Patents
Literature
30results about How to "Low friction surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Process for making abrasion resistant paper and paper and paper products made by the process
InactiveUS20050155731A1Improve optical brightnessLow friction surfacePaper after-treatmentPaper coatingPapermakingPaper sheet
In this papermaking process, a first strength agent is added to a stock suspension containing pulp and optionally other additives prior to its being formed into a web at the wet end of a papermaking machine. The web is then formed and processed into paper. A second strength agent is then applied to the surface of the paper. The strength agents may be selected to have opposite charge.
Owner:NAT GYPSUM PROPERTIES
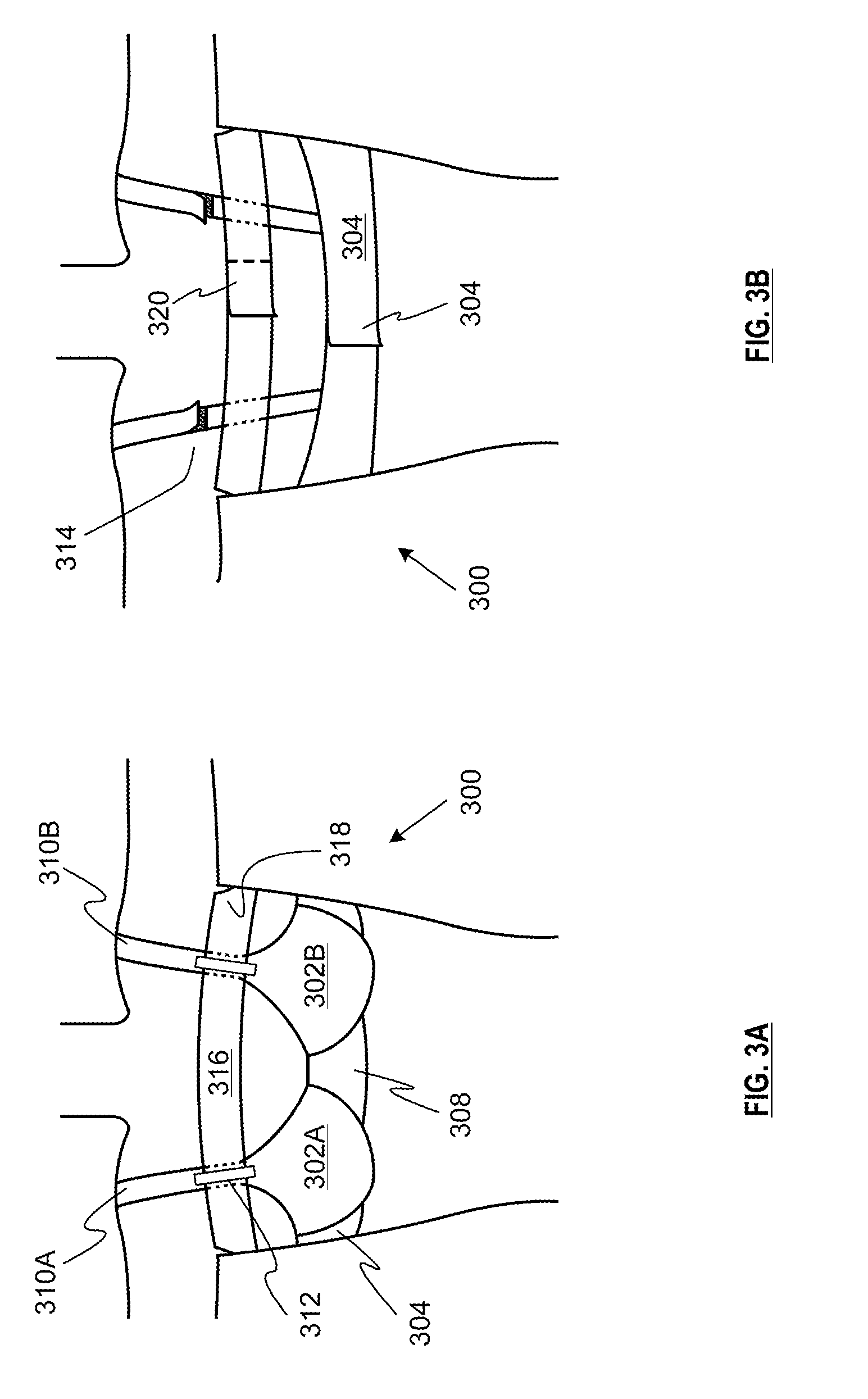
Catheter assembly with bactericidal effect
InactiveUS20060240069A1Reduce decreaseSimple procedureBiocidePharmaceutical containersUrinary catheterOrganic acid
A use in a medical device of at least one salt of organic acid(s), and preferably a benzoate or a sorbate, as an antimicrobial agent is disclosed, and in particular for the manufacturing of an antimicrobial coating for a medical device for the prevention of bacterial infection. This is very useful in medical devices having a hydrophilic coating, such hydrophilic urinary catheters. It is further preferred that the pH of the hydrophilic coating is controlled to be in the range 4.0-8.0, and preferably in the range 5.0-6.0. It is also preferred that the pH of the hydrophilic coating is controlled to be below 7.0. The pH of the hydrophilic coating could be controlled by means of a pH buffer, and preferably a citrate or phosphate buffer. Specifically, the provision of the salt of organic acid in combination with a pH buffer has proven surprisingly efficient for inhibition of bacterial growth, and for prevention of bacterial infections.
Owner:ASTRA TECH SE
Nanostructured chemicals as alloying agents in fluorinated polymers
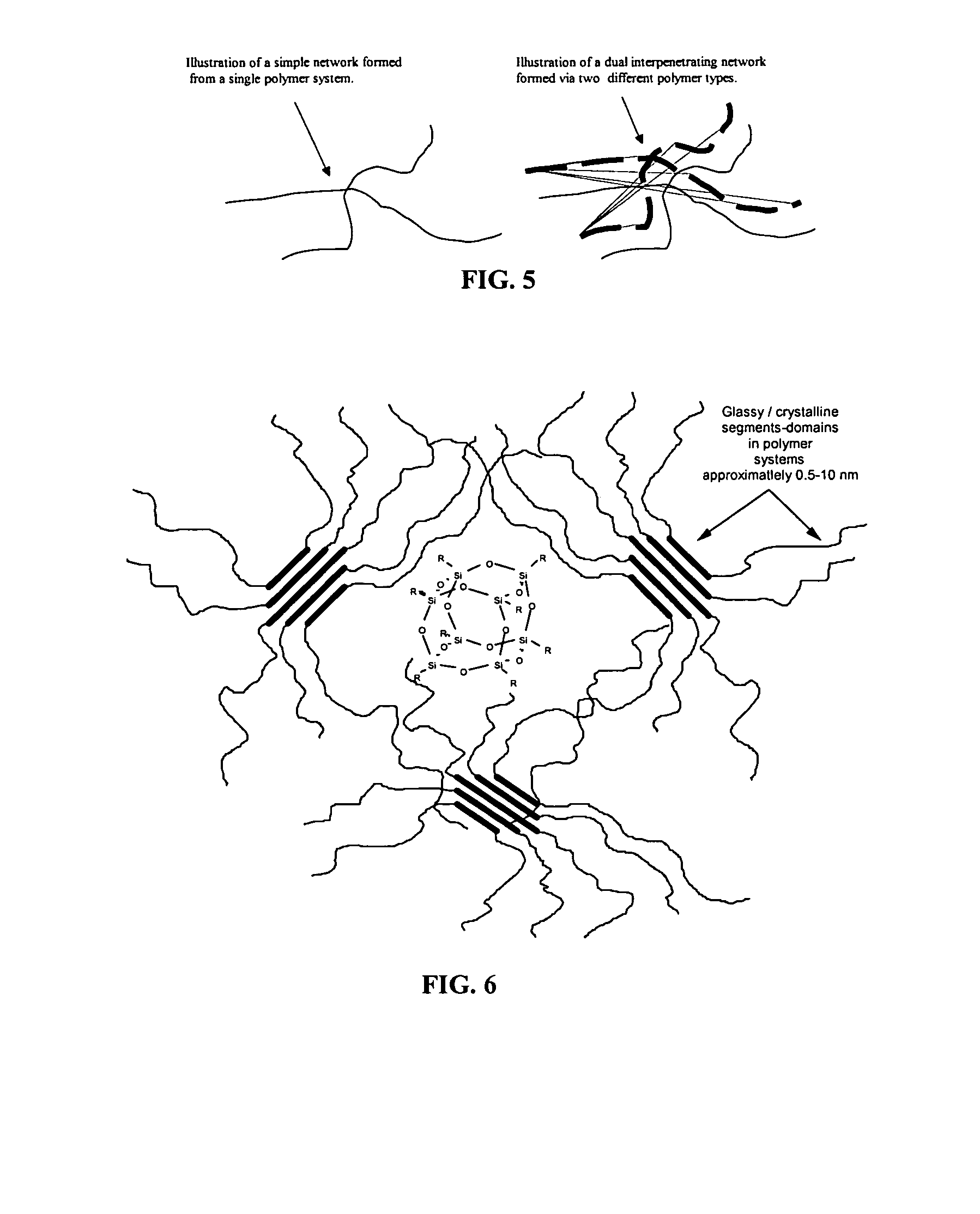
InactiveUS7193015B1Reduce melt viscosityLow dielectric constantMaterial nanotechnologyMolecular levelCompression set
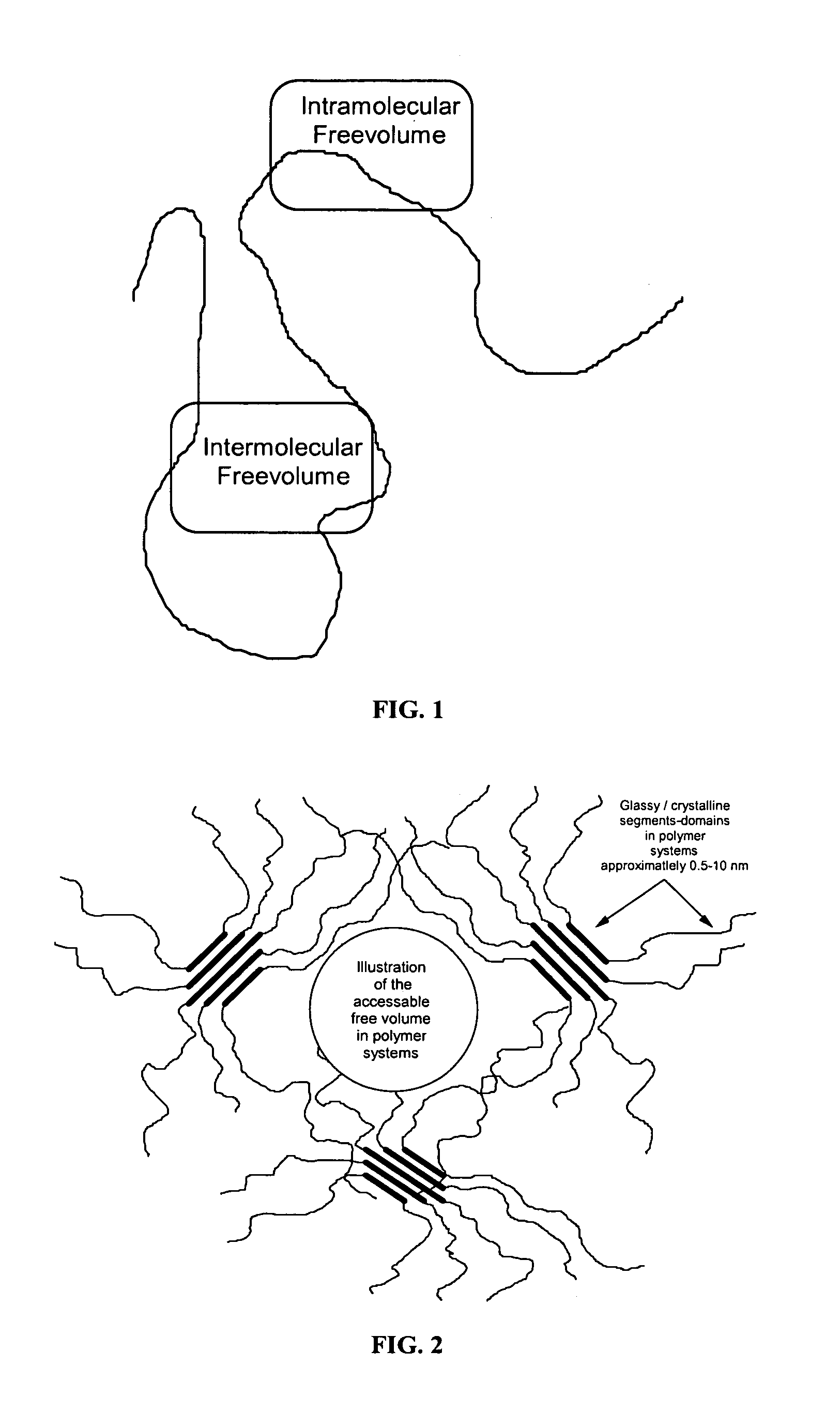
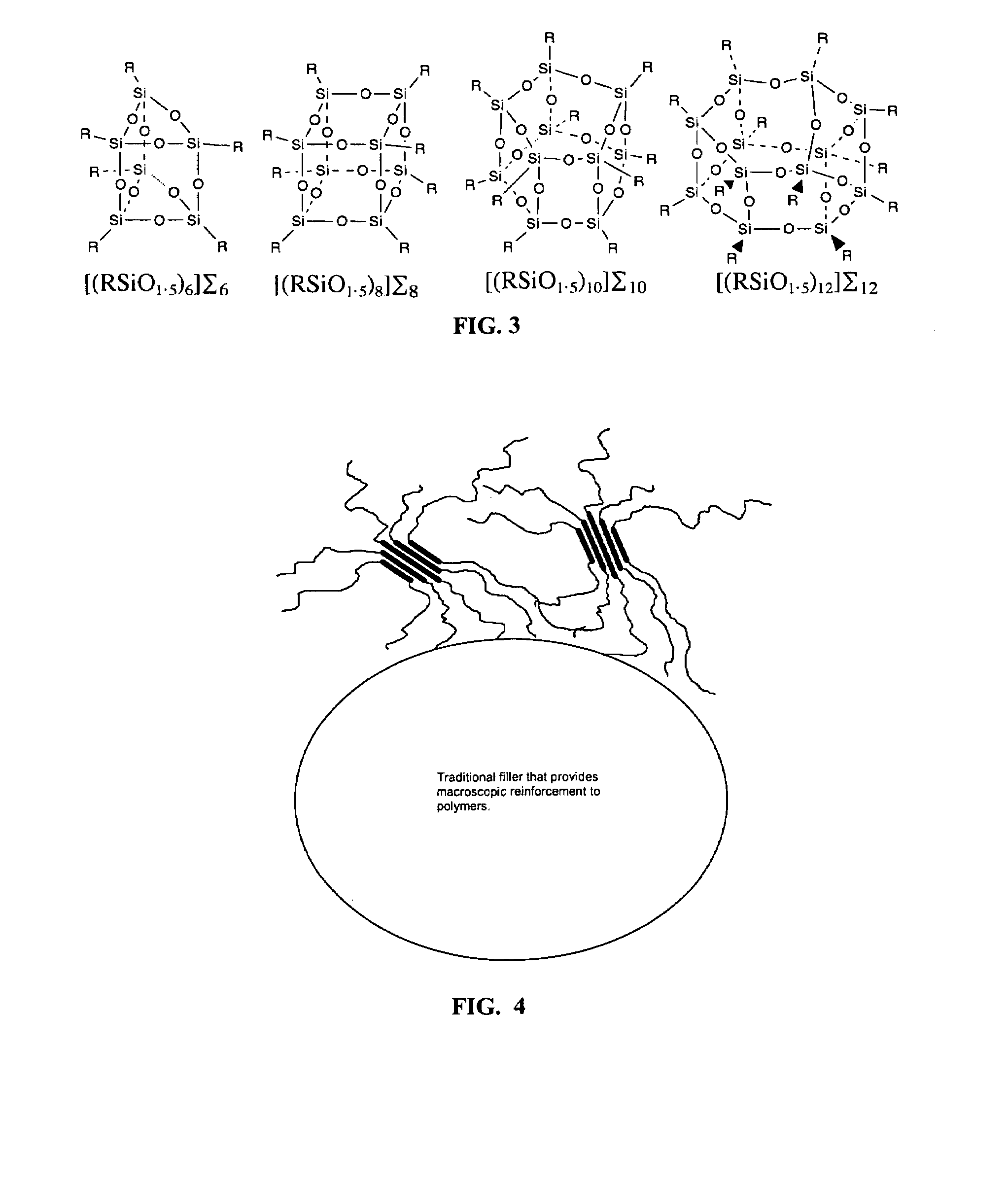
A method of using nanostructured chemicals as alloying agents for the reinforcement of flouropolymer microstructures, including polymer coils, domains, chains, and segments, at the molecular level. Because of their tailorable compatibility with fluorinated polymers, nanostructured chemicals can be readily and selectively incorporated into polymers by direct blending processes. Properties most favorably improved are time dependent mechanical and thermal properties such as heat distortion, creep, compression set, shrinkage, modulus, hardness and abrasion resistance. In addition to mechanical properties, other physical properties are favorably improved, including lower thermal conductivity, fire resistance, and improved oxygen permeability. These improved properties may be useful in a number of applications, including space-survivable materials and creep resistant seals and gaskets. Improved surface properties may be useful for applications such as anti-icing or non-wetting surfaces or as low friction surfaces.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Valve component with multiple surface layers
InactiveUS6935618B2High hardnessIncrease resistanceOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMultiple way valvesSurface layerAmorphous diamond
A sliding component, particularly a disk valve plate. The sliding component includes a multi-layer surface structure comprising a strengthening layer harder than the substrate material, and an amorphous diamond top layer.
Owner:DELTA FAUCET COMPANY
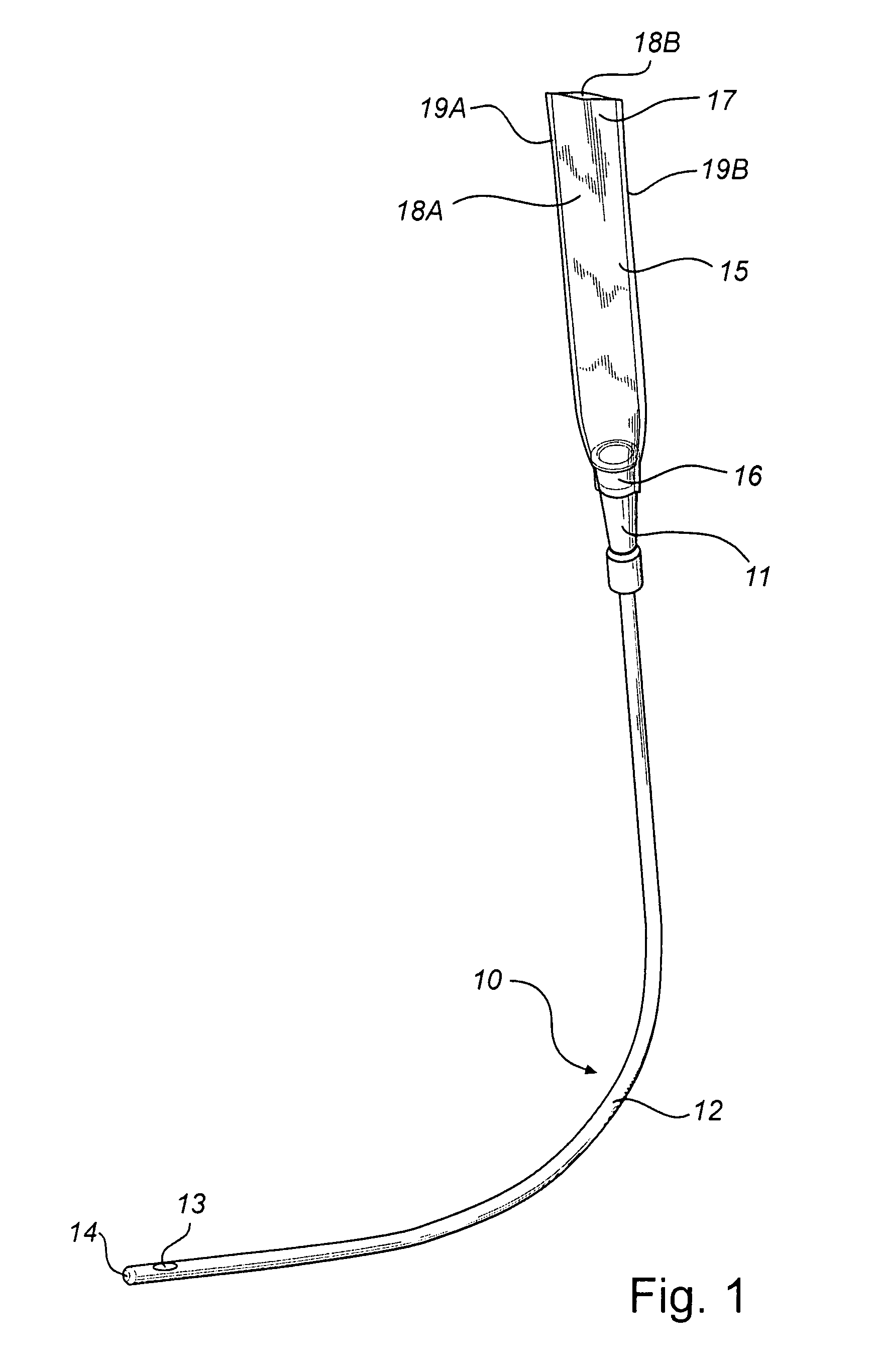
Urinary catheter
ActiveUS8168249B2Improve mechanical propertiesImprove adhesionWound drainsGlovesUrinary catheterPolyolefin
A medical device is disclosed, comprising a substrate, having on its surface, on at least a part thereof, a hydrophilic surface layer providing low-friction surface character of the medical device when wetted by a wetting fluid. The substrate is made of a polymer blend comprising a polyolefin and a composition having molecules with active hydrogen(s), such as polyamide or polyurethane. The hydrophilic surface layer is preferably adhered to the substrate by a polyurea network, whereby said polyurea network forms a covalent bond to said active hydrogen(s) in the substrate. The new substrate material is environmentally acceptable and cost effective, has adequate mechanical and chemical properties and enables the hydrophilic coating to be adequately adhered.
Owner:ASTRA TECH SE
Urinary catheter
ActiveUS20070016169A1Improve mechanical propertiesMaintain good propertiesGlovesWound drainsUrinary catheterPolyolefin
A medical device is disclosed, comprising a substrate, having on its surface, on at least a part thereof, a hydrophilic surface layer providing low-friction surface character of the medical device when wetted by a wetting fluid. The substrate is made of a polymer blend comprising a polyolefin and a composition having molecules with active hydrogen(s), such as polyamide or polyurethane. The hydrophilic surface layer is preferably adhered to the substrate by a polyurea network, whereby said polyurea network forms a covalent bond to said active hydrogen(s) in the substrate. The new substrate material is environmentally acceptable and cost effective, has adequate mechanical and chemical properties and enables the hydrophilic coating to be adequately adhered.
