Method for preparing isobutylene by comprehensively using mixed C4
A technology for mixing C4 and isobutylene, which is applied to chemical instruments and methods, and the production of hydrocarbons and hydrocarbons from oxygen-containing organic compounds, can solve the problems of low added value of mixed C4 and low overall utilization efficiency of mixed C4, etc. To achieve the effect of increasing added value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
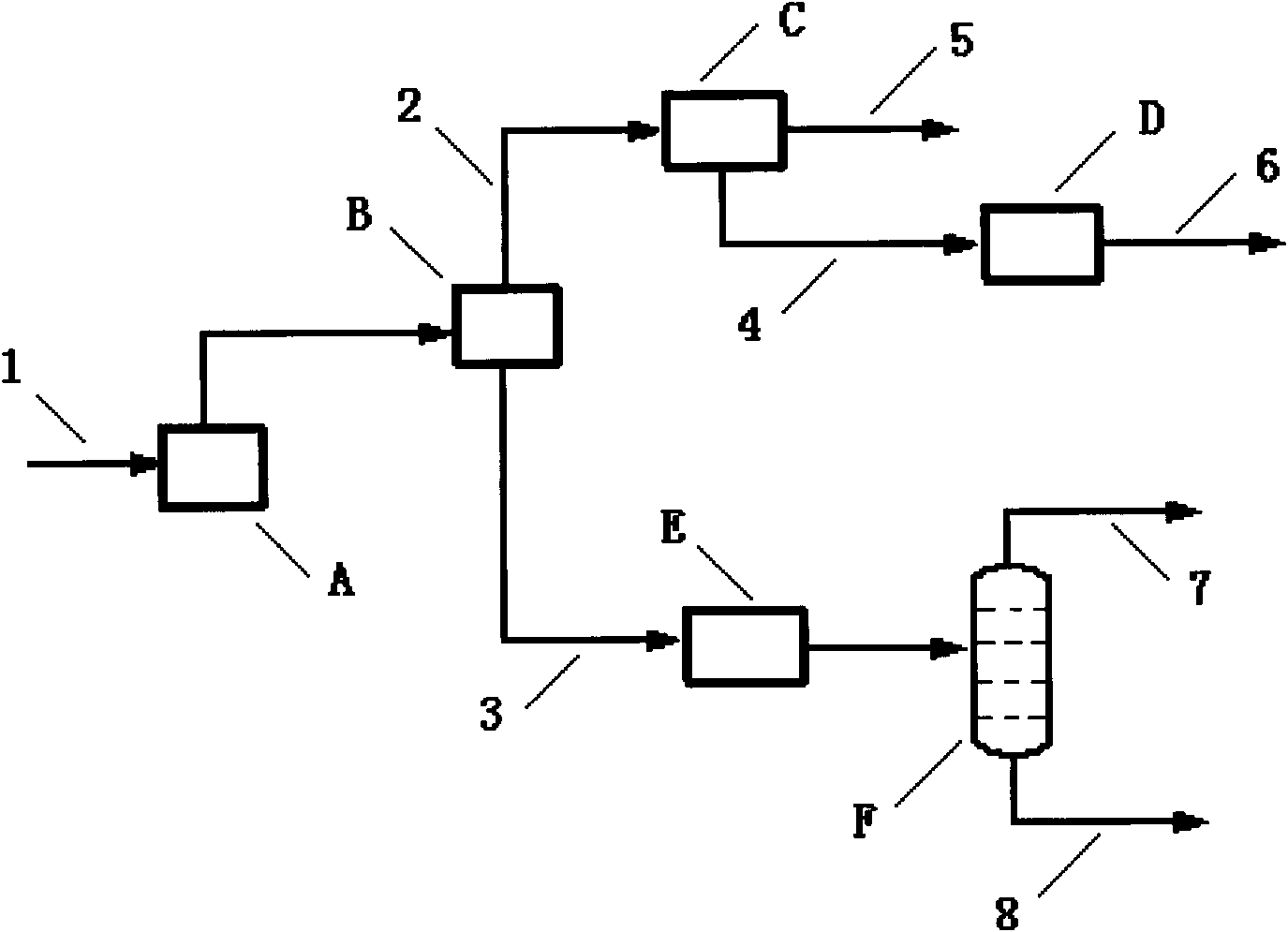
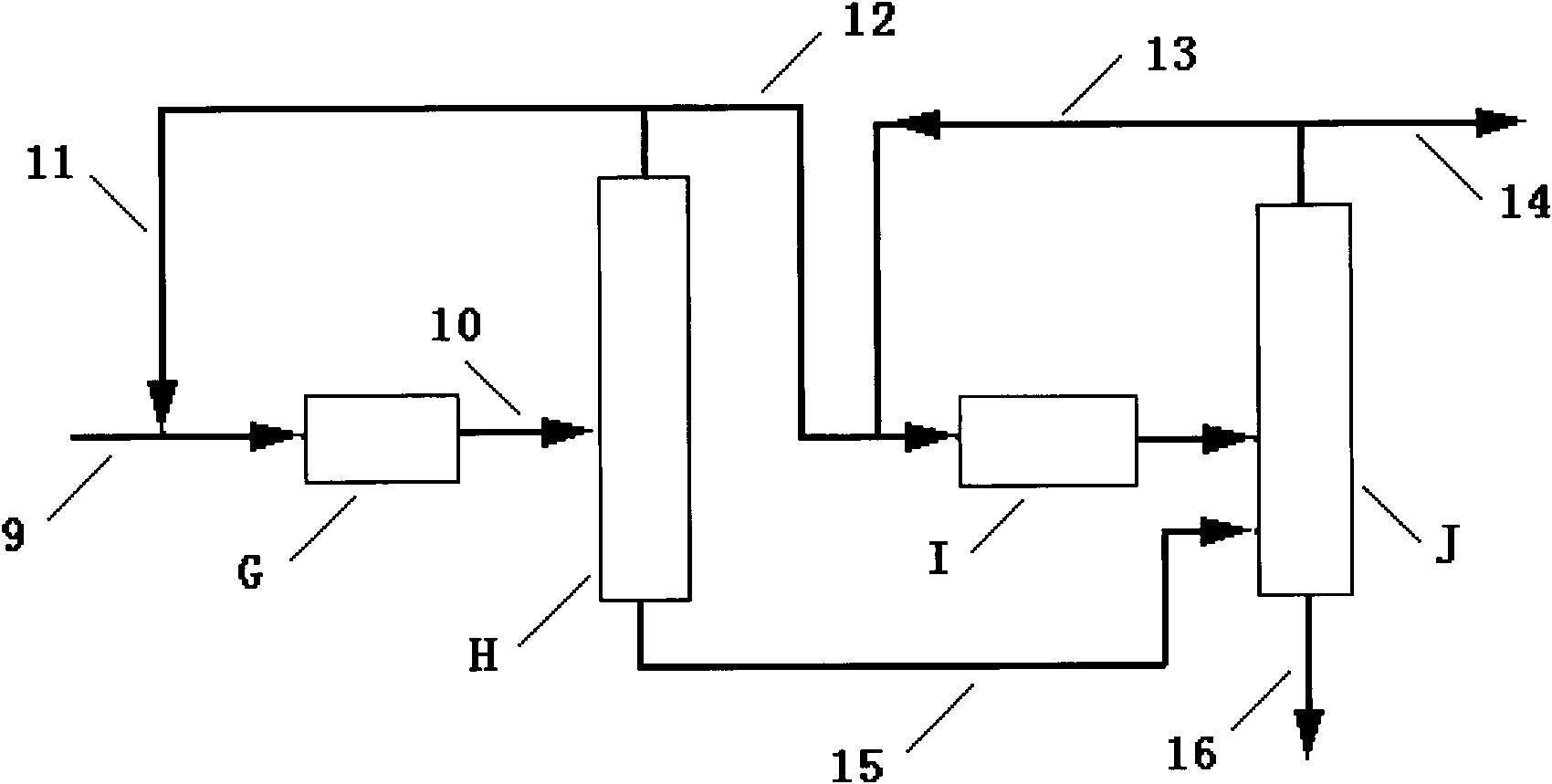
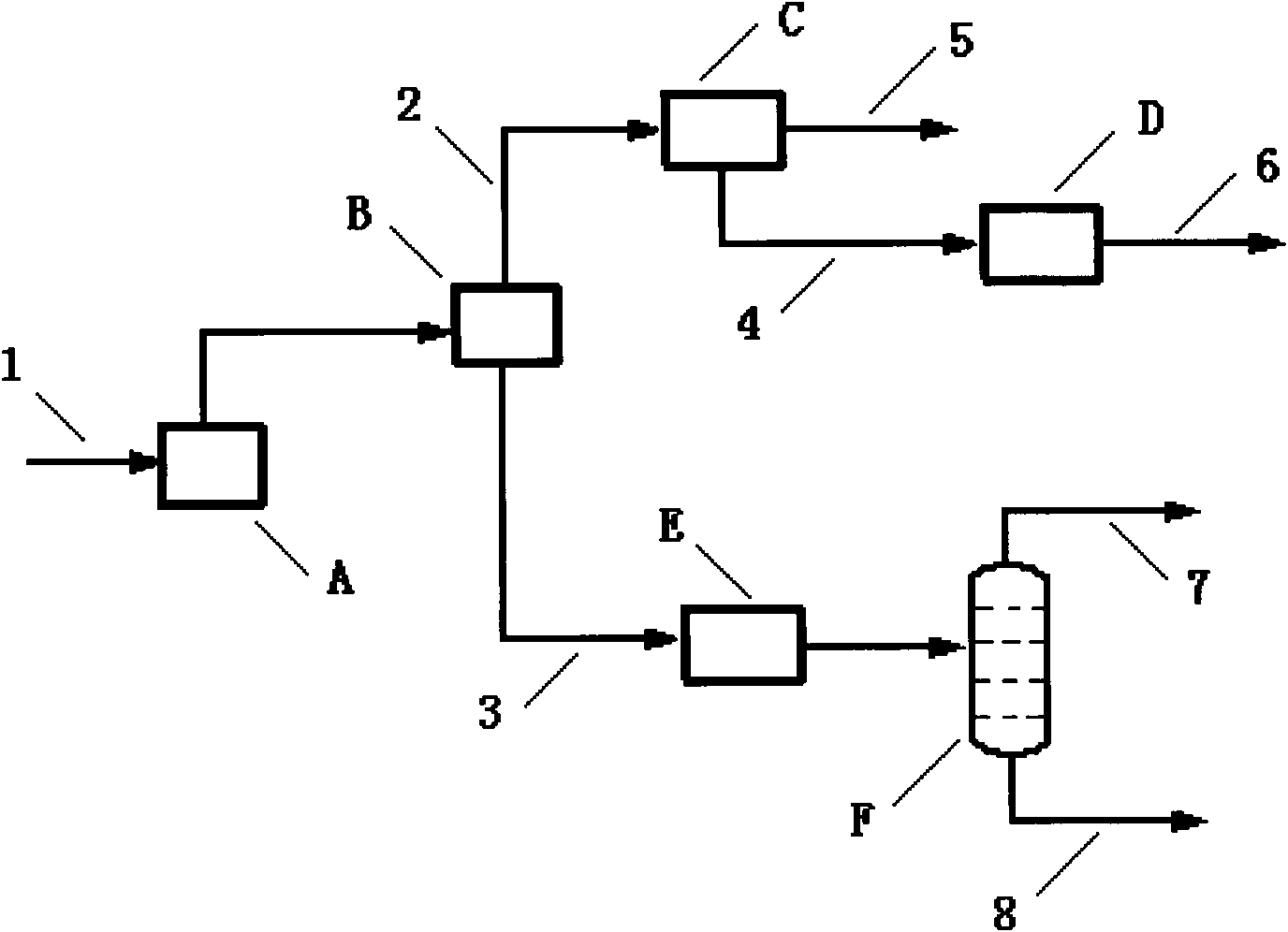
[0036] according to figure 1 As shown, the mixed carbon four composition (% by weight) from the steam cracking unit is: isobutane: 1, n-butane: 2, butadiene: 50, isobutene: 22, butene-1: 14, butene- 2:11. Butadiene selective hydrogenation catalyst is aluminum oxide supported metal nickel and zinc. The common raw material for catalytic distillation is hydrogen, and the hydroisomerization catalyst loaded in the reaction section is metal nickel and zinc supported on alumina. The etherification unit adopts a catalytic distillation reactor, and the catalyst is a macroporous strongly acidic cation exchange resin. Isobutane