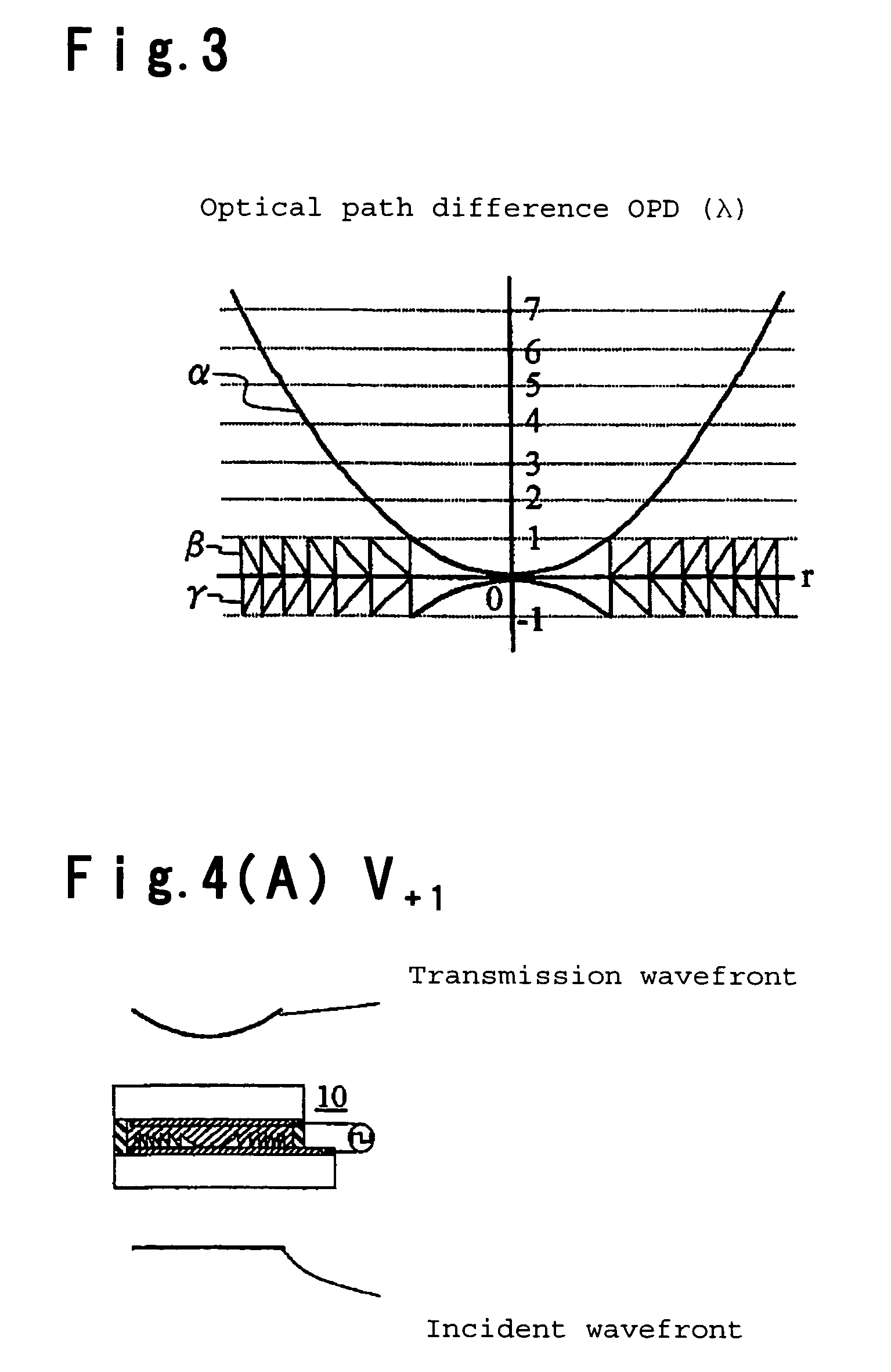
Patents
Literature
86results about How to "Low-voltage driving" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
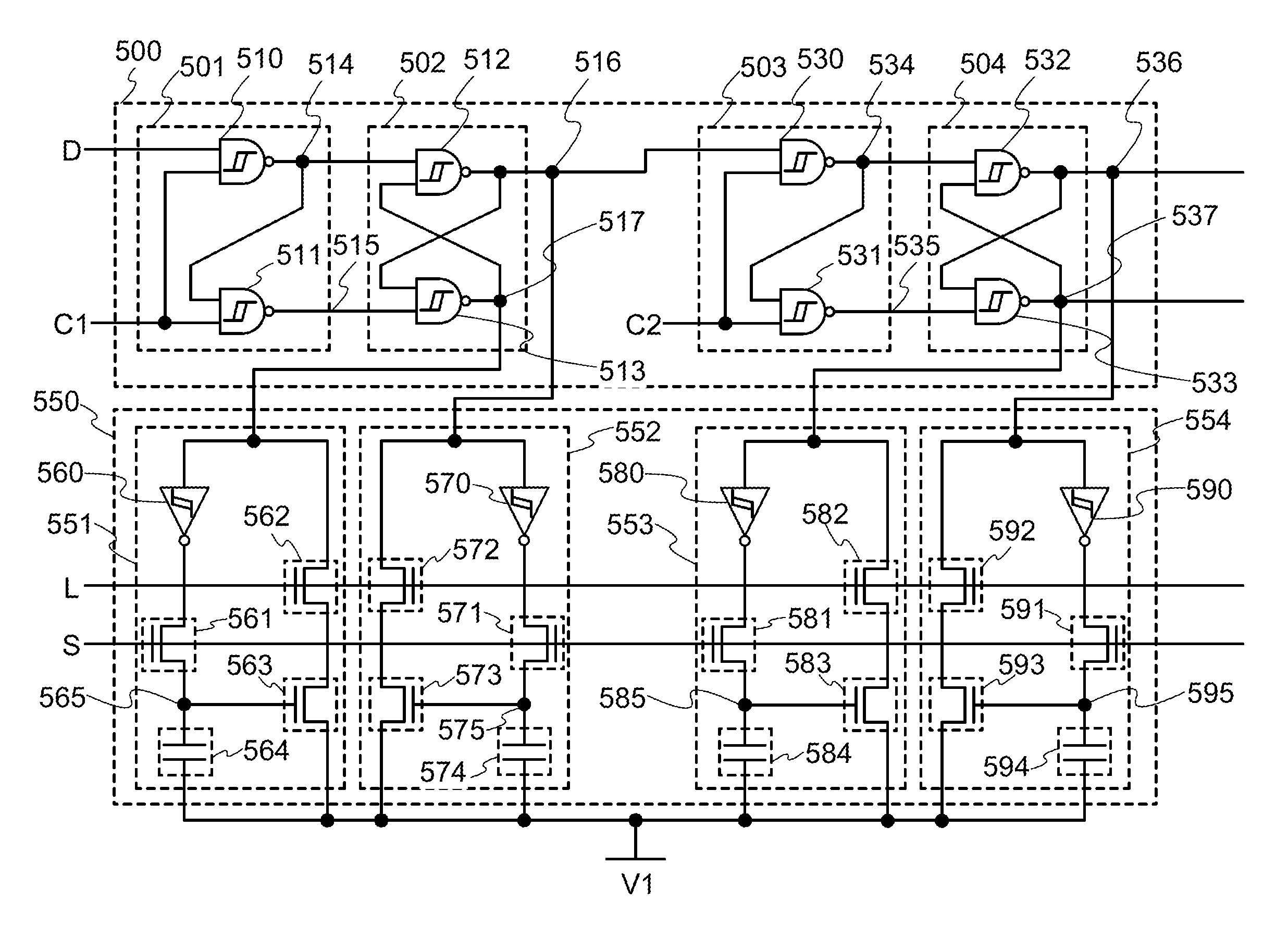
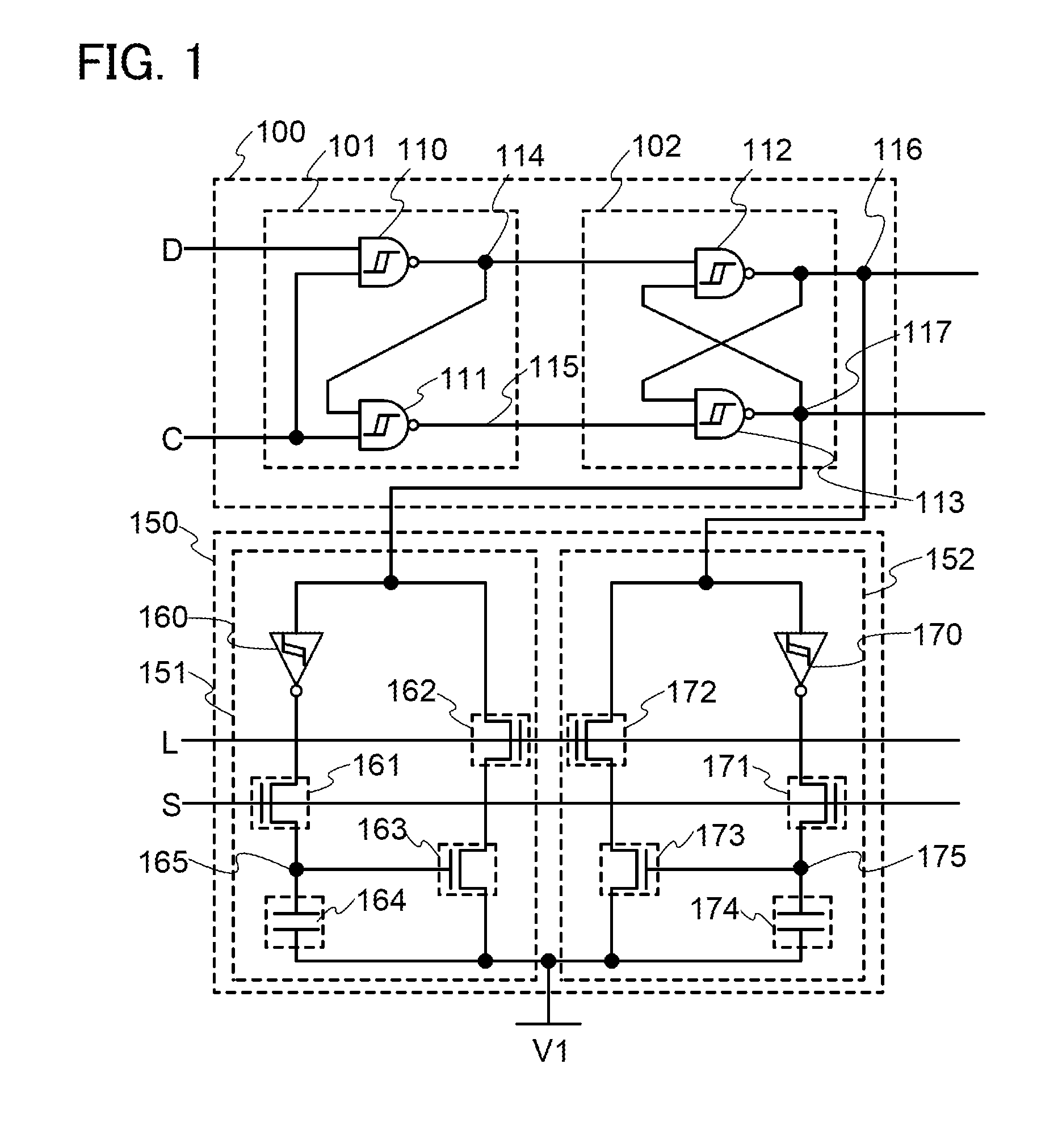
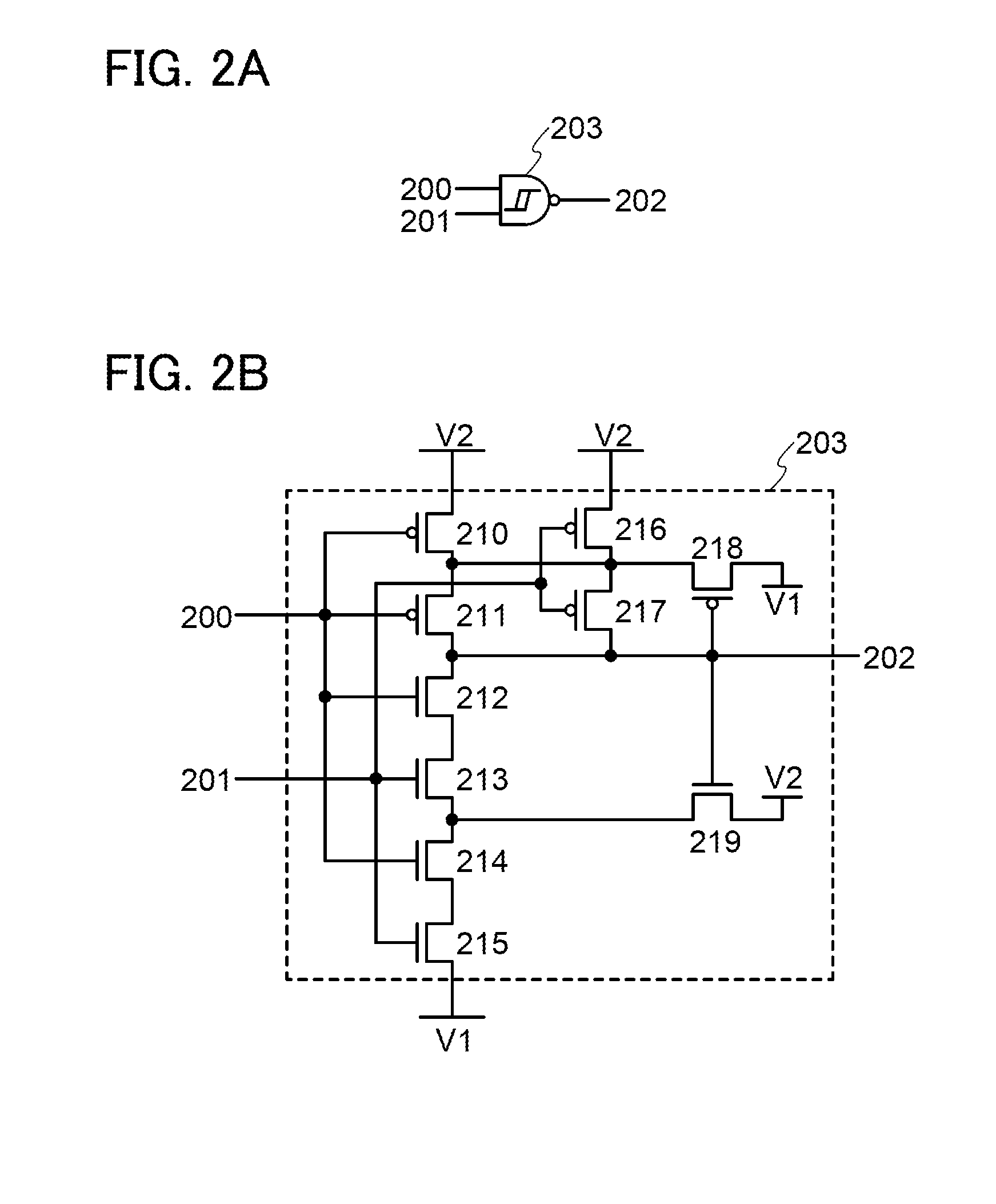
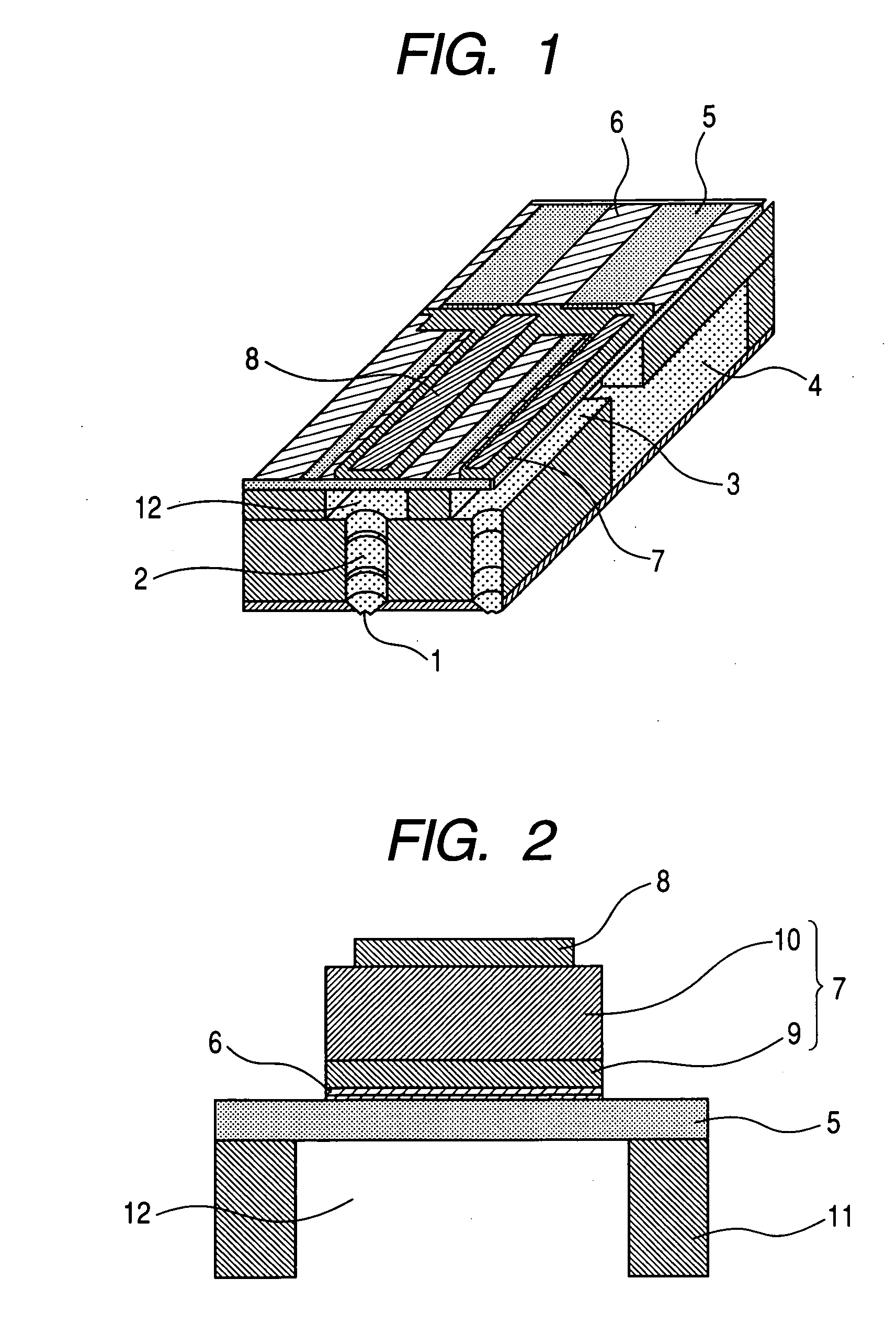
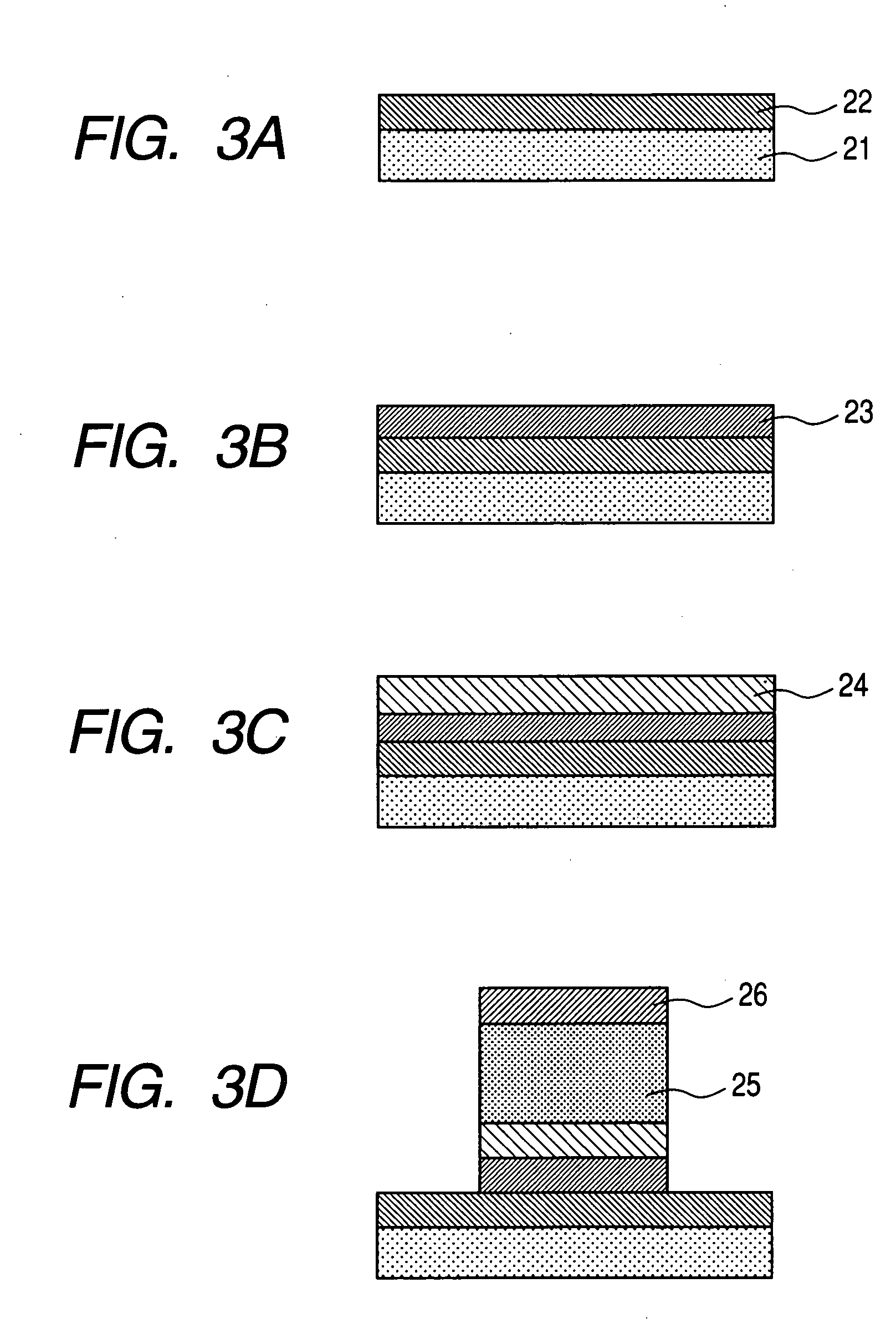
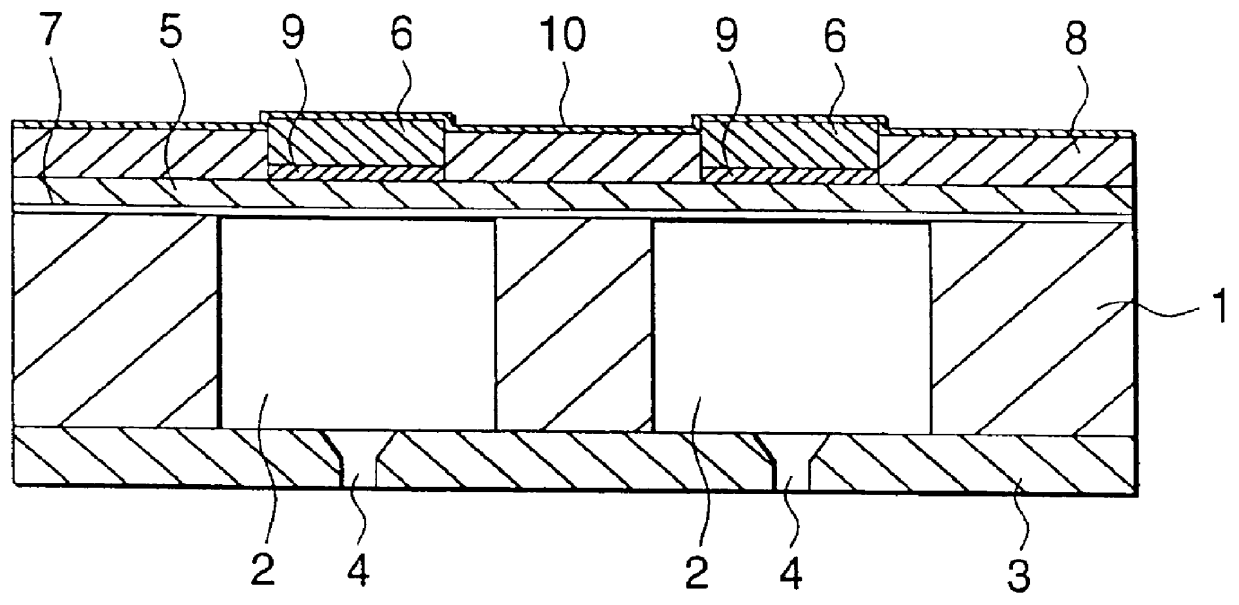
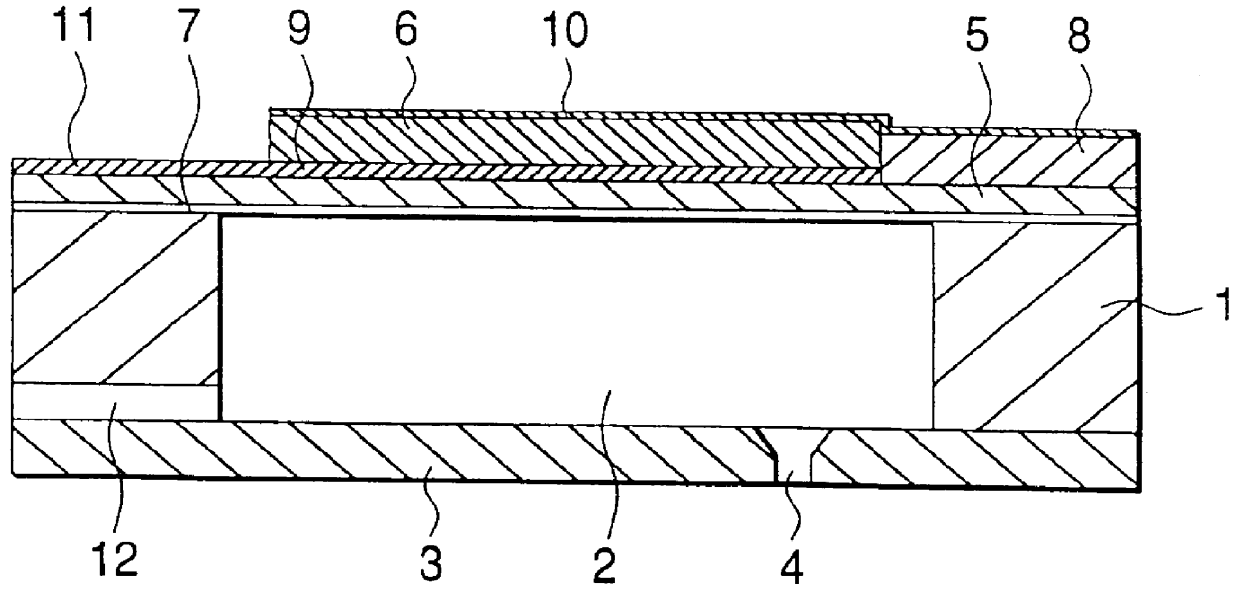
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20140286076A1Low power consumptionReduce power consumptionDigital storagePower semiconductor deviceElectricity
A nonvolatile semiconductor device which can be driven at low voltage is provided. A nonvolatile semiconductor device with low power consumption is provided. A Schmitt trigger NAND circuit and a Schmitt trigger inverter are included. Data is held in a period when the supply of power supply voltage is continued, and a potential corresponding to the data is stored at a node electrically connected to a capacitor before a period when the supply of power supply voltage is stopped. By utilizing a change in channel resistance of a transistor whose gate is connected to the node, the data is restored in response to the restart of the supply of power supply voltage.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Organic electroluminescent device
InactiveUS20060105202A1Improve driving durabilityLow-voltage drivingDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSimple Organic CompoundsHost material
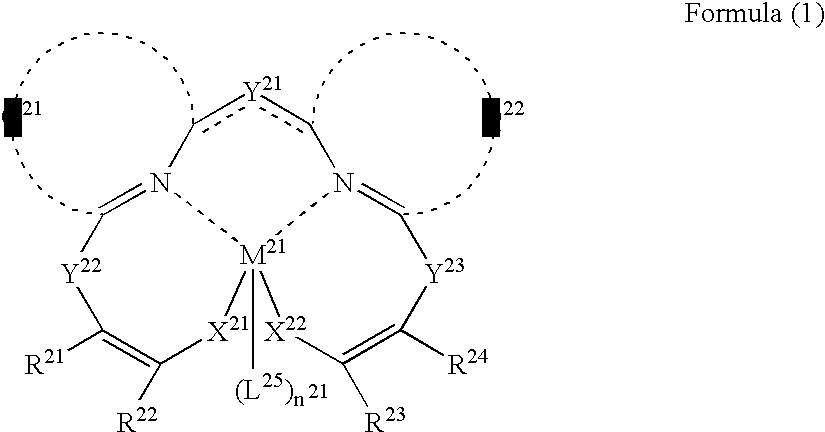
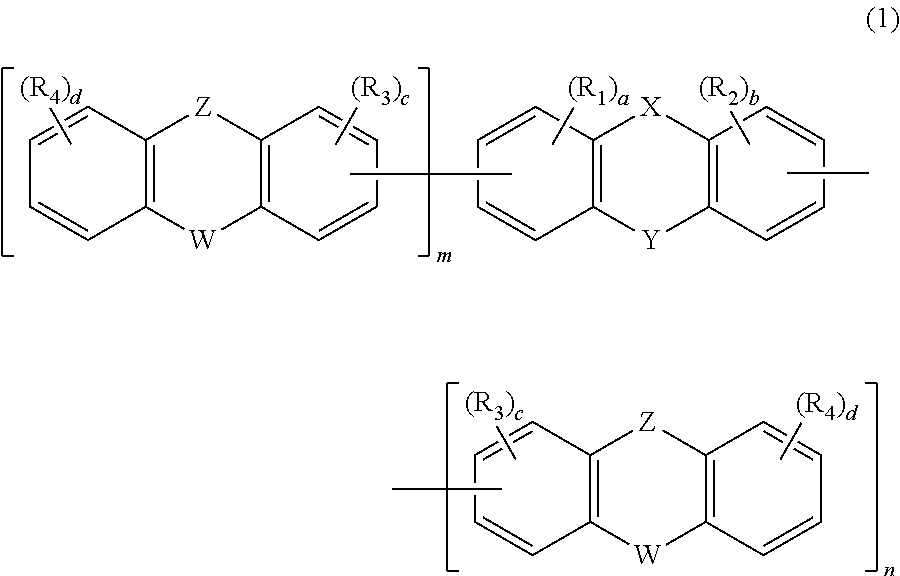
A first aspect of the invention is an organic electroluminescent device that includes a plurality of organic compound layers between a pair of electrodes. The plurality of organic compound layers include a luminescent layer and two or more hole-transporting layers. The hole-transporting layers include a layer adjacent to the luminescent layer. The luminescent layer contains a host material and a luminescent material. The luminescent material is a metal complex containing a tri- or higher-dentate ligand. When the ionization potential of the luminescent layer is designated as Ip0, the ionization potential of the hole-transporting layer adjacent to the luminescent layer among the hole-transporting layers is designated as Ip1, and the ionization potential of the n-th hole-transporting layer from the luminescent layer among the hole-transporting layers is designated as IPn, these values satisfy the relationship represented by the following formula (1). In formula (1) n is an integer of 2 or more. Ip0>Ip1>Ip2> . . . >Ipn-1>Ipn formula (1)
Owner:UDC IRELAND
Film forming apparatus, film forming method, and manufacturing method of light emitting element
InactiveUS20070190235A1Reduce strainReduce defectsElectroluminescent light sourcesVacuum evaporation coatingLow voltageEvaporation
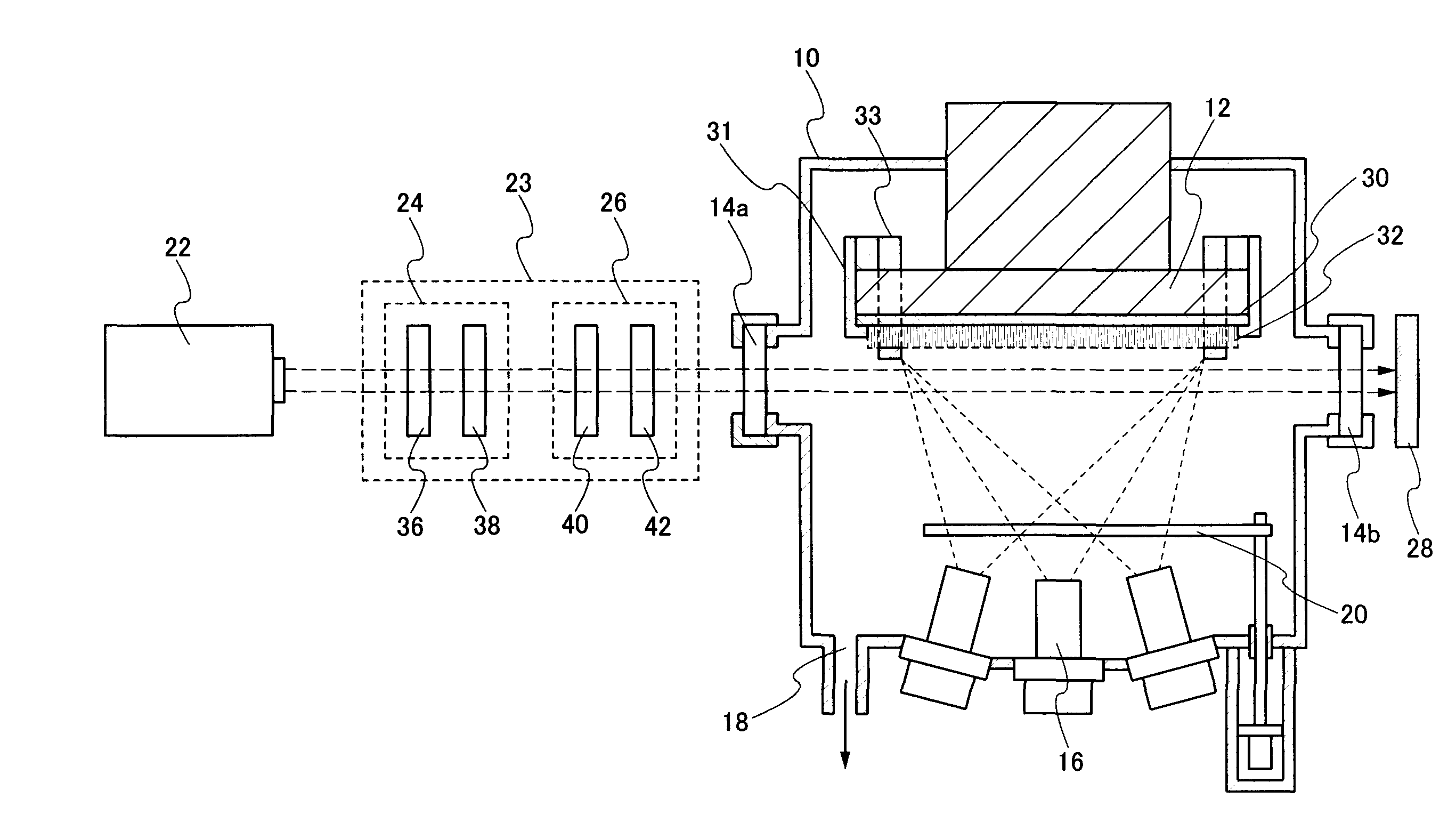
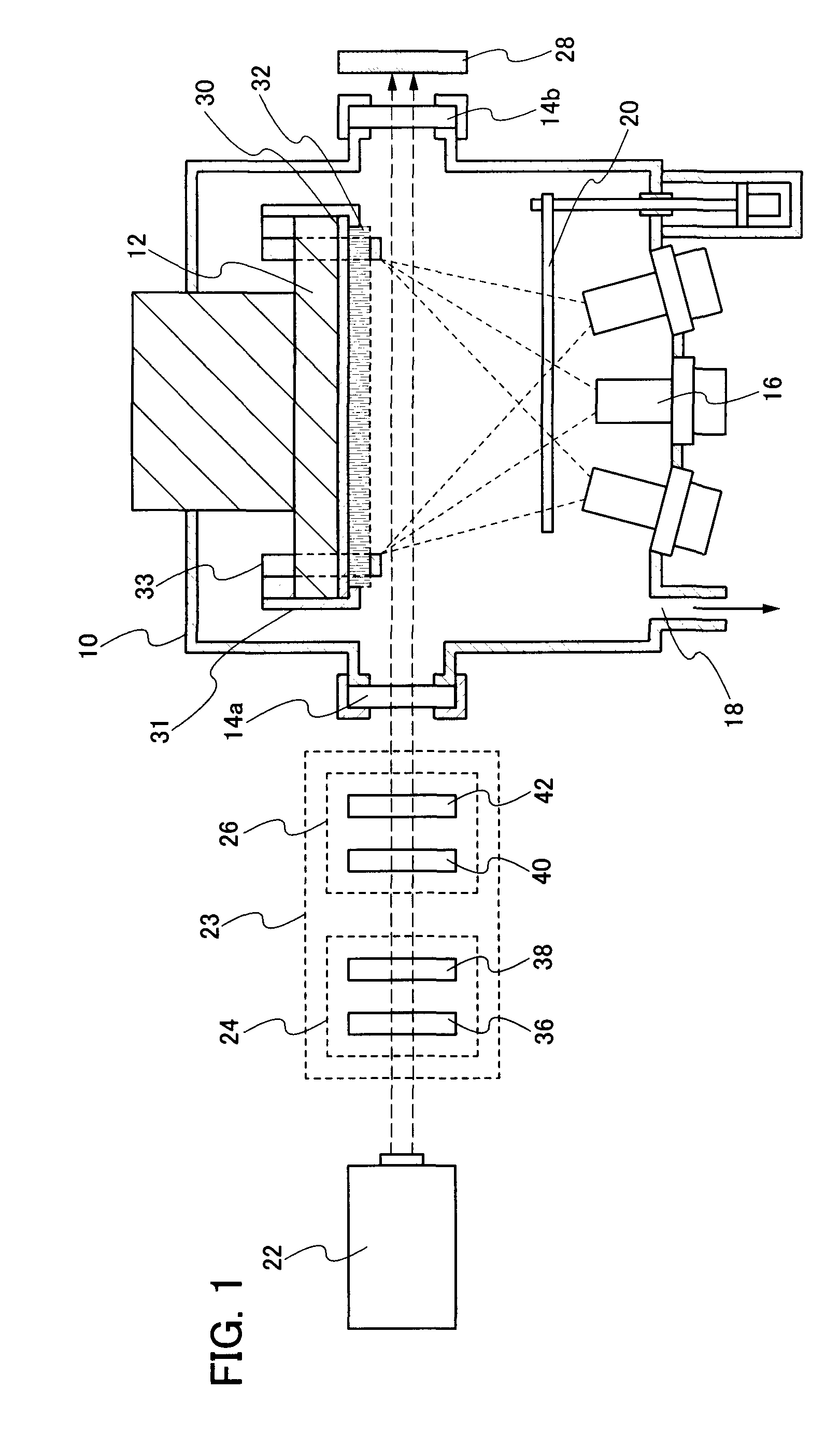
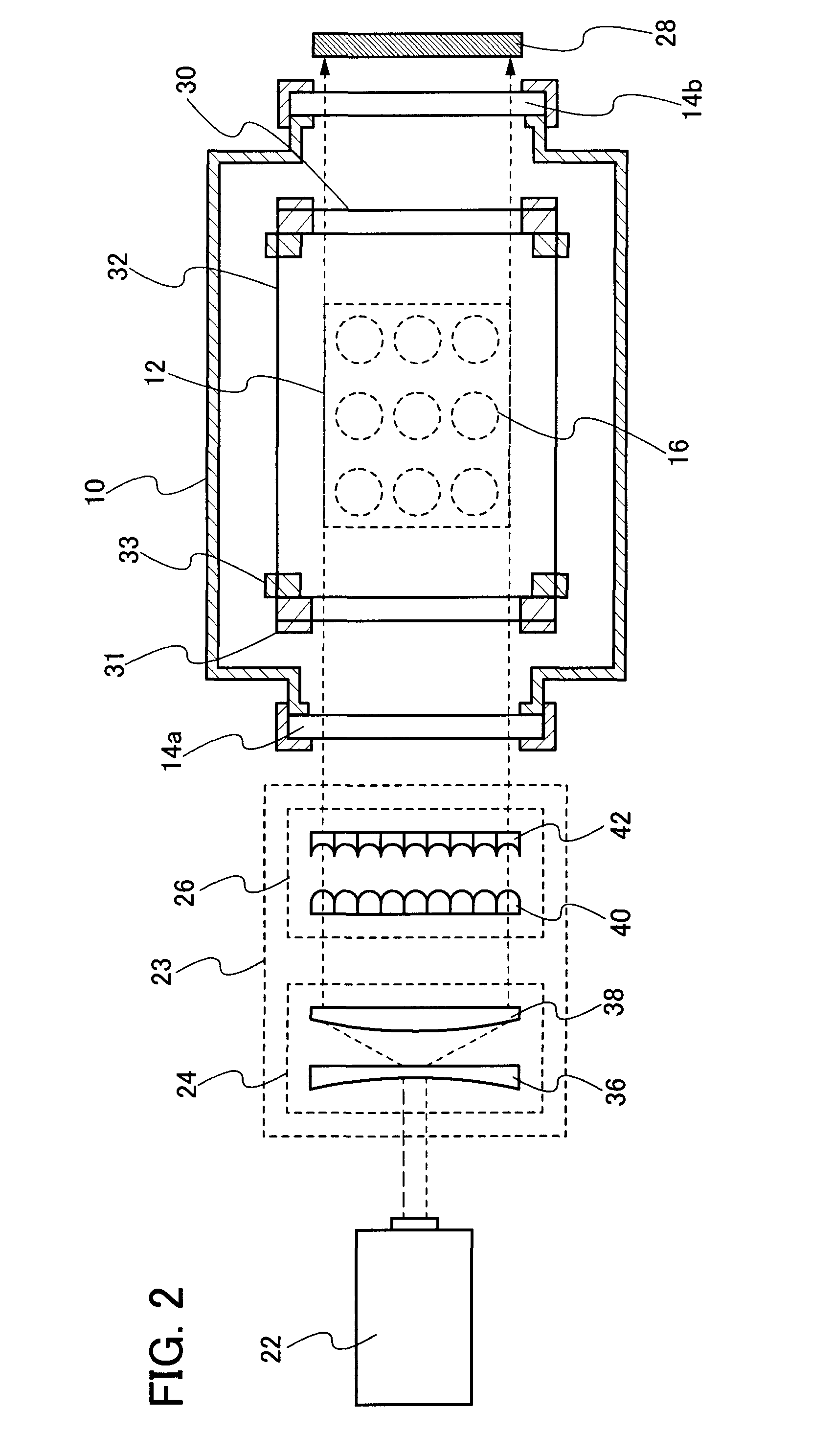
An object of the present invention is to provide a film forming method for forming a film with reduced defect and to provide a film forming method for forming a film with a uniform quality. In addition, another object is to provide a manufacturing method of a light emitting element which can be driven with low voltage. Further, another object is to provide a manufacturing method of a light emitting element with high light emission efficiency. A film with reduced defect and a uniform quality can be formed by fixing a substrate to a substrate holding unit so that at least a part of a surface of the substrate is exposed, evaporating a vapor deposition material from an evaporation source filled with the vapor deposition material, irradiating the vapor deposition material which is evaporated with a laser beam, and depositing the vapor deposition material on the surface of the substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Manufacturing method of display device