Owner:ASTRA TECH SE
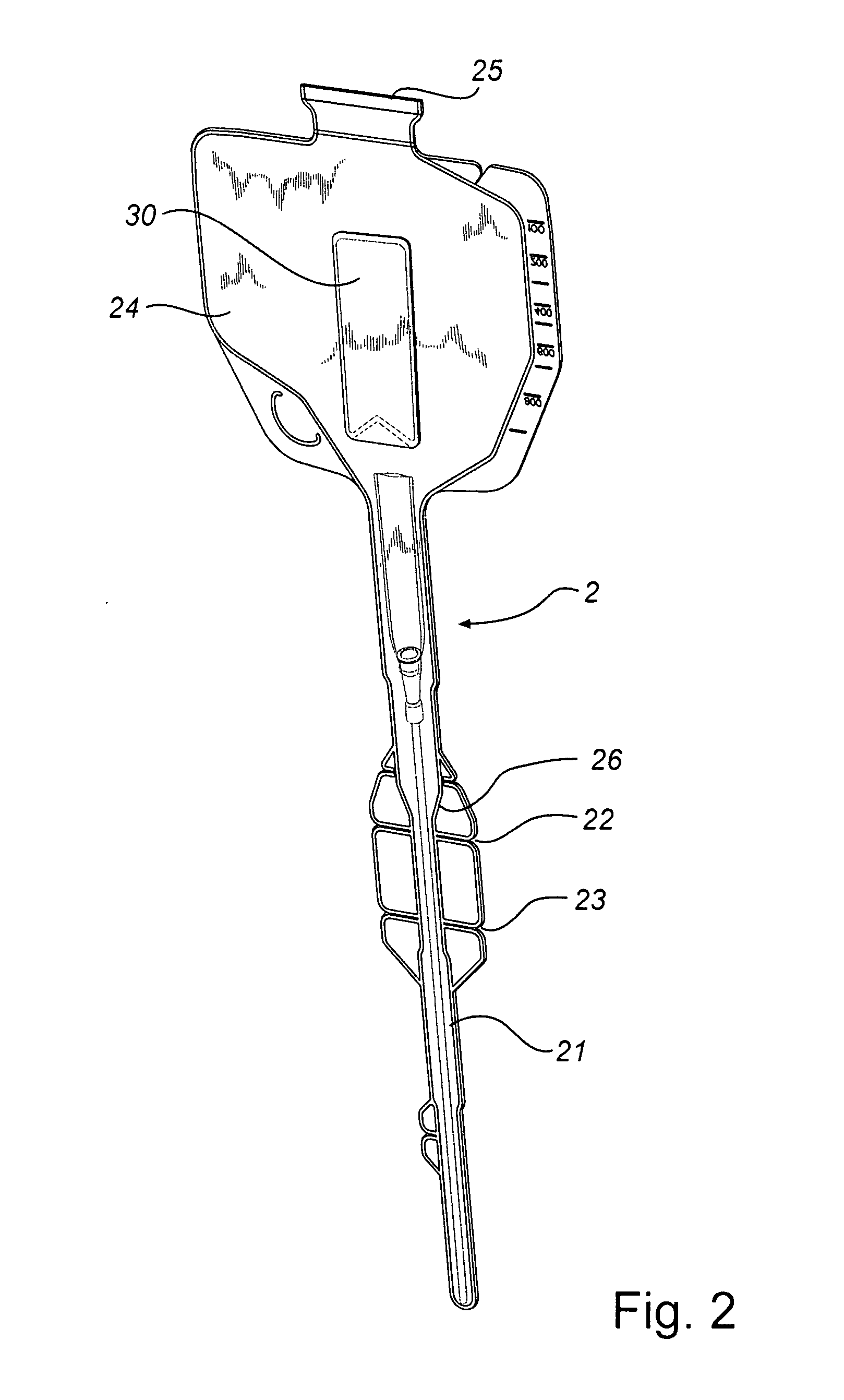
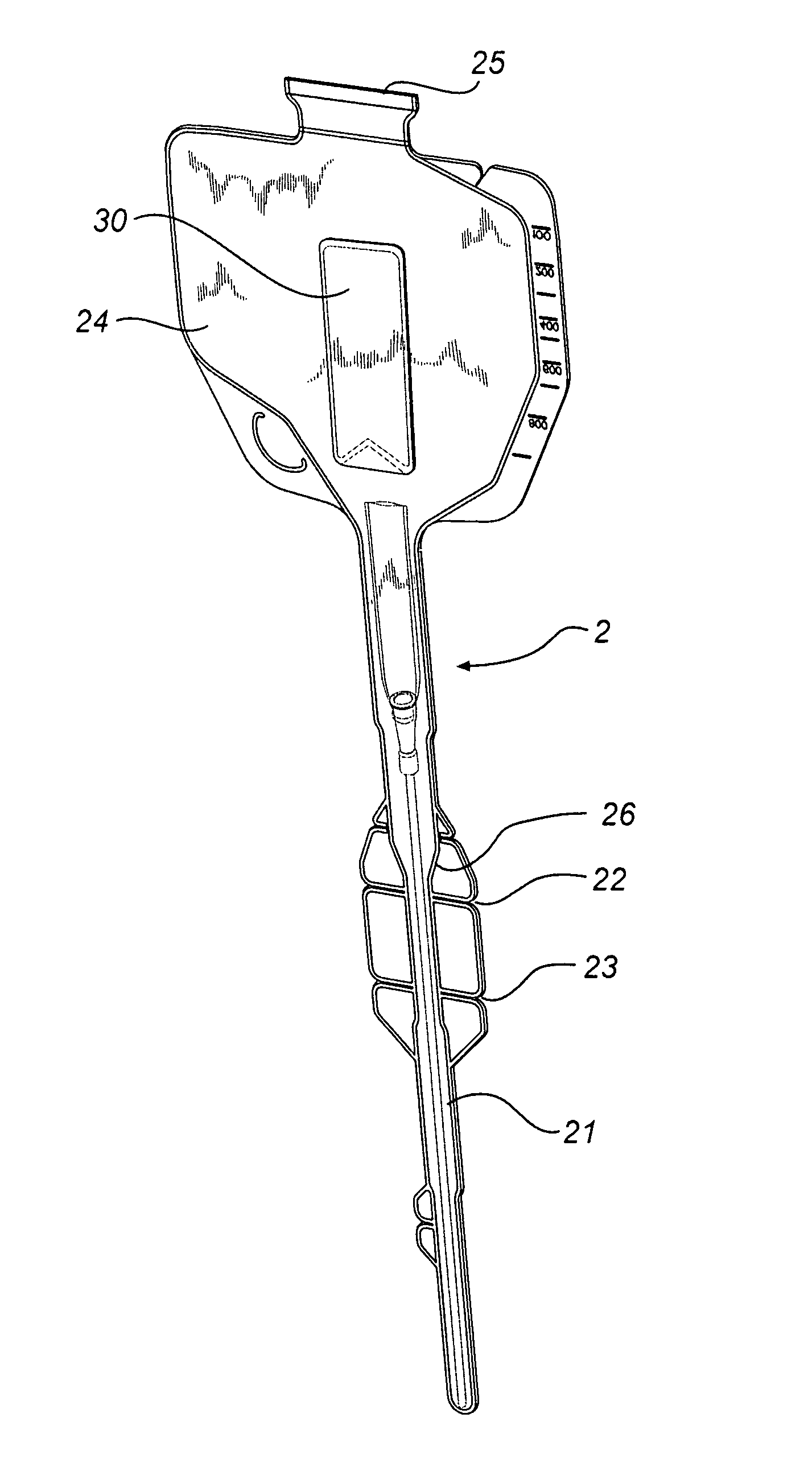
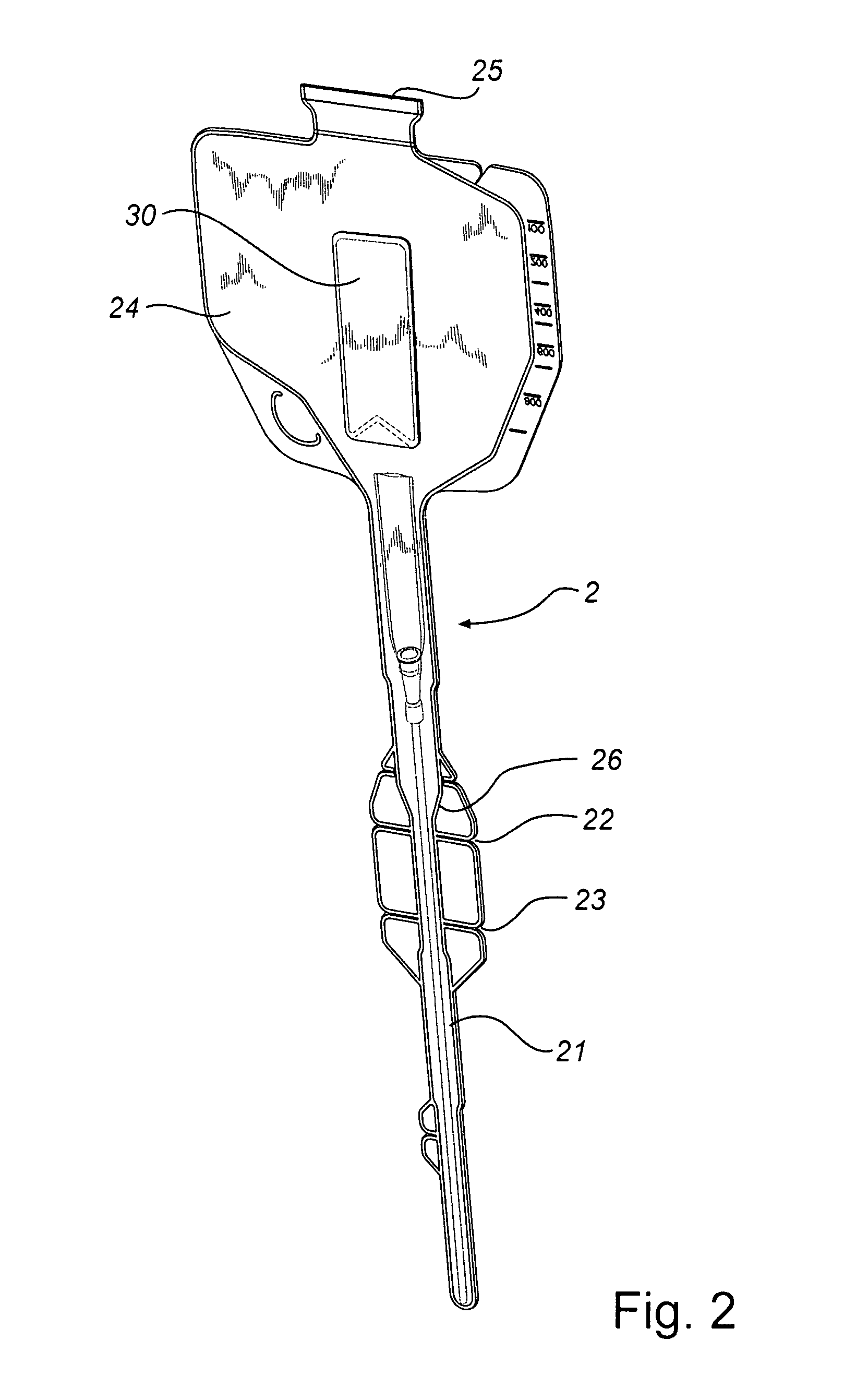
Folded Catheter Assembly With Adhesive Grip
ActiveUS20080200907A1Widely distributedImprove usabilityDispensing apparatusDiagnosticsGuide tubeBiomedical engineering
A catheter assembly is disclosed comprising a catheter and a receptacle enclosing said catheter. The receptacle has a first part and a second part, which parts are foldable over each other. Further, at least one sticky adhesive area is arranged on the surface of one of the parts of the receptacle in such a way that the sticky adhesive area is covered by the other part when the receptacle is in a folded disposition, and exposed to the environment when the receptacle is in an unfolded disposition.
Owner:ASTRA TECH SE
Urinary catheter with one way check valve
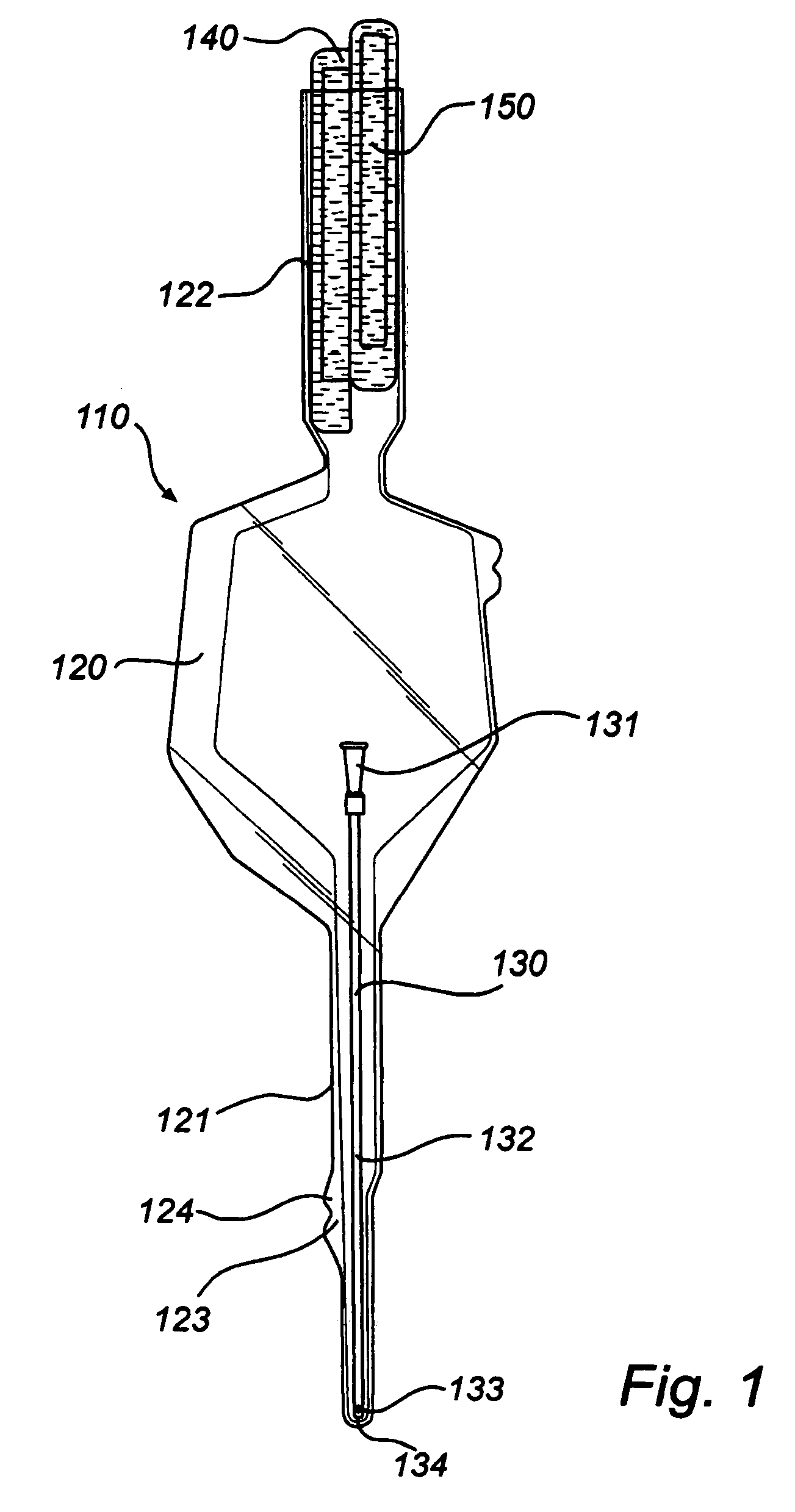
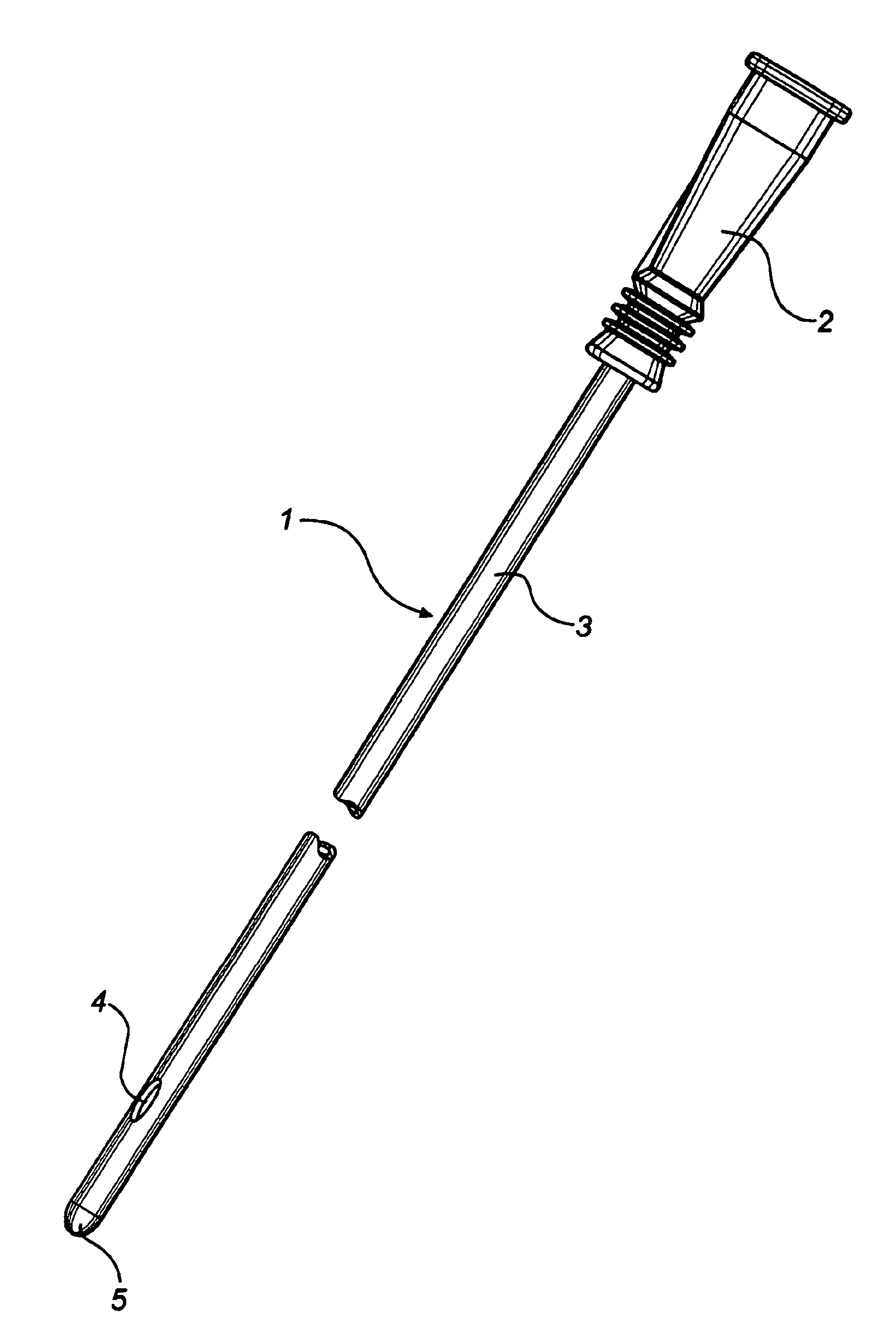
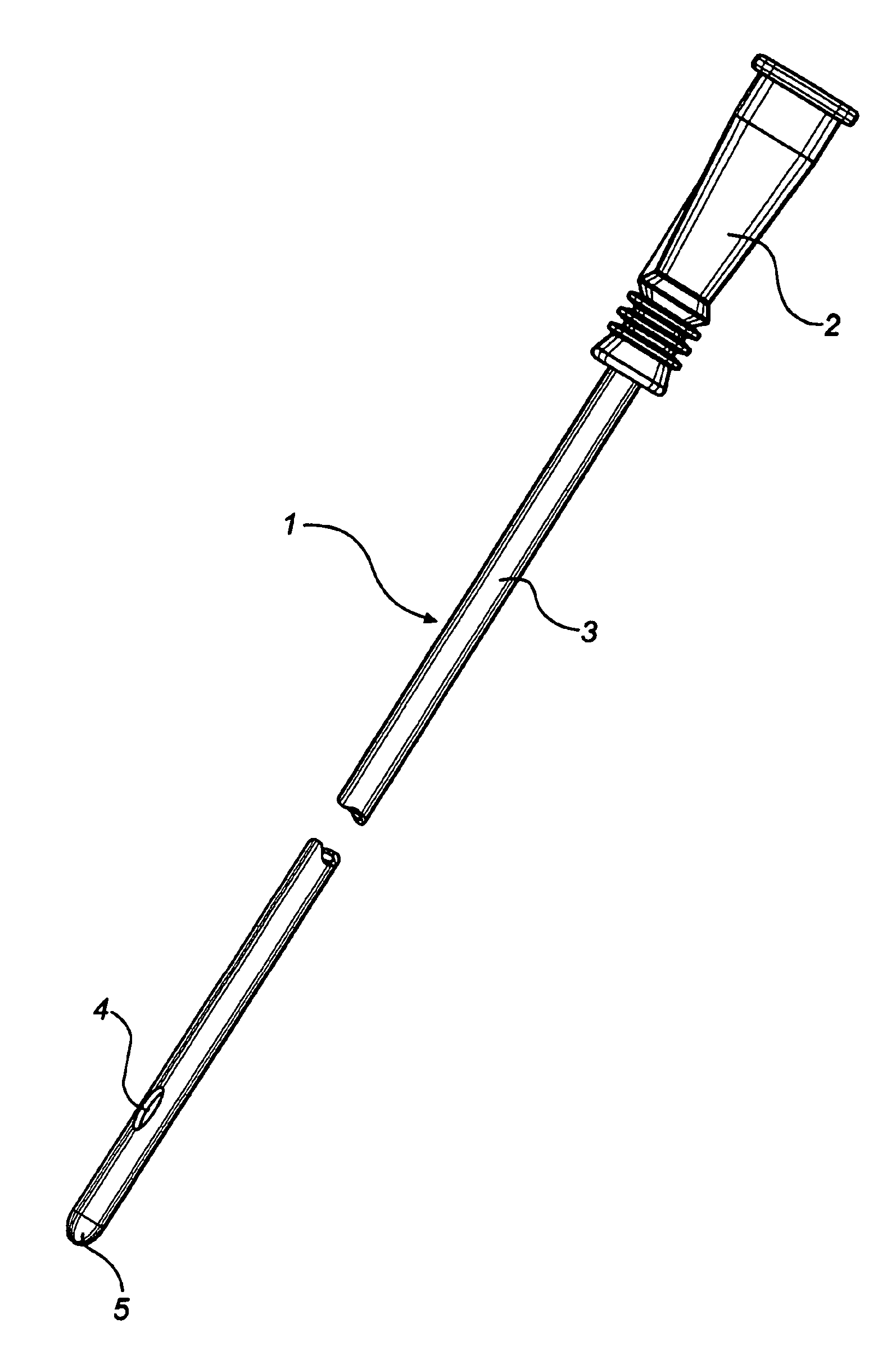
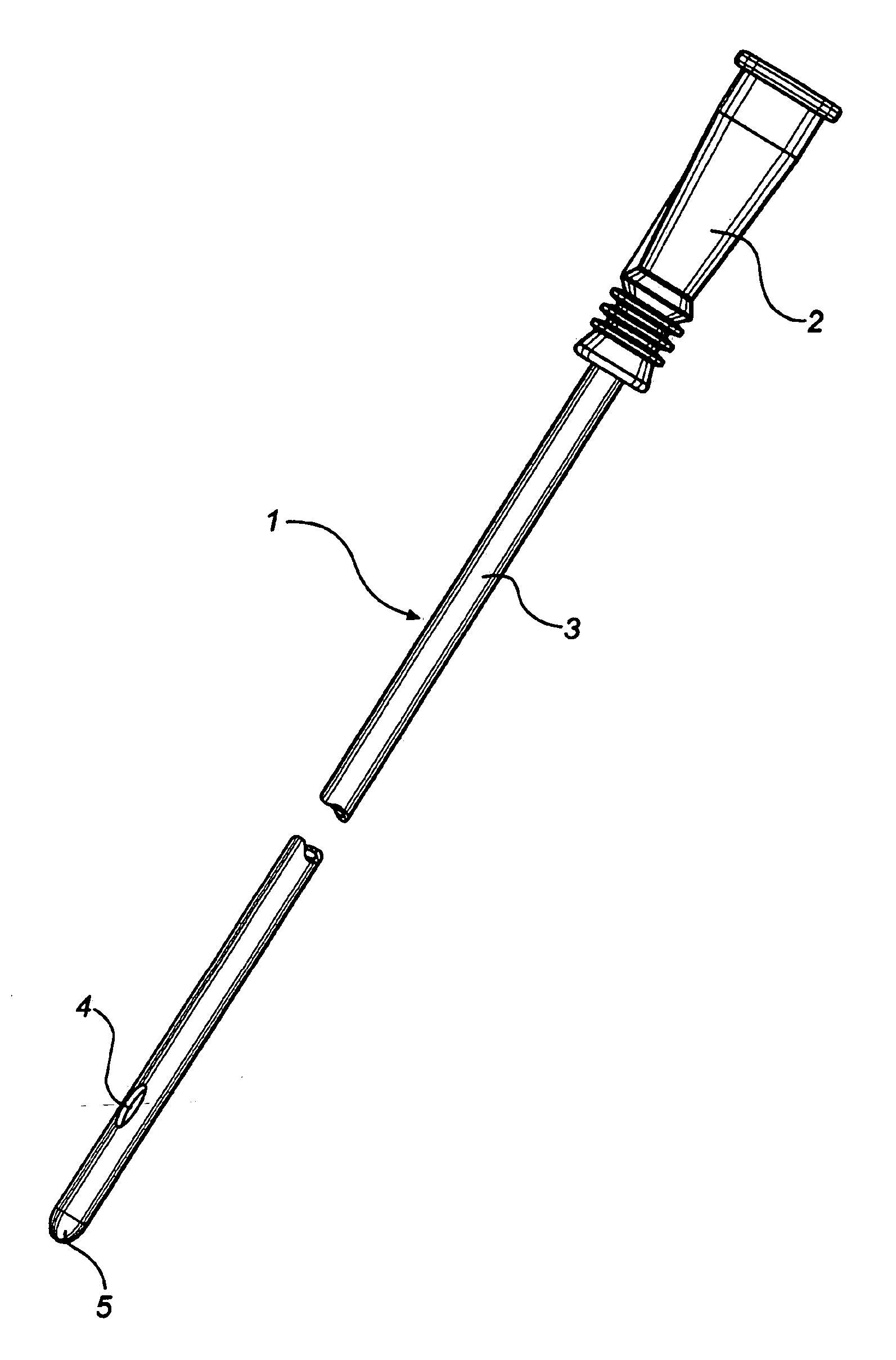
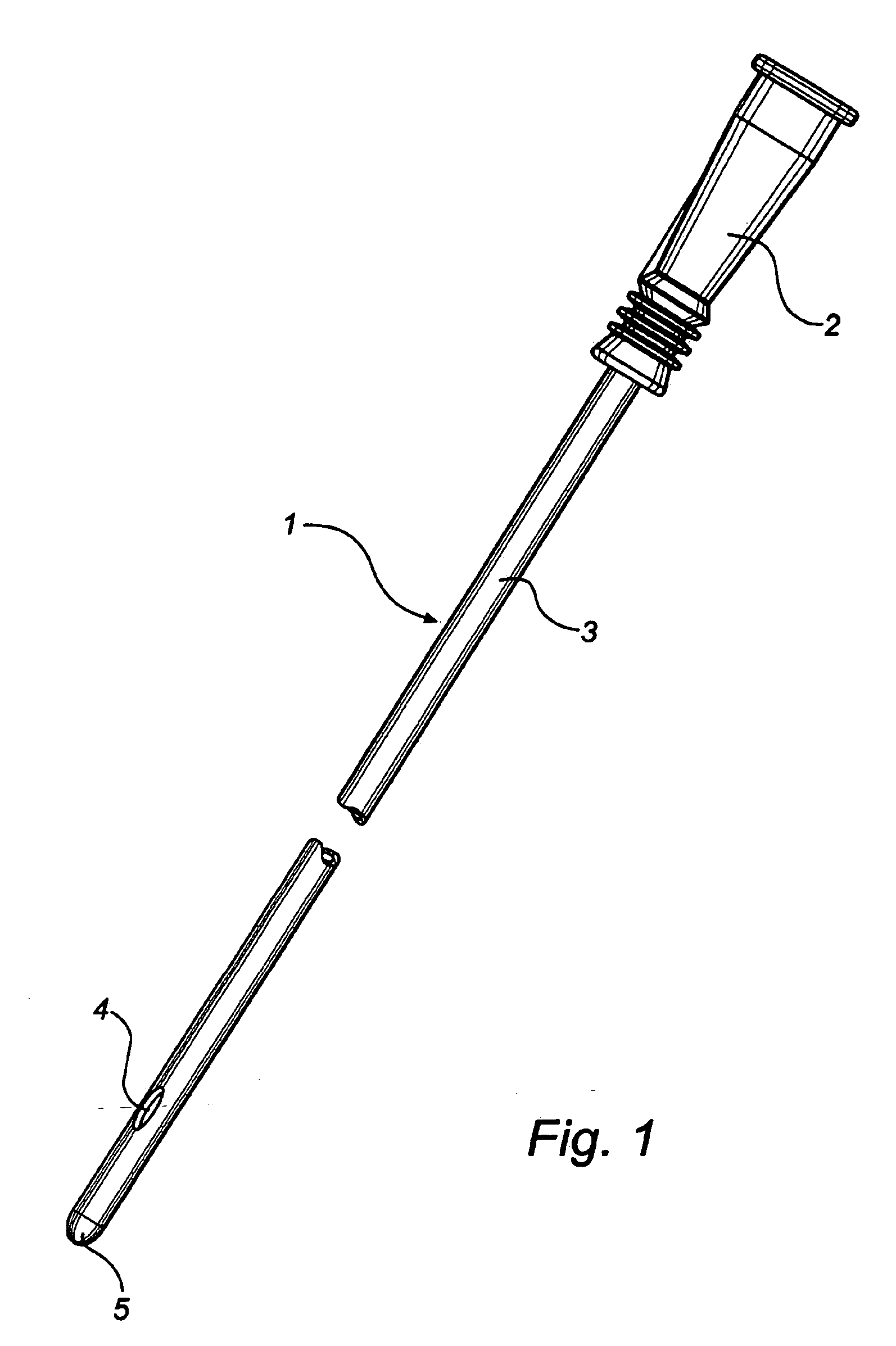
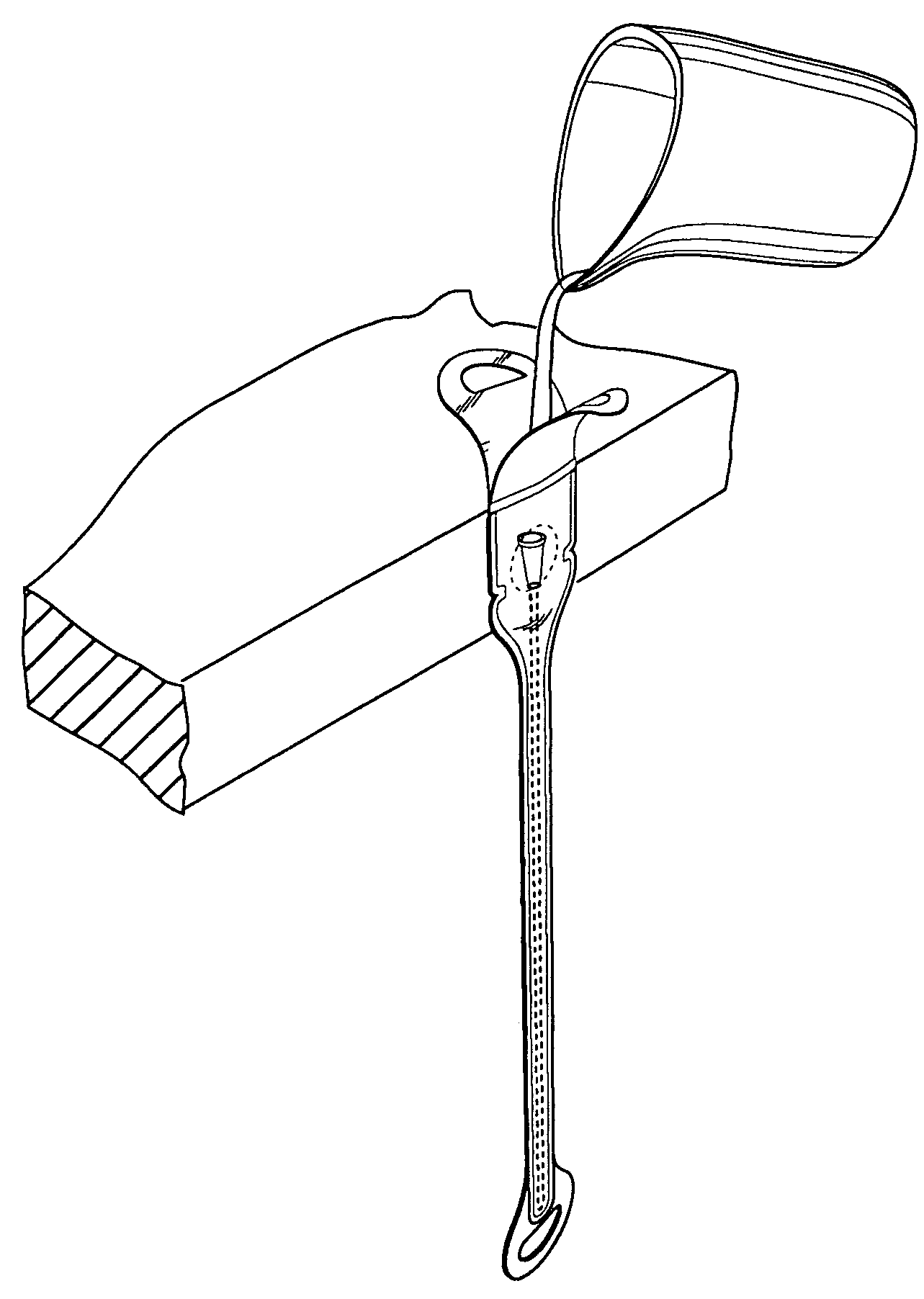
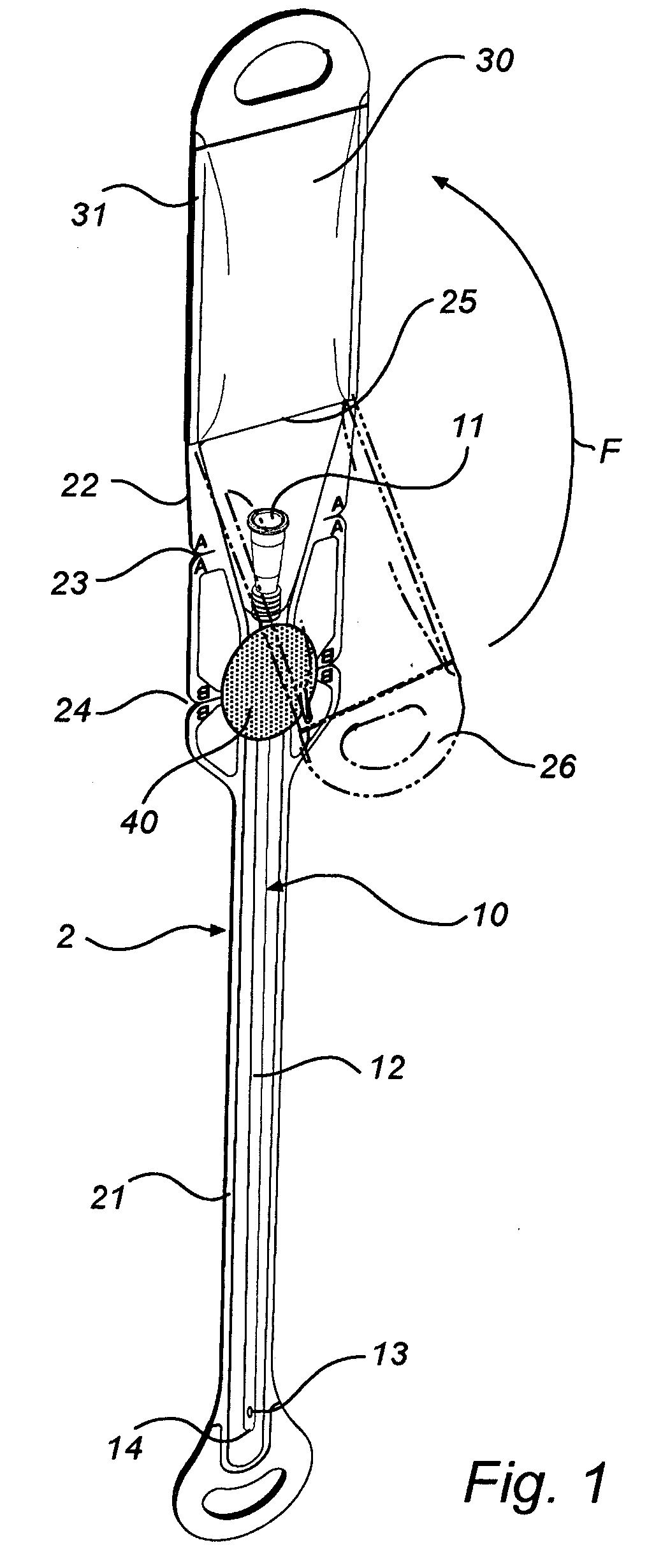
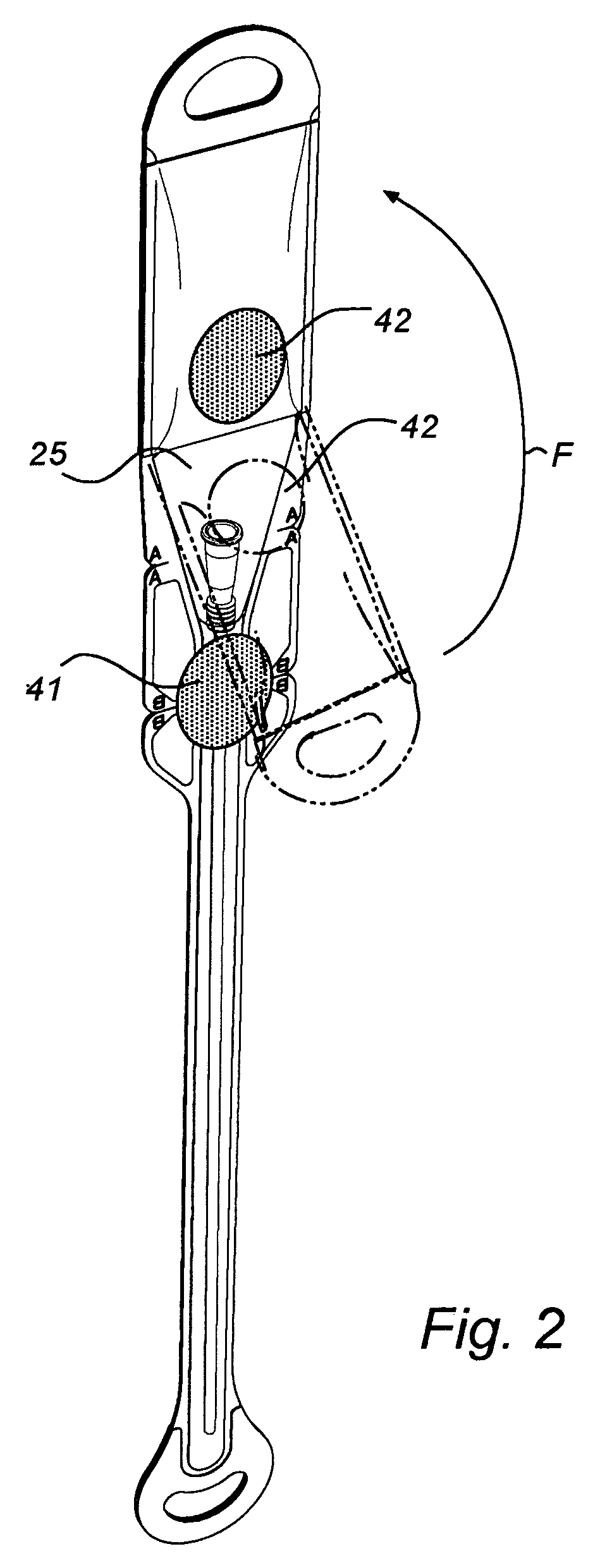
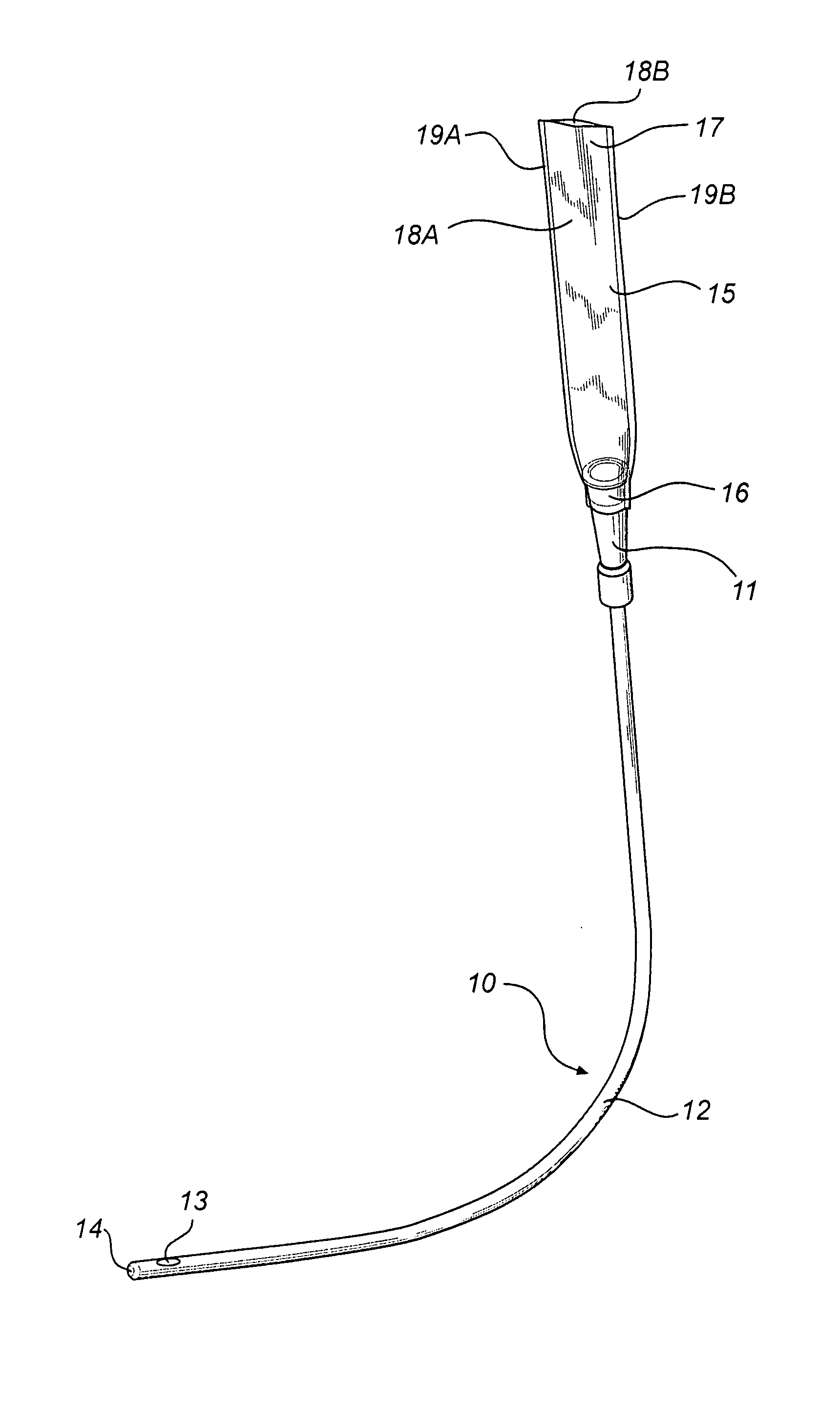
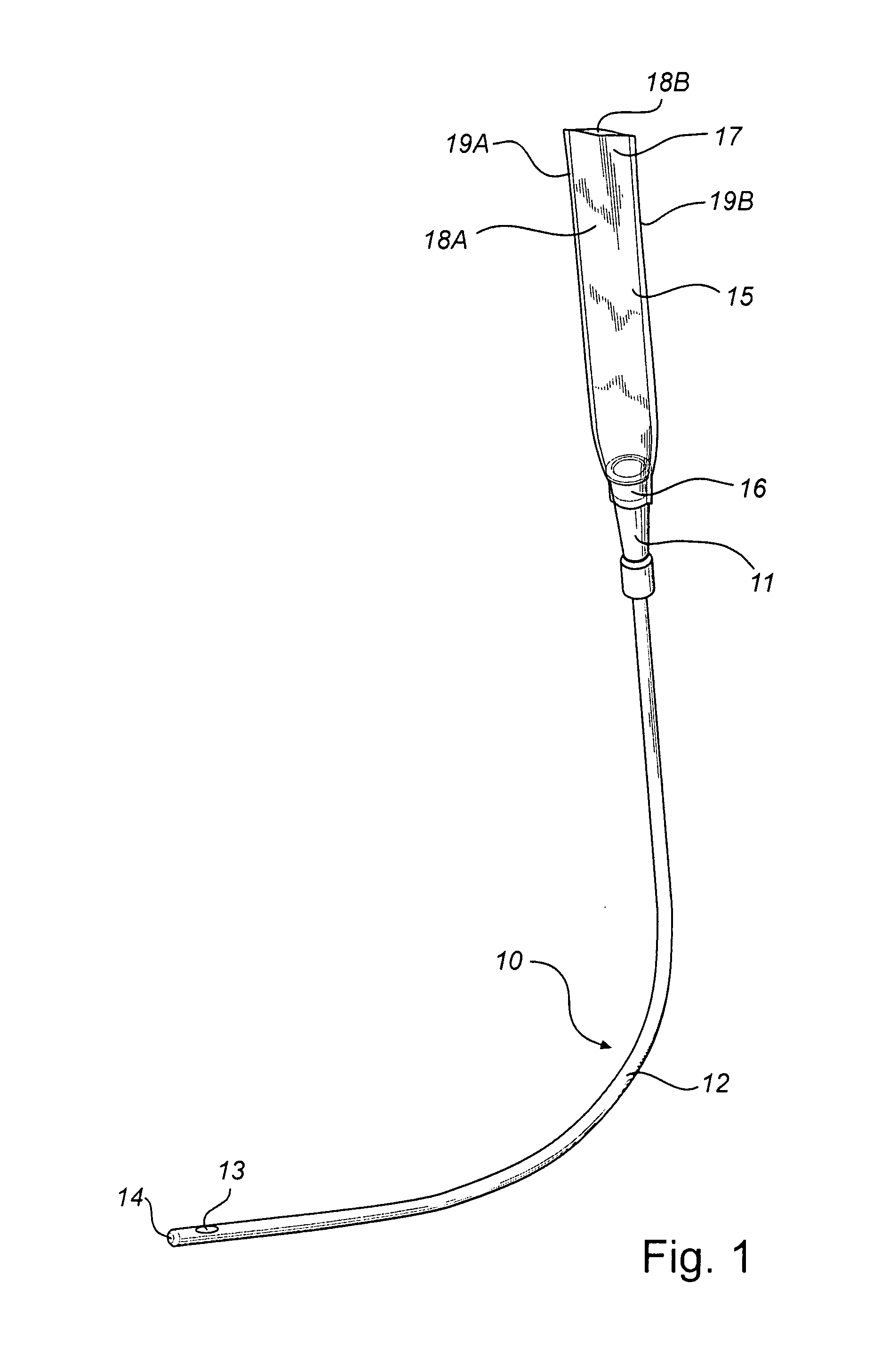
InactiveUS20080051763A1Easy handling and disposalLow-friction surfaceWound drainsCatheterCheck valveUrinary catheter
