Depth uniformity control method for laser surface quenching hardening layer and device thereof
A technology of laser surface quenching and hardened layer depth, which is applied in the direction of temperature control using electric methods, can solve problems such as unevenness, and achieve the effect of uniform hardened layer depth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
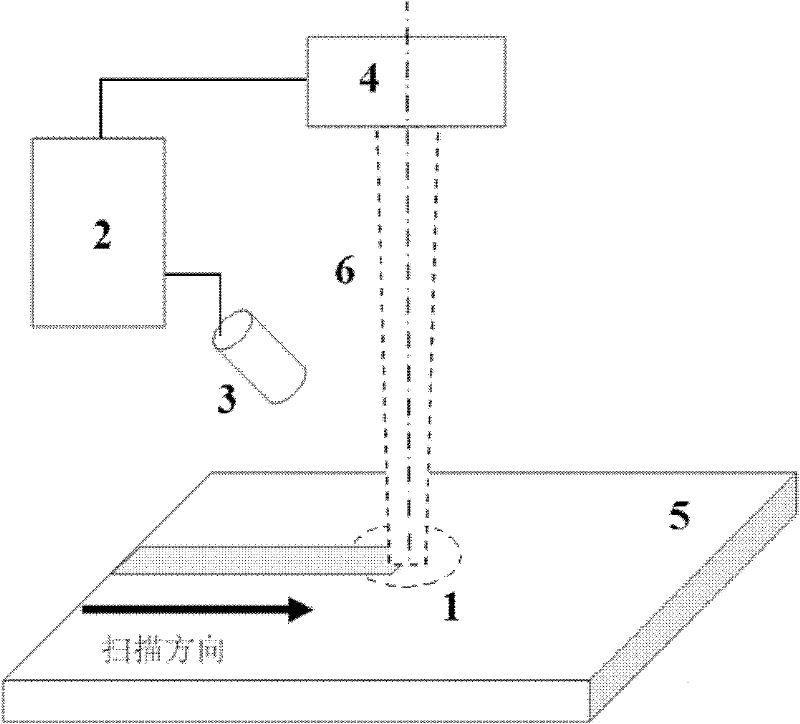
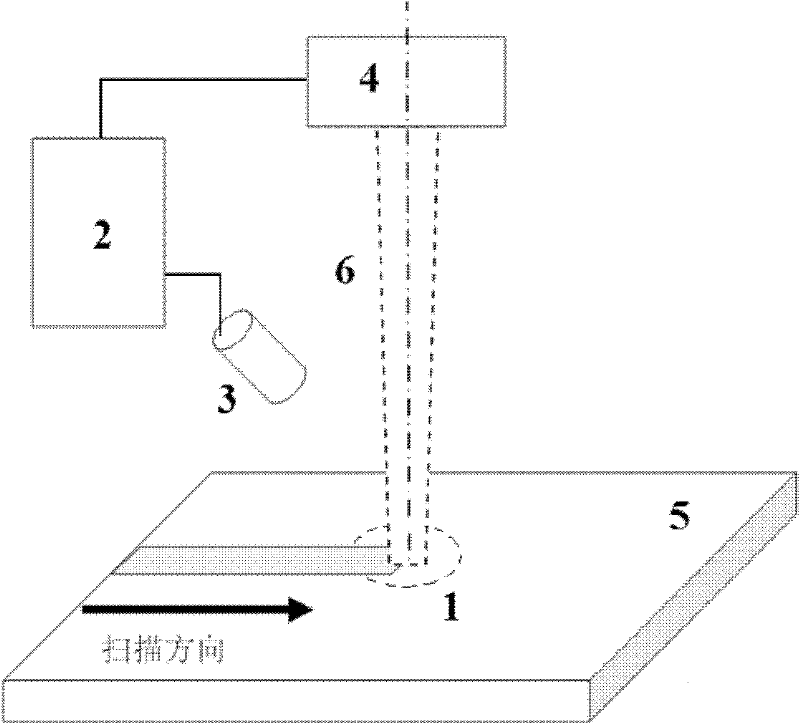
[0023] Such as figure 1 As shown, the control device involved in this embodiment includes: a control module 2 and an infrared enhanced CCD camera 3 and a laser 4 connected thereto respectively, wherein: the control module 2 obtains a molten pool image from the infrared enhanced CCD camera 3 and outputs power The control command is sent to the laser 4, and the output end of the laser 4 and the lens of the infrared enhanced CCD camera 3 face the area 1 to be treated on the substrate 5 respectively.