InactiveUS20070190675A1Defect and distortionReduce crystallinityStatic indicating devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight irradiationDisplay device
A highly functional and reliable display device with lower power consumption and higher light-emitting efficiency is provided. A light-emitting material is irradiated with light; the light-emitting material irradiated with light is dispersed in a solution containing a binder, and a solution containing the light-emitting material irradiated with light and the binder is formed; a first electrode layer is formed; the solution is applied on the first electrode layer, and a light-emitting layer containing the light-emitting material irradiated with light and the binder is formed; and a second electrode layer is formed over the light-emitting layer, and a light-emitting element is manufactured. An insulating layer may be provided between the first electrode layer and the light-emitting layer or between the second electrode layer and the light-emitting layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
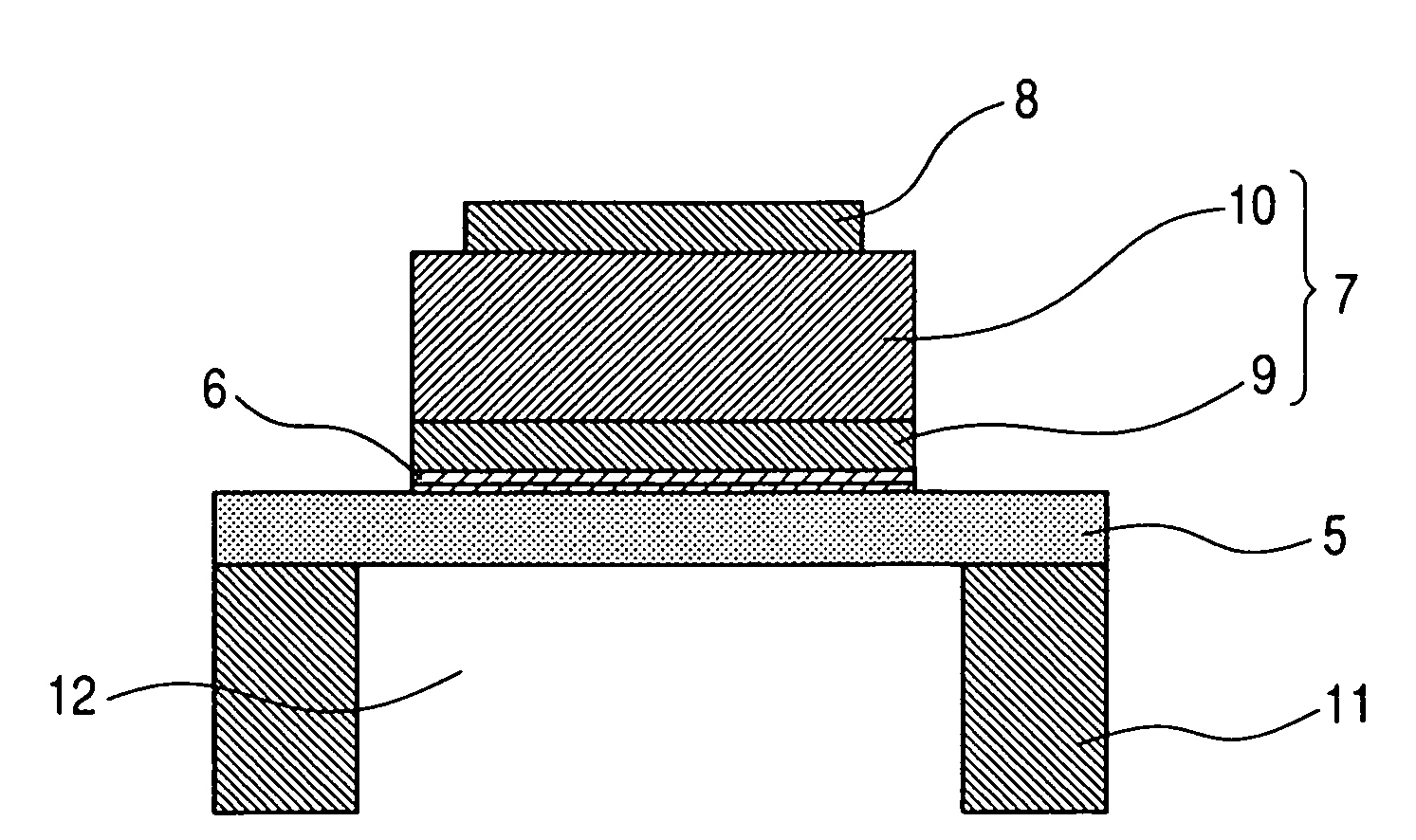
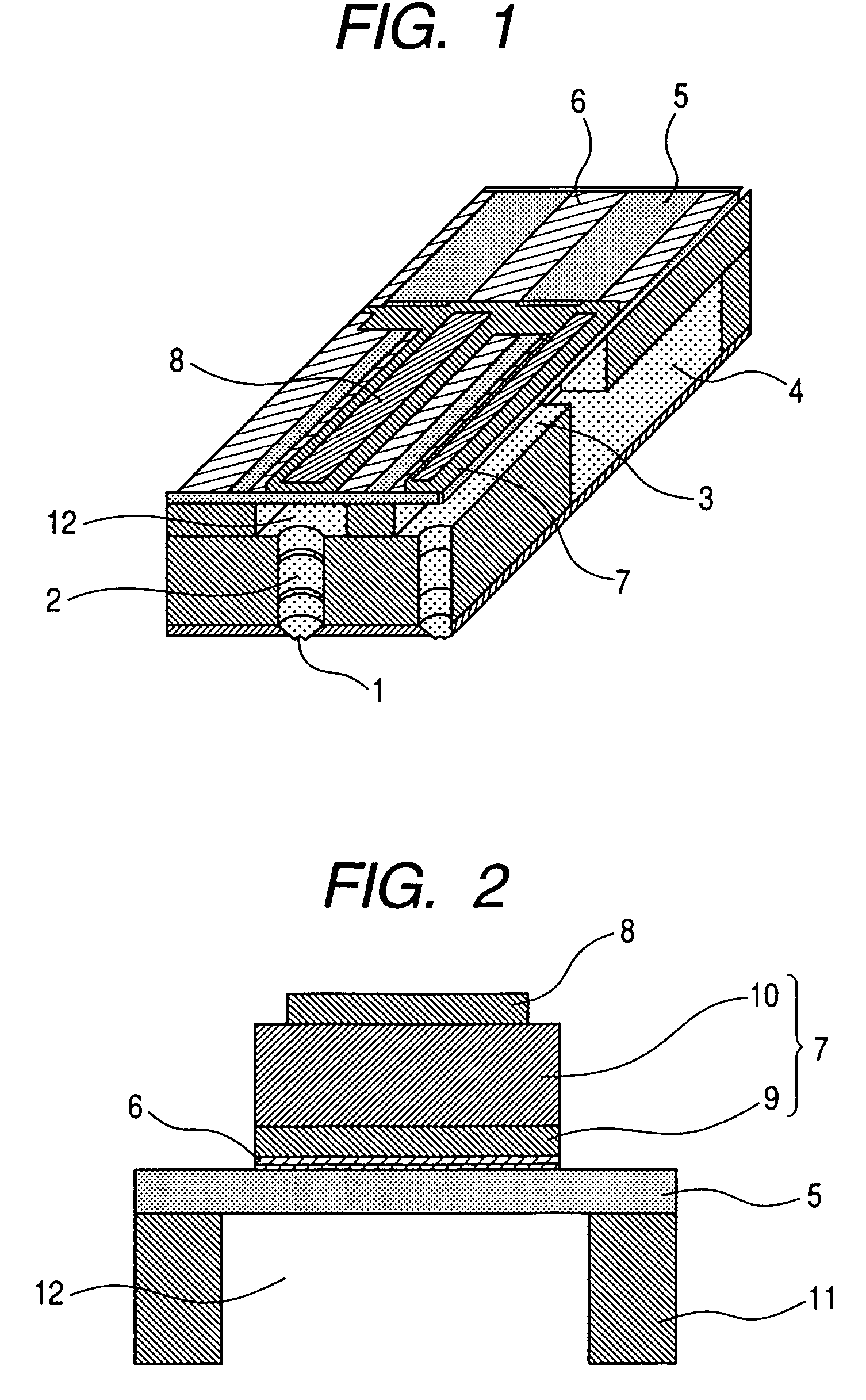
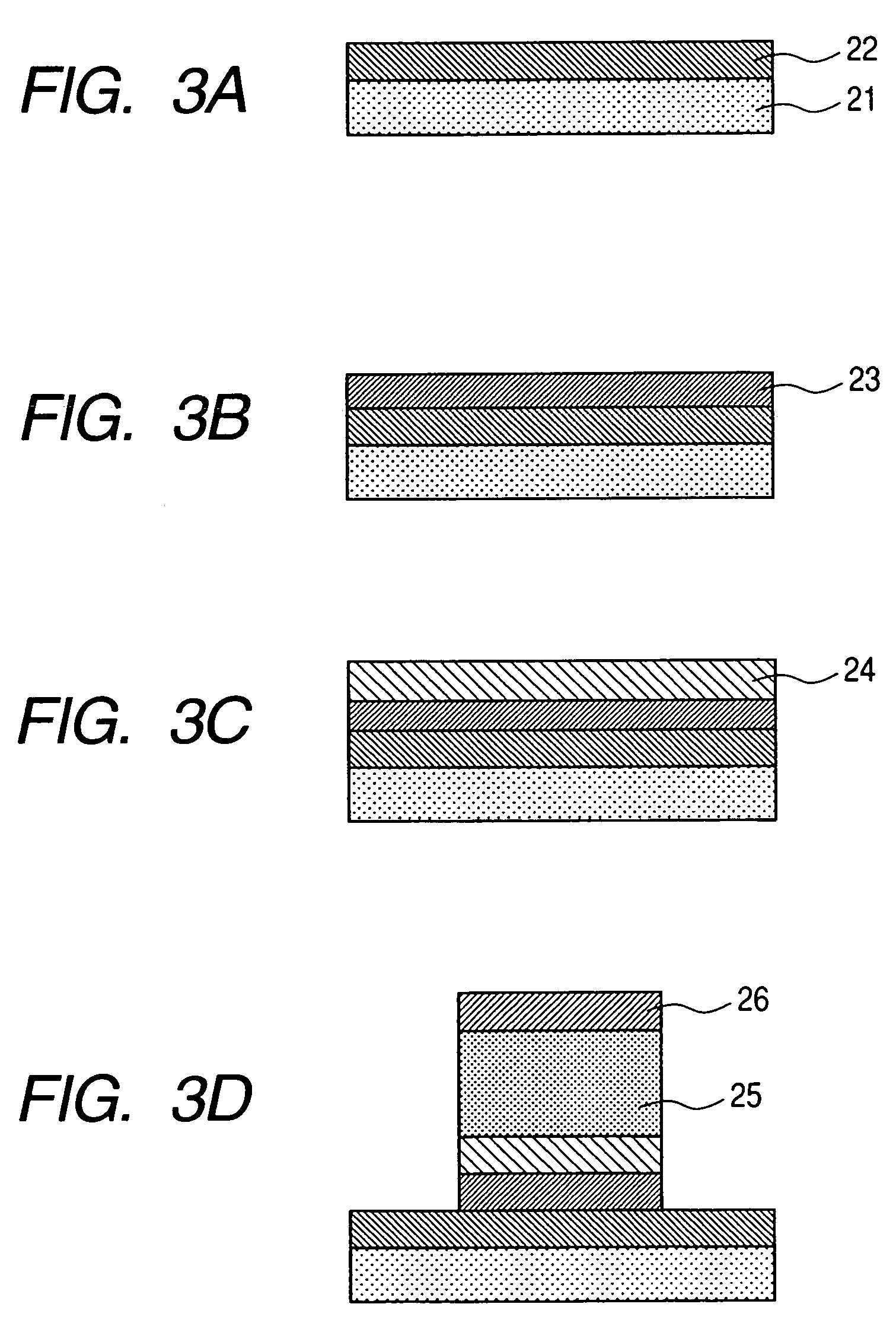
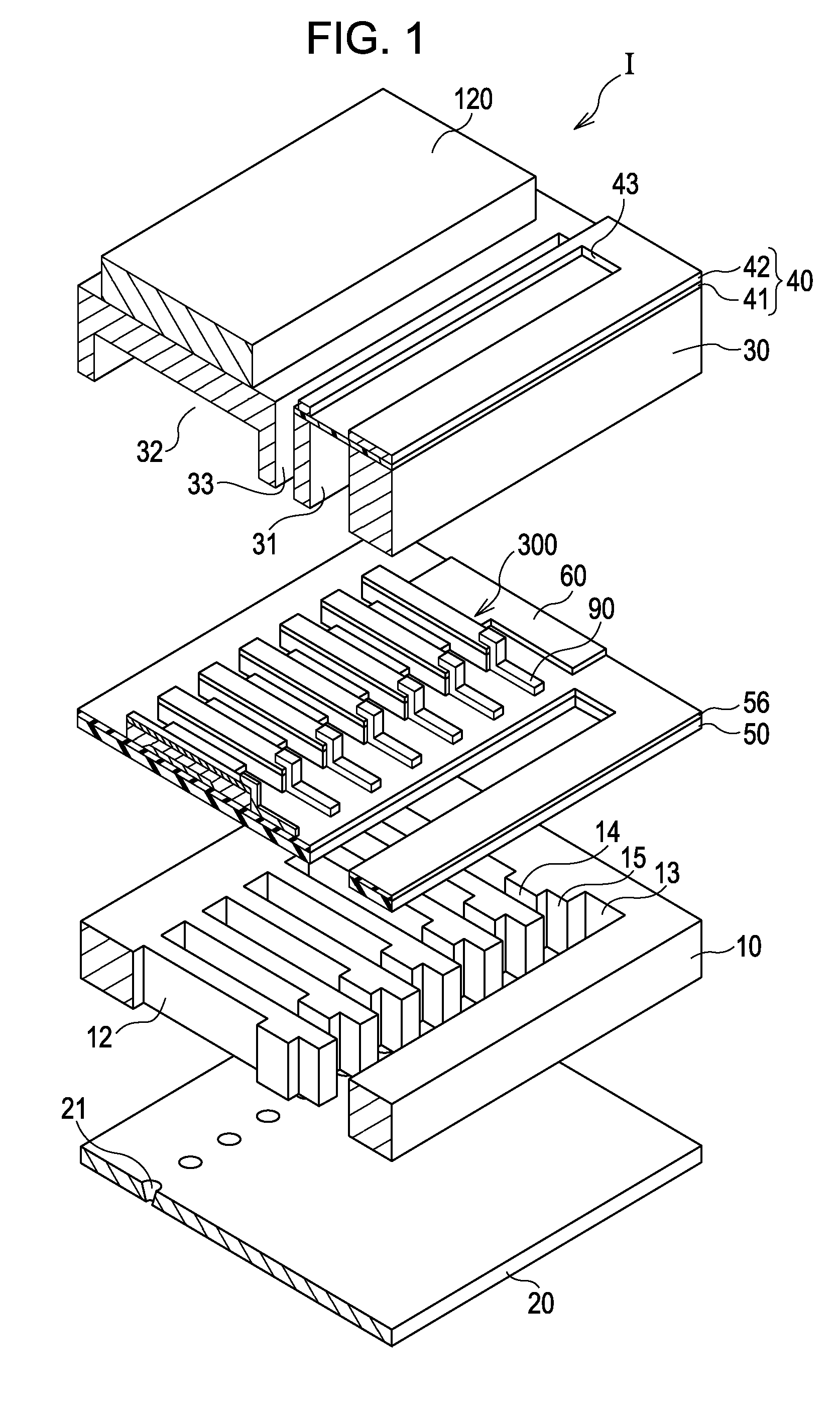
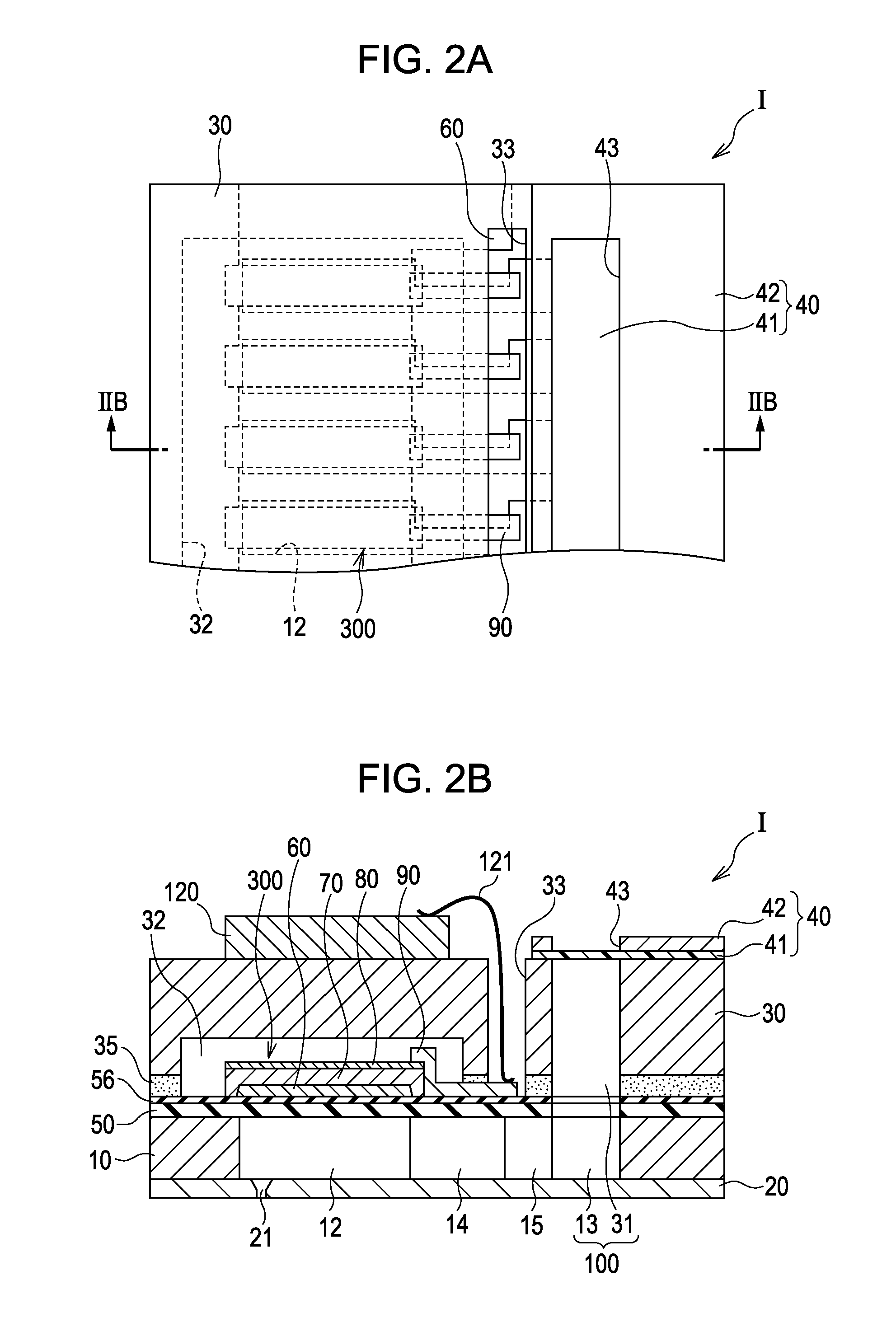
Dielectric element, piezoelectric element, ink jet head and ink jet recording apparatus and manufacturing method of same
InactiveUS20050189849A1Improve featuresLow-voltage drivingPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyInking apparatusDielectric layerMaterials science
A dielectric element having a dielectric layer provided between an upper electrode layer and a lower electrode layer, wherein the dielectric layer has a first dielectric layer and a second dielectric layer mutually different in composition, and composition of at least one component of the first dielectric layer changes as to a thickness direction of the first dielectric layer in proximity to a boundary between the first dielectric layer and the second dielectric layer.
Owner:CANON KK +1
Laminated ink-jet recording head, a process for production thereof and a printer equipped with the recording head
InactiveUS6158847ASmall film thicknessEfficiently issuedInking apparatusPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesLow voltageBiomedical engineering
PCT No. PCT / JP96 / 01924 Sec. 371 Date May 14, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date May 14, 1997 PCT Filed Jul. 11, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 03834 PCT Pub. Date Feb. 6, 1997A laminated ink-jet recording head is provided that has a strong joint between the diaphragm and the piezoelectric vibrating element and which can be driven on low voltage. The recording head is of such a design that a lower electrode is provided on the diaphragm in at lest a region that corresponds to said pressure generating chamber, the lower electrode being overlaid with the piezoelectric vibrating element formed by a hydrothermal method, said piezoelectric vibrating element in turn being overlaid with an upper electrode and having a film thickness of not less than 1 mu m but not more than 10 mu m. The invention further provides a process for producing this recording head, as well as an apparatus such as a printer that is equipped with this recording head.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Anthracene derivatives and organic light emitting device using the same as a light emitting material
