Resistance-type pressure distribution fabric sensor
A technology of resistive pressure and fabric sensors, which is applied in the measurement of properties and forces of piezoelectric devices, can solve the problems of reducing sensor stability, cumbersome wiring, and long-term heating safety, and achieves improved stability and flexibility. Effects of improving connection stability and simplifying circuit structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] Below in conjunction with specific embodiment, further illustrate the present invention. It should be understood that these examples are only used to illustrate the present invention and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention. In addition, it should be understood that after reading the teachings of the present invention, those skilled in the art can make various changes or modifications to the present invention, and these equivalent forms also fall within the scope defined by the appended claims of the present application.
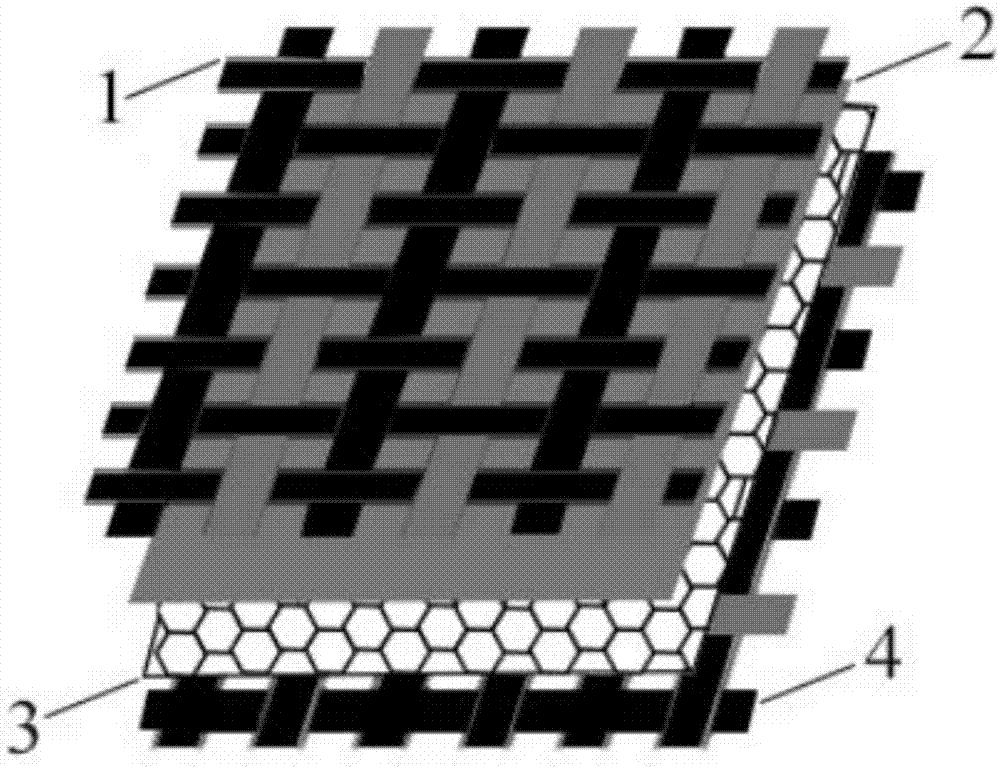
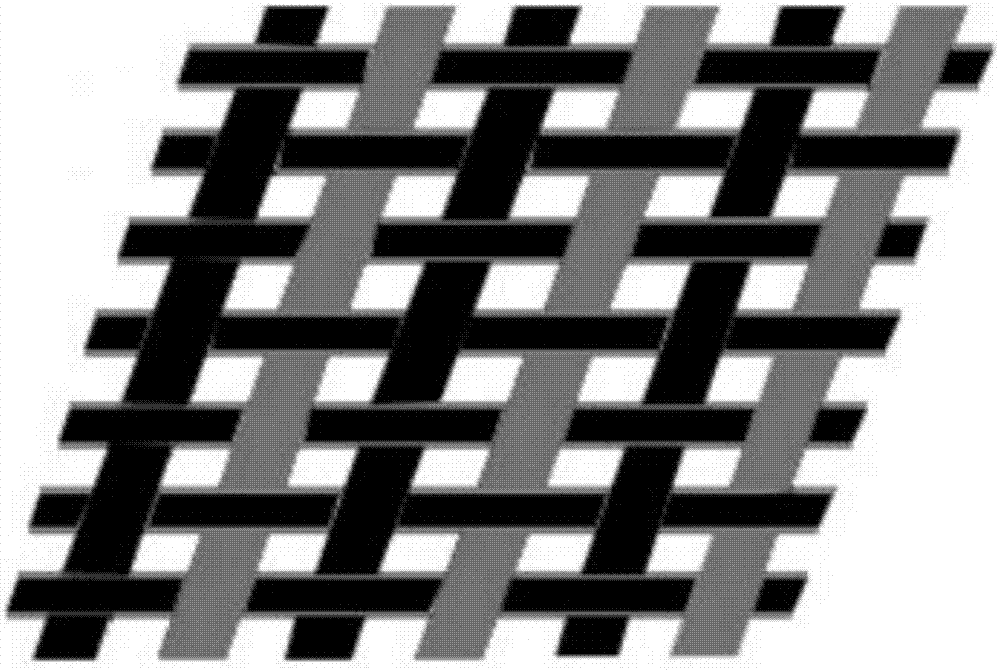
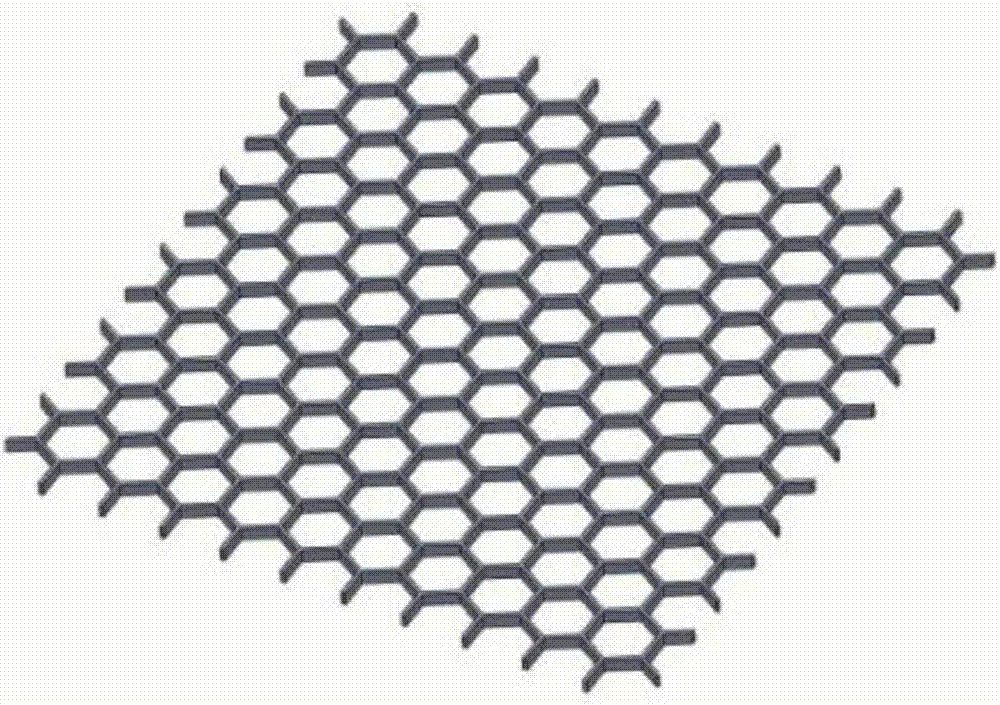
[0033] Embodiments of the present invention relate to a resistive pressure distribution fabric sensor such as figure 1 As shown, it includes an upper electrode layer 1, a conductive layer 2 and a lower electrode layer 4 stacked sequentially from top to bottom; figure 2 As shown, the upper electrode layer 1 and the lower electrode layer 4 are fabrics woven into strips of different widths using conductive yarns and non-conducti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com