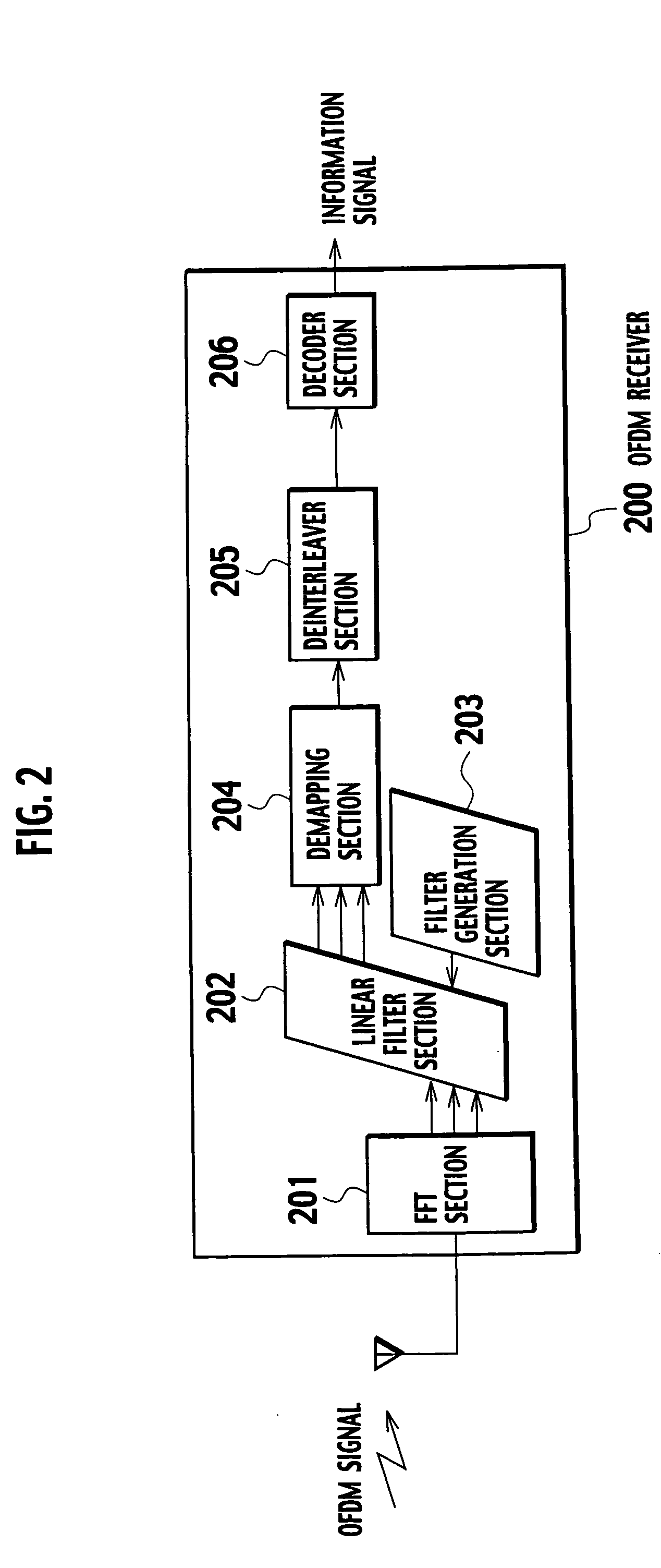
Receiver which demodulates OFDM symbol
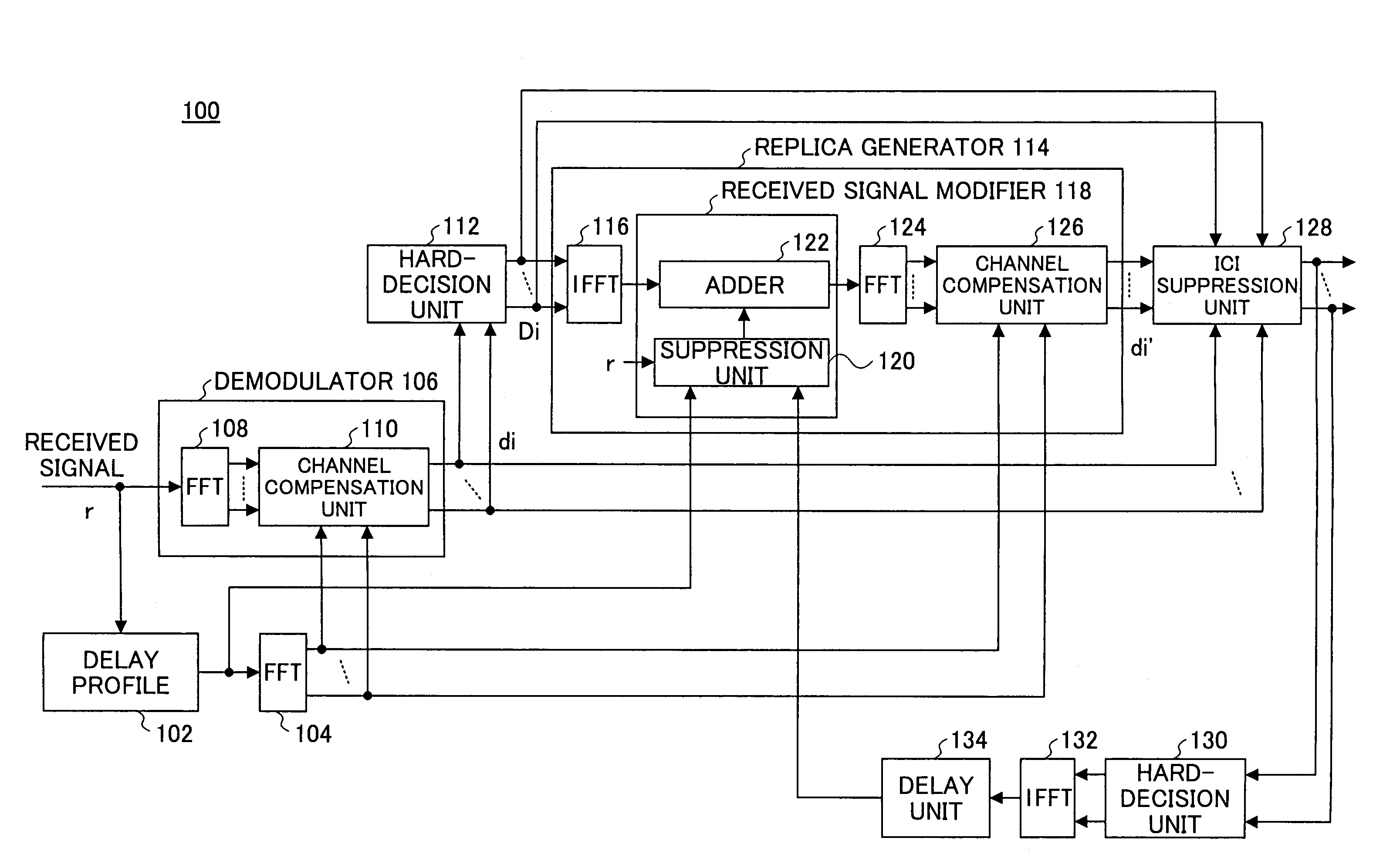
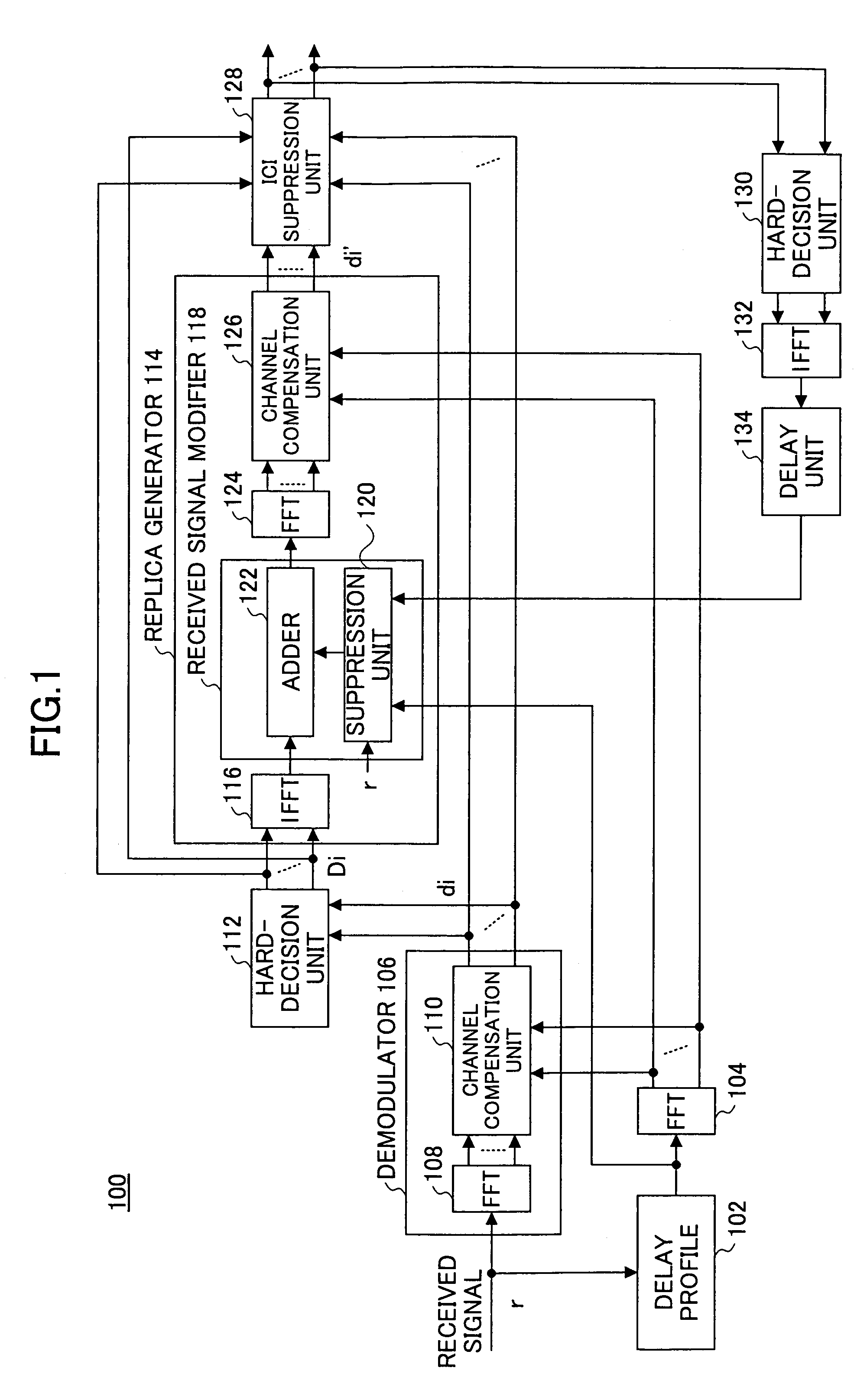
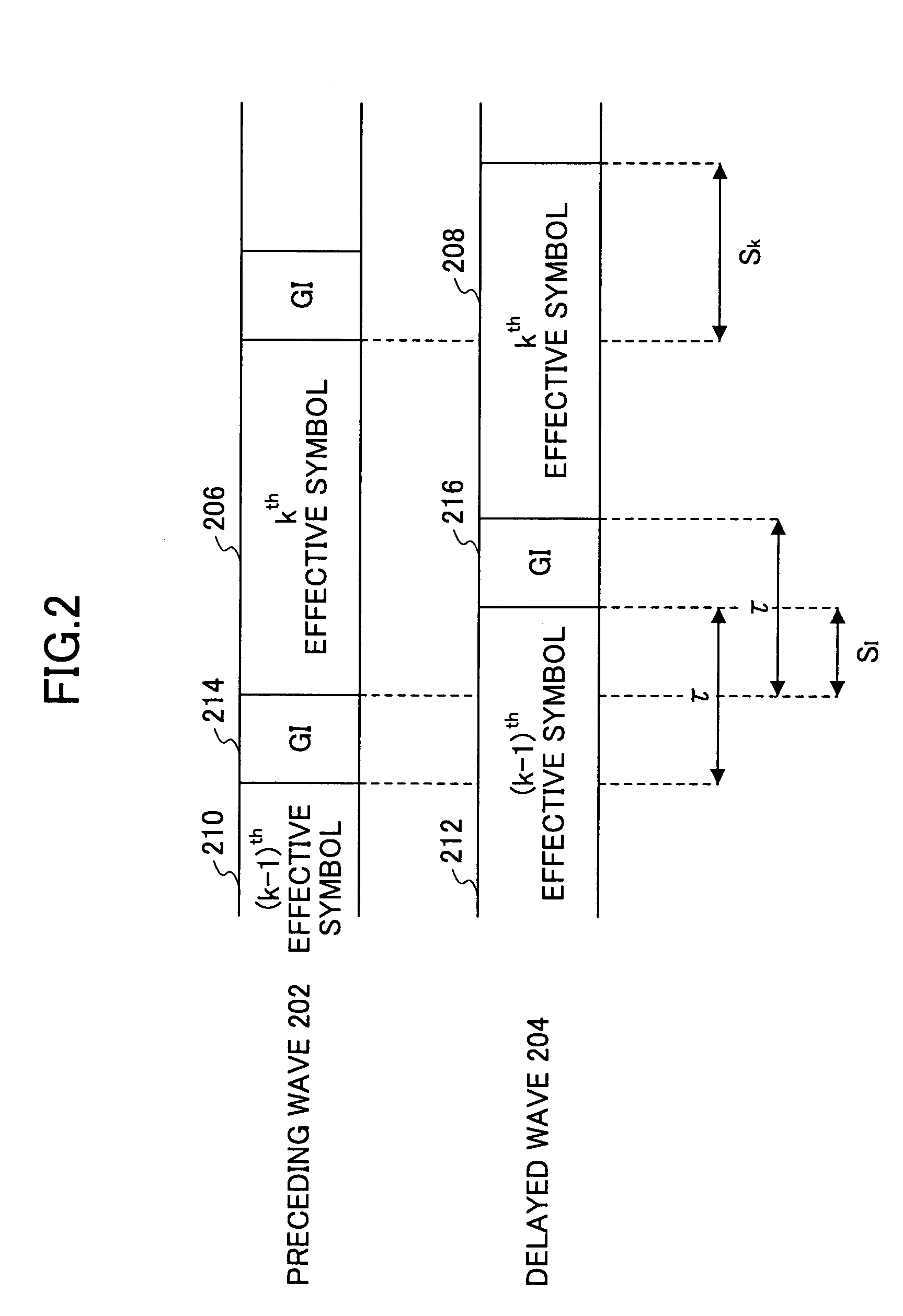
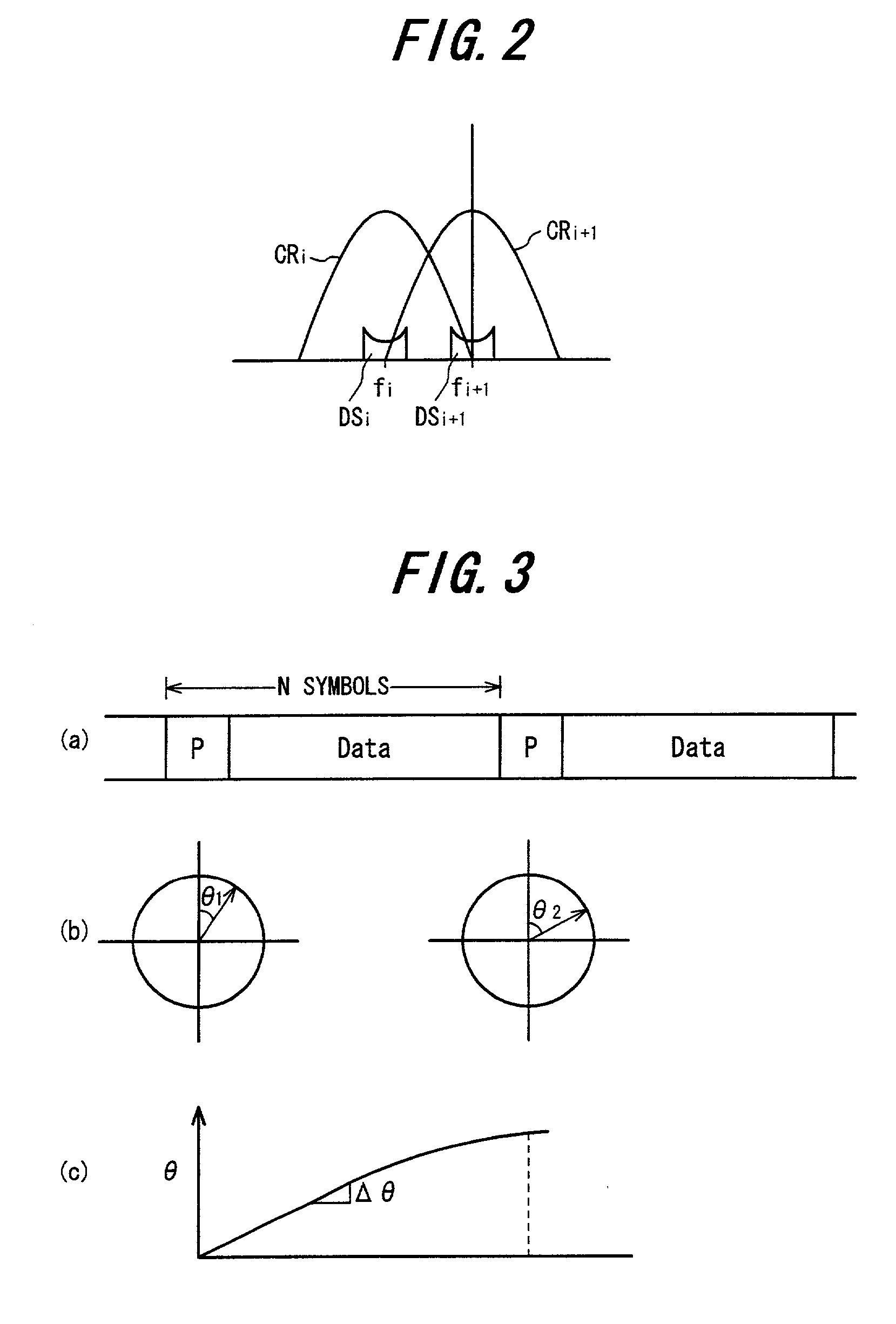
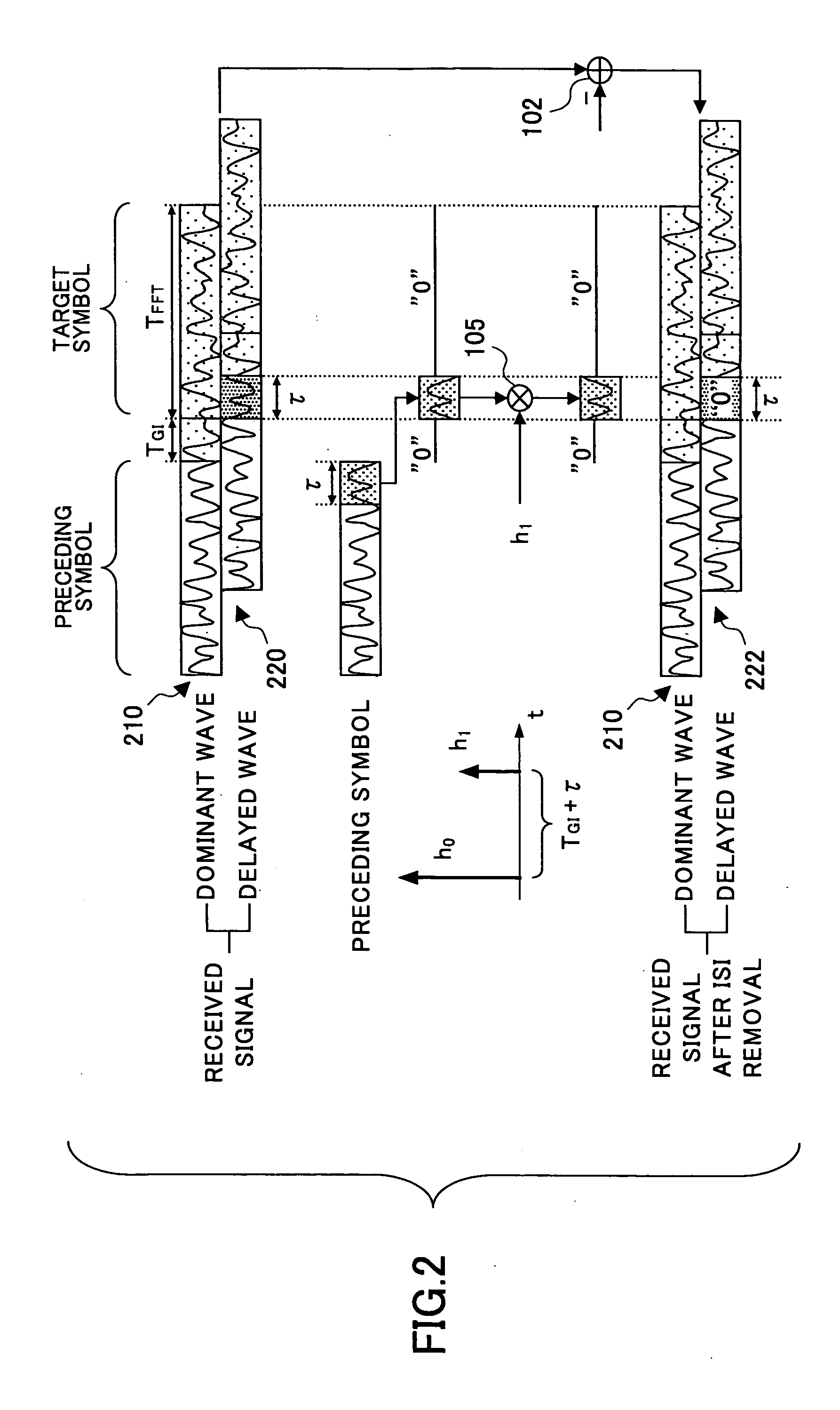
InactiveUS7313189B2Reduce Intersymbol InterferenceError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionCarrier signalLatency distribution
A receiver is disclosed that demodulates an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) symbol transmitted by an OFDM method. The receiver includes a delay profile generation unit that generates a delay profile regarding a preceding wave and a delayed wave included in a received signal, a demodulation unit that demodulates the received signal so as to output a demodulated signal per sub-carrier, a hard-decision unit that makes a hard decision per sub-carrier on a signal point based on the demodulated signal so as to output a hard-decision signal, a replica generation unit that uses the hard-decision signal to generate a replica signal per sub-carrier, and an inter-carrier interference suppression unit that adds a difference between the hard-decision signal and the replica signal to the demodulated signal so as to suppress an inter-carrier interference.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
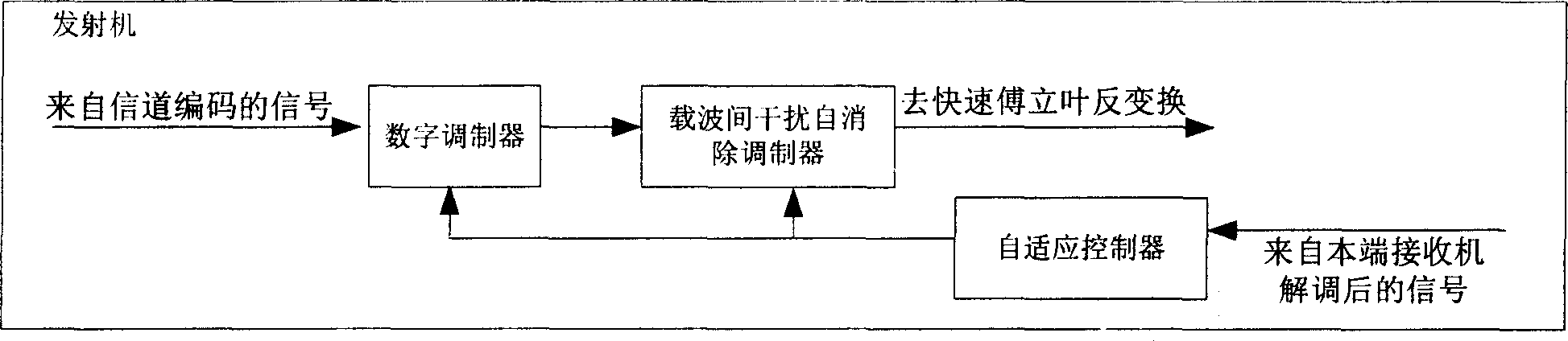
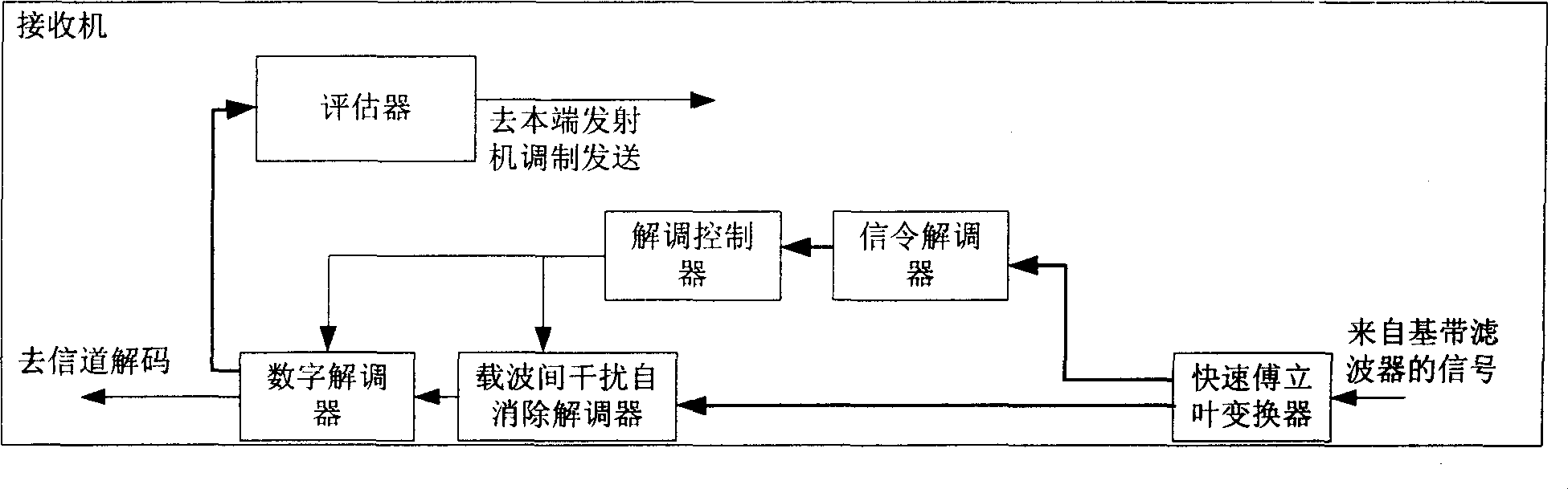
Method of self eliminating interference between self adaptive carriers and receiving and transmitting machine
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SHANGHAI BELL CO LTD
OFDM receiver
InactiveUS7415085B2Reduce the amount of processingSpatial transmit diversityLine-faulsts/interference reductionCarrier signalOfdm transmitter
An OFDM receiver receives an OFDM signal transmitted from an OFDM transmitter by using a sub-carrier. The OFDM receiver includes a channel estimator configured to obtain a channel estimated value of each multi-path based on OFDM signals received through a plurality of multi-paths; a transmission signal estimated value calculator configured to calculate a transmission signal estimated value as an estimated value of the OFDM signal; and an inter-carrier interference compensator configured to extract a multi-path not becoming a form to contain a signal component only of a target symbol in an FFT window based on the transmission signal estimated value and the channel estimated value of each multi-path, and to compensate for inter-carrier interference in the OFDM signal based on signal components corresponding to all sub-carriers of the multi-paths.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
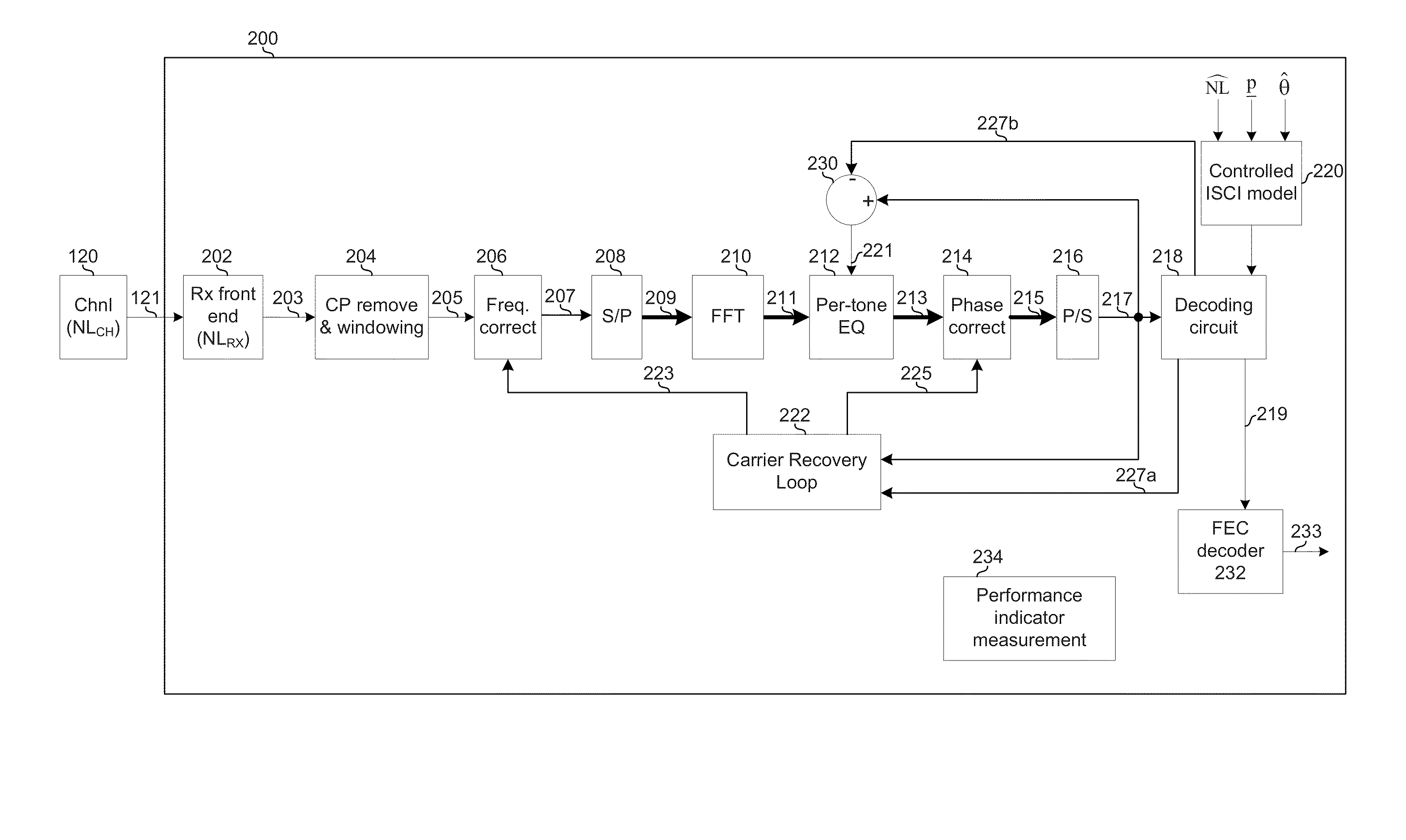
