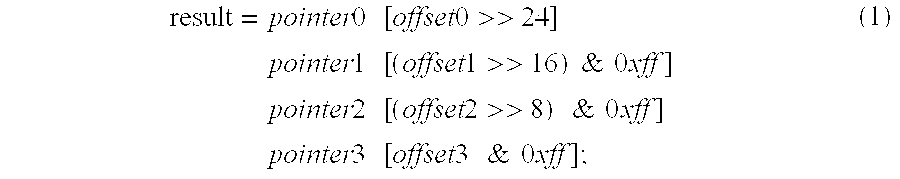Patents
Literature
88 results about "Index register" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
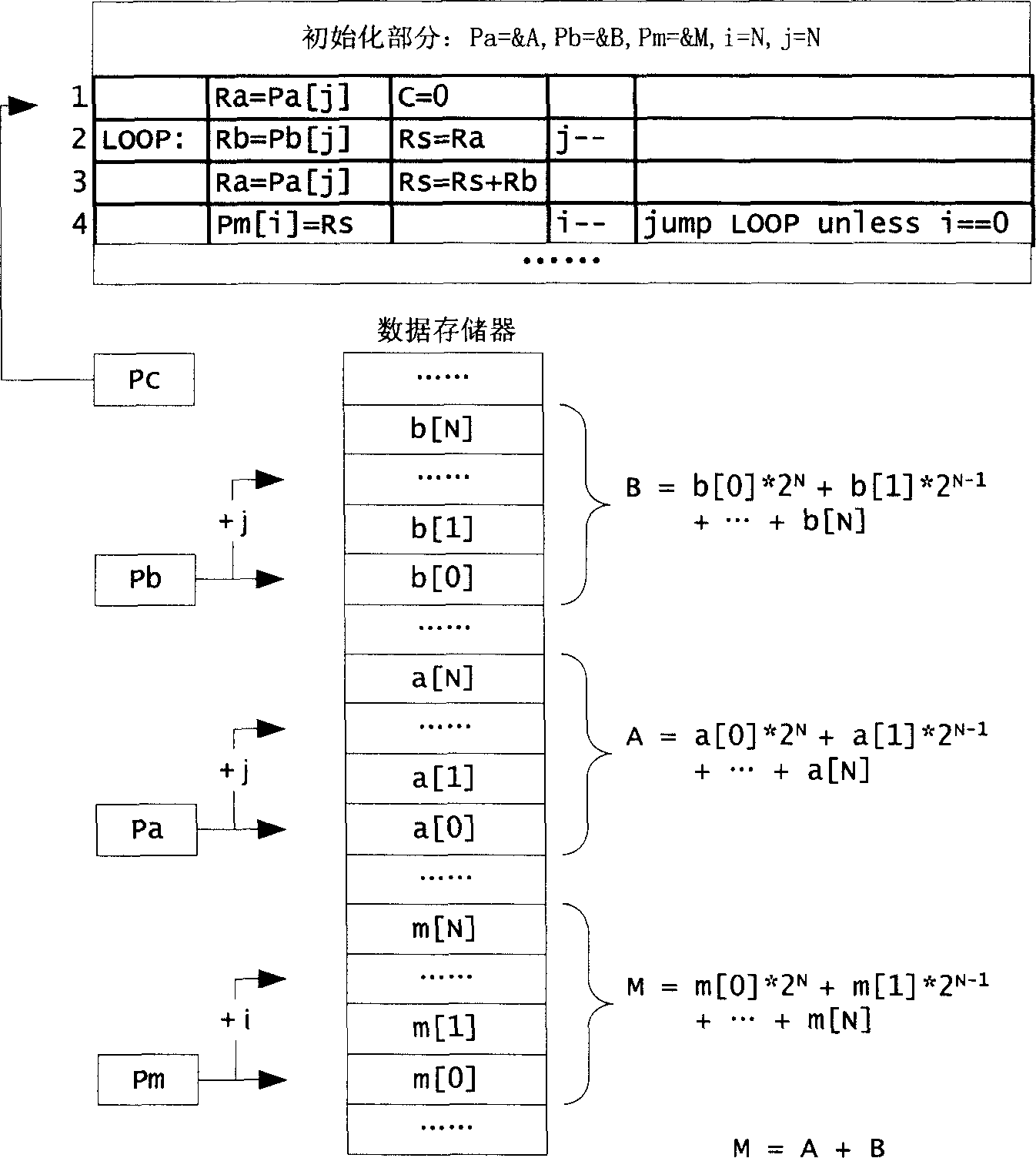
An index register in a computer's CPU is a processor register used for modifying operand addresses during the run of a program, typically for doing vector/array operations. The contents of an index register is added to (in some cases subtracted from) an immediate address (one that is part of the instruction itself) to form the "effective" address of the actual data (operand). Special instructions are typically provided to test the index register and, if the test fails, increments the index register by an immediate constant and branches, typically to the start of the loop. Some instruction sets allow more than one index register to be used; in that case additional instruction fields specify which index registers to use. While normally processors that allow an instruction to specify multiple index registers add the contents together, IBM had a line of computers in which the contents were or'd together.
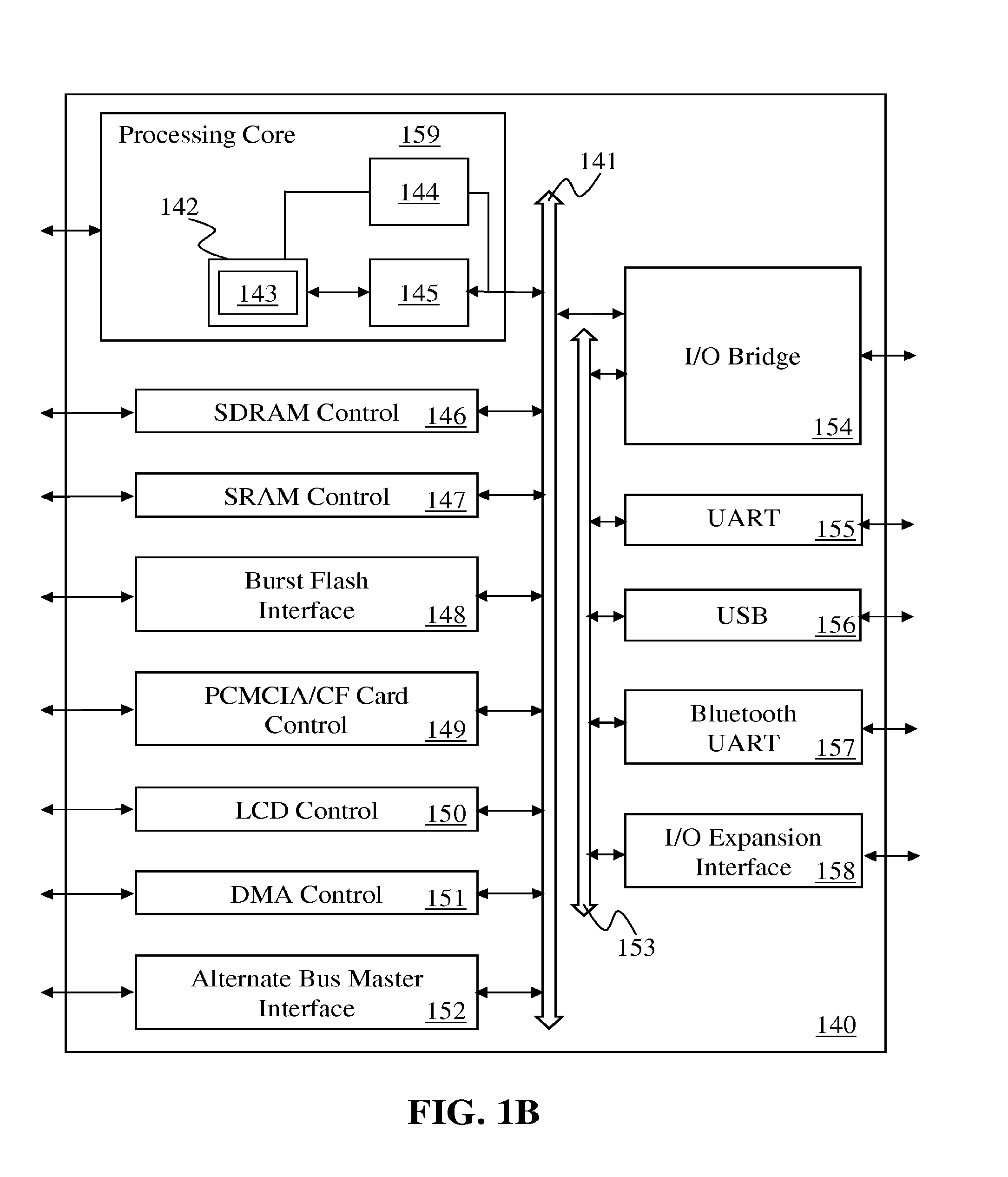
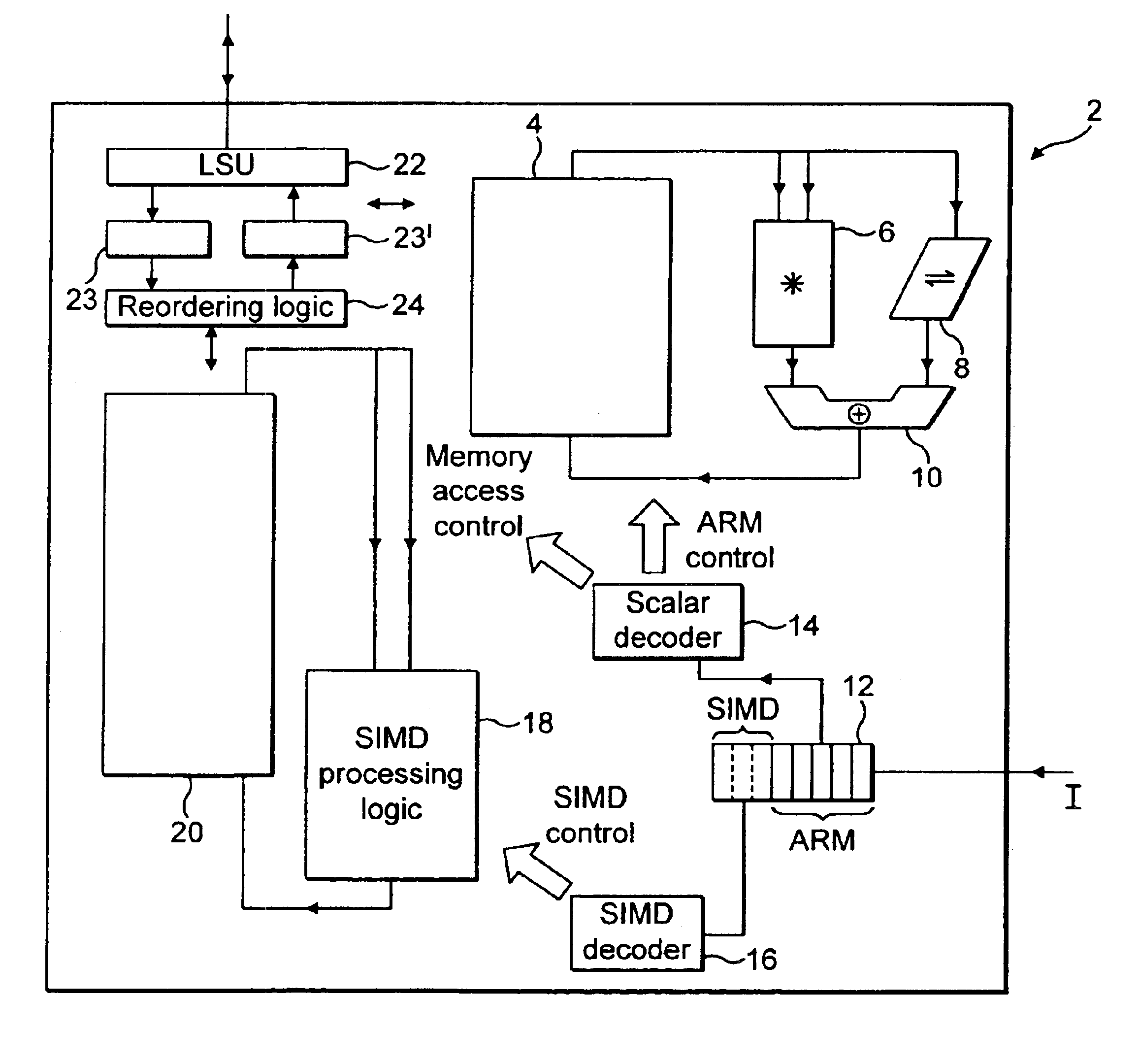
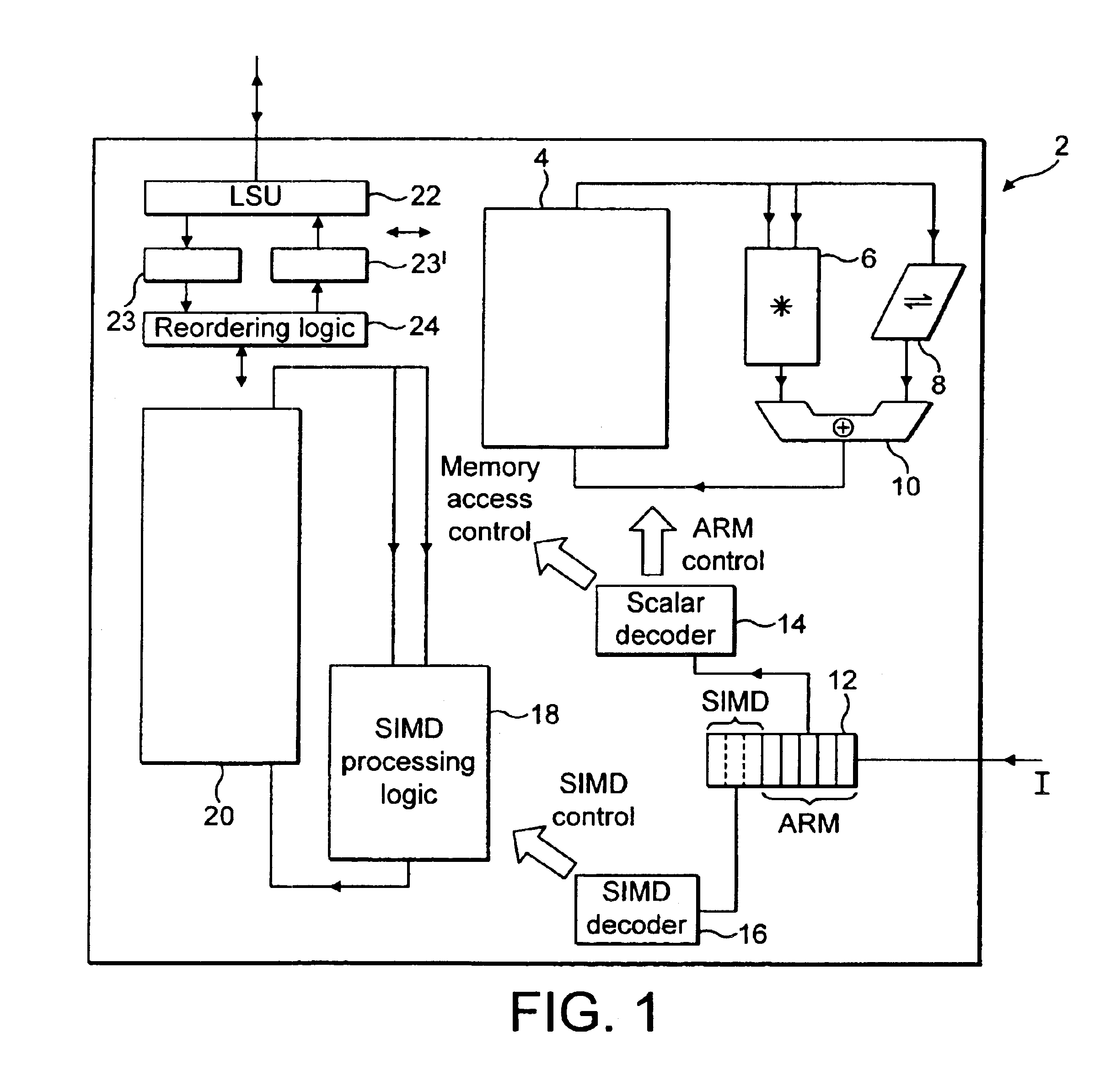
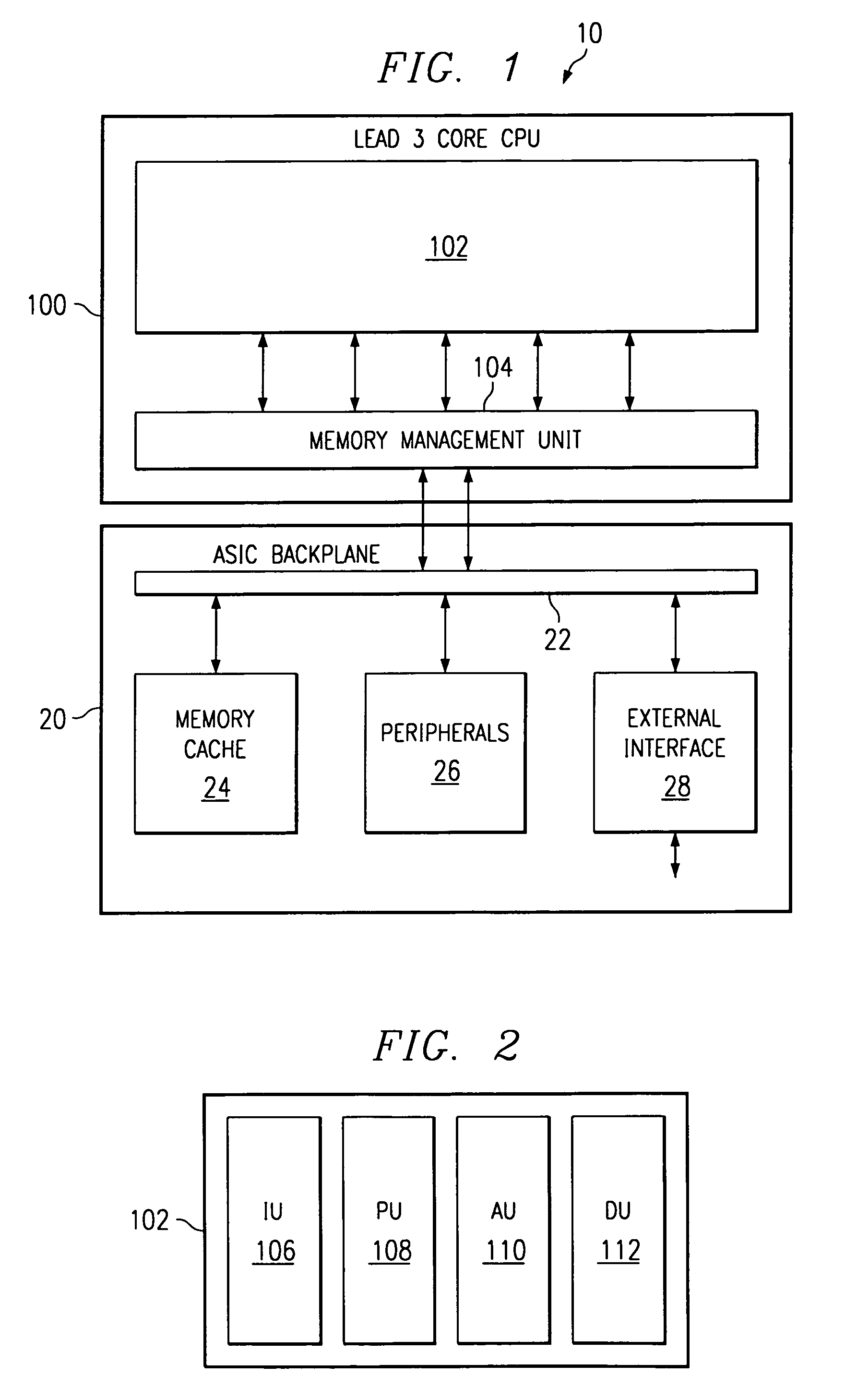
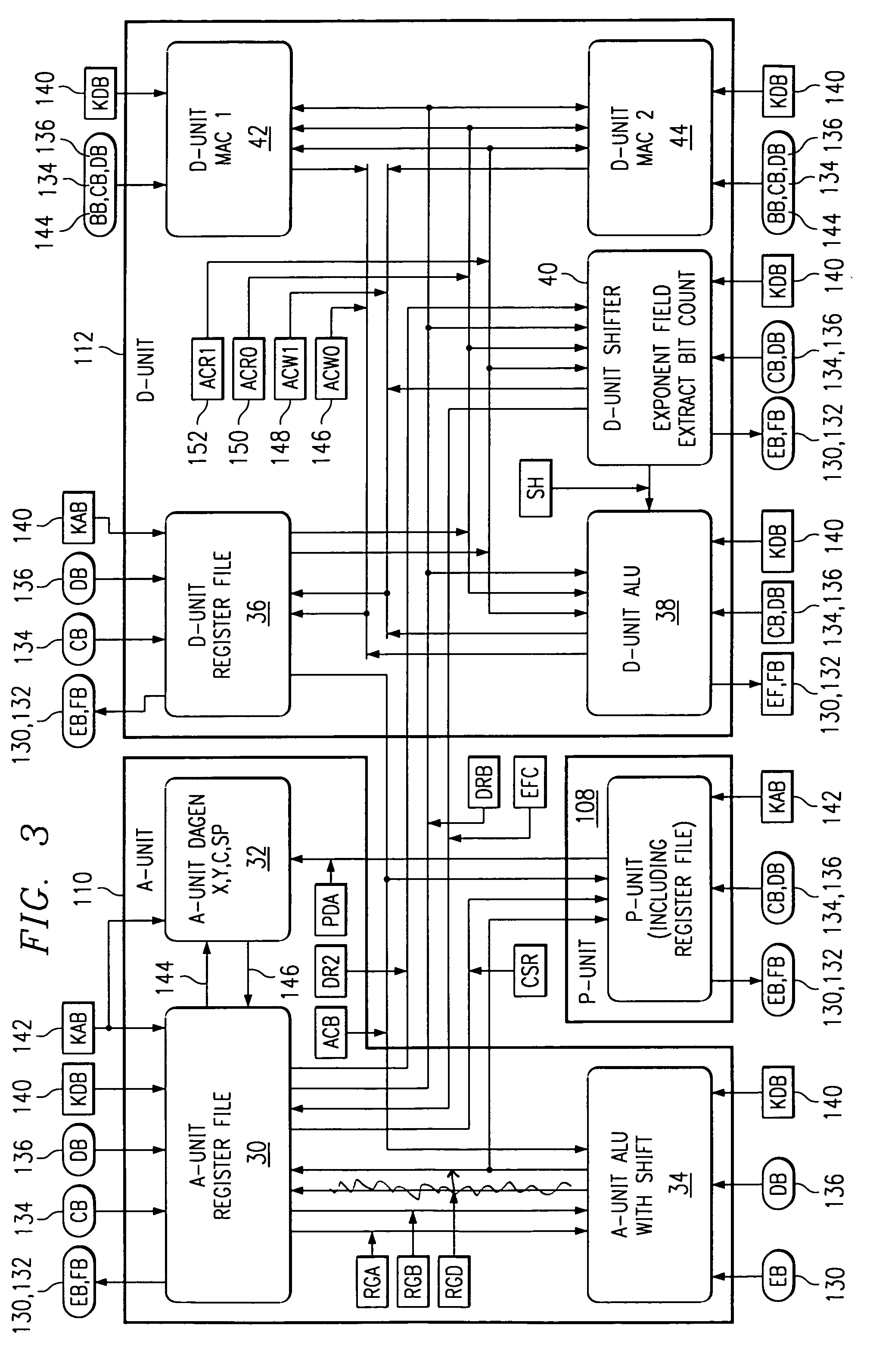
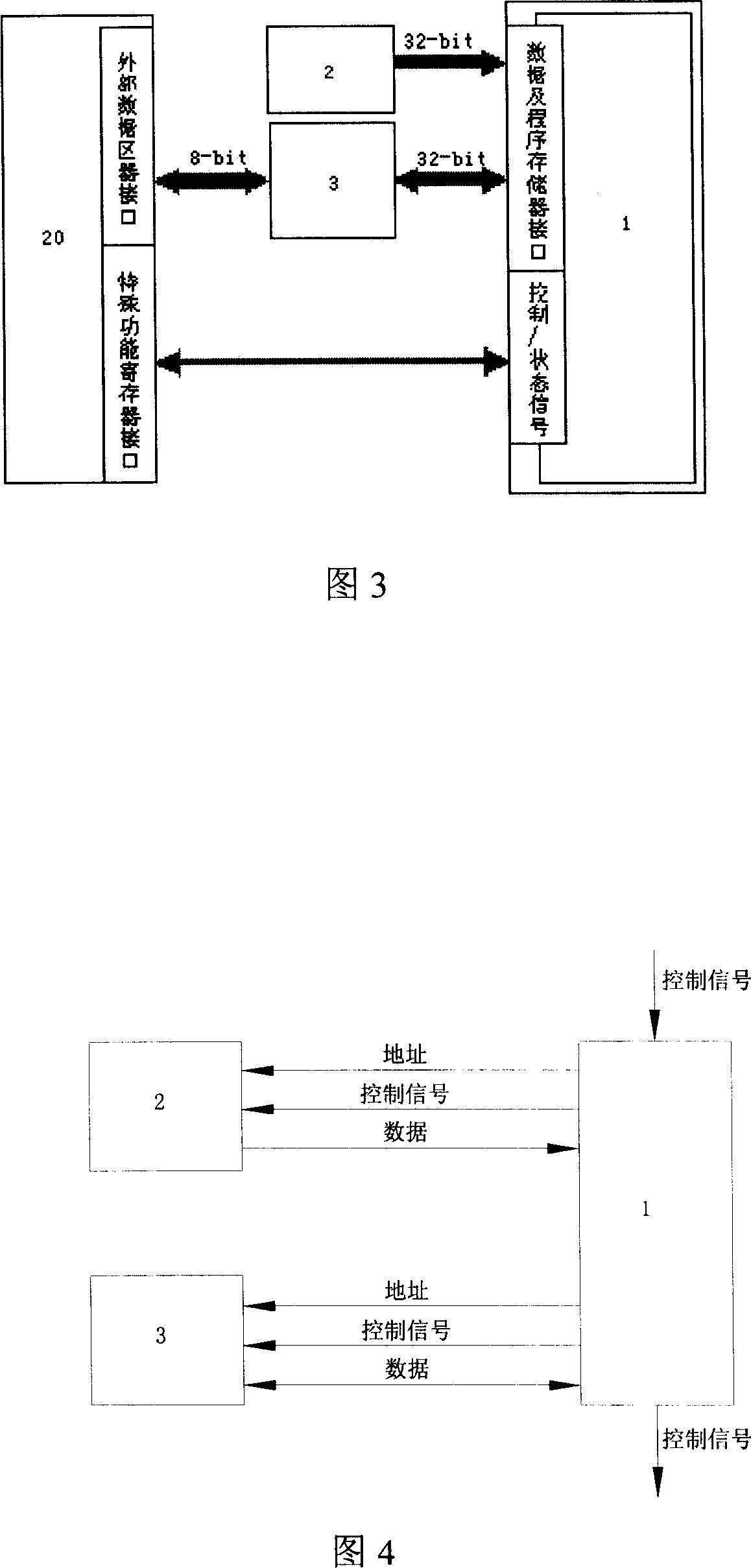
Long Instruction Word Controlling Plural Independent Processor Operations
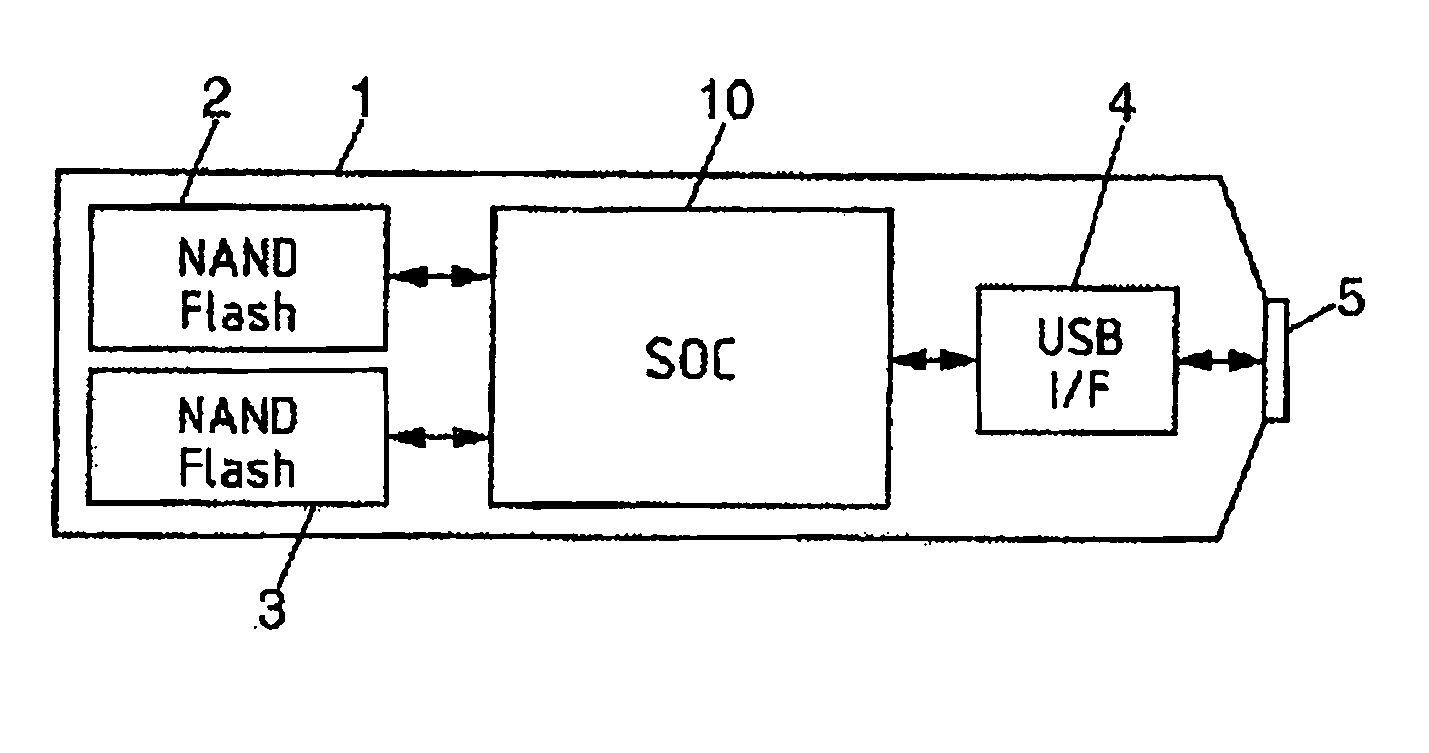
InactiveUS20080077771A1Instruction analysisComputation using non-contact making devicesIntegrated circuitStatus register
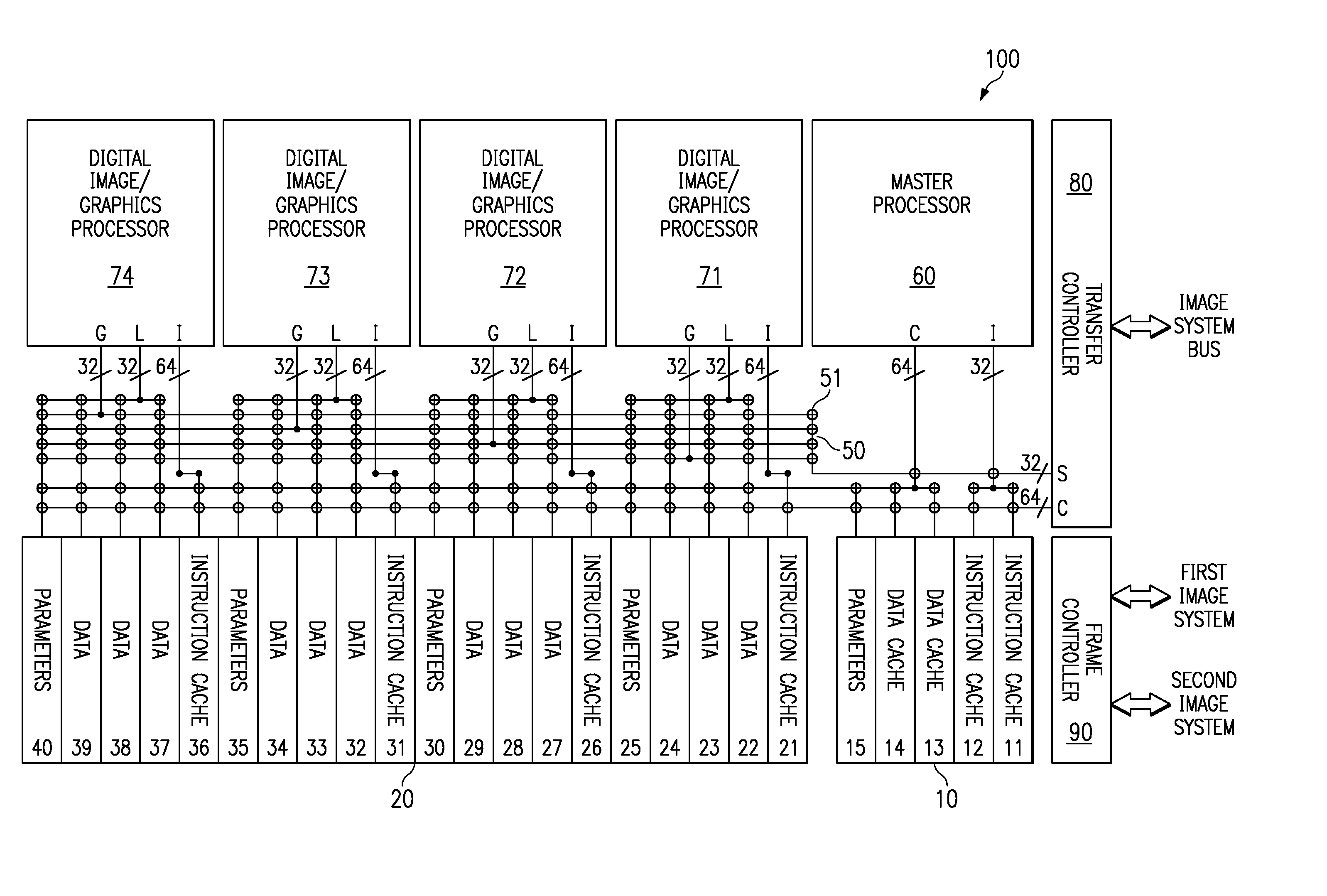
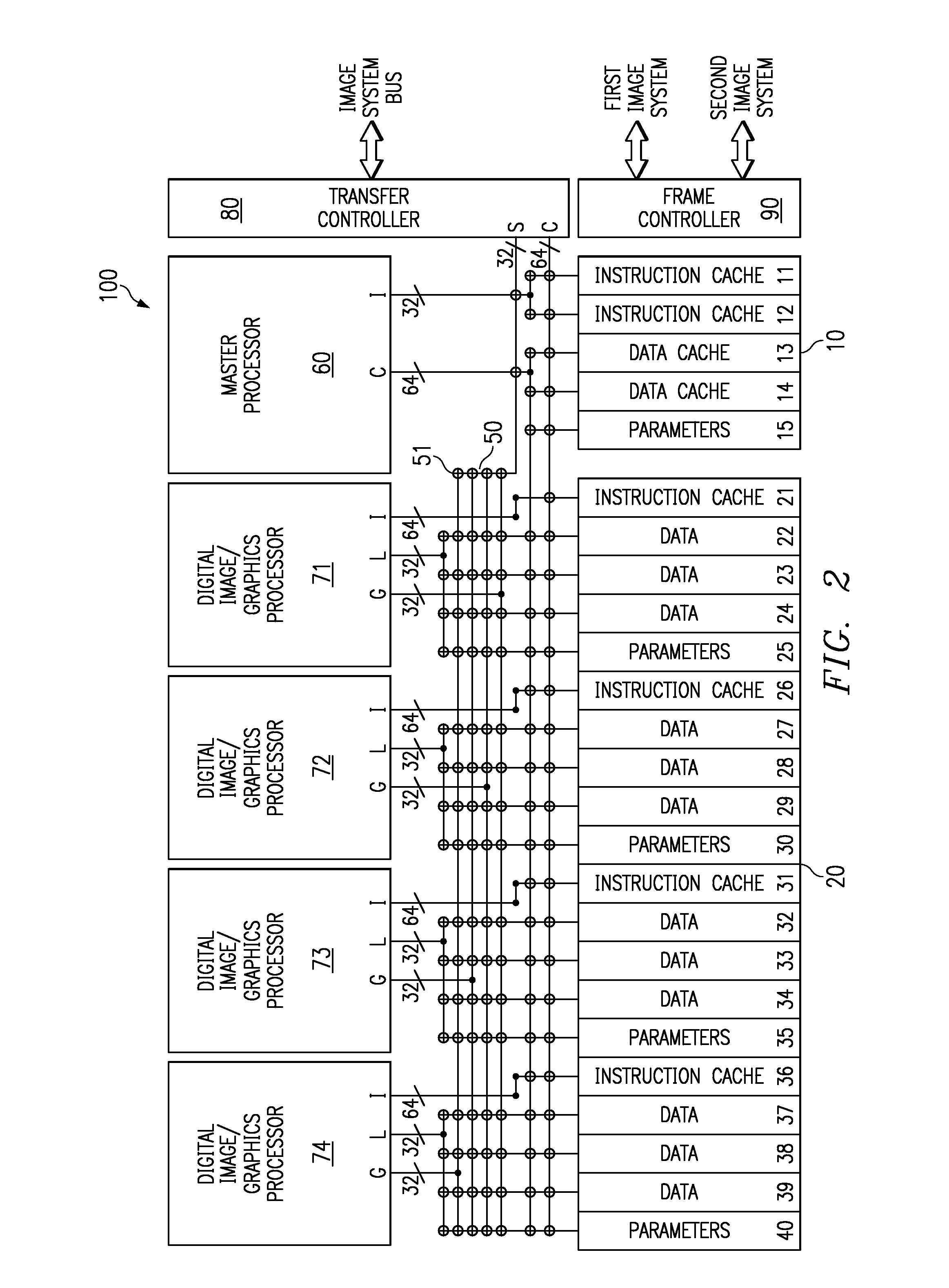
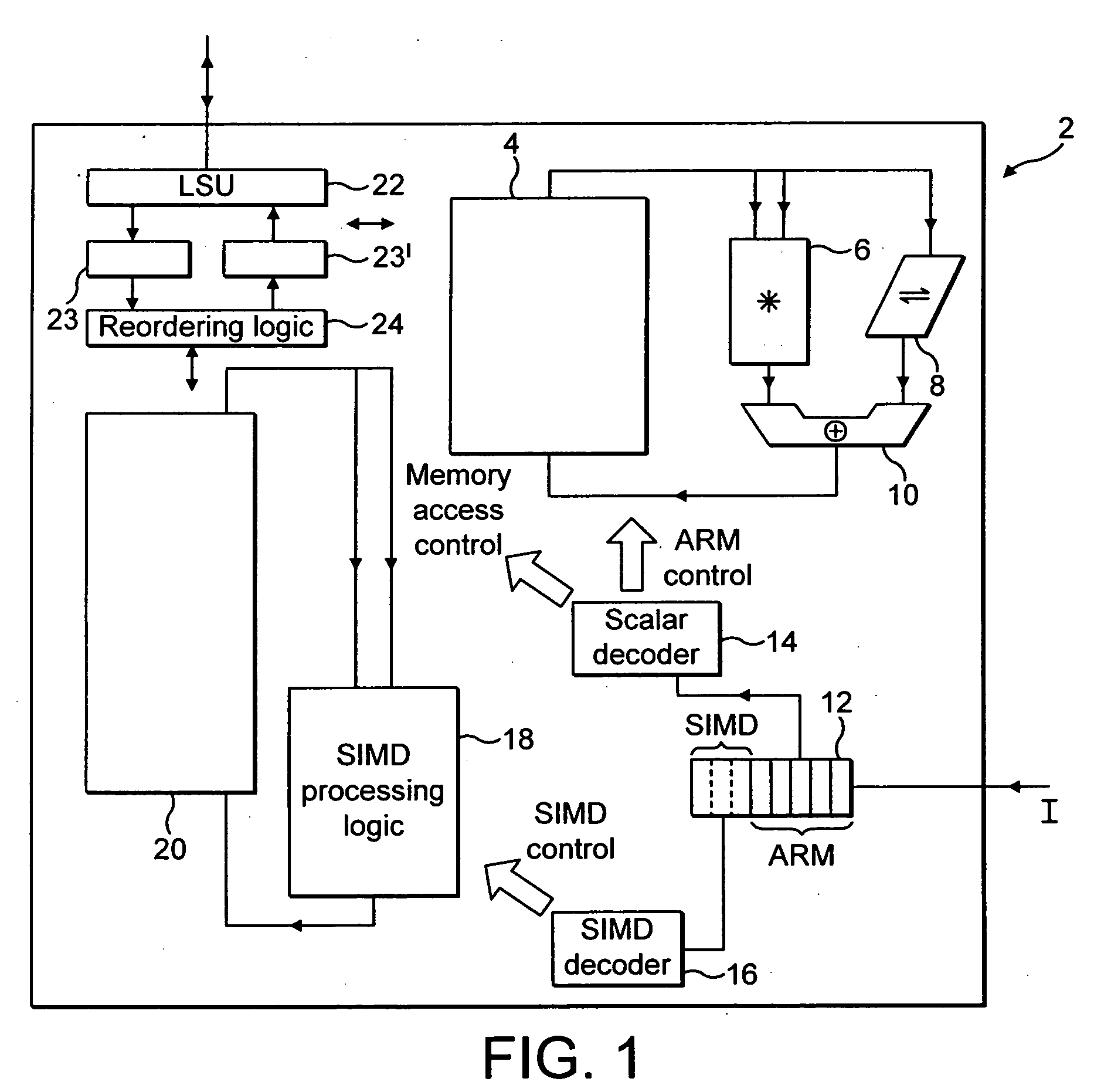
This invention is a data processing apparatus which operates on instruction controlling plural processor actions. Each instruction includes a data unit section and a data transfer section. These instruction sections are independent and may include differing options. In the preferred embodiment, each instruction is 64 bits. The data unit section includes a data operation field that indicates the type of arithmetic logic unit operation and six operand fields. The six operand fields include four source data register fields and two destination register fields. The data unit (110) includes a multiplication unit (220) and an arithmetic logic unit (230). The data unit (110) may include a barrel rotator (235) for one input of the arithmetic logic unit (230). The rotated data may be stored in the first destination register instead of the multiply result. The address unit (120) operations according to the data transfer operation field. This could be a load, a store or a register to register move. Operations may be conditional based upon conditions stored in a status register (210). The status register (210) is set by a prior output of the arithmetic logic unit (230) and the instruction may specify some of the status bits protect from change. The address unit (120) preferably includes a plurality of base address registers (611), a full adder (615) and a left shifter (614). The full adder (615) may add an index as scaled by the left shifter to the base address or subtract the scaled index from the base address. The full adder (615) output may update the base address register (611), either before supply of the address or following supply of the address. The index may be recalled from an index register (612) or an immediate value. In the preferred embodiment of this invention, the data unit (110) including the data registers (200), the multiplication unit (220) and the arithmetic logic unit (230), the address unit (120) and the instruction decode logic (250, 660) are embodied in at least one digital image / graphics processor (71, 72, 73, 74) as a part of a multiprocessor (100) formed in a single integrated circuit used in image processing.
