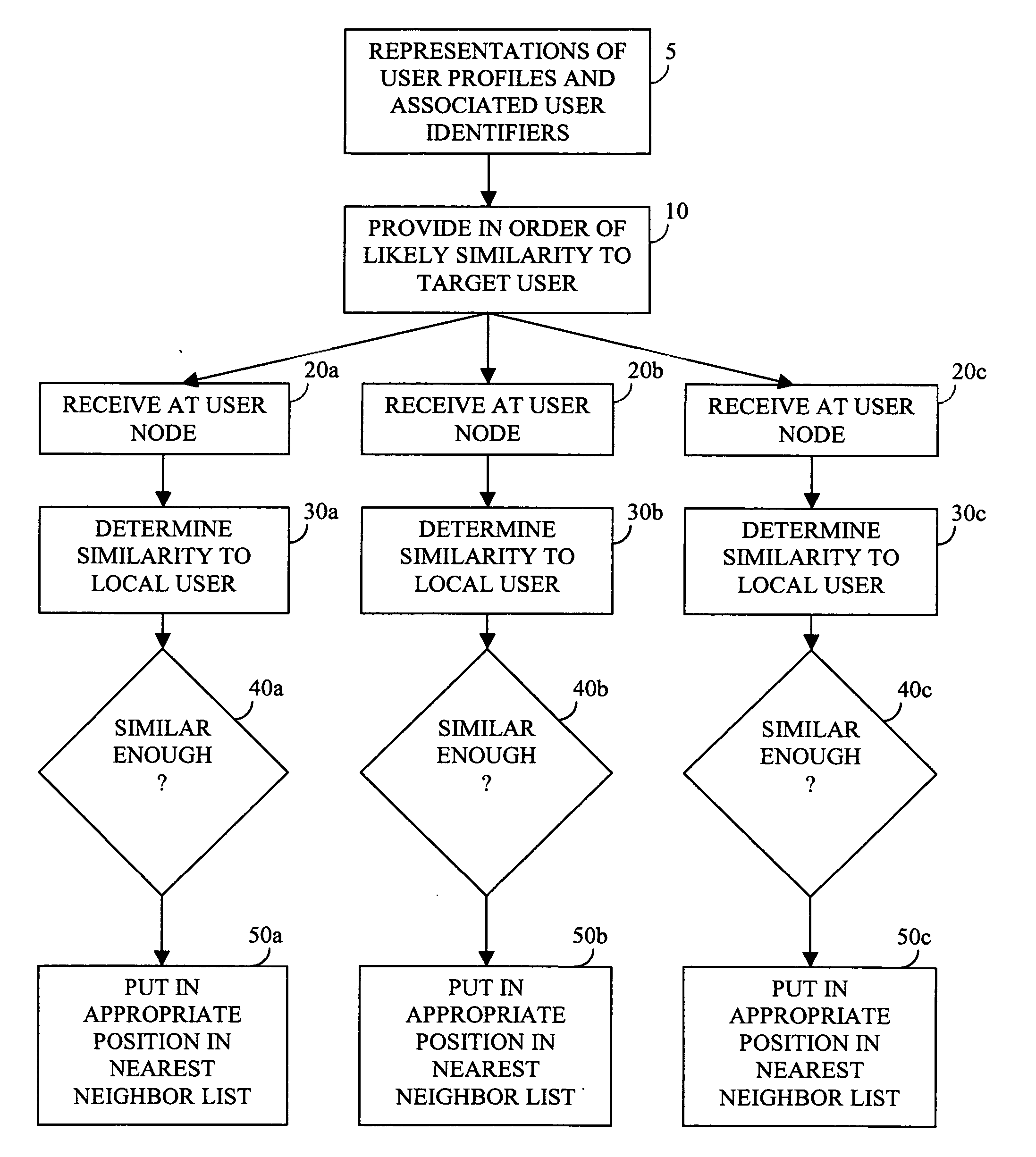
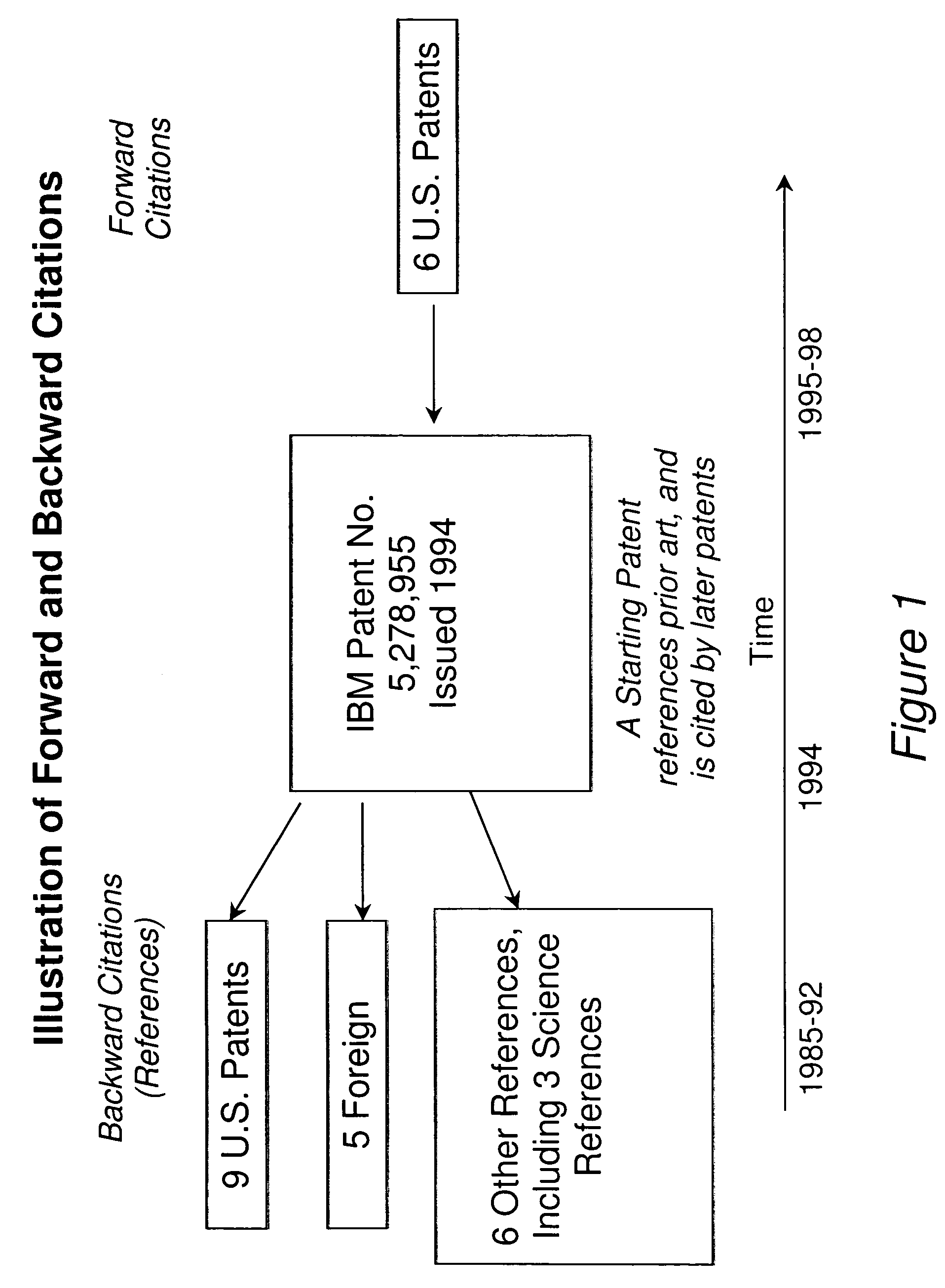
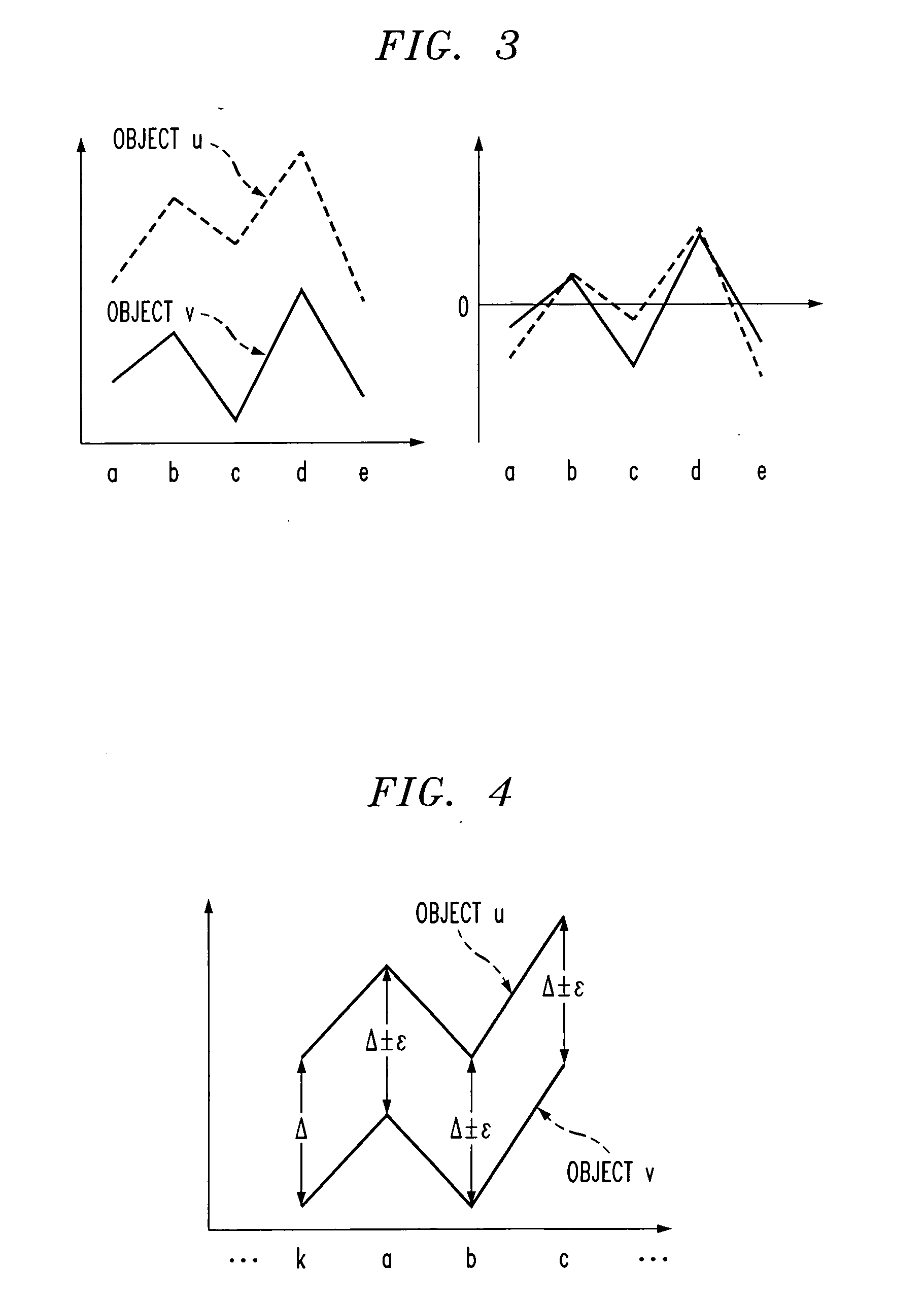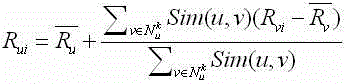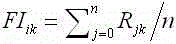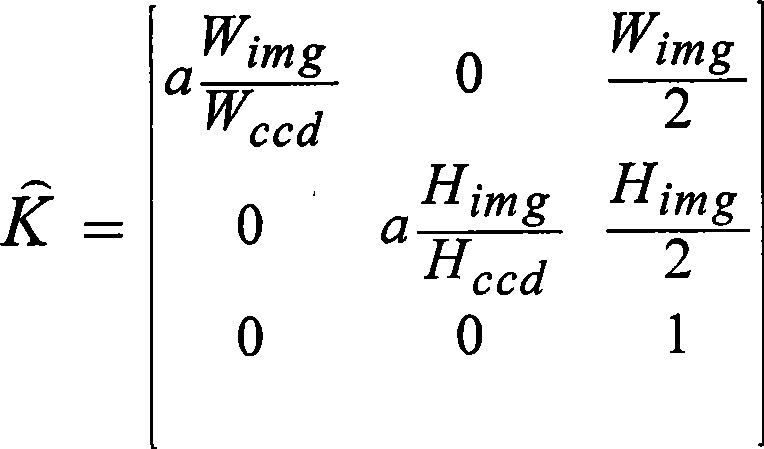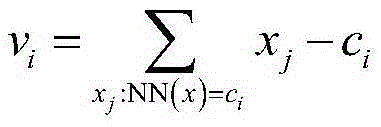Patents
Literature
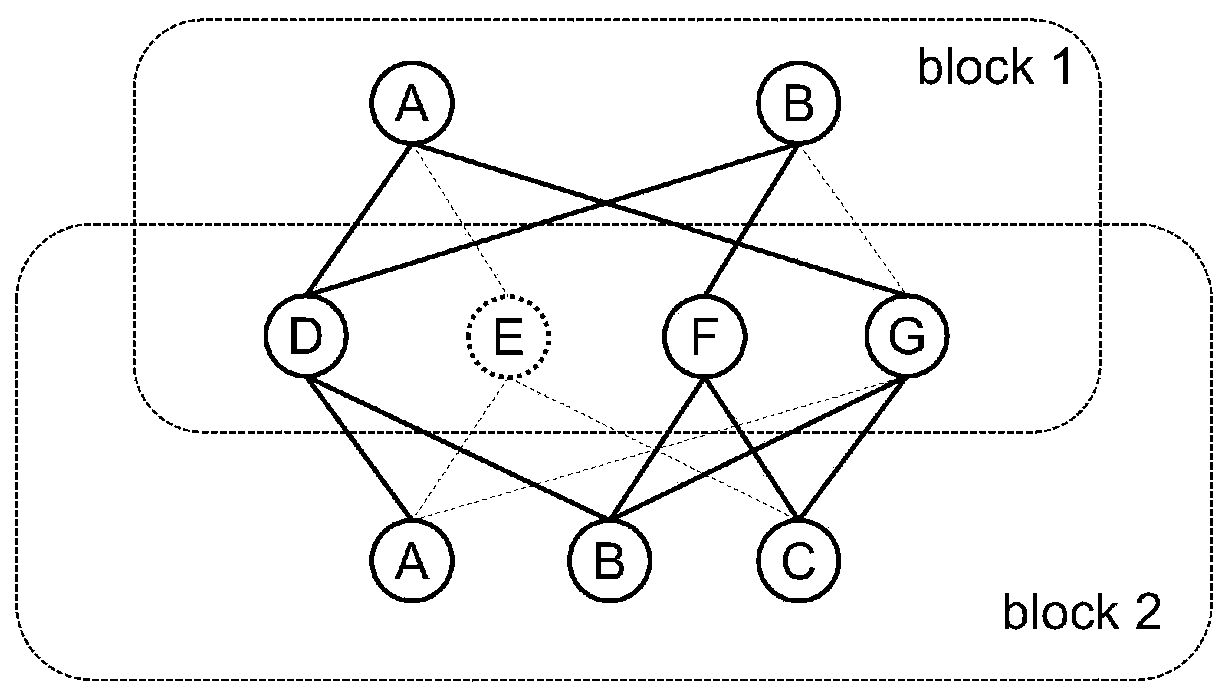
266 results about "Nearest neighbor search" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
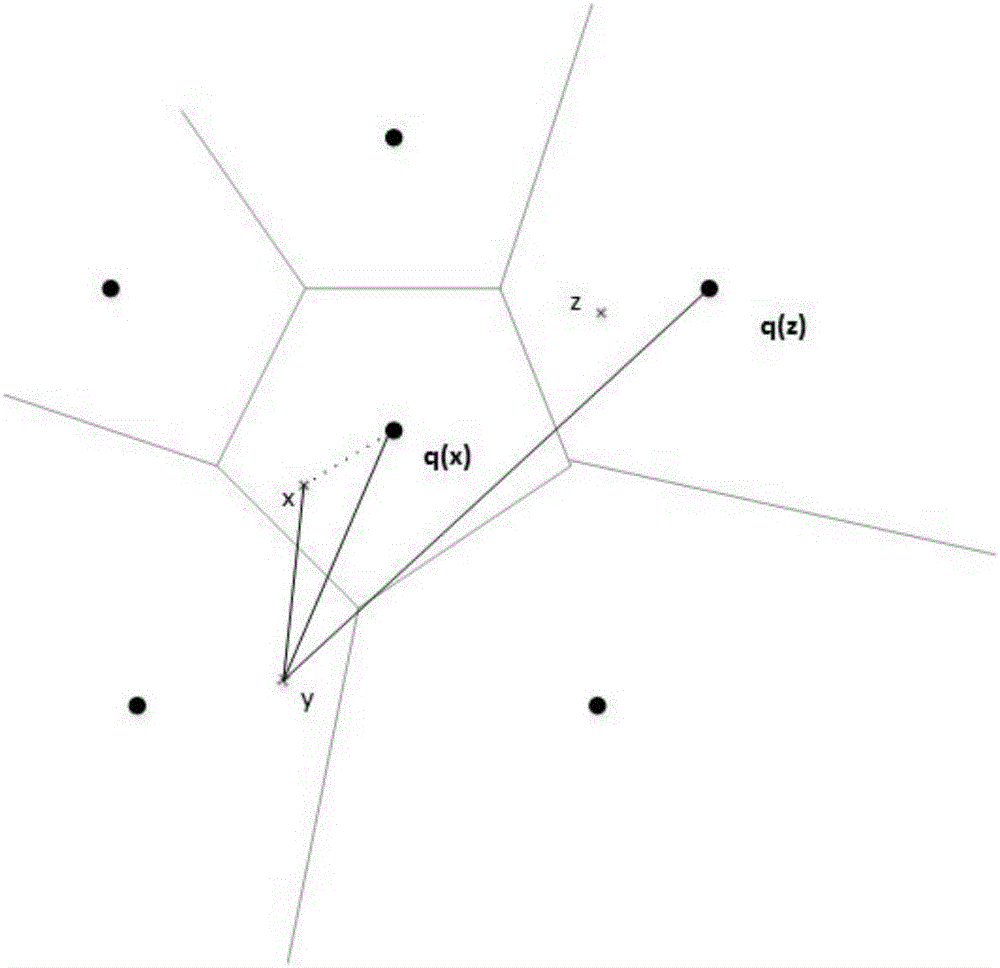
Nearest neighbor search (NNS), as a form of proximity search, is the optimization problem of finding the point in a given set that is closest (or most similar) to a given point. Closeness is typically expressed in terms of a dissimilarity function: the less similar the objects, the larger the function values. Formally, the nearest-neighbor (NN) search problem is defined as follows: given a set S of points in a space M and a query point q ∈ M, find the closest point in S to q. Donald Knuth in vol. 3 of The Art of Computer Programming (1973) called it the post-office problem, referring to an application of assigning to a residence the nearest post office. A direct generalization of this problem is a k-NN search, where we need to find the k closest points.
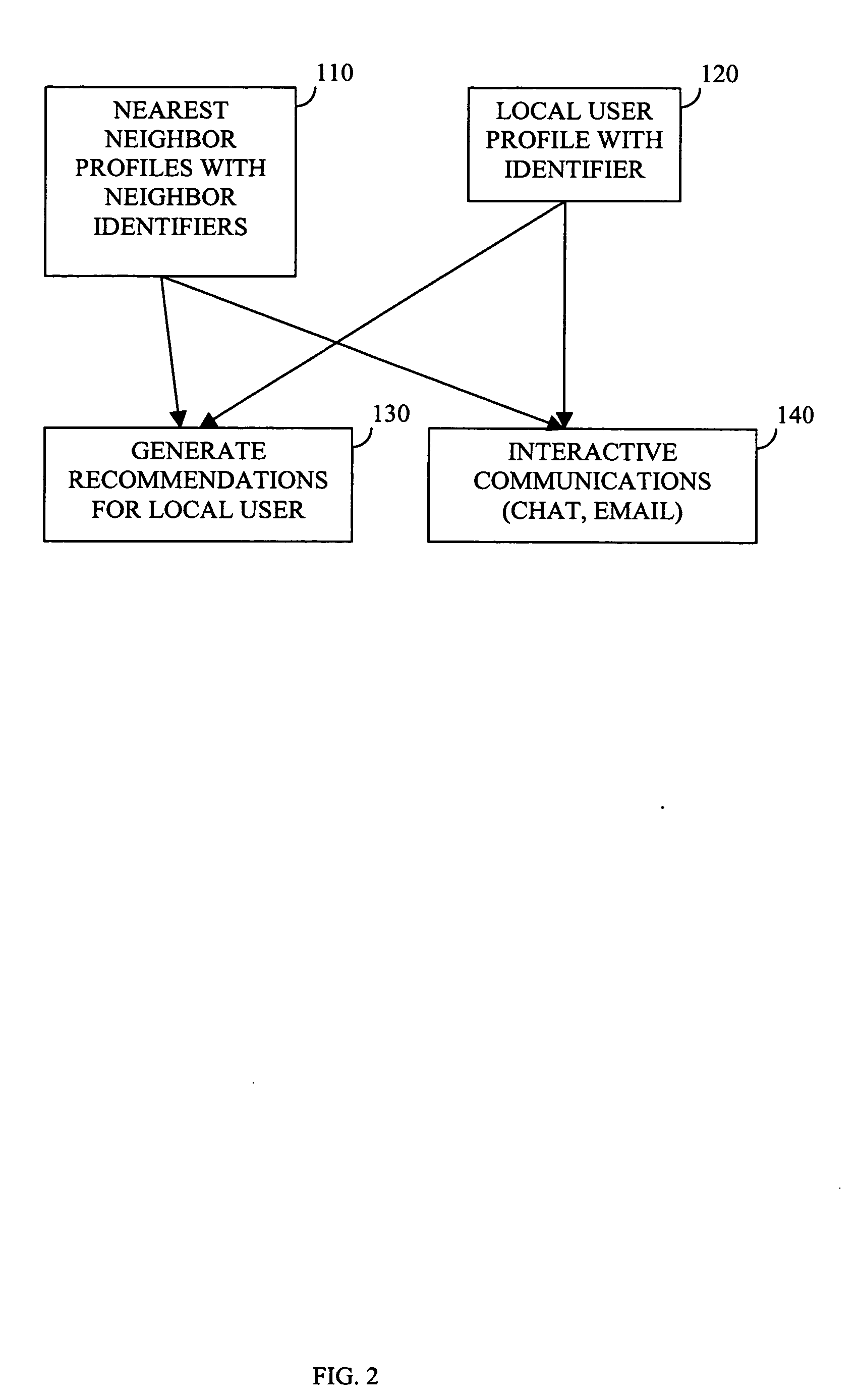
Enabling recommendations and community by massively-distributed nearest-neighbor searching
InactiveUS20060020662A1Reason to have confidenceGreat extremityMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksNear neighborEnd user
The computer associated with each of a potentially large number of end users is harnessed to provide a massively-distributed mechanism for finding the nearest neighbors of each user, according to tastes and / or interests. Once these nearest neighbors are determined, there taste or and / or interest profiles are leveraged for highly accurate recommendations, and their online addresses are leveraged for community purposes.
