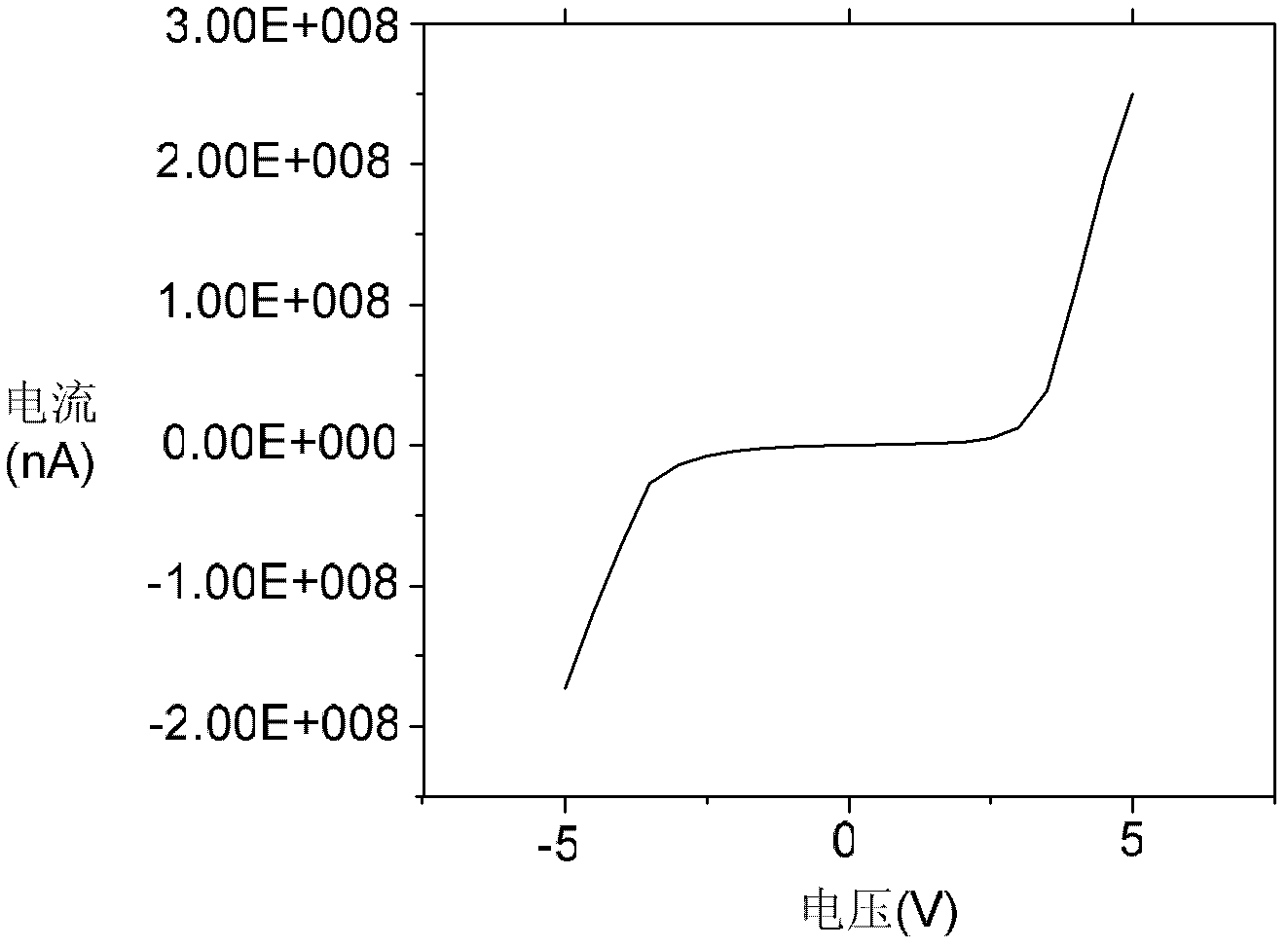
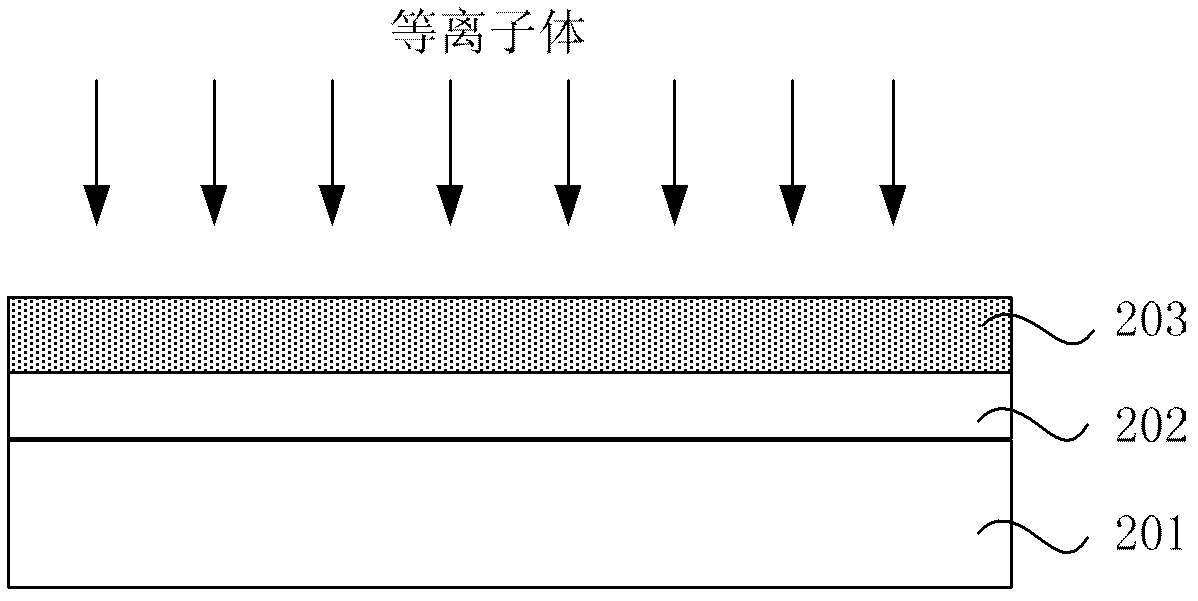
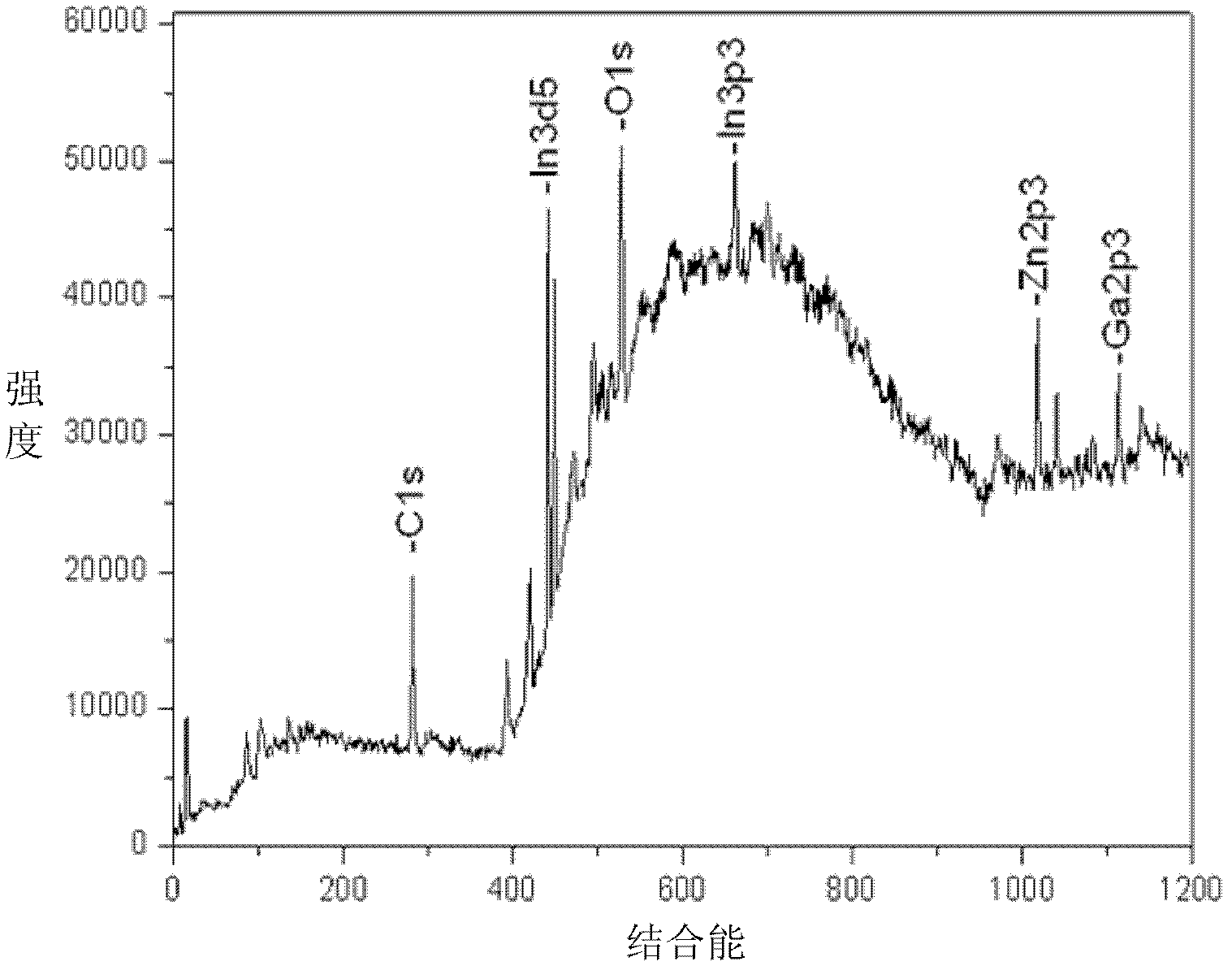
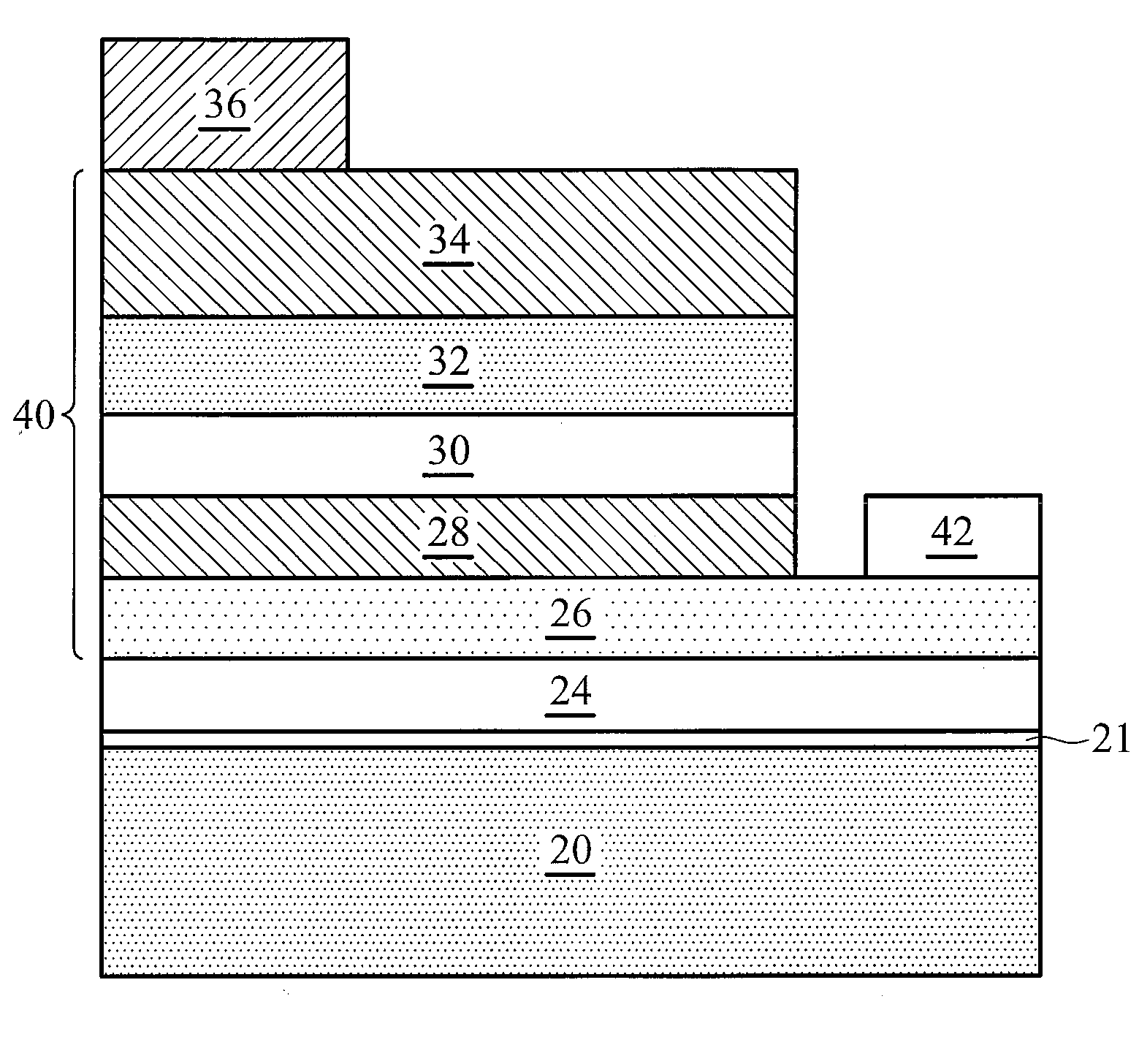
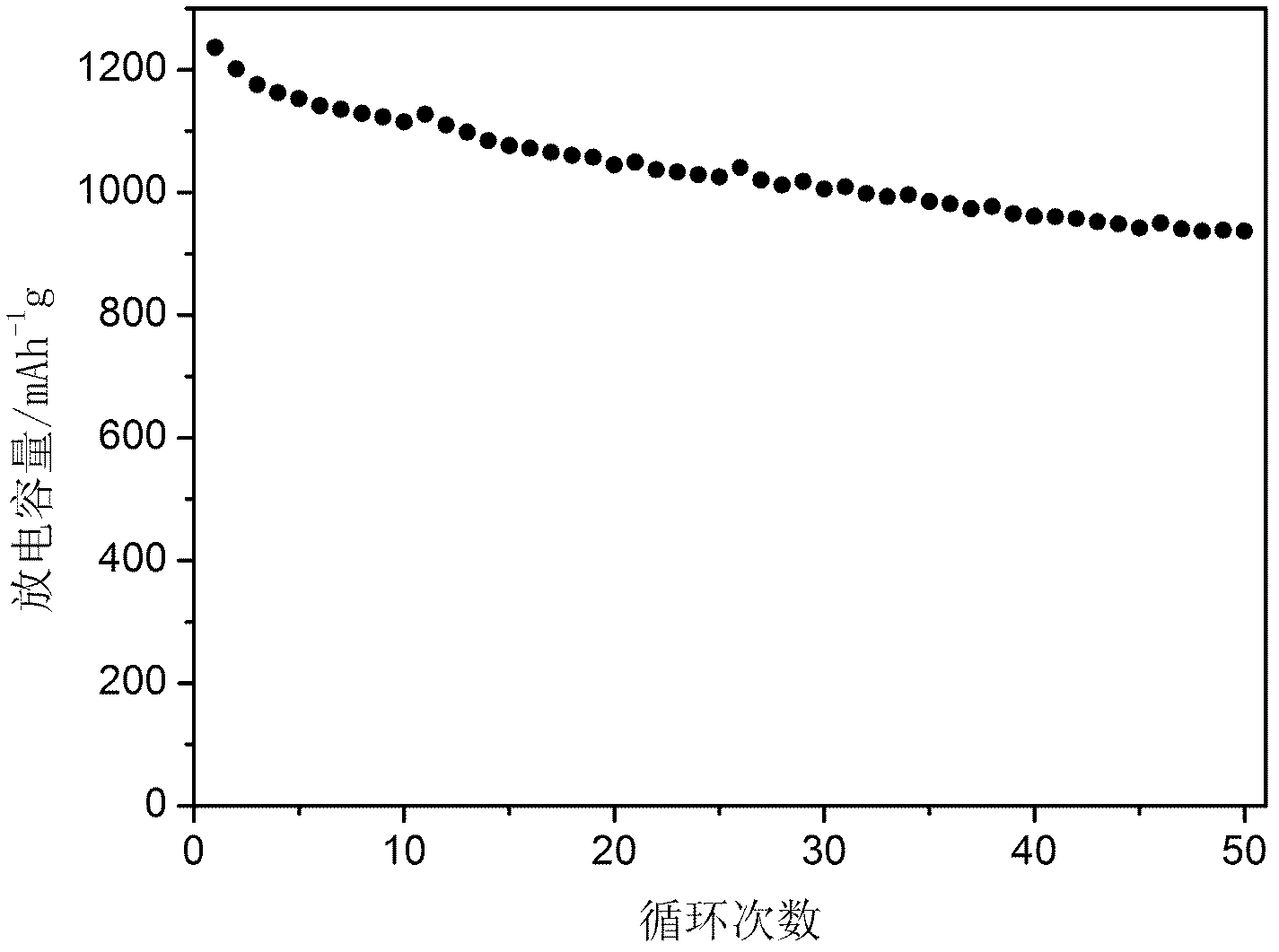
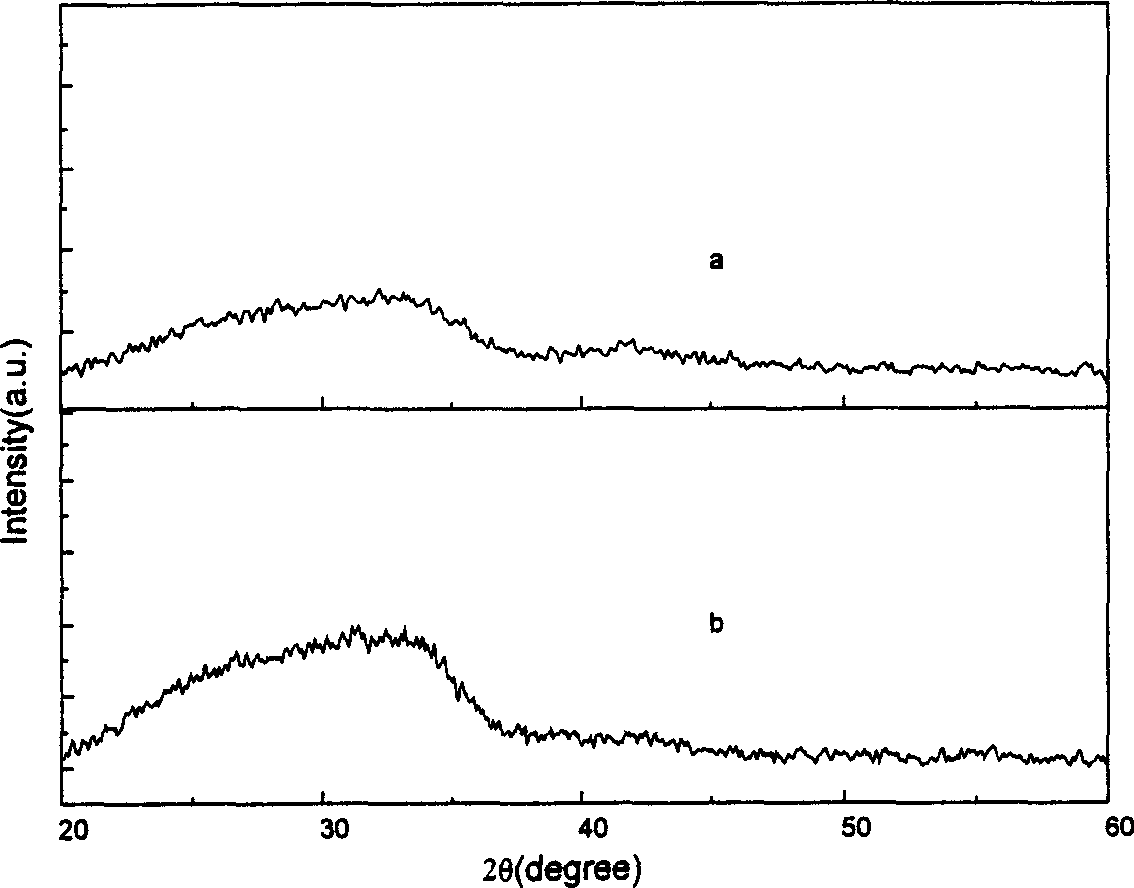
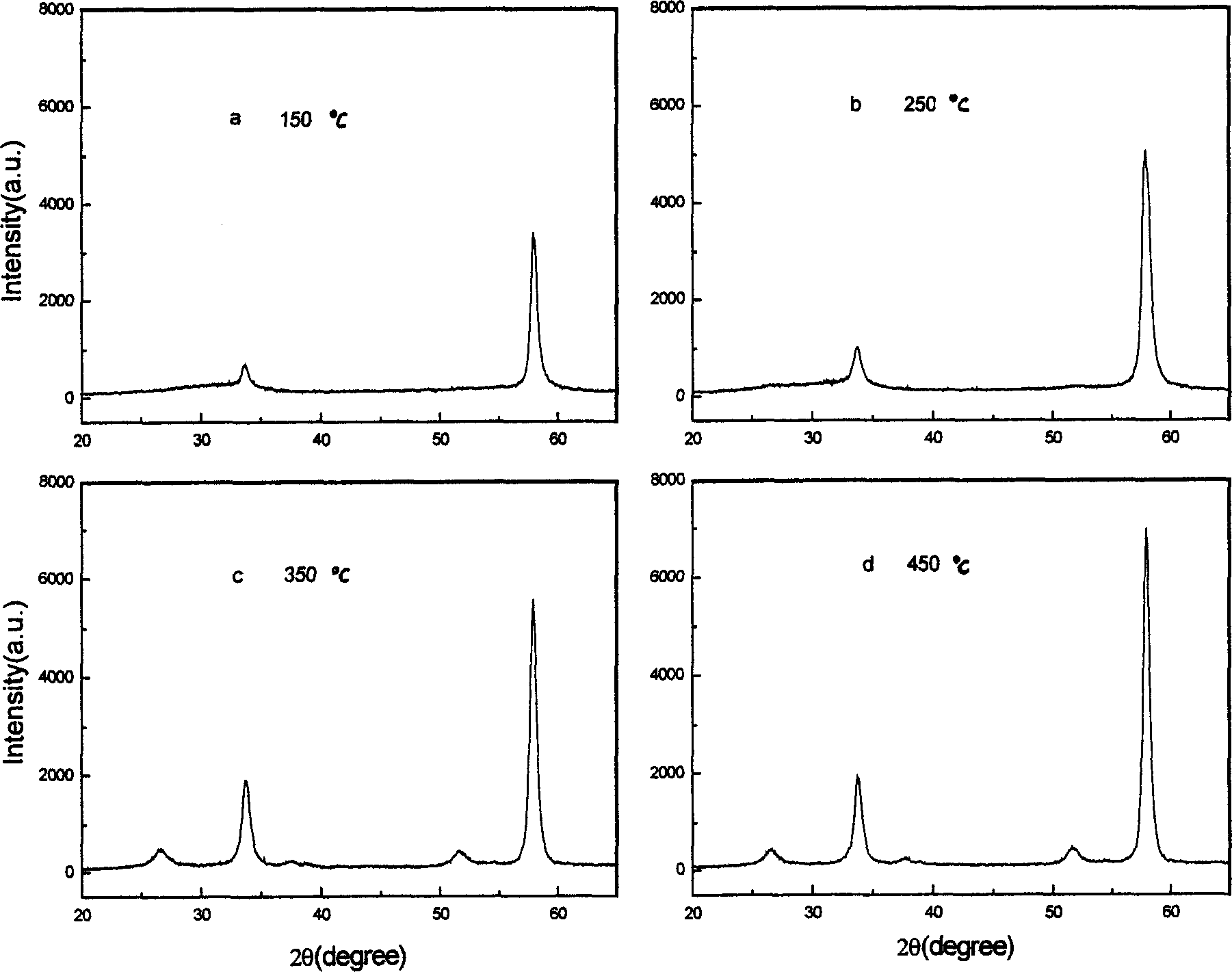
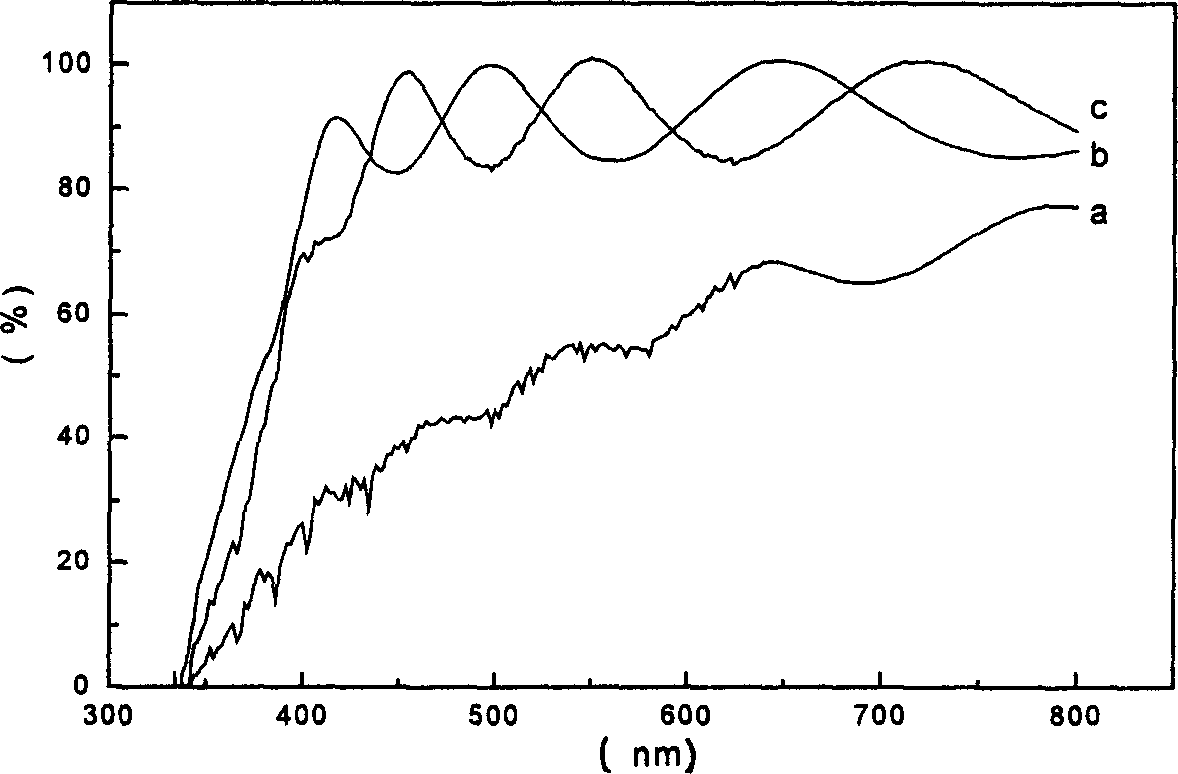
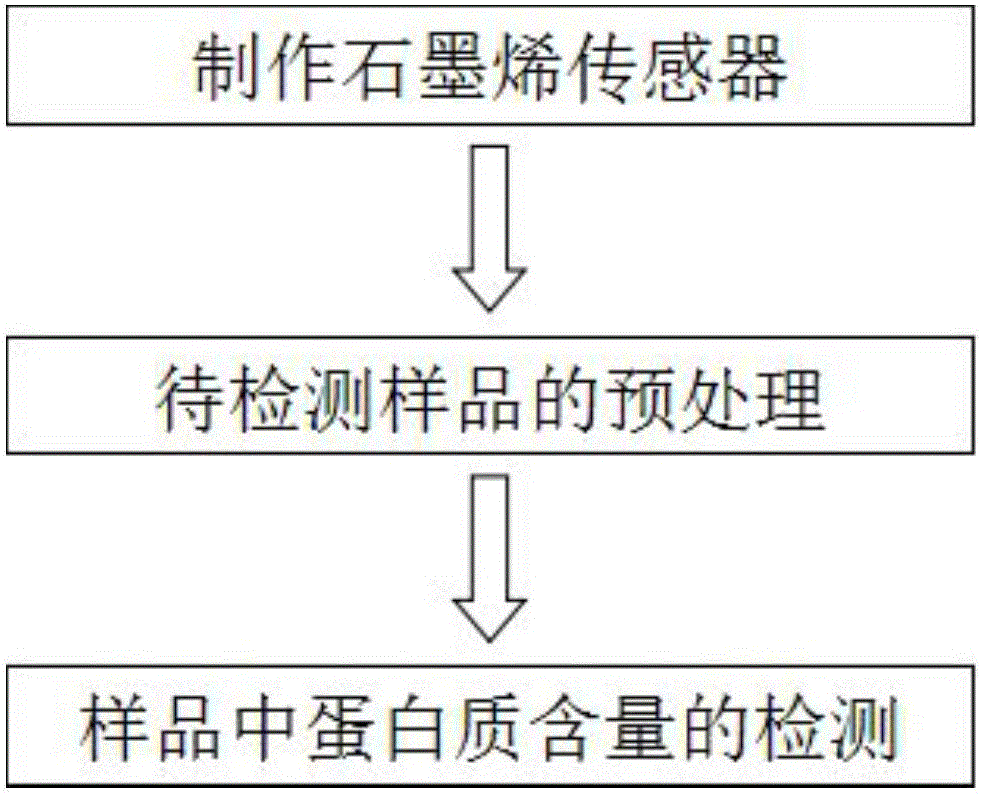
Patents
Literature
