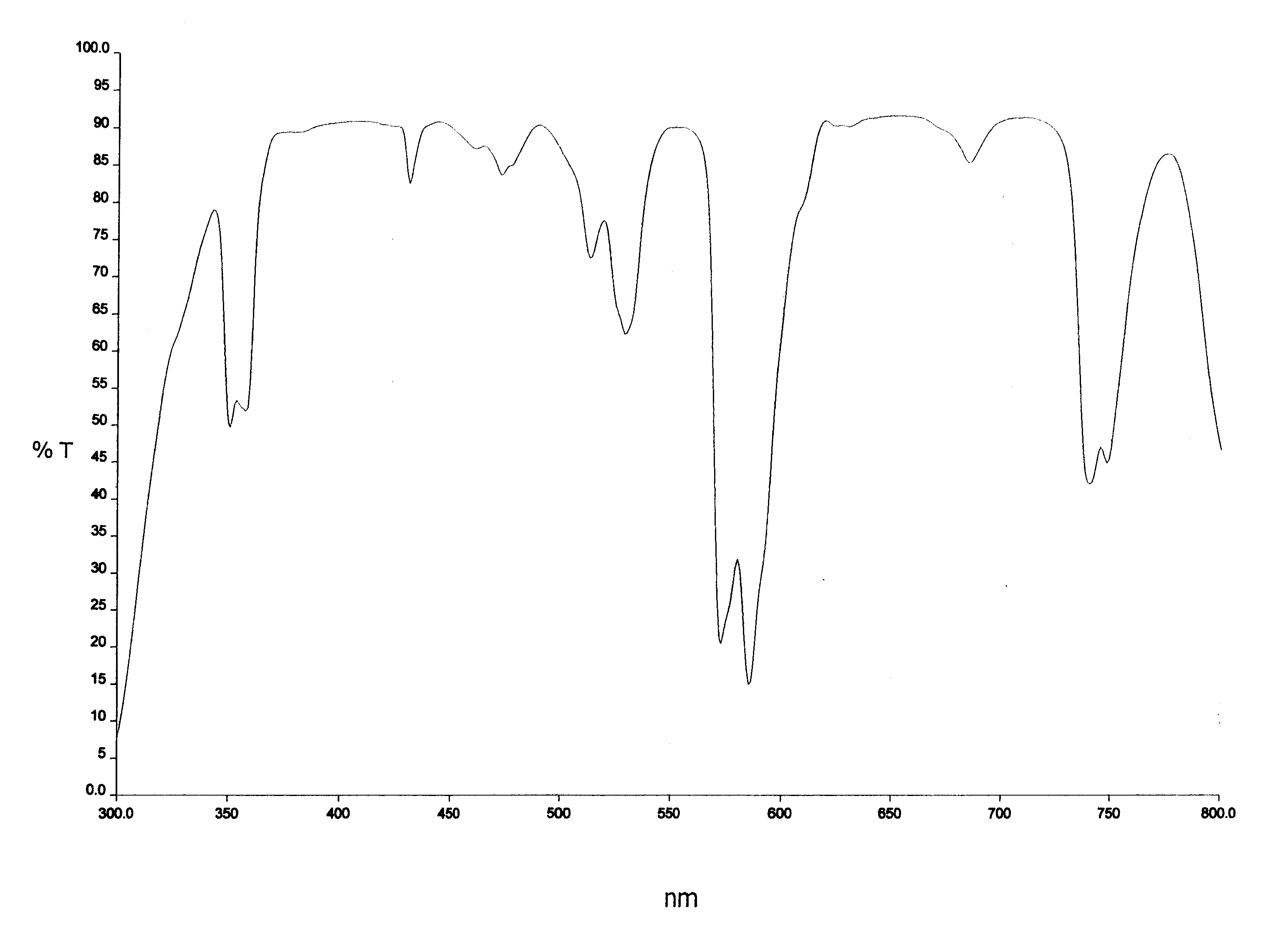Patents
Literature
493 results about "Safety glass" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
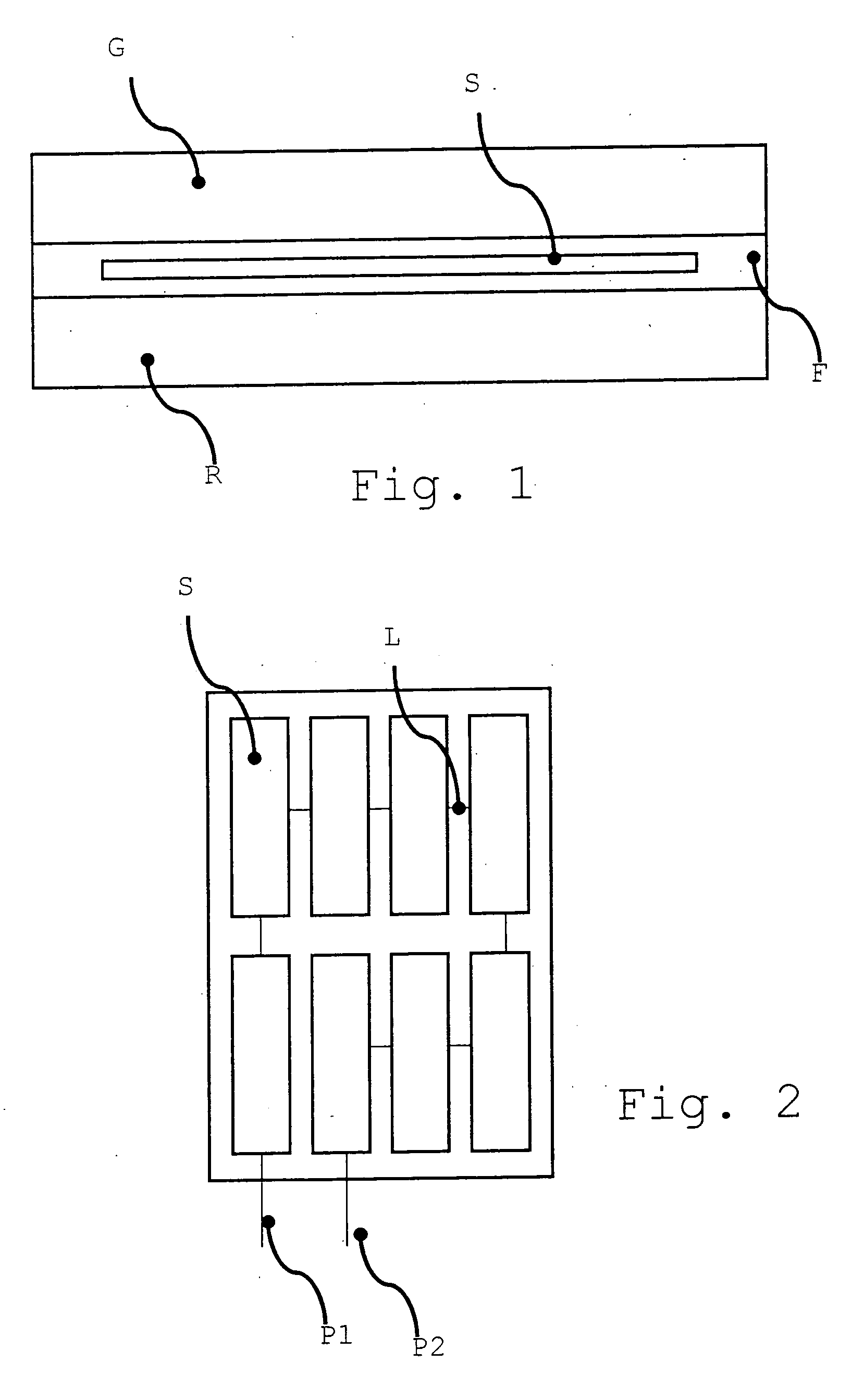
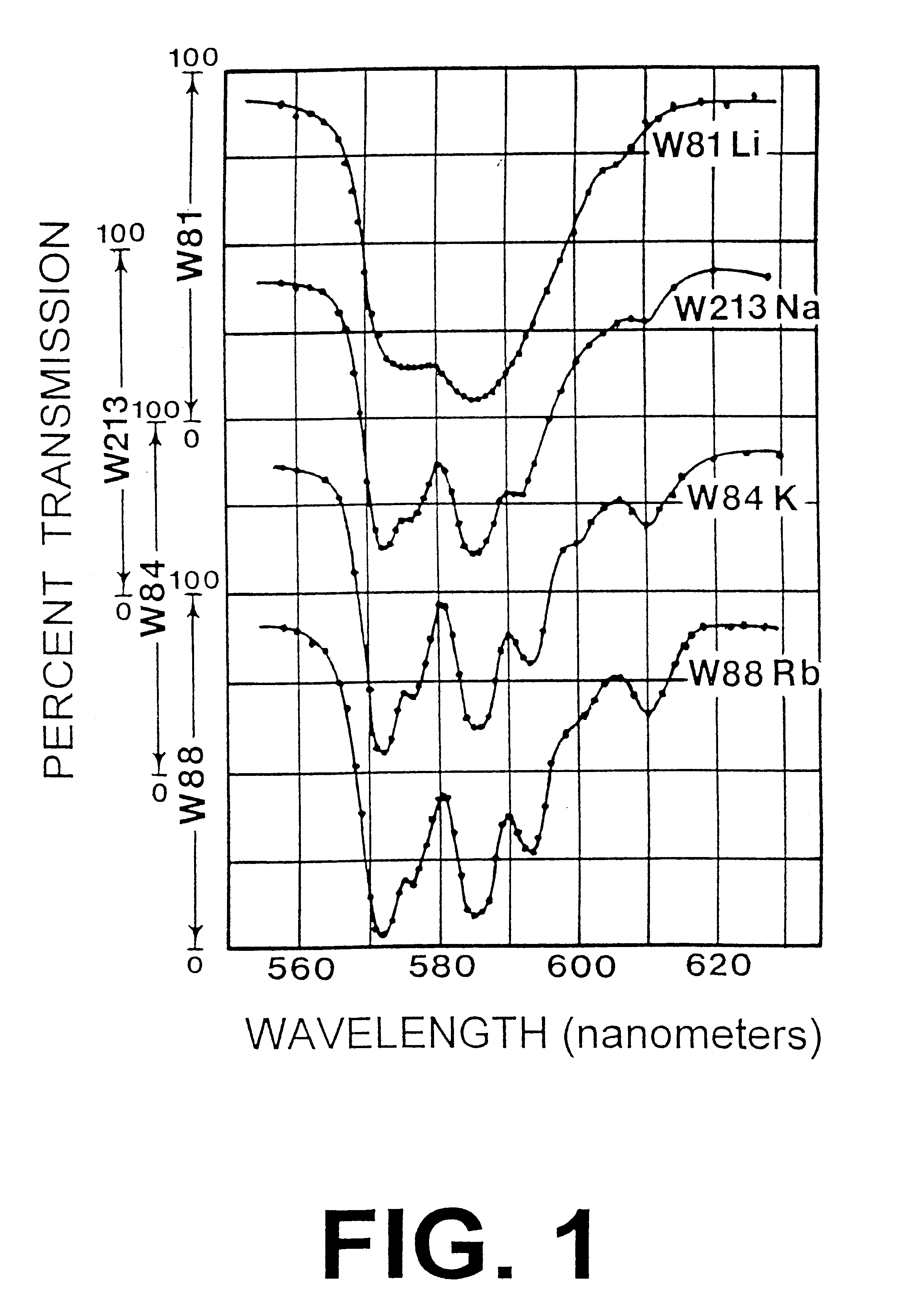
Safety glass is glass with additional safety features that make it less likely to break, or less likely to pose a threat when broken. Common designs include toughened glass (also known as tempered glass), laminated glass, wire mesh glass (also known as wired glass) and engraved glass. Wire mesh glass was invented by Frank Shuman. Laminated glass was invented in 1903 by the French chemist Édouard Bénédictus (1878–1930).
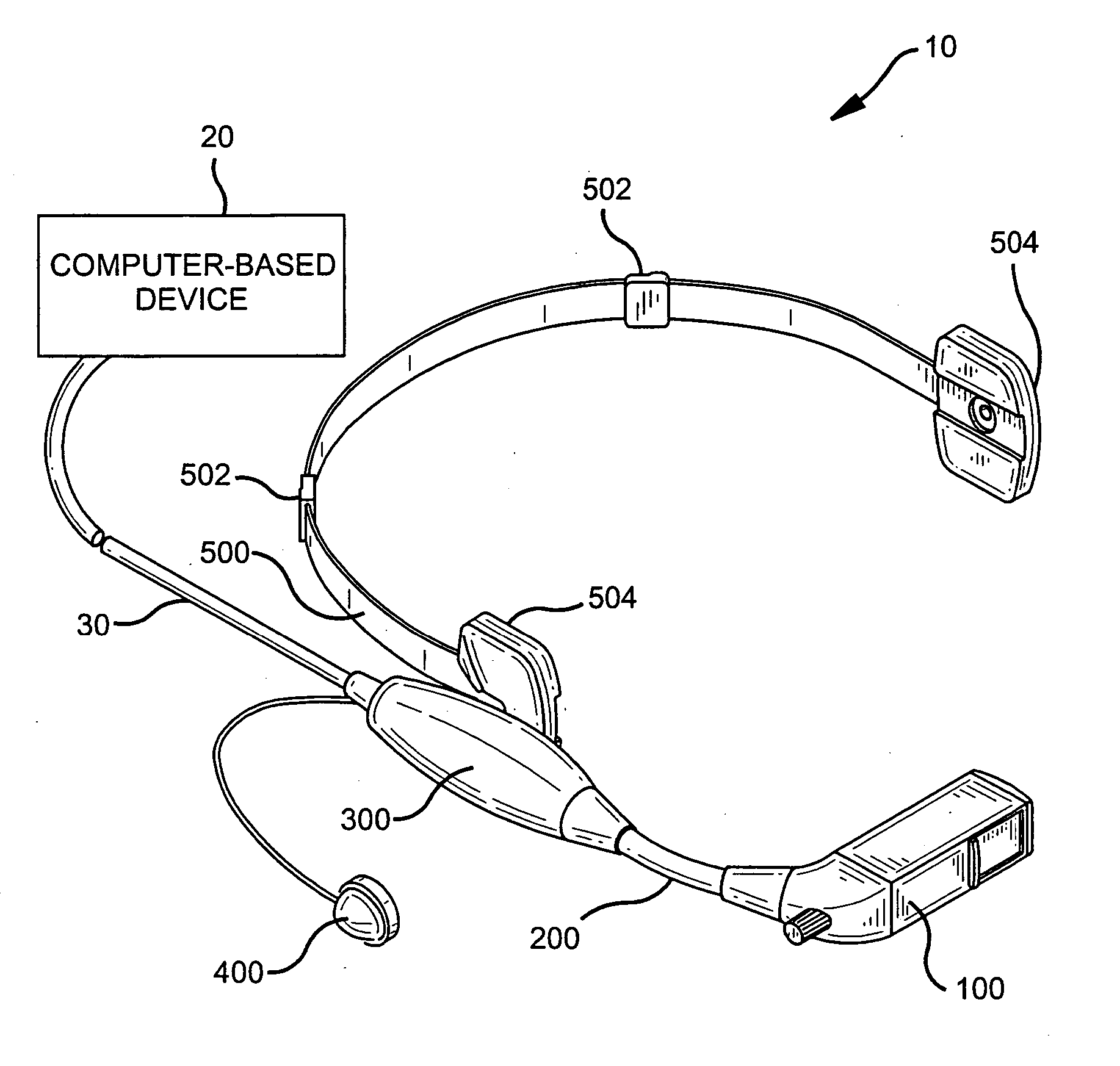
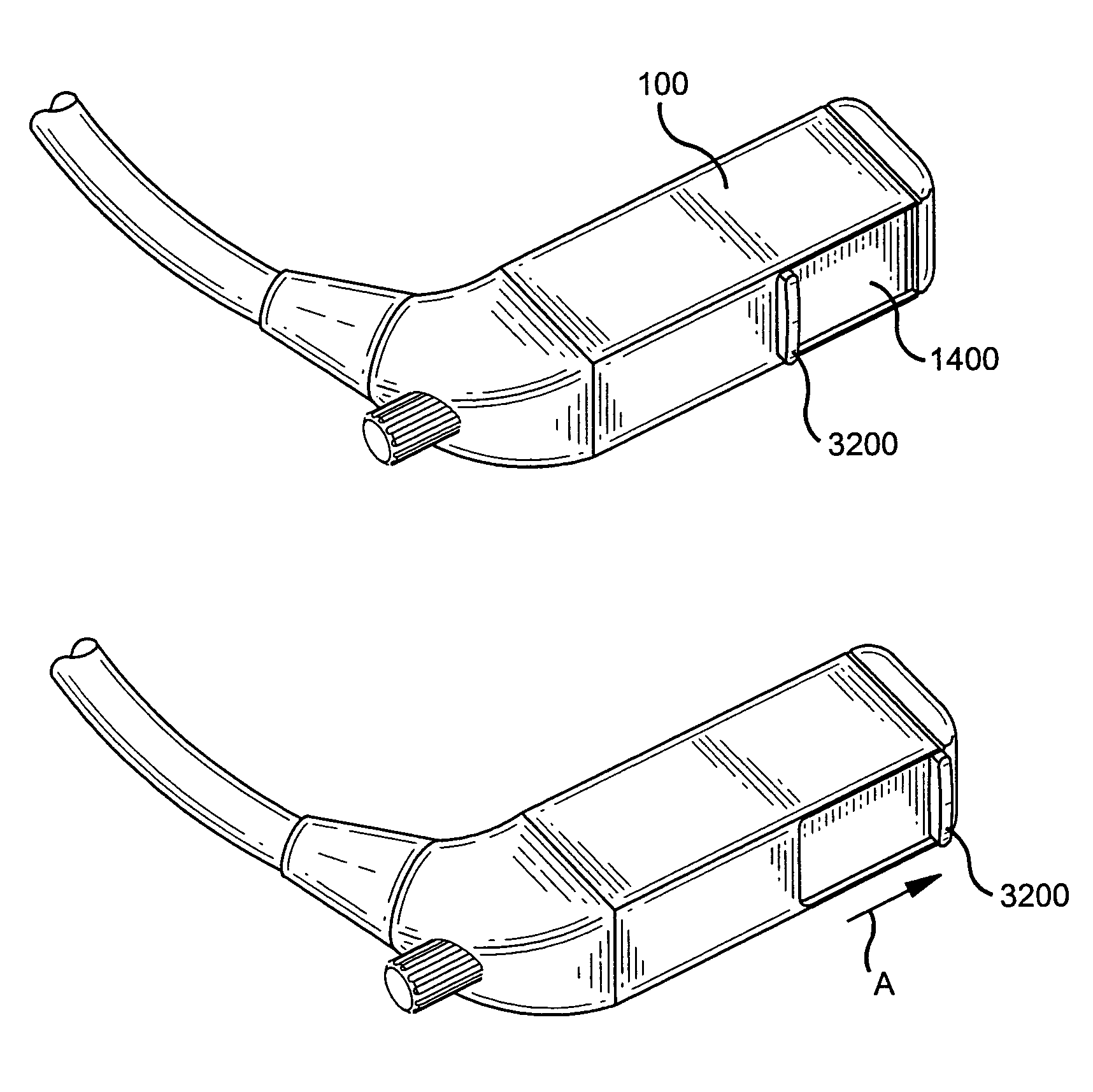
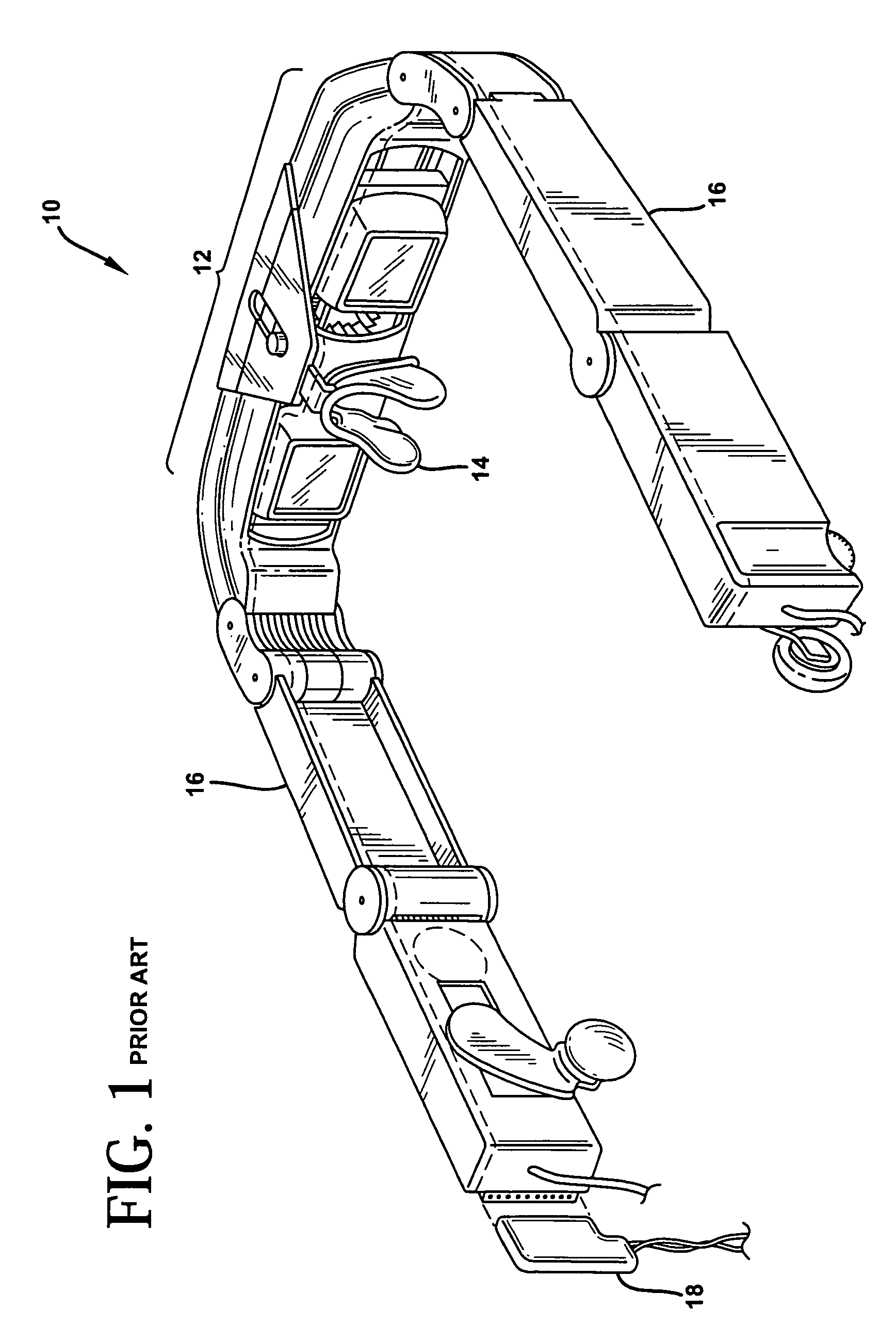
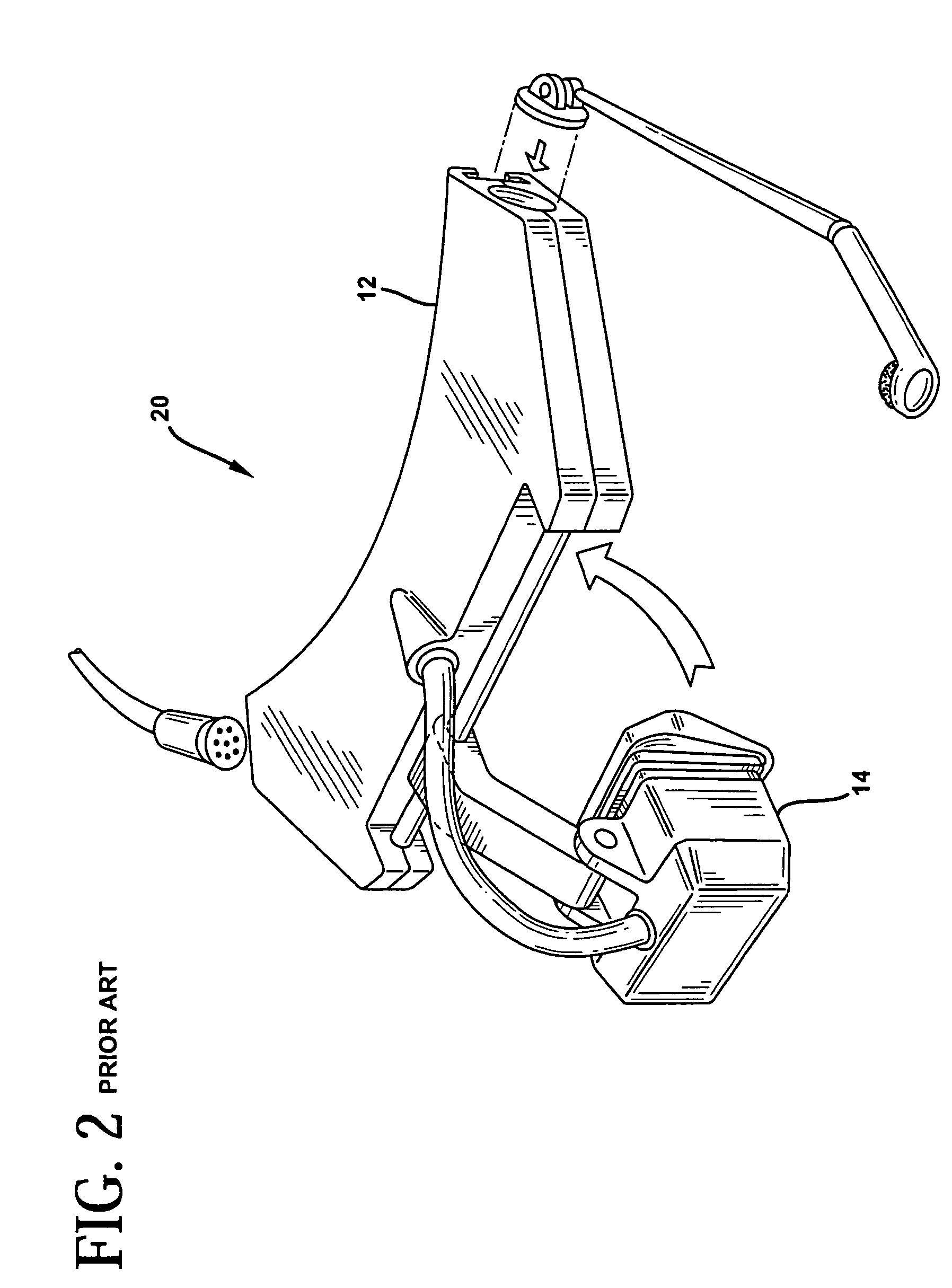
Compact optical system and packaging for head mounted display
ActiveUS20050219152A1Improve convenienceHigh acceptabilityTelevision system detailsPrismsDisplay deviceEngineering
A head mounted virtual image display unit is provided which is compact in size and weight, and incorporates a high performance optical system offering a clear see-through capability. A sliding light shield may be incorporated for those instances when see-through capability is not desired. A focus adjustment may be incorporated to permit the focusing of the image, for example, at a distance of approximately 18 inches to infinity. An adjustable headband may be incorporated that adapts to fit the users head. A flexible boom structure may be incorporated to facilitate fine positional adjustment of the optical assembly. A slider and ball joint mechanism may also be incorporated to facilitate positional adjustment of the optical assembly. A built-in microphone may be incorporated to enable speech input by the user. The head mounted virtual image display unit may be used comfortably in conjunction with eye or safety glasses, and provides a useful image to the user without blocking his view of the surrounding environment. The unit is designed to have a pleasing appearance so as to greatly enhance user acceptability.
