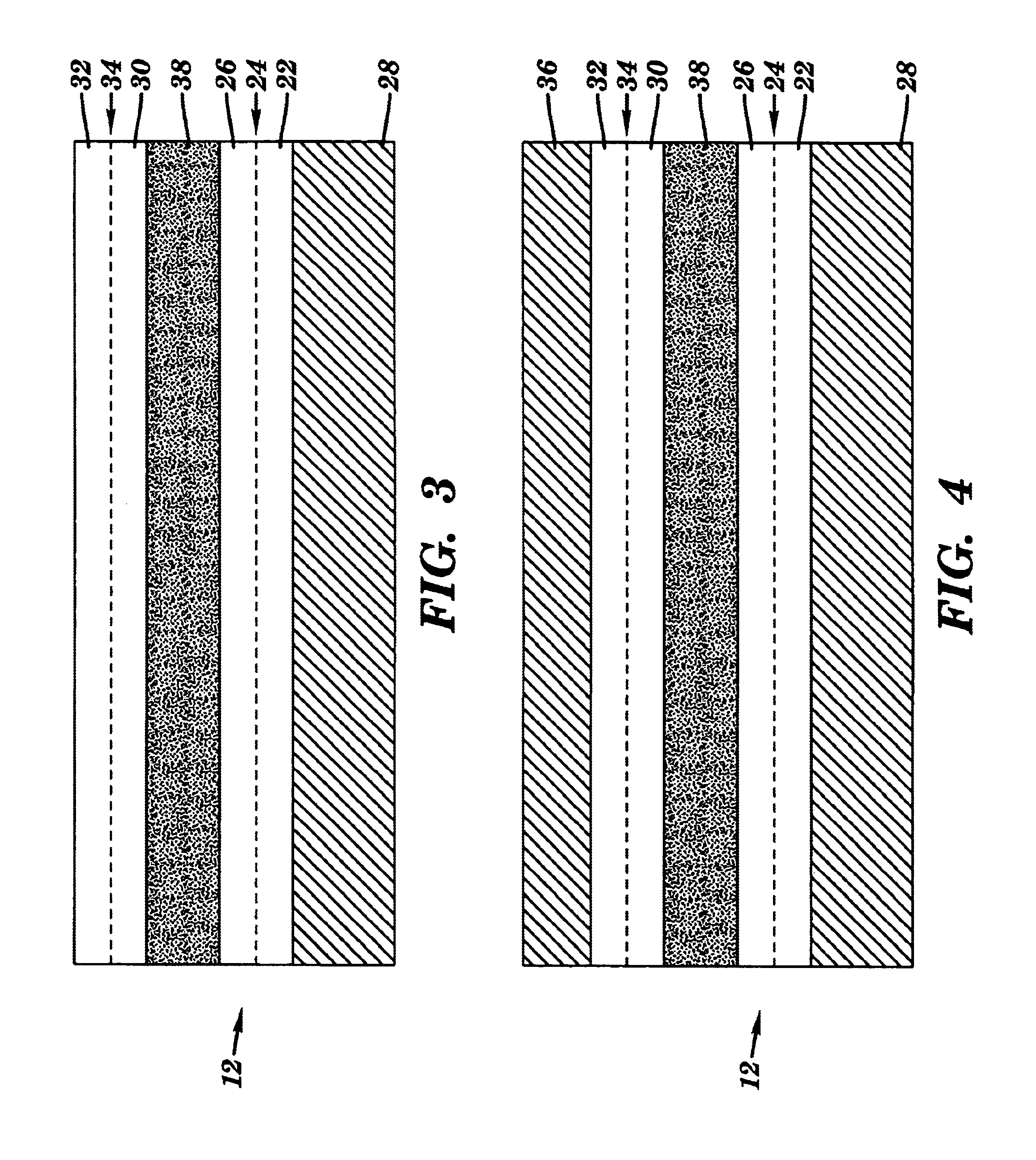
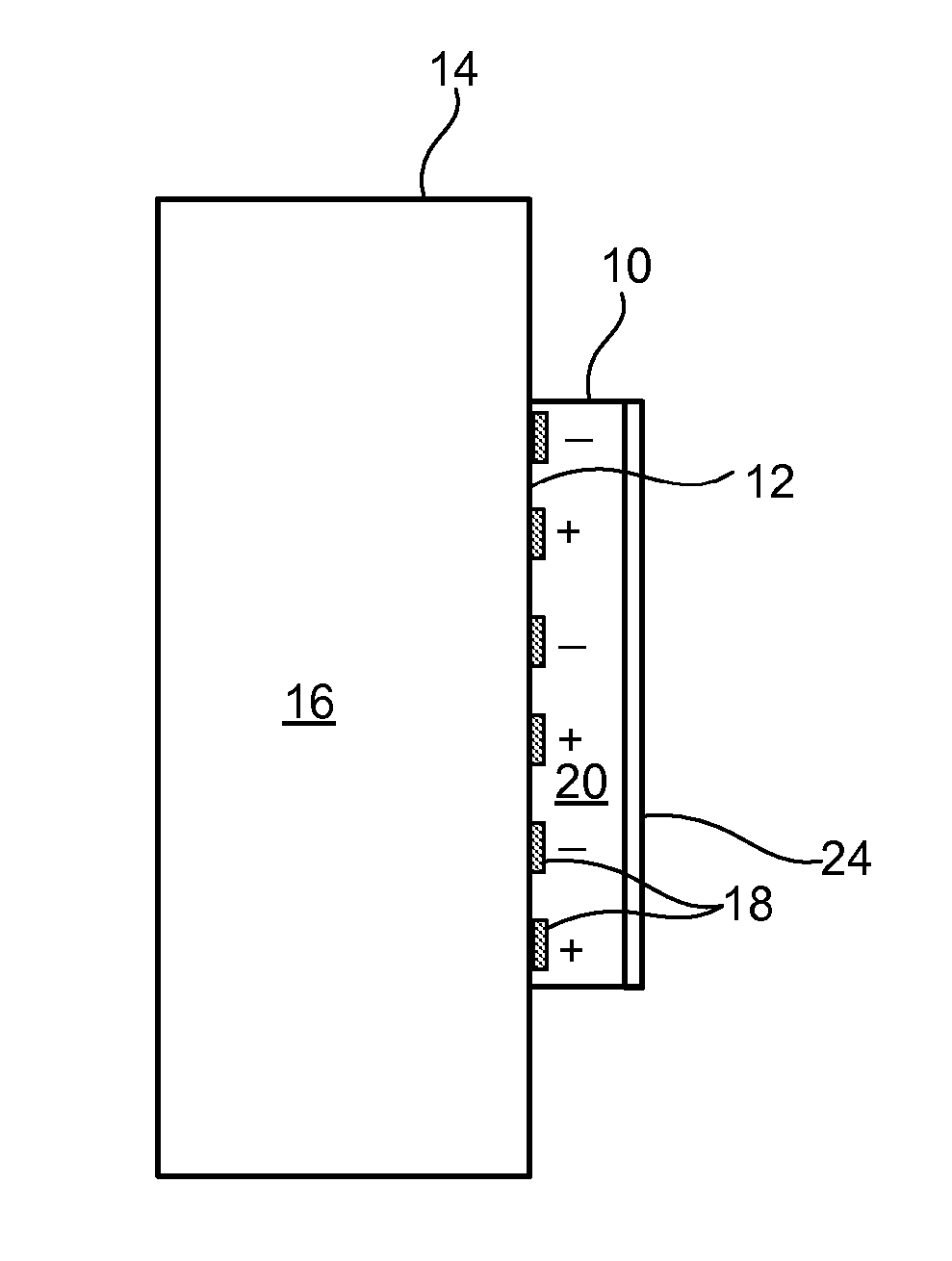
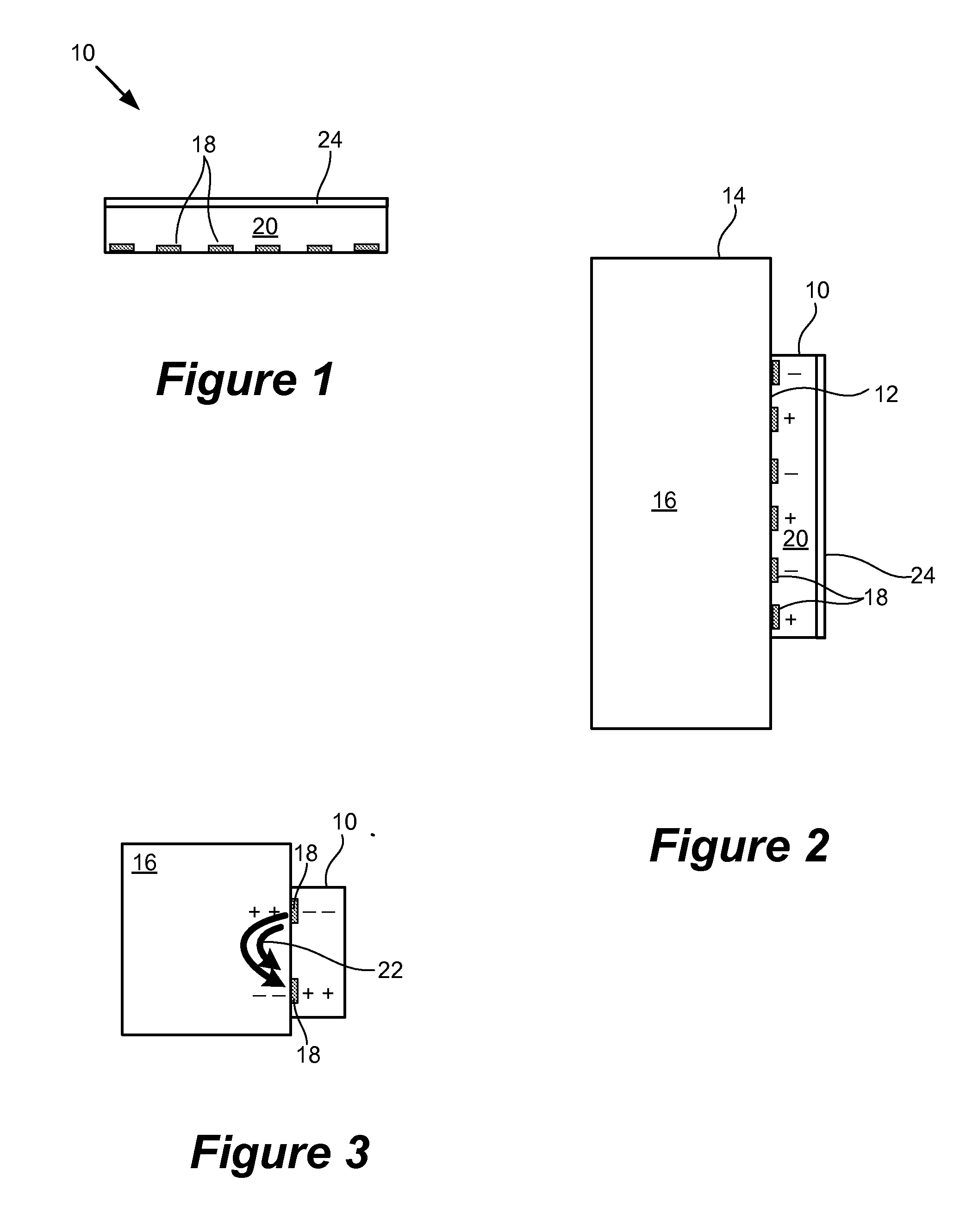
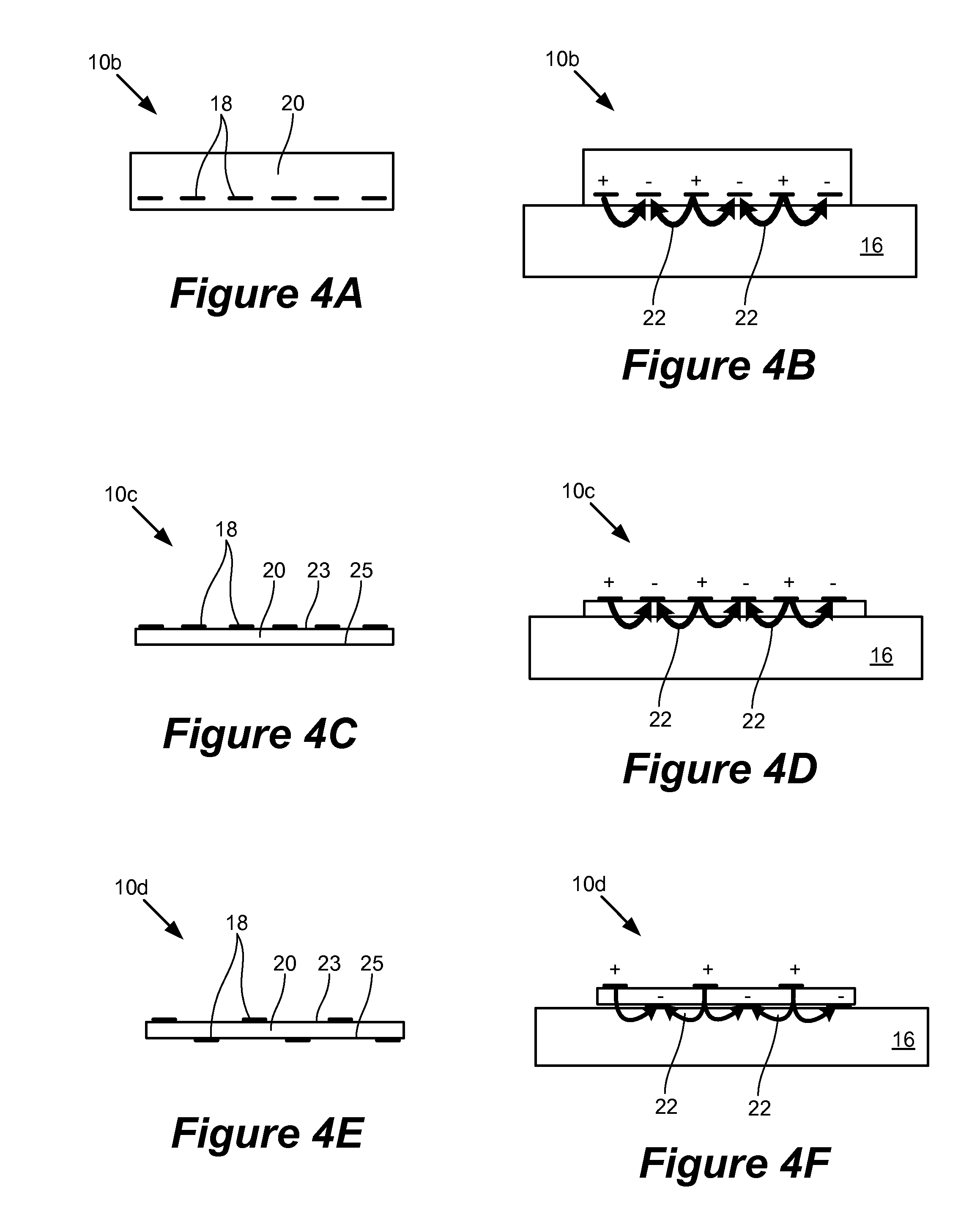
Patents
Literature
910results about "Electrostatic holding devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
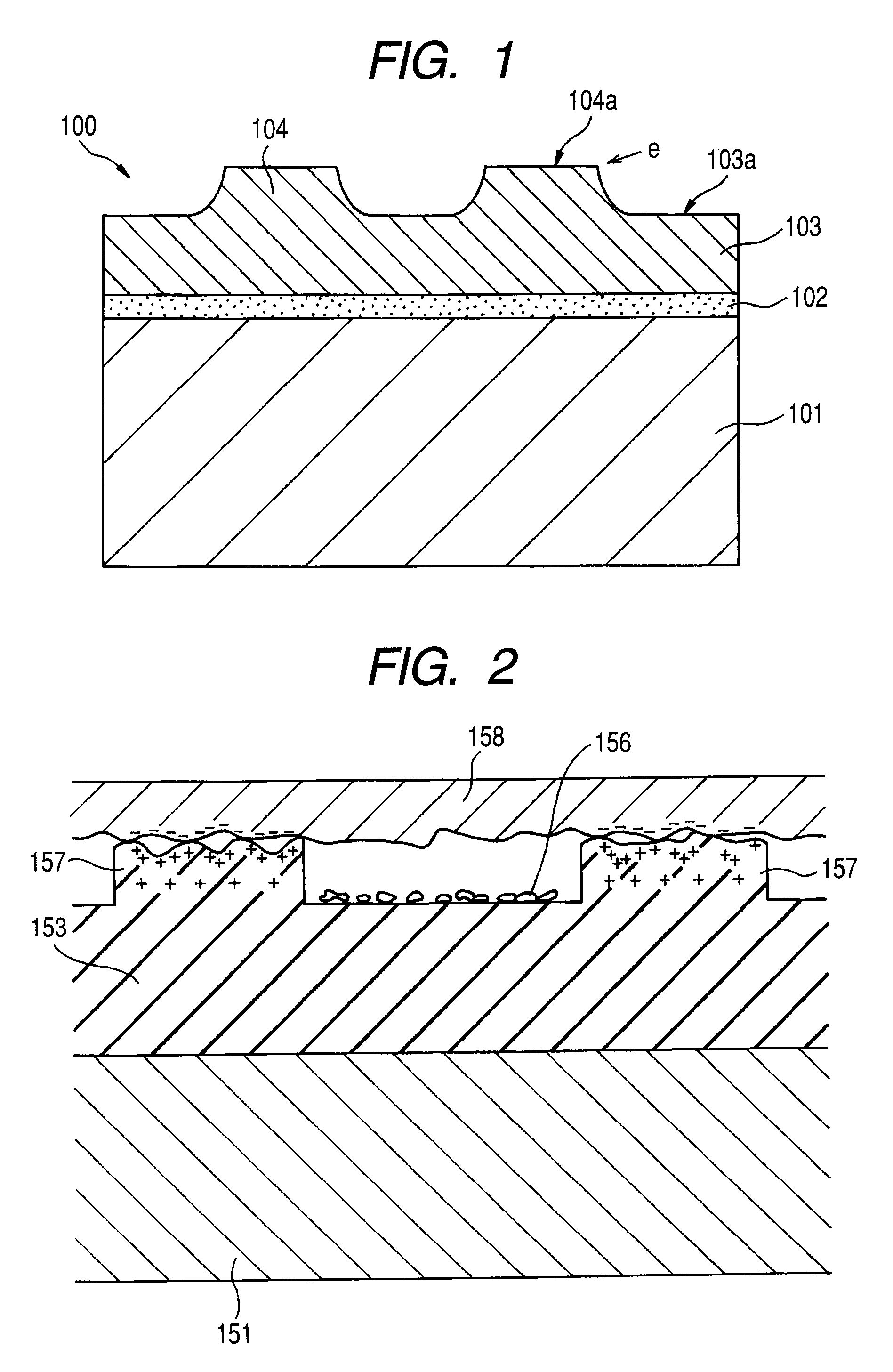
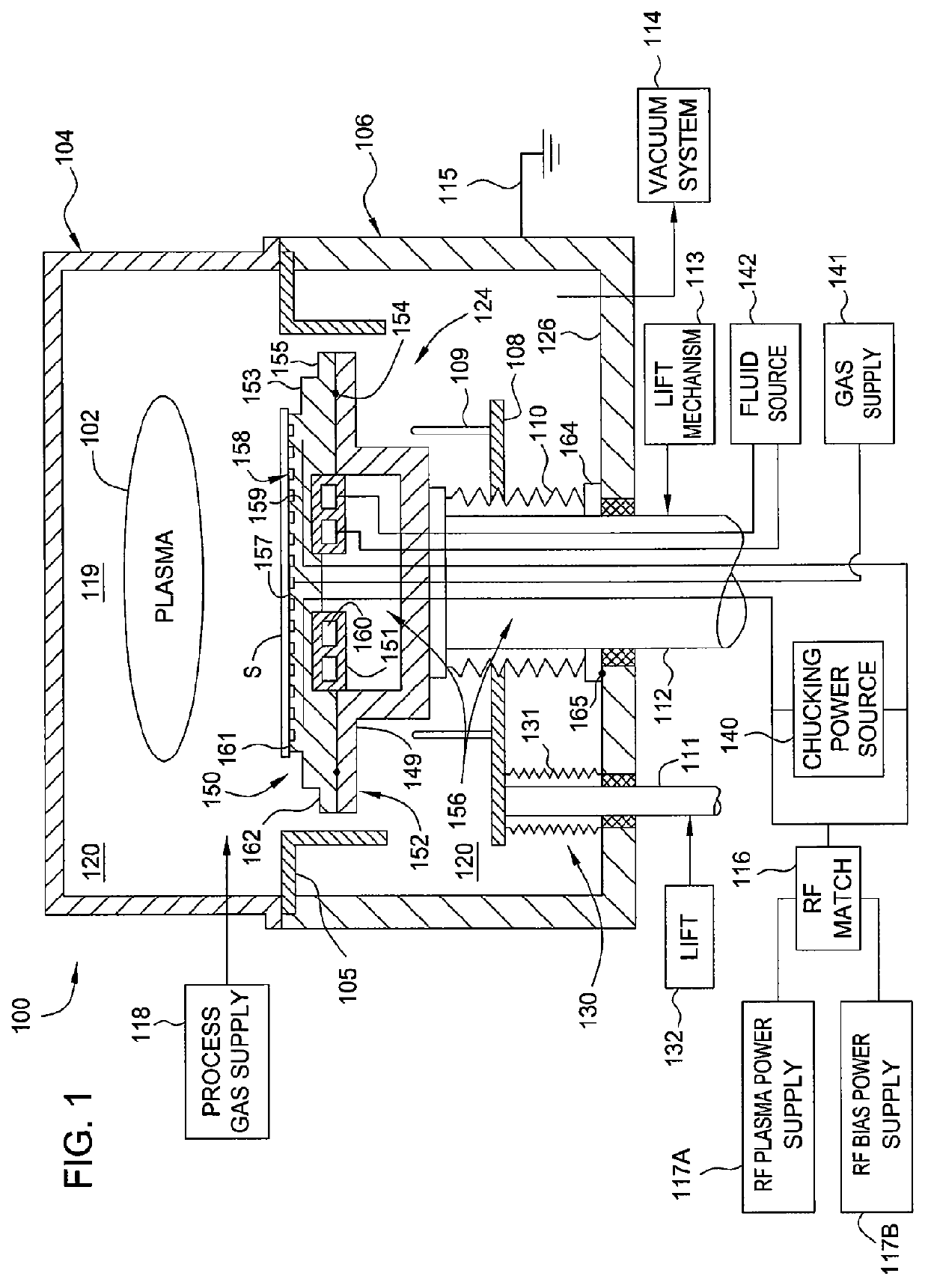
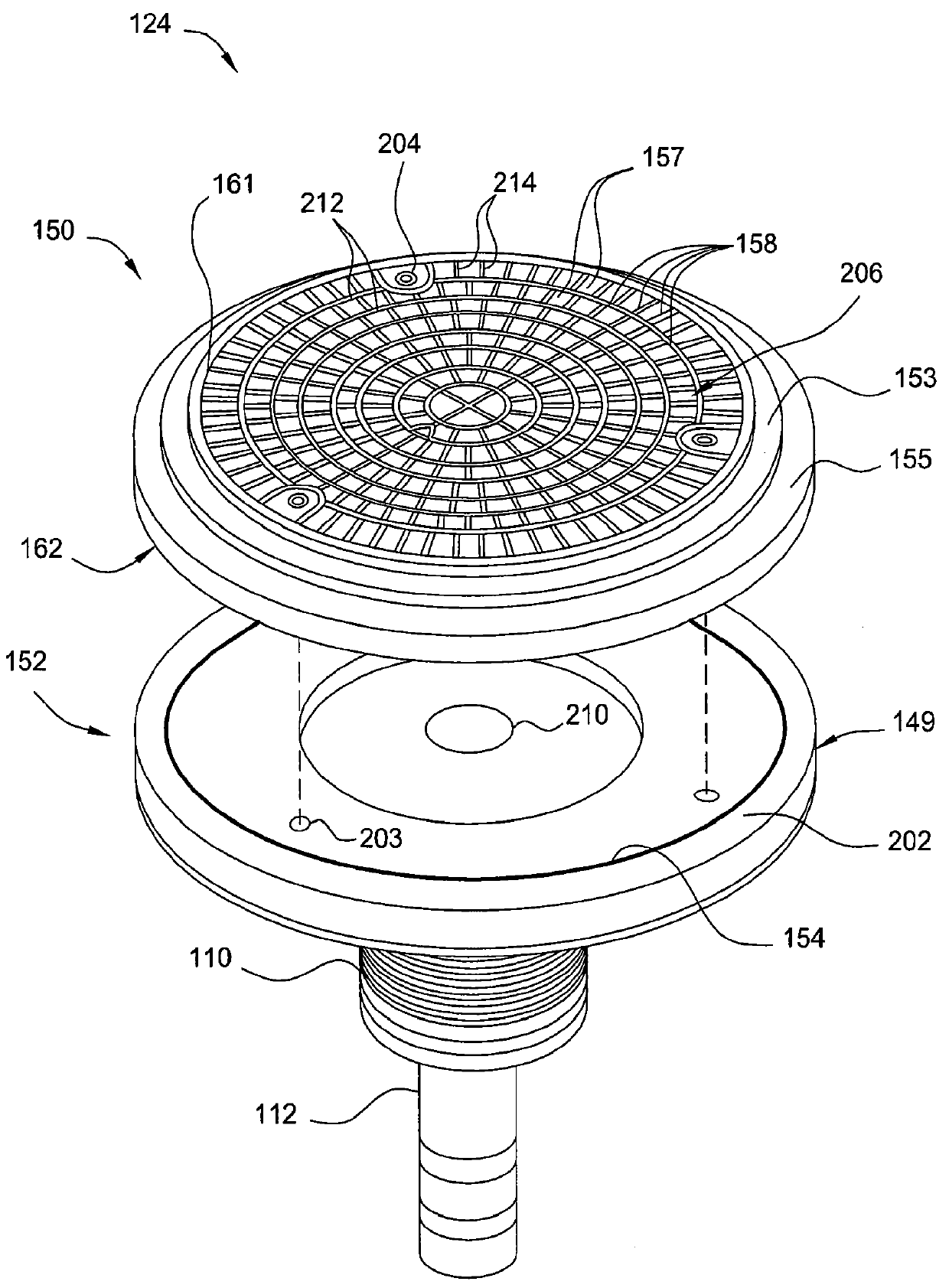
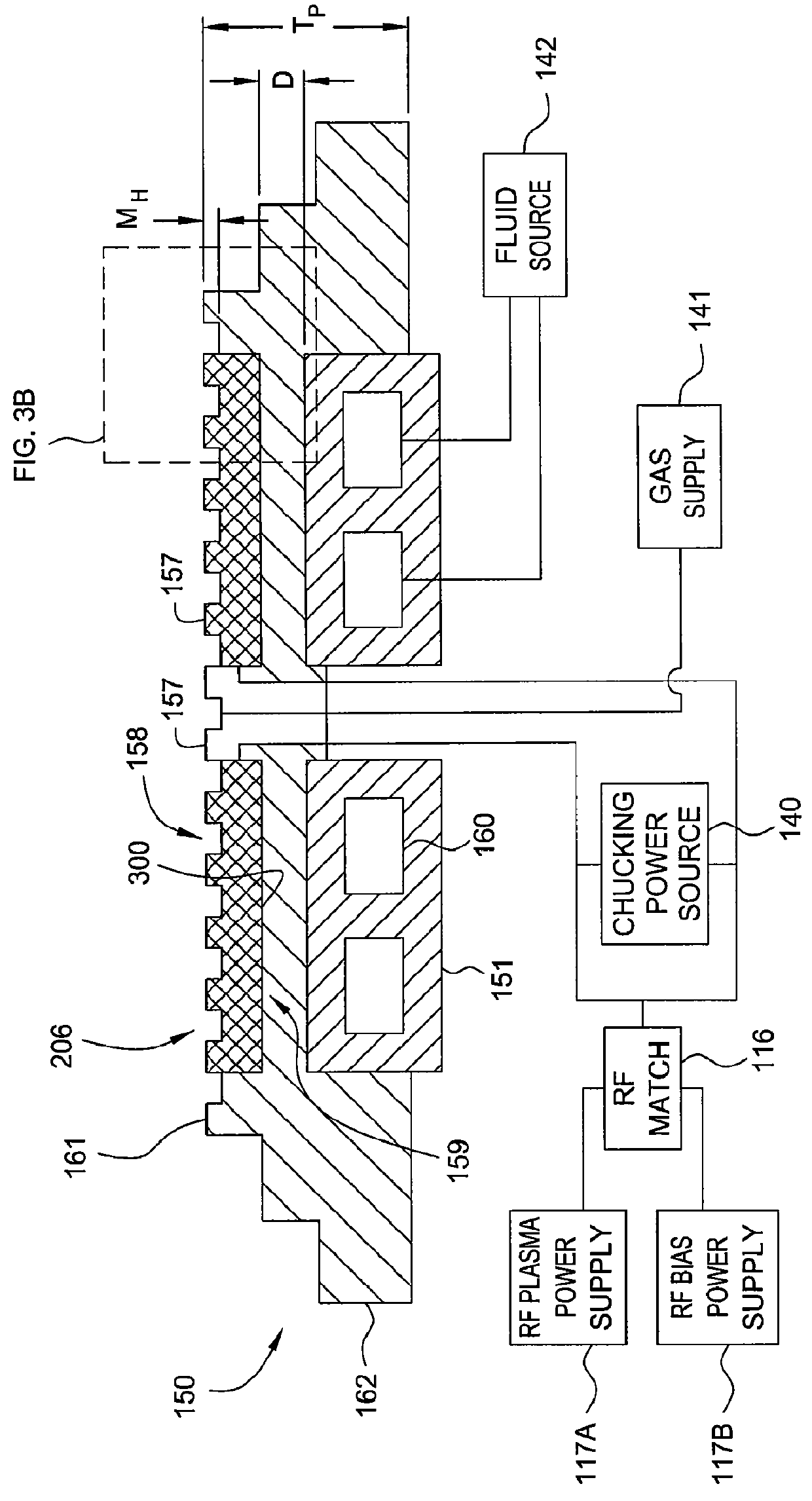
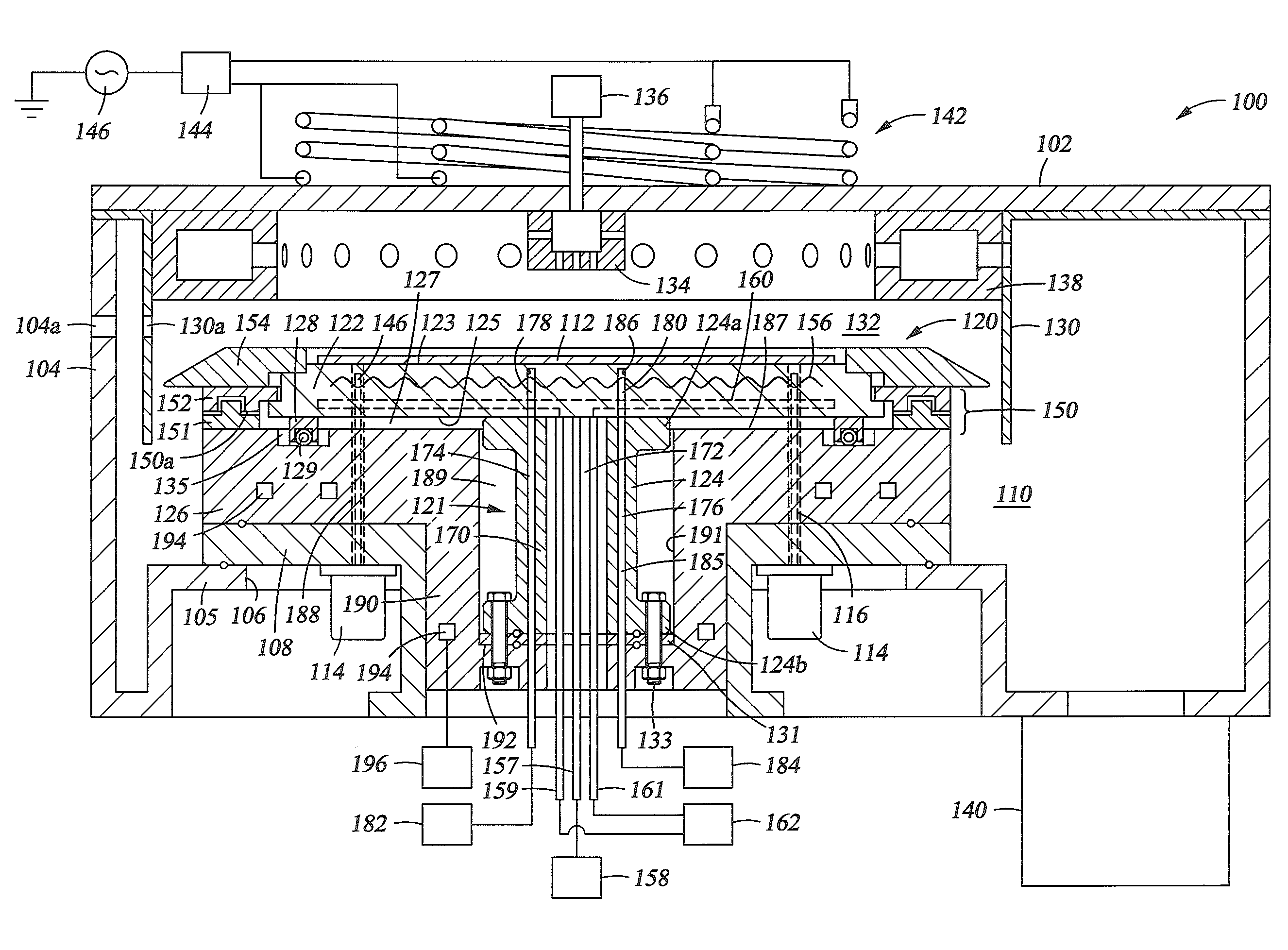
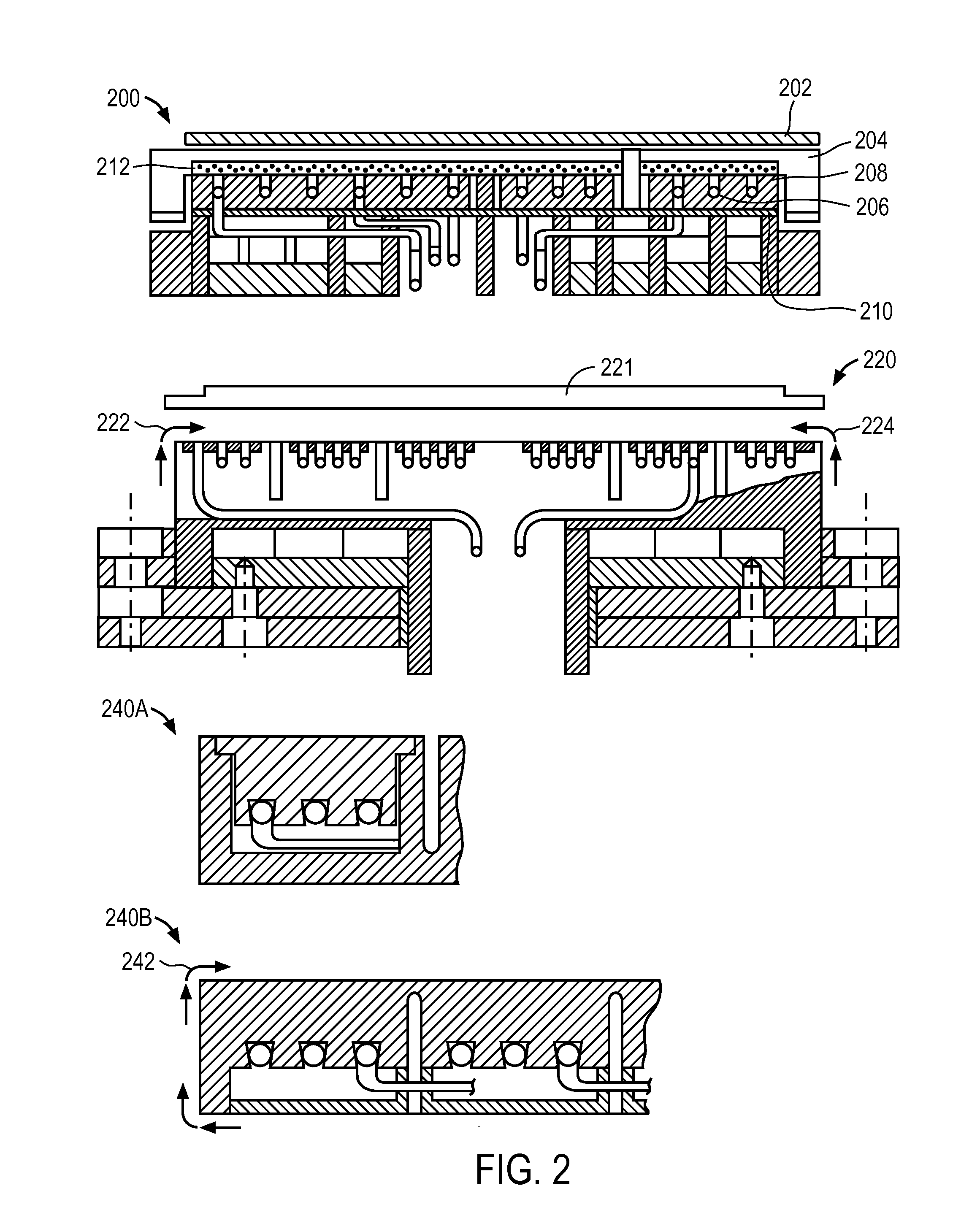
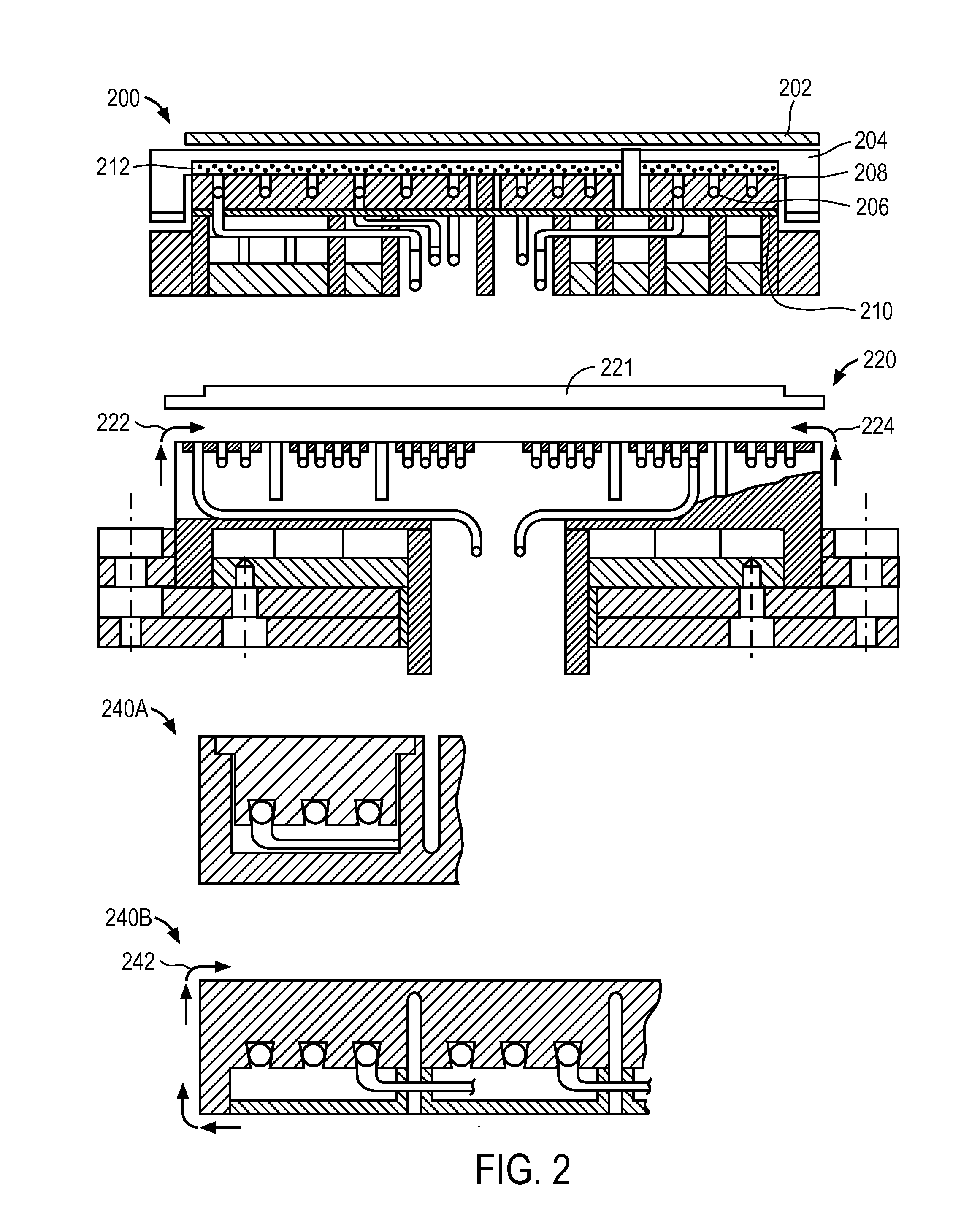
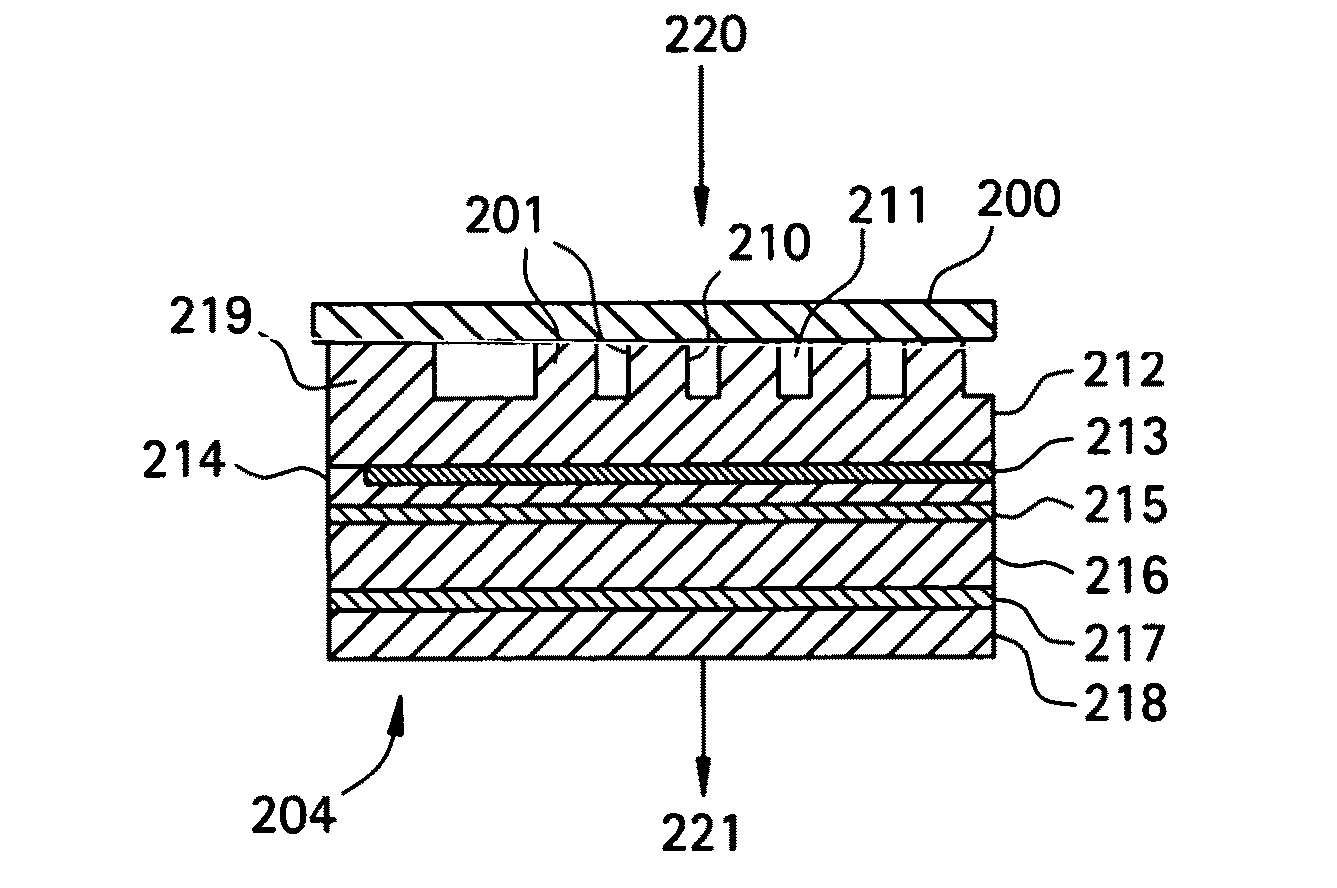
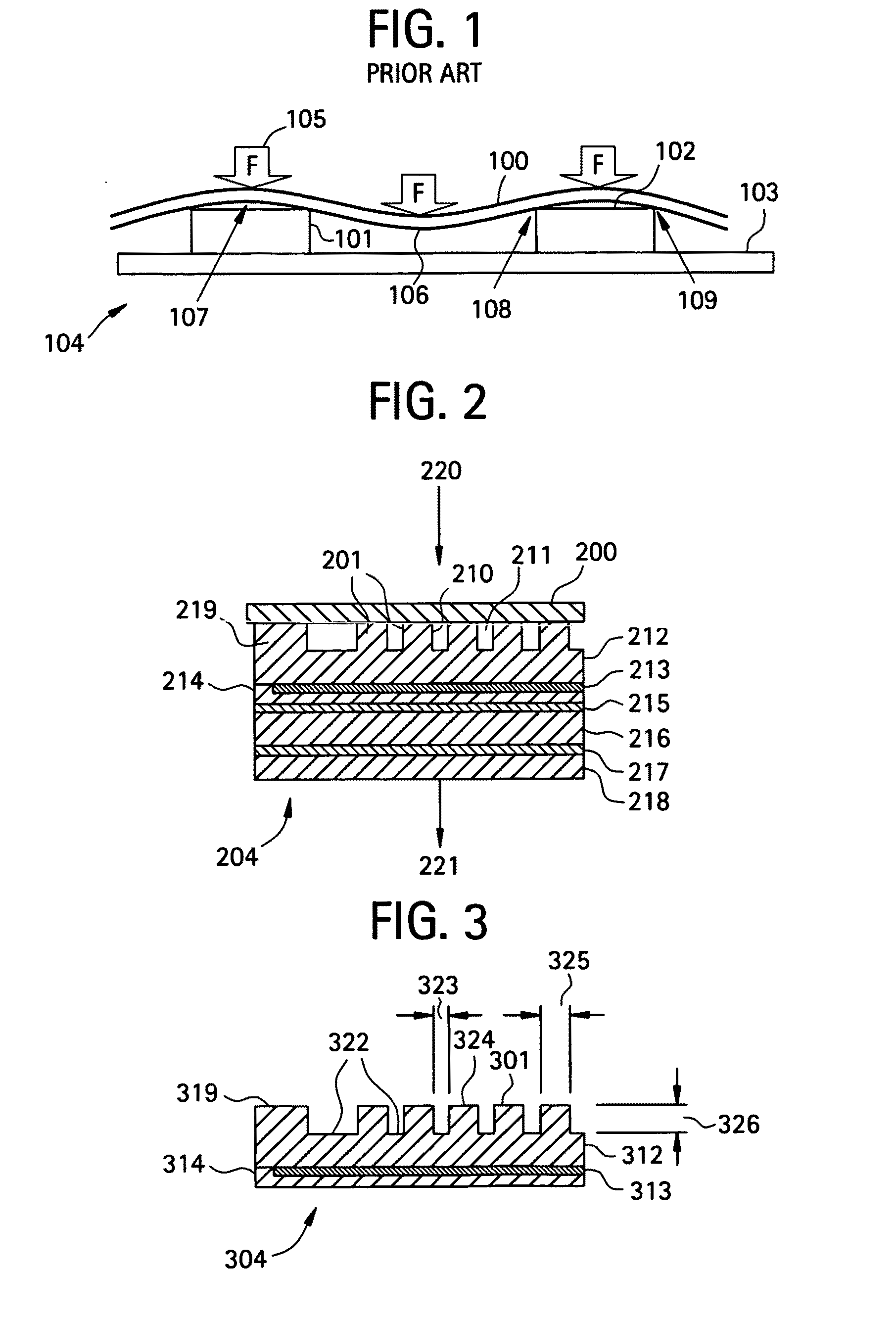
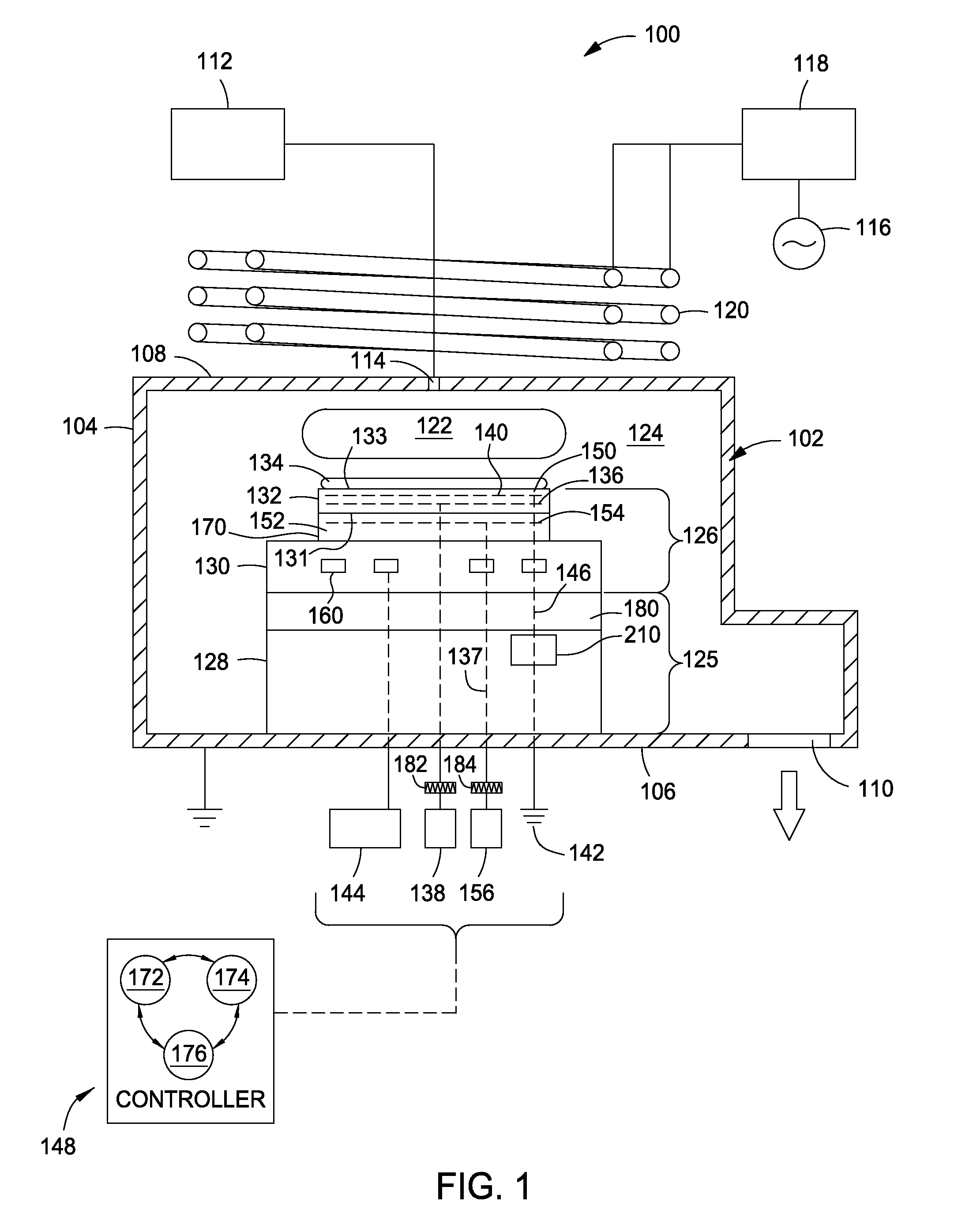
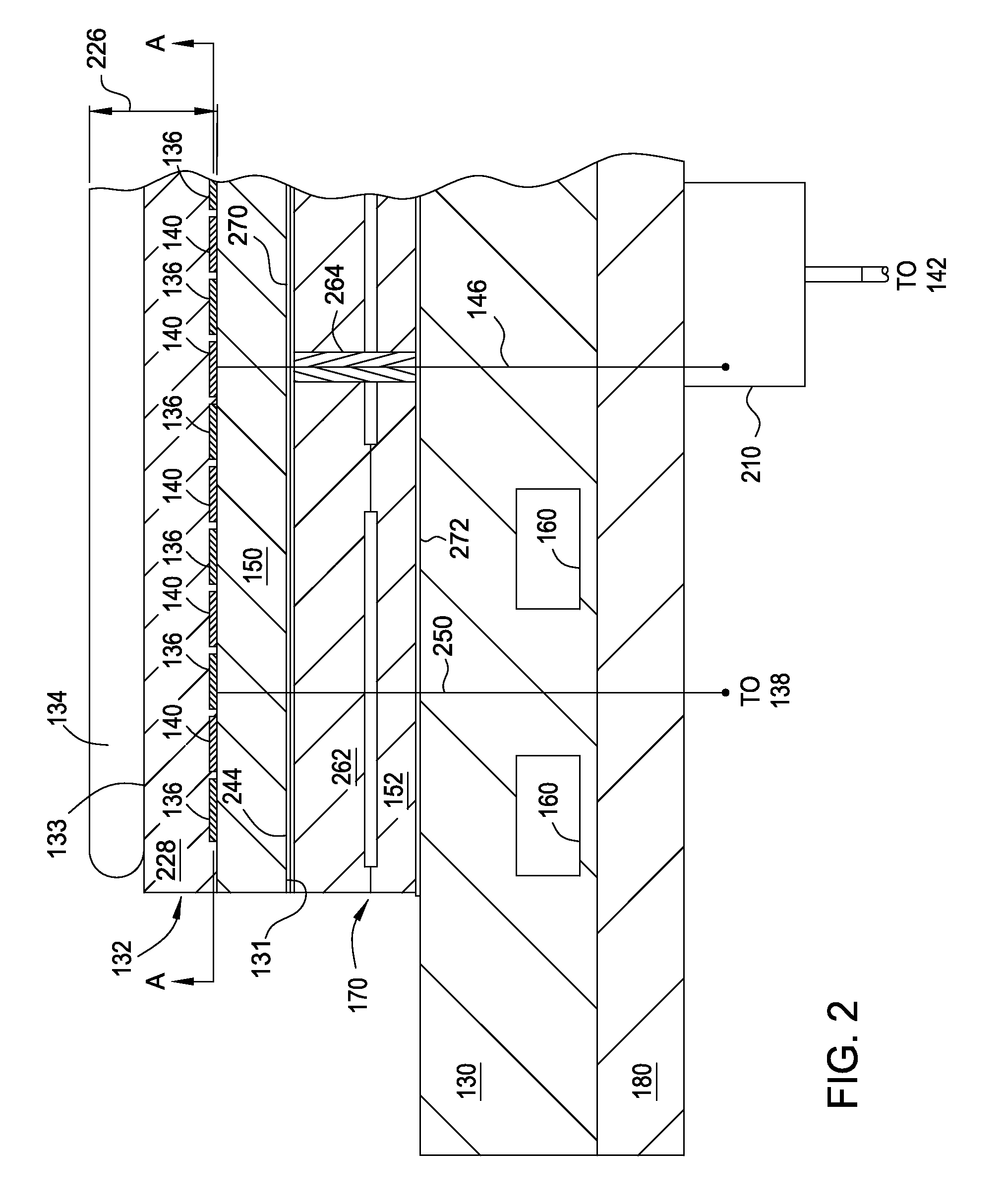
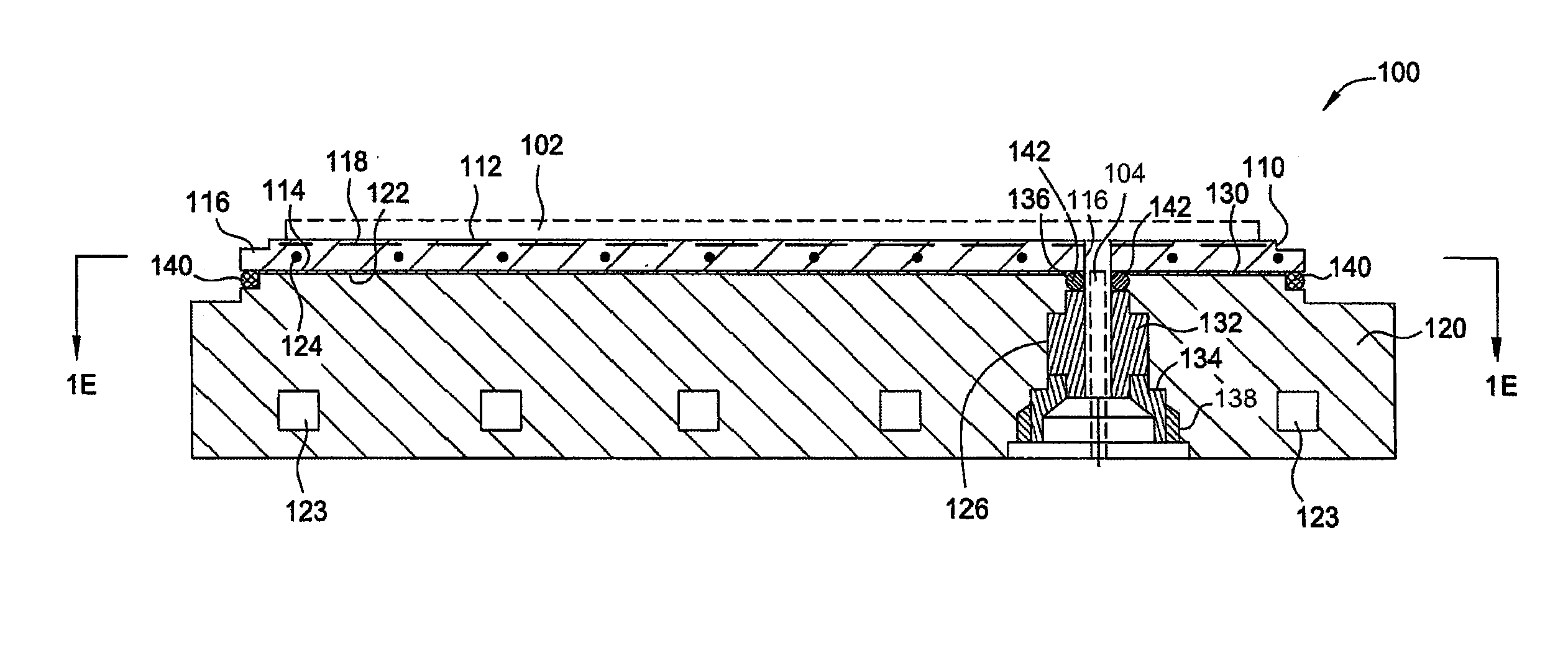
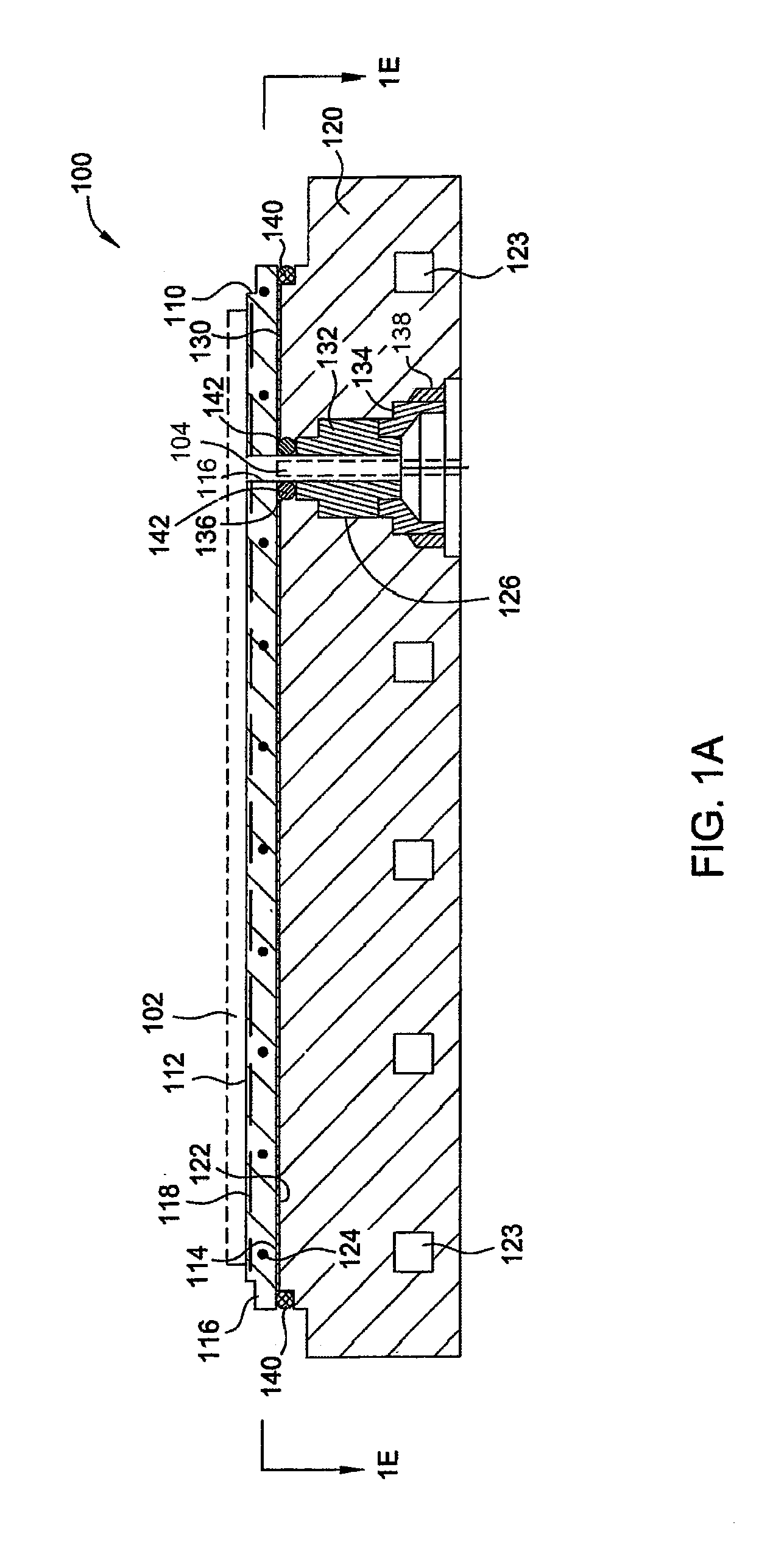
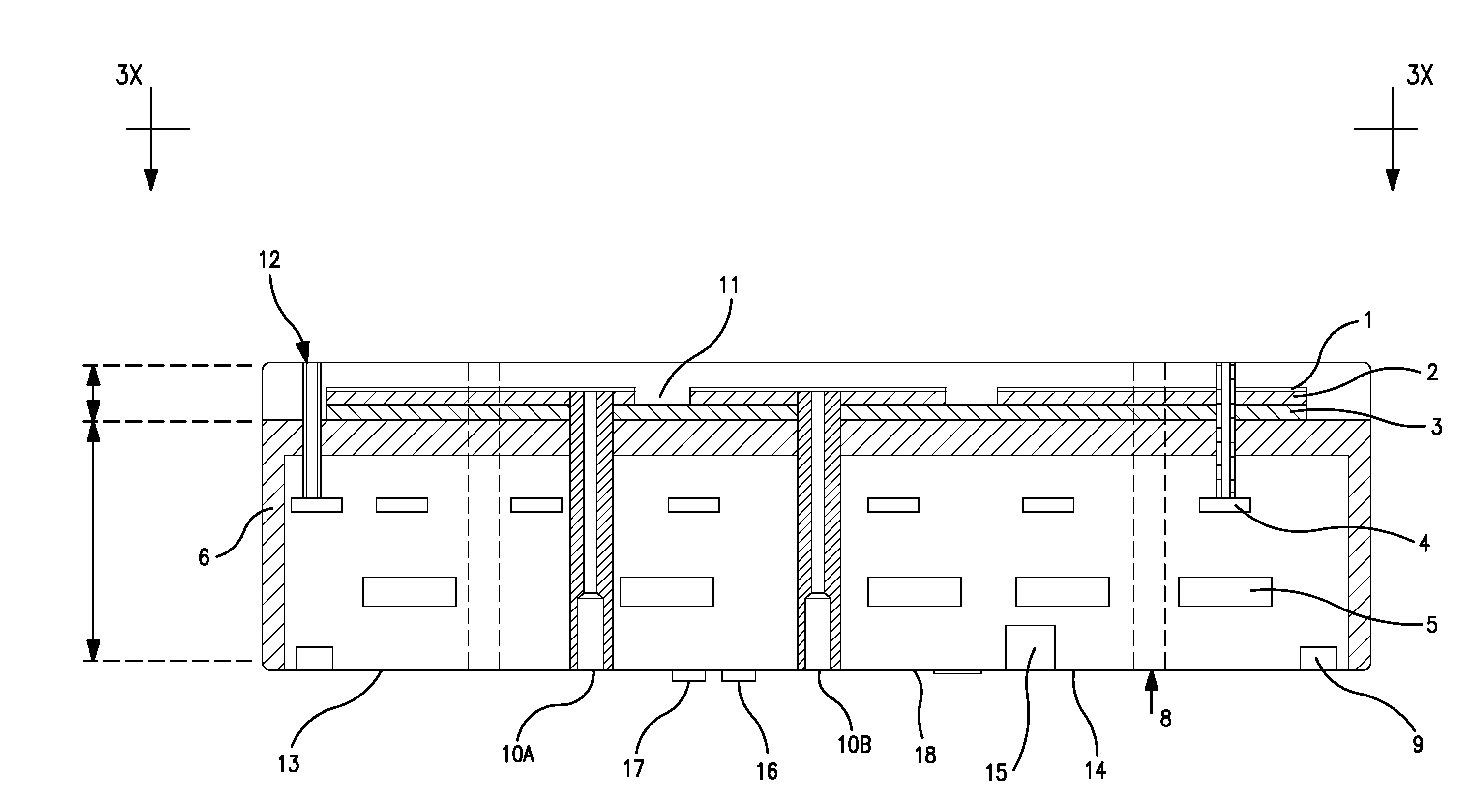
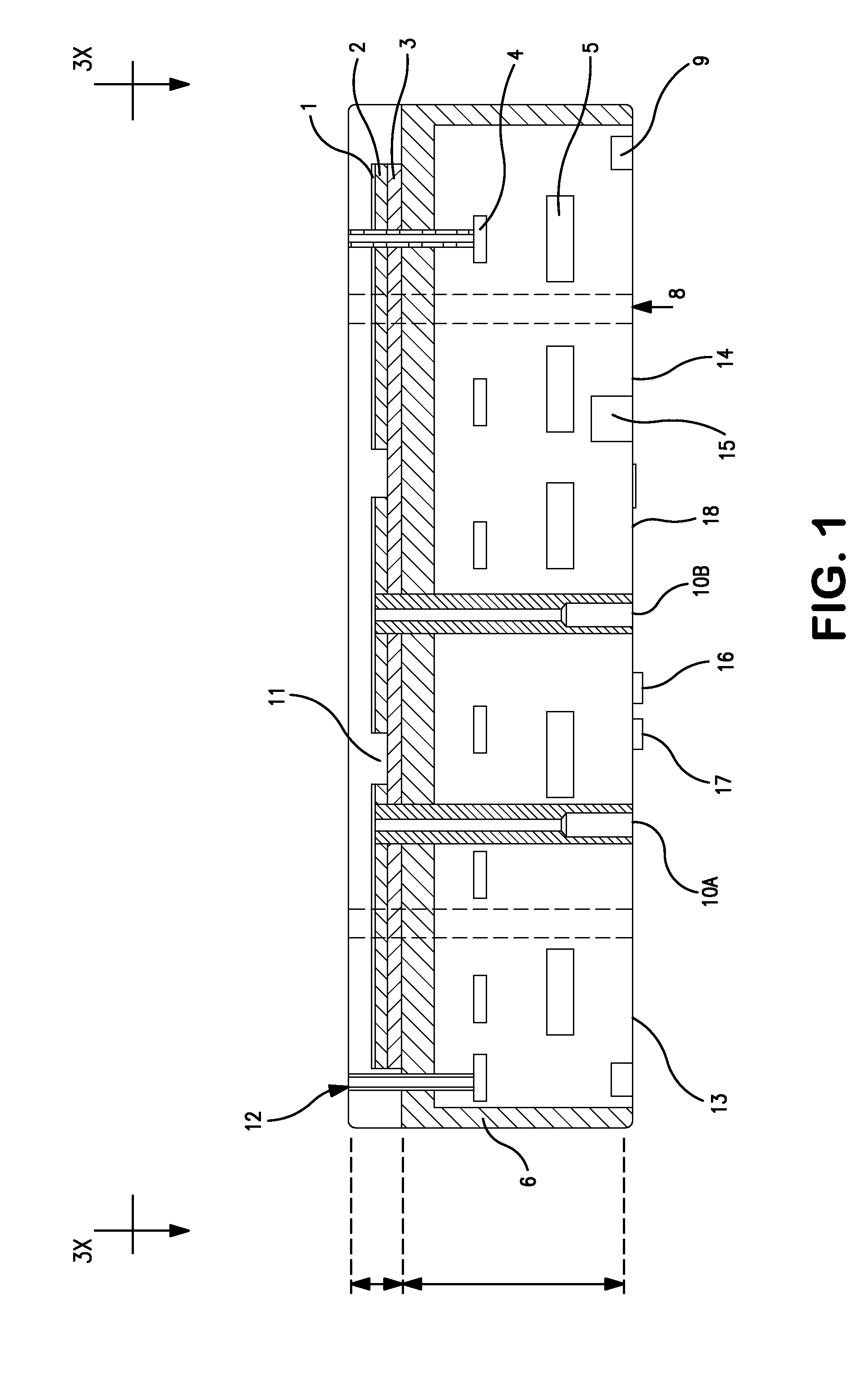
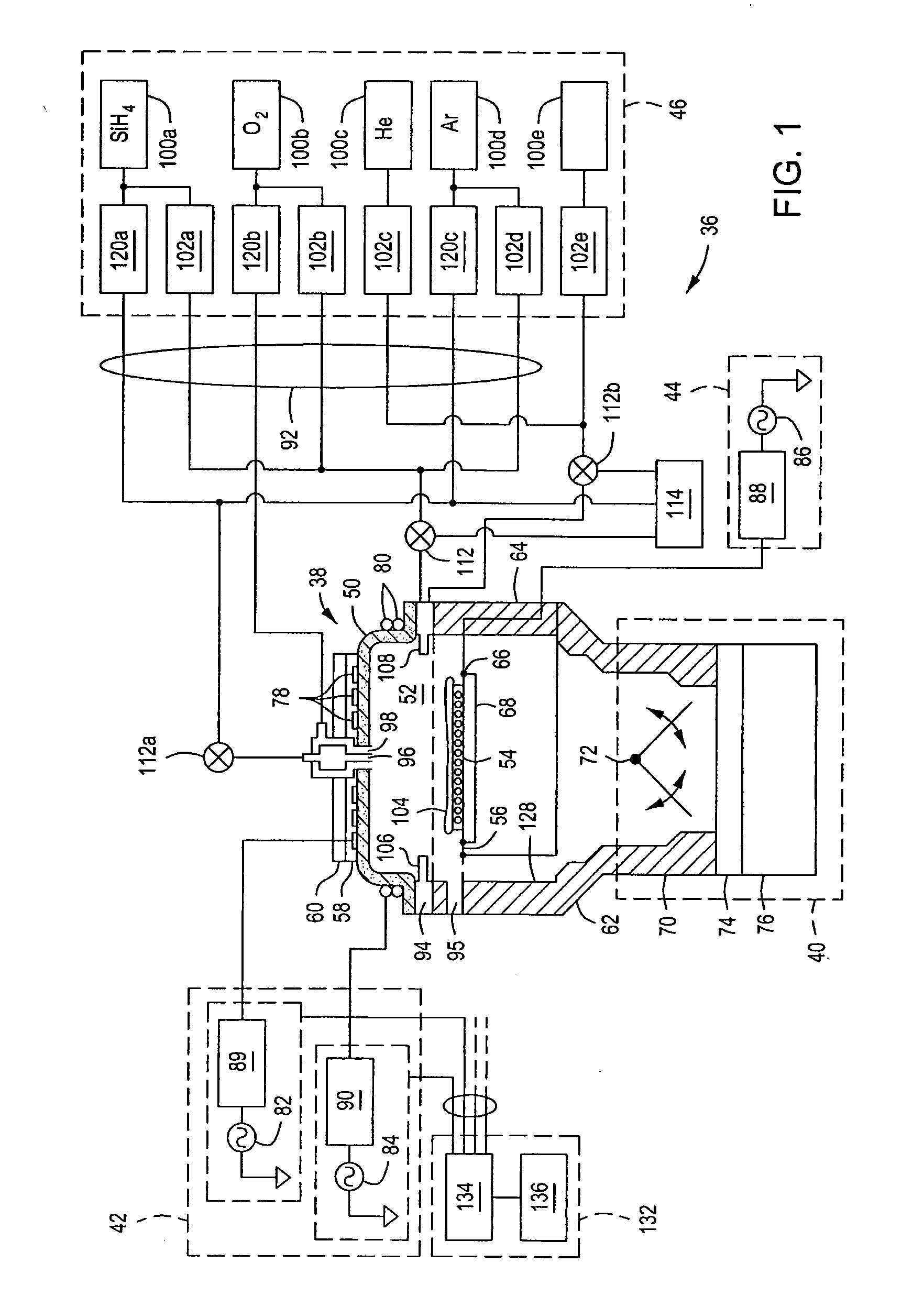
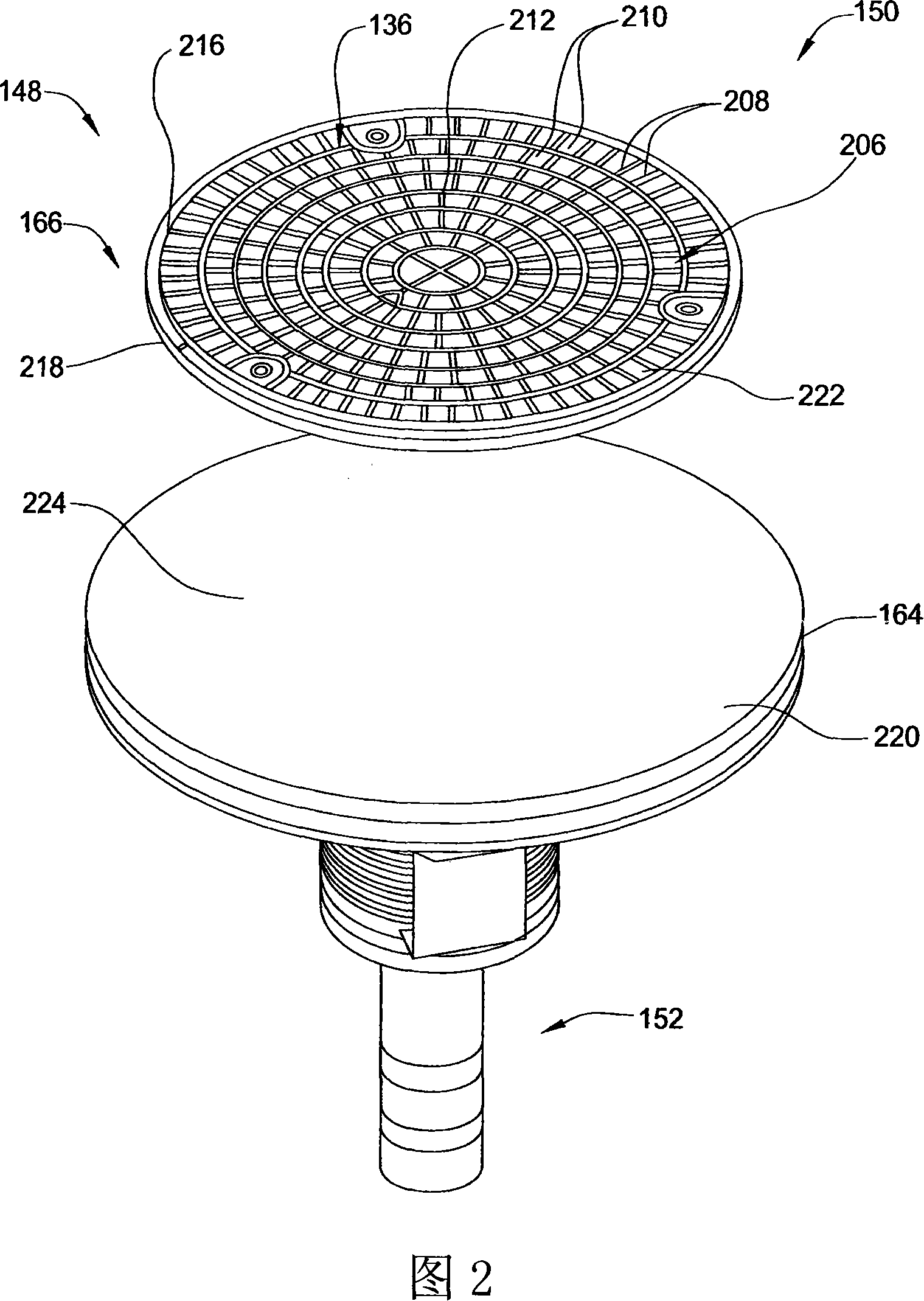
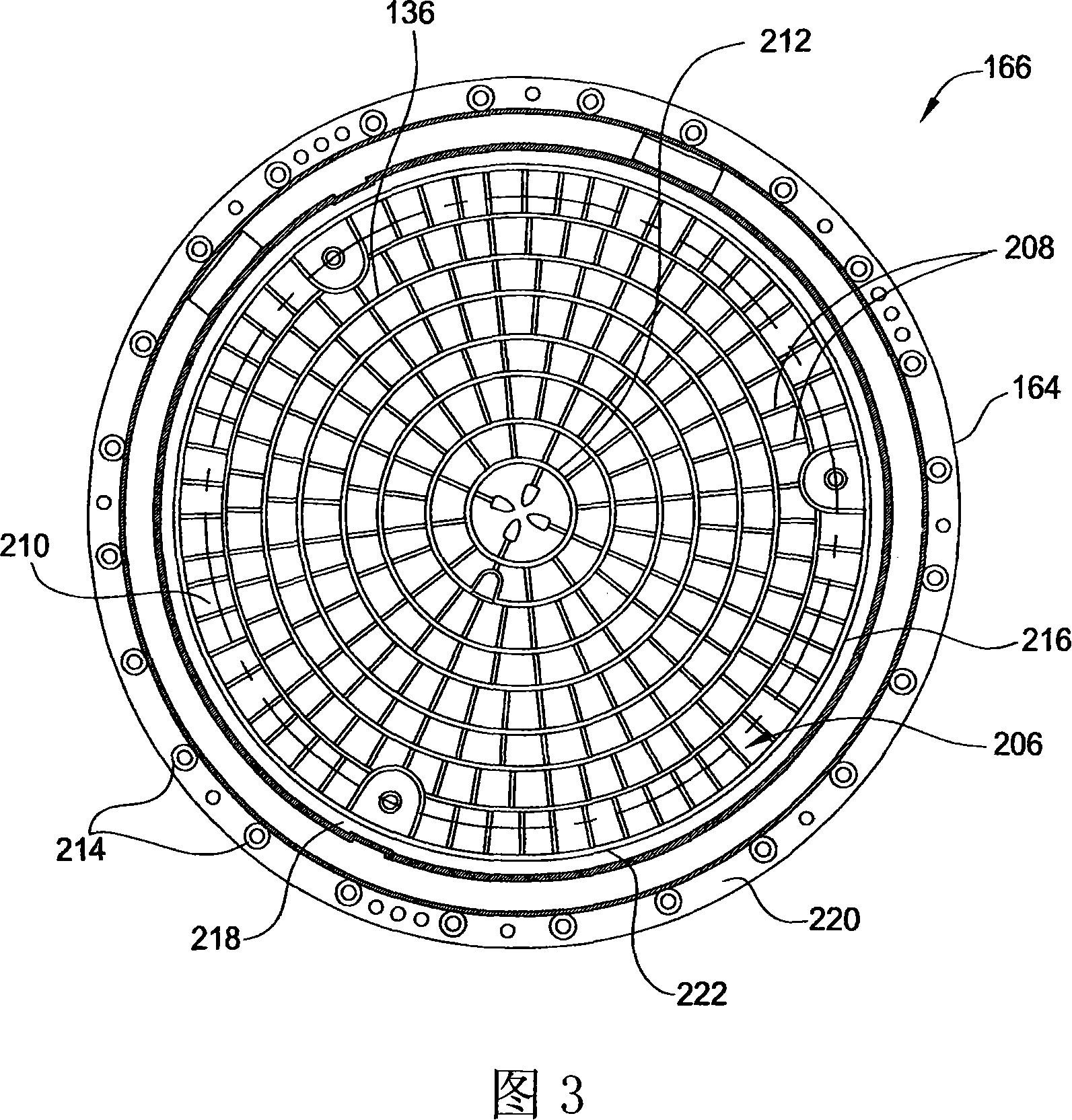
Electrostatic chuck assembly