Owner:EMERGENT MUSIC
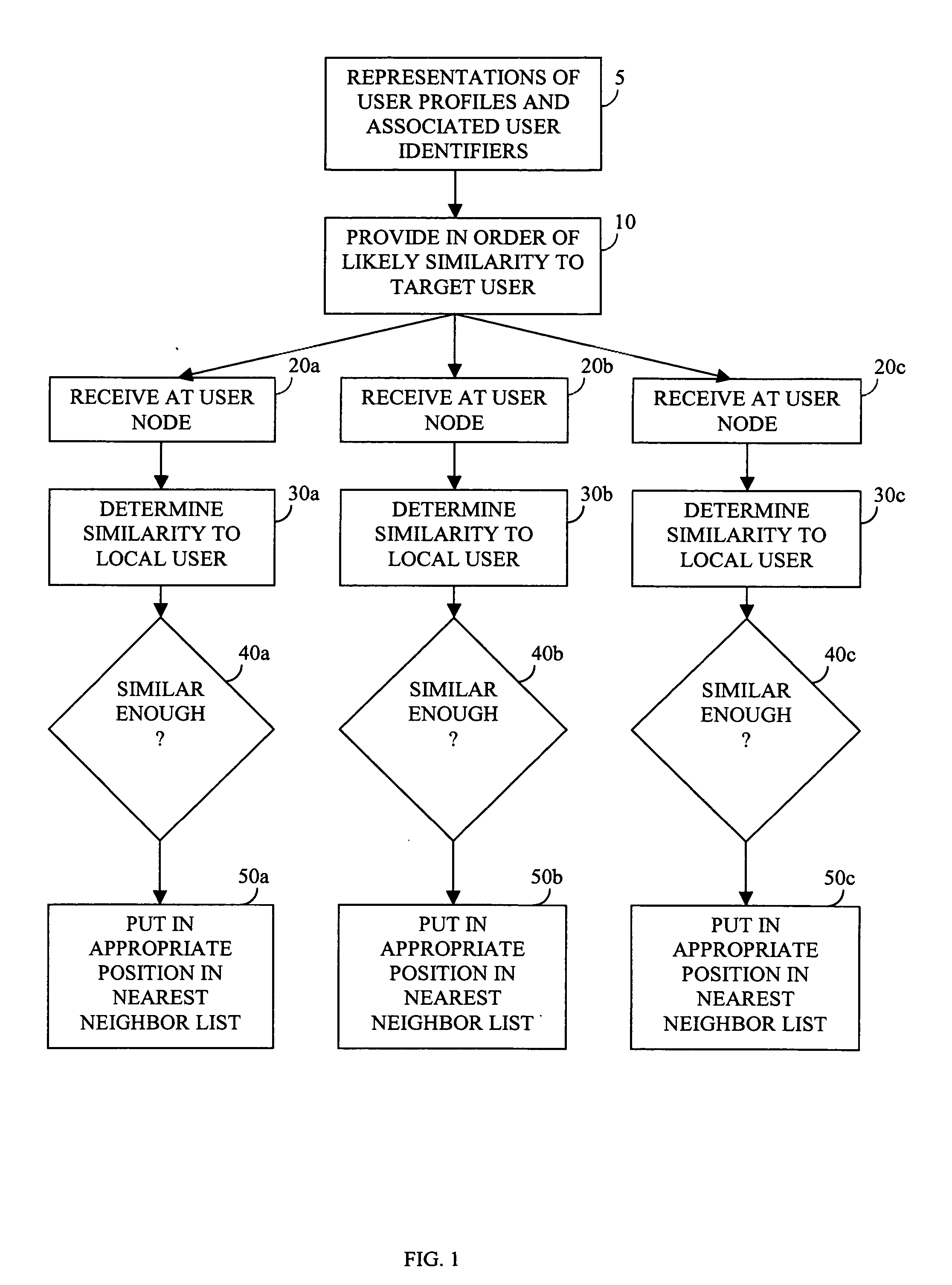
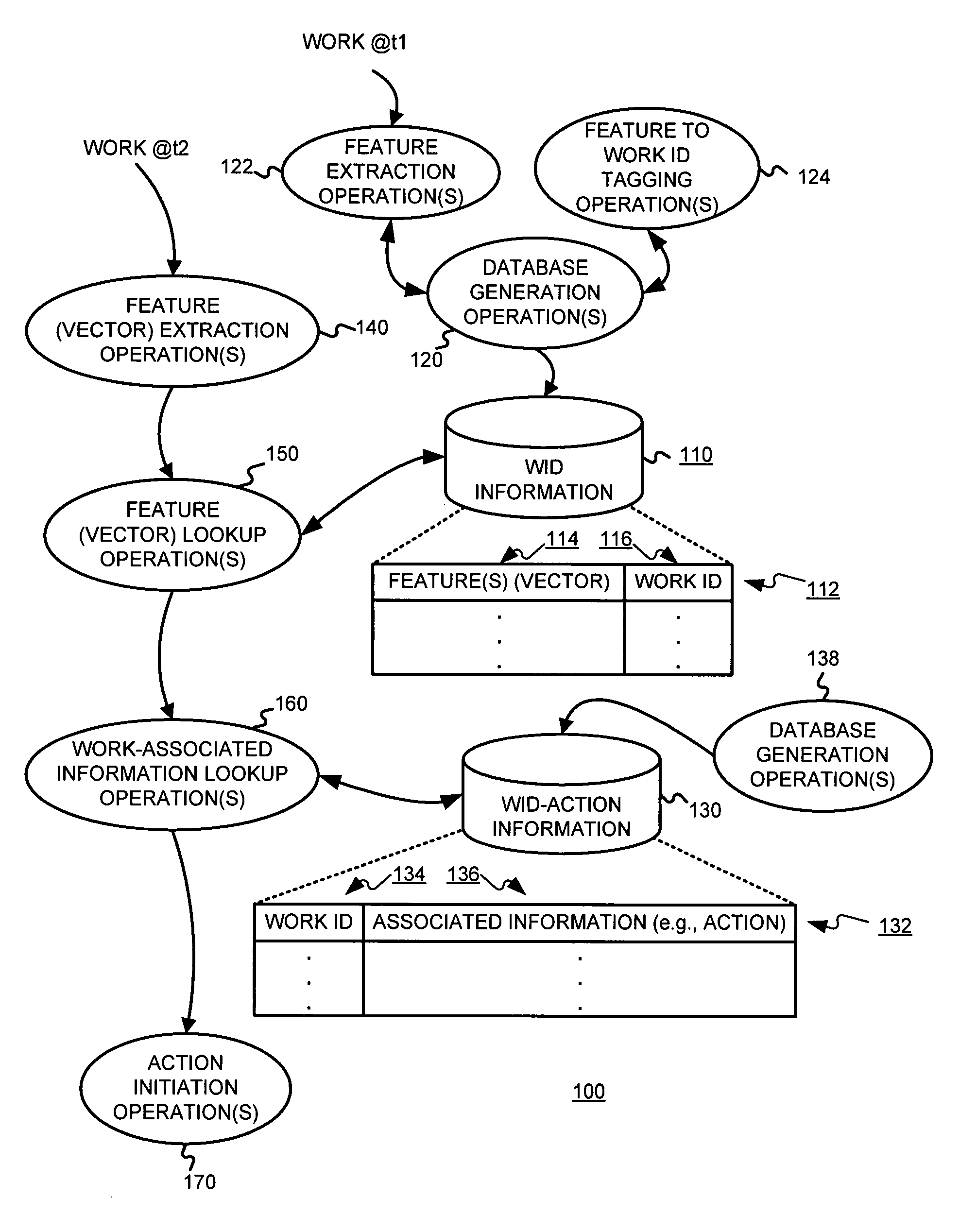
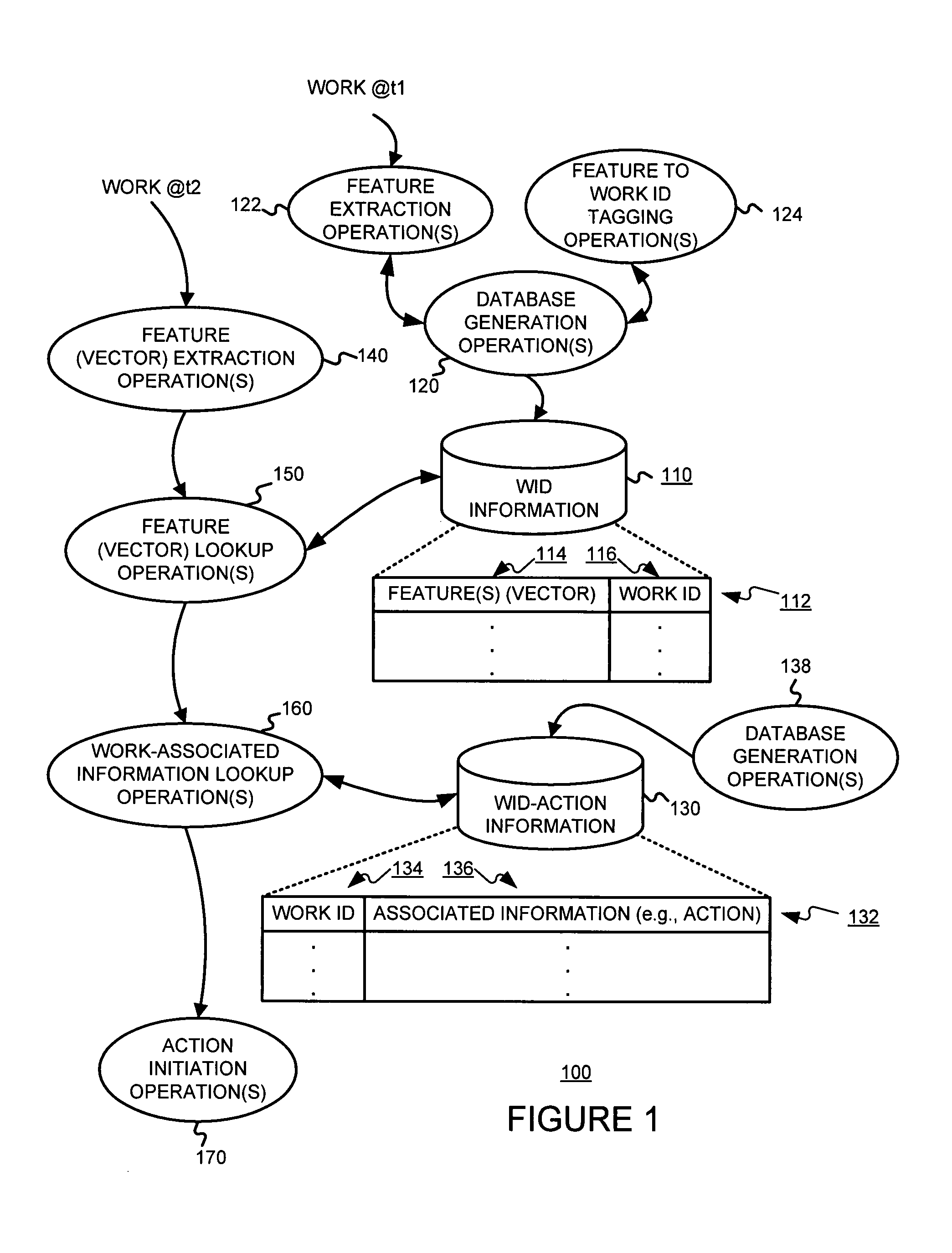
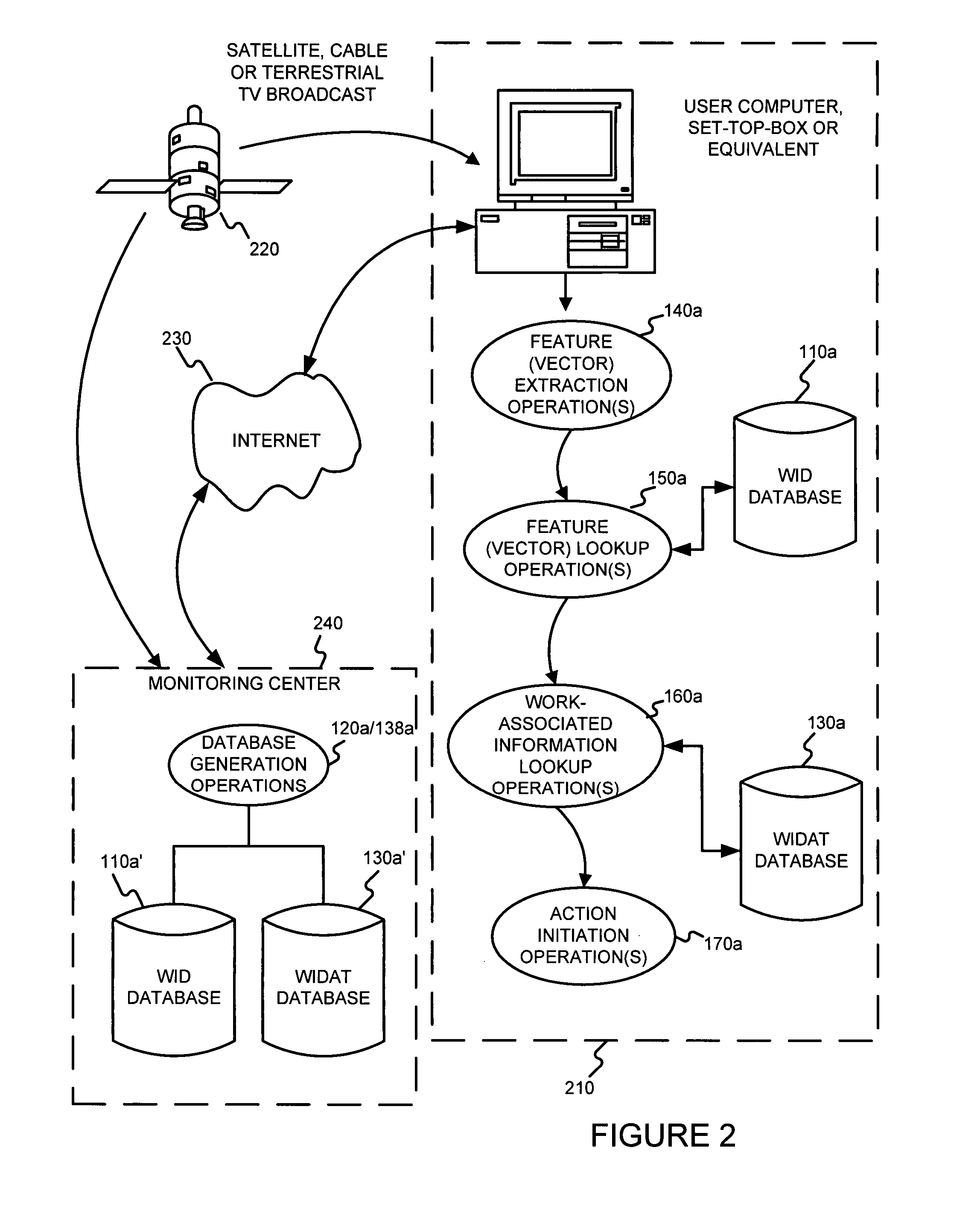
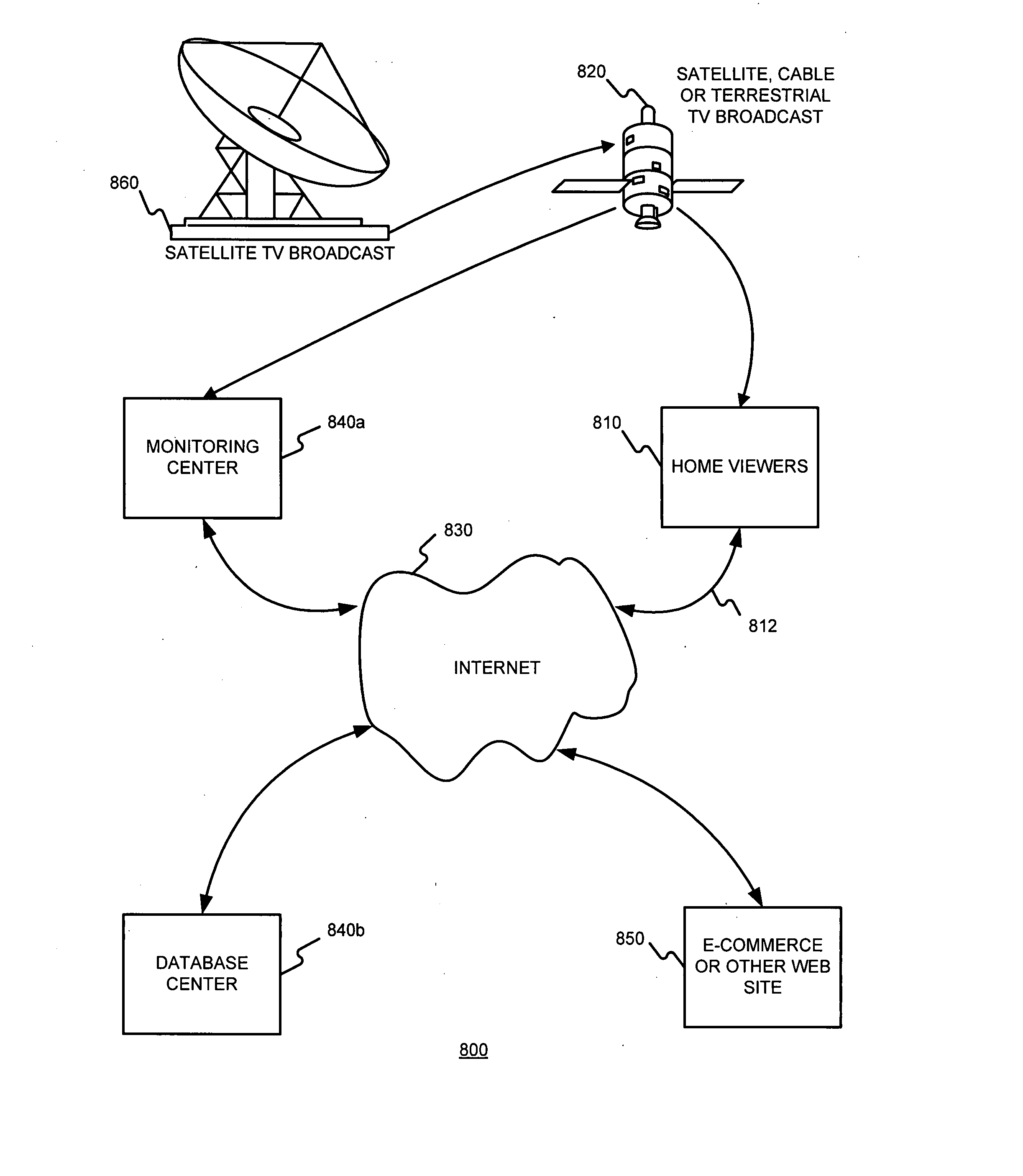
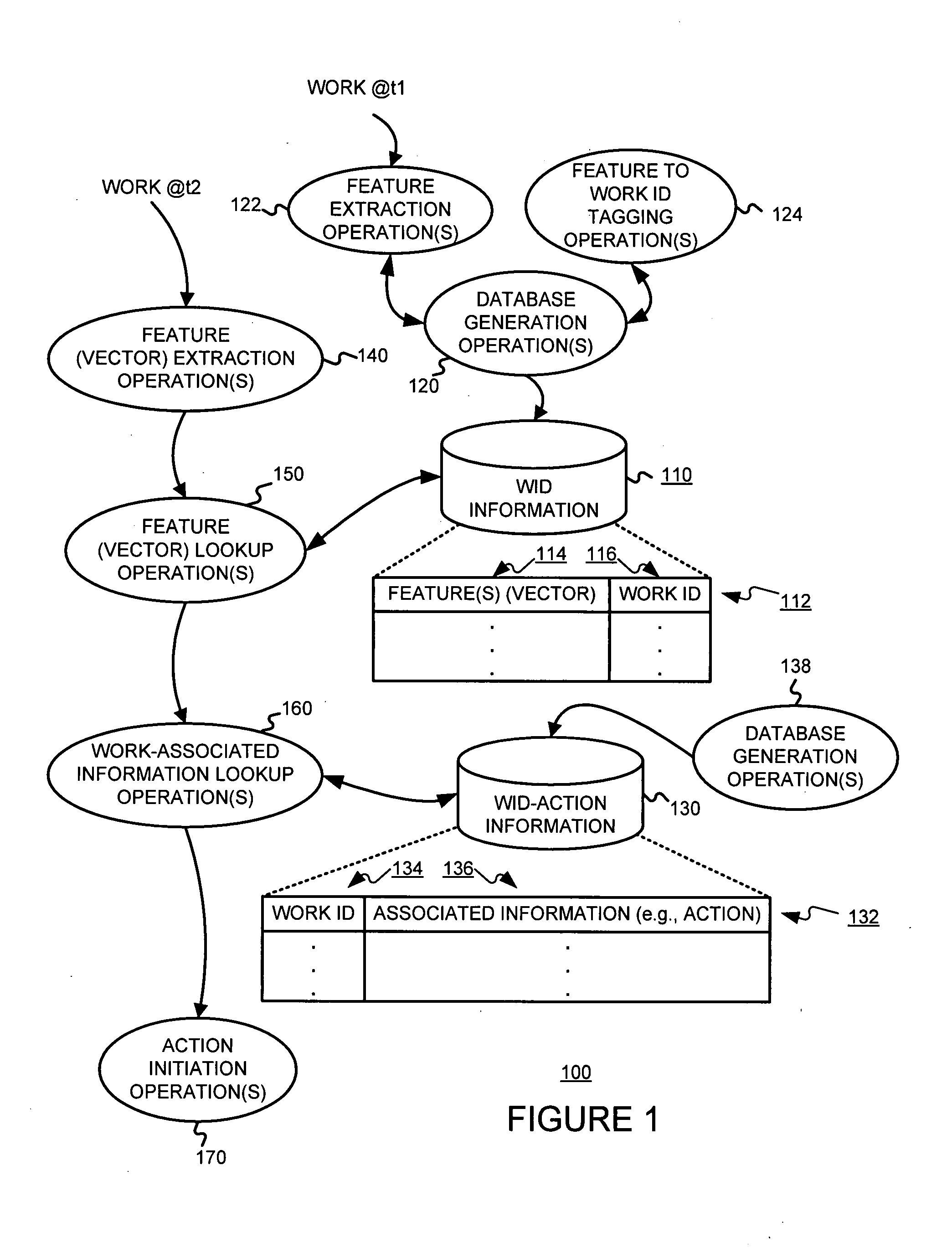
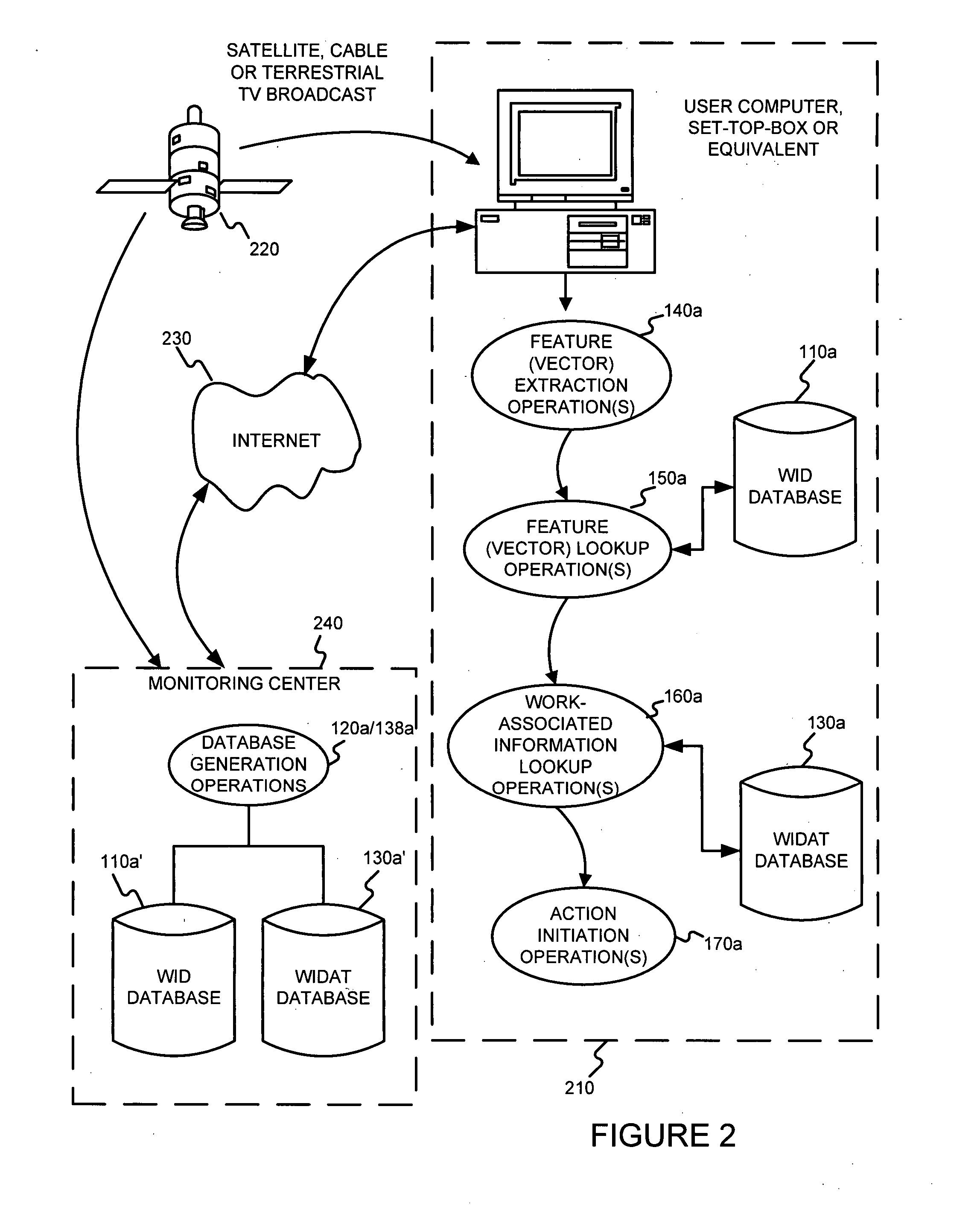
Identifying works, using a sub-linear time search, such as an approximate nearest neighbor search, for initiating a work-based action, such as an action on the internet
A media work may be associated with an action by (a) extracting features from the media work, (b) determining an identification of the media work, based on the features extracted, using a sub-linear time search, such as an approximate nearest neighbor search for example, and (c) determining an action based on the identification of the media work determined. The media work may be an audio work. The features extracted from the work may include (A) a frequency decomposition of a signal of the audio work, (B) information samples of the audio work, (C) average intensities of sampled windows of the audio work, and / or (D) information from frequencies of the audio work.
Owner:NETWORK 1 TECH
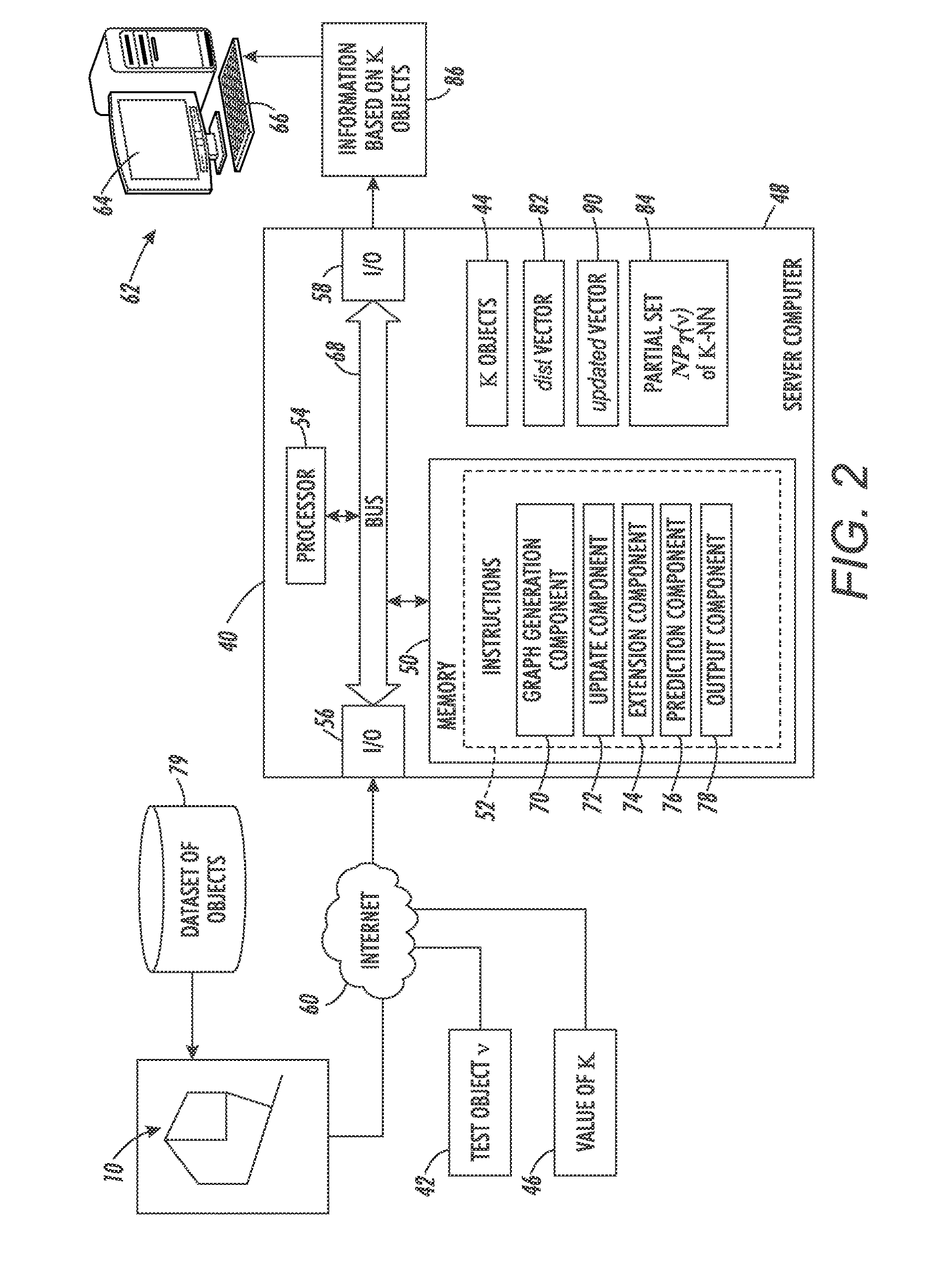
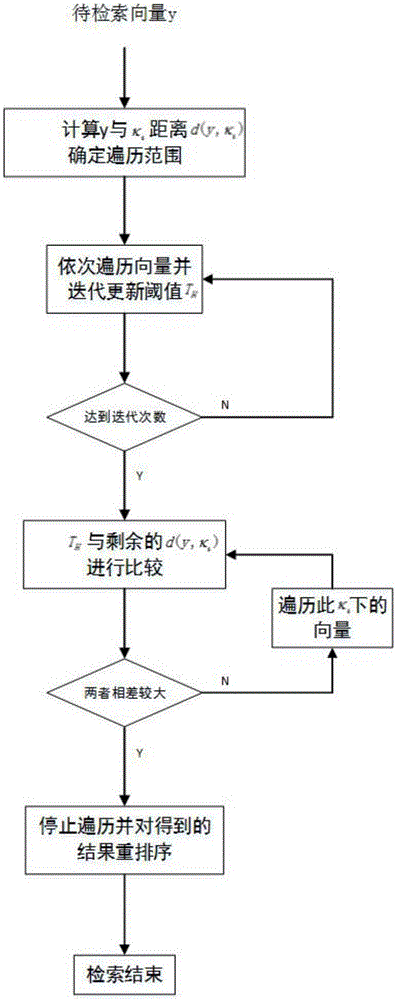
System and method for performing k-nearest neighbor search based on minimax distance measure and efficient outlier detection
A system and method enable a set of dataset objects that are K-nearest neighbors (K-NN), based on their Minimax distances to a test object, to be identified without computing the all-pair Minimax distances directly. A pairwise distance between the test object and each dataset object is computed. Iteratively, one of the dataset objects is selected to add to a K-NN set until the K-NN set includes a predefined number of nearest neighbors. The selected dataset object at each iteration is the one for which there is no other unselected dataset object which has a smaller pairwise distance to any of a current subset of objects than the selected dataset object. The current subset of objects includes the test object and the dataset objects currently in the K-NN set. After the K-NN set is identified it may be output or used to generate other information, such as a test object label.