Owner:IBM CORP
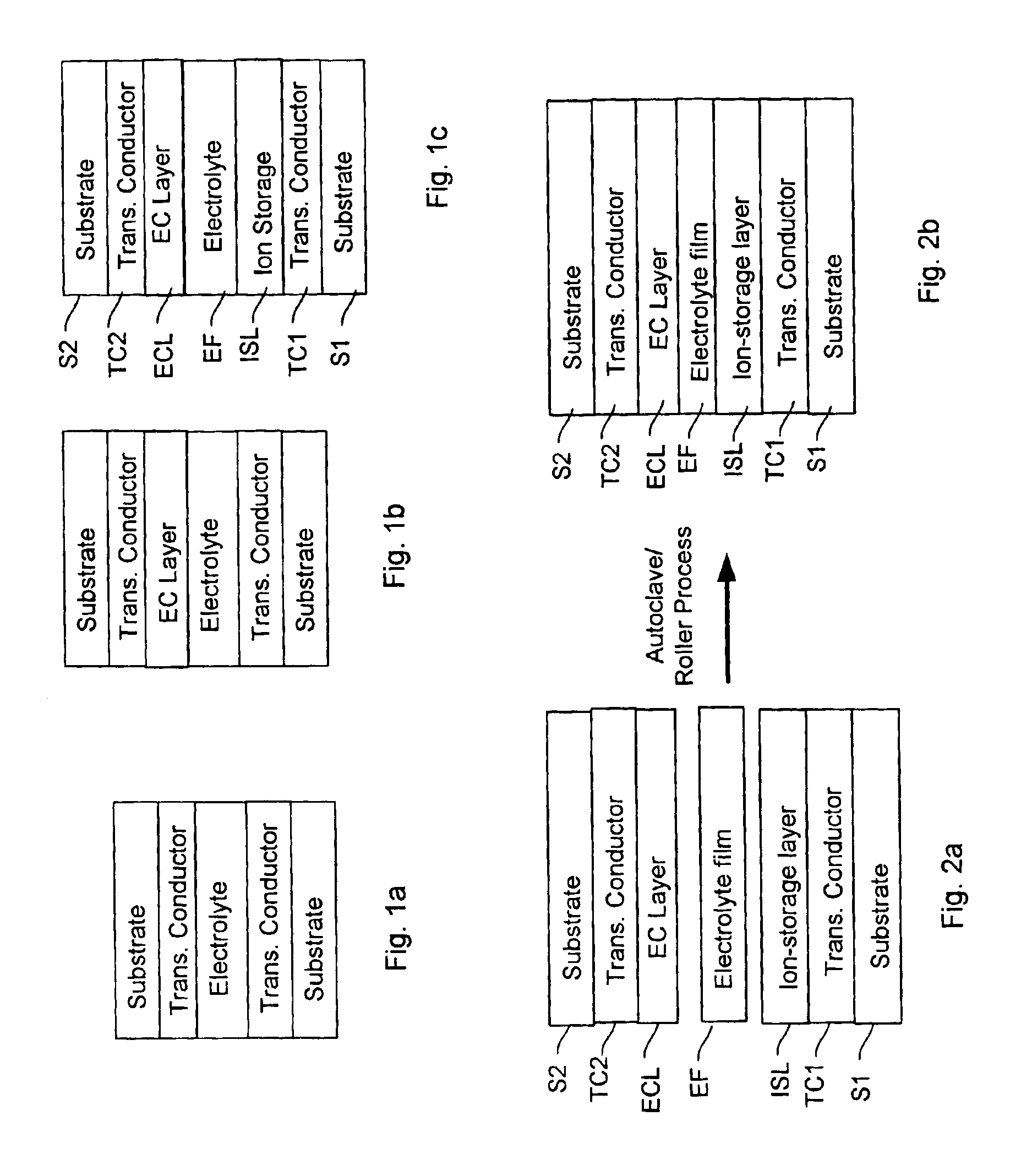
Solar laminates as laminated safety glass
InactiveUS20050284516A1High tensile strengthPrevent penetrationPV power plantsSolid-state devicesEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
Solar modules, with the properties of laminated safety glass, comprising a laminate containing a) a glass pane b) at least one solar cell unit that is located between two PVB-based films, and c) a rear covering and at least one of the PVB-based films has a tensile strength of at least 16 N / mm2, are suitable for use as a facade component, roof surface, winter garden covering, soundproofing wall, or as a component of windows.
Owner:KURARAY EURO GMBH
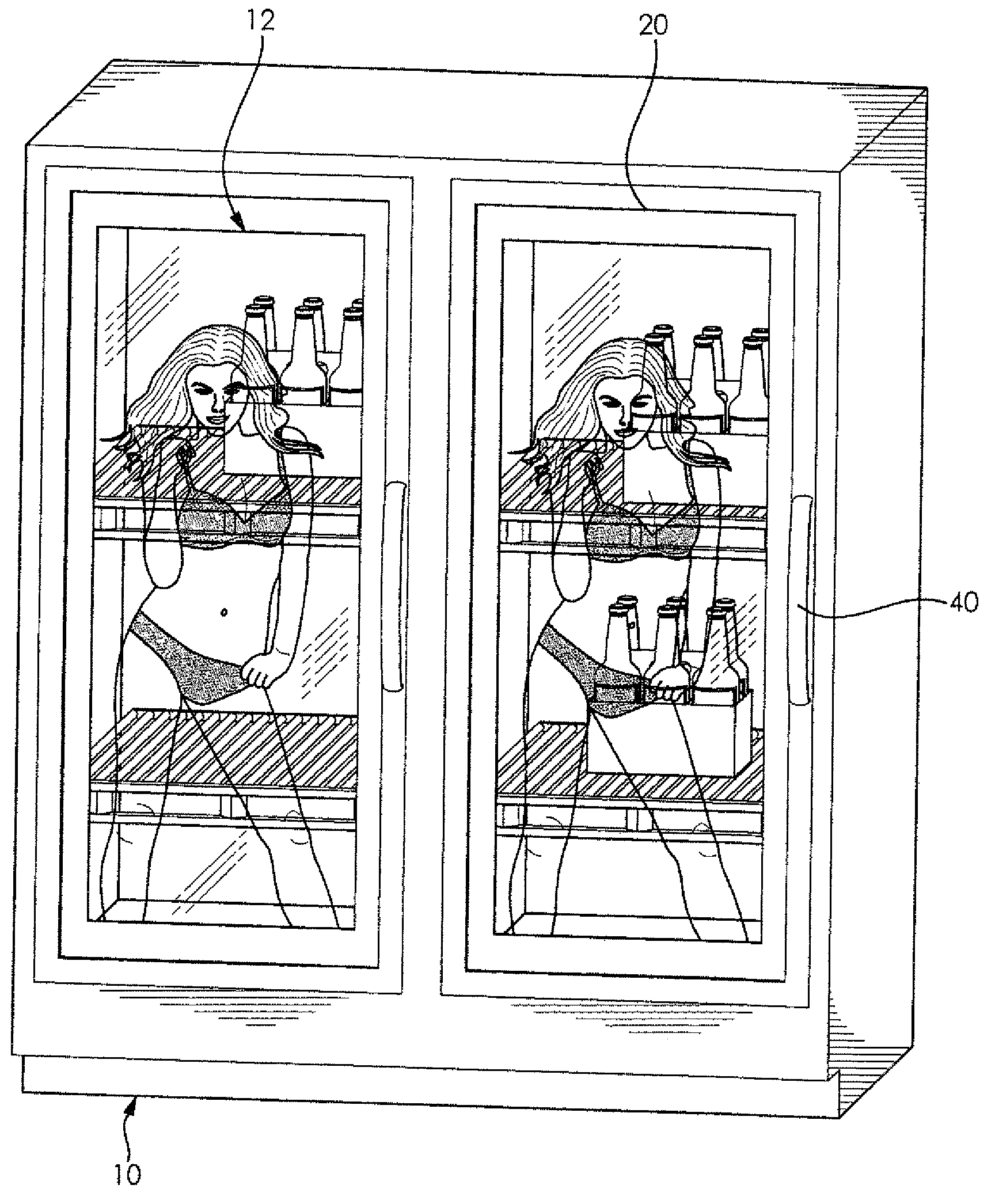
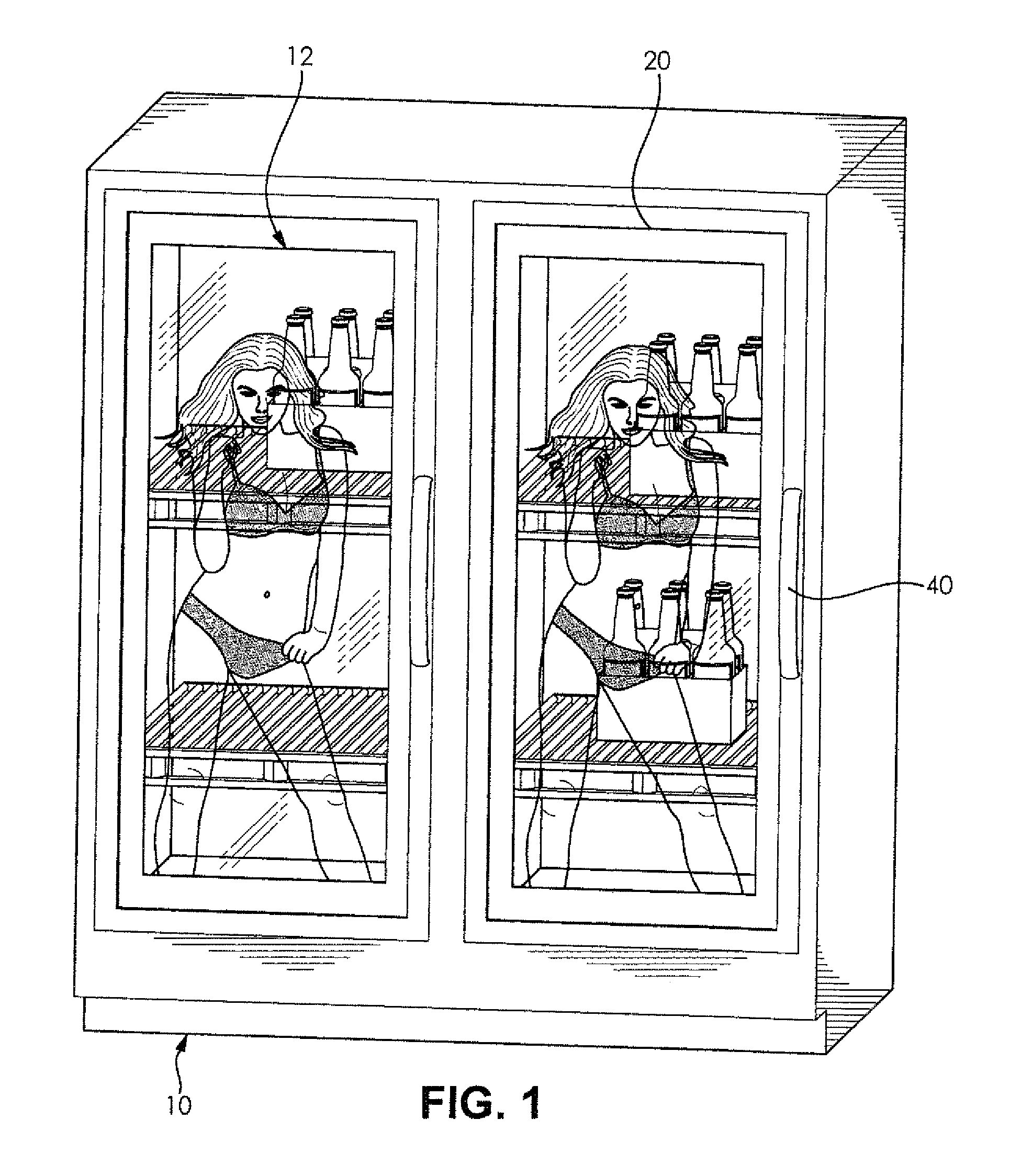
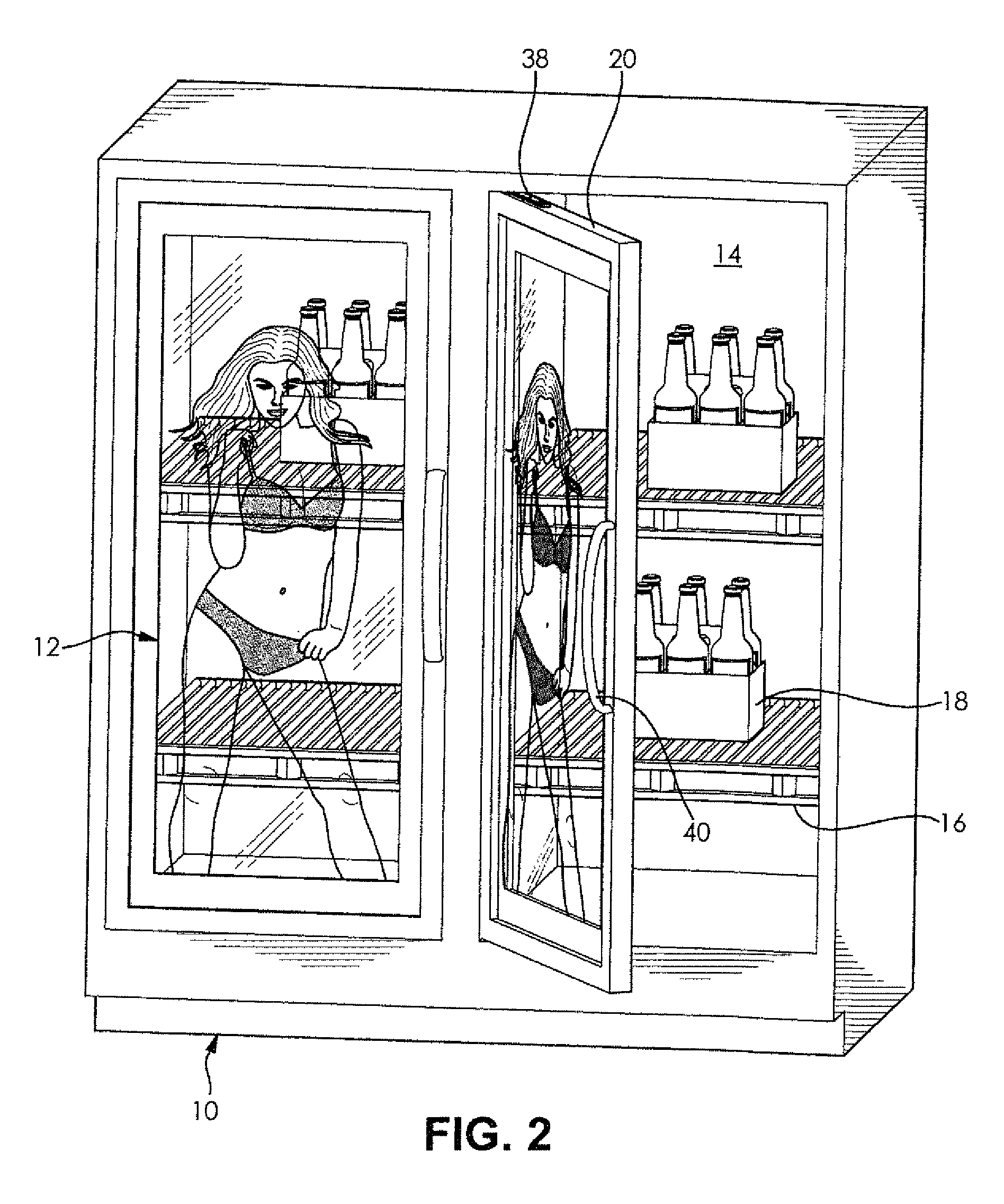
Translucent Digital Display System
ActiveUS20130063326A1Uniform lightShow cabinetsTelevision system detailsDigital videoComputer graphics (images)
A digital display system includes a transparent outer protective panel, a transparent inner protective panel, and a translucent digital video display located between the outer and inner protective panels. An integrated media player is operably connected to the translucent digital video display so that full-motion videos displayed on the translucent digital video display are viewed through the outer protective panel and items can be viewed through the translucent digital video display. The digital display system can be incorporated into any environment where a product is located behind a glass enclosure such as freezers, coolers, security glass, jewelry cases, liquor cases, cosmetic cases, and the like. In retail environments, the digital display systems can also be incorporated into entry doors, windows, drive-thru windows, teller windows, and any other location where there is traditionally glass and you want to focus consumer attention obstructing the customer's line of site.
Owner:STRATACACHE
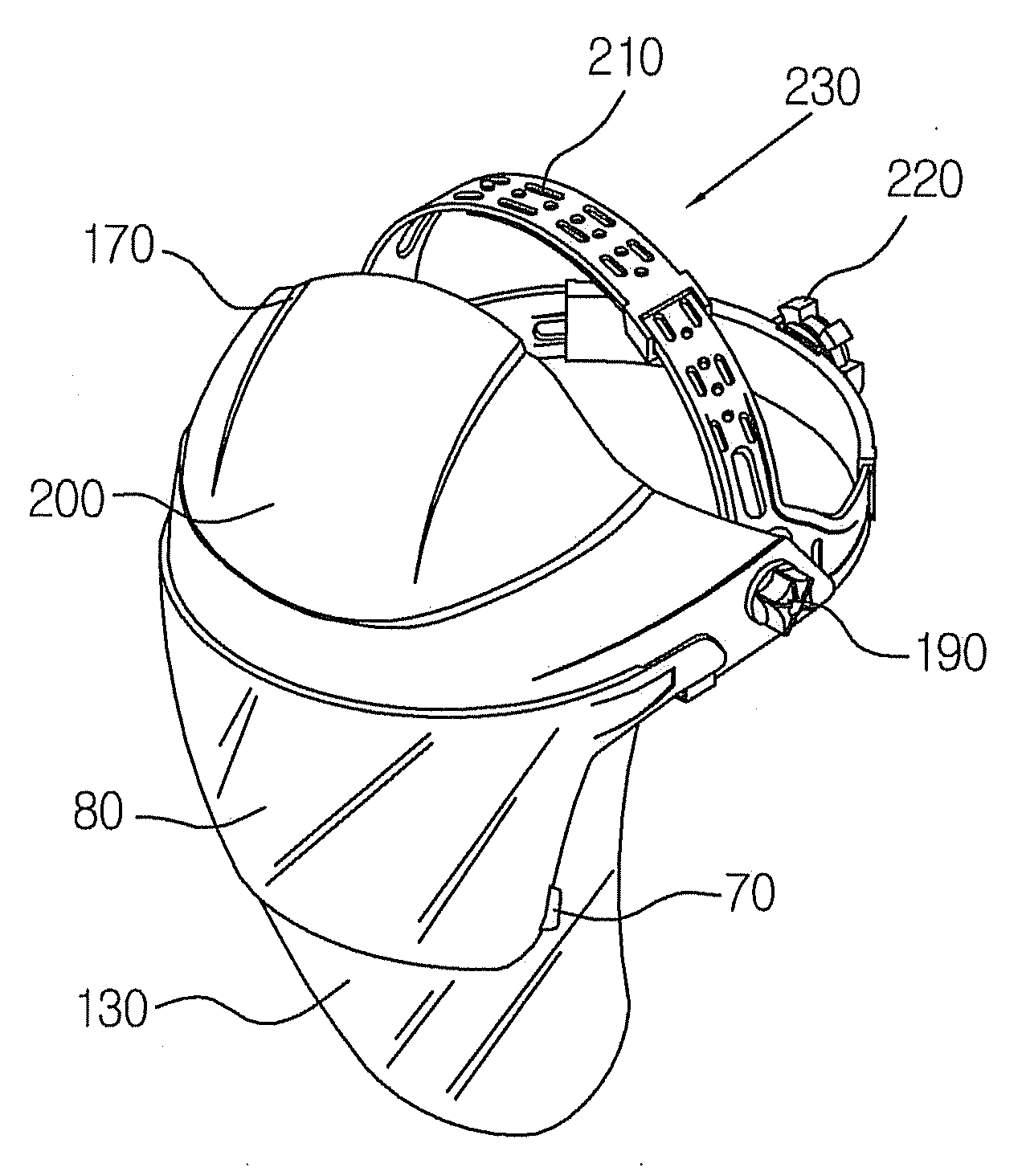
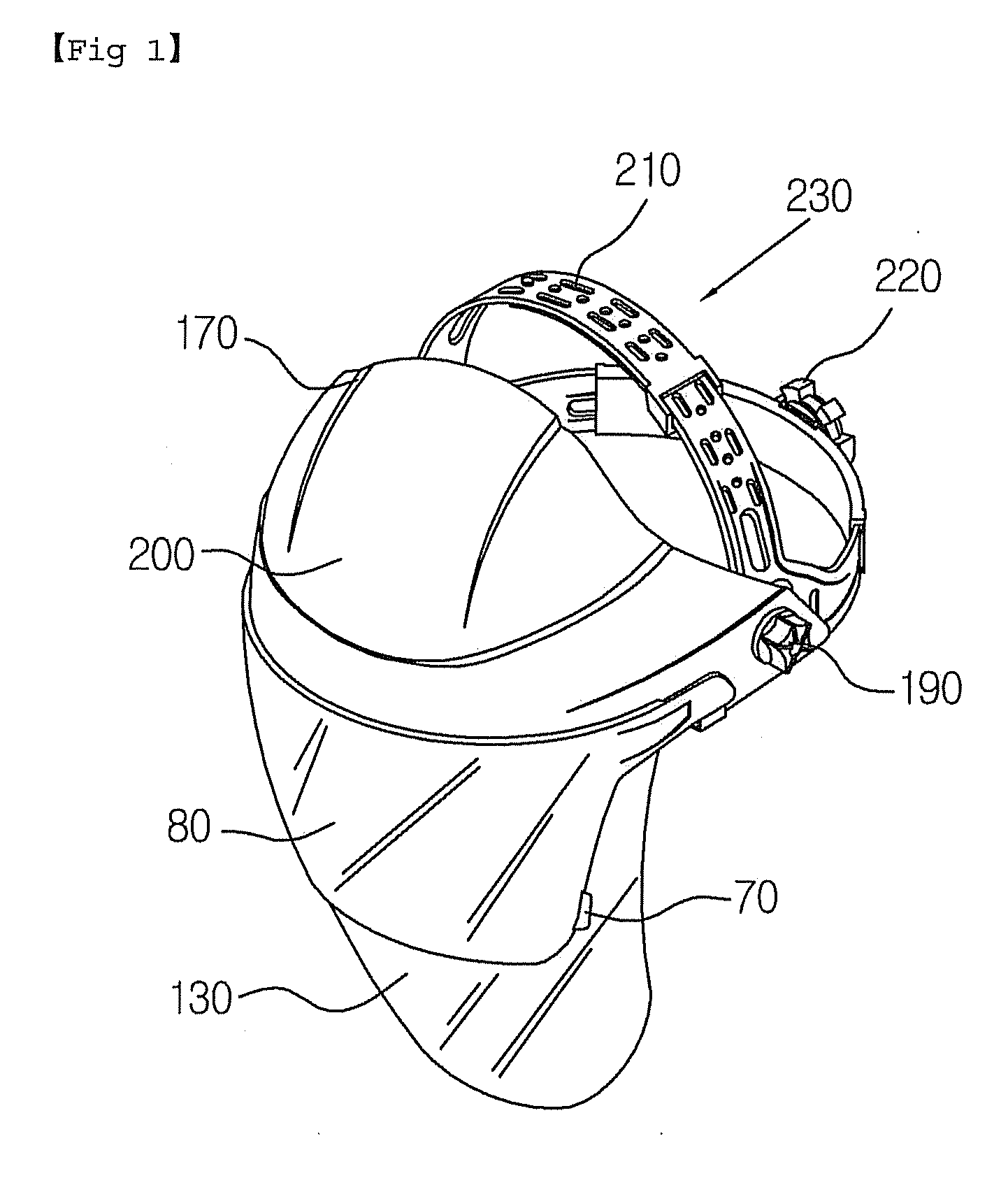
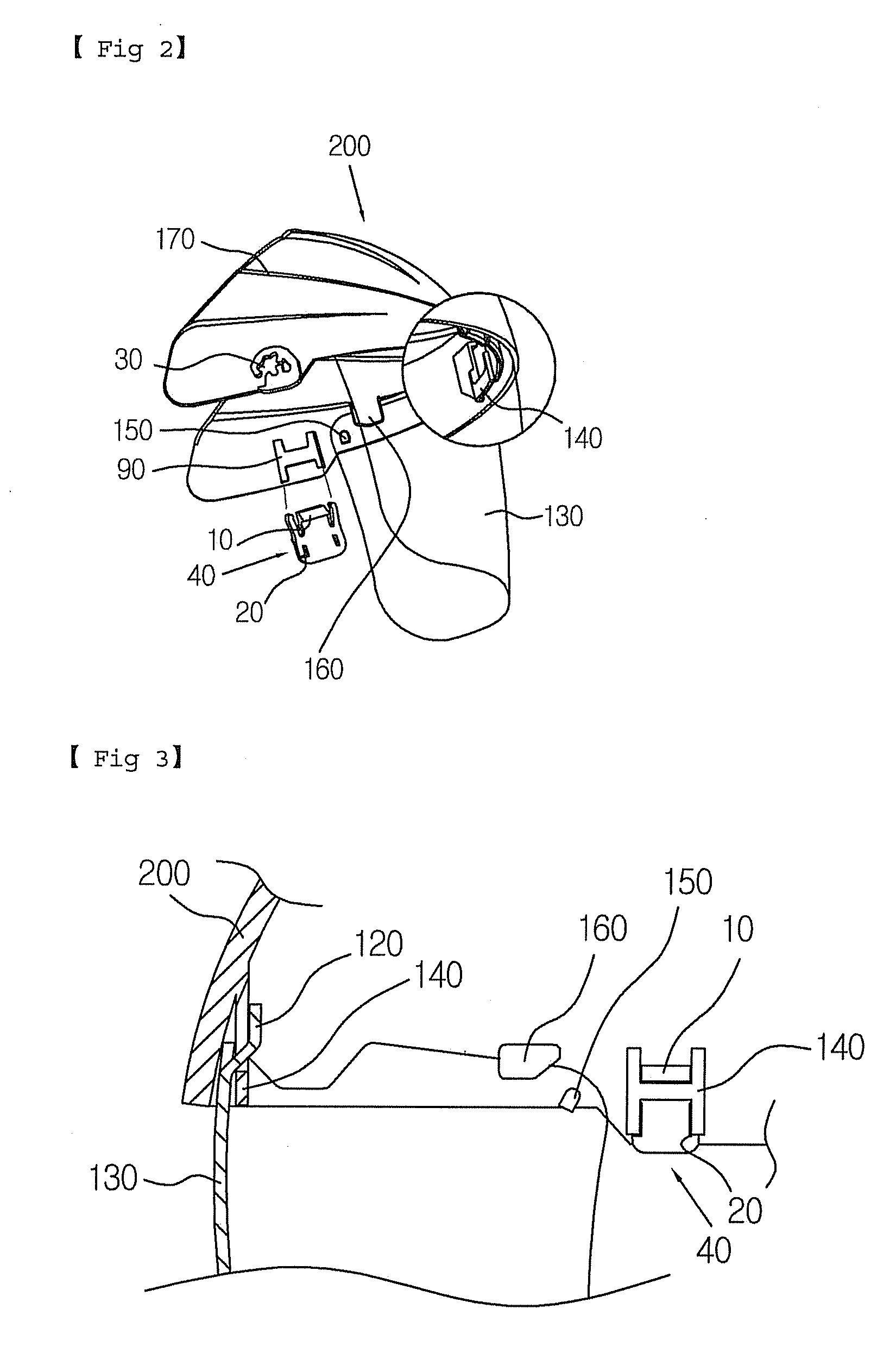
Multi-function face protector
Disclosed herein is a face protector having a protective shade that enables the worker to perform welding as well as grinding while wearing the multi-function face protector and that can be used with safety glasses, goggles and a mask. The multi-function face protector includes a head band, a forehead cover, and a face shield. The face shield comprises resilient hooks formed at its upper central portion, and engaging portions formed at its opposite ends respectively. The forehead cover comprises shield couplings formed at the central portion of its inner surface, and projections formed at the opposite ends of its inner surface respectively. The resilient hooks of the face shield are engaged with the respective shield couplings of the forehead cover.