A catheter and catheter assembly are disclosed comprising a urinary catheter comprising an insertion end, a rearward end, and a one way check valve arrangement. The check valve arrangement comprises a tubular part of a flexible material, connected to the rearward end of the catheter and extending past the rearward end in a direction opposite to the insertion end, thereby substantially limiting the flow through the catheter to a single direction from the insertion end to the rearward end. Hereby, a very effective anti-reflux function is achieved, and at the same time the construction is relatively simple and inexpensive, and does not require any essential modifications of the other parts of the urinary catheter.
Owner:ASTRA TECH SE
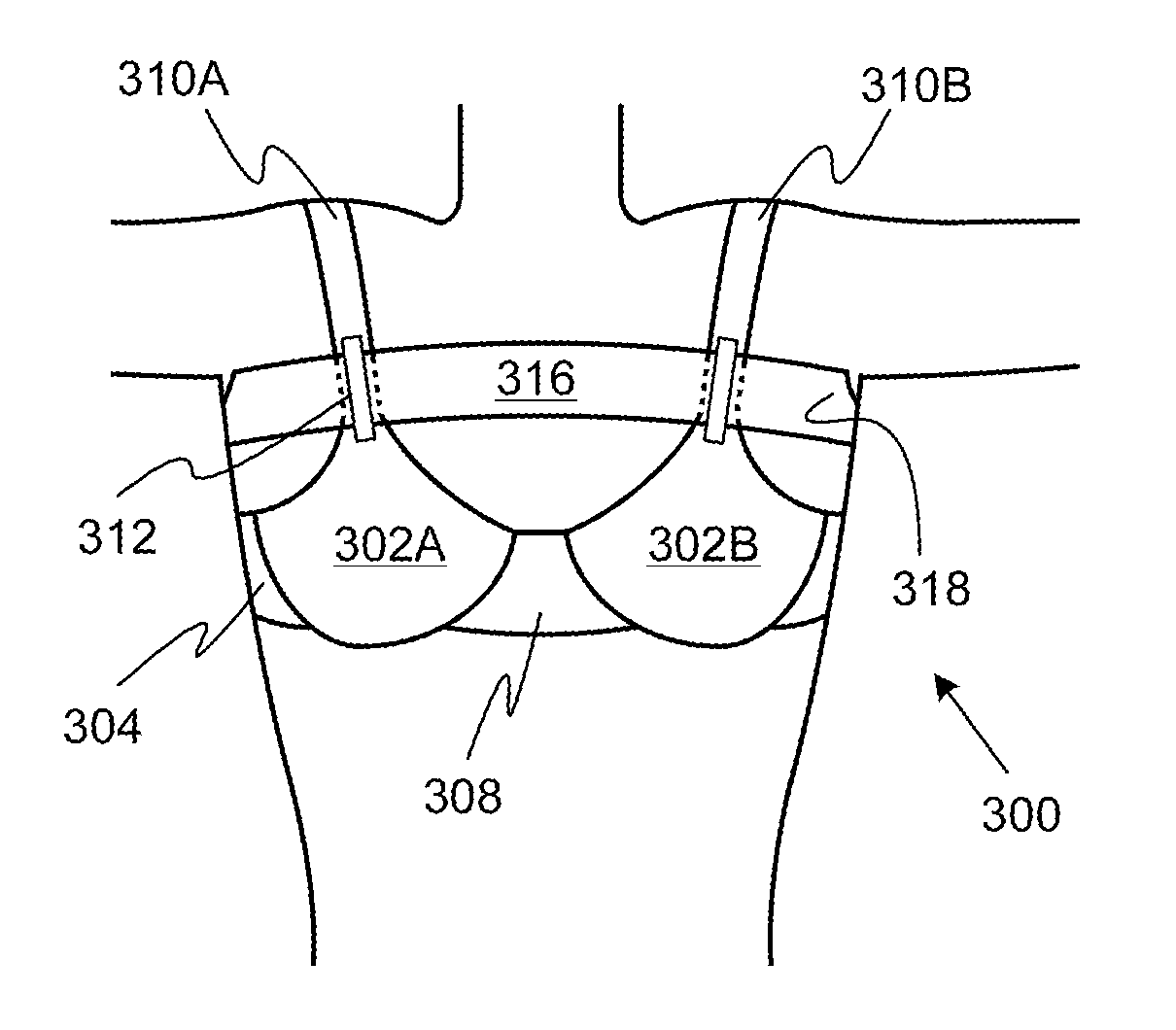
Mammography brassiere
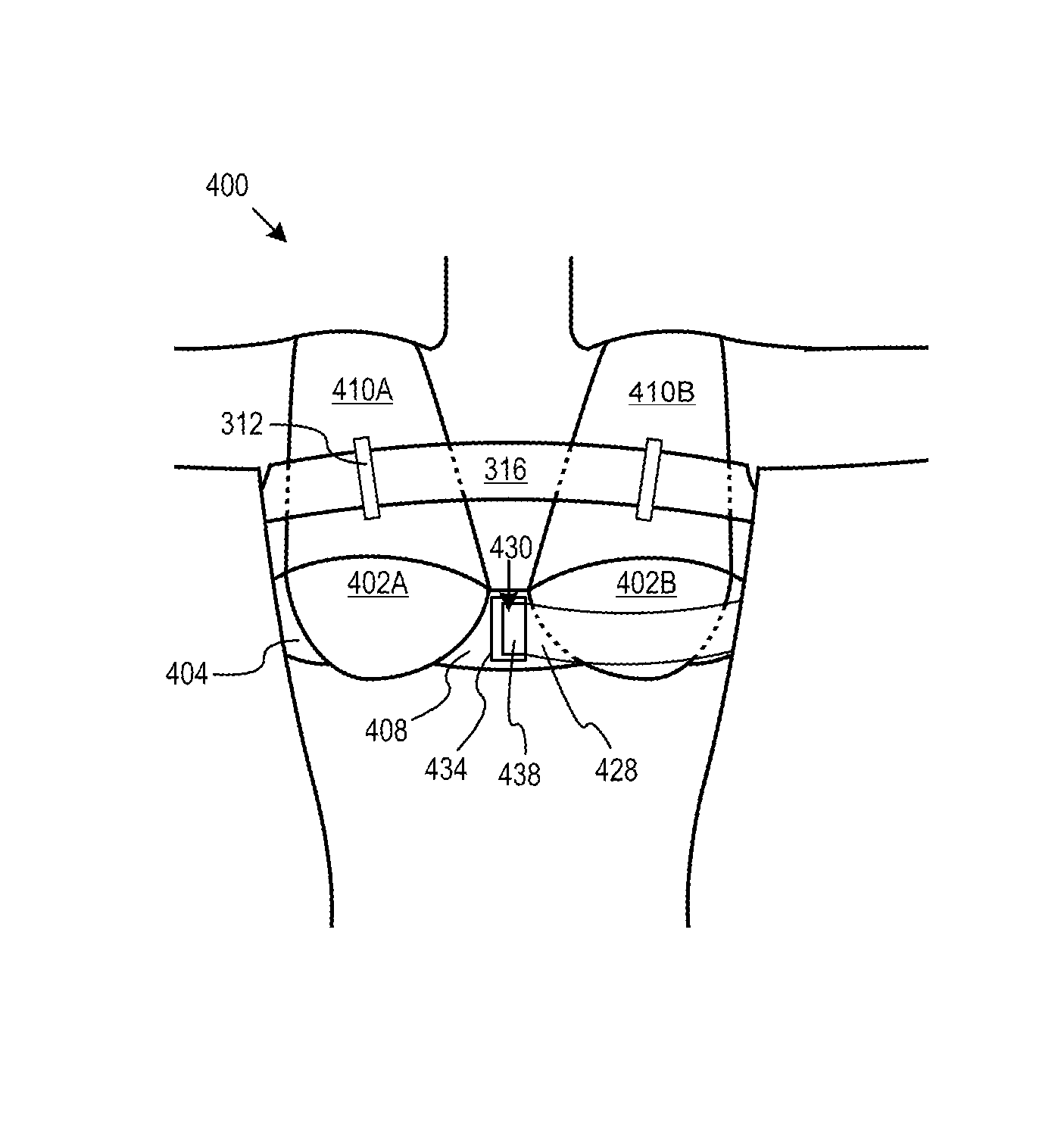
ActiveUS20130316616A1Relieve painReduce feelingsShoulder strapBrassieresEngineeringMechanical engineering
A brassiere that can be worn during a mammogram is devoid of metal and has stretch cups. The brassiere permits a woman to remain at least partially clothed above the waist during a mammogram. In various embodiments, the brassiere includes one or more additional features, in any combination, including a compression band, wide shoulder straps, a bra band, and releasable breast cups. Some of the additional features are expected to reduce the pain experienced by some patients undergoing a mammography.