Owner:CONDUENT BUSINESS SERVICES LLC
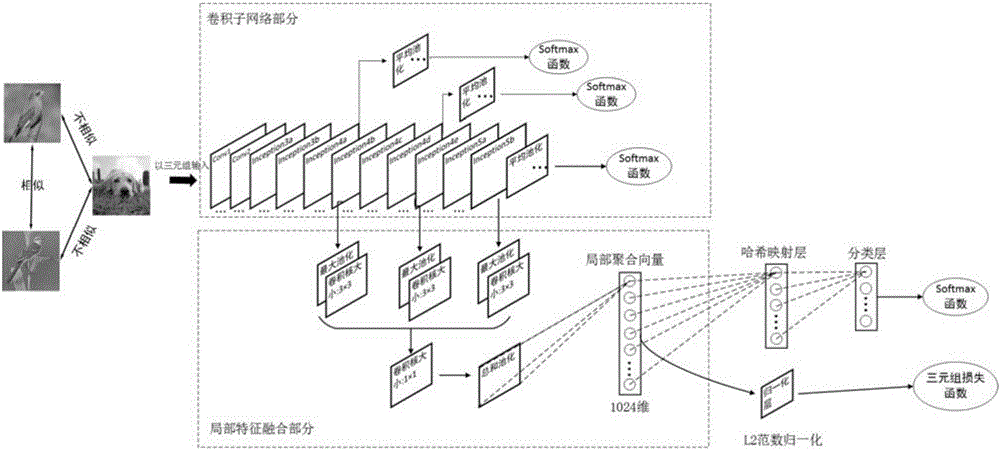
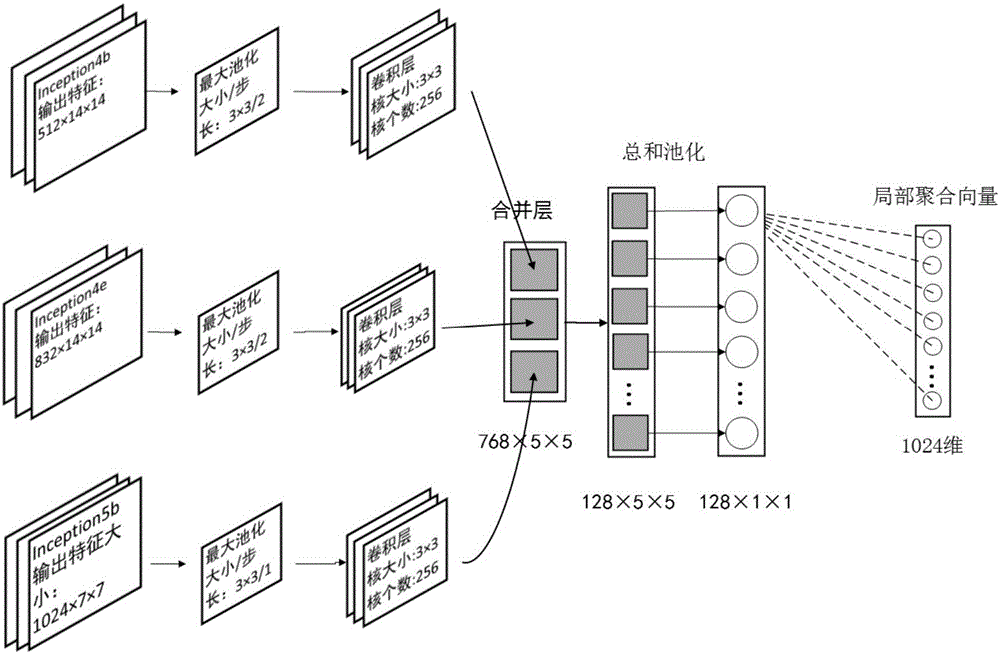
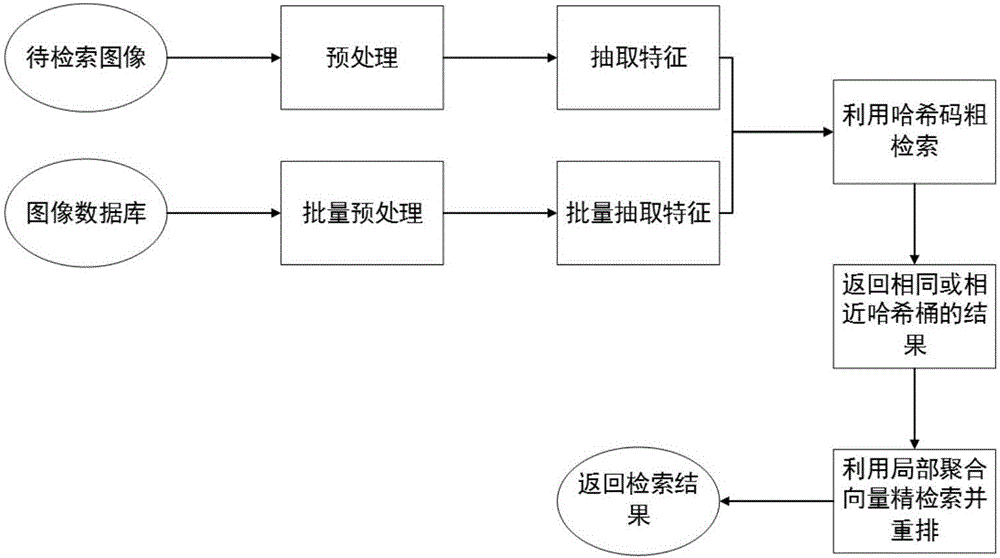
Method for Hash image retrieval based on deep learning and local feature fusion
ActiveCN106682233AFast and Efficient Image Retrieval TasksCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsFloating pointImage retrieval
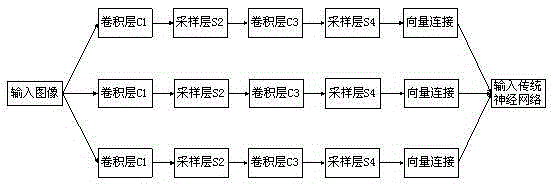
The invention relates to a method for Hash image retrieval based on deep learning and local feature fusion. The method comprises a step (1) of preprocessing an image; a step (2) of using a convolutional neural network to train images containing category tags; a step (3) of using a binarization mode to generate Hash codes of the images and extract 1024-dimensional floating-point type local polymerization vectors; a step (4) of using the Hash codes to perform rough retrieval; and a step (5) of using the local polymerization vectors to perform fine retrieval. According to the method for Hash image retrieval based on deep learning and local feature fusion, an approximate nearest neighbor search strategy is utilized to perform image retrieval after two features are extracted, the retrieval accuracy is high, and the retrieval speed is quick.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Identifying works, using a sub-linear time search, such as an approximate nearest neighbor search, for initiating a work-based action, such as an action on the internet
A media work may be associated with an action by (a) extracting features from the media work, (b) determining an identification of the media work, based on the features extracted, using a sub-linear time search, such as an approximate nearest neighbor search for example, and (c) determining an action based on the identification of the media work determined. The media work may be an audio work. The features extracted from the work may include (A) a frequency decomposition of a signal of the audio work, (B) information samples of the audio work, (C) average intensities of sampled windows of the audio work, and / or (D) information from frequencies of the audio work.
Owner:NETWORK 1 TECH
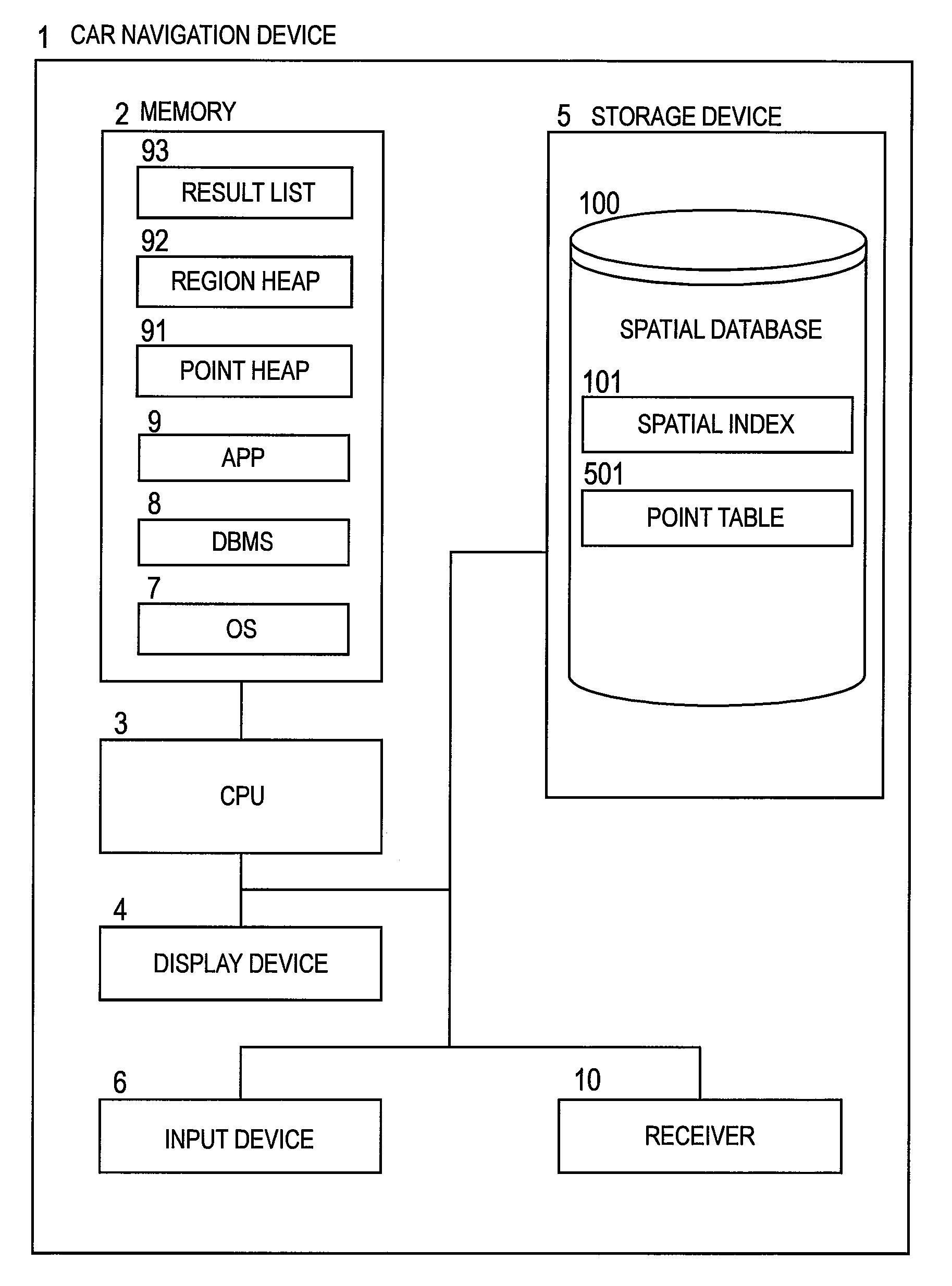
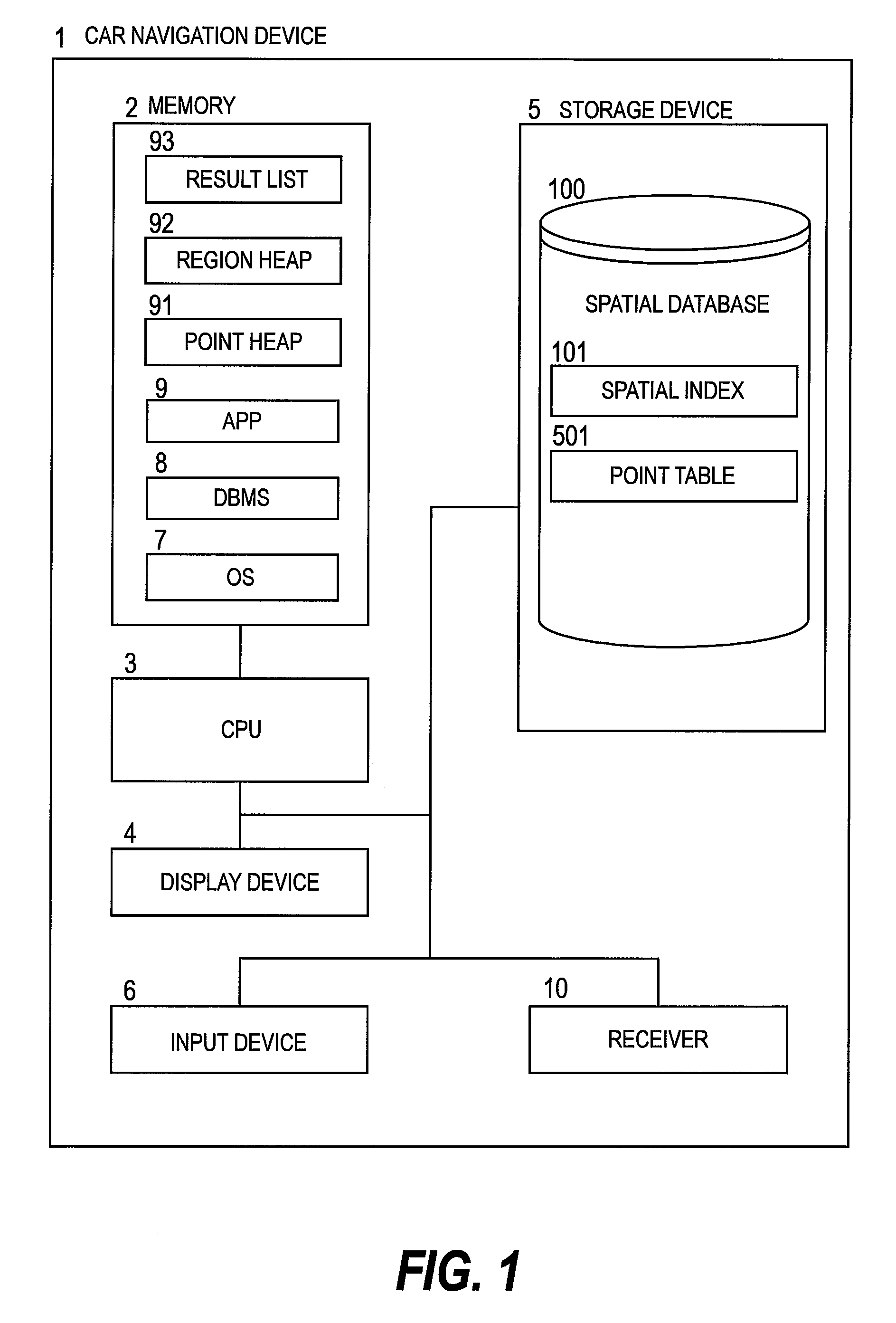
K-nearest neighbor search method, k-nearest neighbor search program, and k-nearest neighbor search device
ActiveUS20090210413A1Increase loadExtension of timeDigital data processing detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionNear neighborIntermediate region
Provided is a k-nearest neighbor search method of searching for a query number k of nearest points to an arbitrary point in a DBMS for creating a spatial index from multidimensional points, comprising setting a search conditions, judging which of a lowest branch and an intermediate branch of the spatial index a nearest region to the query point is, calculating, when the nearest region is judged to be the lowest branch, a distance between the query point and a child region of the nearest region, storing information of a divided region which has become a calculation target, calculating, when the nearest region is judged to be the intermediate region, a distance between the query point and a point included in the nearest region, storing information of the point which has become a calculation target, finishing search processing when the search conditions are satisfied, and obtaining a search result from the DBMS.
Owner:HITACHI SOFTWARE ENG +1
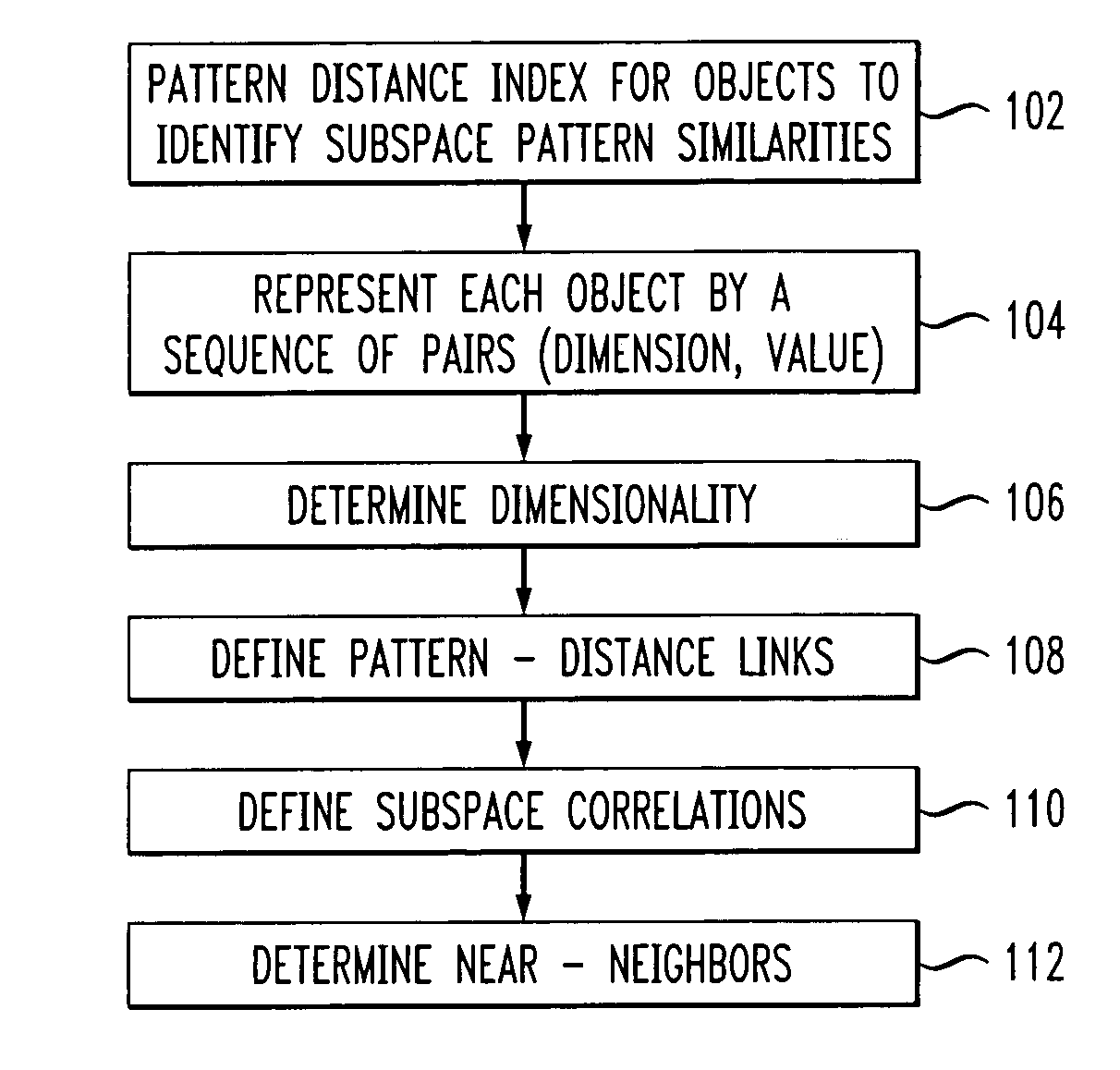
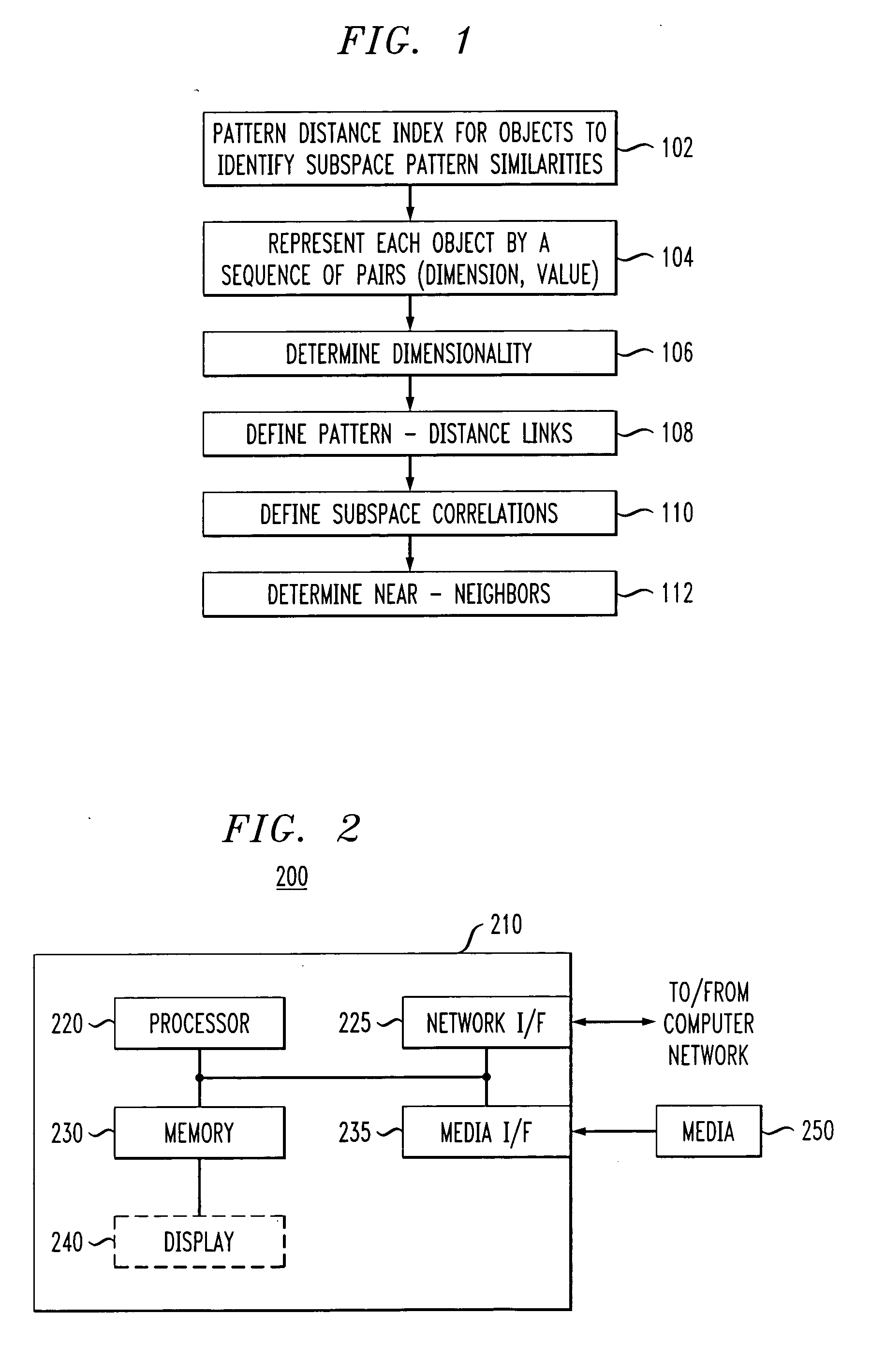
Near-neighbor search in pattern distance spaces
Owner:IBM CORP
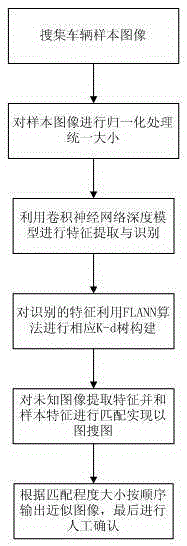
Method for fast retrieving high-similarity image of highway fee evasion vehicle
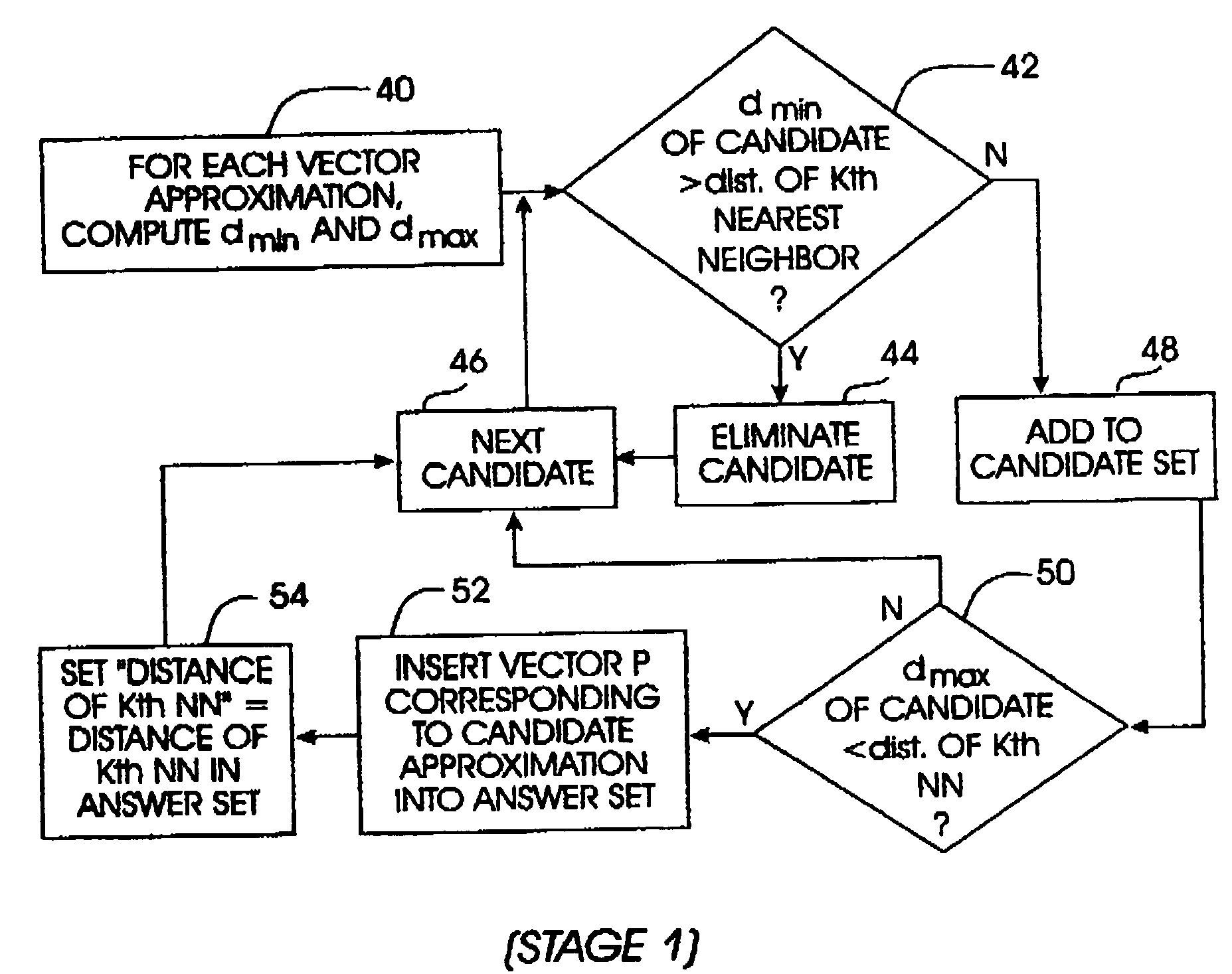
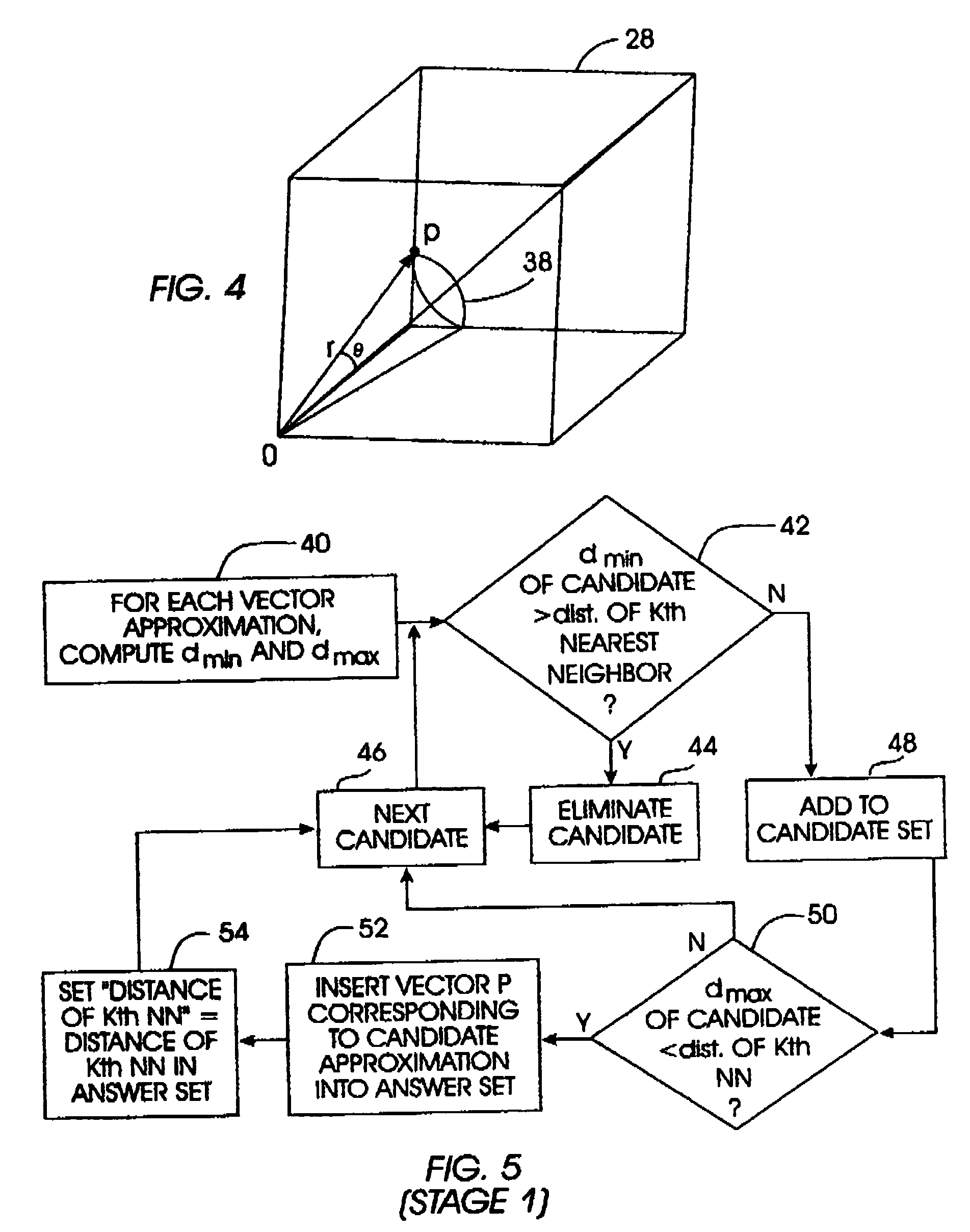
InactiveCN105354273AReduce complexityAvoid Feature ExtractionCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsImage extractionFeature extraction
The present invention discloses a method for fast retrieving a high-similarity image of a highway fee evasion vehicle. The method comprises: performing feature extraction and recognition on a collected sample image of an illegal vehicle by using a convolutional neural network model of a computer, constructing a corresponding K-d tree for the recognized feature, extracting a feature for a collected unknown image by using a fast high-similarity nearest neighbor search algorithm, and matching the feature of the unknown image with the feature of the sample image, to implement fast retrieval of a high-similarity image. According to the method provided by the present invention, better image feature expression can be obtained for retrieving a similar vehicle. Not only a retrieval result is high in similarity, but also retrieval is faster. Therefore, a function of image retrieval for cracking down on fee evasion, gaining evidence, cross-examination and a legal evidence chain can be sufficiently utilized, and behaviors of toll evasion can be fought and prohibited effectively.
