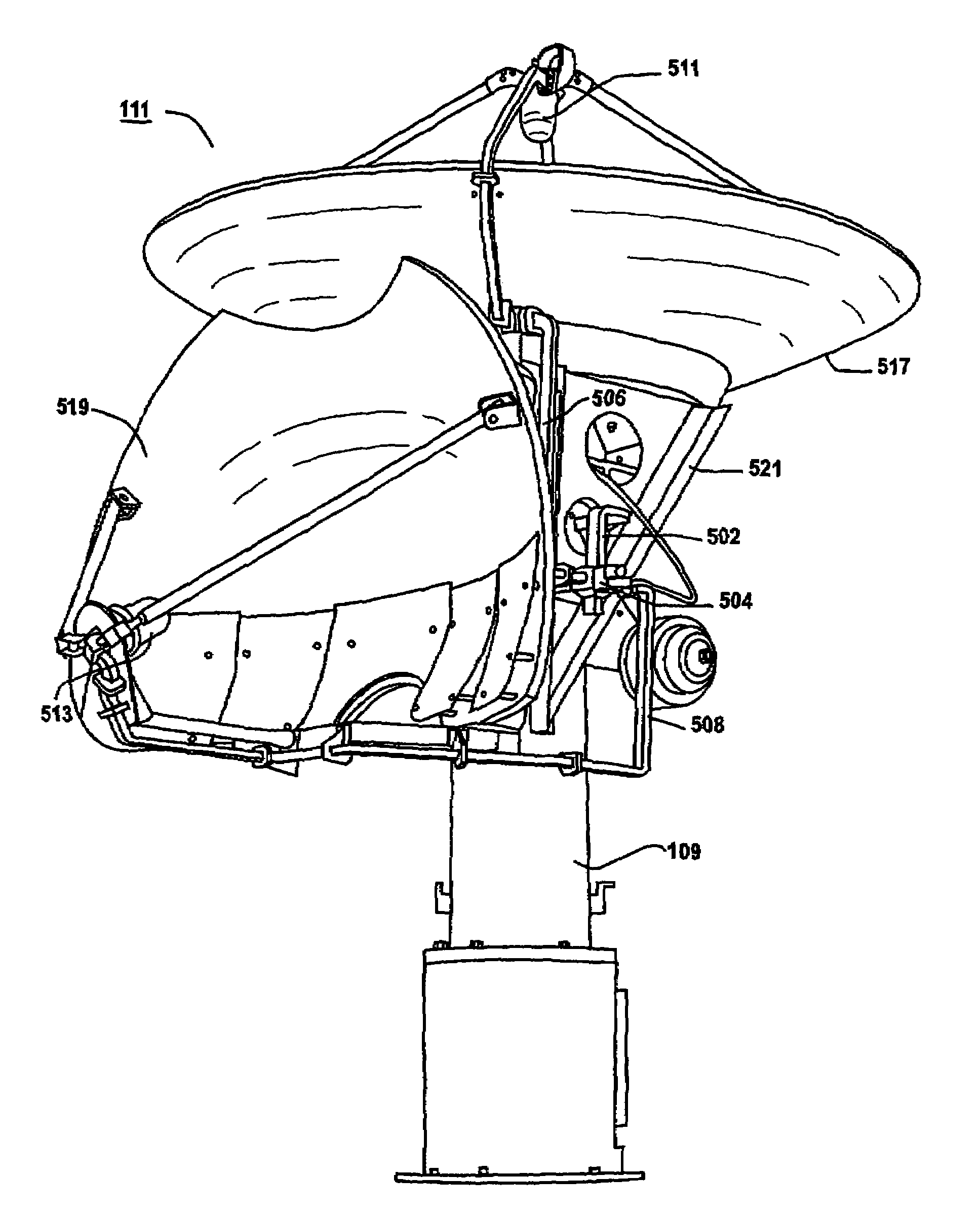
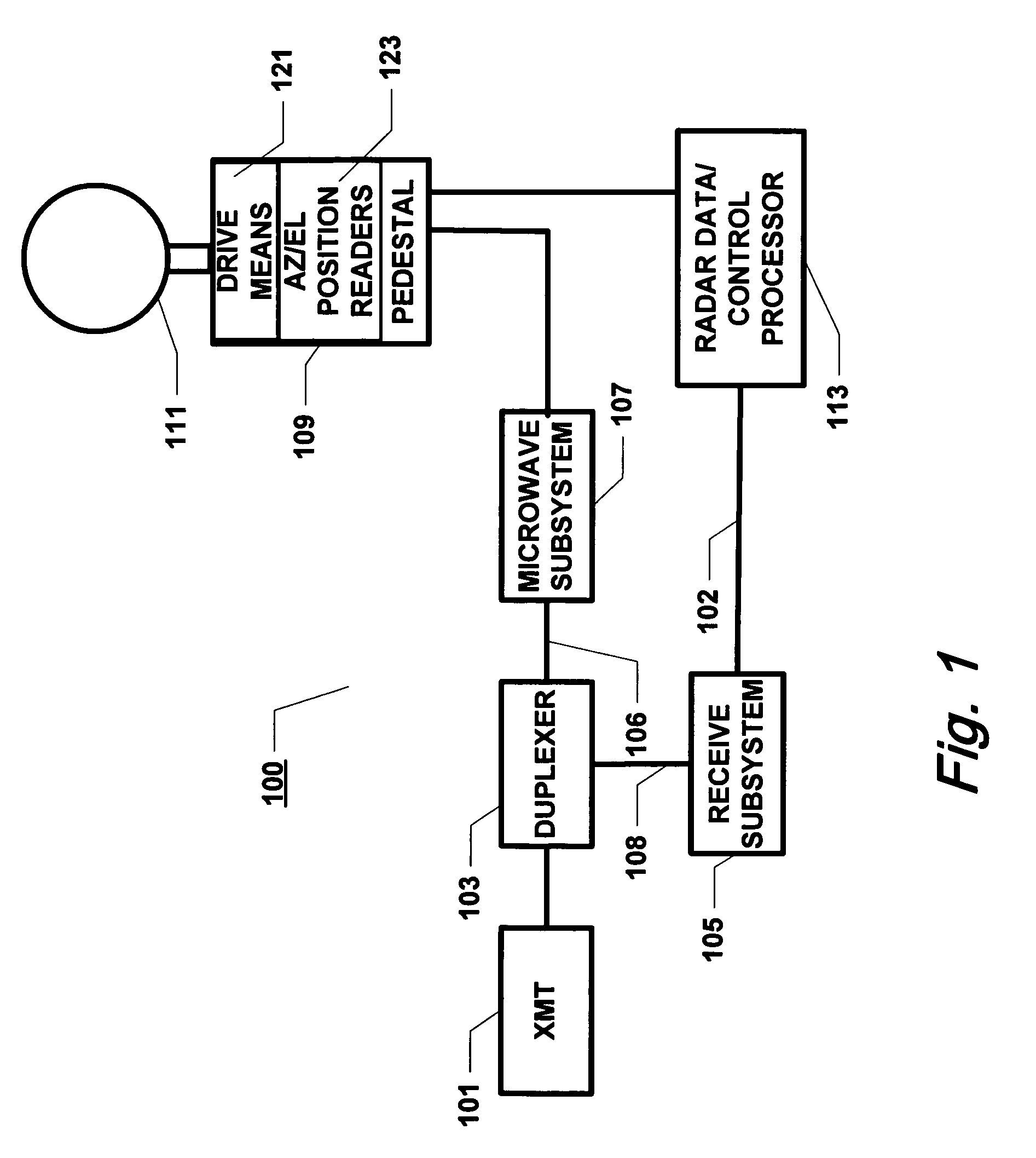
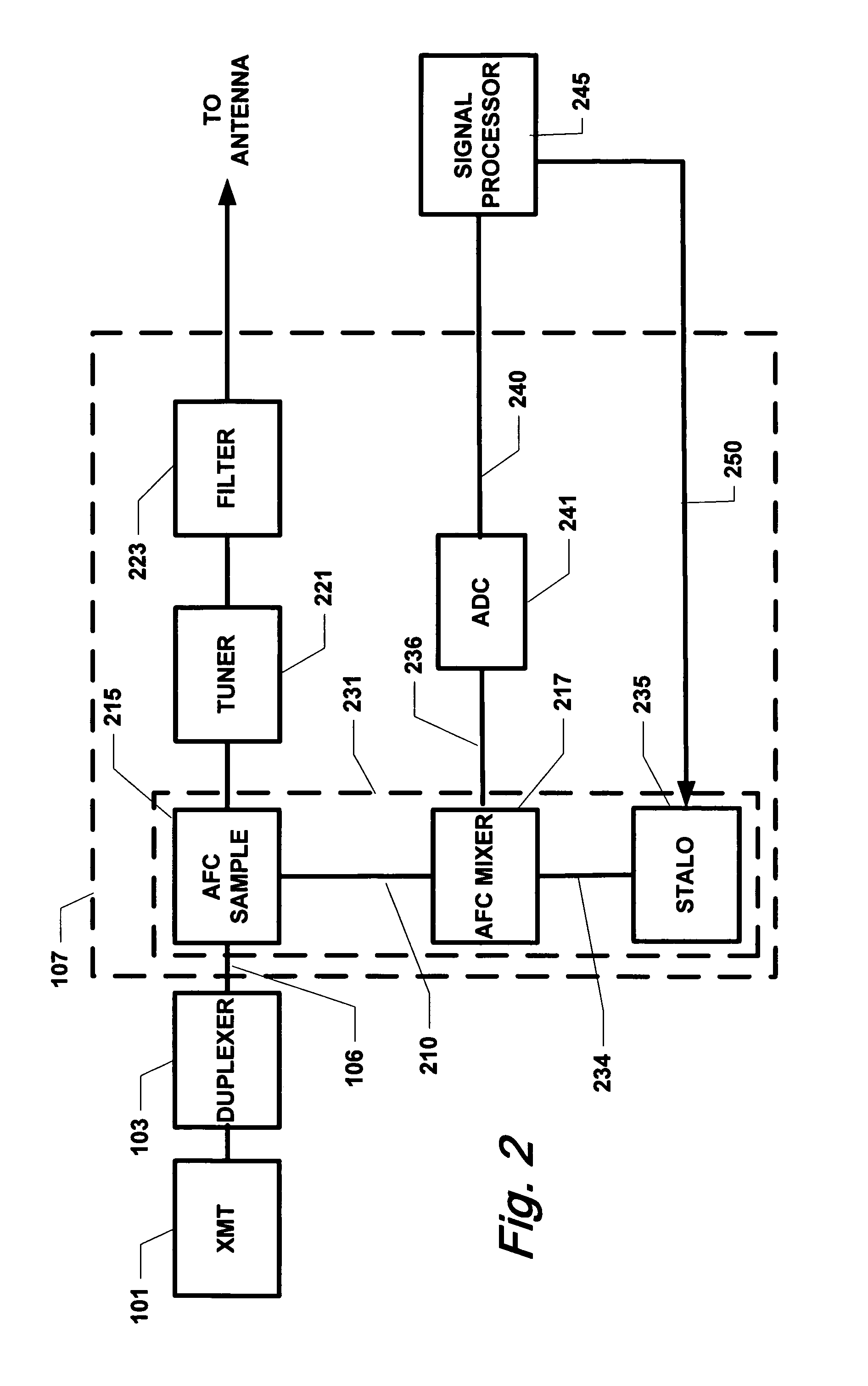
Patents
Literature
77 results about "Secondary surveillance radar" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
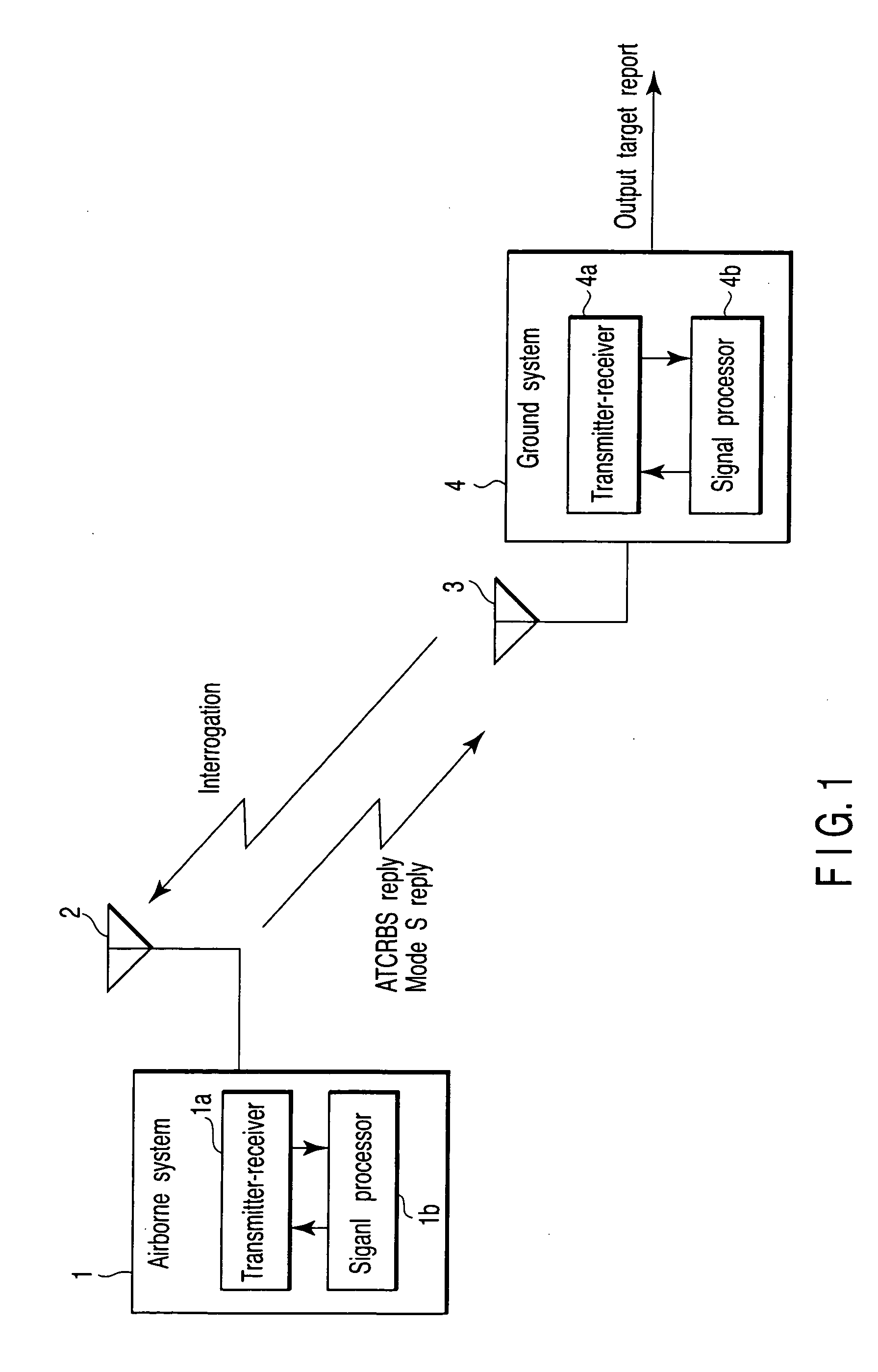
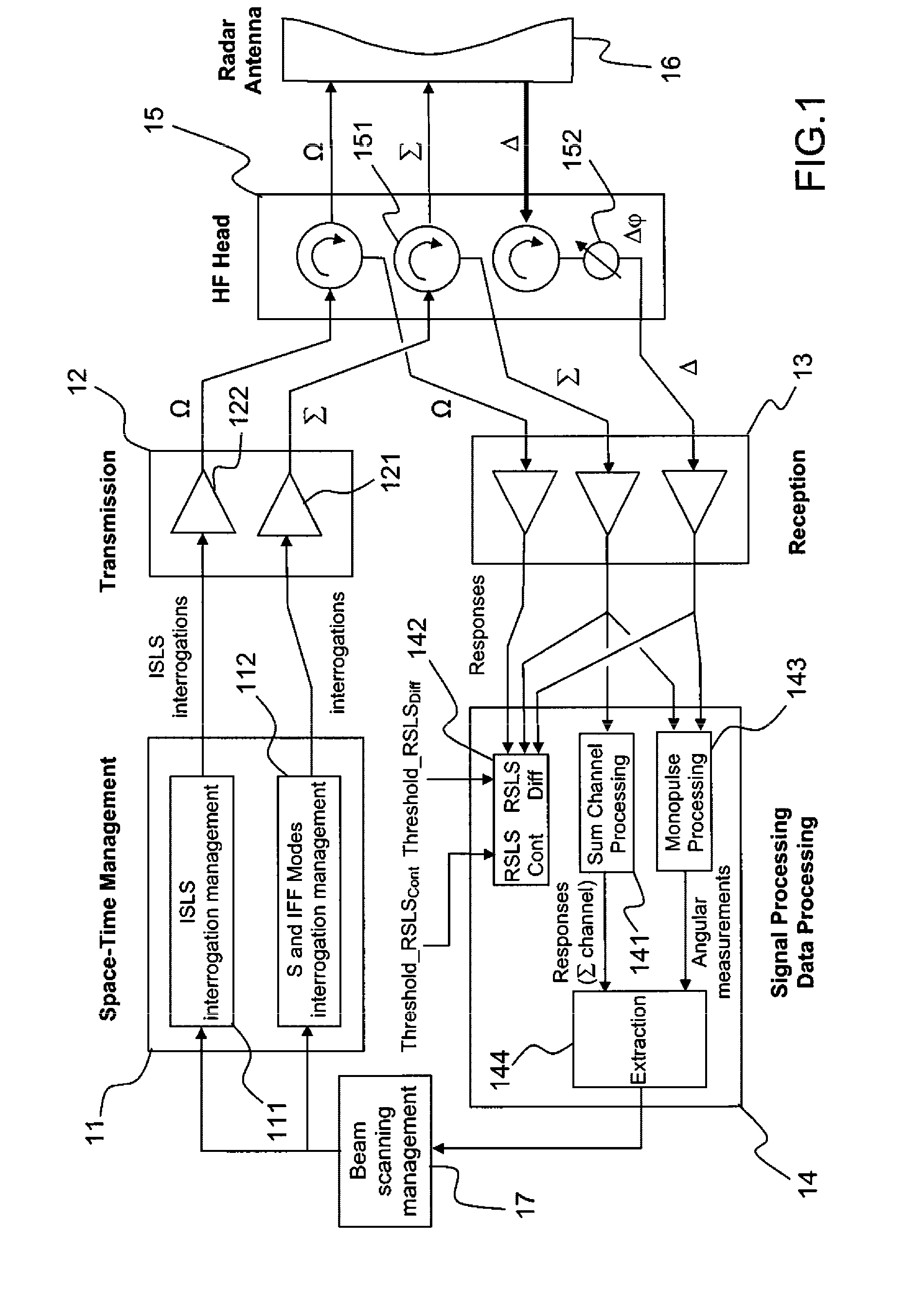
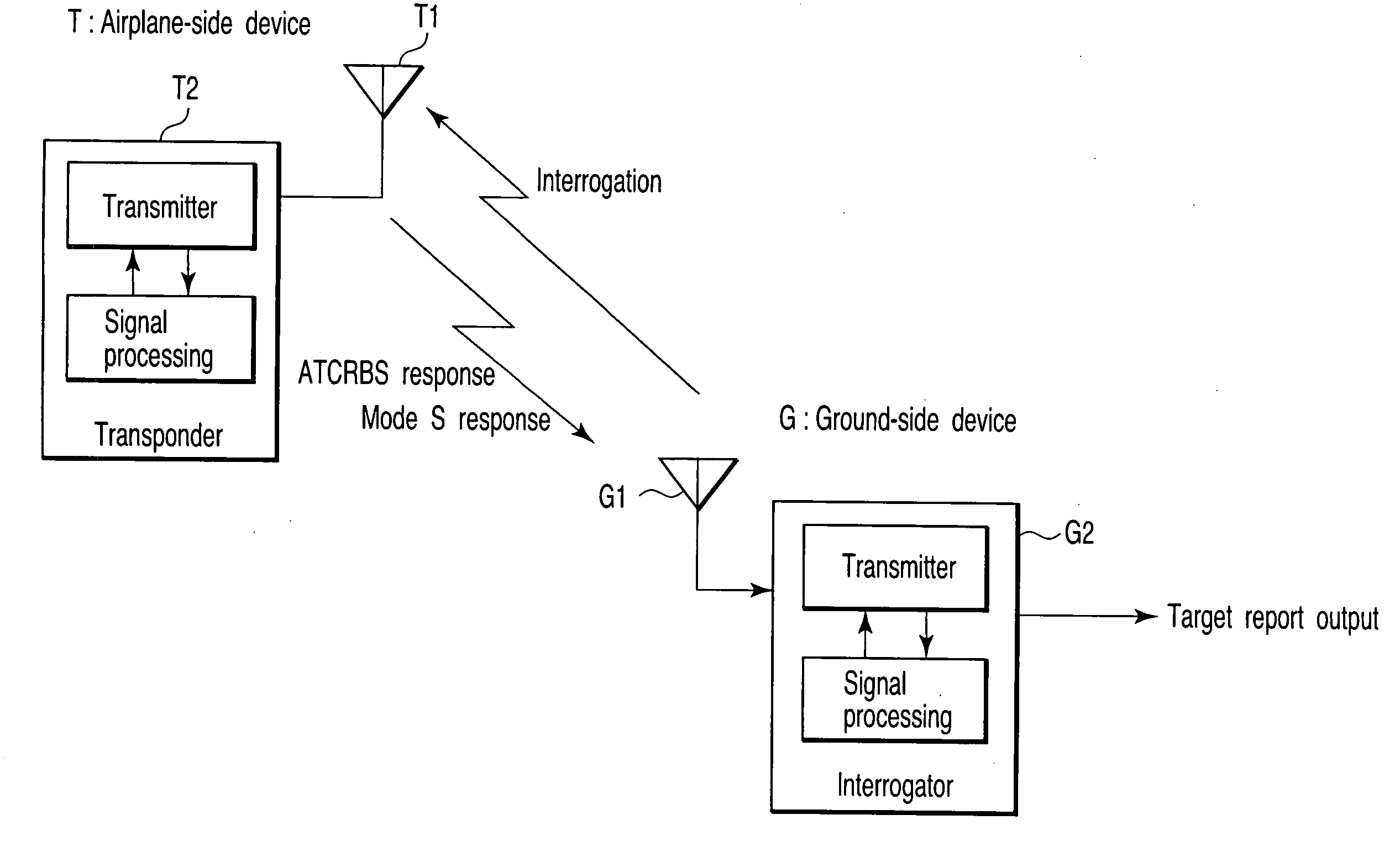
Secondary surveillance radar (SSR) is a radar system used in air traffic control (ATC), that not only detects and measures the position of aircraft, i.e. bearing and distance, but also requests additional information from the aircraft itself such as its identity and altitude. Unlike primary radar systems that measure the bearing and distance of targets using the detected reflections of radio signals, SSR relies on targets equipped with a radar transponder, that replies to each interrogation signal by transmitting a response containing encoded data. SSR is based on the military identification friend or foe (IFF) technology originally developed during World War II, therefore the two systems are still compatible. Monopulse secondary surveillance radar (MSSR), Mode S, TCAS and ADS-B are similar modern methods of secondary surveillance.