ActiveUS20100039747A1Efficient couplingCost effectiveElectric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesUltra-high vacuumThermal expansion
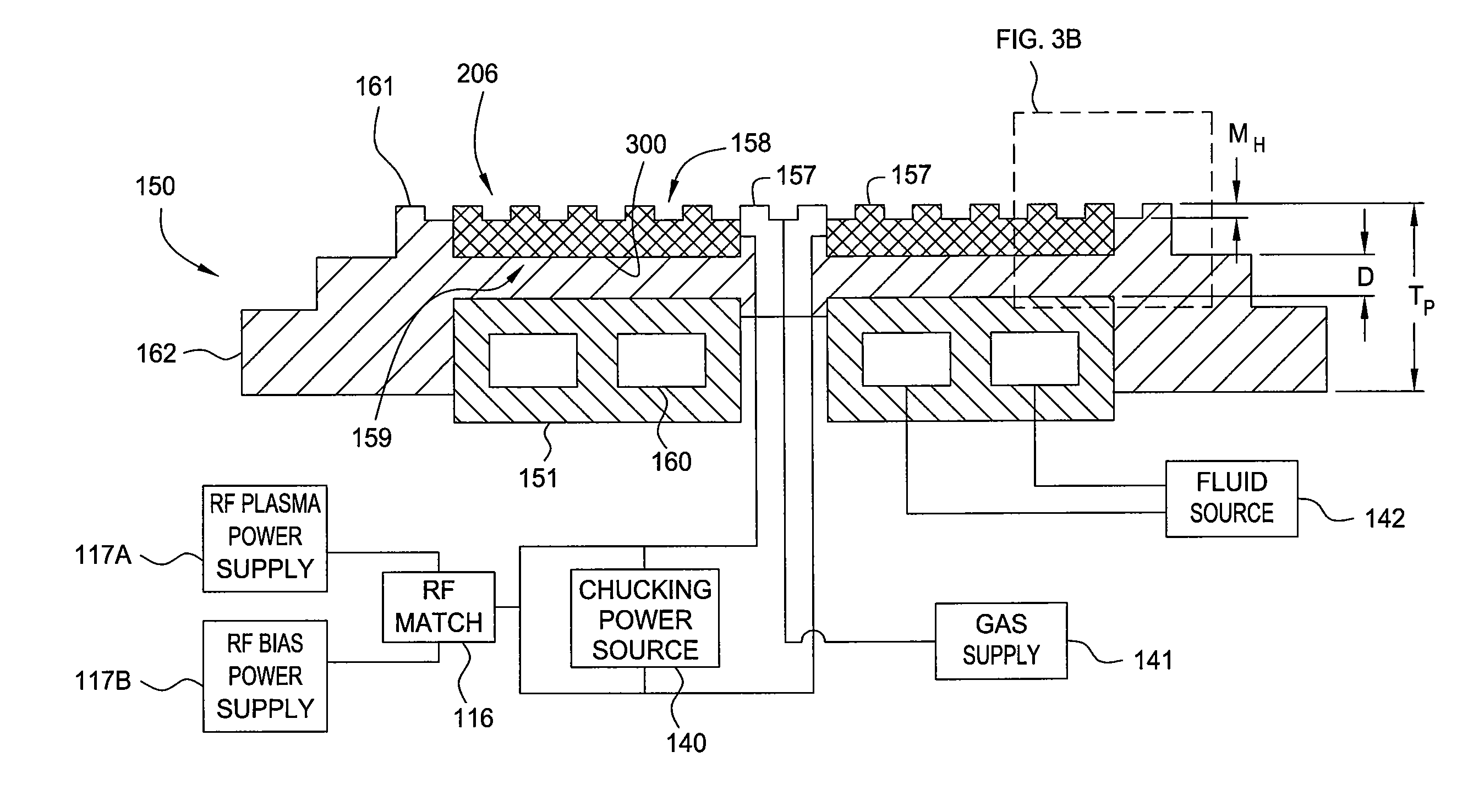
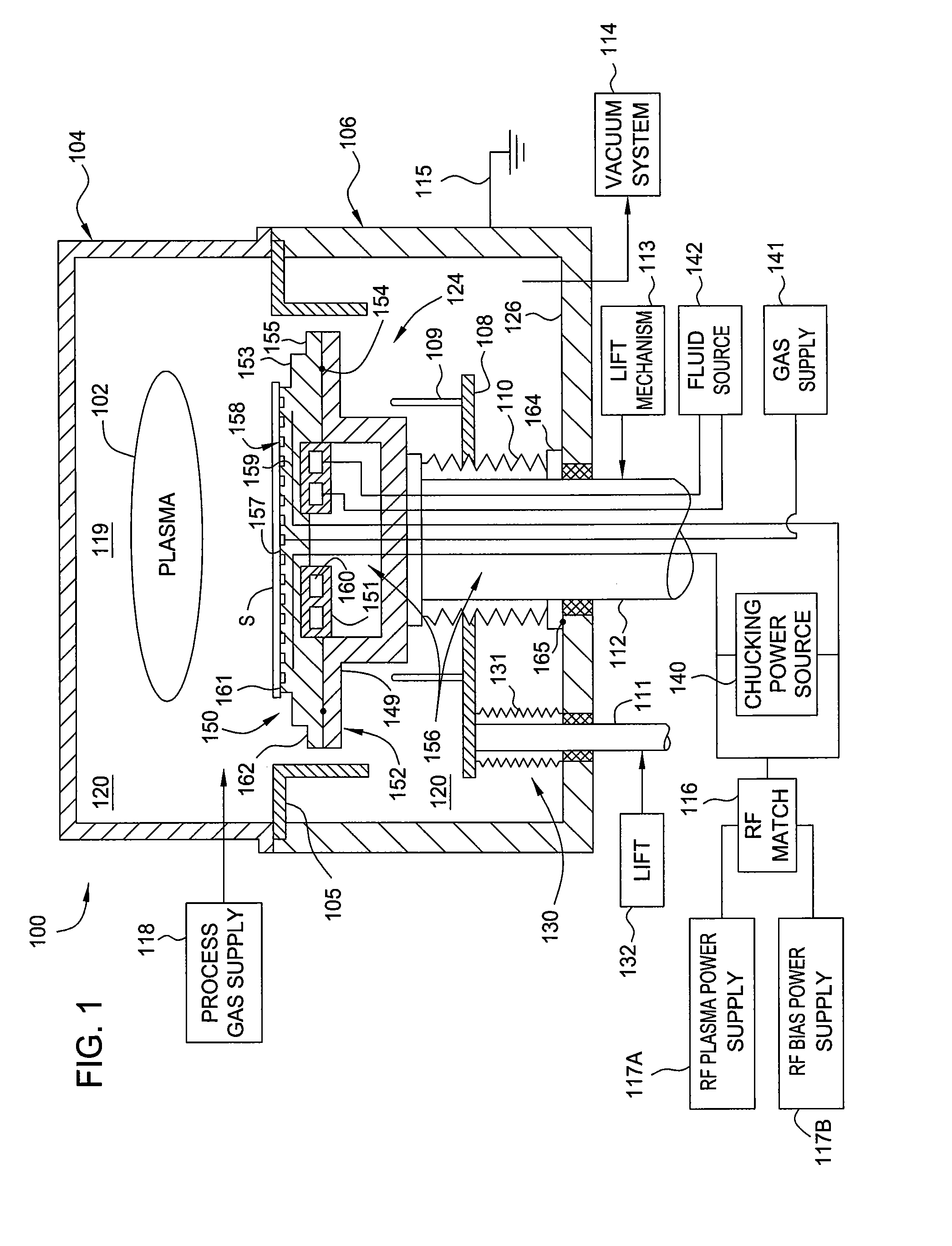
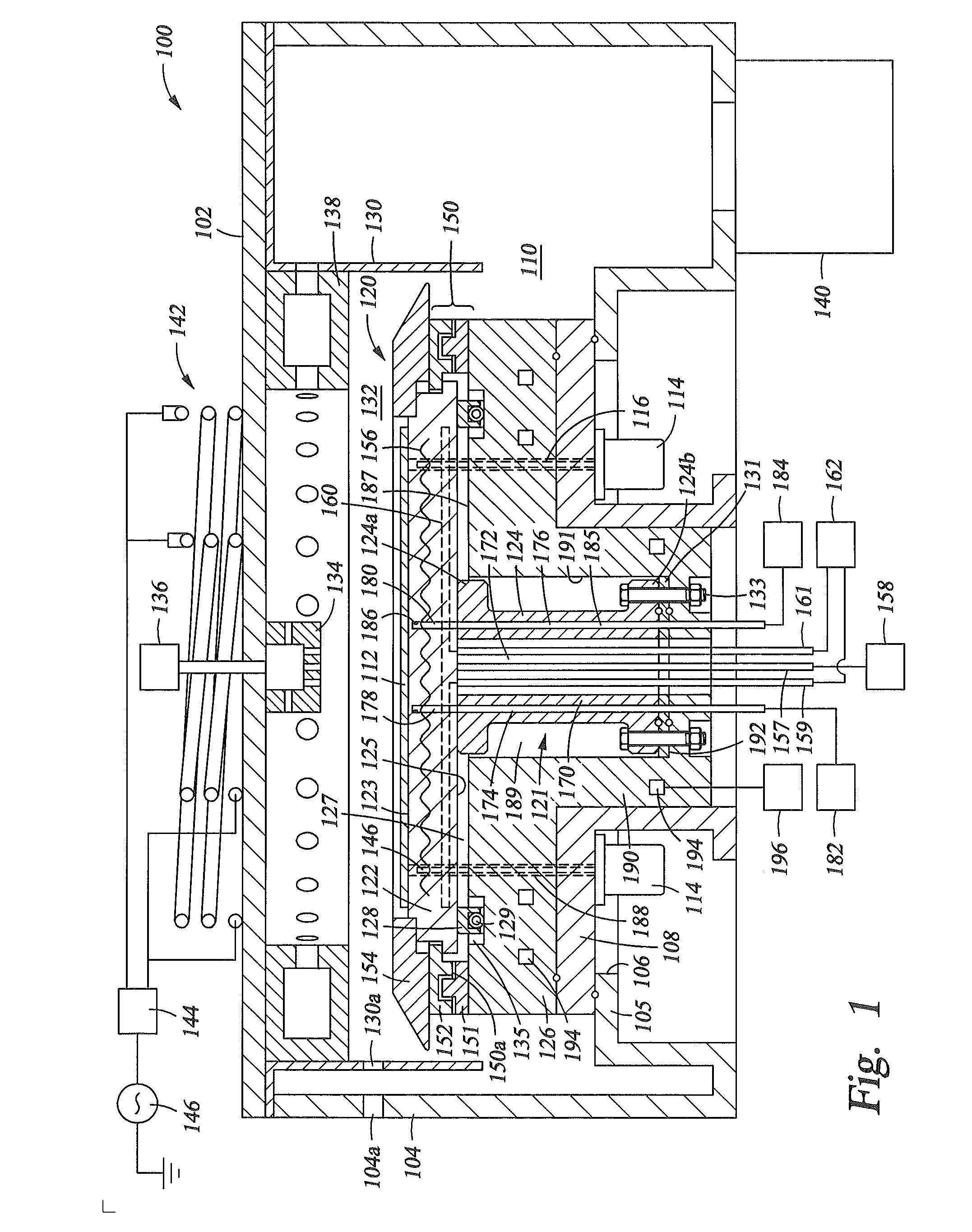
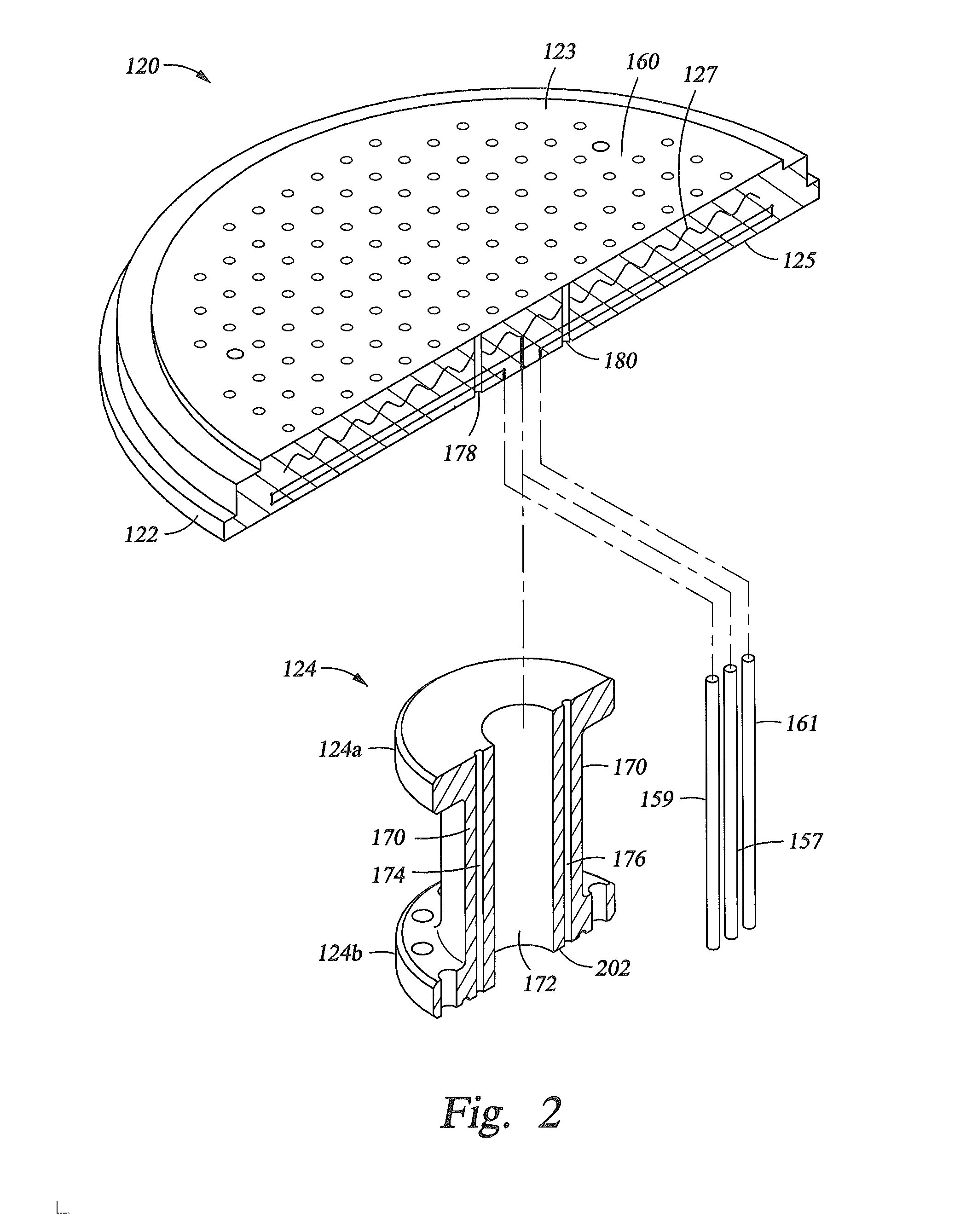
Embodiments of the present invention provide a cost effective electrostatic chuck assembly capable of operating over a wide temperature range in an ultra-high vacuum environment while minimizing thermo-mechanical stresses within the electrostatic chuck assembly. In one embodiment, the electrostatic chuck assembly includes a dielectric body having chucking electrodes which comprise a metal matrix composite material with a coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) that is matched to the CTE of the dielectric body.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
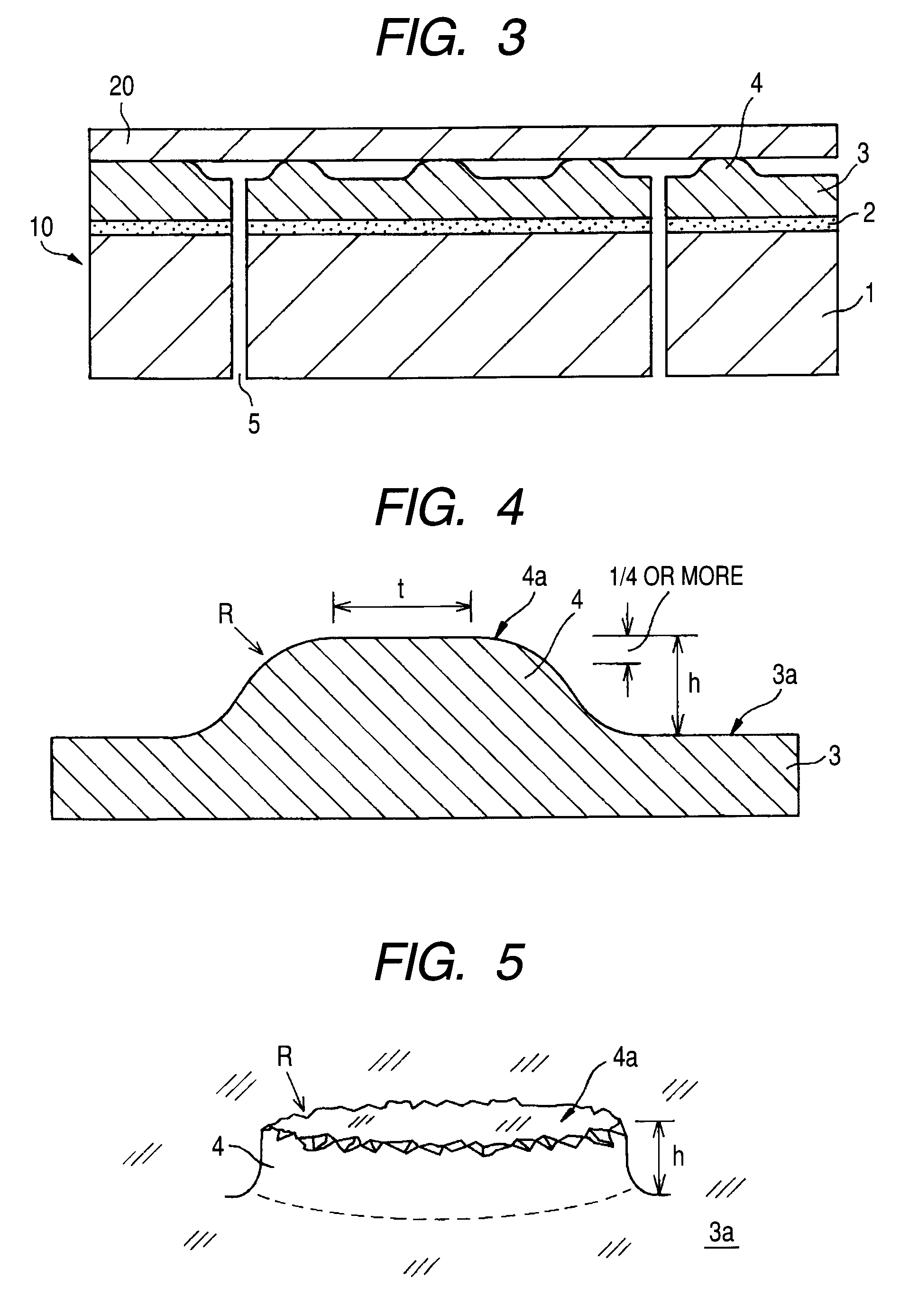
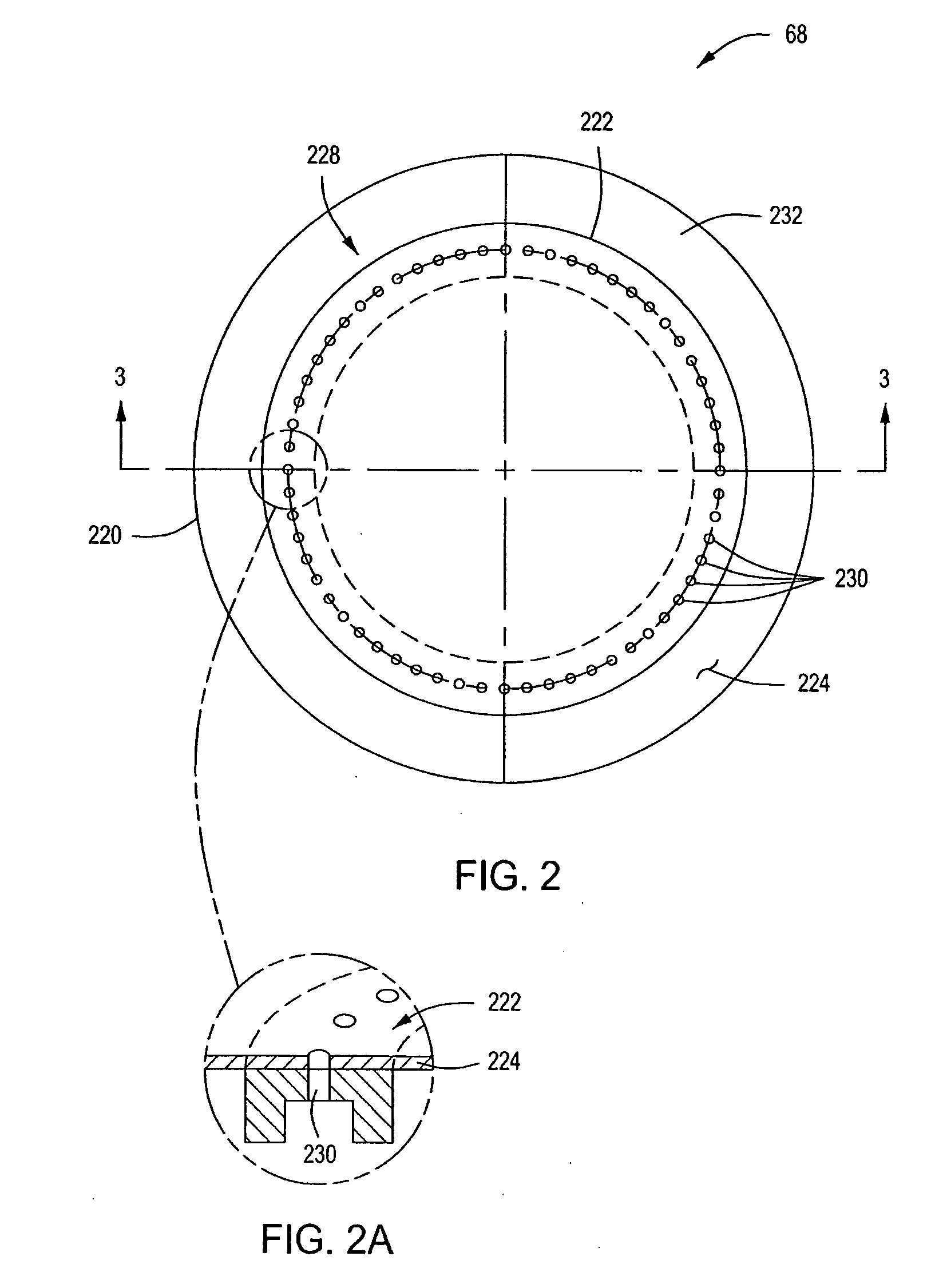
Electrostatic chuck member, method of manufacturing the same, and electrostatic chuck device
InactiveUS20090056112A1Good effectComplicated processingSleeve/socket jointsWave amplification devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