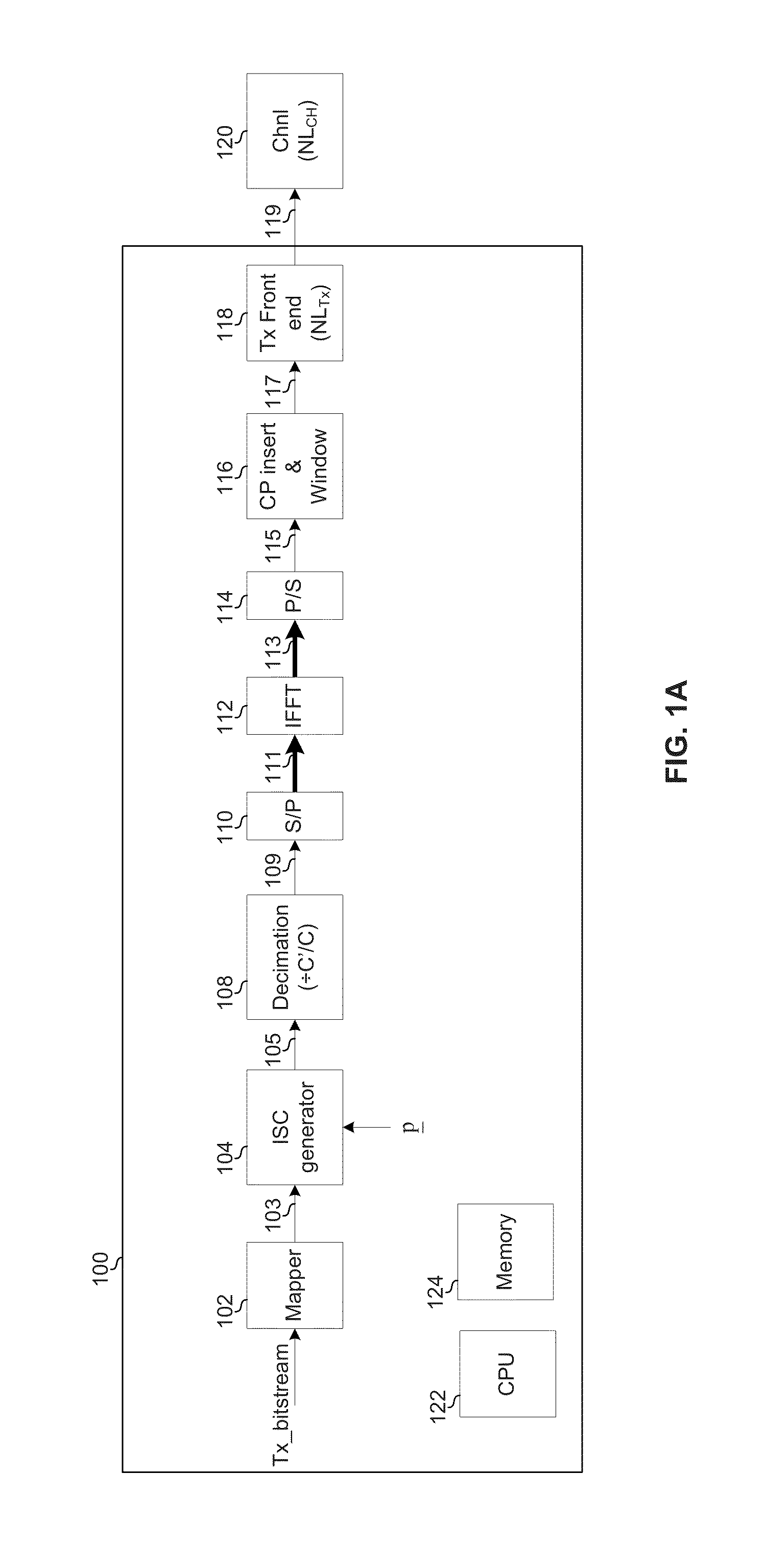
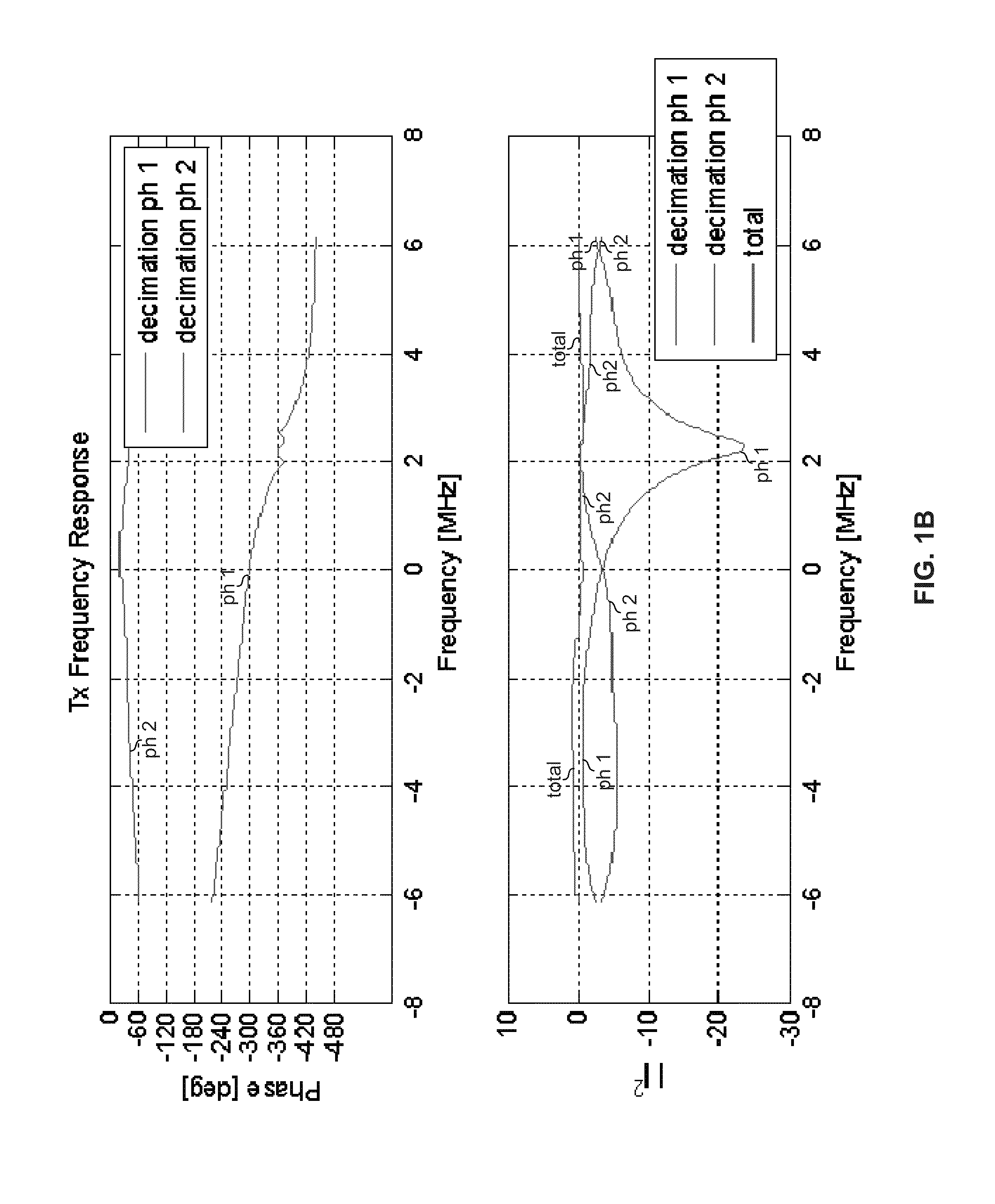
Highly-spectrally-efficient reception using orthogonal frequency division multiplexing
Circuitry for use in a receiver may comprise: a front-end circuit operable to receive an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) symbol on a first number of physical subcarriers. The circuitry may comprise a decoding circuit operable to decode the OFDM symbol using an inter-carrier interference (ICI) model, the decoding resulting in a determination of a sequence of symbols, comprising a second number of symbols, that most-likely correspond to the received OFDM symbol, where the second number is greater than the first number. The sequence of symbols may comprise N-QAM symbols, N being an integer. The ISCI model may be based, at least in part, on non-linearity experienced by the OFDM symbol during transmission by a transmitter, propagation over a channel, and / or reception by the receiver. The ISCI model may be based, at least in part, on phase-noise introduced to the OFDM symbol during transmission by a transmitter, propagation over a channel, and / or reception by the receiver.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Incremental iterative time-varying channel evaluation and inter carrier interference (ICI) elimination method of fast orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system
InactiveCN103107969AMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksInterference (communication)Carrier signal
An incremental iterative time-varying channel evaluation and inter carrier interference (ICI) elimination method of fast orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system is applied in the field of wireless communication channel evolution, and is used for channel evaluation based on pilot frequency in the circumstance that a severe ICI influence of a time-varying channel occurs. The incremental iterative time-varying channel evaluation and ICI elimination method of fast OFDM system is characterized in that the sum of an ICI and a channel noise (SIN) is taken as a denosing object of a Kalman wave filter, and the ICI influence when the Kalman wave filter evaluates is eliminated. In addition, an incremental mode is used by data used for iteration, the number of the sub-carrier waves used for measurement increases slowly along two sides of each pilot frequency point in an iterative process, and thus the influence caused by the ICI is suppressed. The performance of the incremental iterative time-varying channel evaluation and ICI elimination method of fast OFDM system is improved significantly compared with an existing algorithm in the circumstance that signal noise ratio (SNR) is small.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
