Method for preparing edible biological gelatin film with EGCG (epigallocatechin gallate) controlled-release performance
A technology of gelatin film and performance, applied in the field of preparation of edible biological gelatin film
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0025] A kind of preparation method of the edible biological gelatin film with slow-release EGCG performance of the present invention, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0026] Step 1, prepare gelatin solution;
[0027] The specific process of step 1 is as follows:
[0028] Dissolve gelatin in deionized water, let stand at room temperature to swell for 2-10 hours, add glycerin, heat and stir at 50-70°C, and then perform ultrasonic degassing to obtain gelatin solution.
[0029] In step 1, the heating time is at least 20 minutes, and the ultrasonic degassing time is at least 10 minutes.
[0030] The mass ratio of glycerol to gelatin in step 1 is 0.3-1:3.
[0031] Step 2, after cooling the gelatin solution prepared in step 1 to room temperature, adding EGCG, stirring to dissolve, standing at 2-8°C for 10-14 hours to obtain a film-forming solution;
[0032] The mass ratio of EGCG to gelatin solution in step 2 is 1-5:100.
[0033] In step 3, the film-forming solution...
Embodiment 1
[0037] Dissolve 3g of gelatin in 100mL of deionized water, let it swell at room temperature for 2 hours, add 1g of glycerin, heat and stir at 50°C for 30 minutes, then ultrasonically degas for 20 minutes, after the gelatin solution is cooled to room temperature, add EGCG with a mass fraction of 3% gelatin, Stir to dissolve, and stand at 2°C for 10 hours to cross-link. After the cross-linked film-forming solution was heated and dissolved in a 34°C water bath, it was transferred to a mold, and dried in a 20°C constant-temperature blast drying oven to form a film.
Embodiment 2
[0039] Dissolve 3g of gelatin in 100mL of deionized water, let it stand for swelling at room temperature for 6 hours, add 0.3g of glycerin, heat and stir at 60°C for 20 minutes, then ultrasonically degas for 10 minutes, after the gelatin solution is cooled to room temperature, add EGCG with 5% gelatin mass fraction , stir to dissolve, and stand at 4°C for 12h. After the cross-linked film-forming solution was heated and dissolved in a water bath at 37°C, it was transferred to a mold, and dried in a constant temperature blast drying oven at 26°C to form a film.
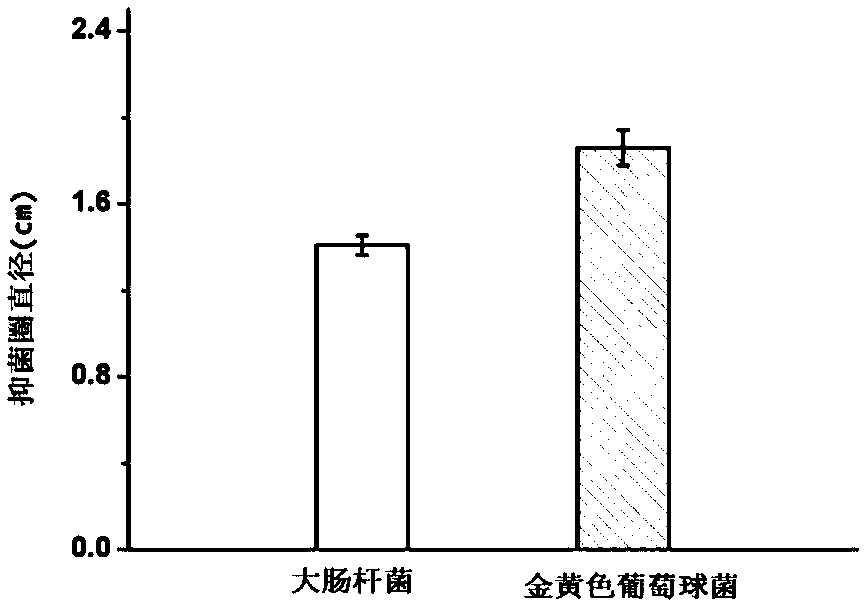
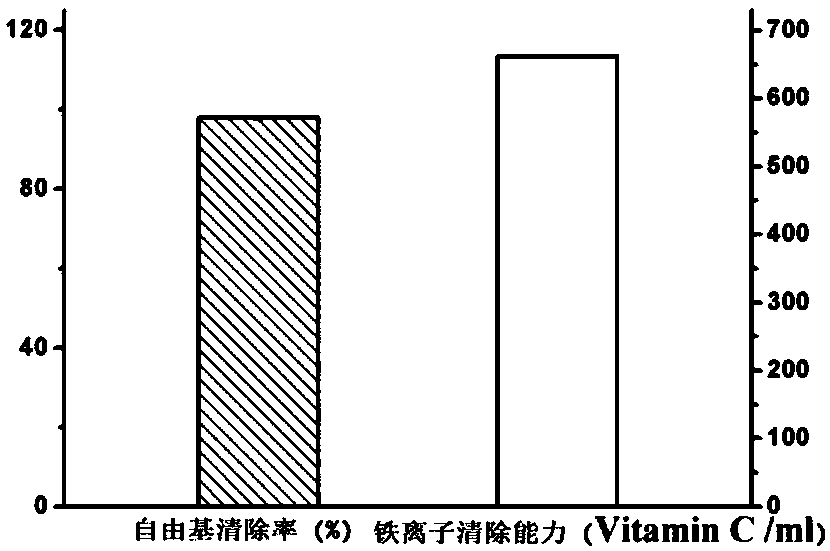
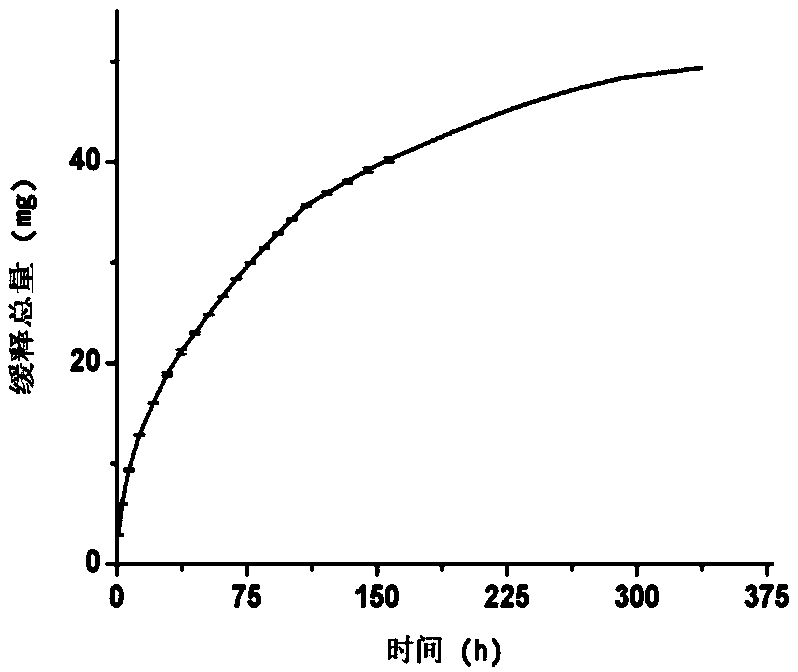
[0040] The antibacterial performance of the dried edible gelatin film was determined by the Oxford cup method, and the tested bacteria were Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. The results showed that the edible gelatin film had good bacteriostatic effect on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus (see figure 1 ). Characterize the antioxidant performance of edible gelatin film by measuring DPPH free radical ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com