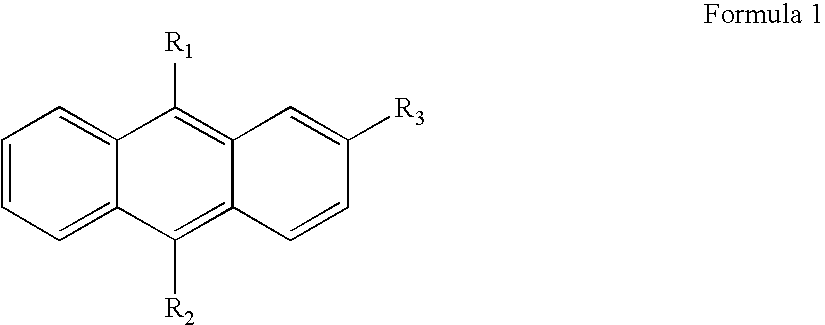
InactiveUS20060046097A1Prolong lifeRealize low voltageOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensAnthraceneOrganic light emitting device
Disclosed is a compound of Formula 1 and an organic light emitting device using the same. In Formula 1, R1, R2, and R3 each independently is selected from the group consisting of a phenyl group, an 1-naphthyl group, a 2-naphthyl group, and a pyrene.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
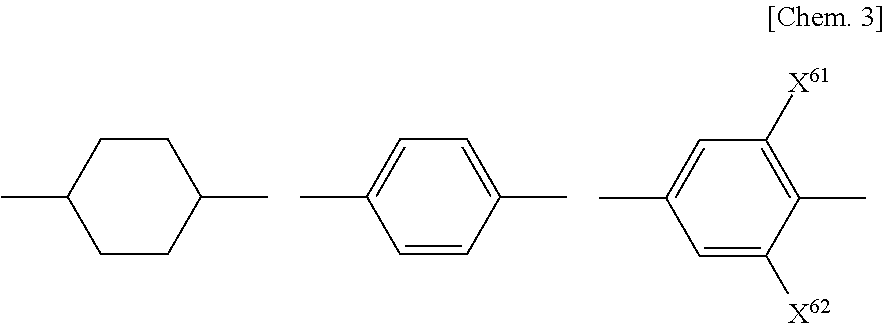
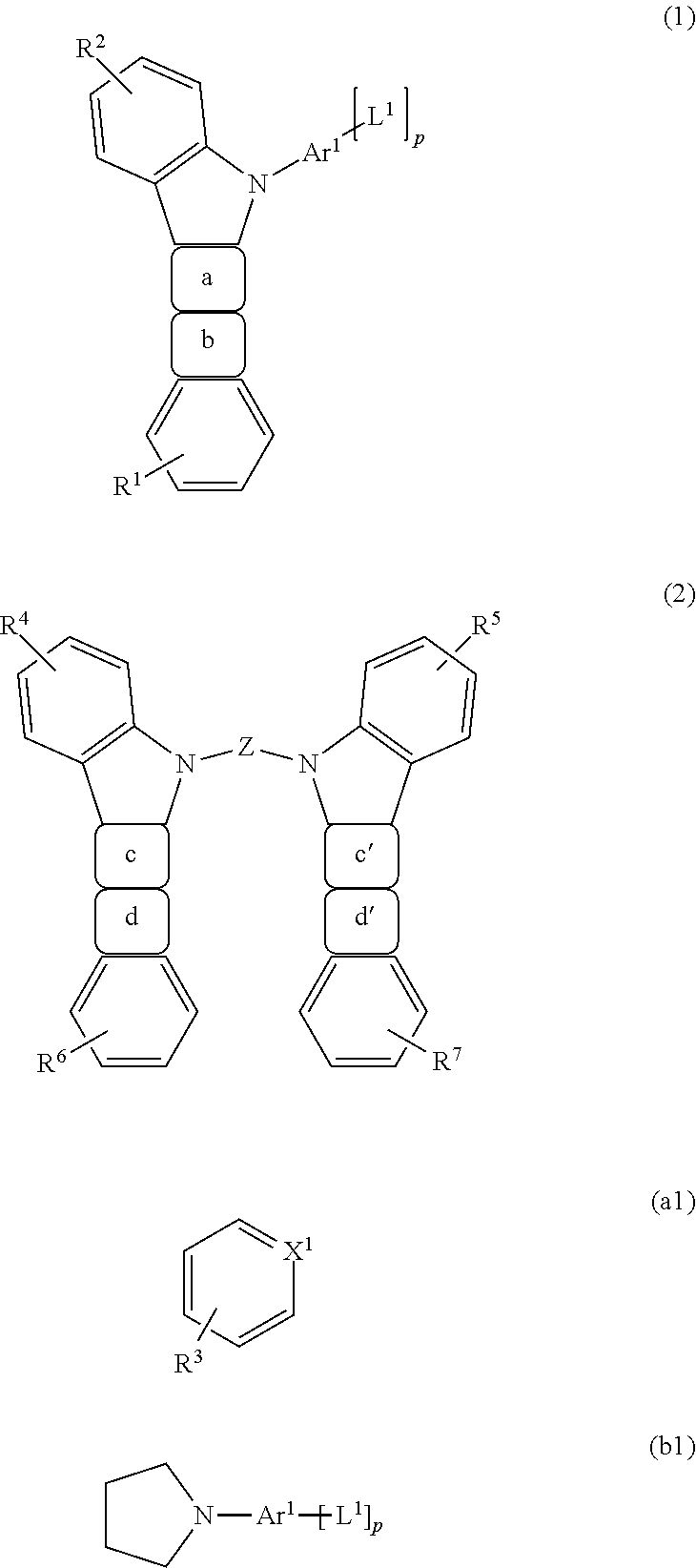
Carbazole Compound, Light-Emitting Element, Light-Emitting Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device
ActiveUS20120302762A1Improve efficiencyGood hole transport propertiesOrganic chemistryCarbazolePhenyl group
A carbazole compound represented by General Formula (G1) is provided.In the formula, α represents a phenylene group, Ar1 represents an alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, a substituted or unsubstituted phenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted naphthyl group, or a substituted or unsubstituted phenanthryl group, Ar2 represents hydrogen, a substituted or unsubstituted phenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted naphthyl group, or a substituted or unsubstituted phenanthryl group, Ar3 represents a substituted or unsubstituted phenyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted naphthyl group, or a substituted or unsubstituted phenanthryl group, and R1 represents hydrogen, an alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, or a substituted or unsubstituted phenyl group. Further, n is 0 or 1.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Liquid crystal lens element and optical head device
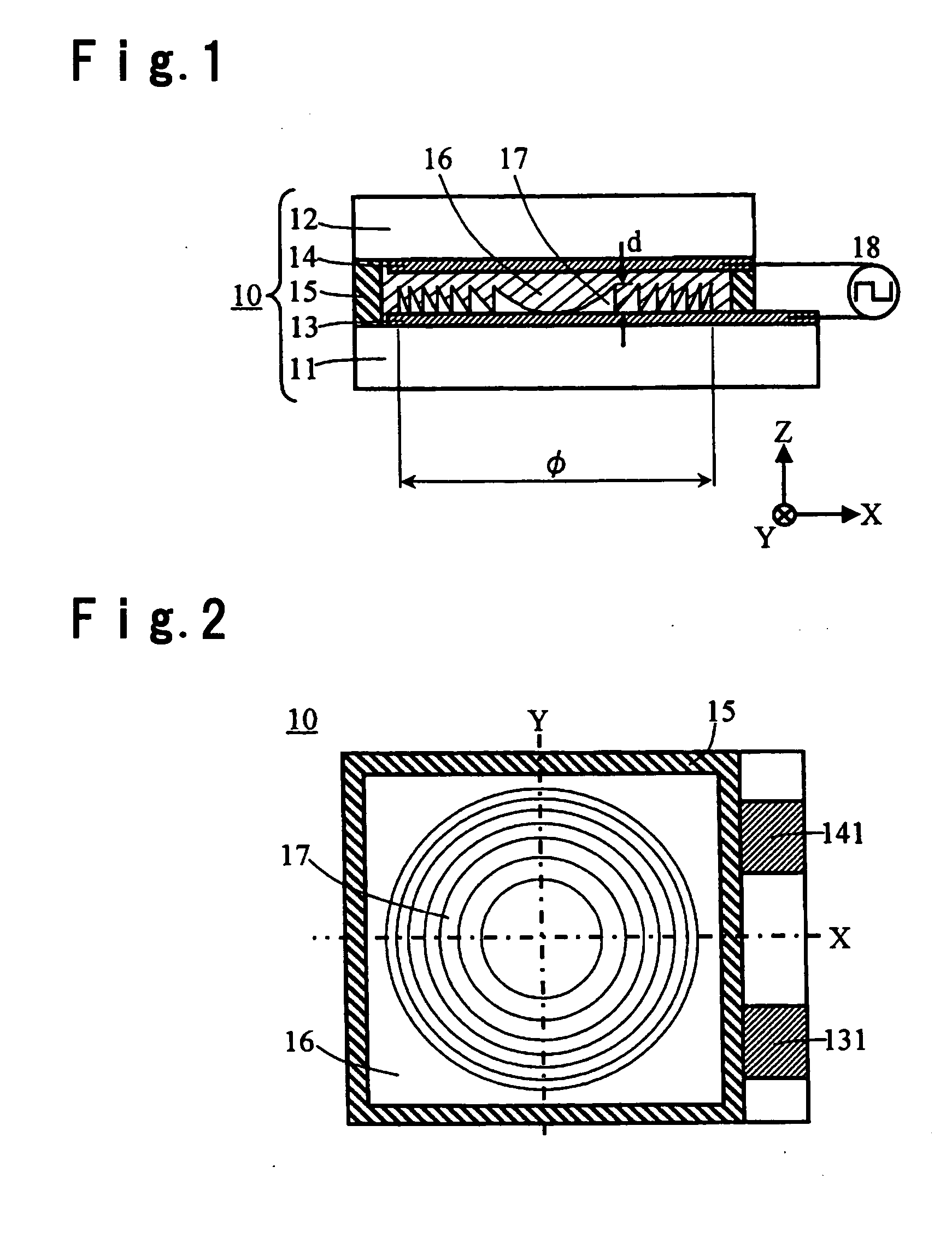
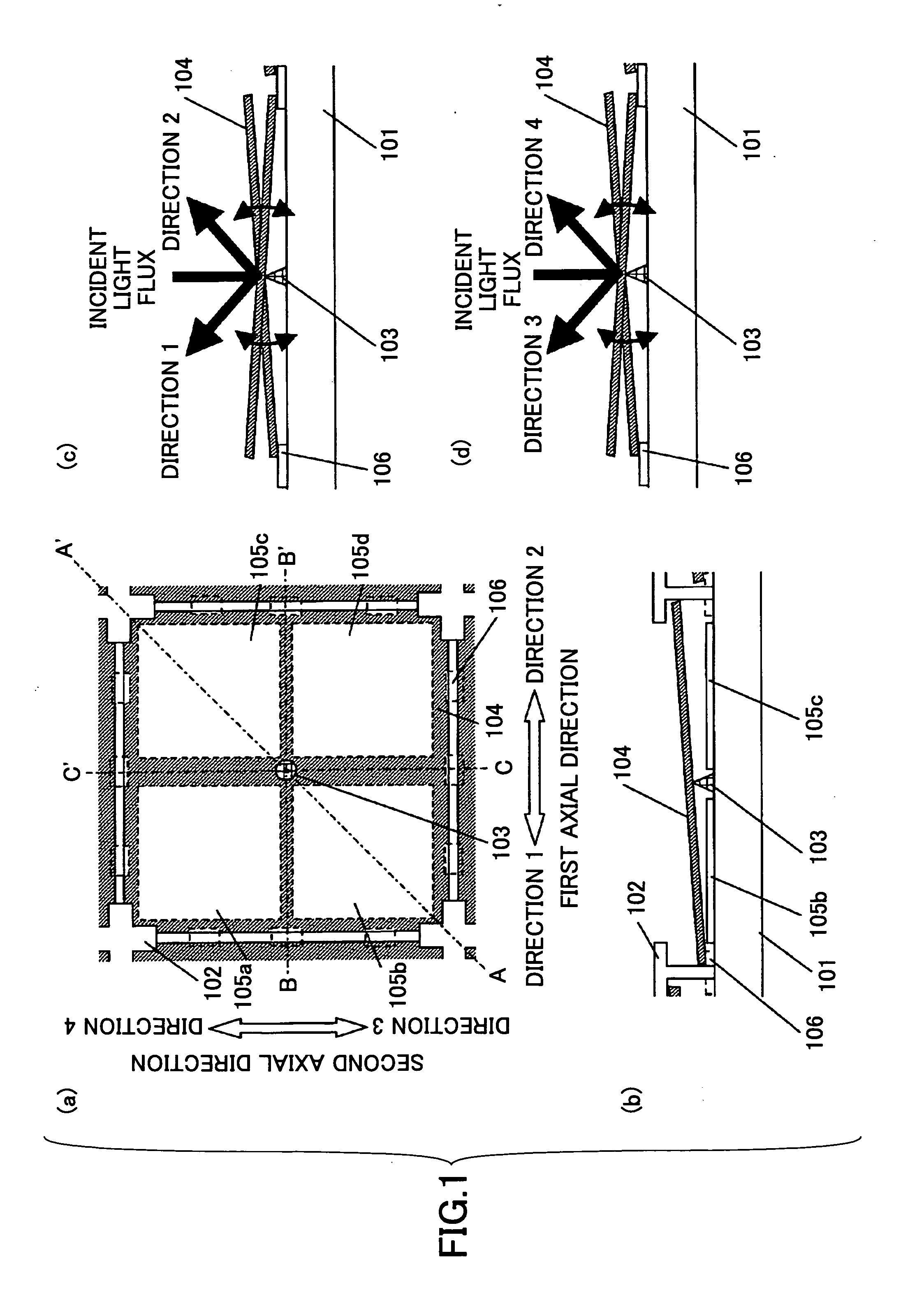
ActiveUS20060280100A1Guaranteed uptimeLow voltage drivingOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageOptical axisRefractive index
A liquid crystal lens element having a lens function is provided, which is small sized without having moving part, and which can stably carry out correction of spherical aberration containing a power component corresponding to focal point change of incident light. A liquid crystal lens element which changes a focal length of light transmitted through a liquid crystal 16 according to the magnitude of the voltage applied to the liquid crystal 16 sandwiched between a pair of transparent substrates 11 and 12, which comprises transparent electrodes 13 and 14 provided on the respective transparent substrates 11 and 12 for applying a voltage for the liquid crystal 16, and a concave-convex portion 17 having a saw-tooth-shaped cross-sectional shape having a rotational symmetry about an optical axis and formed on one surface of the transparent electrode 13 with a transparent material, wherein at least concave portions of the concave-convex portion 17 are filled with the liquid crystal 16 so as to change the substantial refractive index of the liquid crystal 16 according to the magnitude of applied voltage.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Microactuator
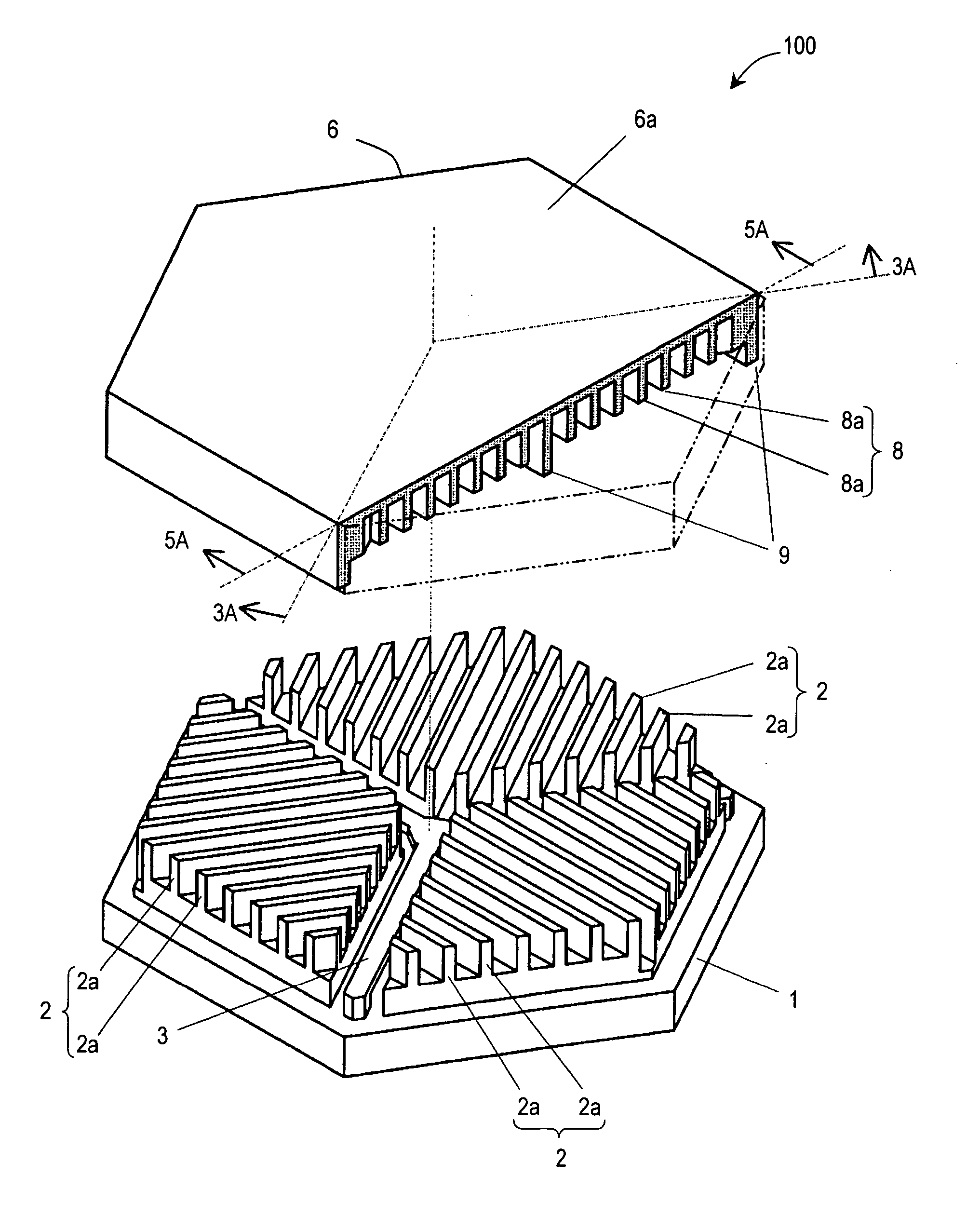
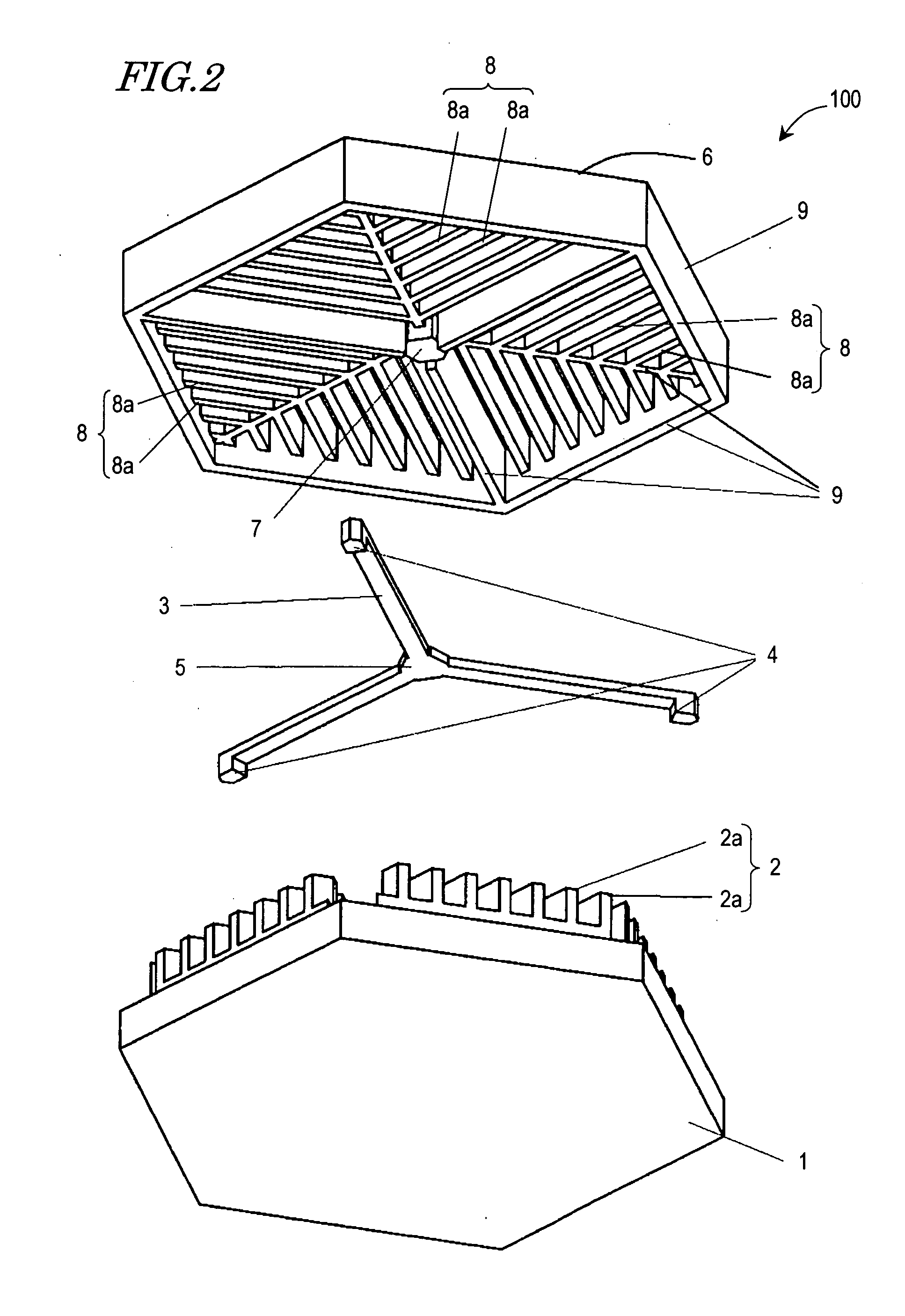
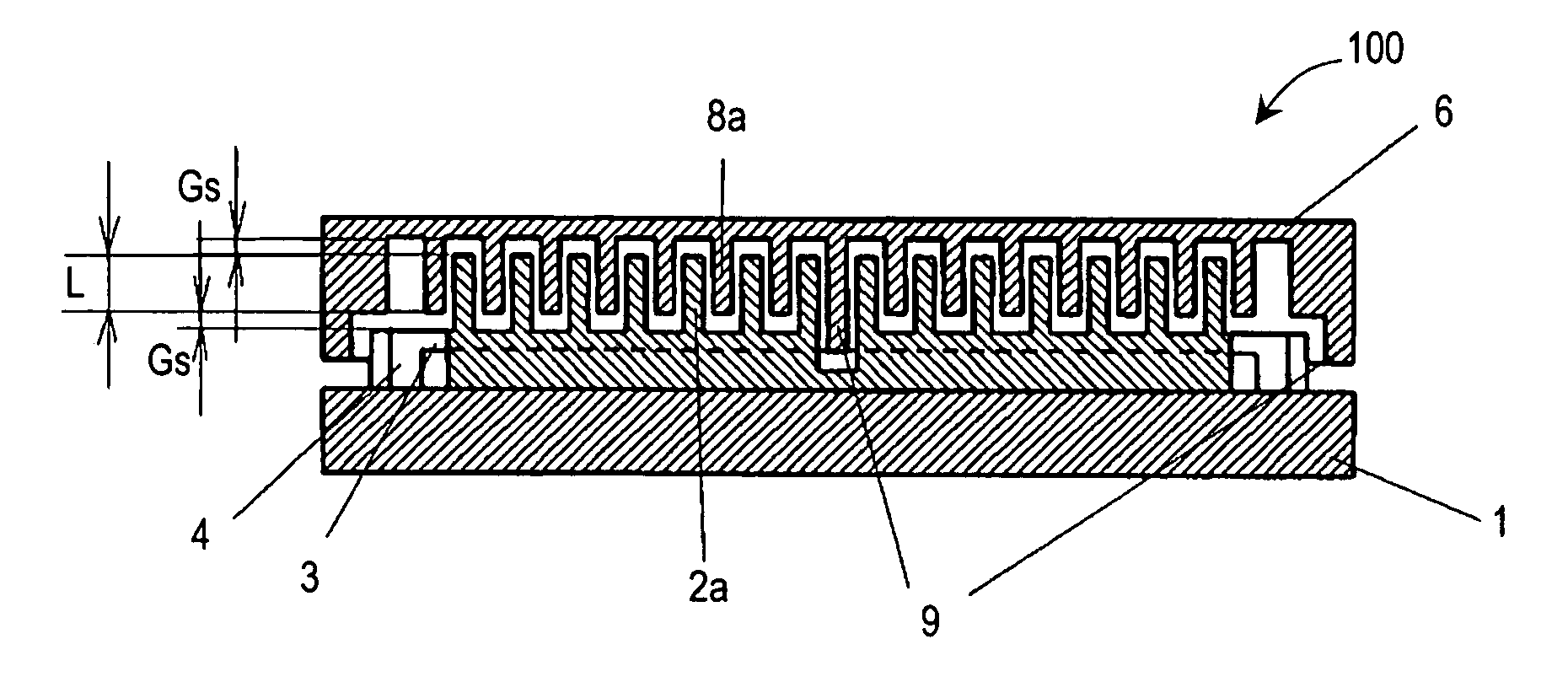
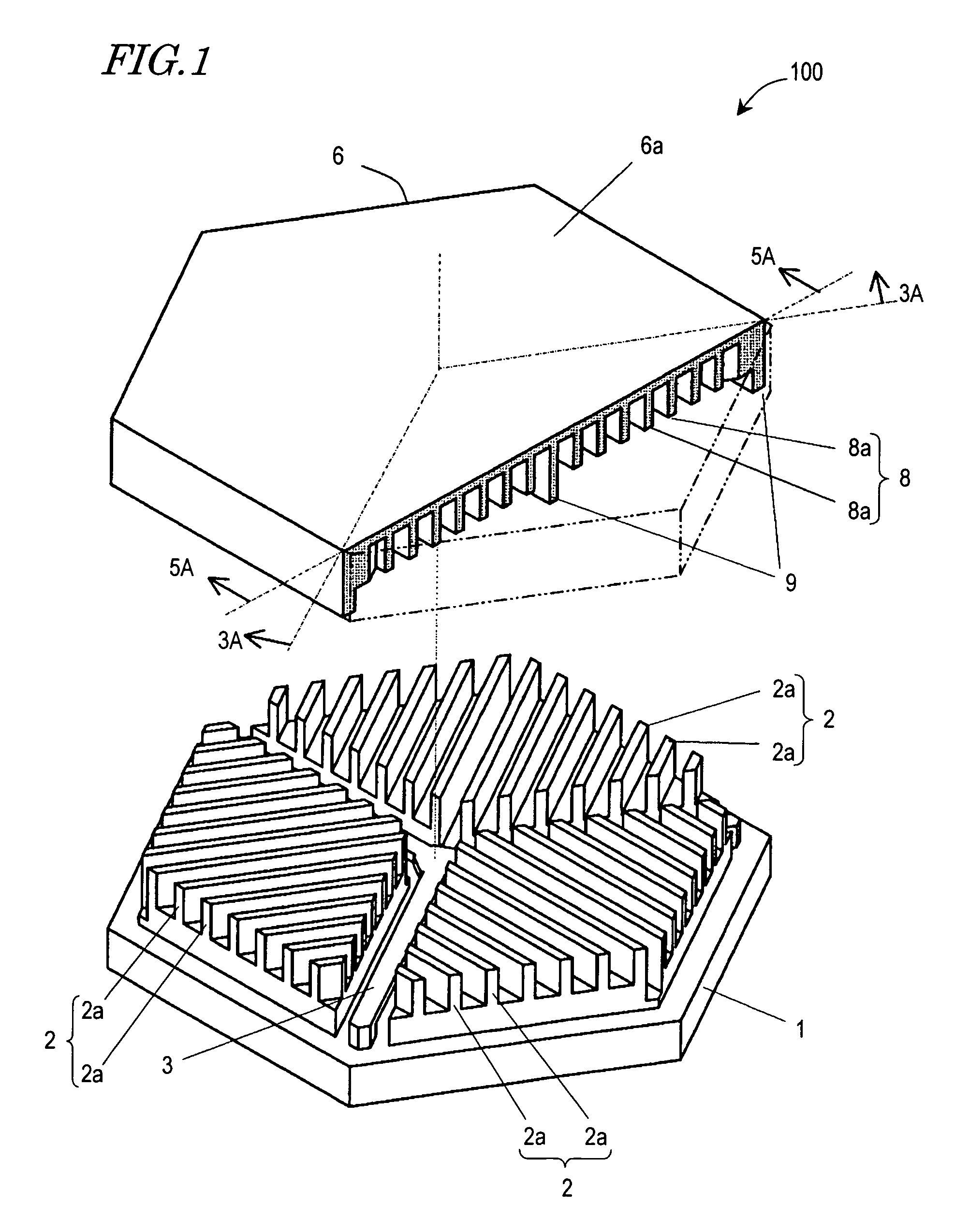
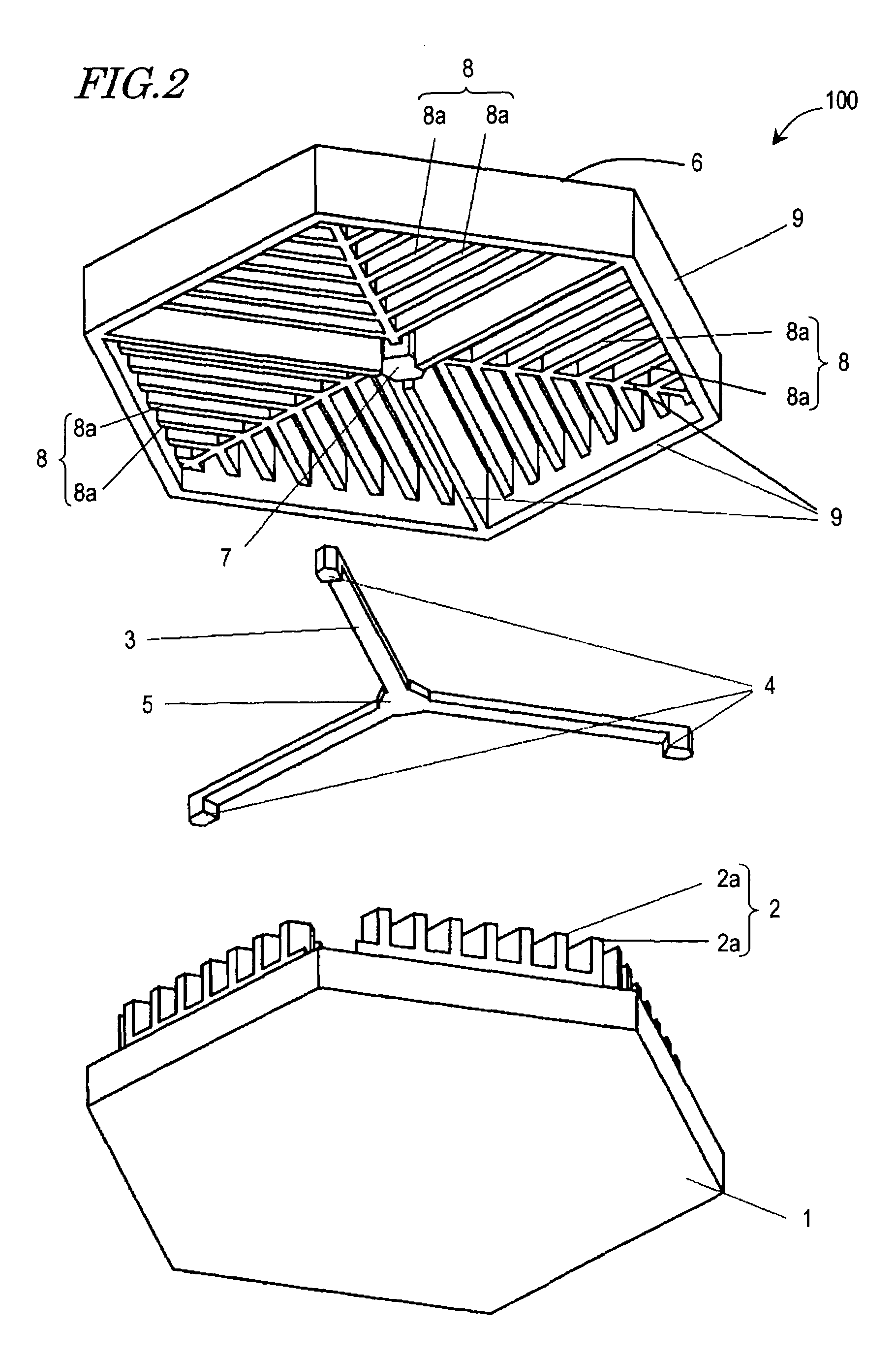
InactiveUS20050236928A1Reduce quality problemsImprove rigidityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesElectrostatic motorsEngineeringMicroactuator