Owner:GUTTAG KARLM +2
Context switch architecture and system
A method and system for performing switch operations utilize non-architectural registers to store context information. Data in a first context register on a peripheral system is accessed (e.g., read or write) until a host computer provides a new index value to an index register on the peripheral system. A context switch occurs, and the context register associated with the new index value is accessed. In some embodiments a system that performs context switching includes a host computer, at least one peripheral system coupled to the host computer, an interface between the host computer and the peripheral system, and a register access circuit coupled to the host computer. The register access circuit is configured to access data in a first or a second register on the peripheral system if the first or a second index value, respectively, is provided by the host computer.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Instruction and logic to provide vector scatter-op and gather-op functionality
ActiveUS20140201498A1Program control using stored programsInstruction analysisMemory addressIndex register
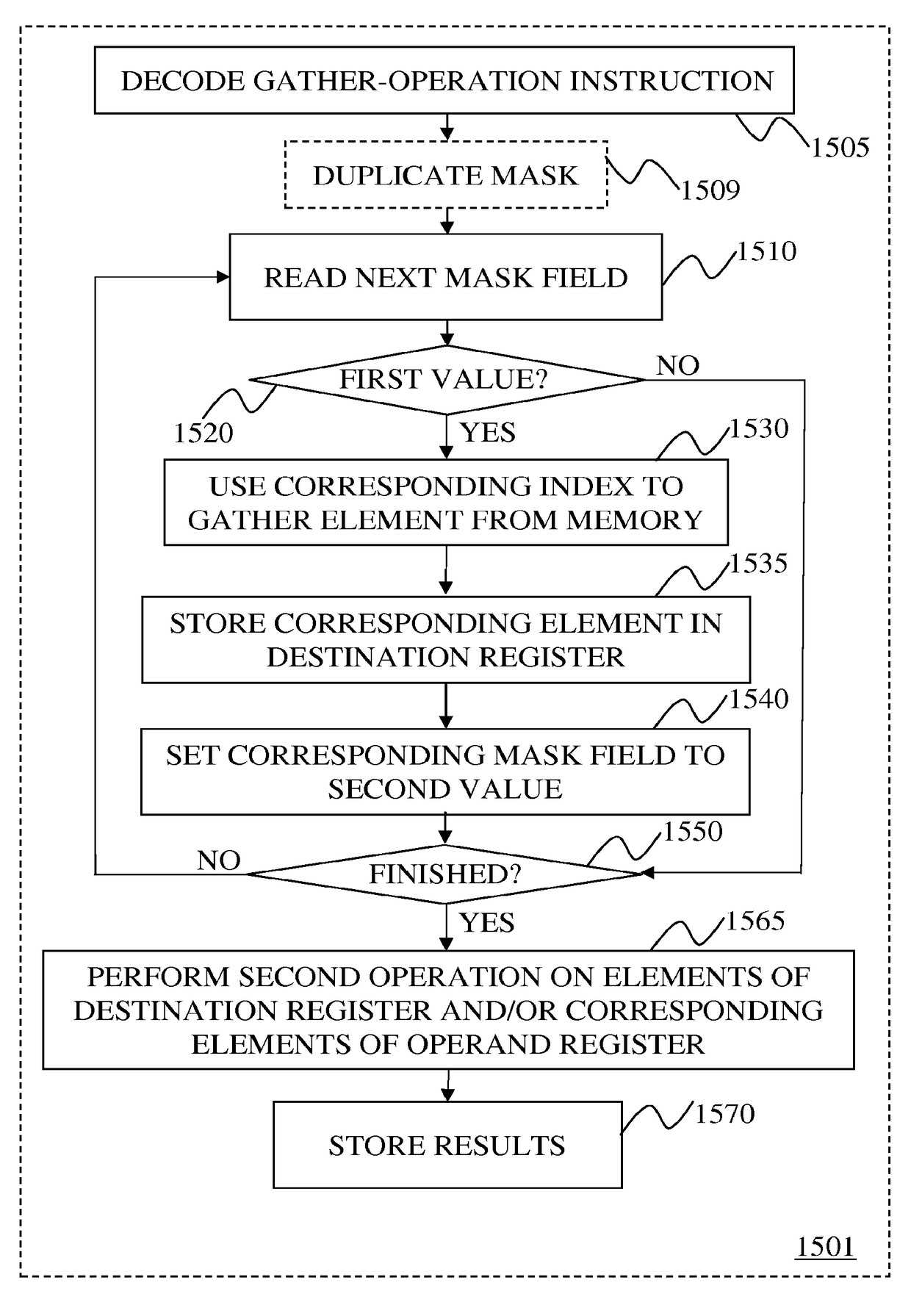
Instructions and logic provide vector scatter-op and / or gather-op functionality. In some embodiments, responsive to an instruction specifying: a gather and a second operation, a destination register, an operand register, and a memory address; execution units read values in a mask register, wherein fields in the mask register correspond to offset indices in the indices register for data elements in memory. A first mask value indicates the element has not been gathered from memory and a second value indicates that the element does not need to be, or has already been gathered. For each having the first value, the data element is gathered from memory into the corresponding destination register location, and the corresponding value in the mask register is changed to the second value. When all mask register fields have the second value, the second operation is performed using corresponding data in the destination and operand registers to generate results.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Table lookup operation within a data processing system
ActiveUS6958718B2Efficient programmingCode conversionGeneral purpose stored program computerData processing systemIndex register
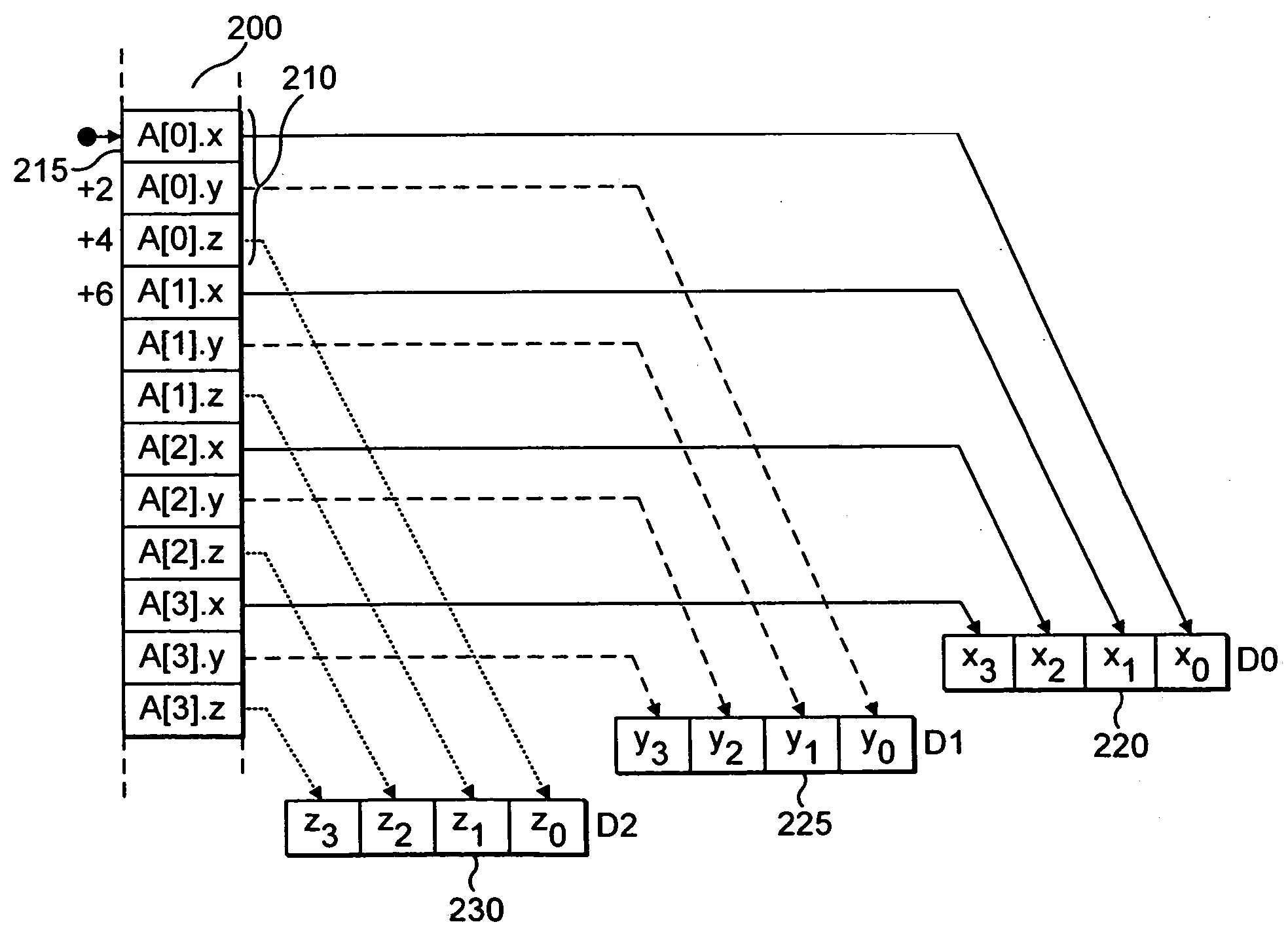
A table lookup extension instruction is provided in which index values stored within an index register D2 are used to select data elements stored within one or more table registers D0, D1 for storage into corresponding positions within a result register D3. Out-of-range index values result in the corresponding locations within the result register being left unchanged U. In this way, an offset can be applied to index values held and then those index values reused with the table registers D0, D1 being reloaded with a different portion of a table so as to give the effect of a larger table than can be directly supported by the number of table registers available.