Owner:OTOS TECH
Laminated glass windscreen intended to be used at the same time as a HUD system reflector
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN VITRAGE SA
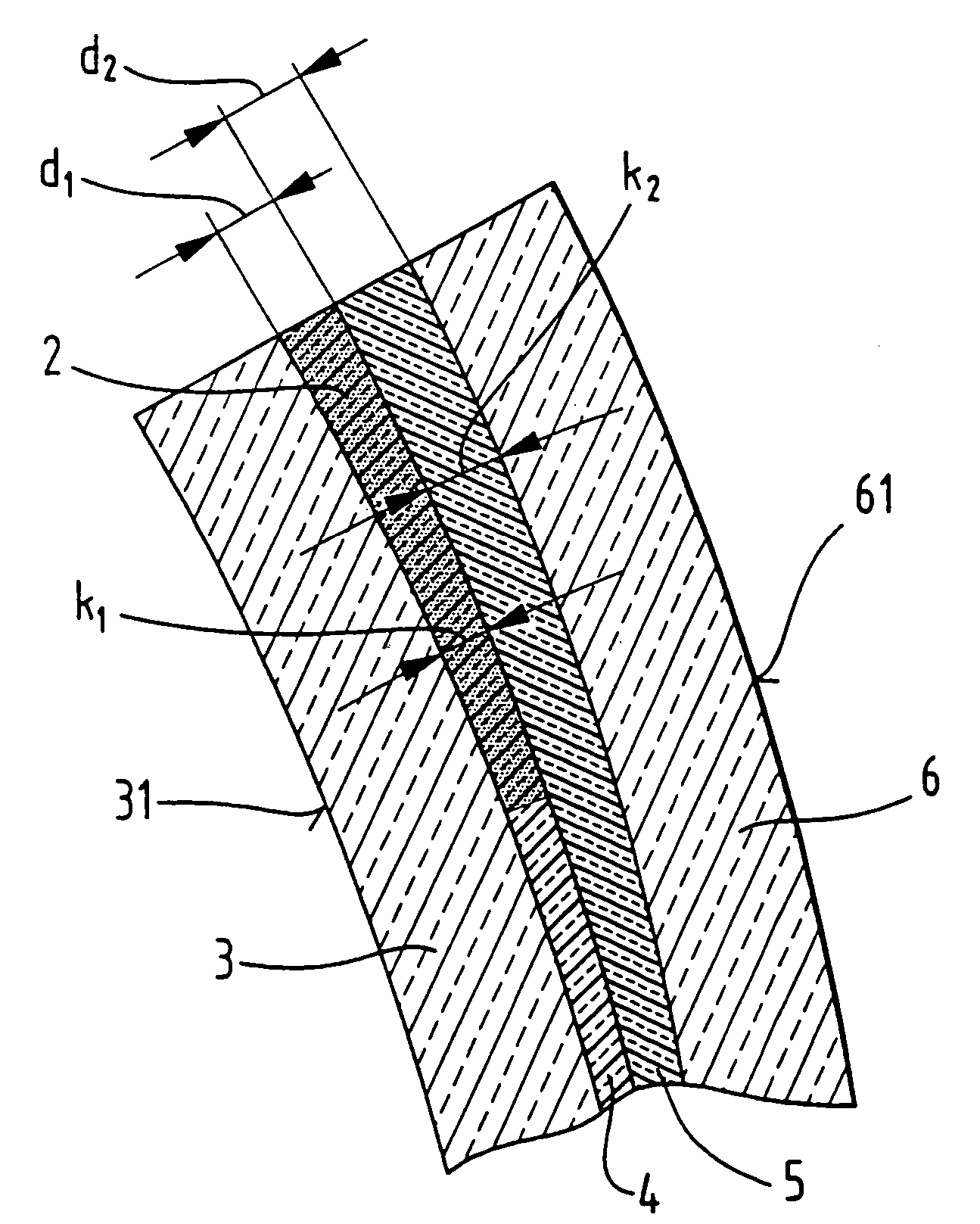
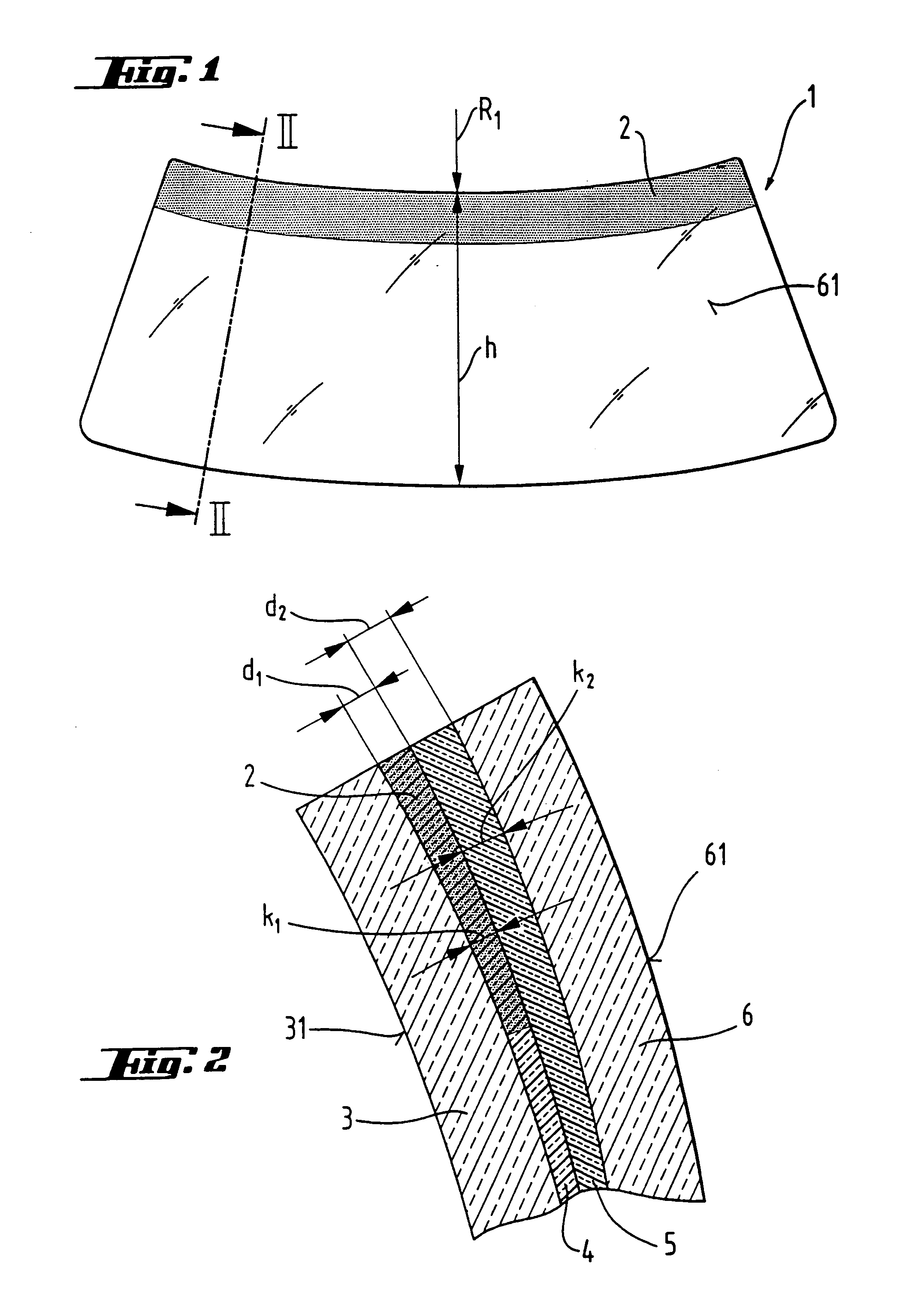
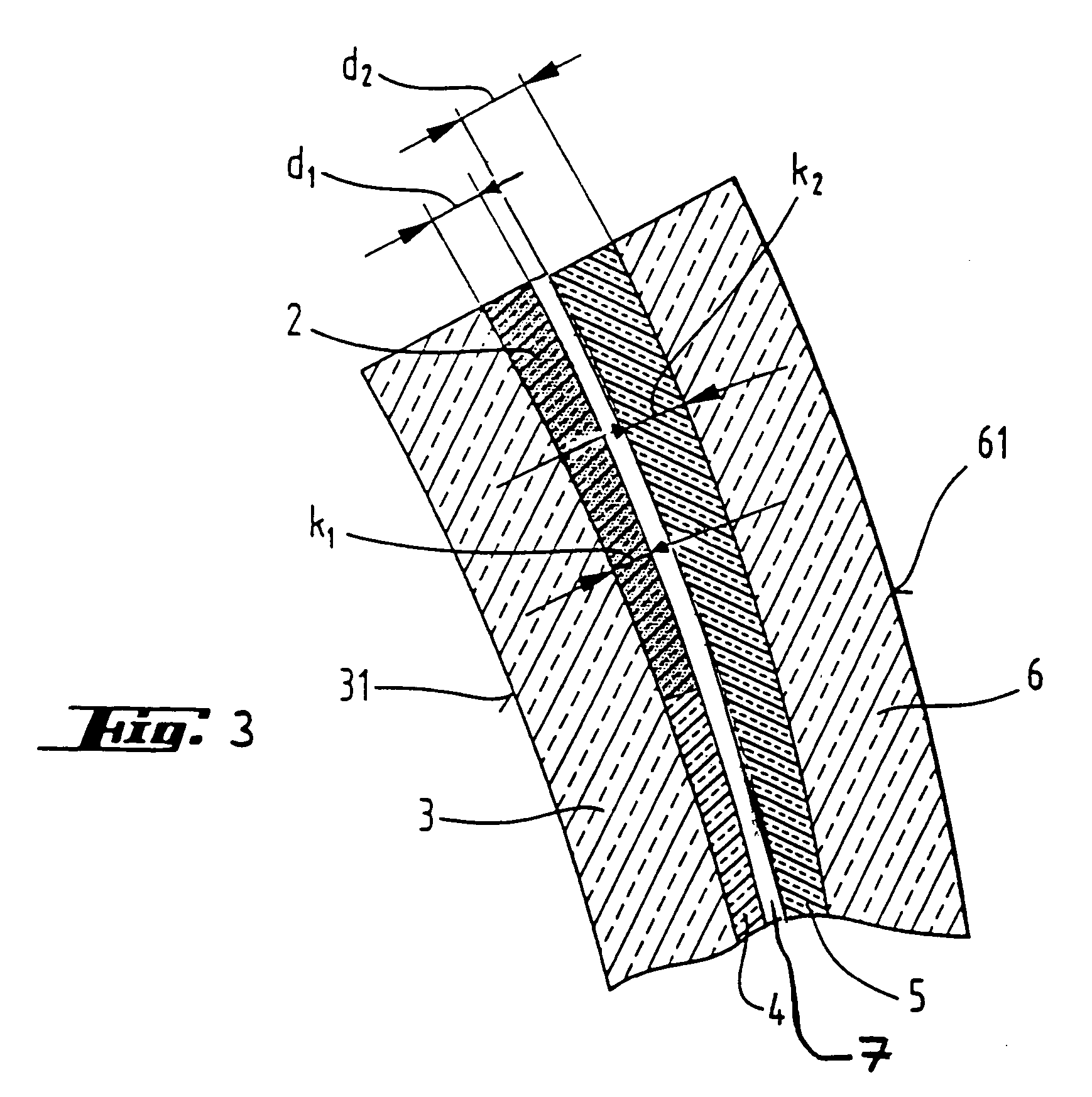
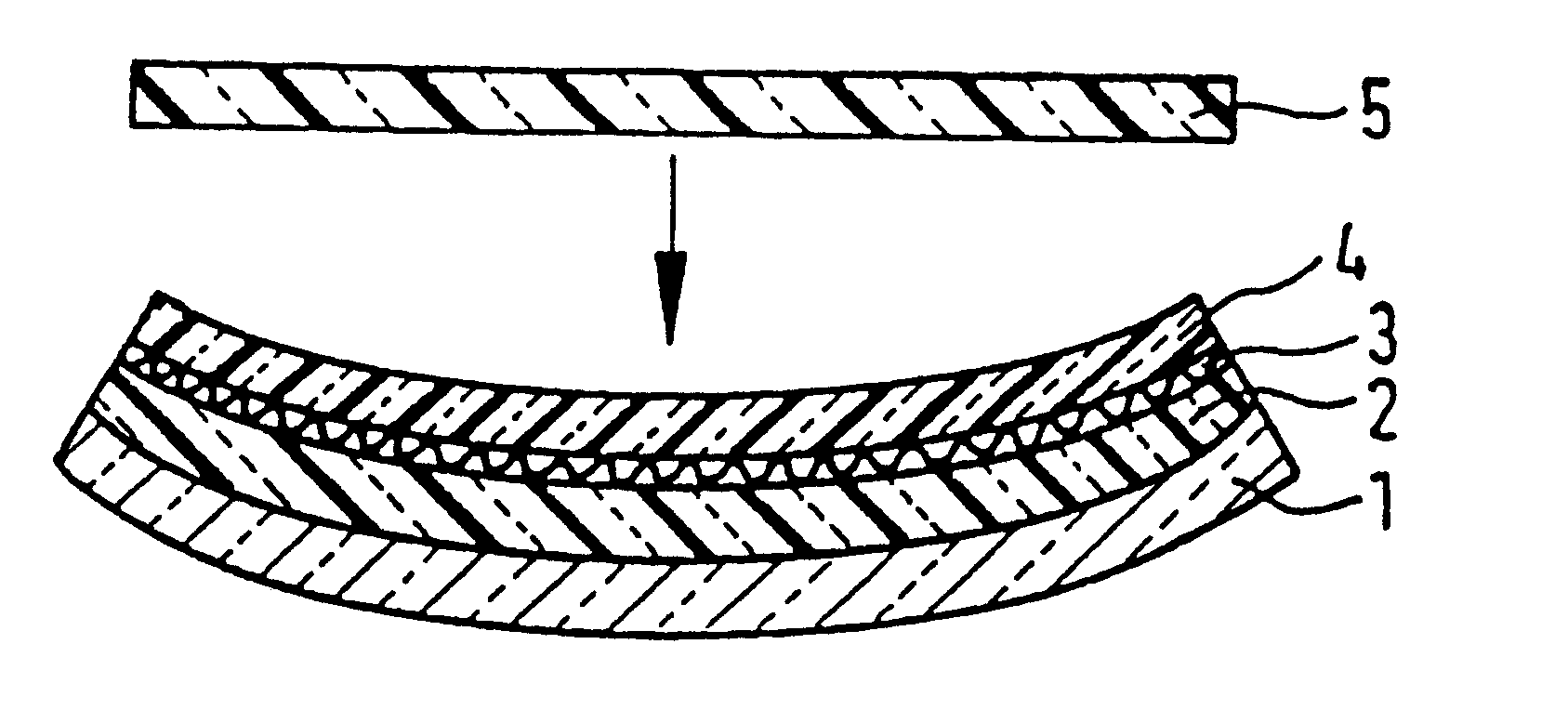
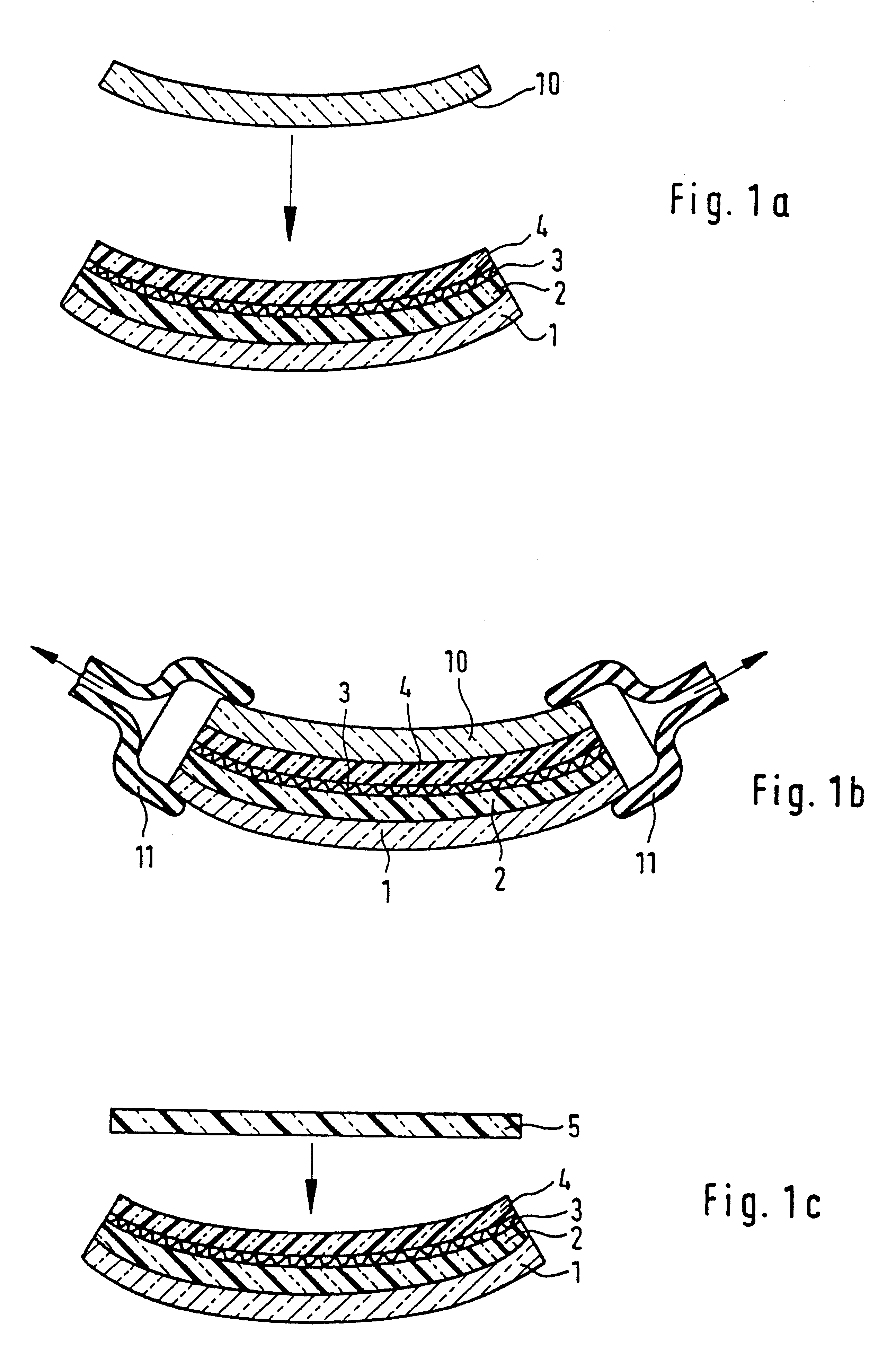
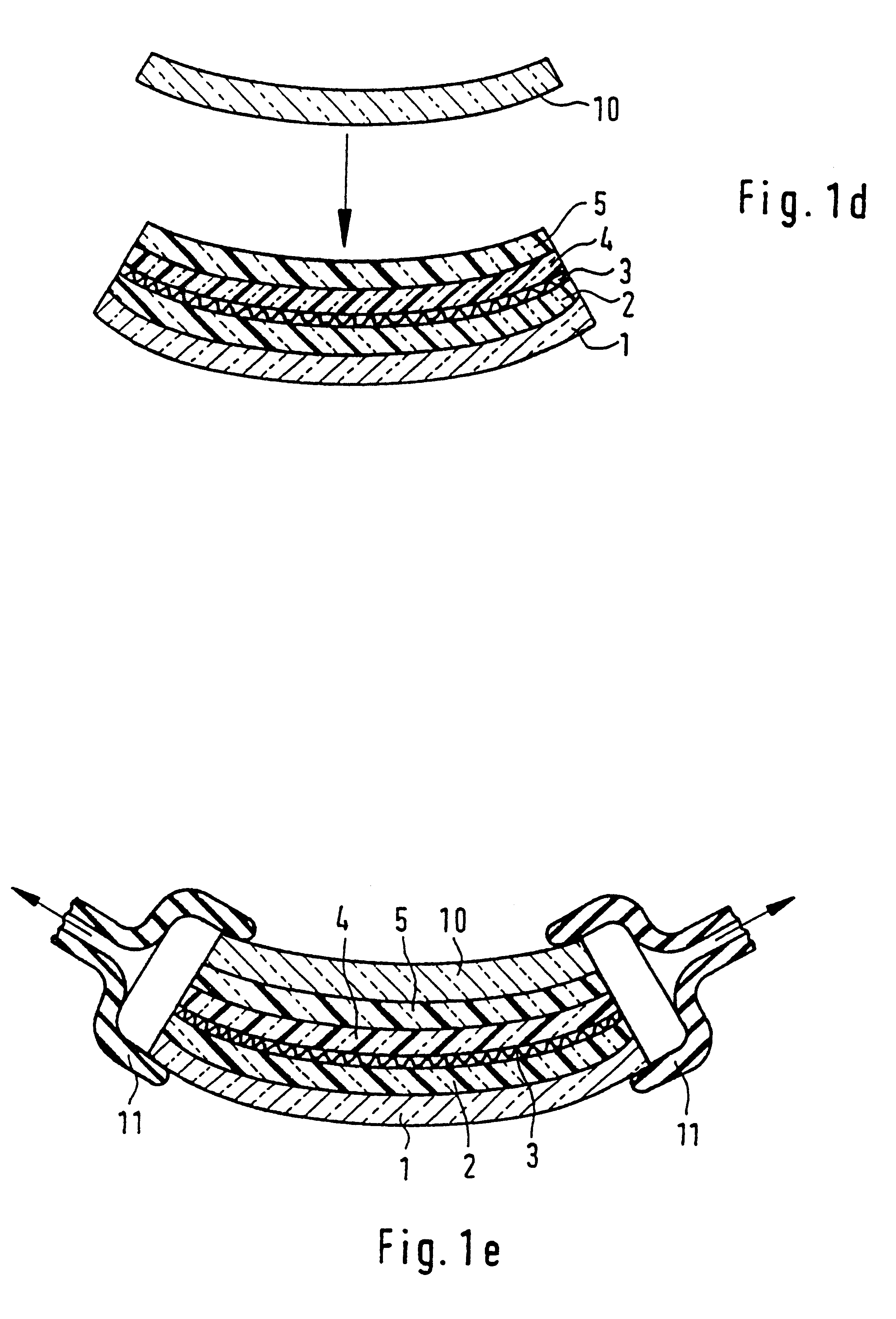
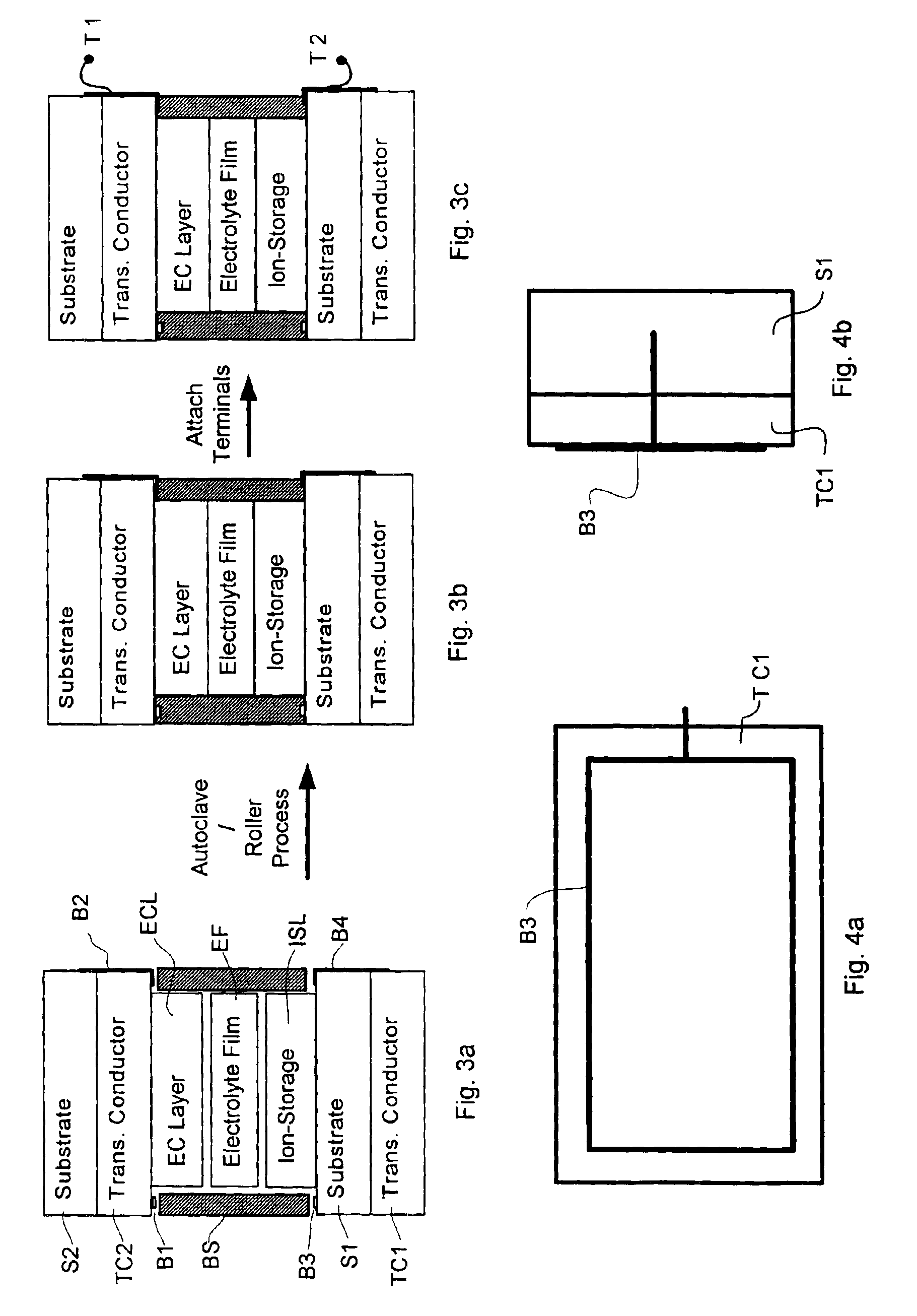
Process for producing a curved laminated safety glass sheet
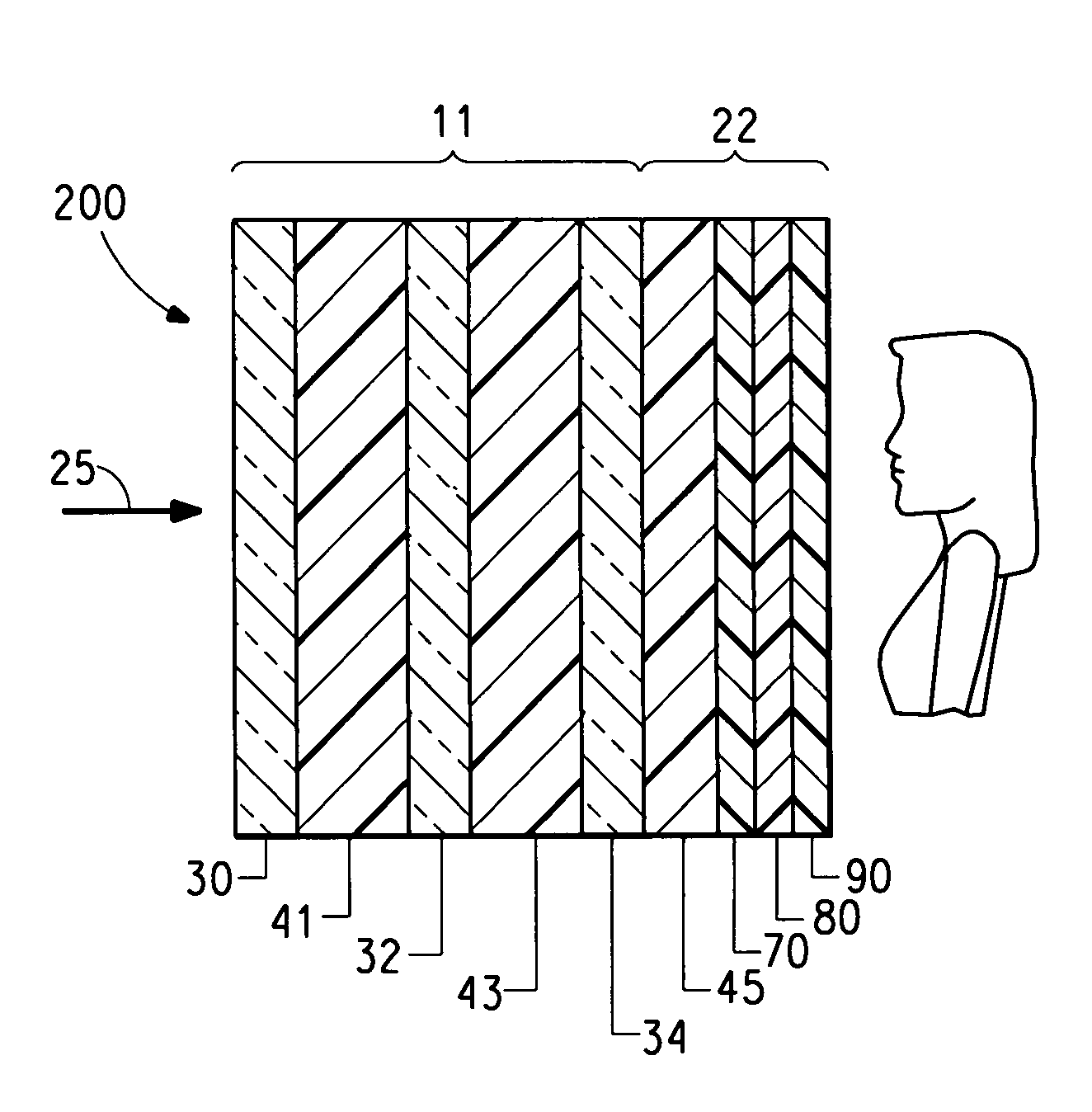
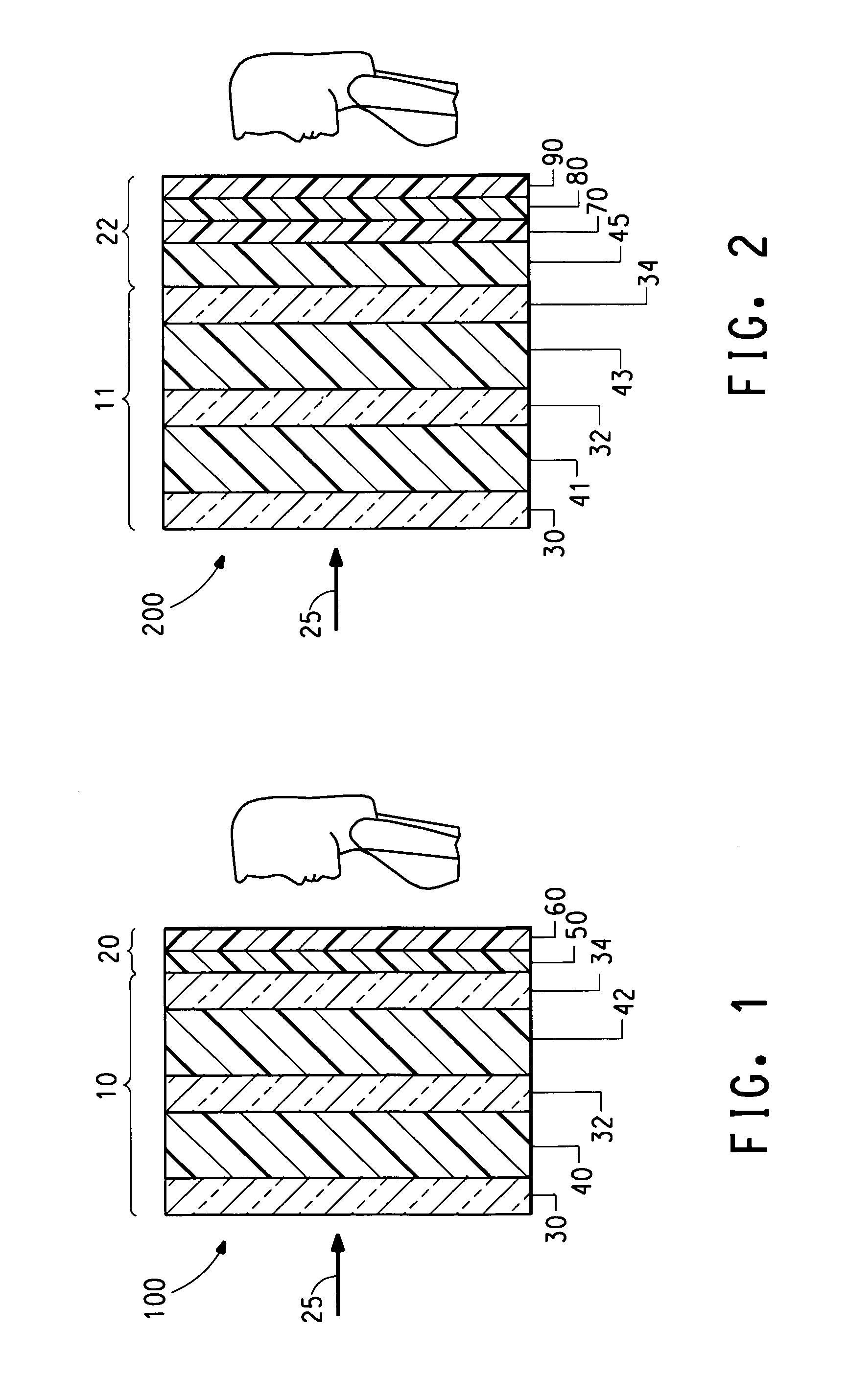
InactiveUS6261398B1Avoid wrinklesSimple preparation processLaminationLamination apparatusThin layerEngineering
This invention concerns a process for producing a curved, laminated safety glass sheet from a first curved glass sheet (1), a first laminated layer (2), a thermoplastic substrate sheet (4) with a biaxially drawn thin-layer system (3), a second laminated layer (5), and a second curved glass sheet (10) conforming to the first one. To avoid formation of folds in the substrate layer, the process has the following steps: (a) a prelaminated sheet consisting of the first laminated layer (2) and the substrate sheet (4) is superimposed with its laminated layer facing the first glass sheet, (b) a bend-resistant cover sheet (10) conforming to the first glass sheet (1) is superimposed on the prelaminated sheet, (c) the glass layer packet formed out of the first glass sheet (1) and the prelaminated sheet with the cover sheet (10) superimposed upon it is preliminarily bonded by removing the air and subjecting it to pressure and heat, (d) the cover sheet (10) is removed, (e) the second laminated layer (5) and the second glass sheet (10) are superimposed on the preliminarily bonded glass-film pocket, (f) the laminate so formed is preliminarily bonded by removing the air and subjecting it to pressure and heat, (g) the preliminarily bonded laminate is finally bonded into a laminated safety glass sheet by subjecting it to pressure and heat.
Owner:PILKINGTON AUTOMOTIVE DEUT GMBH
Intrusion resistant safety glazings and solar cell modules
ActiveUS20080210287A1Lamination ancillary operationsPV power plantsPolyvinyl butyralPhysical chemistry