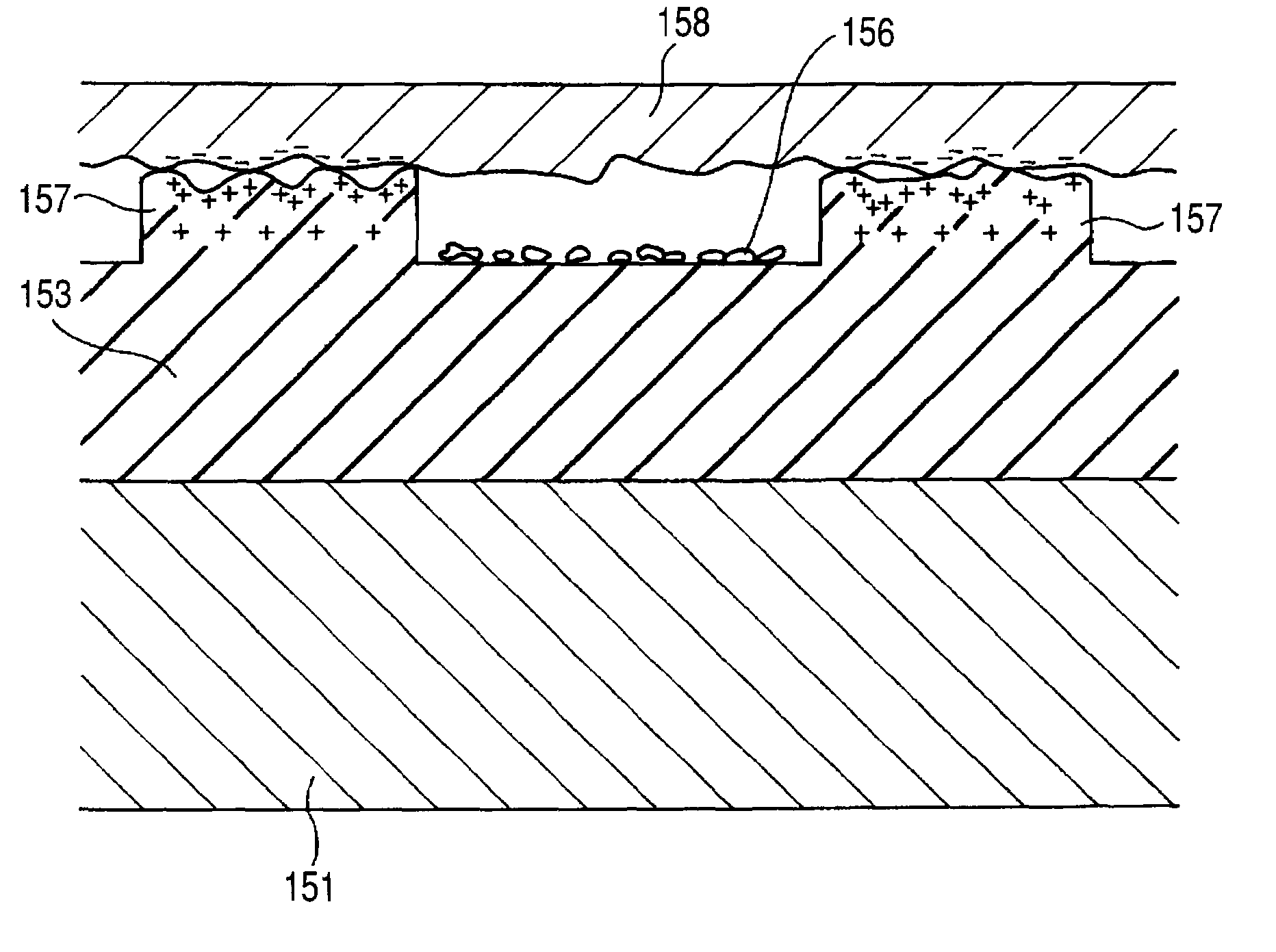
A plurality of protruded portions is formed through embossing and is distributed and arranged regularly or irregularly on an electrostatic chuck surface, and has a circular or almost circular top surface shape and a roundness (R) of 0.01 mm or more is applied to an edge part defined by an intersection of the top surface and a side surface and a portion to which the roundness is applied occupies a quarter of a height h of the protruded portion or more.
Owner:SHINKO ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
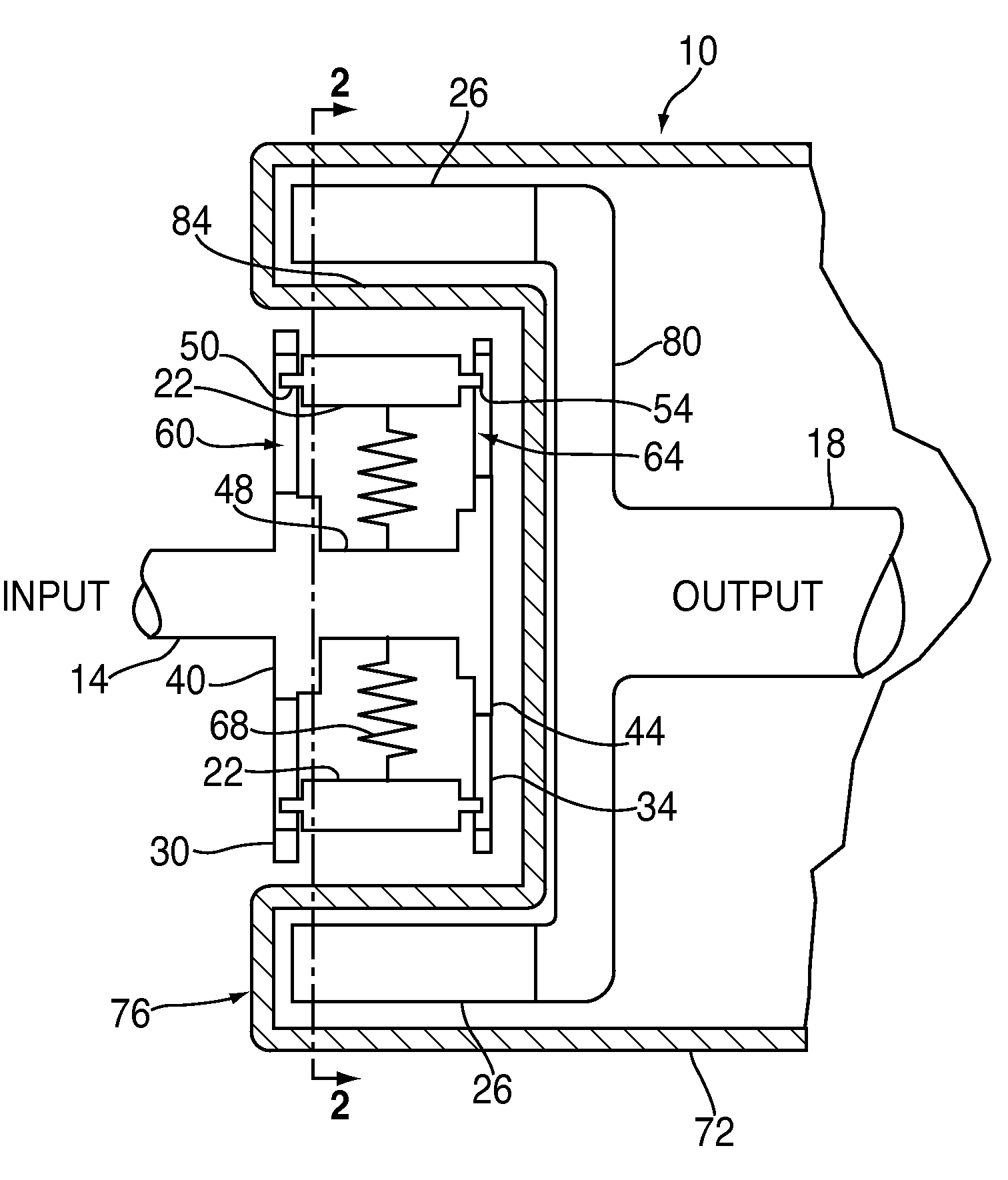
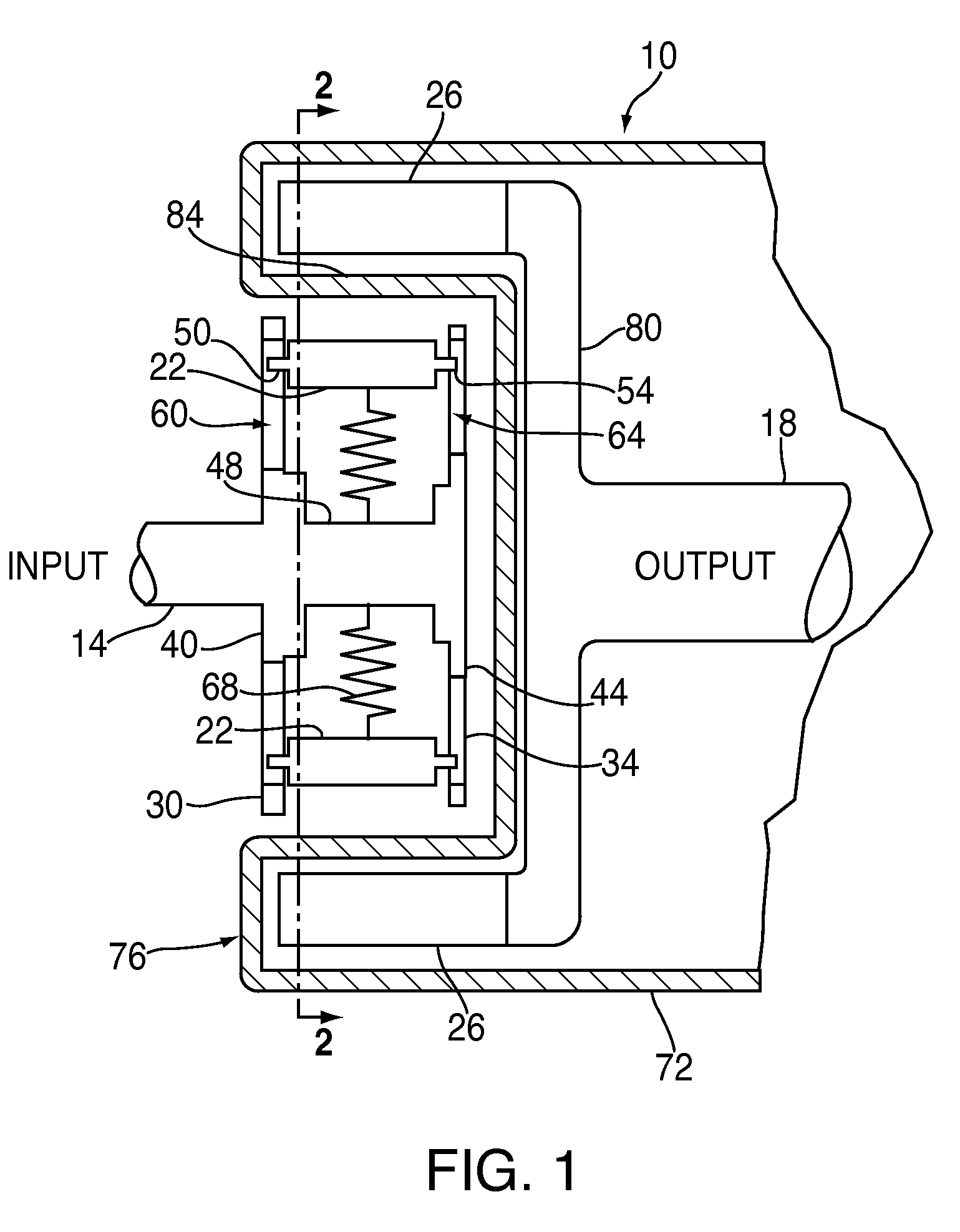
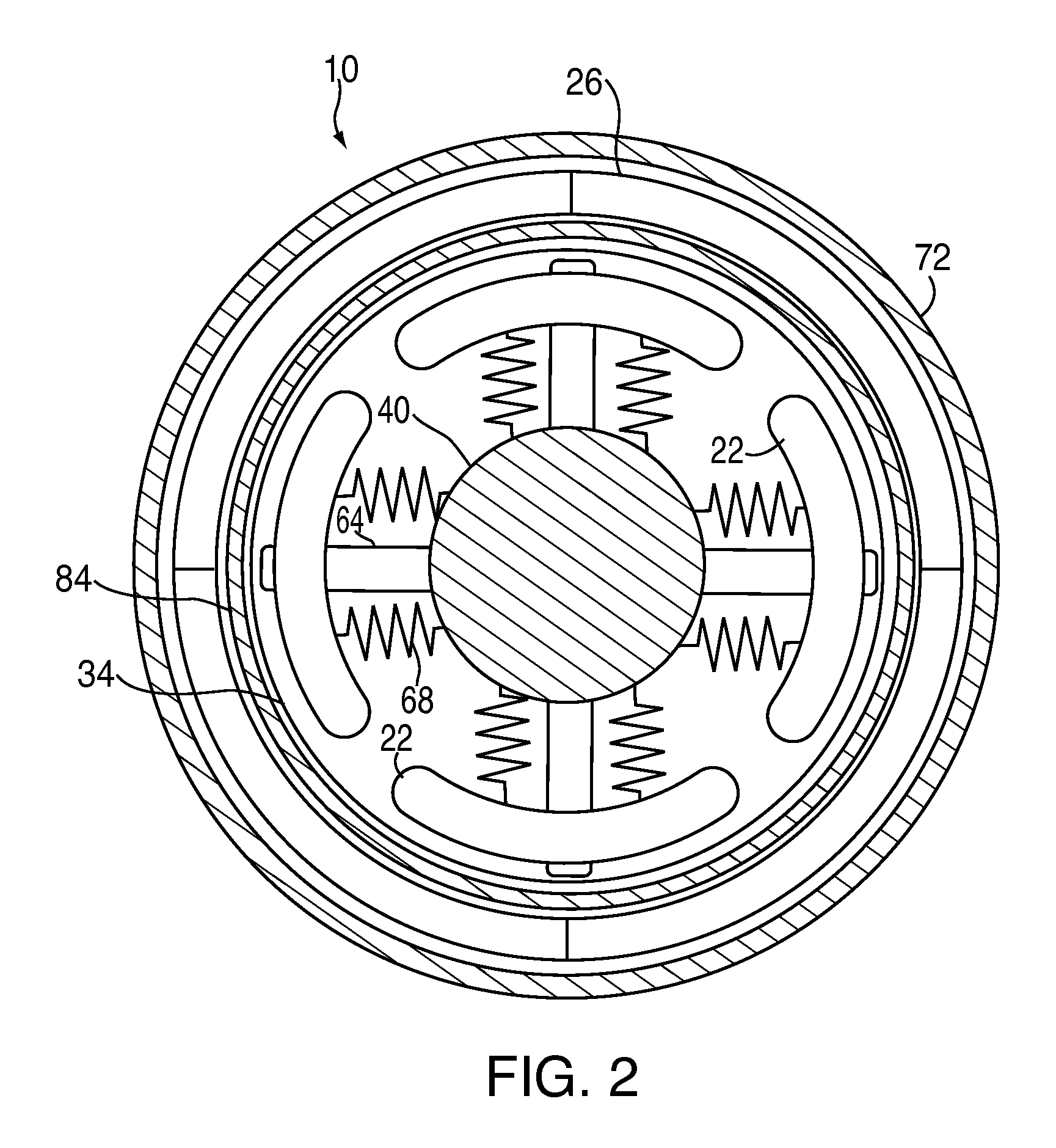
Magnetic torque-limiting device and method
In a torque-limiting device, a first end engages a fastener, a second end receives an applied torque, and a magnetic torque limiter transmits the applied torque from the second end to the first end to rotate the first end in conjunction with the second end when the applied torque is less than a predetermined limit.
Owner:PILLING WECK INC
Electrostatic chuck device
ActiveUS20180254211A1Prolong lifeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPositioning apparatusTemperature controlEngineering
An electrostatic chuck device includes an electrostatic chuck member and a temperature controlling base member. The electrostatic chuck member has a ceramic plate having a mounting surface on which a plate-shaped sample is mounted, and an electrode for electrostatic attraction provided on the other surface on the side opposite the mounting surface of the ceramic plate. The temperature controlling base member is disposed on the surface on the side opposite the ceramic plate side of the electrode for electrostatic attraction and cools the electrostatic chuck member. The ceramic plate has a dike portion which extends to the temperature controlling base member side and surrounds the electrode for electrostatic attraction, the temperature controlling base member has a groove portion accommodating an end part of the dike portion, and a space between the groove portion and the dike portion is filled with a filling part formed of a resin material.