Owner:ARM LTD
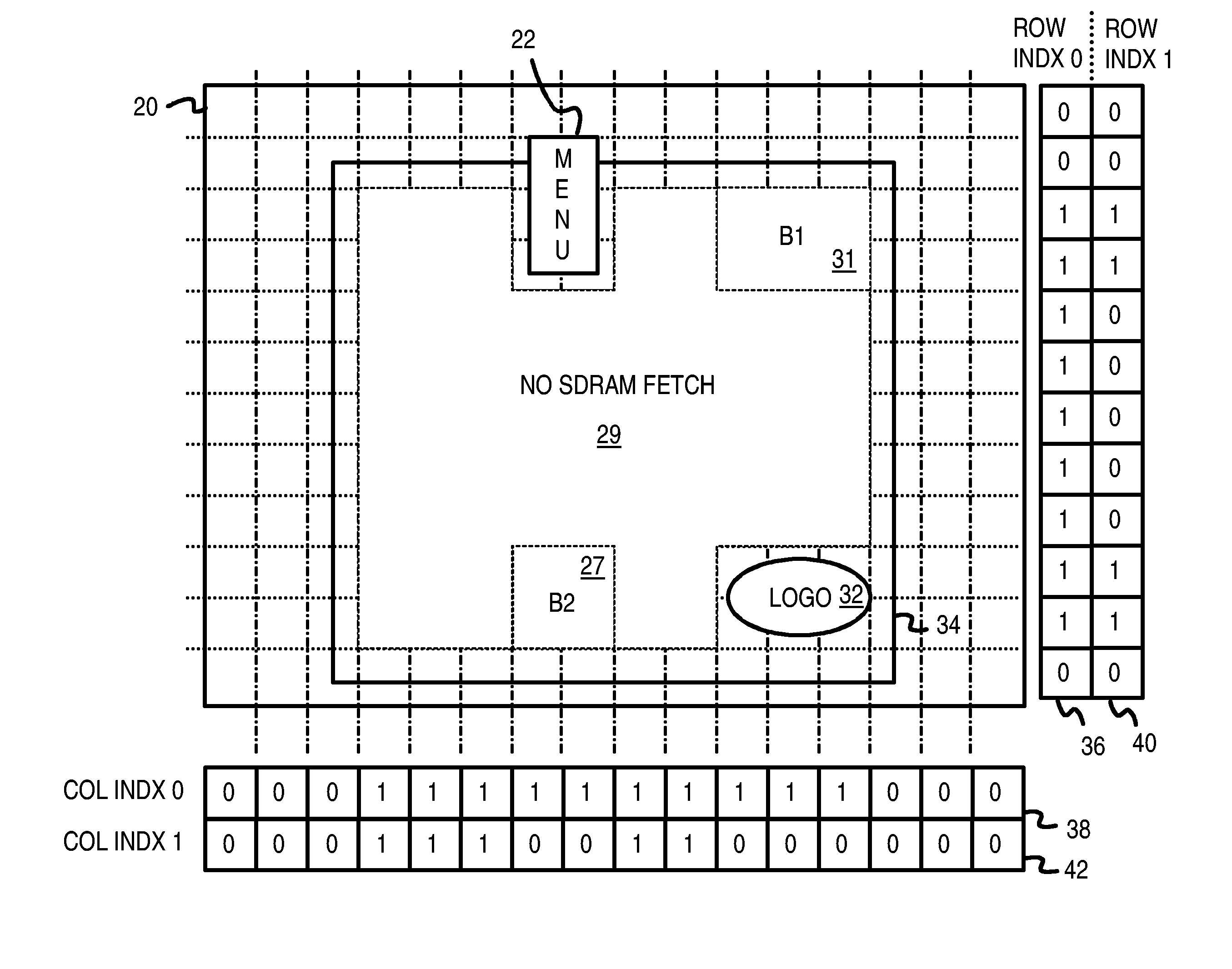
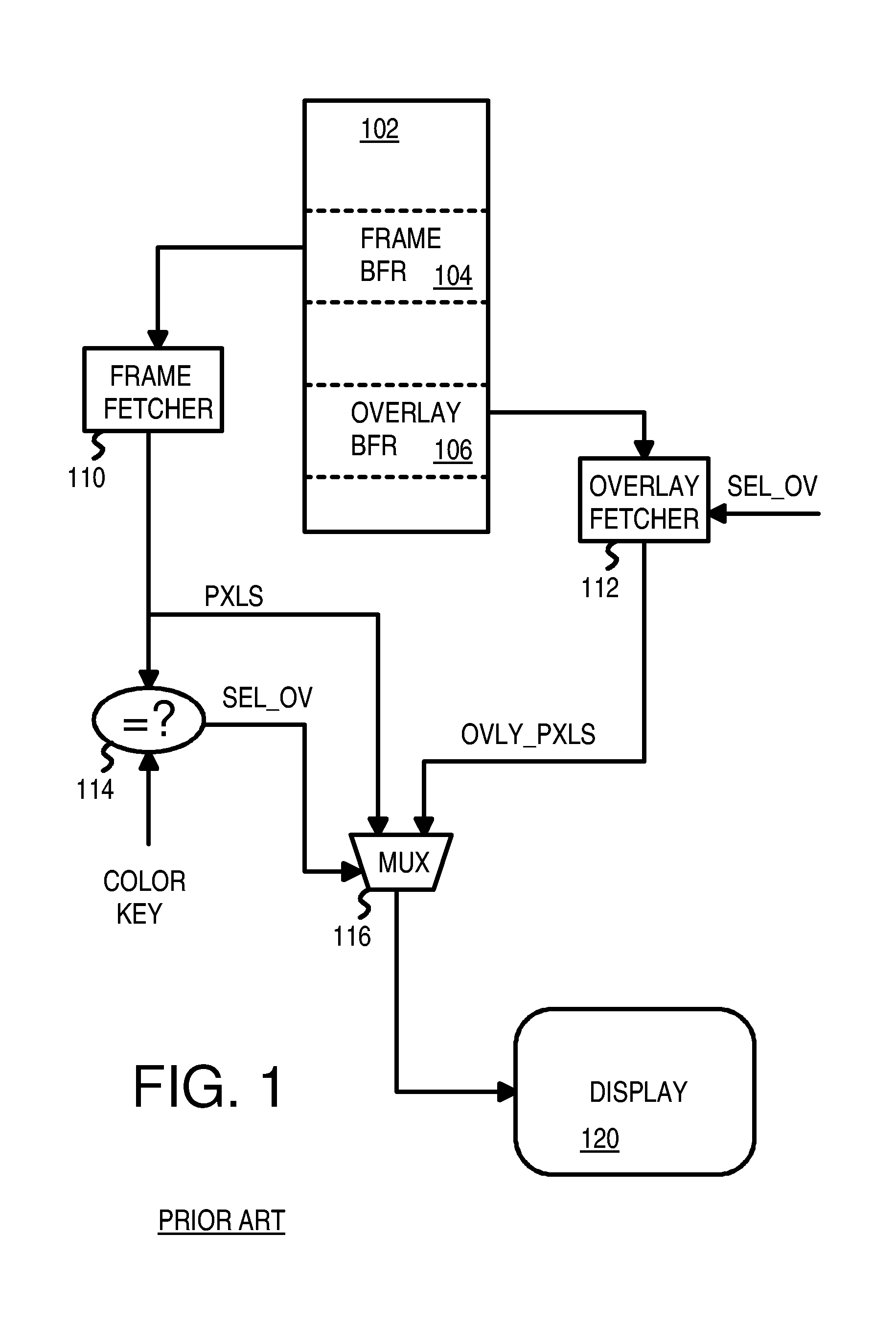
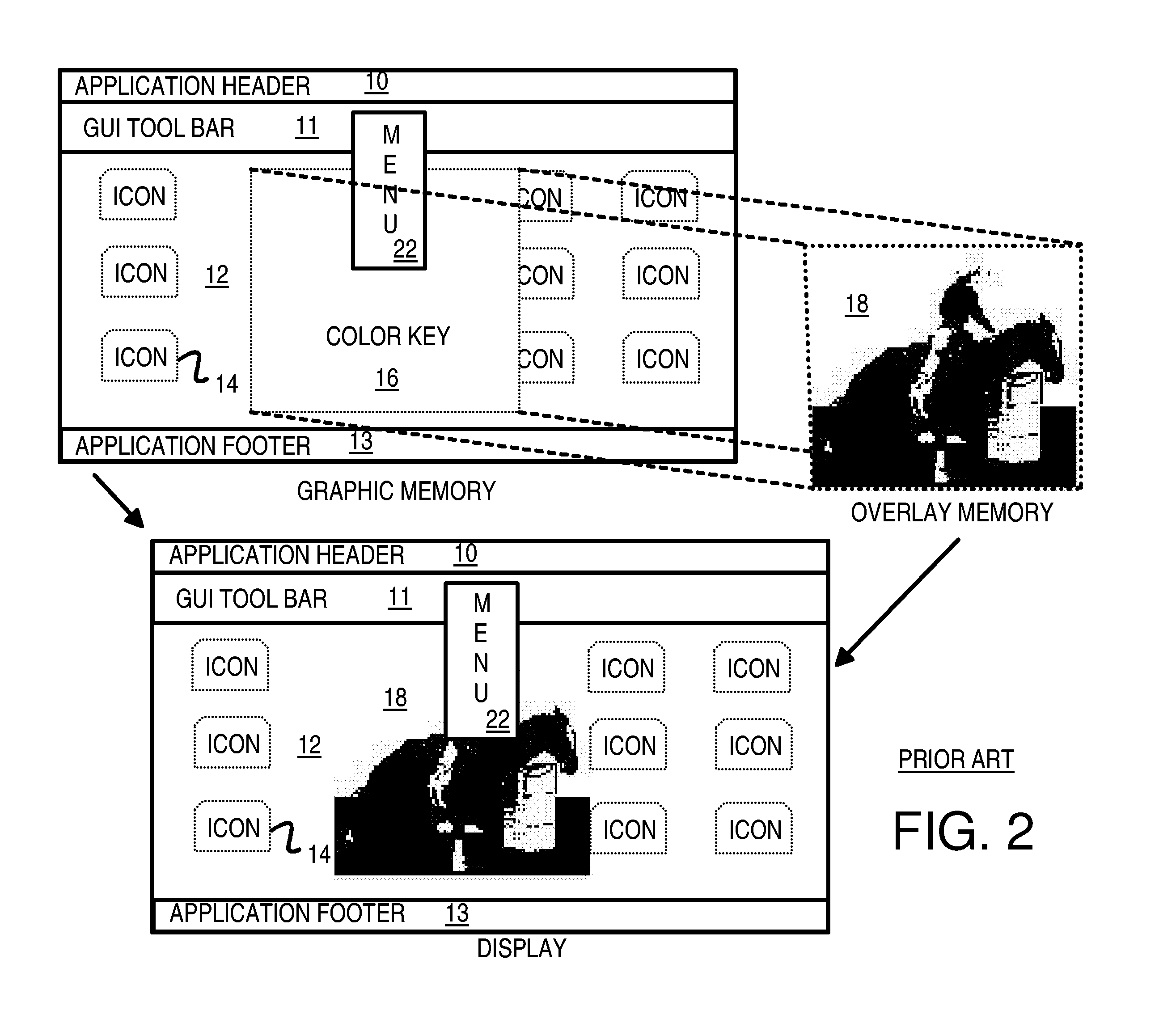
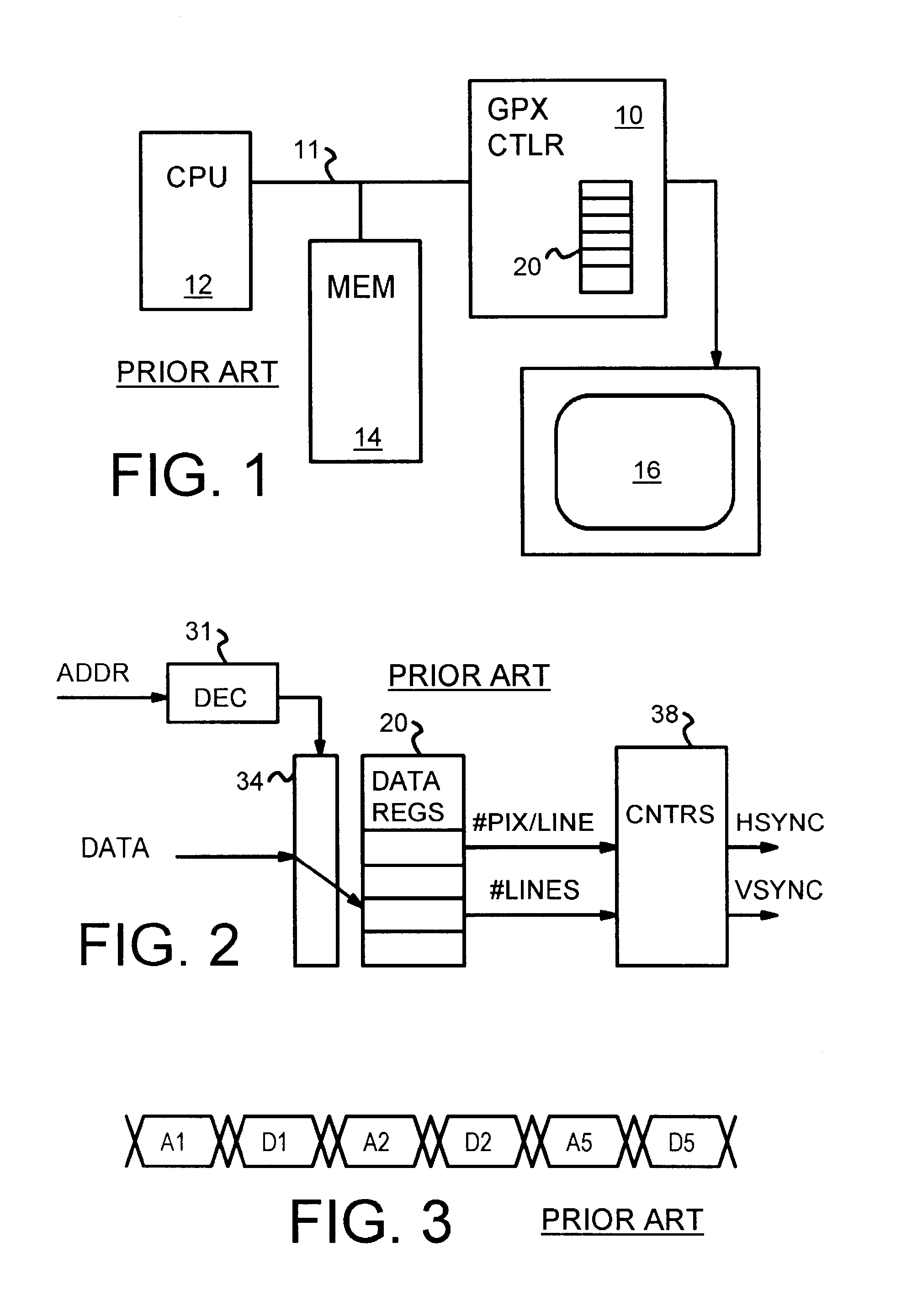
Complex-shaped video overlay using multi-bit row and column index registers
InactiveUS7400328B1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsElectric digital data processingIndex registerGraphic system
A graphics system reduces fetching from memory of color-key pixels when video pixels from a video-overlay window are displayed. A frame buffer is divided into multi-line, multi-pixel blocks that are arranged in block-rows and block-columns. Each block-row has primary and secondary row indicator bits and each block-column has two column indicator bits. When the primary row indicator bit is cleared, all pixels in the block-row are fetched from a frame-buffer memory. When the primary row indicator is set, a secondary row indicator bit selects either first or second column indicator bits for reading. When the selected column indicator bit for a block-column is set, fetching of pixels from the frame buffer memory is skipped. Instead, dummy color-key pixels are generated and inserted into the pixel stream. These dummy pixels match the color key and cause video pixels to be sent to the display. Memory fetching is reduced.
Owner:NEOMAGIC
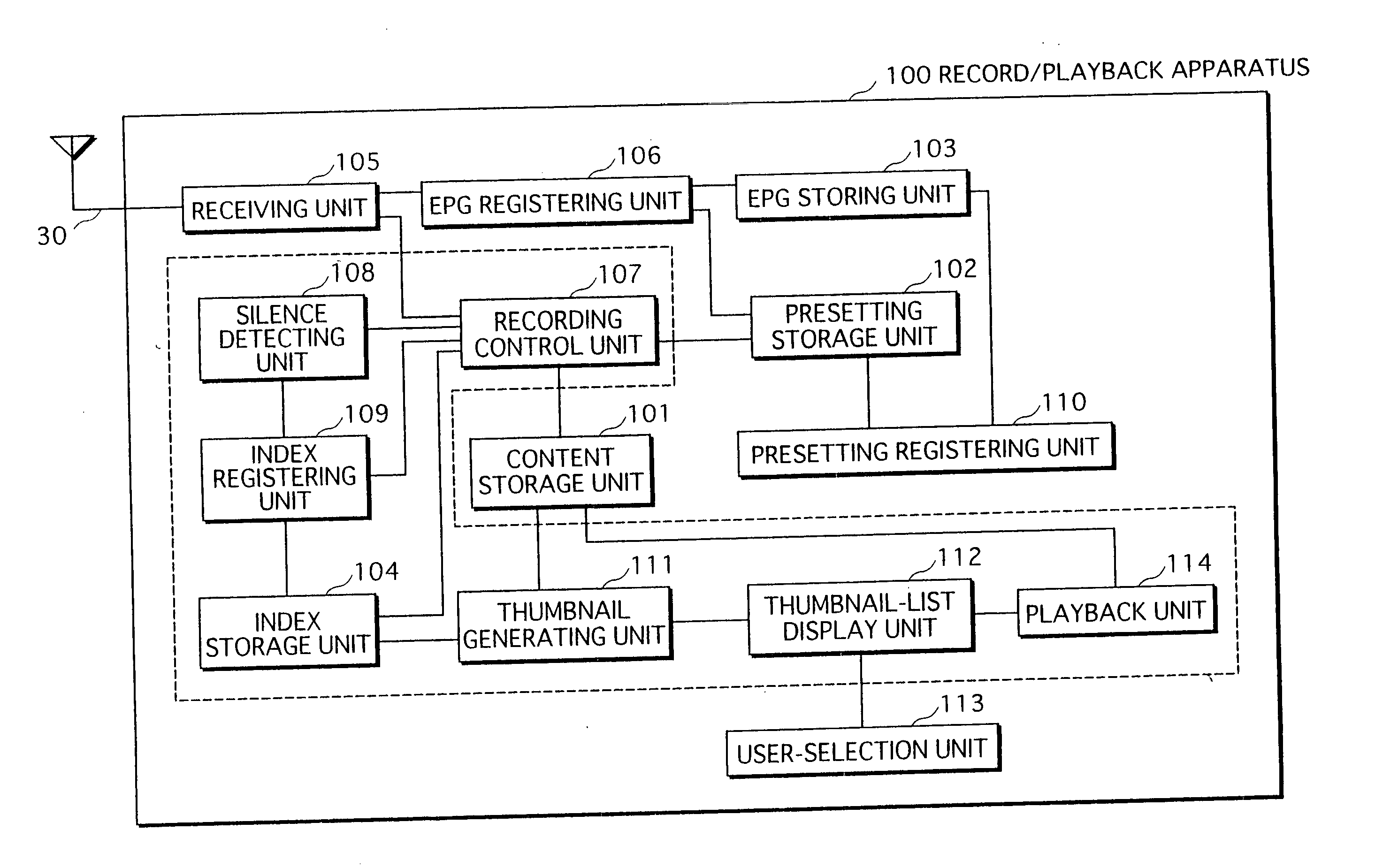
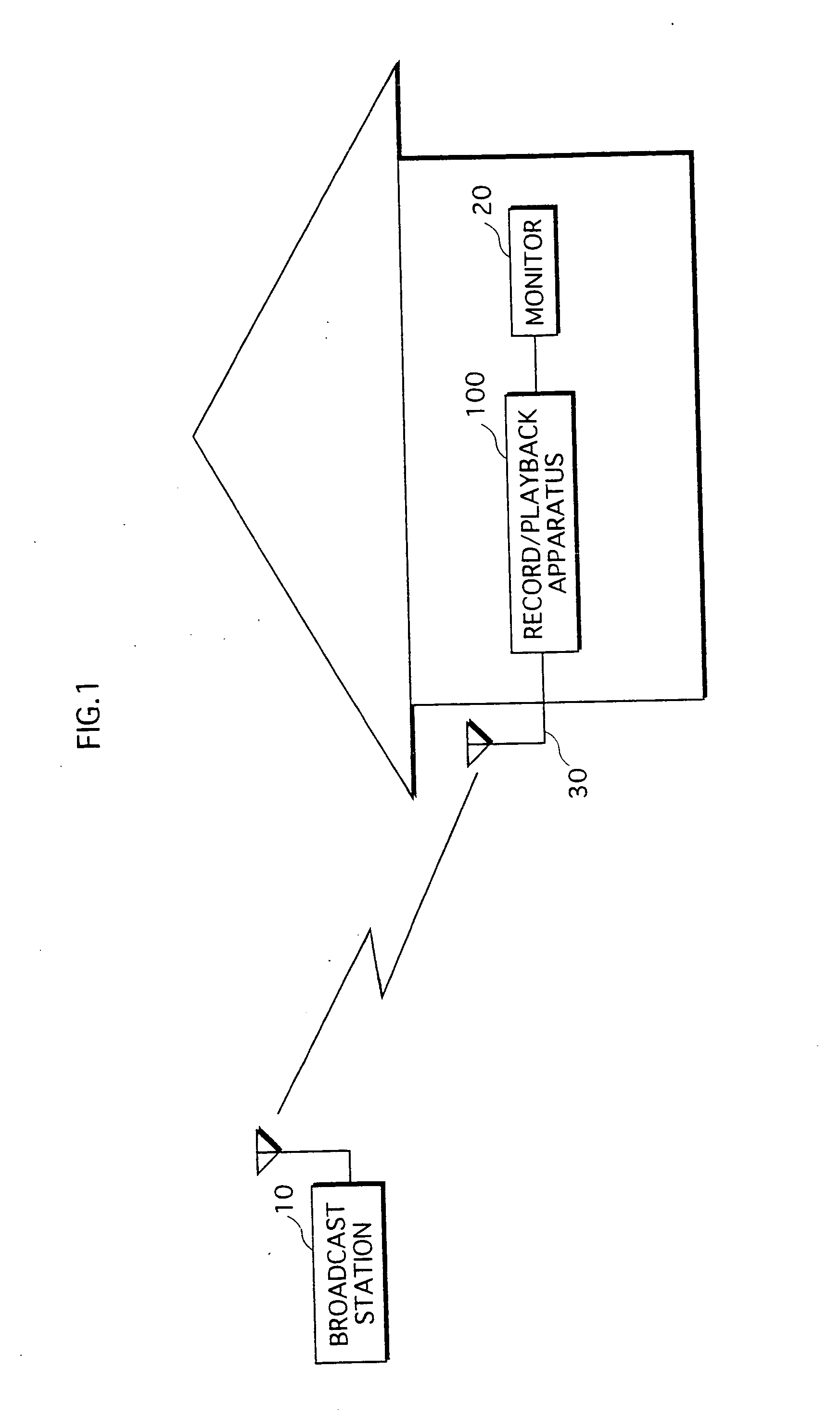
Broadcast program recording apparatus
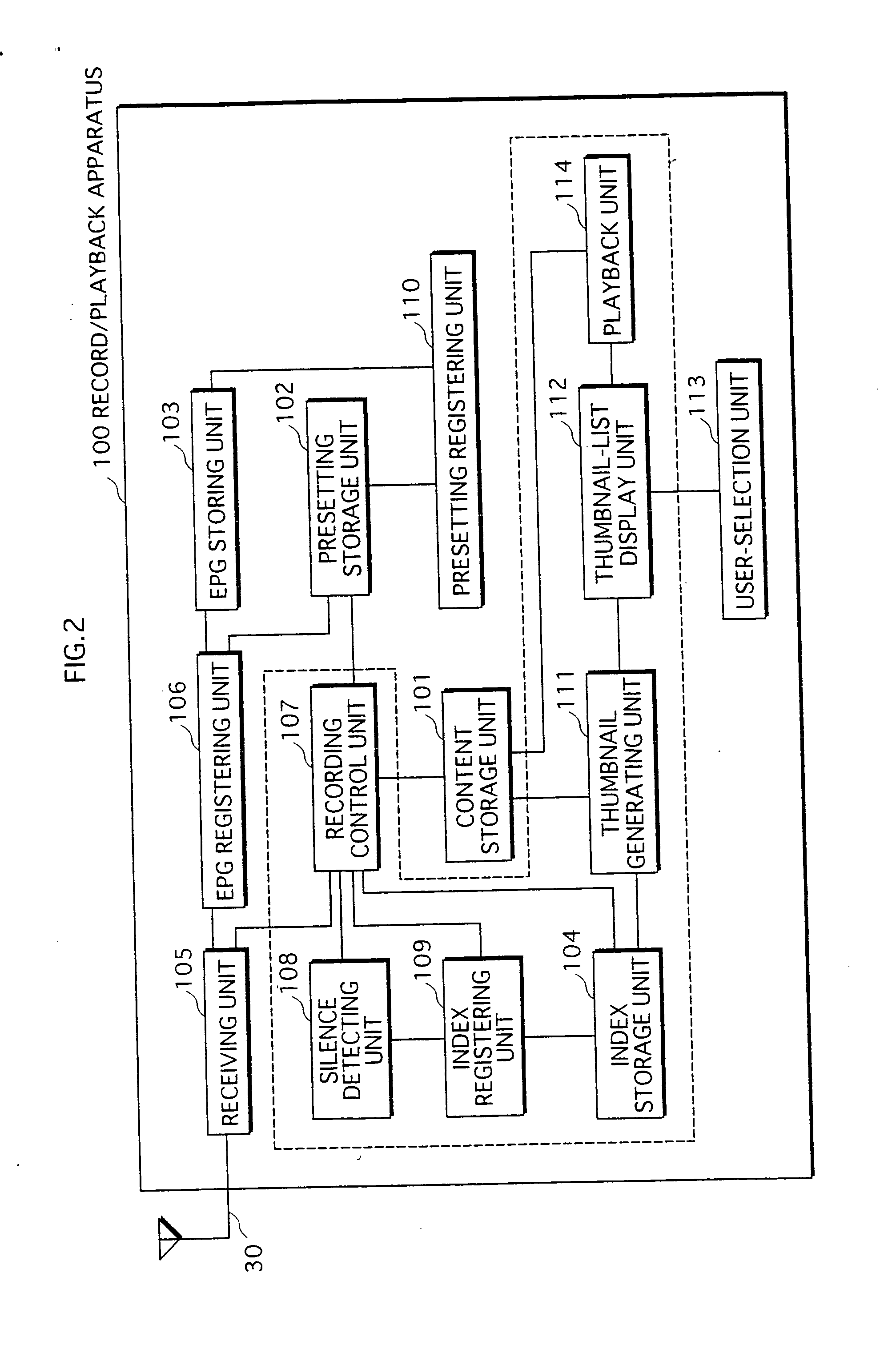
InactiveUS20070183743A1Television system detailsColor television signals processingIndex registerTime segment
A broadcast program recording apparatus locates a start position of a target broadcast program preset to be recorded, even if a program preceding the target broadcast program is broadcast for an extended time period. In a record / playback apparatus 100, a silence detecting unit 108 detects silent frames and calculates a segment period between detected silent frames. An index registering unit 109 judges whether a program broadcast during the segment period is a CM. If judged in the affirmative, the record / playback apparatus 100 adds the segment period to the total CM period. If judged in the negative, it is further judged whether the total CM period exceeds a threshold. On judging that the threshold is exceeded, the record / playback apparatus 100 generates an index entry composed of a content ID and the display time of a silent frame that is broadcast between the CM and a broadcast program, and stores the index entry to the index storage unit 104.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
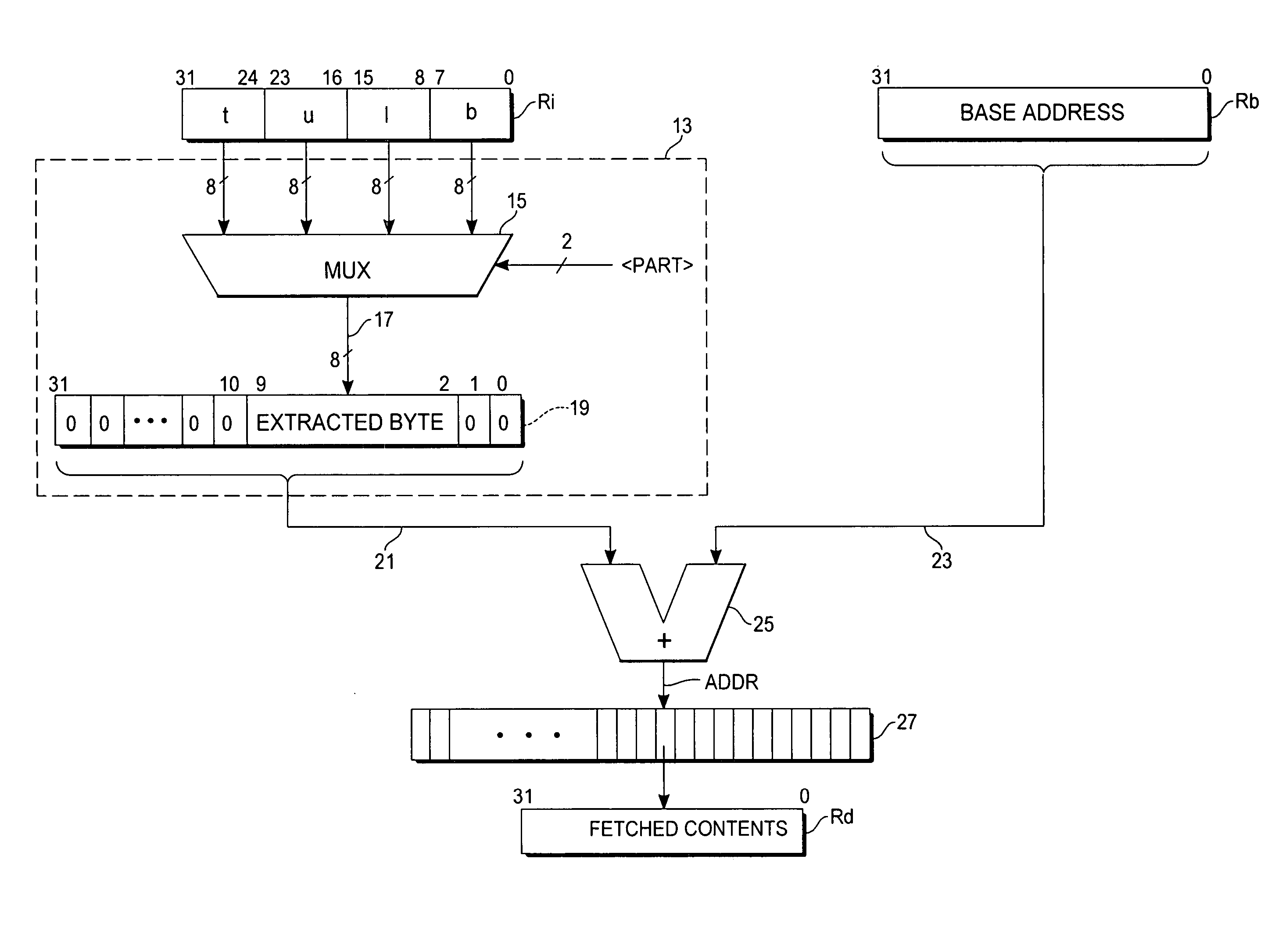
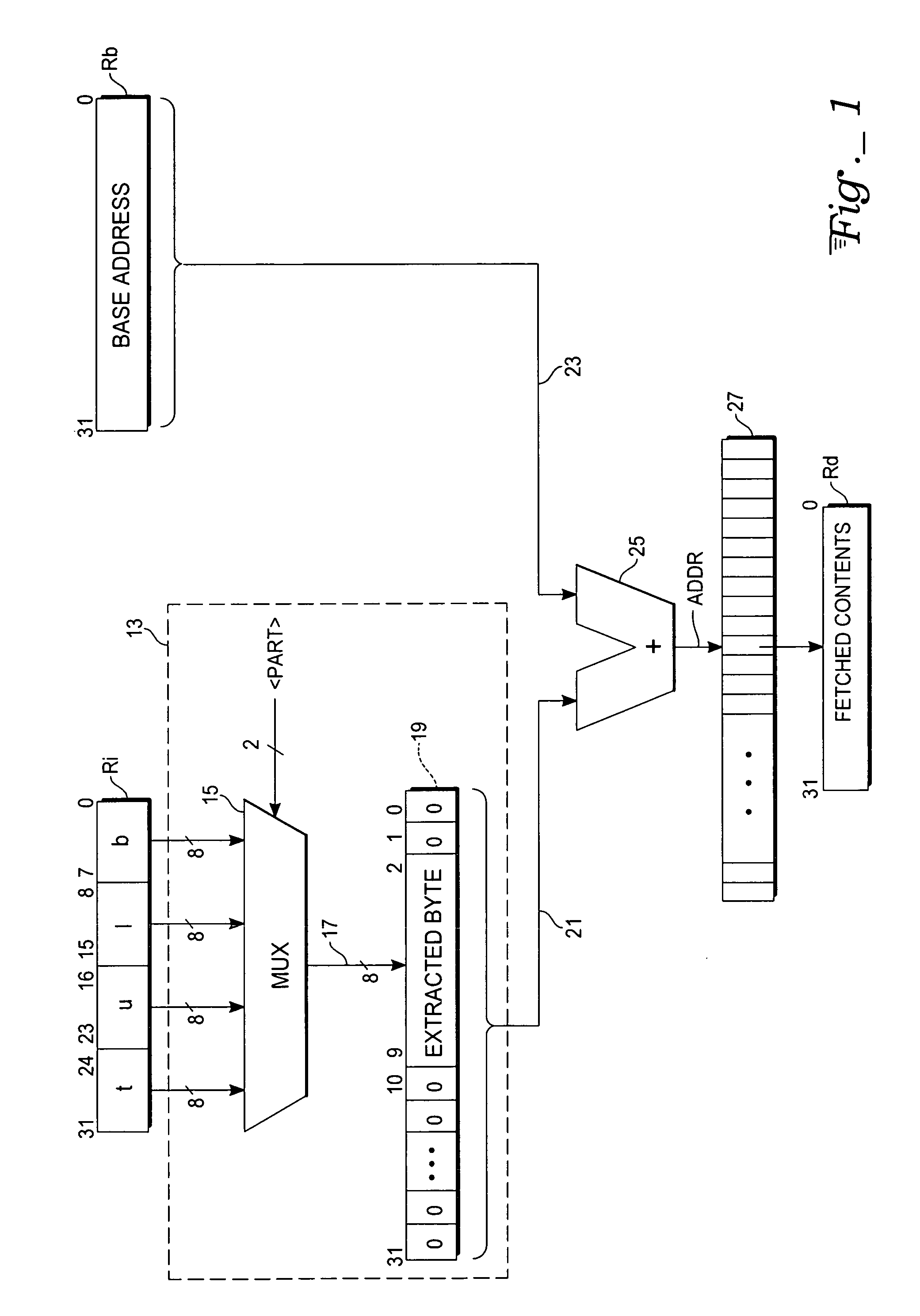
Extracted-index addressing of byte-addressable memories
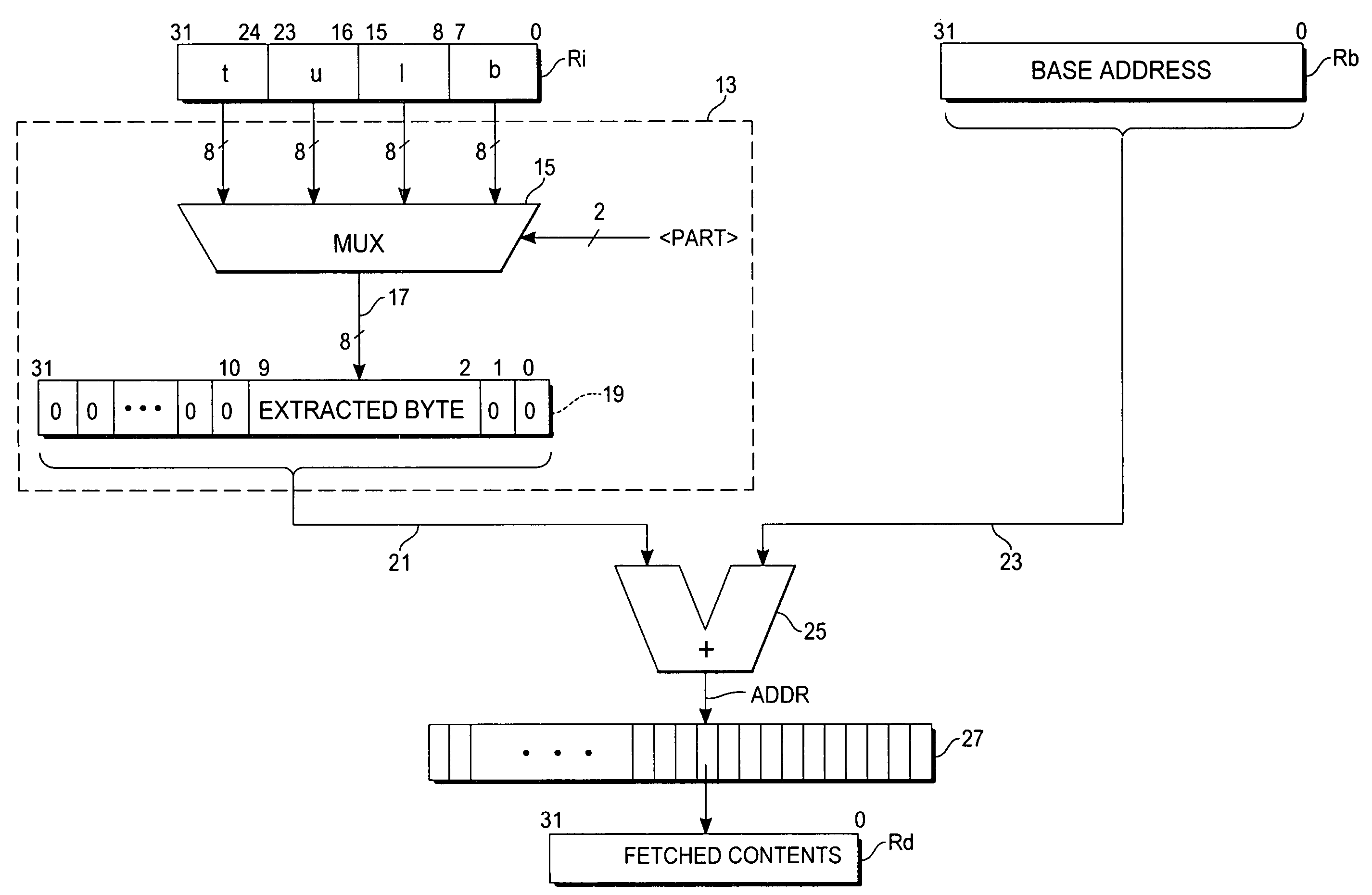
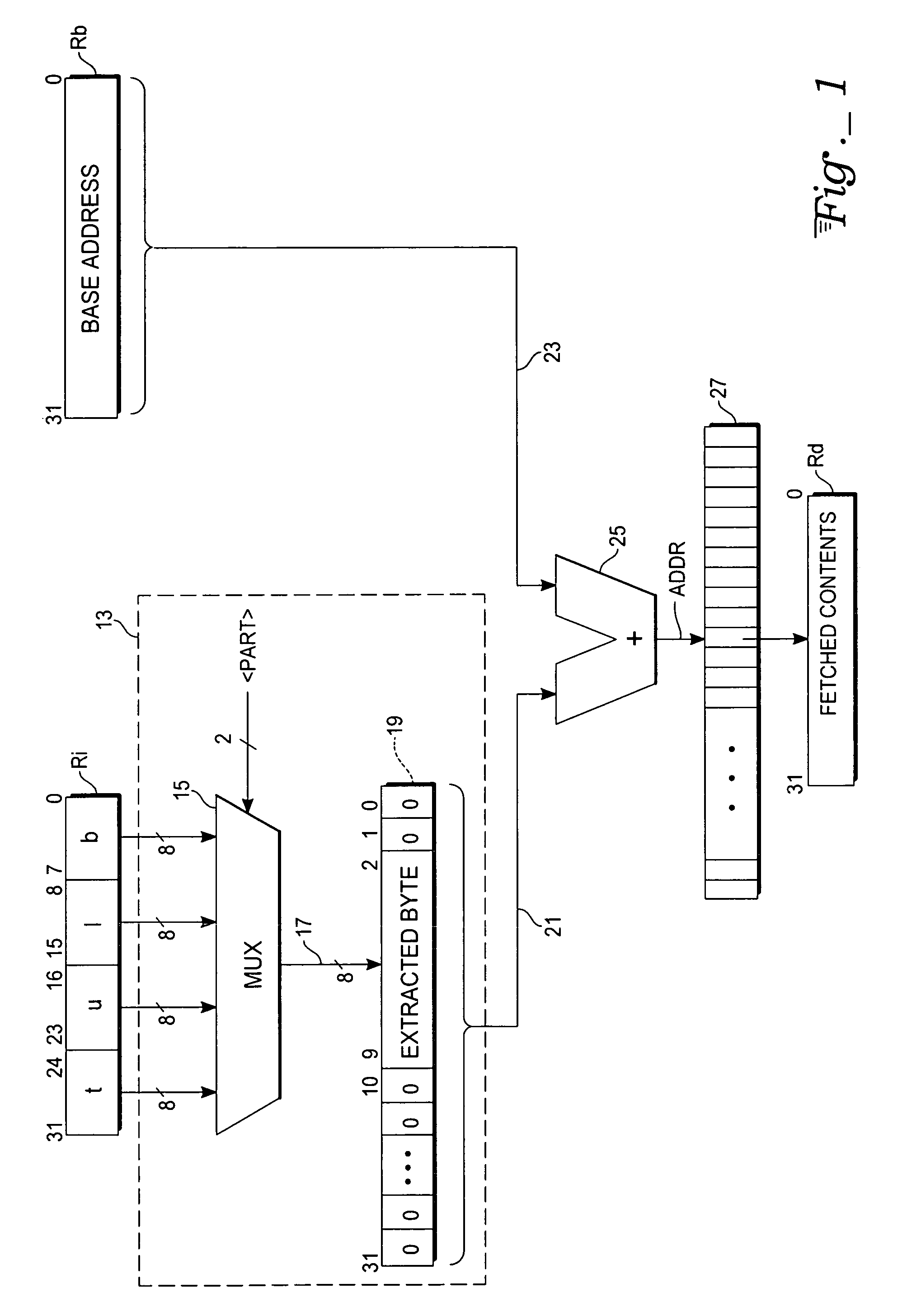
ActiveUS20060271763A1Efficient solutionMemory systemsMicro-instruction address formationIndex registerMultiplexer
A microprocessor circuit useful for indexed addressing of byte-addressable memories includes word-length index, base address, and destination registers designated by an instruction. The instruction also specifies one byte packed within the index register, which is to be extracted. A multiplexer has a word-wide input end accessing all of the bytes of the index register, and responsive to byte selection control passes the specified byte to its output. The extracted byte is provided directly at specific bit positions of a zero-extended address offset word. The offset word is added to the base address, the sum being used to address memory contents that are loaded into the destination register.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Security methodology for devices having plug and play capabilities