493results about How to "Increase the carrier concentration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
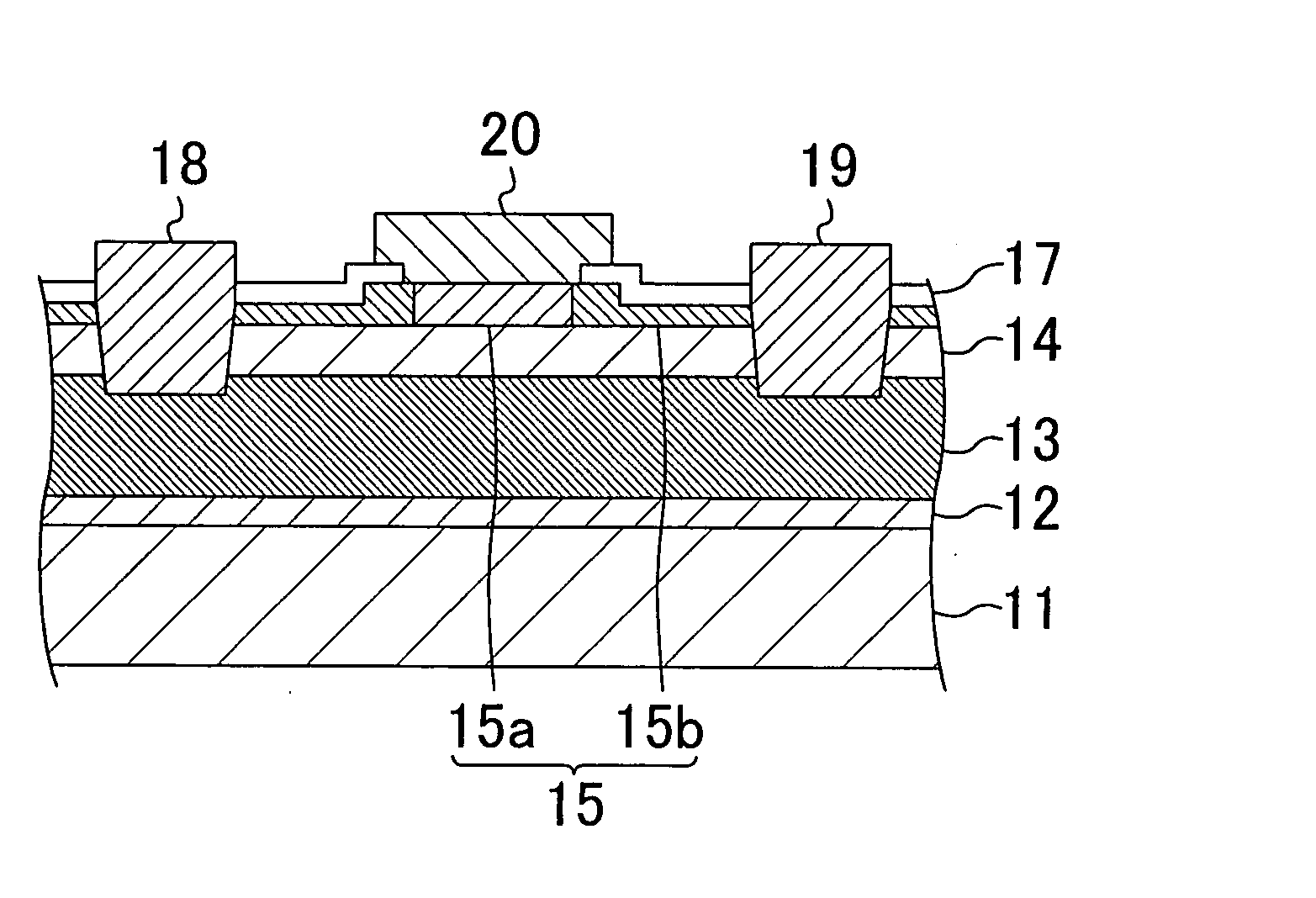
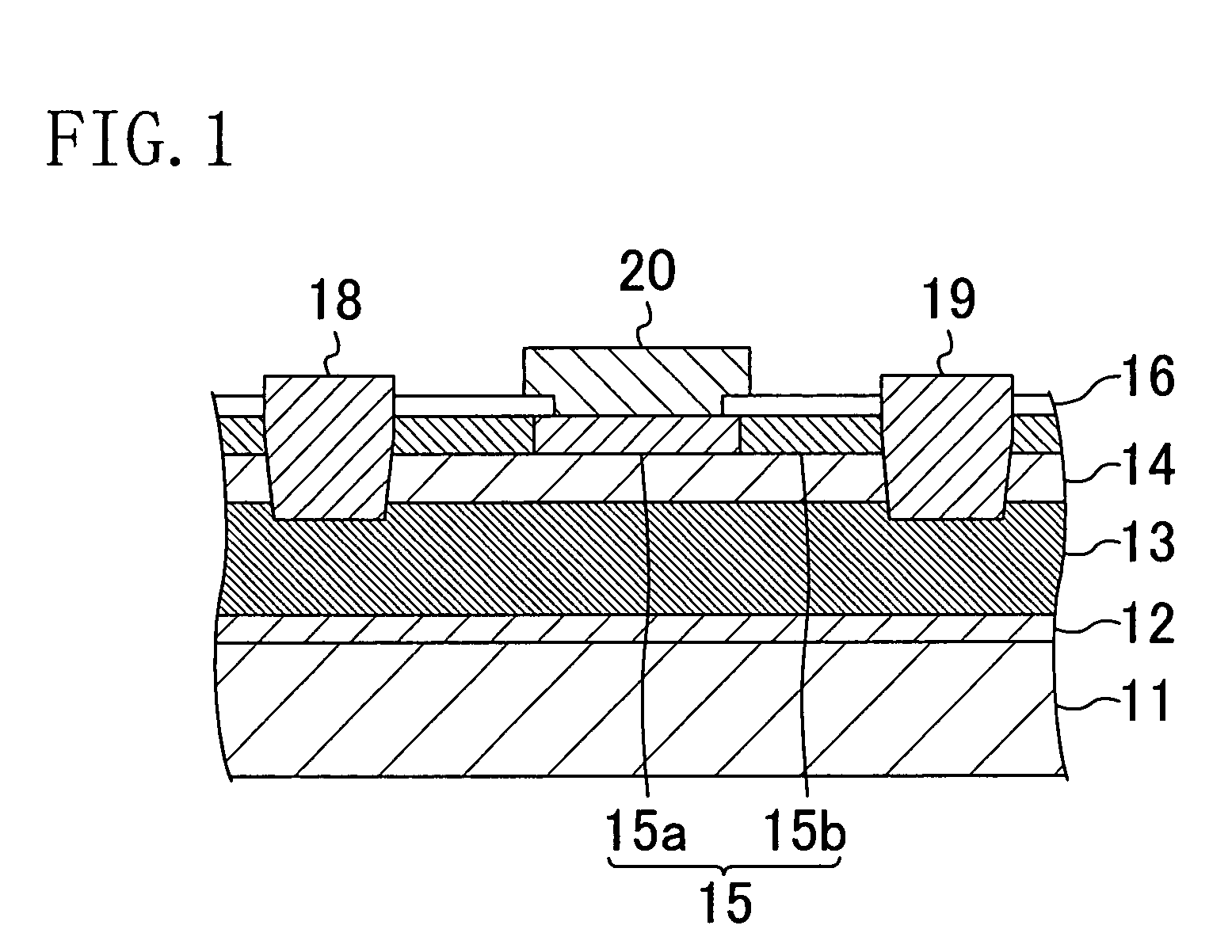
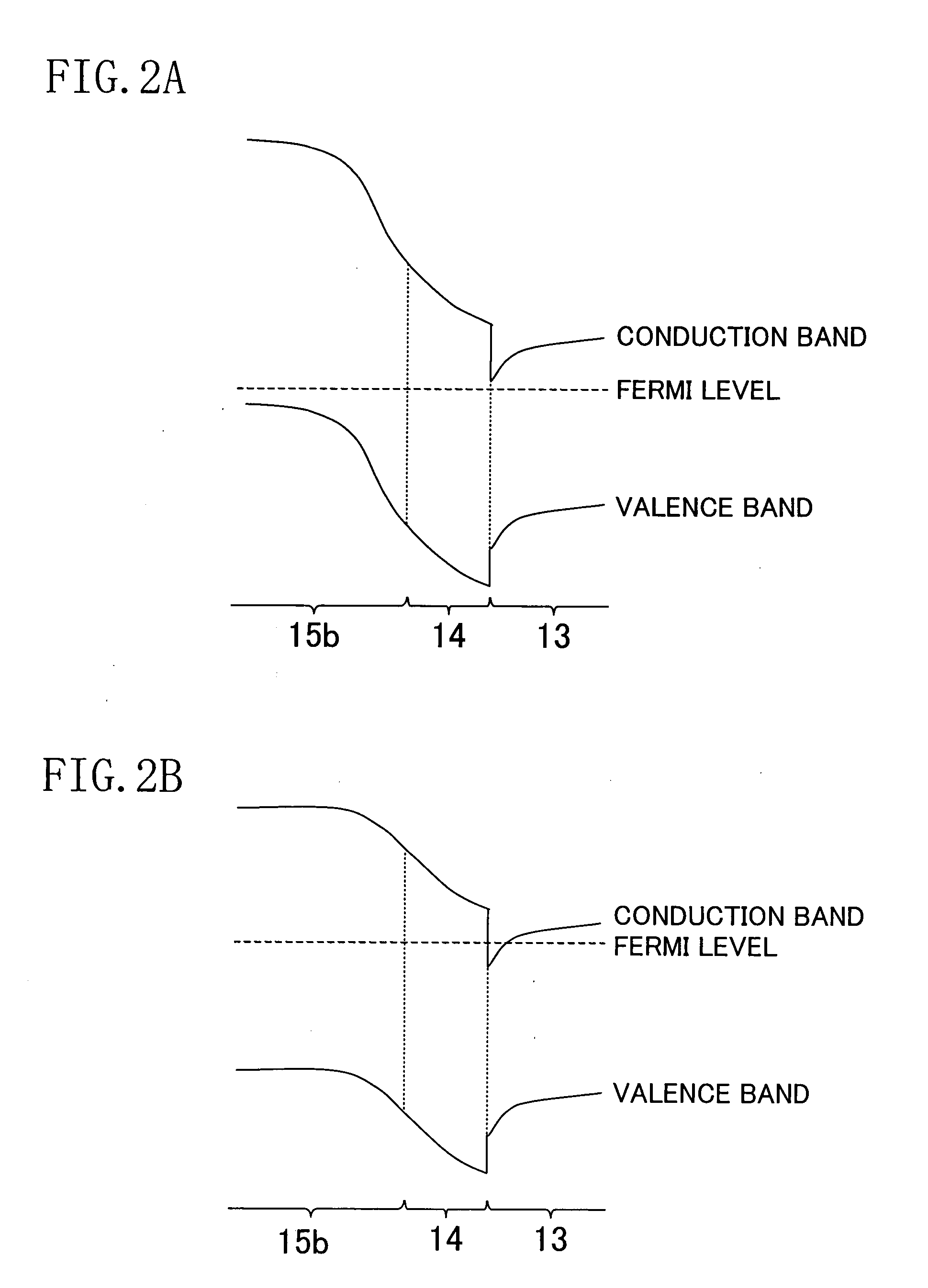
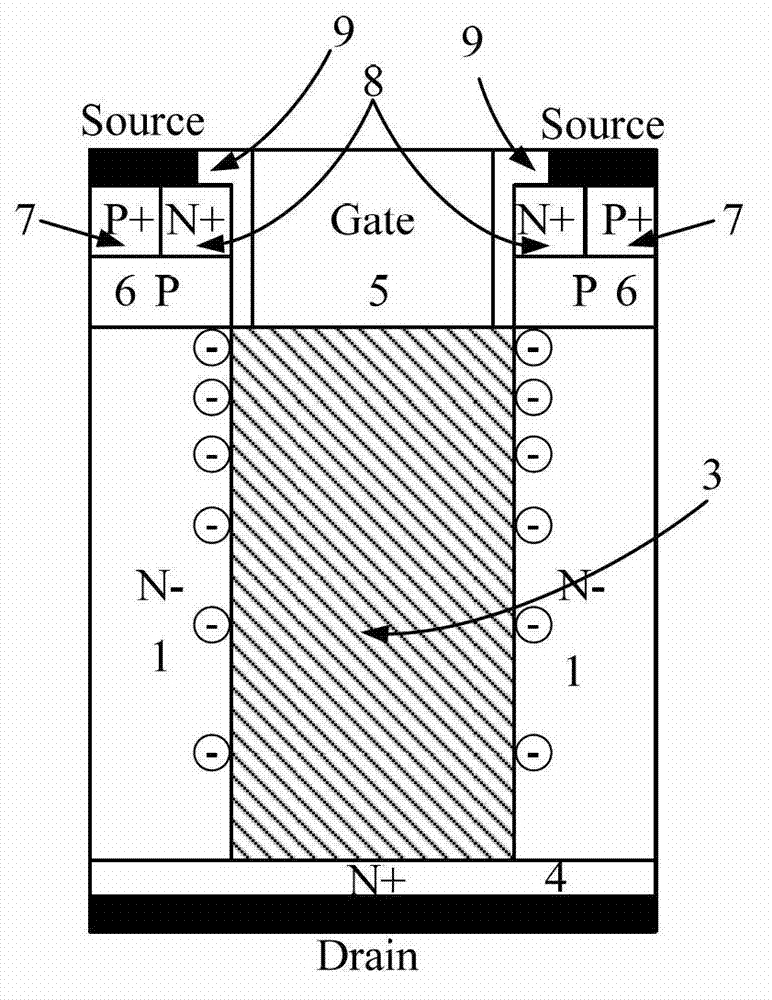
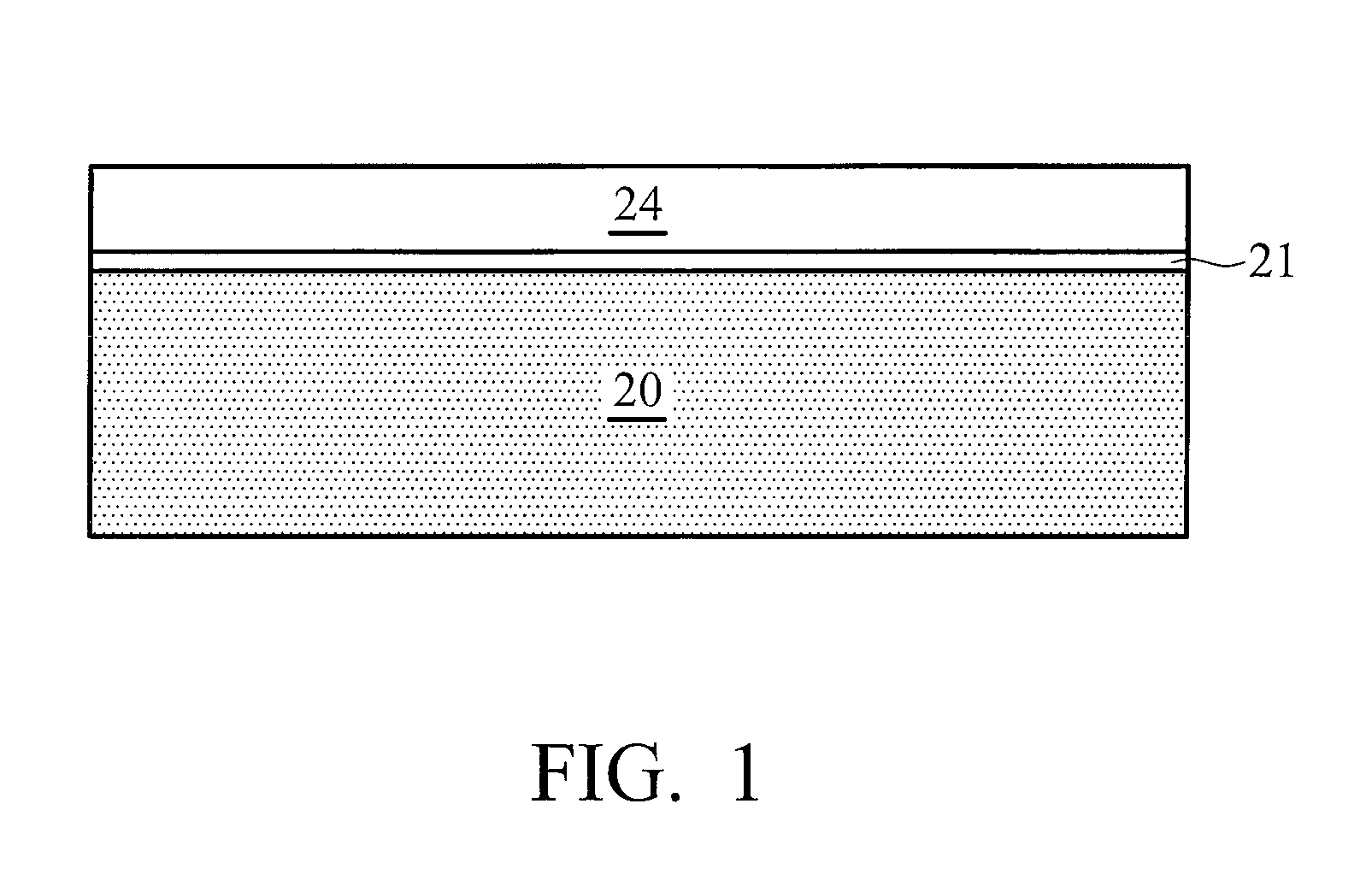
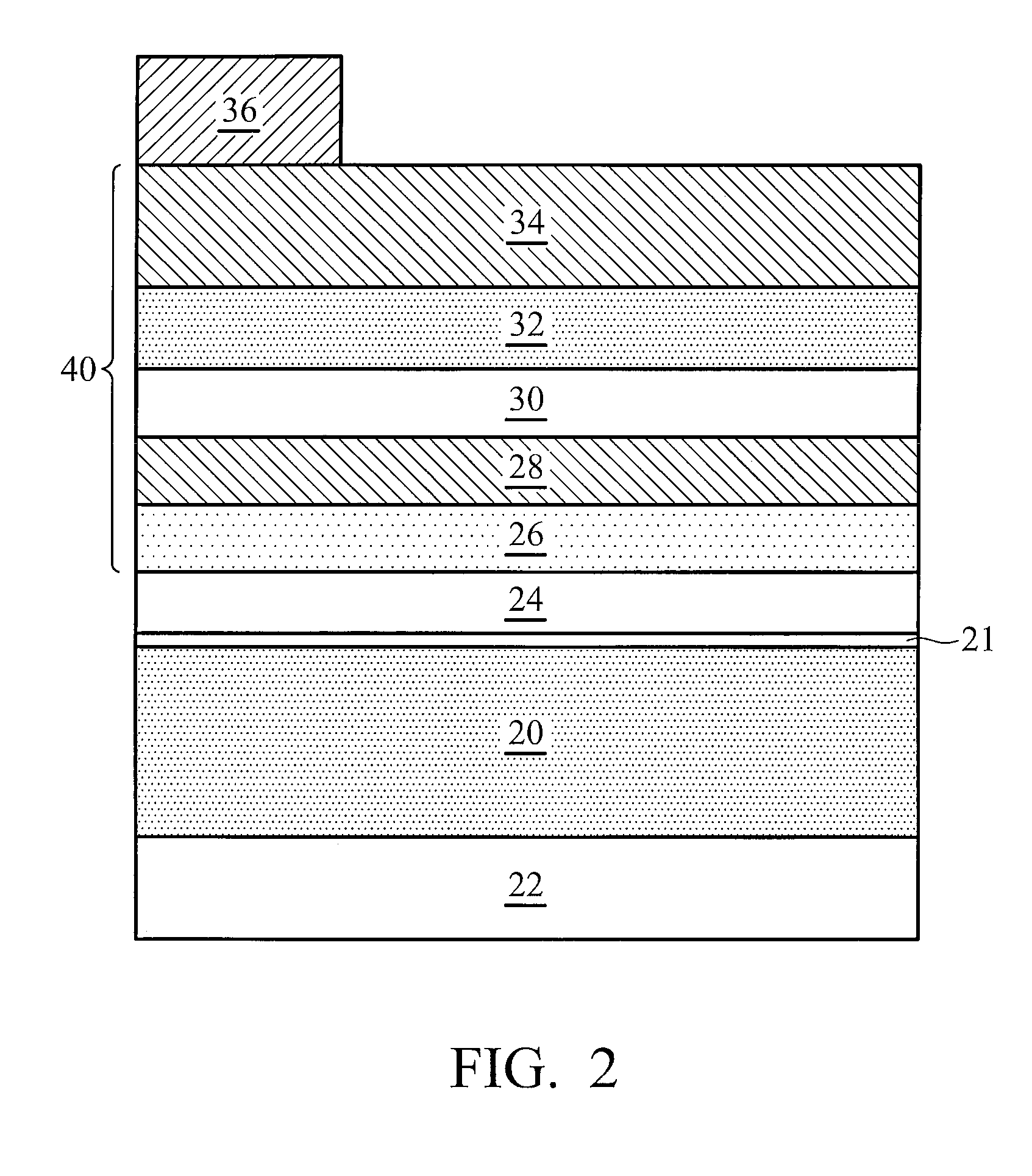
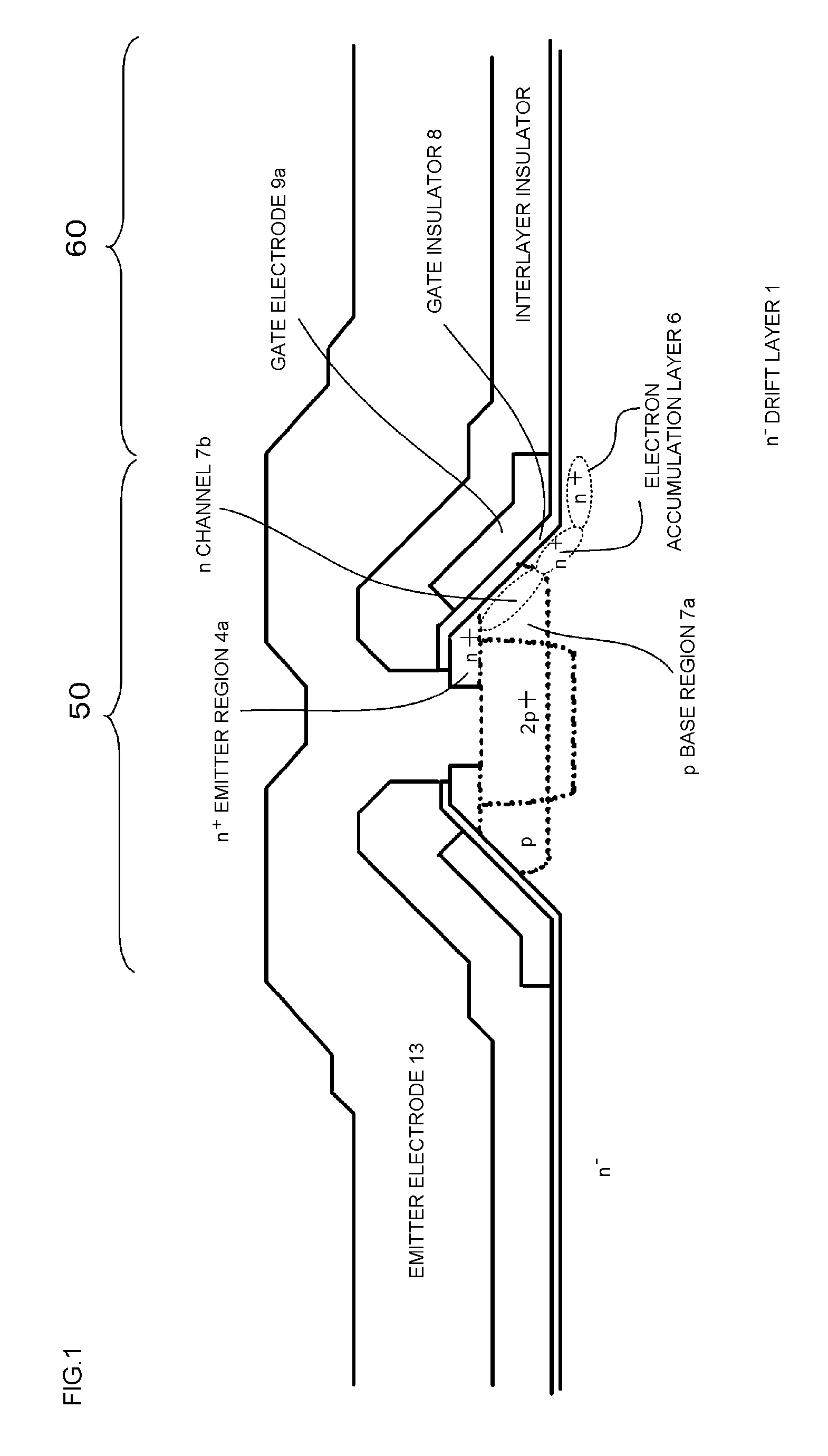