Classification system for radar and sonar applications
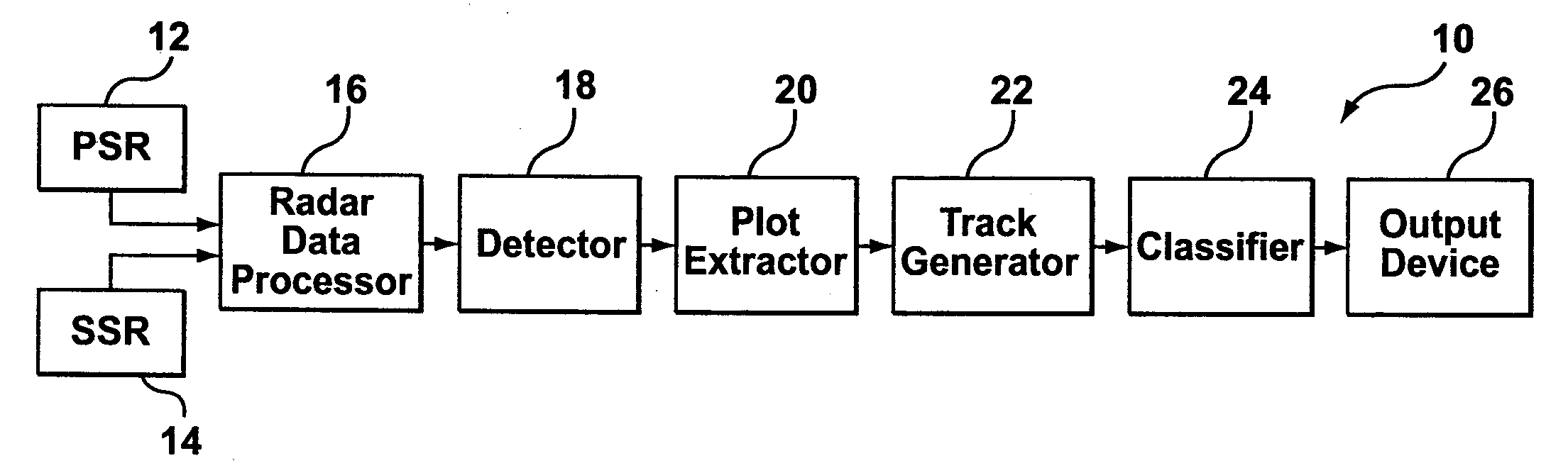
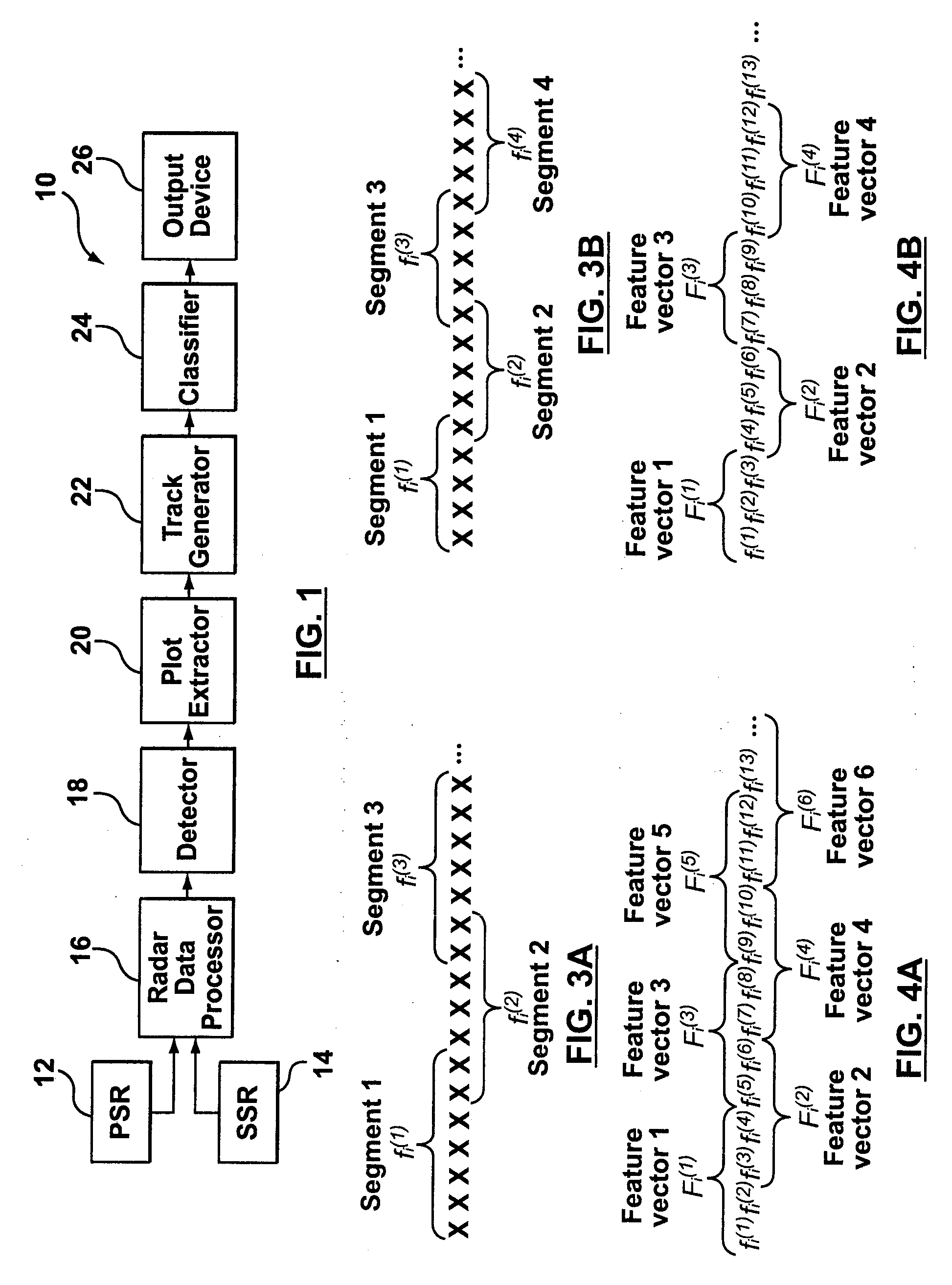
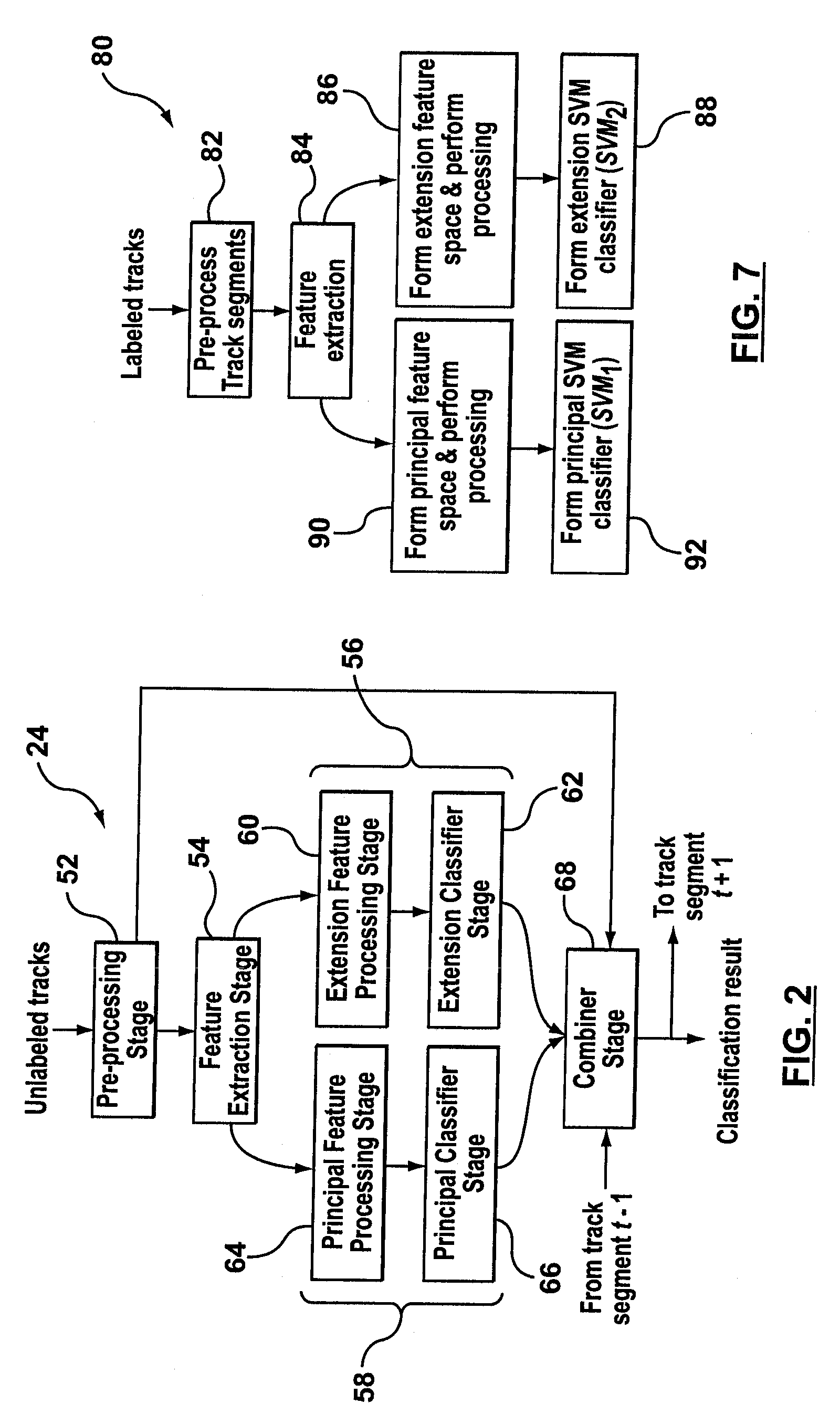
ActiveUS20070024494A1ICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSecondary surveillance radarBiological target
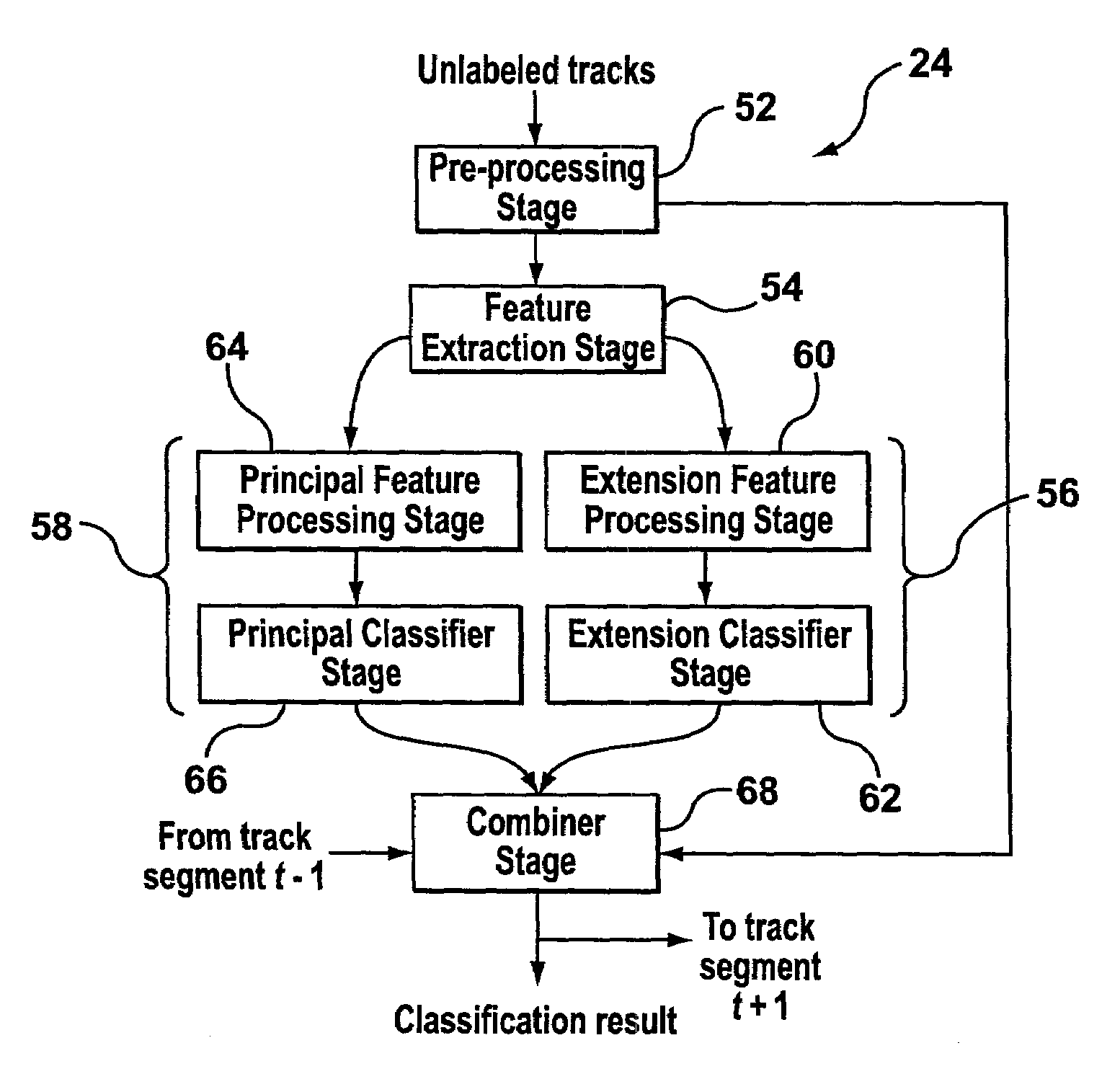
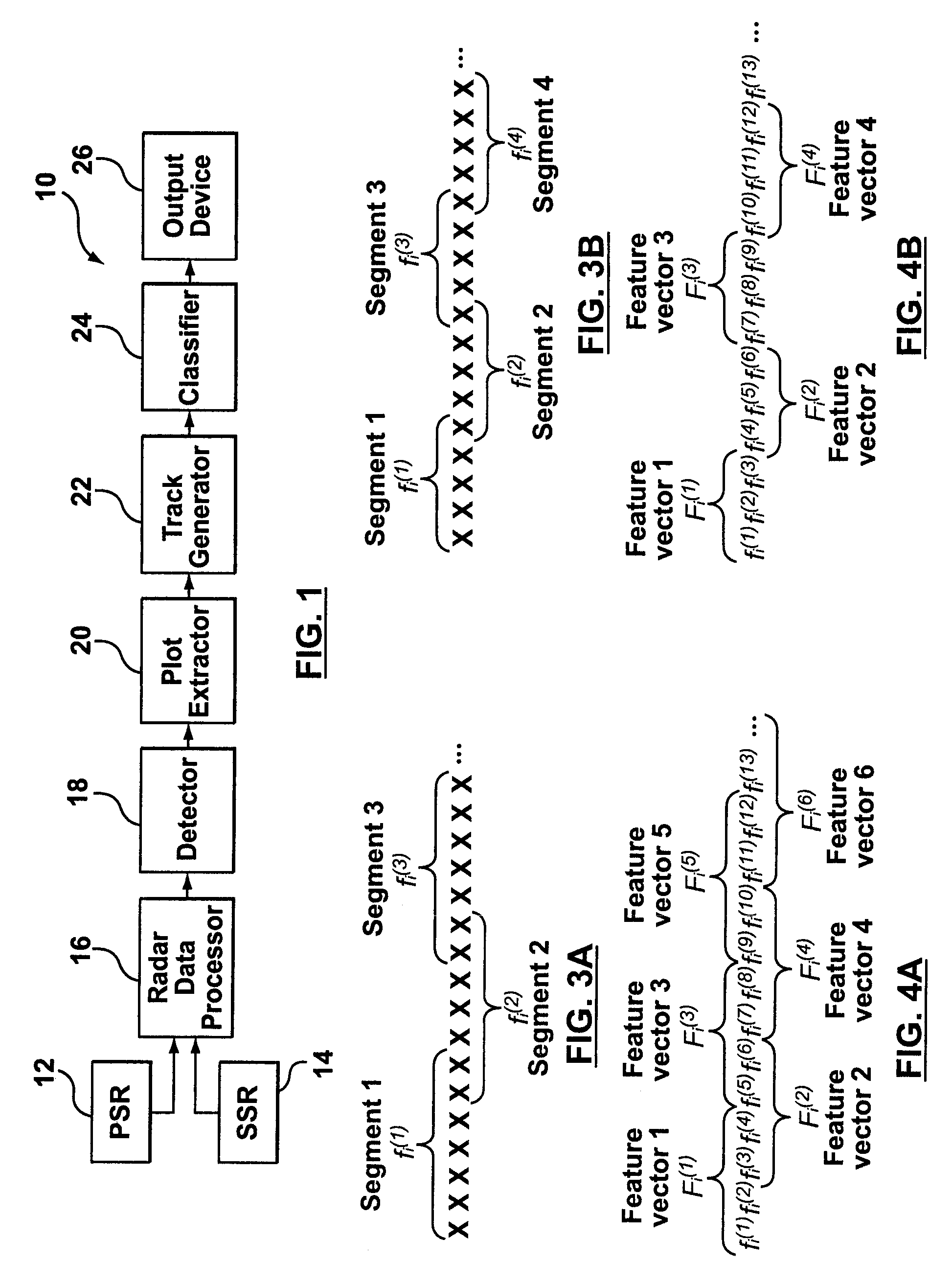
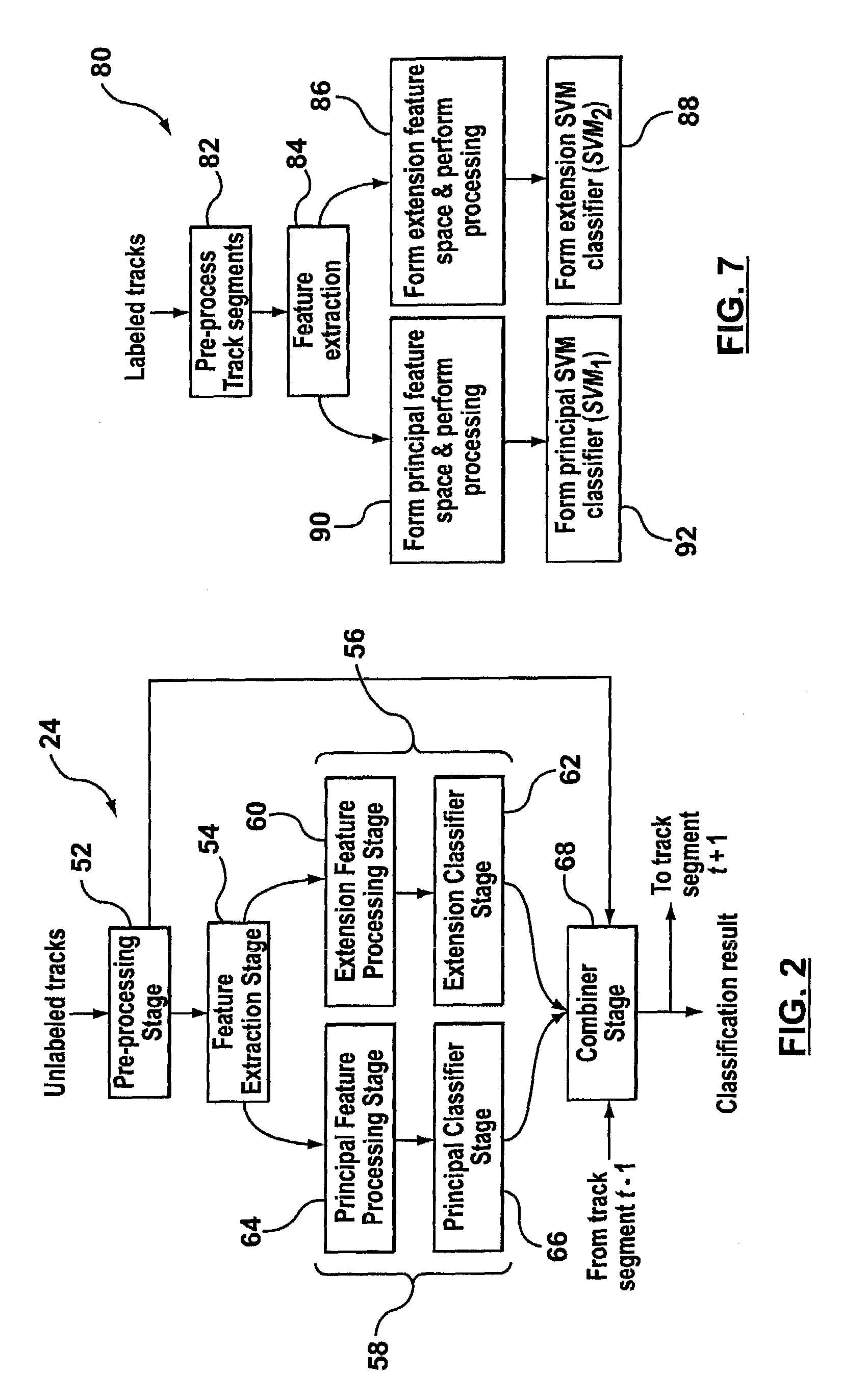
A system and method for target classification for an aircraft surveillance radar is provided. In one implementation, the track classifier provides tracks with an updated probability value based on its likelihood to conform to aircraft and non-aircraft target behavior. The track classifier identifies false tracks that may arise from weather and biological targets, and can detect aircrafts lacking Secondary Surveillance Radar (SSR) data. Various features and combinations of features are evaluated using a proposed clustering performance index (CPI) and used to discriminate between aircrafts and false tracks.
Owner:RAYTHEON CANADA LTD
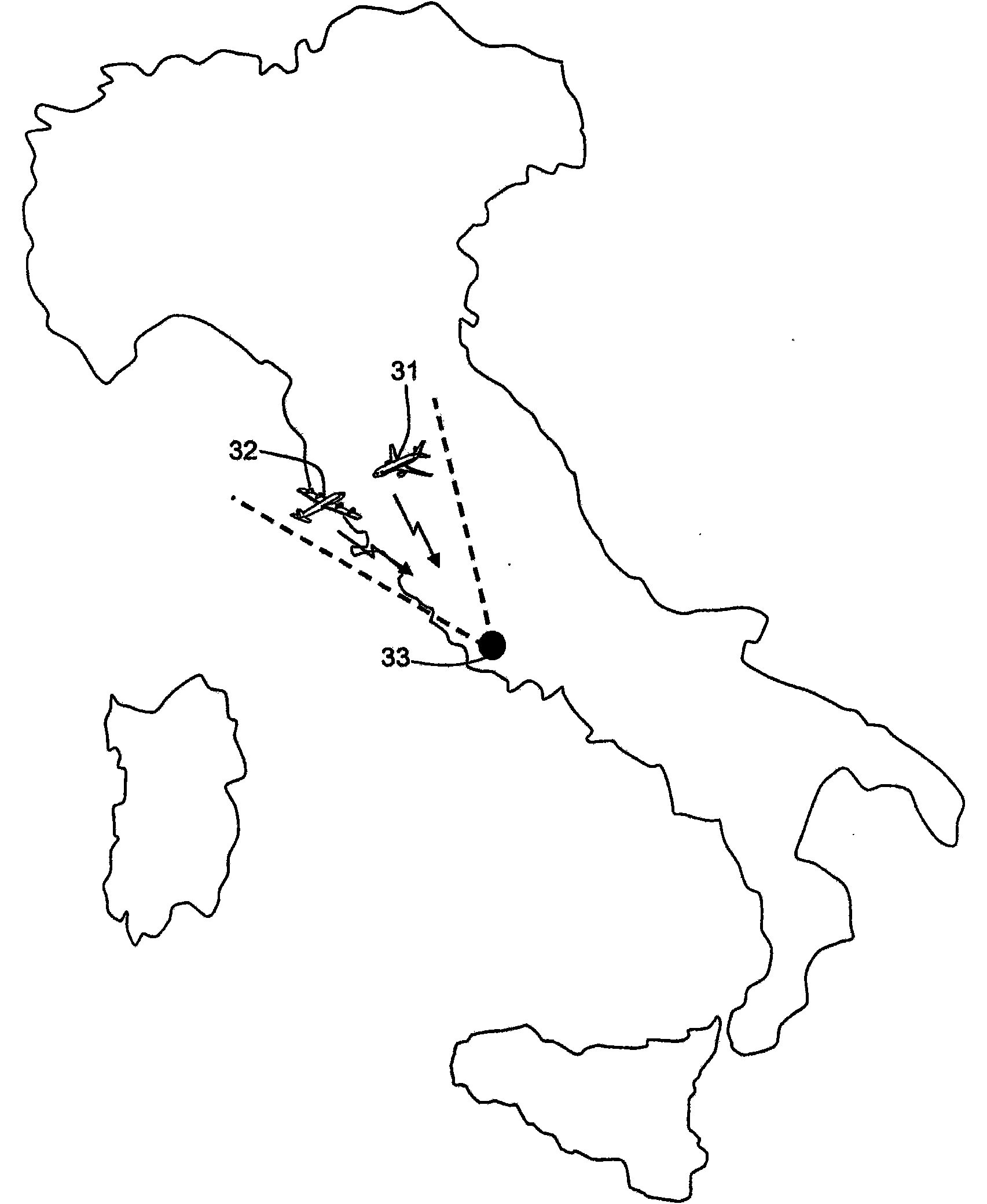
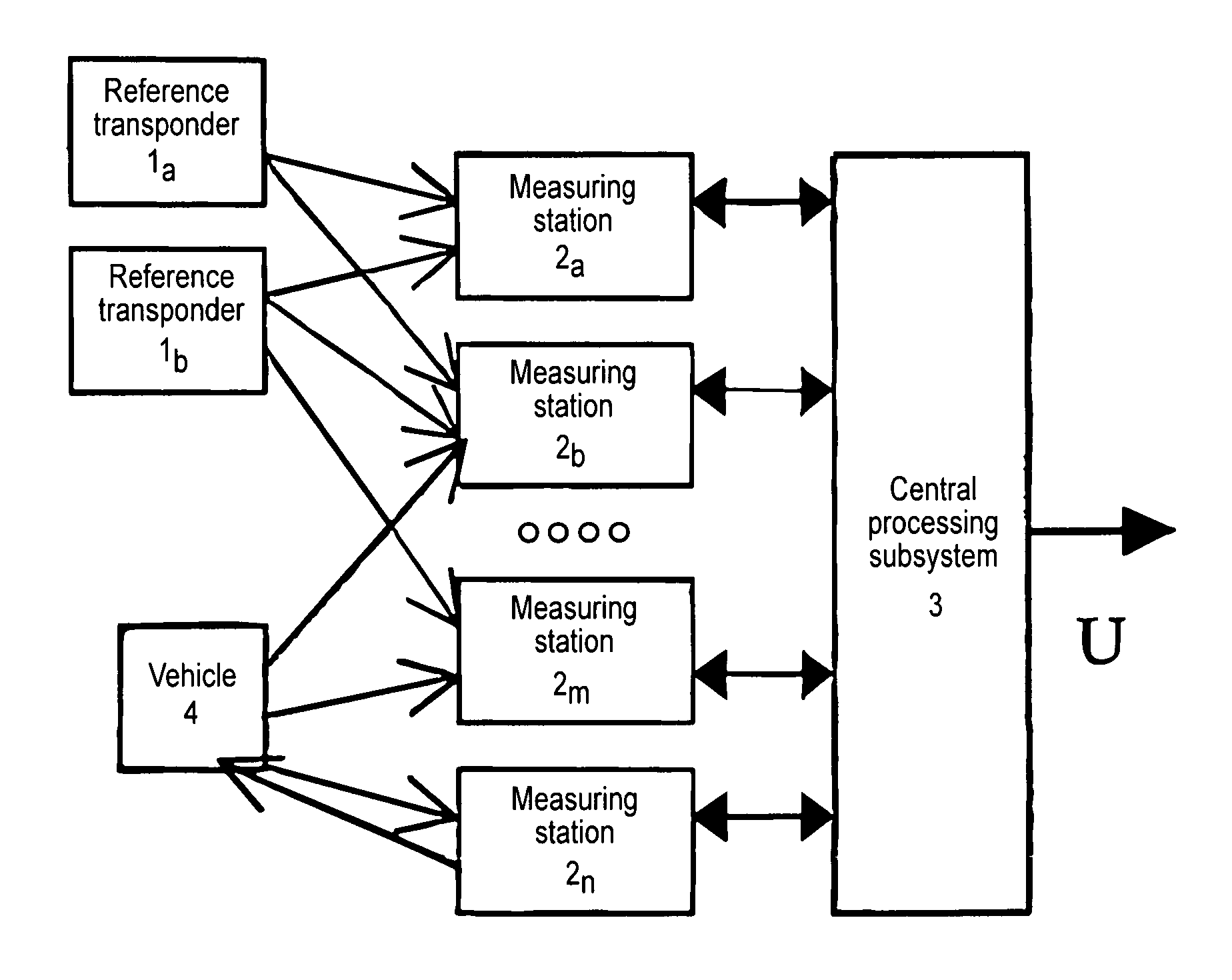
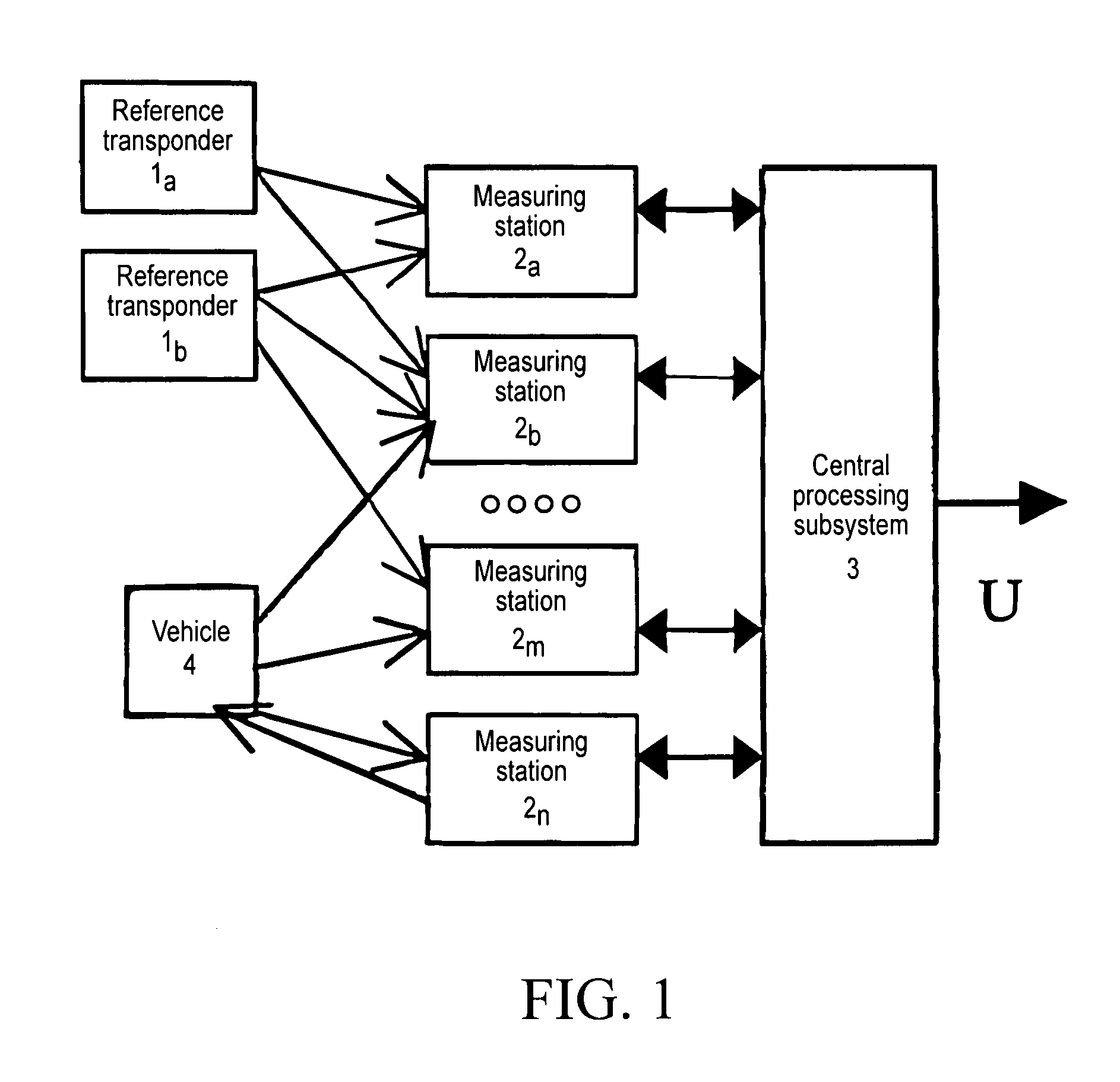
High Precision Surveillance System by Means of Multilateration of Secondary Surveillance Radar (SSR) Signals
ActiveUS20080231494A1Good estimateImprove efficiencyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSecondary surveillance radarSpite
A system able to locate and identify aircraft and vehicles based on the reception and processing, with novel means and methods, of signals emitted by the transponder of the secondary surveillance radar, shortly SSR. The system has a number of fixed stations distributed in the area of interest, e.g. in the airport area; any signal (the well known SSR reply / squitter) transmitted by the on-board transponder is received by four or more stations and the measurement of three or more differences of times of arrival (TOA) permits the reconstruction of the position of the transponder in spite of the fact that the transmission time is unknown. Suitable algorithms based on optimal estimation enhance both the accuracy of TOA measurements and the accuracy of the reconstructed position. The effects of possible overlapping of signal in time are avoided or mitigated by multiple source separation techniques based on least squares algebraic processing.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROME TOR VERGATA
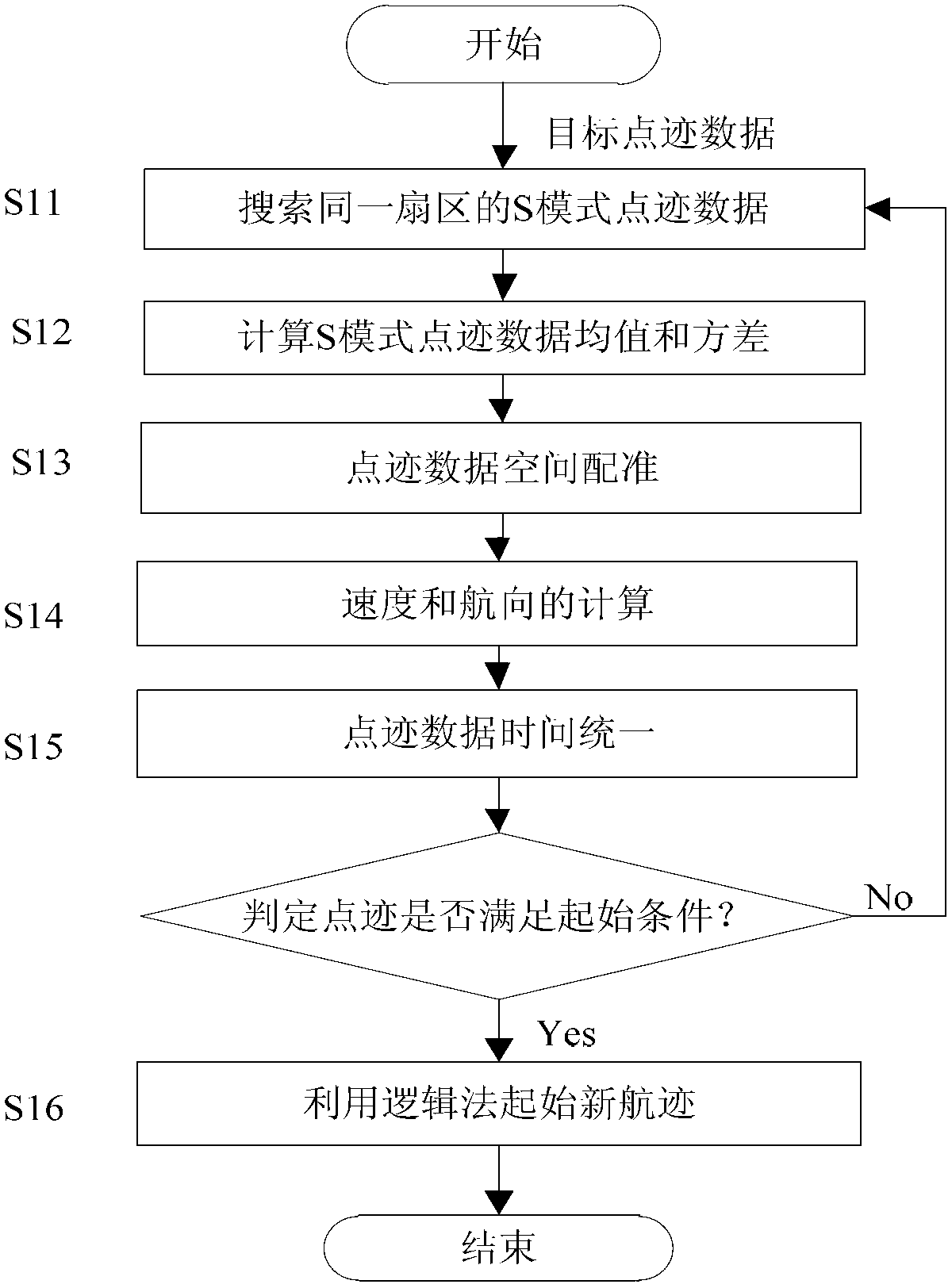
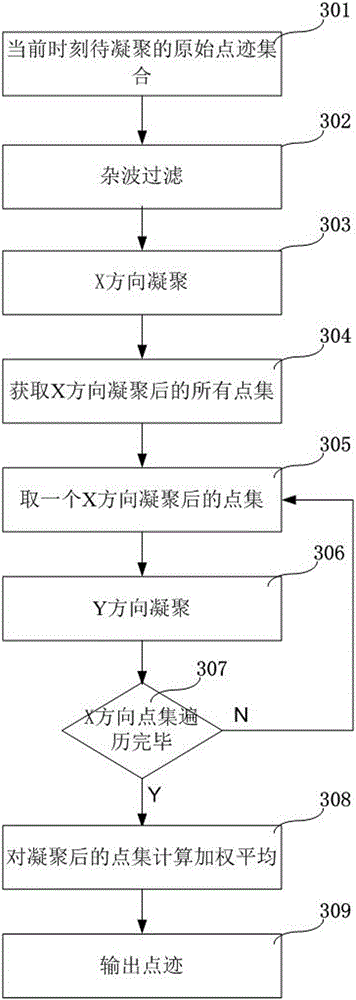
Secondary surveillance radar track extraction method for multimode polling and S-mold roll-calling interrogation
InactiveCN103076605ASolve technical problems that are difficult to removeImprove accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSecondary surveillance radarTime space
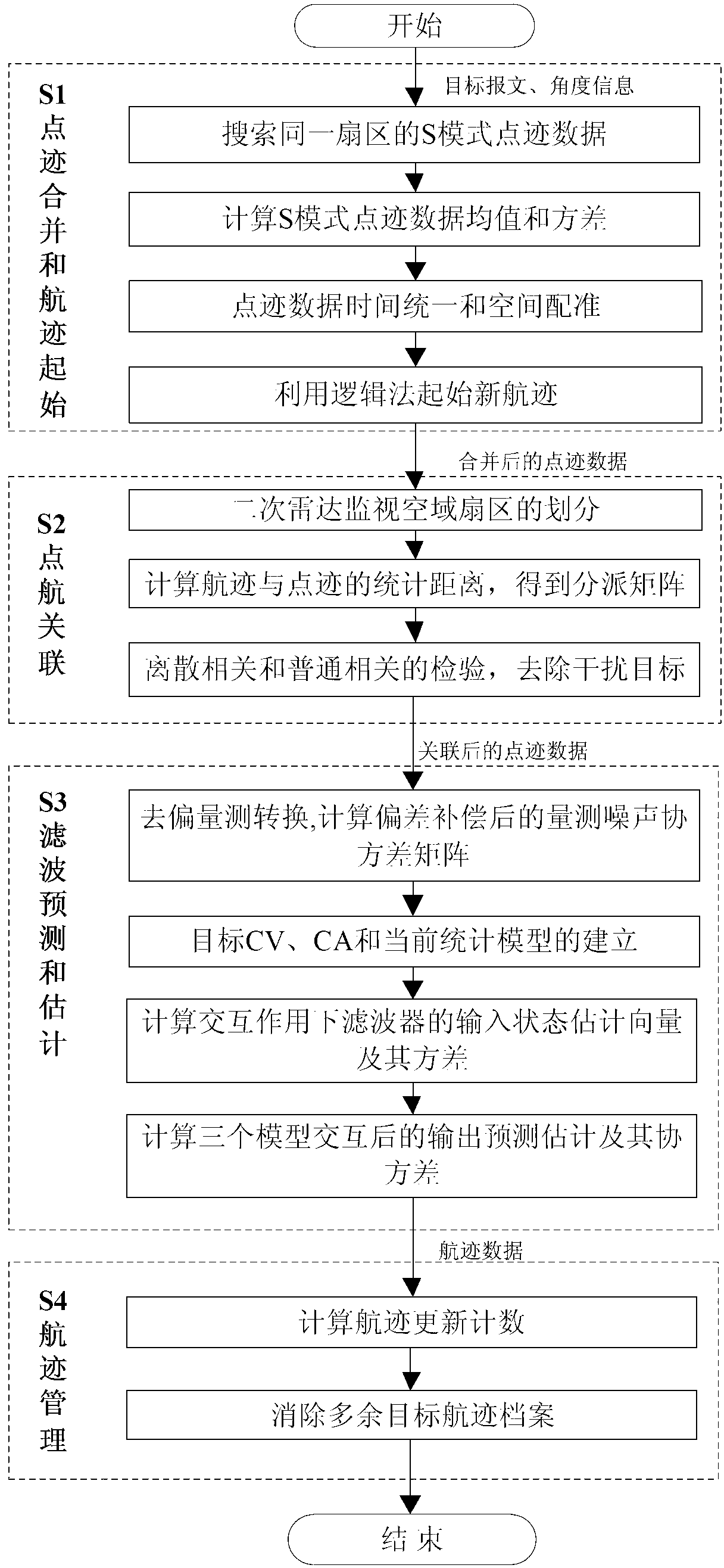
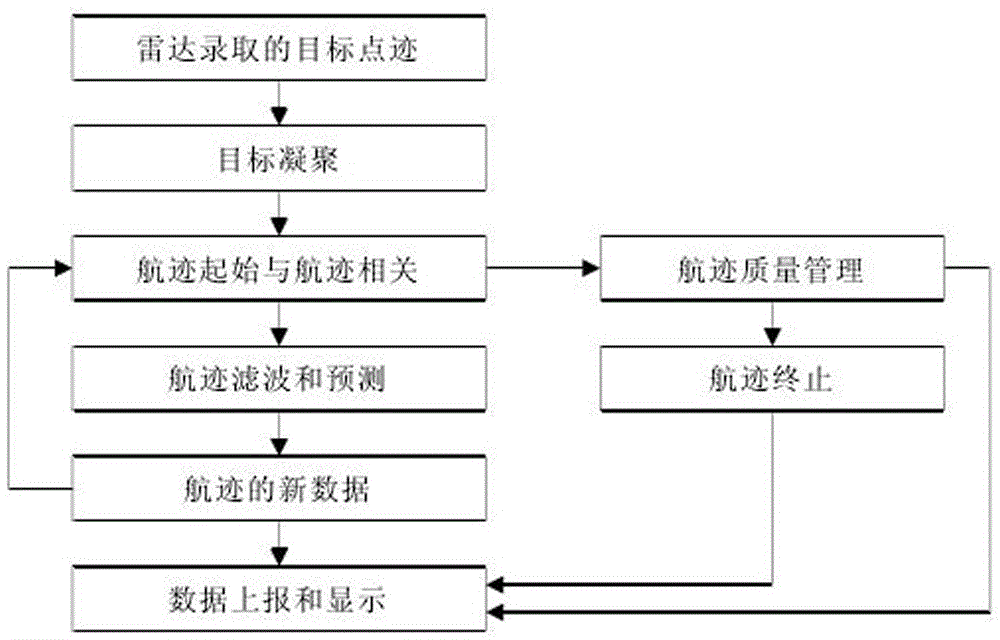
The invention provides a secondary surveillance radar track extraction method for multimode polling and S-mold roll-calling interrogation. By using the method, false targets under an interference environment can be effectively removed and the accuracy and the real-time performance of the S-mode query are improved. The method is realized through the technical scheme that plot combination is conducted to S-mode plot data which is searched from the same sector of a secondary surveillance radar interrogator, the mean value and the variance of the plot data are calculated, and a real track is initiated after time-space registration; the combined plot data is divided according to the sector characteristic of radar and an associated sector window is created to