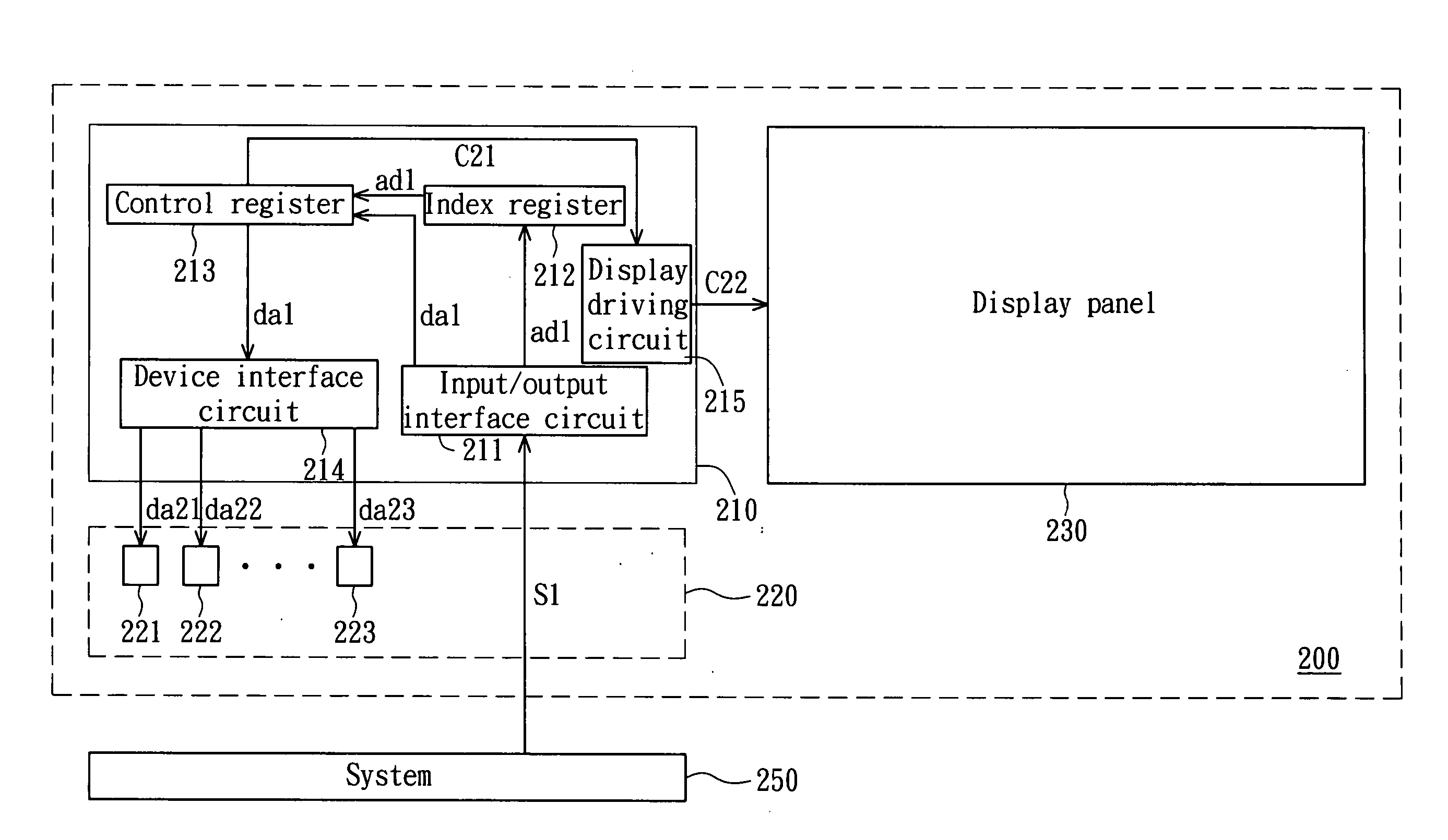
InactiveUS6301665B1Digital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionIndex registerComputerized system
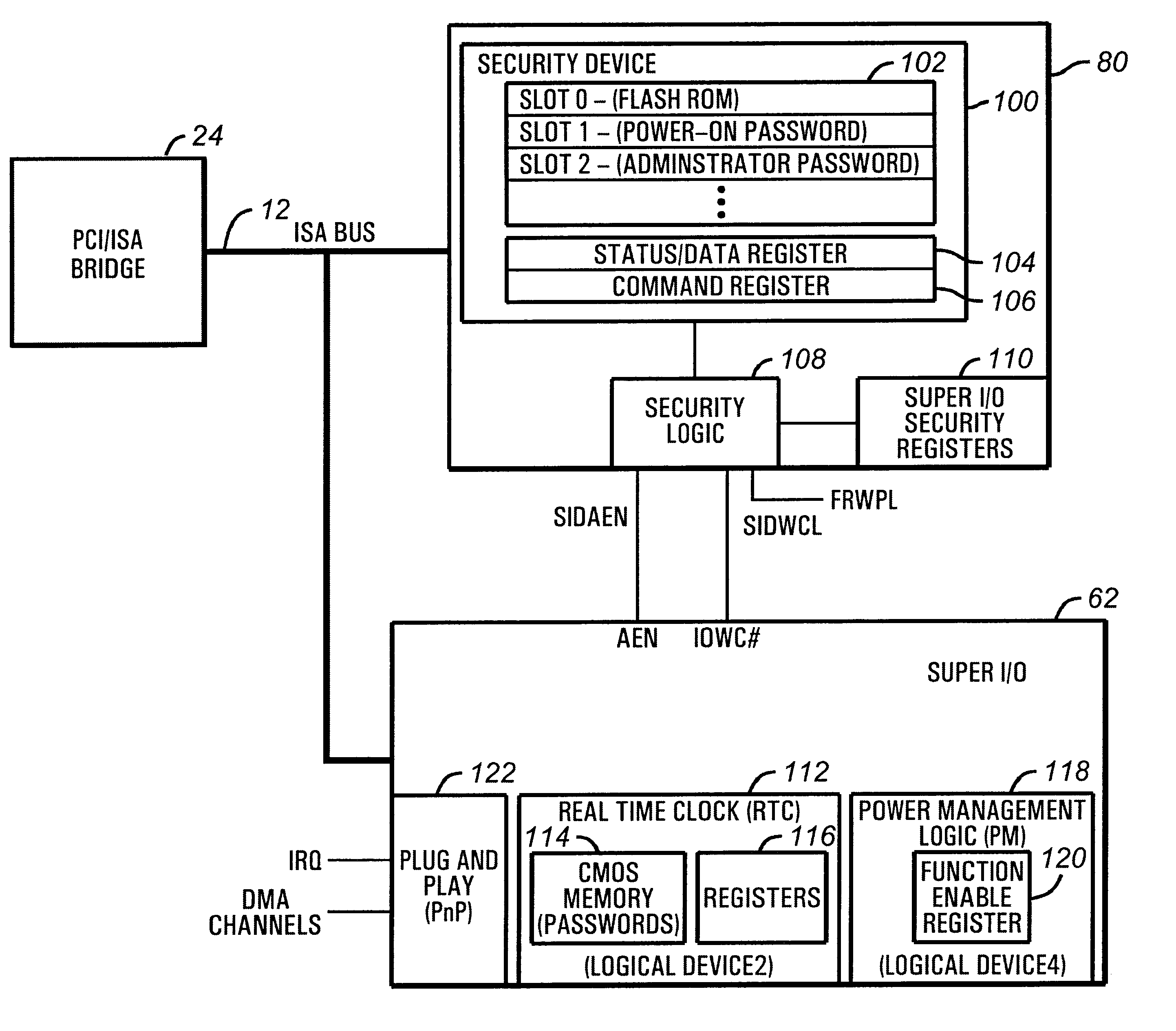
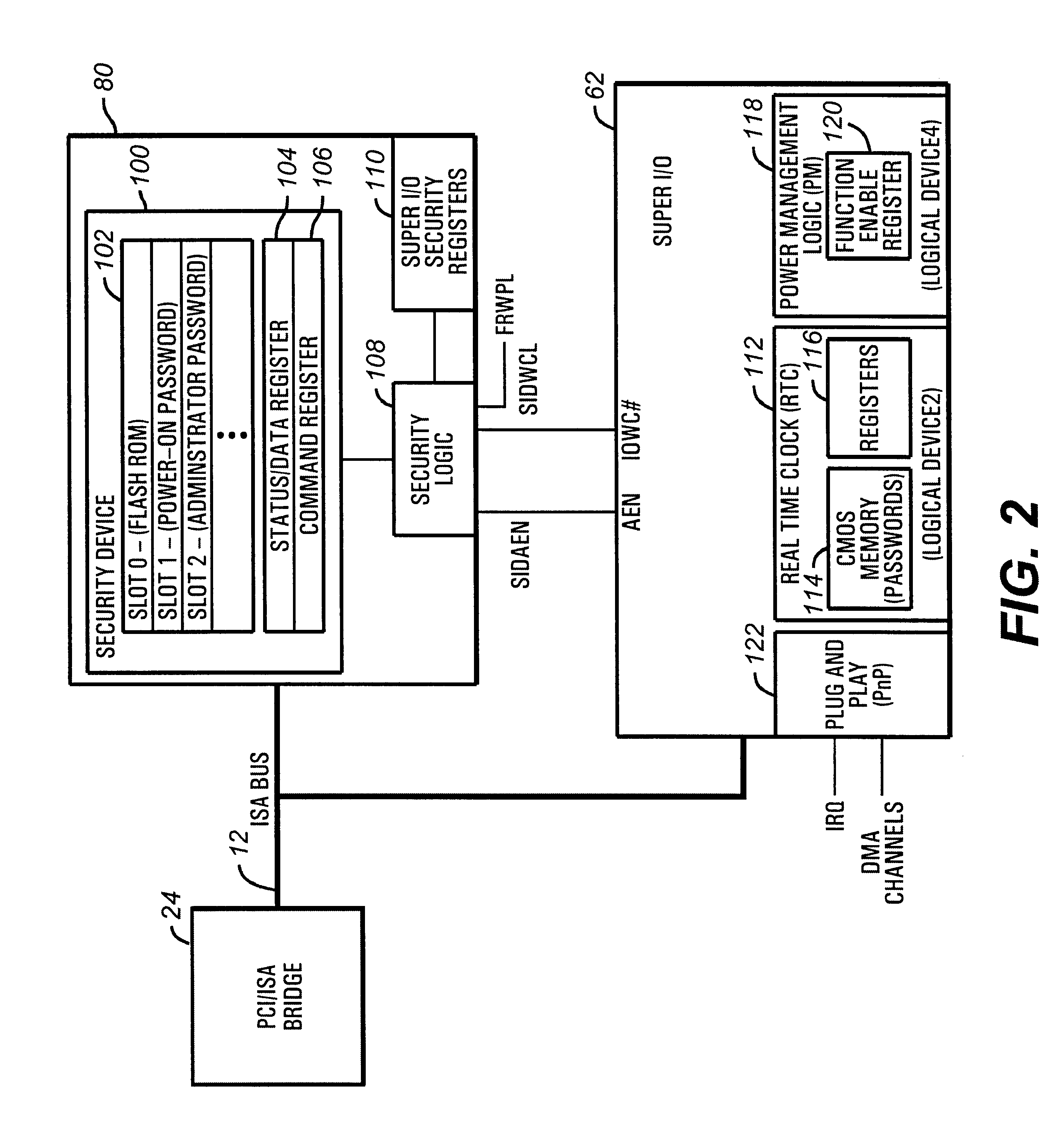
A security methodology and security logic for protecting Plug and Play computer system components from unauthorized access. The security logic prevents modification of the base addresses of specified Plug and Play computer system components by blocking writes to specific index locations programmed into security registers. In the disclosed embodiment of the invention, the base address of a Super I / O chip is protected, as well as the base addresses of specified logical devices in the Super I / O chip. Protecting the base addresses in this manner prevents the security logic from being circumvented by interfering with the address decoding used to track reads and writes to protected index registers. In addition, the security registers are programmed to prevent access to the protected index registers of the logical devices.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Table lookup operation within a data processing system
ActiveUS20050125639A1Efficient programmingCode conversionGeneral purpose stored program computerData processing systemIndex register
A table lookup extension instruction is provided in which index values stored within an index register D2 are used to select data elements stored within one or more table registers D0, D1 for storage into corresponding positions within a result register D3. Out-of-range index values result in the corresponding locations within the result register being left unchanged U. In this way, an offset can be applied to index values held and then those index values reused with the table registers D0, D1 being reloaded with a different portion of a table so as to give the effect of a larger table than can be directly supported by the number of table registers available.
Owner:ARM LTD
Display driver IC and driving method
InactiveUS20060244739A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingIndex registerData signal
Owner:MORGAN STANLEY +1
Hardware circuit for realizing data sequencing and method
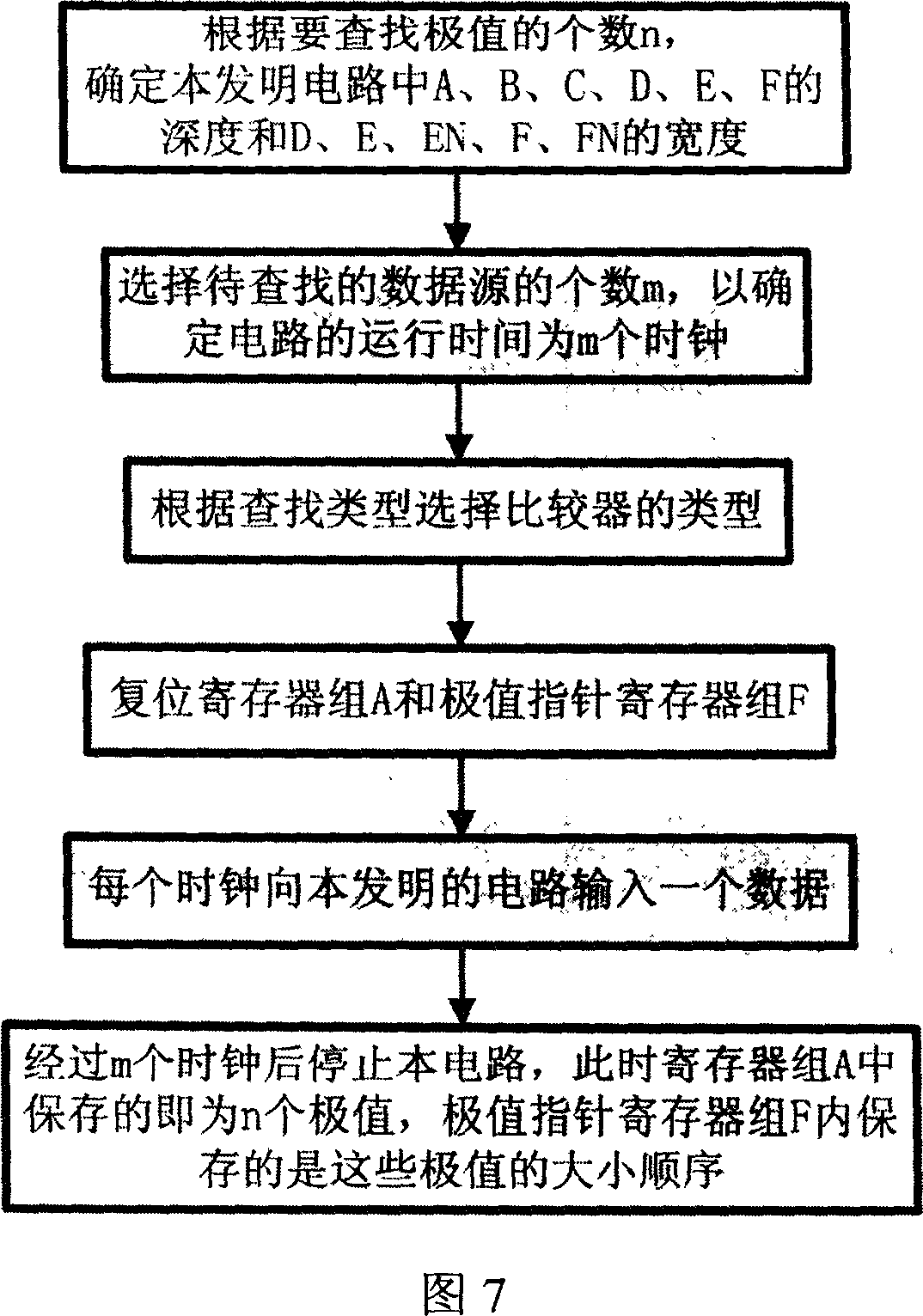
ActiveCN1987771AStrong real-time processingReduce sorting timeHandling data according to predetermined rulesIndex registerTime processing
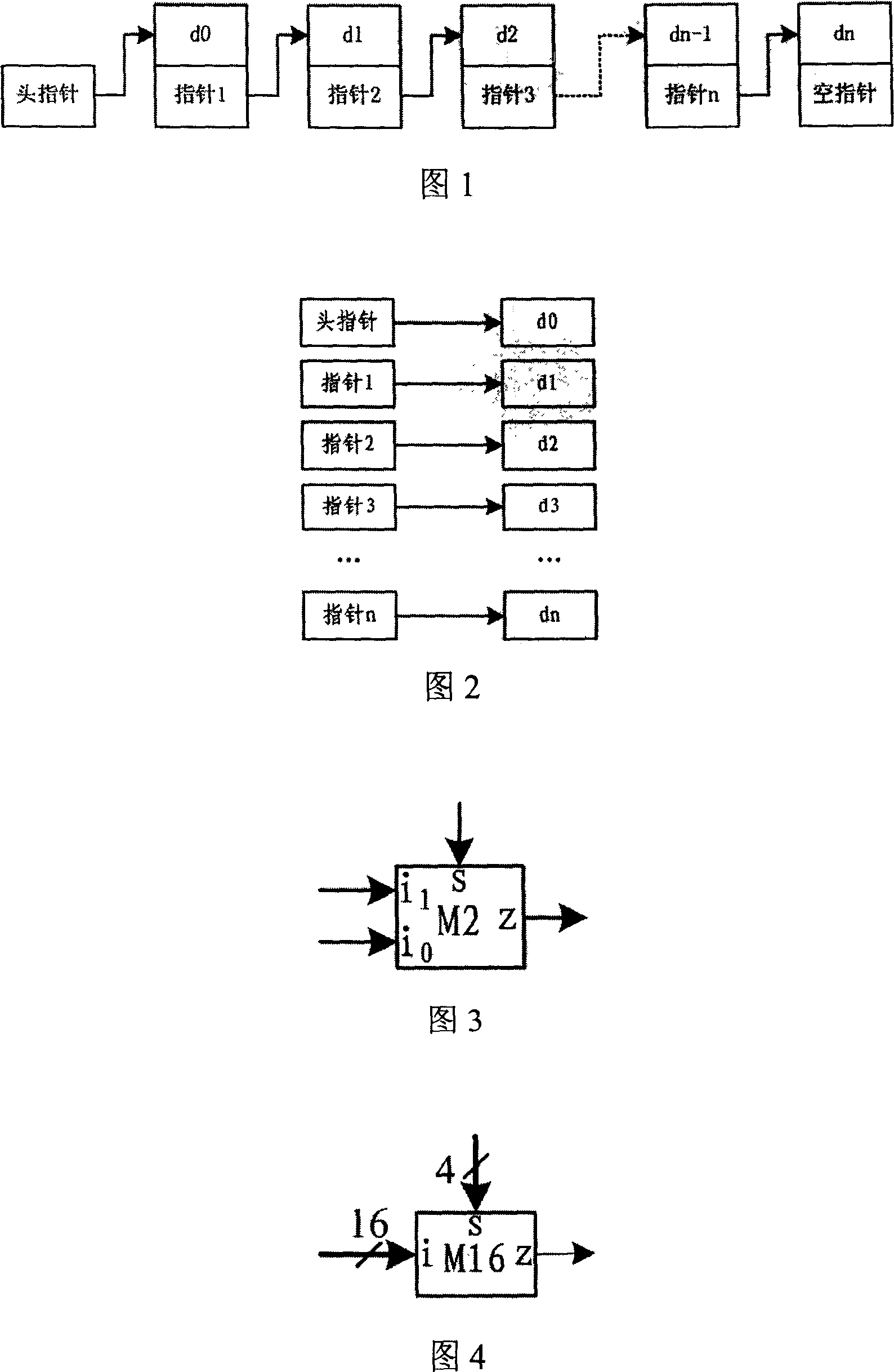
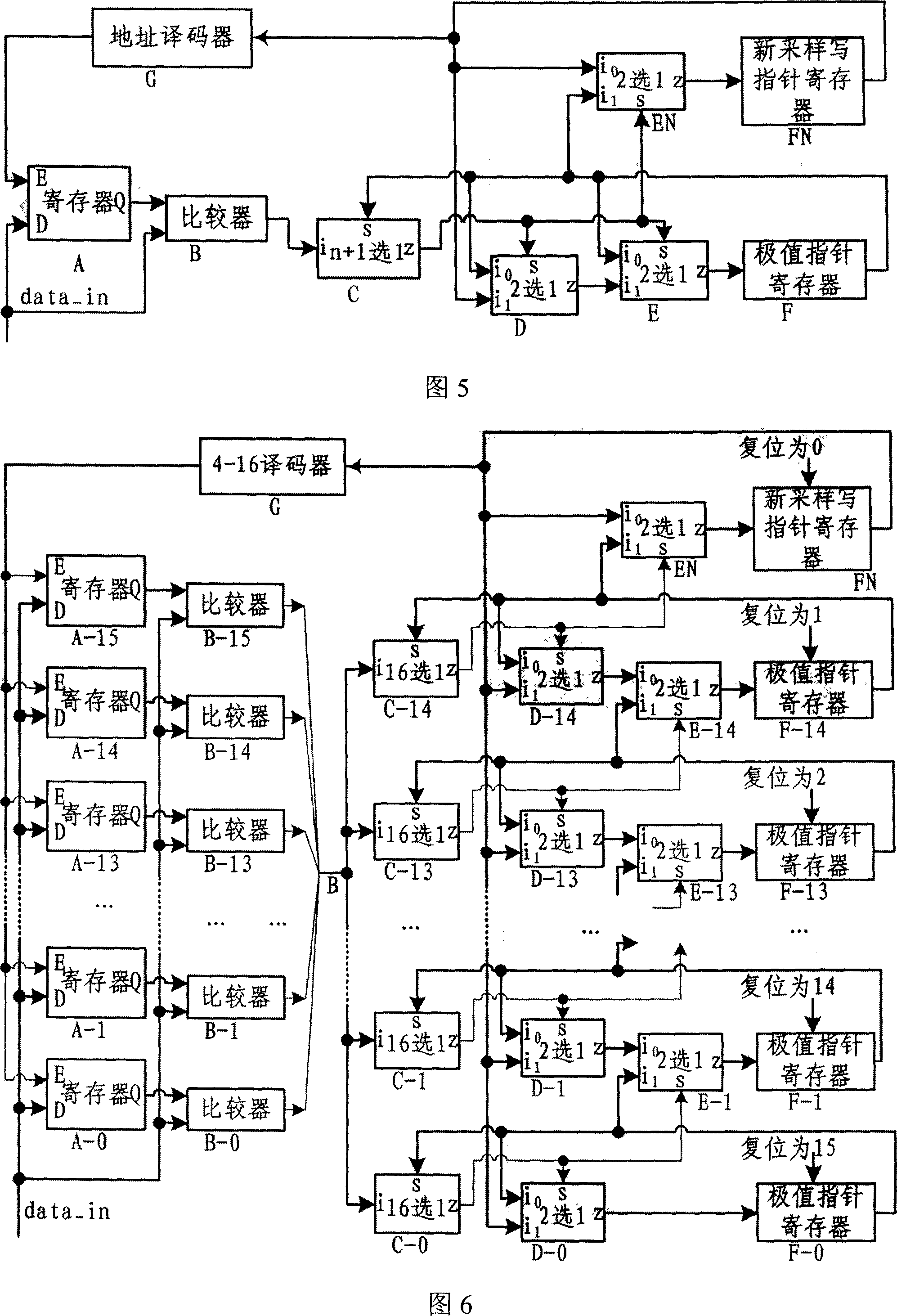
This invention discloses a hardware circuit and method which can realize the sequencing of data. The circuit is used to find n the largest data from m data, m>n, and at the same time realize the sequencing of the n data. It concrete includes a register, a comparator, a multiplex chooser which can choose 1 from n+1, and two multiplex choosers which can choose one from two, and a maximum index register, and a multiplex chooser which can choose one from two, a current sampling index register, an address code converter. The talked method and equipment realize the sequencing of data by the hardware circuit which can process a data each hour, if using many circuits to work, the time of sequencing can reduce large. So the real-time processing of this circuit is strong, it can meet the higher requirement of some situation.