Described certain plasticized poly(vinyl butyral) (PVB) interlayer sheets that may be used to produce safety glass and solar cell laminates having enhanced penetration resistance and adequate adhesion levels. In particular, the stress value of these interlayer sheets at an elongation of 120% is preferably in the range of from about 8 to about 15 N / mm2.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
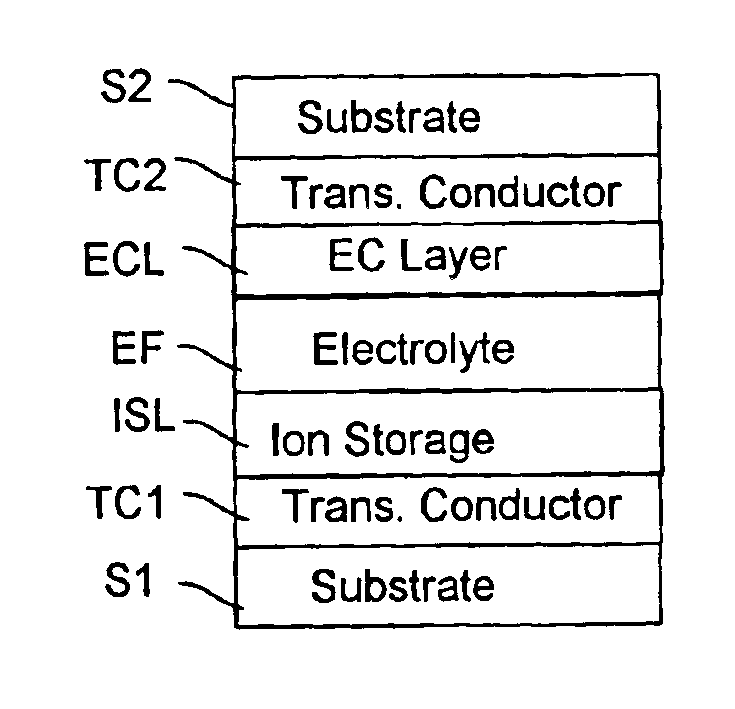
Electrochromic safety glazing
An electrochromic device is achieved that exhibits the characteristics of impact-resistant safety glass by starting with a solid electrolyte sheet material and a peripheral sealant material sandwiched between substrates to heat and pressure such that the electrolyte bonds to the treated surfaces of the substrates with an adhesion of at least 1.8 kg / linear cm width causing the electrolyte to exhibit a tensile strength of at least 5 kg / cm2.
Owner:DONNELLY MAGNA +1
Decorative safety glass
An image-bearing article comprising an interlayer bearing an image wherein the interlayer is an acoustic poly(vinyl acetal) interlayer having a Tg 23° C. or less. The acoustic poly(vinyl acetal) interlayer is preferably laminated to a film layer, a white layer, a second interlayer sheet or a rigid layer. The image-bearing article can preferably be coated on the image-bearing side and over the image with an adhesion promoter.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Interlayers for laminated safety glass with superior de-airing and laminating properties and process for making the same
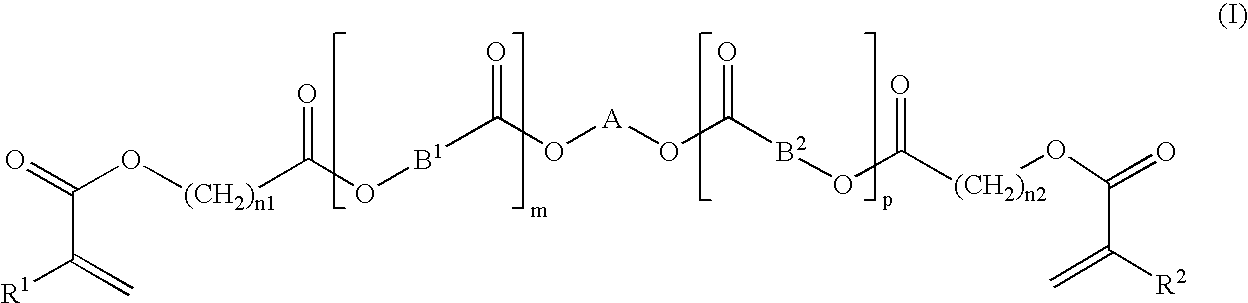
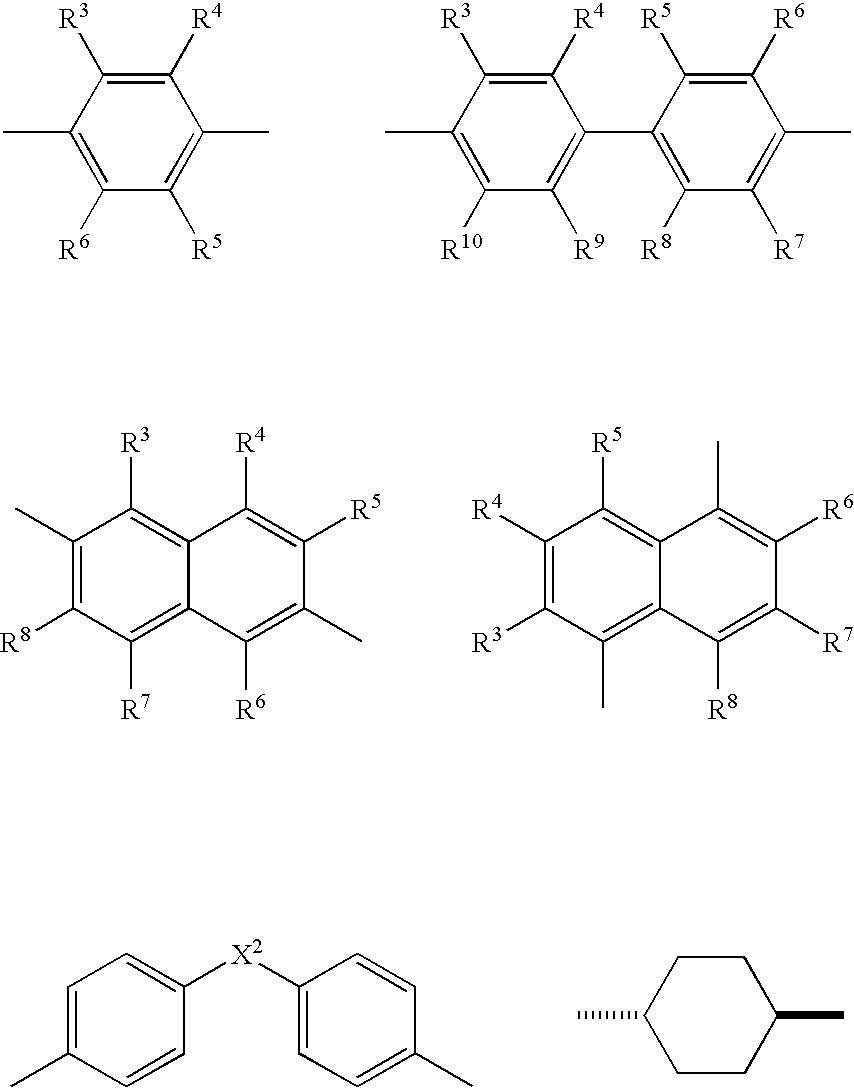
This invention relates to thermoplastic interlayers for laminated safety glass with superior vacuum de-airing at elevated temperatures and superior tacking and edge sealing properties. The sheeting has surface pattern on at least one of the surfaces characterized by flat surfaces with substantially uninterrupted channels for airflow in at least two non-parallel directions. The channels allow for rapid de-airing while the area roughness parameter ratio ARp / ARt in the range of 0.52 to 0.62, ARt being less than 32 μm, and area kurtosis less than 2.5, allow for ease of tacking of the interlayer onto glass and edge sealing after de-airing has been completed. Said surface pattern may also be superimposed onto a pattern which is generated by melt fracture or other means on at least one side to enhance de-airing and aid edge sealing.