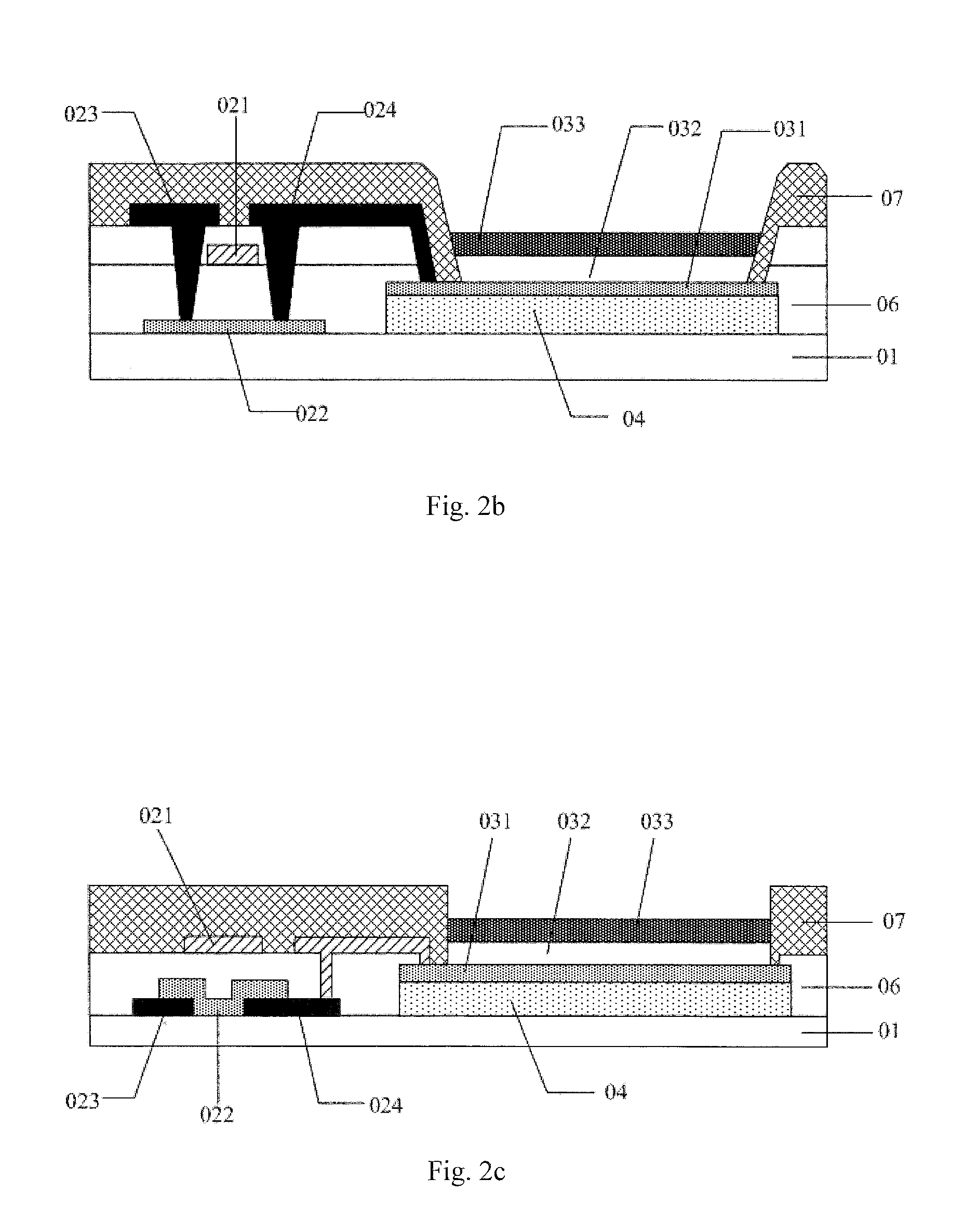
Nitride semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20080087915A1Large operating currentImprove switching characteristicsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh resistanceWide band
A nitride semiconductor device includes: a first nitride semiconductor layer; a second nitride semiconductor layer formed