There has been a trade-off between the rigidity and the mass of a movable section of a microactuator, and also between the rigidity of the movable section and the electrostatic force. A microactuator 100 includes: a base 1; a first comb electrode 2 supported by the base 1; a movable section 6 having a second comb electrode 8 opposing the first comb electrode 2, and at least one reinforcement rib 9 protruding toward the base 1; and an elastic supporting member 3 for supporting the movable section 6 so as to allow the movable section 6 to be displaced with respect to the base 1. The height of the second comb electrode 8 is different from the height of the at least one reinforcement rib 9.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Process for producing a laminated ink-jet recording head
InactiveUS20020018105A1Reduce voltageLow-voltage drivingPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyInking apparatusTitaniumMaterials science
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Electrostatic transportation device, development device and image formation apparatus
InactiveUS6947691B2Efficient and stable transportationSimple configurationElectrographic process apparatusWave shapeImage formation
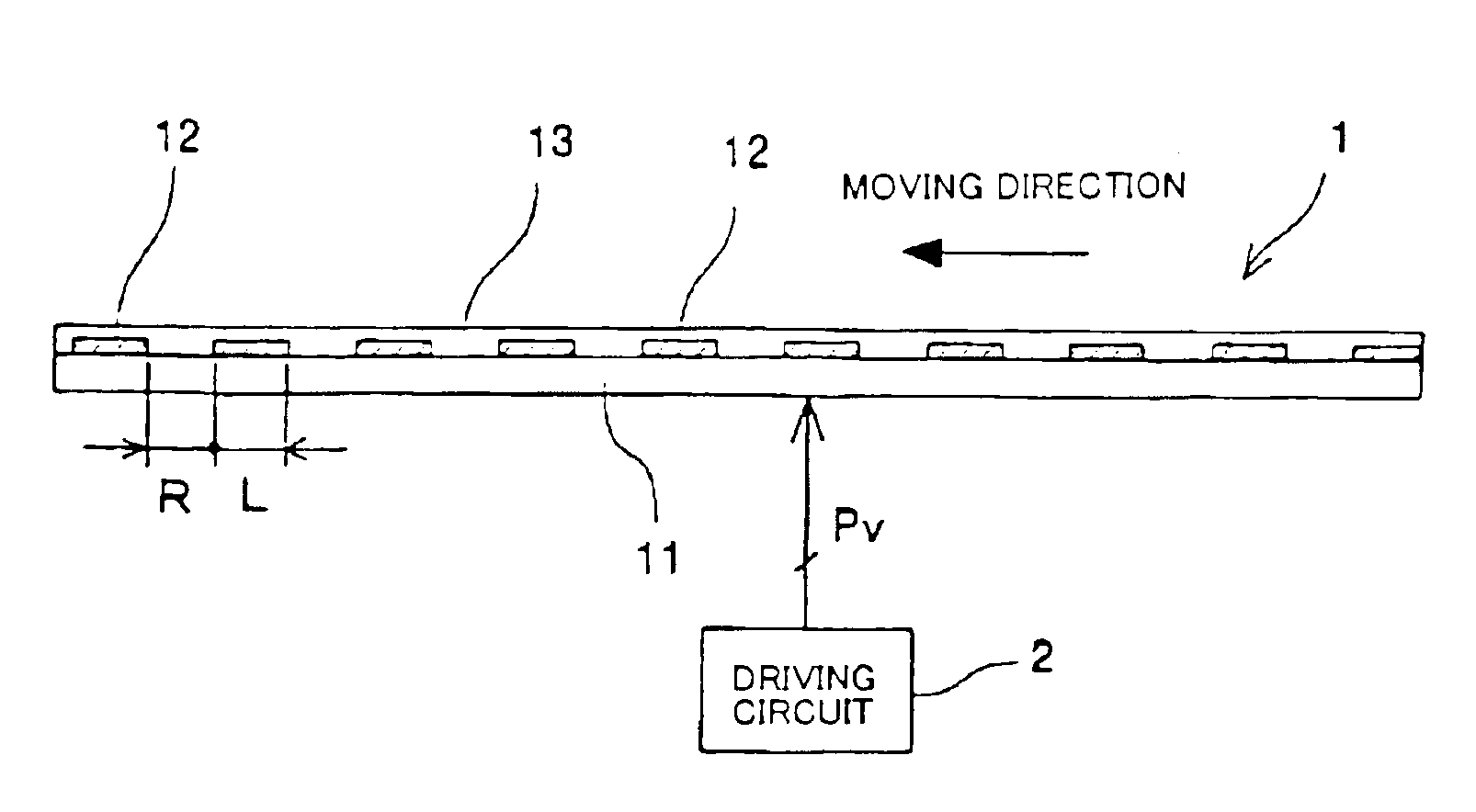
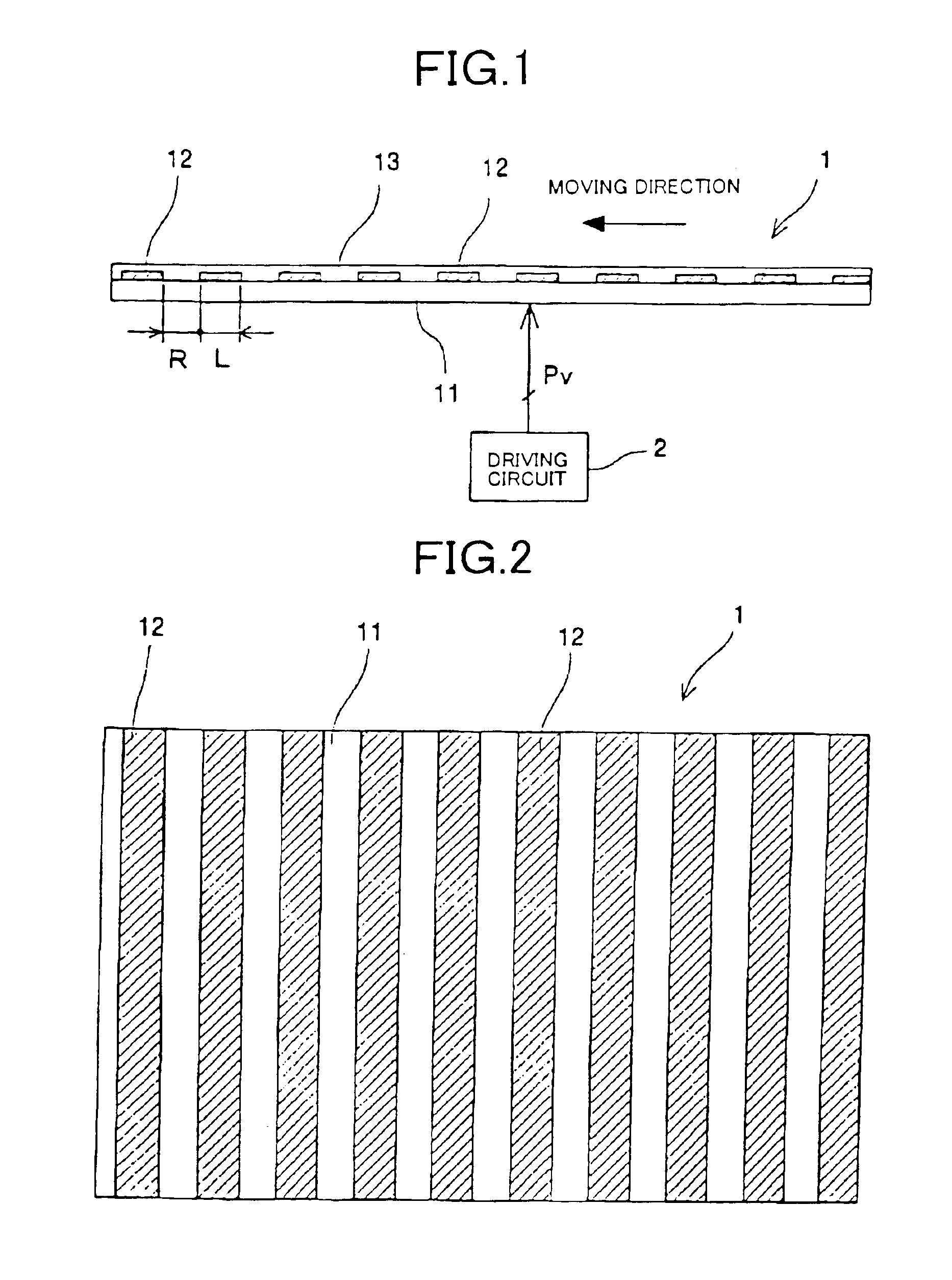
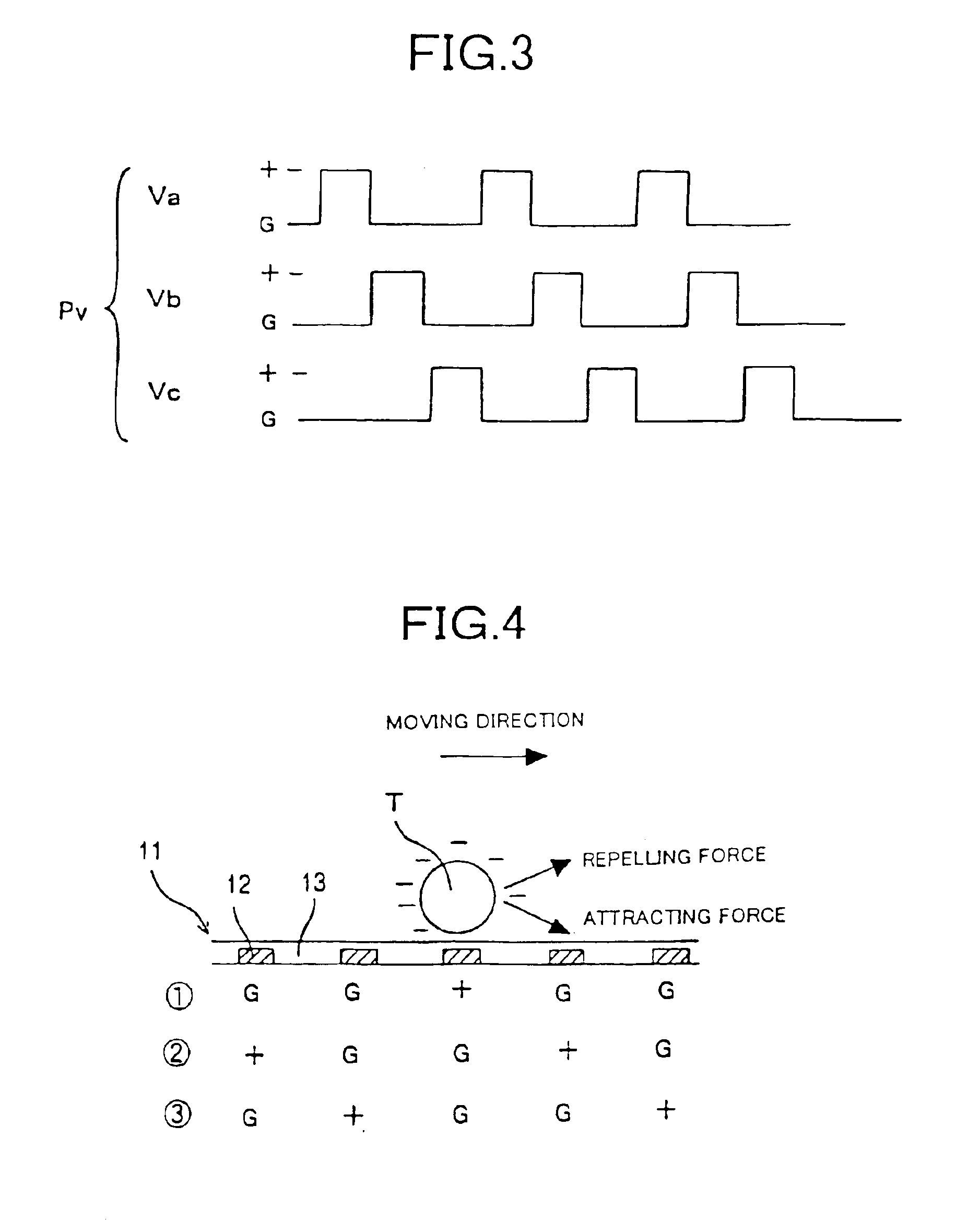
An electrostatic transportation device is provided with a transporting base plate having a plurality of electrodes which generate an electric field which performs transporting and hopping of fine particles by an electrostatic force, wherein a width of each of the electrodes in a travelling direction of the fine particles is set to be in a range of 1 time to 20 times an average particle diameter of the fine particles, a pitch between the electrodes in the travelling direction of the fine particles is set to be in a range of 1 time to 20 times the average particle diameter of the fine particles, and driving waveforms of n phases or more (n is an integer of 3 or more) are applied to respective electrodes.
Owner:RICOH KK
Light deflector, light deflection array, optical system, image forming device, and projection type image display apparatus
InactiveUS20060239009A1High melting pointLittle mechanical deformationTelevision system detailsProjectorsLight reflectionEngineering
A light deflector includes a substrate; a plurality of control members provided at edge parts of the substrate, the control members having upper parts where stoppers are situated; a fulcrum member provided on an upper surface of the substrate, the fulcrum member having a top part; a plate-shaped member movably provided in a space formed by the substrate, the fulcrum member and the stopper, the plate-shaped member having a light reflection area, no fixed end, and a conductive layer; and a plurality of electrodes provided on the substrate, the electrodes facing the conductive layer of the plate-shaped member.
Owner:RICOH KK
Liquid crystal lens element and optical head device
ActiveUS7388822B2Small sizeGuaranteed uptimeOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageOptical axisRefractive index