Owner:浙江高信技术股份有限公司
CNN based quick image search method
ActiveCN105912611AImprove robustnessReduce data volumeCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsFeature extractionVisual perception
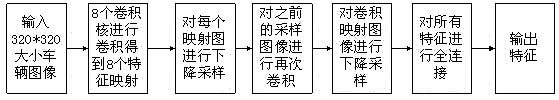
The invention discloses a CNN (Convolution Neural Network) based quick image search method. The method includes: a first step, extracting features of an image to be searched through a CNN so as to obtain a vector feature representing the image; and a second step, performing k neighbor search on the vector feature in a feature database. The method selects CNN features based on a GOOGLENET network, which is a breakthrough in the field of computer vision after deep learning rising; the method is good in robustness; after the CNN features are extracted, based on the PQ quick search idea and an inverted strategy of text search, the method considers the personal data size during application, reasonably arranges a system parameter, and improves reordering of search results; a quick ordering strategy is adopted, and then the detection time is shortened, and the detection efficiency is improved.
Owner:尚特杰电力科技有限公司
Statistical content block matching scheme for pre-processing in encoding and transcoding
ActiveUS20060188020A1Fast computationFast implementationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDistortionNearest neighbor search
Statistical content block matching for video pre-processing, for example in fast motion estimation, uses a second-order distortion criterion for processing steps such as identifying a best reference image portion for comparison with a current image portion. The second-order distortion criterion is a Lagrange-optimized combination of a mean squared error criterion with an entropy criterion. Then a fast motion estimation search advantageously includes performing a diamond search using the second-order distortion criterion to identify a candidate best reference image portion, and performing a nearest neighbor search starting using said second-order distortion criterion to identify the best reference image portion within a search range limited by an adaptive search range cap. A better motion vector can then be calculated.
Owner:MK SYST USA INC
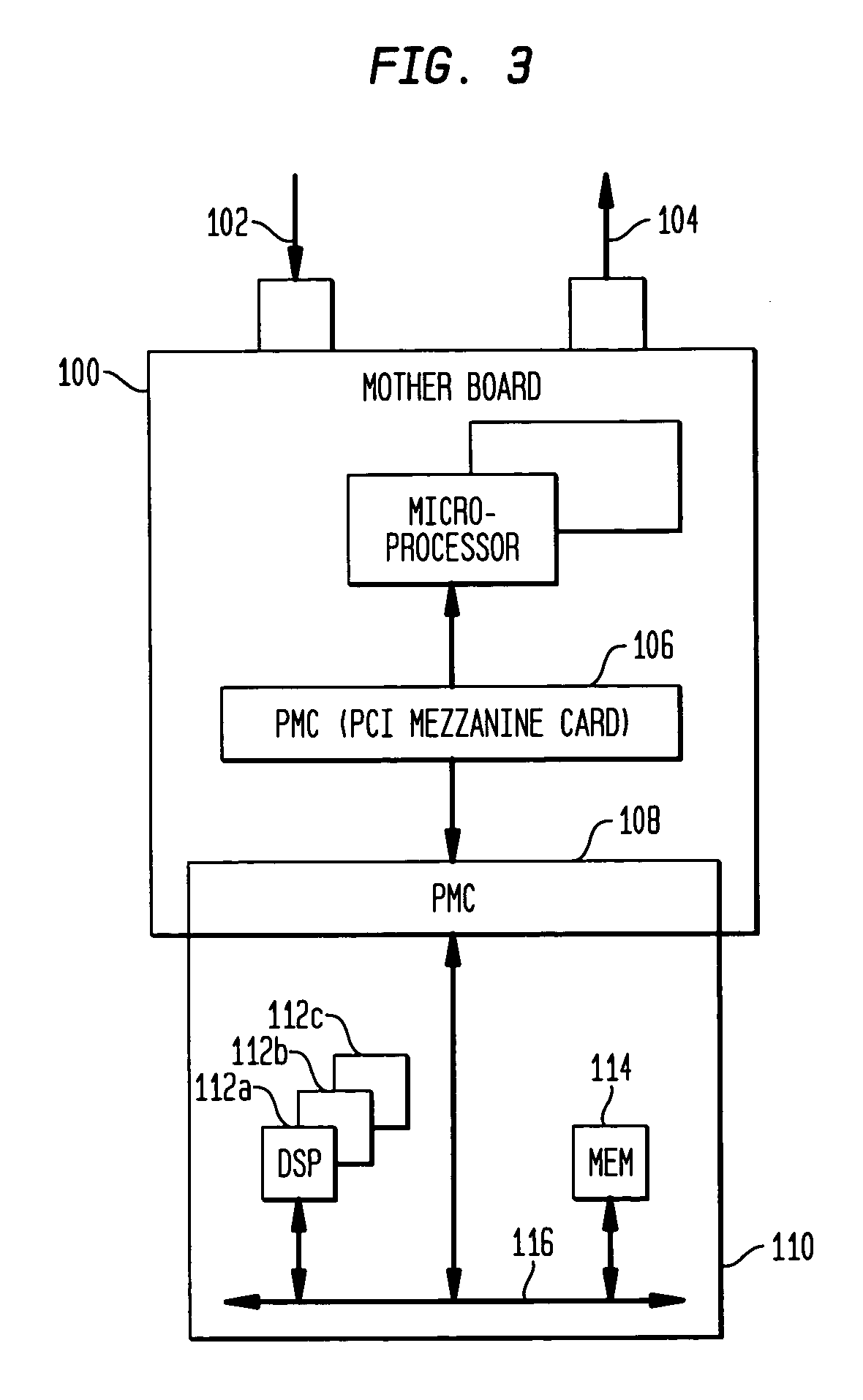
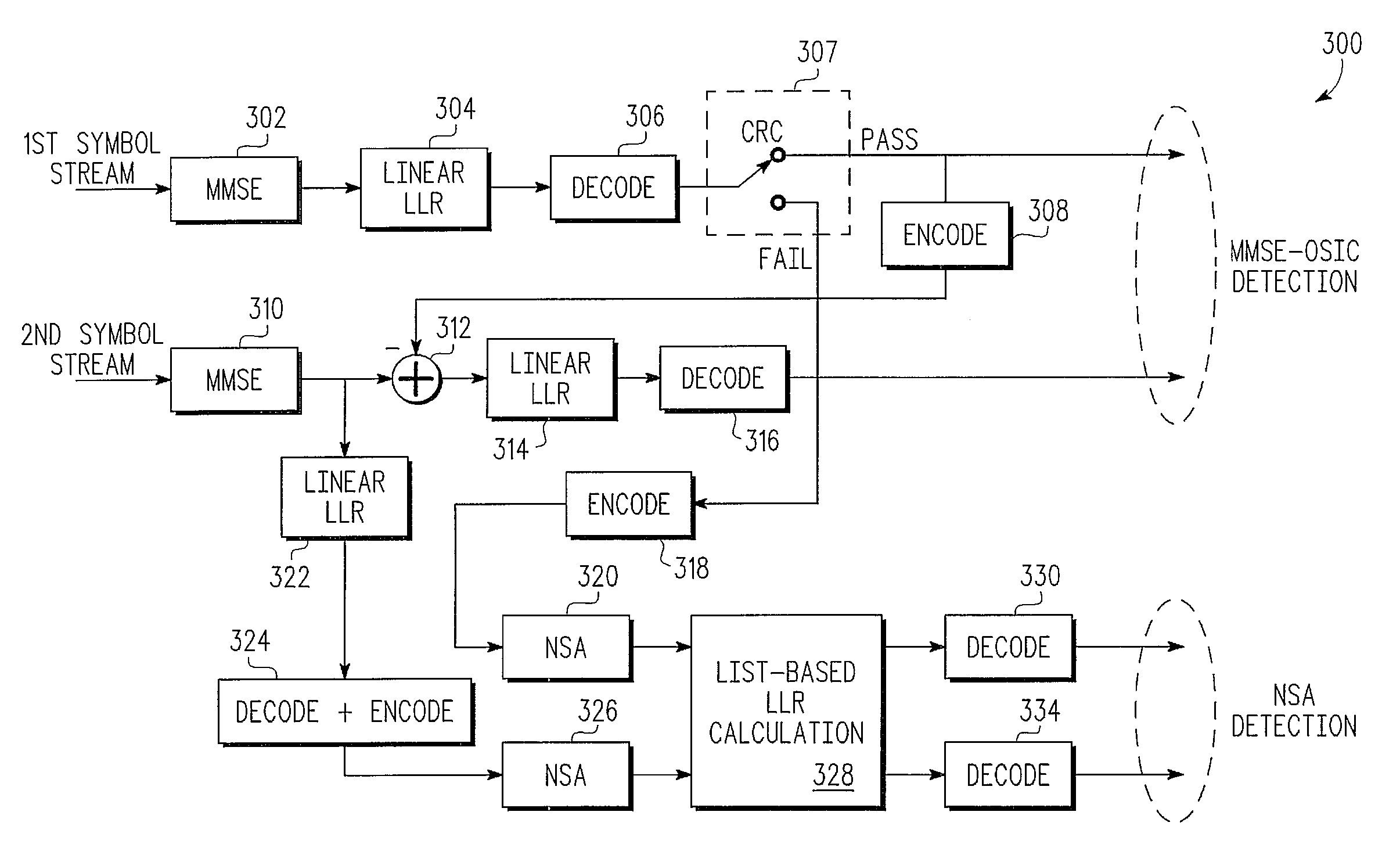
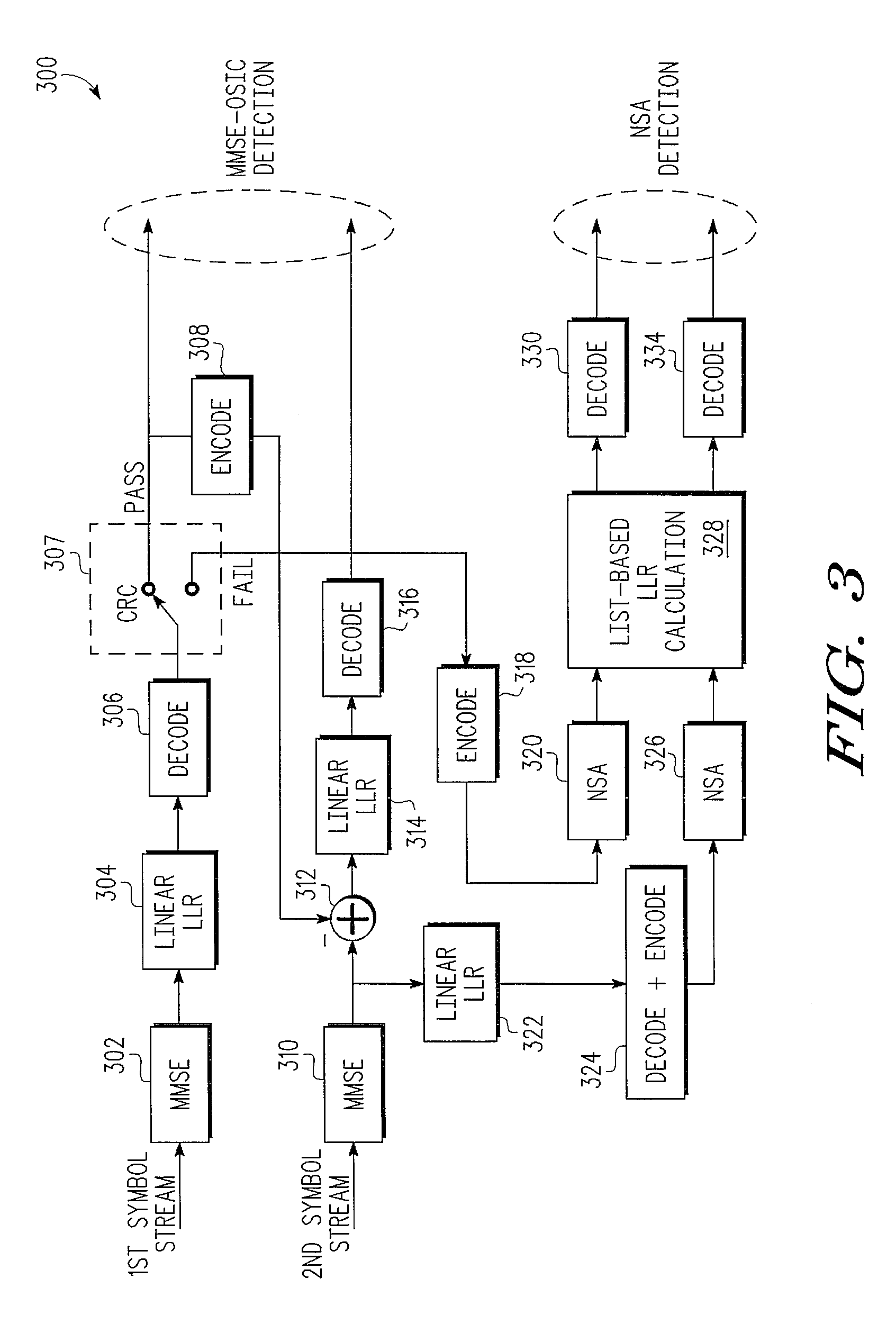
Techniques for Reducing Joint Detection Complexity in a Channel-Coded Multiple-Input Multiple-Output Communication System
ActiveUS20090327835A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsCommunications systemMultiple input
A technique for joint detection of channel-coded signals in a multiple-input multiple-output system includes detecting, when a decoded signal associated with a first symbol stream passes a cyclic redundancy check, channel-coded signals in the first symbol stream and a second symbol stream using minimum mean squared error with ordered successive interference cancellation (MMSE-OSIC) based detection. When the decoded signal associated with the first symbol stream fails the cyclic redundancy check, the channel-coded signals in the first and second symbol streams are detected using neighbor search algorithm (NSA) based detection.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Social association cloud media collaborative filtering and recommending method
ActiveCN104156436AAccurate recommendationAvoid the problem of over-reliance on similaritySpecial data processing applicationsFeature vectorMicroblogging
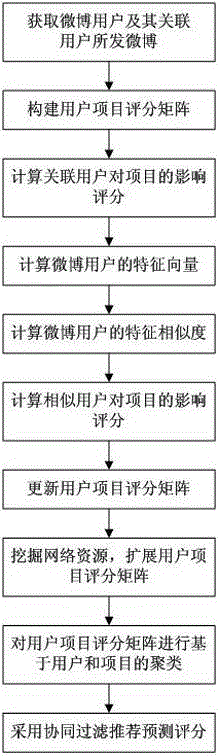
The invention relates to a social association cloud media collaborative filtering and recommending method. The method includes the following steps that micro blogs sent by multiple micro blog users and associated users of the micro blog users are obtained; a user program rating matrix for reflecting the corresponding relation between different users and grading of different programs is built; influence grading of the associated users on the programs is calculated; the feature vector of the micro log users is calculated; feature similarity of the micro log users is calculated; the influence grading of similar users similar to the micro log users on the programs is calculated; the user program grading matrix is updated according to the influence grading of the associated users on the programs and the influence grading of the similar users on the programs; network resources are explored, and the updated user program grading matrix is expanded; cluster is conducted on the user program grading matrix based on the users and the programs respectively; class cluster obtained through the cluster serves as a neighbor search domain, and grading is predicted through collaborative filtering and recommending. By means of the method, network information content which interests the users can be accurately recommended for the users.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
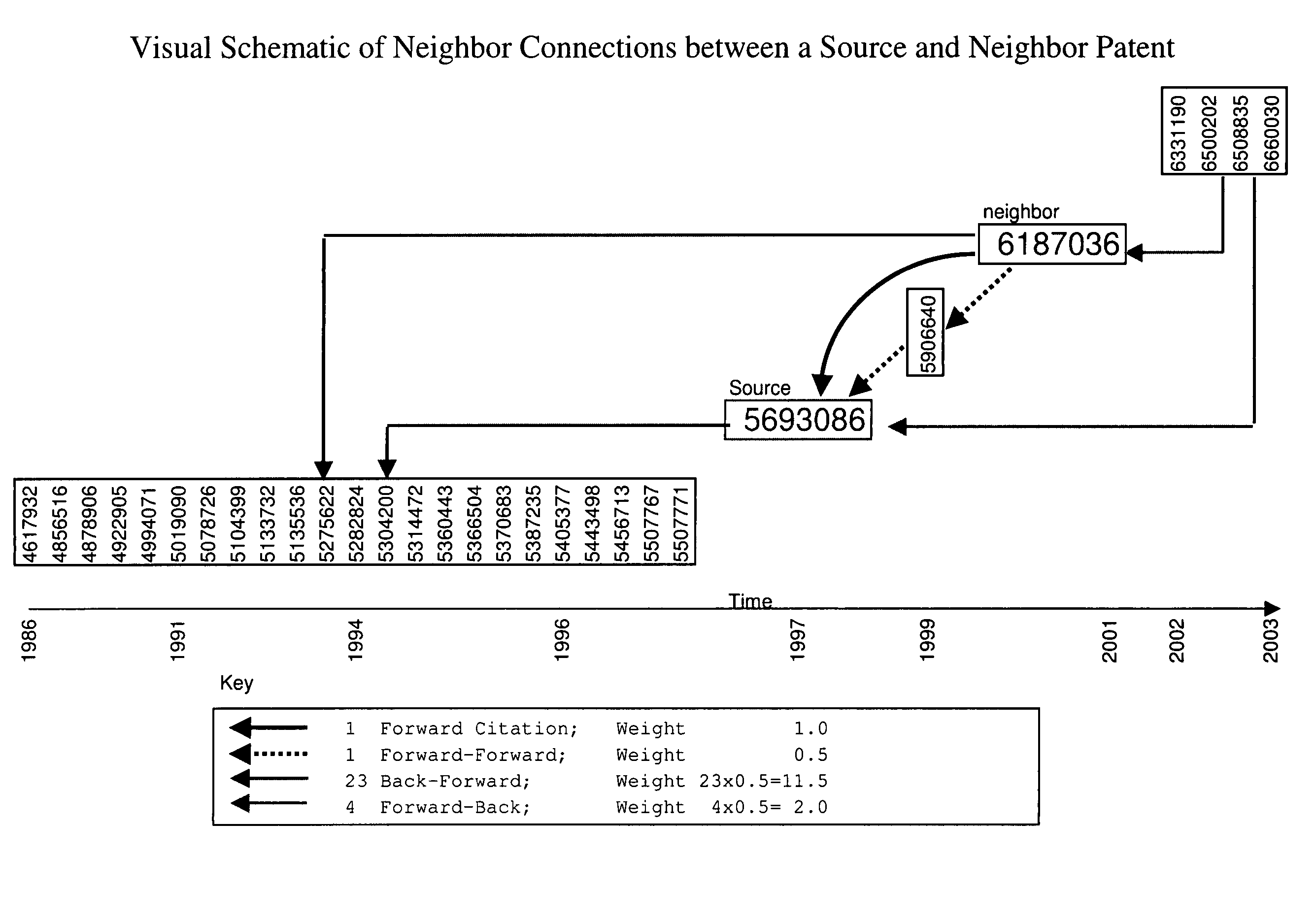
Identification of licensing targets using citation neighbor search process
A portable database can be used by a client organization with substantial numbers of patents to identify target organizations that may be interested in licensing said patents. The database combines the power of citation analysis for identifying licensing targets with the power of citation neighbor searching for identifying similar patents and for overcoming some of the weaknesses inherent with citation analysis. A company can identify targets outside of its core industry that may be interested in licensing the technology in its patents.