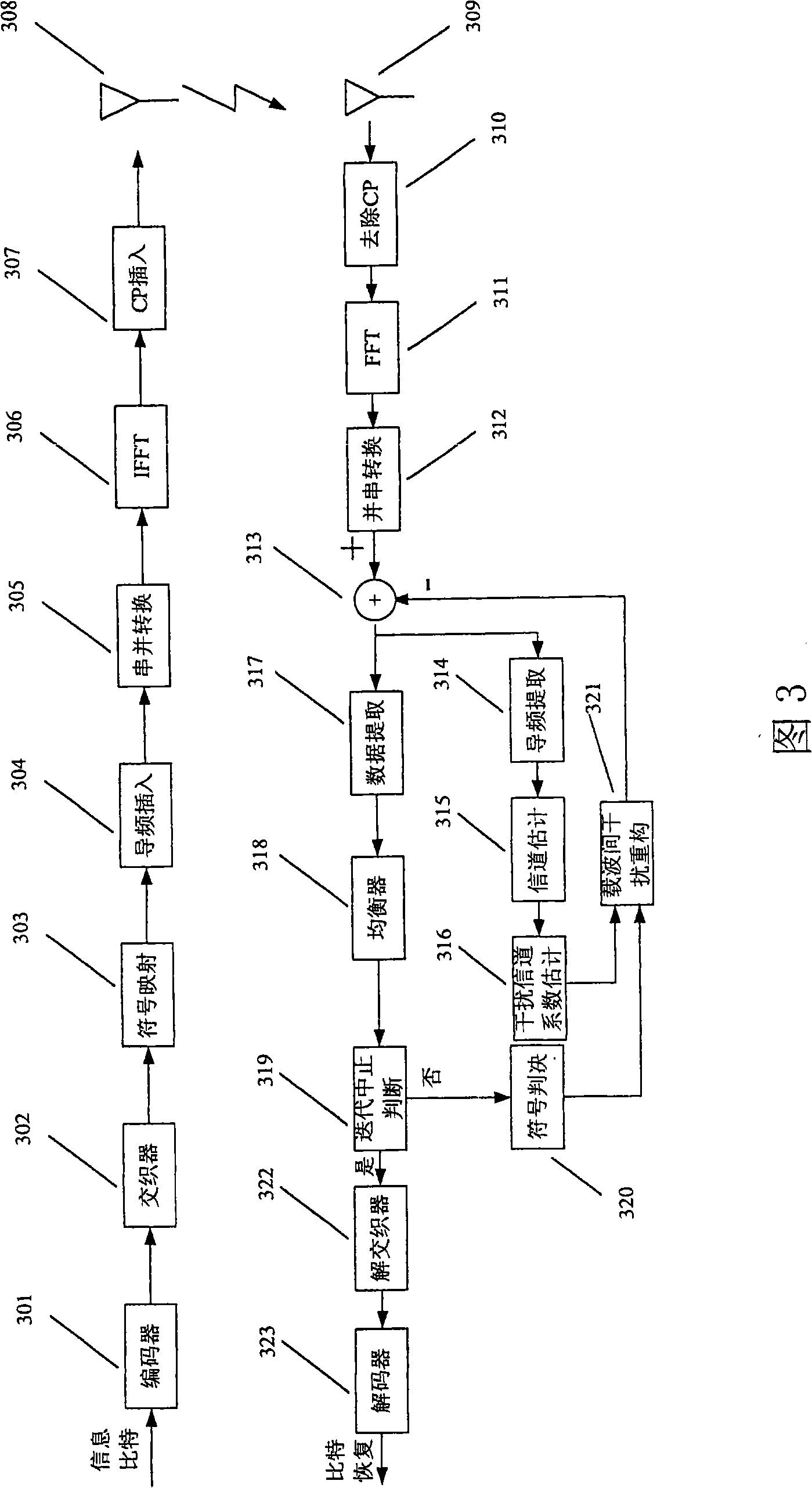
Apparatus and method for processing interference between carriers as well as receiver using the same
InactiveCN101350800ASpatial transmit diversityMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemChannel parameter
The invention provides an inter-carrier interference processing device, a method thereof and a receiver utilizing the device and the method. A reconstruction and cancellation device of the interference between carriers is applied to the receiver of a wireless communication system. The receiver comprises: a pilot frequency extraction unit, a data extraction unit, a signal channel estimation unit and an equalizer unit. The inter-carrier interference processing device comprises: a computing unit of the inter-carrier interference channel parameter for calculating the channel parameter of the channel which causes the inter-carrier interference according to the channel estimation result; a symbol judgment unit for carrying out the symbol judgment on the output and obtaining the symbol of the signal; a reconstruction unit of the inter-carrier interference for reconstructing the inter-carrier interference of the input signal according to the output of the computing unit of the inter-carrier interference channel parameter and the output of the symbol judgment unit; a cancellation processing unit for carrying out the cancellation of the reconstructed inter-carrier interference, and returning the processing result to the pilot frequency extraction unit and the data extraction unit.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
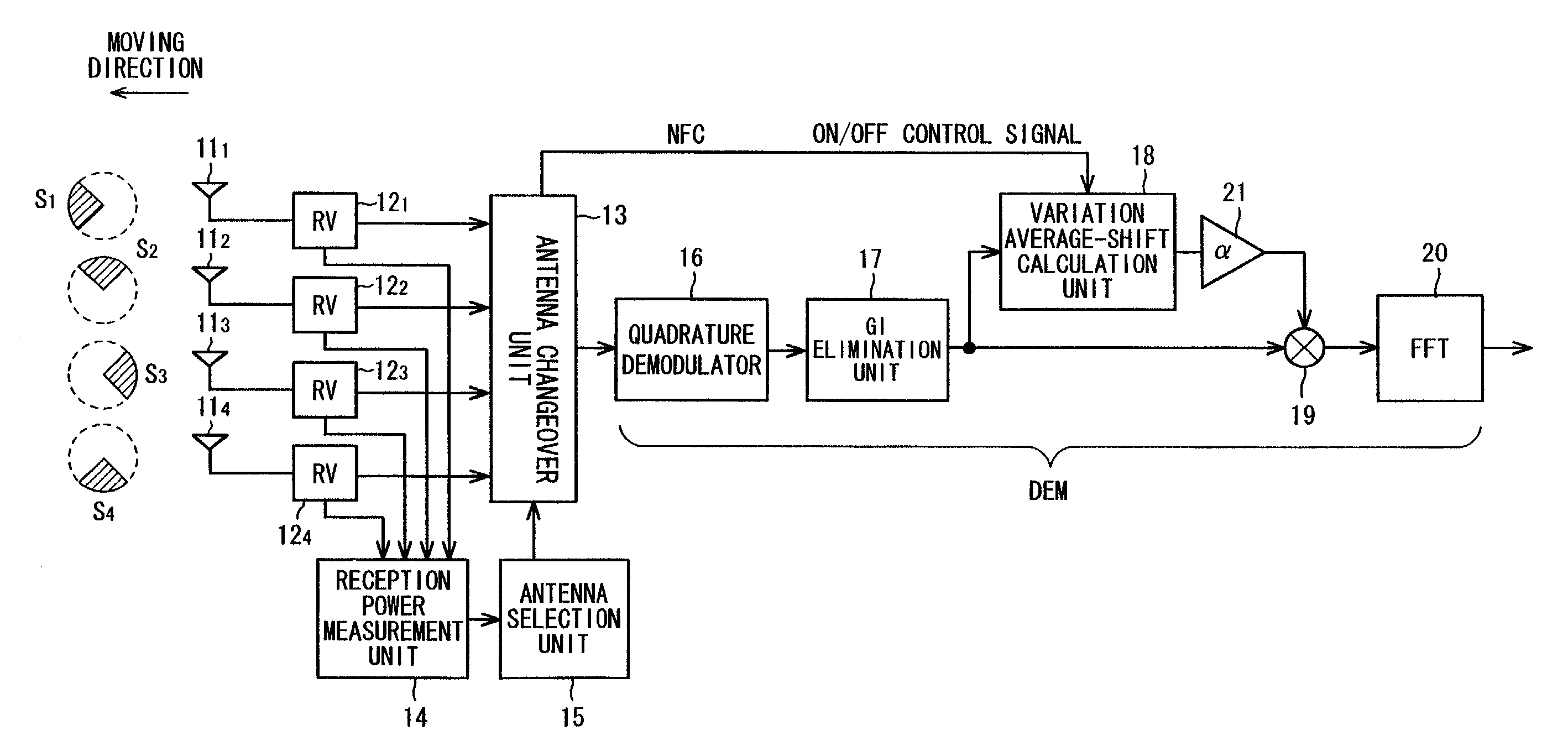
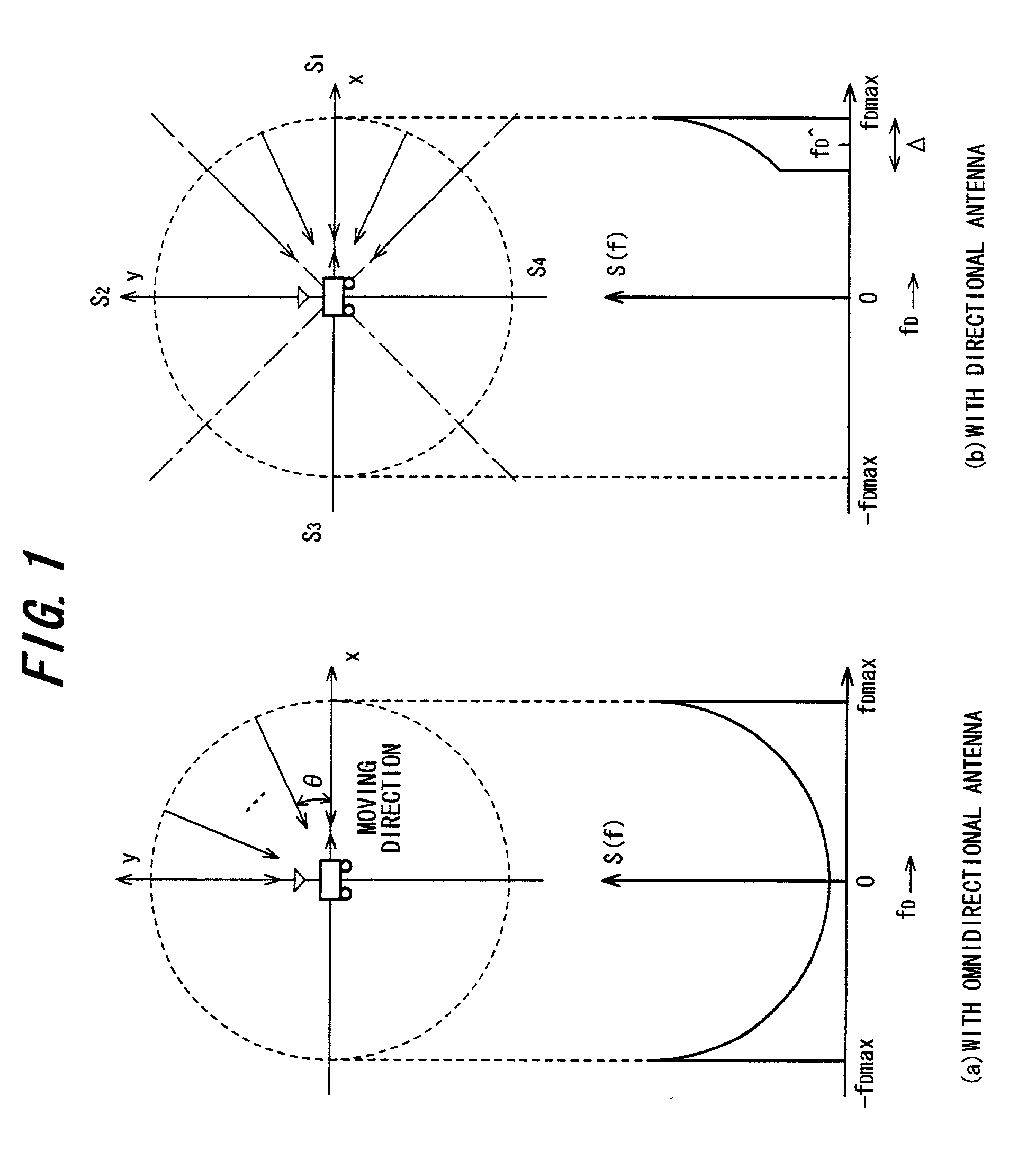
OFDM receiving method and apparatus
InactiveUS7672382B2Without loss of transmission efficiencyImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityCarrier signalDirectional antenna
In order to improve upon a degradation in performances due to inter-carrier interference without loss of transmission efficiency, antennas provided on a mobile body are made directional antennas. An antenna selection unit selects a directional antenna in such a manner that Doppler shift that is caused by movement of the mobile body will keep a constant sign that is positive or negative, a fading-variation calculation unit calculates the average value of fading variation on each path of a multipath environment, and a fading-variation compensation unit compensates the multipath fading variation based upon the average value.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
OFDM system receiver apparatus suppressing inter-symbol interference
InactiveUS20060029143A1Reduce interference inter-carrierReduce inter-symbol interferenceError preventionFrequency-division multiplexCarrier signalEngineering