A liquid crystal lens element having a lens function is provided, which is small sized without having moving part, and which can stably carry out correction of spherical aberration containing a power component corresponding to focal point change of incident light.A liquid crystal lens element which changes a focal length of light transmitted through a liquid crystal 16 according to the magnitude of the voltage applied to the liquid crystal 16 sandwiched between a pair of transparent substrates 11 and 12, which comprises transparent electrodes 13 and 14 provided on the respective transparent substrates 11 and 12 for applying a voltage for the liquid crystal 16, and a concave-convex portion 17 having a saw-tooth-shaped cross-sectional shape having a rotational symmetry about an optical axis and formed on one surface of the transparent electrode 13 with a transparent material, wherein at least concave portions of the concave-convex portion 17 are filled with the liquid crystal 16 so as to change the substantial refractive index of the liquid crystal 16 according to the magnitude of applied voltage.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic derivative and organic electroluminescence device using the same
ActiveUS20120181524A1High luminous efficiencyLong life timeOrganic chemistryElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic electroluminescenceOxygen atom
A nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic derivative represented by the following formula, wherein X1 to X3 are a single bond, CRaRb, NRc, an oxygen atom or a sulfur atom, and when all of X1 to X3 is a single bond, at least one of Ara, Arb and Arc is an aryl group having 6 to 20 ring carbon atoms substituted with a heteroaryl group, an aryloxy group or a heteroaryloxy group, or a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group having 5 to 20 ring atoms.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Light emitting element, light emitting device, and electronic appliance
InactiveUS20070194306A1Long life-timeImprove luminous efficiencyElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesLow voltageInorganic compound
It is an object to provide a light emitting element capable of low-voltage driving; with high luminous efficiency; with high emission luminance; and with long emission lifetime. It is another object to provide a light emitting device and an electronic appliance in which power consumption is reduced; and which can be manufactured at low cost. A light emitting element is provided, including a light emitting layer and a layer including a composite material between a first electrode and a second electrode, where the light emitting layer includes a base material and an impurity element, the layer including the composite material includes an organic compound and an inorganic compound, the layer including the composite material is provided to be in contact with the second electrode, and light emission is obtained by application of a voltage so that an electric potential of the second electrode is higher than that of the first electrode.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Light emitting material, light emitting element, light emitting device and electronic device
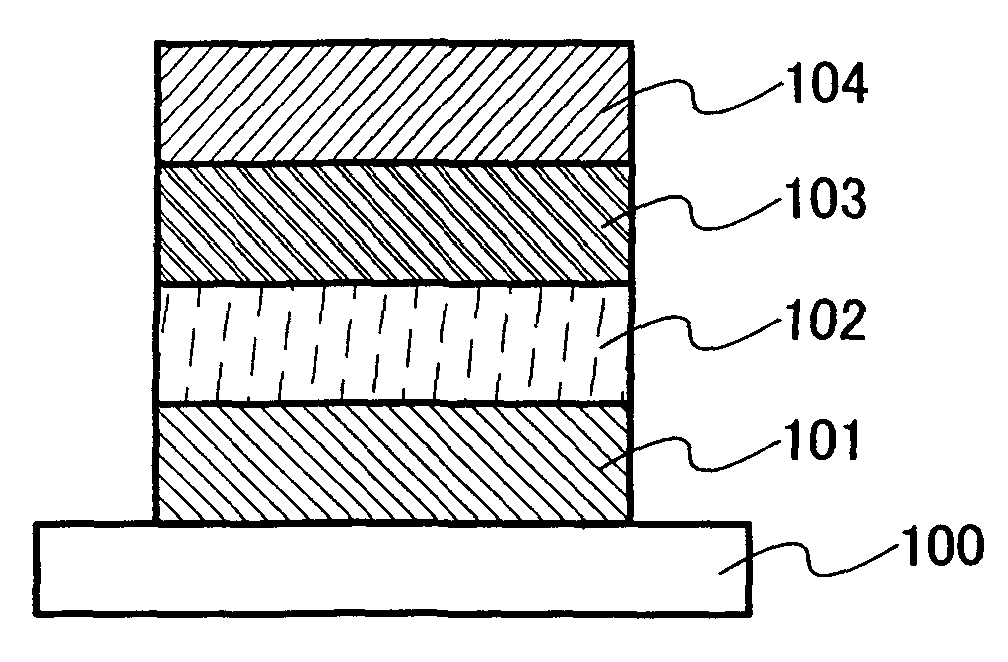
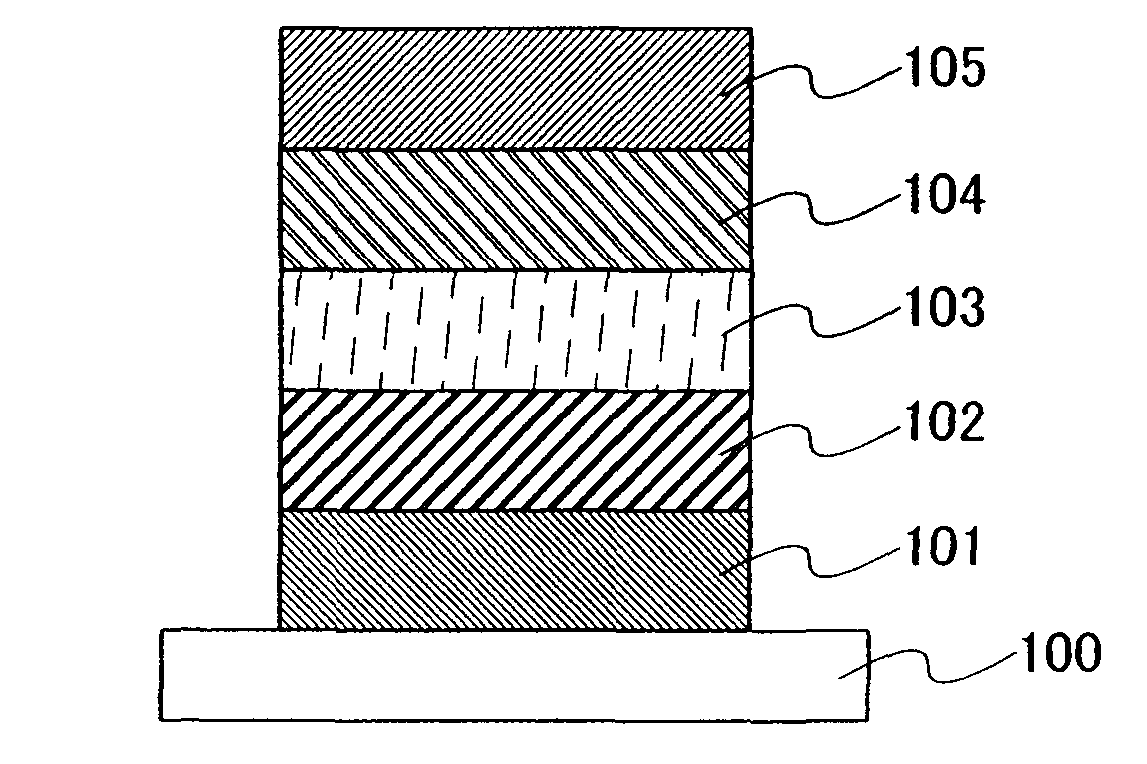
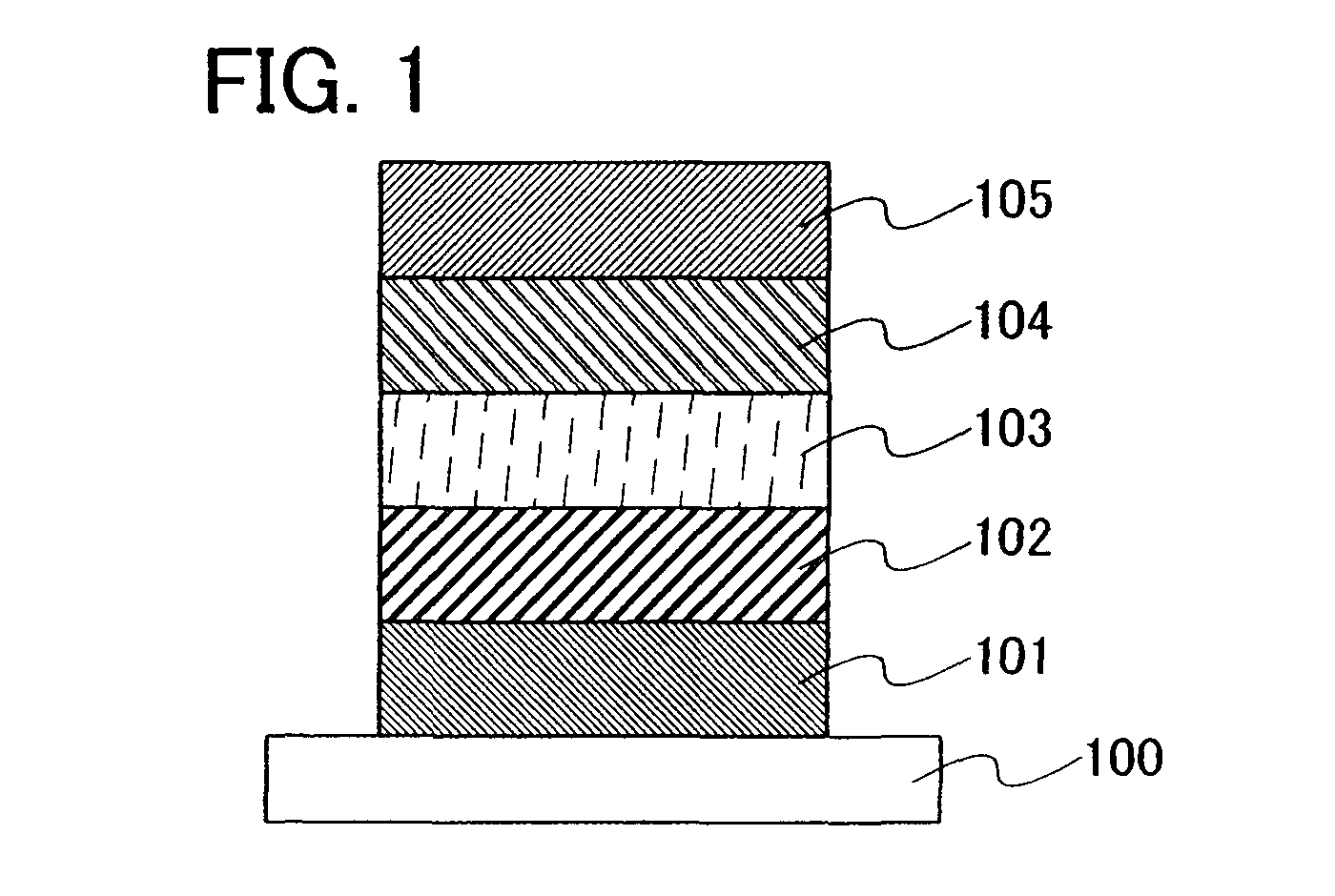
InactiveUS20070221888A1Reduce power consumptionLow costElectroluminescent light sourcesConductive materialLow voltageSulfur
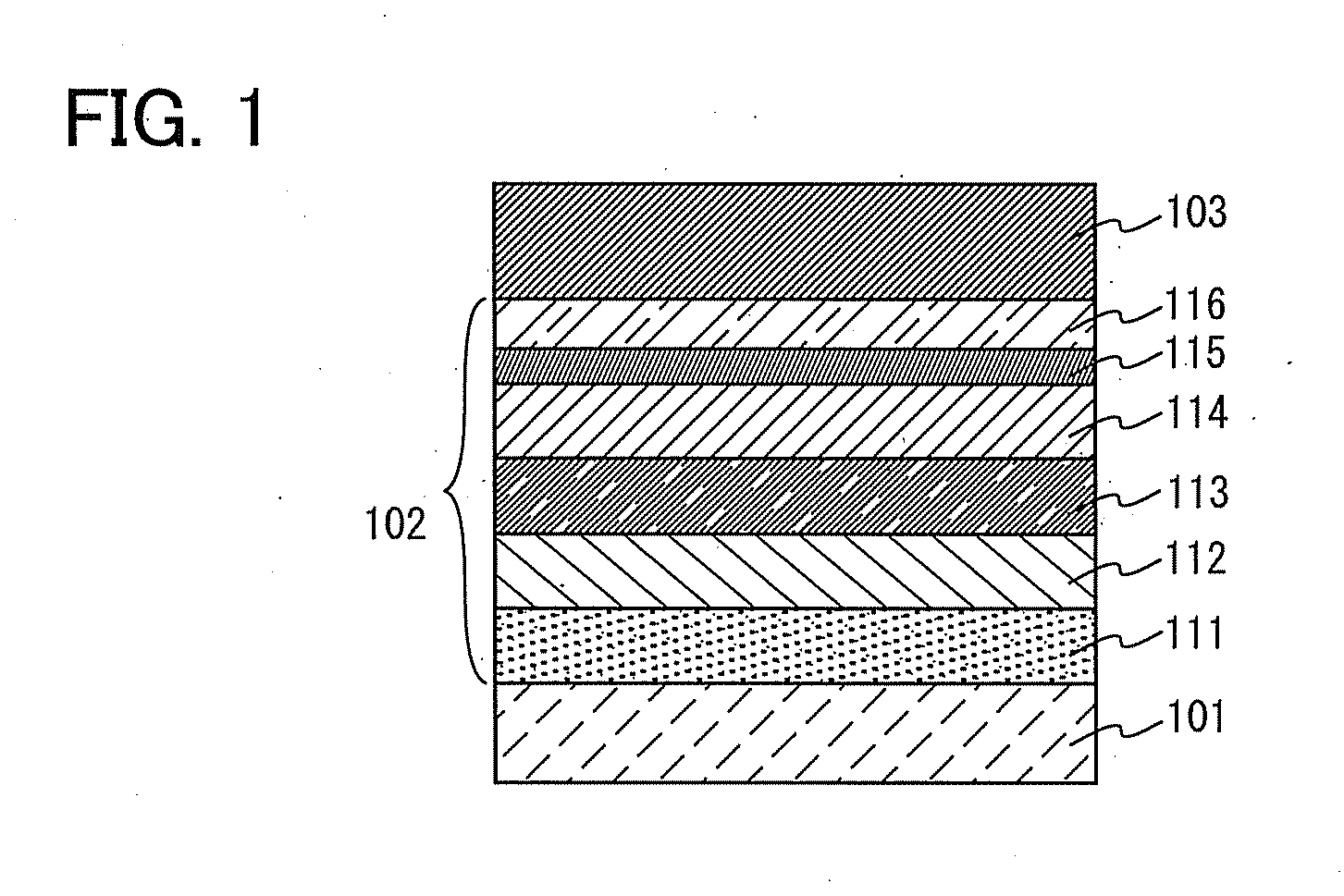
The present invention provides a light emitting material having high emission efficiency, a light emitting element which can be driven at low voltage, and a light emitting device and an electronic device with reduced power consumption. The light emitting element includes, over a substrate 100, a first electrode 101, a first insulating layer 102, a light emitting layer 103, a second insulating layer 104, and a second electrode 105, in which the light emitting layer 103 includes a light emitting element including zinc (Zn), gallium (Ga), manganese (Mn) and sulfur (S).