Owner:CHI RES +1
K nearest neighbor search method for variable weight network
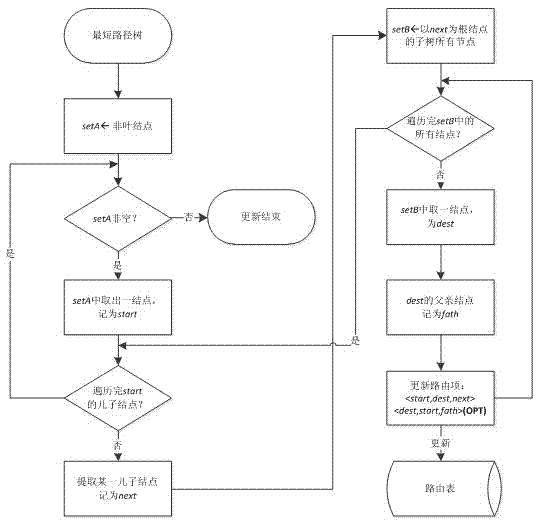
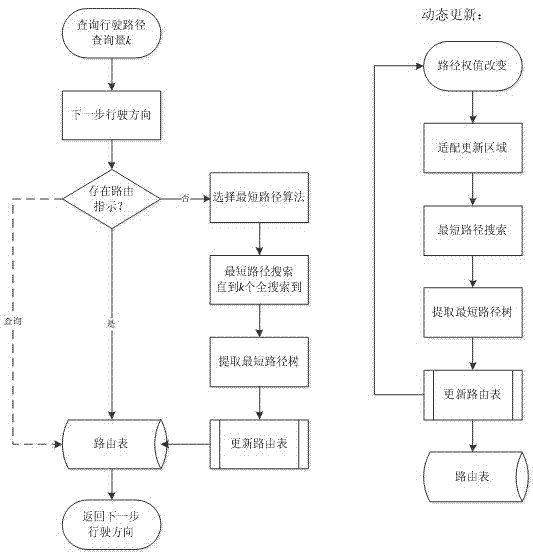
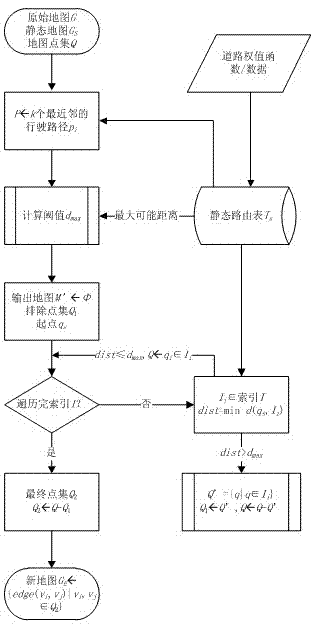
InactiveCN102810118AReduce in quantityNarrow searchSpecial data processing applicationsPathPingRouting table
The invention relates to a k nearest neighbor search method for a variable weight network. The method comprises the steps as follows: routing thinking in a computer network is led in k nearest neighbor query, and predecessor / subsequent information in shortest path tree obtained in computation is taken as history data and is saved in a routing table by designing an update strategy of the routing table. Due to the dynamical update strategy of the routing table, the routing mechanism can adapt to dynamic changes of local road weights in a road net. The k nearest neighbor search method provides the candidate set screening rule and the road net area cutting rule of a non-mobile object as well as the position prediction method and the candidate set screening rule of a mobile object in the dynamical road net, effectively reduces the number of candidate points and narrows down the search range of the k nearest neighbor query, and avoids the defect that indexing and constraint conditions are adjusted frequently because the changes of a k nearest neighbors algorithm are caused by the road weights continuously in the conventional dynamical road net extended from a static road net.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
A K-Nearest Neighbor Query Method Based on Area Coverage
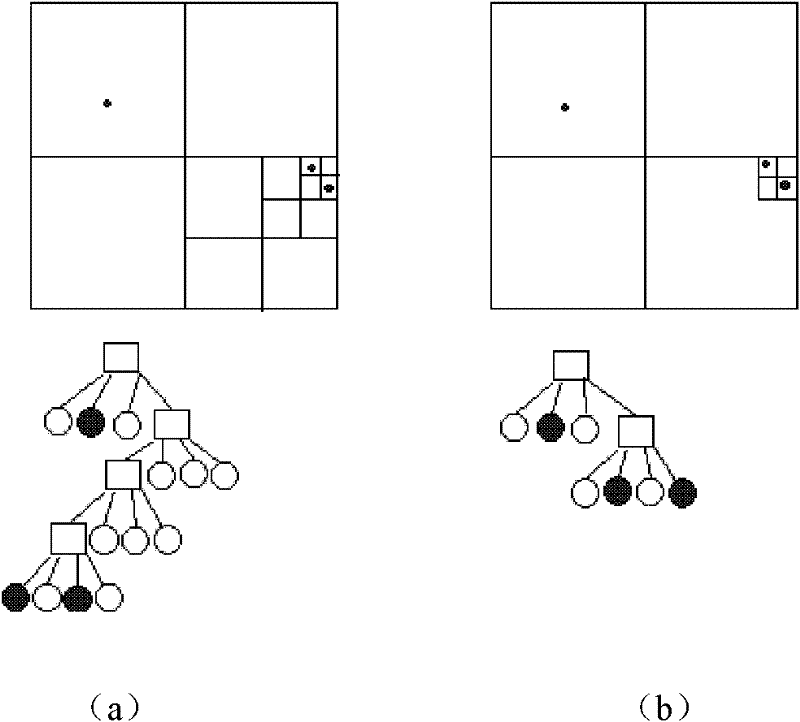
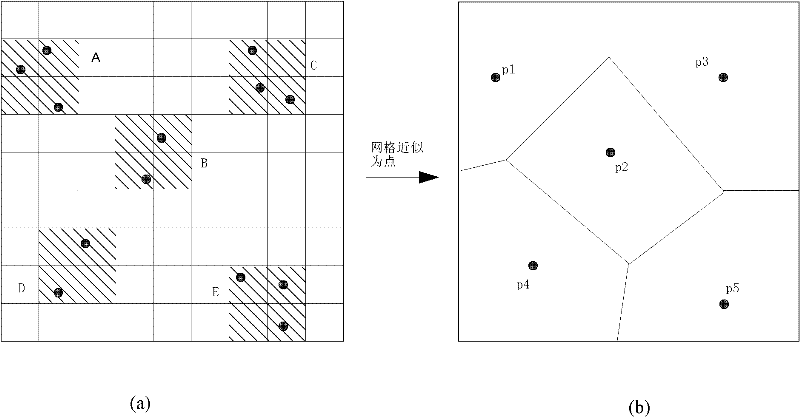
ActiveCN102289466ANeighbors are clearIncrease profitSpecial data processing applicationsNearest neighbor searchData point
The invention provides a k-nearest neighbor searching method based on regional coverage, belonging to the technical field of mobile data indexes. The k-nearest neighbor searching method comprises the steps of: gridding a space, storing data points in corresponding grids, storing grids which are taken as the leaf nodes of a quadtree, meanwhile, storing the grids, which are taken as mobile objects, into a Voronoi image; and during searching, firstly finding out a grid in which an object is located according to coordinates of the object, further finding out the position of the grid in the Voronoi image, structuring the object in the grid according to an ascending order of distances to form a result linked list, meanwhile, putting adjacent grids into an access linked list based on the ascending order of the distances according to the Voronoi image, comparing the distances, and finally finding out K nearest neighbors of the object. In the k-nearest neighbor searching method, an index structure with the Voronoi image and a virtual grid quadtree is comprehensively utilized, and a Hash table is utilized for rapid searching and positioning, so that the searching efficiency is increased.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
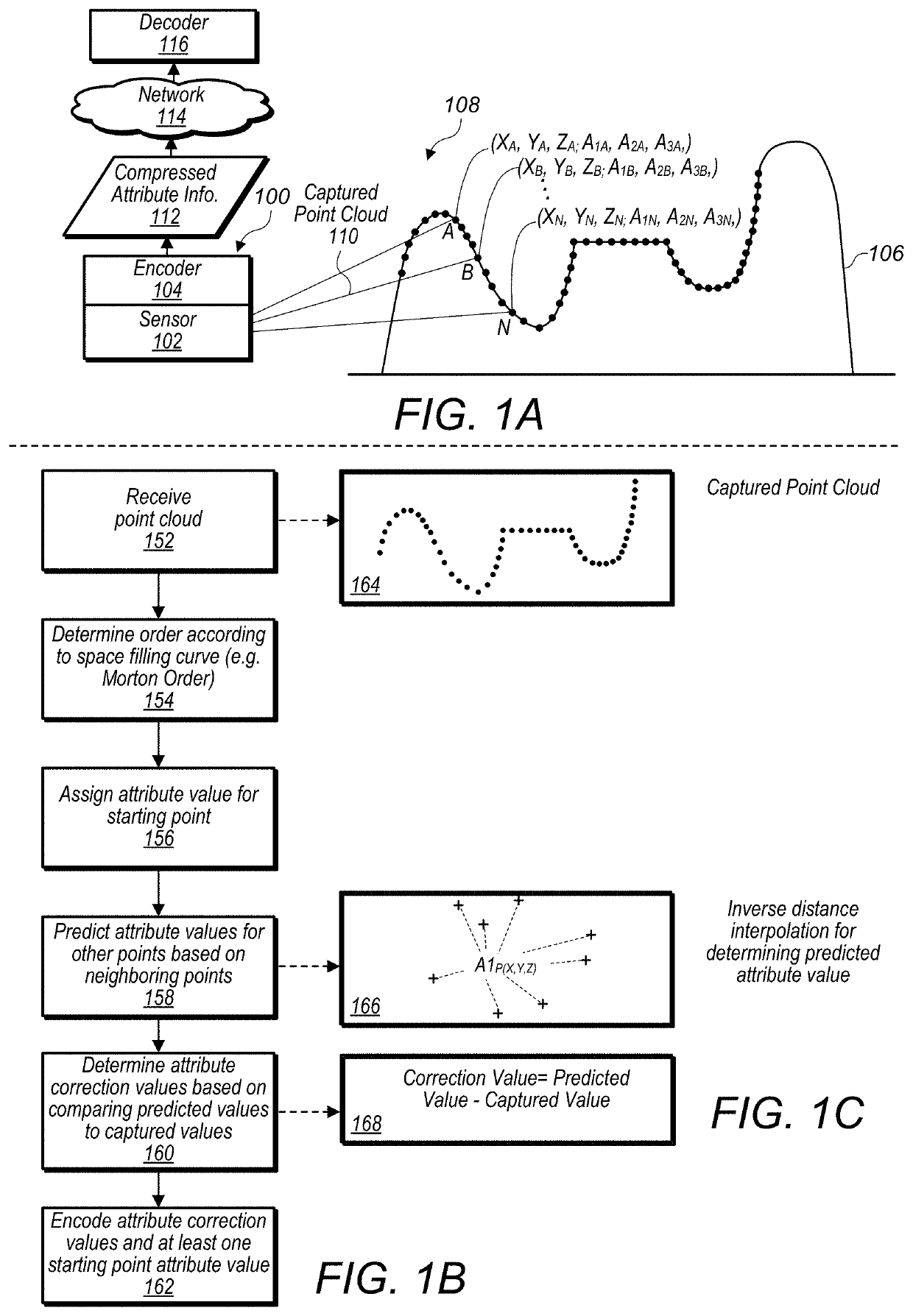
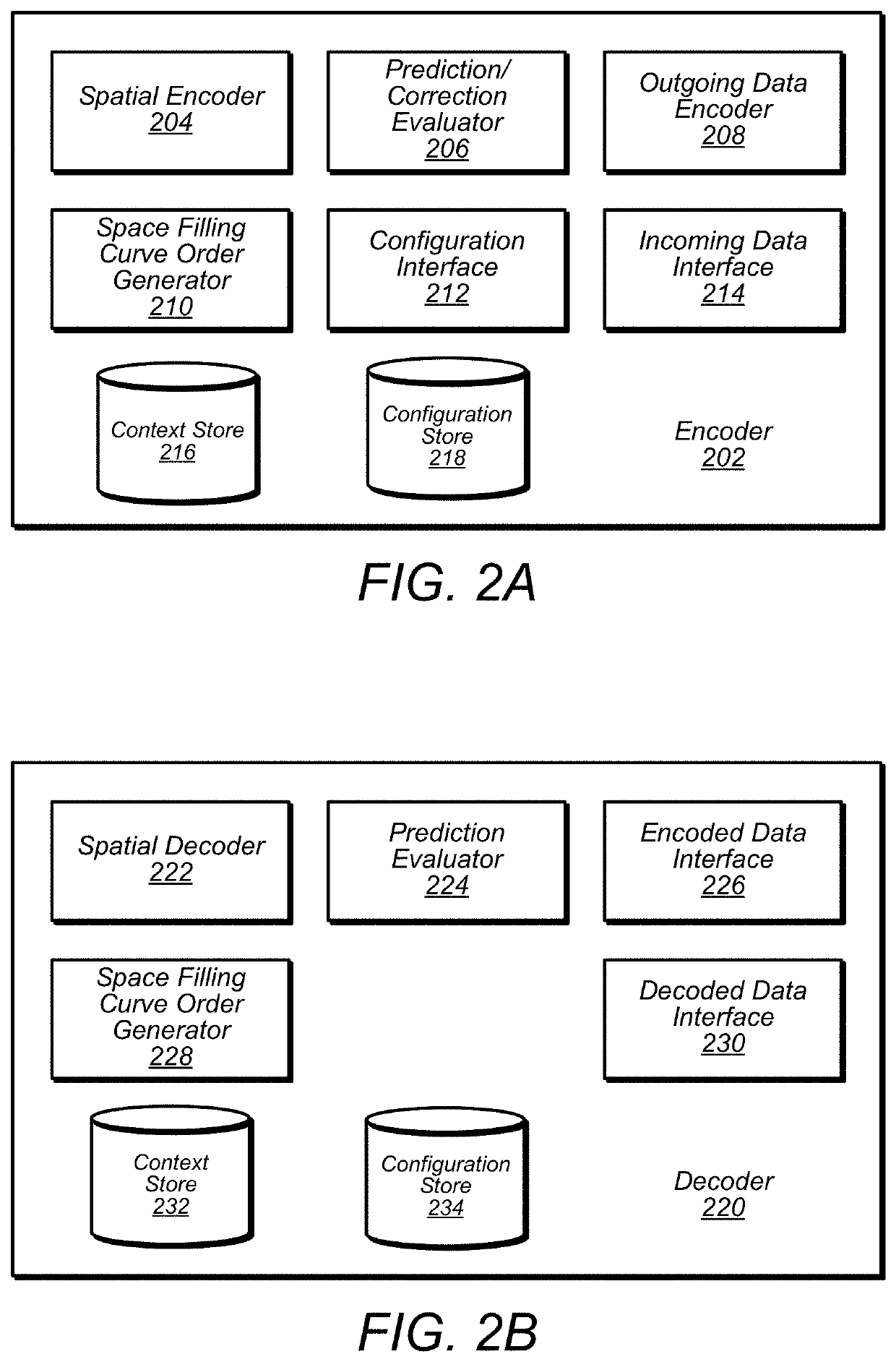
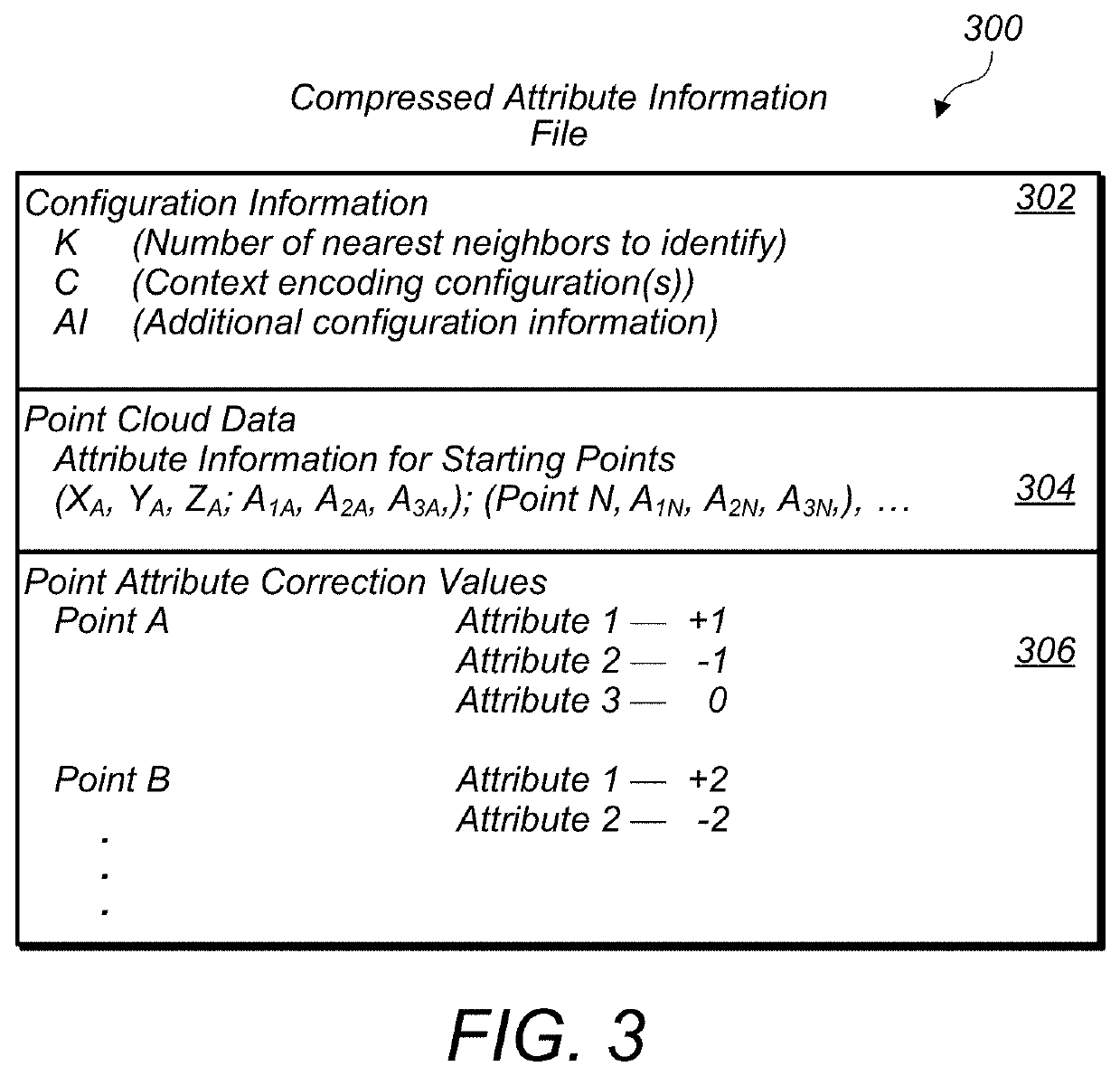
Trimming Search Space For Nearest Neighbor Determinations in Point Cloud Compression
A search space for performing nearest neighbor searches for encoding point cloud data may be trimmed. Ranges of a space filling curve may be used to identify search space to exclude or reuse, instead of generating nearest neighbor search results for at least some of the points of a point cloud located within some of the ranges of the space filling curve. Additionally, neighboring voxels may be searched to identify any neighboring points missed during the trimmed search based on the ranges of the space filling curve.
Owner:APPLE INC
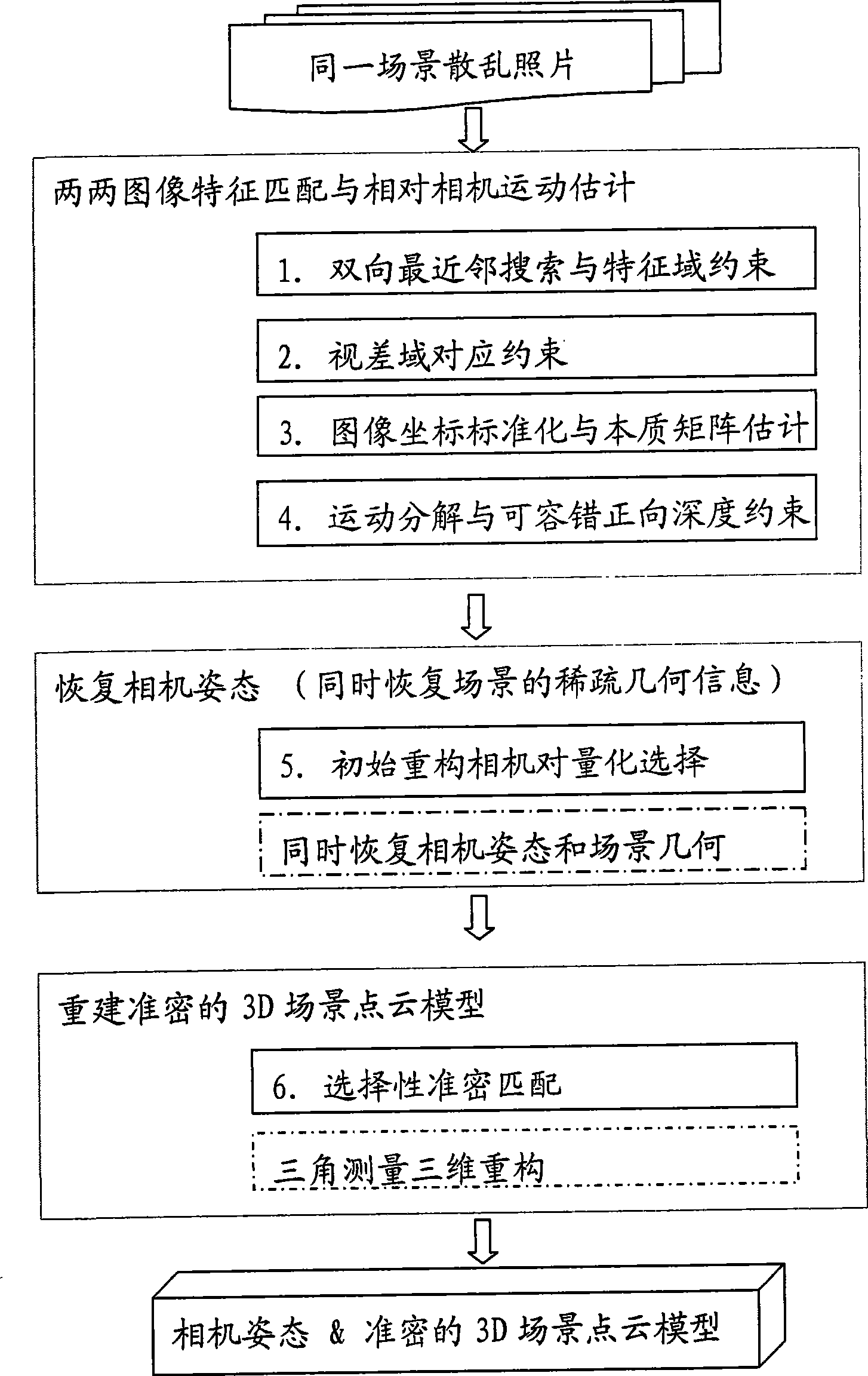
Three-dimensional reconstruction method based on fringe photograph collection of same scene
InactiveCN101398937AImprove stabilityImprove accuracy2D-image generationNearest neighbor searchEssential matrix
A 3D reconstruction method based on scattered photo sets of the same scene is divided into three stages: the first stage: every pairwsie image feature matching and relative camera motion are estimated; and the stage is divided into 4 steps: (1) every two images are subject to the bidirectional nearest neighbor search and feature domain constraint to obtain a candidate correspondence; (2) the candidate correspondence is subject to parallax domain correspondence constraint to obtain a hypothesis correspondence; (3) the image coordinates of the hypothesis correspondence are standardized to solve an essential matrix estimation meeting the hypothesis correspondence; (4) the essential matrix is decomposed to obtain four groups of possible solutions of the camera motion, and the final solution is determined by the fault-tolerant forward depth constraint; the second stage: the optimized initial reconstruction camera pair is selected according to the results of the first stage, the standard sparse reconstruction method is applied, and the camera pose and the sparse geometric information of the scene are restored; the third stage: selective accurate and dense matching is carried out based on the results of second stage, and an accurate and dense 3D scene point cloud model is reconstructed by the triangulation method. The method has the advantages of obtaining reliable camera pose and high-density scene geometric information, greatly shortening the reconstruction time, having relatively high reconstruction efficiency, and is applicable to processing the scattered photo set with large data size.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Indexing system and method for nearest neighbor searches in high dimensional data spaces
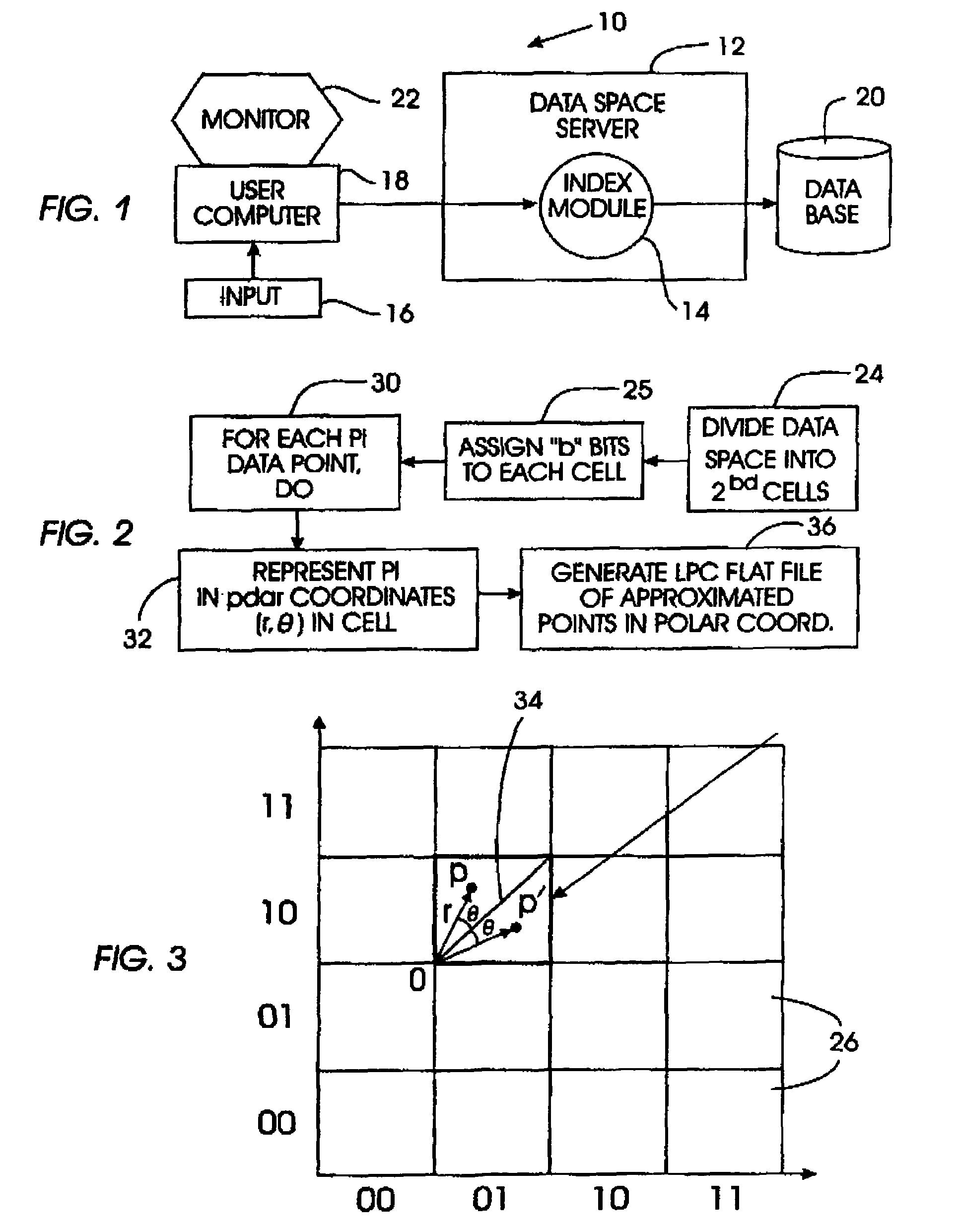
Vectors representing objects in n-dimensional space are approximated by local polar coordinates on partitioned cells of the data space in response to a query, e.g., a query data vector entered with a request to find “k” nearest neighbors to the query vector. A set of candidate near neighbors is generated using the approximations, with the local polar coordinates being independent of the dimensionality of the data space. Then, an answer set of near neighbors is returned in response to the query. Thus, the present invention acts as a filter to reduce the number of actual data vectors in the data set that must be considered in responding to the query.