on the first nitride semiconductor layer and having a wider band gap than the first nitride semiconductor layer; and a third nitride semiconductor layer formed on the second nitride semiconductor layer. A region of the third nitride semiconductor layer located below the gate electrode is formed with a control region having a p-type conductivity, and a region of the third nitride semiconductor layer located between the gate electrode and each of the source electrode and the drain electrode is formed with a high resistive region having a higher resistance than the that of the control region.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Semiconductor device and mehtod
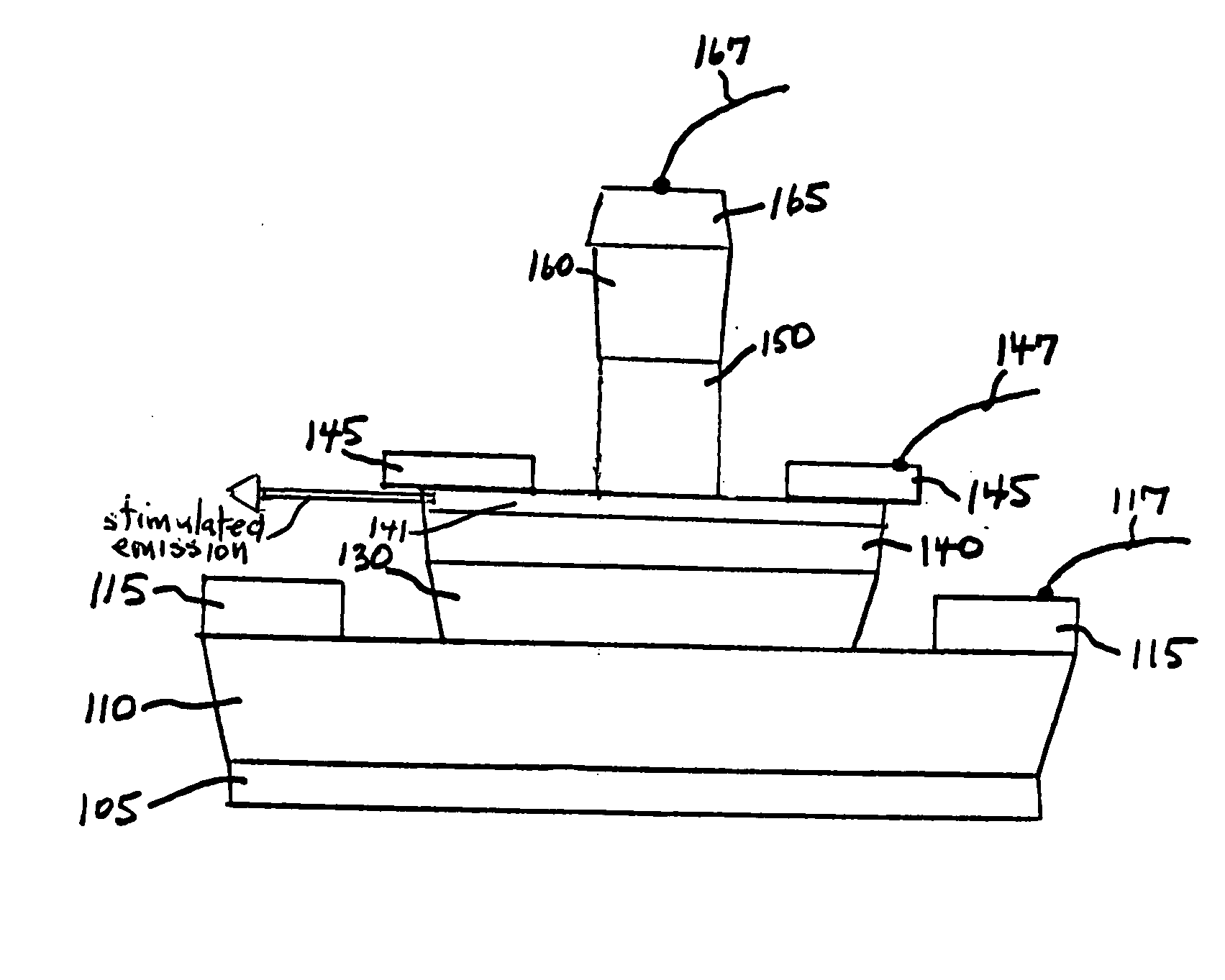
