3D printed bio-ink based on costal cartilage as well as preparation method and application thereof
A 3D printing and bio-ink technology, applied in the field of biomedical materials, can solve the problems of waste of donor materials in engraving surgery, large demand for rib bone extraction, and high exposure rate of biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
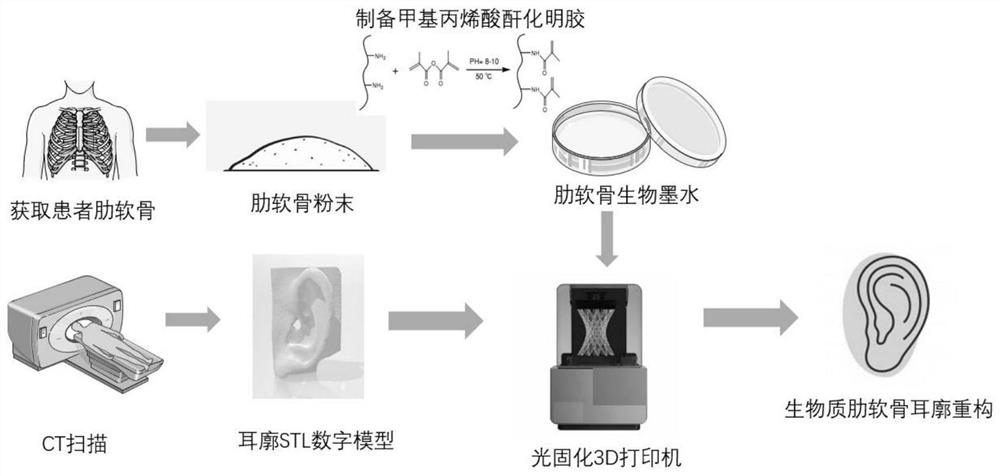
[0052] (1) Costal cartilage biological crushing.
[0053] Take the patient's 7th and 8th costal cartilage (the sixth costal cartilage can be taken if necessary), and use a biological pulverizer to pulverize the costal cartilage in a sterile environment. .
[0054] (2) Configuration of autologous costal cartilage bioink containing photoinitiator
[0055] 20g of gelatin was dissolved in 150mL of alkaline buffered saline solution (0.075mol / L sodium carbonate, 0.175mol / L sodium bicarbonate) at 60°C, then 2mL of methacrylic anhydride was slowly added dropwise to the gelatin solution, and in Stir vigorously at 50 °C for 3 h. After the reaction was completed, 200 mL of deionized water was added to terminate the reaction, and the supernatant was removed by centrifugation, and then the crude product was dialyzed in ultrapure water at 40° C. for 3 days (the cut-off of the dialysis bag was 12-14 KDa). The dialyzed product was then freeze-dried for 3 days to obtain a white porous spong...
Embodiment 2
[0061] In this example, the effects of different autologous costal cartilage bioink formulations on the accuracy of auricle shaping and cartilage remodeling ability were studied. Firstly, the costal cartilage is bio-pulverized, and the 7th and 8th costal cartilages of the patient are taken and crushed with a bio-pulverizer in a sterile environment. The steps and process parameters in this example are the same as those in Example (1), except that the autologous ribs in step (1) have a larger particle size after biological pulverization, and the particle size of the finished product is about 30-80 μm. The effect of its implementation is that the accuracy and resolution of the autologous costal cartilage auricle formed by step (4) 3D printing is worse than that of Example 1, and the order of its forming accuracy is: Example 1>Example 2, this is because the biologically crushed ribs of the printing ink The raw material is rougher, but in this case the pinna has better cartilage re...
Embodiment 3
[0063] In this example, the effects of different autologous costal cartilage bioink formulations on the accuracy of auricle shaping and cartilage remodeling ability were studied. Firstly, the costal cartilage is bio-pulverized, and the 7th and 8th costal cartilages of the patient are taken, and the costal cartilage is crushed with a bio-pulverizer in a sterile environment. The steps and process parameters in this example are the same as those in Example (1), except that the autologous ribs in step (1) have a larger particle size after bio-crushing, and the particle size of the finished product is about 80-130 μm. The effect of its implementation is that the accuracy and resolution of the autologous costal cartilage auricle formed by 3D printing in step (4) is worse than that of Example 2, and the order of its forming accuracy is: Example 1>Example 2>Example 3, this is because the printing ink The bio-crushed rib raw material is rougher, but the auricle of this example has bett...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com