Owner:IBM CORP
Efficient approximate-nearest-neighbor (ANN) search for high-quality collaborative filtering
ActiveUS20150206285A1Need can be replacedEasy to adaptImage enhancementImage analysisNear neighborCollaborative filtering
A computer implemented method of performing an approximate-nearest-neighbor search is disclosed. The method comprises dividing an image into a plurality of tiles. Further, for each of the plurality of tiles, perform the following in parallel on a processor: (a) dividing image patches into a plurality of clusters, wherein each cluster comprises similar images patches, and wherein the dividing continues recursively until a size of a cluster is below a threshold value; (b) performing a nearest-neighbor query within each of the plurality of clusters; and (c) performing collaborative filtering in parallel for each image patch, wherein the collaborative filtering aggregates and processes nearest neighbor image patches from a same cluster containing a respective image patch to form an output image.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
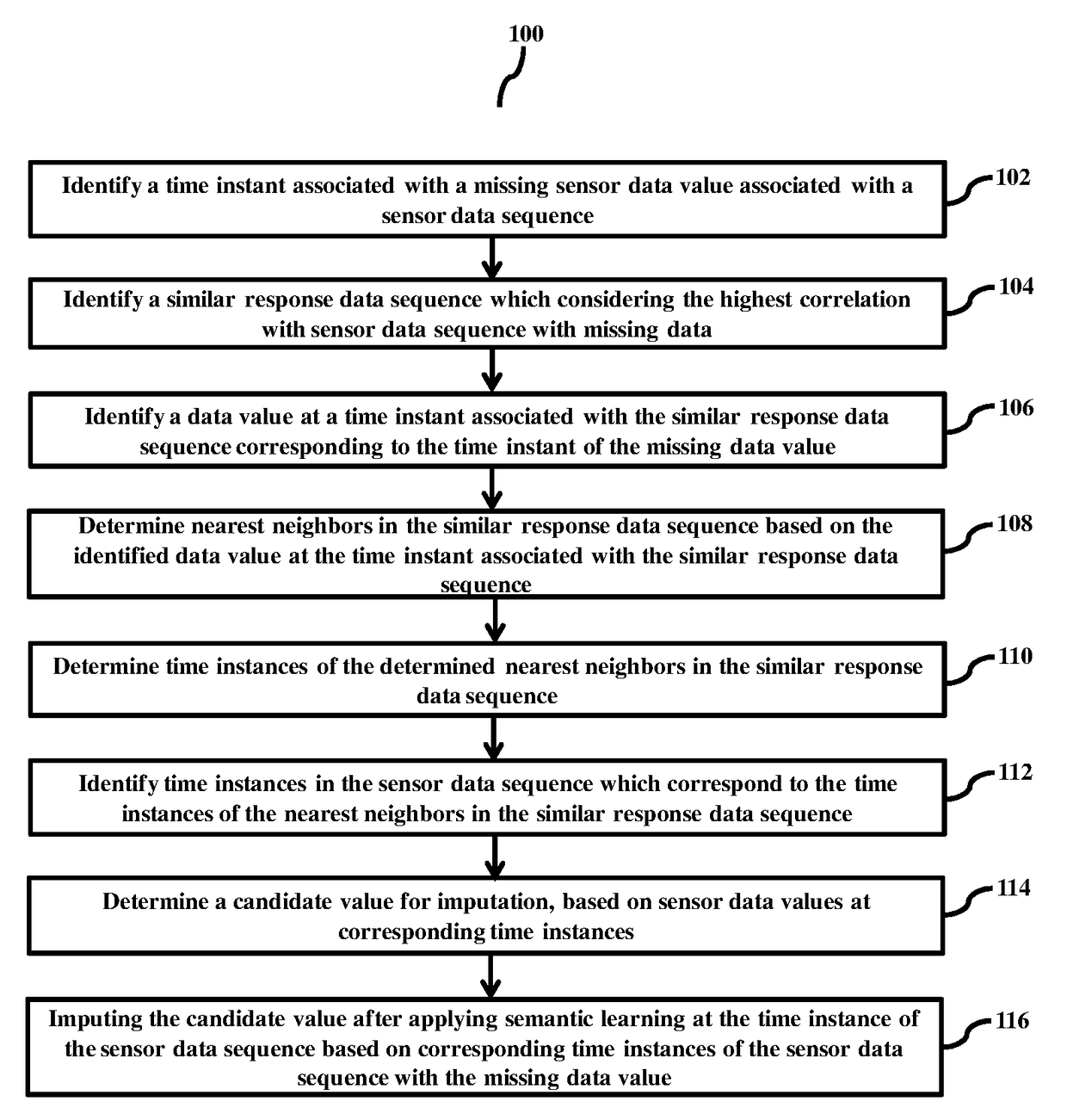
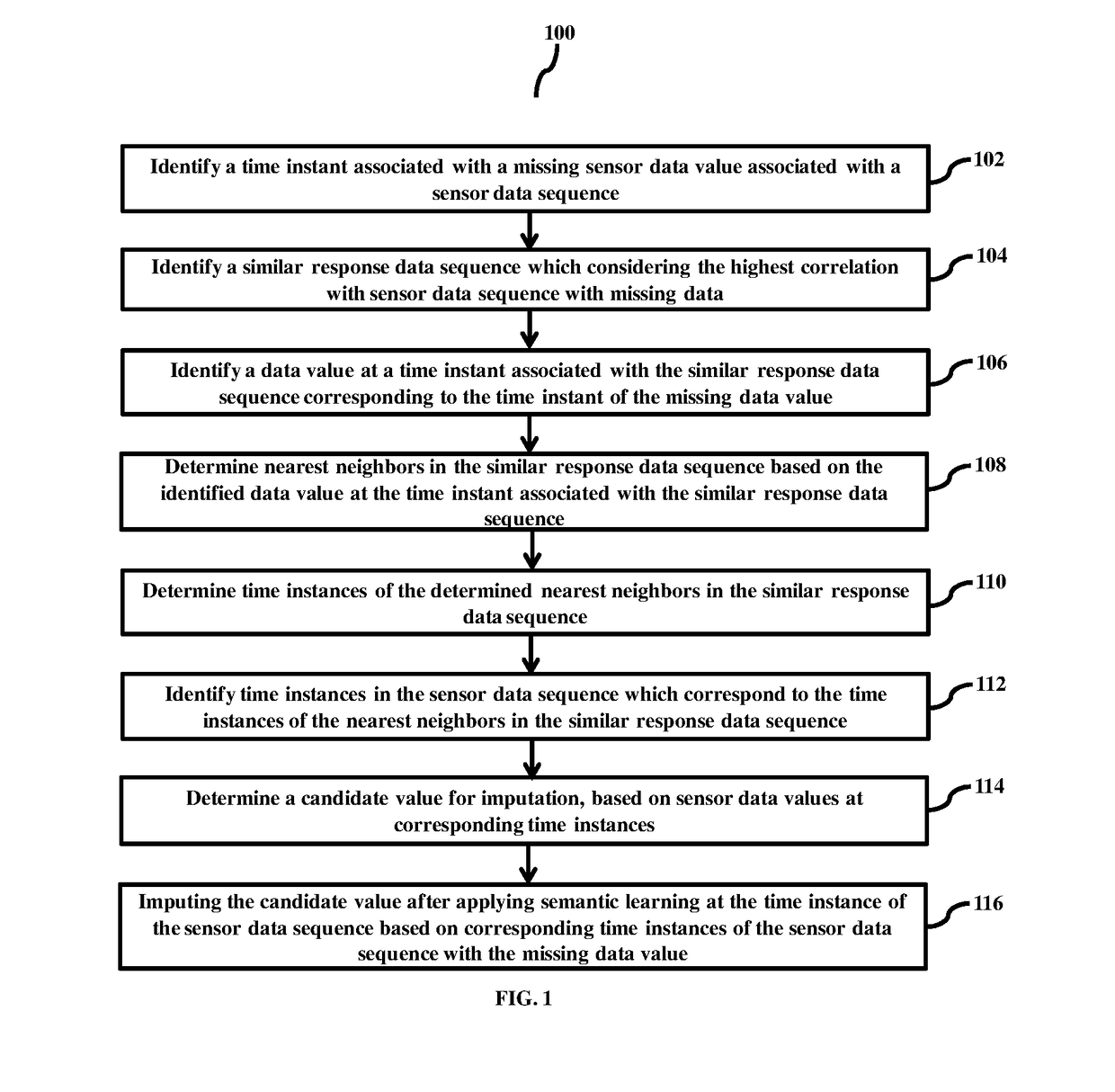
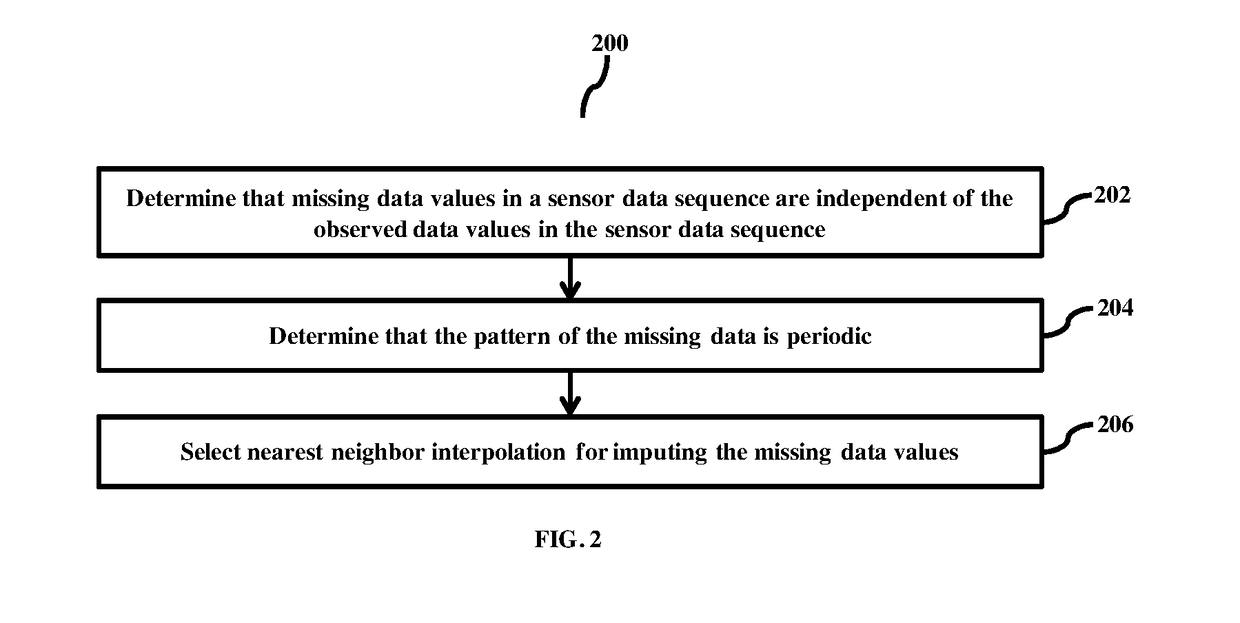
Method for imputing missed data in sensor data sequence with missing data
ActiveUS20180068033A1Reduce errorsError minimizationDigital data information retrievalElectrical measurementsMissing dataDistribution pattern
Embodiments herein provide a method for imputing sensor data, in a sensor data sequence with missing data based on the semantics learning, where semantics is defined by the constraints of the sensor data features. A candidate value for imputation is determined based on sensor data of corresponding time instances of the sensor data sequence using learning based on semantics of features of the sensor data sequence with missing data. The nearest neighbors search has been applied in similar response data sequence using the data values corresponding to the time instant of missing data in sensor data sequence. In case similar response data sequence is not available imputation is performed based on the distribution pattern of missing data.
Owner:INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY +1
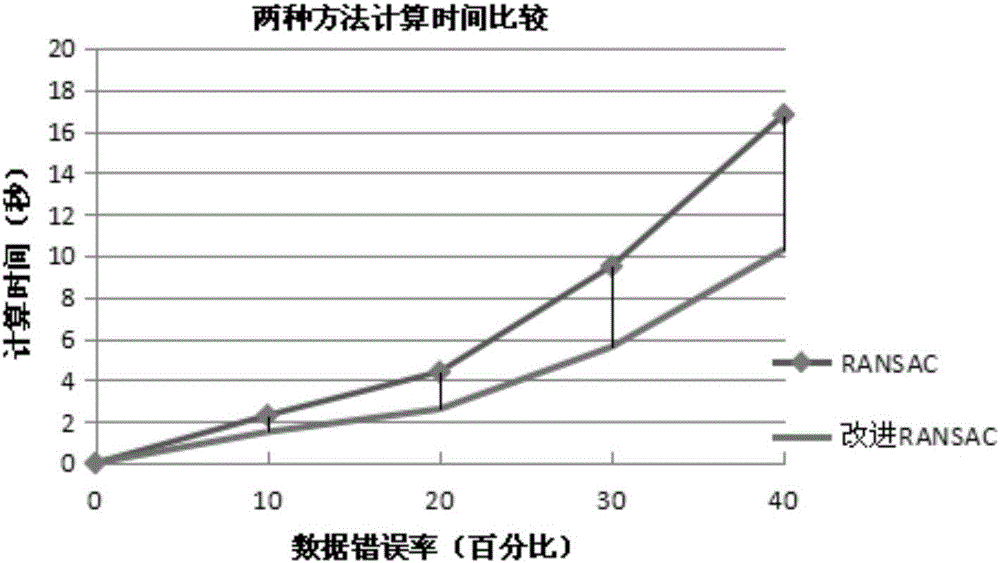
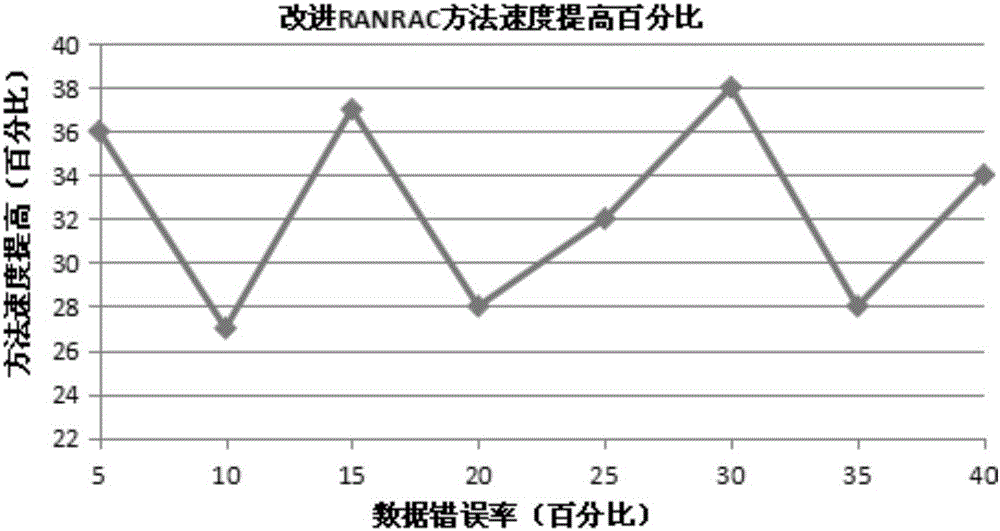
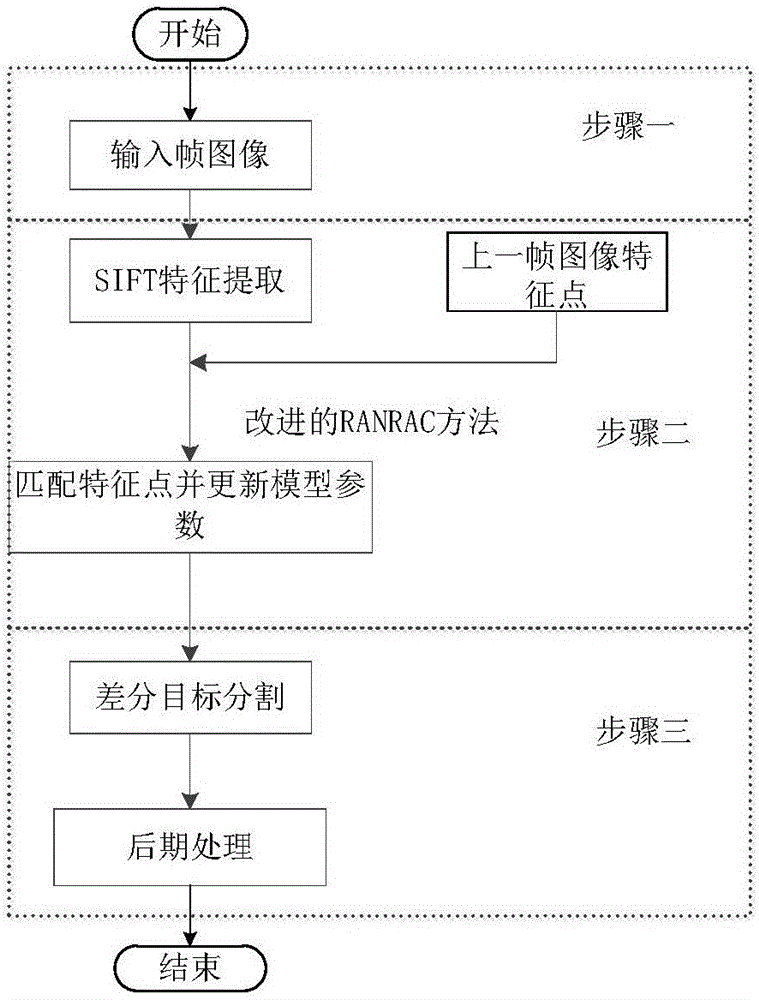
Moving object detection method based on SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) feature matching
InactiveCN105976399AThe detection process is fastLess time complexityImage enhancementImage analysisFeature matchingNearest neighbor search
The invention discloses a moving object detection method based on SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) feature matching. The method comprises steps: an SIFT feature extraction method is firstly used for acquiring feature points of the image; quick and accurate matching is then carried out on the SIFT feature points of the image; a global moving model is built according to features of a dynamic scene, an improved RANSAC (Random Sample Consensus) method is used for excluding influences from an external point, a least square method is used for solving a global moving parameter, the moving parameters are updated timely according to feature point change, an updating strategy based on a residual image block is used for updating, and a second nearest neighbor search area restricting method is used for ensuring the accuracy of feature matching; and finally, a differential target segmentation method is used for realizing detection on a moving target. An experiment proves that compared with the traditional image block-based matching detection method, the method improves the computing speed by 31.26%, background interference can be effectively eliminated, the detected target image is distinct, and the method is particularly applicable to real-time detection on the moving target in the dynamic scene.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
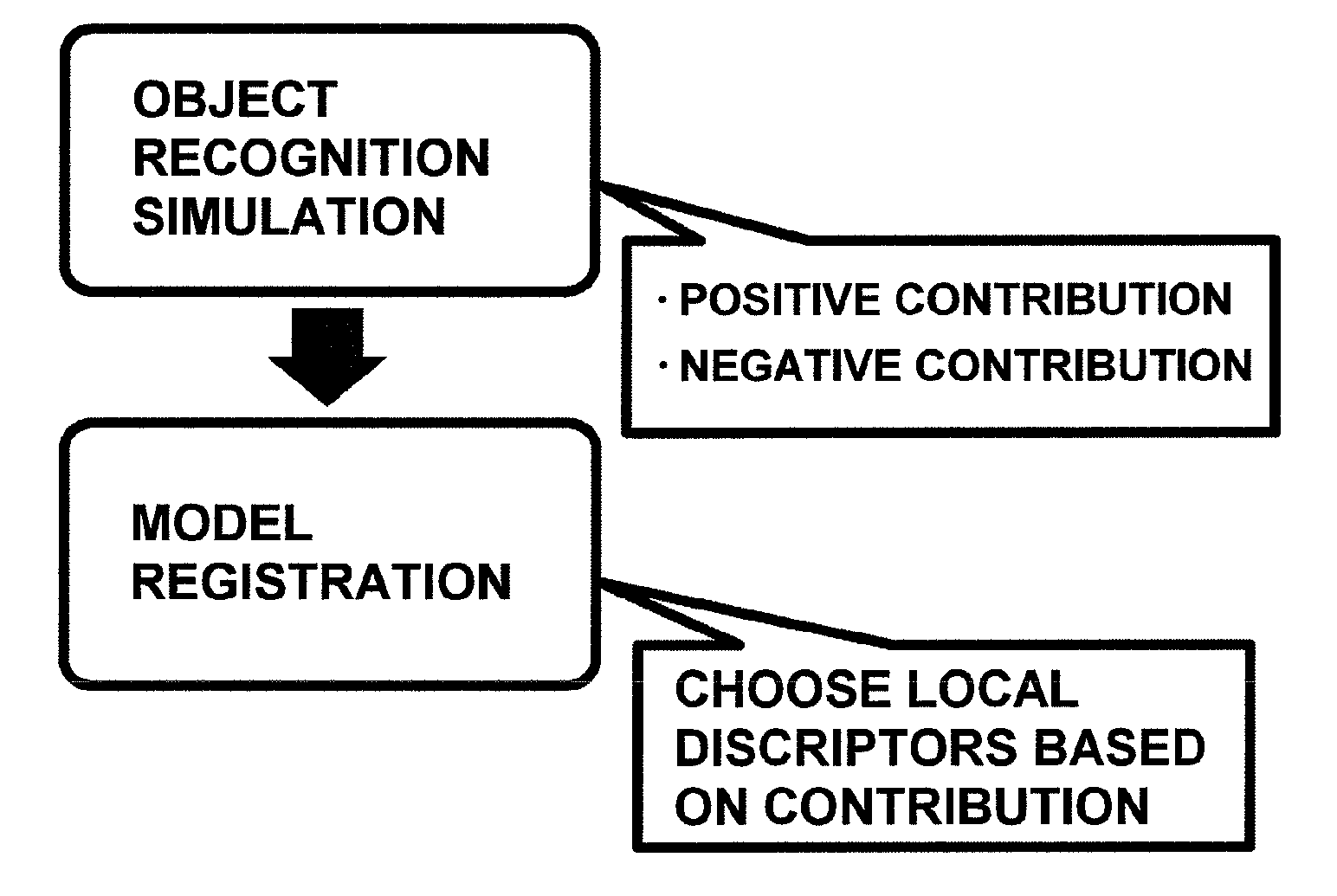
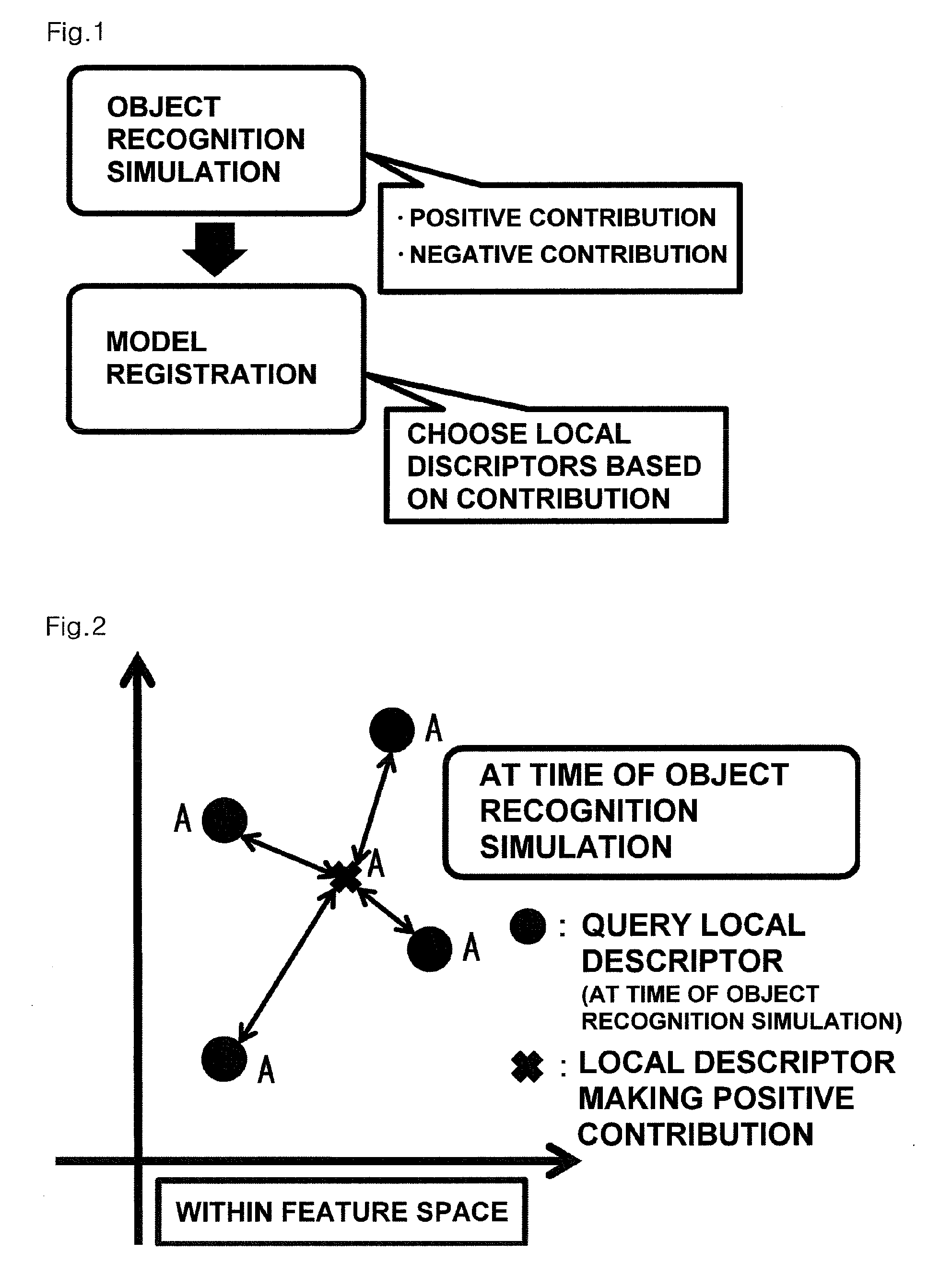
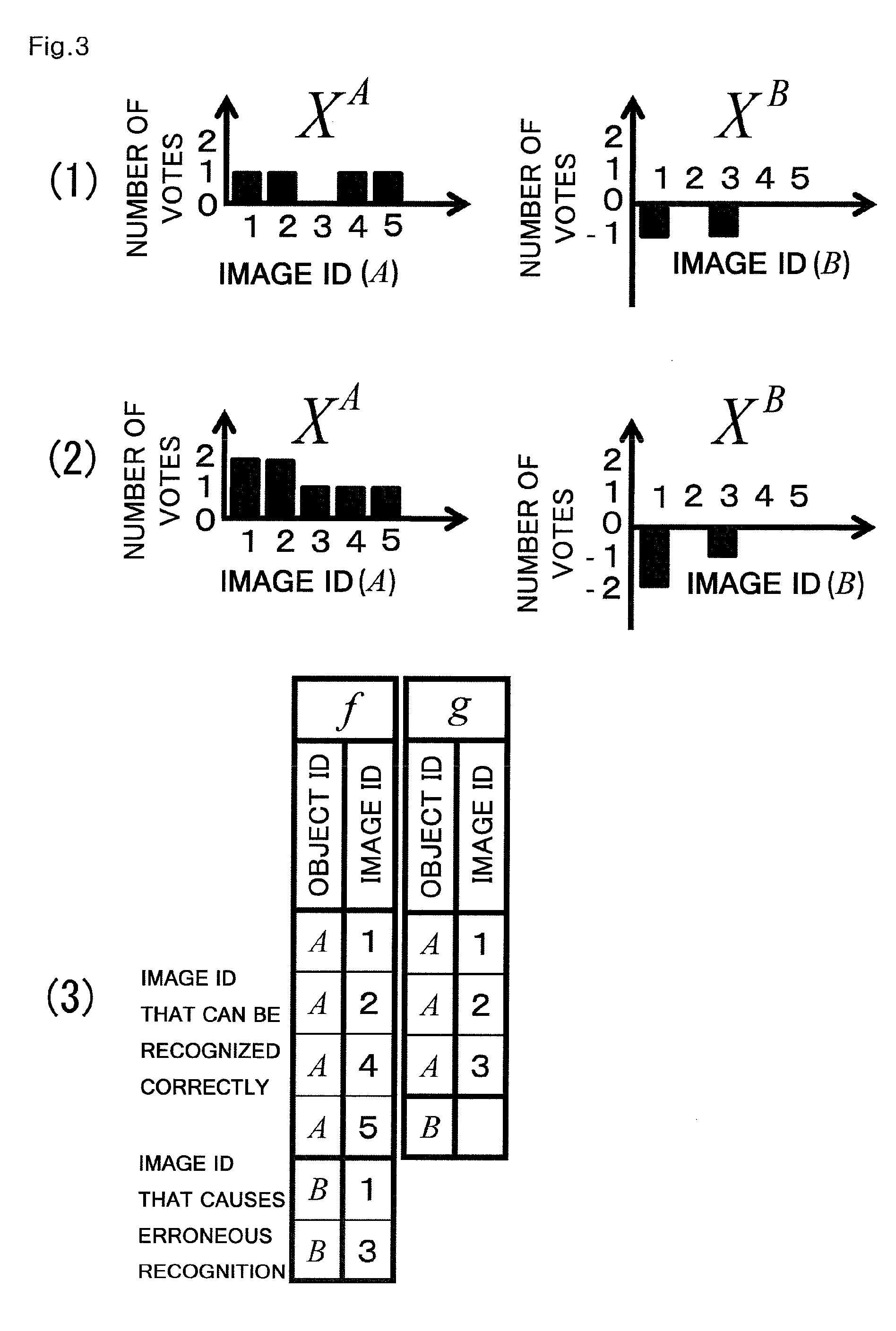
Method of compiling three-dimensional object identifying image database, processing apparatus and processing program
InactiveUS20110058733A1Low recognition rateAccurate recognition of objectDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionImage extractionViewpoints
Provided are a method of generating a low-capacity model capable of identifying an object with high accuracy, and creating an image database using the model, a processing program for executing the method, and a processing apparatus that executes the process. The method for compiling an image database that is used for a three-dimensional object recognition includes a steps of extracting vectors as local descriptors from a plurality of images each image showing a three-dimensional object as seen from different viewpoints, a model creating step of evaluating the degree of contribution of each local descriptor to identification of the three-dimensional object, and creating a three-dimensional object model systematized to ensure approximate nearest neighbor search using the individual vectors which satisfy criteria, and a registration step of adding an object identifier to the created object model and registering the object model into an image database. In the model creating step, the local descriptor to be used in the model is selected based on the contributions of the individual vectors which are evaluated in such a way that when a vector extracted from one image of one three-dimensional object is an approximate nearest neighbor to another vector relating to an image of the three-dimensional object seen from a different viewpoint, the vector has a positive contribution, whereas when the vector is an approximate nearest neighbor to another vector relating to a different three-dimensional object, the vector has a negative contribution. The processing program is designed to execute the method, and the processing apparatus executes the process.