ActiveUS20050054172A1Increase speedImprove mobilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialStimulated emission
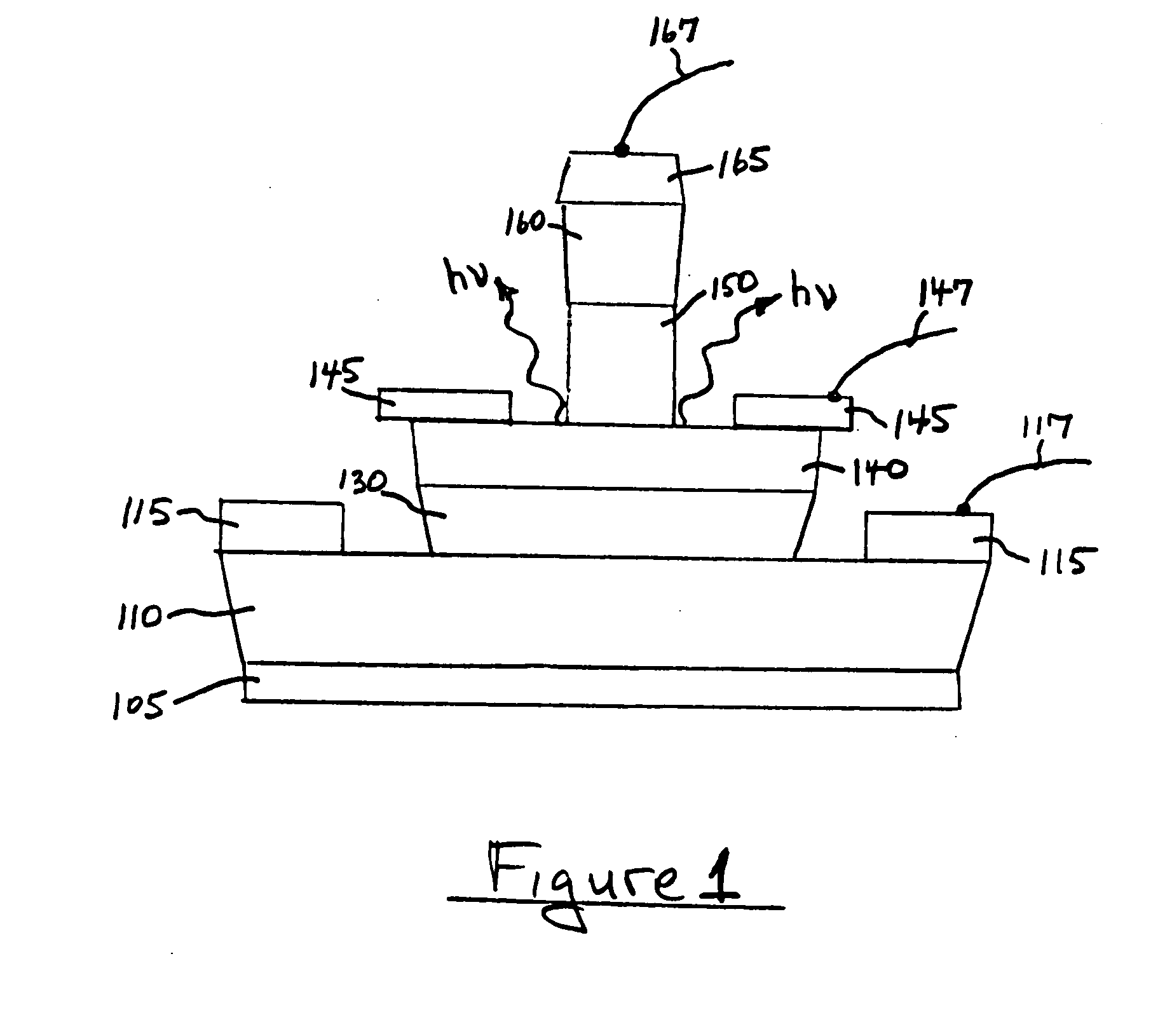
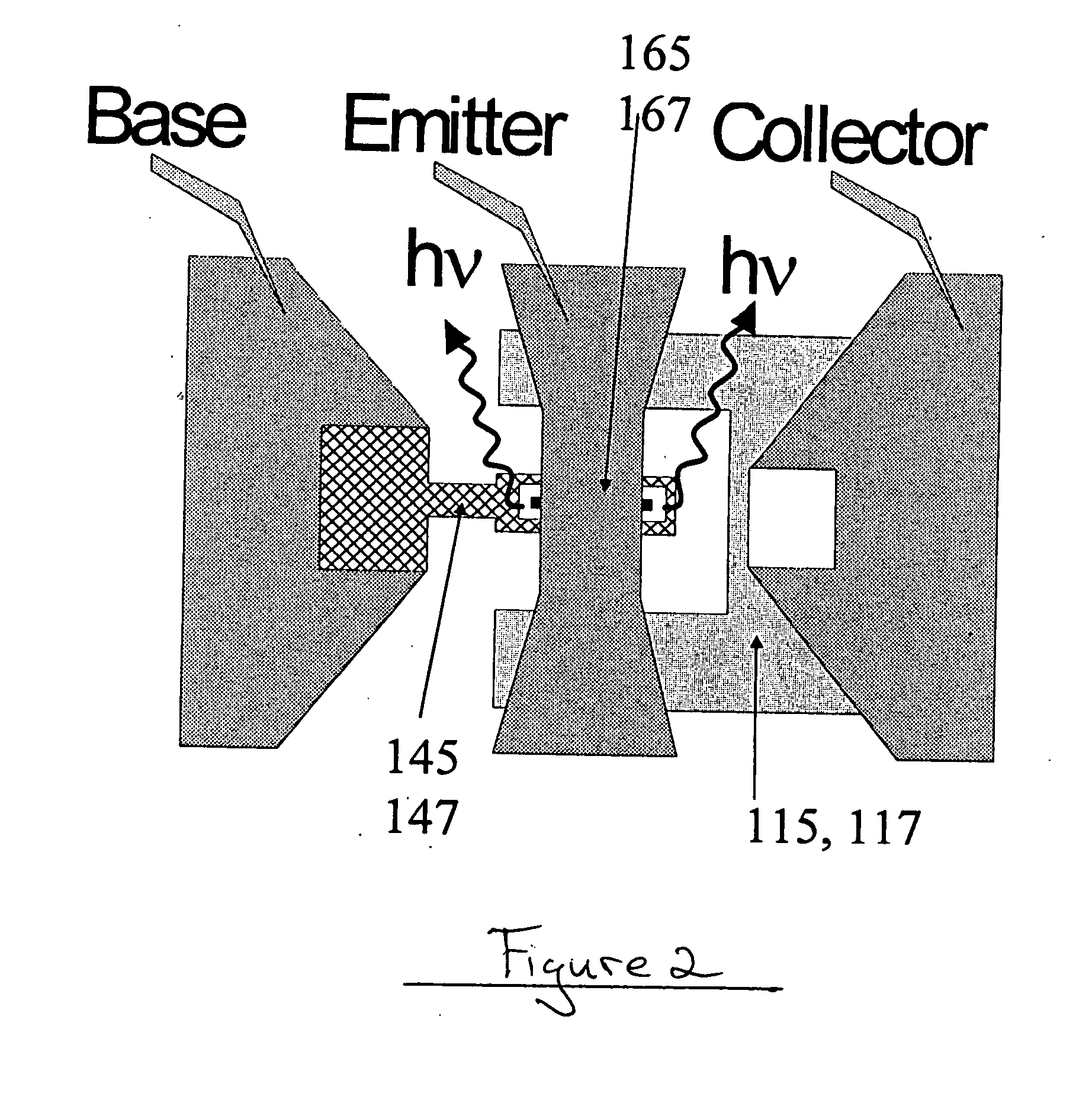
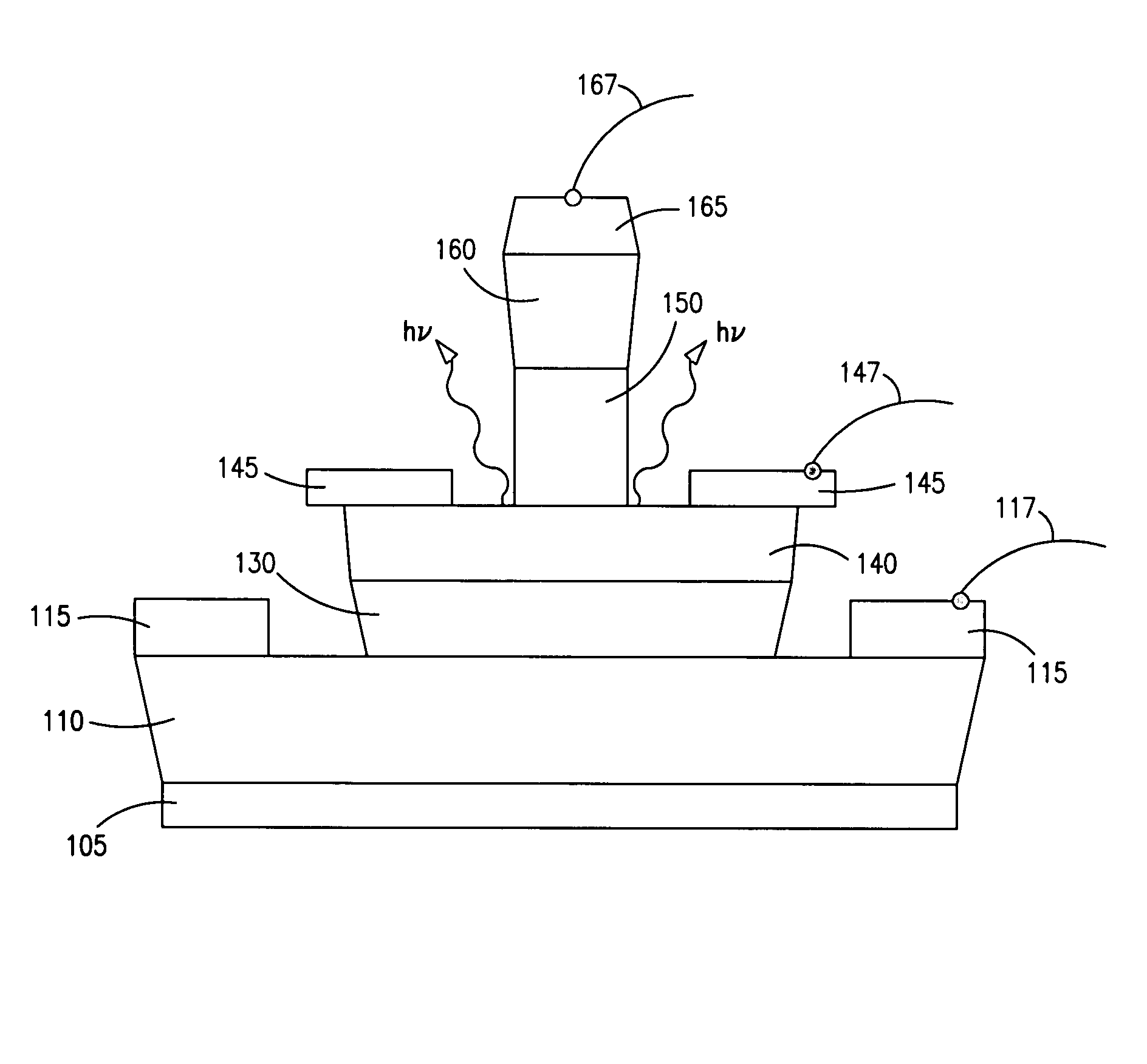
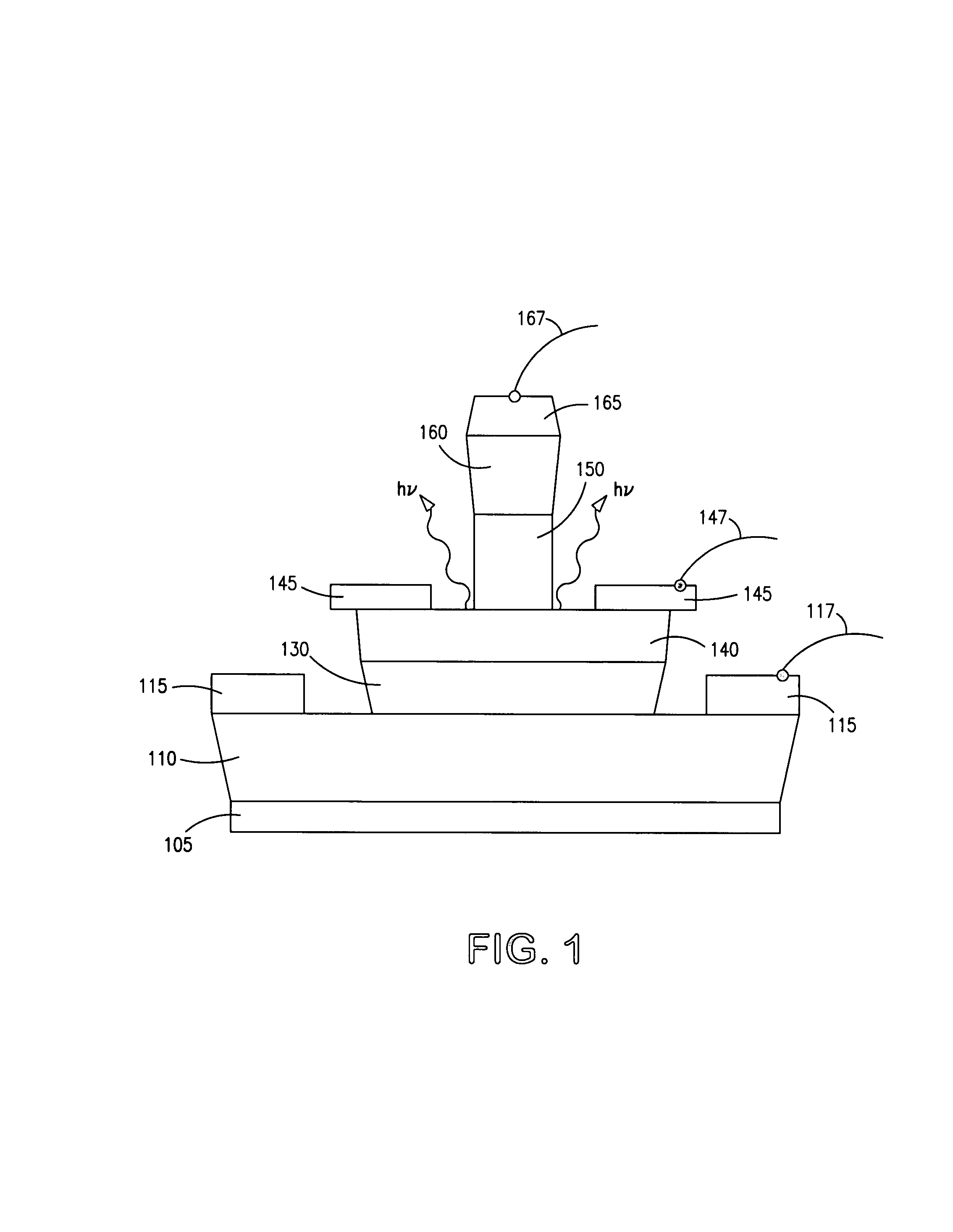
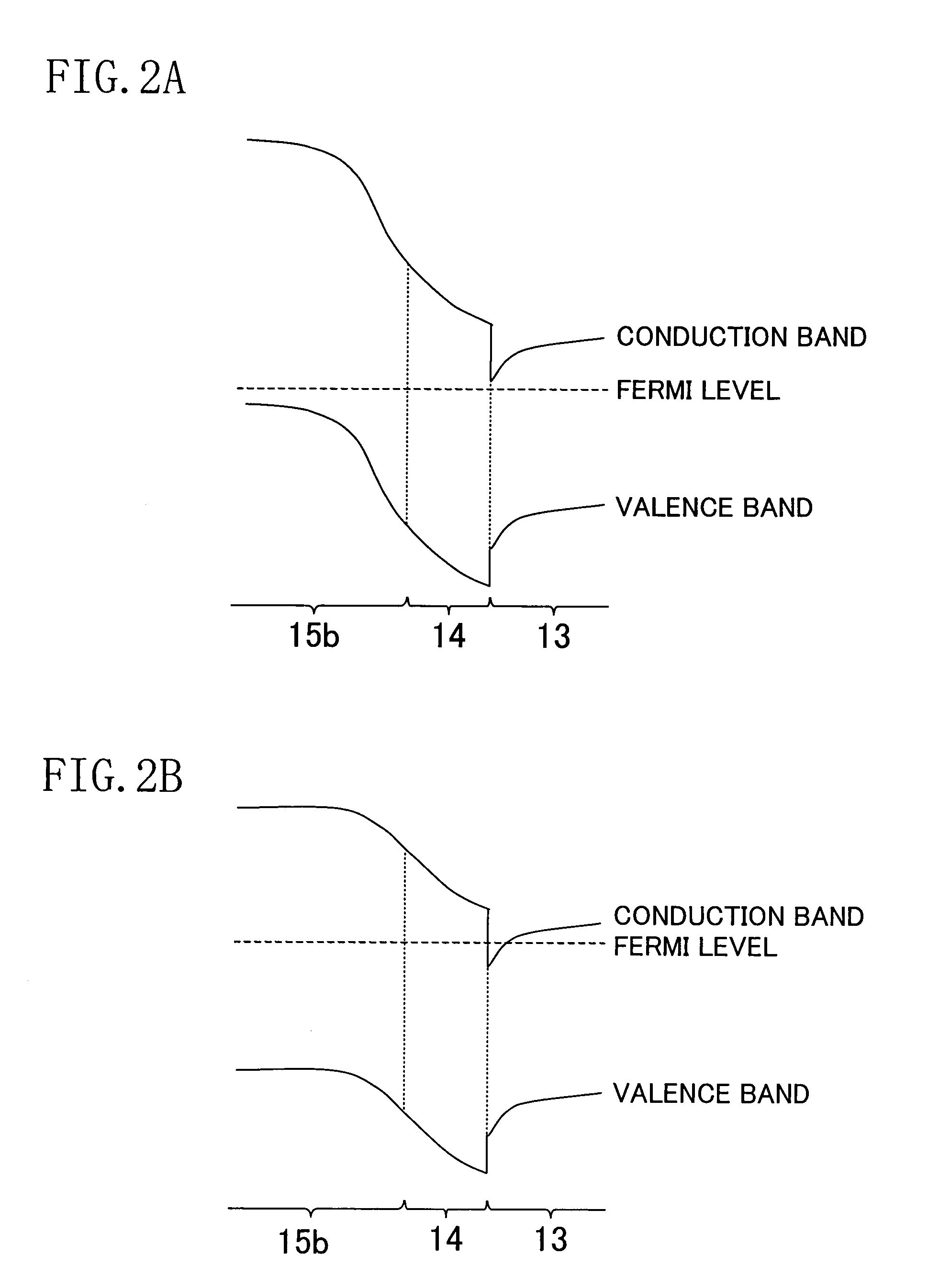
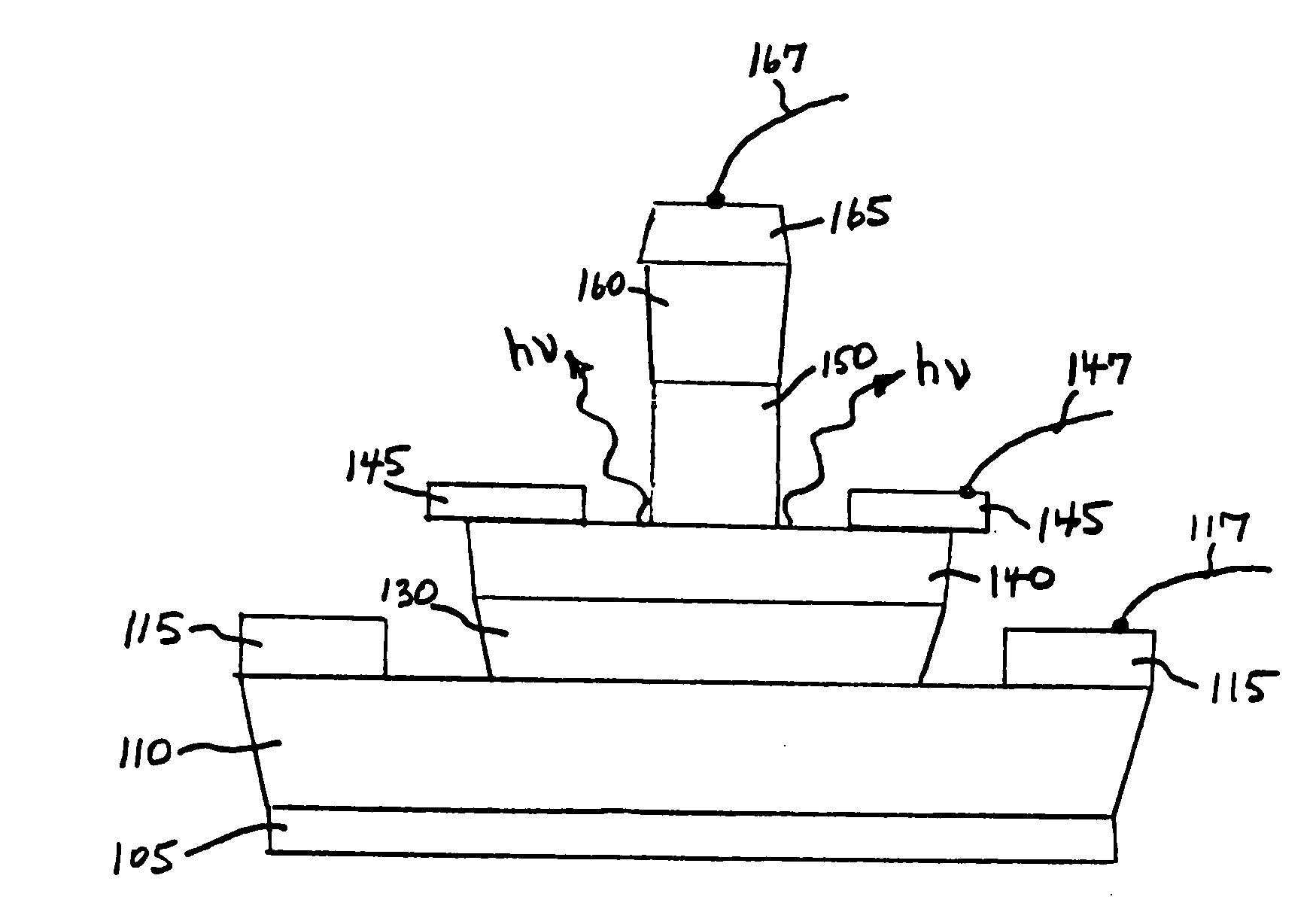
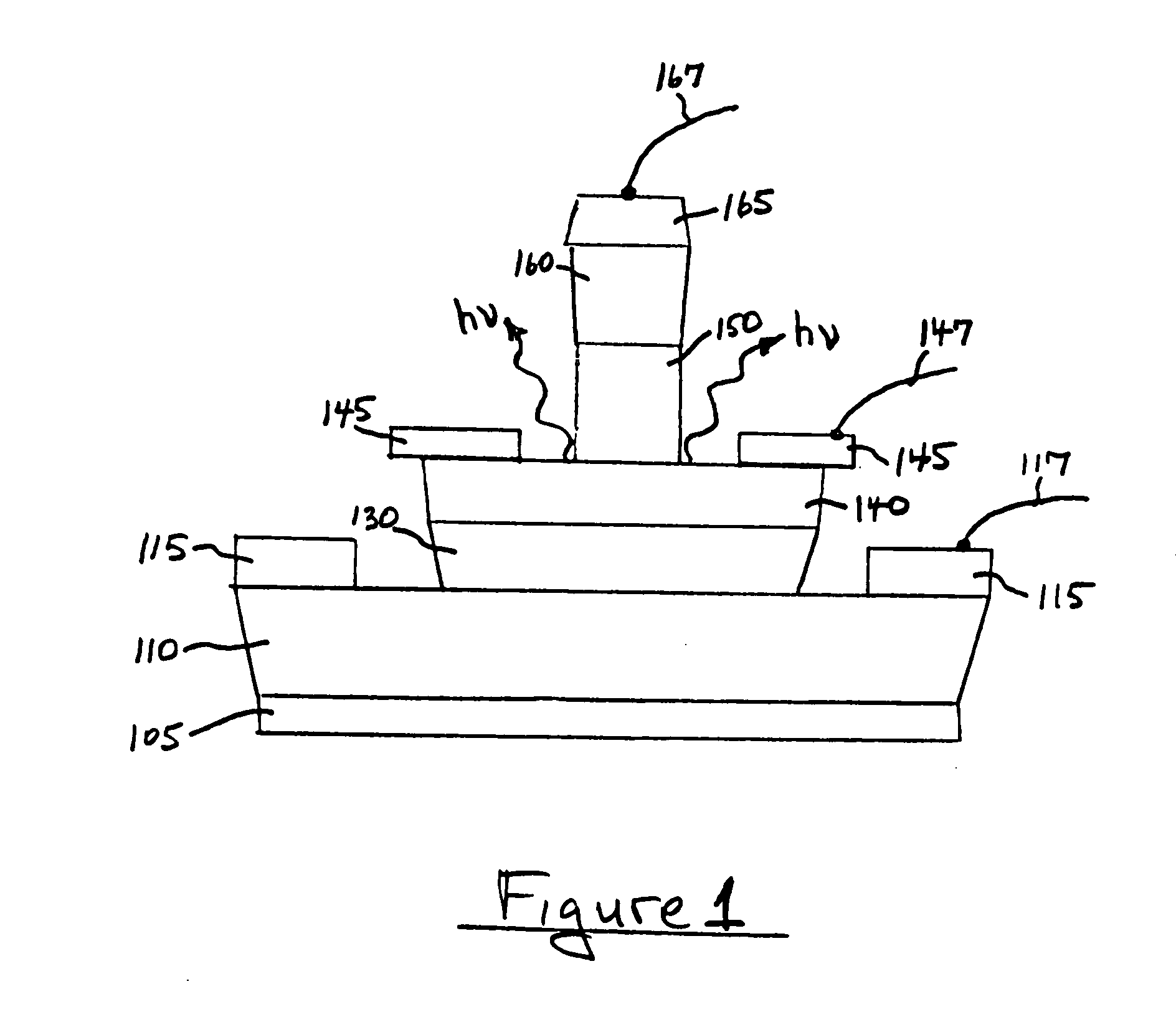
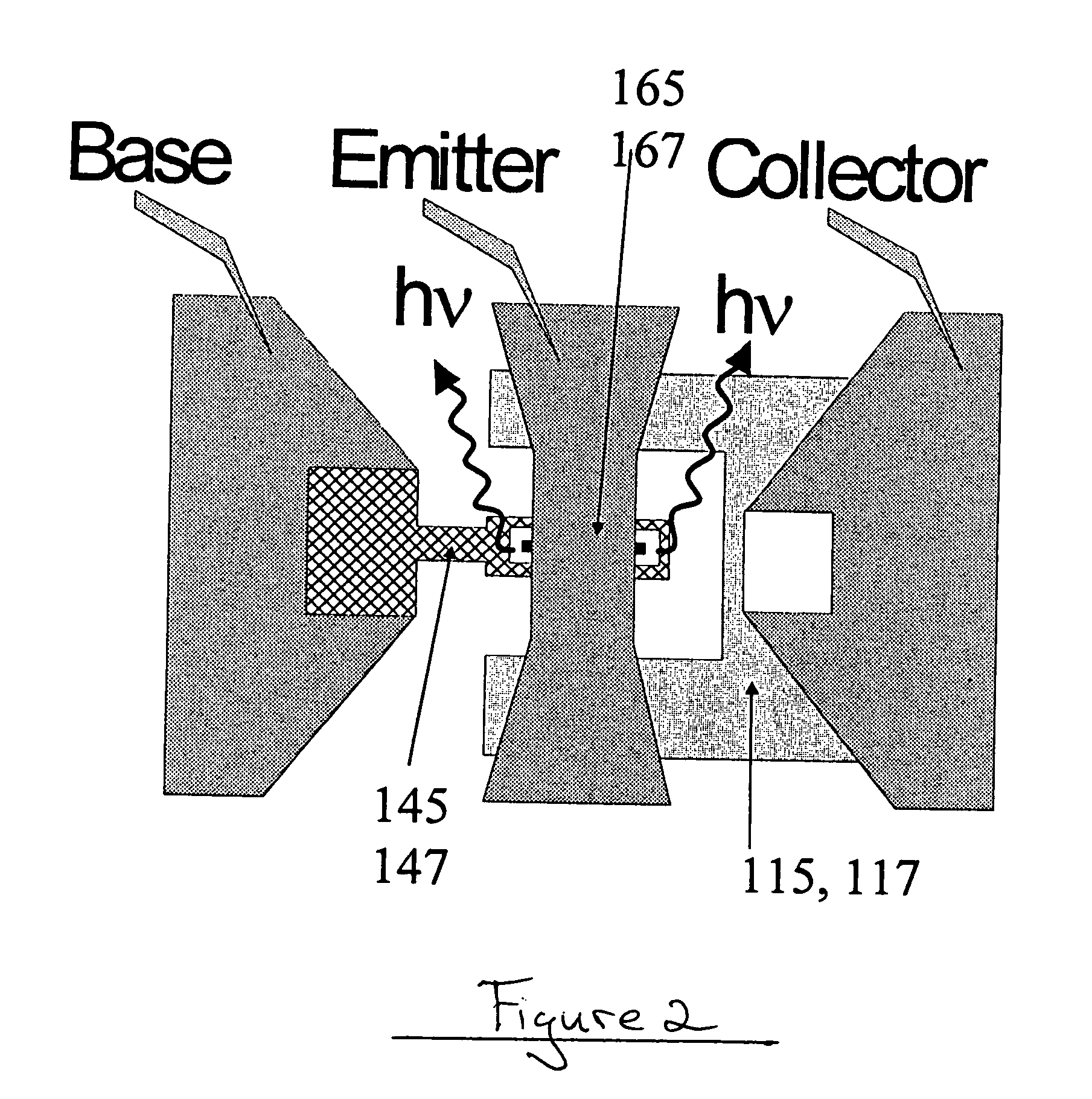