enter a plot and track processing flow; firstly de-biased measurement conversion is conducted to the associated plot data, a CV (Constant Velocity) model, a CA (Constant Acceleration) model and a current statistical model are combined into a target multi-model, and the interactive input state estimation vector and the variance of each filter under an interactive effect are calculated; interference targets are removed by adopting interference target removing strategies; and unnecessary target files are removed through track management, tracking is ended and a correct target track extraction result of the secondary surveillance radar is given.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
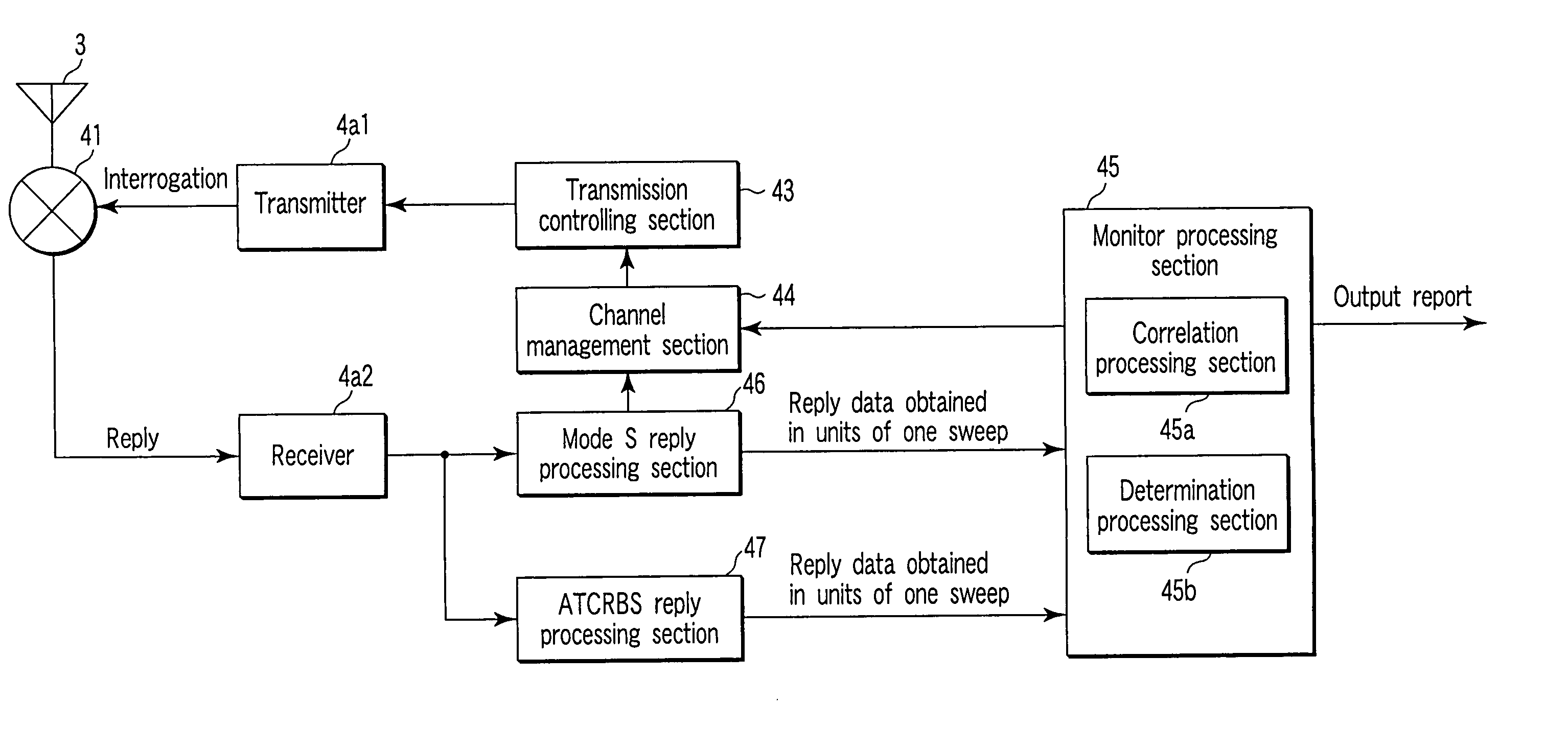
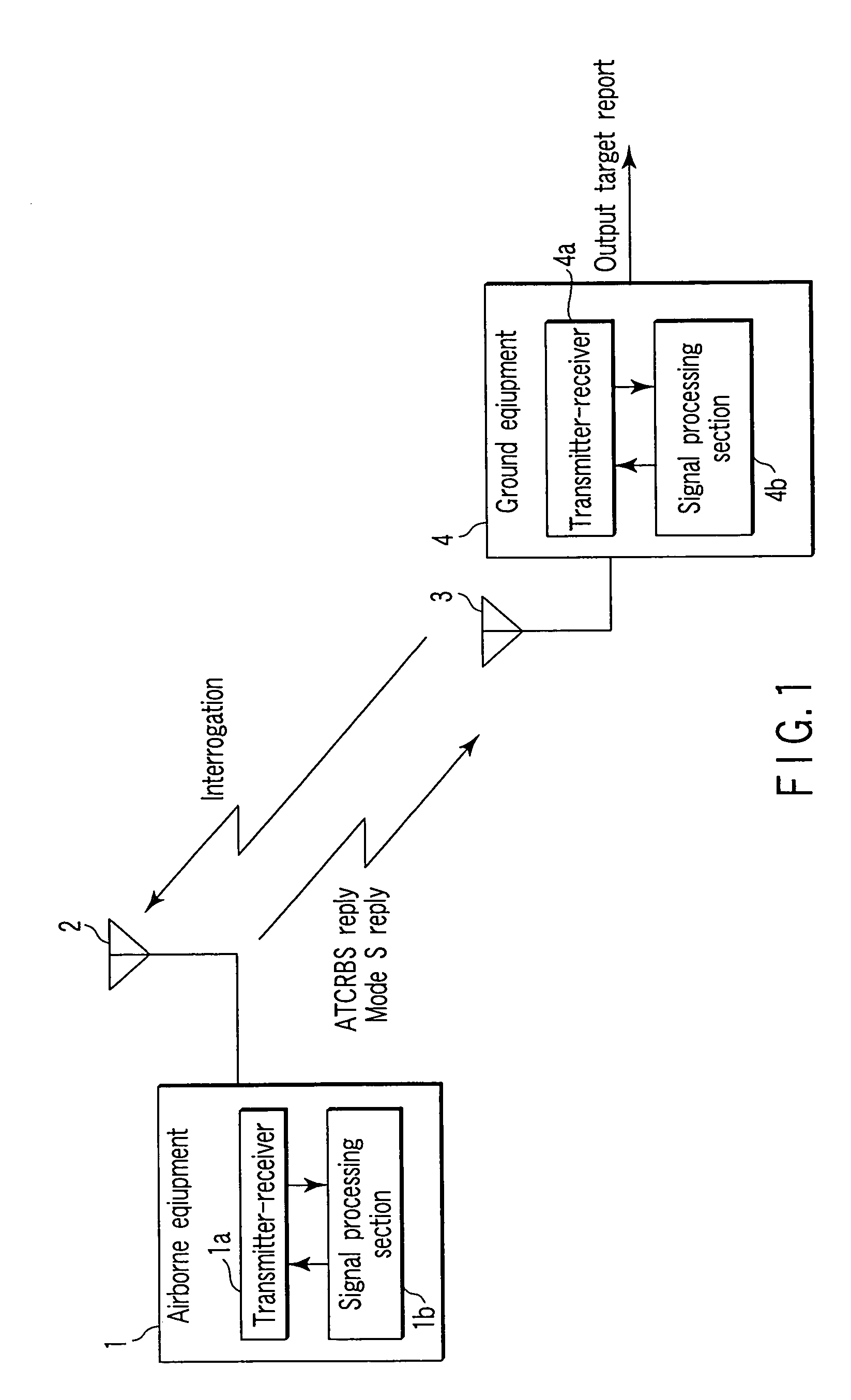
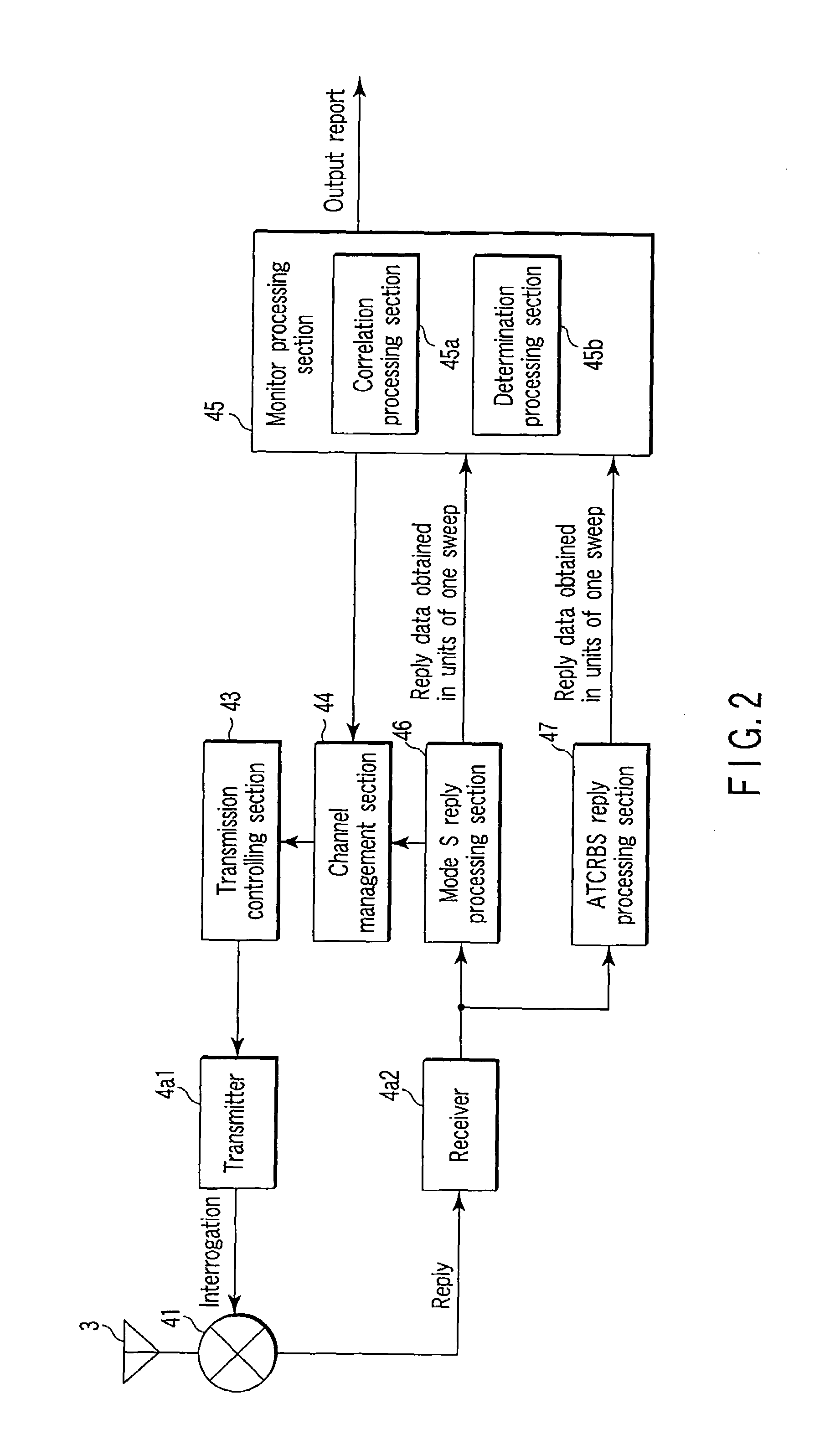
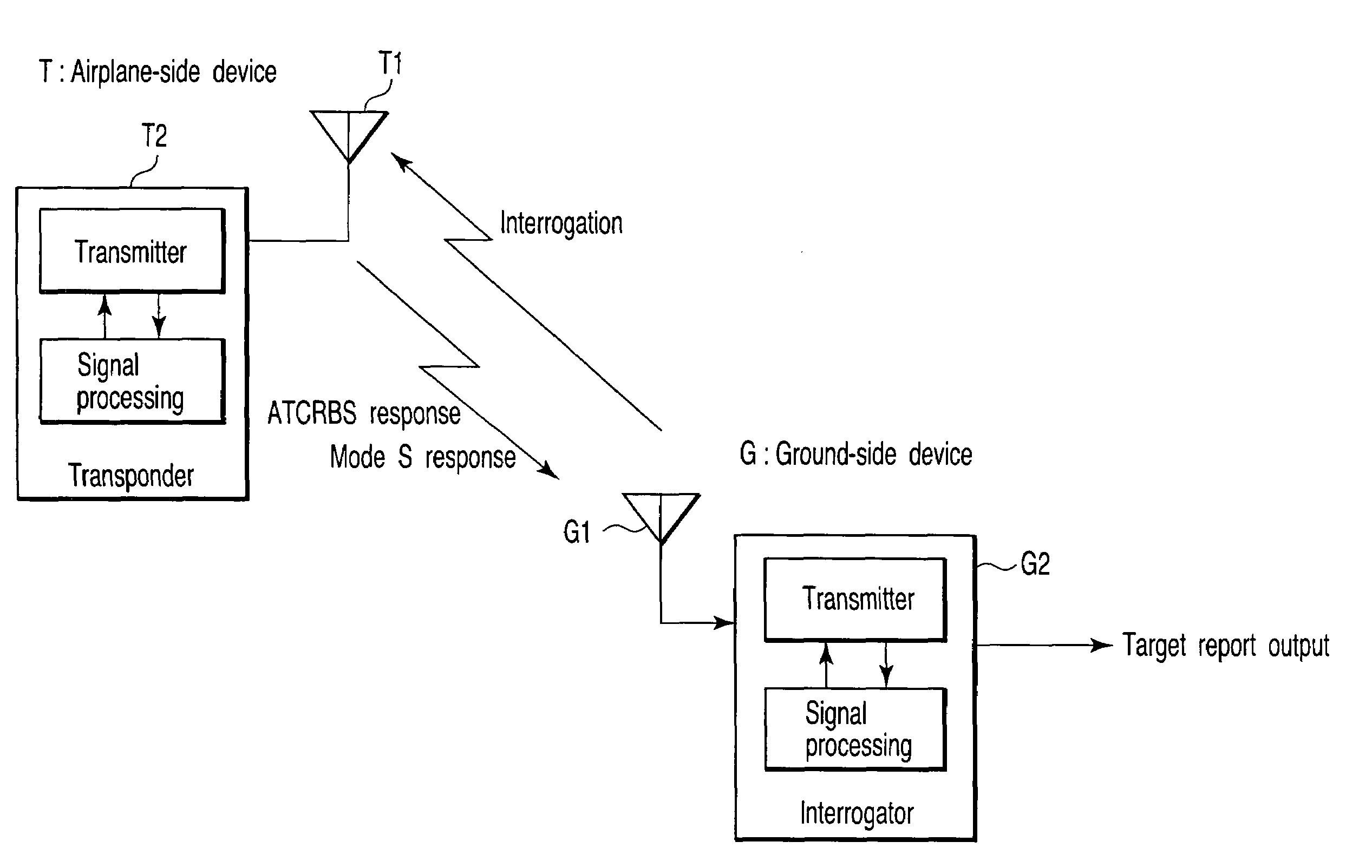
Secondary surveillance radar system, ground equipment for use therein, and response signal checking method applied thereto
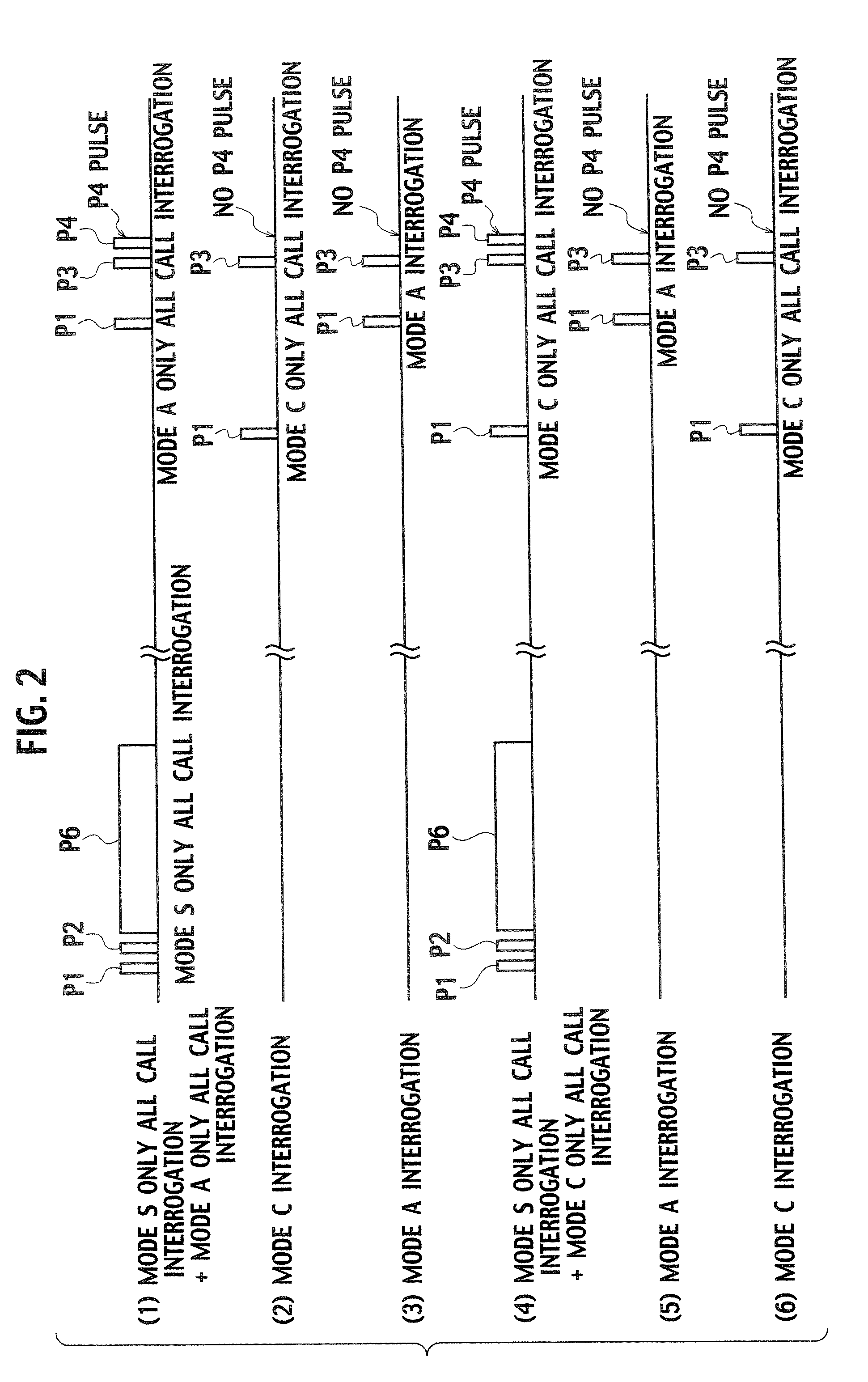
A secondary surveillance radar system for use in surveillance of an airspace, which reliably achieves surveillance of the airspace even when an aircraft including a mode S transponder and an aircraft including an ATCRBS transponder are both located in the airspace, wherein both of a time interval between time when transmission of an all-call interrogation signal specific for mode S is completed and time when the transmission of an all-call interrogation signal specific for mode A is started and a time interval between time when transmission of the all-call interrogation signal specific for mode S is completed and time when transmission of an all-call interrogation signal specific for mode C is started is varied in units of one all-call time period.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method for increasing the time for illumination of targets by a secondary surveillance radar
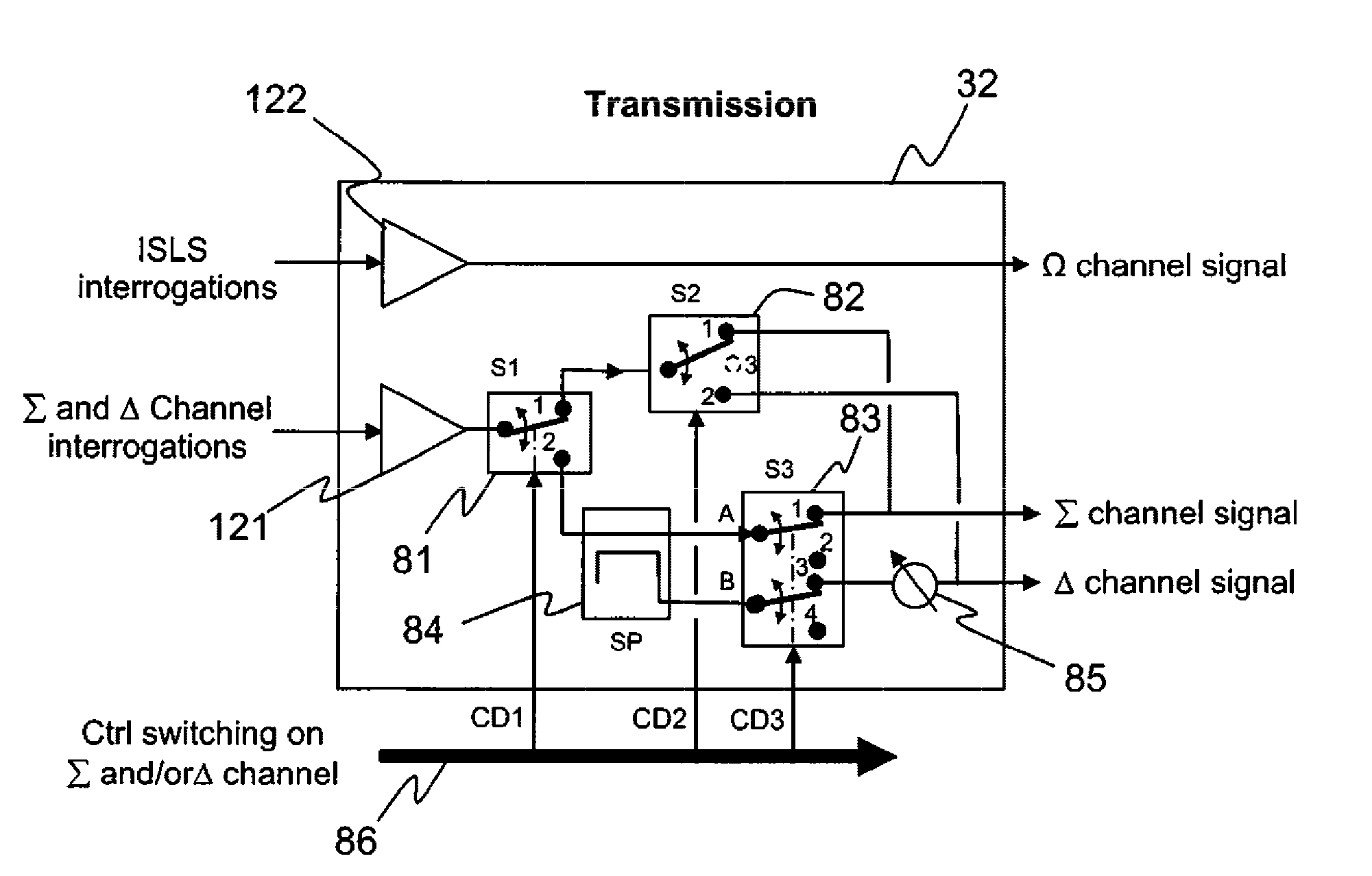
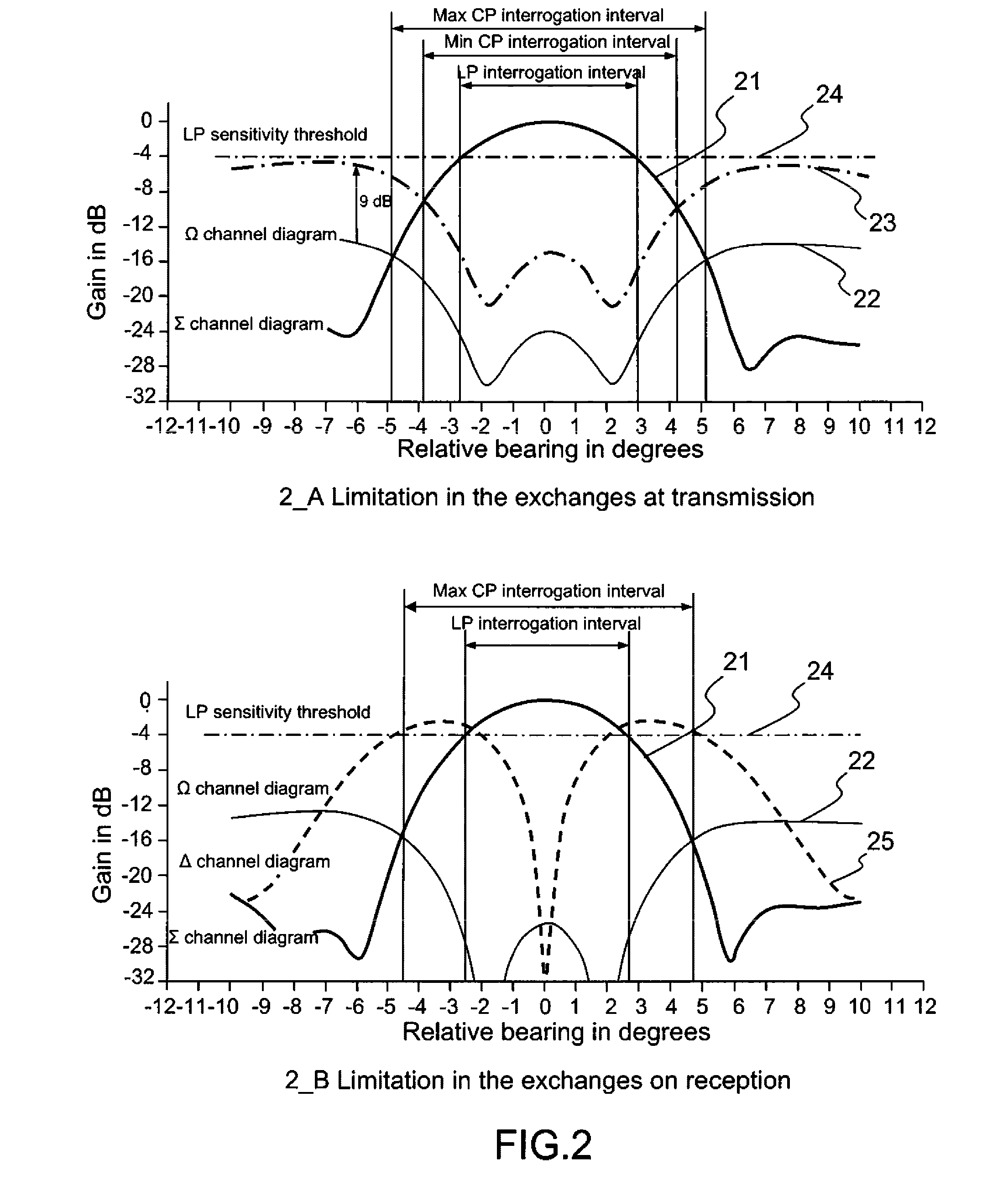
ActiveUS8674872B2Radio wave reradiation/reflectionAcoustic wave reradiationSecondary surveillance radarTransmission channel
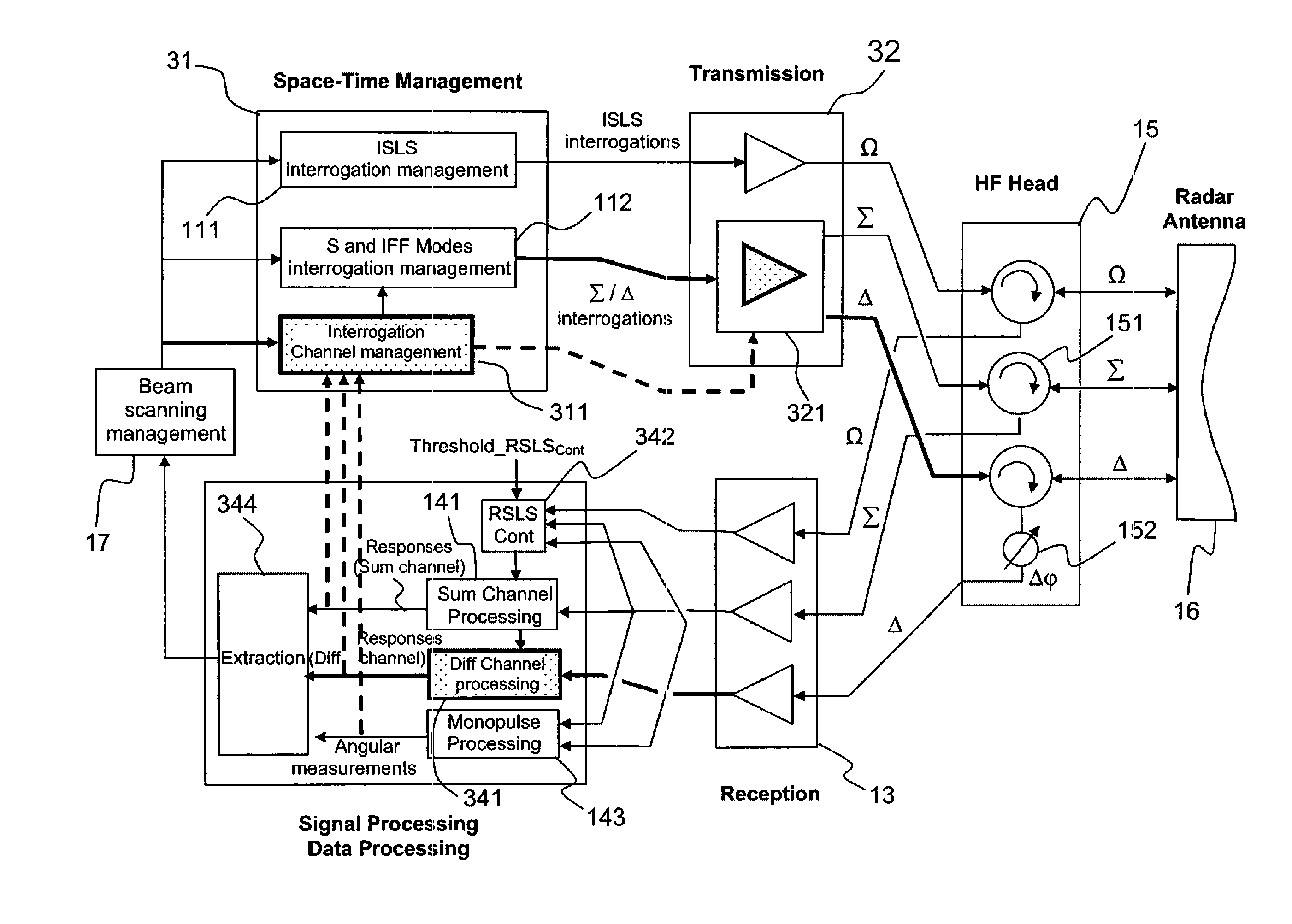
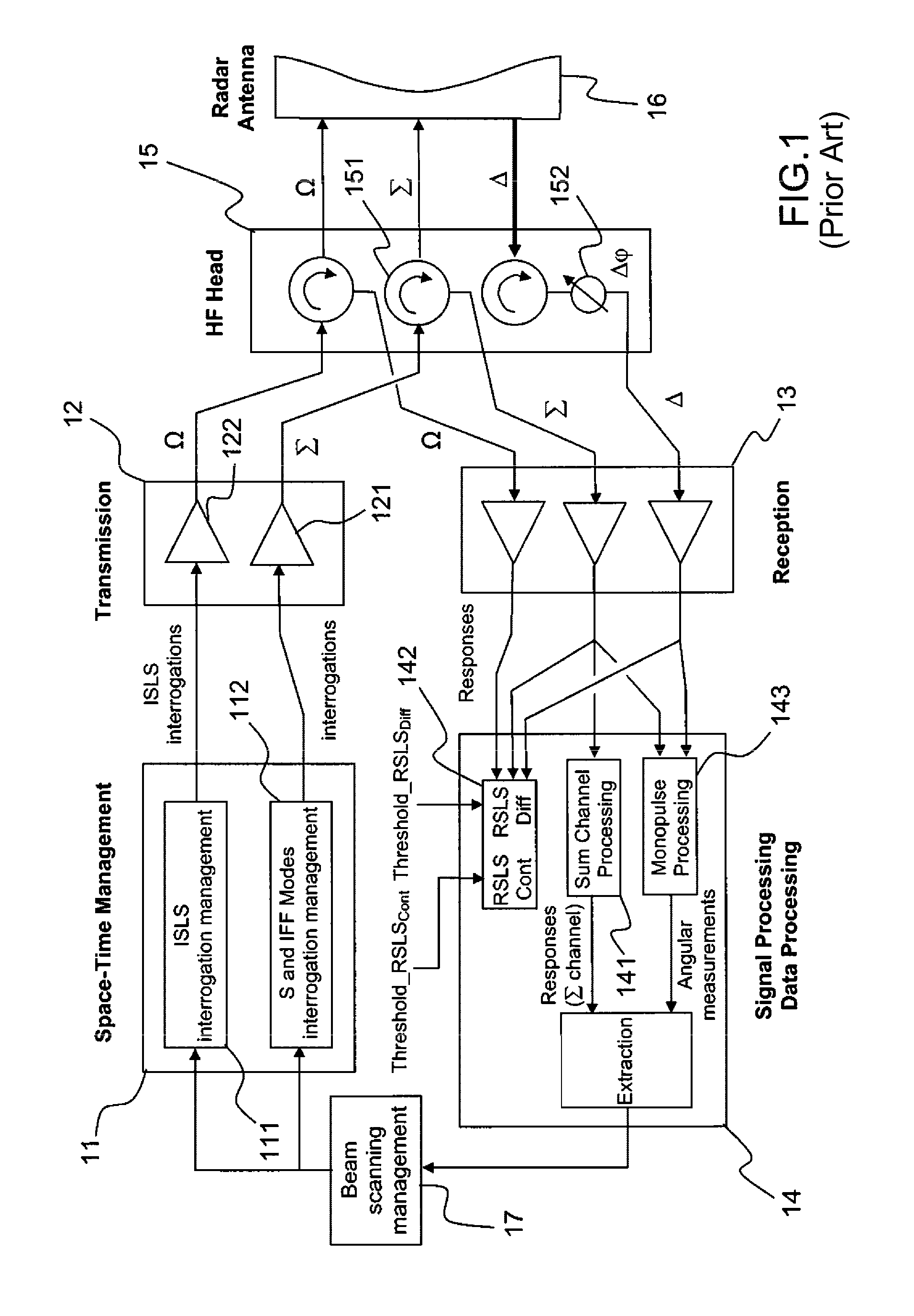
A secondary surveillance radar with rotating antenna, configured for transmitting interrogations in S or IFF mode and processing the responses to these interrogations. The radar includes an antenna having a lobe with three channels, a Sum channel, a Difference channel and a Control channel, whose transmission means are configured for transmitting interrogation messages over the Sum and Difference channels and whose reception and processing means are configured so as to carry out, aside from conventional detections by the Sum channel, detections by the Difference channel of the responses from the aircraft having been subjected to interrogation by this same channel. The radar also includes means for Space-Time Management configured for generating interrogation messages and determining whether a given message is to be transmitted by the Sum channel, by the Difference channel or by the two channels simultaneously and controlling its transmission by the corresponding transmission channel.
Owner:THALES SA
Interferometer system based secondary surveillance radar response signal direction-finding method
ActiveCN102944866AReduce power consumptionLow costDirection findersSecondary surveillance radarSide lobe
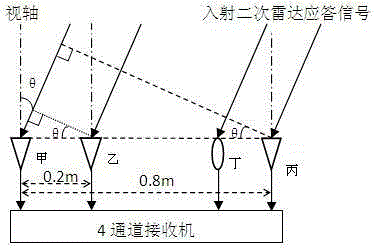