Owner:PUBLIC UNIVERSITY CORPORATION OSAKA CITY UNIVERSITY
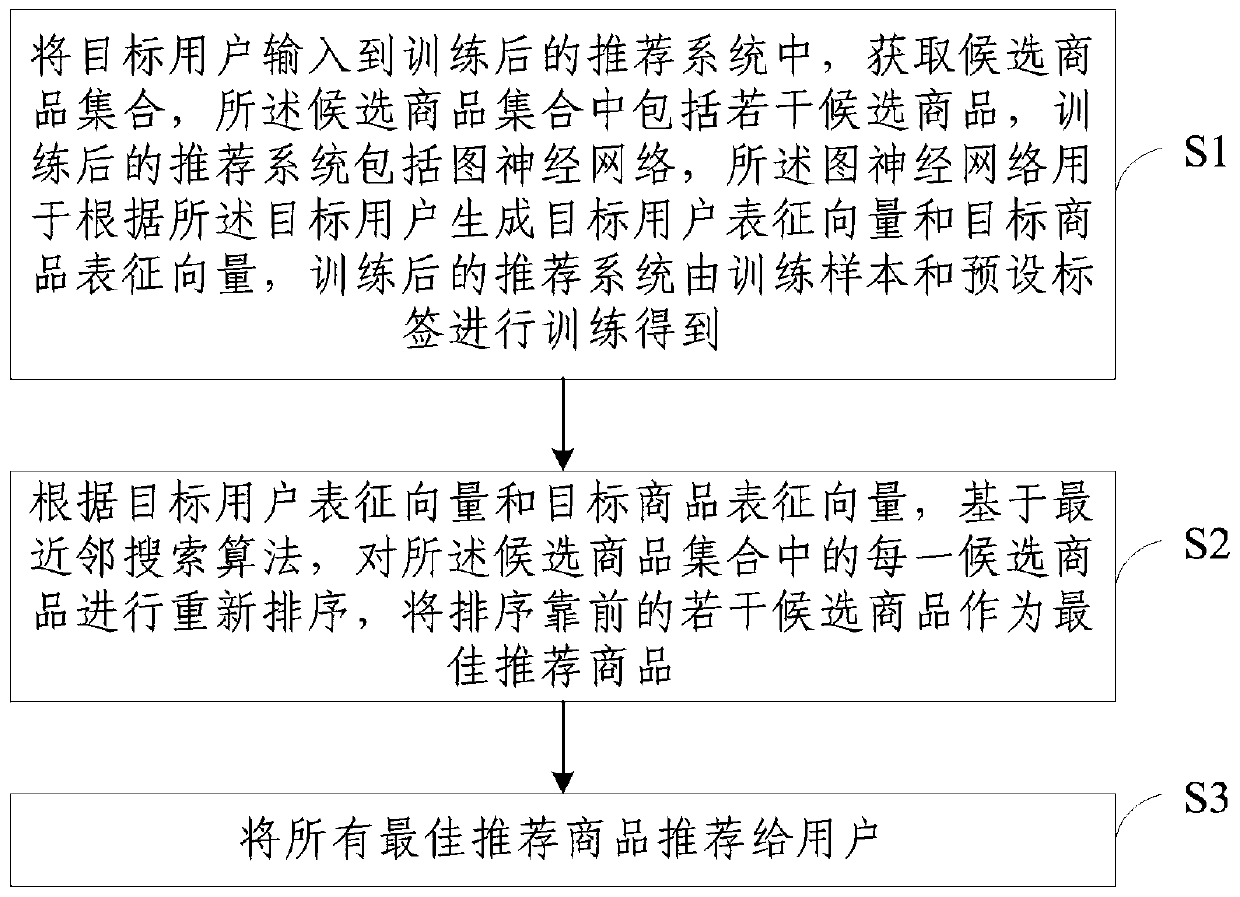
Commodity recommendation method and device
PendingCN110969516AIncrease diversityImprove accuracyDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionGraph neural networksOperations research
The embodiment of the invention provides a commodity recommendation method and device. The commodity recommendation method comprises the steps: inputting a target user into a trained recommendation system, and obtaining a candidate commodity set; reordering each candidate commodity in the candidate commodity set based on a nearest neighbor search algorithm according to the target user representation vector and the target commodity representation vector, and taking a plurality of candidate commodities sorted in the top as optimal recommended commodities; and recommending all the optimal recommended commodities to the user. The commodity recommendation method and device generate the target user representation vector and the target commodity representation vector according to the similarity between the target user and each commodity, based on the recommendation system constructed by the graph neural network, so that the diversity of the candidate commodities is improved, and the diversityof the best recommended commodities is improved, and the commodity with the maximum probability is recommended to the user through the commodity recall stage, and the recommendation accuracy is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
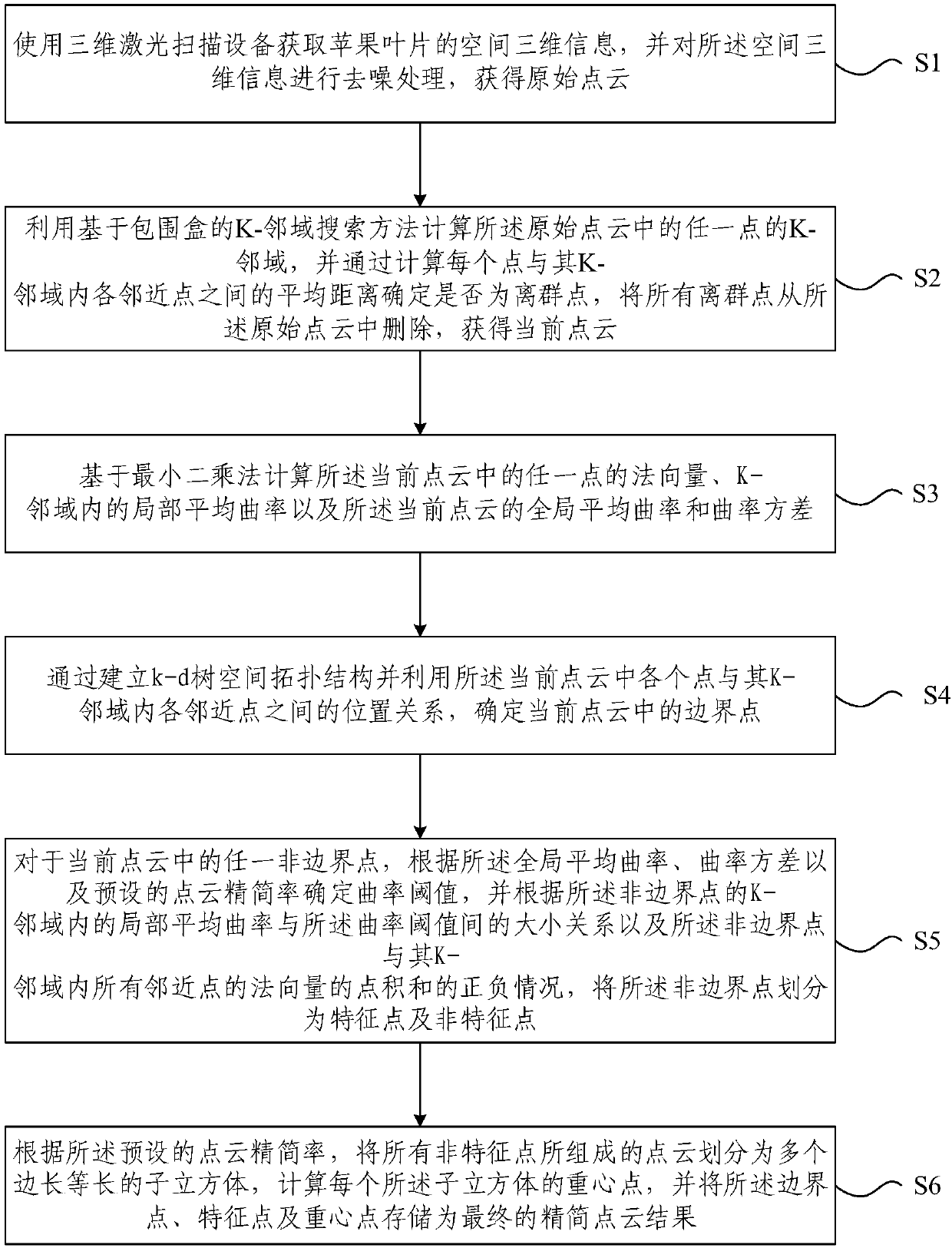
Method and apparatus for simplifying point cloud of apple leaf
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus for simplifying the point cloud of the apple leaf. The method comprises: using a bounding box method to perform fast K-nearest neighbor search,establishing a kd-tree space storage structure of the point cloud, setting different thresholds to identify the point cloud boundary of the leaf and extracting the point cloud boundary of the leaf; and by calculating the normal vector, the curvature, and the like of the feature parameters of the point, calculating neighborhood point position information, distinguishing feature points and non-feature points, and further carrying out simplification processing on the non-feature points. According to the technical scheme of the present invention, boundary point clouds and non-boundary point clouds can be quickly and conveniently obtained, and a simplification result can be further obtained; during the process, different K values and multiple thresholds can be set according to requirements, the obtained point result accuracy is relatively high, the calculation process is convenient and the calculation method is reasonable, the obtained point result accuracy is suitable for automatic programming, the waste of computer resources is effectively reduced, and the operating efficiency can be improved to some extent.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
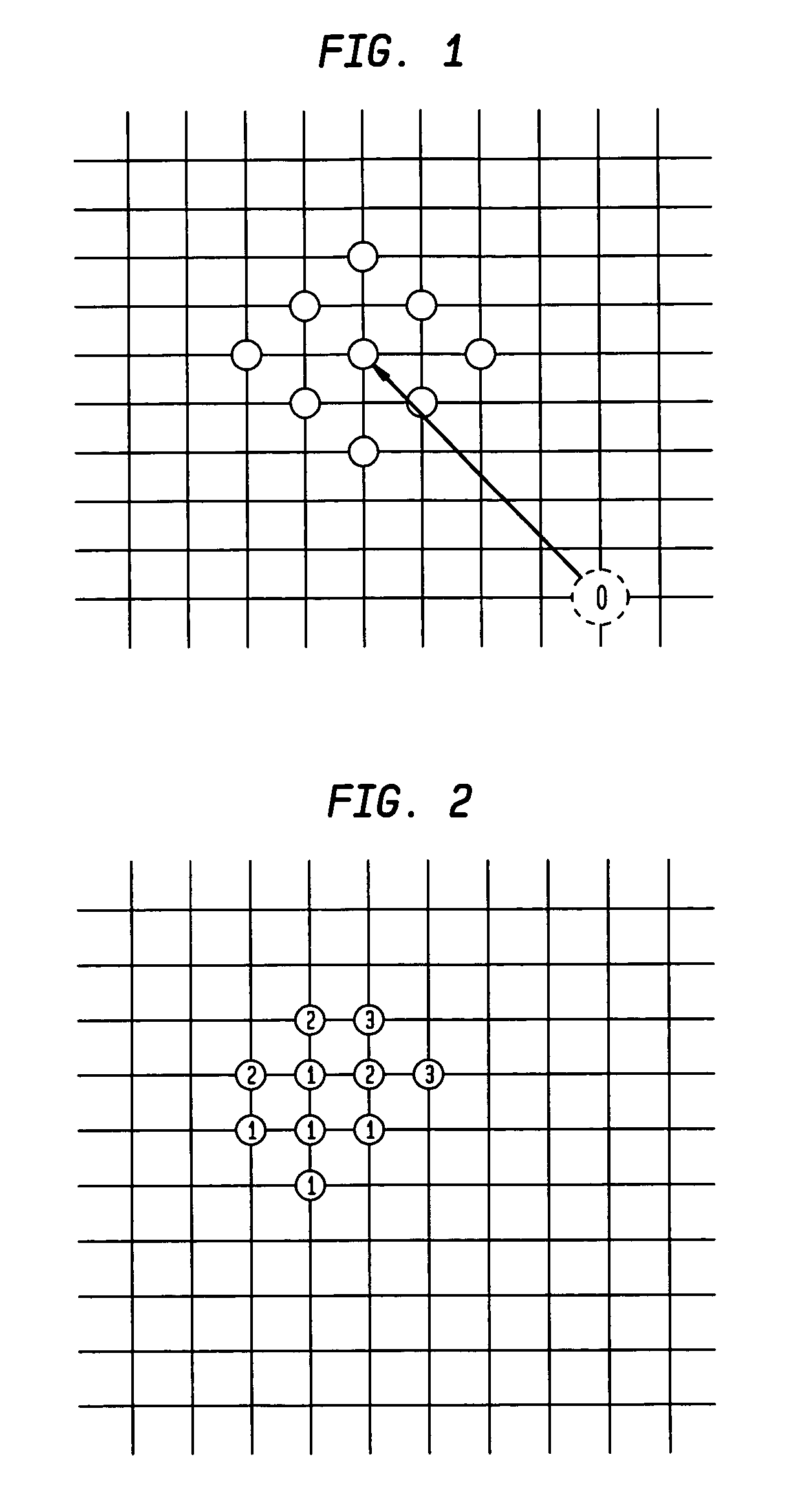
K nearest neighbor search method for point cloud simplification
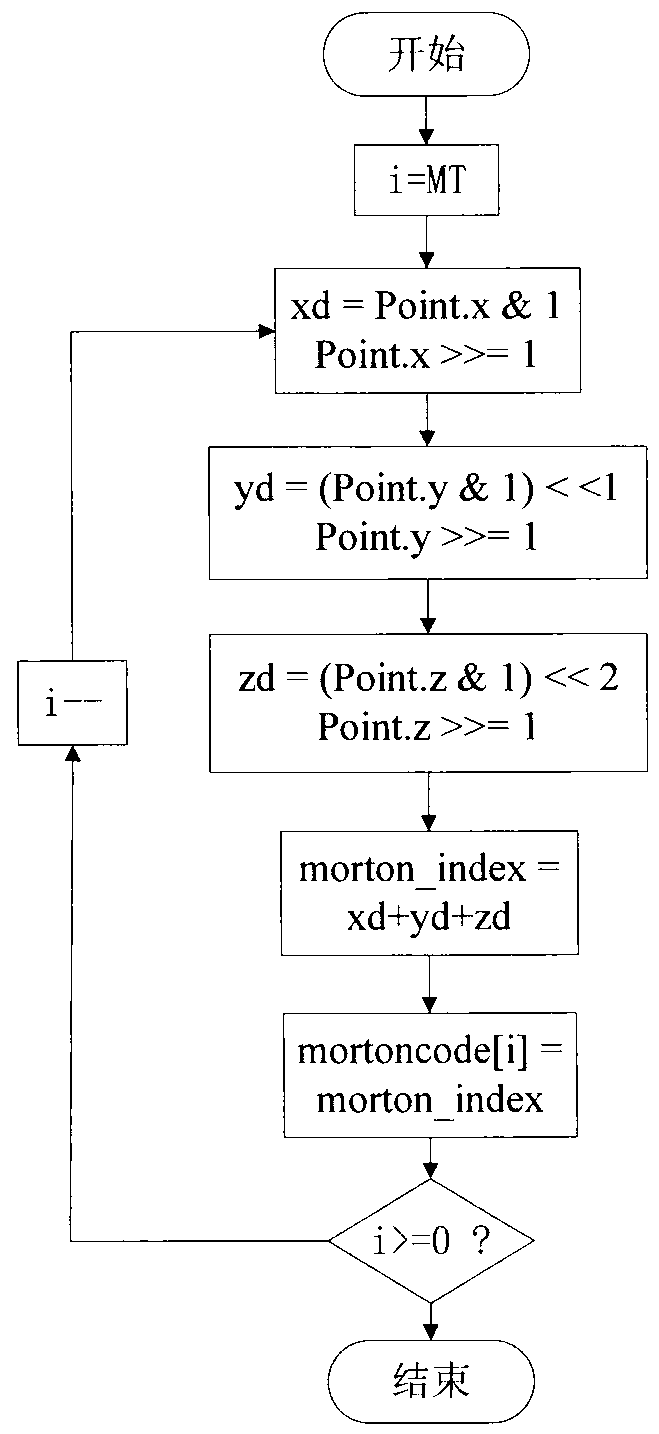
The invention discloses a K nearest neighbor search method for point cloud simplification. The K nearest neighbor search method for the point cloud simplification comprises the following steps: enlarging original data and horizontally moving the original data to map the original data to positive integer space, obtaining Morton codes of any point in the positive integer space through a displacement calculation method, ranking the Morton codes from small to big, respectively obtaining N*K points from the front and the back of the center point, calculating three-dimensional distances between the 2*N*K points and the center point, and selecting advanced K points as the K nearest neighbor.