Owner:SUMITOMO OSAKA CEMENT CO LTD
Electrostatic chuck assembly
ActiveUS8390980B2Efficient couplingCost effectiveElectric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesUltra-high vacuumThermal expansion
Embodiments of the present invention provide a cost effective electrostatic chuck assembly capable of operating over a wide temperature range in an ultra-high vacuum environment while minimizing thermo-mechanical stresses within the electrostatic chuck assembly. In one embodiment, the electrostatic chuck assembly includes a dielectric body having chucking electrodes which comprise a metal matrix composite material with a coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) that is matched to the CTE of the dielectric body.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
High temperature electrostatic chuck with real-time heat zone regulating capability
ActiveUS20130284374A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChucksTemperature controlHigh heat
Embodiments of the present invention provide electrostatic chucks for operating at elevated temperatures. One embodiment of the present invention provides a dielectric chuck body for an electrostatic chuck. The dielectric chuck body includes a substrate supporting plate having a top surface for receiving a substrate and a back surface opposing the top surface, an electrode embedded in the substrate supporting plate, and a shaft having a first end attached to the back surface of the substrate supporting plate and a second end opposing the first end. The second end is configured to contact a cooling base and provide temperature control to the substrate supporting plate. The shaft is hollow having a sidewall enclosing a central opening, and two or more channels formed through the sidewall and extending from the first end to the second end.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
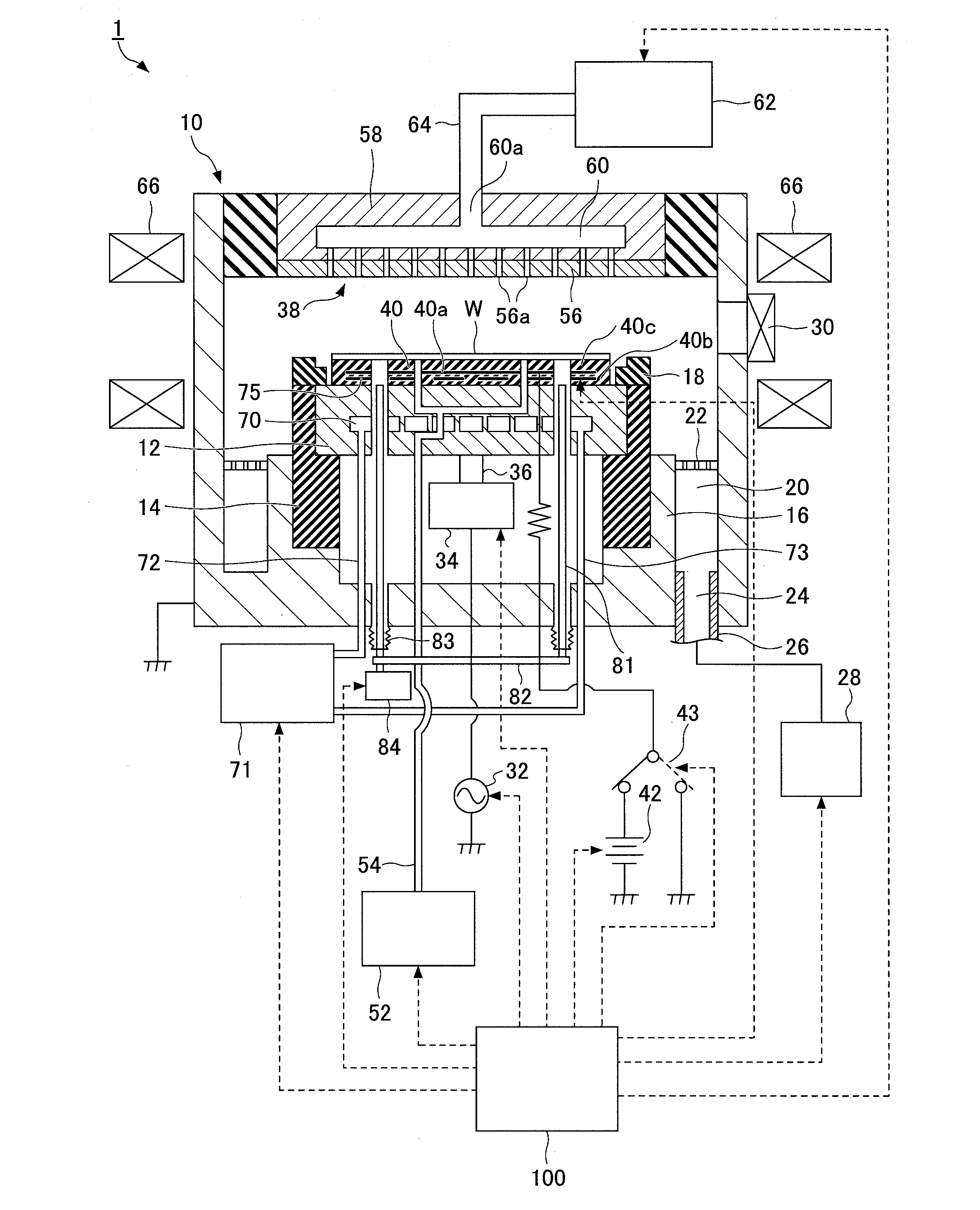
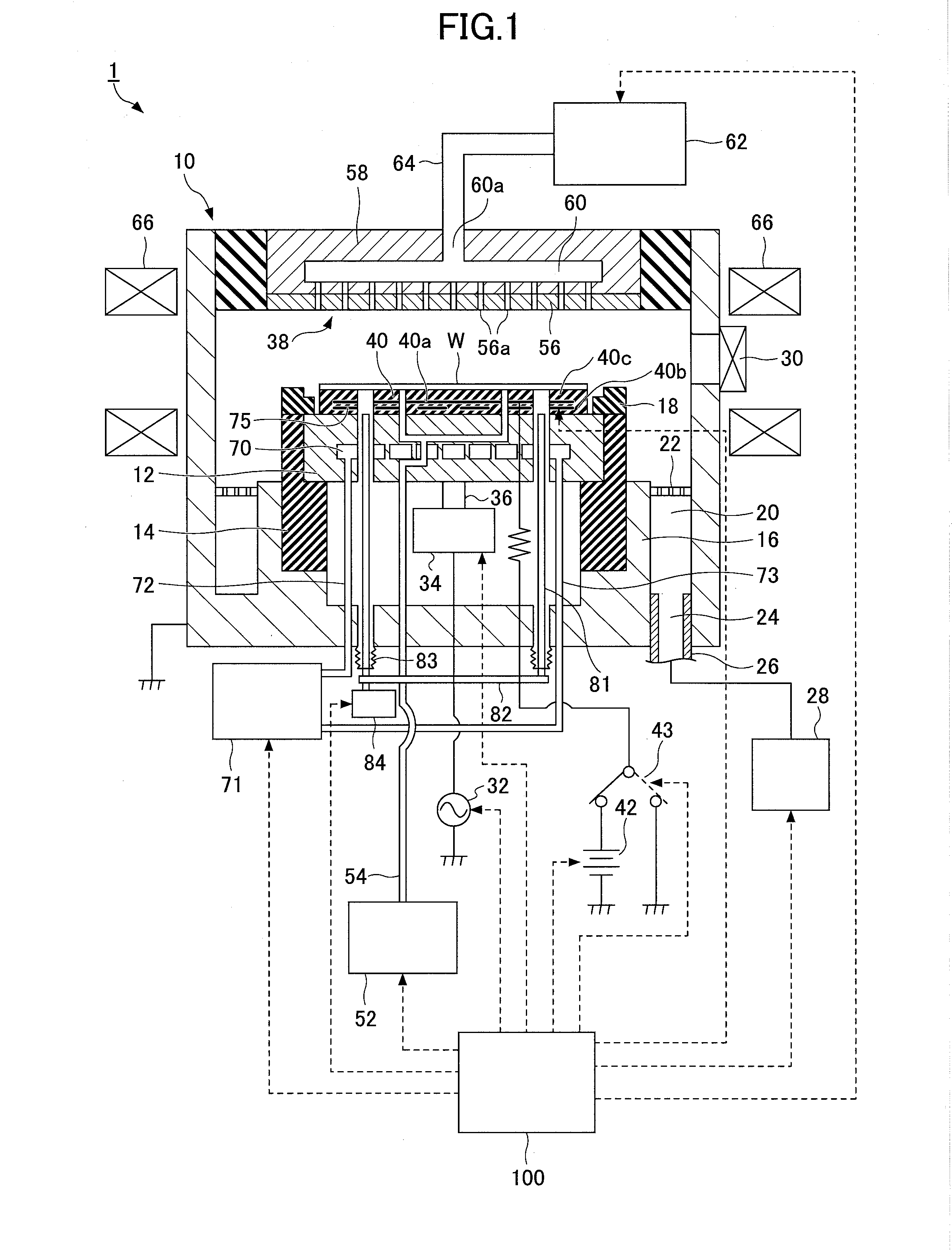
Electrostatic chuck with advanced RF and temperature uniformity
ActiveUS8937800B2Improve the level ofIncrease the diameterWorkpiece holdersSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringRadio frequency
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Electrostatic chuck with advanced RF and temperature uniformity
ActiveUS20130279066A1Improve the level ofIncrease the diameterWorkpiece holdersSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringRadio frequency
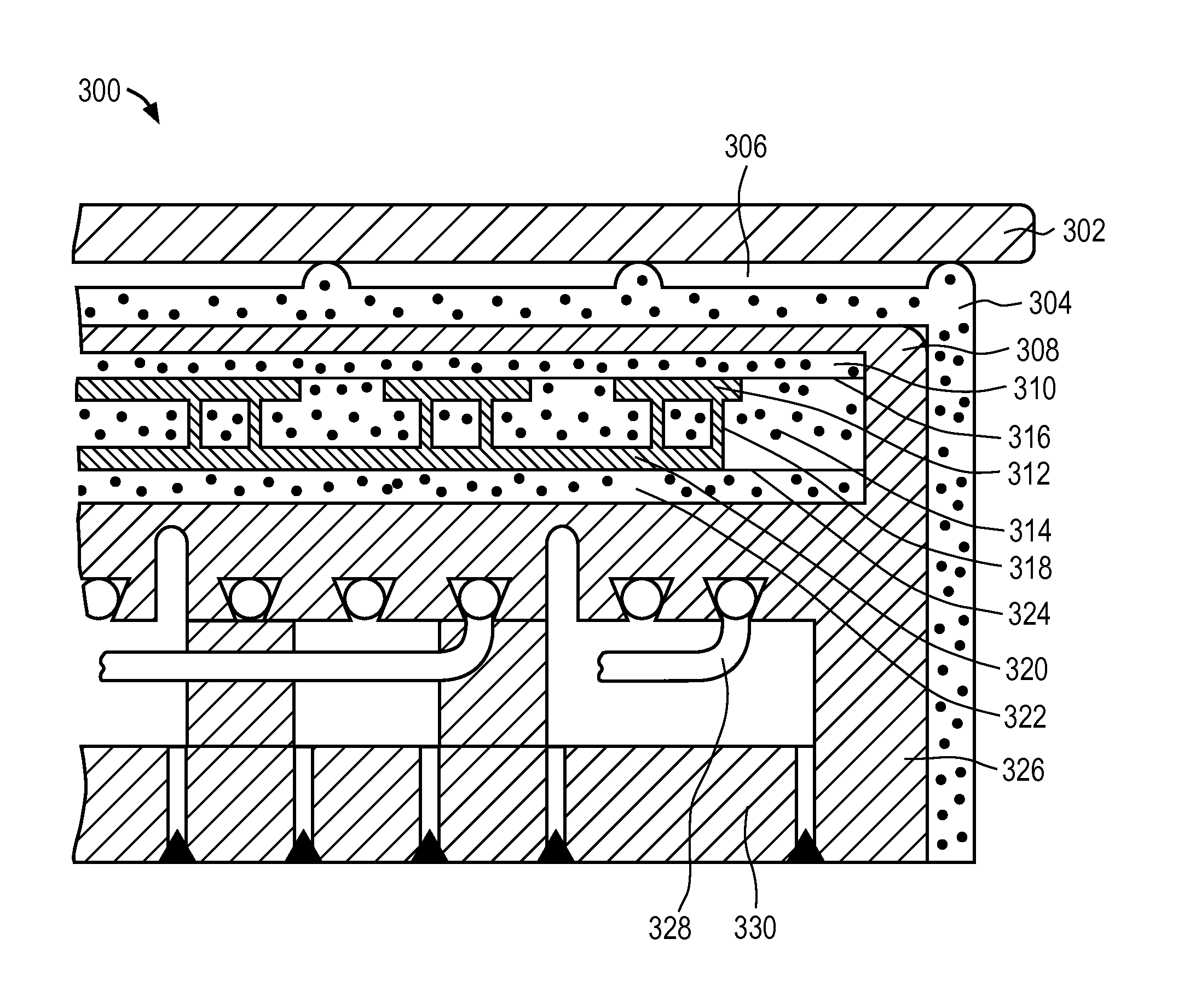
Electrostatic chucks (ESCs) with RF and temperature uniformity are described. For example, an ESC includes a top dielectric layer. An upper metal portion is disposed below the top dielectric layer. A second dielectric layer is disposed above a plurality of pixilated resistive heaters and surrounded in part by the upper metal portion. A third dielectric layer is disposed below the second dielectric layer, with a boundary between the third dielectric layer and the second dielectric layer. A plurality of vias is disposed in the third dielectric layer. A bus power bar distribution layer is disposed below and coupled to the plurality of vias. A fourth dielectric layer is disposed below the bus bar power distribution layer, with a boundary between the fourth dielectric layer and the third dielectric layer. A metal base is disposed below the fourth dielectric layer. The metal base includes a plurality of high power heater elements housed therein.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
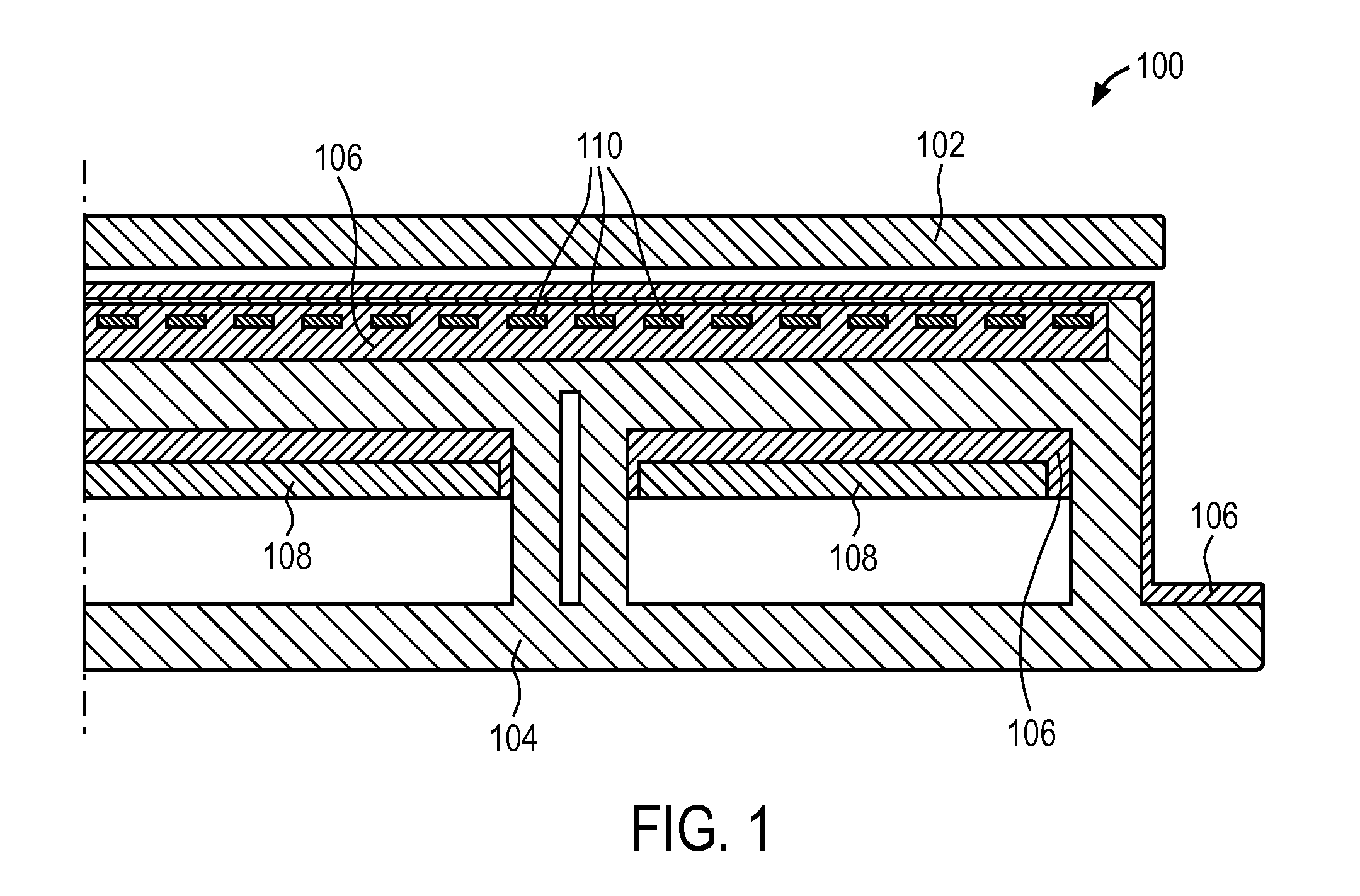
Electrostatic chuck
ActiveUS20090284894A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic holding devicesSurface layerEngineering
In accordance with an embodiment of the invention, there is provided an electrostatic chuck comprising an electrode, and a surface layer activated by a voltage in the electrode to form an electric charge to electrostatically clamp a substrate to the electrostatic chuck. The surface layer includes a plurality of protrusions extending to a height above portions of the surface layer surrounding the protrusions to support the substrate upon the protrusions during electrostatic clamping of the substrate. The protrusions are substantially equally spaced across the surface layer as measured by a center to center distance between pairs of neighboring protrusions.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Pixelated capacitance controlled ESC
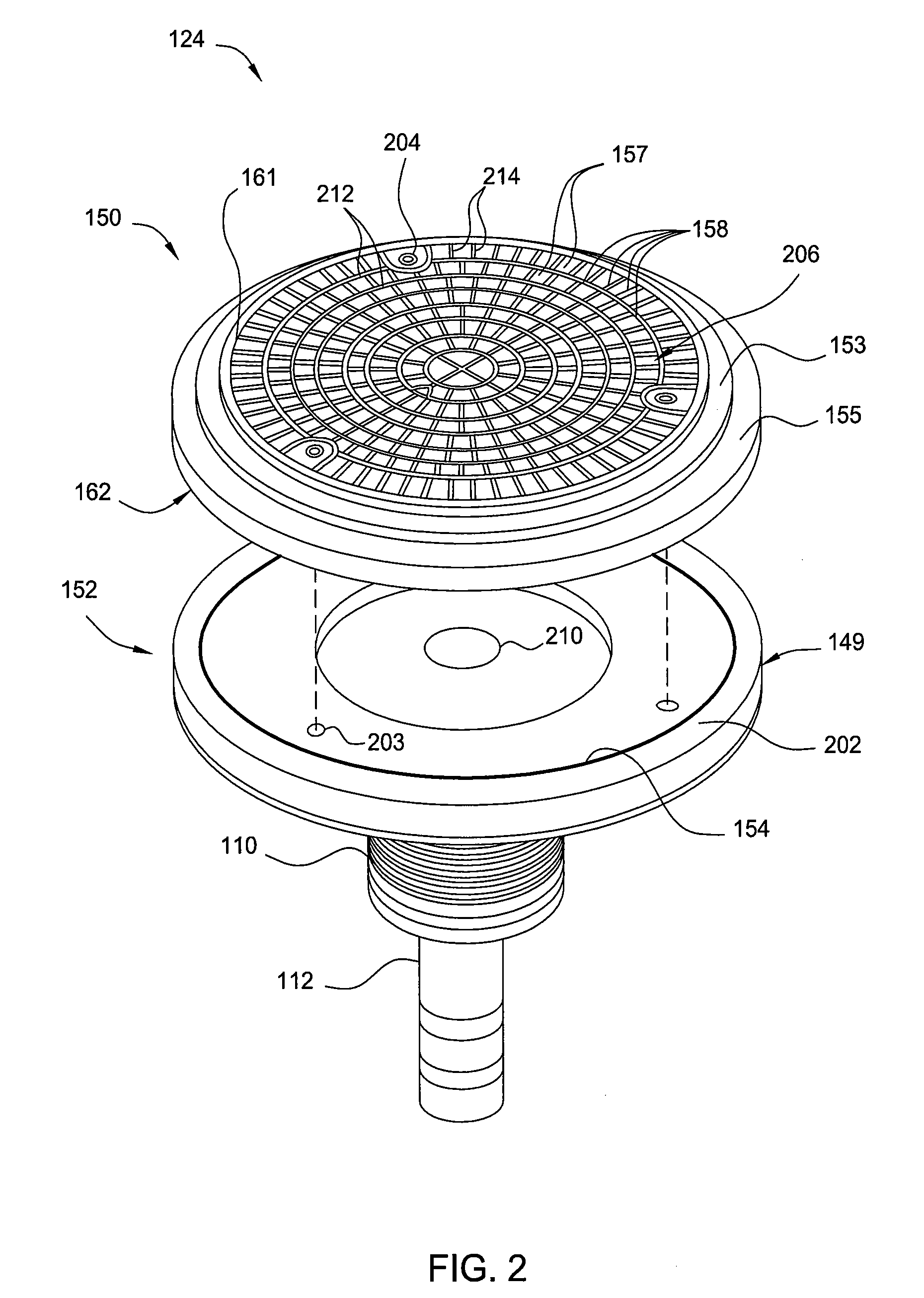
Implementations described herein provide a pixilated electrostatic chuck which enables both lateral and azimuthal tuning of the RF coupling between an electrostatic chuck and a substrate placed thereon. In one embodiment, the pixilated electrostatic chuck (ESC) may include a dielectric body having a workpiece support surface configured to accept a substrate thereon, one or more chucking electrodes disposed in the pixilated ESC, and a plurality of pixel electrodes. The plurality of pixel electrodes are switchable between a floating state and a grounded state, having variable capacitance to ground, or both. The pixel electrodes and the chucking electrodes form a circuit operable to electrostatically chuck the substrate to the workpiece support surface.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
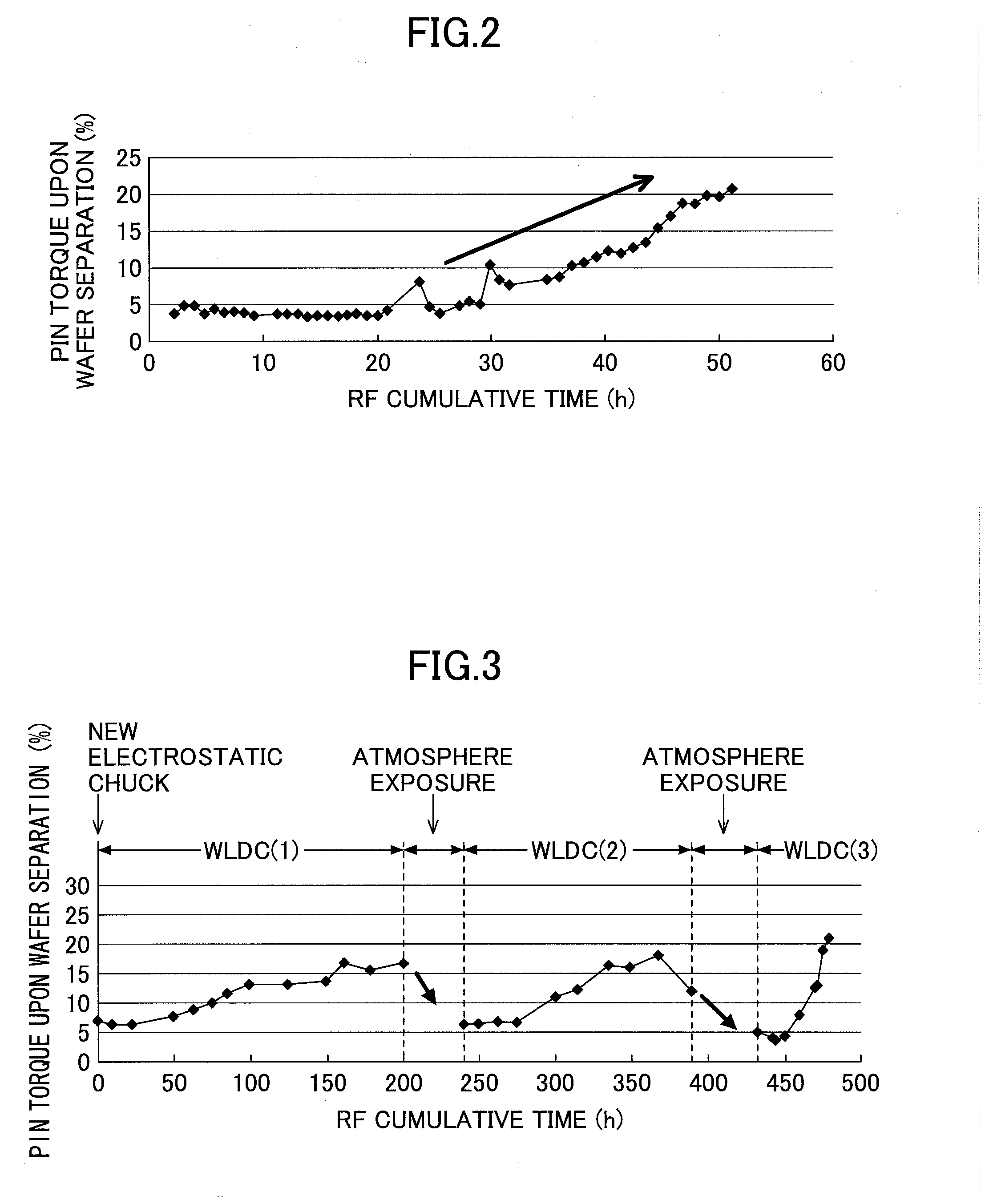
Methods and apparatus toward preventing esc bonding adhesive erosion