Owner:PERFORMANCE MATERIALS NA INC
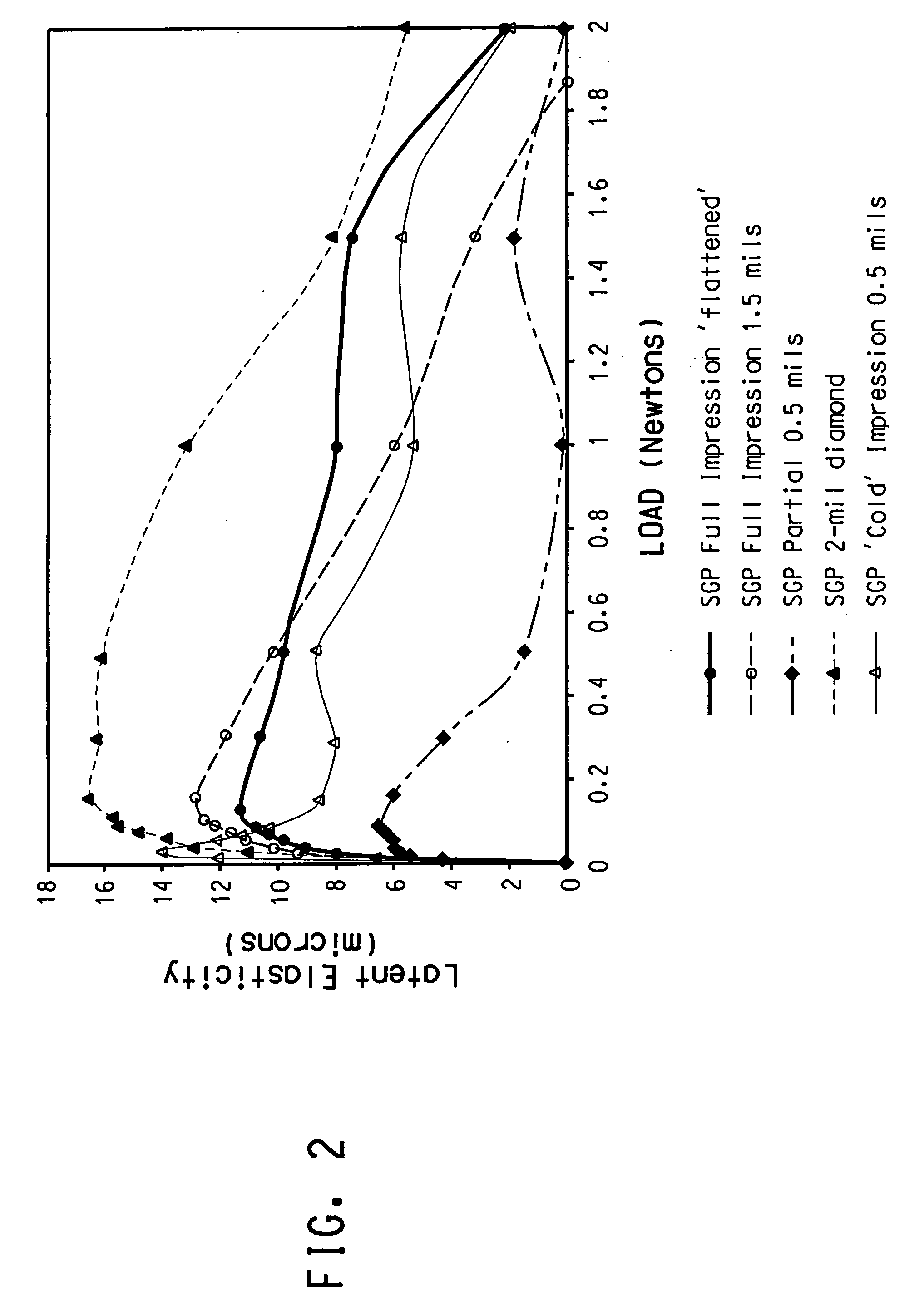
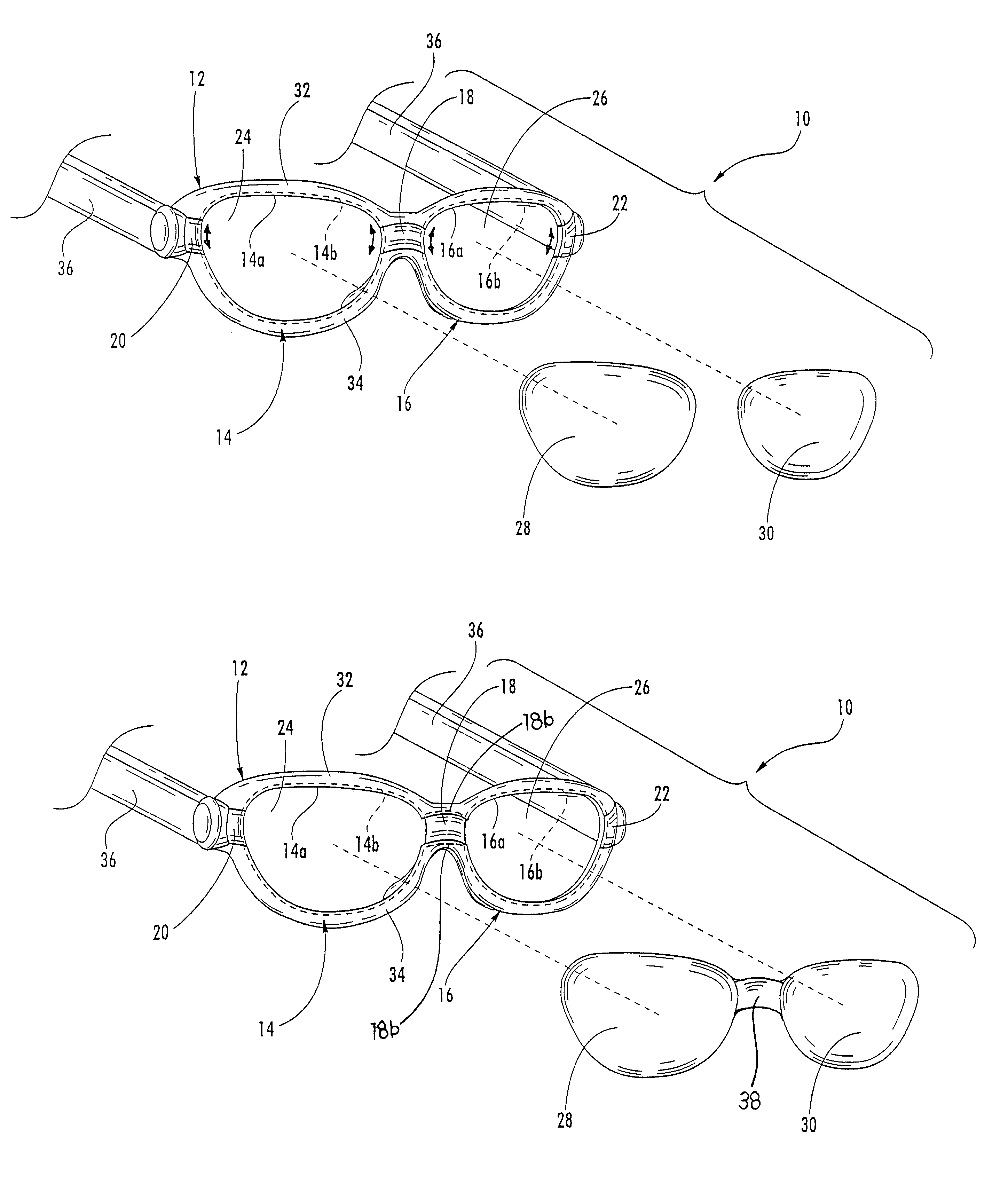
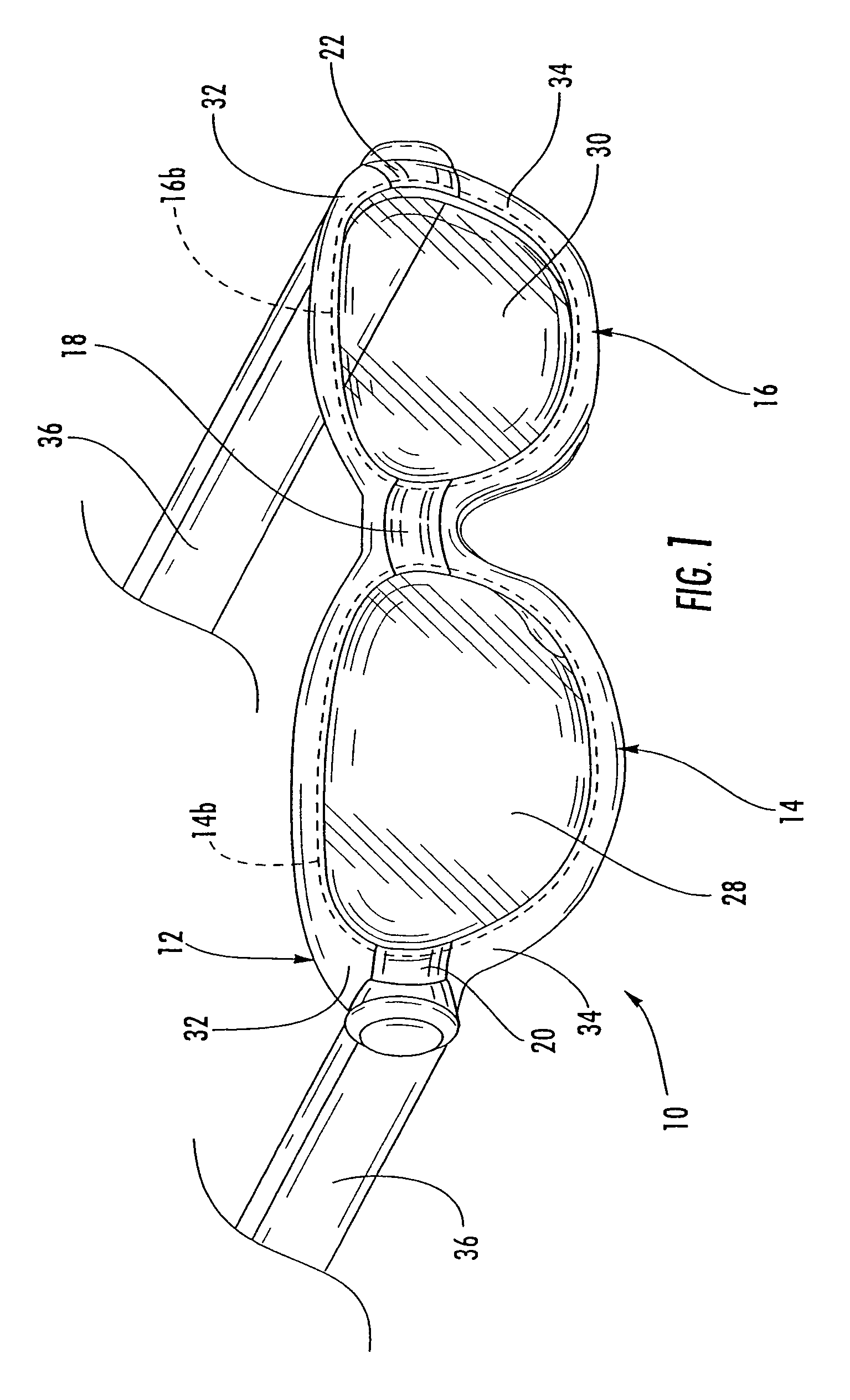
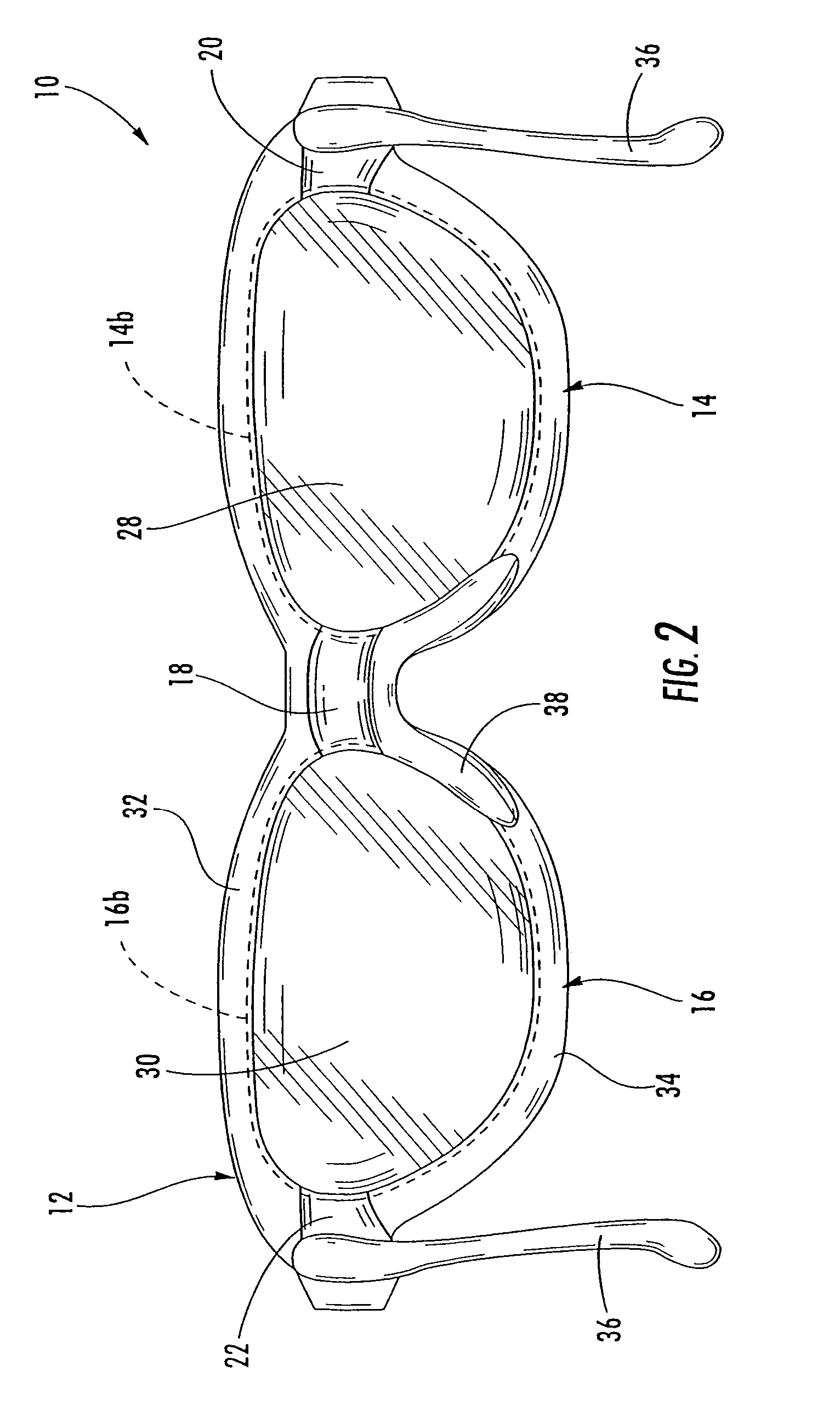
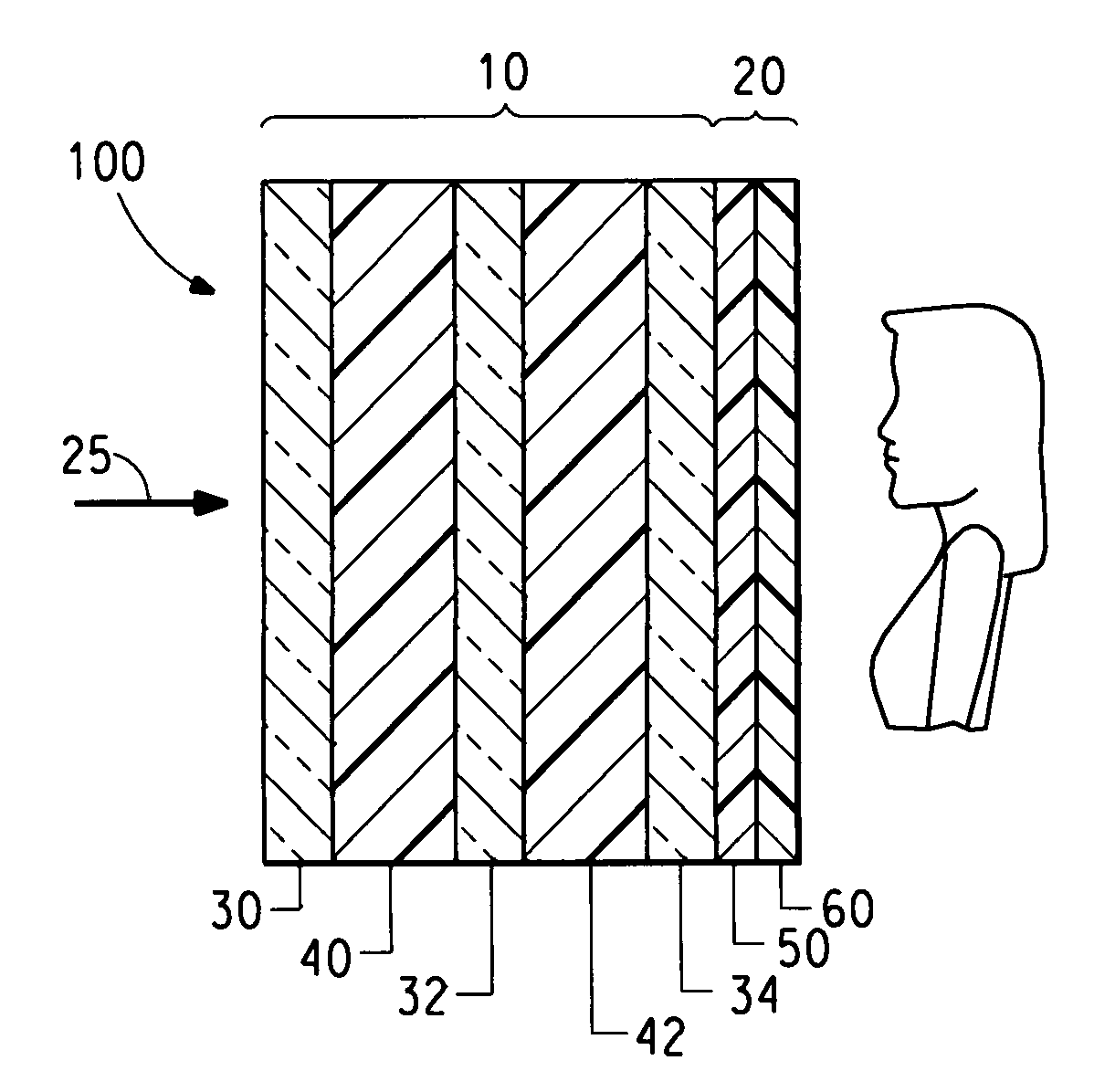
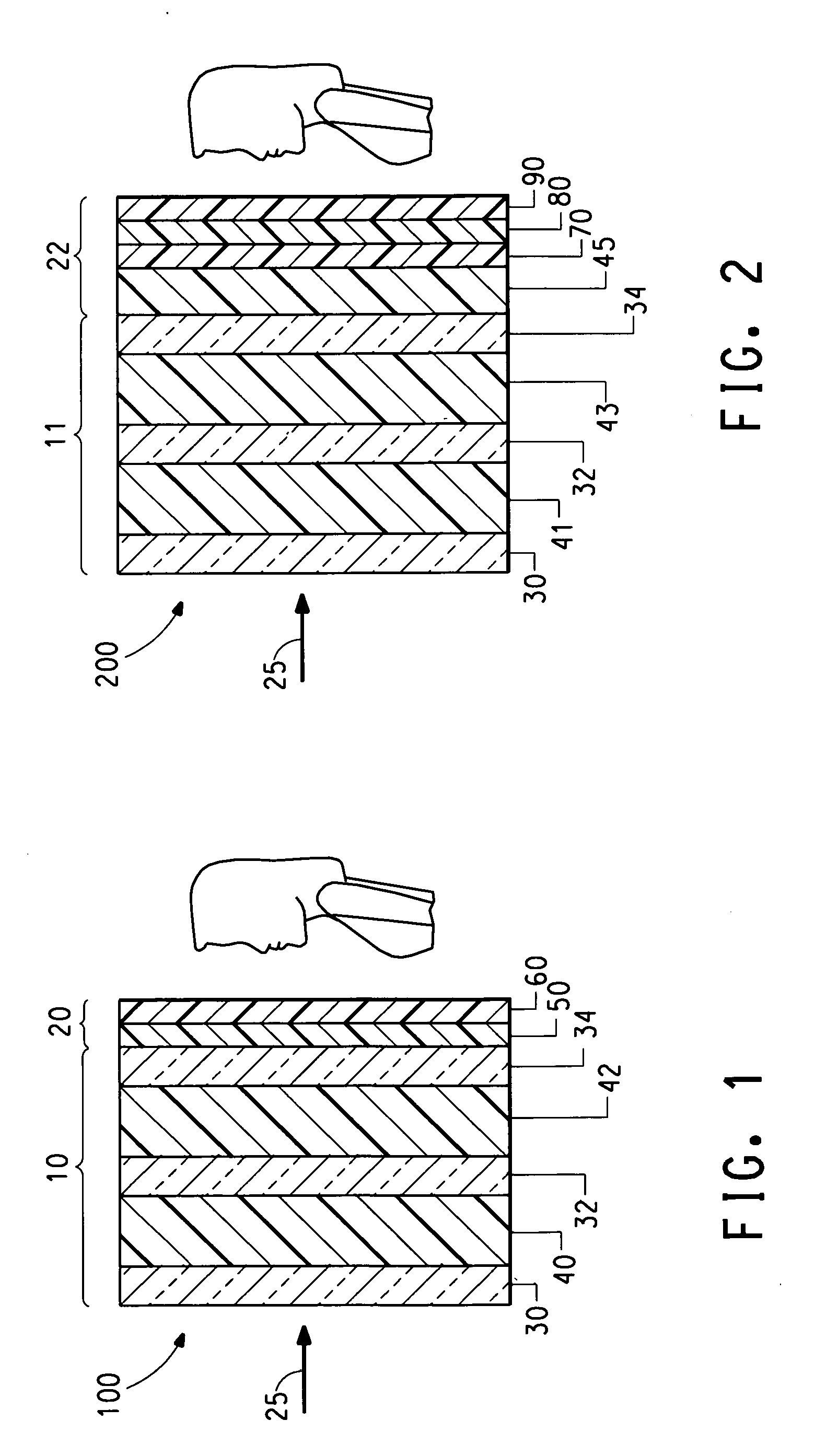
Safety glasses with flexible frame and interchangeable dual-lenses
Safety eyewear (10) having interchangeable lens(es) (28,30) is provided. To provide for interchange of the lenses (28,30) in the frame (12), upper and lower frame members (32,34) are molded from a harder, more rigid plastic while lateral temple portions (20,22), and a central nose bridge portion (18) are molded from a softer, more elastic material. The entire frame structure (12) is preferably molded as a unitary piece to form a unitary frame having rigid upper and lower frame portions (32,34) joined by flexible intermediate portions (18,20,22). In this regard, the upper and lower frame portions (32,34) can be flexed or stretched relative to each other to temporarily separate the frame portions (32,34) and open up the lens openings (24,26).
Owner:SPERIAN EYE & FACE PROTECTION
Transparent light-weight safety glazings
Provided is a transparent and light-weight ballistic resistant safety glazing comprising an ionomer sheet. The ionomer sheet comprises an ionomer derived from a parent acid copolymer that comprises copolymerized units of an α-olefin having 2 to 10 carbon atoms and, based on the total weight of the acid copolymer, about 20 to about 30 wt % of copolymerized units of an α,β-ethylenically unsaturated carboxylic acid having 3 to 8 carbon atoms. The ionomer is neutralized to a level of about 5% to about 90%, based on the total carboxylic acid content of the acid copolymer, and further comprises at least one cation. Further provided are articles comprising the light-weight ballistic resistant safety glazing.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Thermoplastic resin compositions suitable for use in laminated safety glass
The present invention is a polymeric resin composition having improved toughness, suitable for use in transparent glazing, comprising an at least partially neutralized ethylene acid copolymer metal carboxylate resin, wherein the metal carboxylate consists essentially of zinc metal counter-ions.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Multilayer laminates comprising twisted nematic liquid crystals
ActiveUS20070154718A1Low hazeMaintain structureLiquid crystal compositionsDiffusing elementsHalf waveEnergy consumption
Provided are multilayer laminates having one or more layers comprising twisted nematic liquid crystals and one or more layers of a polymeric sheet comprising a polymer with a modulus of 20,000 psi (138 MPa) or less. The twisted nematic liquid crystal layers reflect infrared radiation. Thus, the multilayer laminates are useful to reduce the transmission of infrared energy. For example, in some embodiments the multilayer laminates are useful as windows to reduce energy consumption necessary to cool the interior of a structure such as an automobile or building. Preferably, the multilayer laminates retain the beneficial properties of safety glass. The multilayer laminates may include additional layers such as infrared absorbing layers, half wave plates, and the like, to minimize the transmission of infrared energy. The multilayer laminates may also include further additional layers such as polymeric films, polymeric sheets, rigid sheets, and the like.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
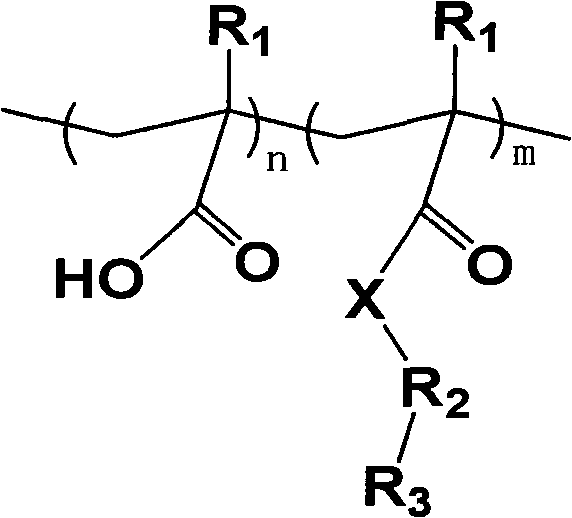
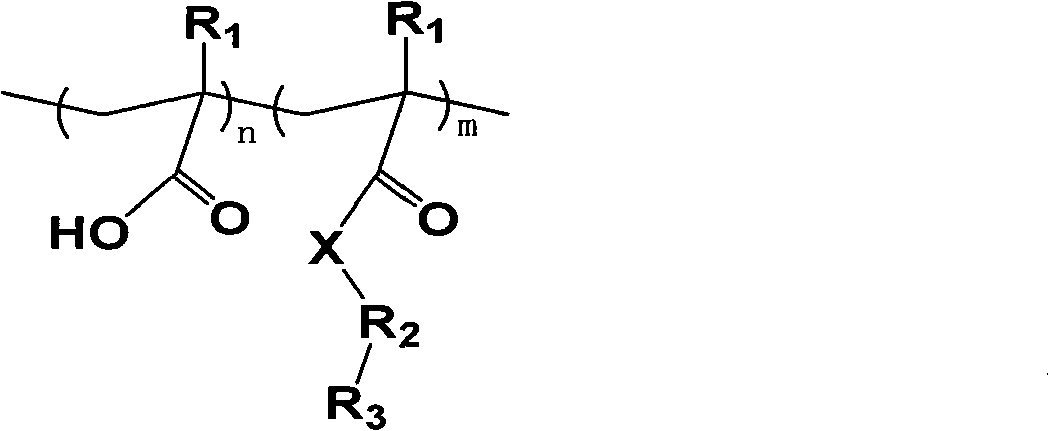
Compound safety glass and PVB foil for the production thereof
InactiveUS6887577B1Easy to processImprove sound insulationPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsSynthetic resin layered productsHydrogenPolyvinyl alcohol
Known intermediate foils for compound glasses with improved sound insulation consist of several layers or special materials which cannot be further processed in conventional plants. The aim of the present invention is to provide an intermediate foil for compound glasses with improved sound insulation, whereby said foil consists of one layer as far as possible and is based upon PVB. Said intermediate foil allows for an improved sound insulation of the compound glasses in room temperature and has essentially unchanged working properties, whereby said compound glasses are produced from the intermediate foil. To resolve the aim of the invention, an intermediate foil is provided which contains: 50 to 80 wt. % PVB (partially acetalised polyvinyl alcohol), 20 to 50 wt. % of a softener mixture containing 30 to 70 wt. %, calculated as a portion of the softener mixture, of one or more polyalkylene glycoles of the group consisting of polyalkylene glykoles of the general formula HO—(R—O)n-H with R=alkylene and n>5, block copolymers made of ethylene- and propylene glycole of the general formula HO—(CH2-CH2-O)n-(CH2-CH(CH3)-O)m-H with n>2, m>3 and (n+m)<25, derivatives of block copolymers made of ethylene- and propylene glycole of the general formula R1O—(CH2-CH2-O)n-(CH2-CH(CH3)-O)m-H or HO—(CH2-CH2-O)n-(CH2-CH(CH3)-O)m-R1 with n>2, m>3 and (n+m)<25 and R1 as the organic radical, derivatives of polyalkylene glycols of the general formula R1-O—(R2-O)n-H with R2=alkylene and n>2, wherein the hydrogen of one of the two terminal hydroxygroups of the polyalkylene glycol is replaced by an organic Rest R1, derivatives of polyalkylene glycols of the general formula R1-O—(R2-O)n-R3 with R2=alkylene and n>5, wherein the hydrogen of the two terminal hydroxygroups of the polyalkylene glycol is replaced by an organic Rest R1 or R3.