The invention discloses an interferometer system based secondary surveillance radar response signal direction-finding method, which relates to the technical field of radio monitoring. The method comprises the following steps that: a 4-array-element direction-finding antenna array with a receiving sidelobe suppression antenna unit receives secondary radar response signals, and four receiving channels respectively carry out digital measuring on frequency, amplitude and phase parameters; then, an operation of controlling the receiving sidelobe suppression of an instantaneous direction-finding range and an operation of exhaustion based long-short baseline resolving phase ambiguity are performed; and finally, the orientation resolving is completed through phase orientation mapping. A secondary radar response signal direction-finding system using the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high direction-finding precision, rapid direction-finding speed, large instantaneous direction-finding range, low power consumption, low cost, capability of carrying out passive direction-finding, and the like, and has a good application prospect and economic benefits in promoting the air surveillance range in the field of air management and monitoring.
Owner:SICHUAN JIUZHOU ELECTRIC GROUP
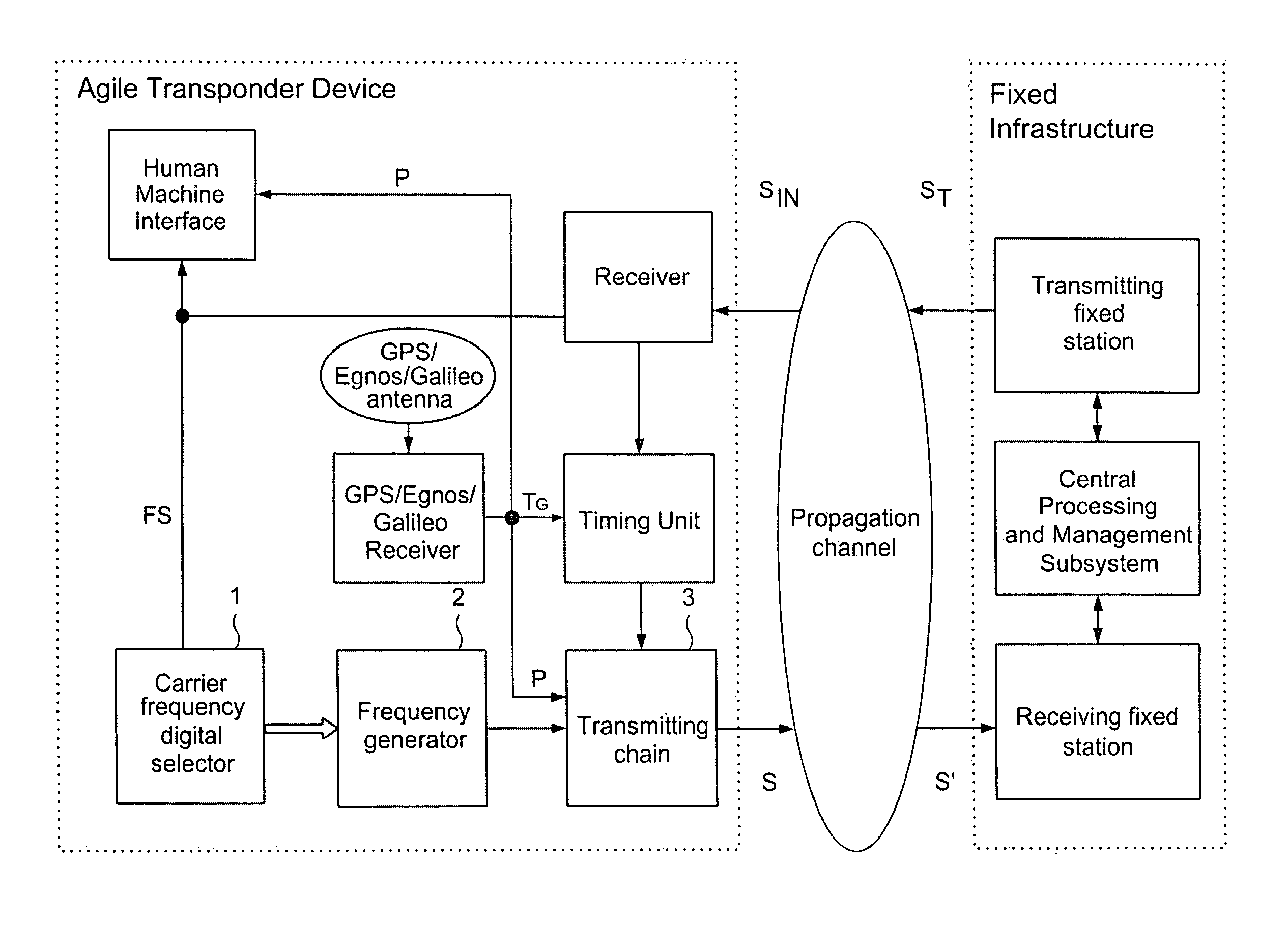
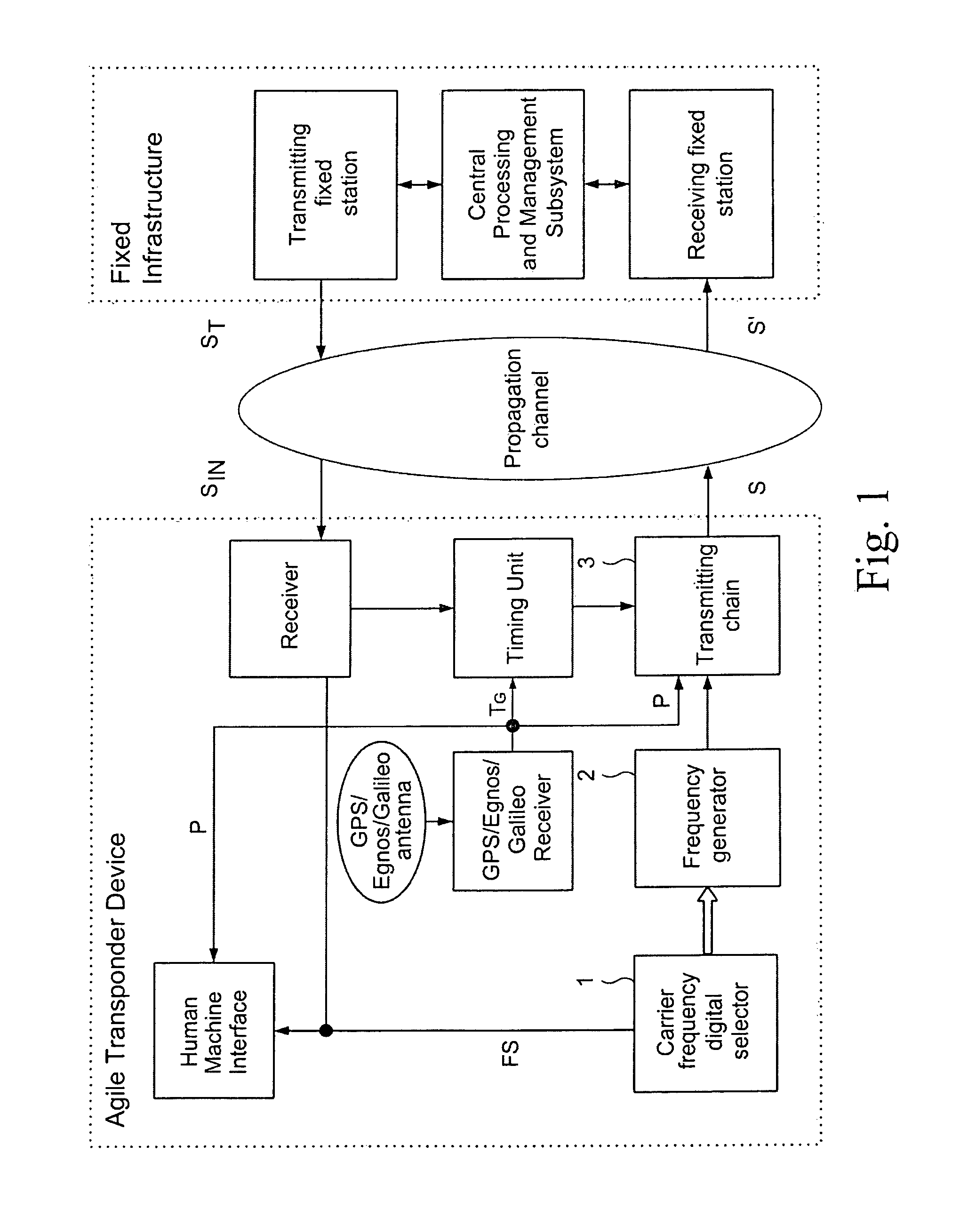
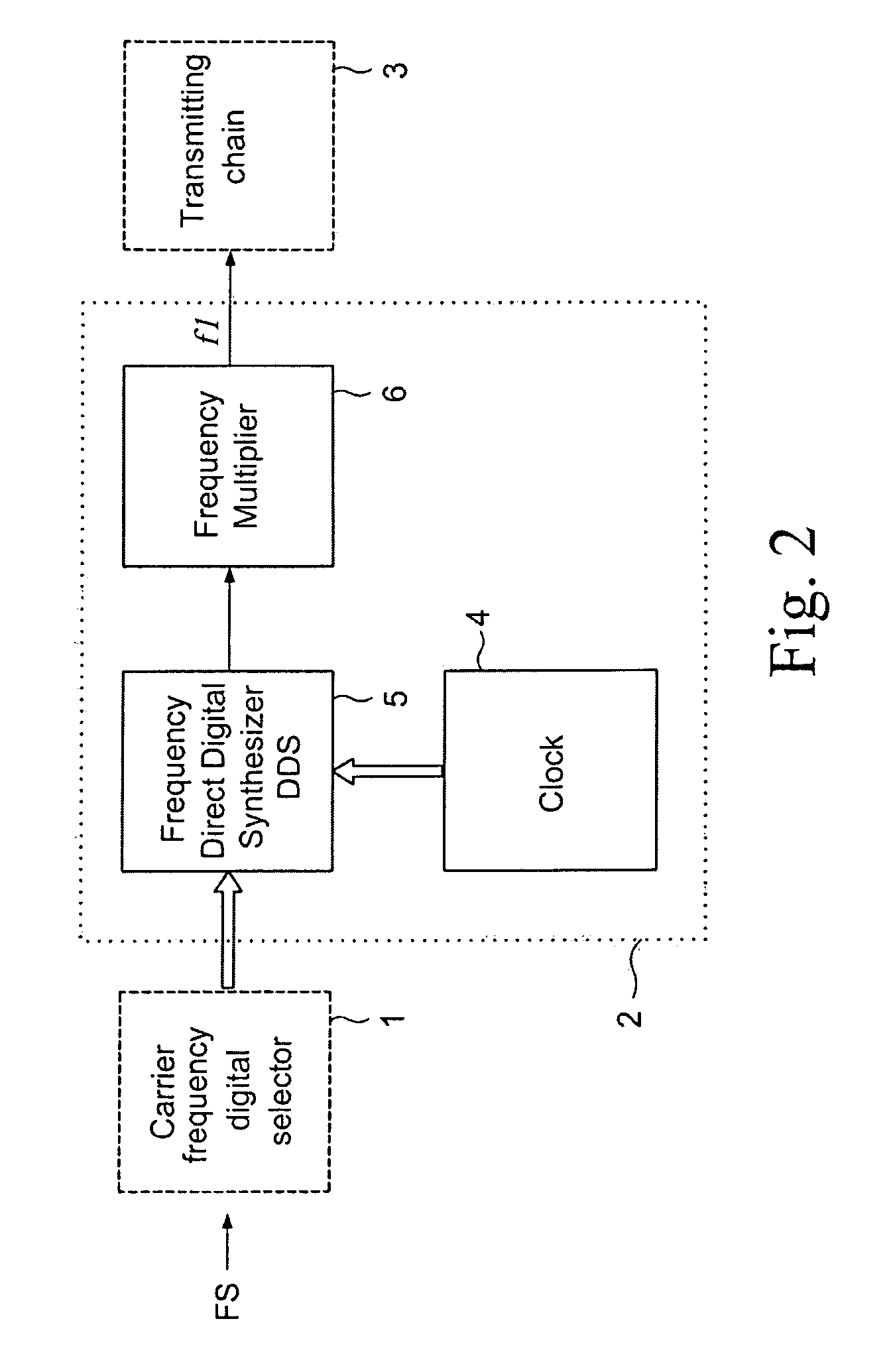
High-Capacity Location and Identification System for Cooperating Mobiles With Frequency Agile and Time Division Transponder Device on Board
InactiveUS20080106457A1Easy to operateOvercome limitationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionOn boardGround vehicles
Cooperating mobiles (ground vehicles, aircraft) are located and identified by Multilateration and Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) techniques using the frequency band and the format of the Secondary Surveillance Radar (SSR) signals in high traffic situations. Standard messages, transmitted by the mobile on the downlink channel, i.e. to a set of fixed receiving stations, and including the identification code, permit the location of the mobile by multiple time measurements (Multilateration) from a subset of the set of fixed receiving stations; when the message contains the position (GPS and, later, Galileo datum) the mobile may be located with the ADS-B when in view even of a few stations or of a single station. In order to overcome the problem that arises with high traffic, i.e. the superimposition of signals, called garbling.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROME TOR VERGATA
Dual mode weather and air surveillance radar system
InactiveUS7719458B1Maximize useLow costIndependent non-interacting antenna combinationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSecondary surveillance radarRadar systems
A radar system having first and second modes of operation comprising a dual antenna assembly comprising first and second antennas having respective first and second antenna waveguides coupled to a waveguide switch operable to divert RF energy to or from either said antenna waveguide, said waveguide switch coupled to a common waveguide, said dual antenna assembly mounted to an antenna support assembly, said first and second antennas being designed for use in said first and second modes respectively and operable for coupling said RF energy to a transmit medium, and for coupling reflected RF energy from transmit medium to said first or second antenna waveguide; and a control processor configured with control logic operable to control the functions of said radar system wherein said first and second antennas are mounted generally perpendicularly in the vertical plane with respect to each other and wherein said radar system operates in only one of said modes of operation at any time.