Owner:SANECHIPS TECH CO LTD
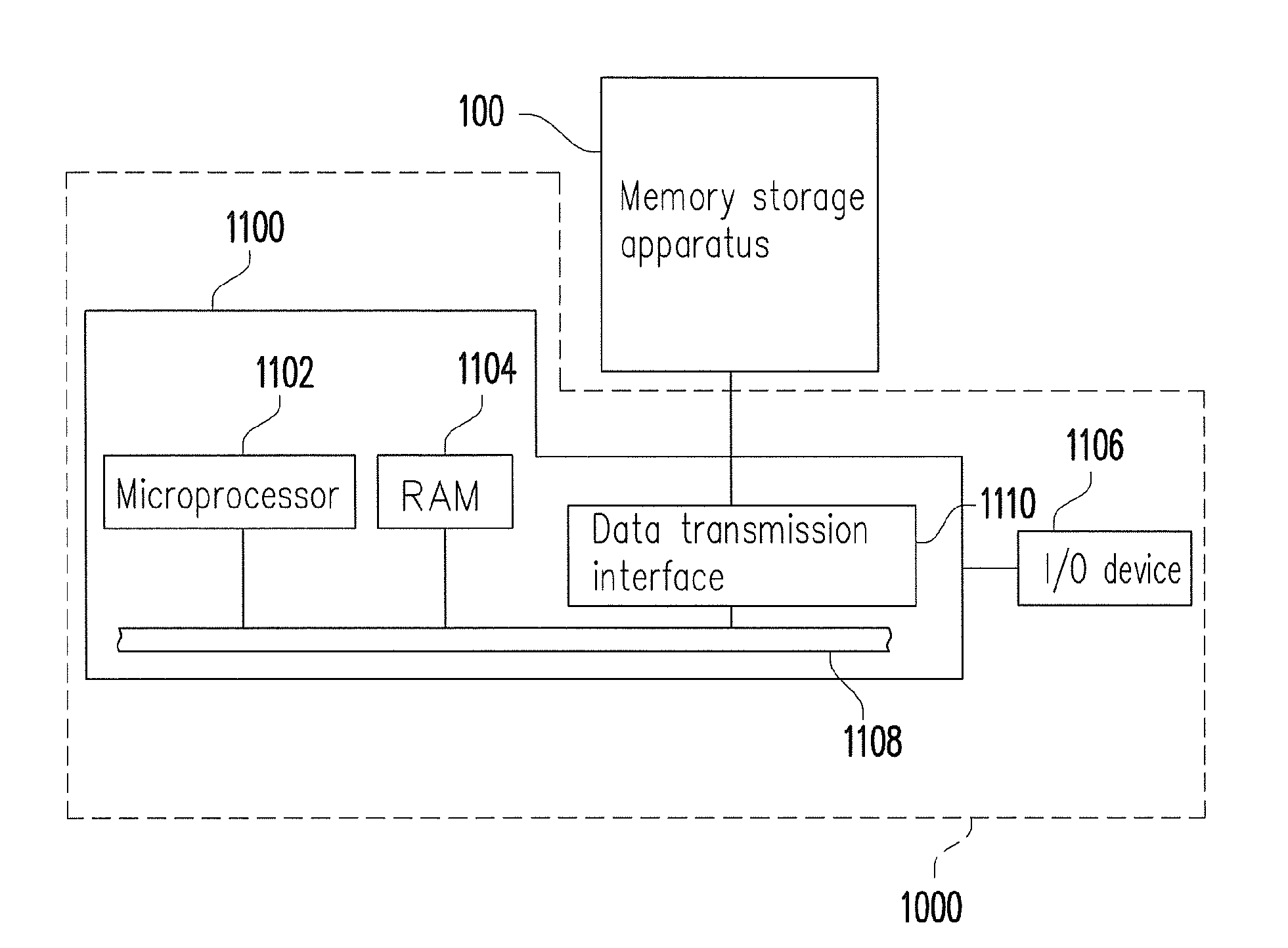
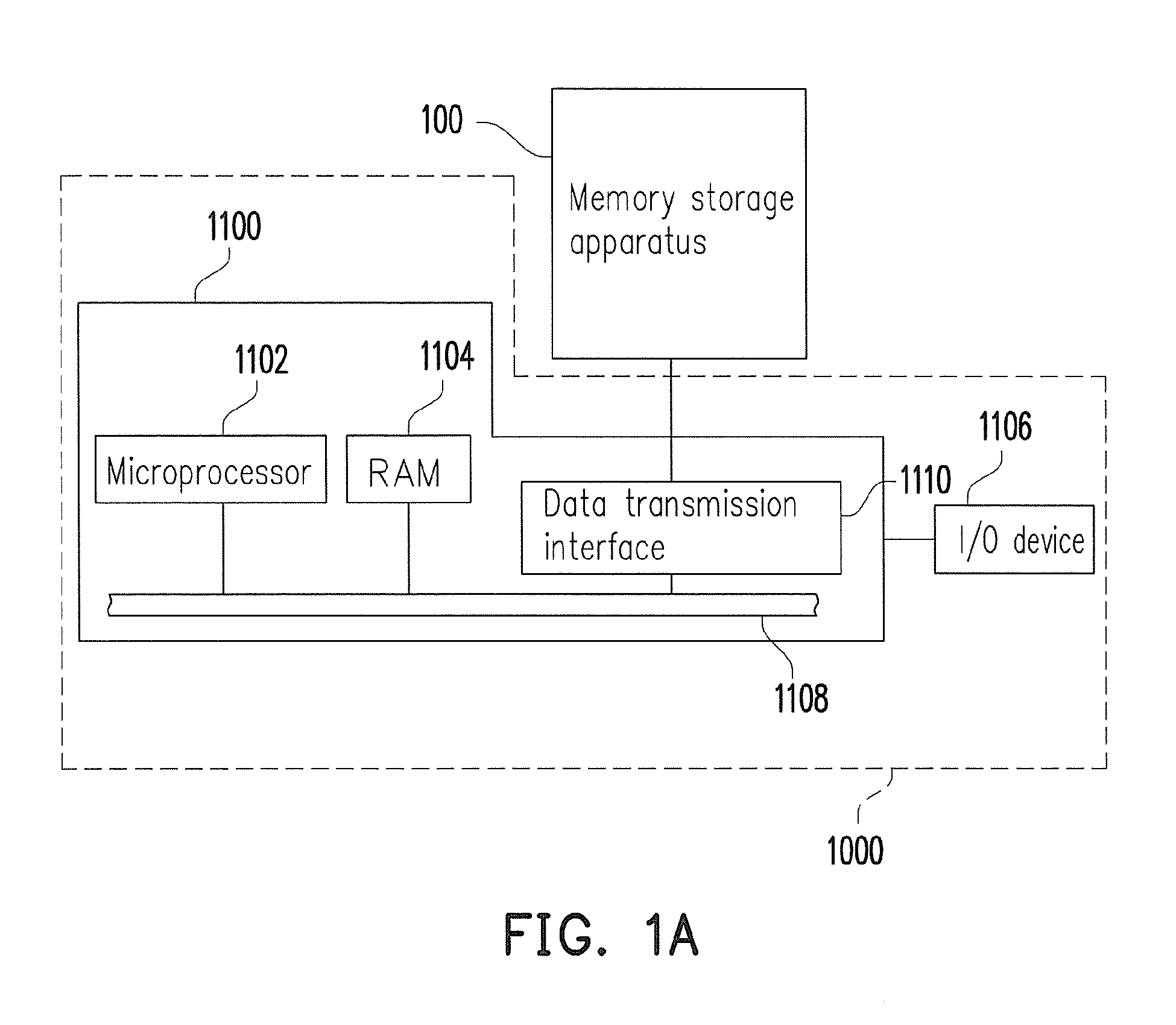
Method for managing commands in command queue, memory control circuit unit and memory storage apparatus
ActiveUS20150012687A1Efficient managementInput/output to record carriersMemory systemsIndex registerMemory controller
A method for managing commands in a command queue, a memory controller, and a memory storage apparatus are provided. The method includes: storing at least one first command in a command queue register according to a plurality of first indication bits and updating the first indication bits according to a current storage status of the command queue register; generating a plurality of updated second indication bits according to the updated first indication bits and a plurality of second indication bits. The method also includes: obtaining at least one first command index corresponding to at least one register block storing the at least one first command in the command queue register according to the updated second indication bits and adding the at least one first command index into a command index register; executing commands corresponding to un-executed command indices in the command queue register.
Owner:PHISON ELECTRONICS
Systems and methods for utilizing an extended translation look-aside buffer having a hybrid memory structure
InactiveUS20080172524A1Well formedEnergy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory addressVirtual memory
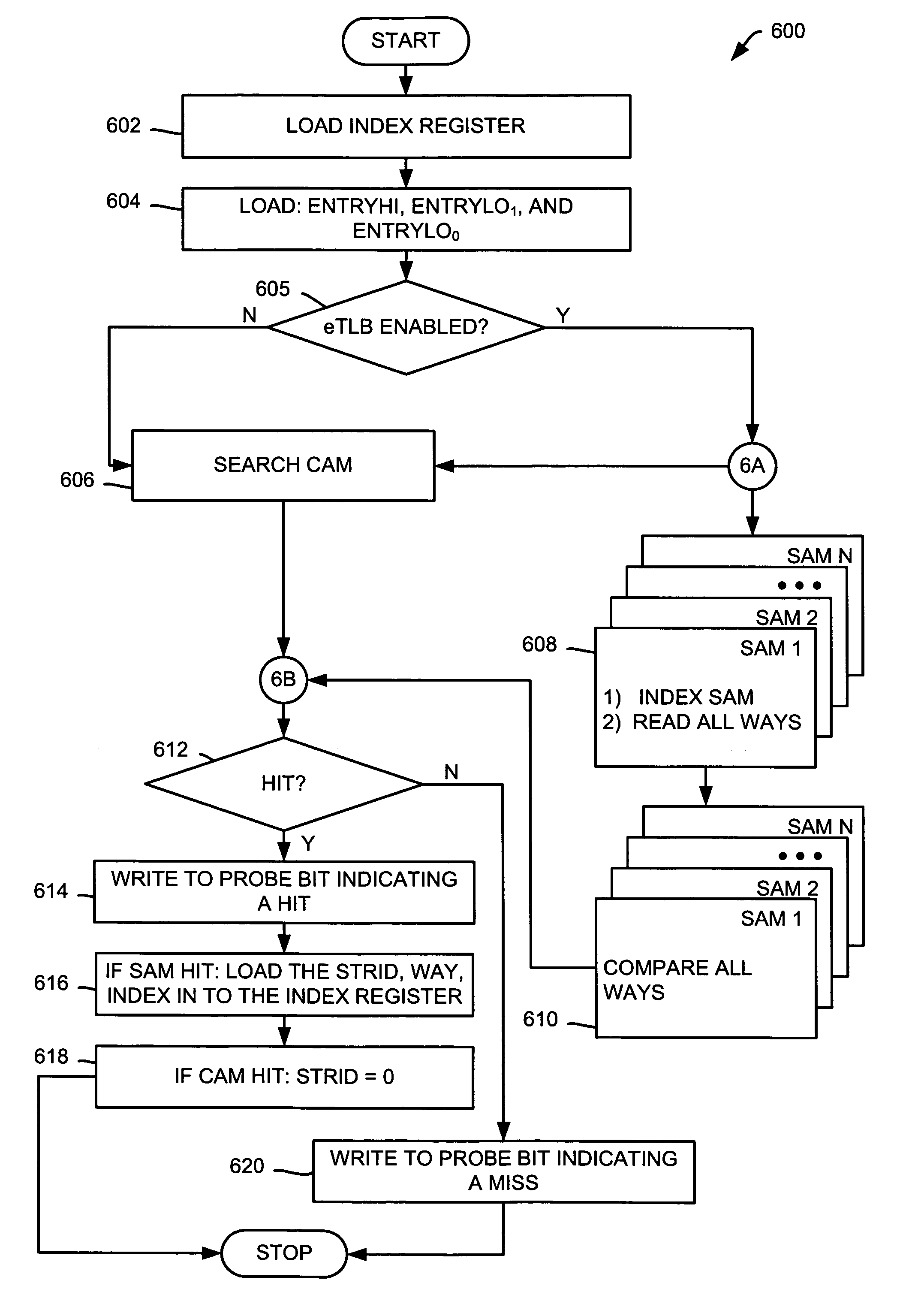
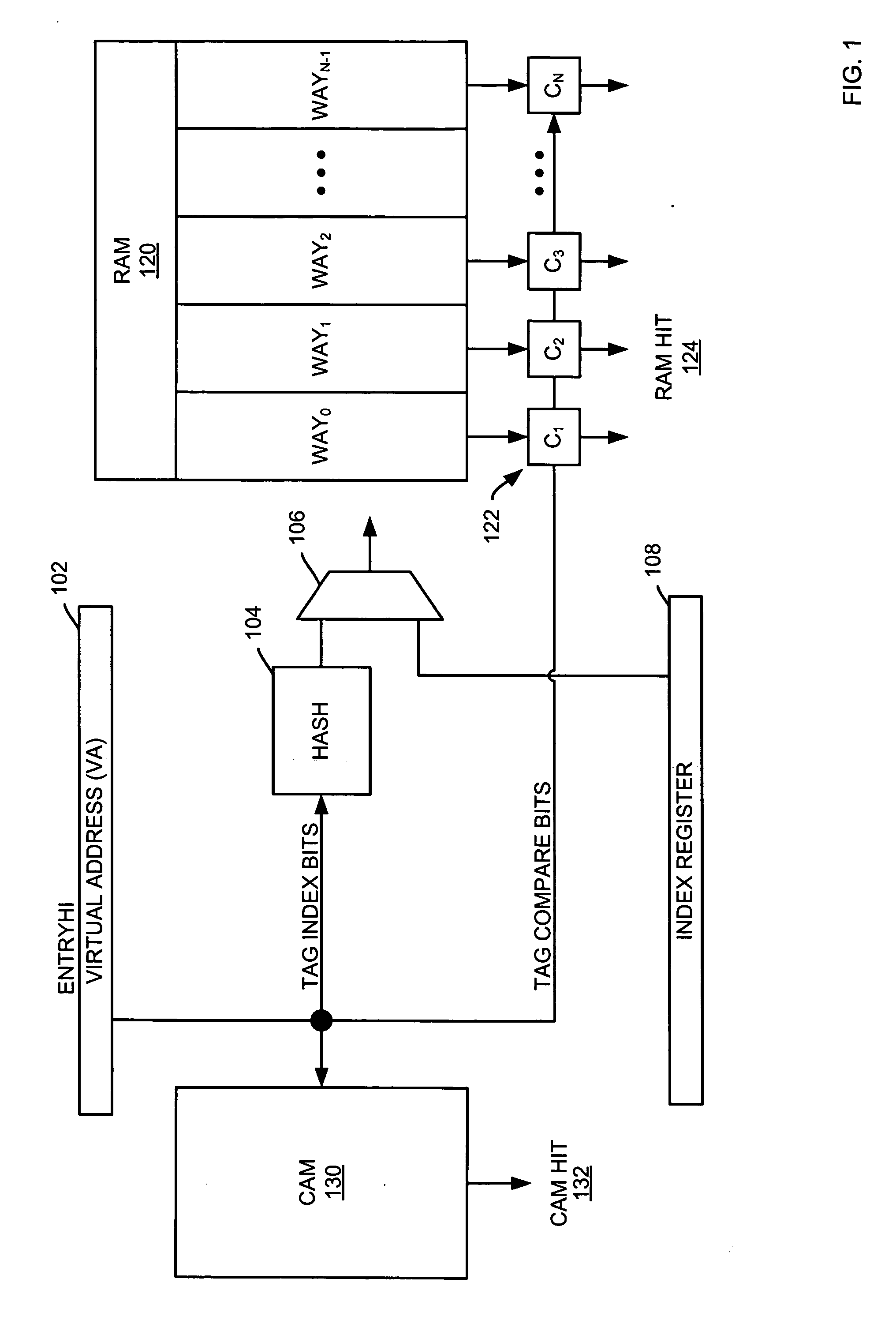
Extended translation look-aside buffers (eTLB) for converting virtual addresses into physical addresses are presented, the eTLB including, a physical memory address storage having a number of physical addresses, a virtual memory address storage configured to store a number of virtual memory addresses corresponding with the physical addresses, the virtual memory address storage including, a set associative memory structure (SAM), and a content addressable memory (CAM) structure; and comparison circuitry for determining whether a requested address is present in the virtual memory address storage, wherein the eTLB is configured to receive an index register for identifying the SAM structure and the CAM structure, and wherein the eTLB is configured to receive an entry register for providing a virtual page number corresponding with the plurality of virtual memory addresses.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE +1
Lookup table addressing system and method
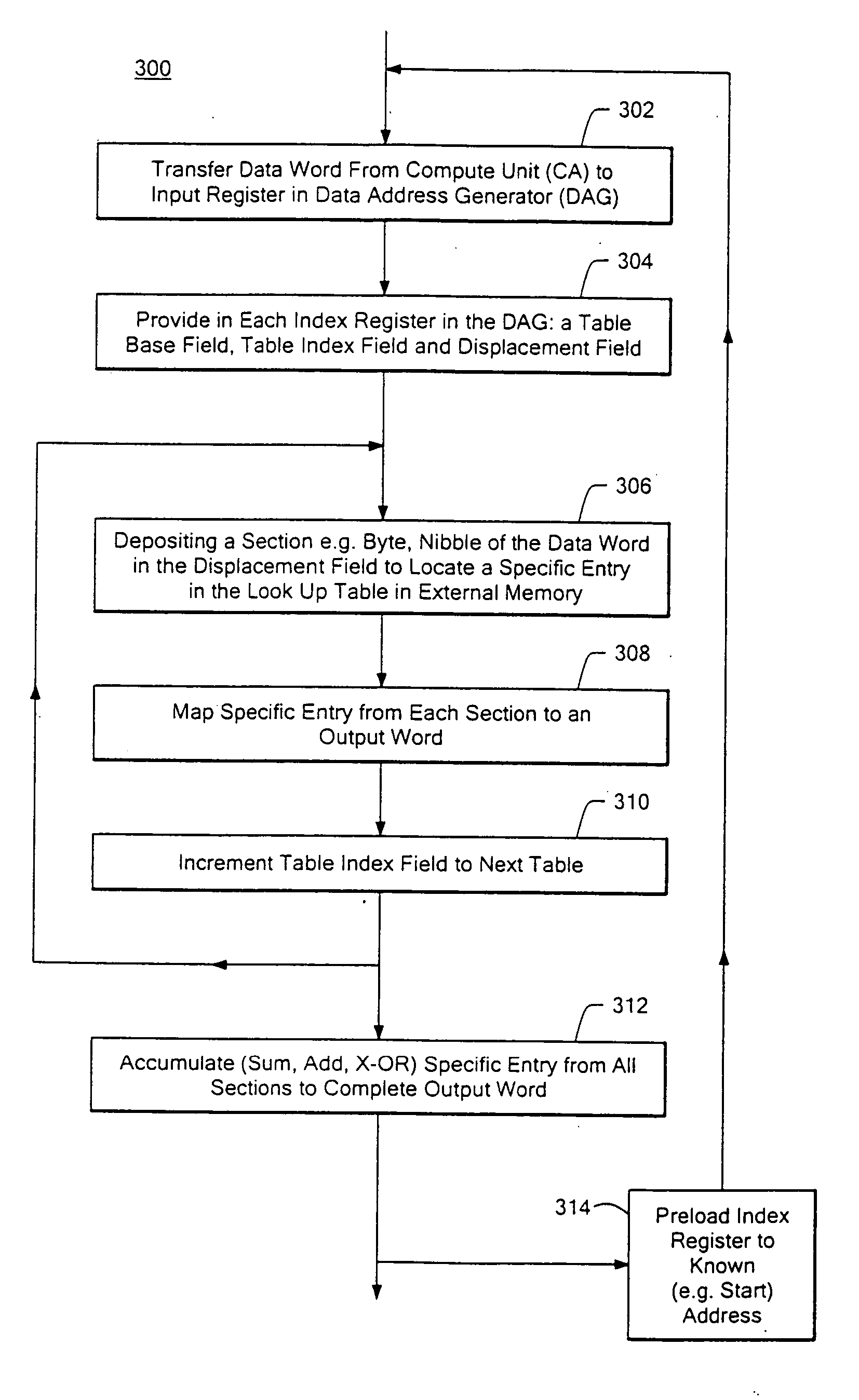
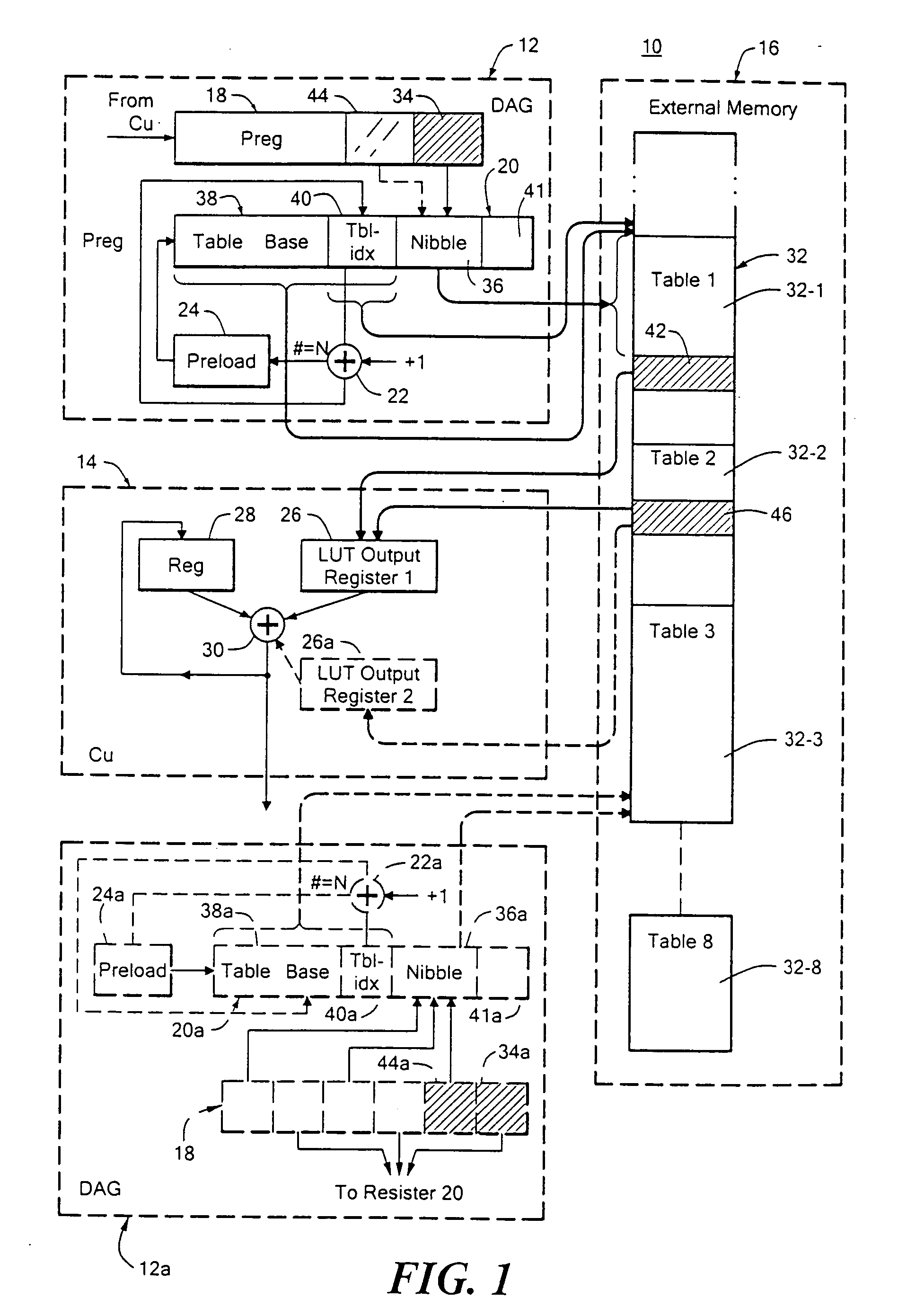
InactiveUS20070094474A1Minimizes pipeline stallEasy to operateEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesCathode-ray tube indicatorsExternal storageIndex register
Lookup table addressing of a set of lookup tables in an external memory is achieved by: transferring a data word from a compute unit to an input register in a data address generator; providing in at least one deposit-increment index register in the data address generator including a table base field for identifying the location of the set of tables in memory, and a displacement field; and depositing a section of the data word into a displacement field in the index register for identifying the location of a specific entry in the tables.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Extracted-index addressing of byte-addressable memories
ActiveUS7243210B2Efficient solutionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationIndex registerMultiplexer
A microprocessor circuit useful for indexed addressing of byte-addressable memories includes word-length index, base address, and destination registers designated by an instruction. The instruction also specifies one byte packed within the index register, which is to be extracted. A multiplexer has a word-wide input end accessing all of the bytes of the index register, and responsive to byte selection control passes the specified byte to its output. The extracted byte is provided directly at specific bit positions of a zero-extended address offset word. The offset word is added to the base address, the sum being used to address memory contents that are loaded into the destination register.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