An receiver apparatus according to an OFDM system includes a inter-symbol interference suppressing unit configured to modify to a predetermined content a portion of a dominant wave included in a received signal and to modify to a predetermined content a portion of at least one delayed wave included in the received signal, a tentative demodulation unit configured to demodulate a signal inclusive of the modified dominant wave and the modified delayed wave or inclusive of the unmodified dominant wave and the modified delayed wave according to the OFDM system so as to output a tentatively demodulated target symbol, and an inter-carrier interference suppressing unit, wherein the inter-carrier interference suppressing unit includes a first unit configured to further modify the modified portion of the modified delayed wave in response to the tentatively demodulated target symbol, a second unit configured to further modify the modified portion of the modified dominant wave and the modified portion of the modified delayed wave in response to the tentatively demodulated target symbol, and a selecting unit configured to select one of the first unit and the second unit in response to a delay profile.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
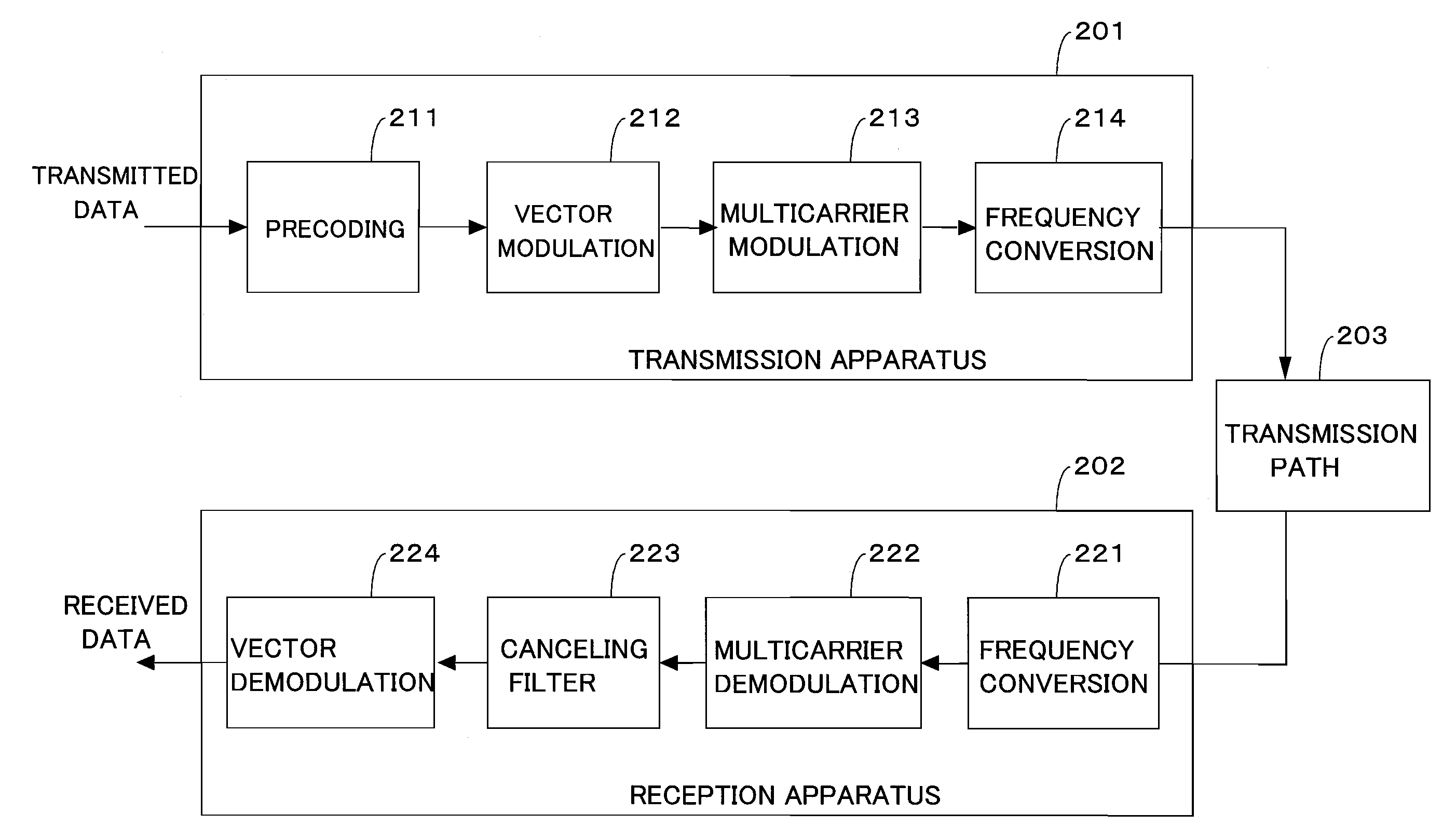
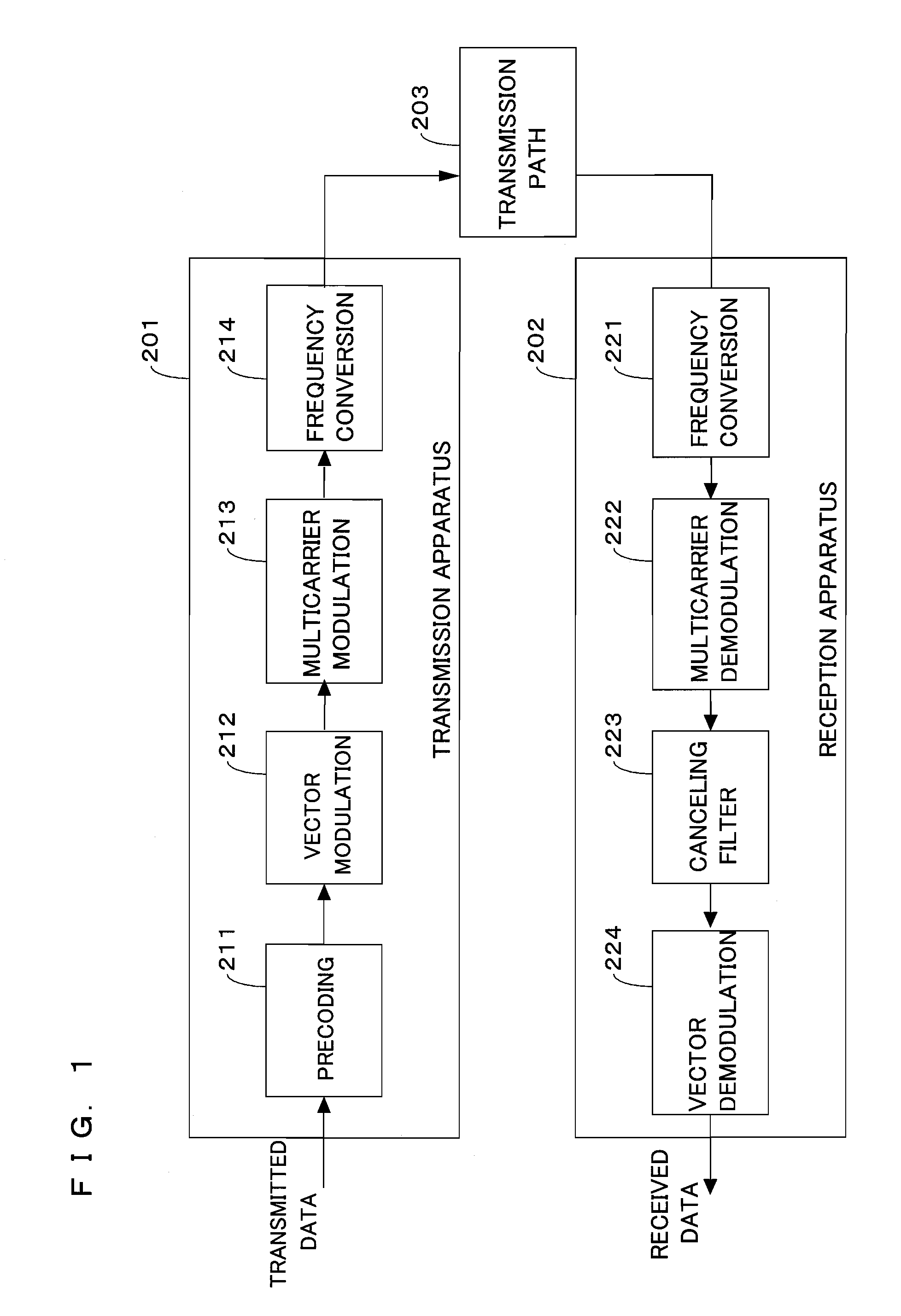
Transmission apparatus and a reception apparatus in a multicarrier transmission system and a transmission method and a reception method using the multicarrier transmission system
ActiveUS20090180566A1Low efficiencyHigh mobile communicationError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionPrecodingCarrier signal
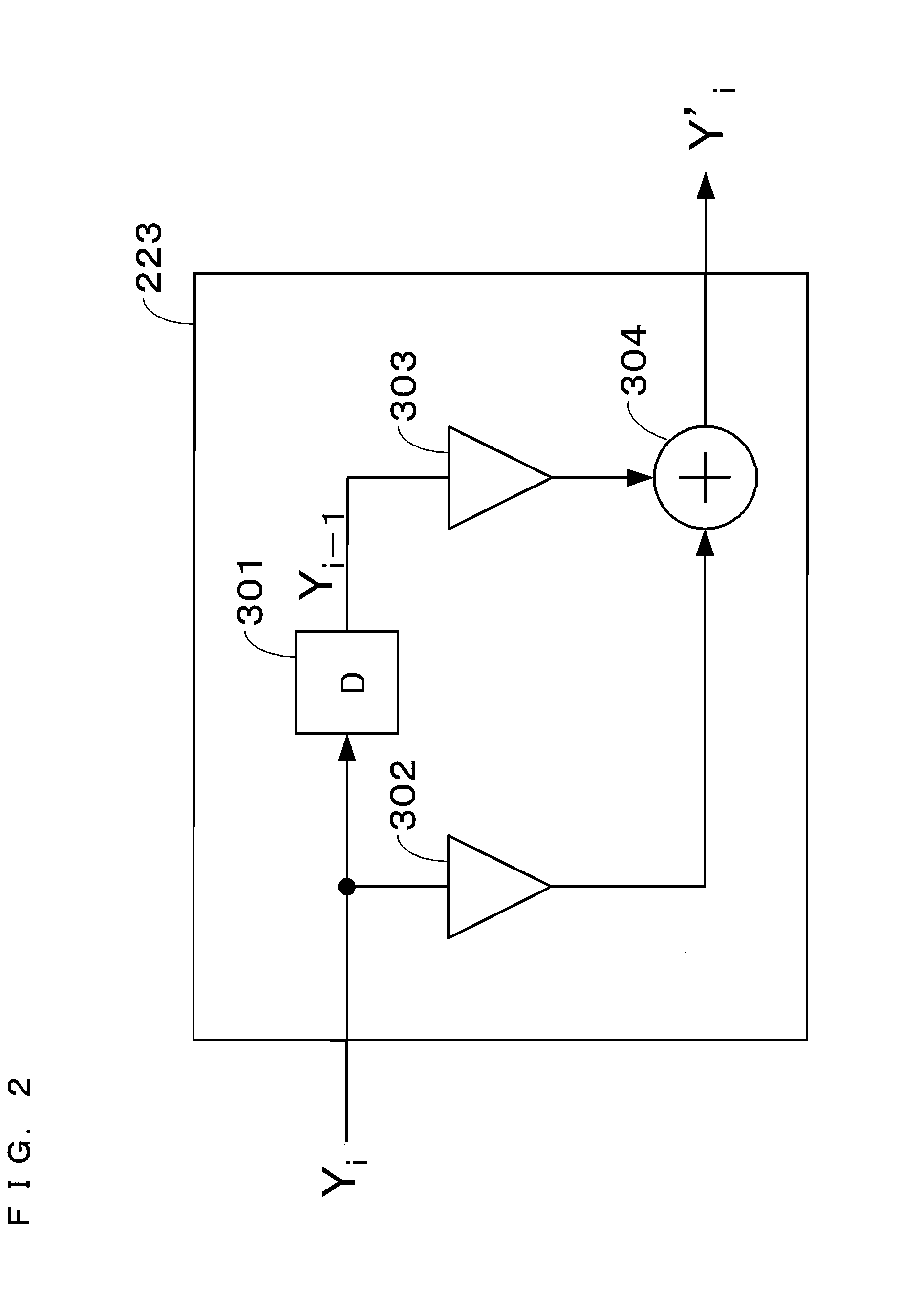
An object is to reduce inter-carrier interference caused by frequency fluctuations, amplitude fluctuations, phase fluctuations, or the like without reducing a transmission efficiency. On a receiving end, a canceling filter section (223) is provided, alleviating the inter-carrier interference caused by the frequency fluctuations, the amplitude fluctuations, the phase fluctuations, or the like through filtering processing. On a transmitting end, a precoding section (211) is provided, facilitating determination of demodulation data in a vector demodulation section (224) on the receiving end through precoding processing. Or on the receiving end, a trellis decoding section (225) is provided, decoding the demodulation data through trellis decoding processing.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
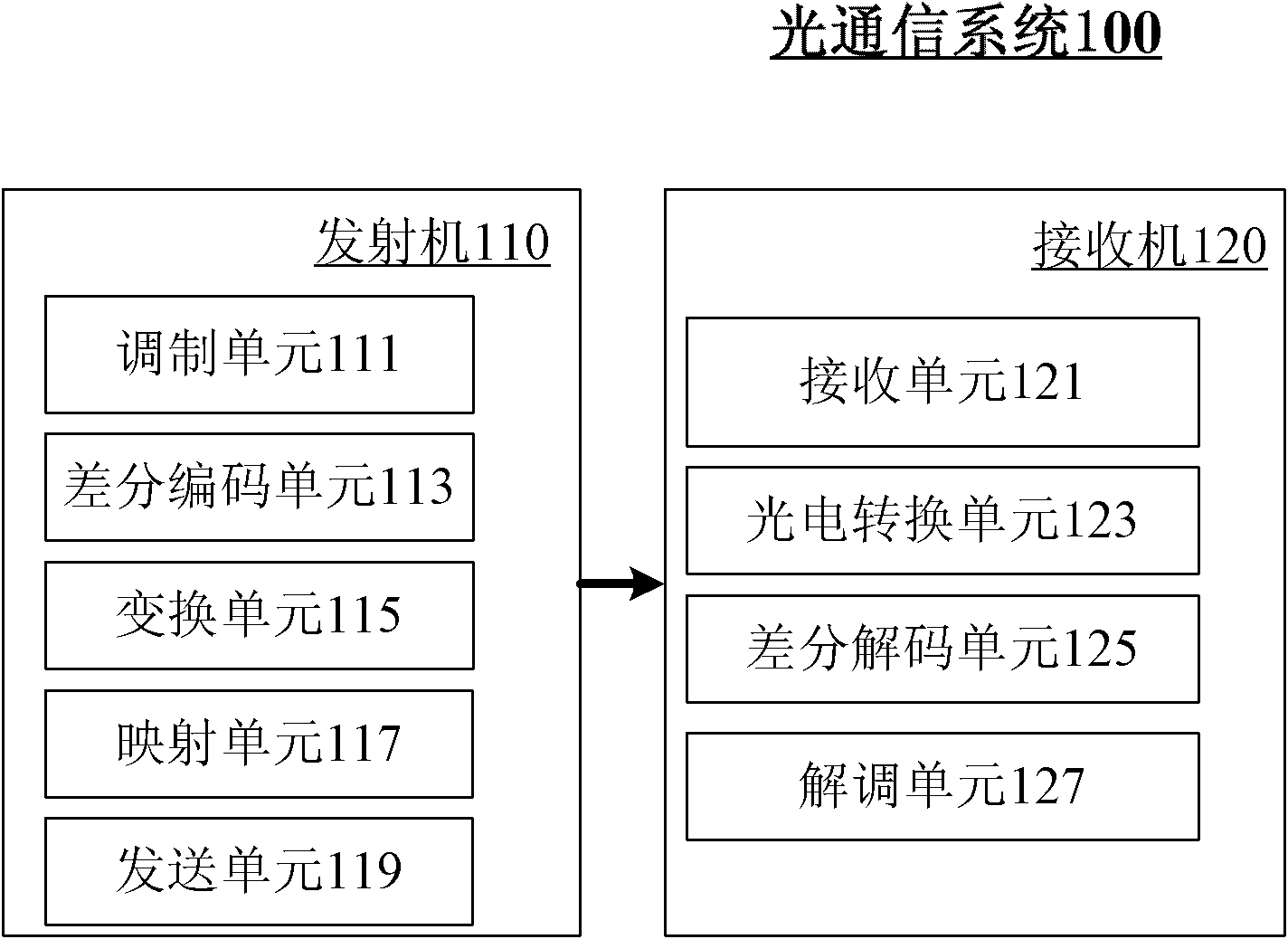
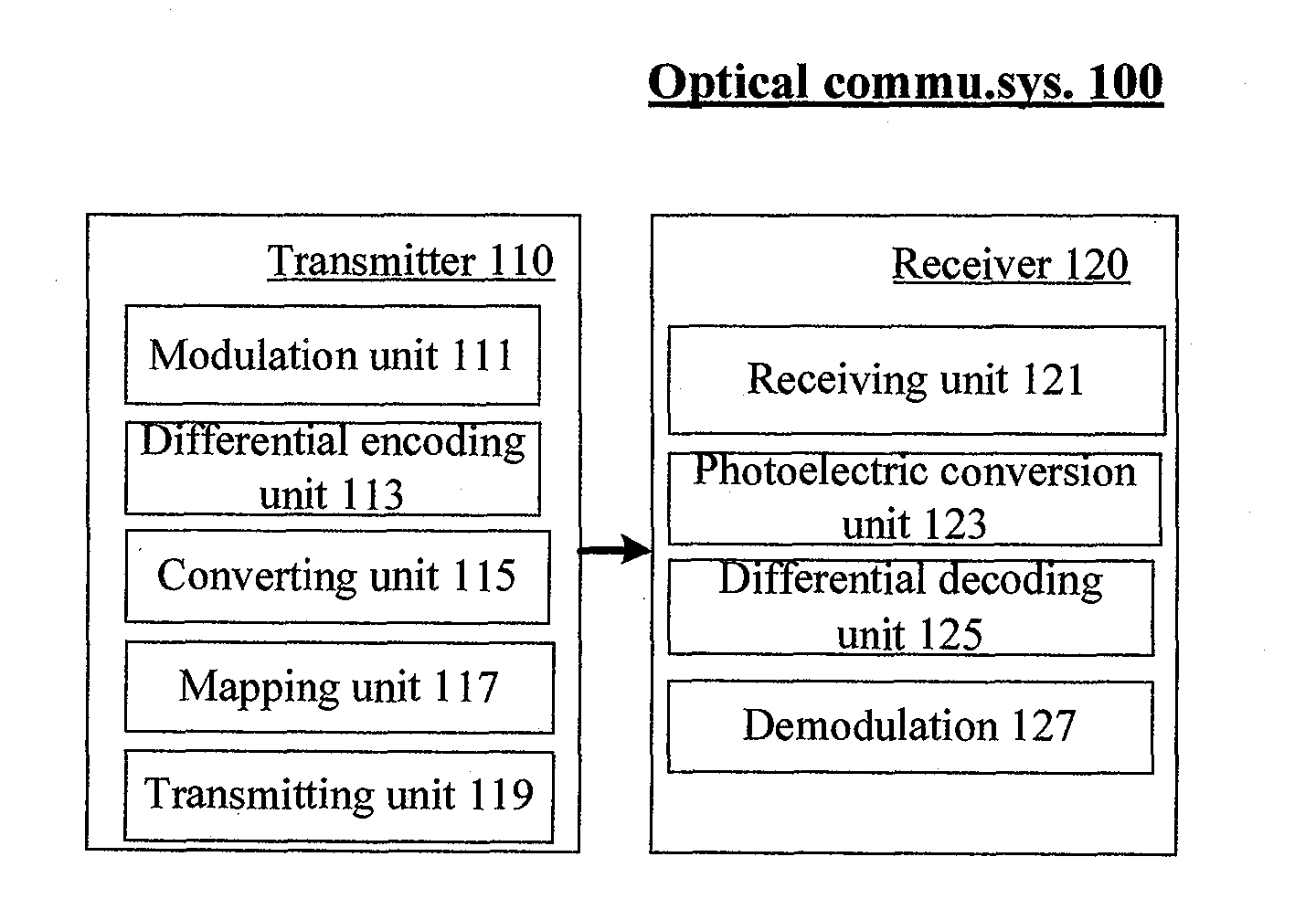
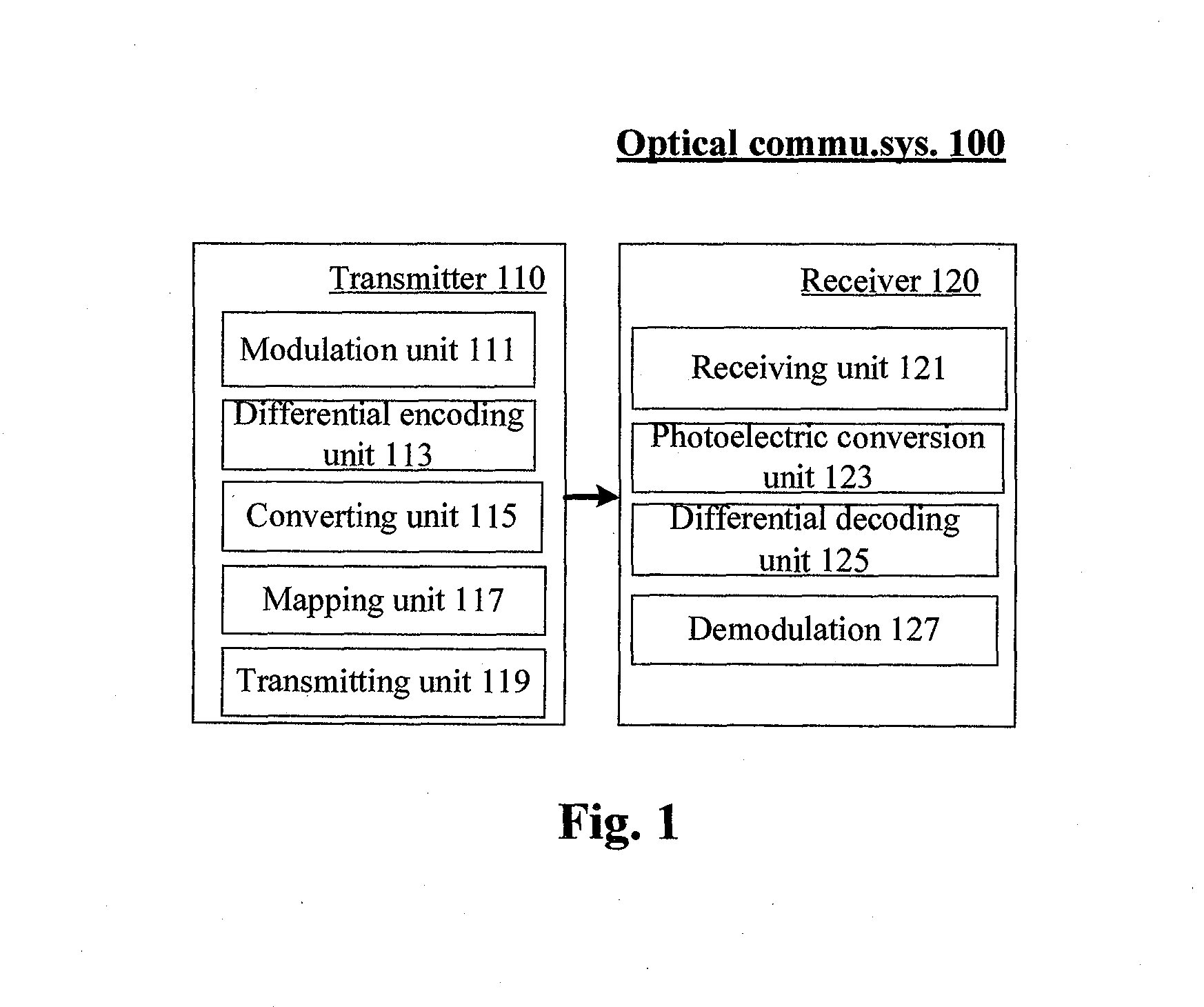
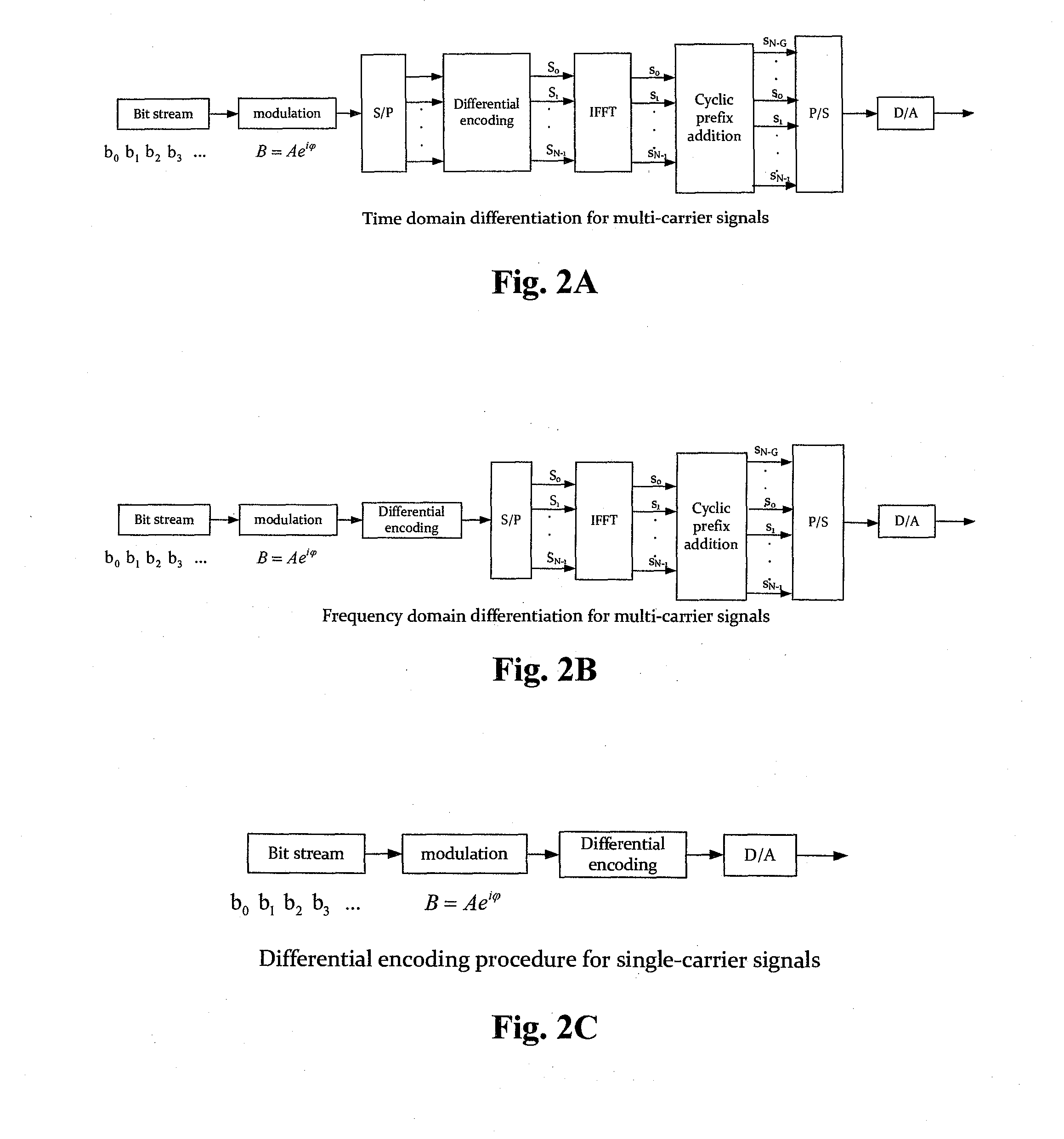