Owner:BARON SERVICES
Dual mode weather and air surveillance radar system
InactiveUS7671785B1Maximize useLow costIndependent non-interacting antenna combinationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSecondary surveillance radarRadar systems
A radar system having first and second modes of operation comprising a dual antenna assembly comprising first and second antennas having respective first and second antenna waveguides coupled to a waveguide switch operable to divert RF energy to or from either said antenna waveguide, said waveguide switch coupled to a common waveguide, said dual antenna assembly mounted to an antenna support assembly, said first and second antennas being designed for use in said first and second modes respectively and operable for coupling said RF energy to a transmit medium, and for coupling reflected RF energy from transmit medium to said first or second antenna waveguide; and a control processor configured with control logic operable to control the functions of said radar system wherein said first and second antennas are mounted generally perpendicularly in the vertical plane with respect to each other and wherein said radar system operates in only one of said modes of operation at any time.
Owner:BARON SERVICES
ADS-B and secondary surveillance radar monitoring information data integration method and device
ActiveCN106371091AAchieving time-space alignmentGuaranteed continuityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAircraft traffic controlSecondary surveillance radarData integration
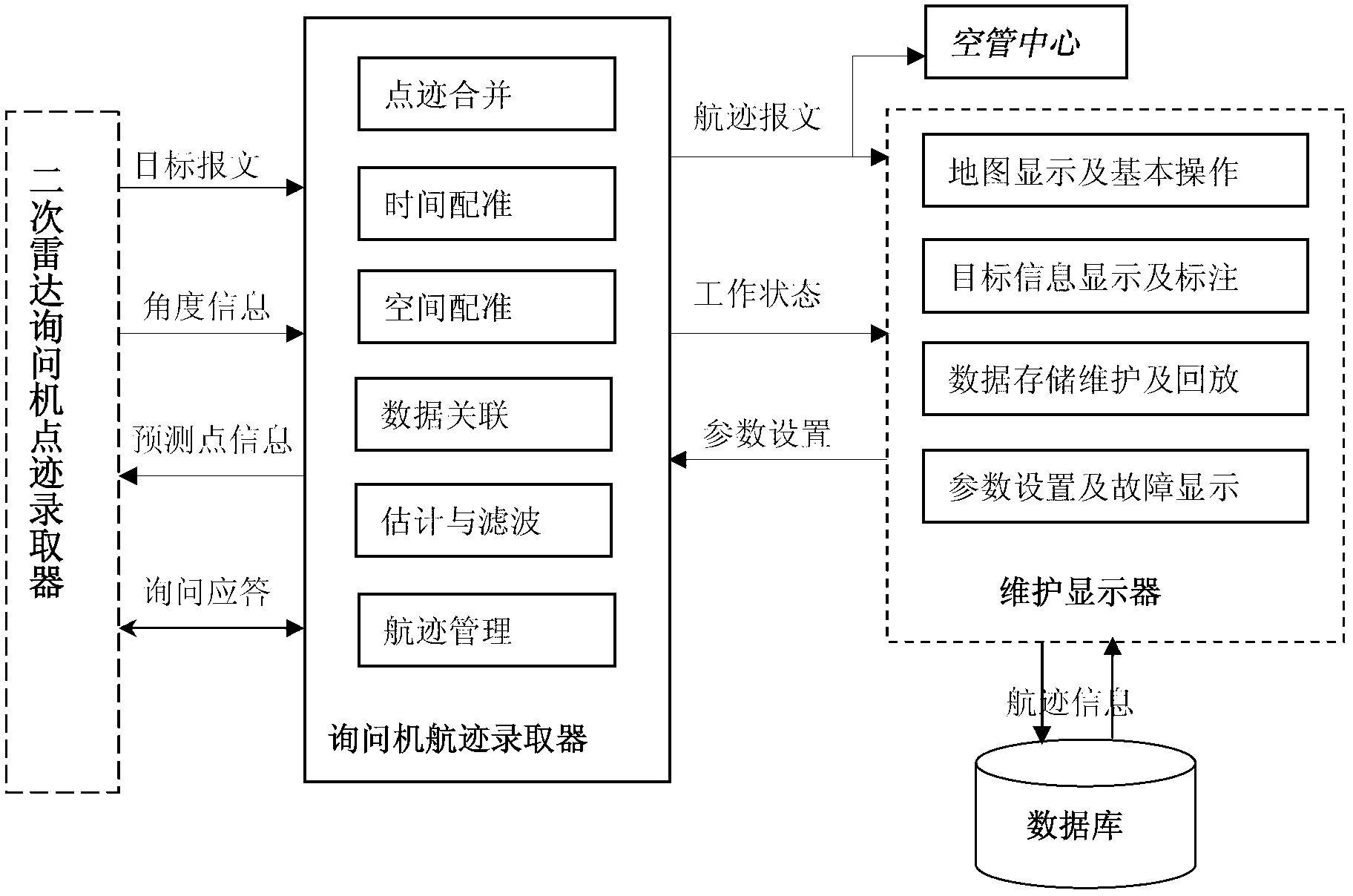
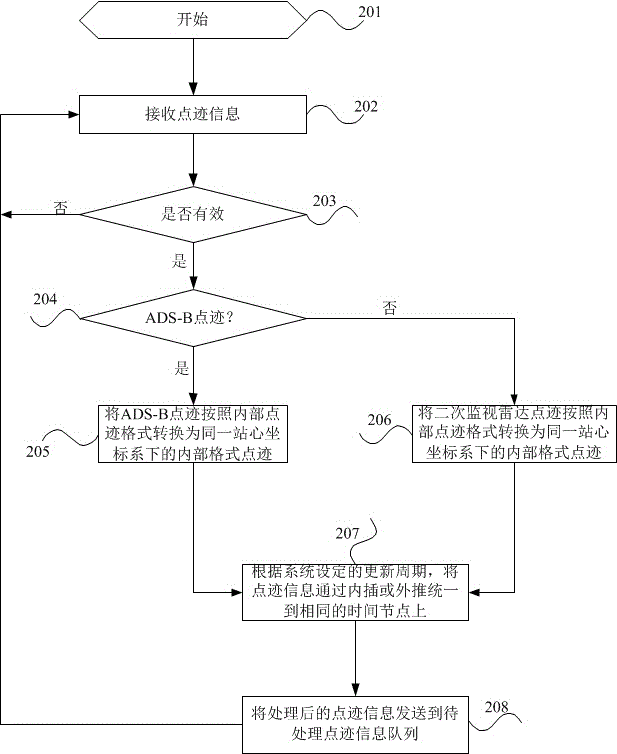
The invention relates to the track processing technology, in particularly, to an ADS-B and secondary surveillance radar monitoring information data integration method and device. With the object of solving the problems in the prior art, a data integration method and device are provided so as to realize the integrated tracking processing of ADS-B surveillance information and the secondary surveillance radar information, to make the tacking keep a constantly updated state and to ensure the continuity and the correctness of surveillance. The method comprises the following steps: converting the coordinates of different types of tracking information into a unified station-centered orthorhombic coordinate system; through the interpolation method or the extrapolation method, achieving time and space alignment and sending the processed point tracking information to a pre-processing point tracking line; from the pre-processing point tracking line, reading the point tracking information and using the local optimal proximity algorithm to have the determined tracking in the tracking line and the tentative tracking correlated; and finally, according to the tracking in the tracking line, performing extrapolation of tracking or removing the missing targets or the tentative track from the processing tracking line so as to maintain and protect the tracking.
Owner:四川九洲空管科技有限责任公司
Classification system for radar and sonar applications
ActiveUS7567203B2ICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSecondary surveillance radarBiological target
A system and method for target classification for an aircraft surveillance radar is provided. In one implementation, the track classifier provides tracks with an updated probability value based on its likelihood to conform to aircraft and non-aircraft target behavior. The track classifier identifies false tracks that may arise from weather and biological targets, and can detect aircrafts lacking Secondary Surveillance Radar (SSR) data. Various features and combinations of features are evaluated using a proposed clustering performance index (CPI) and used to discriminate between aircrafts and false tracks.
Owner:RAYTHEON CANADA LTD
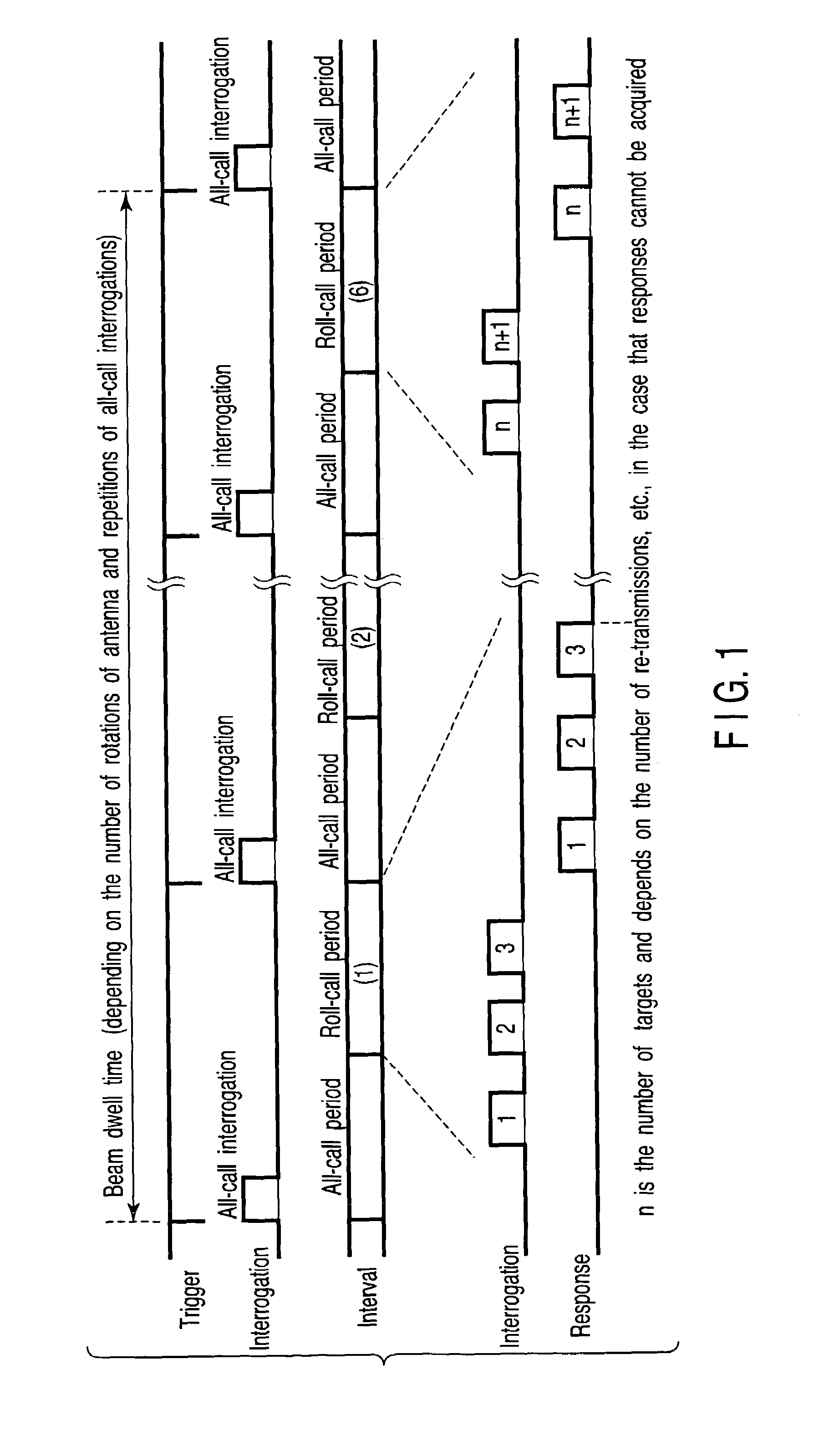
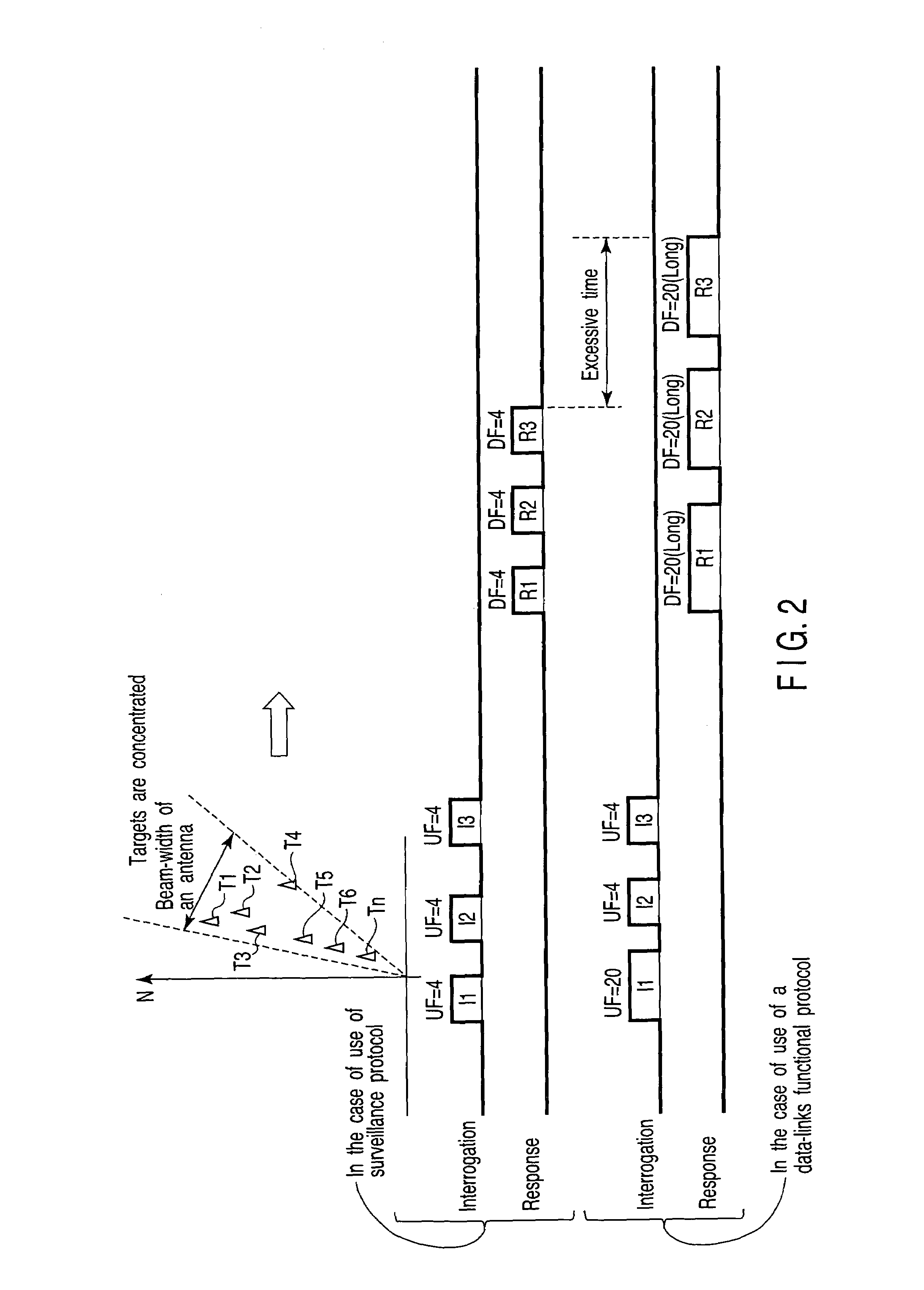
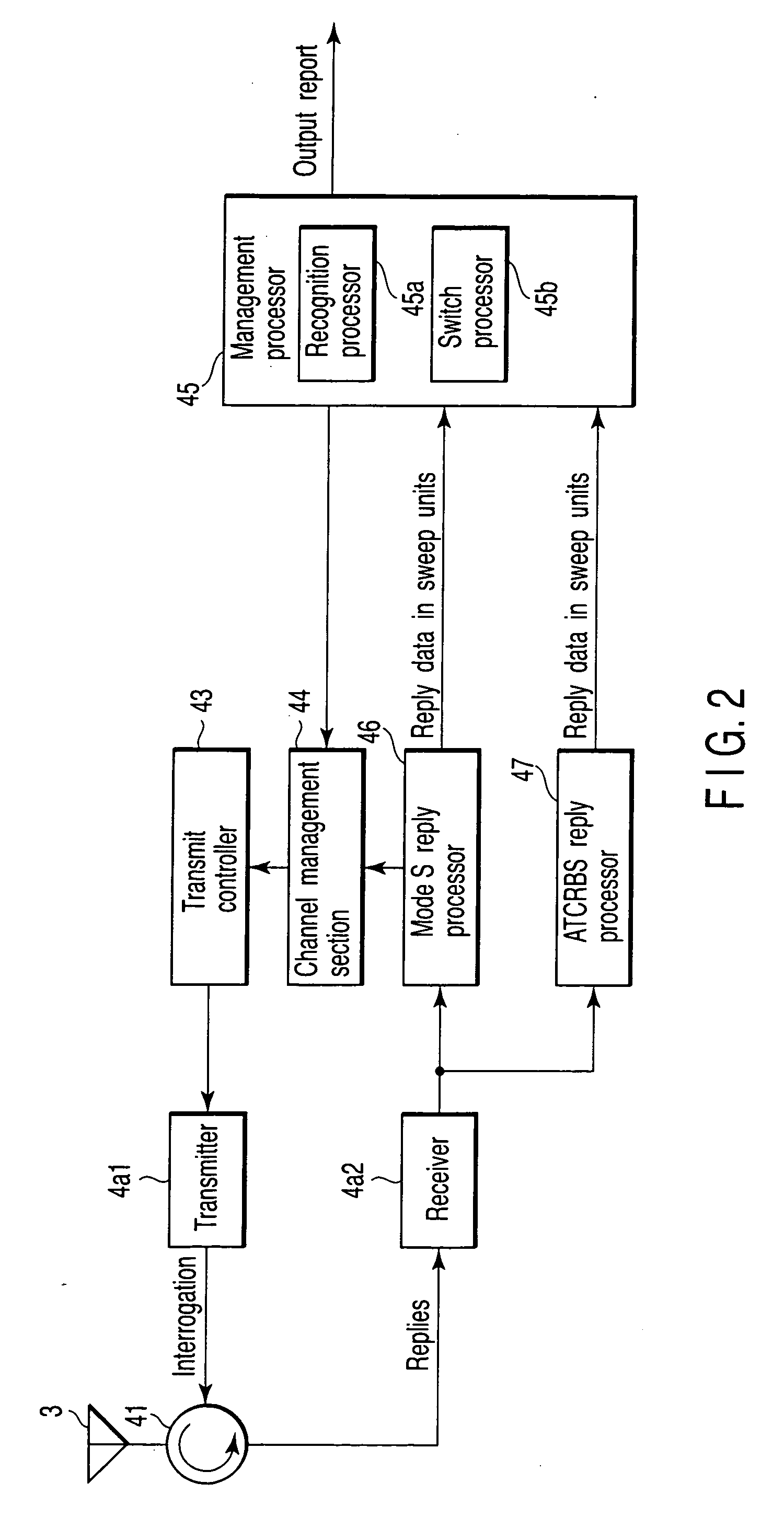
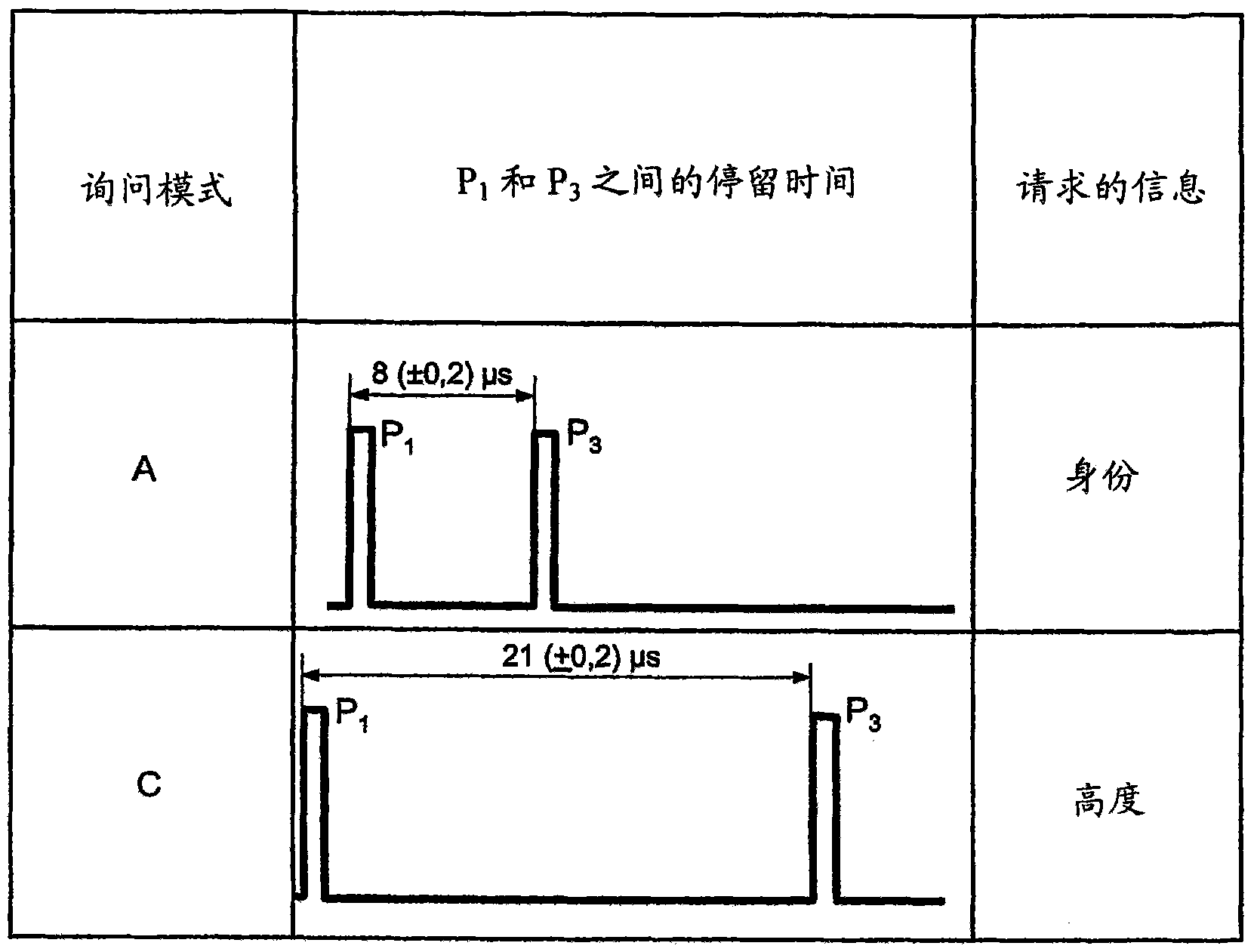
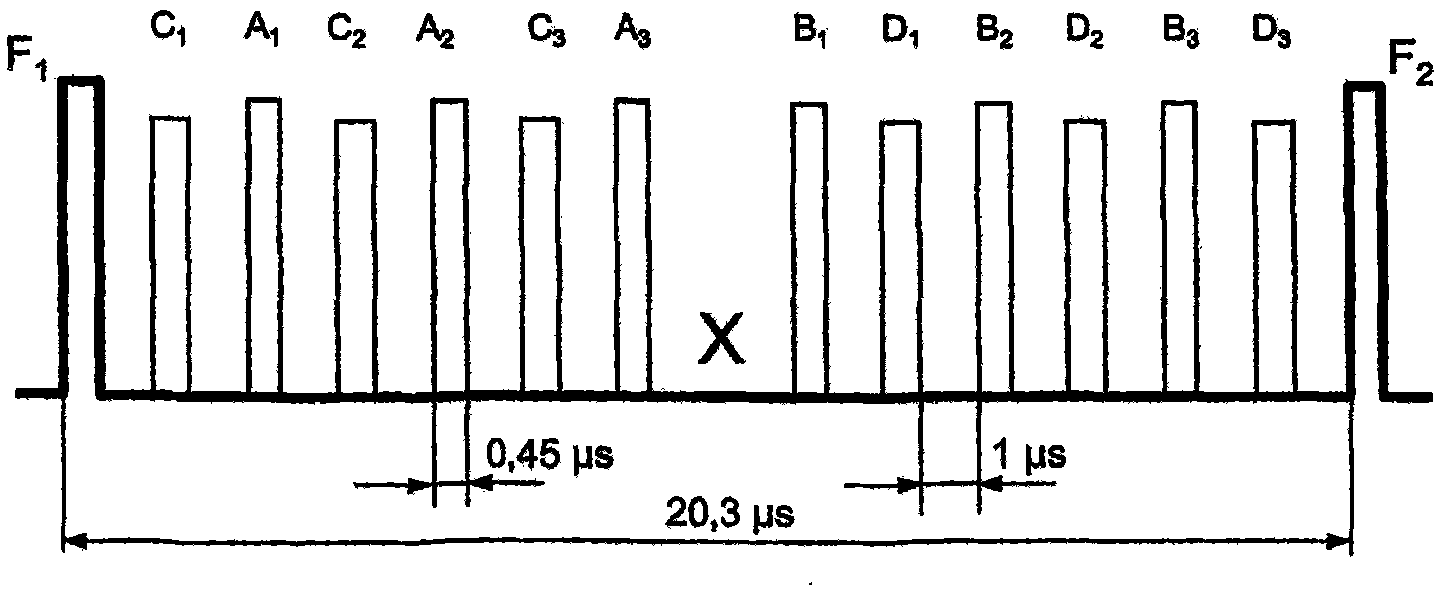
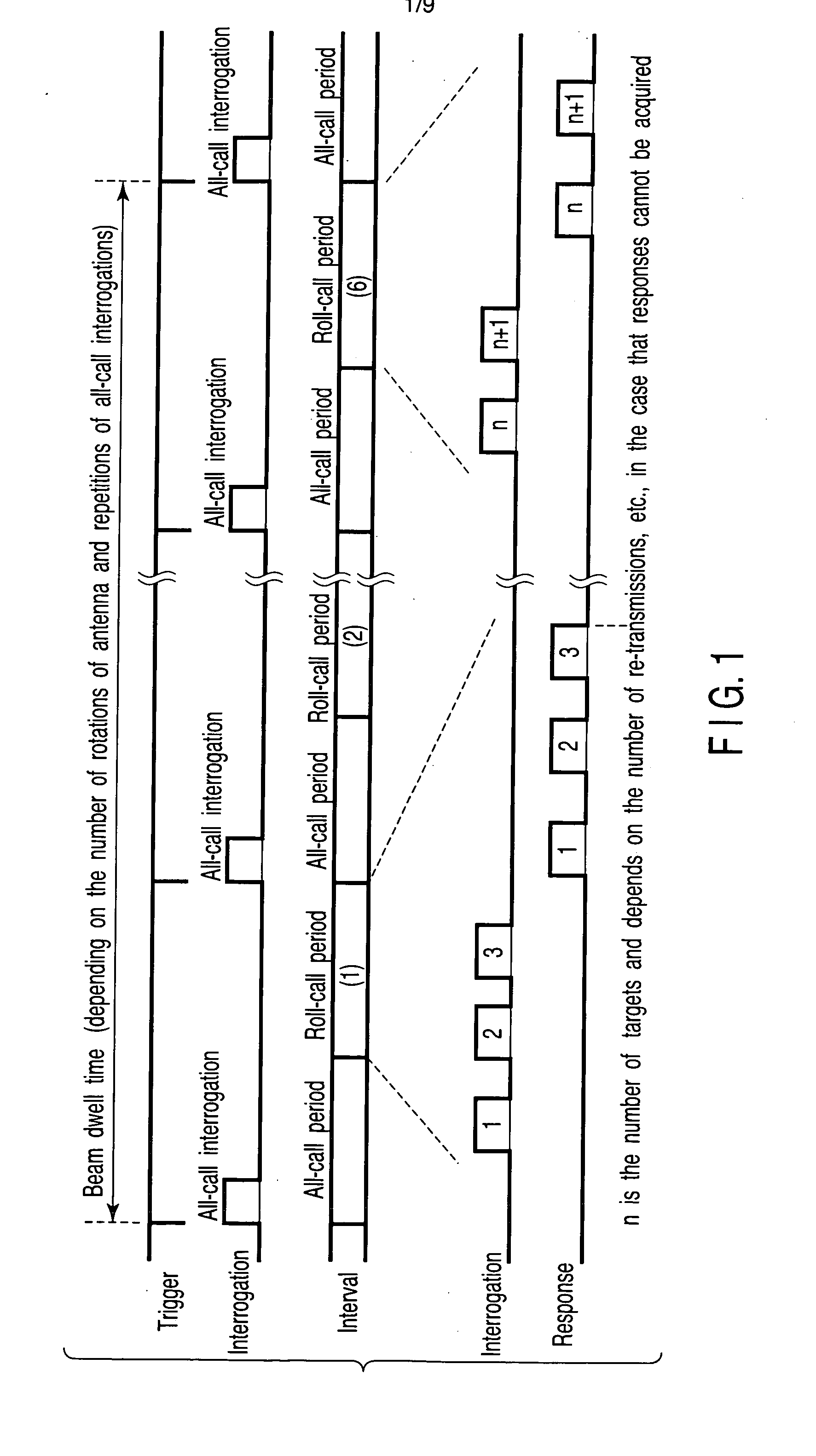
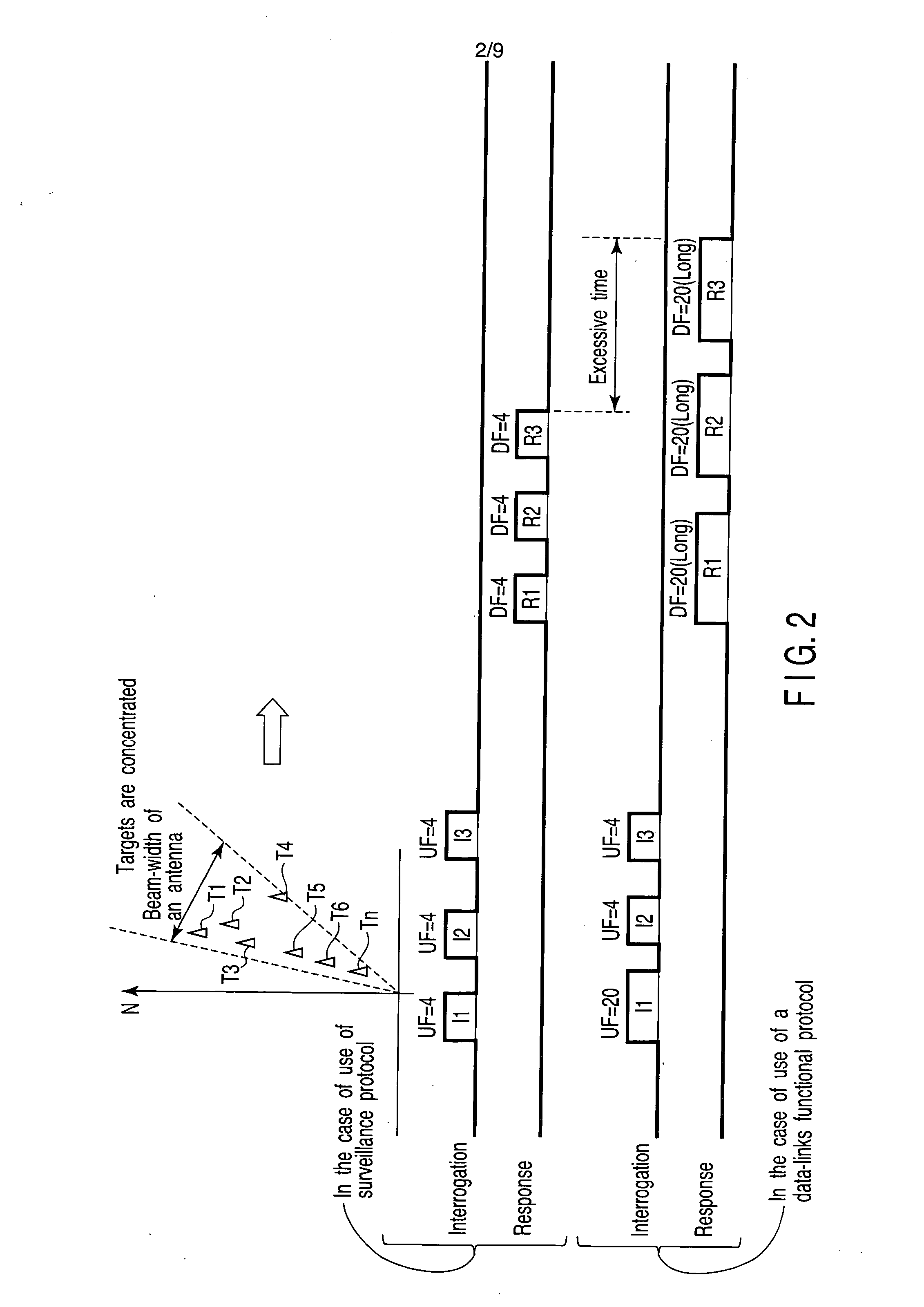
Secondary surveillance radar and its interrogation transmission method
InactiveUS7408498B2Securing timeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSecondary surveillance radarEnvironmental geology
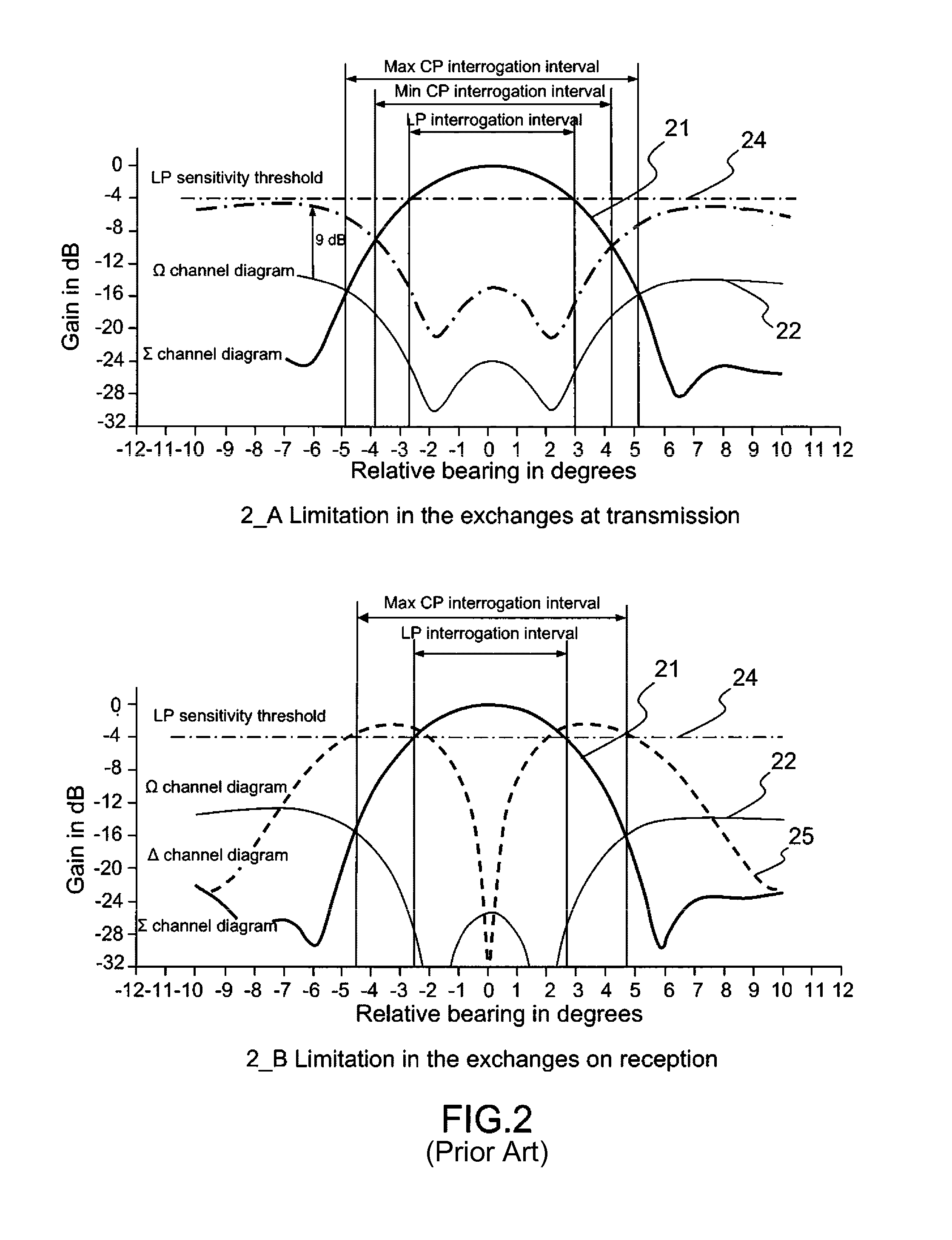
An interrogation transmission method of a secondary surveillance radar compares prediction angle ranges for transmitting interrogations with a beam-width of an antenna, and transmits the interrogations at every roll-call period if the prediction angle ranges for transmitting interrogations are narrower than the beam-width of the antenna. In contrast, if the prediction angle ranges for transmitting the interrogations are wider than the beam-width of the antenna, the radar respectively sets a period to transmit the interrogations and a period not to transmit the interrogations until responses can be received, and transmits interrogations at every roll-call period after the responses can be received (even if a receiving error or downlink occurs).
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Secondary surveillance radar system, and ground system for use therein
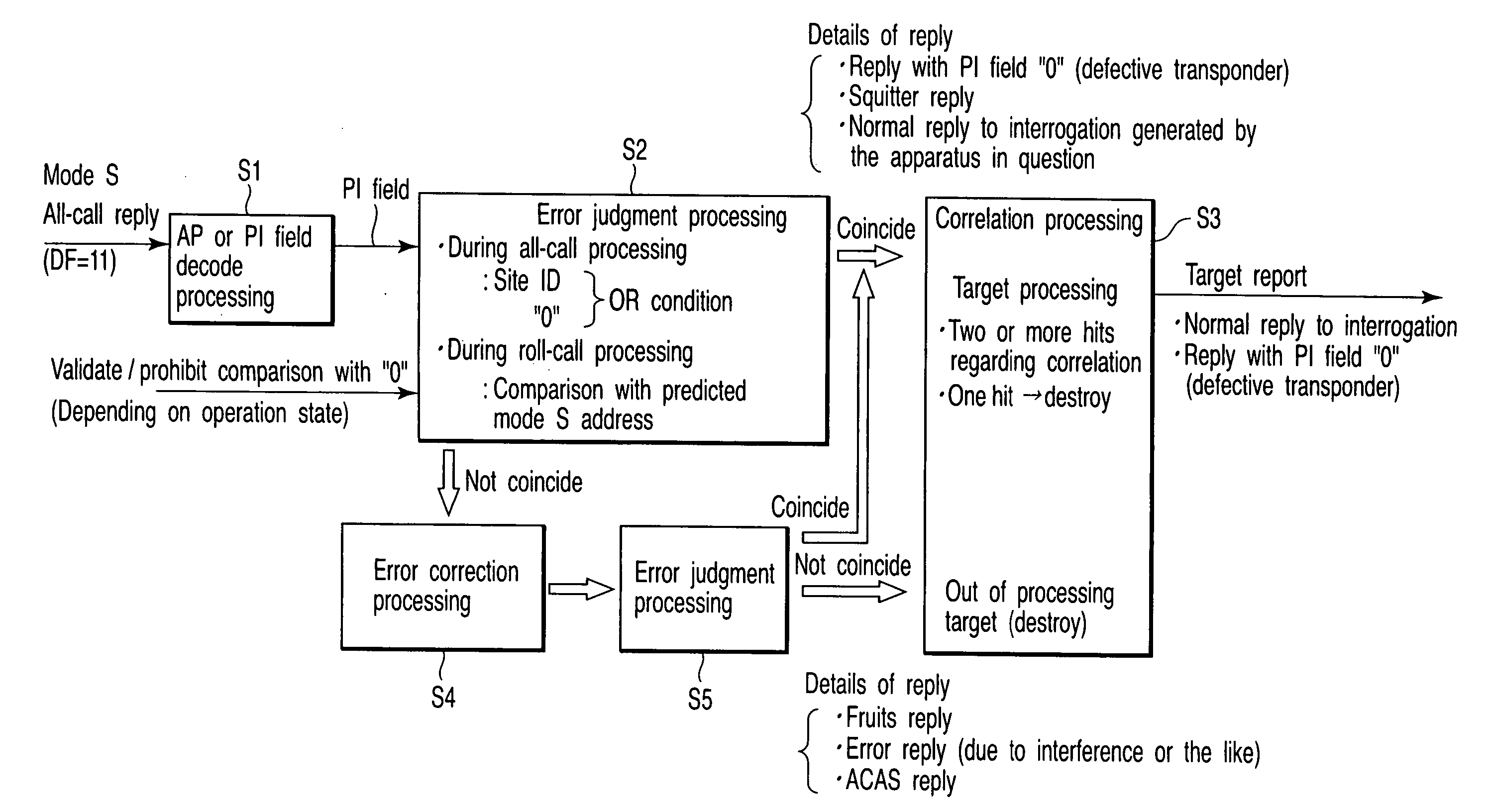