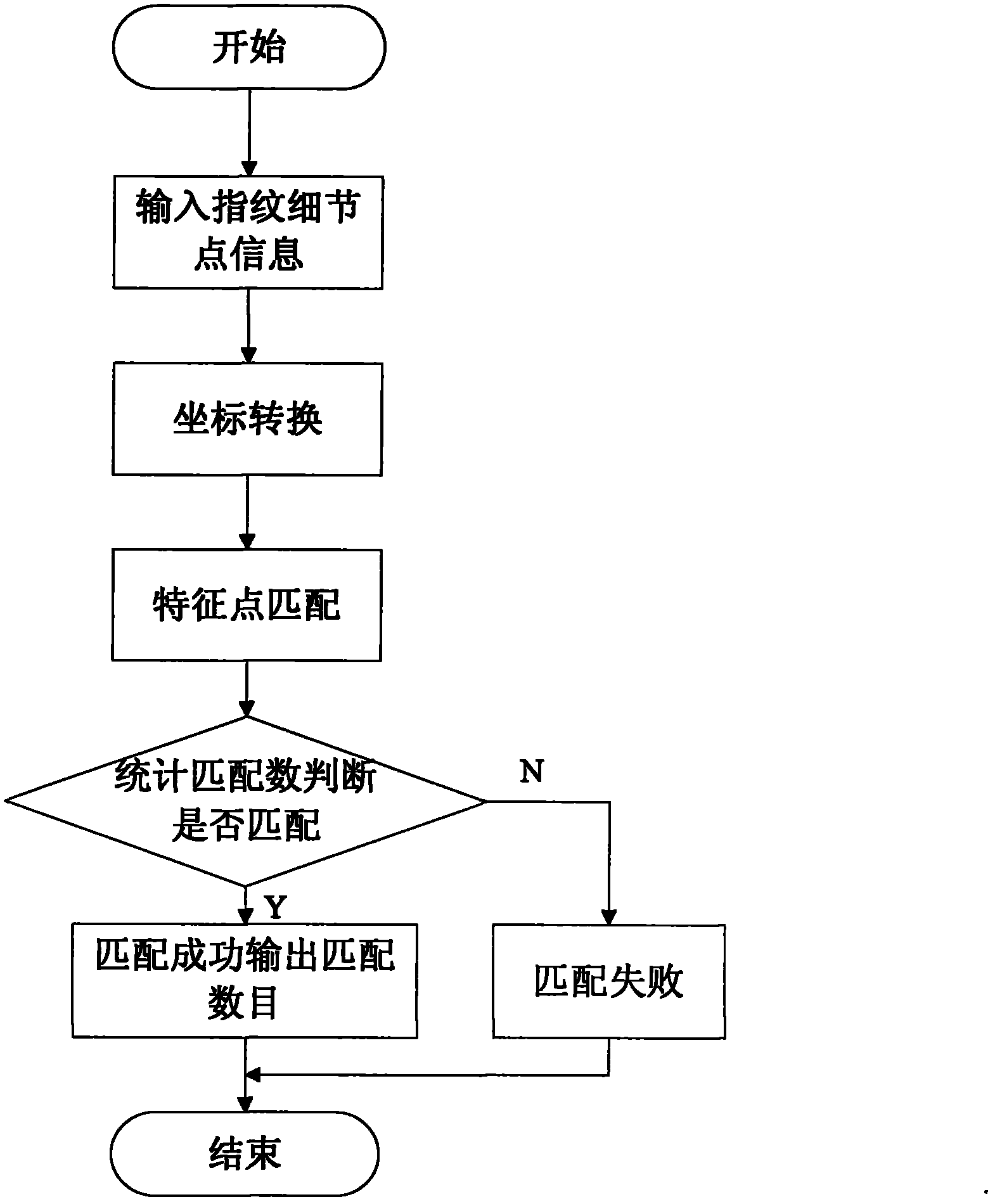
Method for searching fingerprint database based on quantum algorithm
InactiveCN102495886ASolve the speed problemSolve the accuracy problemCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsIndex registerGrover's algorithm
The invention relates to a method for searching a fingerprint database based on a quantum algorithm; the matching method comprises the following steps of: (1) collecting and preprocessing fingerprints, extracting detail minutiae, selecting reference points, and transferring an input fingerprint and a set of the detail minutiae in N template fingerprints to polar coordinates based on respective reference points; (2) obtaining a total matching number of all the template fingerprints and the input fingerprint at a time according to quantum parallelism principle, and storing the total matching number in a matching score database; (3) improving Oracle operators in a Grover algorithm so that the Grover algorithm comprises two databases, and finally carrying out one-to-one correspondence on the N states obtained in index registers and the positions of the all obtained matching score databases; and (4) rotating average values of all the states in the index registers, and measuring the index registers, and finally obtaining the researched target fingerprint. According to the method, the efficiency and the accuracy of fingerprint searching in the non-structured fingerprint database are improved by using the quantum algorithm.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
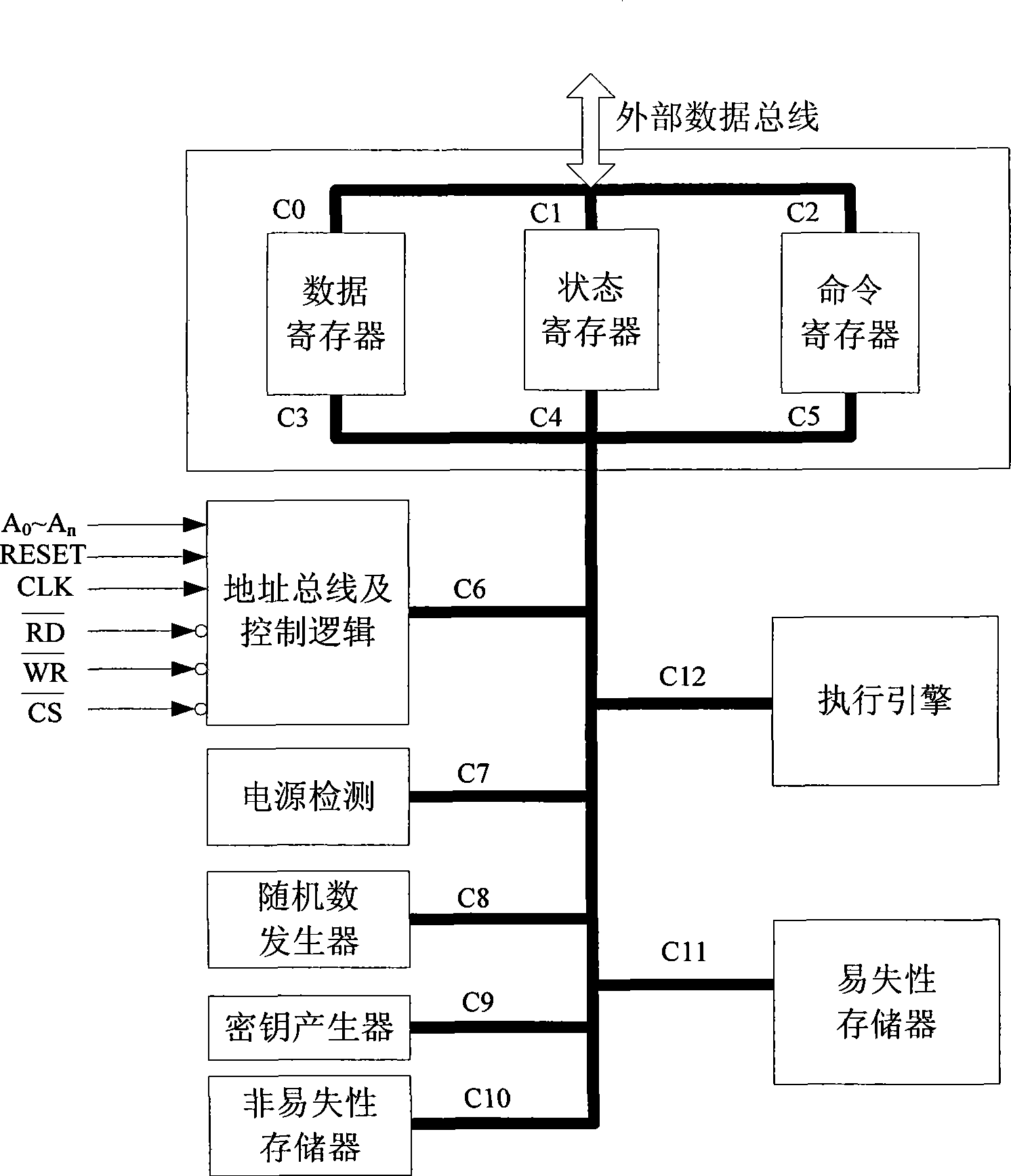
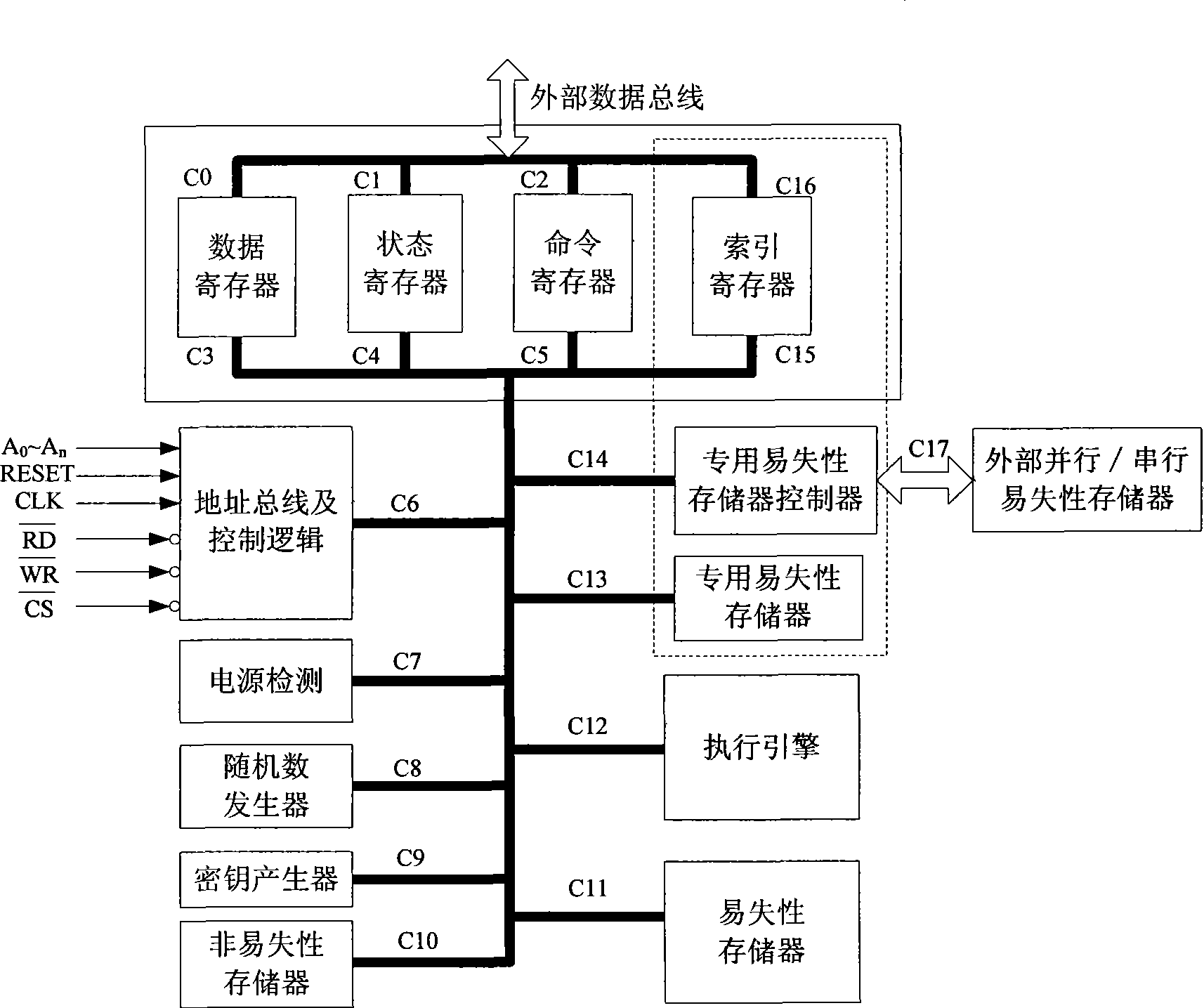
Cipher processor supporting thread-level encryption and decryption and its cipher operation method
InactiveCN101431407AExpandable and flexibleKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data protectionData streamIndex register
The present invention discloses a cipher processor that support thread level encryption and decryption and the method of cipher, which belongs to digital communication technology field. The cipher processor comprises data register, status register, command register, address bus, control logic, power supply test, random number generator, key generator, nonvolatile memory, volatile memory, execution engine, special volatile memory, special volatile memory controller and index register, wherein thread level encryption and decryption is done inside after interactive operation among special volatile memory, special volatile memory controller, index register and execution engine. Multi-thread processing is realized through initialization thread operation to each data stream at the first encryption and decryption and operation of different thread encryption and decryption switching by the cipher processor. The invention settles the problem of multi-key and randomized cross encryption and decryption of cipher processor, and can support existing cryptosystems and all working mode.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
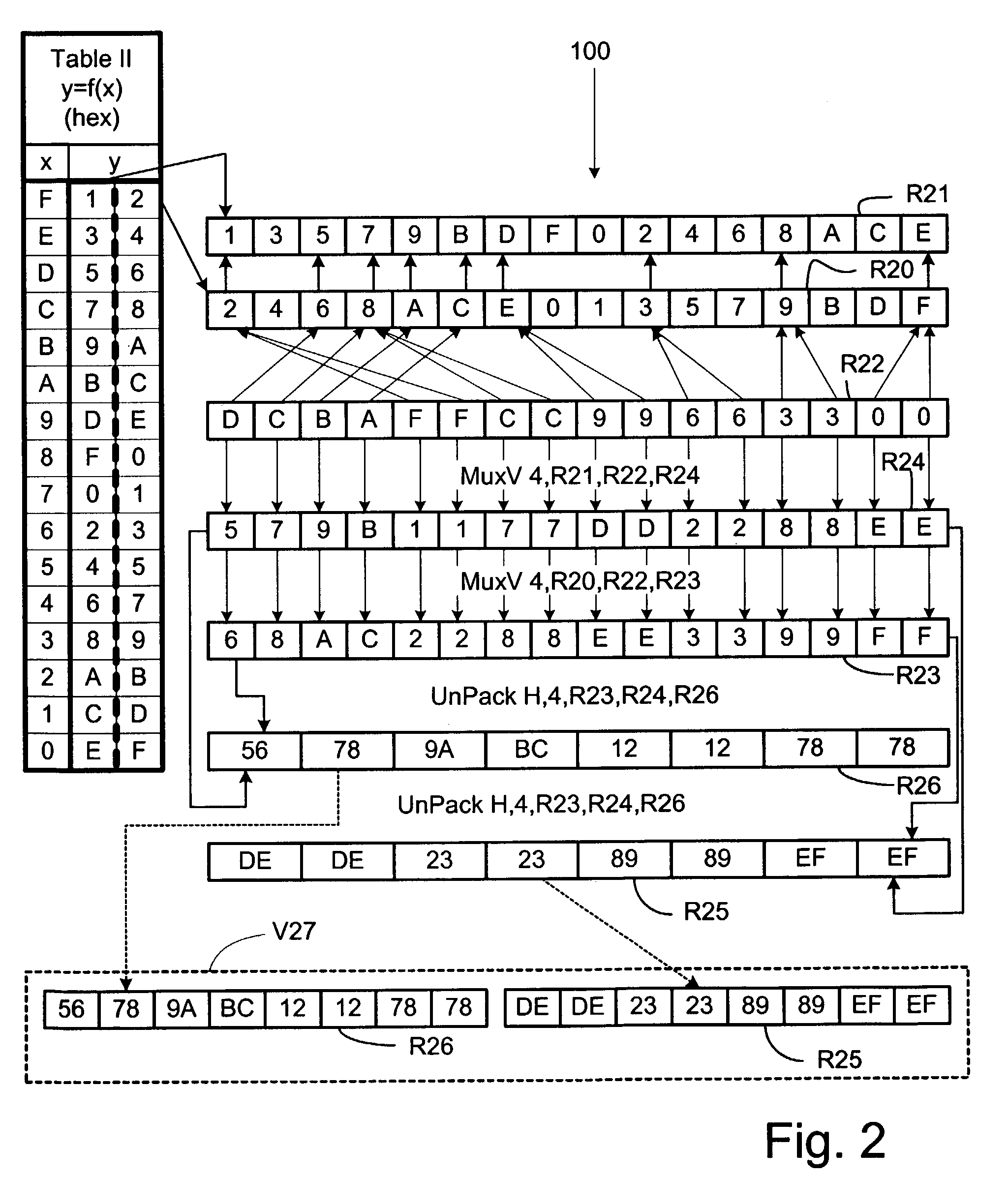
Variable reordering (Mux) instructions for parallel table lookups from registers
InactiveUS7424597B2Wider and more parallel data processorEconomical and simpleGeneral purpose stored program computerProcessor architectures/configurationIndex registerParallel computing
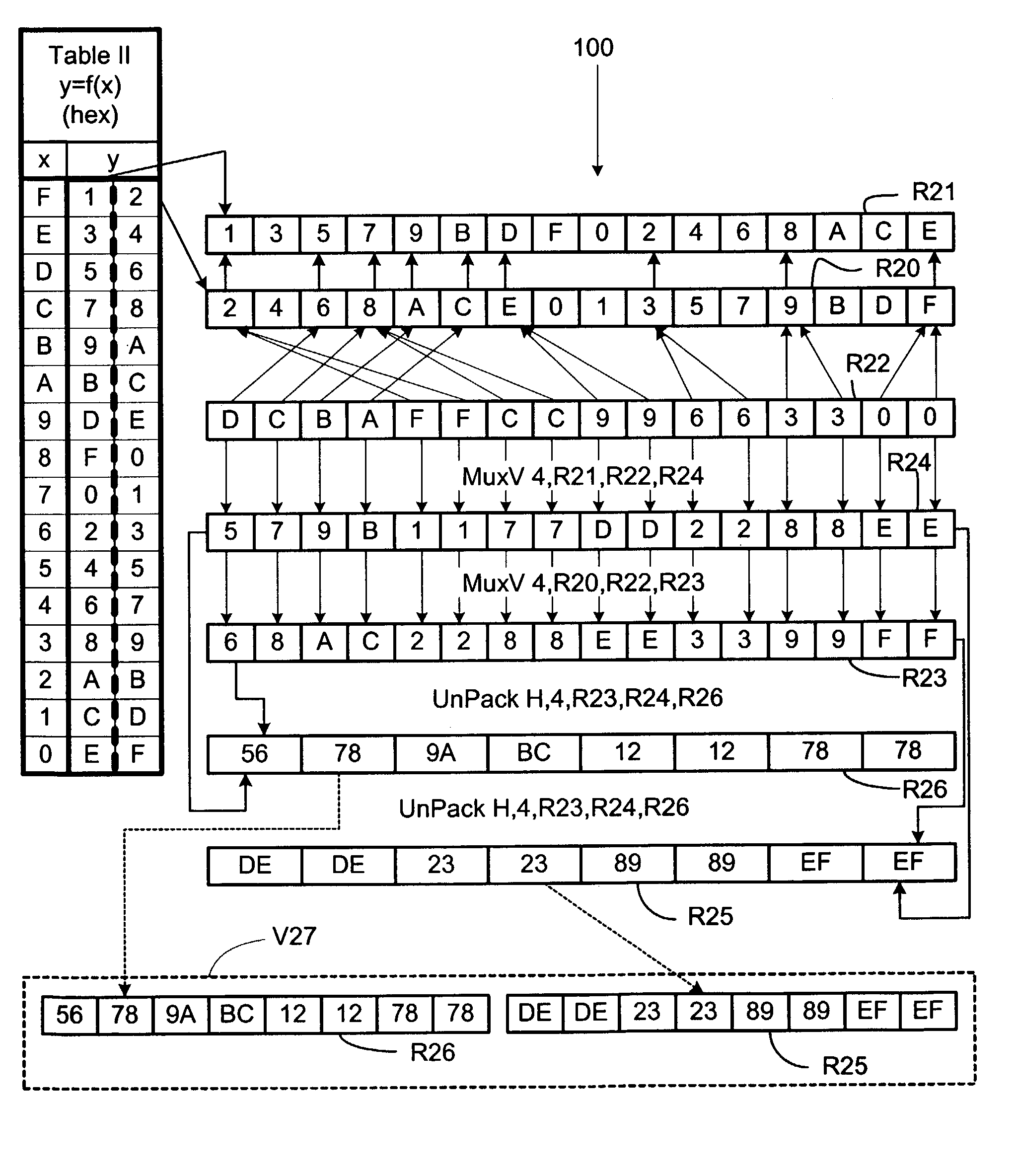
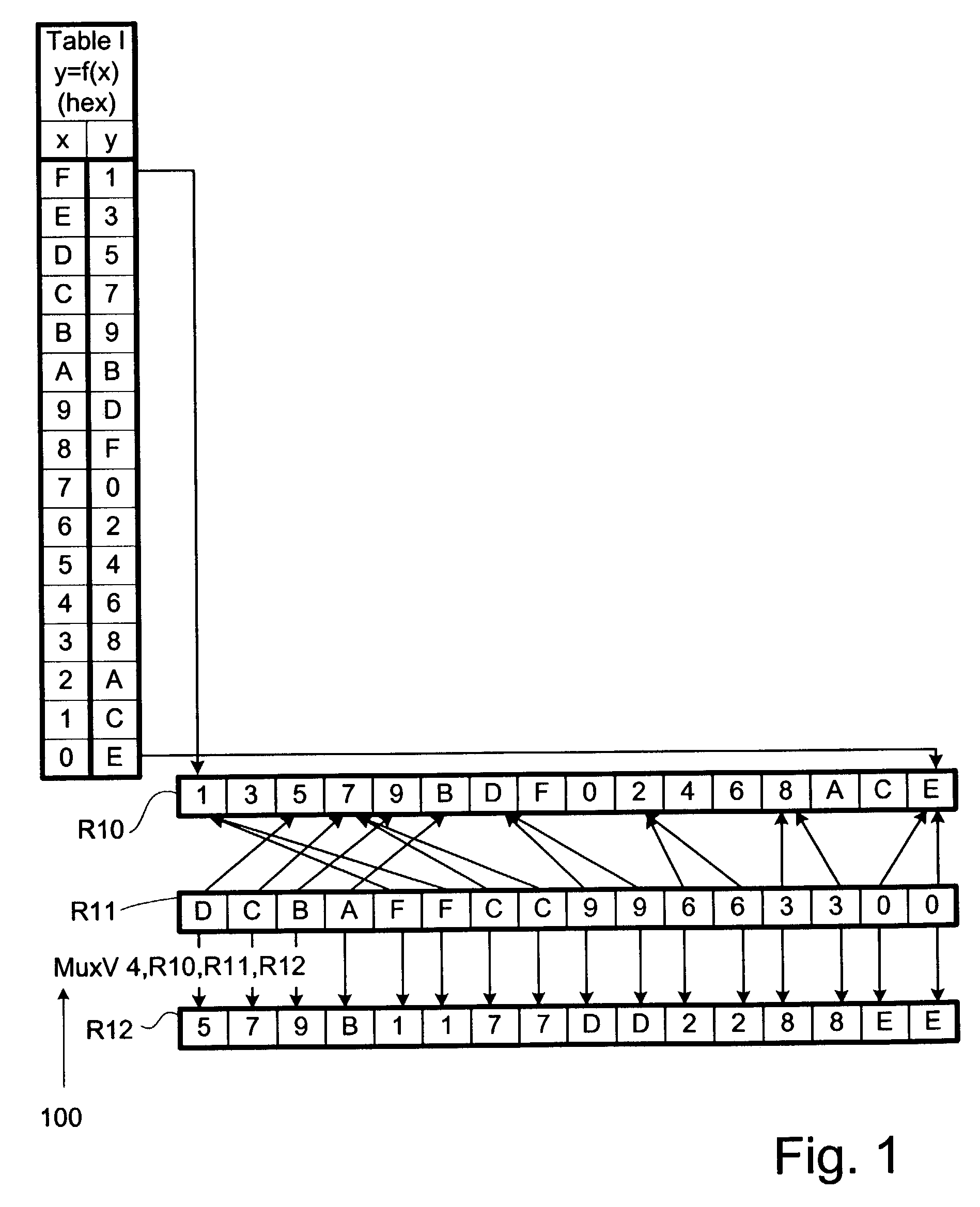
Parallel table lookups are implemented using variable Mux instructions to reorder data. Table data can be represented in a “table” register, while the desired ordering can be represented in an “Index” register. A direct variable Mux instruction can specify the table register and the index register as arguments, along with a result register. The instruction writes at least some of the data from the table register into the result register as specified in the index register. If the entire table cannot fit within a single register, entries can be divided between two or more table registers. An indirect variable Mux instruction can specify both a table-register-select register and a subword-location-select register. Both the direct and indirect Mux instructions can be used with entry data that is divided in accordance with significance between registers. In that case, plural Mux instructions are used with UnPack instructions that concatenate portions of the table entries.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