Optical communication method and system
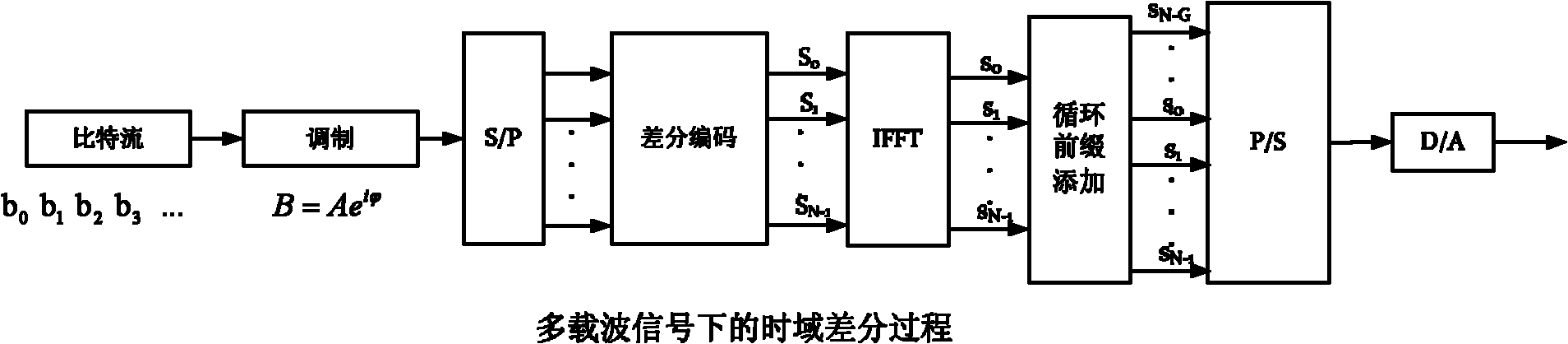
InactiveCN102427387AIncrease line widthEnhanced ability to resist inter-carrier interferenceBaseband system detailsElectromagnetic transmissionFrequency spectrumStream data
The invention provides an optical communication method which comprises the steps of: modulating obtained bit stream data to obtain a modulating signal; carrying out differential coding on the modulating signal to obtain a differential coding signal; converting the differential coding signal into an electrical signal; mapping the electrical signal on an optical carrier to form an optical signal; and then transmitting the optical signal. By using the method, on the premise that a frequency spectrum utilization rate is not reduced, the system capability of resisting disturbance among carriers is enhanced; thus, the tolerance of the existing optical communication sysem for resisting laser linewidth, quick change PMD (Physical Media Dependent), nonlinear fiber, disturbance among channels and other damage is enhanced; and system performance is greatly enhanced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
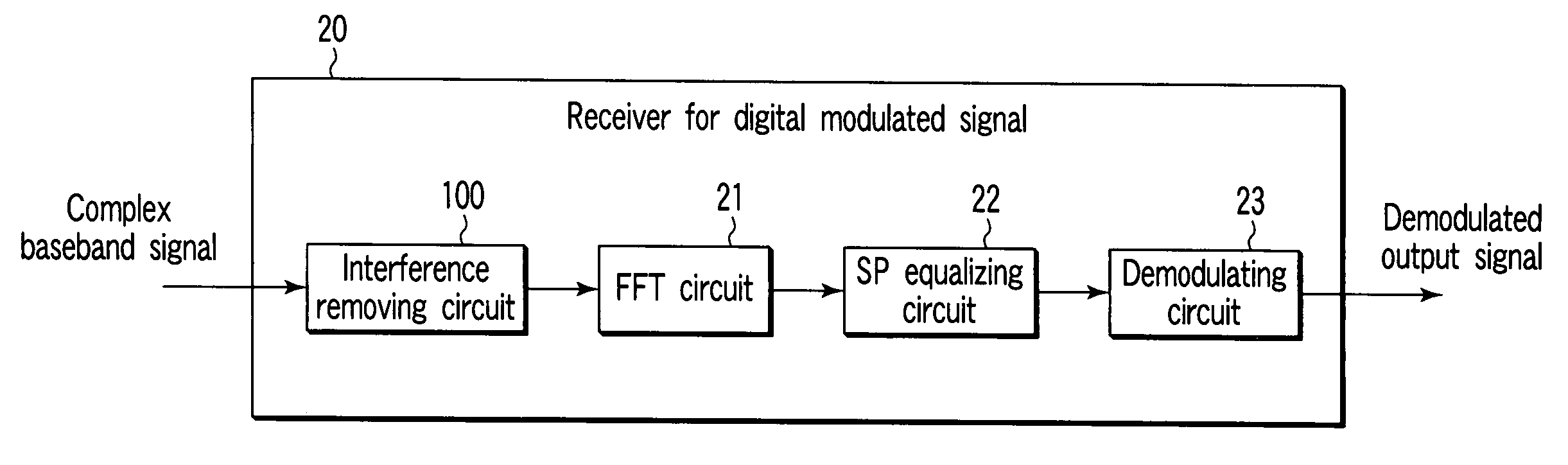
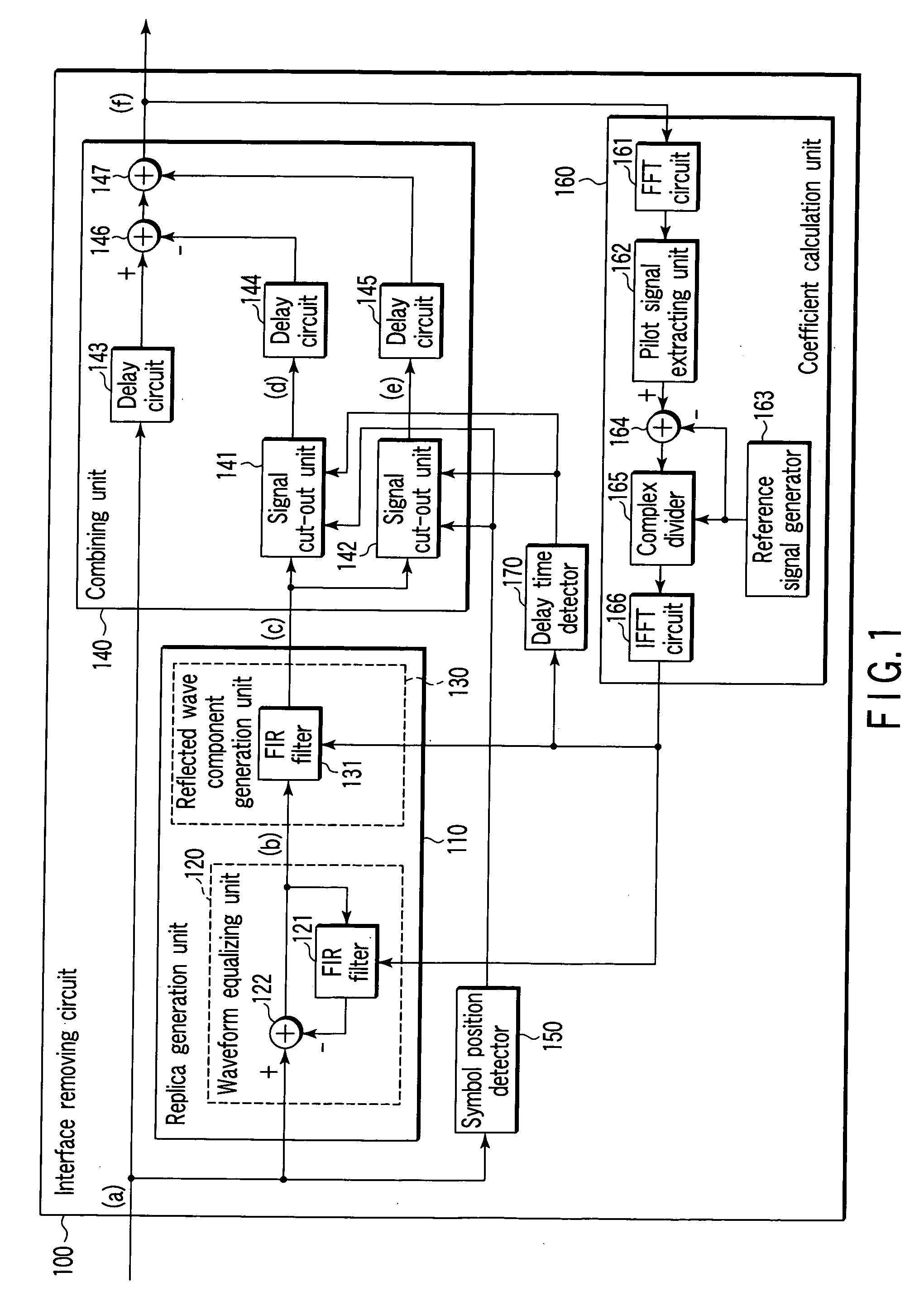
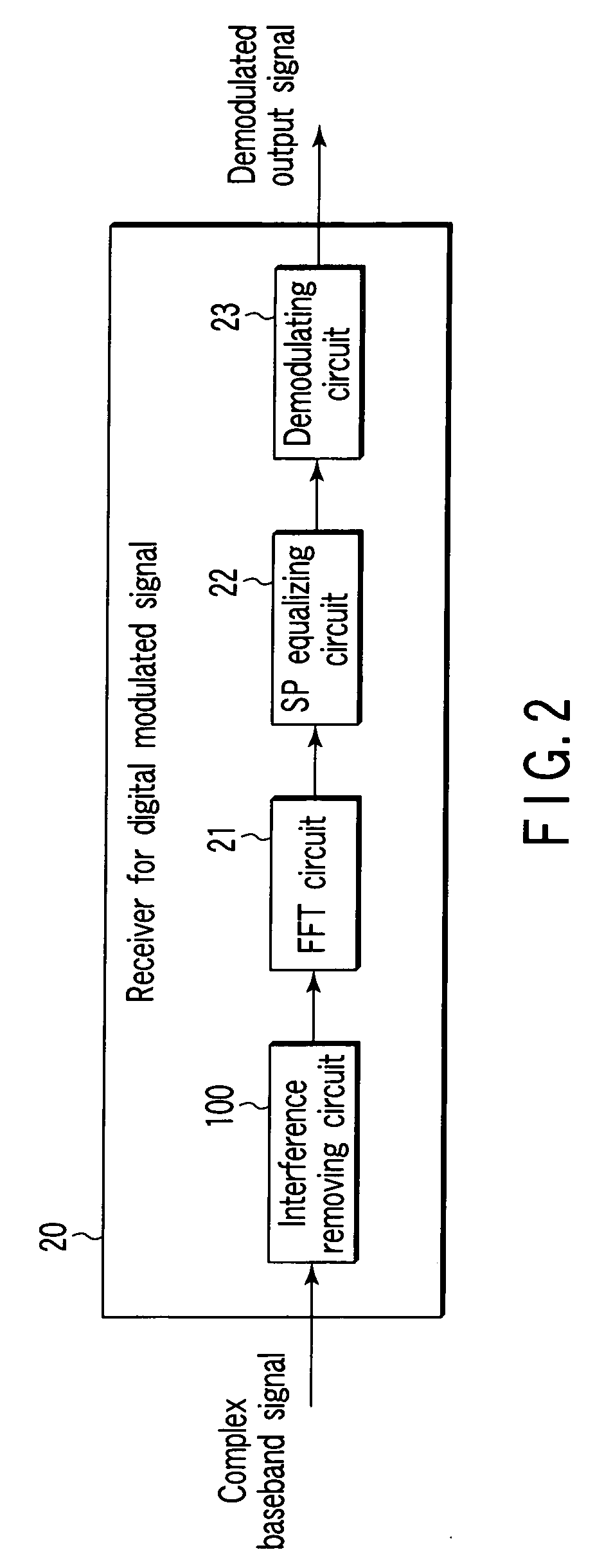
Receiver for digital modulated signal and receiving method for the same
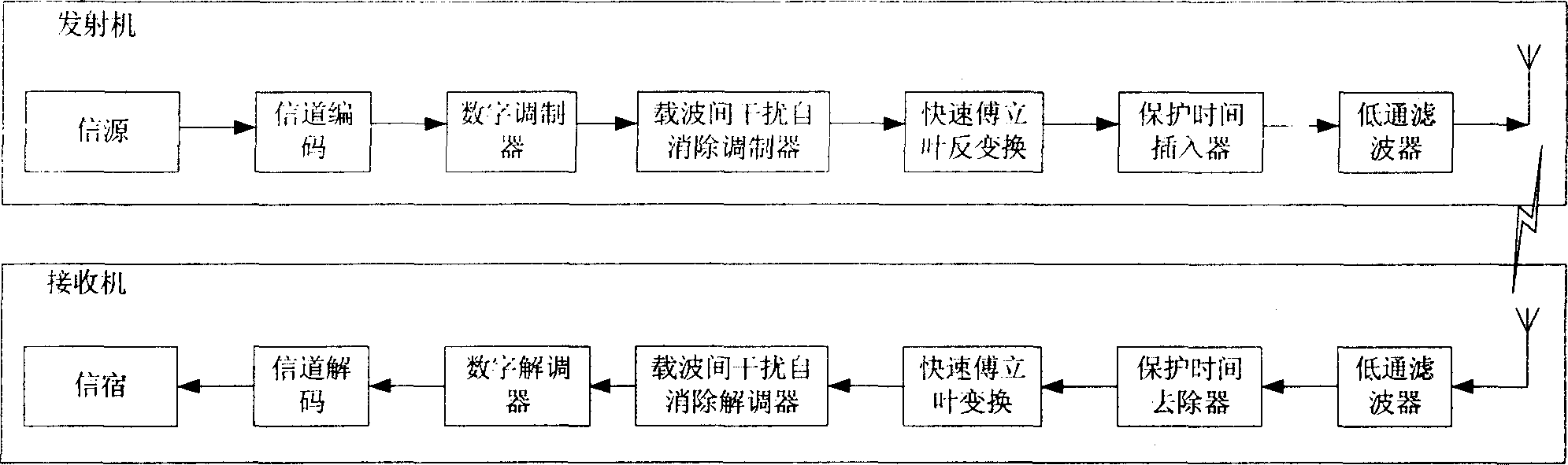
ActiveUS20060291375A1Reduce signalingReduce distractionsModulated-carrier systemsOrthogonal multiplexTransformerCarrier signal
A receiver for a digital modulated signal which receives a multi-carrier modulated signal and demodulates a receiving signal by converting it from a time region into a frequency region by Fourier transform is provided. The receiver comprises a Fourier transformer which performs Fourier transform of the receiving signal and an interference removing circuit which reduces an inter-symbol interference or an inter-carrier interference of the receiving signal. The removing circuit is disposed in a front stage of the Fourier transformer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
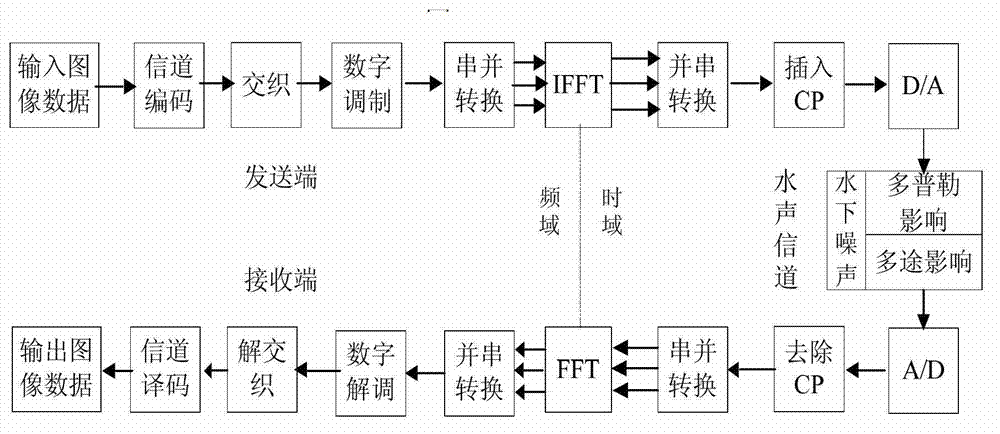
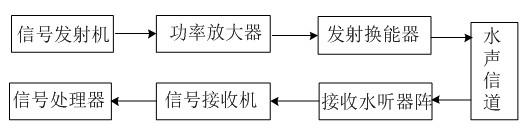
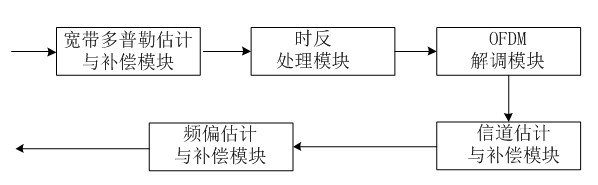
Underwater sound communication device and method based on time reversal and orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) combined treatment
InactiveCN102546511AReduce multipath effectsEliminate delayMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksEngineeringCombined treatment