Embodiments of the present invention provide chamber components having a protective element for shielding bonding material from processing environments in a processing environment. The protective element may include protective seals, protective structures, erosion resistive fillers, or combinations thereof. Embodiments of the present invention reduce erosion of bonding material used in a processing chamber, thus, improving processing quality and reducing maintenance costs.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Electrostatic chuck member
InactiveUS20090080136A1Avoid damageAvoid layeringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic holding devicesSurface roughnessSpray coating
An electrostatic chuck member comprises an electrode layer and an electric insulating layer, wherein a spray coating layer of an oxide of a Group 3A element in the Periodic Table is formed as an outermost layer of the member and a surface of the spray coating layer is rendered into a densified re-melting layer having an average surface roughness (Ra) Of 0.8-3.0 μm.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD +1
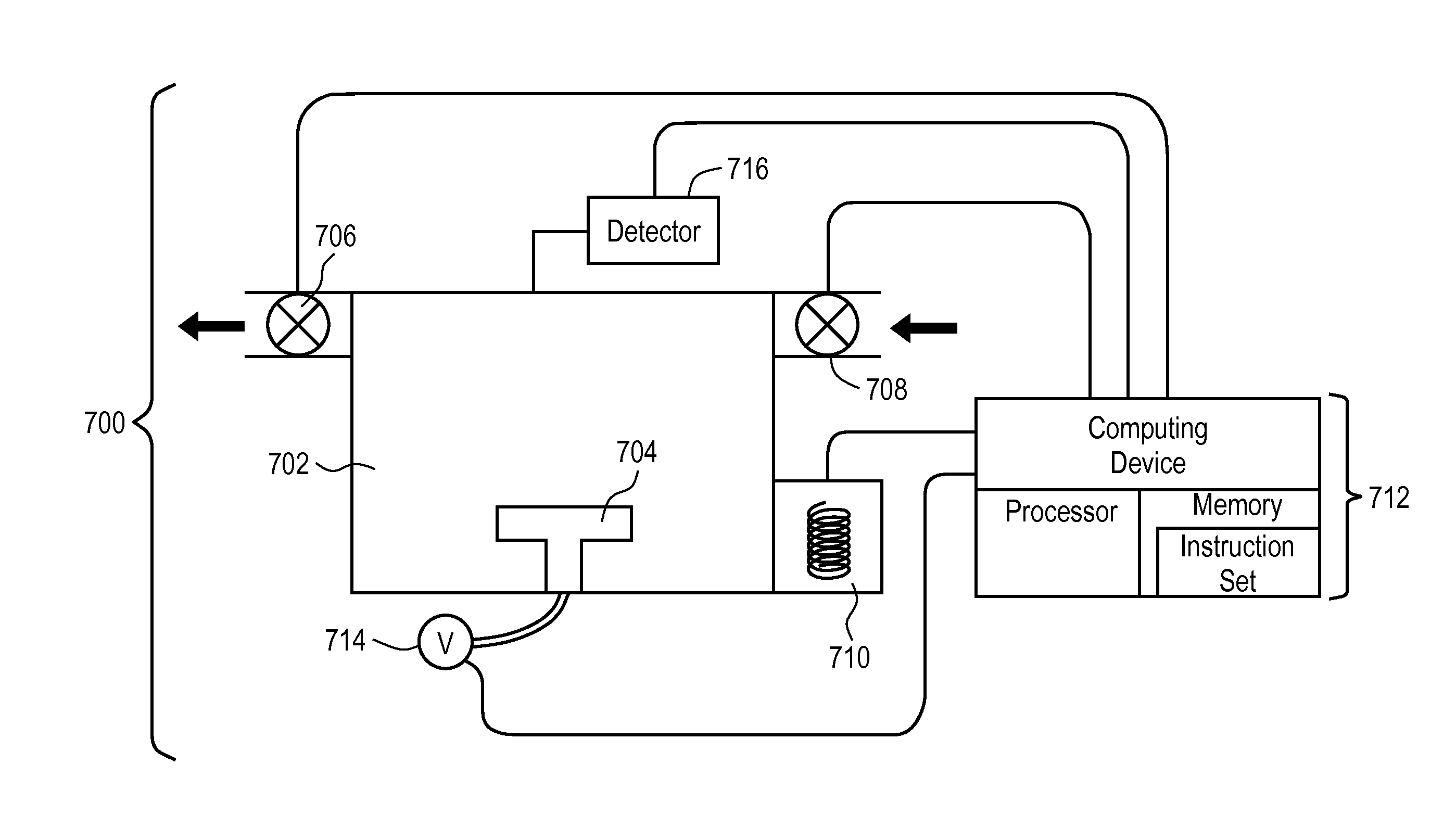
Method of modifying electrostatic chuck and plasma processing apparatus
ActiveUS20140158154A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh frequency powerHydrogen
A method of modifying an electrostatic chuck that electrostatically attracts a processing object is provided. The method includes a gas supplying step of supplying a gas containing hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) into a chamber accommodating the electrostatic chuck having a surface that is fluorinated; and a modifying step of turning the gas supplied to the chamber into plasma using a high frequency power, exposing the electrostatic chuck to the plasma, and modifying the fluorinated surface of the electrostatic chuck.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
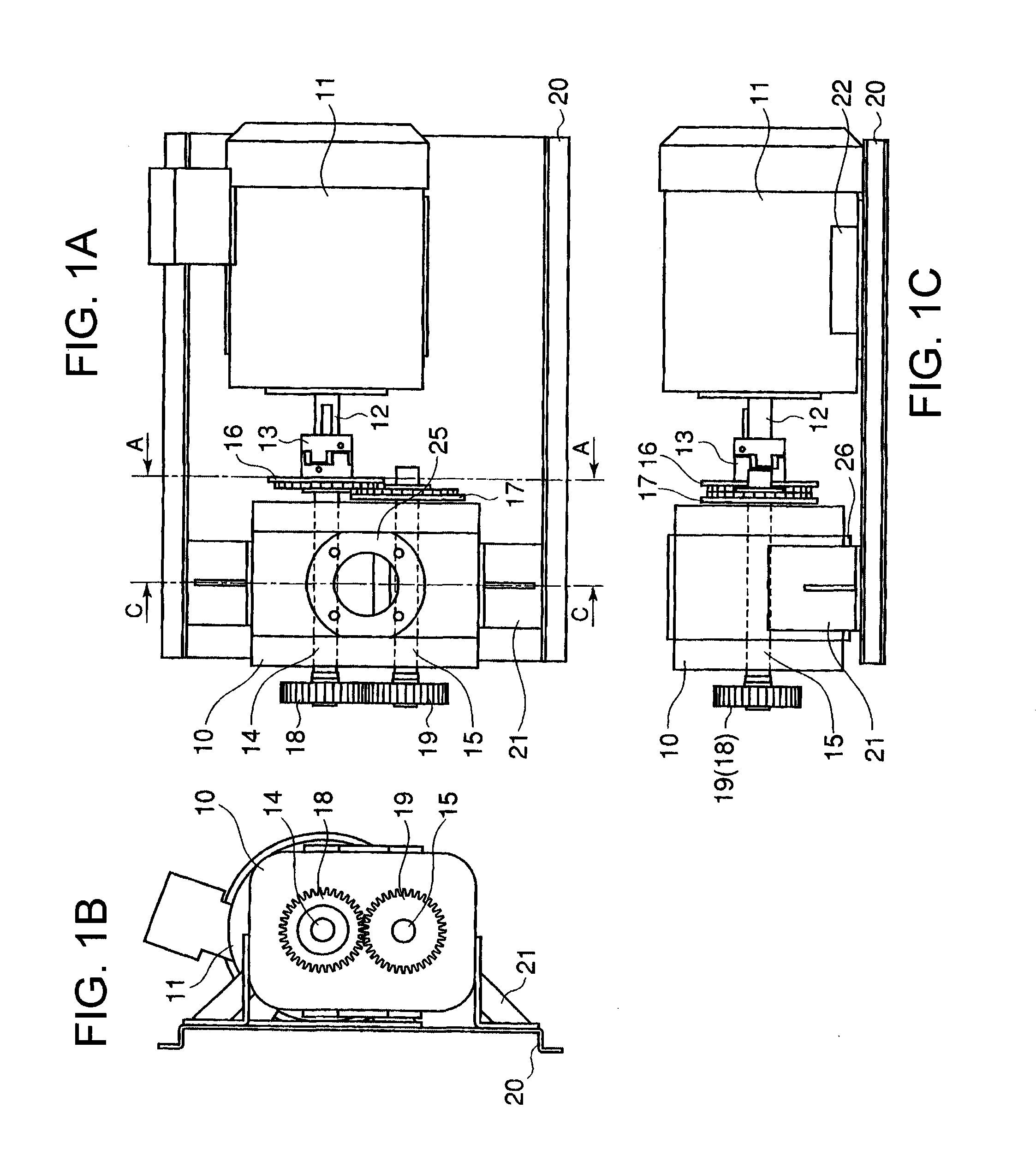
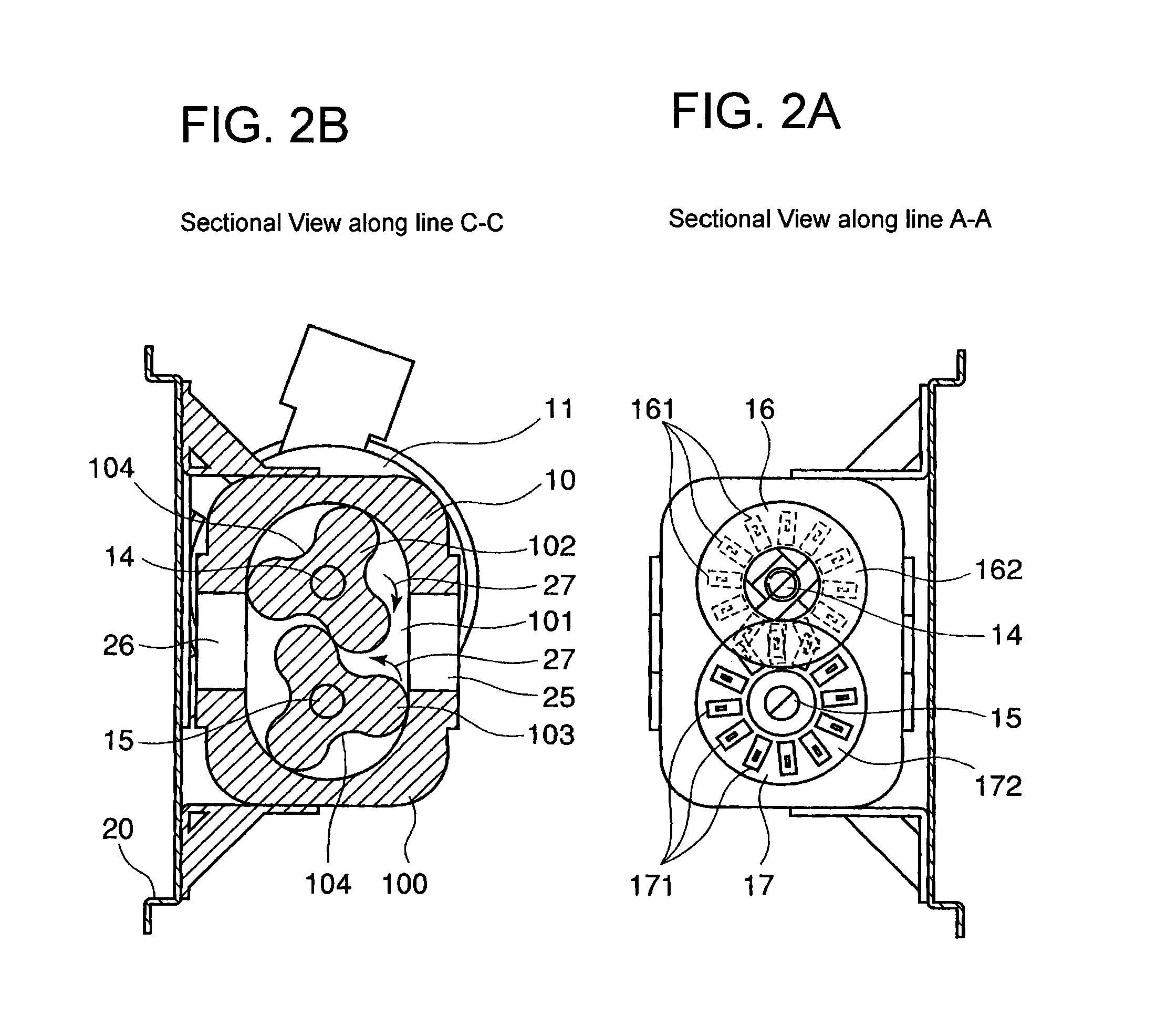
Drive transmission mechanism between two or more rotary shafts and oil-free fluid machine equipped with the mechanism
InactiveUS20080181804A1Reduced service lifeEliminate pollutionDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesEngine of counter-engagement typePlastic materialsOil free
A drive transmission mechanism for transmitting torque between two or more rotary shafts in synchronization with one another without need for lubrication thereby eliminating occurrence of oil contamination, and an oil-free fluid machine equipped with the mechanism, are provided. A magnetic drive disk 16 and a synchronization gear 18 are attached to a rotary shaft 14 connected to a drive motor 11, a magnetic drive disk 17 and a synchronization gear 19 is attached to a rotary shaft 15, torque transmission from the rotary shaft 14 to the rotary shaft 15 is carried out in two ways, via the magnetic drive disks 16, 17 and via the synchronization gears 18, 19, and at least one of the synchronization gears is made of plastic material. With the construction, torque transmit load between the rotary shafts via the synchronization gears is decreased, and a plastic gear or gears can be adopted for synchronization gears without reducing life of the gears without need for lubrication oil.
Owner:ANEST IWATA CORP
Electrostatic levitation and attraction systems and methods
InactiveUS6841917B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital storageEngineeringElectrostatic interaction
An electrostatic interaction system includes a first structure having a first fixed electrostatic charge and a second structure having a second fixed electrostatic charge. The polarity of the first and second fixed electrostatic charges determines a positional relationship of the first structure to the second structure.
Owner:ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Electroadhesion
ActiveUS20080089002A1Great tractionPermit controllable adherenceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic holding devicesElectric fieldElectroadhesion
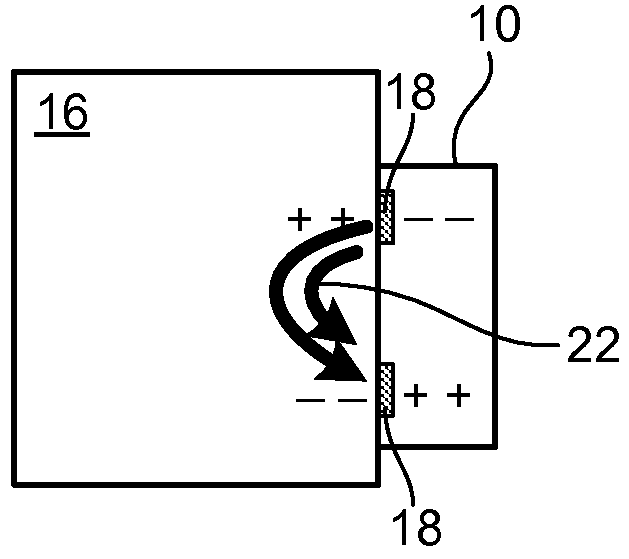
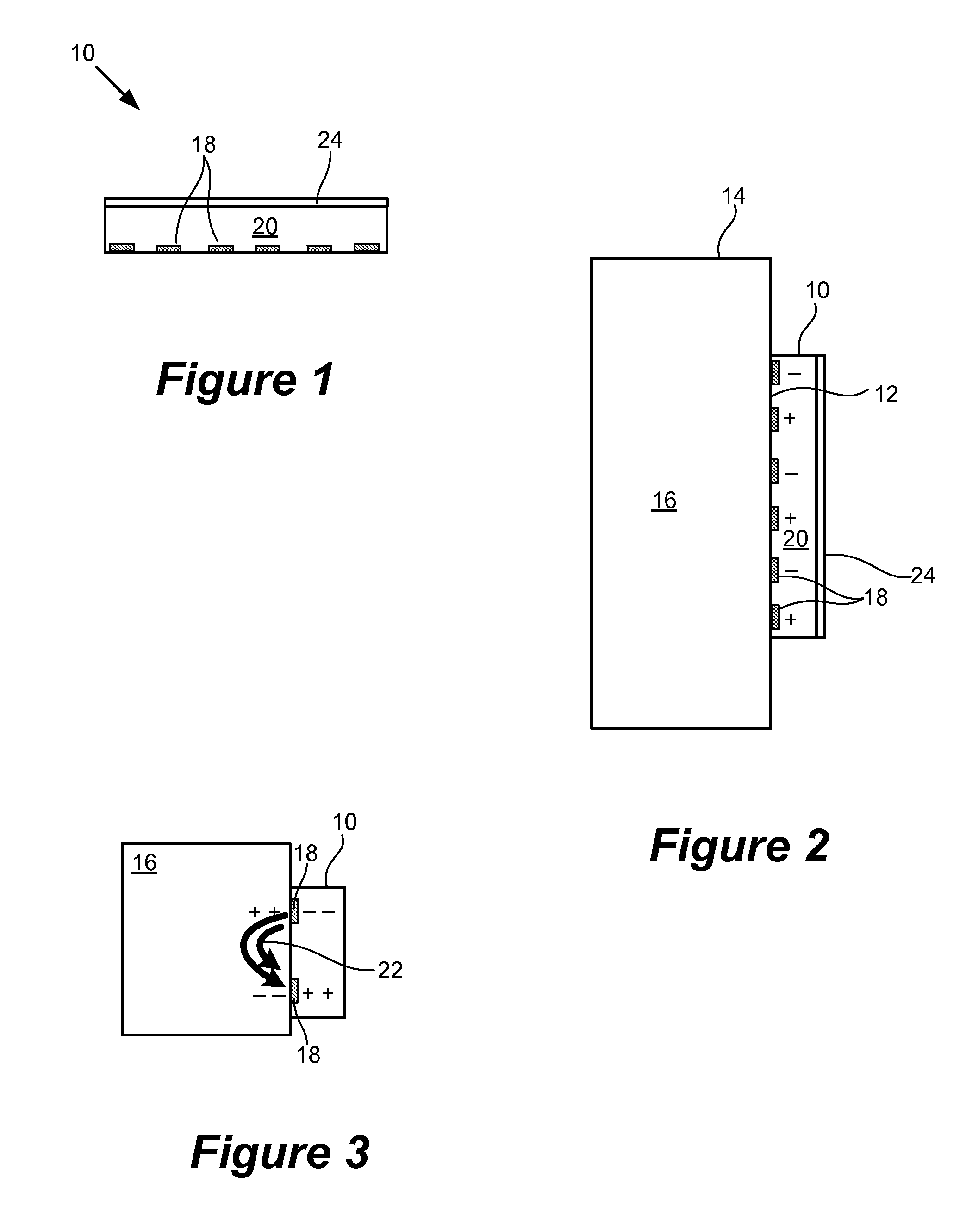
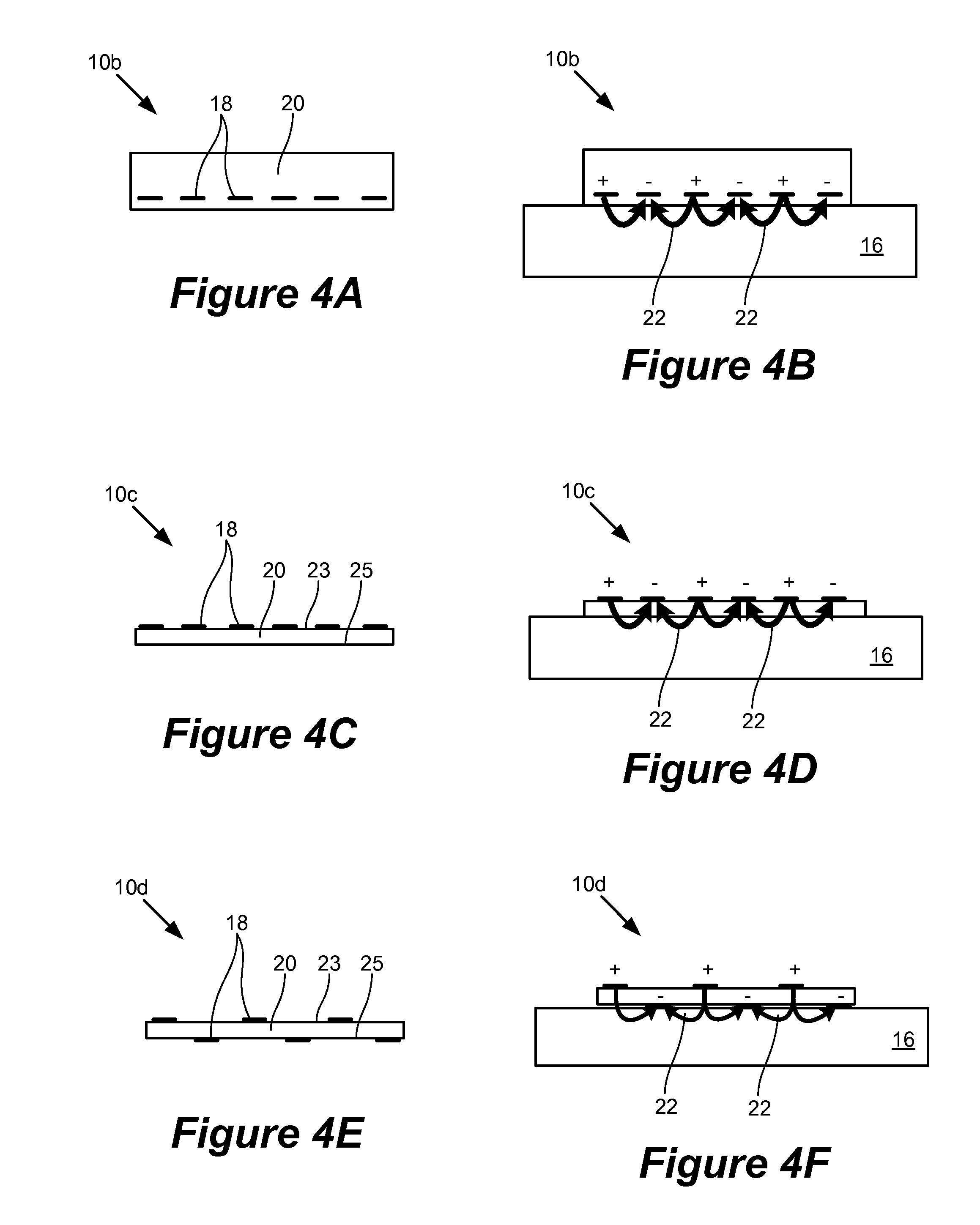
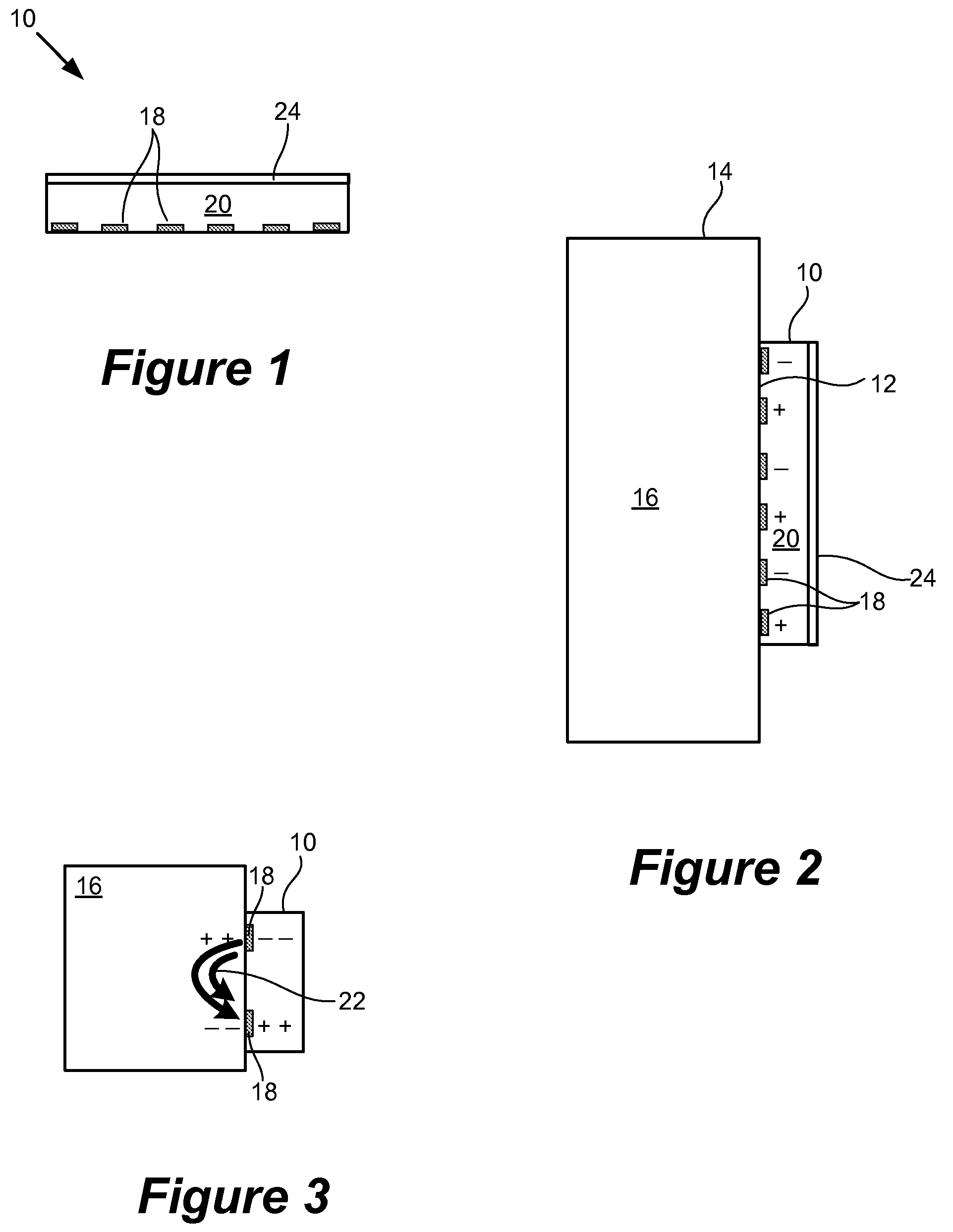
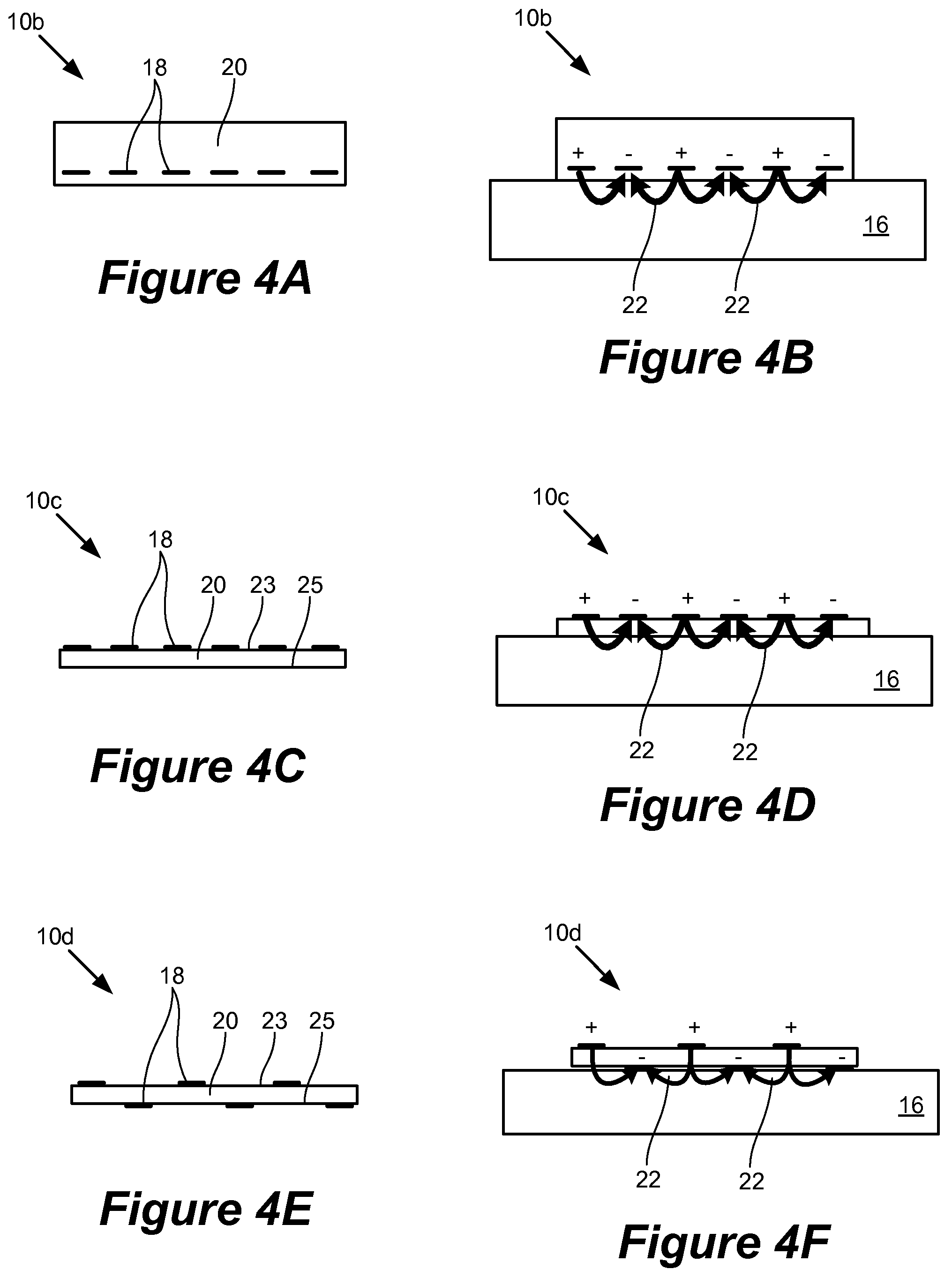
Described herein is electroadhesion technology that permits controllable adherence between two objects. Electroadhesion uses electrostatic forces of attraction produced by an electrostatic adhesion voltage, which is applied using electrodes in an electroadhesive device. The electrostatic adhesion voltage produces an electric field and electrostatic adherence forces. When the electroadhesive device and electrodes are positioned near a surface of an object such as a vertical wall, the electrostatic adherence forces hold the electroadhesive device in position relative to the surface and object. This can be used to increase traction or maintain the position of the electroadhesive device relative to a surface. Electric control of the electrostatic adhesion voltage permits the adhesion to be controllably and readily turned on and off.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Electroadhesion
ActiveUS7551419B2Great tractionControllablySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic holding devicesEngineeringElectric control