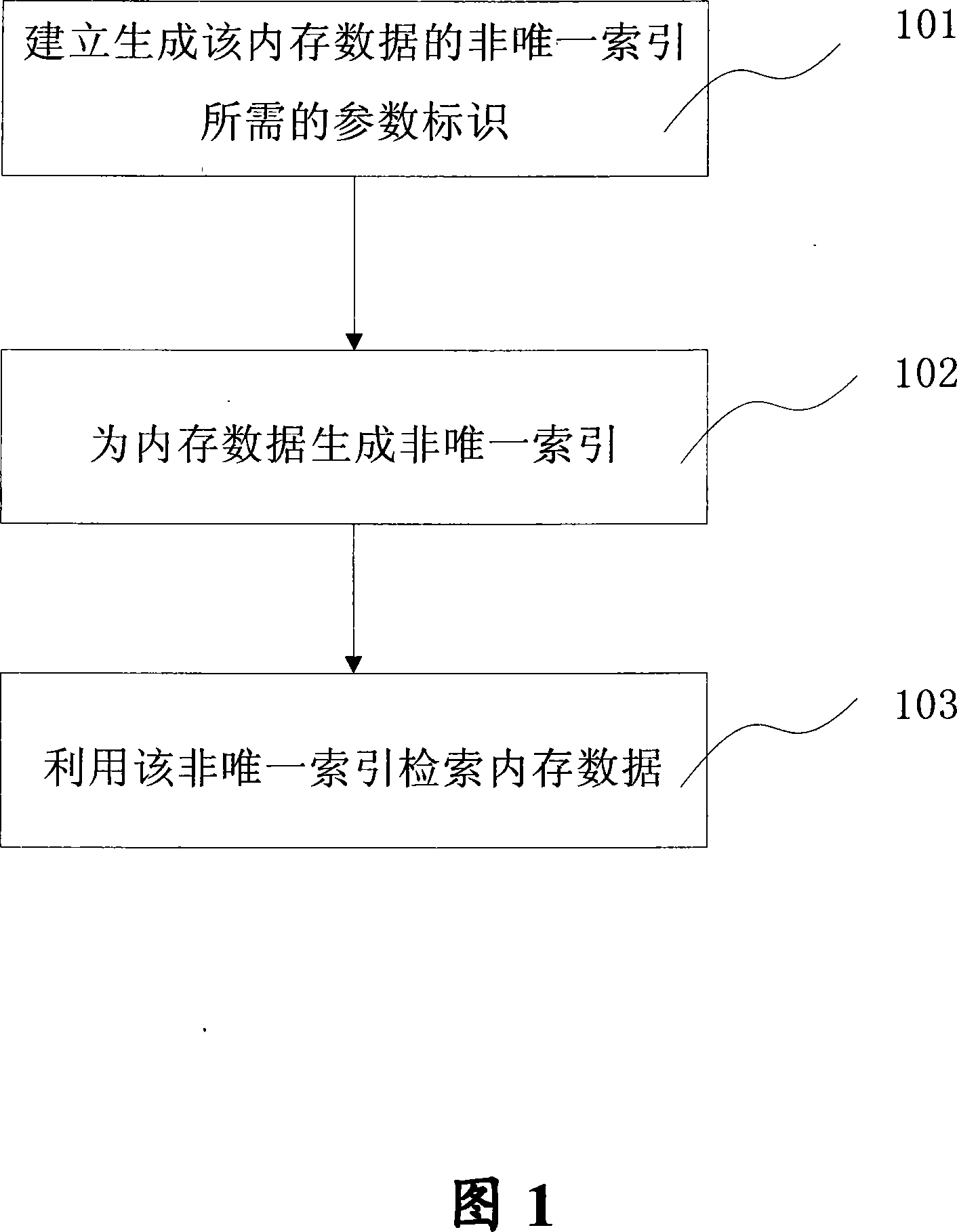
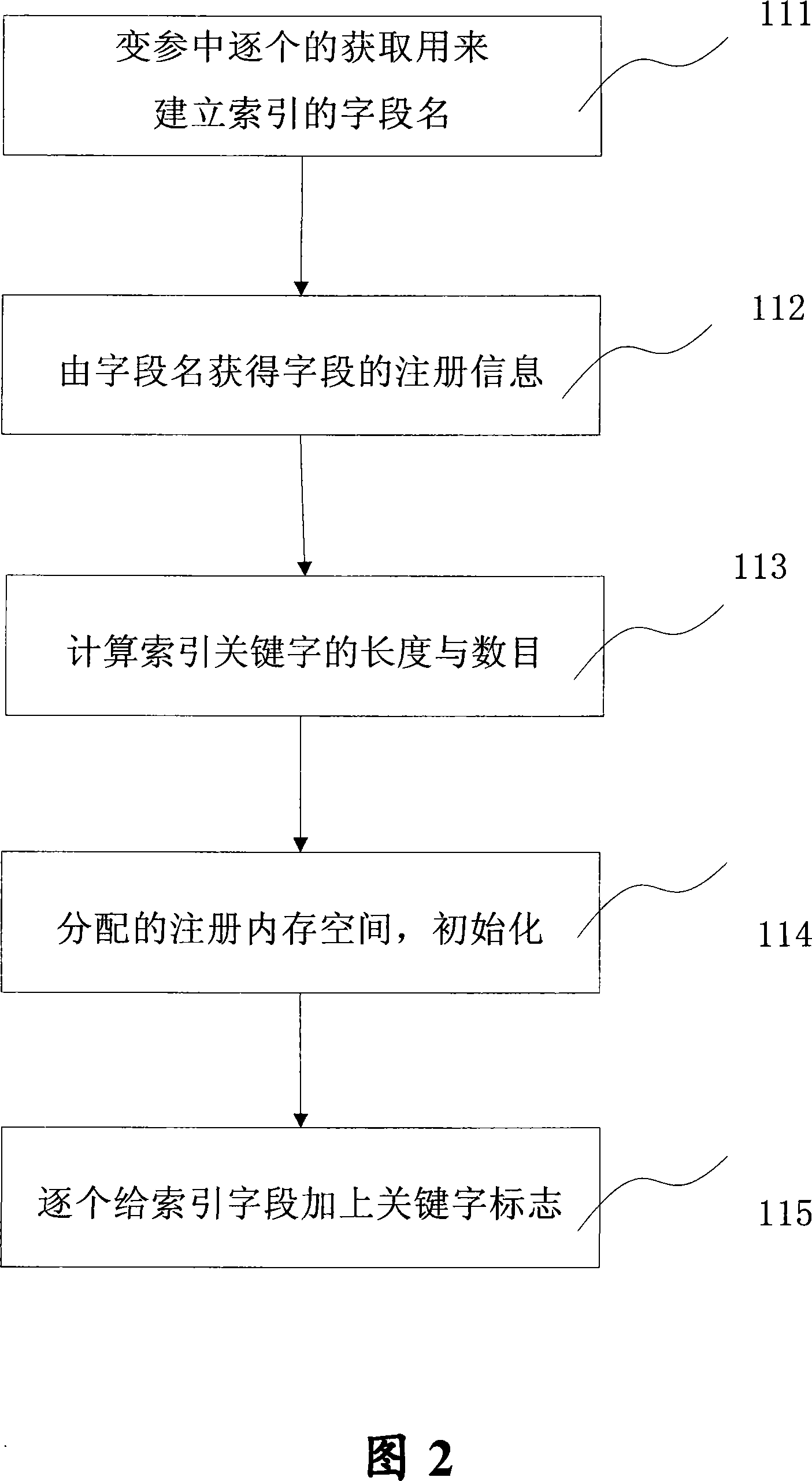
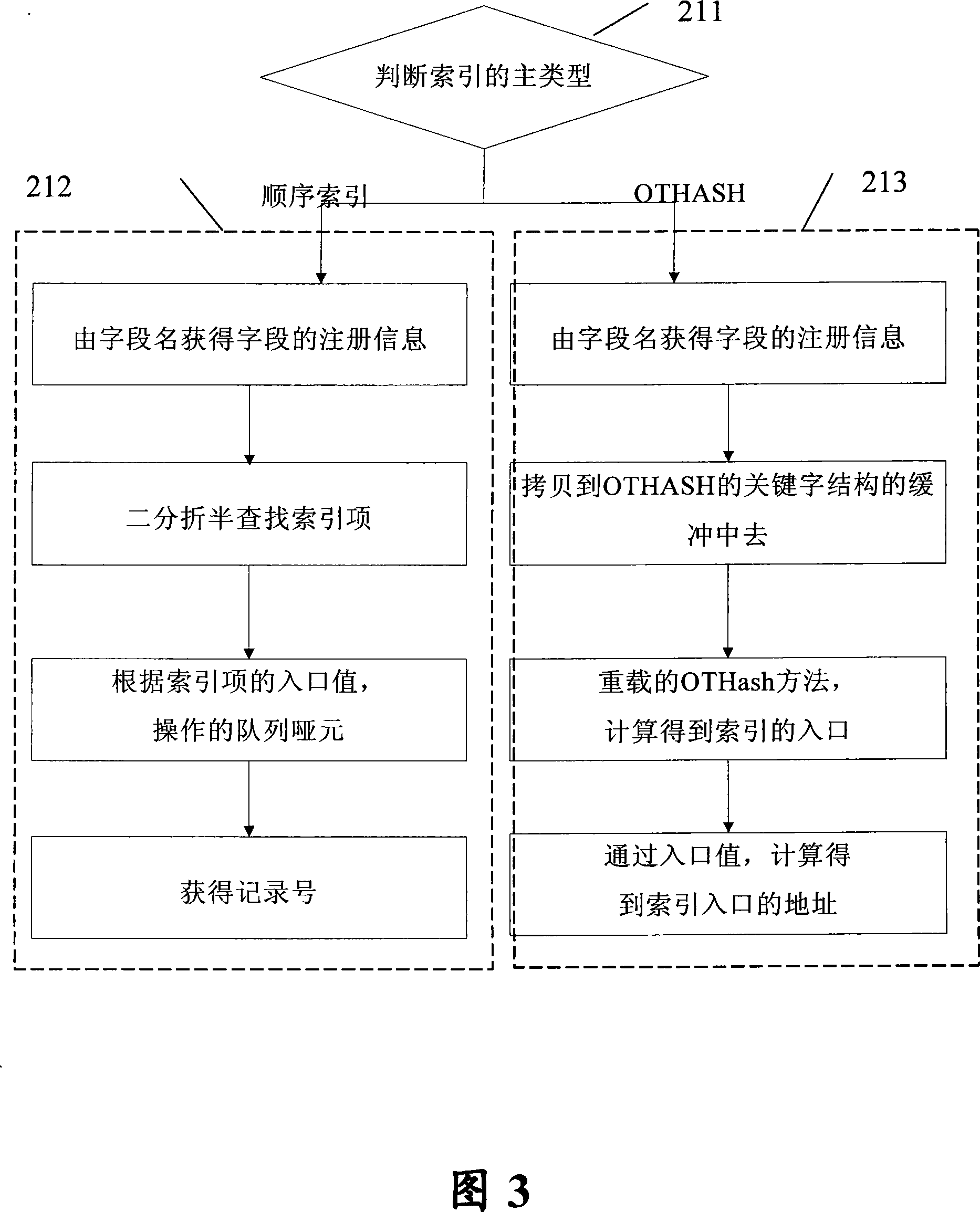
Non-only indexes search method for internal memory data
InactiveCN101082935ACode conciseSpeed up developmentSpecial data processing applicationsInternal memoryIn-memory database
The invention discloses a non-unique index searching method of internal memory data, which comprises the following steps: (1) building to generate the non-unique parameter mark of the internal memory data; distributing the index register list according to the parameter mark; (2) building the non-unique index for the internal memory data according to the index register list; (3) utilizing the non-unique index to search the internal memory data. The inveniton simplifies the code of operating mode of database, which reduces the coupling of database operating mode and internal memory database.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Optimizing Memory Accesses for Network Applications Using Indexed Register Files
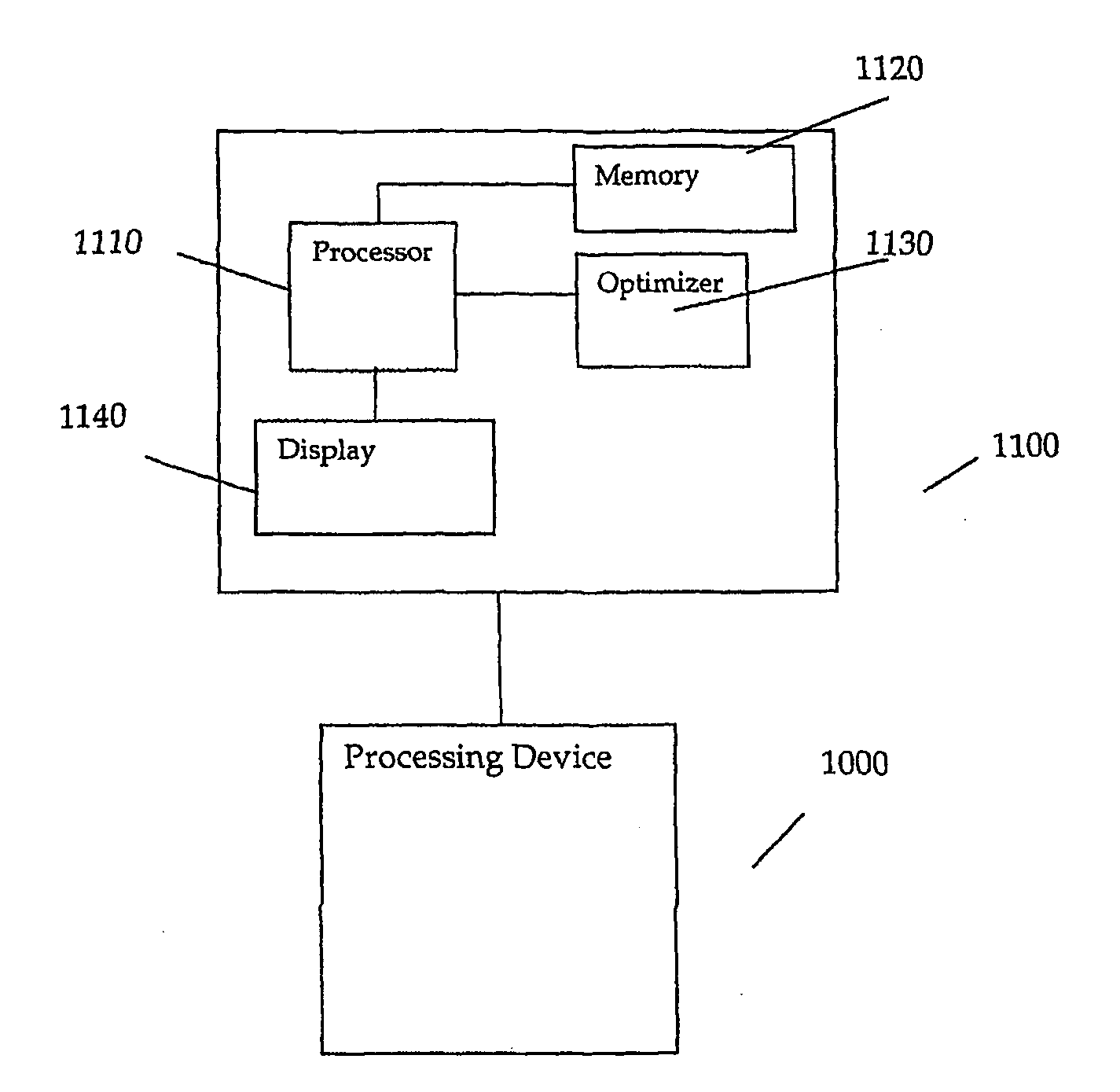
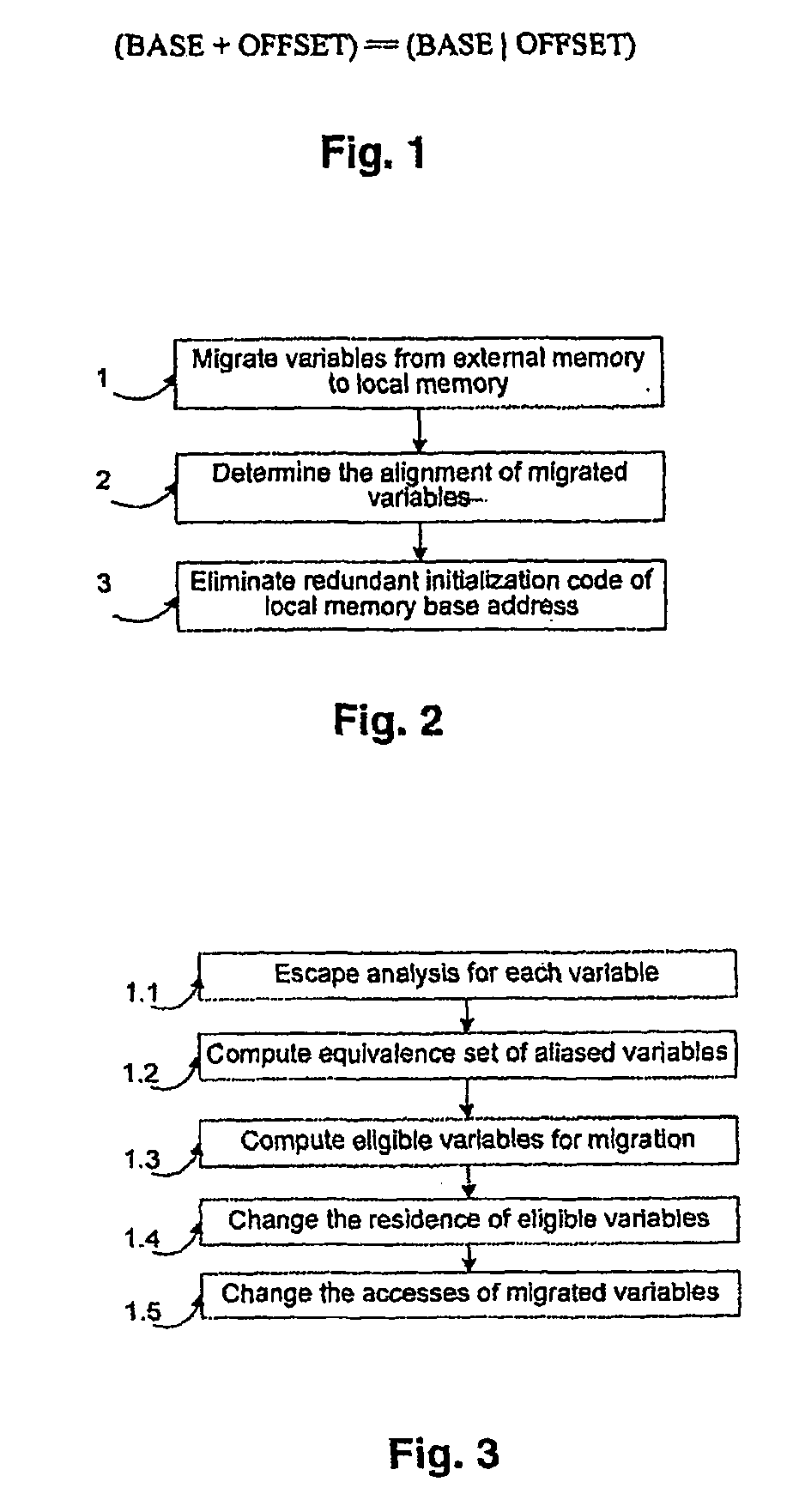
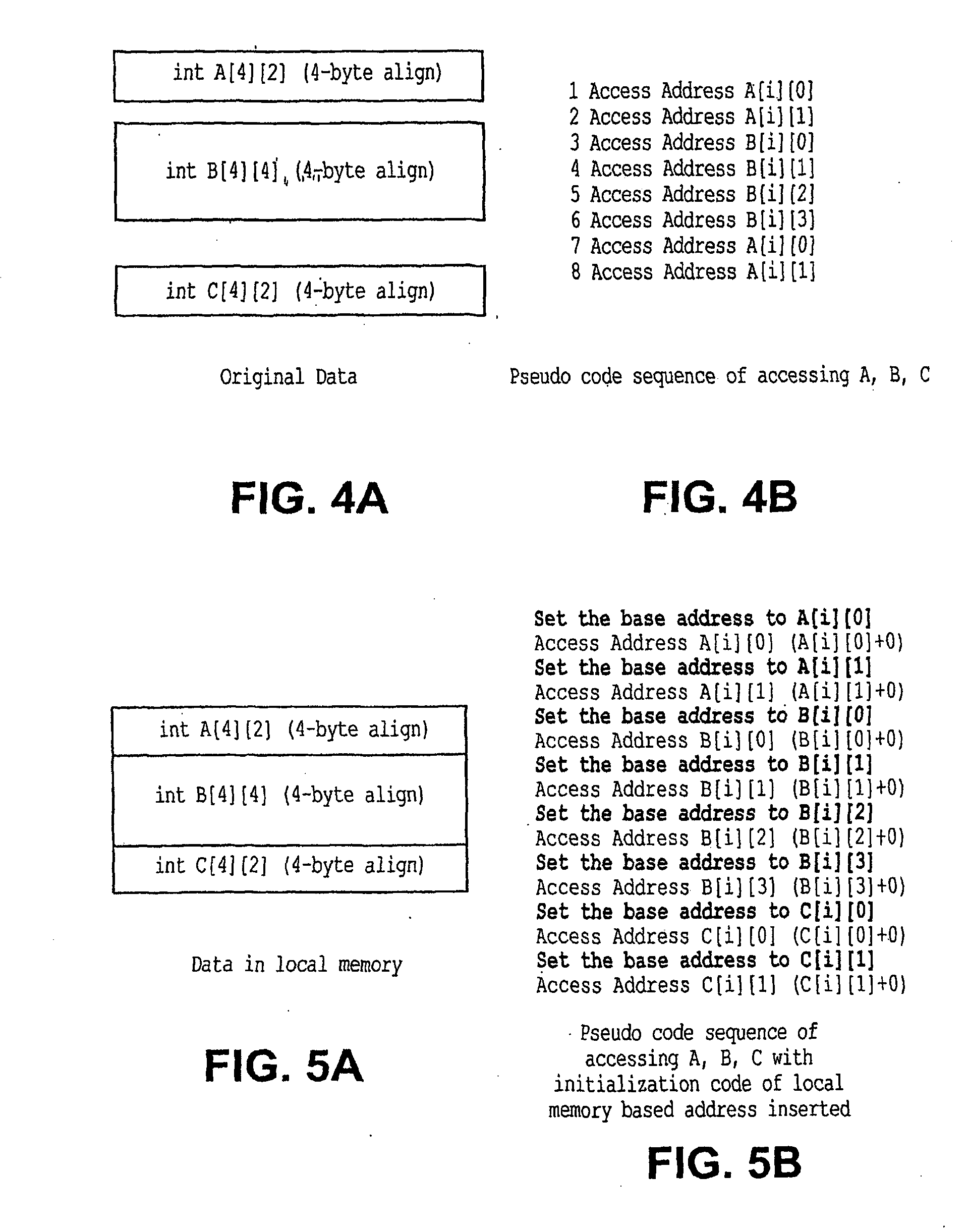
InactiveUS20080288737A1Improve performanceMinimizing initializationSoftware engineeringDigital computer detailsExternal storageIndex register
A processing device includes an optimizer to migrate objects from an external memory of a network processing to local memory device to registers connected to a processor. The optimizer further aligns and eliminates redundant unitialization code of the objects.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Processor with a computer repeat instruction
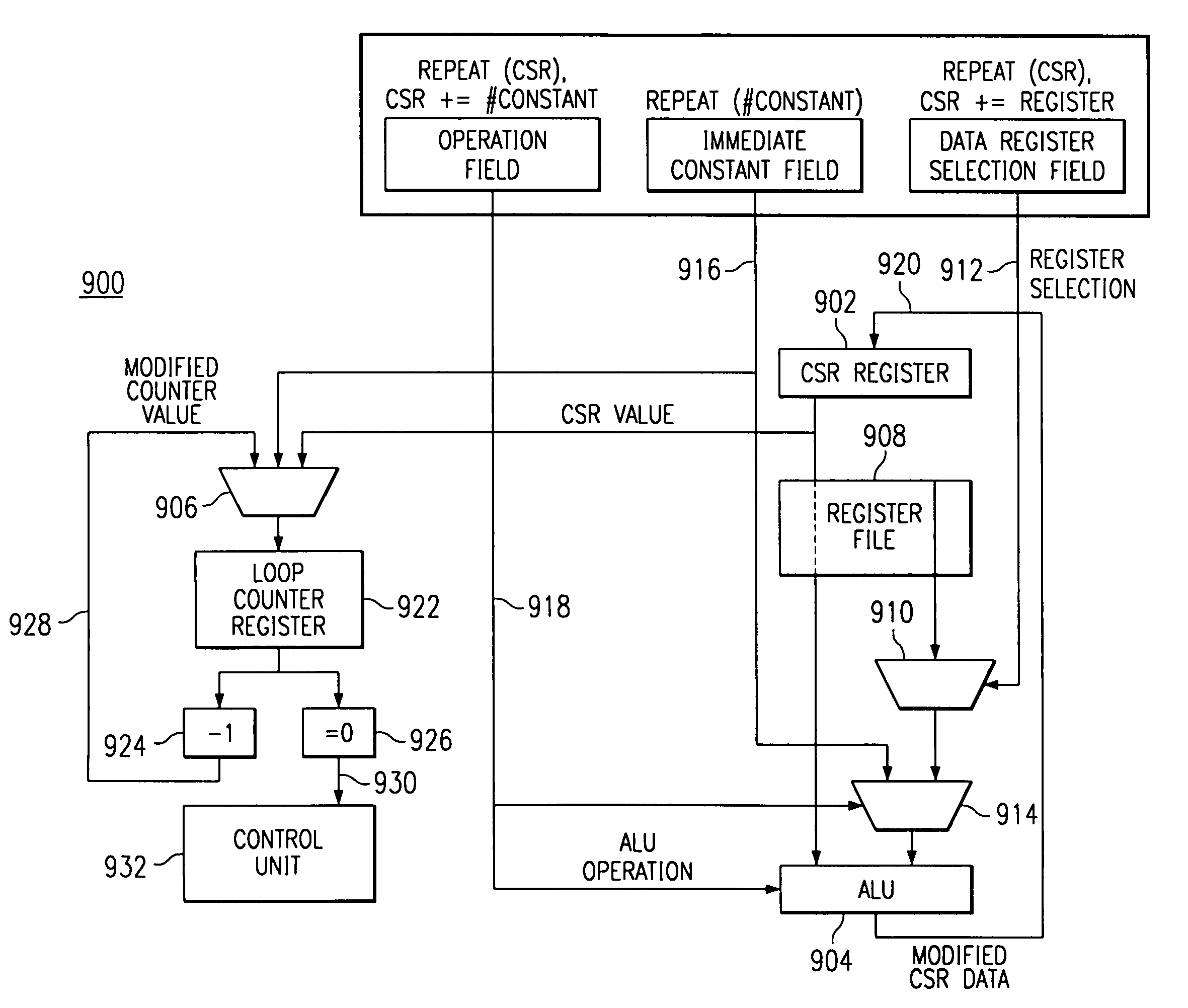
InactiveUS6990570B2Reduce power consumptionSuitable for useInstruction analysisDigital computer detailsIndex registerDigital signal processor
A processing engine, such as a digital signal processor, includes an execution mechanism, a repeat count register and a repeat count index register. The execution mechanism is operable for a repeat instruction to initialize the repeat count index register with the content of the repeat count register, and to modify the content of the repeat count register. The repeat instruction comprises two parts, the first of which initializes the repeat count index register and initiates repeat of a subsequent instruction, and the second part of which modifies the content of the repeat count register.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
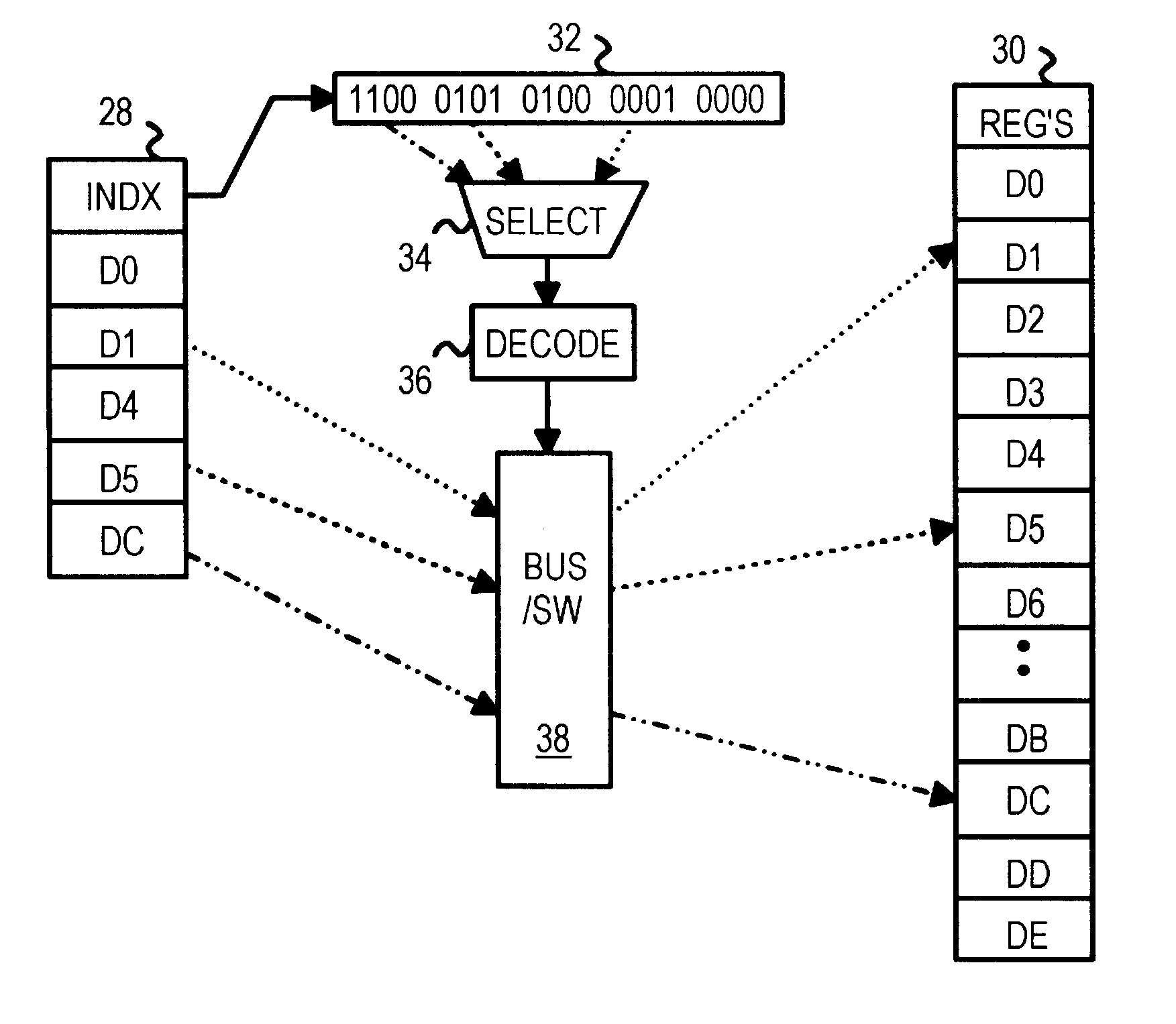
Graphics engine command FIFO for programming multiple registers using a mapping index with register offsets
InactiveUS6741257B1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsConcurrent instruction executionGraphicsIndex register
A host writes graphics commands and data to programmable registers through a command FIFO that is read by a graphics controller or BitBlt engine. Rather than write an address and a data value for each register programmed, the host writes one address, one index, and several data values. The address points to an index register. The index is a mapping index word with several multi-bit mapping fields. Each multi-bit mapping field in the index identifies a register to be programmed with one of the data values. Since N bits are used for each mapping field, the mapping field can select one register in a bank of 2<N>-1 registers. The registers in the bank can be programmed in any order, and registers can be skipped. Since only one index is stored in the command FIFO for programming several registers, less memory space and fewer bus cycles are required.