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for manufacturing organic electroluminescent device
ActiveUS20090081357A1Improve light emission efficiencyLong life timeMaterial nanotechnologySolid-state devicesQuantum efficiencyElectricity
Disclosed is an organic EL device having high external quantum efficiency, long emission life and low driving voltage. Also disclosed are an illuminating device and a display. Specifically disclosed is an organic electroluminescent device comprising, on a supporting substrate, at least an anode, a cathode and an organic compound layer which is arranged between the anode and the cathode and includes at least one light-emitting layer. This electroluminescent device is characterized in that the anode, cathode and organic compound layer are respectively formed by coating.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Microactuator having increased rigidity with reduced mass
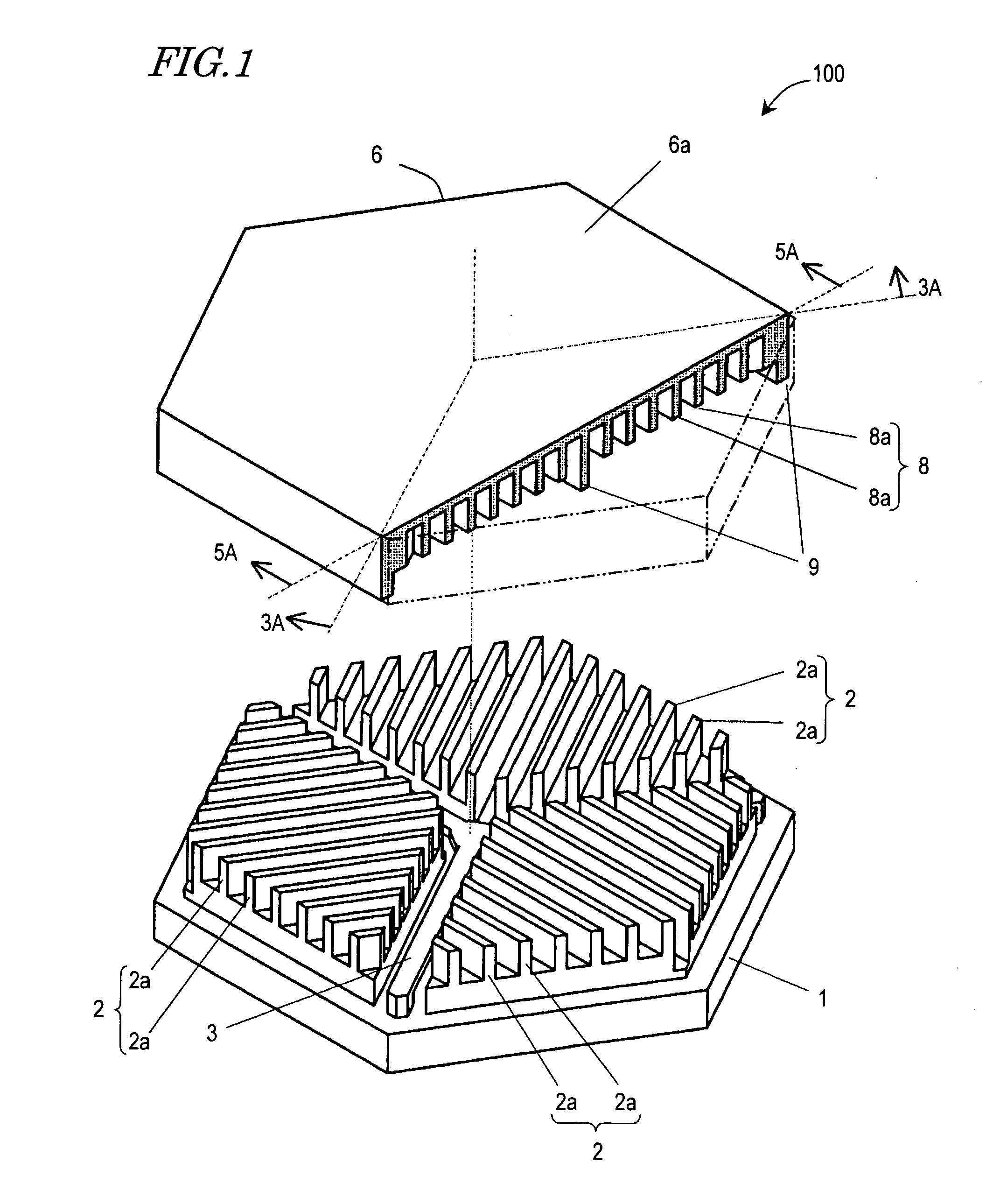
InactiveUS7538471B2Reduce quality problemsImprove rigidityElectrostatic motorsPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesEngineeringReduced mass
There has been a trade-off between the rigidity and the mass of a movable section of a microactuator, and also between the rigidity of the movable section and the electrostatic force. A microactuator 100 includes: a base 1; a first comb electrode 2 supported by the base 1; a movable section 6 having a second comb electrode 8 opposing the first comb electrode 2, and at least one reinforcement rib 9 protruding toward the base 1; and an elastic supporting member 3 for supporting the movable section 6 so as to allow the movable section 6 to be displaced with respect to the base 1. The height of the second comb electrode 8 is different from the height of the at least one reinforcement rib 9.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
High emission low voltage electron emitter
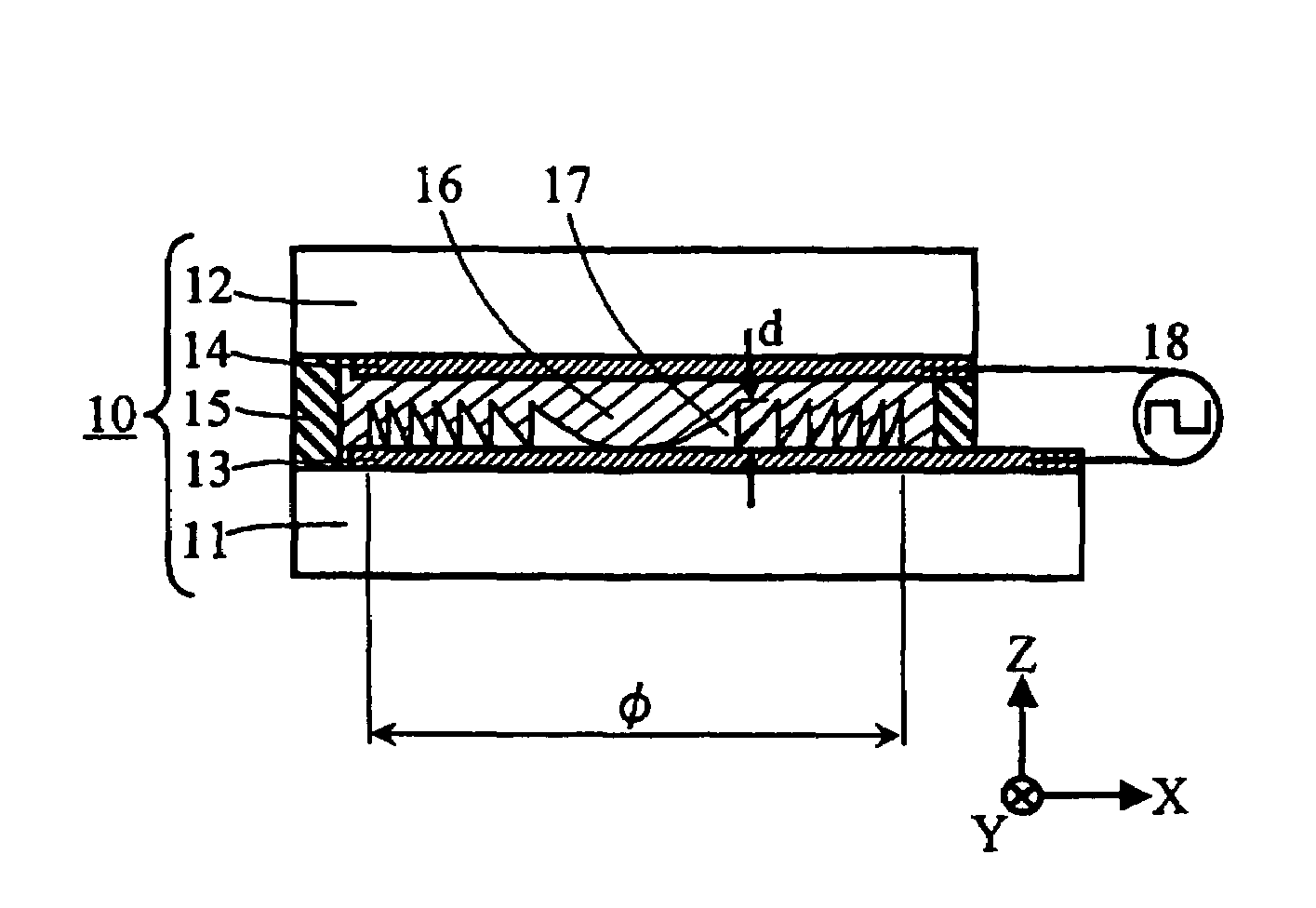
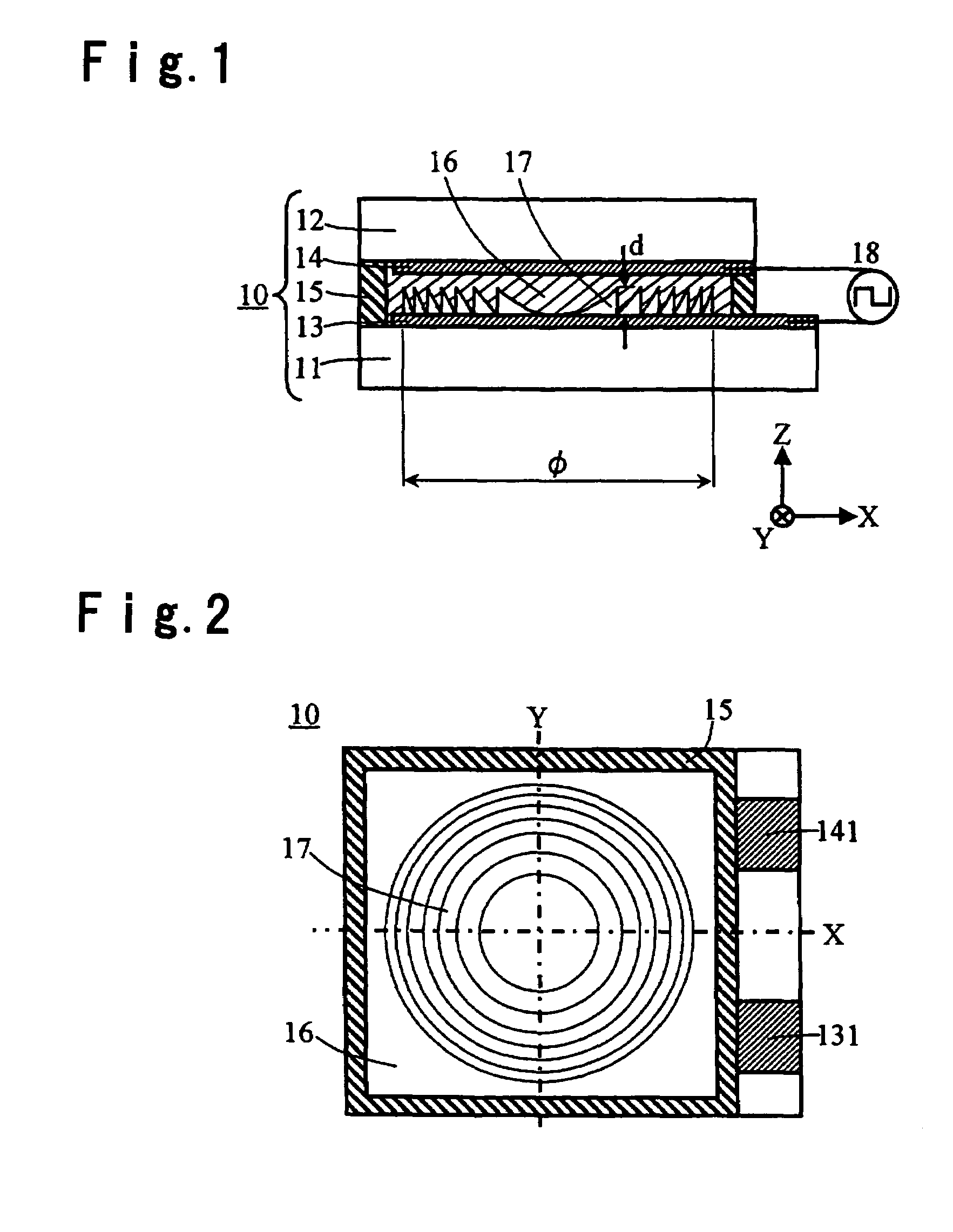
InactiveUS7176609B2Easily producing high electric field concentrationLarge outputStatic indicating devicesNanoinformaticsLow voltageElectron
An electron emitter has an emitter made of a dielectric material, and an upper electrode and a lower electrode to which a drive voltage is applied to emit electrons. The upper electrode is formed on a first surface of the substance serving as the emitter, and the lower electrode is formed on a second surface of the substance serving as the emitter. The upper electrode has a plurality of through regions through which the emitter is exposed. The upper electrode has a surface which faces the emitter in peripheral portions of the through regions and which is spaced from the emitter.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Aromatic heterocyclic derivative and organic electroluminescence device using the same
InactiveUS20120273766A1High luminous efficiencyLow voltage drivingGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesOrganic electroluminescenceHeterocyclic derivatives
An aromatic heterocyclic derivative represented by the following formula (1), a material for an organic electroluminescence device and an organic electroluminescence device including these:
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Light modulating device and exposure apparatus using the same
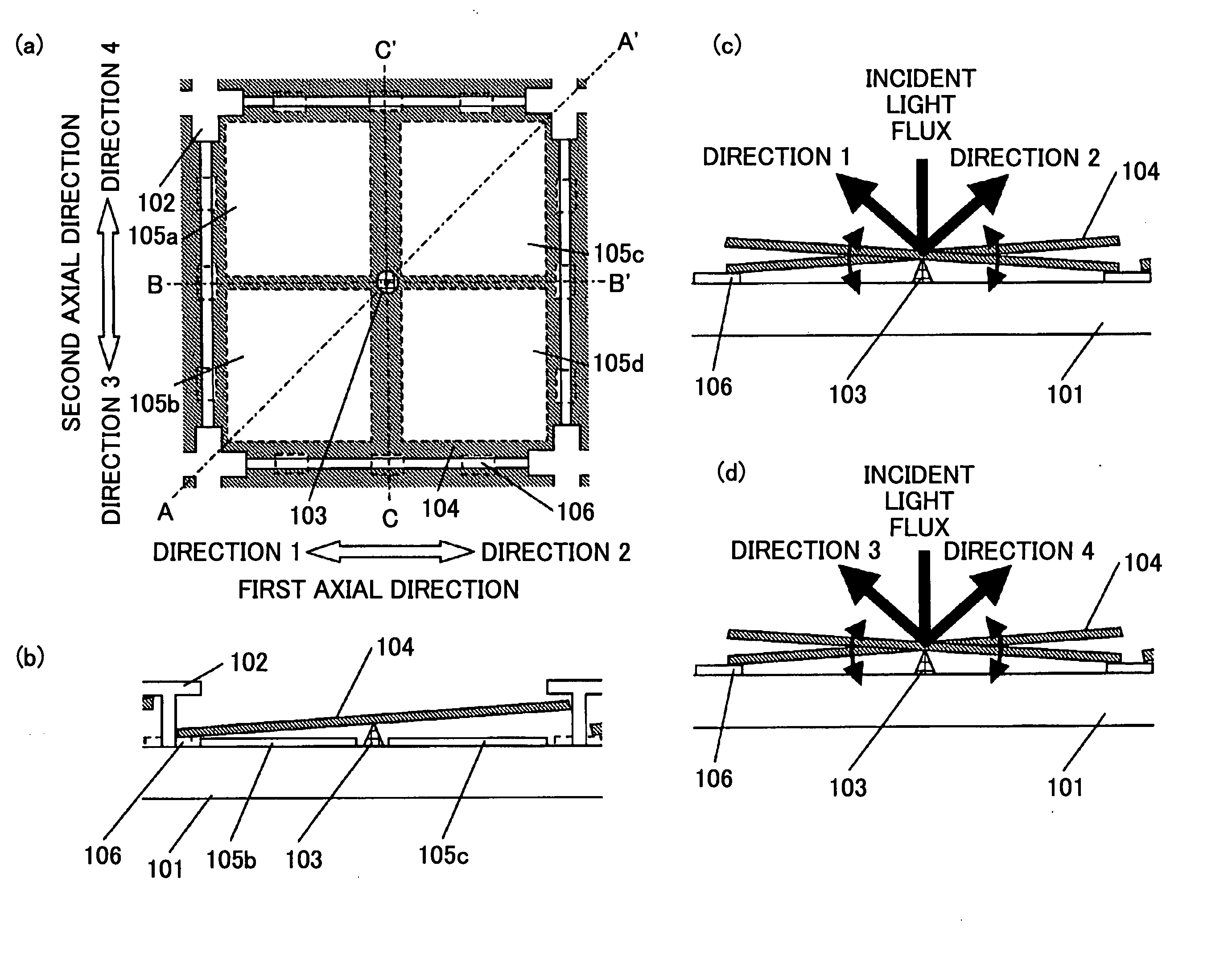
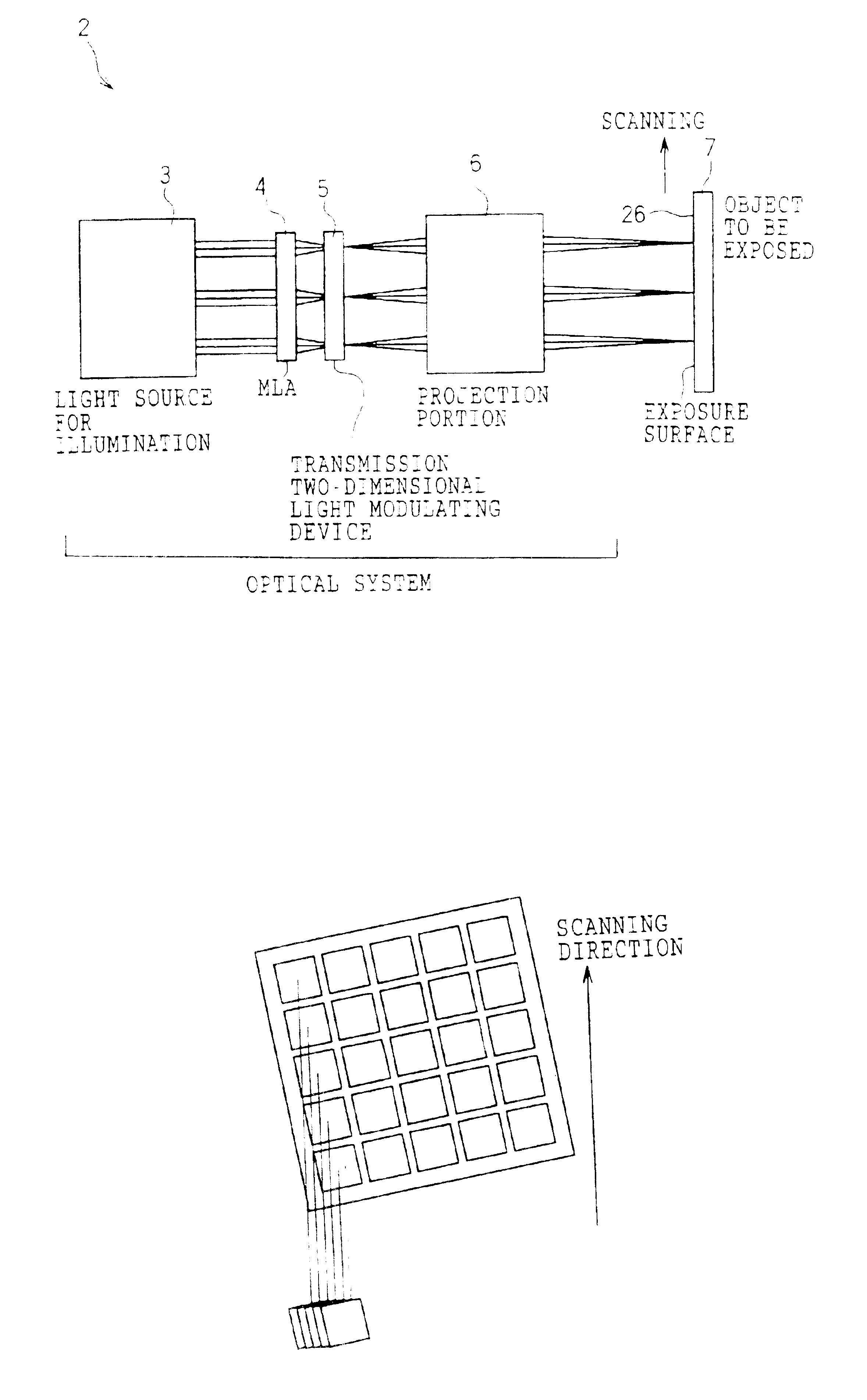
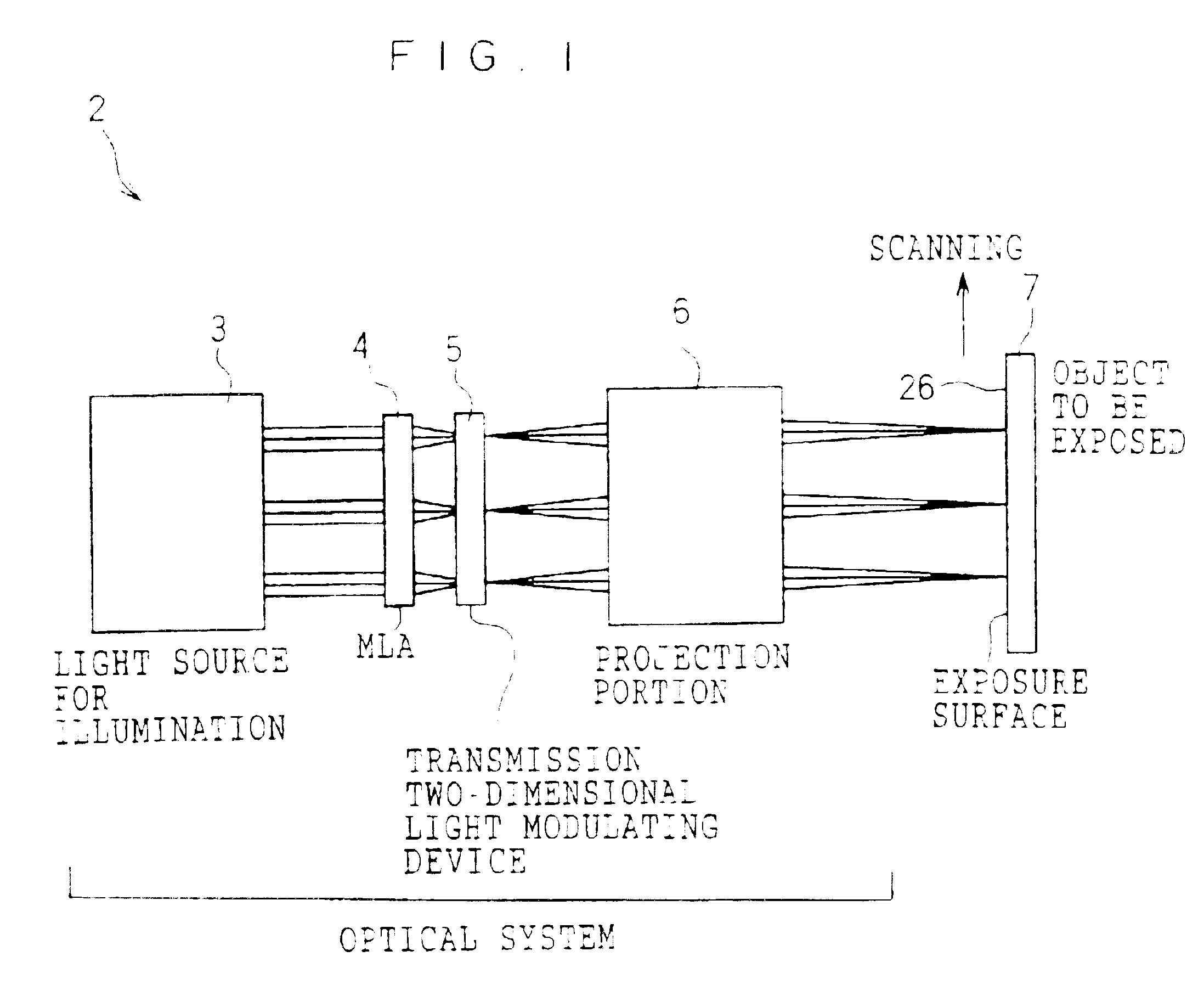
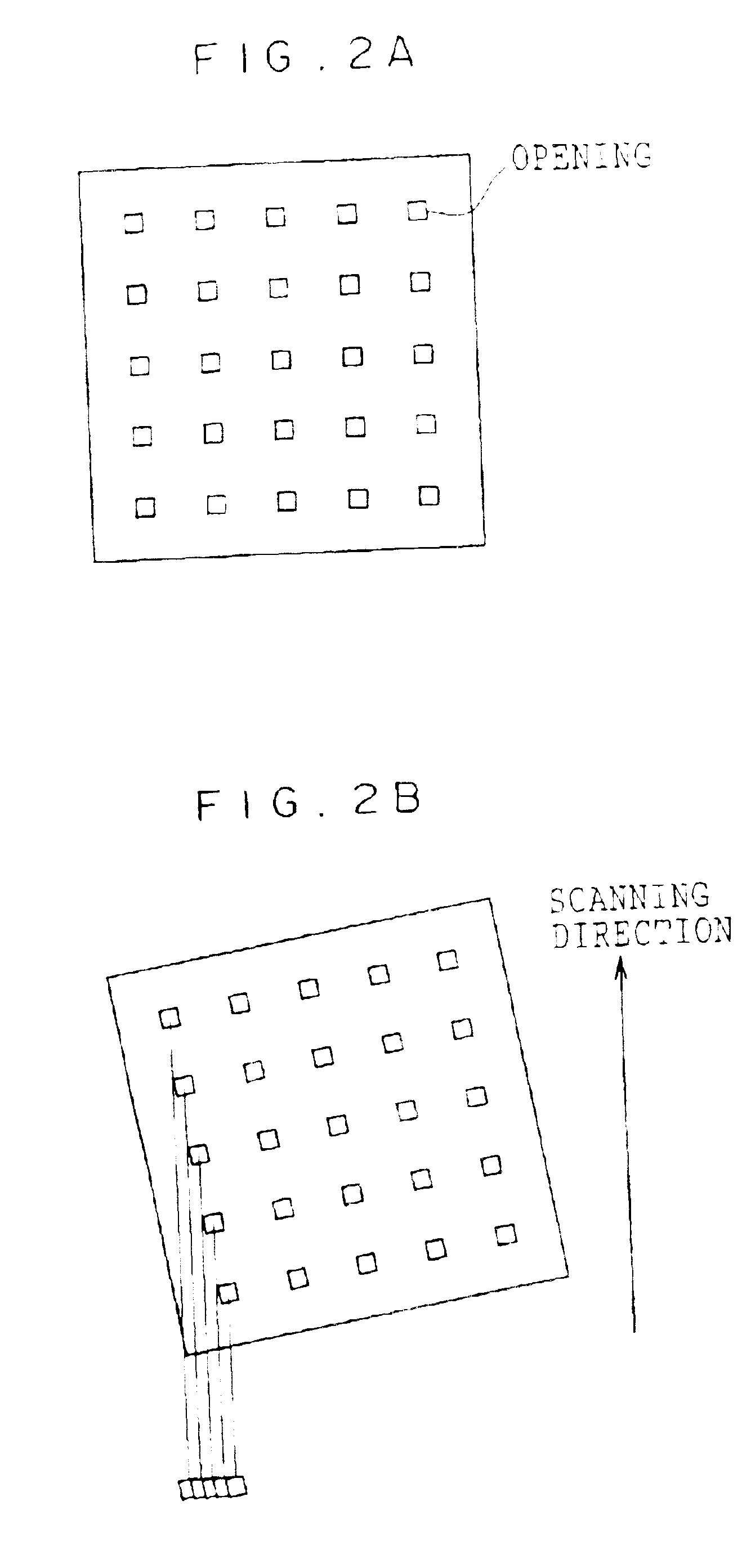
InactiveUS6953268B2Improve usabilityHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsPoint-like light sourceImage resolutionTransmittance
A light modulating device comprising a plurality of light modulating elements modulating the light that is incident thereto and emitting the light, wherein each of the light modulating elements is formed from a micro electronic machinery which is two-dimensionally arranged, and the transmittance can be controlled so as to vary for each of the light modulating elements. The light modulating device further comprises a lens array on a light-incident side of the light modulating elements, and the lens array condenses the incident light, which impinges on each of the light modulating elements, into a region whose area is smaller than an area occupied by each of the light modulating elements at a light-incident side thereof. Consequently, the light modulating device, in which usability of the light is improved and resolution is increased in the projection exposure, and the exposure apparatus using the same can be obtained.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Dielectric element, piezoelectric element, ink jet head and ink jet recording apparatus and manufacturing method of same