Described herein is electroadhesion technology that permits controllable adherence between two objects. Electroadhesion uses electrostatic forces of attraction produced by an electrostatic adhesion voltage, which is applied using electrodes in an electroadhesive device. The electrostatic adhesion voltage produces an electric field and electrostatic adherence forces. When the electroadhesive device and electrodes are positioned near a surface of an object such as a vertical wall, the electrostatic adherence forces hold the electroadhesive device in position relative to the surface and object. This can be used to increase traction or maintain the position of the electroadhesive device relative to a surface. Electric control of the electrostatic adhesion voltage permits the adhesion to be controllably and readily turned on and off.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
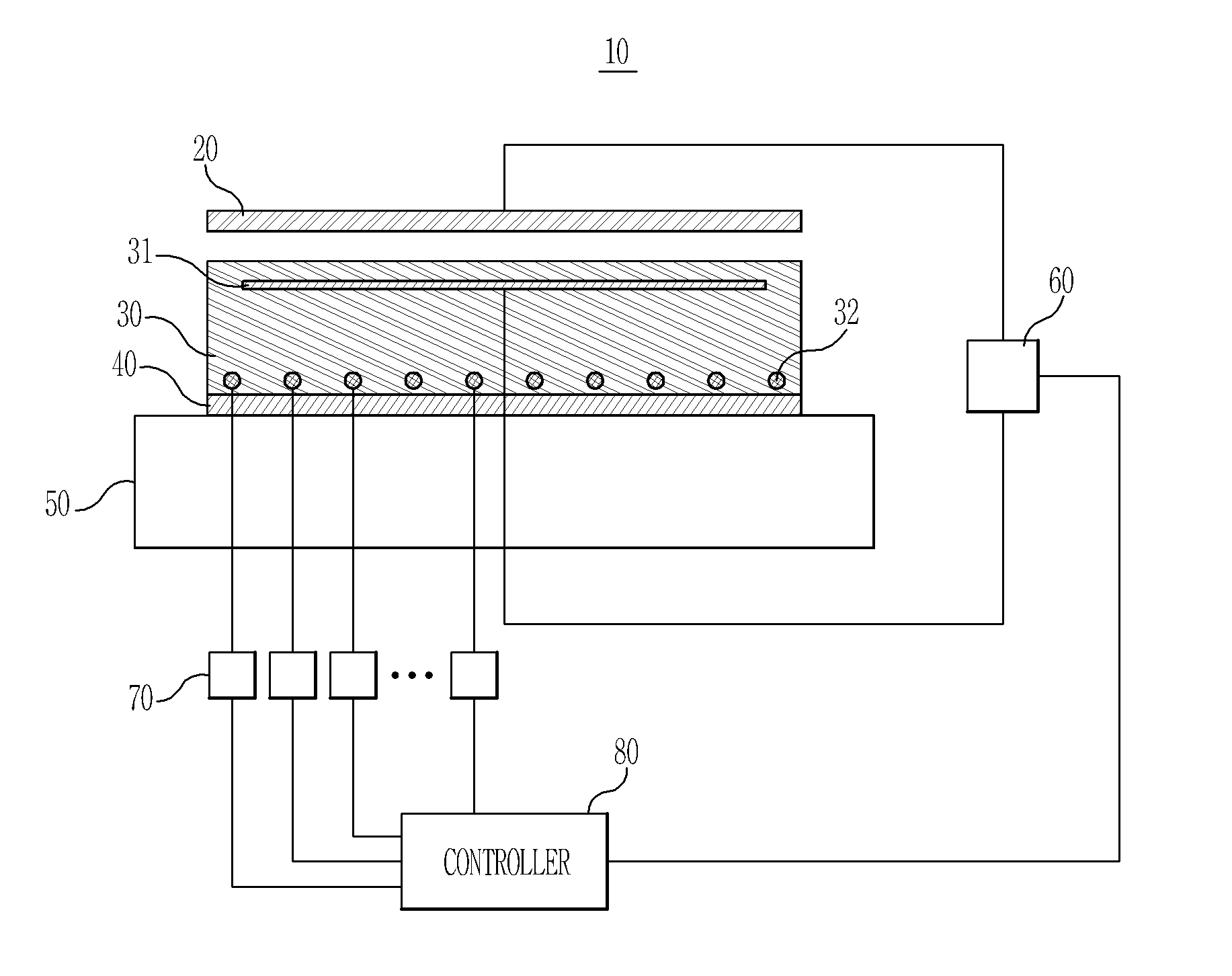
Electrostatic chuck and manufacturing method for the same, and alumina sintered member and manufacturing method for the same
ActiveUS20050152089A1High volume resistivityImprove insulation performanceSleeve/socket jointsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRoom temperatureElectrode
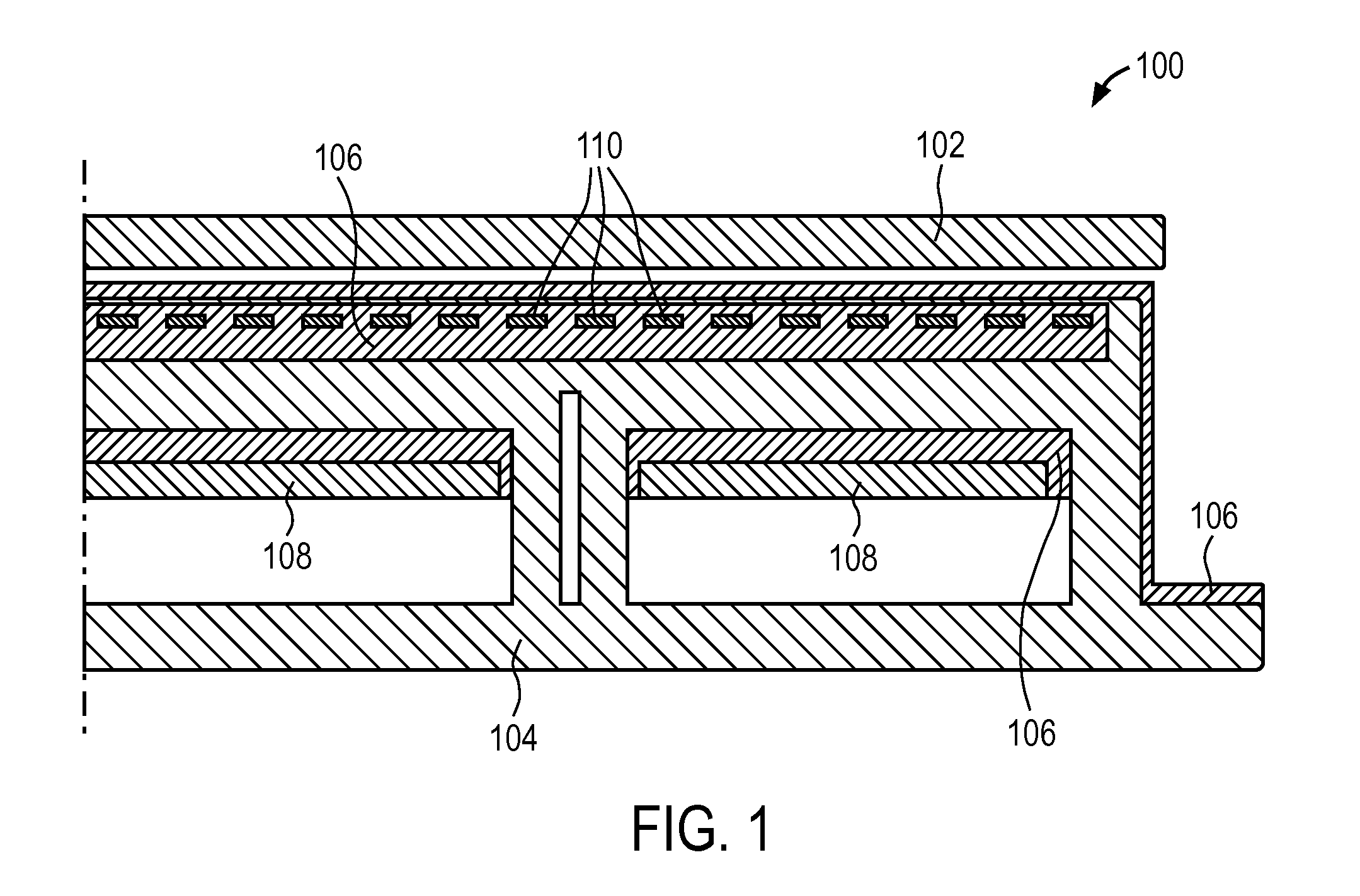
An electrostatic chuck comprises a dielectric ceramic layer made of an alumina sintered body having a volume resistivity equal to or greater than about 1×1017Ω·cm at room temperature and a volume resistivity equal to or greater than about 1×1014Ω·cm at 300° C., and an electrode formed on one surface of the dielectric ceramic layer.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Electrostatic chuck and production method therefor
InactiveUS6215643B1Small resistivityImprove the forceSleeve/socket jointsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConductive pasteElectrostatic attraction
An electrostatic chuck according to the present invention exhibits a greater attractive force by virtue of the Johnson-Rahbeck effect, while ensuring satisfactory insulation in a ceramic portion present below an electrostatic attraction electrode thereof in a temperature range of 250 to 450° C. The electrostatic chuck is produced by superposing green sheets printed with a conductive paste and green sheets not printed with the conductive paste in a predetermined order with a binding liquid applied on the respective green sheets, heat- and press-bonding the superposed green sheets and firing the heat- and press-bonded green sheets. During the production, a conductive component of the electrostatic attraction electrode is diffused into the ceramic portion present between the electrode and an attractive surface of the chuck.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Electrostatic chuck and processing apparatus for insulative substrate
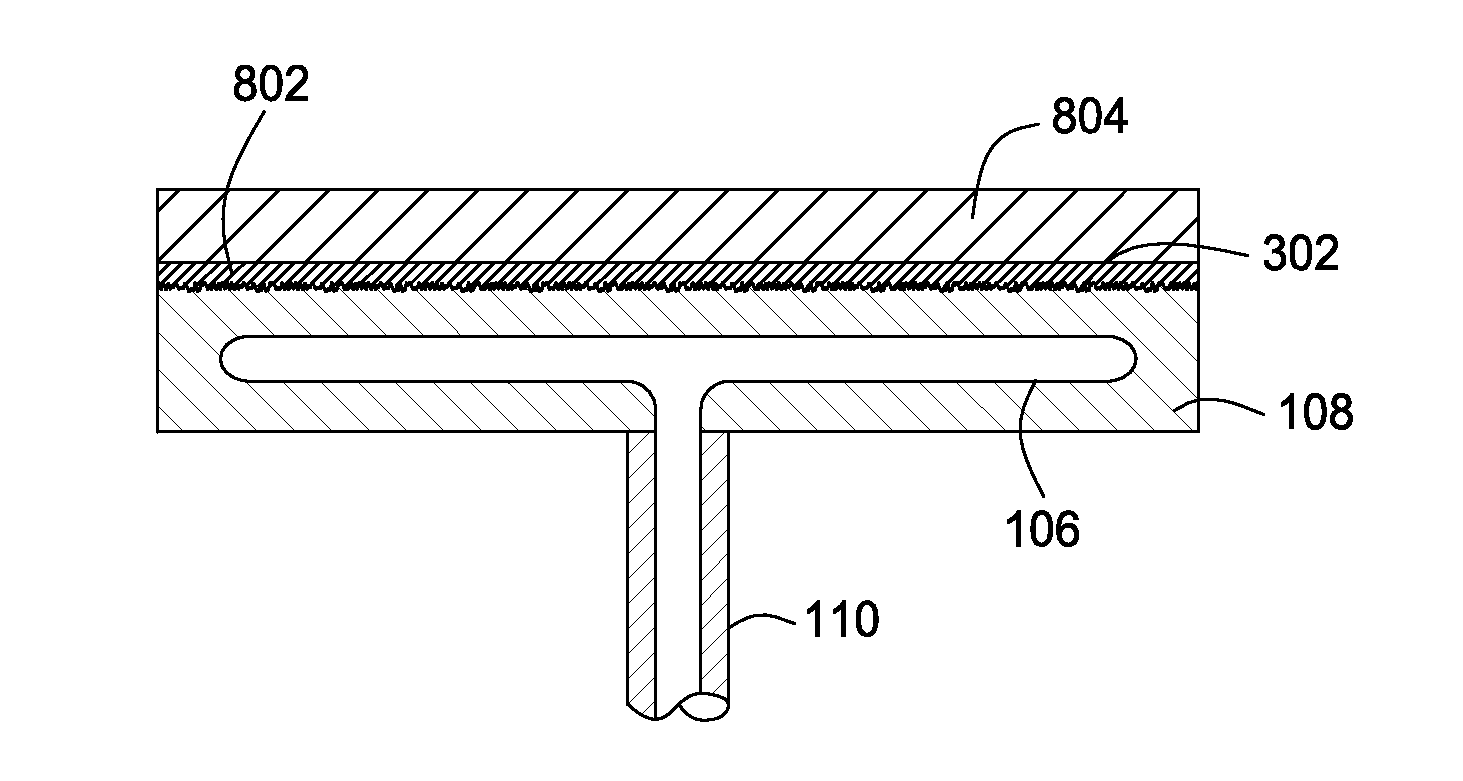
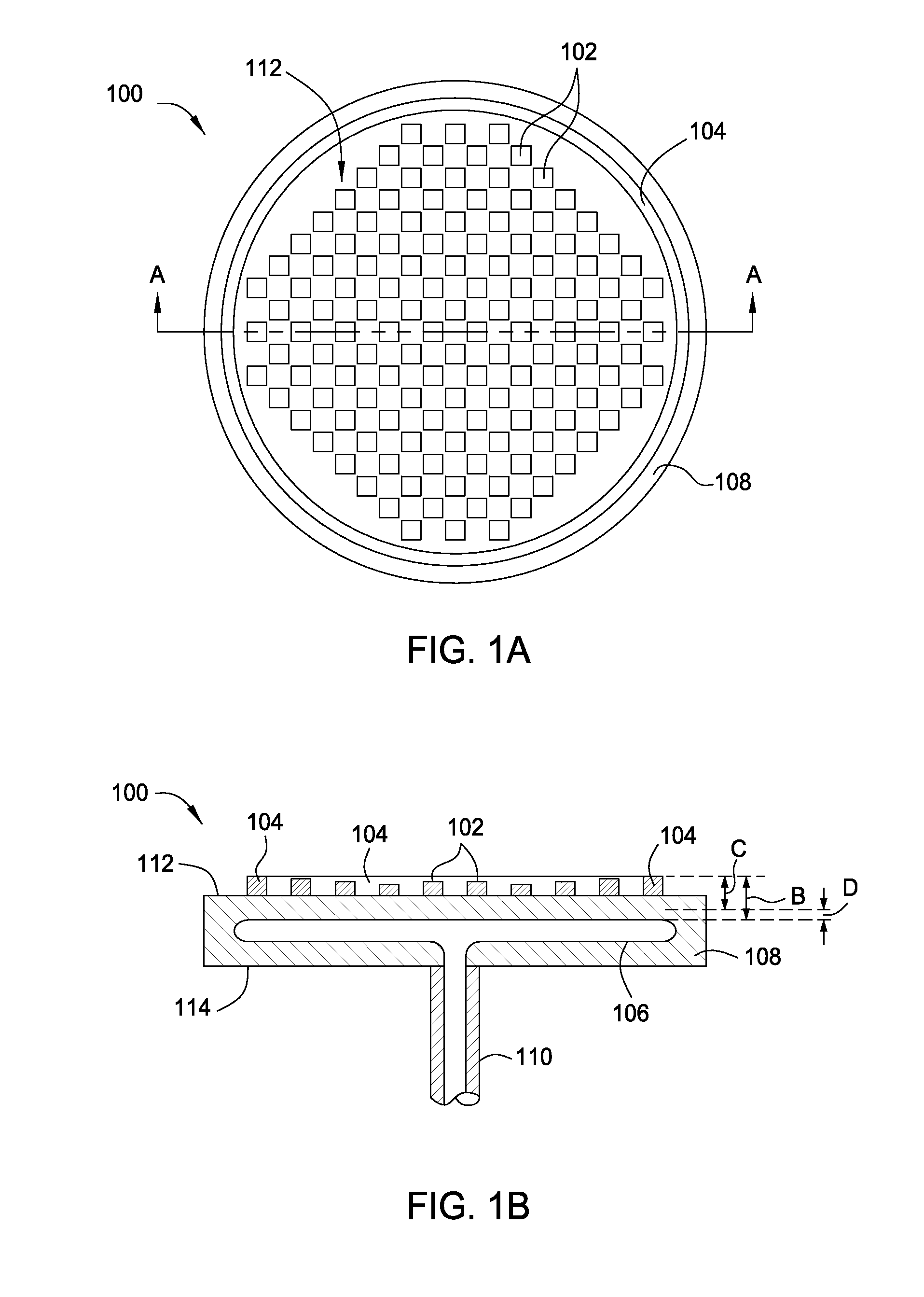
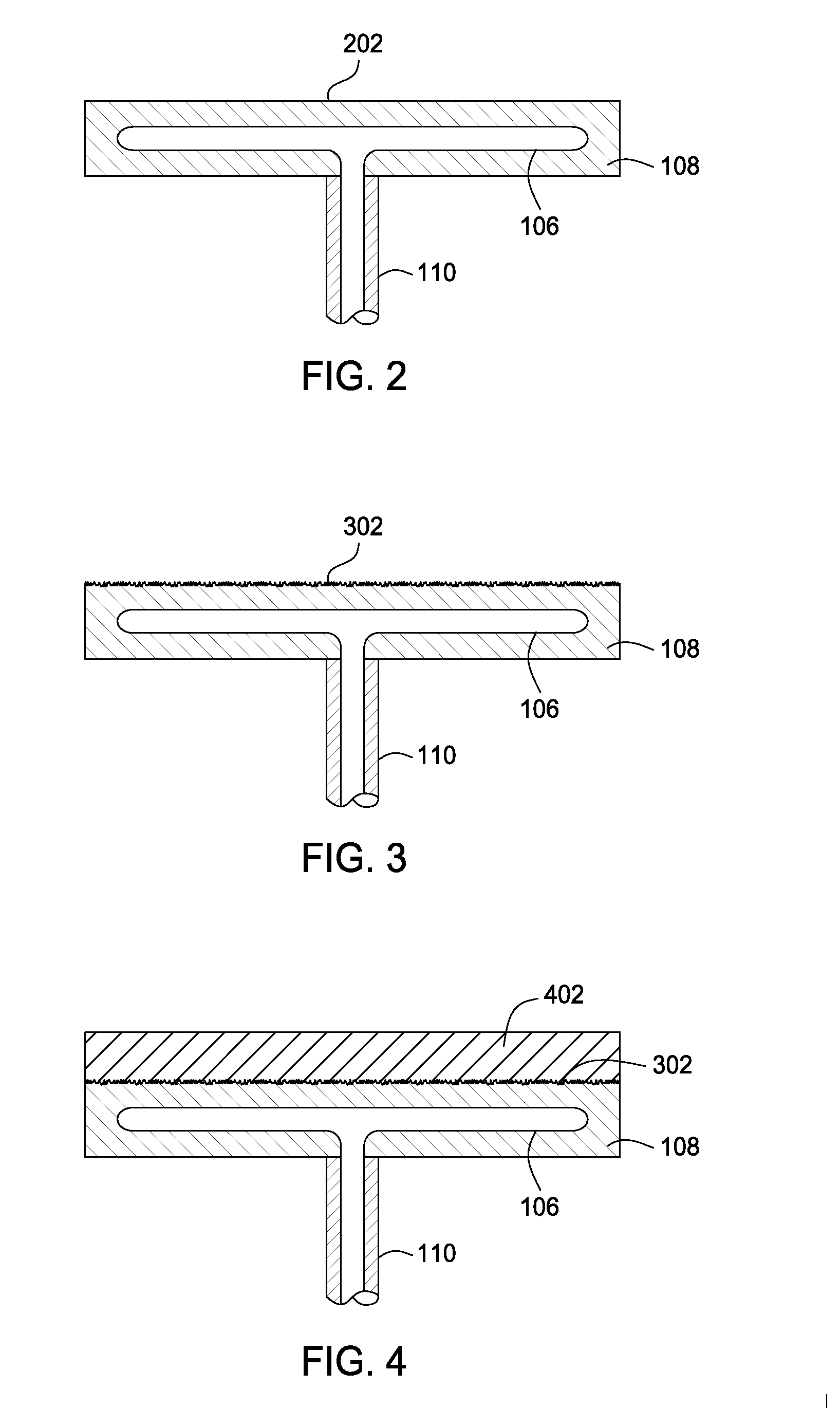
InactiveUS6768627B1The overall thickness is thinSmall distanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPositioning apparatusElectrical connectionEngineering
An electrostatic chuck for attracting an insulative substrate, used under a vacuum atmosphere, comprises: a dielectric layer having a first surface which attracts an insulative substrate, and a second surface on which are provided a plurality of electrodes; an insulative support base plate fixing the dielectric layer thereon; a plurality of electrically conductive terminals provided on the insulative support base plate; and an electrical connection between the electrodes and the electrically conductive terminals.
Owner:ULVAC INC +1
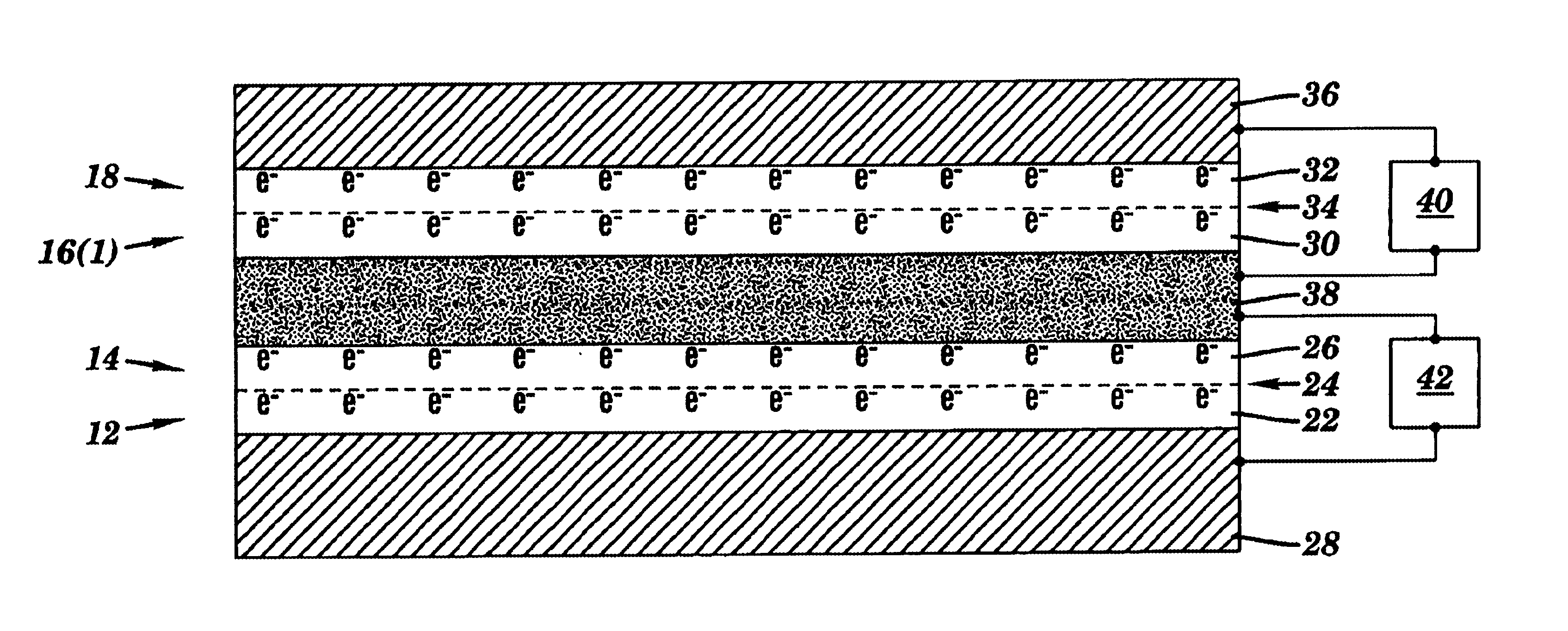
Polyceramic e-chuck
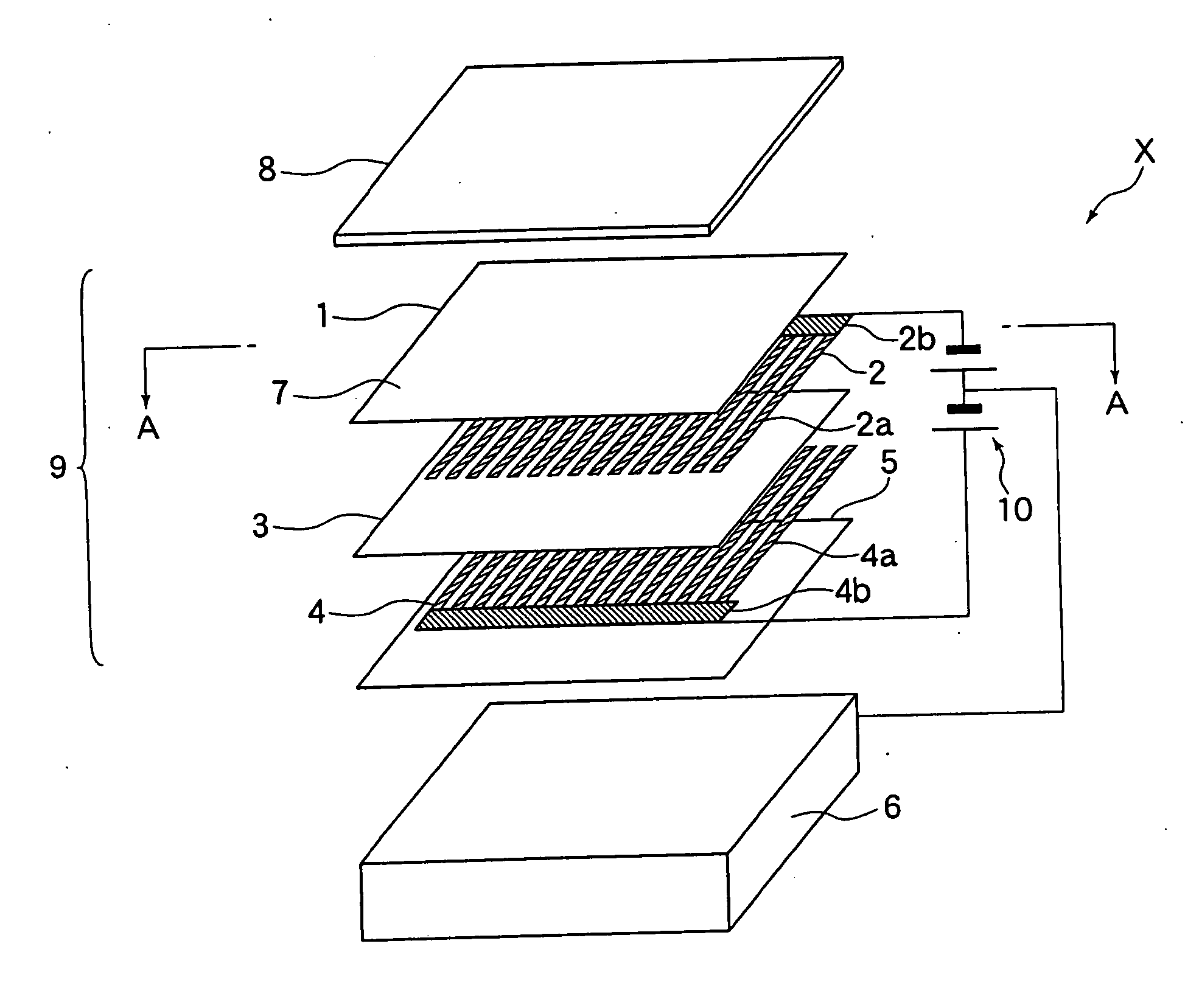
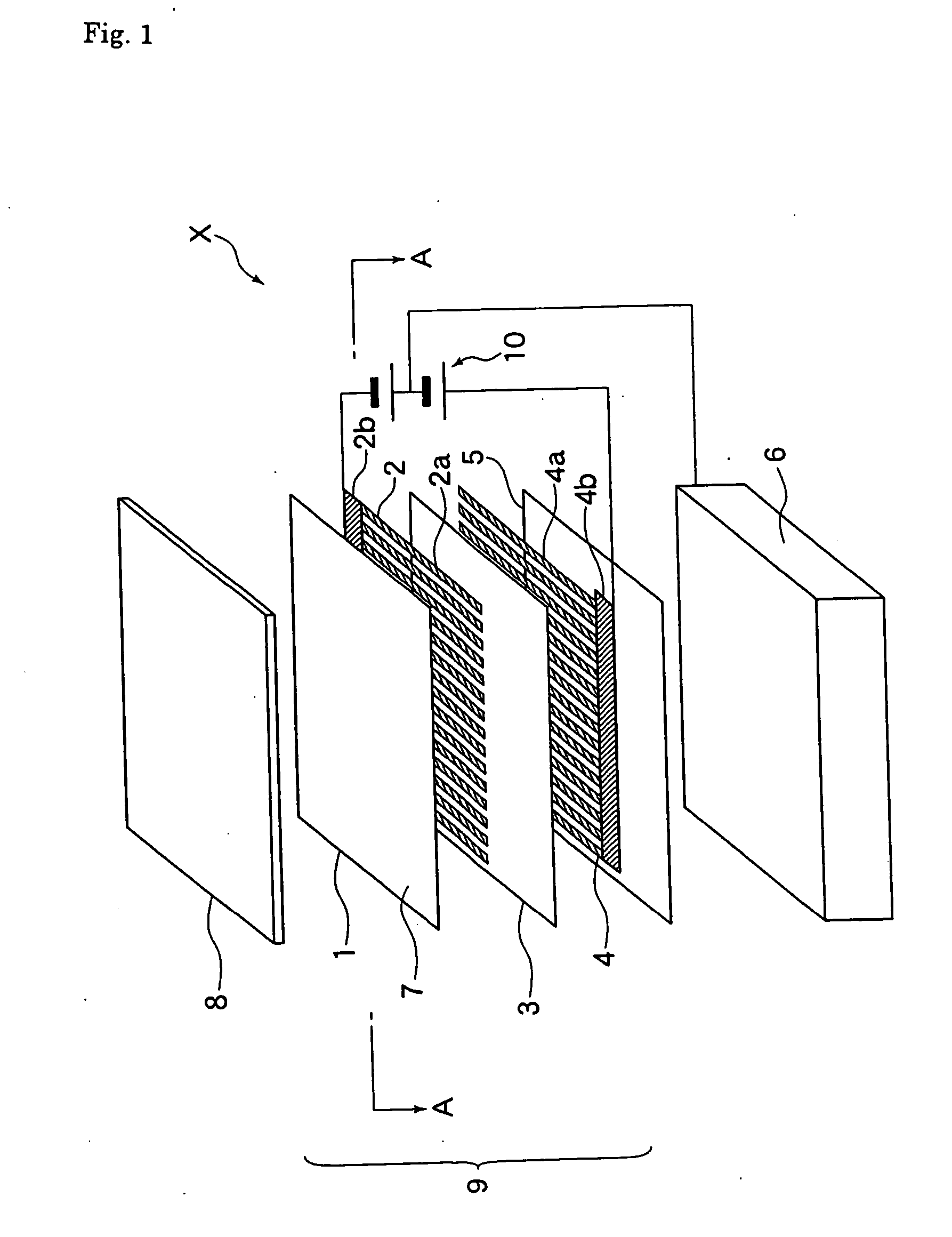
ActiveUS20090002913A1Reduce thermal stressEasy to controlSleeve/socket jointsElectric discharge tubesCapacitanceDielectric layer
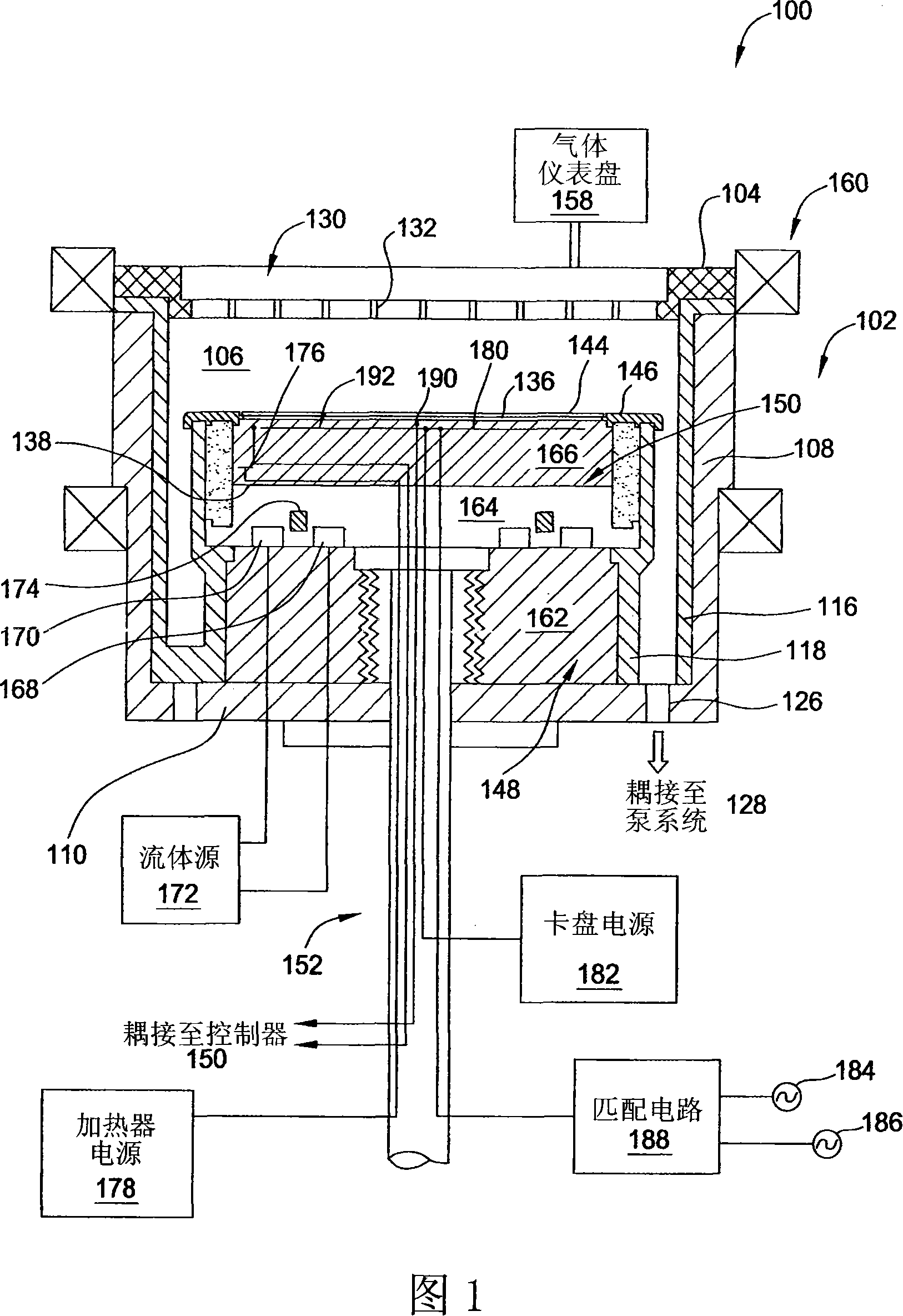
The present invention discloses an electrostatic chuck for clamping work substrates, said chuck comprising three layers, where the dielectric constant of included non-conductive layers is selected to provide overall lower capacitance to the chuck. In the chuck assembly of the present invention, the top dielectric layer that is in contact with a substrate, such as, for example, a wafer, has a dielectric constant that is preferably greater than about 5, with a resistivity that is preferably greater than about 1E6 ohm.m, whereas the bottom dielectric layer has a dielectric constant that is preferably less than about 5 and a resistivity that is preferably greater than about 1E10 ohm.m. The intermediate layer preferably has a conductive layer where the resistivity is less than about 1 ohm.m. The electrostatic chuck may be bonded to heat sinks coated with anti-arc dielectrics. The heat sink can also be used as an RF electrode. The heat sink may have provisions for coolants and gas channels to feed a cooling gas to the backside of a wafer. The heat sink may have feed thrus to power the segmented electrodes in the electrostatic chuck. The passages for the feed thrus, gas feed holes and lift pins may be lined with ceramics or polymers to prevent any discharge to the heat sink. The electrostatic chuck is for clamping work substrates like Si, GaAs, SiO2, etc. used in semiconductor tools.