A secondary surveillance radar system comprising a ground system which observes an observation area where an aircraft equipped with a mode S transponder and an aircraft equipped with an ATCRBS transponder possibly coexist, wherein the ground system comprises a transmit processor which transmits to the observation area an all-call interrogation signal specific for mode S including an identification code of the ground system, a receive processor which receives a reply signal to the interrogation signal transmitted by the transmit processor, and a recognition processor which recognizes the reply signal as a processing target when identification information included in the reply signal received by the receive processor coincides with the identification code of the ground system, and wherein the recognition processor recognizes the reply signal as the processing target also when the identification information included in the reply signal received by the receive processor coincides with null information.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Reply detection in a secondary surveillance radar
The present invention relates to a detecting device (10; 20; 20') for detecting an SSR signal having a characteristic structure. The detecting device (10; 20, 20') comprises filtering means (11; 21) matched to the characteristic structure of the SSR signal, and means for maintaining a false-alarm rate at a substantially constant value (12; 22; 22'). The characteristic structure of the SSR signal comprises either a preamble or an initial pulse and a final pulse separated by a fixed dwell time. The means for maintaining a false-alarm rate at a substantially constant value (12; 22; 22') comprisecomputing means configured to compute a detection threshold on the basis of a signal supplied by the filtering means (11; 21), and decision means configured to detect the SSR signal on the basis of the detection threshold and of the signal supplied by the filtering means (11; 21).
Owner:SELEX SISTEMI INTEGRATI
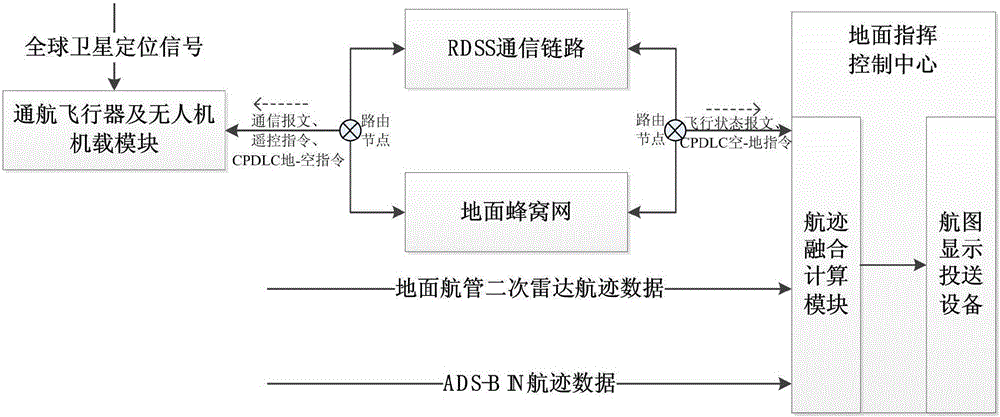
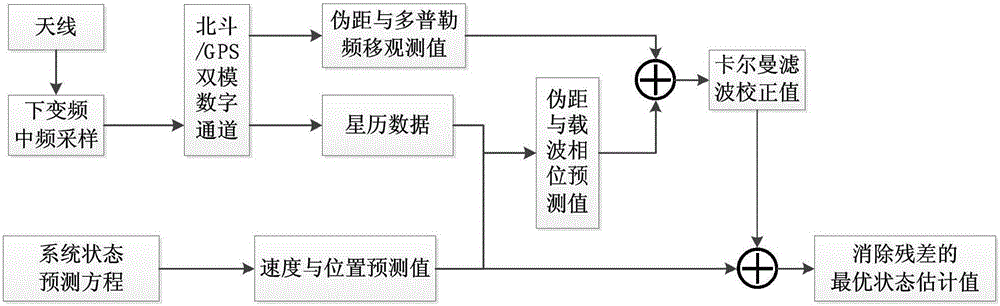
Safety monitoring method for universal aerial vehicle and unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN105867272AEfficient managementEnable seamless monitoringProgramme controlComputer controlSecondary surveillance radarIntellectual property
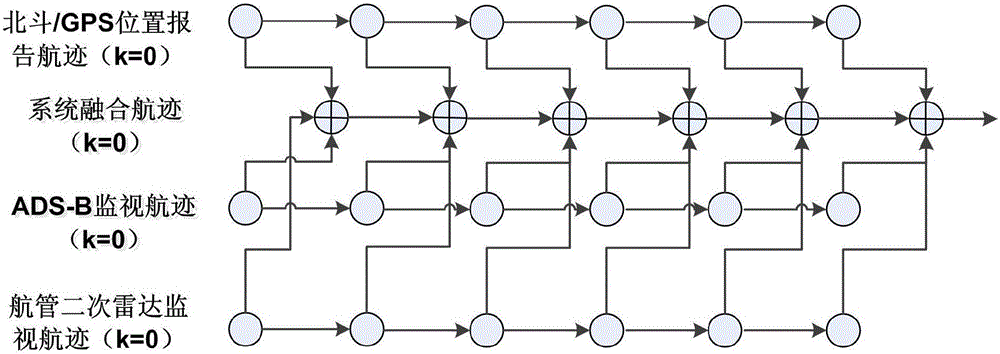
The invention provides a safety monitoring method for a universal aerial vehicle and an unmanned aerial vehicle. The safety monitoring method aims at problems of single safety monitoring facility and low strength in existing low-altitude flight. Beidou RNSS and GPSL1 combined passive positioning technology, RDSS and ground cellular network communication technology are used for finishing flight state reporting and flight route service pushing of the universal aerial vehicle and the unmanned aerial vehicle. The safety monitoring method is characterized in that in cities and areas with large population density and ground cellular network coverage, comprehensive monitoring is performed through a ground secondary surveillance radar, ADS-B ground station equipment and Beidou / GPS double-mode positioning technology, thereby ensuring high accuracy of an aerial vehicle track; and in undeveloped and remote mountainous regions and areas without secondary surveillance radar or ADS-B ground station coverage, a lowest monitoring performance standard of the aerial vehicle is kept by means of Beidou / GPS double-mode positioning and Beidou RDSS communication. The safety monitoring method according to the invention is the low-altitude space domain safety monitoring method which has advantages of high universality, easy disposition and Chinese proprietary intellectual property right.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
Broadband amplitude monopulse system secondary radar monopulse angle measurement visualization method
InactiveCN102520398AStore response data in real timeEasy to set upRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSecondary surveillance radarTerminal equipment
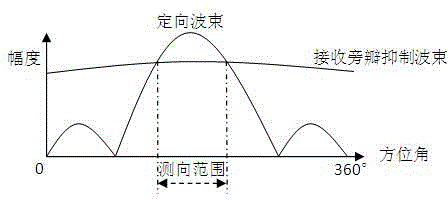
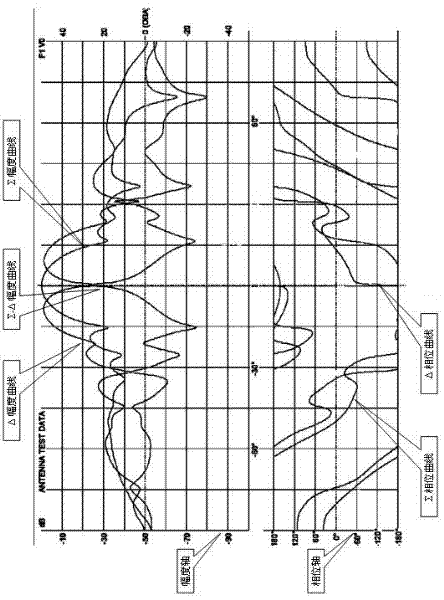
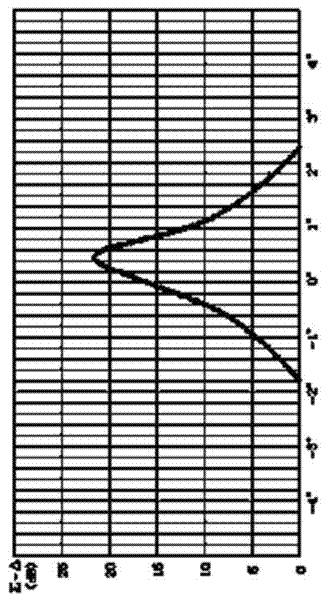
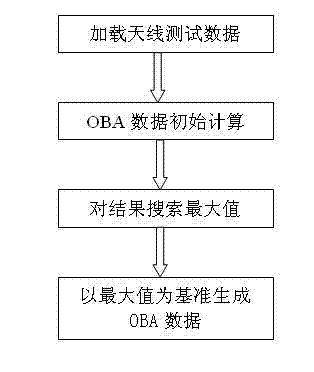
The invention, which relates to the radar signal processing field, discloses a broadband amplitude monopulse system secondary radar monopulse angle measurement visualization method. The method comprises the following steps that: a monopulse device sends information of a response signal and target data to terminal equipment according to a predetermined format; the terminal equipment receives the information of the response signal and the target data and then loading and generation of static data are carried out; loading is carried out by employing a graphical mode and an antenna directional diagram is displayed; and a monopulse secondary surveillance radar off-boresight angle (OBA) table is generated by the antenna directional diagram. Because the loading is carried out by employing the graphical mode and the antenna directional diagram is displayed, a main beam shape, the width, sigma and delta channel phase distribution situations of the antenna directional diagram can be displayed visually, so that it is convenient for engineering personnel to arrange a monopulse parameter under a corresponding antenna feed system. Besides, it is convenient to realize amplitude monopulse system secondary radar monopulse angle measurement function verification and a precision analysis under a broadband condition; a requirement for maintenance equipment by a system is reduced; high flexibity is realized; and maintenance cost can be effectively controlled.