ActiveUS7453188B2Improve featuresLow-voltage drivingPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesDielectric layerMetal
A dielectric element includes a lower electrode layer provided on a substrate, a dielectric layer provided on the lower electrode layer and an upper electrode layer provided on the dielectric layer. The dielectric layer has a first dielectric layer provided on a side of the lower electrode layer, and a second dielectric layer provided on a side of the upper electrode layer. The second dielectric layer is a layer comprised mainly of an oxide including four or more kinds of metal element components, and the first dielectric layer does not substantially include at least one component selected from metal elements included in the oxide layer of the second dielectric layer and is comprised mainly of an oxide including at least three components selected from the remaining metal elements without substantially including Ti and Zr elements.
Owner:CANON KK +1
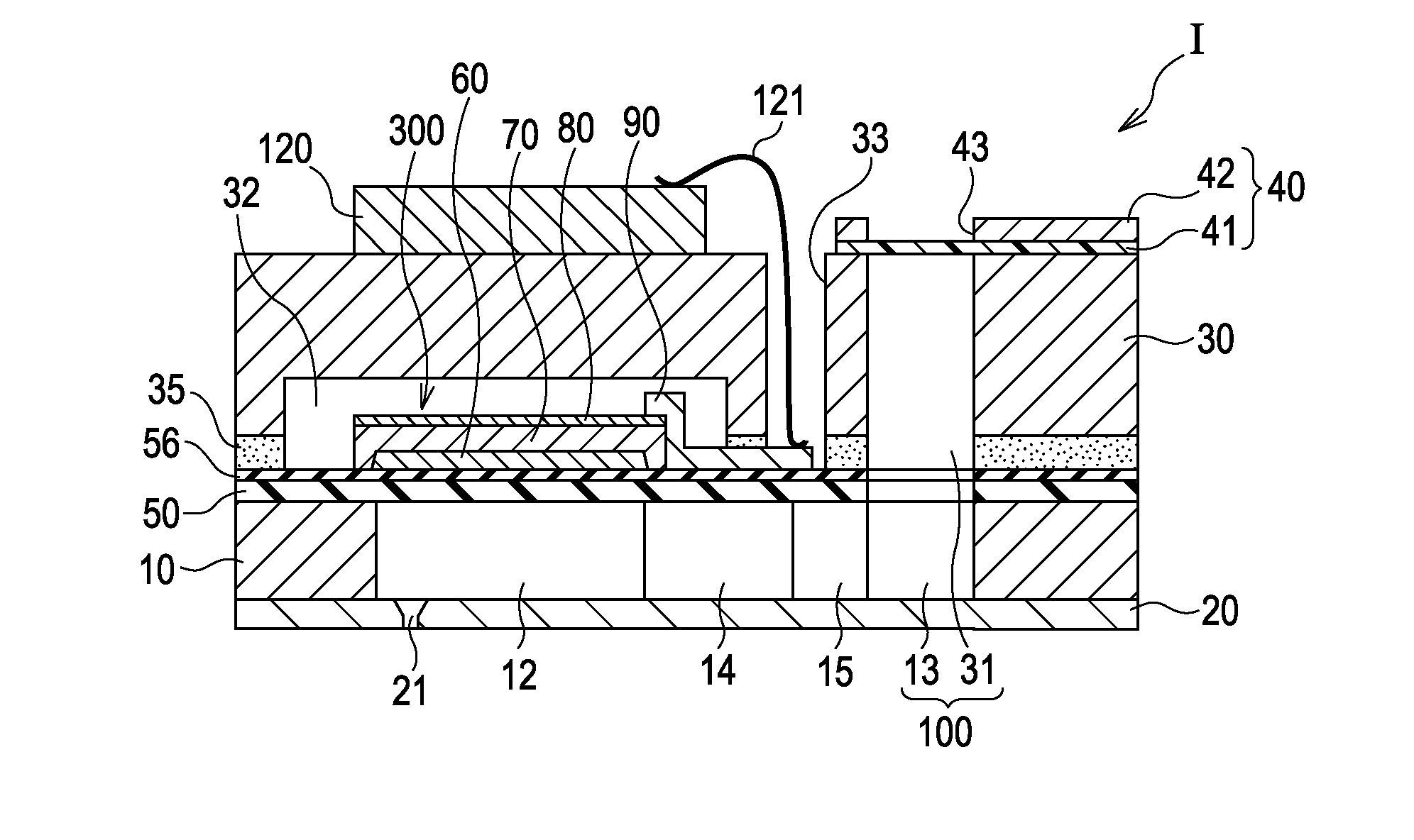
Liquid-ejecting head and liquid-ejecting apparatus
InactiveUS20110216135A1Reduce contentLess negative impactPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesPrintingSaturation polarizationEngineering
A liquid-ejecting head includes a pressure-generating chamber communicating with a nozzle opening and includes a piezoelectric element including a piezoelectric layer and electrodes. The piezoelectric layer contains bismuth sodium potassium titanate and satisfies the inequality 0≦Pr / Pm≦0.25 at 25° C., where Pm and Pr are the saturation polarization and remanent polarization, respectively, of the piezoelectric layer.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
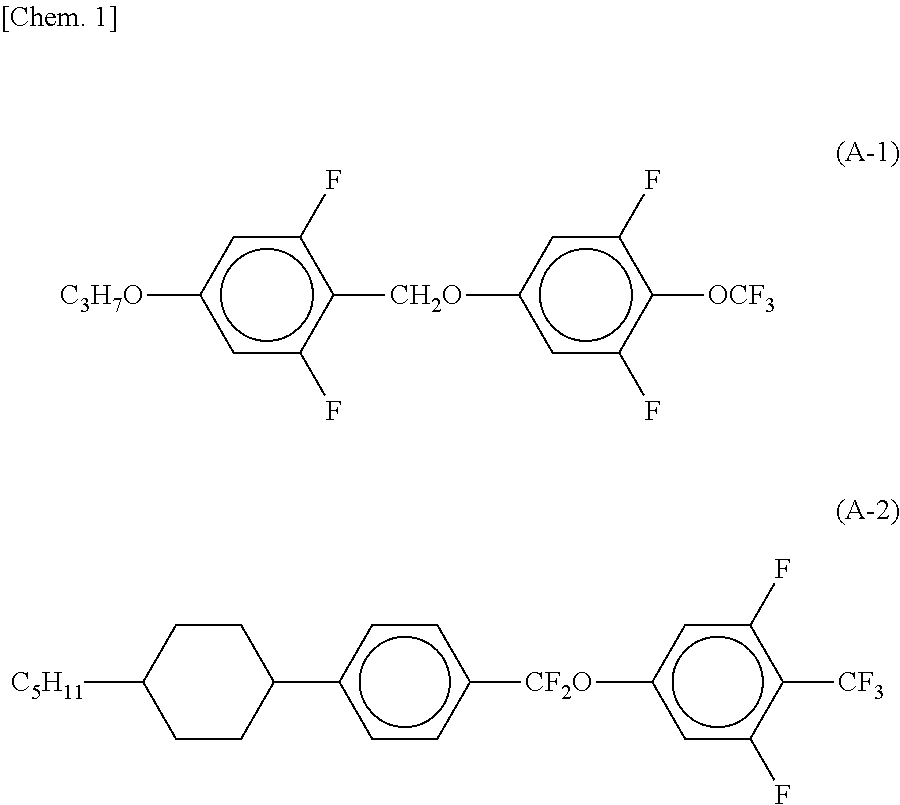
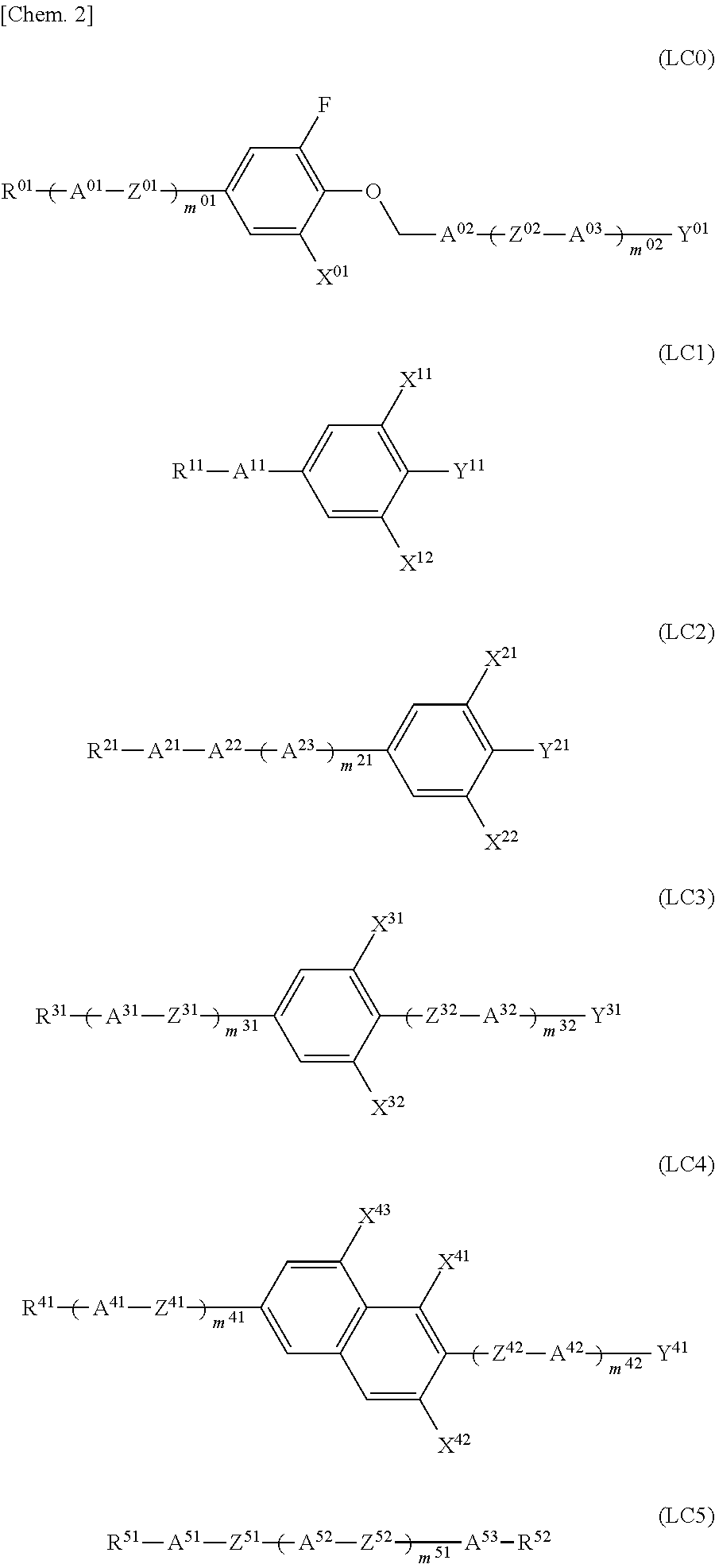
Nematic liquid crystal composition
ActiveUS9039929B2Improve reliabilitySignificant valueLiquid crystal compositionsNon-linear opticsDielectric anisotropyRefractive index
A nematic liquid crystal composition of the present invention is used in liquid crystal display devices of the TN mode, OCB mode, ECB mode, IPS mode, or VA-IPS mode. The liquid crystal composition has positive dielectric anisotropy. Since the refractive index anisotropy and the nematic phase-isotropic liquid phase transition temperature are decreased and the increase in the lower limit temperature of the nematic phase is suppressed, the viscosity of the liquid crystal composition is sufficiently low without degrading the nematic phase temperature range. The liquid crystal composition also offers excellent features such as high-speed response, good display quality, and less display failures and is thus suitable as a practical liquid crystal composition.
Owner:DAINIPPON INK & CHEM INC
Organic electroluminescent element
ActiveUS20180083201A1Containment leakImprove featuresOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesDopantCarbazole
Provided is an organic EL device having high efficiency and high driving stability while being driven at a low voltage. The organic electroluminescent device includes one or more light-emitting layers between an anode and a cathode opposite to each other. At least one of the light-emitting layers contains a host material and a light-emitting dopant, and (i) a first host formed of an indolocarbazole compound having one or two indolocarbazole rings, and (ii) a second host formed of a carbazole compound having a plurality of carbazole rings and having a bond structure represented by the following general formula (3) are used as the host material.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CHEMICAL CO LTD
Organic electroluminescent device
ActiveUS20150325796A1Improve luminous efficiencyGuaranteed smooth progressOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesDopantCarbazole
Provided is a practically useful organic EL element having high efficiency and high driving stability while being capable of being driven at a low voltage. The organic EL element has a light-emitting layer and any other organic layer between an anode and a cathode opposite to each other. The light-emitting layer contains at least two host materials and at least one light-emitting dopant. At least one of the host materials is a host material selected from compounds each having one or two indolocarbazole skeletons, and at least one of the other host materials is a host material selected from carbazole compounds each substituted with a dibenzofuran or a dibenzothiophene.