The invention discloses an underwater sound communication device and a method based on time reversal and orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) combined treatment. The underwater sound communication device comprises a signal transmitter, a power amplifier, a transmitting transducer, a receiving hydrophone array, a signal receiver and a signal processor, wherein the signal processor comprises a broadband Doppler estimation and compensation module, a time reversal processing module, an OFDM demodulation module, a channel estimation and compensation module and a frequency deviation estimation and compensation module. In the underwater sound communication device, the space time focusing characteristics of the time reversal are utilized to eliminate the multipath influence of the channel; a pulse channel response length can be shortened by the time reversal so as to reduce the length of an OFDM symbol guard interval and improve the communication efficiency; and because the guard interval is reduced, the length of the OFDM symbol can be shortened so as to enlarge a subcarrier frequency interval. With the method disclosed by the invention, interference among subcarriers can be reduced, and the available rate of the OFDM underwater sound communication is further improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and apparatus for ici cancellation in communication systems
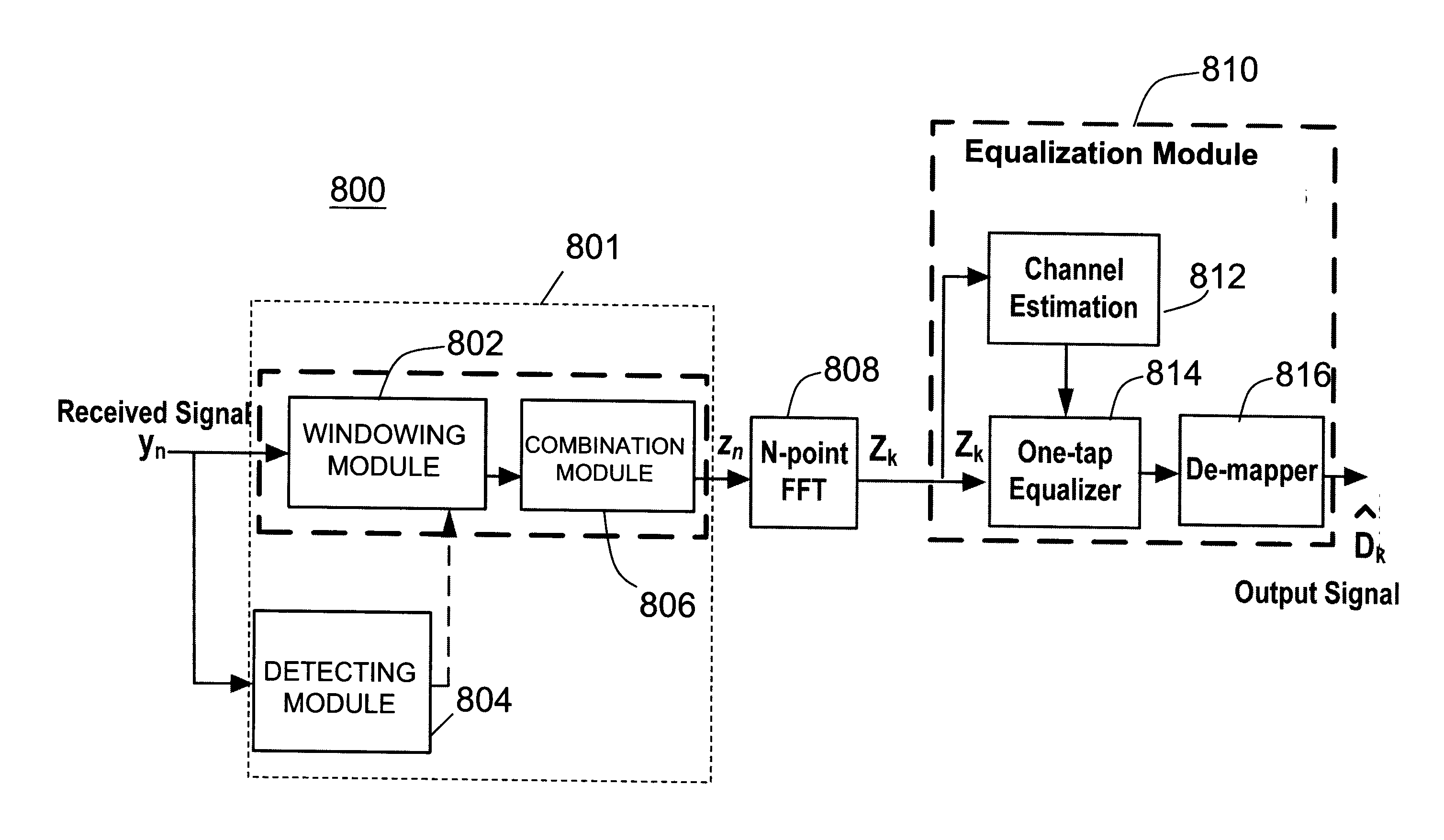
ActiveUS20090059781A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexTime domainCommunications system
An apparatus capable of inter-carrier interference (ICI) cancellation in a communication system, the apparatus comprising a detecting module configured to detect an ISI-free region free from inter-symbol interference (ISI) in a guard interval (GI) of a symbol in time domain, a windowing module configured to provide a windowing function in time domain, identifying a weight value in the windowing function based on the ISI-free region, and multiplying a channel response related to the symbol by the windowing function in time domain to obtain a windowing result, wherein the windowing result comprises a first portion corresponding to the ISI-free region and a second region corresponding to an end portion of the symbol, the end portion and the ISI-free region having the same length, and a combination module configured to combine the first portion and the second portion of the windowing result in time domain.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
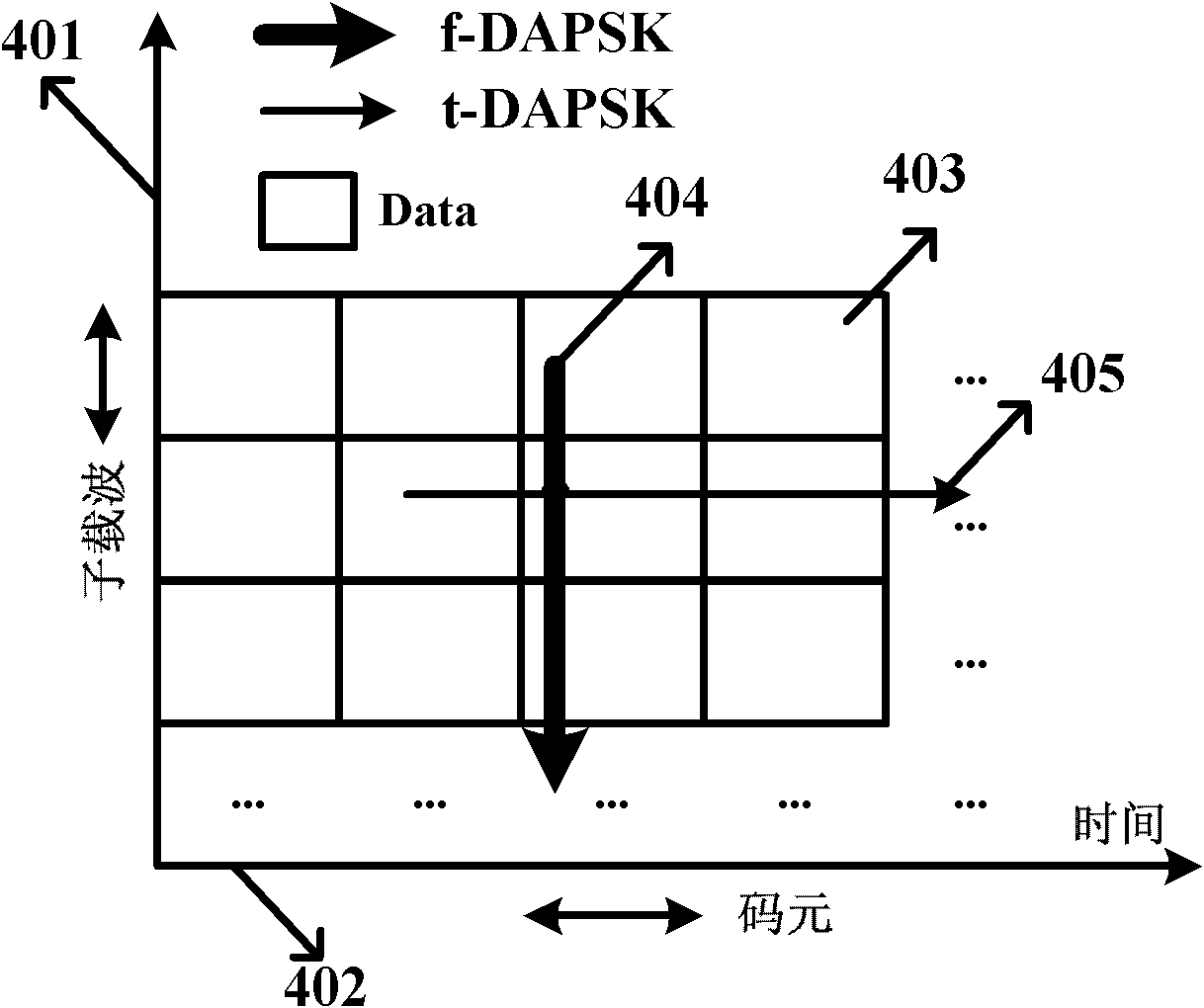
Multi-carrier Optical Communication Method and System Based on DAPSK
ActiveUS20130070866A1Improve toleranceSpectrum efficiency of spectrum is reducedError preventionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsFrequency spectrumStream data