Owner:THOMPSON ELIZABETH CHABNER
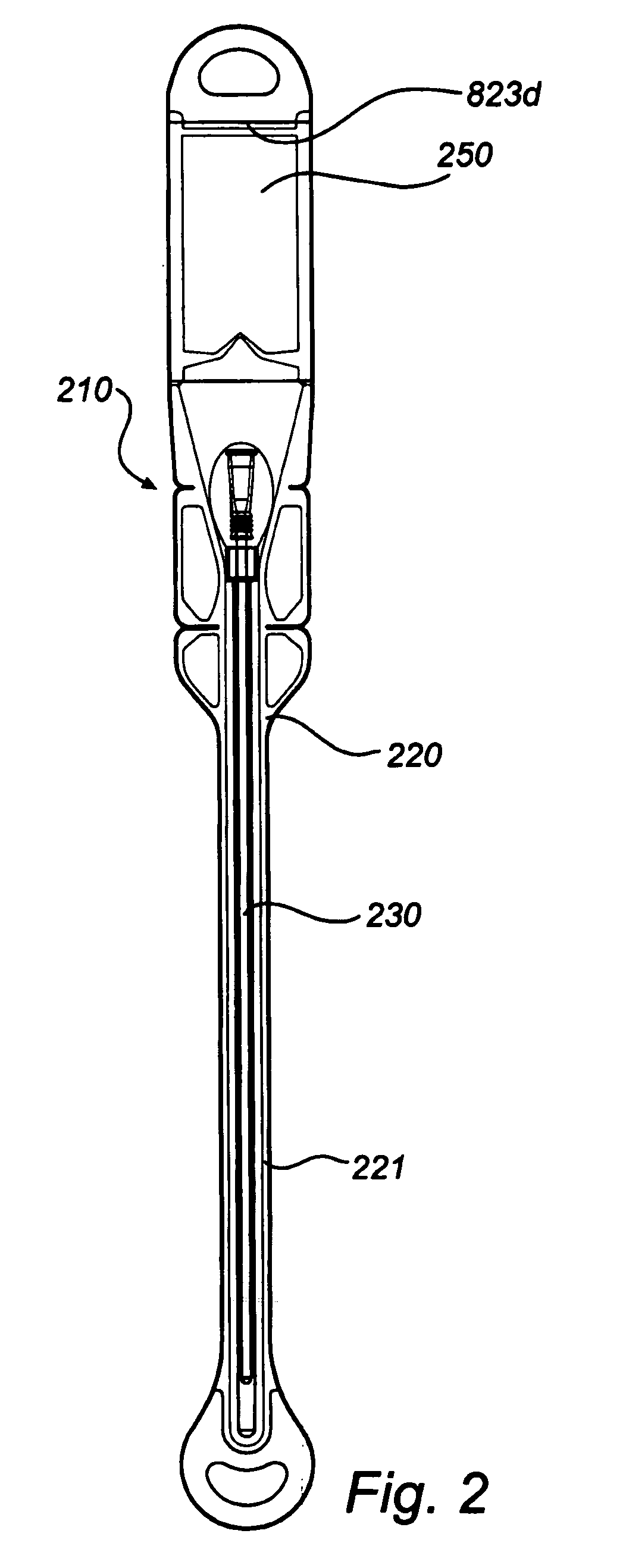
Urinary catheter with one way check valve
A catheter and catheter assembly are disclosed comprising a urinary catheter comprising an insertion end, a rearward end, and a one way check valve arrangement. The check valve arrangement comprises a tubular part of a flexible material, connected to the rearward end of the catheter and extending past the rearward end in a direction opposite to the insertion end, thereby substantially limiting the flow through the catheter to a single direction from the insertion end to the rearward end. Hereby, a very effective anti-reflux function is achieved, and at the same time the construction is relatively simple and inexpensive, and does not require any essential modifications of the other parts of the urinary catheter.
Owner:ASTRA TECH SE
Airflow boosting assembly for a forced air circulation and delivery system
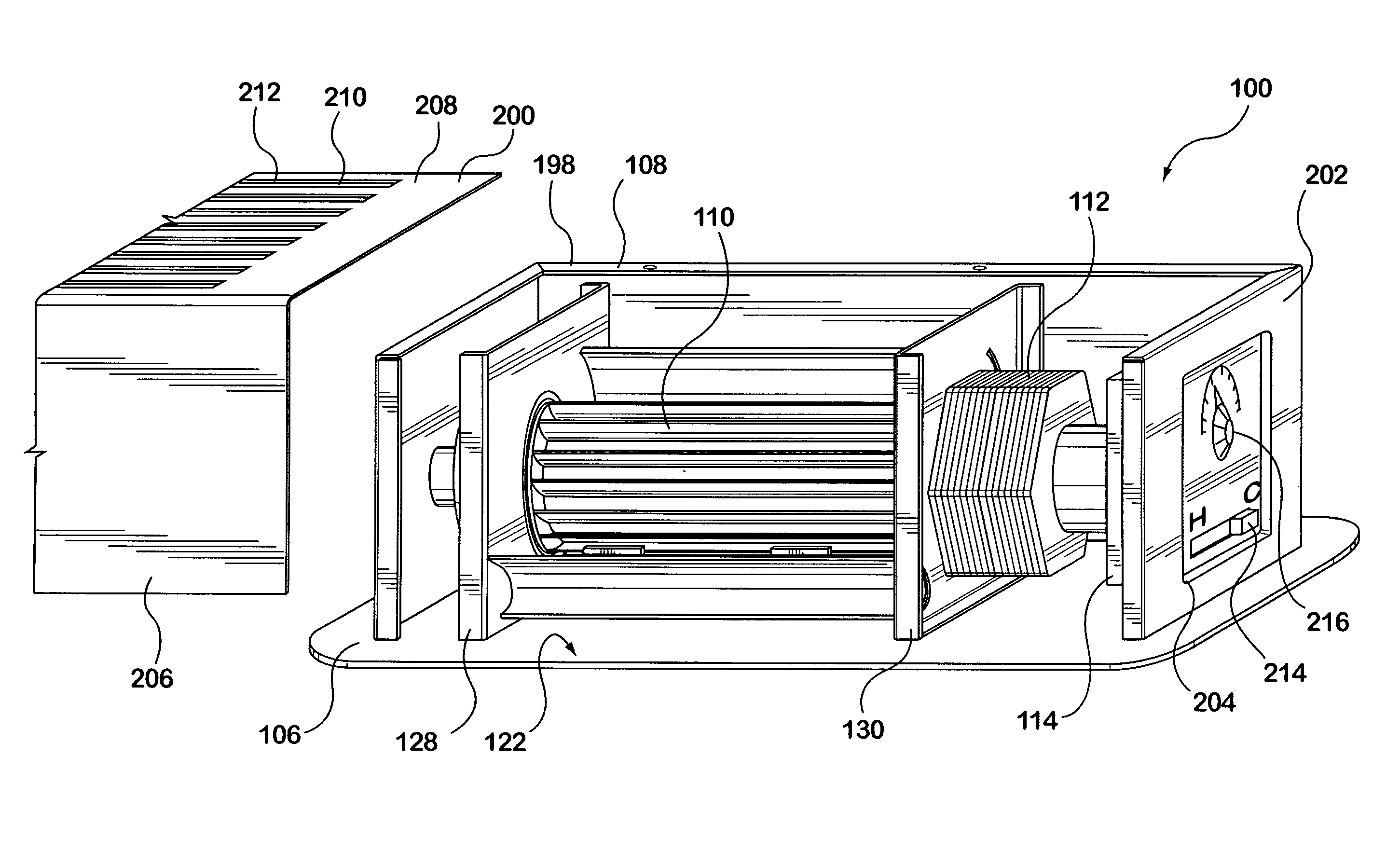
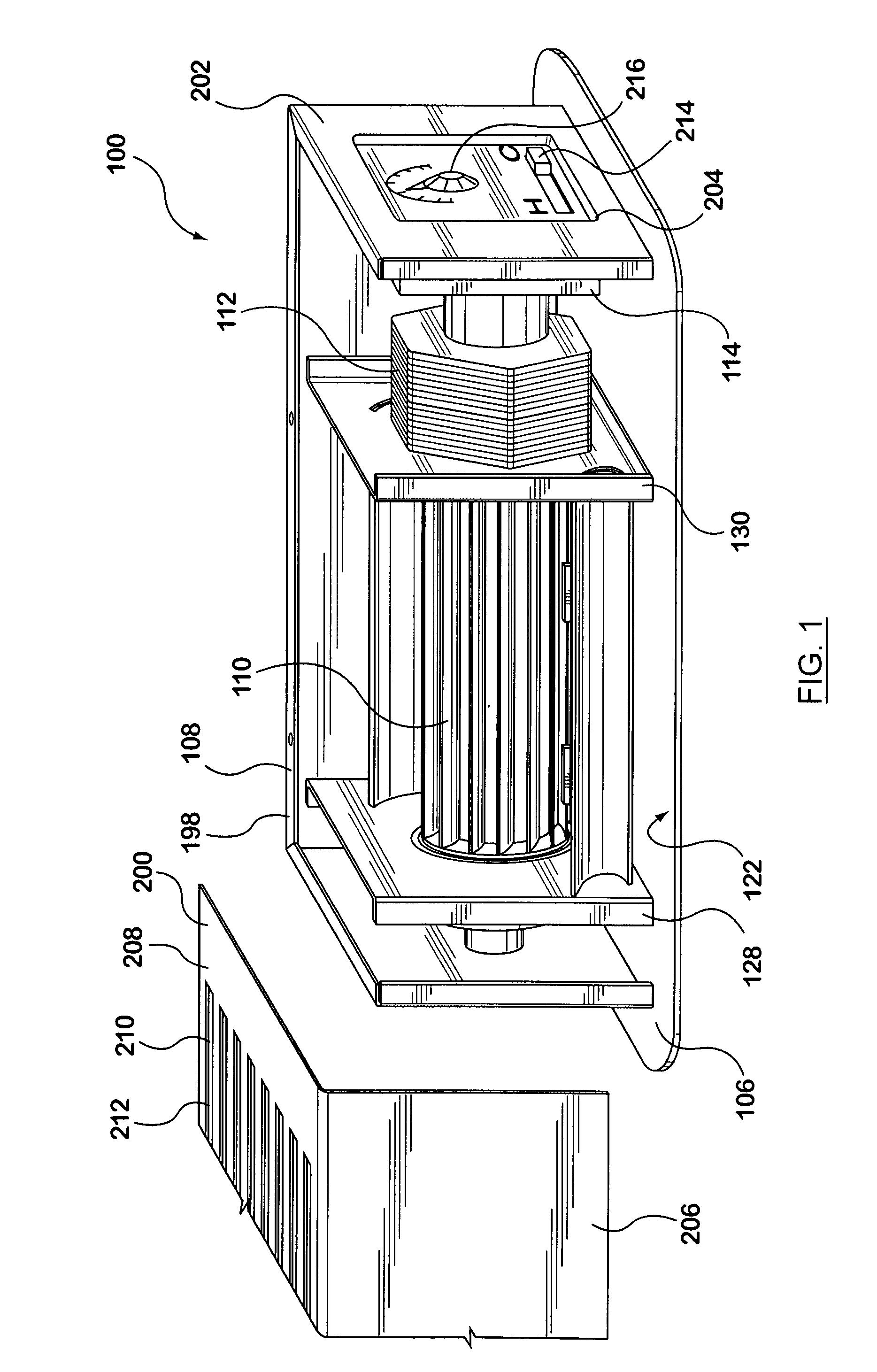
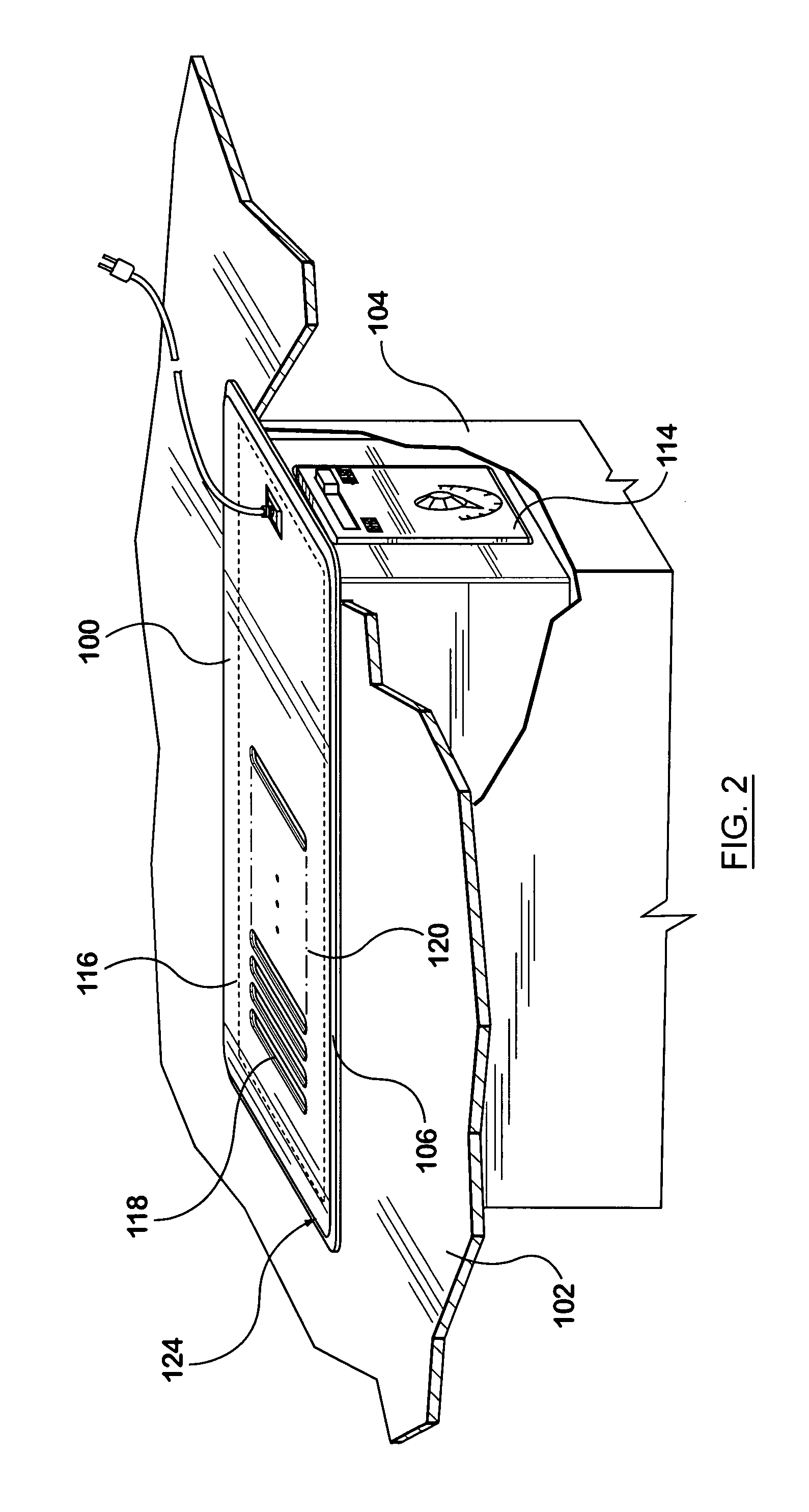
InactiveUS20100015905A1Low friction surfaceDucting arrangementsYielding couplingForced inductionAirflow
The invention relates generally to the field of airflow boosting devices. In particular, the invention relates to a booster fan for installation into a vent opening of a duct system in a forced air circulation and delivery system. In an embodiment, the booster fan includes a register plate for covering a vent opening. An opening or openings on the register plate provide an air outlet. A housing is secured to the register plate for enclosing a crossflow fan therein. The crossflow fan is disposed adjacent and spaced from the register plate and resiliently supported at both ends. A motor is resiliently connected to the crossflow fan. The housing also has an aperture for providing an air inlet communicating with the duct system. Preferably, two arcuate air deflection panels are provided in the housing for connecting the air inlet and air outlet to form a guided air passageway.
Owner:NORTH AMERICA RANGE HOODS
Mammography brassiere
A brassiere that can be worn during a mammogram is devoid of metal and has stretch cups. The brassiere permits a woman to remain at least partially clothed above the waist during a mammogram. In various embodiments, the brassiere includes one or more additional features, in any combination, including a compression band, wide shoulder straps, a bra band, and releasable breast cups. Some of the additional features are expected to reduce the pain experienced by some patients undergoing a mammography.
Owner:THOMPSON ELIZABETH CHABNER
Dropped deck center beam rail road car with shallow center sill
A center beam rail road car has a center sill that runs along the car from end to end. The center sill is dog-legged, having end portions mounted over rail car trucks, and a downwardly stepped central portion between the trucks. A central beam assembly stands upwardly of the center sill. A lading supporting deck structure extends laterally to either side of the center sill. The deck structure has a depressed medial portion between the trucks, and raised end portions over the trucks. The deck portions have lading bearing interfaces. The medial portion of the center sill has a top flange that is carried at a height that lies flush with, or below, the level of the lading bearing interface of the medial portion of the center sill. In one embodiment, a column member for carrying buff and draft loads is spaced upwardly from the medial portion of the center sill. The car may be constructed in a version having a top truss, or having a top chord member that lies within the profile of vertical posts of the central beam assembly. In embodiments having a narrow top chord, the car may be provided with a top chord cover.
