Ecological sound identification method on basis of rapid sparse decomposition and deep learning
A sparse decomposition, deep learning technology, applied in the field of ecological sound recognition, can solve the problem that the classification effect is not as good as GMM or HMM
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
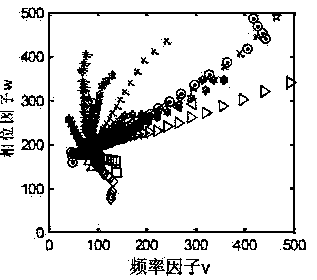
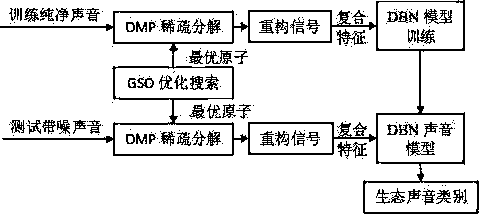
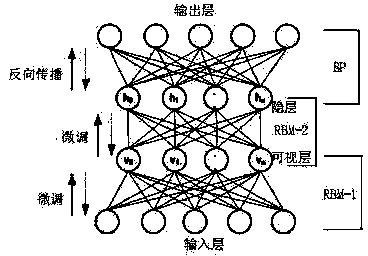
[0037] The invention utilizes the method of fast sparse decomposition and deep learning to recognize ecological sounds. Firstly, use Orthogonal Matching Pursuit (OMP) based on Firefly Algorithm (GSO) to decompose and reconstruct the sound signal with finite times of sparseness, retain high correlation components and filter out low correlation noise; secondly, extract according to atomic time-frequency information and frequency domain information Composite anti-noise features; finally, combined with deep belief network (DBN) to classify and recognize ecological sounds in different environments and signal-to-noise ratio situations. Experiments show that the performance of OMP sparse denoising is better than that of spectral subtraction and wavelet denoising. Compared with the commonly used methods of MFCCs and SVM, this method has different degrees of improvement in the recognition performance of ecological sounds under different signal-to-noise ratios. It has good noise immunit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com