Owner:FM INDS
Method for refurbishing an electrostatic chuck with reduced plasma penetration and arcing
ActiveUS20090034149A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic holding devicesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method for refurbishing at least a portion of an electrostatic chuck. The method comprises removing a first dielectric component from a fluid distribution element of the electrostatic chuck and replacing the first dielectric component with a second dielectric component.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Mechanical drive system operating by magnetic force
InactiveUS7057320B2Magnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetically actuated clutchesMagnetic tension forceDrive shaft
A mechanical drive system operating by magnetic force, to be fitted on a pump, comprises a basic structure on which a drive shaft, which extends along a longitudinal axis, is supported rotatably. A driving element operatively connected to the drive shaft is provided with driving magnets arranged in a ring. A driven element provided with driven magnets arranged in a ring is also mounted on the basic structure. A bell is inserted between the driving element and the driven element and isolates the environment containing the driven element. The driving element and the driven element comprise respective cages each having seats for housing the respective driving magnets or driven magnets.
Owner:C D R POMPE
Wall crawling devices
ActiveUS7554787B2Great tractionControllablySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic generators/motorsEngineeringElectric control
Described herein is electroadhesion technology that permits controllable adherence between two objects. Electroadhesion uses electrostatic forces of attraction produced by an electrostatic adhesion voltage, which is applied using electrodes in an electroadhesive device. The electrostatic adhesion voltage produces an electric field and electrostatic adherence forces. When the electroadhesive device and electrodes are positioned near a surface of an object such as a vertical wall, the electrostatic adherence forces hold the electroadhesive device in position relative to the surface and object. This can be used to increase traction or maintain the position of the electroadhesive device relative to a surface. Electric control of the electrostatic adhesion voltage permits the adhesion to be controllably and readily turned on and off.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Electrostatic chuck for holding wafer
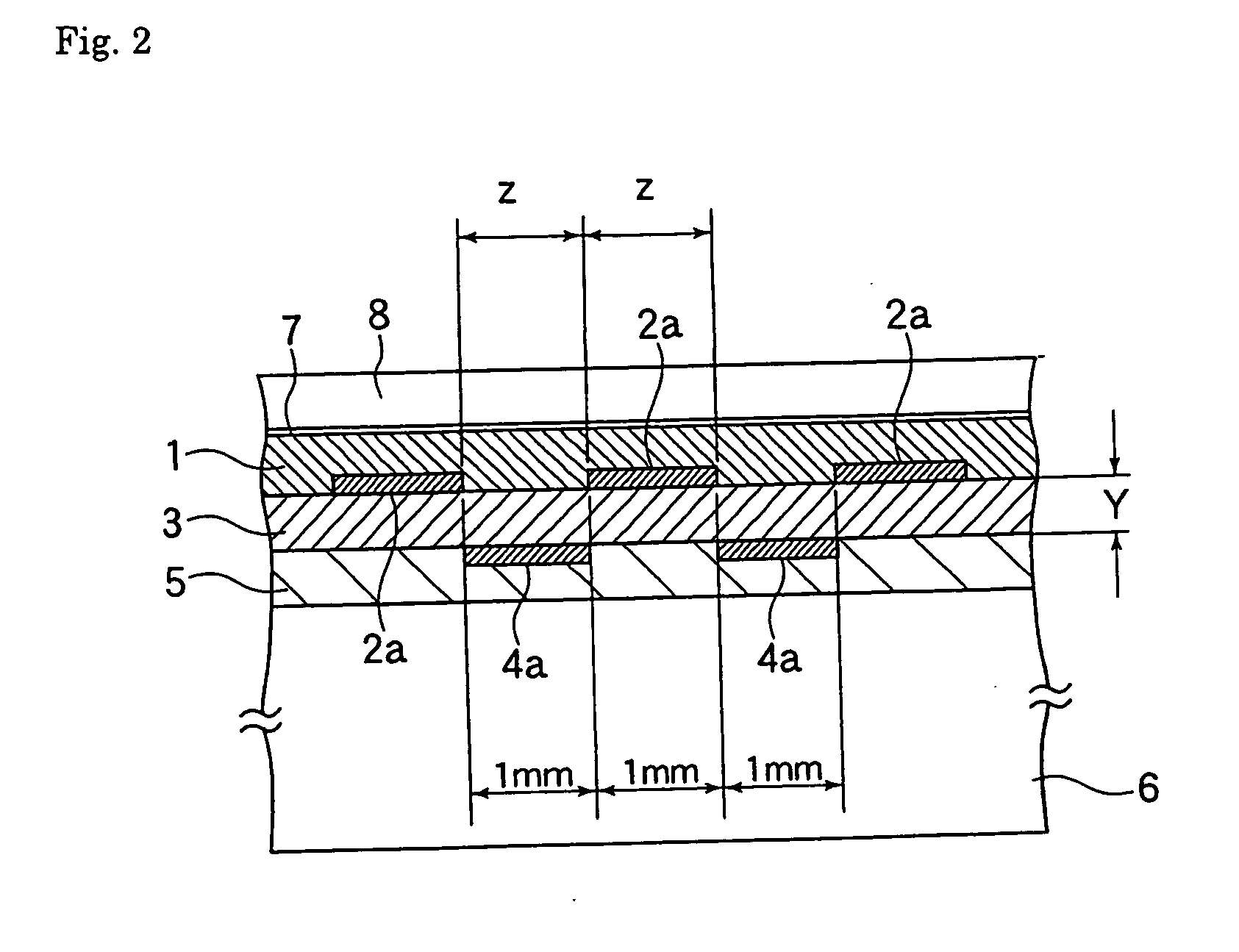
InactiveUS20030161088A1Emergency protective arrangement detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetallurgyWaviness
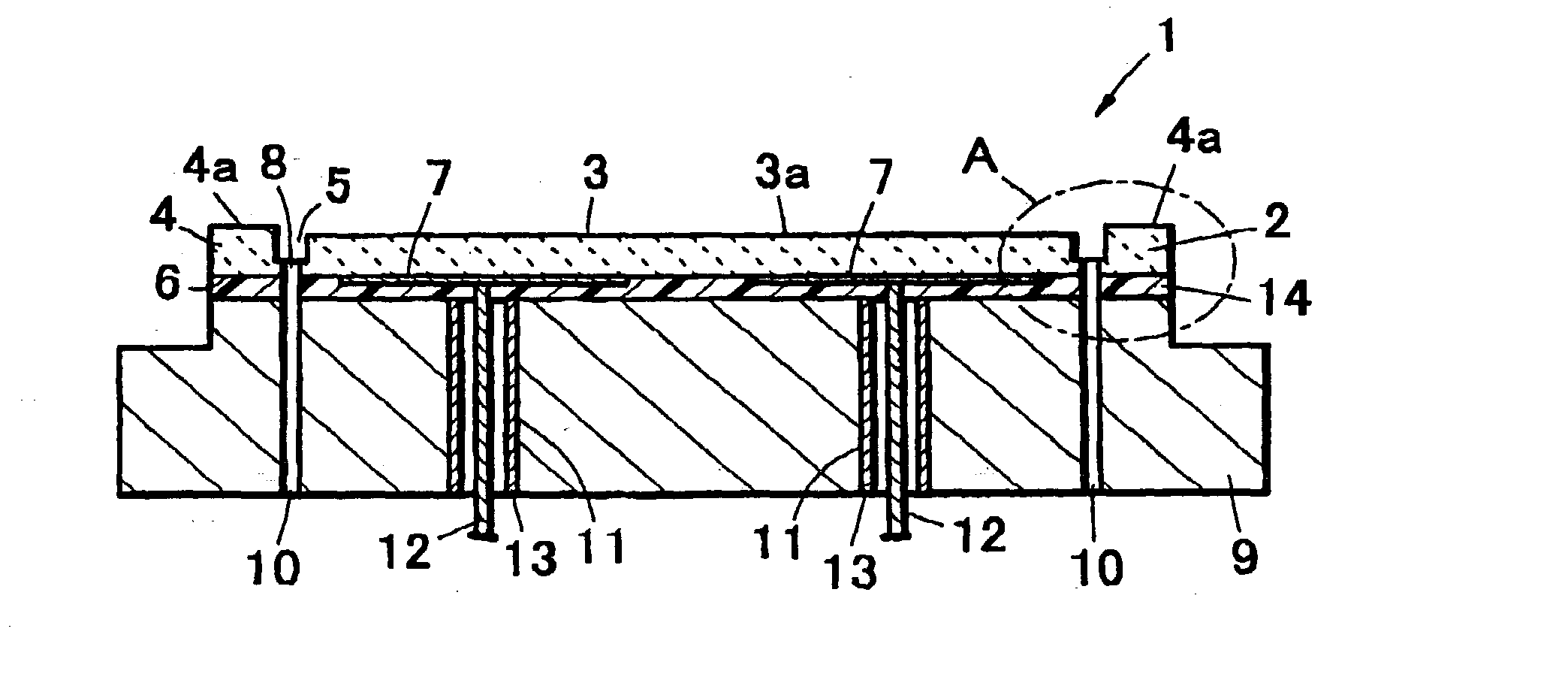
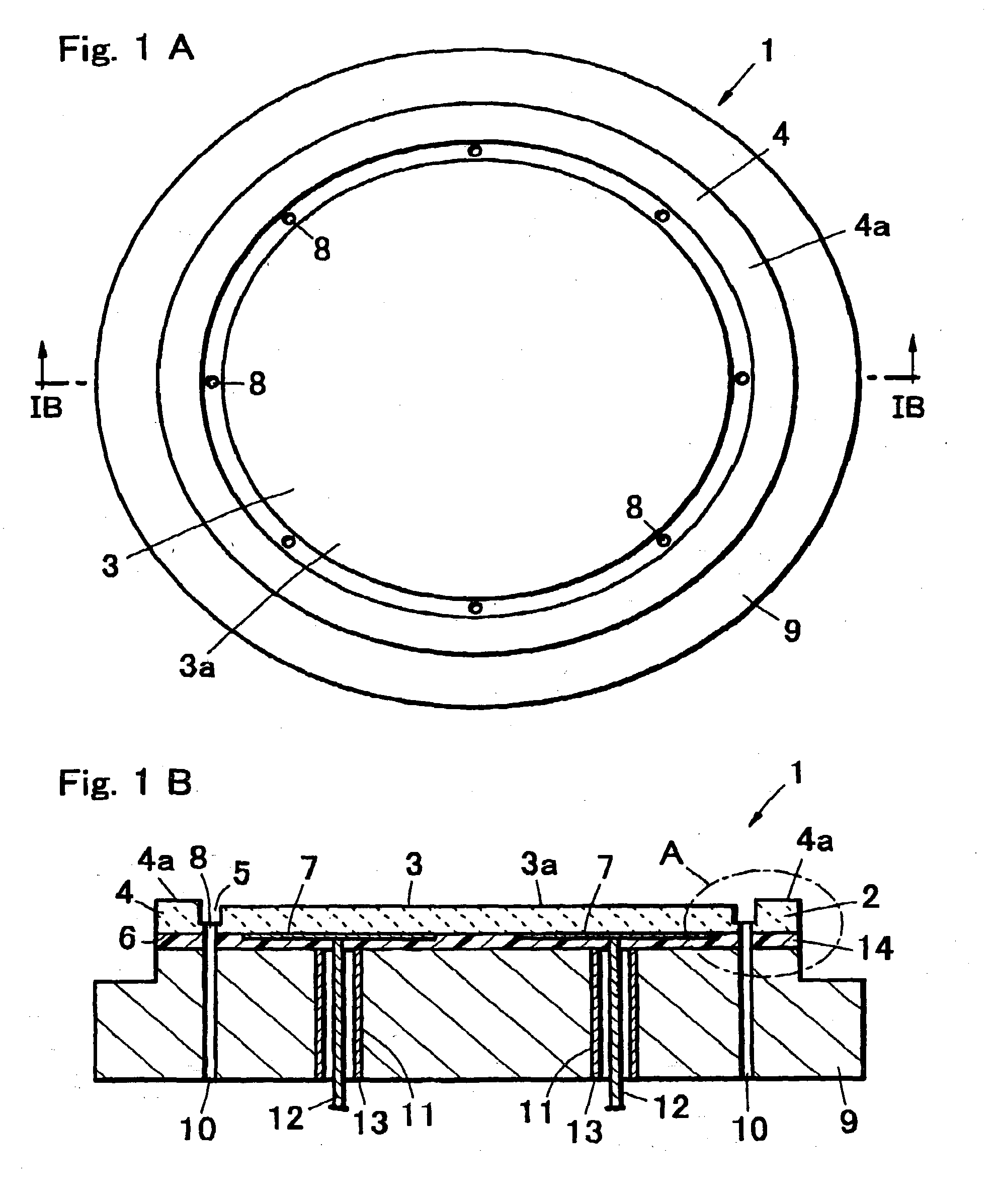
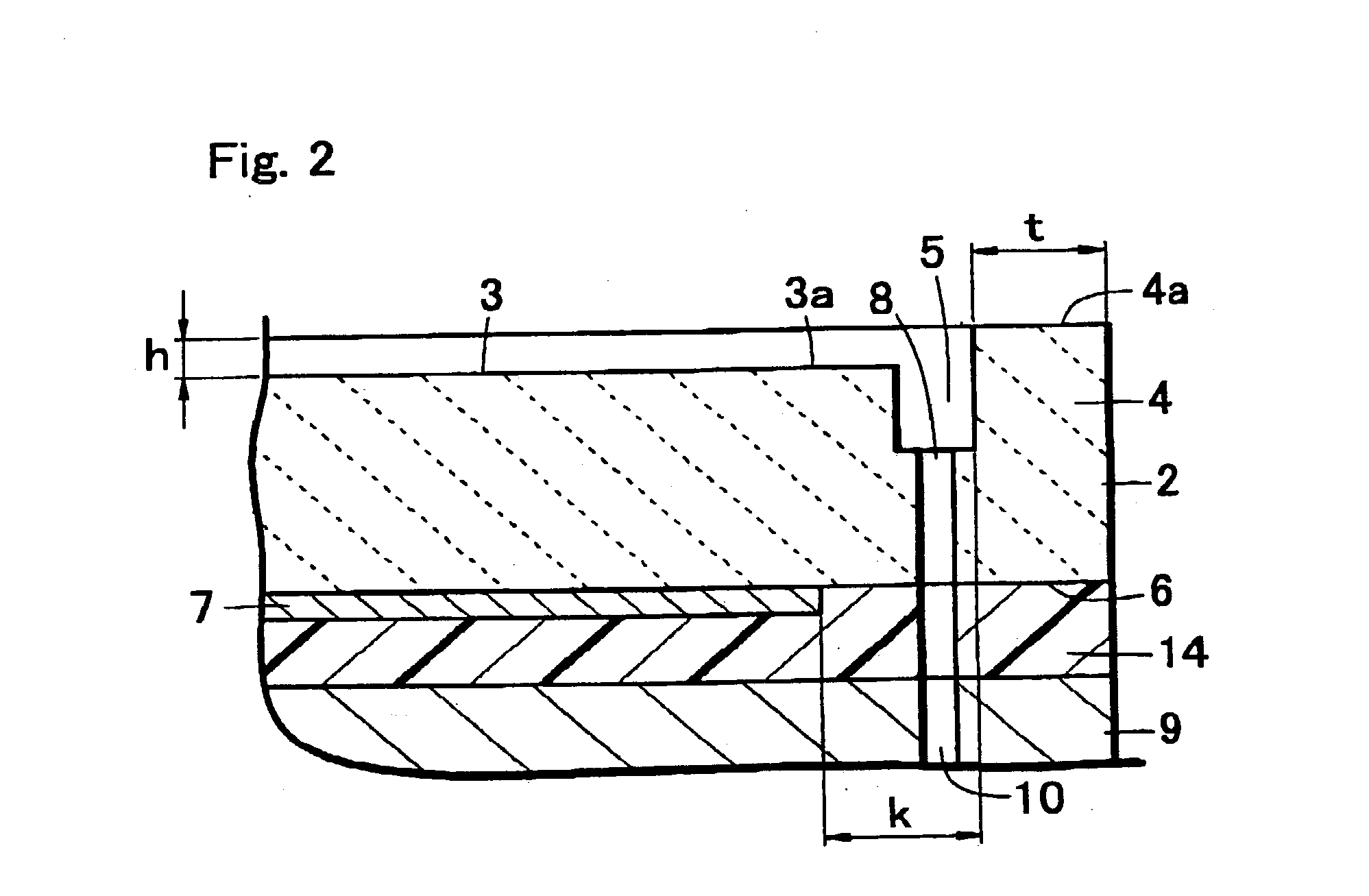
An electrostatic chuck for holding a wafer includes a ceramic plate of which one main surface is formed to work as a mounting surface for mounting the wafer, and electrostatic attraction electrodes formed on a lower surface of the ceramic plate or in the ceramic plate. A recess portion having a depth in a range of from 3 to 10 mum is formed on one main surface of the ceramic plate excluding an outer peripheral portion thereof. The waviness of a top face of the outer peripheral portion is set to 1 to 3 mum, a gas groove is provided to a peripheral portion of a bottom surface of the recess-portion bottom surface, and electrostatic attraction electrodes are disposed in the ceramic plate disposed below the bottom surface of the convex portion. In the electrostatic chuck thus constructed, even a wafer having a deformation such as a warped portion can be firmly attracted, a uniform temperature distribution over a wafer surface can be implemented, leakage of a heat-conductive gas can be suppressed, and moreover, high wafer-dechucking sensitivity can be exhibited.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Substrate support with a protective layer for plasma resistance
ActiveCN101118865AVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRare earthMetal
Embodiments of the present invention provide a substrate support assembly having a protective layer with enhanced plasma corrosion resistance. In one embodiment, a substrate support assembly includes an electrostatic chuck having an upper substrate support surface, and a protective layer disposed on the electrostatic chuck, wherein the protective layer is made of a ceramic material including a rare earth metal.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Bipolar Electrostatic Chuck
InactiveUS20070223173A1Sufficient performanceEliminate dischargeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic holding devicesDielectric breakdown strengthDepth direction
A bipolar electrostatic chuck which has excellent dielectric breakdown strength and provides excellent attracting performance. The bipolar electrostatic chuck eliminates difficulty in dismounting a sample from a sample attracting plane as much as possible after application of a voltage to electrodes is finished. The bipolar electrostatic chuck is provided with a first electrode and a second electrode in an insulator and permits a surface of the insulator to be the sample attracting plane. The insulator has the first electrode, an interelectrode insulating layer and the second electrode in this order from the sample attracting plane in the depth direction. The second electrode has a region not overlapping with the first electrode in a normal line direction of the sample attracting plane.
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
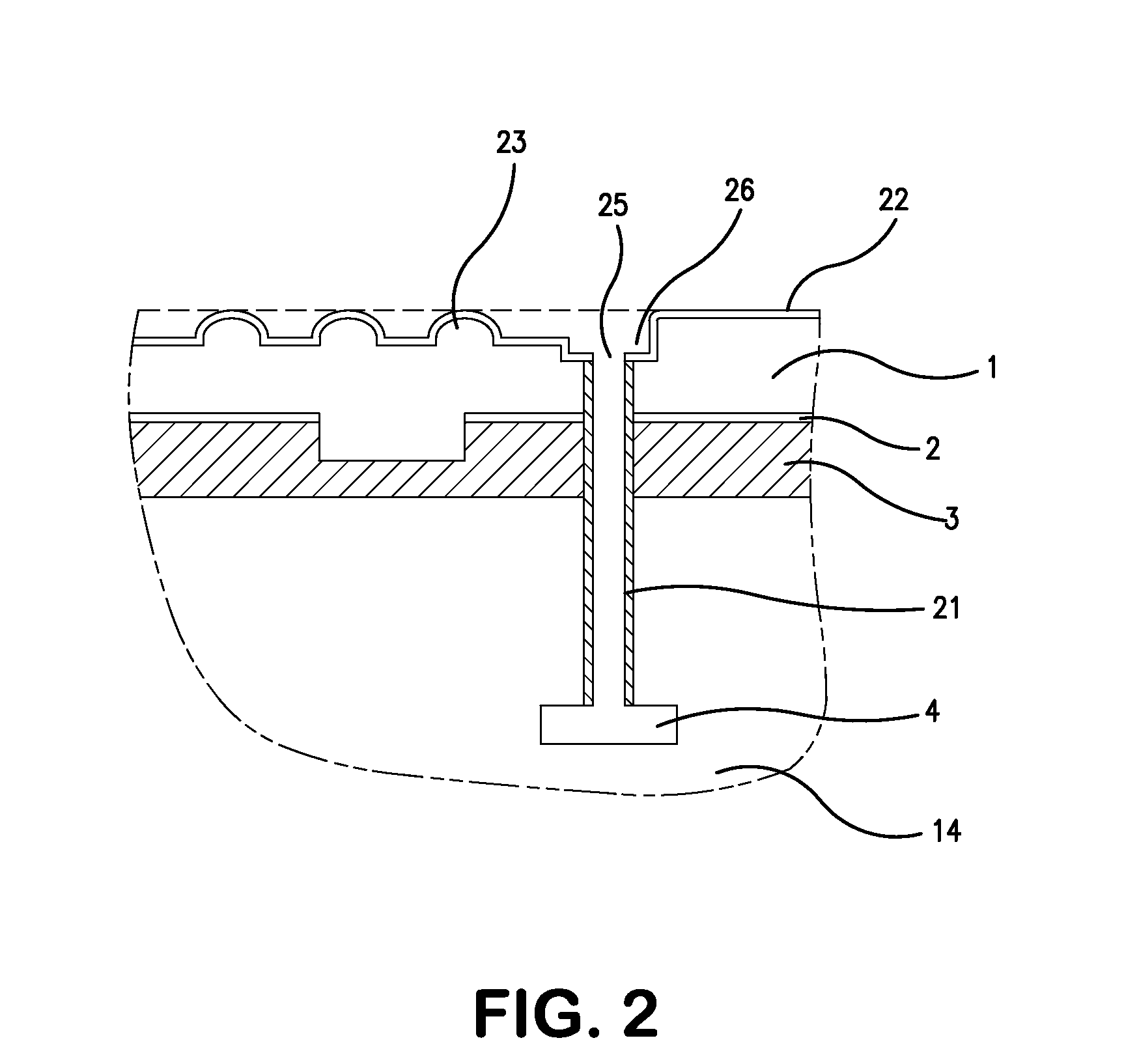
Electrostatic chuck aln dielectric repair
ActiveUS20120307412A1Improve adhesionSmooth edgesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingArc welding apparatusEngineeringDielectric layer
The present invention generally relates to a refurbished electrostatic chuck and a method of refurbishing a used electrostatic chuck. Initially, a predetermined amount of dielectric material is removed from the used electrostatic chuck to leave a base surface. Then, the base surface is roughened to enhance the adherence of new dielectric material thereto. The new dielectric material is then sprayed onto the roughened surface. A mask is then placed over the new dielectric material to aid in the formation of mesas upon which a substrate will sit during processing. A portion of the new dielectric layer is then removed to form new mesas. After removing the mask, edges of the mesas may be smoothed and the refurbished electrostatic chuck is ready to return to service after cleaning.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Centrifugal magnetic clutch
A centrifugal magnetic clutch device includes, an input shaft and, a plurality of input magnets that are rotatable about an axis of the input shaft, and are radially movable relative to the input shaft axis, and are rotationally fixed to the input shaft. The device further includes, a plurality of output magnets rotatable about the input shaft axis and in axial alignment with the plurality of input magnets, and an output shaft rotationally fixed to the plurality of output magnets. The device further includes, a housing for fluidically sealing the plurality of output magnets and the output shaft relative to the plurality of input magnets and the input shaft.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
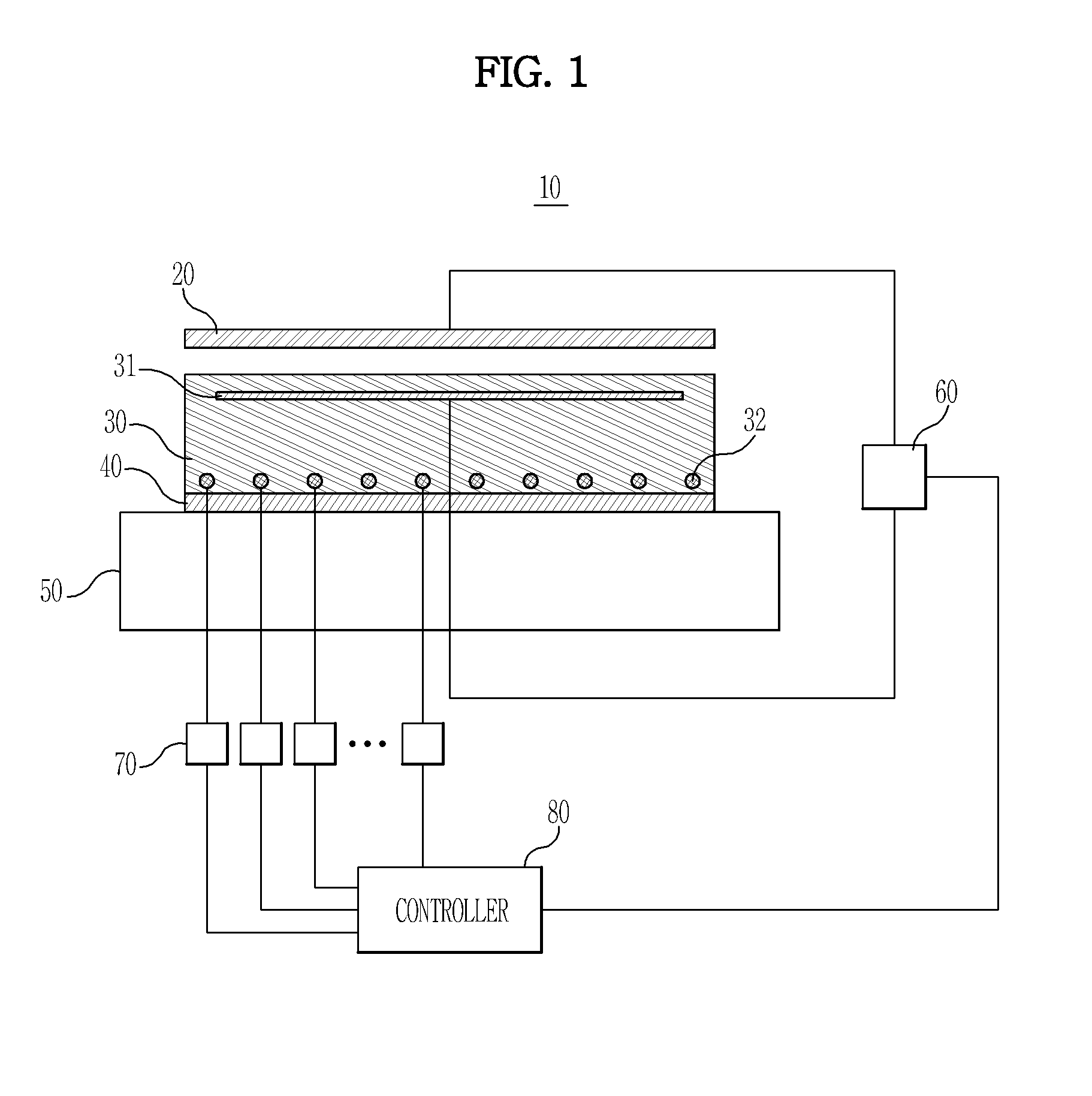
Electrostatic chuck device and control method thereof
InactiveUS20130224675A1Add temperature control functionCharge supportsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
An electrostatic chuck device includes a surface to support a substrate, an electrode to generate electrostatic force for the substrate, and a plurality of heaters to heat different regions of the surface. The plurality of heaters include a first heater to heat a first region to a first temperature, a second heater to heat a second region to a second temperature, and a third heater to heat a third region to a third temperature between the first and second temperatures. The second region is closer to a peripheral area of the surface than the first region, and the third region between the first and second regions.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com