Owner:SICHUAN JIUZHOU ELECTRIC GROUP
High precision surveillance system by means of multilateration of secondary surveillance radar (SSR) signals
ActiveUS7570194B2Easy to operateGood precisionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSecondary surveillance radarSpite
A system able to locate and identify aircraft and vehicles based on the reception and processing, with novel means and methods, of signals emitted by the transponder of the secondary surveillance radar, shortly SSR. The system has a number of fixed stations distributed in the area of interest, e.g. in the airport area; any signal (the well known SSR reply / squitter) transmitted by the on-board transponder is received by four or more stations and the measurement of three or more differences of times of arrival (TOA) permits the reconstruction of the position of the transponder in spite of the fact that the transmission time is unknown. Suitable algorithms based on optimal estimation enhance both the accuracy of TOA measurements and the accuracy of the reconstructed position. The effects of possible overlapping of signal in time are avoided or mitigated by multiple source separation techniques based on least squares algebraic processing.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROME TOR VERGATA
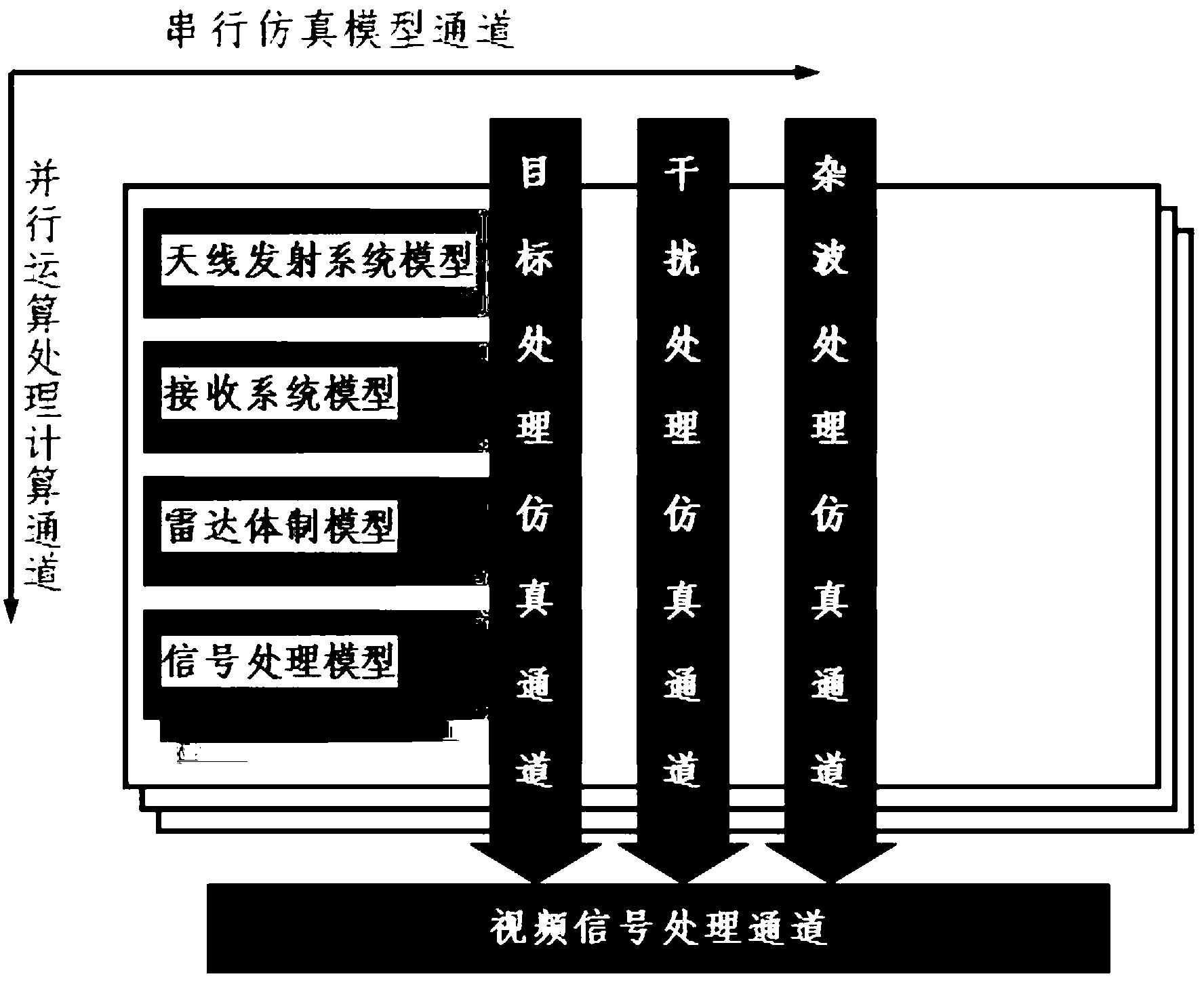
General performance simulation method and framework of air surveillance radar
ActiveCN103246556AImprove scalabilityConvenient replacementMultiprogramming arrangementsSpecial data processing applicationsSecondary surveillance radarReal-time simulation
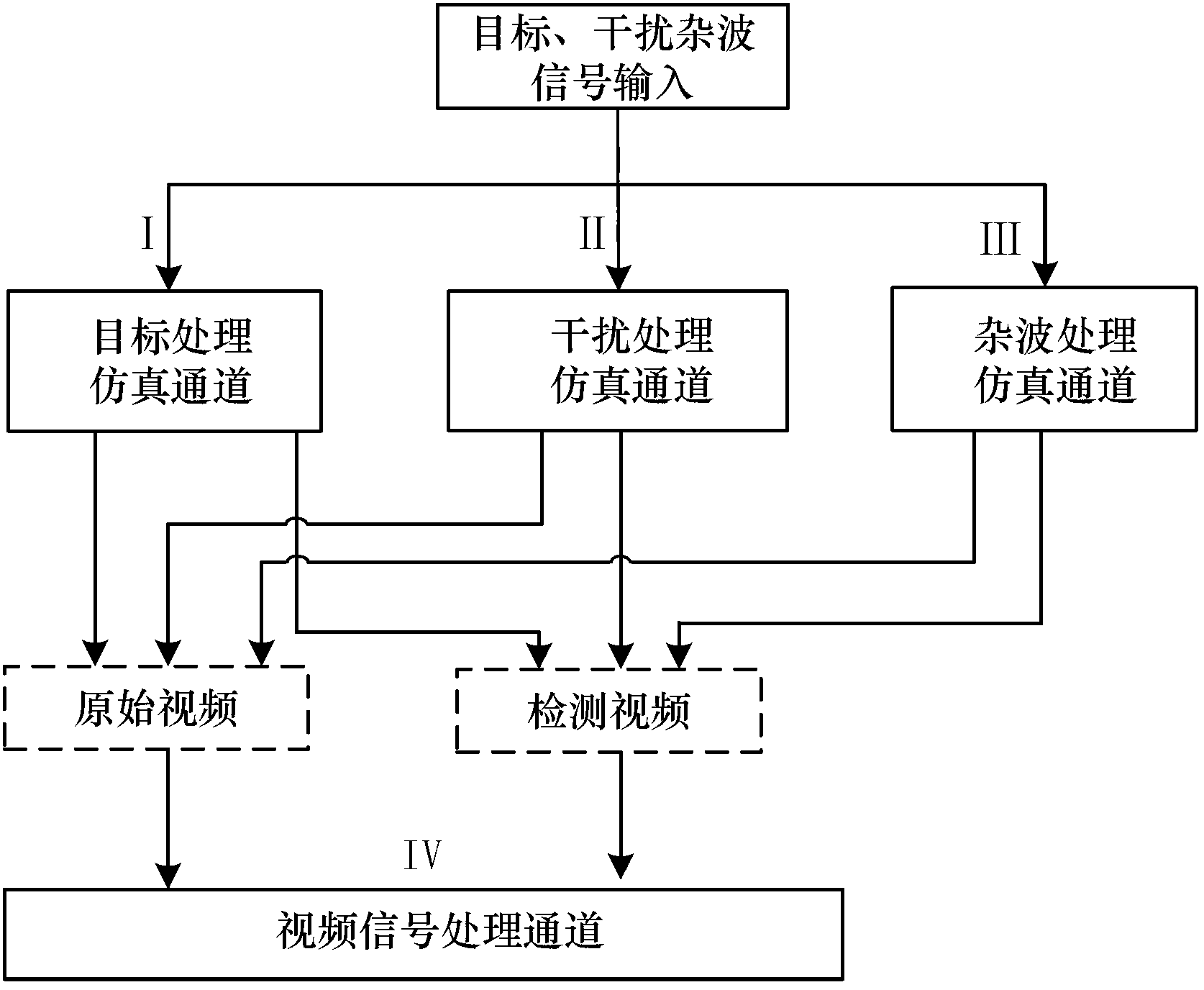
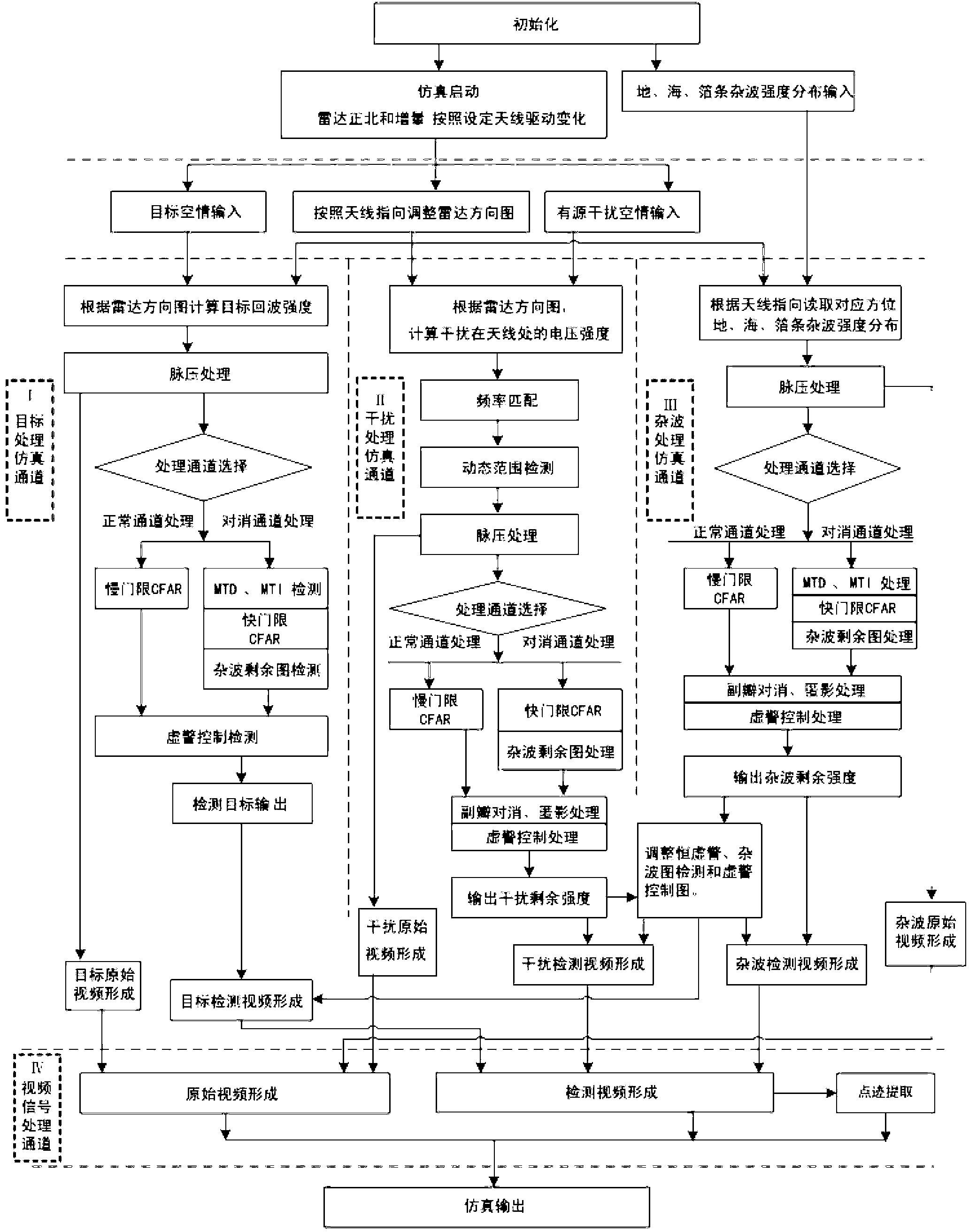
The invention relates to a general performance simulation method and a framework of an air surveillance radar. General real-time simulation of detection performance of the air surveillance radar is achieved due to the utilization of a structure of a plurality of serial simulation module channels and parallel computation processing calculation channels. Processing modules related to the radar are serially connected through the serial simulation module channels according to treating processes of radar real installation signals to form into a simulation process of processing of at least a radar signal. Parallel simulation calculations of treating processes of a target signal, an interference signal and a clutter signal are respectively performed through a parallel calculation processing structure based on the serial simulation module channels and then various signals are performed composition and point trace cohesion to form and output a radar simulation result. The serial simulation module channels are reconfigurable; module composed structures and parameters can be changed; and an existing module or a new construct module can be utilized to achieve general performance simulation of the air surveillance radar.
Owner:中国人民解放军防空兵学院
Target cluster method and device suitable for field surveillance radar
ActiveCN106093946AImprove efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSecondary surveillance radarRectangular coordinates
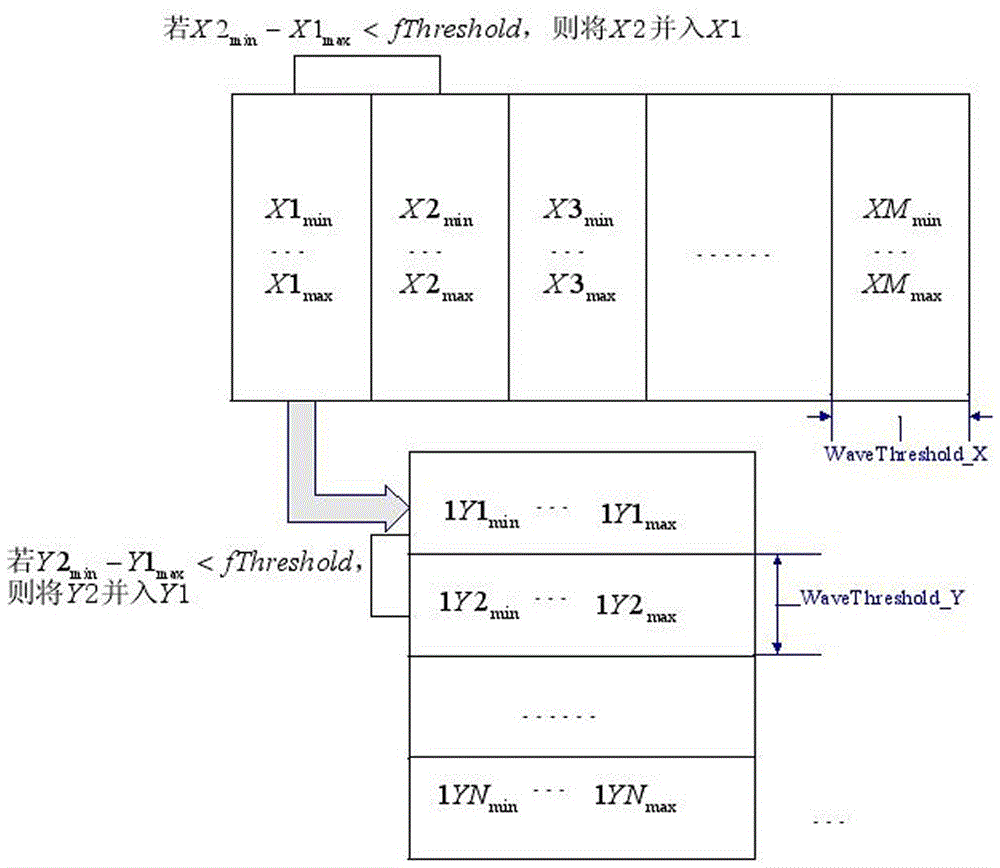
The invention relates to the radar data processing technology and particularly relates to a target cluster method and device suitable for field surveillance radar. The invention provides a target cluster method and device directed to the problem in the prior art. The position of radar serves as a system center point, the radar detecting range is taken as the boundary, and the control space is changed into a rectangular coordinate system plane by projection. Firstly, an original trace point set is distributed in corresponding space units in a direction, then, the space units are subjected to condensation in sequence to obtain a cluster result in the direction, and on this basis, the first cluster result is subjected to condensation in another direction to obtain a final condensation result. The algorithm conducts linear scanning in one-dimensional direction for once condensation, and is better than the traditional algorithm considering two dimensions, thereby being named a dimension-reducing algorithm. In addition, calculation of a distance between any two points is omitted, and the time complexity of algorithm is linear, so that the efficiency is high.
Owner:四川九洲空管科技有限责任公司
High-capacity location and identification system for cooperating mobiles with frequency agile and time division transponder device on board
InactiveUS7570195B2Increase the stationIncrease system capacityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionOn boardGround vehicles
Cooperating mobiles (ground vehicles, aircraft) are located and identified by Multilateration and Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) techniques using the frequency band and the format of the Secondary Surveillance Radar (SSR) signals in high traffic situations. Standard messages, transmitted by the mobile on the downlink channel, i.e. to a set of fixed receiving stations, and including the identification code, permit the location of the mobile by multiple time measurements (Multilateration) from a subset of the set of fixed receiving stations; when the message contains the position (GPS and, later, Galileo datum) the mobile may be located with the ADS-B when in view even of a few stations or of a single station. In order to overcome the problem that arises with high traffic, i.e. the superimposition of signals, called garbling.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROME TOR VERGATA
Method for Increasing the Time for Illumination of Targets by a Secondary Surveillance Radar
ActiveUS20120068878A1Radio wave reradiation/reflectionSecondary surveillance radarTransmission channel
A secondary surveillance radar with rotating antenna, configured for transmitting interrogations in S or IFF mode and processing the responses to these interrogations. The radar includes an antenna having a lobe with three channels, a Sum channel, a Difference channel and a Control channel, whose transmission means are configured for transmitting interrogation messages over the Sum and Difference channels and whose reception and processing means are configured so as to carry out, aside from conventional detections by the Sum channel, detections by the Difference channel of the responses from the aircraft having been subjected to interrogation by this same channel. The radar also includes means for Space-Time Management configured for generating interrogation messages and determining whether a given message is to be transmitted by the Sum channel, by the Difference channel or by the two channels simultaneously and controlling its transmission by the corresponding transmission channel.
Owner:THALES SA
Secondary surveillance radar and its interrogation transmission method
InactiveUS20060055586A1Securing timeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSecondary surveillance radarEnvironmental geology
An interrogation transmission method of a secondary surveillance radar compares prediction angle ranges for transmitting interrogations with a beam-width of an antenna, and transmits the interrogations at every roll-call period if the prediction angle ranges for transmitting interrogations are narrower than the beam-width of the antenna. In contrast, if the prediction angle ranges for transmitting the interrogations are wider than the beam-width of the antenna, the radar respectively sets a period to transmit the interrogations and a period not to transmit the interrogations until responses can be received, and transmits interrogations at every roll-call period after the responses can be received (even if a receiving error or downlink occurs).
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
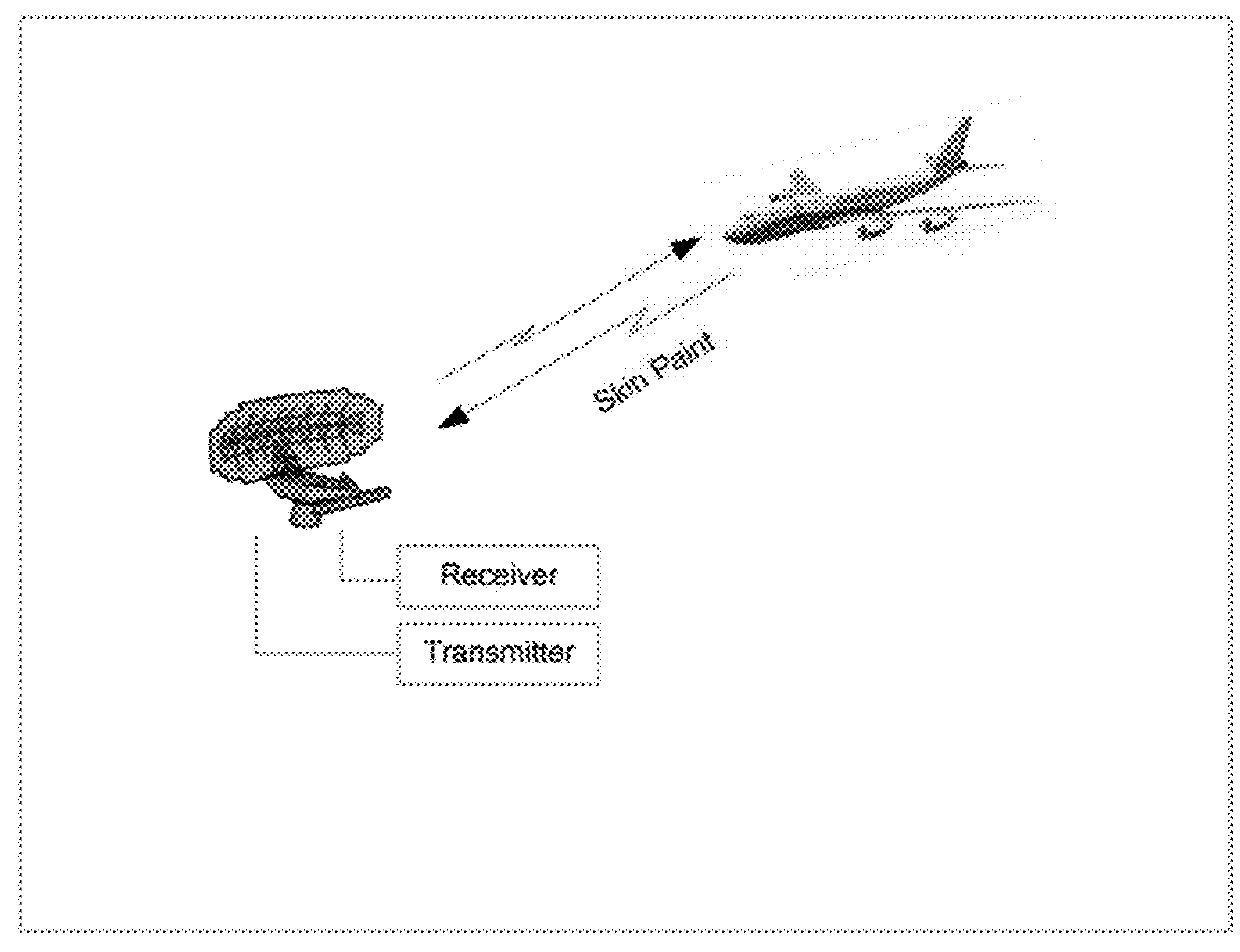
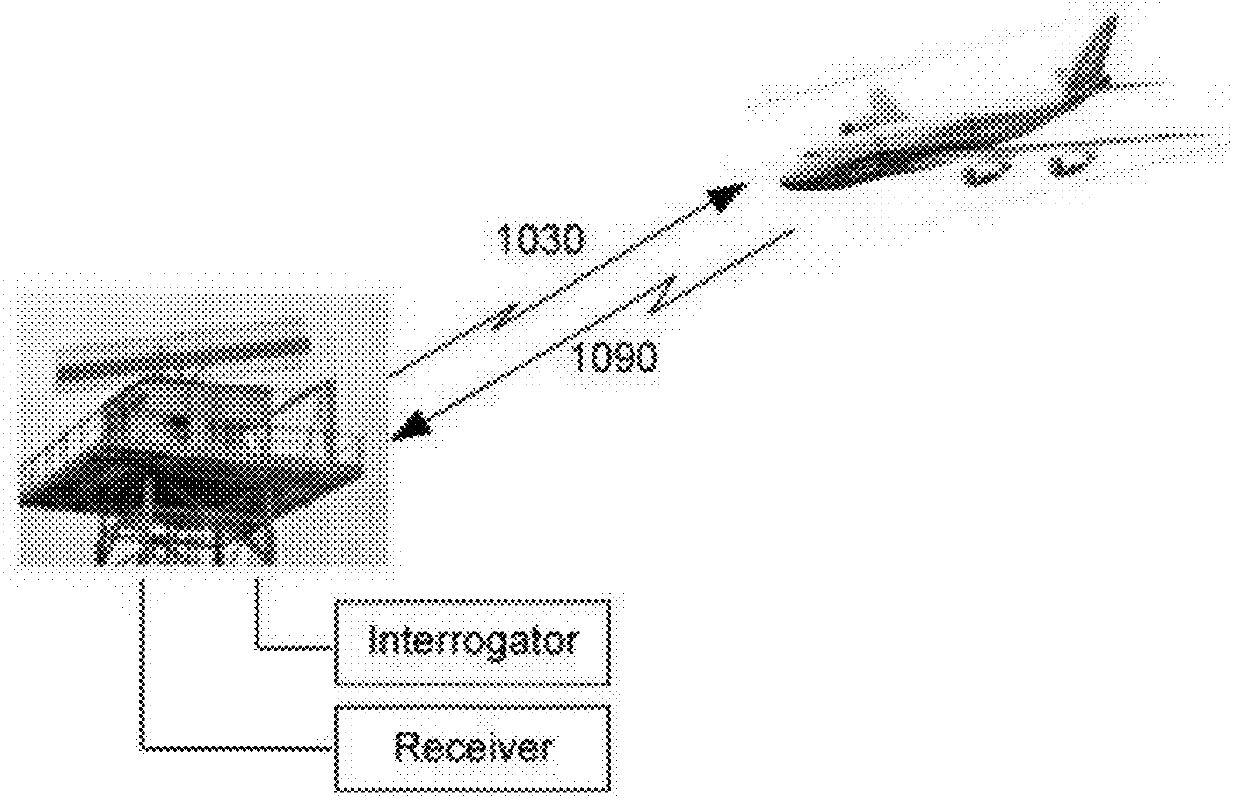
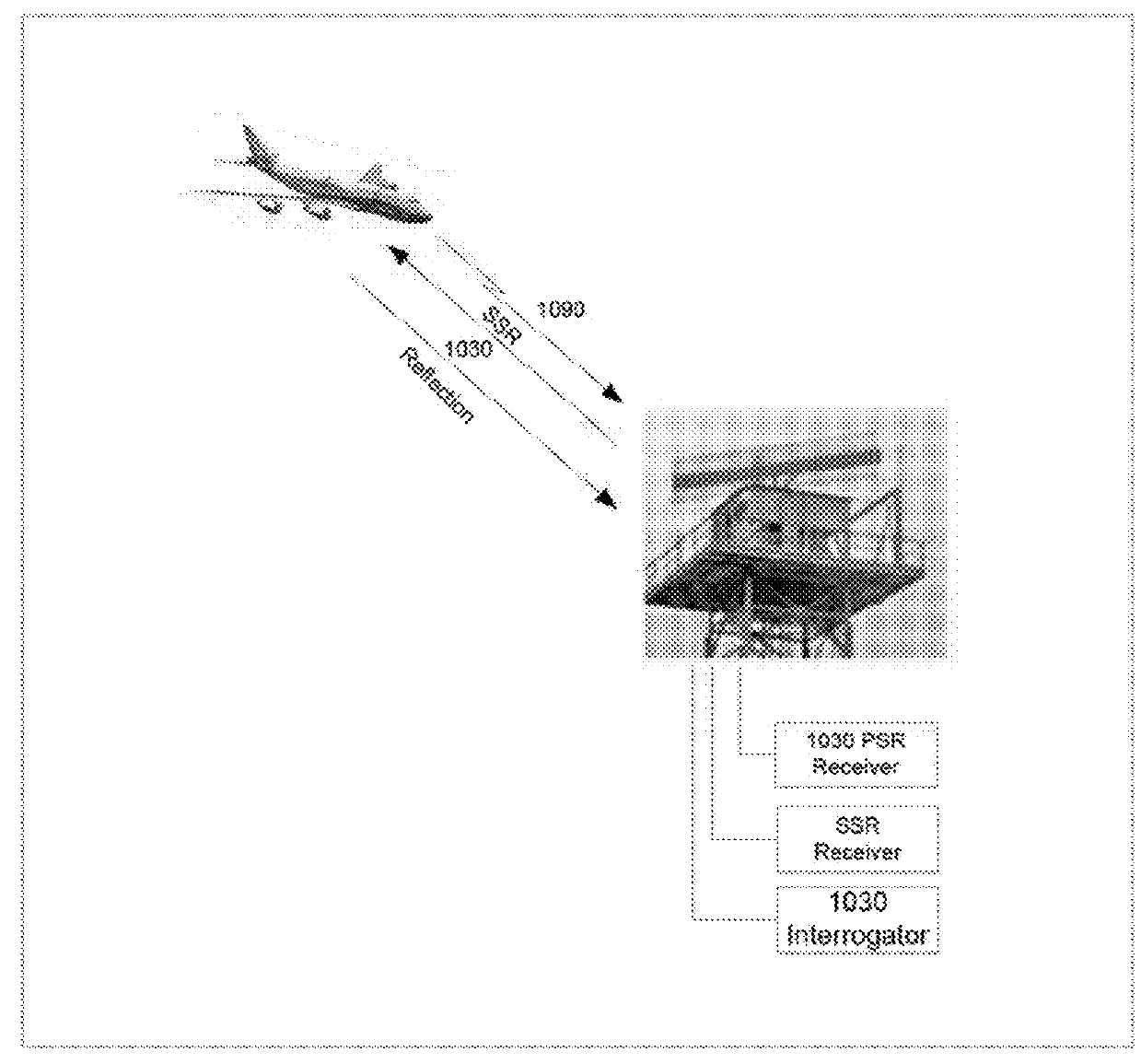
Secondary surveillance radar signals as primary surveillance radar
Systems and methods relating to the use of one type of radar technology to accomplish the function of another type of radar technology. Secondary Surveillance Radar / Identification Friend or Foe (SSR / IFF) technology can be used as if it was Primary Surveillance Radar (PSR) to gain the advantages of both systems. Radar signals useful for SSR / IFF are used as PSR signals. Reflections of the SSR / IFF signal off of both airborne and ground based aircraft, and ground based vehicles and items are used to locate and identify these aircraft, vehicles and items. For SSR / IFF transponder equipped aircraft, the reflected SSR / IFF signals provide (prove dial) dual confirmation of the aircraft's presence while for non-transponder equipped aircraft, the reflected signals provide an indication of the aircraft's presence. The use of SSR / IFF signals reflected off of ground based vehicles and items provides an indication of ground based vehicles and items present around the installation receiving the reflected SSR / IFF signals.