Owner:SERVSTOR TECHNOLOGIES LLC +1
Debugging support unit for microprocessor
A debug-enabled processing device includes a processor, a communication transceiver circuit, and a debug support unit. The debug support unit has a plurality of dedicated debug registers to facilitate debugging a software program under execution by the processor. One of the plurality of debug registers is a control register having at least four bits, which are used to enable / disable a plurality of debugging operations. Others of the debug registers include a set of index registers that may be configured to pass data to and from the processor.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS BEIJING R& D
Management of indexed registers in a system on a chip
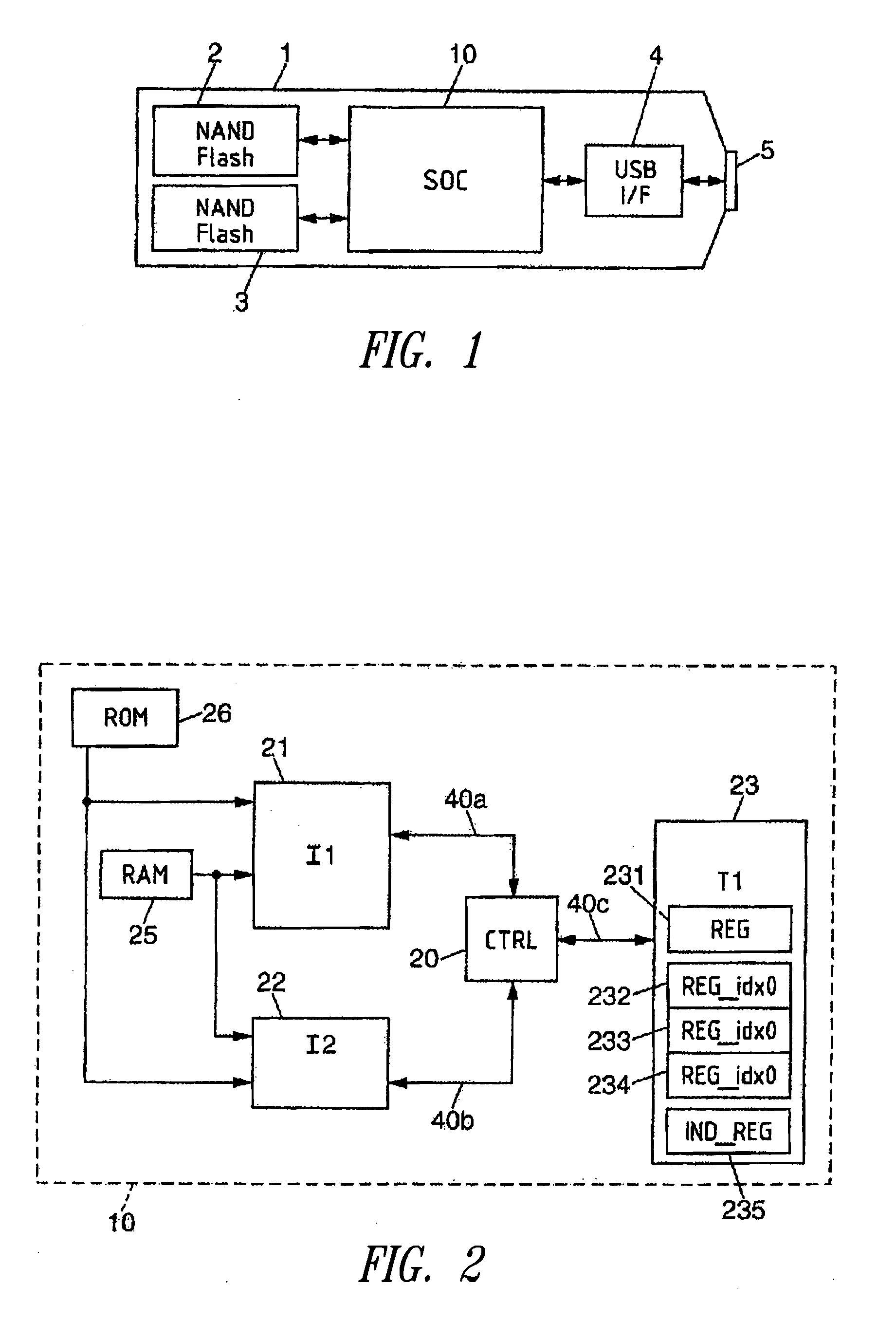
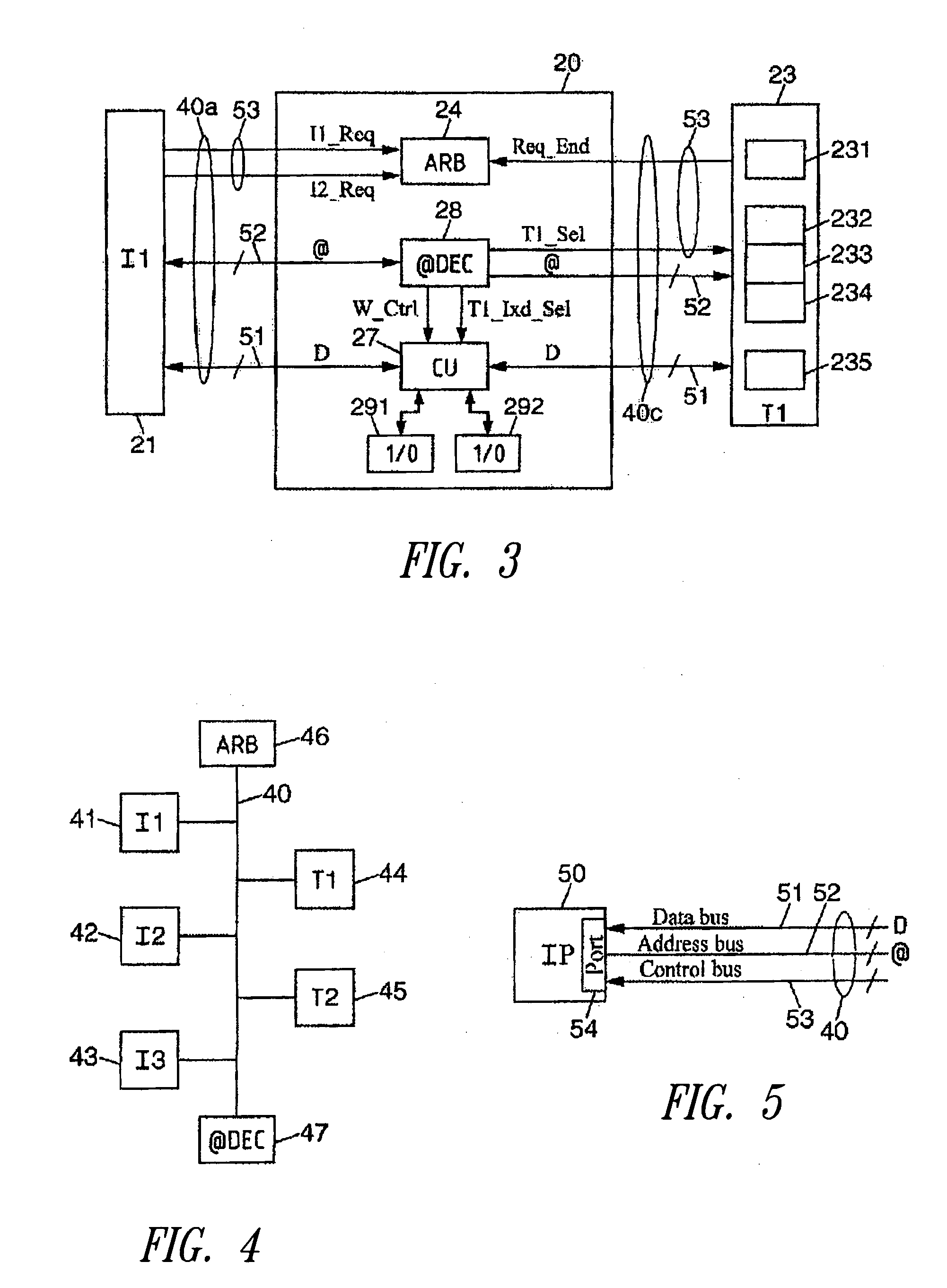
InactiveUS20050256993A1Eliminate riskEasy accessResource allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationElectronic systemsIndex register
An electronic system comprises a control unit for ordering the storage of an index value for indexed registers, in an additional index register linked to a defined initiator module, in response to a request to write the index value in an index register linked to the indexed registers, initiated by the initiator module. In response to any request to access an indexed register initiated by a defined initiator module, the control unit copies the index value from the additional index register linked to this initiator module to the index register linked to this indexed register, prior to execution of the access request. This enables management of access to indexed registers associated with an arbitration mechanism provided for managing conflicting access requests initiated by different functional modules in a system on a chip.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Micro-processor kernel used for cryptography arithmetic
ActiveCN101131719AHave versatilityEasy to integrateGeneral purpose stored program computerInternal/peripheral component protectionAddress generation unitMemory interface
A kind of micro-processor inner core used for cryptology calculation relates to the cryptology technology in the information security field. The invention is connected with the program memory and data memory, used for accelerating the cryptology calculation. The invention includes: instruction register, instruction decode unit, register stack including program counter, stack pointer, data pointer, accelerating module pointer, data register, index register, comparison register and bit register, data calculation unit, program address generation unit, program memory interface, data memory interface, cryptology calculation module interface and cryptology calculation module. Comparing with current technology, the invention can not only get higher calculation speed but also make the algorithm function more flexible and more general with the way to bond the software and hardware, and it is characterized in low-cost, high performance, function collocation, flexibility and generality.
Owner:BEIJING TONGFANG MICROELECTRONICS
Command queue management method, memorizer controller and memorizer storage device
ActiveCN104281413AEfficient managementInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer hardwareIndex register
The invention provides a command queue management method, a memorizer controller and a memorizer storage device. The method comprises the following steps of storing at least one first command in a command queue register according to a plurality of first indicator bits, and updating the first indicator bits according to the current storage state of the command queue register; updating second indicator bits according to the updated first indicator bits and a plurality of second indictor bits. The method also comprises steps of obtaining a first command index of a temporary storage block for correspondingly storing the first command in the command queue register according to the updated second indictor bits, and adding the first command index into a command index register; executing a command, corresponding to an unexecuted command index, in the command queue register.
Owner:PHISON ELECTRONICS
Gather-op instruction to duplicate a mask and perform an operation on vector elements gathered via tracked offset-based gathering
ActiveUS9747101B2Program control using stored programsInstruction analysisMemory addressIndex register
Instructions and logic provide vector scatter-op and / or gather-op functionality. In some embodiments, responsive to an instruction specifying: a gather and a second operation, a destination register, an operand register, and a memory address; execution units read values in a mask register, wherein fields in the mask register correspond to offset indices in the indices register for data elements in memory. A first mask value indicates the element has not been gathered from memory and a second value indicates that the element does not need to be, or has already been gathered. For each having the first value, the data element is gathered from memory into the corresponding destination register location, and the corresponding value in the mask register is changed to the second value. When all mask register fields have the second value, the second operation is performed using corresponding data in the destination and operand registers to generate results.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Graphics engine command FIFO for programming multiple registers using a mapping index with register offsets
InactiveUSRE41523E1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsConcurrent instruction executionGraphicsIndex register
A host writes graphics commands and data to programmable registers through a command FIFO that is read by a graphics controller or BitBlt engine. Rather than write an address and a data value for each register programmed, the host writes one address, one index, and several data values. The address points to an index register. The index is a mapping index word with several multi-bit mapping fields. Each multi-bit mapping field in the index identifies a register to be programmed with one of the data values. Since N bits are used for each mapping field, the mapping field can select one register in a bank of 2N−1 registers. The registers in the bank can be programmed in any order, and registers can be skipped. Since only one index is stored in the command FIFO for programming several registers, less memory space and fewer bus cycles are required.
Owner:XYLON LLC +1
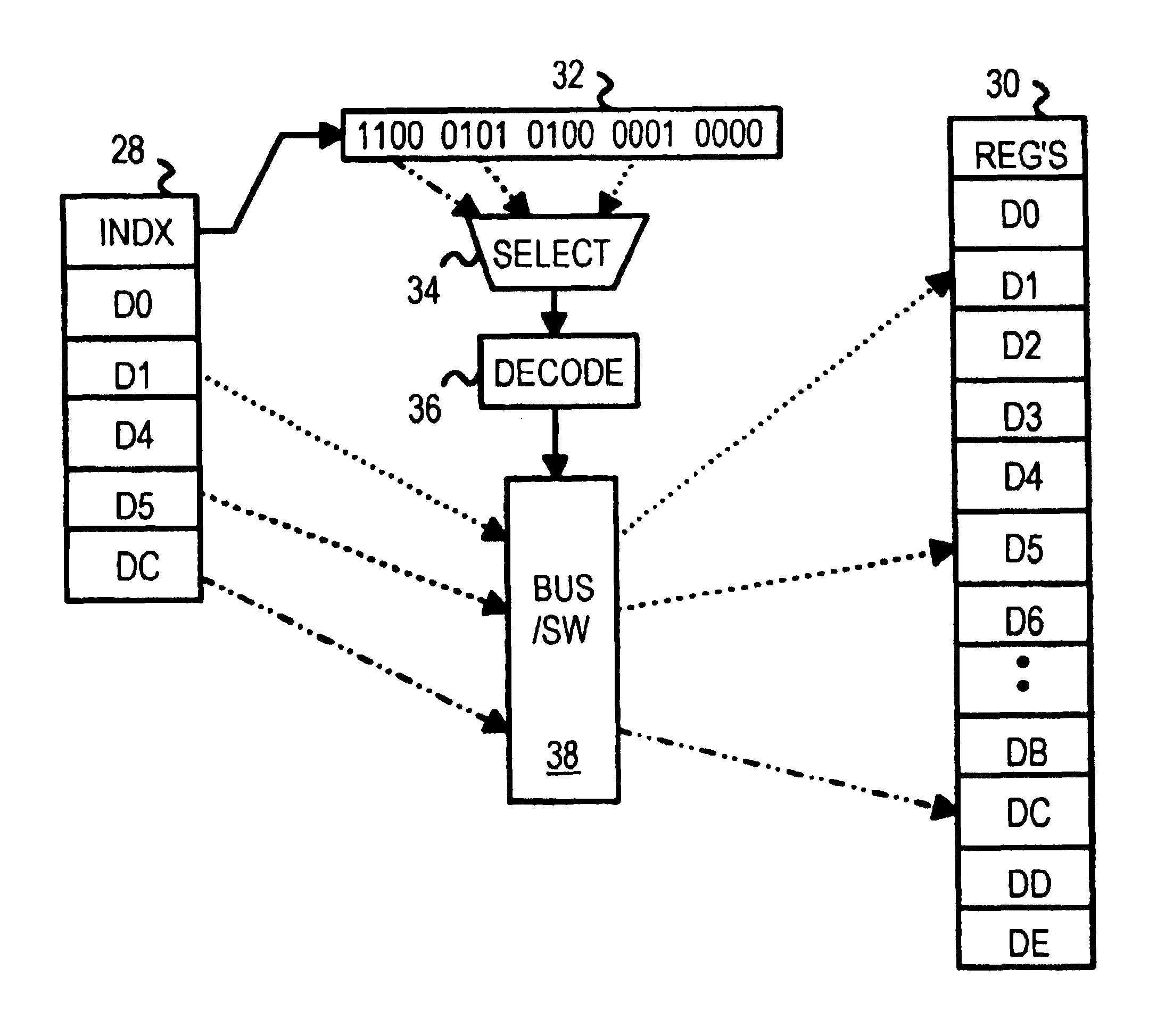
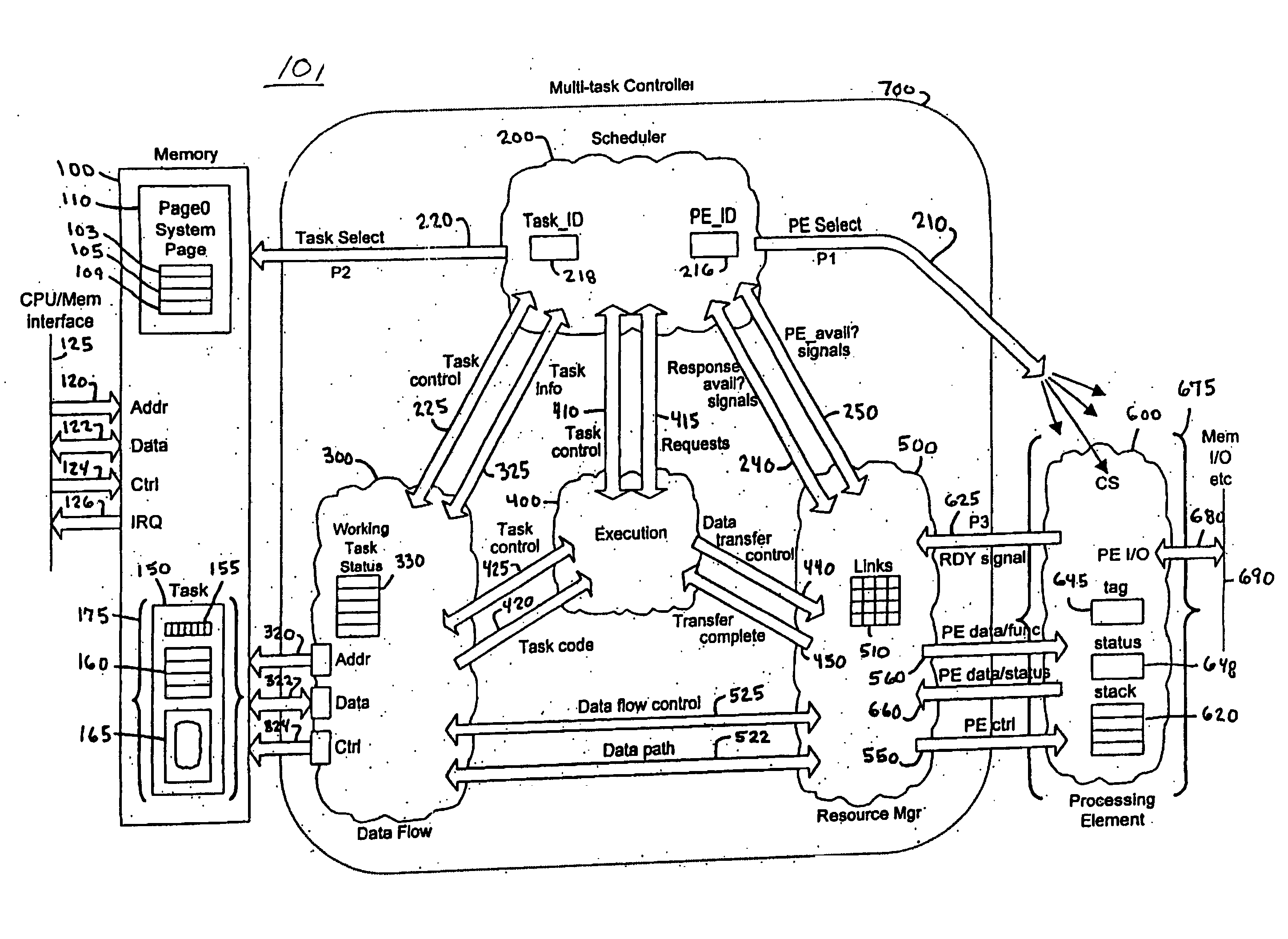
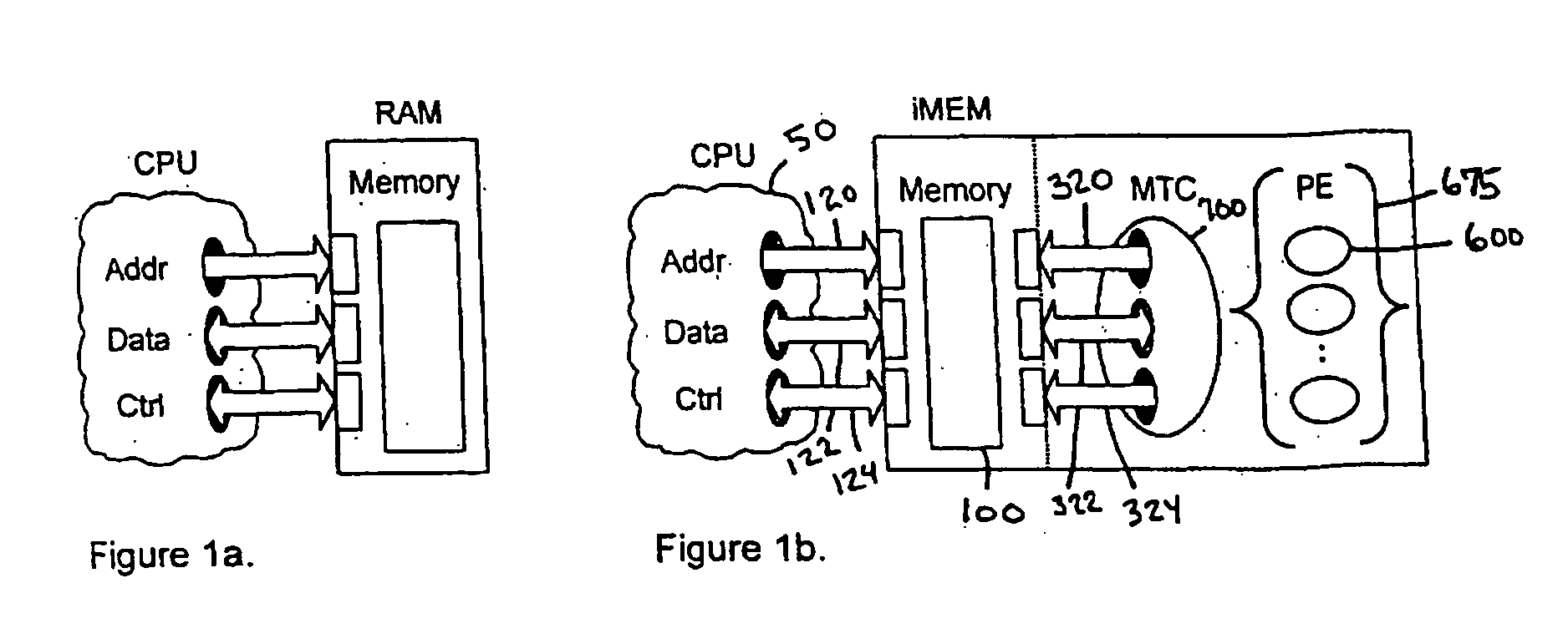
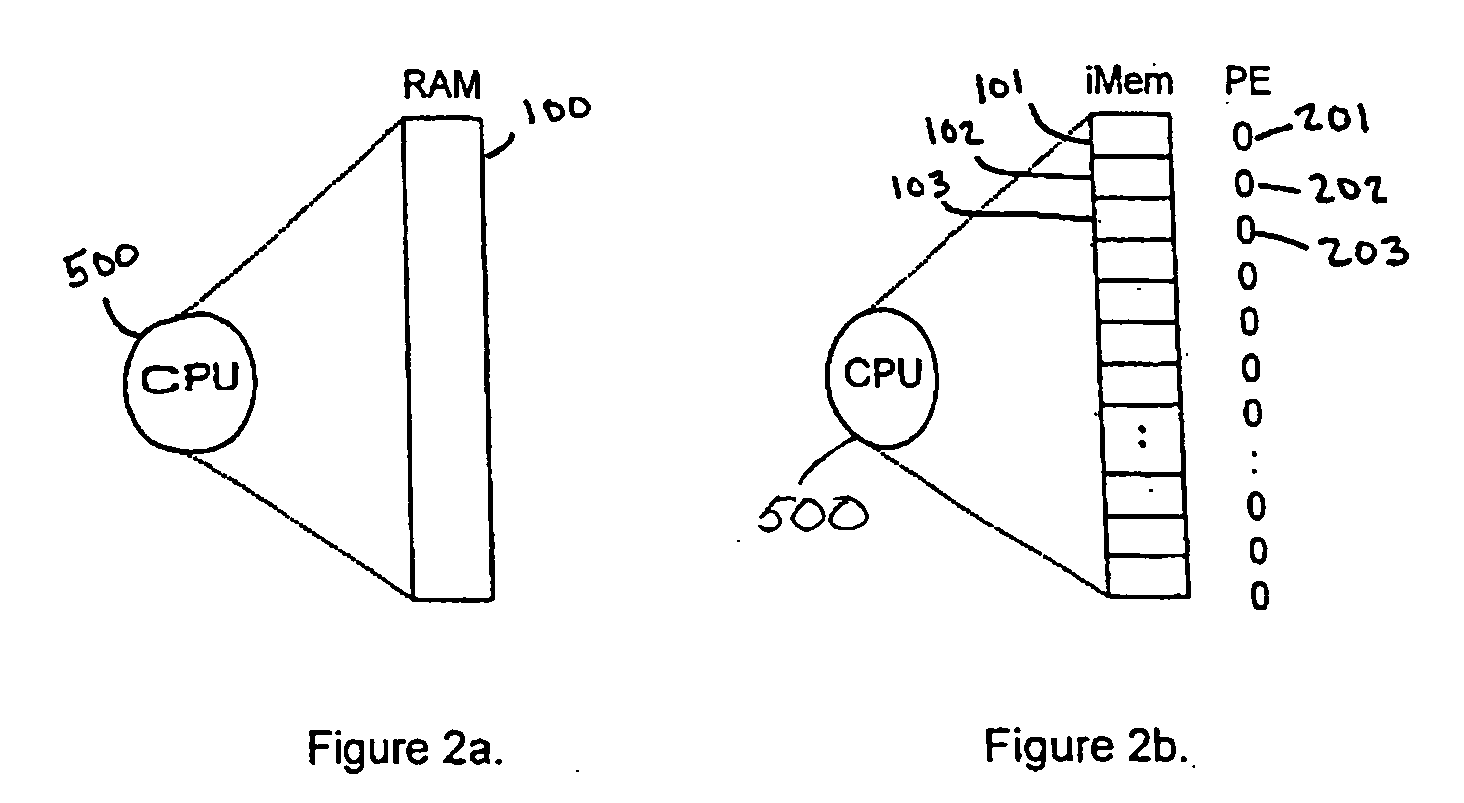
iMEM task index register architecture
InactiveUS20050172090A1Extraordinary capabilityEconomic benefitGeneral purpose stored program computerMultiprogramming arrangementsComputer architectureIndex register
A computing system that includes a number of processing elements, a memory and a multi-task controller is disclosed. The memory has an interface that includes a task page mechanism with an index register. A portion of the multi-task controller also has a task page register for accessing the memory via another interface. The task page mechanism provides access to the memory by the host processor. The index register can be loaded by either the address or data bus of the host processor. In one embodiment, the task page mechanism includes a comparator and a counter to facilitate a polling scan of the status of the various tasks in the memory.
Owner:KLINGMAN REVOCABLE TRUST
Method and device for the controlled editing and broadcasting of compressed multimedia files
InactiveUS20100063984A1Maximum comfortDigital data processing detailsTransmissionDigital transformationIndex register
The present application relates to a method for editing and broadcasting compressed multimedia files composed of binary data blocks originating from digital transformations applied to an audiovisual or multimedia content according to the format of a parent file, said parent file having been separated into a first modified file having the format of the nominal parent file and into a complementary file including information on the modifications brought to the parent file, the method comprising prior to the transmission from a portal to the receiving terminal:a step of preparation including analyzing said first file for extracting time-codes therefrom,a second step including generating an index register table from said first modified file,a third step including generating a modified multimedia file according to the format of the parent file containing information of said first modified file and meta-data,a step of transmission of said modified multimedia file separate from said modified multimedia file, the elements of said complementary file making it possible to recreate a partial synthesis of the original audiovisual file.
Owner:UBICMEDIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com