Owner:NATIONAL STEEL CAR
Automobile Wheel Changing Tool
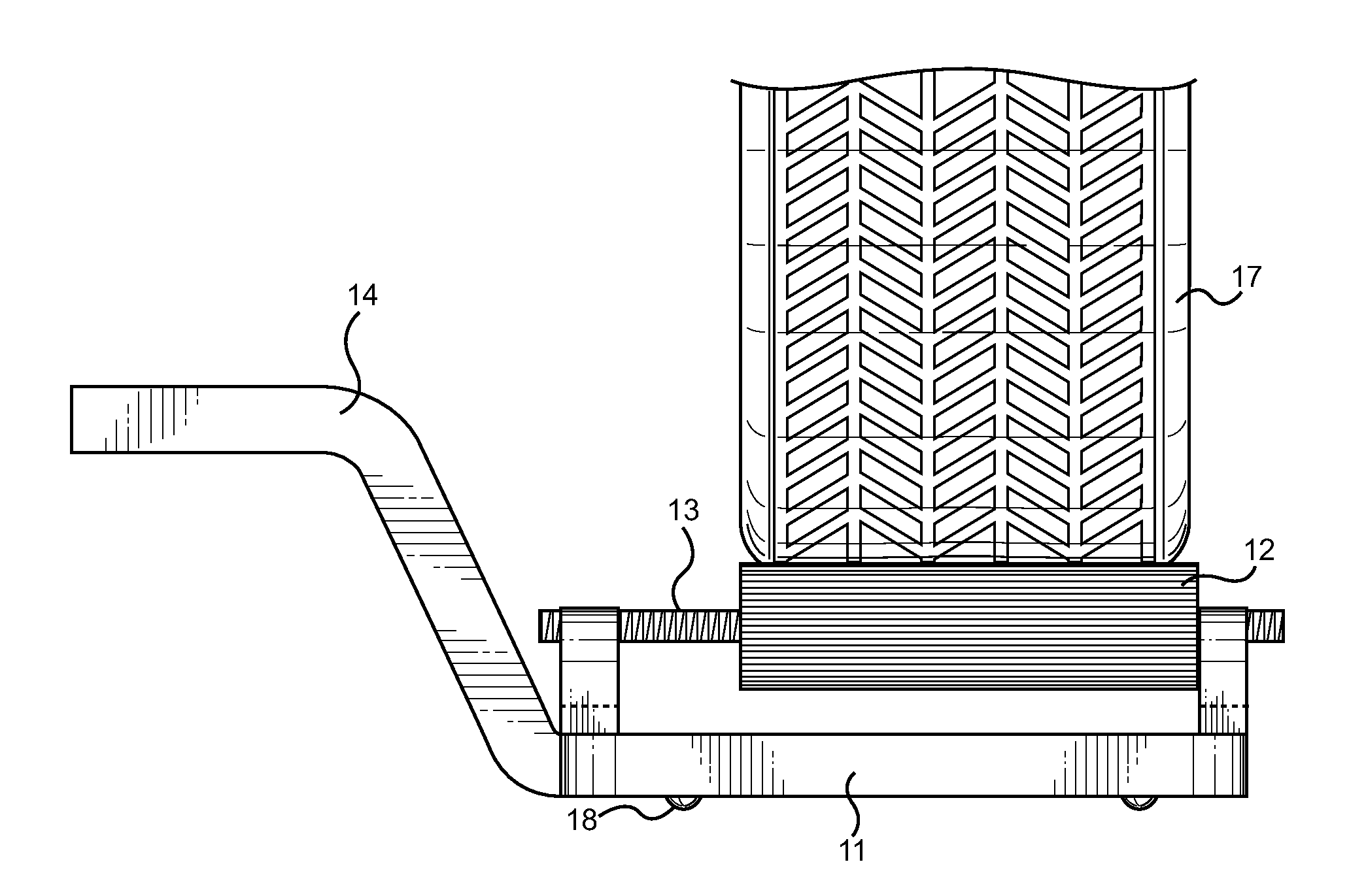
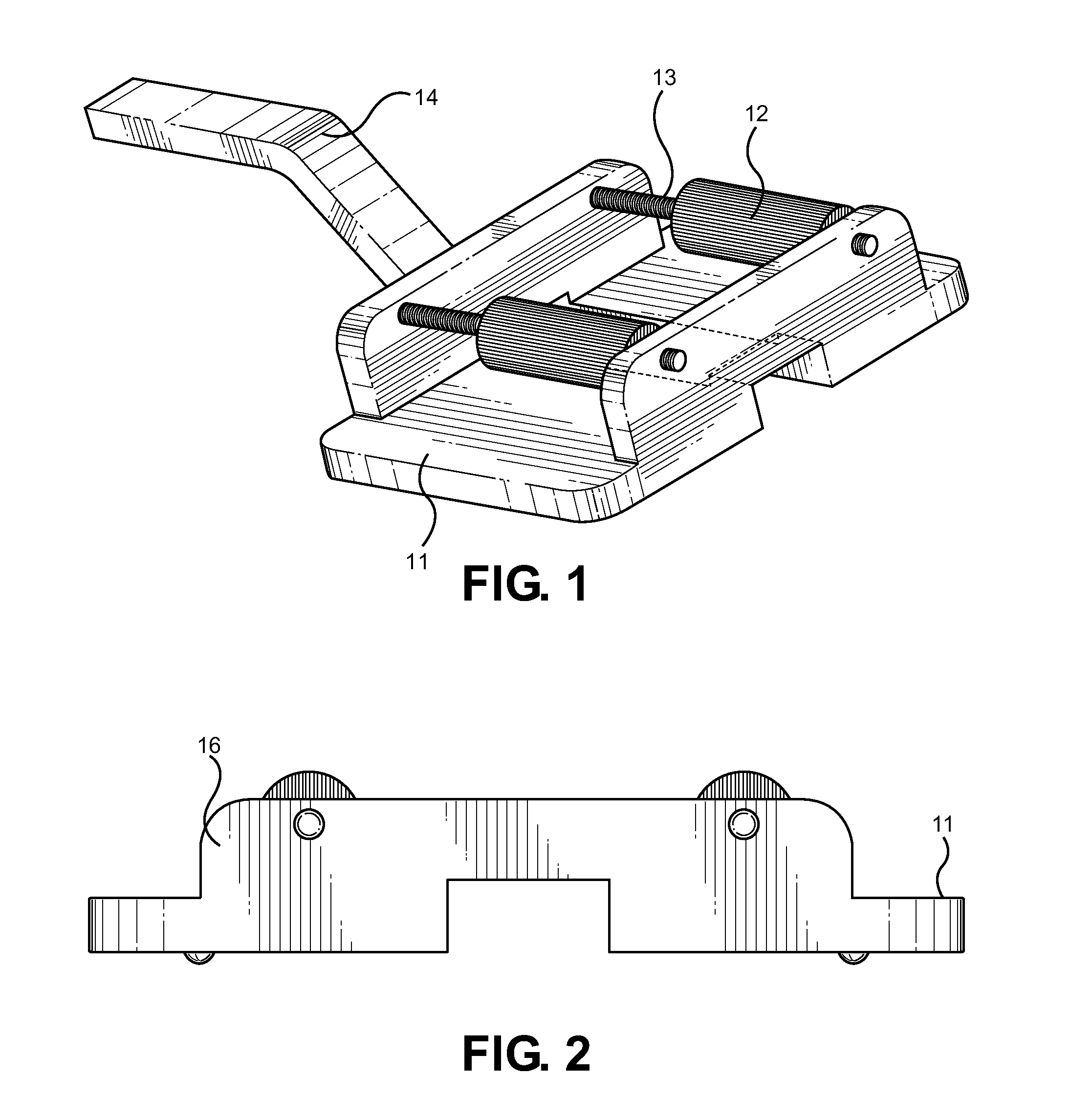
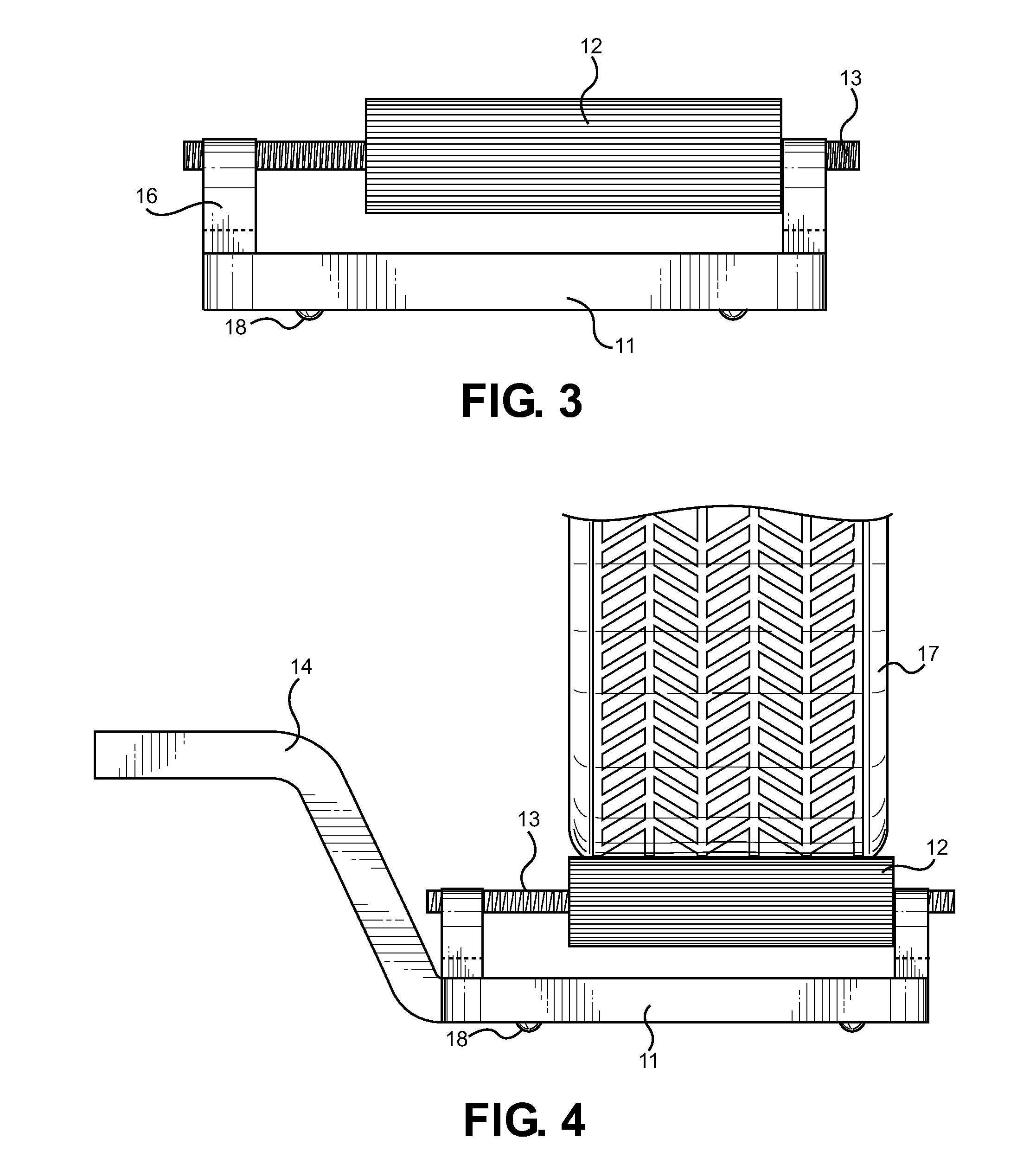
InactiveUS20120224940A1Help positioningImprove balanceWheel mounting apparatusManual conveyance devicesSlide plateFixed position
An automobile wheel-changing assistant tool, comprising a base member, a plurality of roller rails with rollers mounted thereto. The roller rails are secured to upstanding walls of the base member and have rollers mounted thereon. The rollers rotate freely about the roller rails and may slide therealong. A tunnel cutout is centrally disposed along the bottom surface of the base member such that a lever arm may be inserted under the device. Once inserted, the upper portion of the lever arm may be pushed downward to lift the device and a tire to be installed. A slider plate comprising a low-friction surface allows the assembly to slide freely when it is placed thereon, allowing easy handling of the device and associated wheel. In use, a tire is placed onto the rollers, slid into position near a vehicle wheel well, pressed forward along the rollers and rotated into position for securement.
Owner:ANDREWS DANA
Workbench
ActiveUS20130062823A1Avoid damageLow friction surfaceWork benchesPositioning apparatusEngineeringWorkbench
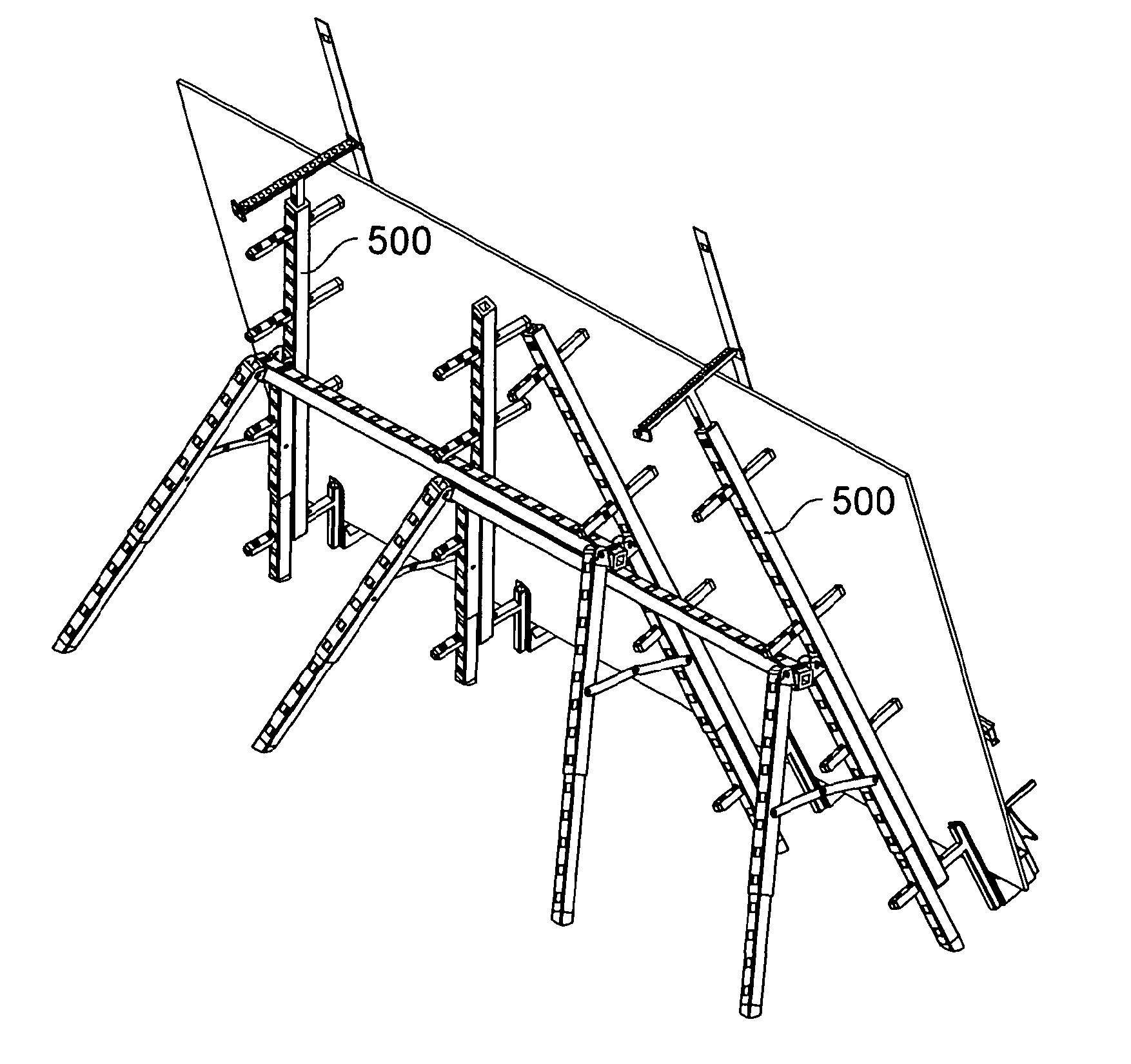
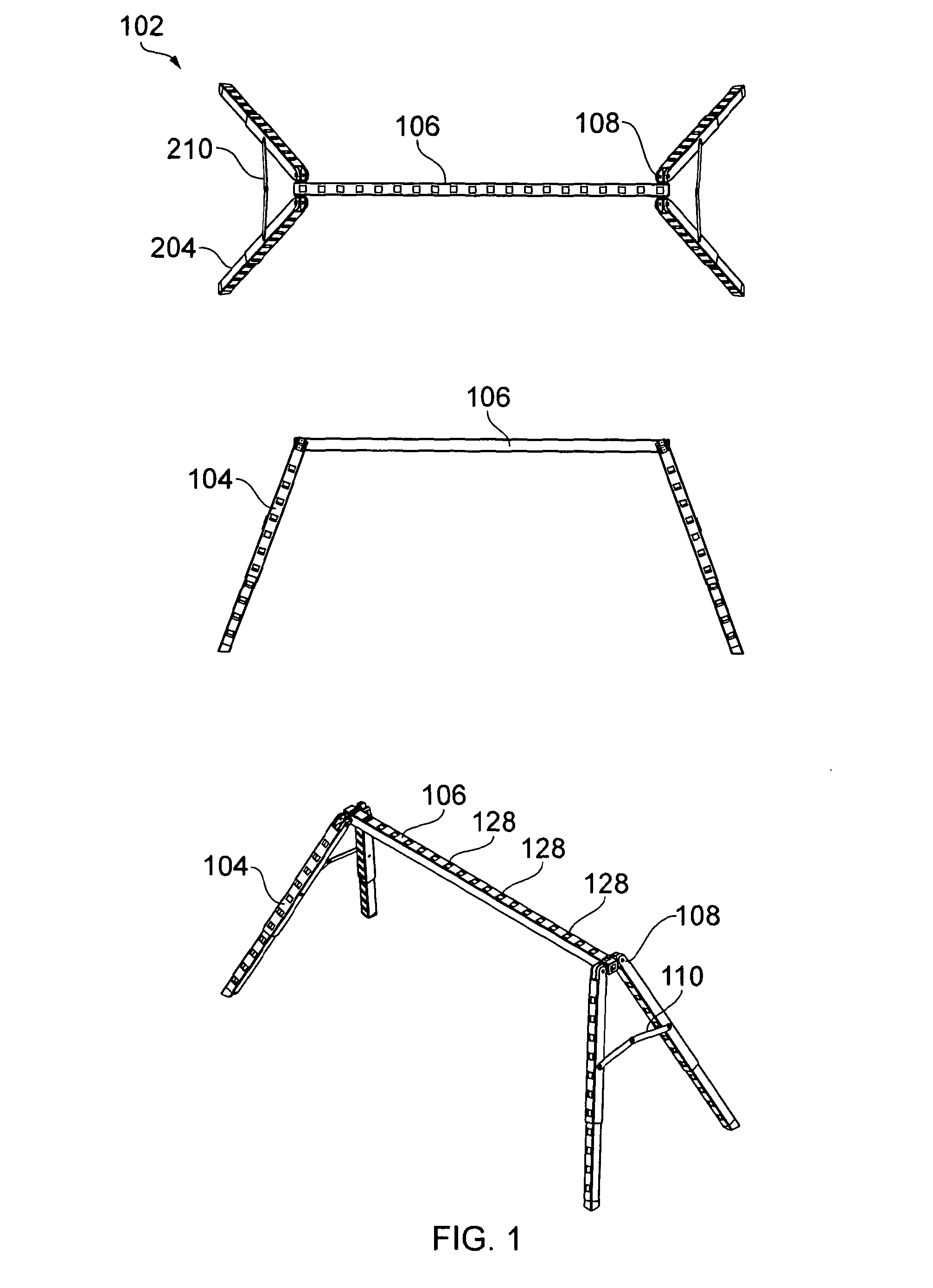
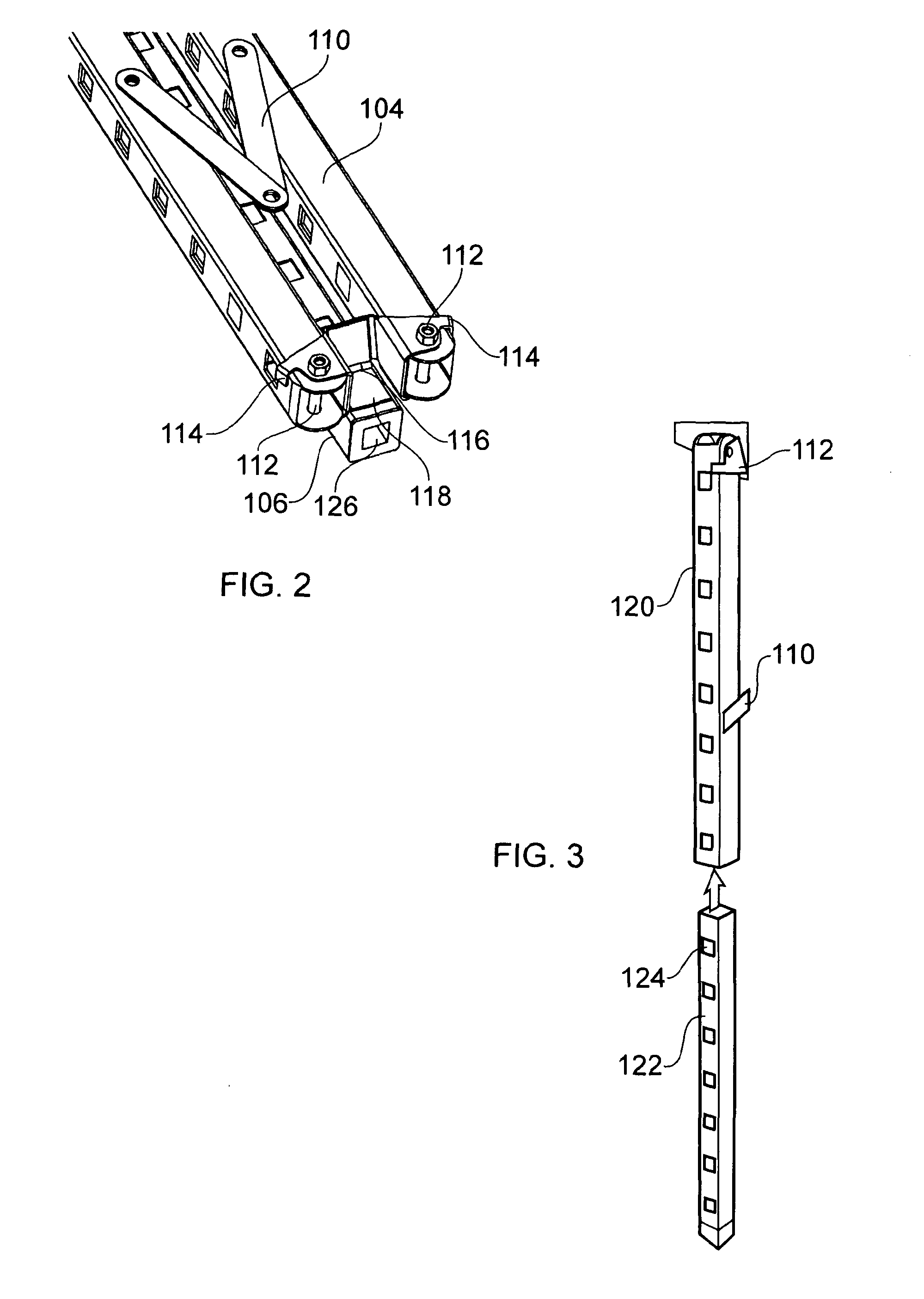
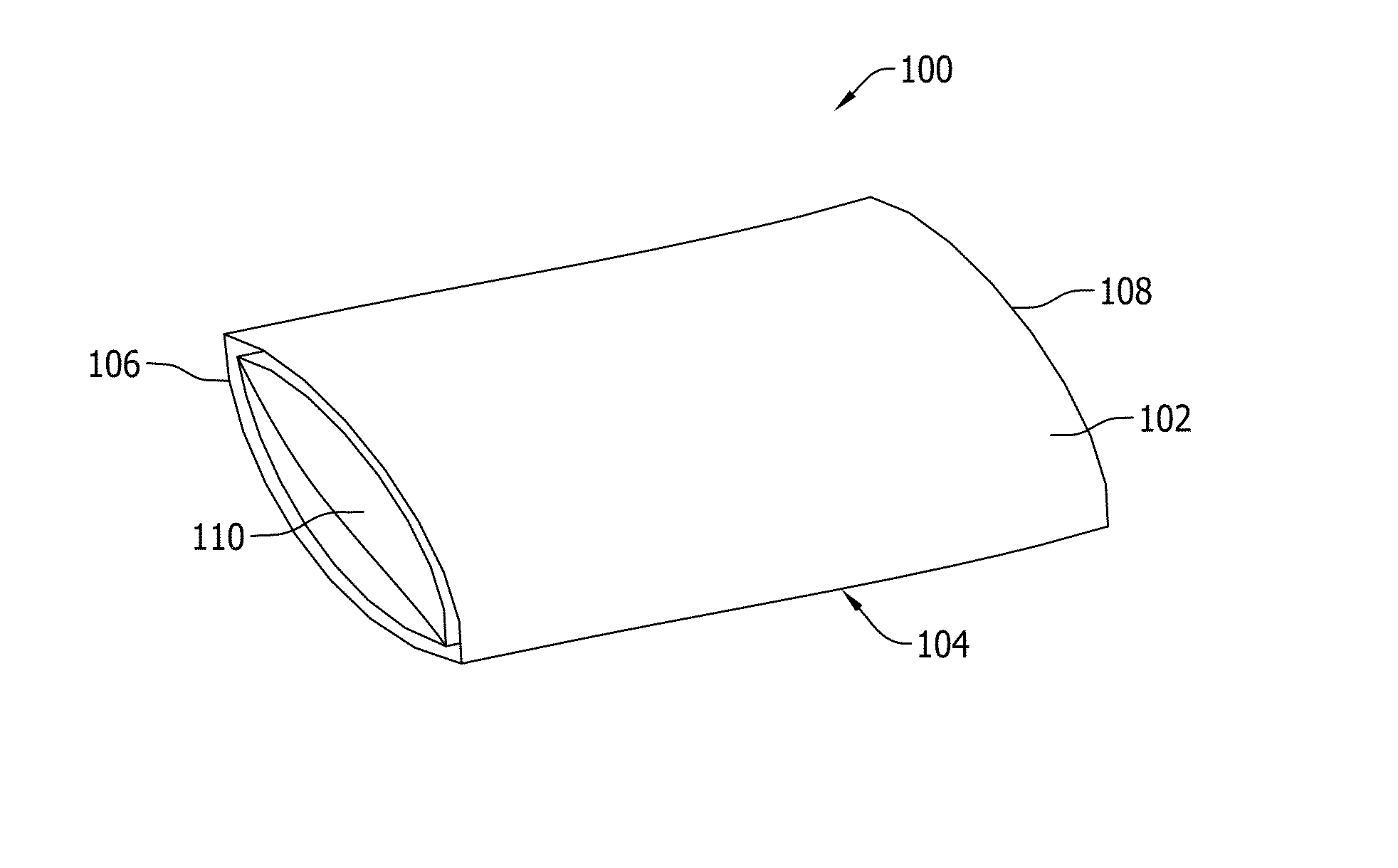
The workbench includes one or more trestle units (102) having pairs of legs (104) joined to each end of a cross-piece (106) by a hinge unit (108) which allows the legs to fold flat against each other and against the cross-piece of the trestle for storage. The hinge has a stop which allows the legs to be positioned away from each other and away from the crosspiece of the trestle to form a stable trestle unit. The workbench further includes a plurality of beams (500), wherein said beams are adapted to be connected to at least one trestle so as to form a supporting framework for a work piece. A folding brace (110) between pairs of legs further stabilises the trestle. The beams and trestles have holes (126) in their ends, and the beams and the trestles have regularly spaced holes (128) in them. Pegs can be inserted into and through the holes, and they have locking parts on them, allowing them to lock onto the trestle or beam. Pegs can have two latches for attachment to different beams or trestles. Trestles and beams may be thus interconnected to form a supporting framework.
Owner:MB INNOVATIONS LTD
Anti-Wrinkle Fabric Arrangement
A fabric arrangement is designed to prevent skin lines, wrinkle formation, or other skin damage while improving sleep using combinations of fabrics, cooling technologies and scents. The fabric arrangement is designed with a specific fabric and material combination that create a surface in which the shear stresses causing skin lines, wrinkles, and other skin damage are eliminated. Multiple layers making up the fabric arrangement include a top layer comprising a stretchable material and a second layer comprising a low friction material relative to the top layer. Supporting the first two layer is a support layer such as foam. Lower layers may comprise a cooling material, an antimicrobial or anti-allergenic material and a scent layer.
Owner:BATISTE STAN +1
Catheter assembly with bactericidal effect
InactiveUS8747882B2Reduce decreaseSimple procedureBiocidePharmaceutical containersOrganic acidHydrophilic coating
A use in a medical device of at least one salt of organic acid(s), and preferably a benzoate or a sorbate, as an antimicrobial agent is disclosed, and in particular for the manufacturing of an antimicrobial coating for a medical device, e.g., hydrophyllic urinary catheters, for the prevention of bacterial infection. The pH of the hydrophilic coating may be controlled to be in the range 4.0-8.0, preferably in the range 5.0-6.0, and preferably to be below 7.0. The pH of the hydrophilic coating could be controlled by means of a pH buffer, and preferably a citrate or phosphate buffer. A salt of organic acid in combination with a pH buffer has proven surprisingly efficient for inhibition of bacterial growth, and for prevention of bacterial infections.
Owner:ASTRA TECH SE
Concealed top track system for sliding doors
InactiveUS20070033874A1Low friction surfaceLarge caliberWing suspension devicesEngineeringTubular formation
A concealing guide track assembly for the top of a pair of sliding doors of a wardrobe having top rails. An elongated top track for mounting on the top wall of the wardrobe has a base wall and spaced channels. First and second elongated guides have a tubular formation along one side edge thereof slidably seated in one of the U-shaped portions of the top track and the other side edge engaged with one of the top rails so as to be slidable therewith. The guides have a bridge portion extending between the side edges, and the second guide bridge portion extends over the bridge portion of the first guide.
Owner:RENIN CORP US
Method for producing polymeric surfaces with low friction
InactiveUS20070256696A1Reduce friction and wearReduce staticDiagnosticsSurgeryPolymeric surfacePlasma deposition
The invention relates to the use of ceramic, plasma-deposited, layers for manufacturing plastic articles whose function requires low-friction surface. The invention further provides a process of manufacturing a polymer object having a low-friction surface, comprising i) providing a mold defining the shape of said object; ii) coating said mold that defines the shape of said low-friction surface with a ceramic layer, the layer being formed by plasma deposition; and iii) molding the polymer in said mold. The invention also provides a polymer article having a low-friction surface created by molding on a plasma-deposited ceramic surface.