The present invention provides an optical communication method, comprising: performing modulation on the obtained bit stream data to generate modulated signals; performing differential encoding on the modulated signals to generate differentially encoded signals; converting the differentially encoded signals into electrical signals; and mapping the electrical signals onto optical carriers to generate optical signals for transmission. With the present invention, it is possible to enhance the system's capability of resisting inter-carrier interference without decreasing spectrum efficiency, hence improving the tolerance of existing optical communication systems towards laser linewidth, fast-changing PMD, optical fiber nonlinearity, inter-channel interference and other damages, greatly enhancing system performances.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
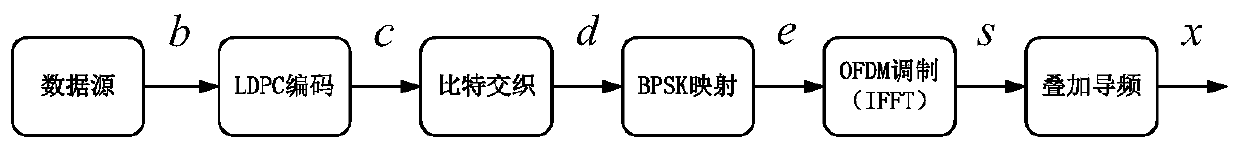
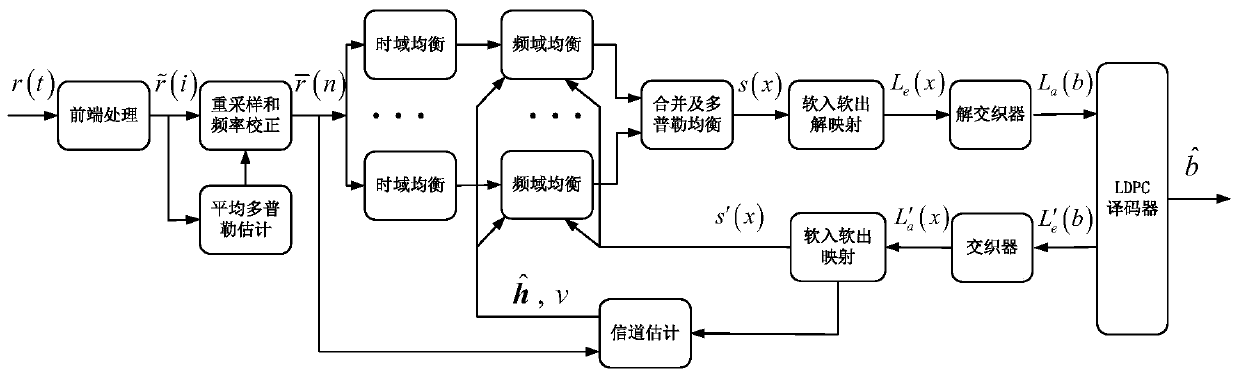
An OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) underwater acoustic communication method with high spectral efficiency under a time-varying double-spread channel condition
ActiveCN109743118AImprove reliabilityReduce complexityMulti-frequency code systemsBandpass filteringFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses an OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) underwater acoustic communication method with high spectral efficiency under a time-varying double-spread channel condition, and belongs to the technical field of underwater acoustic communication. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out band-pass filtering on a received signal r (k), carrying out front-endprocessing such as ADC (Analog to Digital Converter) conversion into a digital signal, carrying out down-conversion and low-pass filtering, estimating average Doppler by utilizing a fuzzy function method, carrying out resampling and frequency correction, multiplexing the signal, carrying out time domain equalization and frequency domain equalization, carrying out diversity combination, and then adopting the OMP-DCD algorithm to perform residual Doppler compensation. an iterative signal processing technology is adopted, an LDPC decoder and an equalizer are cascaded through soft-in soft-out mapping / demapping and an interleaver / deinterleaver, close information interaction is achieved in the two modules, soft information transmitted in a reciprocating mode is fully utilized, and interferenceof a time-varying double-spread channel is effectively resisted. According to the method, the complexity and the performance can be well compromised, and serious inter-symbol interference, inter-carrier interference and pilot frequency-pilot frequency interference in the transmission process are efficiently solved. And the method is low in complexity and can be realized on the DSP in real time.