Owner:PIONEER CORP +2
Semiconductor device
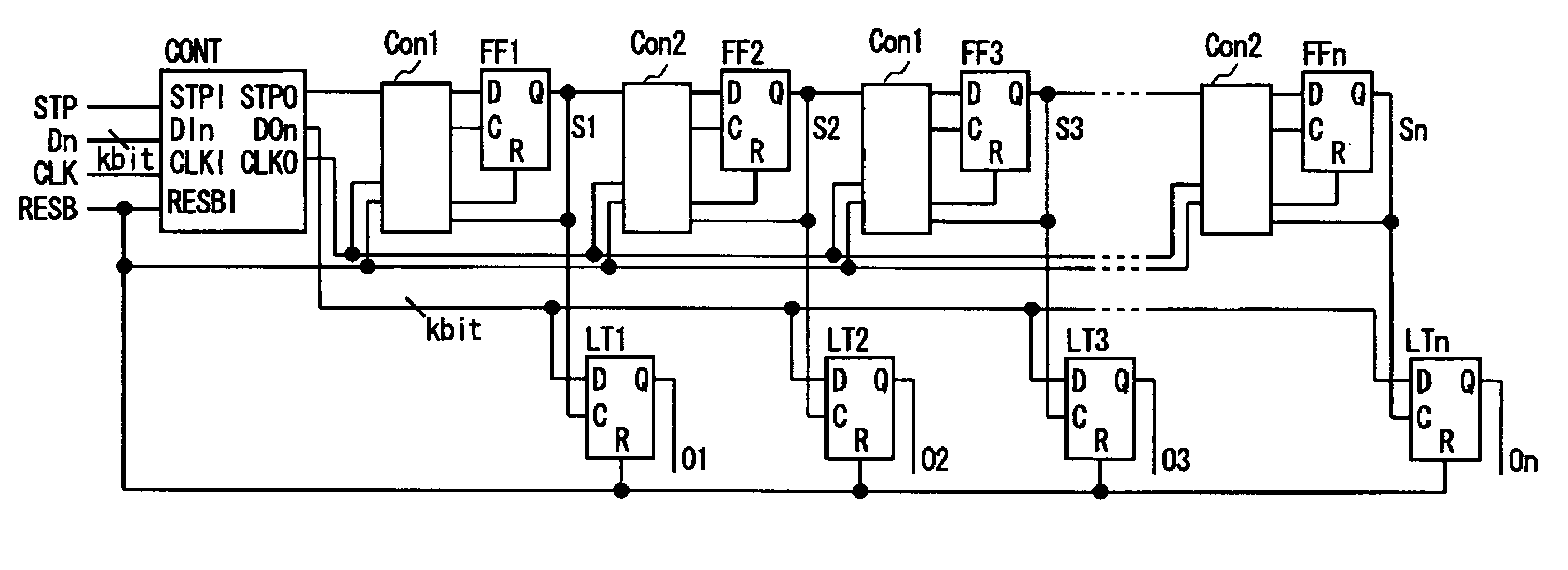
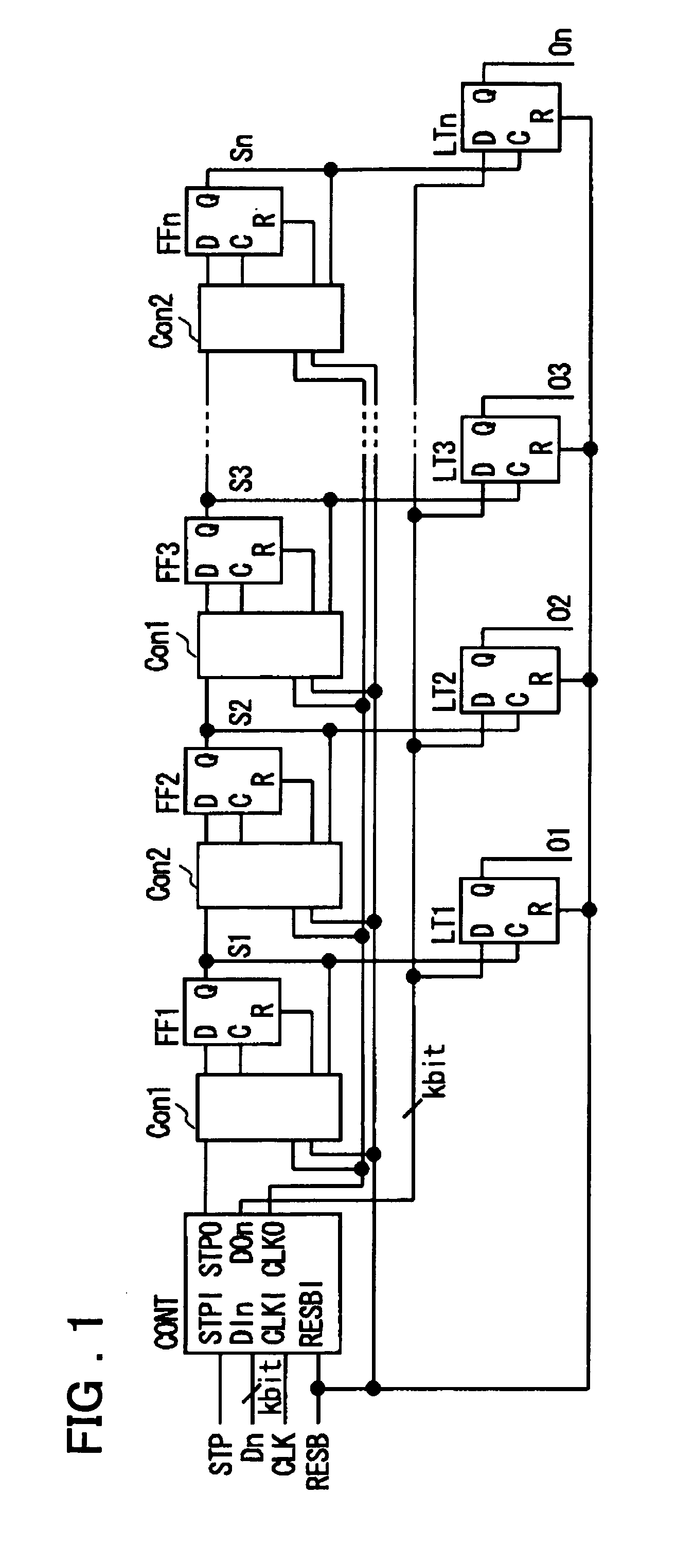
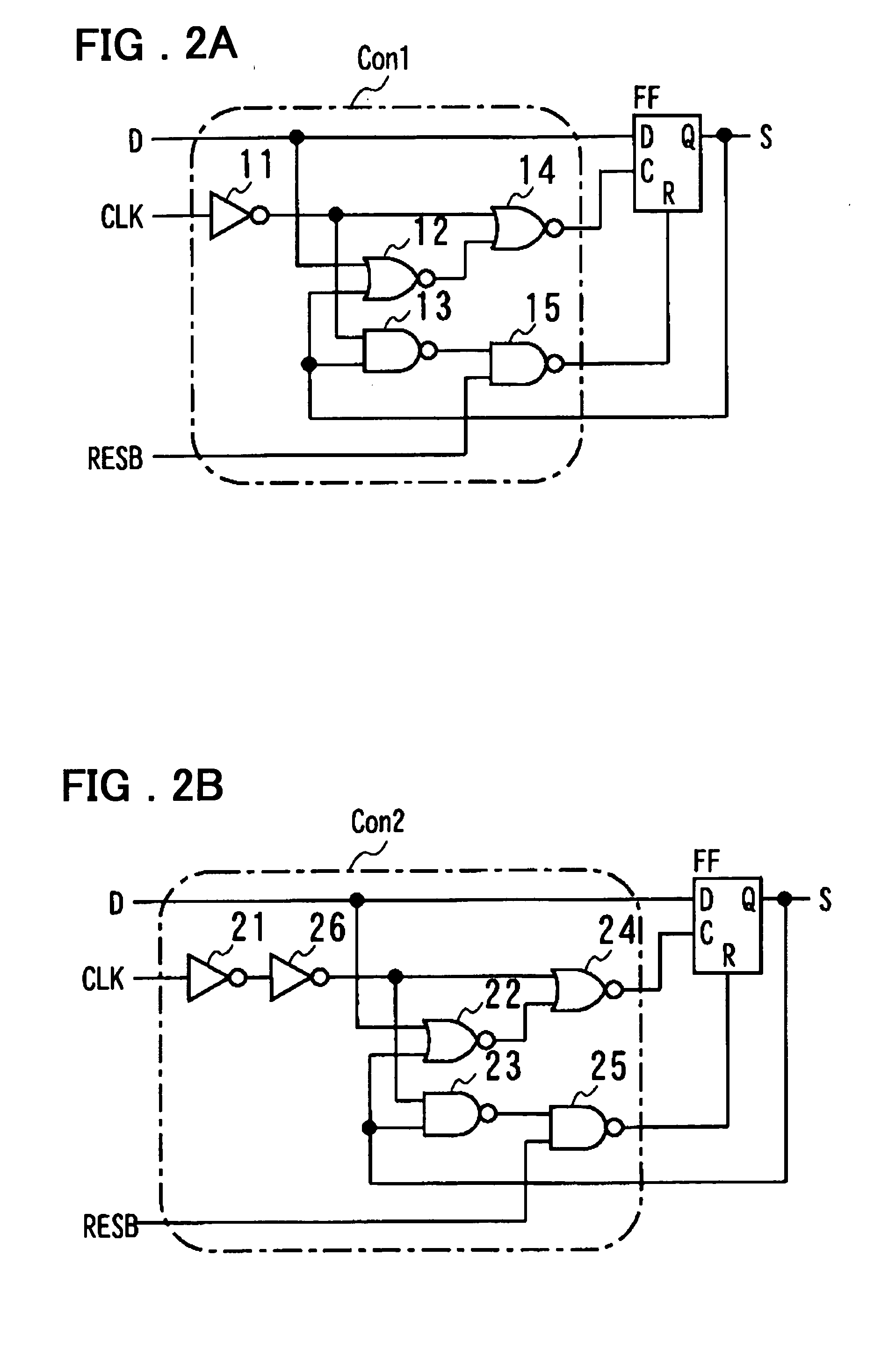
InactiveUS20050206535A1Reduce voltageEasy to operateElectric signal transmission systemsParallel/series conversionShift registerDevice material
Disclosed is a serial to parallel conversion circuit in which the shift clock frequency is lowered to close to the frequency on the data line to achieve low power dissipation. The serial to parallel conversion circuit at least includes a shift register (FF1 to FFn), to the first stage of which is entered a data transfer start signal STPO and which sequentially transfers the data transfer start signal by input shift clock signal, a plural number of latch circuits (LT1 to LTn) receiving signals sequentially output from the shift register as latch clock signal to latch a data signal serially supplied to a data line, and control circuits (Con1 and Con2) receiving at least shift clock signal CLKO supplied to flip-flops and the output signals of the flip-flops. If, in case the output signals of the flip-flops are in active states, the shift clock signal supplied to the flip-flops undertakes a transition to an inactive state, the control circuits reset the flip-flops to inactivate the output signals of the flip-flops. The neighboring ones of the flip-flops sample and output signals entered to the data terminals, using one and the other of the rising and falling edges of the shift clock signal supplied from the clock line. The shift clock signal is operated at a frequency equal to one-half the data signal transfer frequency.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Display panel and display device
ActiveUS20200251689A1Lesser refractive indexSmall distanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight beamDisplay device
Owner:FUZHOU BOE OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD +1
Infrared sensor module using rotary ultrasonic motor
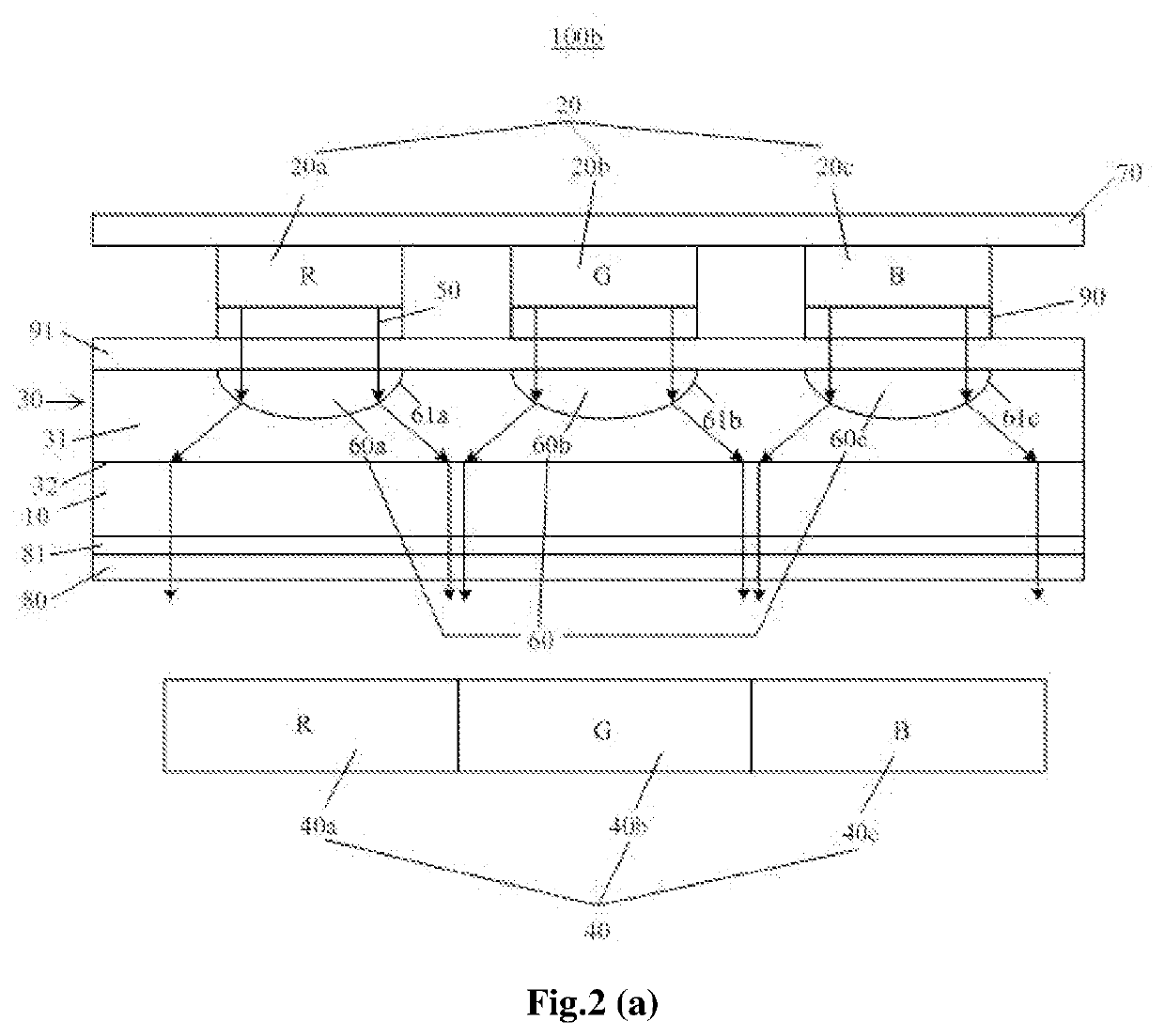
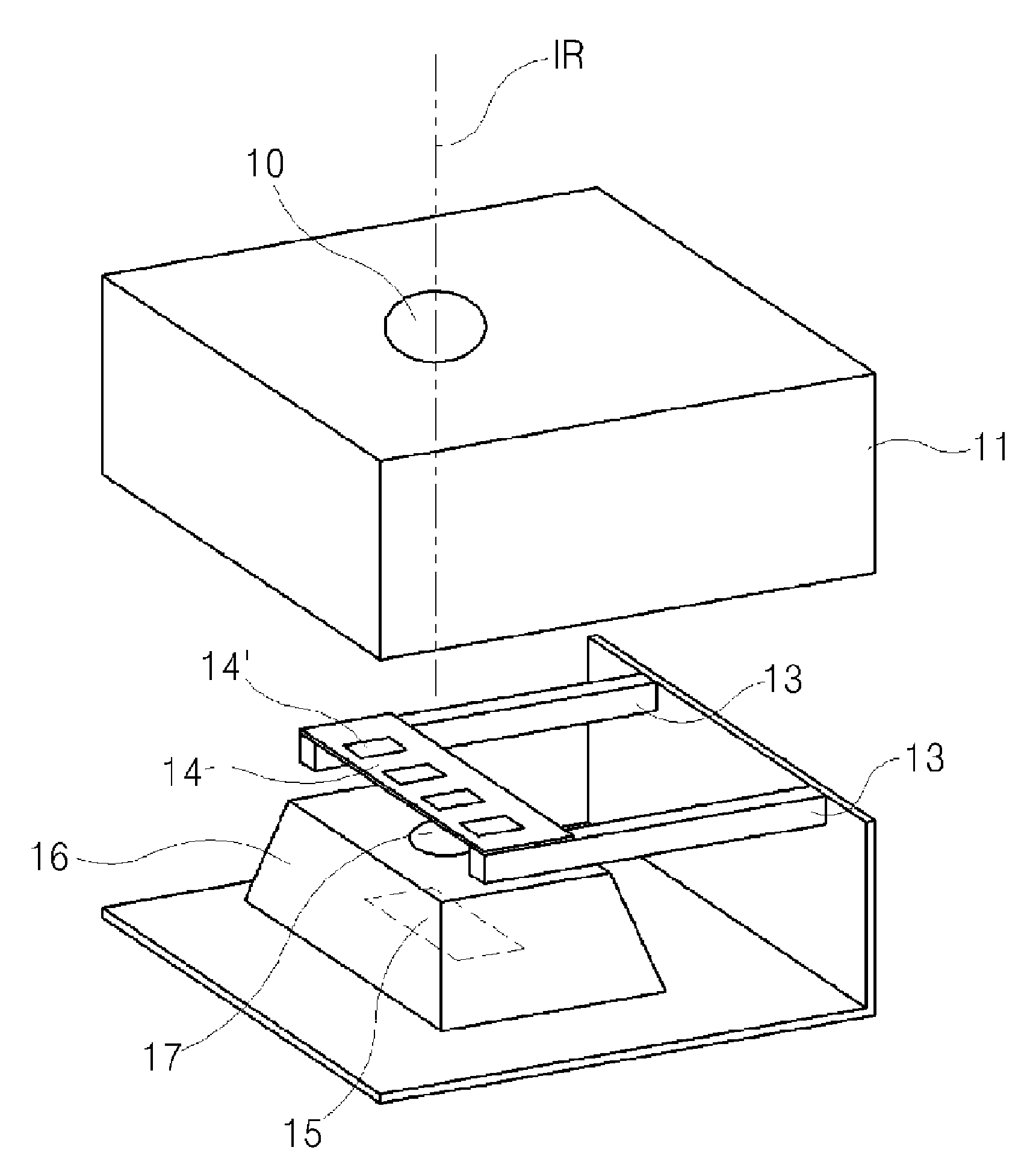
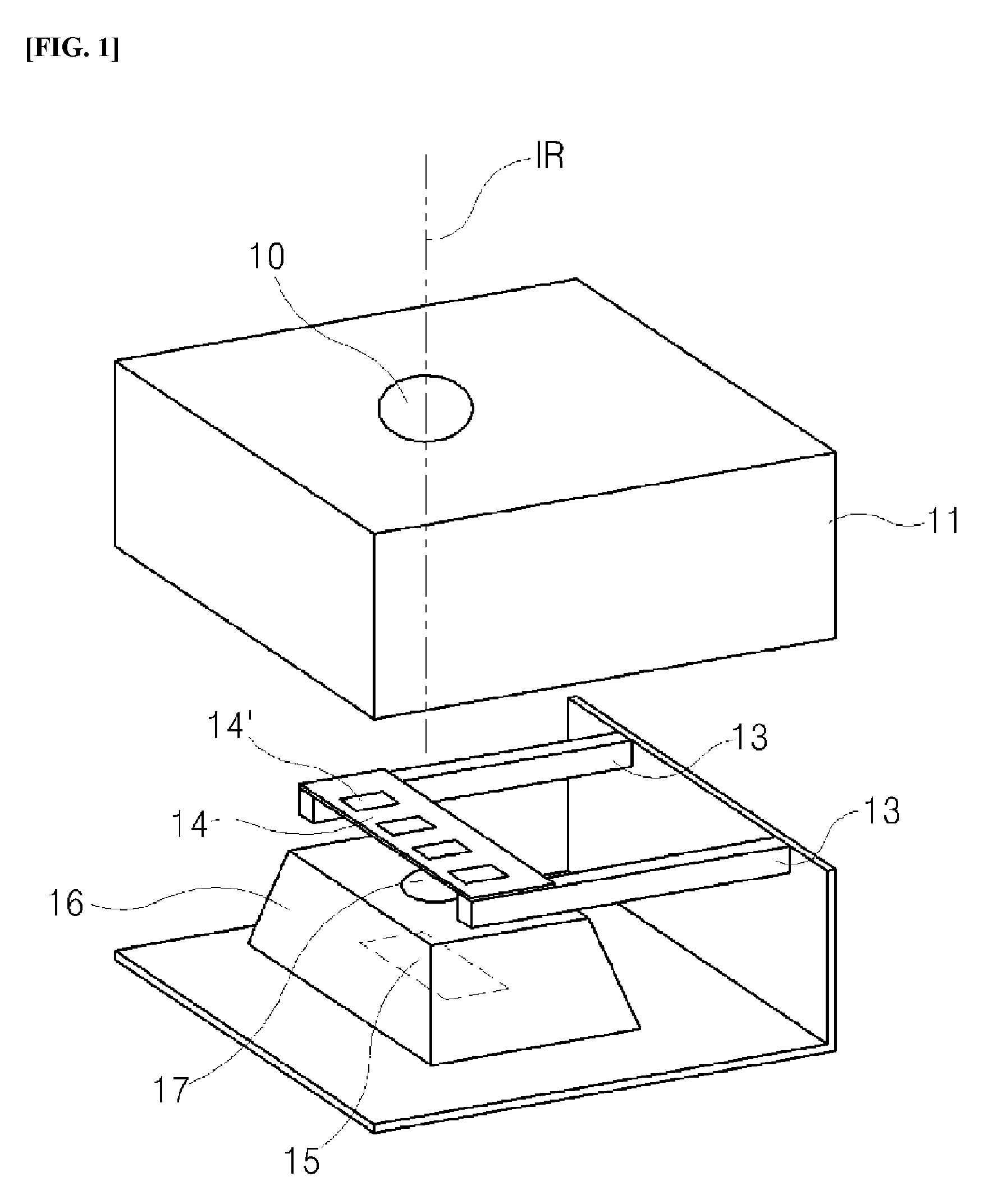
InactiveUS20160320239A1Low voltage drivingSimple structureSensing radiation from moving bodiesPhotometry electrical circuitsInfraredElectricity
An infrared sensor module utilizing a rotary ultrasonic motor is disclosed. The infrared sensor module utilizing a rotary ultrasound motor according to one embodiment of the present invention comprises: an infrared sensor for detecting an object that radiates infrared rays; a rotary ultrasonic motor including a piezoelectric diaphragm having a partitioned electrode structure in a pinwheel shape in a plate body formed with a piezoelectric material and a ring-shaped rotator driven by torsional vibrations generated along the side surfaces of the piezoelectric diaphragm; a Fresnel lens rotatably provided by being coupled to the rotator to control intermittent blocking of the infrared rays incident in the front direction of the infrared sensor; an oscillation unit for outputting a square wave required for the rotary ultrasonic motor; and a control unit for controlling the oscillation unit by using a signal detected by the infrared sensor and controlling the driving of the rotary ultrasonic motor.
Owner:ECO DM LAB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com