Owner:KURARAY EURO GMBH
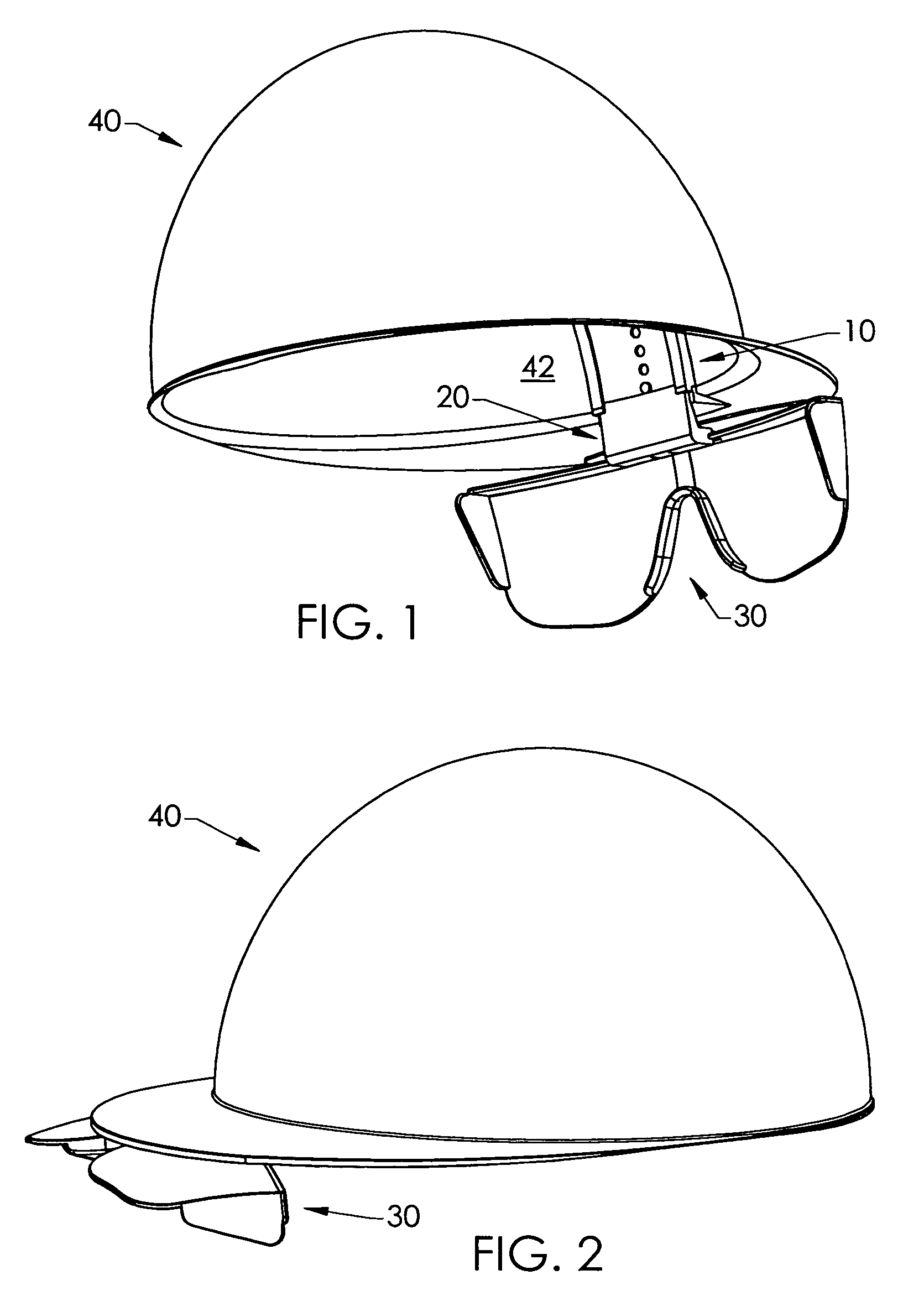
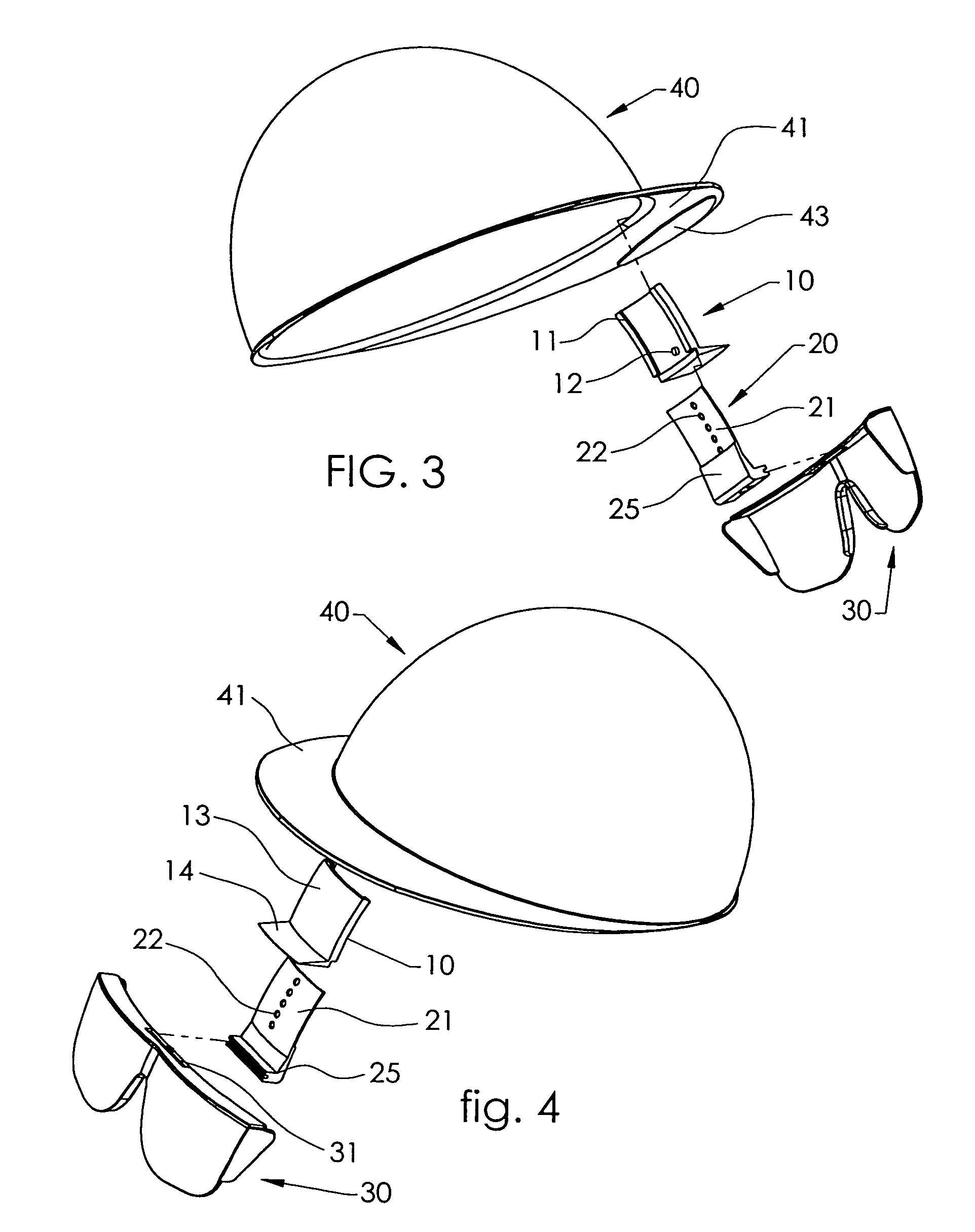
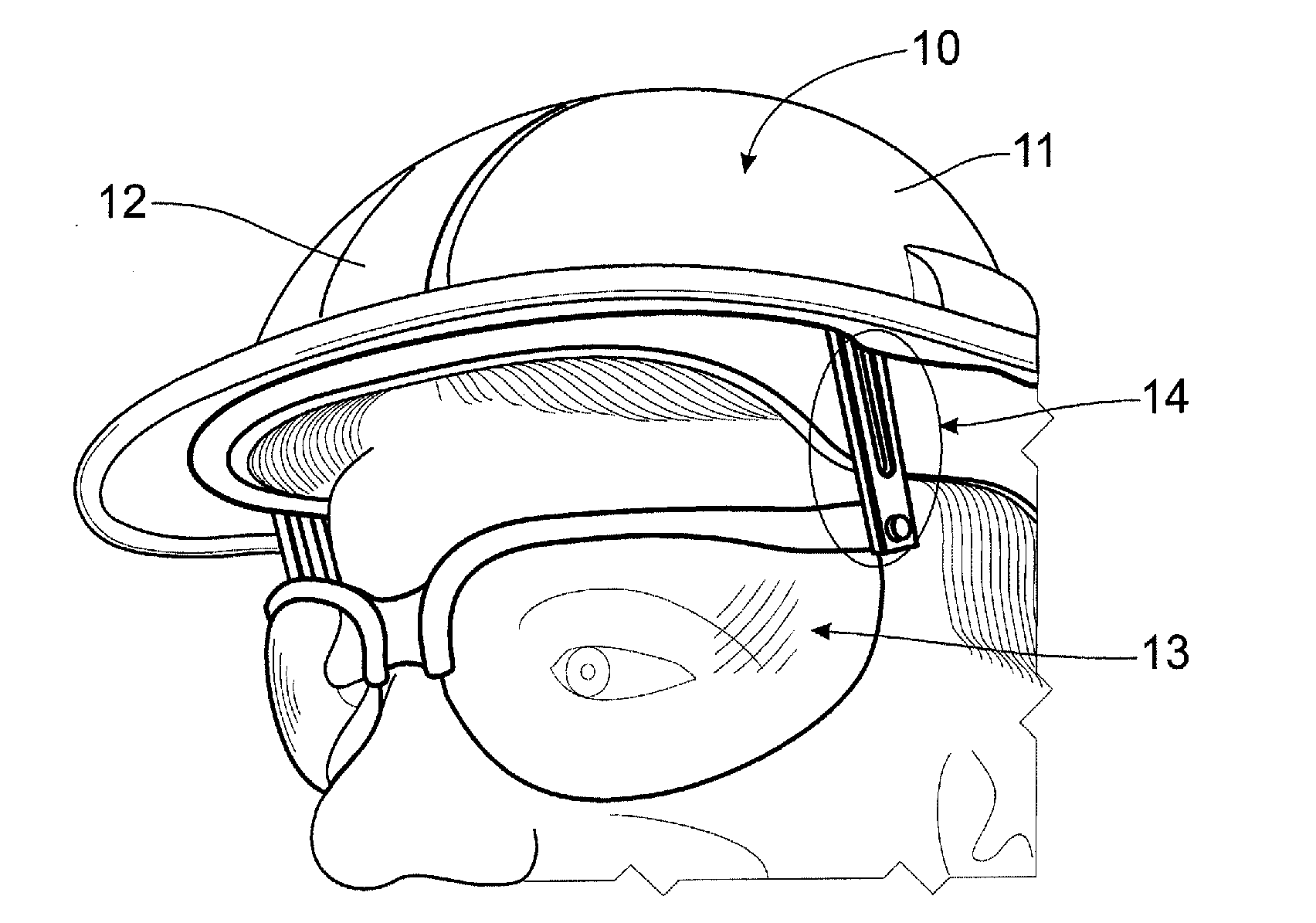
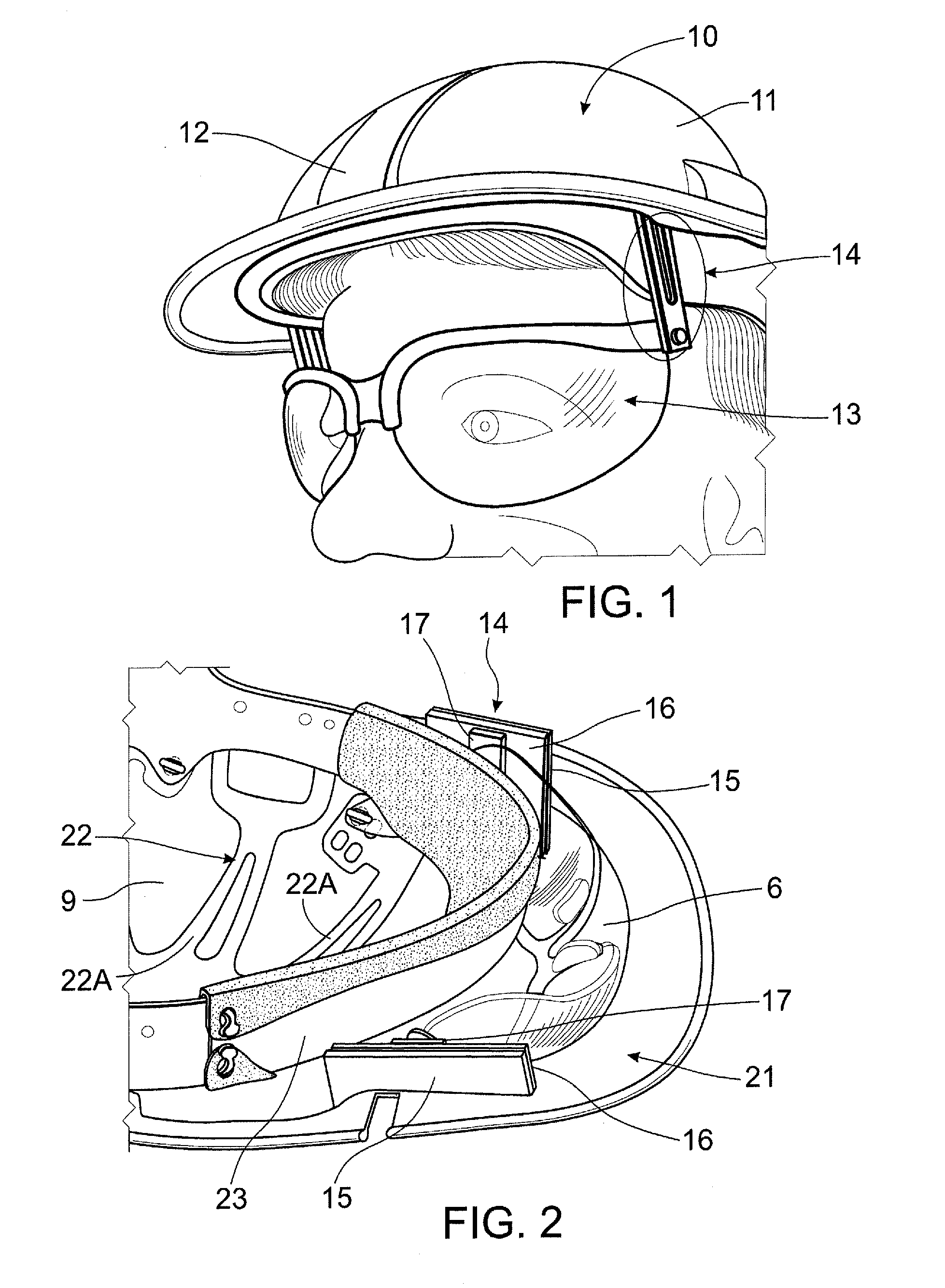
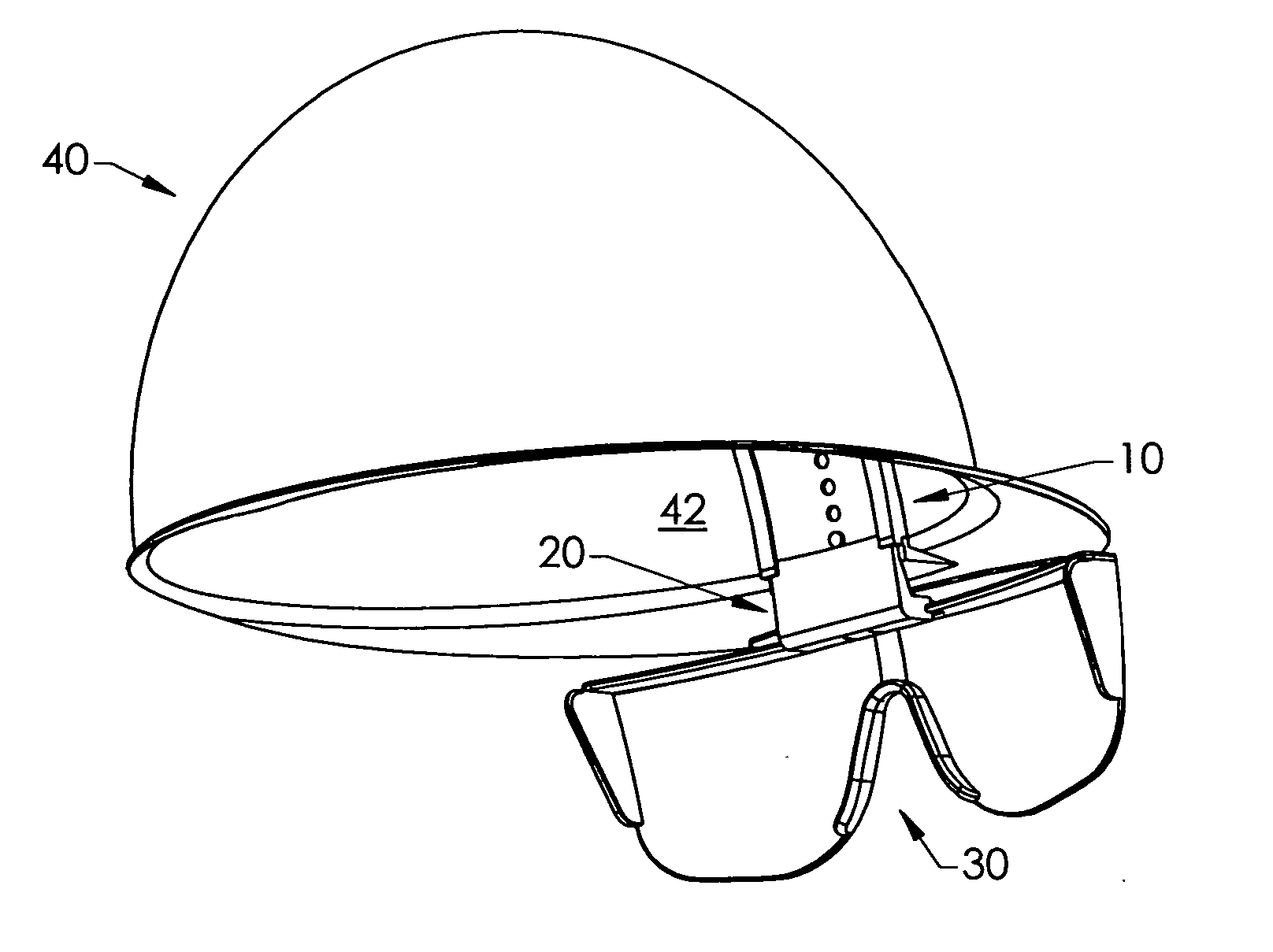
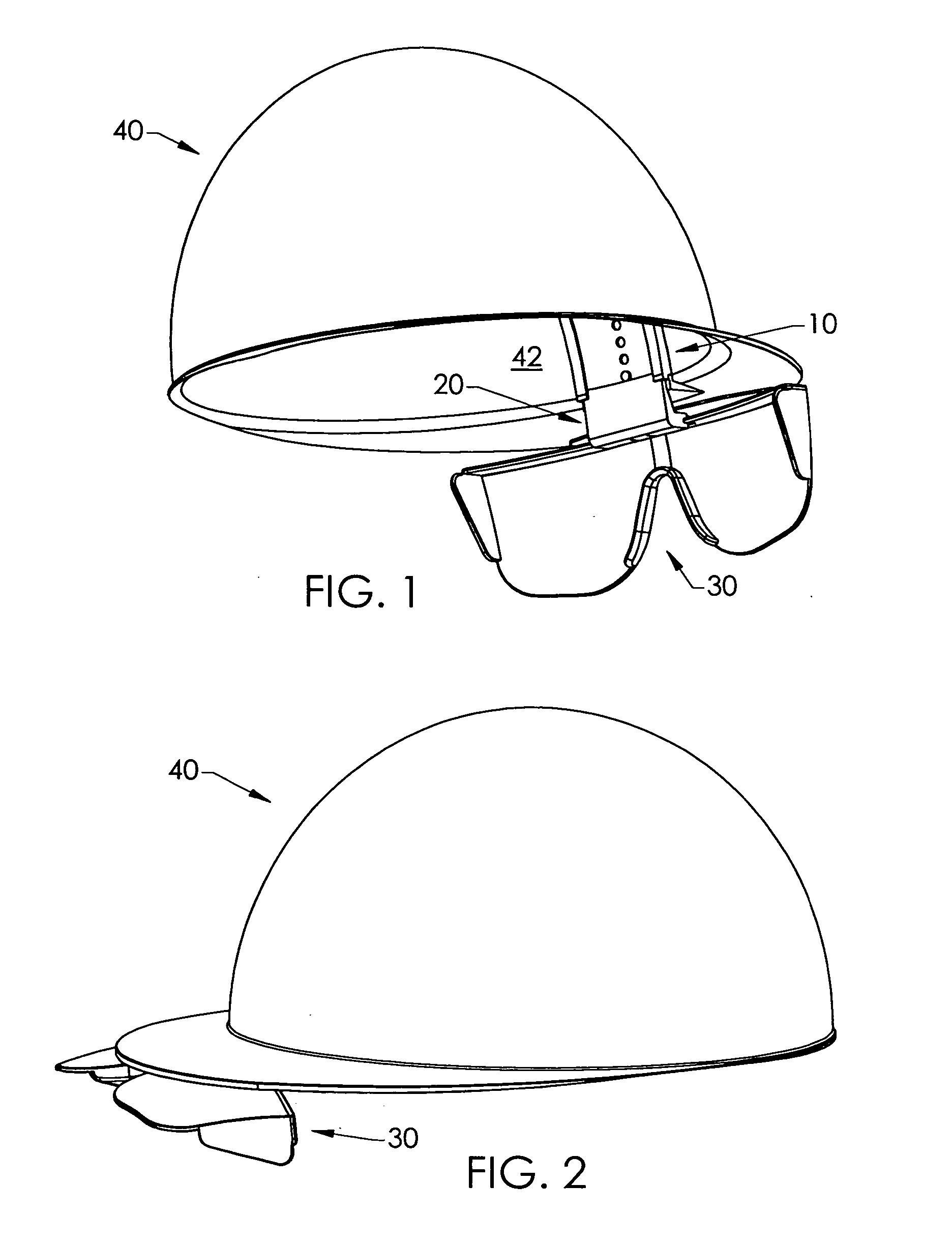
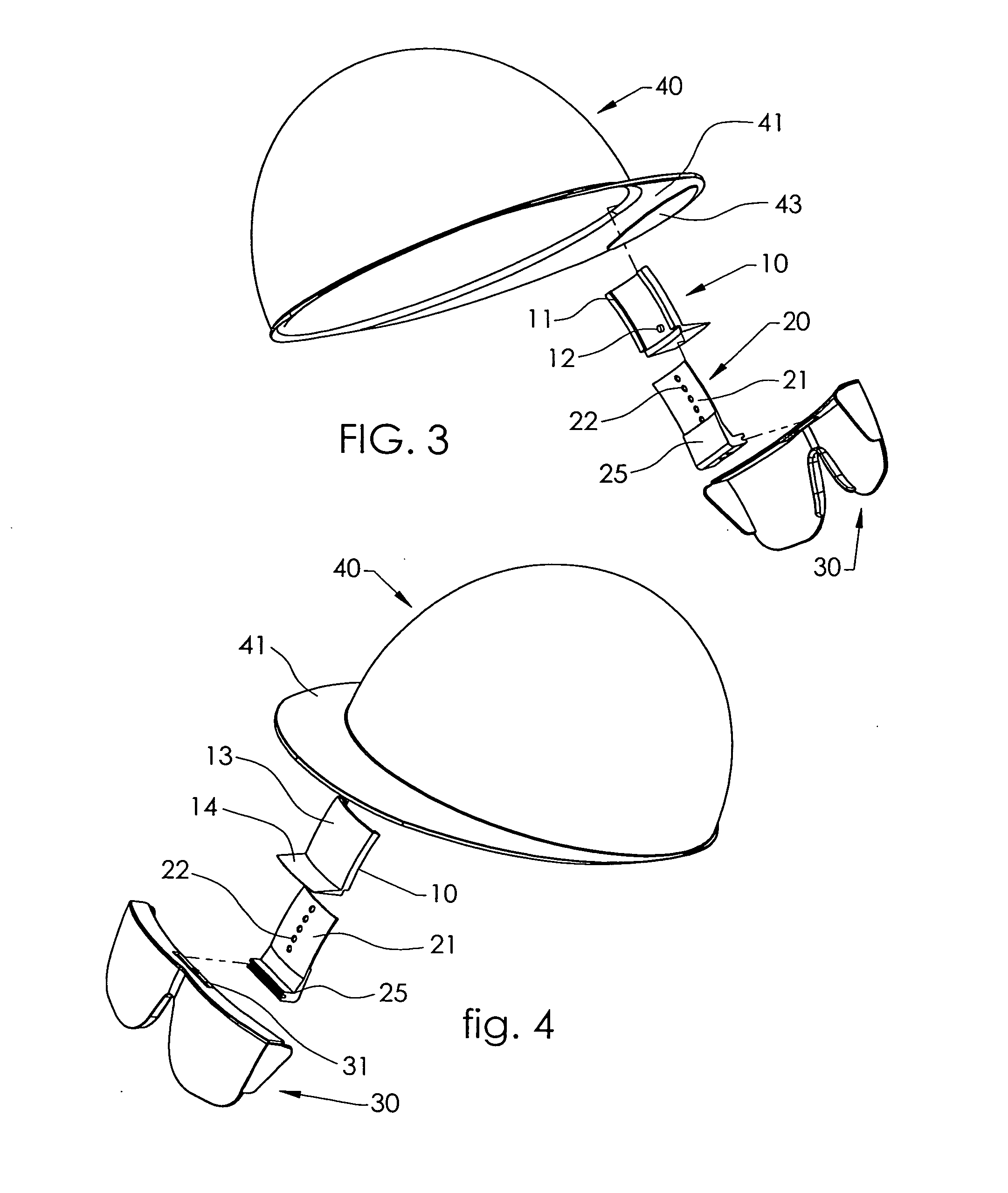
Hard-hat flip-up safety glasses
A system for attaching safety glasses to headwear often called a “helmet” or a “hard-hat” has multiple adjustments that fit the glasses to the individual user and that allow the user to flip the glasses back and forth between in-use and removed positions. The preferred system includes a base piece that attaches to the interior or underside of the helmet, near the wearer's face at or near the junction of the helmet's bill / brim and dome. A preferred second piece receives a portion of the glasses at its distal end, and, at its proximal end, slideably connects to the base piece. The second piece may be locked at various positions relative to the base piece, to adjust, either incrementally or continuously, the distance of the glasses from the helmet. This slidable adjustment between the base piece and second piece makes it possible to adjust the glasses in a generally vertical direction, that is, generally parallel to the plane of the lenses of the glasses when being used, as best suits the particular user. The clamping or gripping mechanism on the second piece distal end allows the glasses to pivot relative to the second piece and, hence, to the helmet. Thus, the user may pivot the glasses up from the eyes, out of his line of sight, or down in front of the eyes as close to the user's face as desired. This pivoting, then, provides some horizontal adjustment in the position of the glasses relative to the eyes and nose. Further, at least some portions of the preferred system are flexible or are flexibly connected to the helmet to absorb shock created when the helmet or safety glasses are struck.