Owner:CHANGSHU RES INSTITUE OF NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
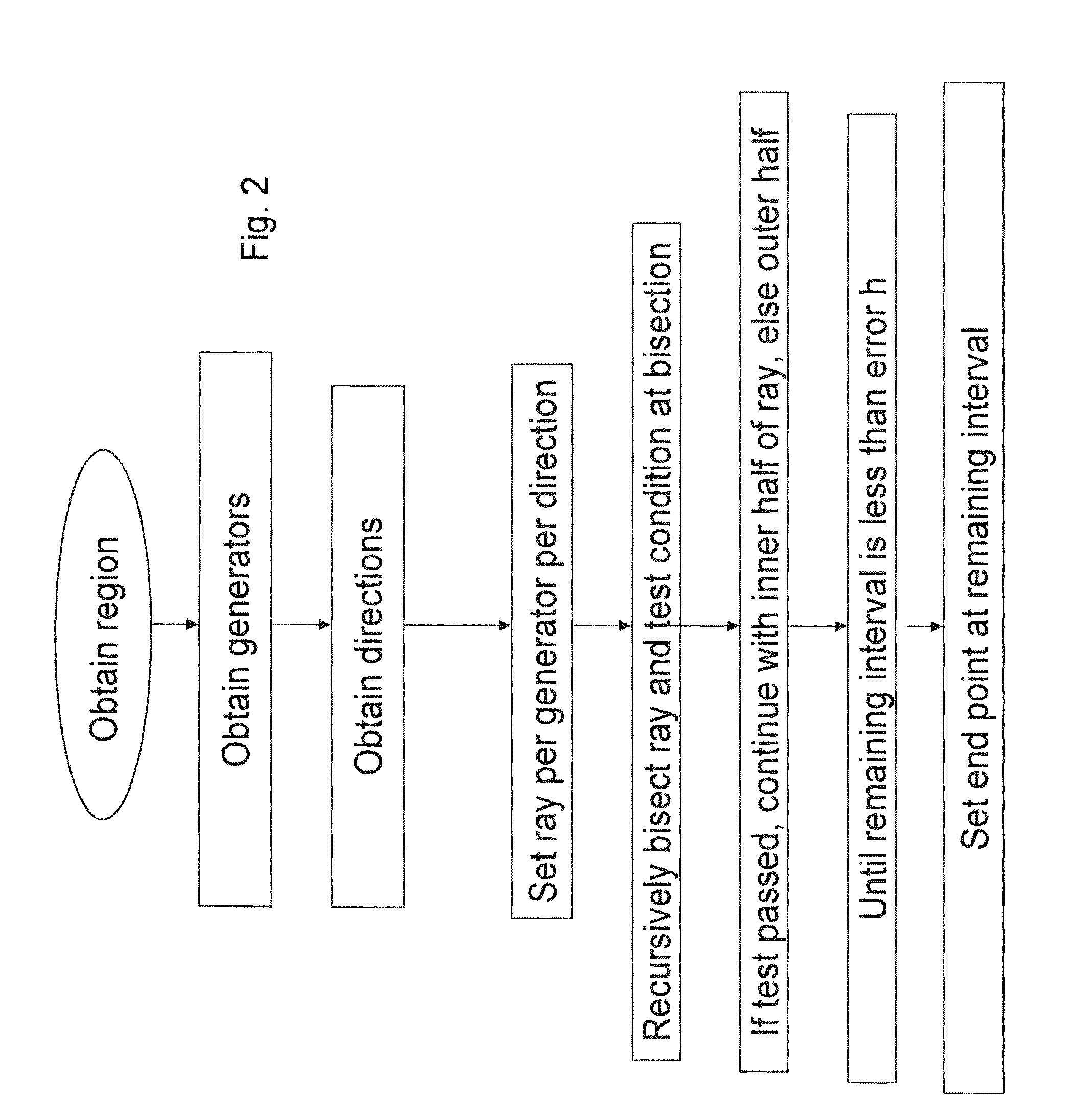
Efficient computation of Voronoi diagrams of general generators in general spaces and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100036647A1Character and pattern recognitionComputation using non-denominational number representationData compressionCollision detection
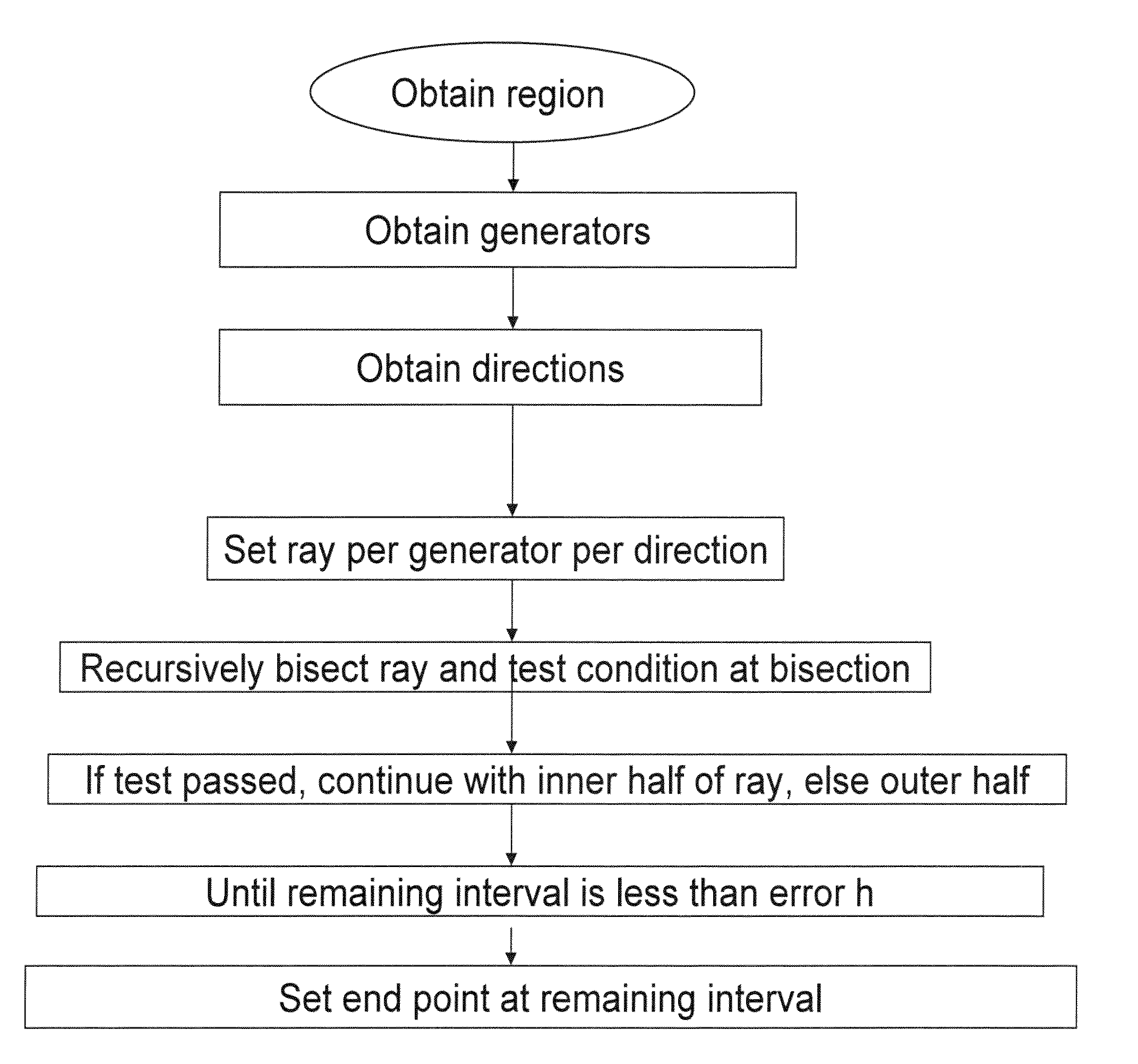
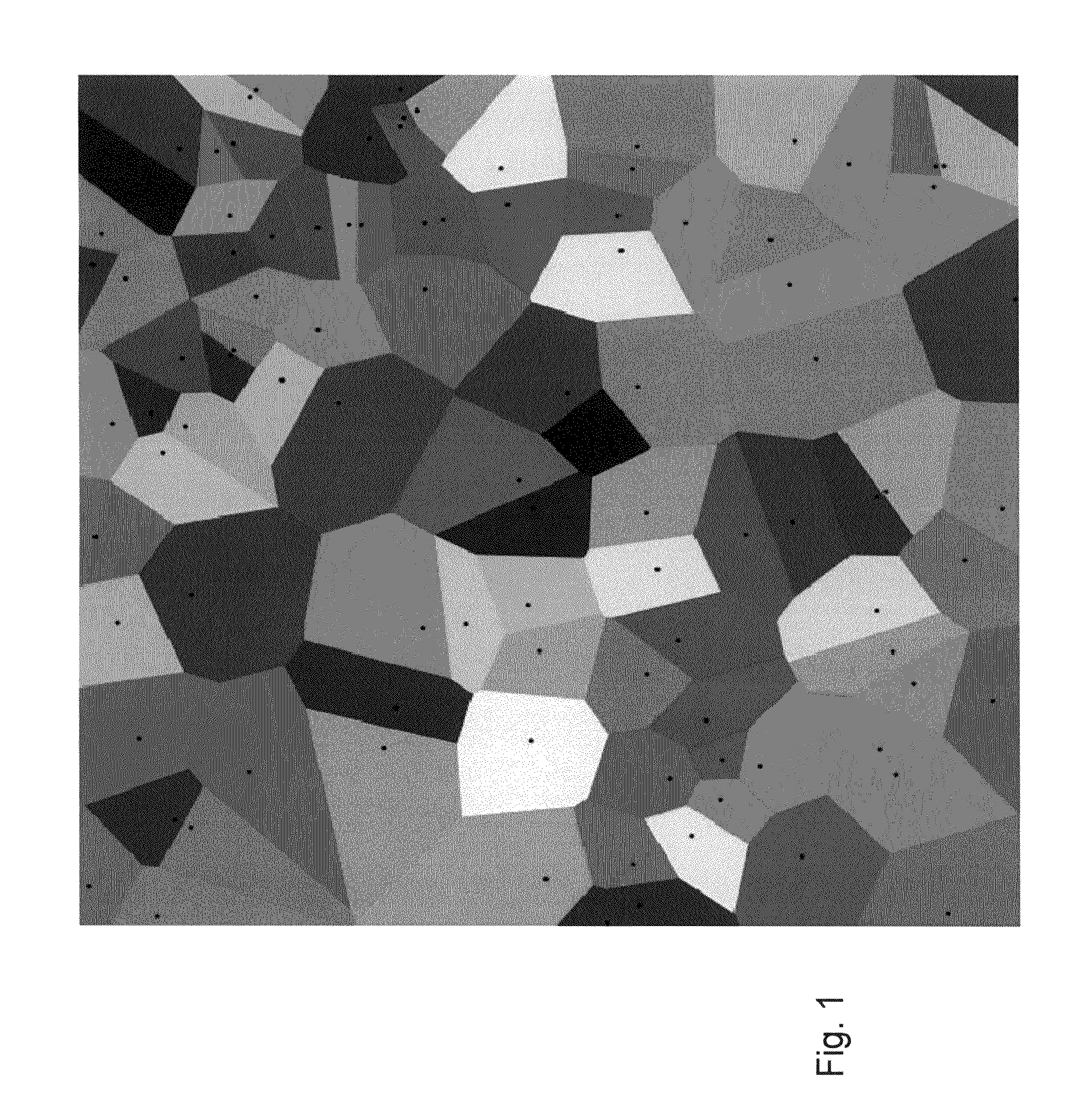
A computerized method of computing the Voronoi diagram has applications including communications networks, robotics, three-dimensional networks, materials science, searching image processing, data clustering, data compression, control of a groups of methods for image processing and the like, design of electronic circuits, geographic information systems, solutions of the efficient location problem, face recognition, mesh generation and re-meshing, curve and surface generation / reconstruction, solid modeling, collision detection, controlling motion of vehicles, navigation, accident prevention, data clustering and data processing, proximity operations, nearest neighbor search, numerical simulations, weather prediction, analyzing and modeling proteins and other biological structures, designing drugs, finding shortest paths, pattern recognition and as an artistic tool. The Voronoi diagram is a decomposed region X made into cells, the decomposition being induced by a set of generators (Pk)k-K, and a distance function, and involves finding for each generator Pk a cell, which is a set of all the points in X satisfying the condition that the distance to the current generator P=Pk is not greater than the distance thereof to the union A of the other generators, The method comprising: for each generator, and for each point p in this generator, selecting a set of directions, then for each direction recursively testing a ray in that direction, until a certain interval on the ray is of length less than or equal to a given error parameter. A point corresponding to the interval on the ray is then selected as an end point, the cells are defined from the end points, thus forming the Voronoi diagram.
Owner:REICH SIMEON +1
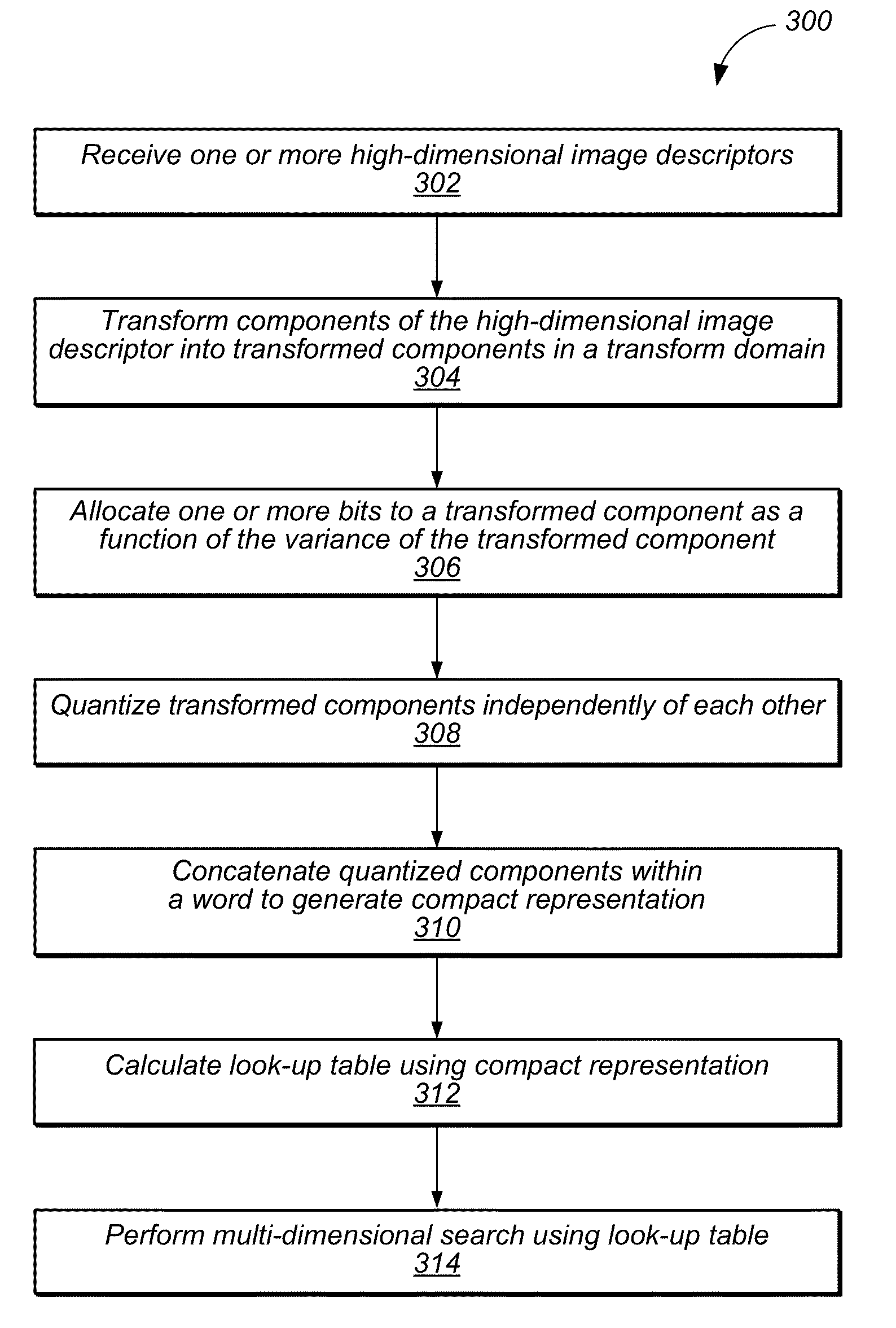
Systems and methods for large scale, high-dimensional searches
ActiveUS8428397B1Increase speedImprove effectivenessCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer visionHigh dimensional
Methods and systems for fast, large scale, high-dimensional searches are described. In some embodiments, a method comprises transforming components of a high-dimensional image descriptor into transformed components in a transform domain, allocating one or more bits available within a bit budget to a given transformed component within a first subset of transformed components as a function of a variance of the given transformed component, independently quantizing each transformed component within the first subset of transformed components, generating a compact representation of the high-dimensional image descriptor based, at least in part, on the independently quantized components, and evaluating a nearest neighbor search operation based, at least in part, on the compact representation of the high-dimensional image descriptor.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Model identification method based on local characteristic aggregation descriptor
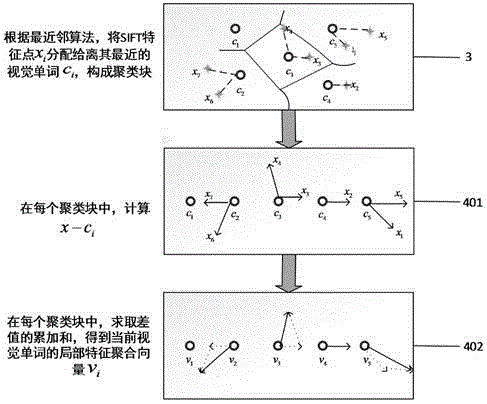
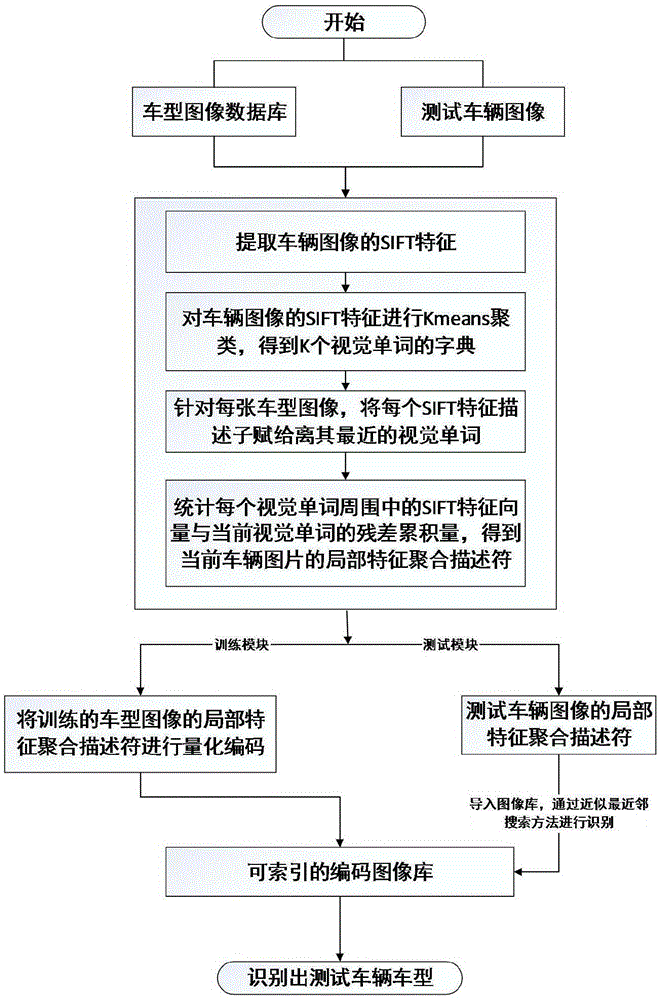
InactiveCN105335757AImprove recognition accuracyImprove practicalityCharacter and pattern recognitionEuclidean vectorVisual perception
The invention discloses a model identification method based on a local characteristic aggregation descriptor. First of all, SIFT characteristics of vehicle images in a model database are extracted; then Kmeans clustering is performed on the SIFT characteristics of all the vehicle images so as to form K cluster centers and obtain a dictionary with K visual words; then, each SIFT characteristic is endowed with a closest visual word for each model image; a residual error cumulant between SIFT characteristic vectors around each visual word and current visual words is counted, and the local characteristic agglomeration descriptor of a current vehicle picture is obtained; finally, an indexable coding image database of n model types is obtained through quantification coding from local characteristic agglomeration descriptors of n model images of a training module; and for a test vehicle image, the local characteristic agglomeration descriptor of the test vehicle image is extracted in the same way as a query vector for introduction into an image database for indexing, and the model of a test vehicle is identified through matching by use of an approximation nearest neighbor search method.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
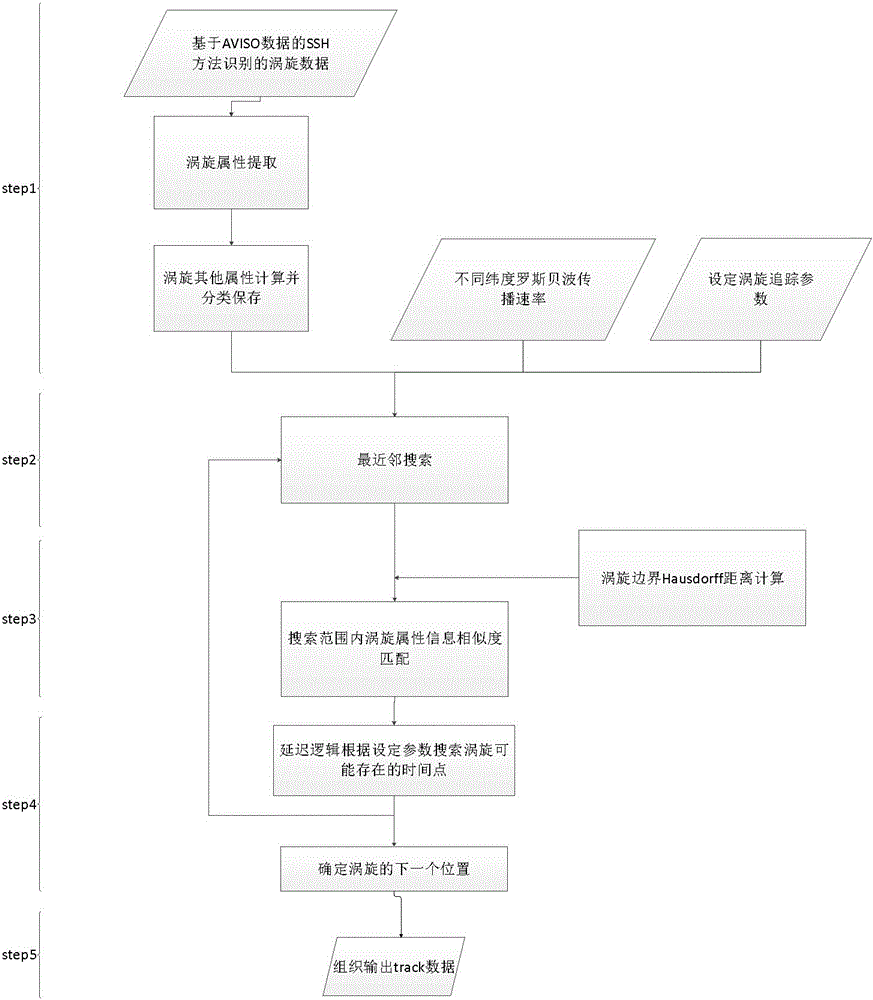
Long-time-series mesoscale eddy tracing method based on hybrid algorithm
InactiveCN105787284AUnderstanding Migration EvolutionTrusted Tracking PathSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsAlgorithmSea-surface height
The invention belongs to the crossing field of physical oceanography and computer graphics and image processing, and particularly relates to a mesoscale eddy tracing method based on a hybrid algorithm. The hybrid algorithm mainly comprises nearest neighbor search, deformation control based similarity match and delay logic. The method comprises the following steps: step one, for the nearest neighbor search, eddies in a search range are delineated according to global mesoscale eddy data recognized with an SSH (sea surface height) method; step two, for a deformation control based similarity match method, the eddies in the range and attributes of the eddies are subjected to similarity calculation of area, amplitude, kinetic energy, relative vorticity and Hausdorff distance, the eddy with the maximum similarity is selected as the position of the next eddy, and jump of an eddy path is avoided through combination of physical attributes and geometric attributes of the eddies; step three, the delay logic is adopted, search at multiple time points is considered, the eddies temporarily disappearing at certain time points are processed, and discontinuity of the eddy path is avoided, so that the purpose of multi-year long-term efficient tracing on the eddies is achieved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
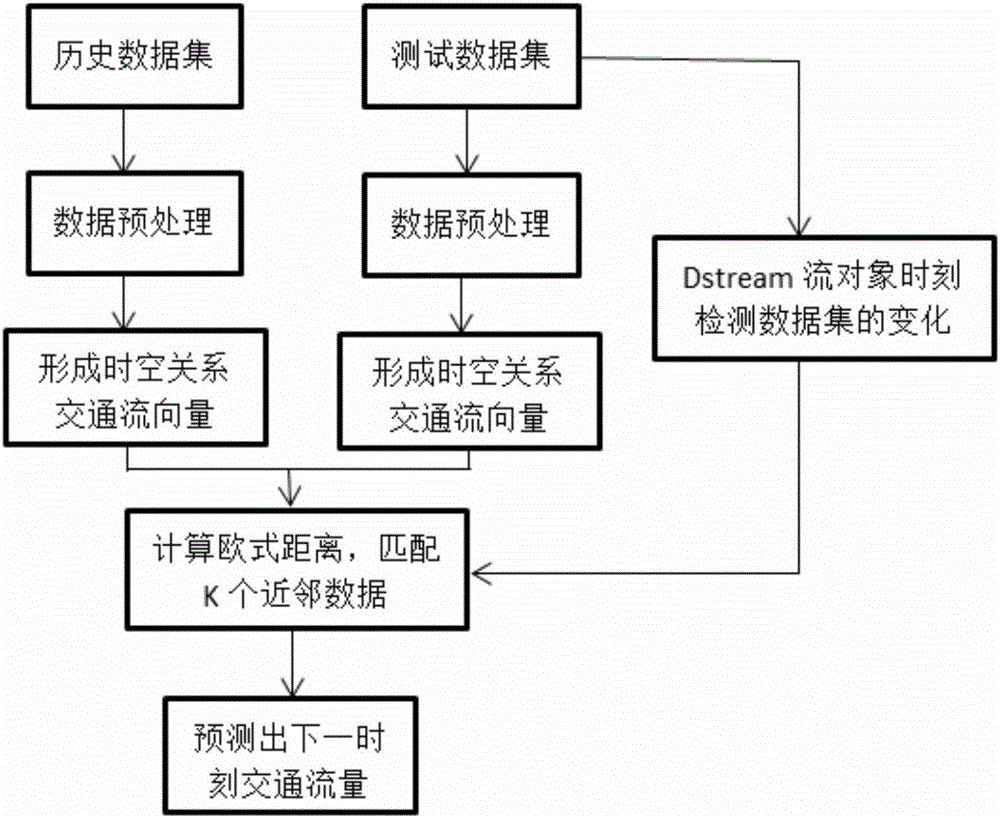
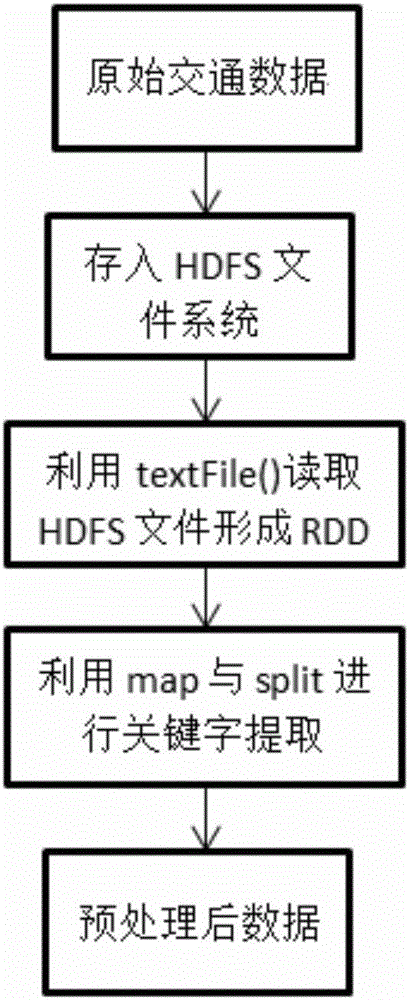
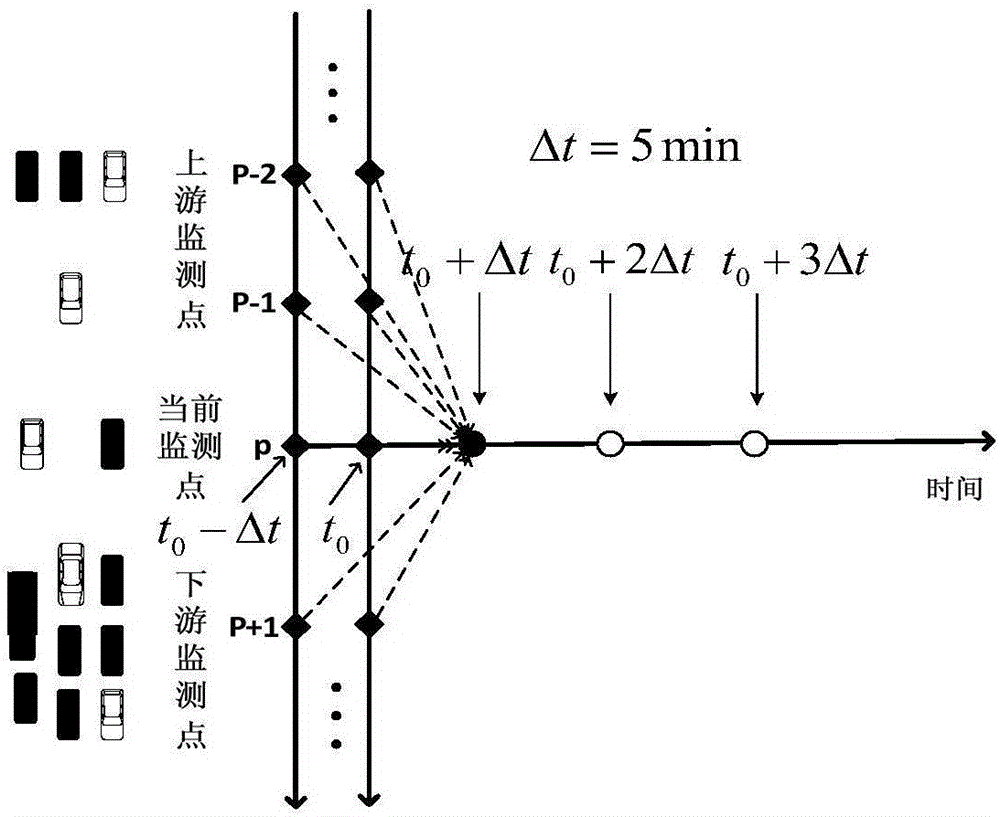
Short-term traffic flow prediction method based on Spark platform
ActiveCN106128100AReduce data volumeImprove computing efficiencyDetection of traffic movementExtensibilityPrediction algorithms
The invention provides a short-term traffic flow prediction method based on a Spark platform. A parallel KNN algorithm is applied to the field of short-term traffic flow prediction. Compared with the conventional KNN algorithm based on single-computer computing, the problems of small system storage capacity and slow computing speed in performing data computing on the single physical computer can be solved by the method, and the problem of low neighbor matching efficiency in the neighbor search process of the KNN algorithm can also be solved by the method. According to the method, the computing efficiency of the algorithm can be enhanced under the premise of guaranteeing prediction precision, the practicality of the KNN prediction algorithm can be effectively improved and the system has great extensibility and speed-up ratio. The method also has reference meaning for other applications requiring large-scale data processing.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com