dehydrogenation uses a fluidized bed reactor, and the catalyst is platinum and zinc supported on alumina. The isomerization of butene-2 to isobutene adopts a single-stage fixed-bed reactor, and the catalyst is a magnesium metal-modified zeolite molecular sieve. Experiments have proved that the yield of isobutene by the method of the present invention is 88% ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] according to figure 1Shown, the mixed carbon four composition (% by weight) from the steam cracking unit is: isobutane: 1, n-butane: 2, butadiene: 50, isobutene: 22, butene-1: 14, butene- 2:11. Butadiene selective hydrogenation catalyst is aluminum oxide supported metal palladium and zinc. The common raw material for catalytic distillation is hydrogen, and the hydroisomerization catalyst loaded in the reaction section is metal palladium and zinc supported on alumina. The etherification unit adopts a catalytic distillation reactor, and the catalyst is ZSM-5 molecular sieve. Isobutane dehydrogenation uses a fluidized bed reactor, and the catalyst is platinum and zinc supported on alumina. The isomerization of butene-2 to isobutene adopts a fluidized bed reactor, and the catalyst is alkali metal modified SAPO-11 molecular sieve. Experiments show that the yield of isobutene of the present invention is 81%, n-butane is 5%, and the others are unconverted mixed carbon fo...
Embodiment 3
[0040] according to figure 1 As shown, the mixed carbon four composition (% by weight) from the catalytic cracking unit of the refinery is: isobutane: 34, n-butane: 10, butadiene: 0, isobutene: 15, butene-1: 13, butene En-2:28. No butadiene selective hydrogenation unit. The common raw material for catalytic distillation is hydrogen, and the hydroisomerization catalyst loaded in the reaction section is metal palladium and zinc supported on alumina. The etherification unit adopts a catalytic distillation reactor, and the catalyst is ZSM-5 molecular sieve. Isobutane dehydrogenation uses a fluidized bed reactor, and the catalyst is platinum and zinc supported on alumina. The isomerization of butene-2 to isobutene adopts a single-stage fixed-bed reactor, and the catalyst is zeolite molecular sieve modified by magnesium alkali metal. Experiments show that the yield of isobutene of the present invention is 83%, that of n-butane is 3%, and that the others are unconverted mixed c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com