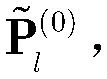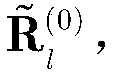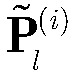Clutter suppression method based on knowledge-assisted sparse iterative covariance estimation
A technology of covariance estimation and knowledge assistance, applied in the field of radar, it can solve the problems of complexity, large amount of calculation, increase of calculation amount, etc., and achieve the effect of suppressing complex and strong ground clutter, good real-time performance, and small calculation amount of estimation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Traditional STAP needs to select the echo data near the unit to be detected as a training sample to estimate it. The selected training sample and the data of the unit to be detected must satisfy the independent and identical distribution conditions. However, in fact, airborne radar usually works in non-uniform noise. In the wave environment, the IID assumption is difficult to satisfy in the actual environment, resulting in a significant decrease in the clutter suppression performance of STAP. In view of the above non-uniformity problems, various methods of suppressing non-uniform clutter have appeared, and the traditional STAP has been improved. The common ones are the rank reduction method and the structuring method. The accuracy of clutter suppression is improved, but the computational load and complexity are also increased. Therefore, the improvement of traditional STAP can effectively suppress ground clutter, significantly improve the detection performance of weak a...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The clutter suppression method based on knowledge-assisted sparse iterative covariance estimation is the same as that of Embodiment 1, and the construction of the first intermediate variable D and the second intermediate variable ρ(i) described in step 2 is as follows:
[0049] is the initial estimated clutter power matrix Iterates continuously to correct the clutter power matrix to make the final estimate To make it closer to the true value, it is necessary to construct two intermediate variables for the iterative process, and construct the value of the first intermediate variable D(Nc×1), whose expression is:
[0050]
[0051] Among them, a(f s,m ) means that the normalized spatial frequency is f s,m The spatial steering vector of the corresponding mth clutter block, the superscript H represents the complex conjugate operation, m∈{1,2,…,Nc}, Nc represents the number of independent clutter blocks on the equidistant ring, and tr represents the matrix trace opera...
Embodiment 3
[0057] The clutter suppression method based on knowledge-assisted sparse iterative covariance estimation is the same as that of Embodiment 1-2, and the lth unit data x to be detected after the ith iteration described in step 3 l Clutter power matrix on a clutter ridge Specifically:
[0058] After the i-th iteration, the l-th unit data x to be detected l The power of the mth clutter block on the clutter ridge Its expression is:
[0059]
[0060] Among them, a(f s,m ) means that the normalized spatial frequency is f s,m the spatial steering vector of the corresponding mth clutter block, Represents the spatial covariance matrix of the lth unit data to be detected reconstructed after the ith iteration, () -1 Represents the matrix inversion operation, and the superscript H represents the conjugate transpose operation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com