Owner:THE STATE OF ISRAEL MINIST OF AGRI & RURAL DEV AGRI RES ORG ARO VOLCANI CENT
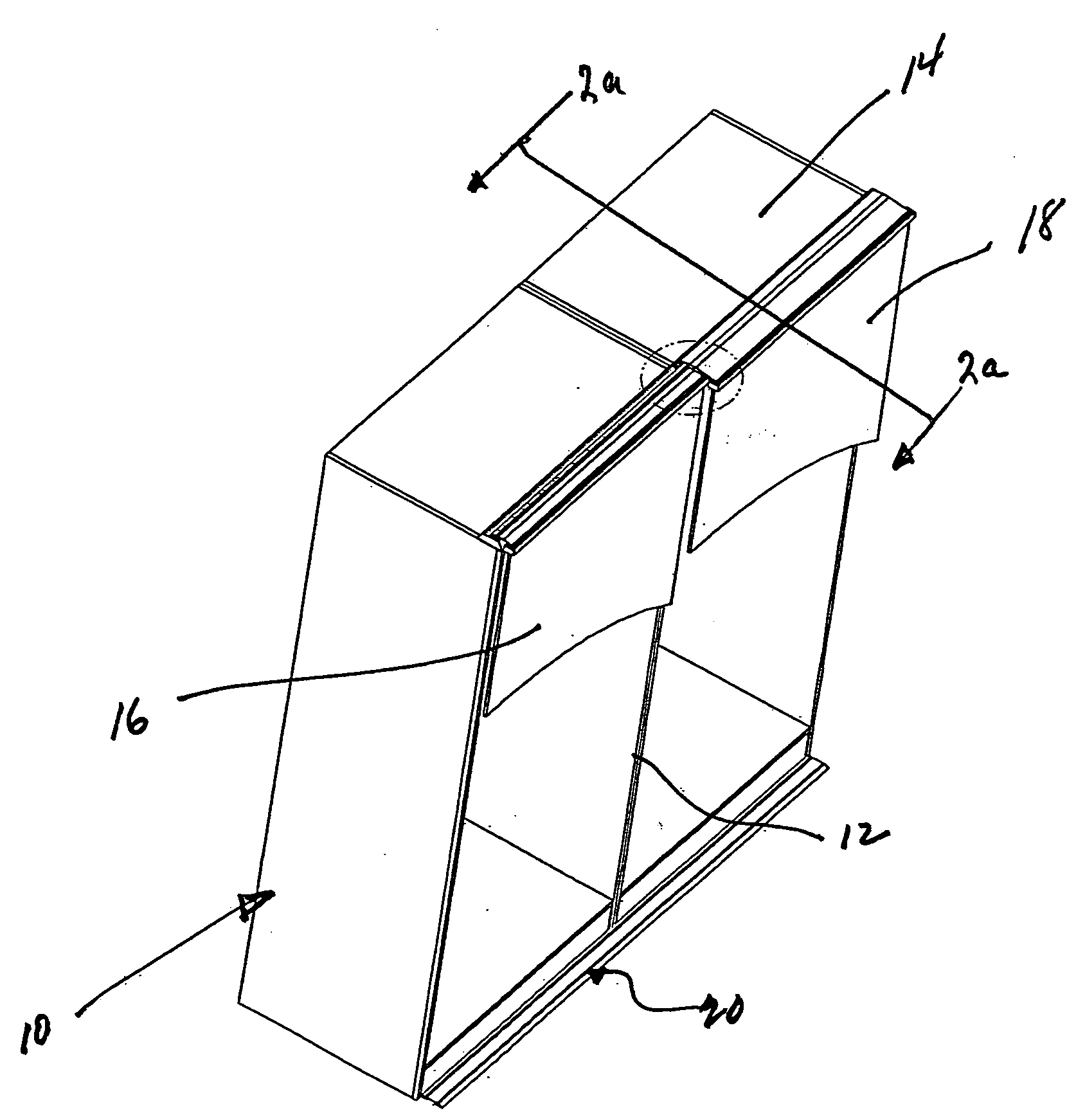
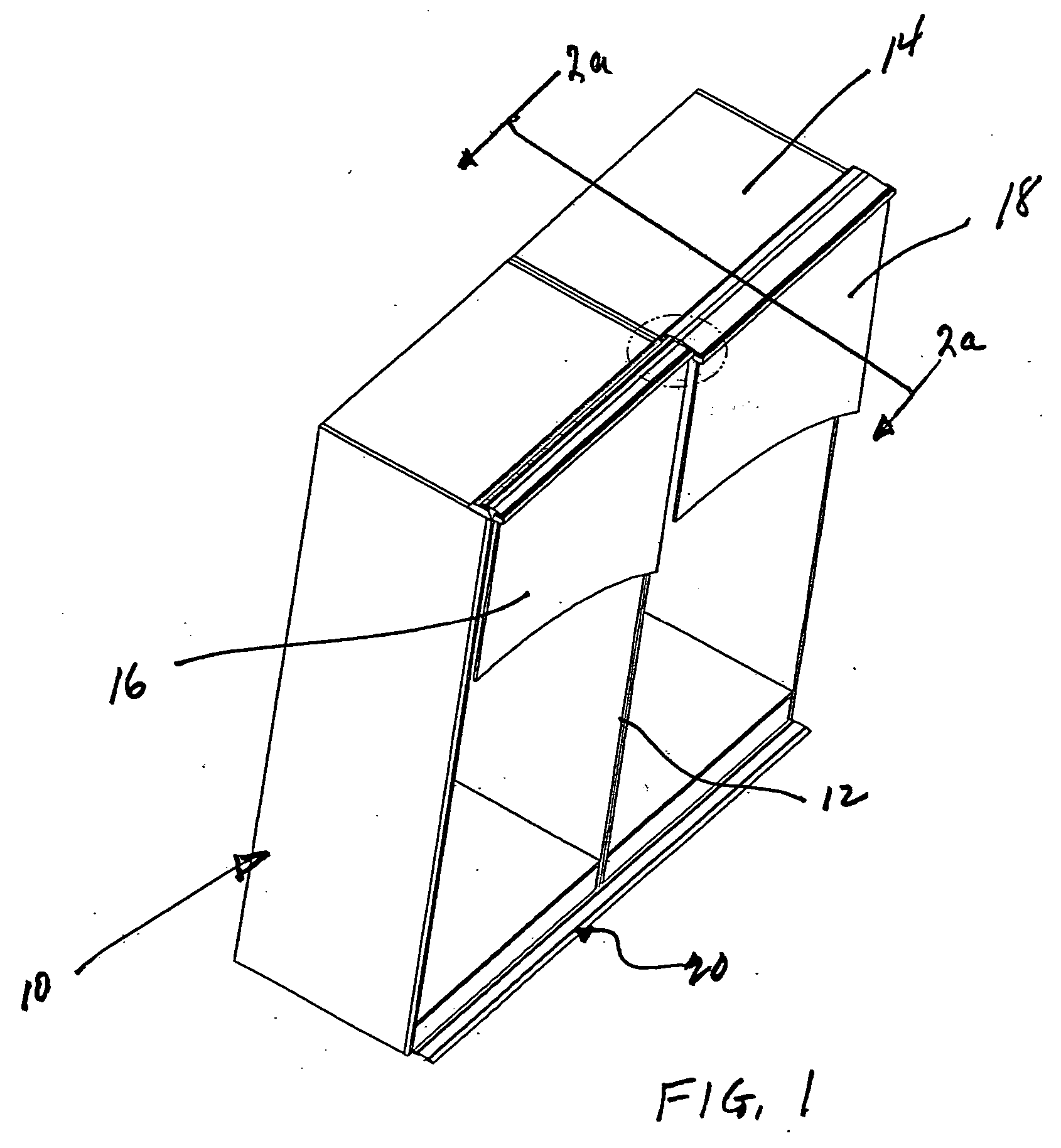
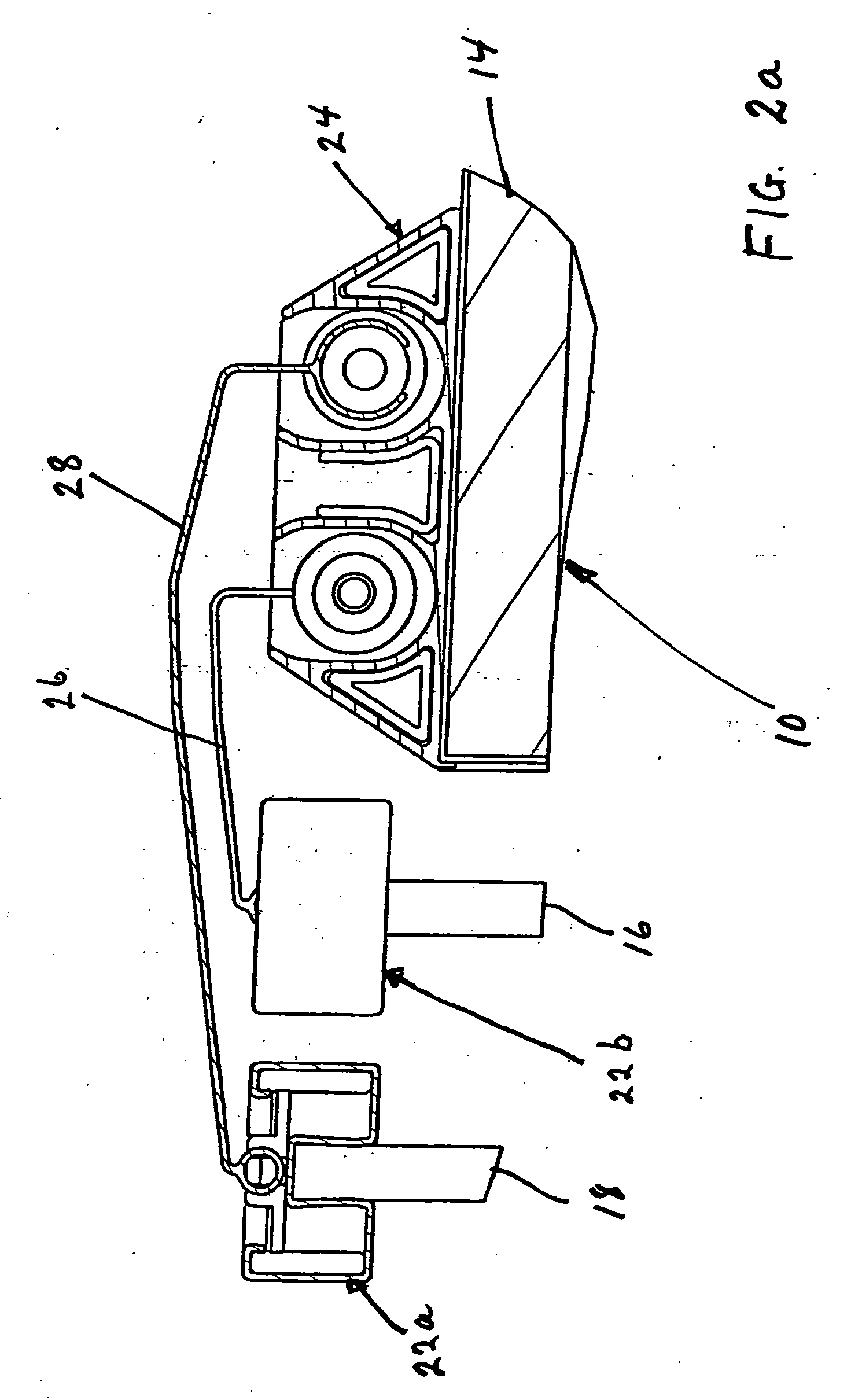
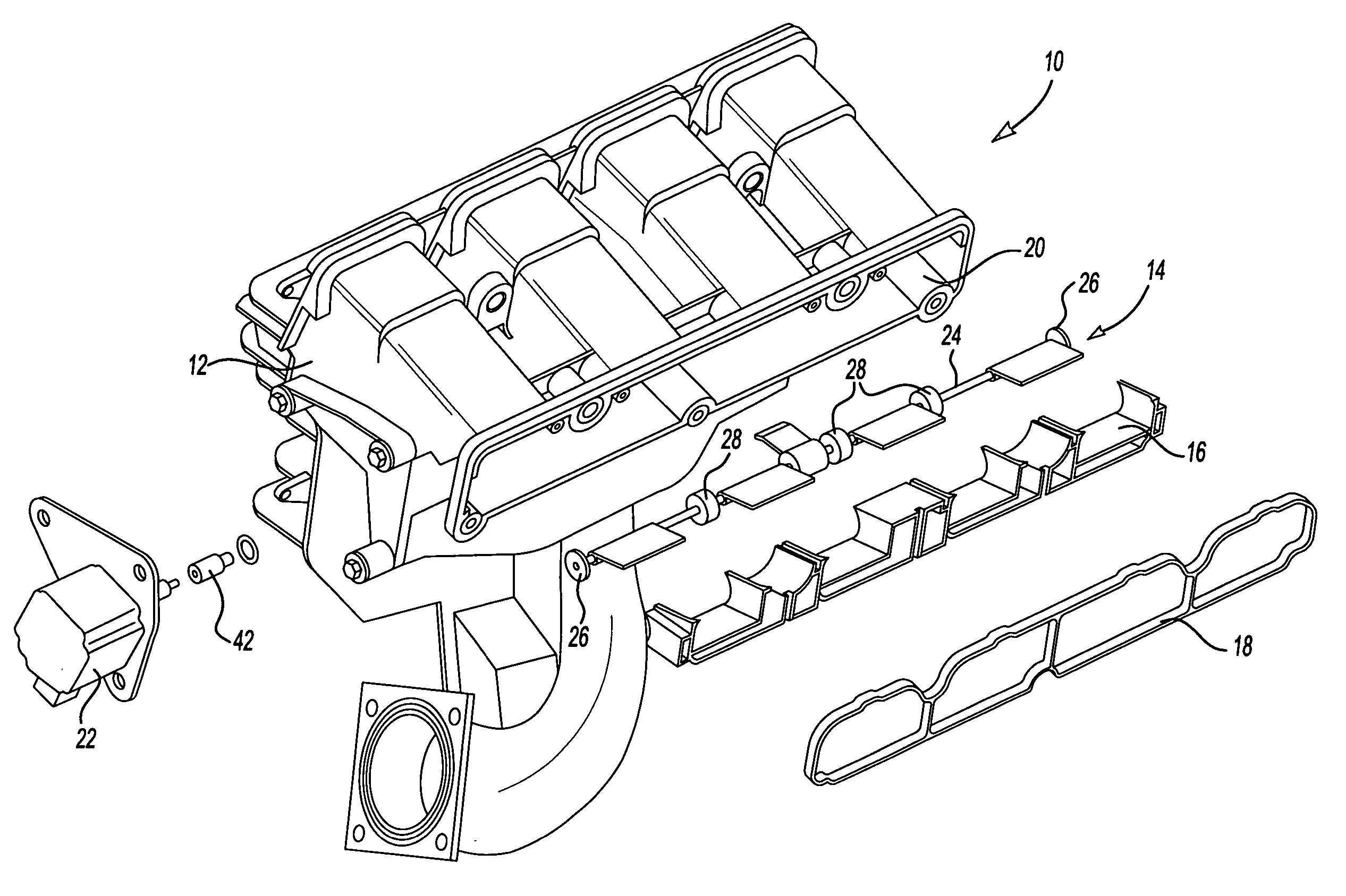
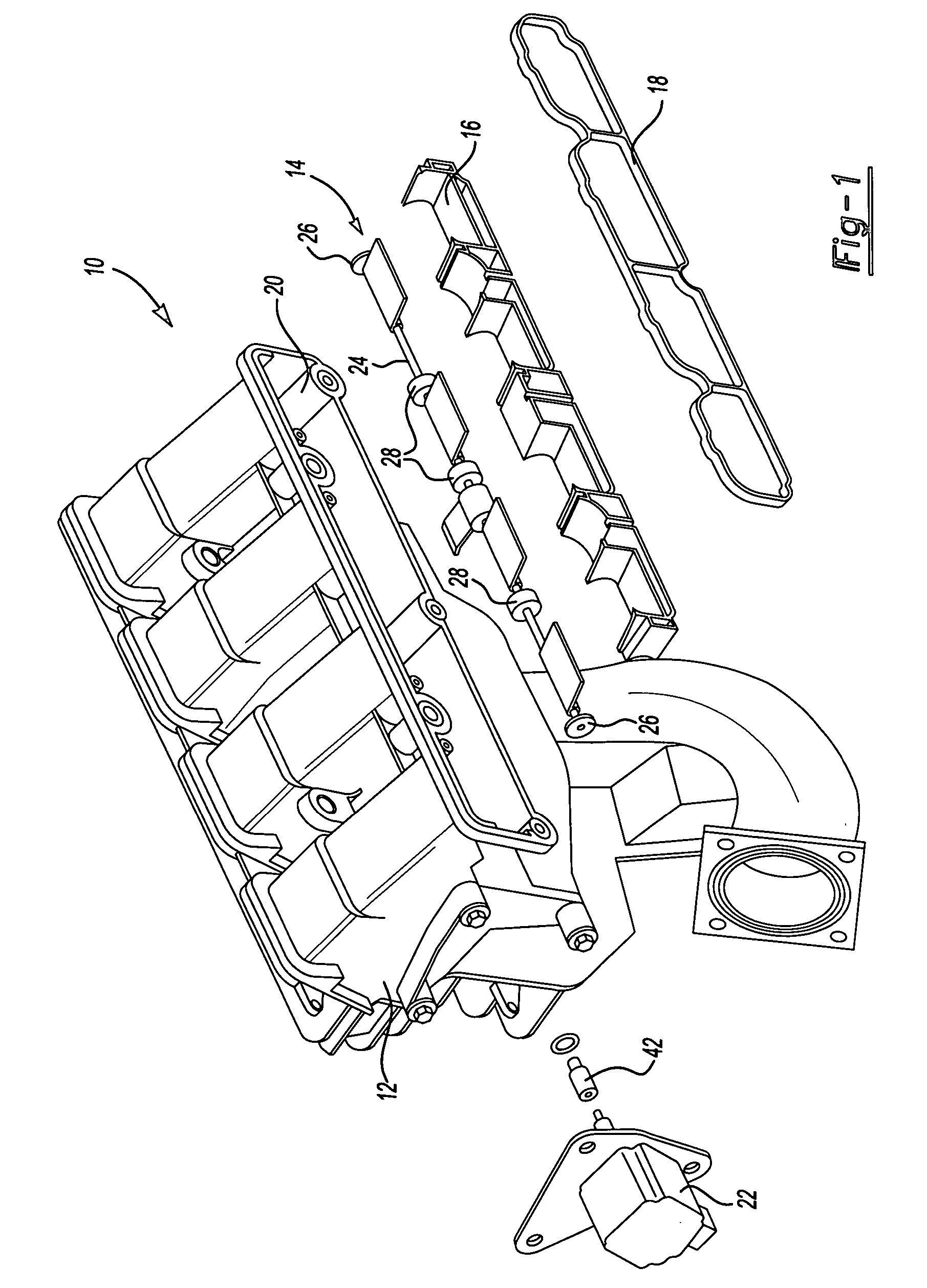
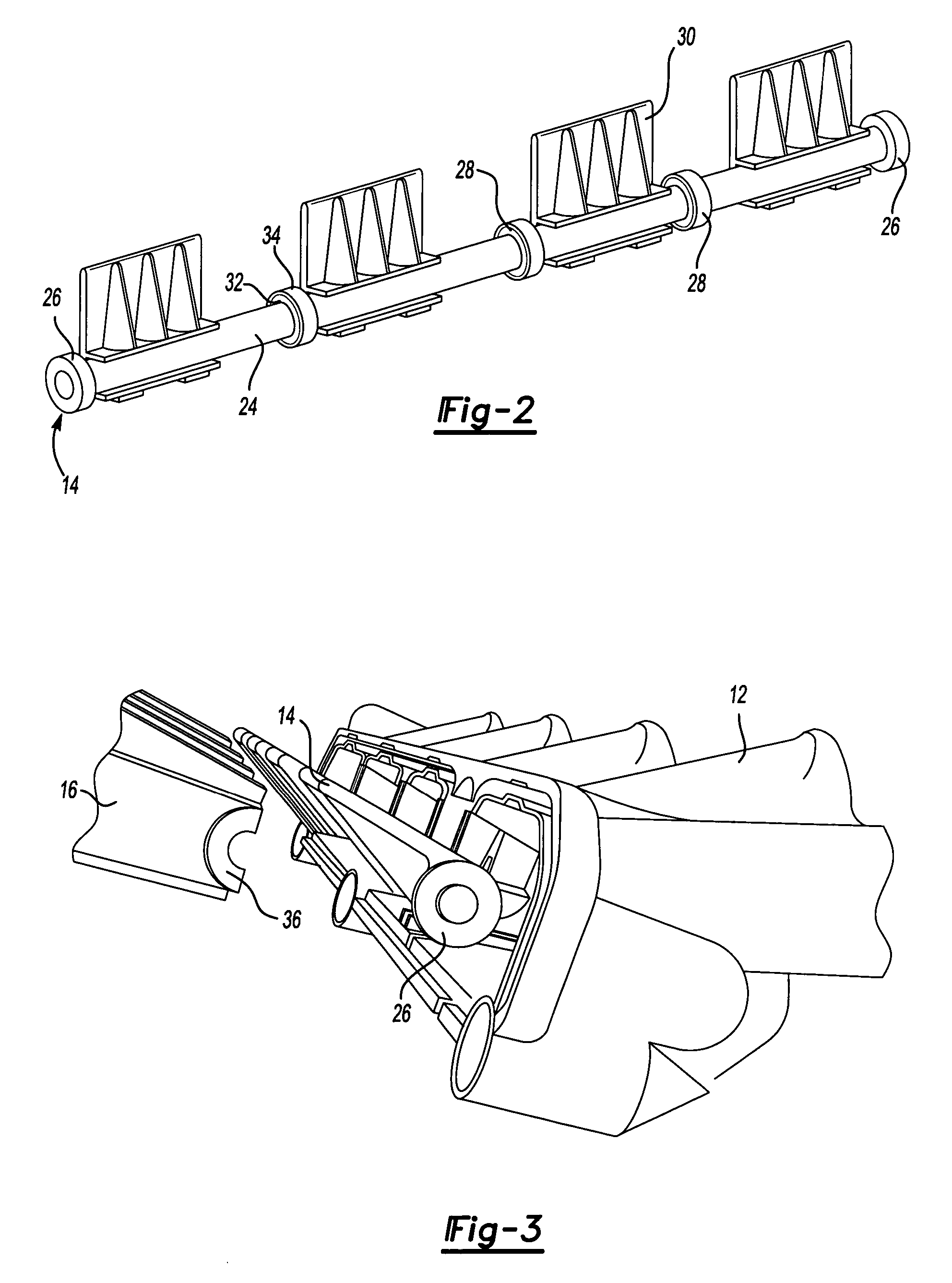
Intake manifold with low chatter shaft system
ActiveUS20070017469A1Reduce frictionPrecise rotationEngine controllersMachines/enginesFree rotationEngineering
An intake manifold assembly includes a housing, a shaft assembly, and an intake insert. The shaft assembly has a metal shaft with bearings located at each end to provide hard mounting surfaces for the shaft assembly when assembled in the housing. The bearings support the shaft within the housing and allow the shaft to freely rotate. Bushings are spaced along the shaft to absorb vibrations and assist is providing a low friction surface for shaft assembly rotation. Journal pockets in the housing and in the intake insert surround the bushings. Isolators located within the journal pockets and housing surround the bushings and assist in dampening vibrations.
Owner:SIEMENS VDO AUTOMOTIVE INC
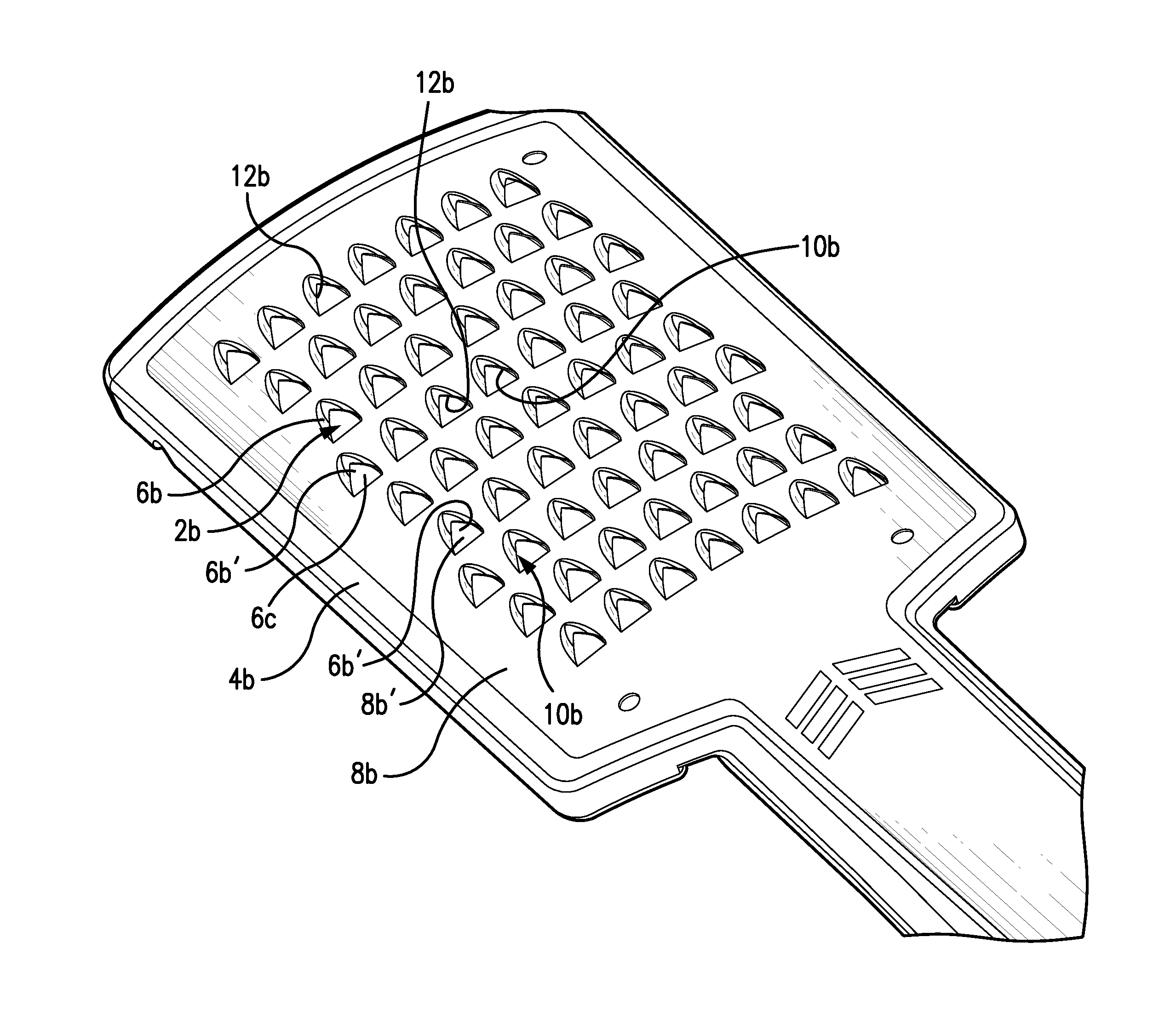
Formed or domed cutting teeth formed by improved double etching process
InactiveUS20140217215A1High strengthLittle strengthKitchen equipmentGrain treatmentsEngineeringFood contact
A device and method for manufacture thereof having a one or more cantilevered cutting teeth integrally formed in raised configuration on a flat base fro cutting food items moved along said base. The free end portion is formed by upper and lower etched out portions of the upper end of said cutting teeth to form a cutting edge. The upper surface of the upper cut-out portion of the teeth is situation at a position out contact with food items being cut. A substantially portion of the teeth is coated with a low friction material, except for the cutting edge In a second embodiment one or more domed cutting elements are cut out of base sheet and may include a leading V-shaped cutting edge.