Owner:HOLM BARENT
Neodymium oxide doped motor vehicle windshield and safety glazing material
Motor vehicle windshields and safety glazing material, suitable for use as motor vehicle windshields and safety glazing material for automobiles, trucks, buses, motorcycles, locomotives. sport utility vehicles, all terrain vehicles, and vans. The motor vehicle windshields and safety glazing material contains Neodymium Oxide, a rare earth compound. The Neodymium Oxide filters out the yellow portion of the spectrum, reducing glare. Incorporation of yellow light in the spectrum desaturates colors and reduces contrast. Improvement in contrast and a reduction in glare permits, for example, a motor vehicle driver to better discriminate the contrast of objects when there is no daylight and the only illumination is artificial. For drivers, in particular, elimination of the yellow light lessens eye strain currently resulting from light emitted by the conventional headlights of oncoming vehicles during hours of darkness. Neodymium Oxide can also be added to safety glazing materials for use in bullet resistant shields.
Owner:KARPEN DANIEL NATHAN
Polyvinyl butyral transparent film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102863917ANon-macromolecular adhesive additivesFilm/foil adhesivesPolymer scienceComposite film
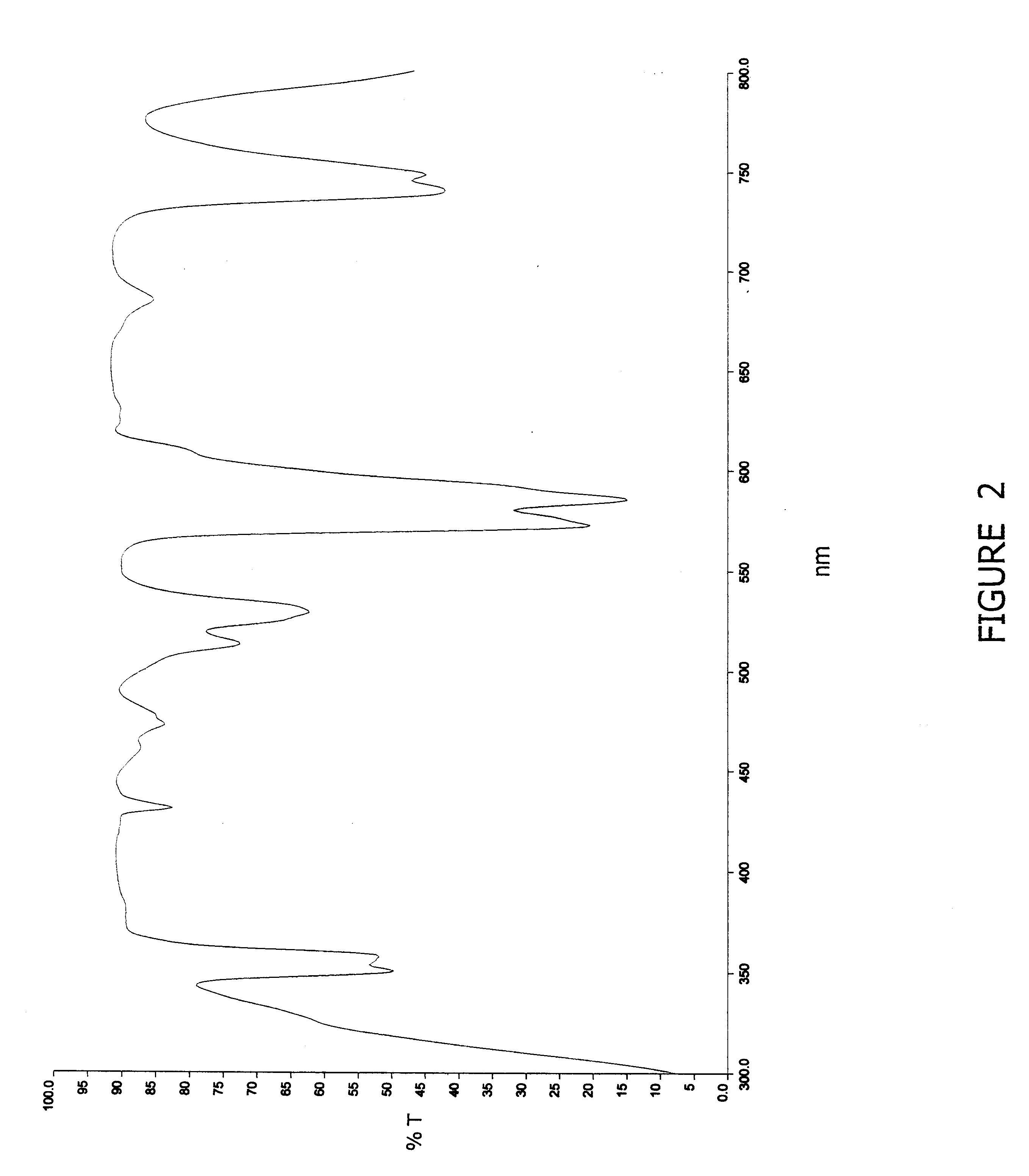
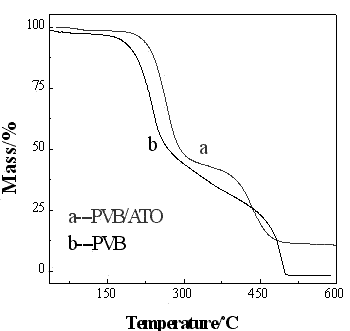
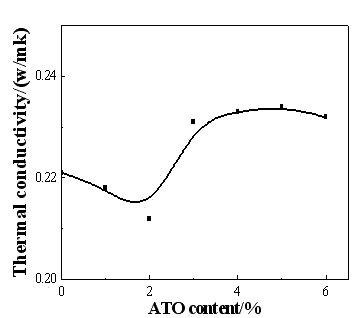
The invention belongs to the field of polymer / nanoparticle composite materials, and relates to an infrared thermal reflection and anti-ultraviolet polyvinyl butyral (PVB) transparent film for laminated safety glass and a preparation method thereof. According to the method, nano-indium stannum oxide (ATO) is selected as functional particles, is subjected to double processing through a coupling agent and a dispersing agent and is poured into a mold to be formed and compounded after being directly and uniformly mixed with purchased or self-made polyvinyl butyral, plasticizer, antioxidant and filming agent by means of ultrasonic wave to prepare a heat-insulating PVB nano composite film. The nano-ATO particles are subjected to the double processing and the special ultrasonic dispersion process, so that the problem of agglomeration of the ATO is effectively improved; and the prepared PVB nano composite film has superior mechanical property and higher infrared reflectivity and visible light transmittance, and can be directly used for processing and producing heat-insulating, sound-insulating, anti-ultraviolet, transparent and impact-resistant multi-functional safety glass.
Owner:CHANGZHOU XIAOGUO INFORMATION SERVICES
Compact optical system and packaging for head mounted display
ActiveUS8289231B2Great convenience and acceptabilityCompact in size and weightTelevision system detailsPrismsDisplay deviceSpherical shaped
A head mounted virtual image display unit is provided which is compact in size and weight, and incorporates a high performance optical system offering a clear see-through capability. A sliding light shield may be incorporated for those instances when see-through capability is not desired. A focus adjustment may be incorporated to permit the focusing of the image, for example, at a distance of approximately 18 inches to infinity. An adjustable headband may be incorporated that adapts to fit the users head. A flexible boom structure may be incorporated to facilitate fine positional adjustment of the optical assembly. A slider and ball joint mechanism may also be incorporated to facilitate positional adjustment of the optical assembly. A built-in microphone may be incorporated to enable speech input by the user. The head mounted virtual image display unit may be used comfortably in conjunction with eye or safety glasses, and provides a useful image to the user without blocking his view of the surrounding environment. The unit is designed to have a pleasing appearance so as to greatly enhance user acceptability.
Owner:IBM CORP
Antifogging coating, special antifogging coating composition and antifogging product thereof
InactiveCN101591494AGood anti-fog performanceImprove water resistanceCoatingsEthylene HomopolymersHigh surface
The invention discloses an antifogging coating, a special antifogging coating composition and a special antifogging product thereof. The antifogging coating composition comprises the following components: 0.5 to 58 mass portions of homopolymer or copolymer taking acrylic acid or methylacrylic acid as a monomer, 0.05 to 6 mass portions of aziridine crosslinking agent, 0.5 to 58 mass portions of inorganic nano-particles and 40 to 98 mass portions of solvent. The coating composition has excellent antifogging property and excellent water resistance; the coating has high bonding strength with a substrate; and the antifogging coating formed by coating the substrate of the coating has good surface hardness. The antifogging product coated with the antifogging coating has excellent surface smoothness and clearness, excellent appearance, high surface strength and good wear resistance, and can be used for bathroom mirrors, eyeglasses, helmets, safety glasses, automobile lampshades, instrument panels and the like.
Owner:BEIJING RIBIO BIOTECH
Translucent digital display system
A digital display system includes a transparent outer protective panel, a transparent inner protective panel, and a translucent digital video display located between the outer and inner protective panels. An integrated media player is operably connected to the translucent digital video display so that full-motion videos displayed on the translucent digital video display are viewed through the outer protective panel and items can be viewed through the translucent digital video display. The digital display system can be incorporated into any environment where a product is located behind a glass enclosure such as freezers, coolers, security glass, jewelry cases, liquor cases, cosmetic cases, and the like. In retail environments, the digital display systems can also be incorporated into entry doors, windows, drive-thru windows, teller windows, and any other location where there is traditionally glass and you want to focus consumer attention obstructing the customer's line of site.
Owner:STRATACACHE
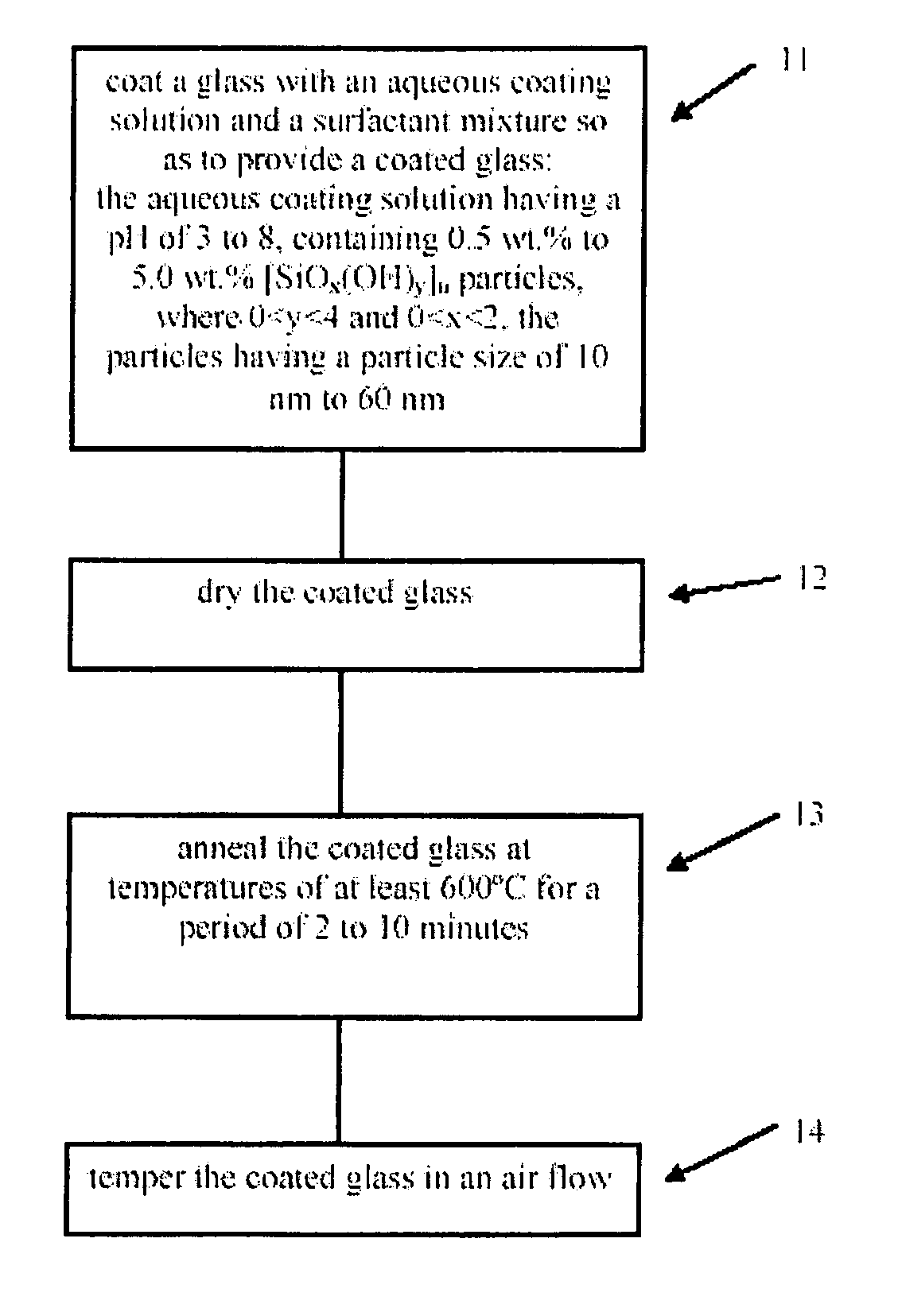
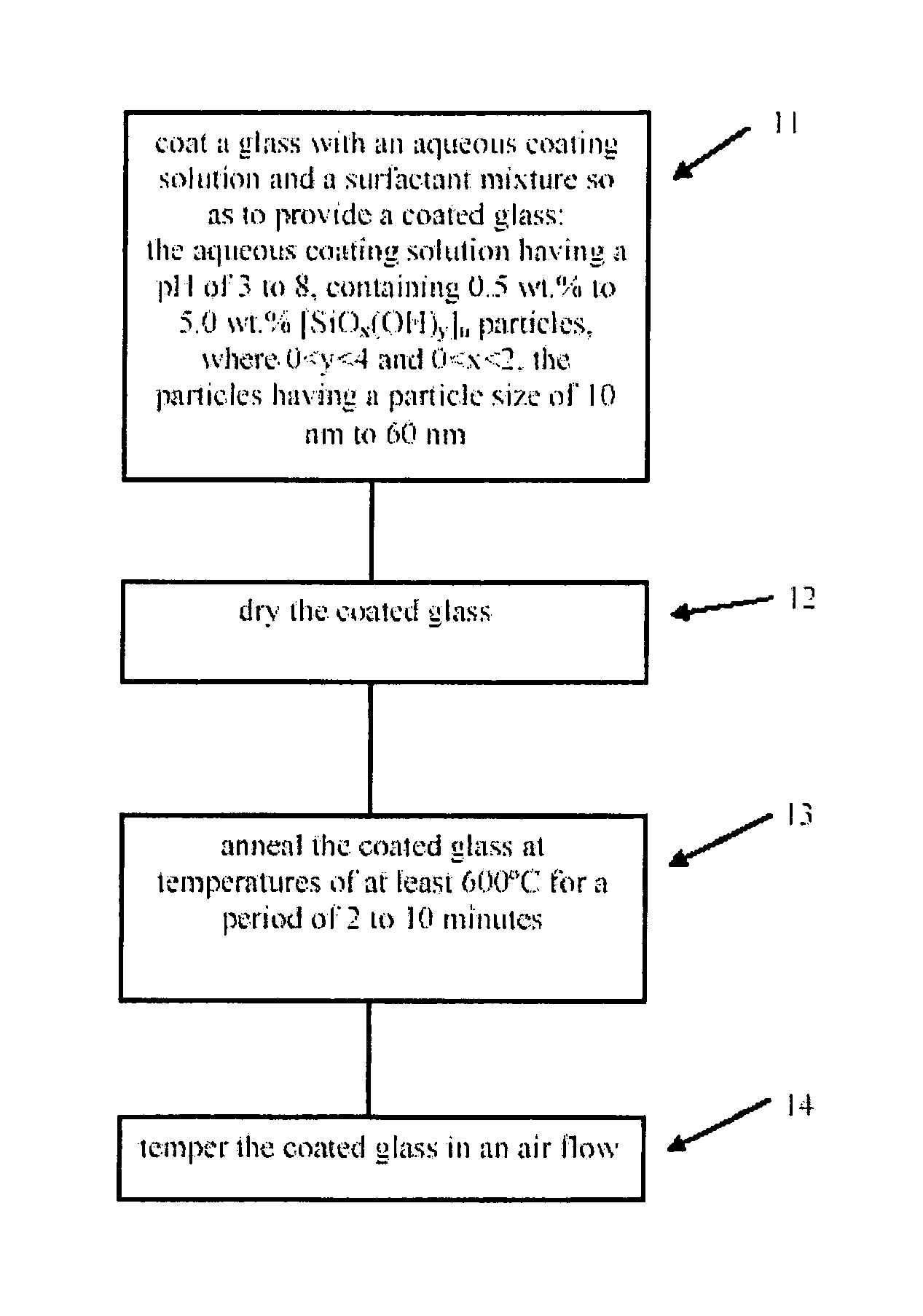
Method for making thermally tempered glass comprising a non-abrasive, porous, SiO2 antireflection layer
InactiveUS7128944B2Easy to operateSpread the wordLayered productsPretreated surfacesRefractive indexPolymer chemistry
The invention relates to thermally tempered safety glass comprising an non-abrasive and porous SiO2 layer which is stable during sintering and has a refractive index of between 1.25 and 1.40. The inventive safety glass can be obtained by coating standard soda-lime glass with an aqueous coating solution having a pH value of between 3 and 8 and containing between 0.5 and 5.0 wt. % of [SiOx(OH)y]n particles (0<y<4 and 0<x<2) having a particle size of between 10 and 60 nm, and a surfactant mixture. The coated glass is then dried, thermally hardened at temperatures of at least 600° C. for several minutes, and thermally tempered by a flow of air.
Owner:DUCATT NV
Decorative Safety Glass
An image-bearing article comprising a rigid sheet bearing an image which is coated on the image-bearing side and over the image with an adhesion promoter.A process of preparing an image-bearing article comprising a coated image-bearing rigid sheet:(a) providing a rigid sheet;(b) printing an image on the rigid sheet so as to produce an image-bearing rigid sheet containing an image-bearing side; and(c) coating an adhesion promoter on the image-bearing side and over the image to produce a coated image-bearing rigid sheet containing a coated image-bearing side.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Hard hat with attached safety glasses
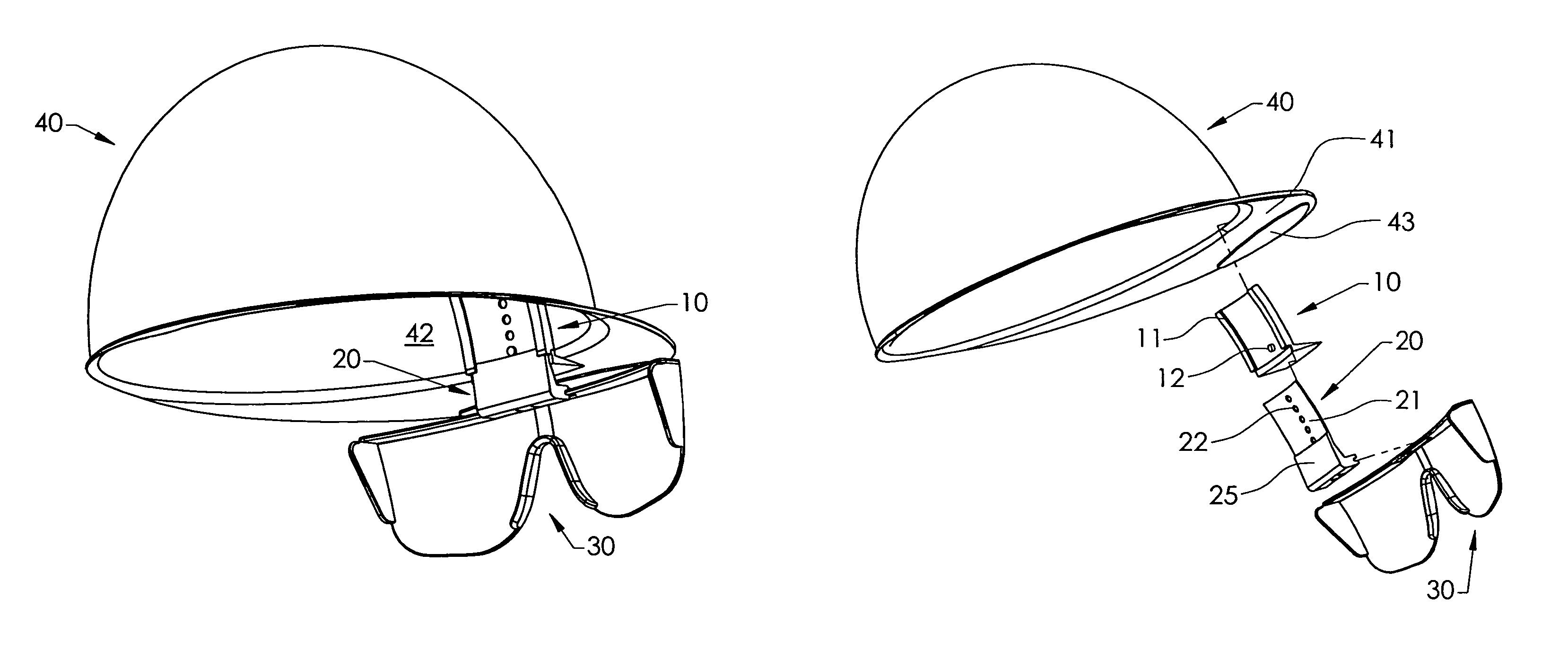
InactiveUS20090235437A1Uncomfortable to wearImprove eyesightGogglesHatsUses eyeglassesHorizontal axis
A hard hat with attached glasses including a hard hat including a dome portion, the dome portion having an interior surface defining a dome space for receiving a wearer's head and said interior surface including a generally vertical front portion, a pair of glasses and a connection system connecting said pair of glasses to said hard hat, the connection system adapted to allow adjustment of the position of the glasses inside said dome space and down out of said dome space and pivotable about a substantially horizontal axis.