[0024] The infrared enhanced CCD camera 3 uses a special filter to filter visible light and laser light. After correction, the gray value of the captured image can reflect the temperature value of the corresponding point.
[0025] The control module 2 includes: a serial communication unit, an analog signal output unit, a human-machine interface unit, and a computer signal processing unit, wherein: the serial communication unit is connected with an infrared enhanced CCD camera and tr...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Such as figure 1 Shown, in the present embodiment, workpiece size is the die steel of 150mm * 60mm * 10mm (long * wide * thick); The heating peak temperature is set to be 1350 ℃ on the computer, and the focus size of the laser beam 6 that semiconductor laser outputs is 7.0mm * 1.5 mm, the focus of the laser beam 6 is located on the surface of the workpiece; when the laser beam 6 irradiates the surface of the workpiece at a scanning speed of 1.3m / min, a quenching zone is formed in the area scanned by the laser beam 6.
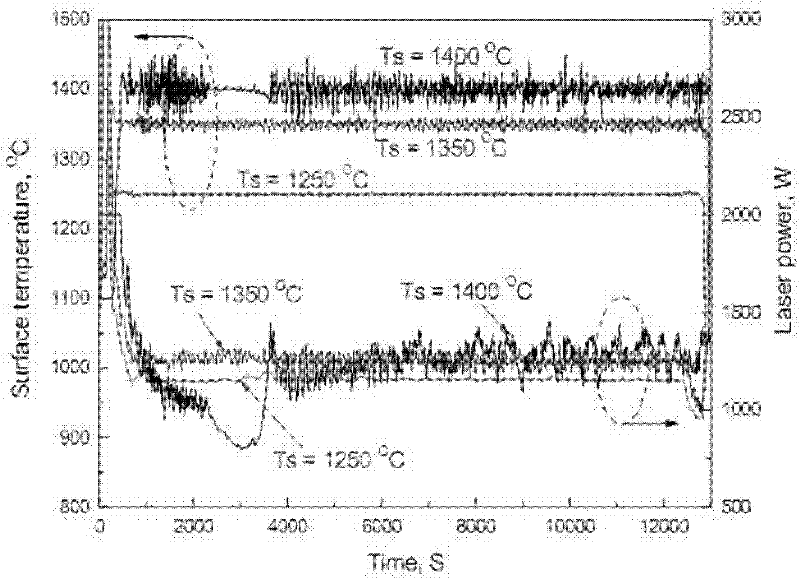
[0031] Such as figure 2 As shown, during the laser surface quenching process, the actual heating peak temperature of the workpiece surface detected by the infrared enhanced CCD camera is basically controlled at 1350°C; at the beginning, the workpiece is in a cold state, and a large laser power is required to ensure the actual heating peak of the workpiece surface When the temperature reaches 1350°C, as the workpiece is heated to a hot state, the laser p...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Such as figure 1 Shown, in the present embodiment, workpiece size is the die steel of 150mm * 60mm * 10mm (long * wide * thick); The heating peak temperature is set to be 1400 ℃ on the computer, and the focus size of the laser beam 6 that semiconductor laser outputs is 7.0mm * 1.5 mm, the focus of the laser beam 6 is located on the surface of the workpiece; when the laser beam 6 irradiates the surface of the workpiece at a scanning speed of 1.3m / min, a quenching zone is formed in the area scanned by the laser beam 6.
[0034] Such as figure 2 As shown, during the laser surface quenching process, the actual heating peak temperature of the workpiece surface detected by the infrared enhanced CCD camera fluctuated around 1400°C, and the laser power also fluctuated greatly; it was observed that there were traces of partial melting on the surface of the workpiece after quenching, indicating that the actual heating peak The temperature has reached above the melting point of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com