Owner:三亚哈尔滨工程大学南海创新发展基地
Adaptive pilot design for mobile system
A method, and device implementing the method, for adaptively allocating pilot signals in a wireless communication system. The method includes receiving channel data, including channel length (L) data, inter-carrier interference power (PICI) data, coherence time (CT) data, and a number of subcarriers (N). The method further includes selecting, when L is greater than a first channel length threshold (LTH1), a first number of pilot signals between a minimum value of L and a maximum number of pilot signals NP,MAX, wherein the first number of pilot signals NP are equally spaced in time according to the CT data, and equally spaced in frequency. Further, the method includes selecting, when L is less than LTH1 and PICI is less than a power threshold (PTH), a second number of pilot signals such that the second number of pilot signals is between the minimum value of L and NP,MAX, wherein the second number of pilot signals are equally spaced in time according to the CT data, and equally spaced in frequency. Finally, the method includes selecting, when L is less than LTH1 and PICI is greater than PTH, a third number of pilot signals such that the third number of pilot signals is equal to n times L (nL), wherein n is an integer, the third number of pilot signals being equally spaced in time according to the CT data, and allocated according to a cluster(n) clustered pilot scheme with a cluster size equal to n, the n-sized clusters being clustered in frequency.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
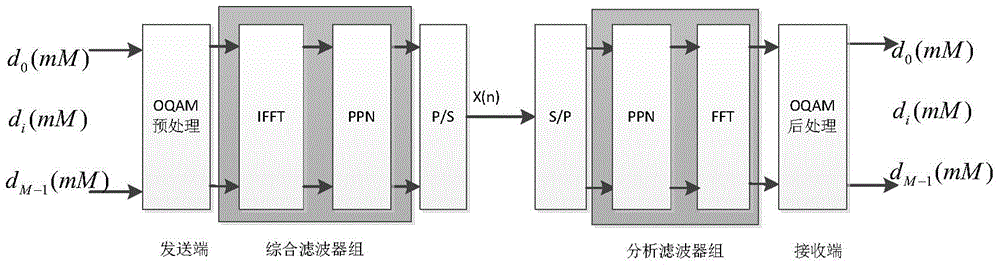
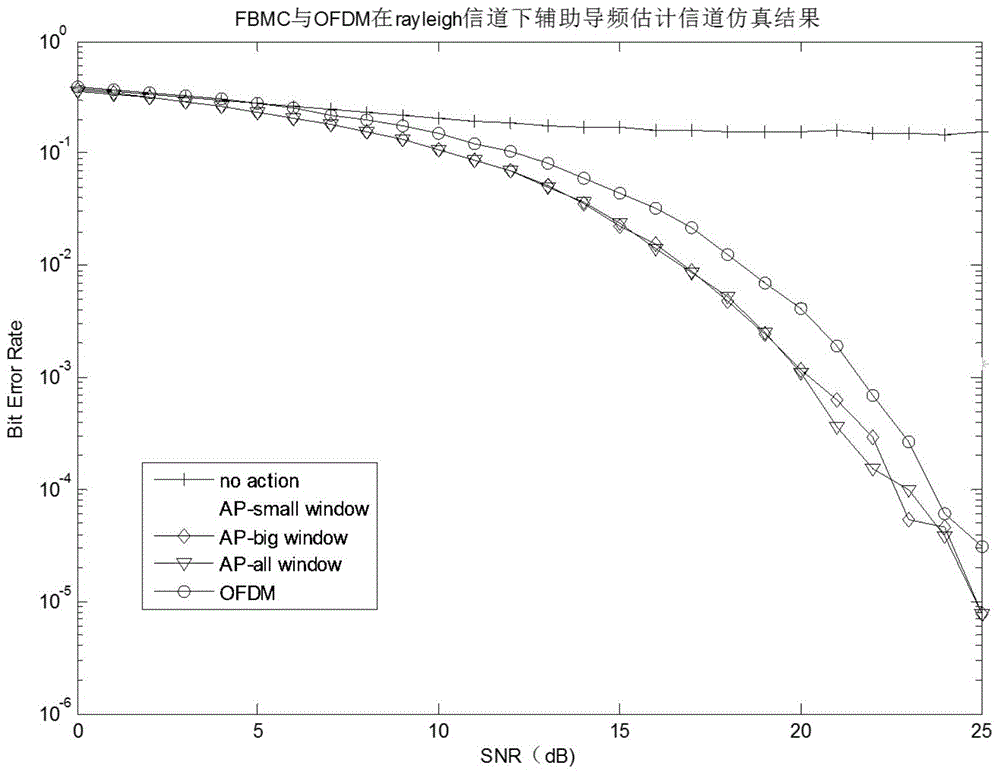
Auxiliary pilot method used for FBMC (Filter Bank Multicarrier) system channel estimation
InactiveCN104954299AInherent interference cancellationAccurate channel estimationChannel estimationInterference factorCarrier signal
FBMC (Filter Bank Multicarrier) is a special carrier communication mode. Being different from OFDM (Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing), subcarriers of the FBMC are not orthogonal to one another, so that intersymbol interference and inter-carrier interference naturally exist. A traditional OFDM channel estimation method is built on the basis of no intersymbol interference and inter-carrier interference, thereof, to carry out accurate channel estimation, the interference of surrounding symbols to a pilot symbol must be eliminated, and surrounding interference factors are definite under a certain filter bank structure and a prototype filter design. An auxiliary pilot method is such a method that an auxiliary pilot is placed nearby the position of an actual pilot, the value of the auxiliary pilot is determined by virtue of the values of the surrounding symbols and the corresponding interference factors, and the interference of the surrounding symbols to the pilot position is eliminated by virtue of the auxiliary pilot, so as to carry out accurate channel estimation.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
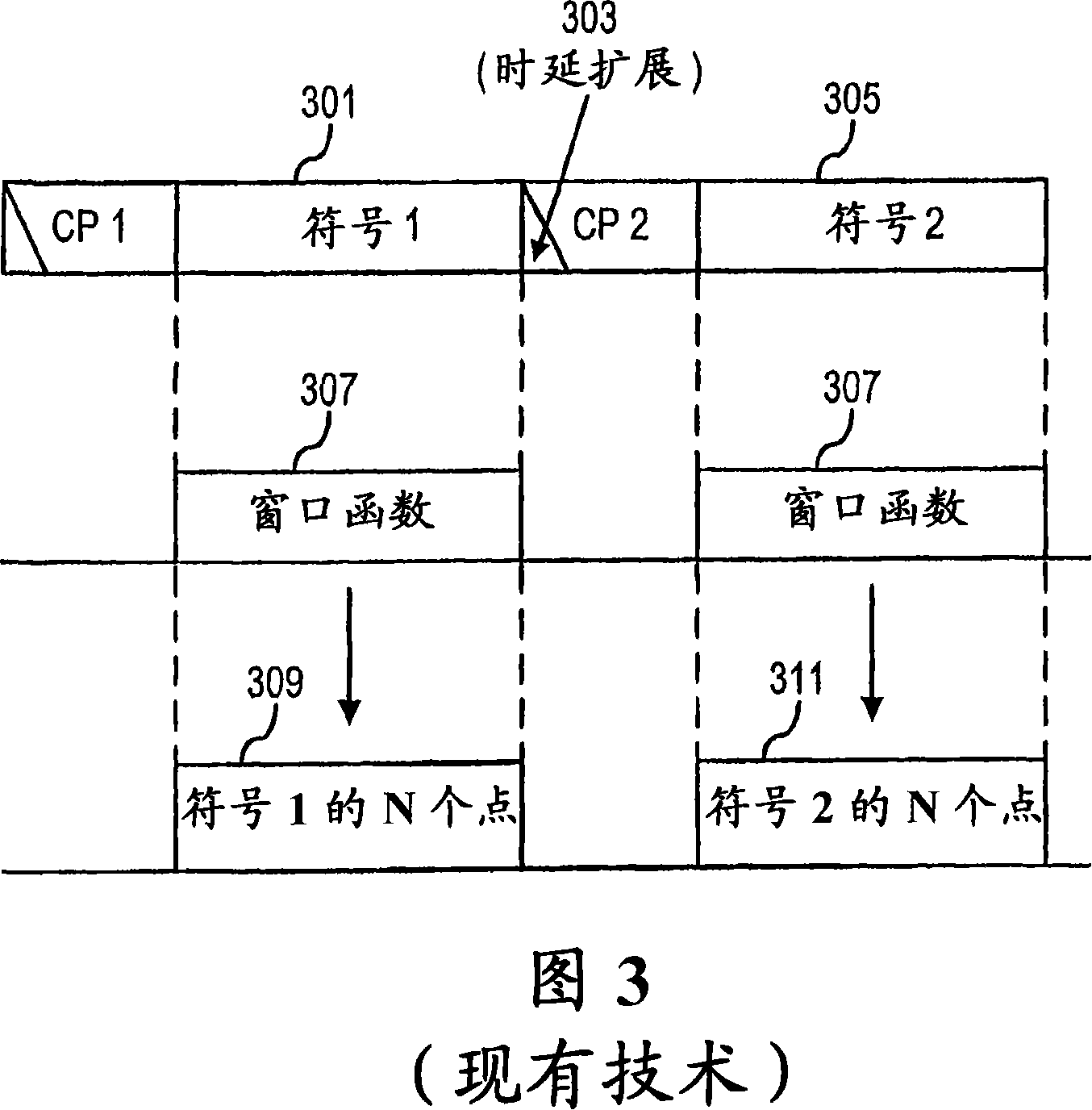
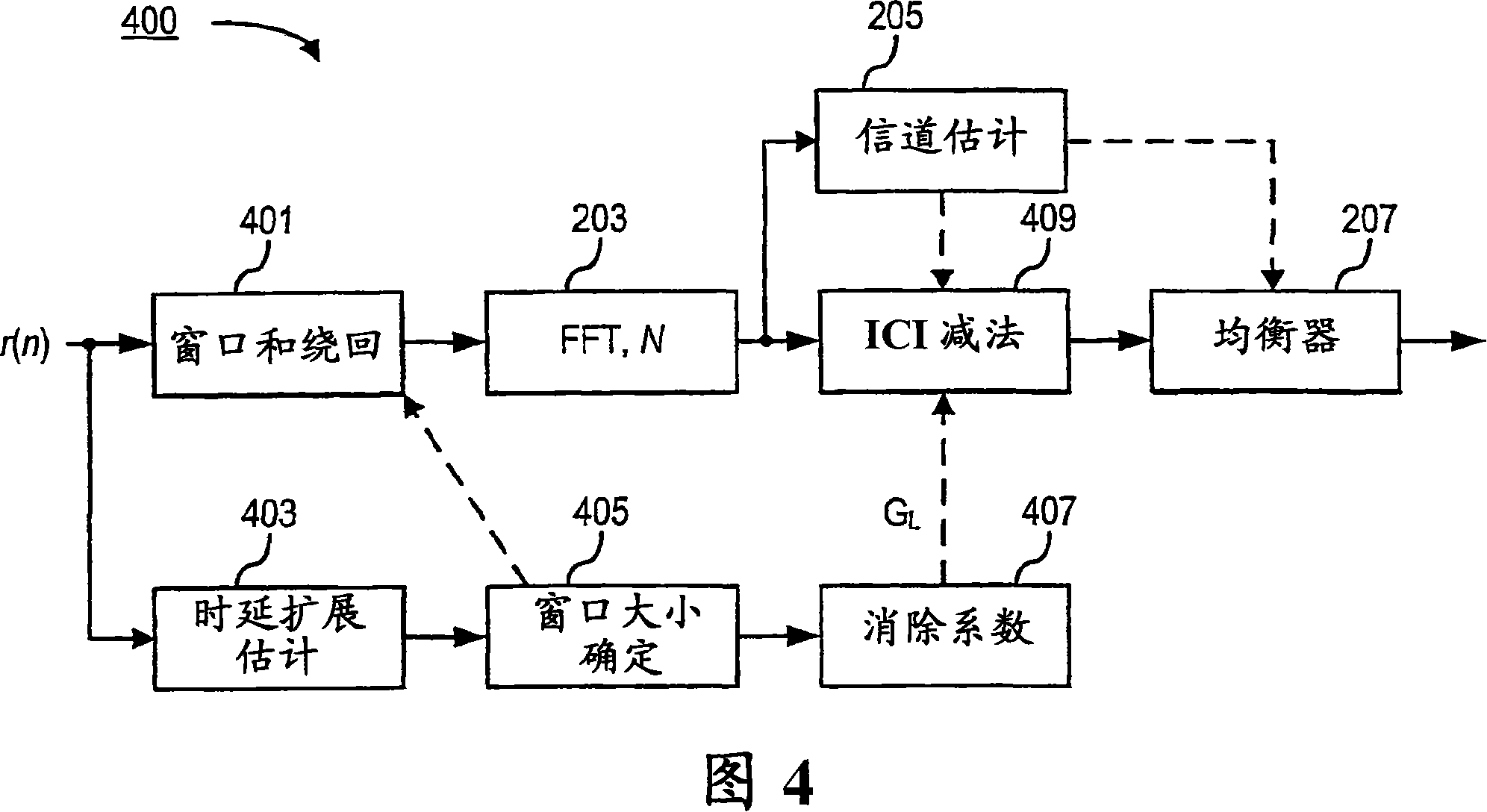
Time domain windowing and inter-carrier interference cancellation
InactiveCN101204057AMulti-frequency code systemsTransmission noise suppressionTime domainCarrier signal
Inter-carrier interference (ICI) in a kth sub-carrier of an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) signal received at time t is reduced, wherein the received OFDM signal comprises a plurality of sub-carriers. This is achieved by generating a self-interference term, ICIk−L,k−L, for a signal received on sub-carrier k−L, wherein L ∈ [ . . . , −3,−2,−1,1,2,3, . . . ], and wherein the self-interference term is an estimate of the data received at time t on the sub-carrier k−L, weighted by a rate of change of the channel through which sub-carrier k−L passes at time t. An ICI cancellation coefficient, GL is obtained, and an estimated ICI term is generated by adjusting the self-interference term, ICIk−L,k−L, by an amount based on the ICI cancellation coefficient, GL. The estimated ICI term is then subtracted from a term representing a signal received on the kth sub-carrier at time t.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com