Owner:SPRINGER DAVID J +1
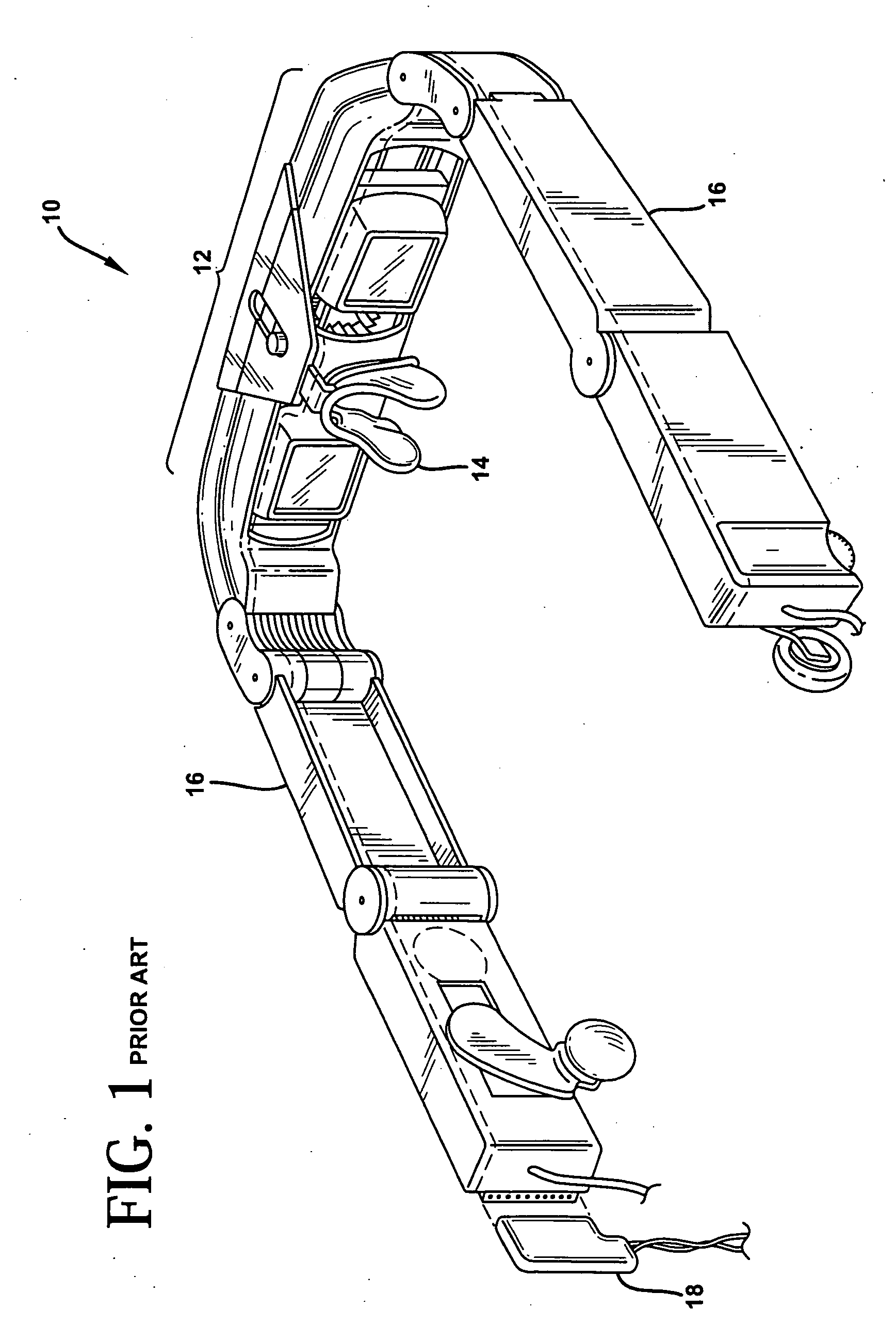
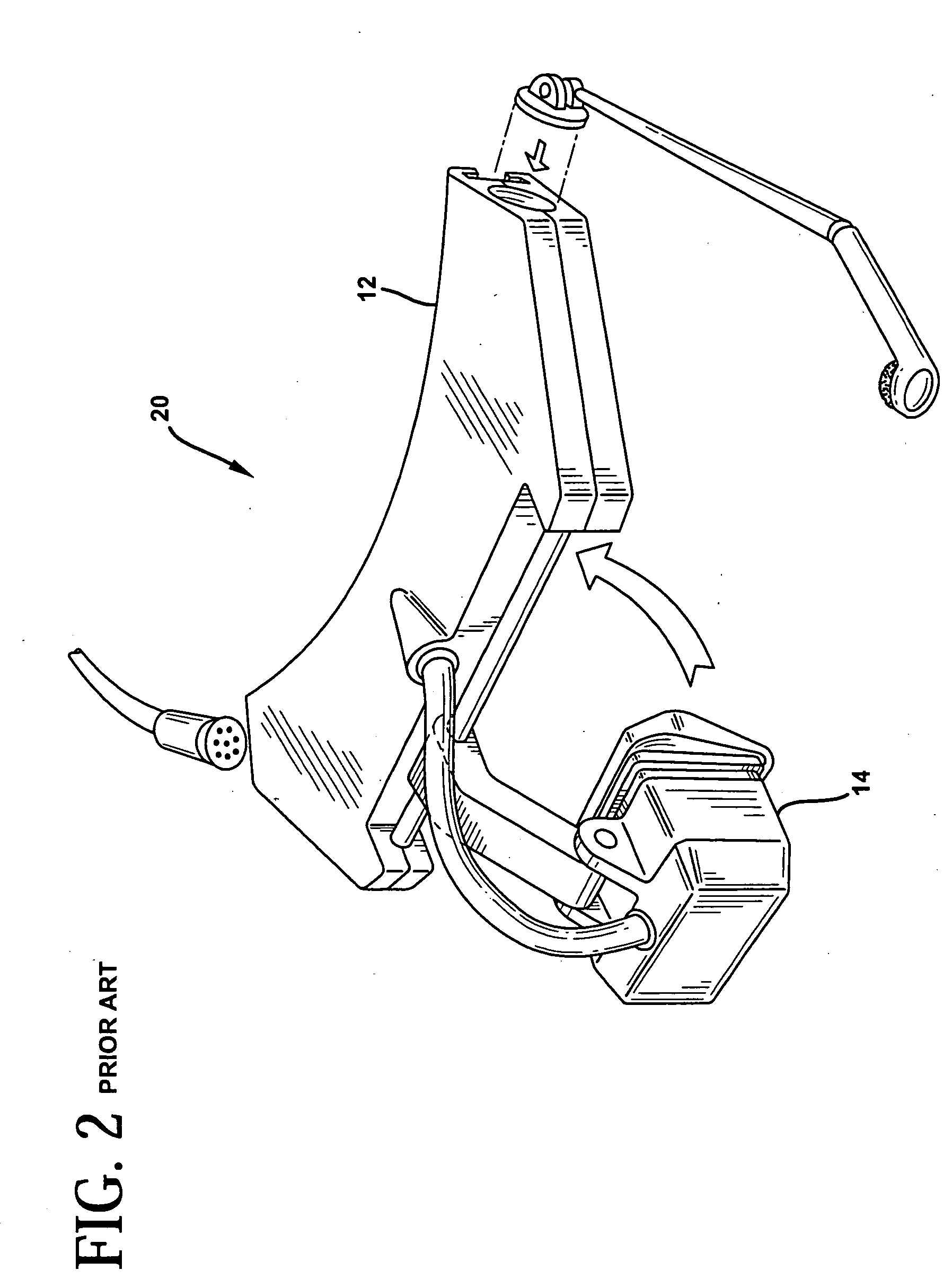
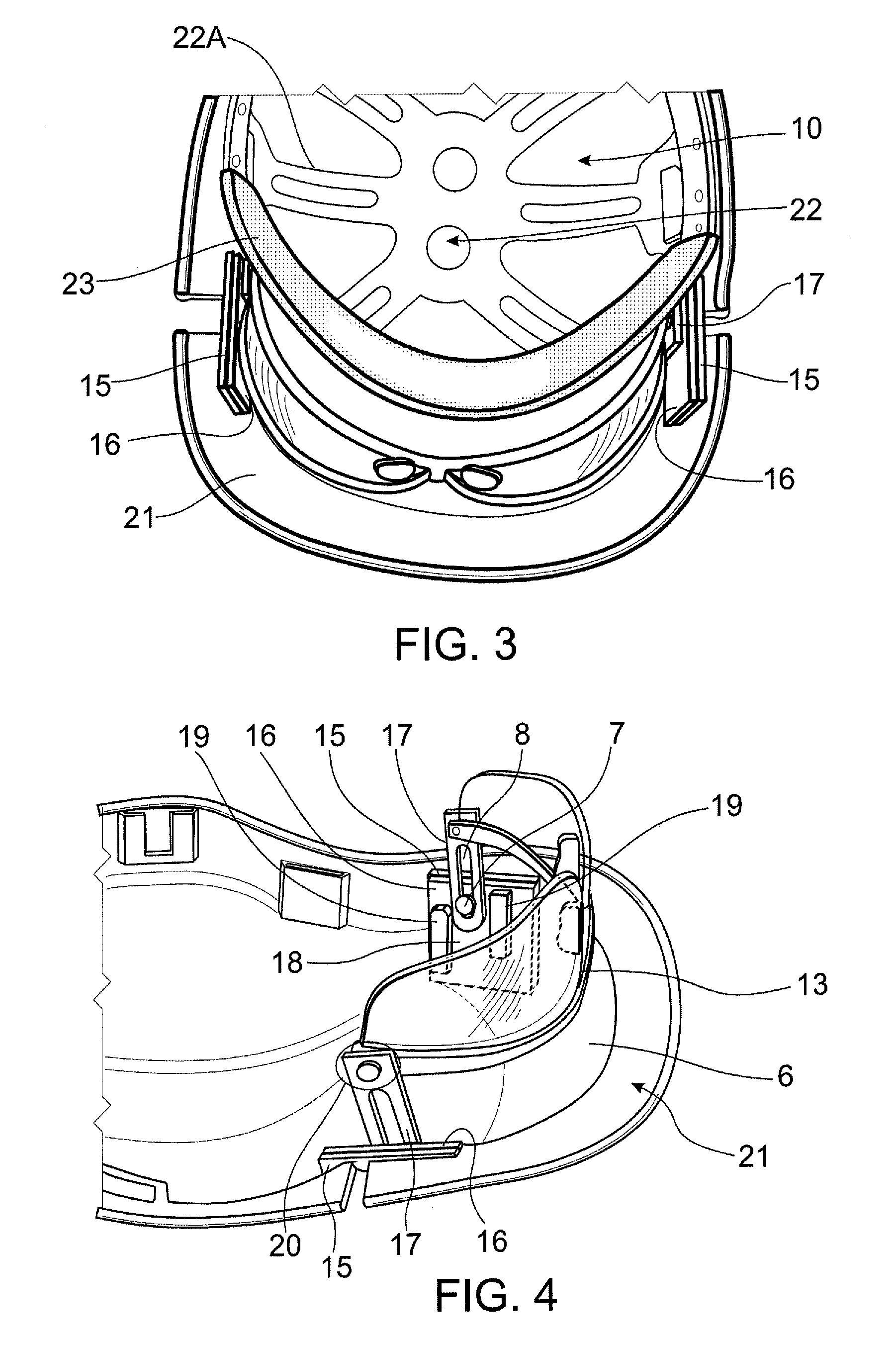
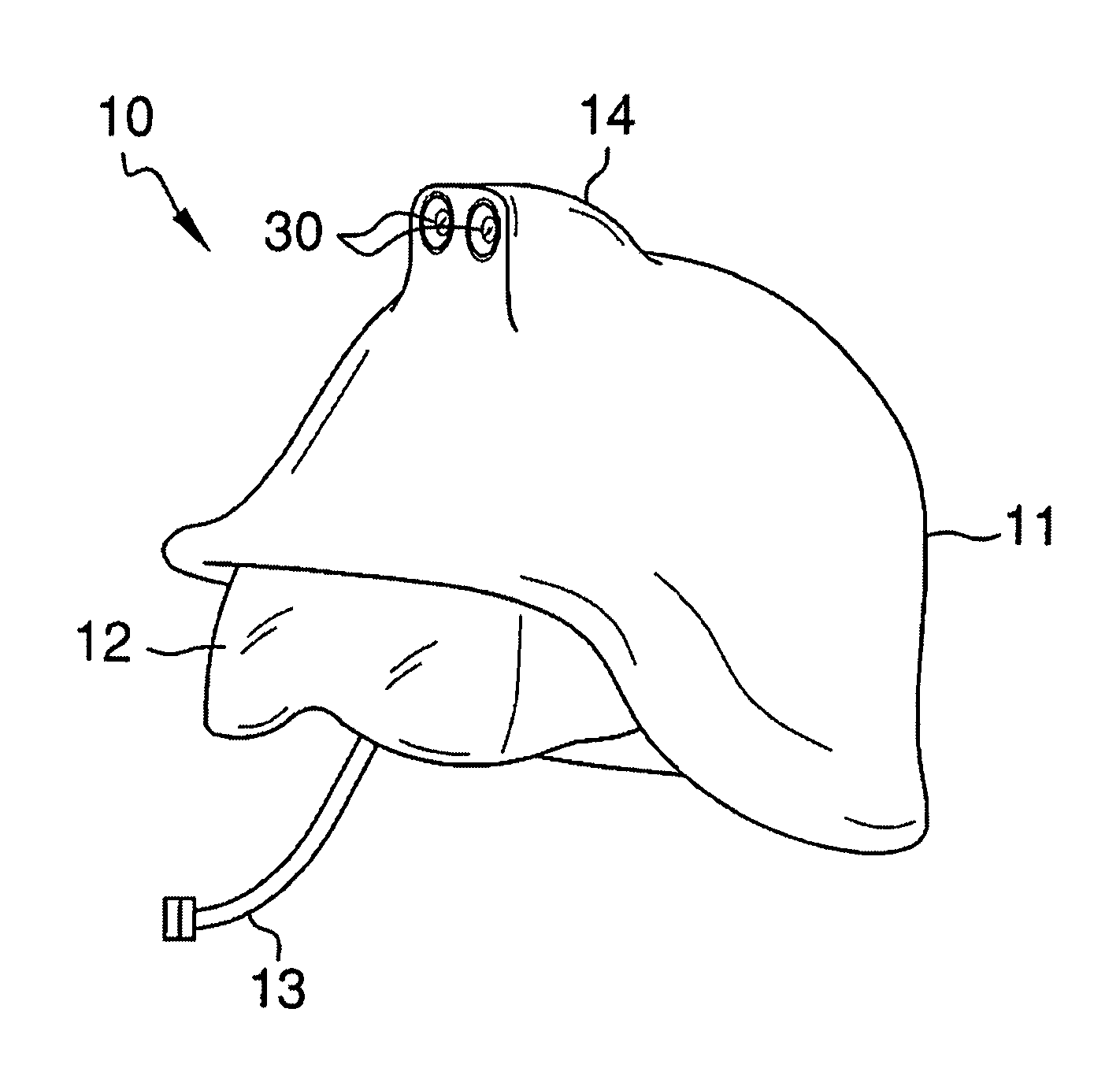
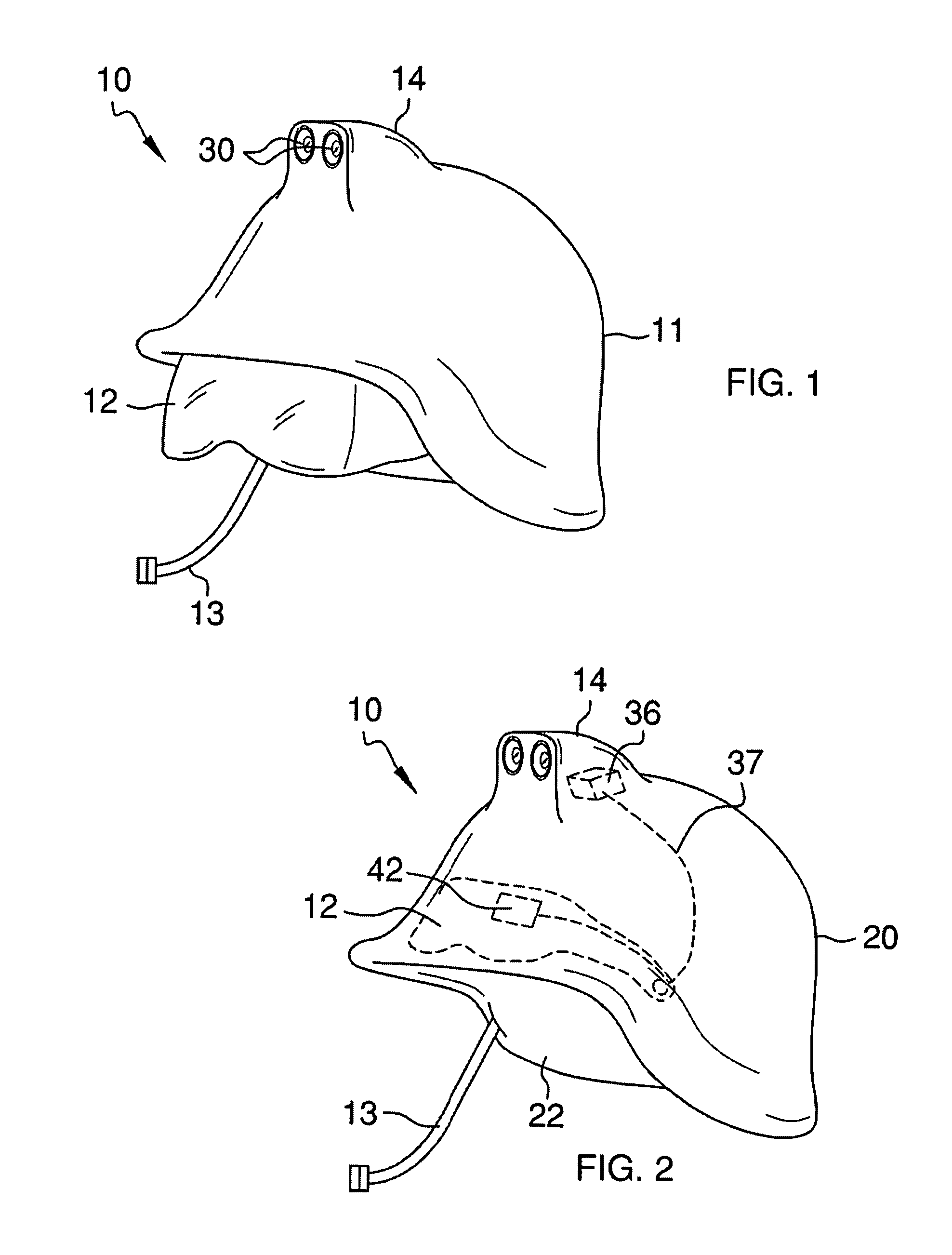
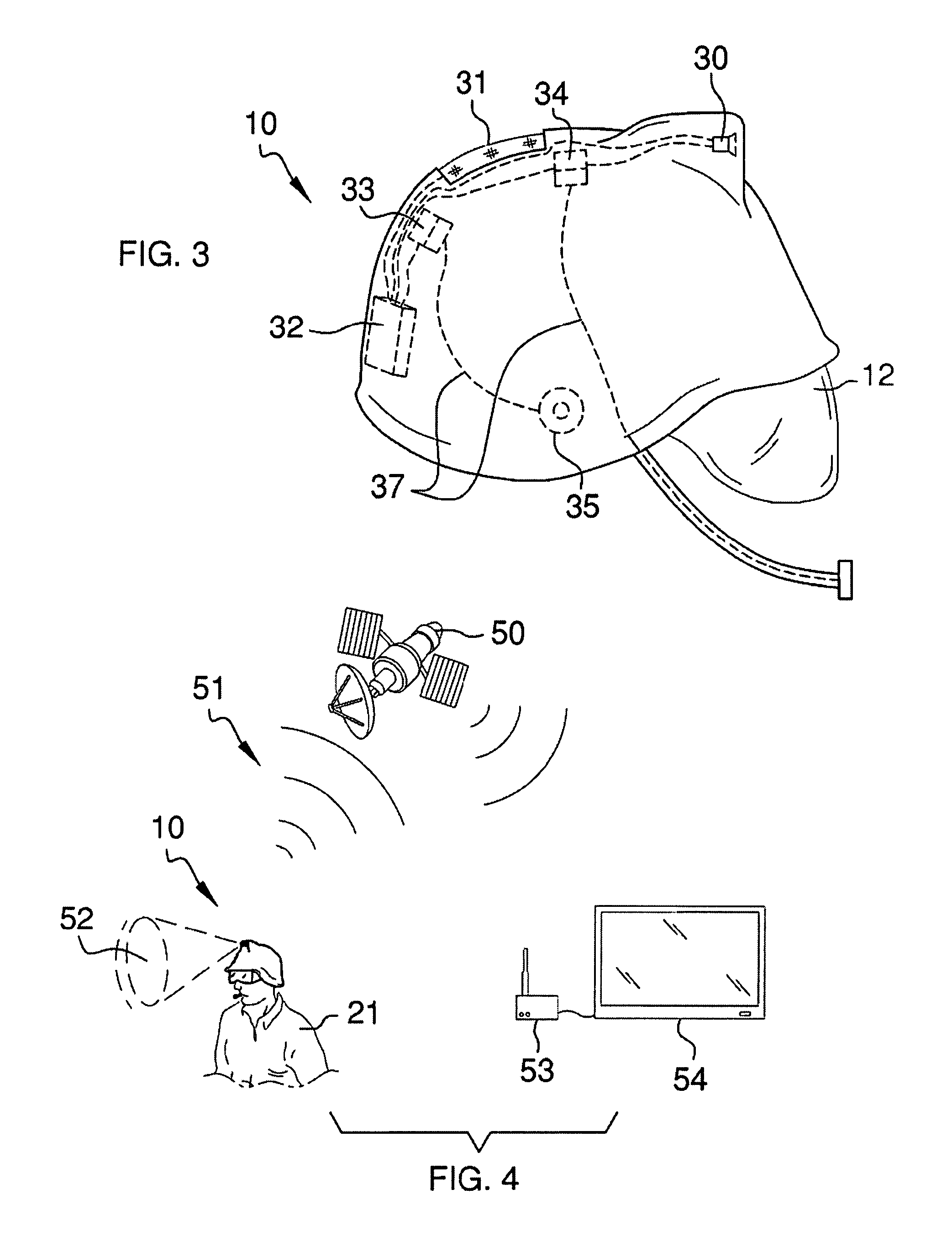
Helmet safety system
InactiveUS8009229B1Problem and limitationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsHead-up displayCommunications system
The present invention discloses a helmet with a plurality of electronic safety devices. The safety devices of the present invention include an audio and video communication system. The video communication system features include a video camera system that can transmit images to a central location, and a display system that can display images transmitted via satellite on a unique heads up display located within the helmet's pivotal safety glasses. The helmet's pivotal safety glasses have a specially designed display that allows users to view images broadcasted to them without having the bulky designs and limited sight problems associated with the traditional display apparatuses of the prior art.
Owner:PETERSON ALLEN
Self-cleaning nano glass and its production process
The disclosed process technique for nano-level self-cleaning coated glass comprises: etching or laser drilling on glass surface to obtain micro pores with size, distance and depth all within 20-100nm; coating SiO2 / TiO2 nano gel film or Ti film or nano Ag film all with super light transmission, hydrophilicity and lipophilicity for self cleaning activated UV ray. This invention has wide application.
Owner:刘明前
Decorative laminated safety glass utilizing a rigid interlayer and a process for preparing same
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Transparent light-weight safety glazings
Provided is a transparent and light-weight ballistic resistant safety glazing comprising an ionomer sheet. The ionomer sheet comprises an ionomer derived from a parent acid copolymer that comprises copolymerized units of an α-olefin having 2 to 10 carbon atoms and, based on the total weight of the acid copolymer, about 20 to about 30 wt % of copolymerized units of an α,β-ethylenically unsaturated carboxylic acid having 3 to 8 carbon atoms. The ionomer is neutralized to a level of about 5% to about 90%, based on the total carboxylic acid content of the acid copolymer, and further comprises at least one cation. Further provided are articles comprising the light-weight ballistic resistant safety glazing.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Hard-hat flip-up safety glasses
A system for attaching safety glasses to headwear often called a “helmet” or a “hard-hat” has multiple adjustments that fit the glasses to the individual user and that allow the user to flip the glasses back and forth between in-use and removed positions. The preferred system includes a base piece that attaches to the interior or underside of the helmet, near the wearer's face at or near the junction of the helmet's bill / brim and dome. A preferred second piece receives a portion of the glasses at its distal end, and, at its proximal end, slideably connects to the base piece. The second piece may be locked at various positions relative to the base piece, to adjust, either incrementally or continuously, the distance of the glasses from the helmet. This slidable adjustment between the base piece and second piece makes it possible to adjust the glasses in a generally vertical direction, that is, generally parallel to the plane of the lenses of the glasses when being used, as best suits the particular user. The clamping or gripping mechanism on the second piece distal end allows the glasses to pivot relative to the second piece and, hence, to the helmet. Thus, the user may pivot the glasses up from the eyes, out of his line of sight, or down in front of the eyes as close to the user's face as desired. This pivoting, then, provides some horizontal adjustment in the position of the glasses relative to the eyes and nose. Further, at least some portions of the preferred system are flexible or are flexibly connected to the helmet to absorb shock created when the helmet or safety glasses are struck.
Owner:HOLM BARENT
High strength multilayer laminates comprising twisted nematic liquid crystals
ActiveUS20070116945A1Lower energy requirementsEasy to useLiquid crystal compositionsDiffusing elementsHigh intensityHalf wave
Provided are multilayer laminates having one or more layers comprising twisted nematic liquid crystals and one or more layers of a polymeric sheet comprising a polymer with a modulus between 20,000 psi (138 MPa) and 100,000 psi (690 MPa). The twisted nematic liquid crystal layers reflect infrared radiation. Thus, the multilayer laminates are useful to reduce the transmission of infrared energy. For example, in some embodiments the multilayer laminates are useful as windows to reduce energy consumption necessary to cool the interior of a structure such as an automobile or building. Preferably, the multilayer laminates retain the beneficial properties of safety glass. The multilayer laminates may include additional layers such as infrared absorbing layers, half wave plates, and the like, to minimize the transmission of infrared energy. The multilayer laminates may also include further additional layers such as polymeric films, polymeric sheets, rigid sheets, and the like.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com