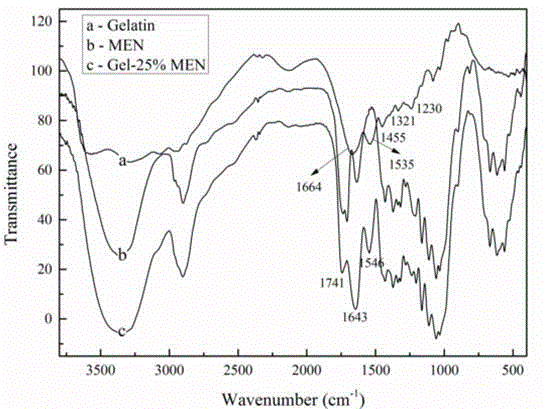
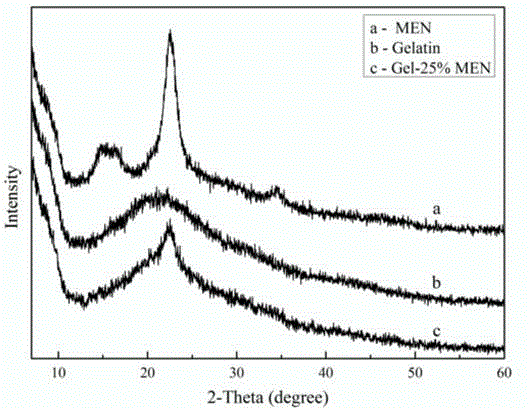
Cellulose chemical crosslinking based gelatin film and preparation method thereof
A technology of chemical cross-linking and cellulose is applied in the field of gelatin film based on chemical cross-linking of cellulose and its preparation to achieve the effects of improving light-blocking performance, light-blocking performance and hydrophobicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] A kind of synthetic method of novel macromolecular cross-linking agent based on cellulose:
[0060] (1) Synthesis of EDTA dianhydride (EDTAD):
[0061] Dissolve 20g of EDTA disodium salt in 100ml of water to form a transparent solution, add 1.5 mol / L HCl dropwise during stirring until a white precipitate appears, and filter to obtain EDTA; weigh 18g of EDTA and 24ml of acetic anhydride in 31 ml of pyridine to form a suspension, and magnetically stirred in an oil bath at 65 °C for 24 h. After the reaction was completed, it was washed with distilled water and ether, then suction filtered, and vacuum-dried at 50 °C to obtain white powdery solid EDTA dianhydride (EDTAD).
[0062] (2) Preparation of EDTAD functionalized microcrystalline cellulose (ME):
[0063] Weigh 3 g of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) and 9 g of EDTAD in 150 ml DMF, and stir magnetically in an oil bath at 70 °C for 24 h. ml of distilled water and 20 ml of ethanol were washed, then suction-filtered, an...
Embodiment 2
[0117] (1) Synthesis of EDTA dianhydride (EDTAD):
[0118] Weigh 30g of EDTA disodium salt and dissolve it in 150ml of water to form a transparent solution, add 1 mol / L HCl dropwise during the stirring process until white precipitate appears, and filter to obtain EDTA; weigh 21g of EDTA and 30ml of acetic anhydride in 40 ml of pyridine to form a suspension, stirred in an oil bath at 72 °C for 24 h, washed with distilled water and then with diethyl ether after the reaction, then vacuum-dried at 50 °C to obtain white powdery solid EDTA dianhydride (EDTAD).
[0119] (2) Preparation of EDTAD functionalized microcrystalline cellulose (ME):
[0120] Weigh 3 g of MCC and 12 g of EDTAD in 150 ml of DMF, and stir magnetically in an oil bath at 73°C for 30 h. Suction filtration after washing, and vacuum drying at 50°C to obtain a light yellow powdery solid compound, namely, EDTAD functionalized microcrystalline cellulose ME;
[0121] (3) Preparation of N-hydroxysuccinimide-activated f...
Embodiment 3
[0129] (1) Synthesis of EDTA dianhydride (EDTAD):
[0130] Weigh 40g of EDTA disodium salt and dissolve it in 200ml of water to form a transparent solution. During stirring, add 2 mol / L HCl dropwise until a white precipitate appears, and filter to obtain EDTA; weigh 25g of EDTA and 40ml of acetic anhydride in 50 ml pyridine to form a suspension, stirred in an oil bath at 75 °C for 36 h, washed with distilled water and then with diethyl ether after the reaction, then vacuum-dried at 50 °C to obtain white powdery solid EDTA dianhydride (EDTAD).
[0131] (2) Preparation of EDTAD functionalized microcrystalline cellulose (ME):
[0132] Weigh 3 g of MCC and 10 g of EDTAD in 120 ml of DMF, and stir magnetically in an oil bath at 65 °C for 20 h. Suction filtration after washing, and vacuum drying at 50°C to obtain a light yellow powdery solid compound, namely, EDTAD functionalized microcrystalline cellulose ME;
[0133] (3) Preparation of N-hydroxysuccinimide-activated functional c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com