Owner:SMITH RICHARD S +1
Synthetic resin hose
ActiveCN101484306ALow friction surfaceIncrease stickinessLayered productsFlexible pipesPolymer scienceSynthetic resin
Surface tackiness of a hose is improved without using a partially crosslinked resin. By heat-molding a hose while mixing a plurality of synthetic resins having different molecular weights in the surface of the hose, particles of the synthetic resins having high molecular weights remain in the molten synthetic resins having low molecular weights, thereby forming fisheyes in the hose surface. Fine projections and recesses due to the fisheyes make the hose surface into a low friction surface.
Owner:TOYOX CO LTD
Brush assembly
ActiveUS20200182226A1Lower impedanceReduce voltage dropRotary current collectorConnection to earthPhysicsScrub brushes
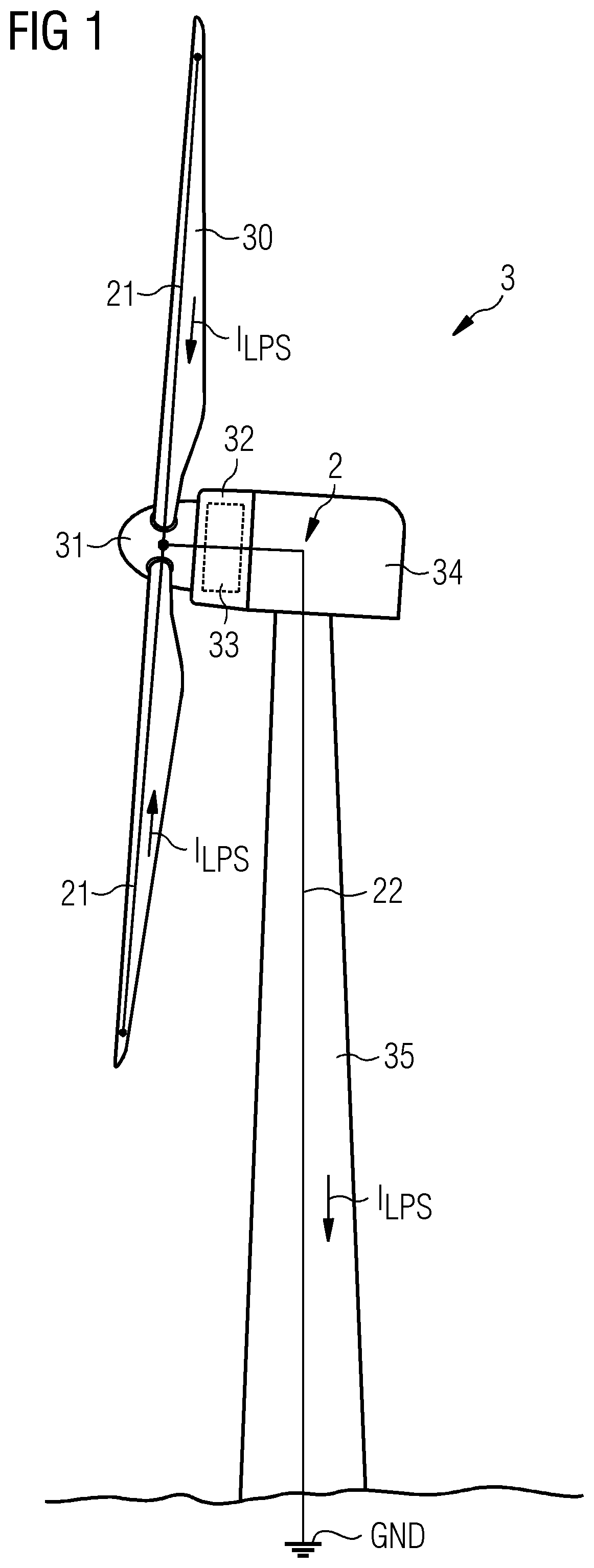
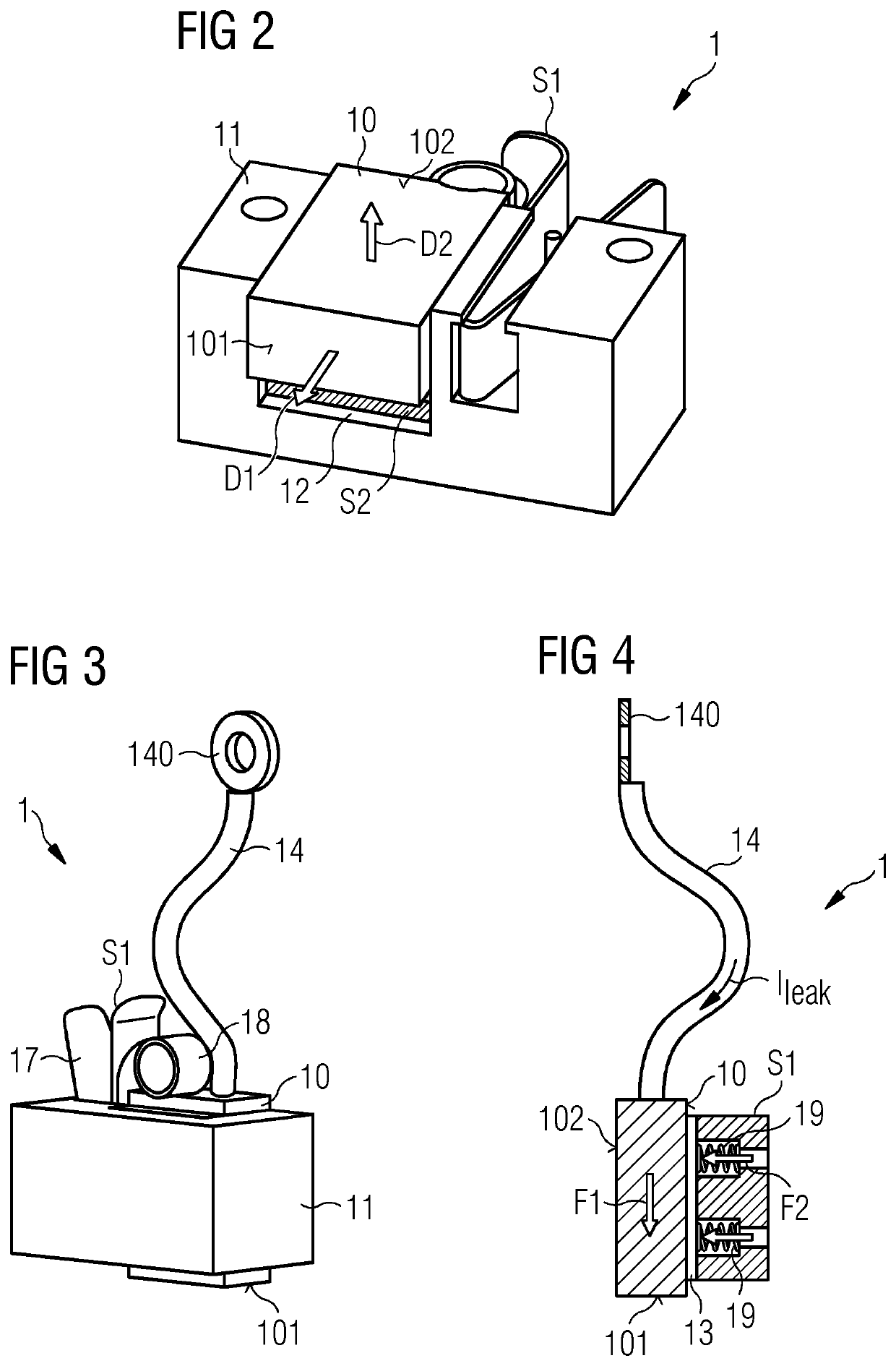
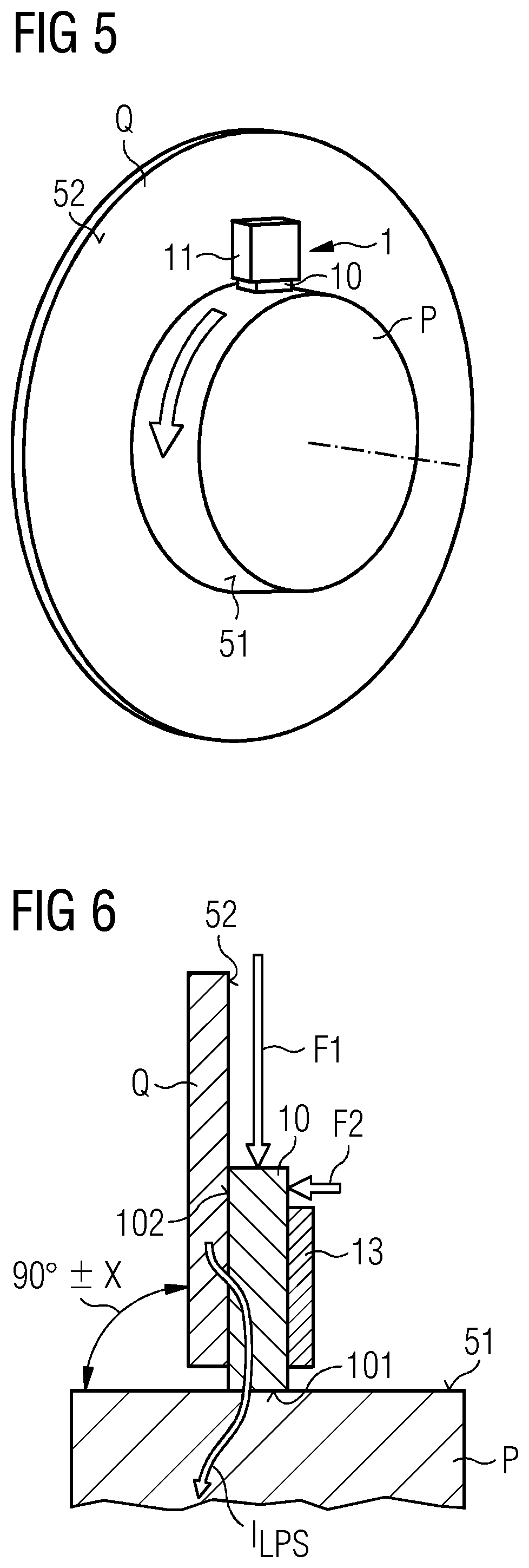
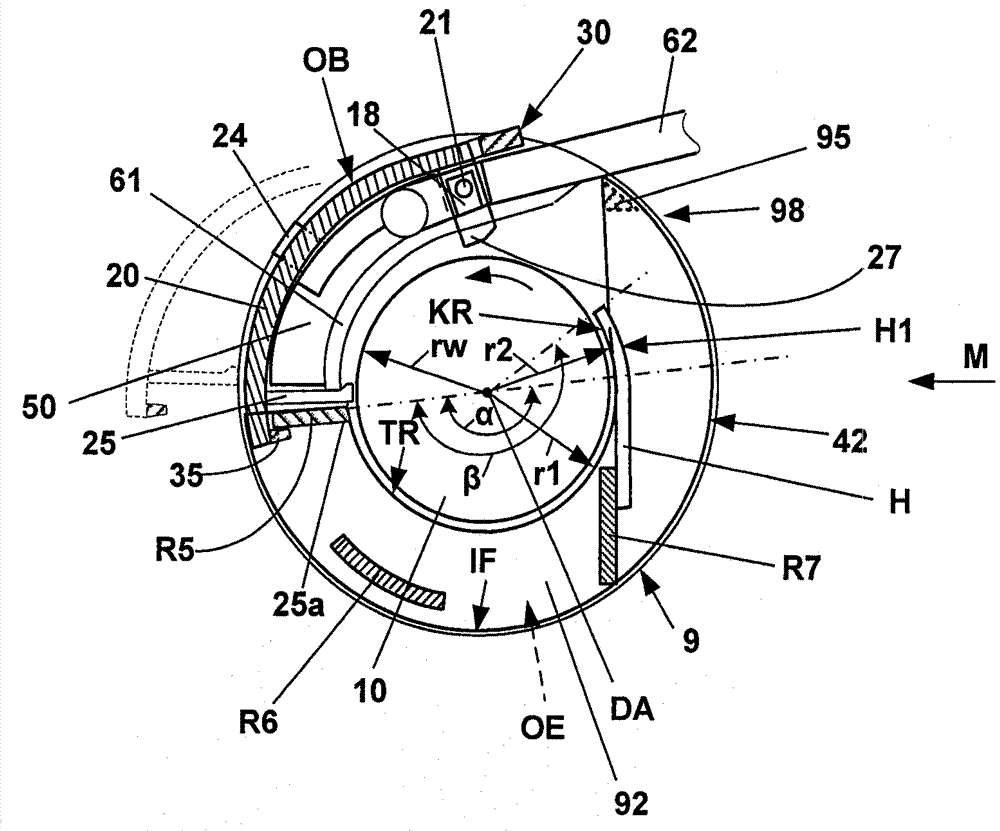
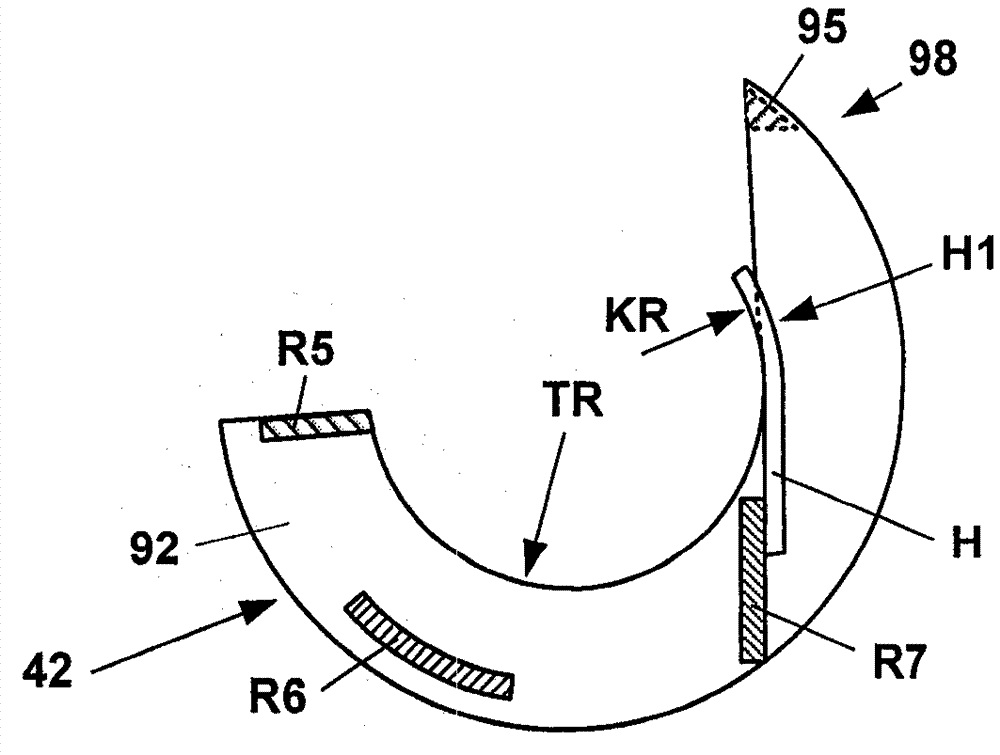
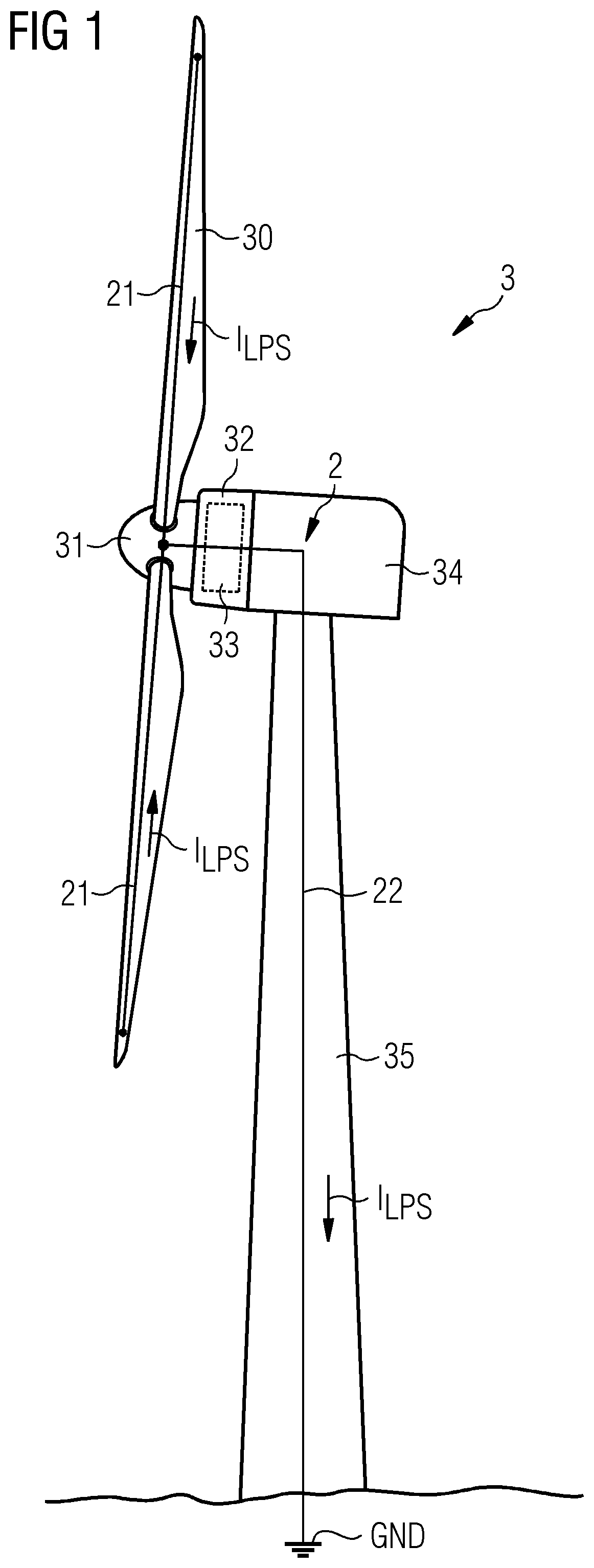
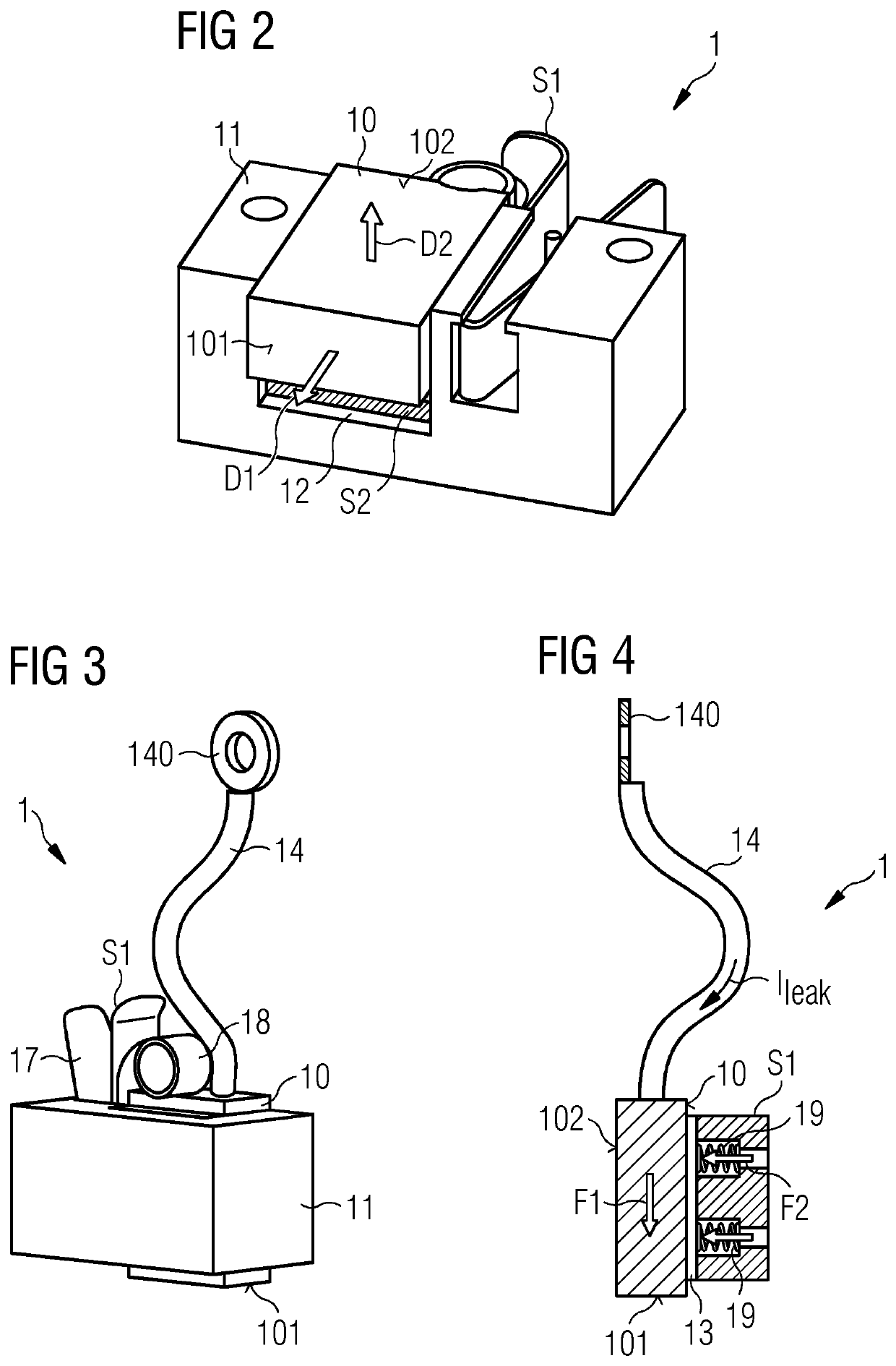
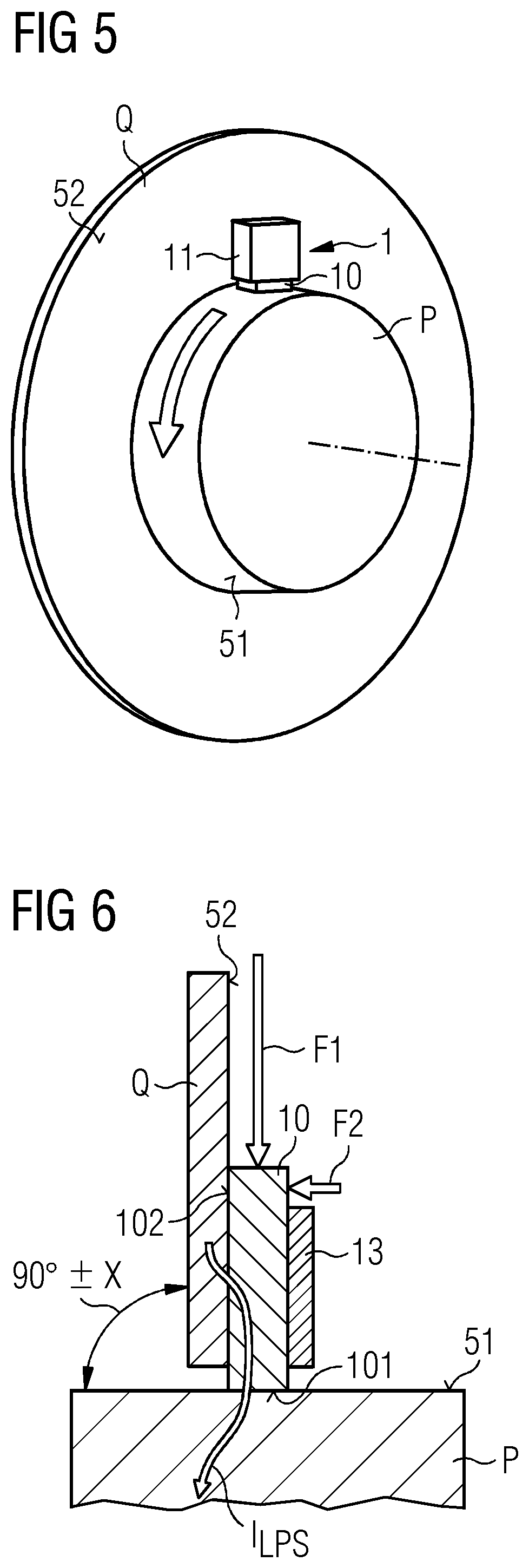
Provided is a brush assembly for transferring lightning current between a first structure and a second structure, which brush assembly includes a holder realized for mounting to one of the two structures; a recess formed in the holder, which recess is shaped to accommodate a brush and to expose a first brush face; and a first displacement means arranged to move the first exposed brush face against a surface of the first structure; and wherein the recess is shaped to also expose a second brush face, and the brush assembly further includes a second displacement means arranged to move the second exposed brush face against a surface of the second structure. Further provided is a lightning protection circuit of a wind turbine; and a wind turbine.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
Spinning machine with compact equipment
Owner:MASCHINENFABRIK RIETER AG
Brush assembly
ActiveUS11187209B2Lower impedanceReduce voltage dropRotary current collectorConnection to earthScrub brushesTurbine
Provided is a brush assembly for transferring lightning current between a first structure and a second structure, which brush assembly includes a holder realized for mounting to one of the two structures; a recess formed in the holder, which recess is shaped to accommodate a brush and to expose a first brush face; and a first displacement means arranged to move the first exposed brush face against a surface of the first structure; and wherein the recess is shaped to also expose a second brush face, and the brush assembly further includes a second displacement means arranged to move the second exposed brush face against a surface of the second structure. Further provided is a lightning protection circuit of a wind turbine; and a wind turbine.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