Owner:HARVEY JAMES FRANCIS
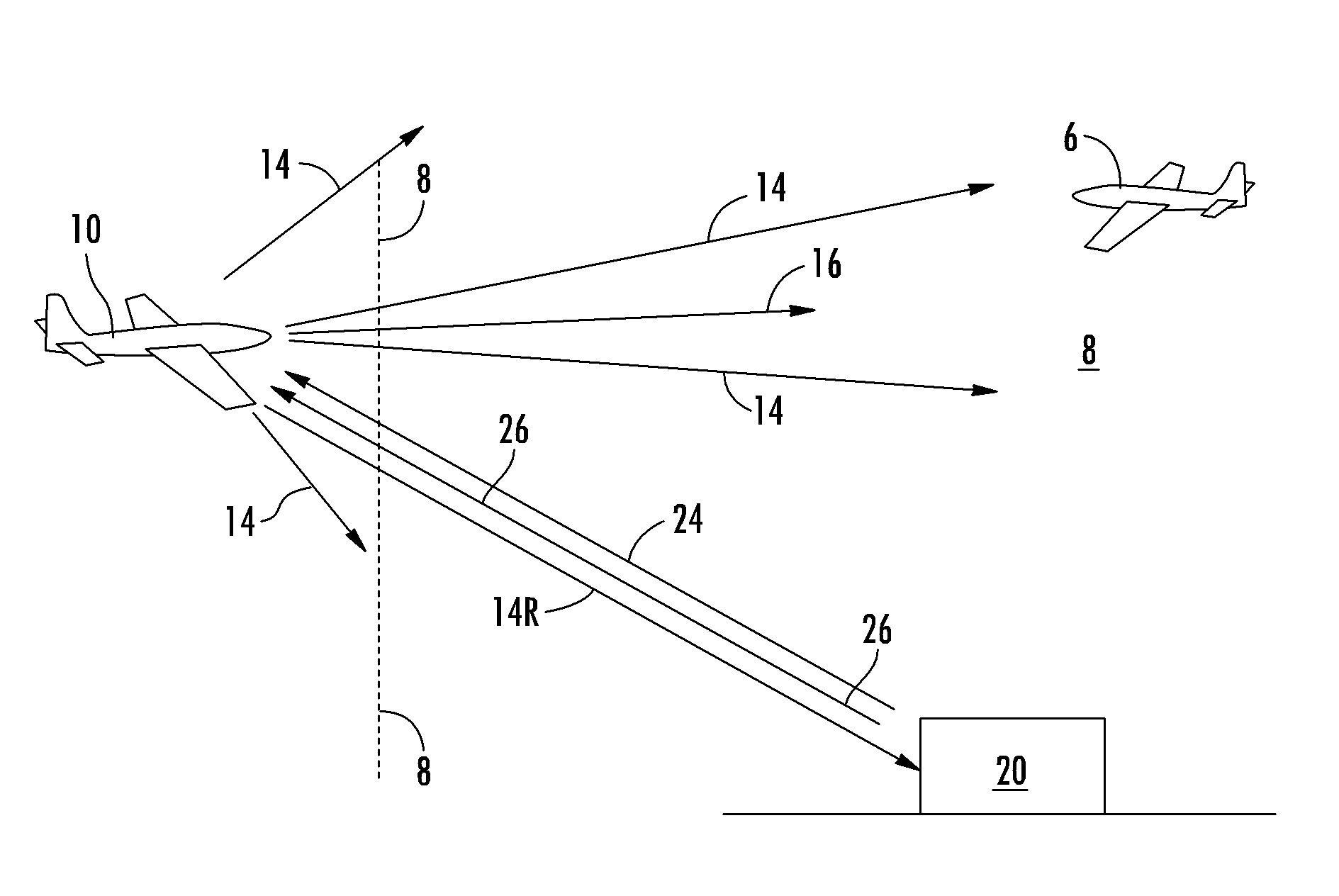
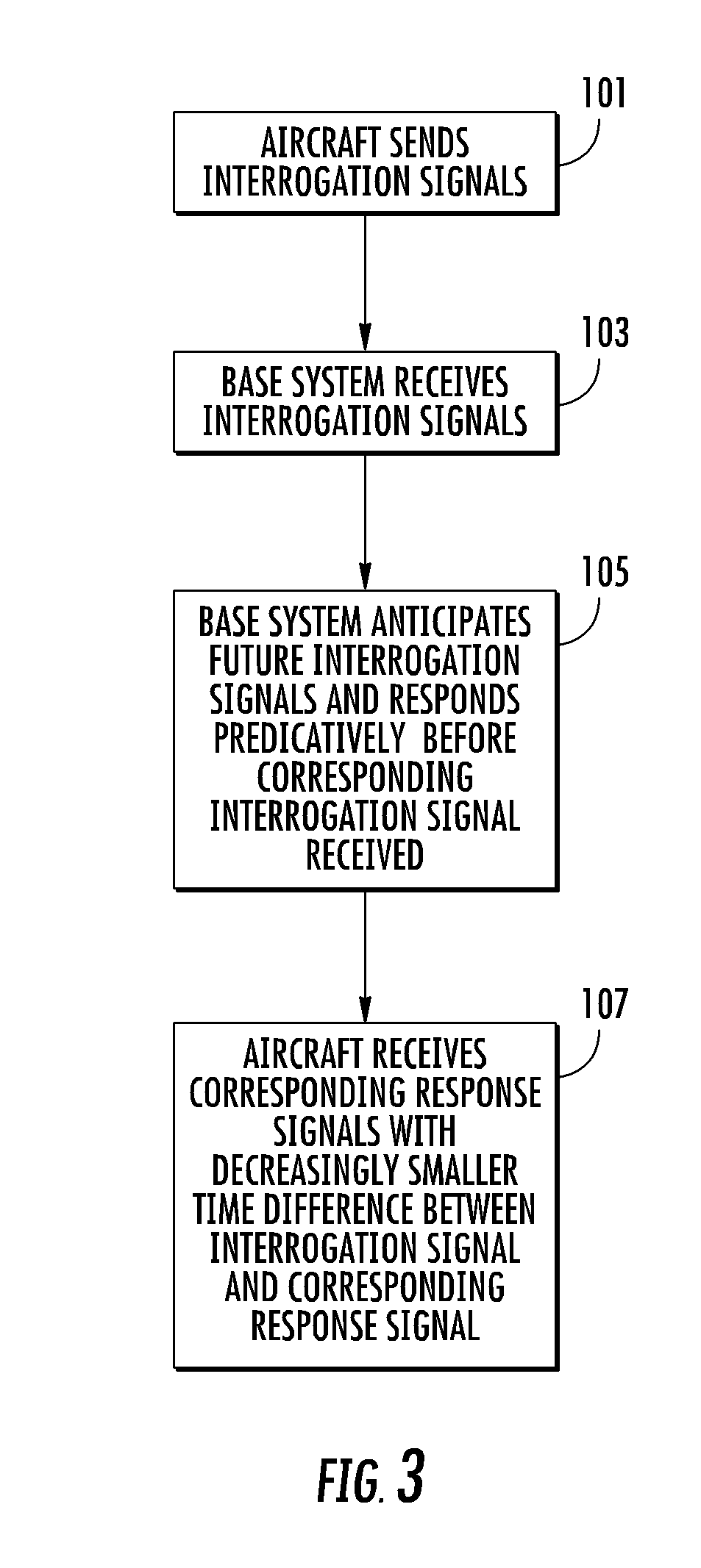
Method and system for preventing anti-aircraft warfare engagement with neutral aircraft
InactiveUS8477061B1Engage with obstructionShorten the timePosition fixationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSecondary surveillance radarTime difference
A method and system that prevents engagement with neutral aircraft utilizes secondary surveillance radar (SSR) in conjunction with traffic alert collision avoidance systems (TCAS) conventionally found on various commercial aircraft. The system and method provide for detecting interrogating signals sent out by a TCAS system of an interrogating aircraft searching for another aircraft that may pose a threat for collision. The system and method of the invention provide for a base system generating signals responsive to the interrogation signals such that there is a decreasing time difference between the interrogating signals and the responsive signals. The decreasing time difference indicates to the interrogating aircraft that another aircraft is approaching its airspace urging the neutral aircraft to change course and avoid entering a guarded tactical airspace thus avoiding unnecessary engagement of the aircraft.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
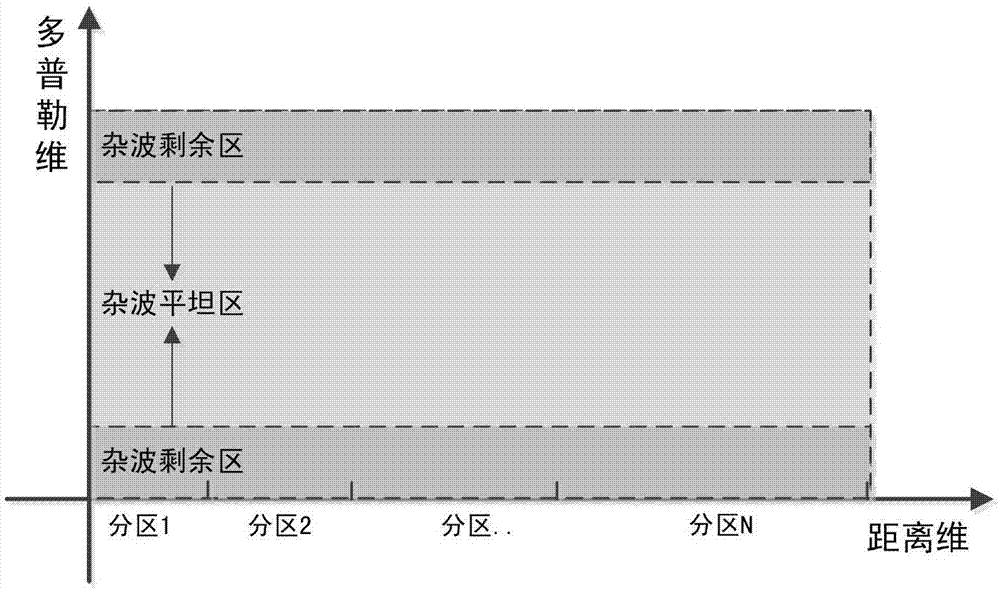
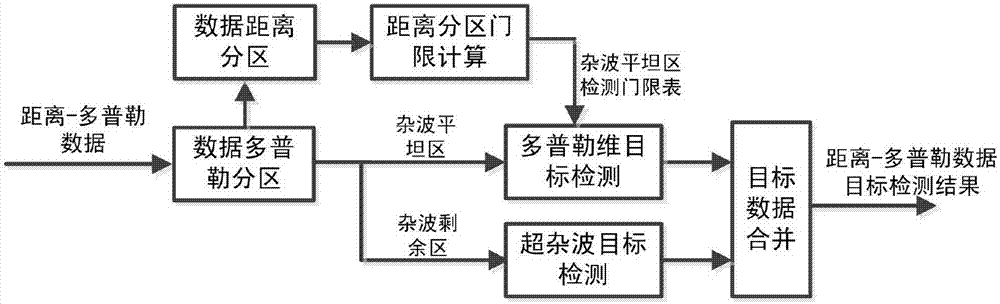
Low false alarm rate rapid target detection method for ground surveillance radar
ActiveCN107015221AControl false alarm rateReduce target false alarmRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSecondary surveillance radarRadar systems
The invention discloses a low false alarm rate rapid target detection method for a ground surveillance radar, relating to the target detection of the ground surveillance radar in the field of radio measurement. The method includes the processing steps of data distance partition, distance partition threshold table calculation, data Doppler division, Doppler rapid target detection, super clutter target detection, and target data merging. This method performs the partition processing on the distance-Doppler data on two dimensions, and realizes the rapid target detection with low false alarm rate. The method has the characteristics of high target detection probability, low false alarm rate, fast calculating speed, and simple engineering realization, solving the problems of high false alarm rate or complex target detection algorithm of a radar system in a ground clutter environment, and being especially suitable for the constant false alarm detection of ground surveillance radars and battlefield reconnaissance radars.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
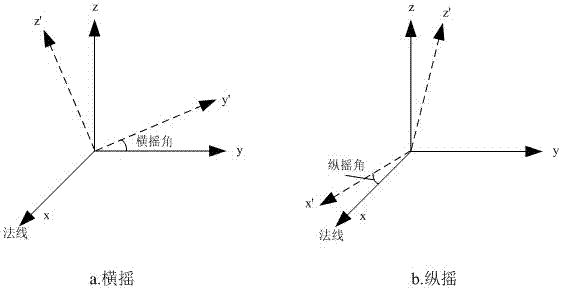
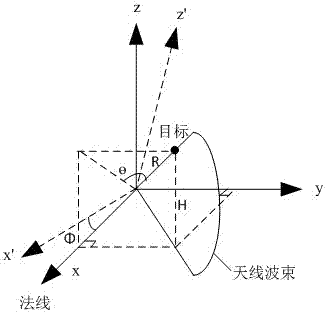
Angle correction method and angle correction system for secondary surveillance radars
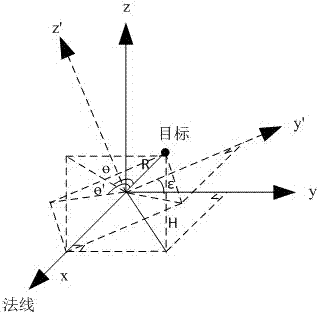
ActiveCN106872952ASolve the phenomenon of out-of-tolerance azimuth measurementBig spaceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSecondary surveillance radarGreek letter epsilon
The invention provides an angle correction method and an angle correction system for secondary surveillance radars. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a roll angle Epsilon and a pitch angle Phi produced by swing of a secondary surveillance radar carrier; judging whether the roll angle Epsilon and the pitch angle Phi are within set threshold scopes; and if the roll angle Epsilon and the pitch angle Phi are within the set threshold scopes, acquiring a measured azimuth angle Theta', a range R and a C-mode height H obtained through target detection by the secondary surveillance radar when the roll angle Epsilon and the pitch angle Phi are within the set threshold scopes, and correcting the azimuth angle. Compared with the prior art, the problem that the azimuth measured by a mobile platform secondary surveillance radar is out of tolerance due to swing of the carrier under the condition of not using a mechanical stabilizing method is solved; and the angle is corrected through a software method, the use of heavy mechanical stabilizing facilities is avoided, the space is expanded and the weight is reduced for the carrier platform, the requirement on the processing ability of the system is not high, compensation can be made in real time, and the correction precision is high.
Owner:四川九洲空管科技有限责任公司
Angle measurement method for secondary surveillance radar
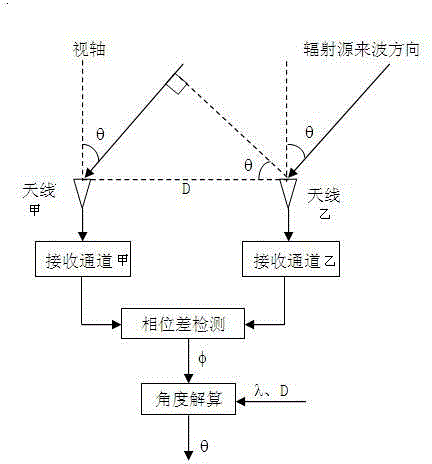
ActiveCN103389496ARealize monitoringEasy to controlRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSecondary surveillance radarPhase difference
The invention provides an angle measurement method for a secondary surveillance radar. The method comprises the step that a direction of an incoming wave is determined by utilizing a two-dimensional phase interferometer, conducting two-dimensional angle measurement computation and utilizing a phase difference formed by a radio wave on a base line. With the adoption of the method, surveillance and control of a secondary surveillance radar system to a target can be achieved; the method is simple to achieve, and has a certain application value to a special application occasion of the secondary surveillance radar; and the problem that one-dimensional angle measurement is inaccurate is solved.
Owner:四川九洲空管科技有限责任公司
Pulse waveform for field surveillance radar
InactiveCN102540151AReduce the amount of equipmentStrong ability to distinguish multiple targetsWave based measurement systemsSecondary surveillance radarRadar waveforms
The invention belongs to the technology of radar waveform design and relates to an improved pulse waveform for a field surveillance radar. The improved pulse waveform is characterized in by comprising narrow pulses and broad pulses alternately one by one; and one pulse waveform period is composed of one period of narrow pulse and one period of broad pulse, wherein the narrow pulse is composed of single-carrier frequency sine wave signals. The pulse waveform has the advantages of less amount of needed equipment, strong multi-target resolution capacity and low emission peak power.
Owner:中国航空工业第六〇七研究所
Secondary surveillance radar and method of analyzing replies for secondary surveillance radar
ActiveUS20100253566A1Improved in capability of eliminatingImprove abilitiesAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficSecondary surveillance radarAtmospheric sciences
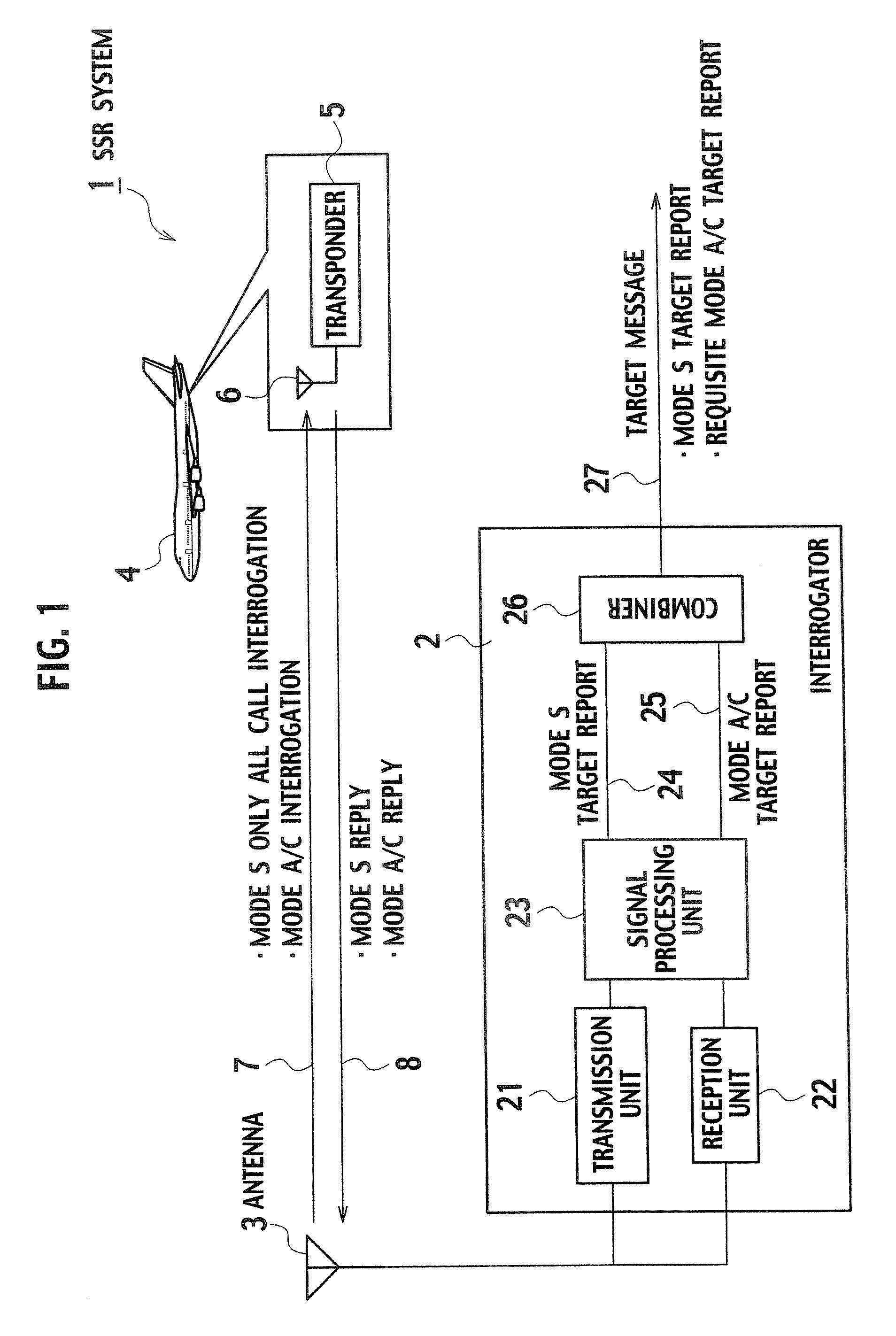
Provided is a secondary surveillance radar with an improved capability of eliminating an unnecessary Mode A / C target report, which includes a transmission unit transmitting interrogations, a reception unit receiving replies, from a transponder, corresponding respectively to the interrogations, and a signal processing unit generating a Mode S target report and a Mode A / C target report from the replies. The radar also includes a combiner generating a Mode S track and a Mode A / C track respectively from the Mode S and the Mode A / C reports, and then judging whether the Mode S report and the Mode A / C report are of the same target on the basis of the Mode S and the Mode A / C tracks. When the Mode S and the Mode A / C reports are of the same target, the combiner rejects the Mode A / C report.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
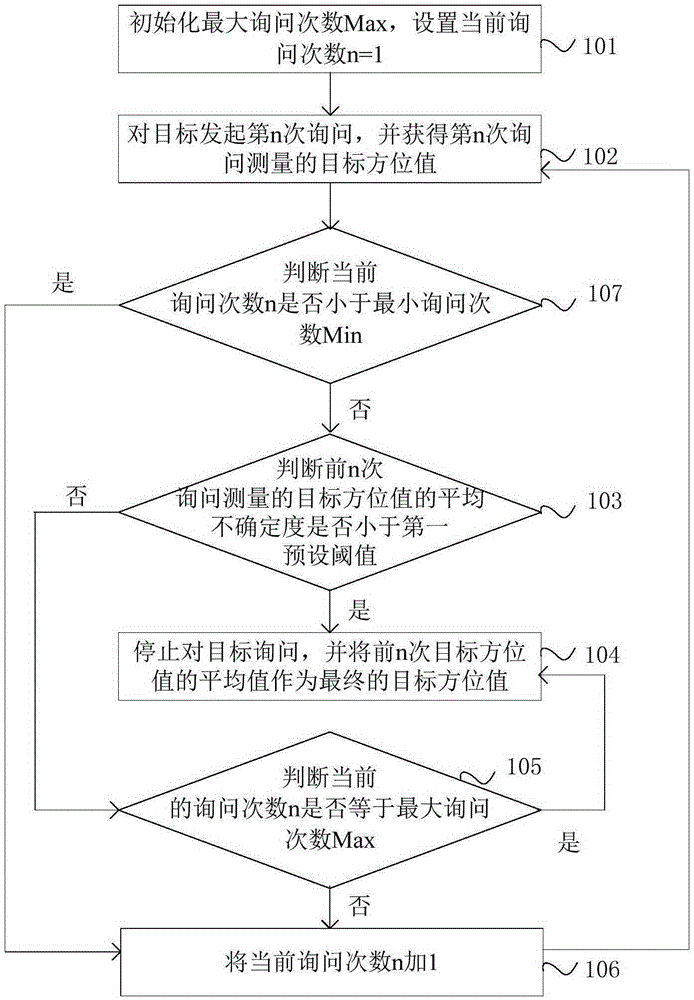
Self-adaptive control method and apparatus for inquiry frequency of secondary surveillance radar
InactiveCN105242265AHigh measurement accuracyMeet the requirements of measurement accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSecondary surveillance radarControl objective
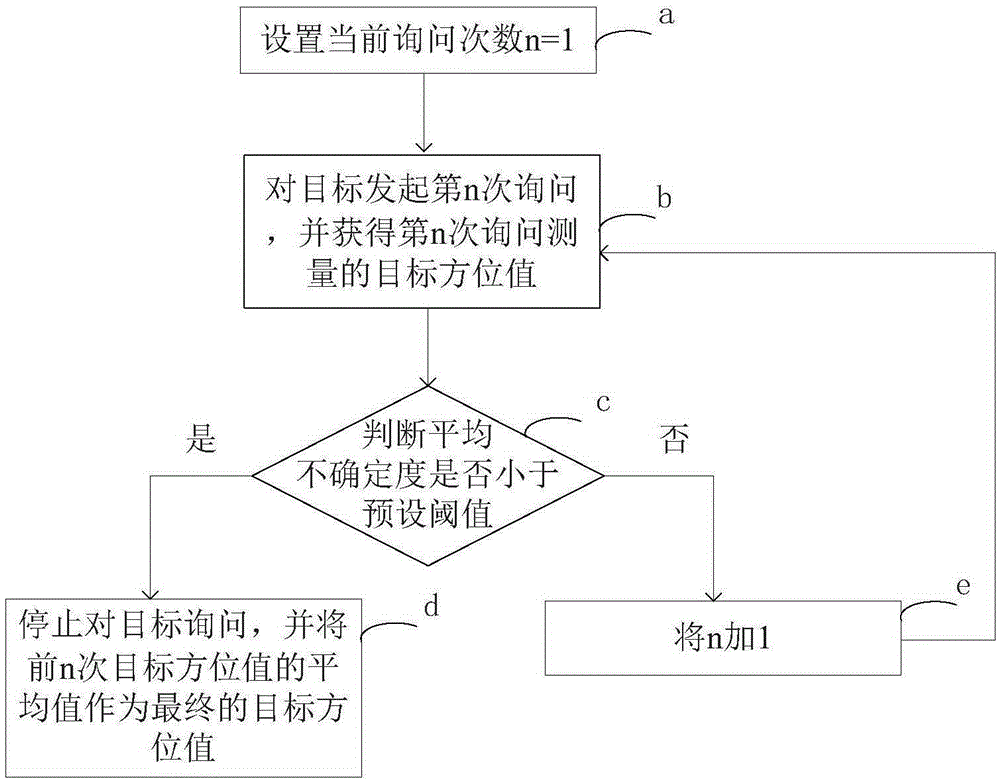
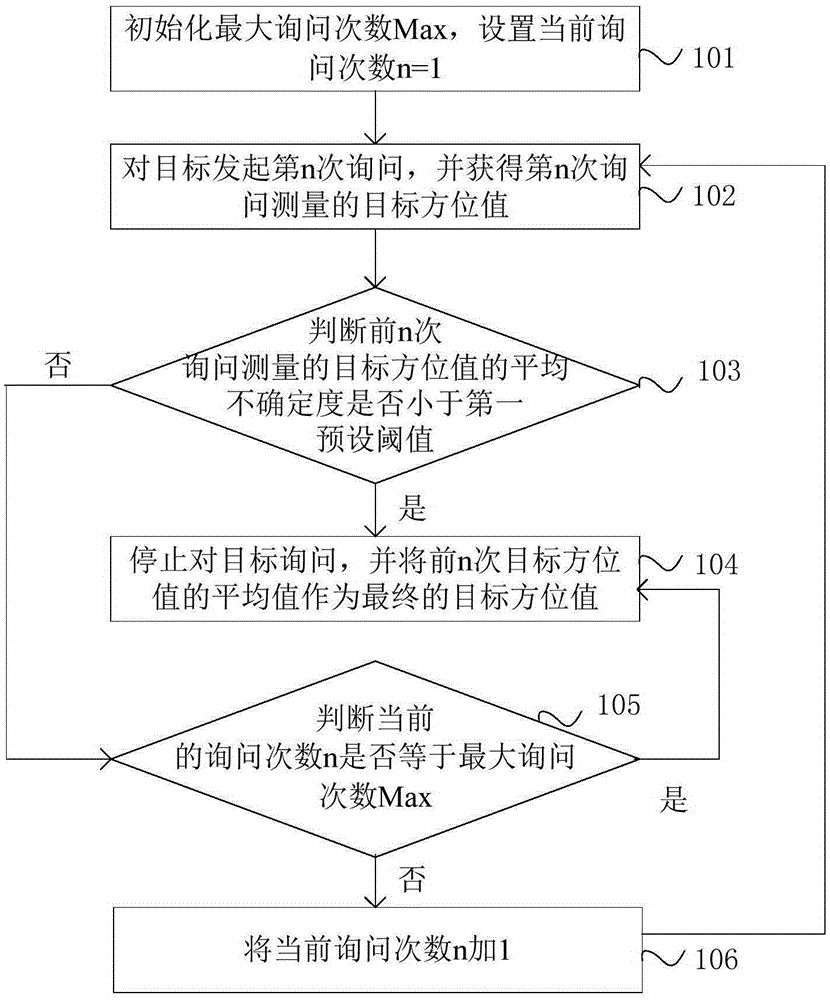
The invention provides a self-adaptive control method and apparatus for the inquiry frequency of secondary surveillance radar. The method includes the steps: a, initializing the maximum inquiry frequency Max, and setting the current inquiry frequency n=1; b, conducting the n inquiry for a target, and obtaining a measured target direction value during the n inquiry; c, calculating the average uncertainty of target direction values measured during the previous n times of inquiry, determining whether the average uncertainty is smaller than a preset threshold, stopping target inquiry if the average uncertainty is smaller than the preset threshold and taking the average value of the previous n times of target direction values as a final target direction value, and performing the step d if the average uncertainty is not smaller than the preset threshold; and d, determining whether the current inquiry frequency n is greater than the maximum inquiry frequency Max, taking the average value of the previous n times of target direction values as a final target direction value if the current inquiry frequency n is greater than the maximum inquiry frequency Max, otherwise, adding 1 to the current inquiry frequency n and going back to the step b. According to the method, the measurement precision of a target direction value can be ensured, the target inquiry frequency can be controlled in a self-adaptive manner, and signal crosstalk and interference in a system can be minimized.
Owner:SICHUAN JIUZHOU ELECTRIC GROUP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com