Spinning machine with compact equipment
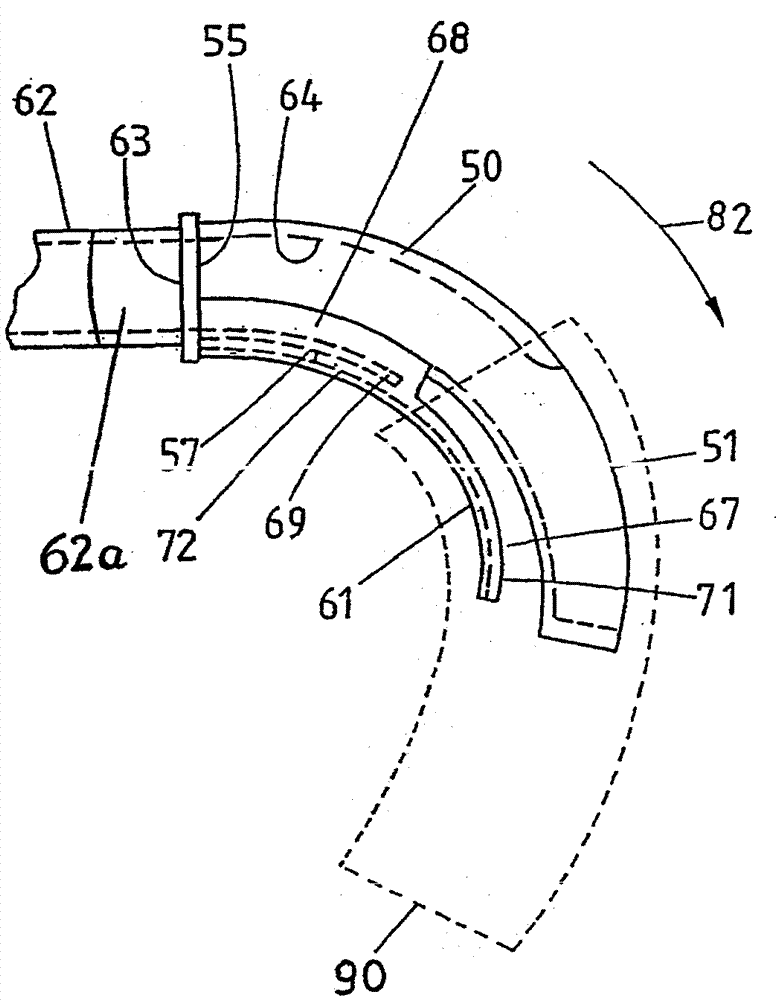
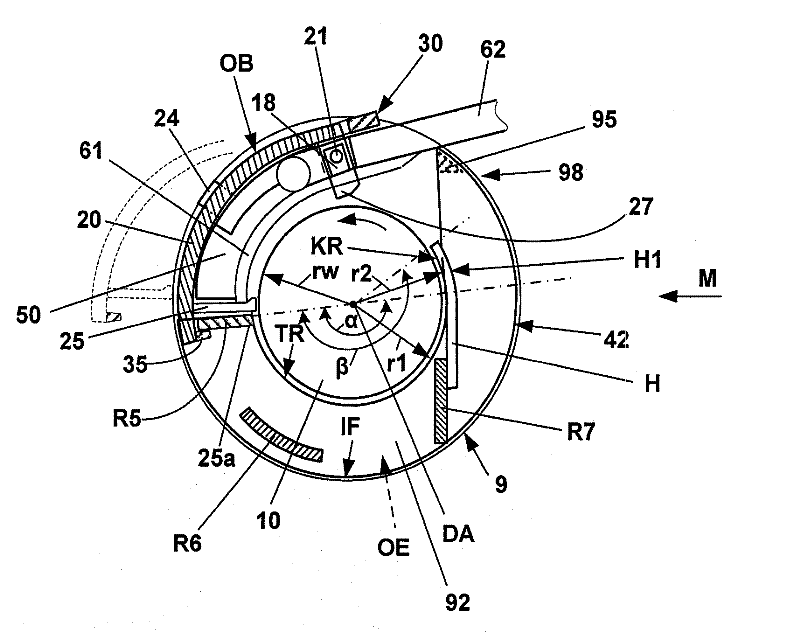
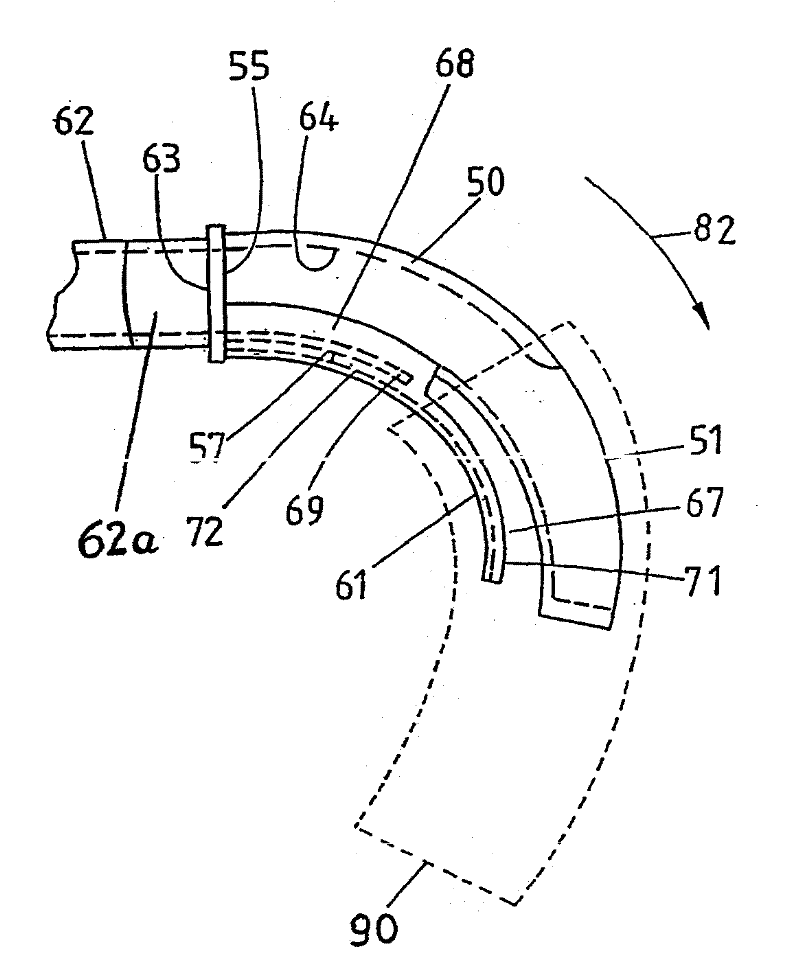
The invention relates to a covering device (42) for suction drums (9), one of compacting devices adjacent drafting units of a spinning machine, wherein the suction drums (9) are disposed coaxially on a longitudinal shaft (10) and on their axially spaced apart, opposite sides annular opening (OE), through each of which a suction source connected to a suction liner (50) projects into the interior of the respective suction drum. To the interior of the suction drums (9) to protect against contamination and uncontrolled air currents, it is proposed that the capping device (42) between the adjacent suction drums (9) is attached and from the opposite which is connected to webs (R1, R2, R3, R4) covering elements (84, 85) exists, each of the adjacent to the respective suction insert remaining annular openings (OE) of the suction drums face (9) and overlapping this at least partially.
Owner:MASCHINENFABRIK RIETER AG
Synthetic resin hose
ActiveCN101484306BLow friction surfaceIncrease stickinessLayered productsFlexible pipesPolymer scienceSynthetic resin
Surface tackiness of a hose is improved without using a partially crosslinked resin. By heat-molding a hose while mixing a plurality of synthetic resins having different molecular weights in the surface of the hose, particles of the synthetic resins having high molecular weights remain in the molten synthetic resins having low molecular weights, thereby forming fisheyes in the hose surface. Fine projections and recesses due to the fisheyes make the hose surface into a low friction surface.
Owner:TOYOX CO LTD
Lubricant supported electric motor
ActiveCN111183569AReduce torqueLow friction surfaceGear lubrication/coolingMagnetic circuit stationary partsEngineeringLubricant
Owner:NEAPCO INTPROP HLDG LLC
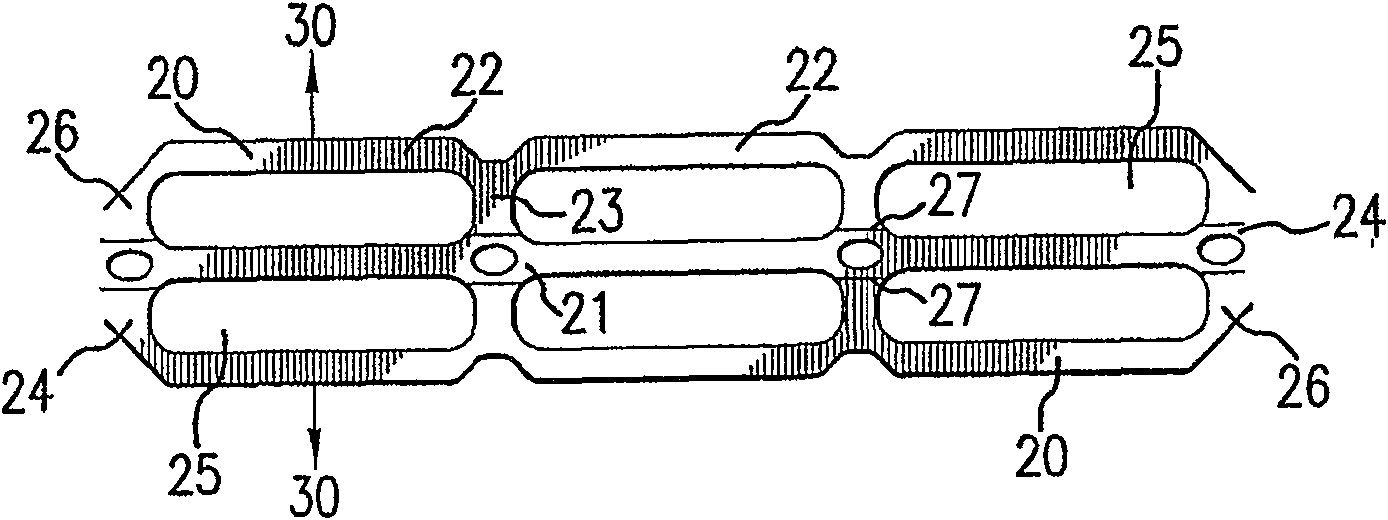
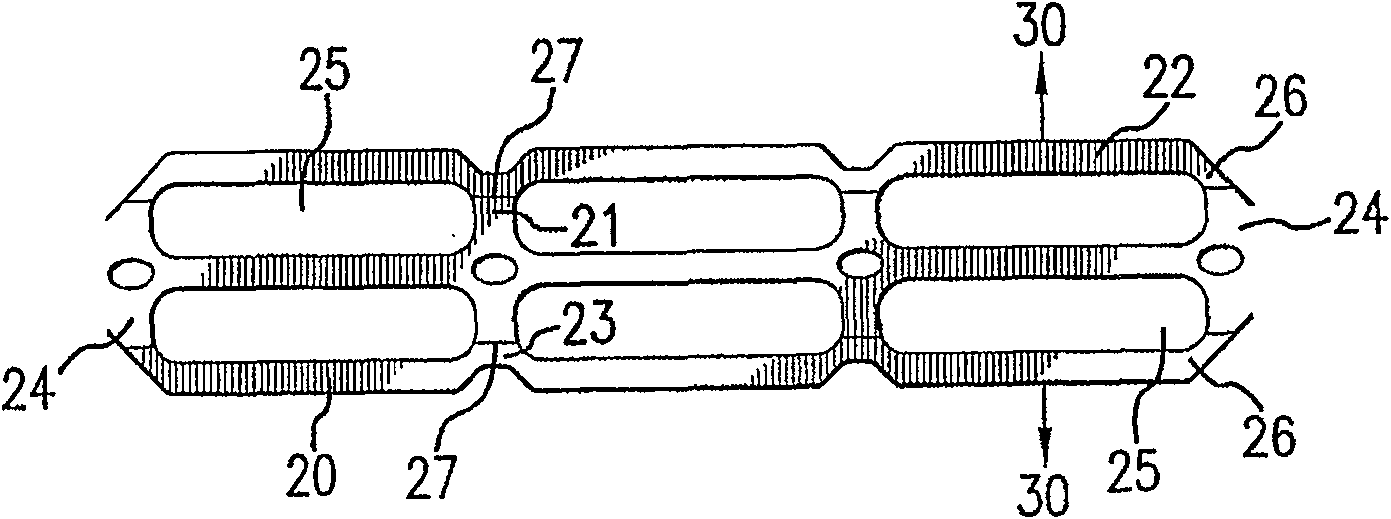
Flexible carrier having regions of higher and lower energy treatment
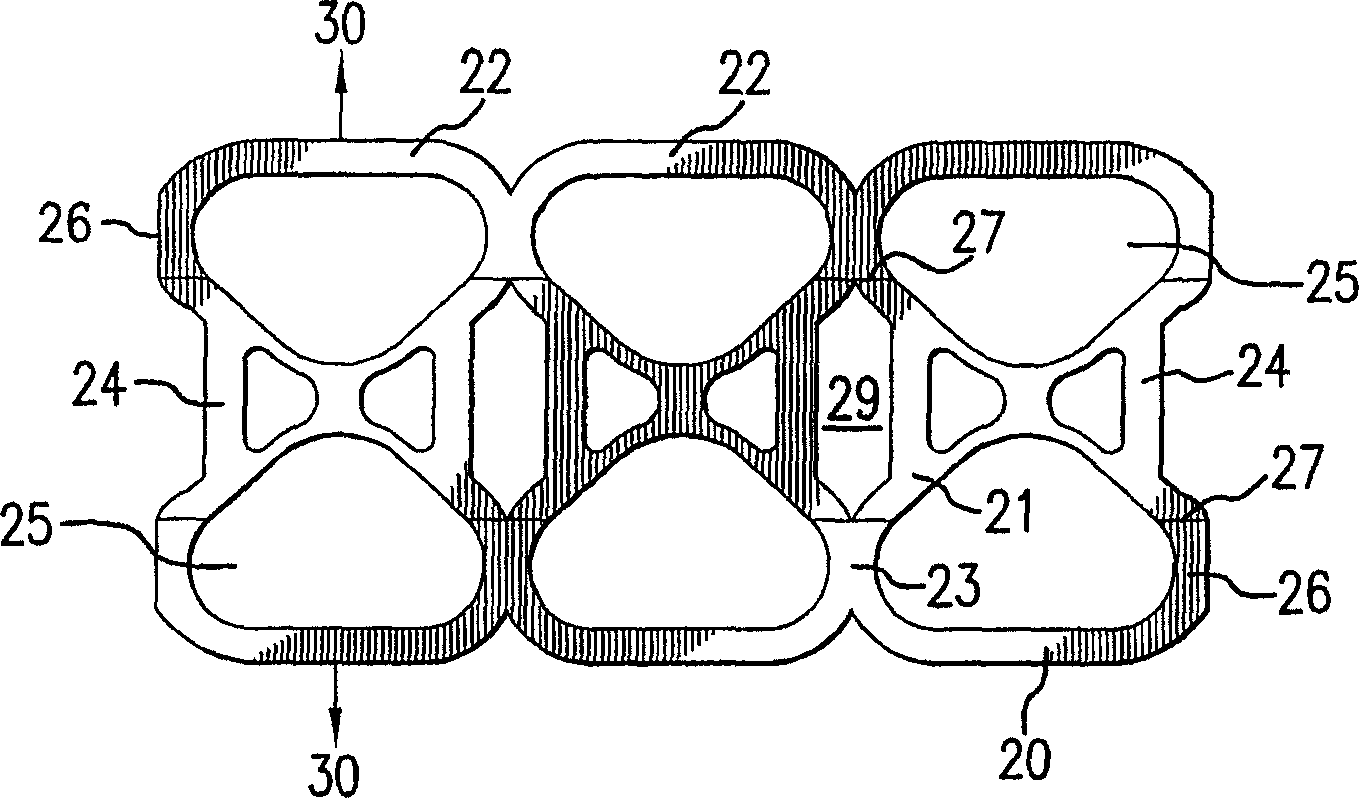
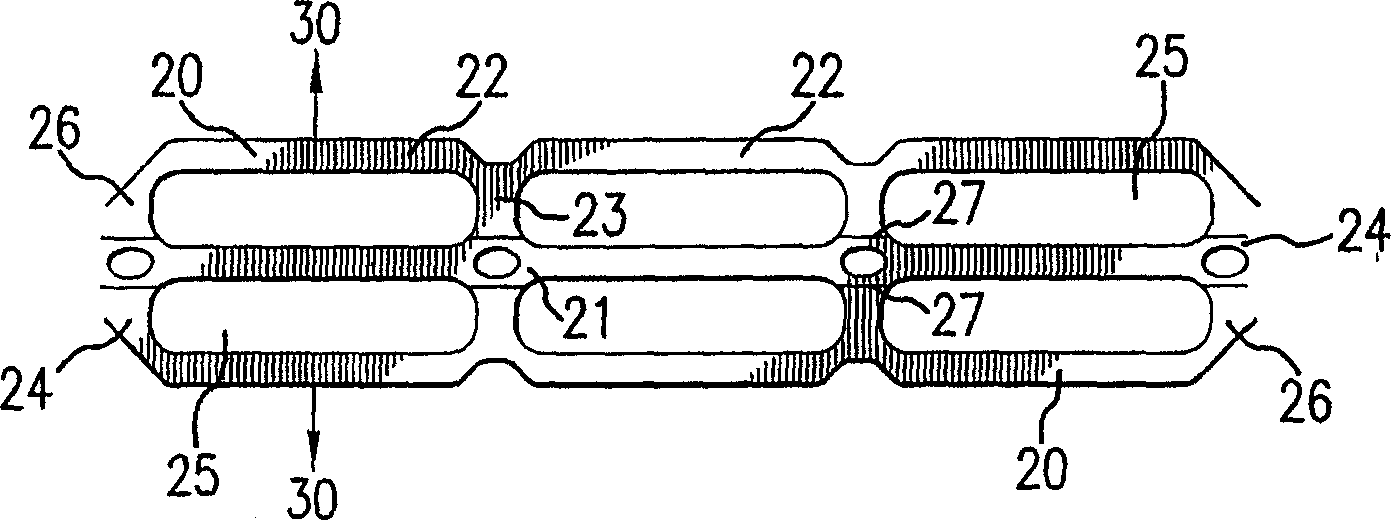
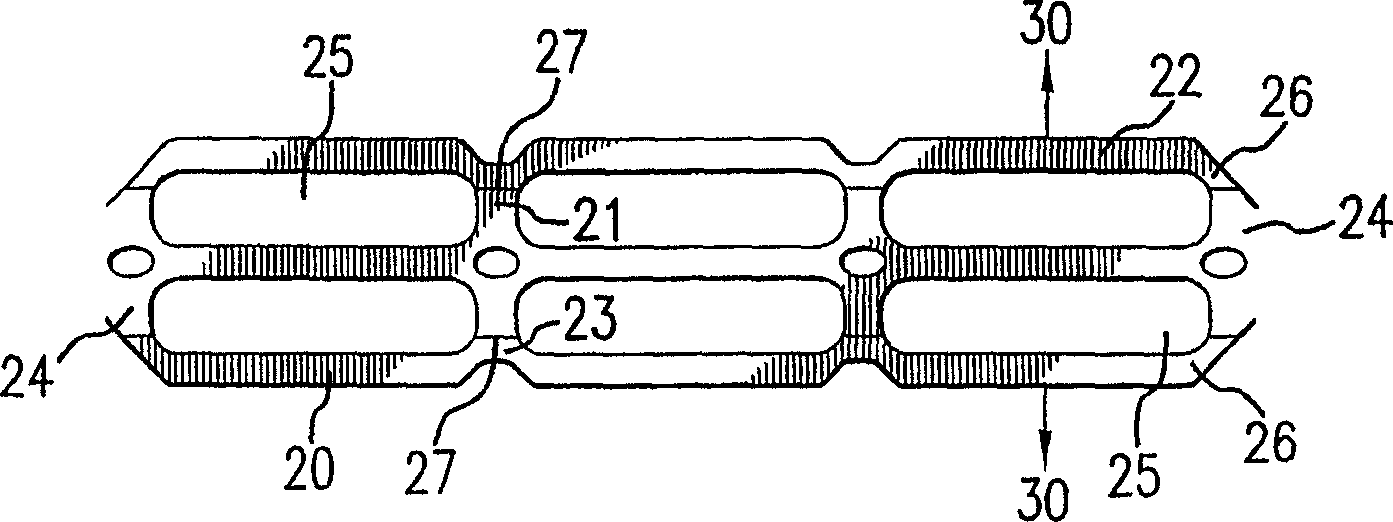
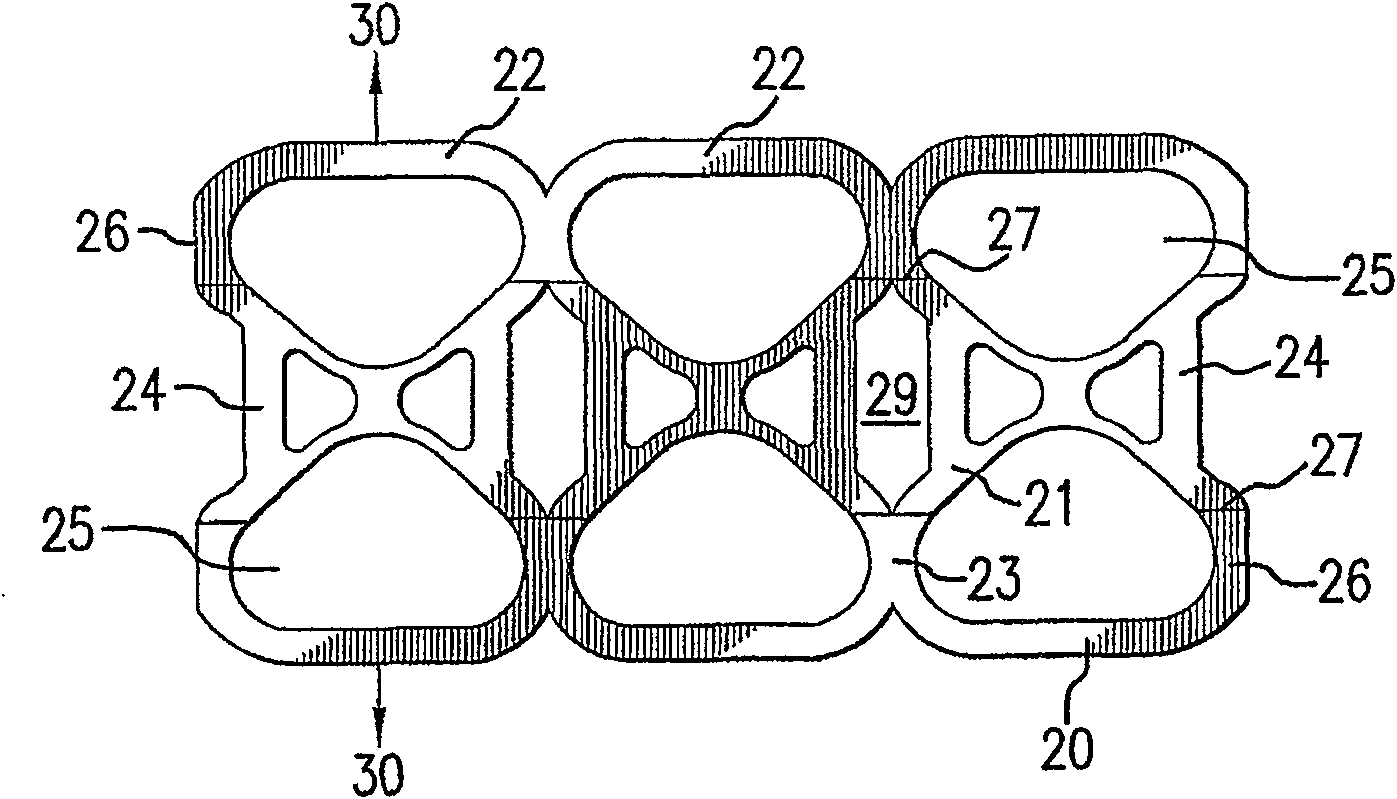
A flexible carrier (30) for carrying a plurality of beverage containers includes a plurality of container holders (25), each having a portion with higher energy treatment (26) and a portion with lower energy treatment (24). The energy treatment is corona or plasma treatment. The portions with higher energy treatment (26) provide better carrier-to container friction. By varying the level of energy treatment and the relative size of the portions being treated, the amount of overall friction between the flexible carrier (30) and the containers can be controlled.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Flexible carrier having regions of higher and lower energy treatment
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com