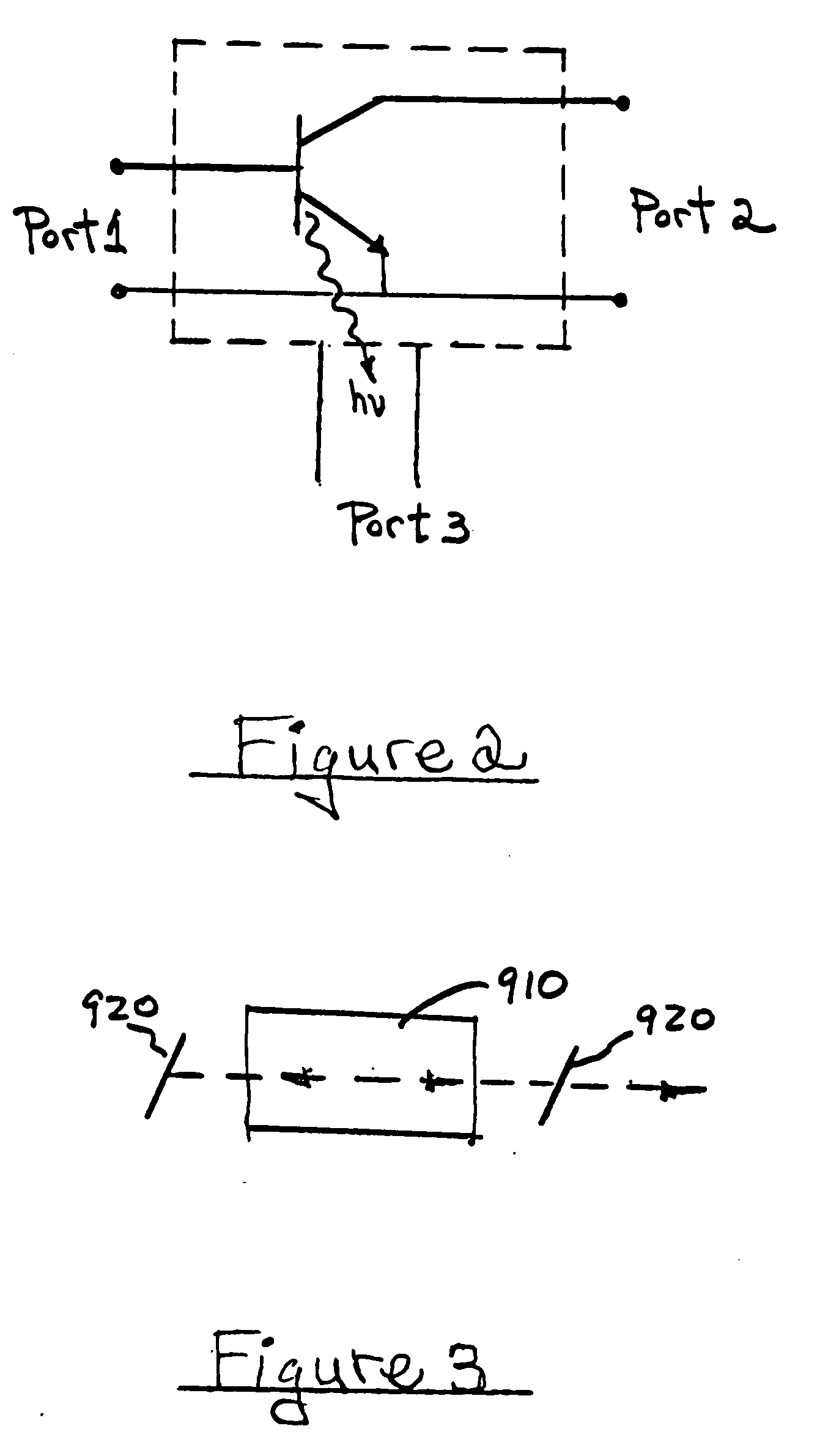
A method for increasing the speed of a bipolar transistor, includes the following steps: providing a bipolar transistor having emitter, base, and collector regions; providing electrodes for coupling electrical signals with the emitter, base, and collector regions; and adapting the base region to enhance stimulated emission to the detriment of spontaneous emission, so as to reduce carrier recombination lifetime in the base region.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Semiconductor laser devices and methods
InactiveUS7286583B2Increase speedImprove mobilityLaser detailsNanoopticsResonant cavitySemiconductor materials
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Boron-Doped Single-Walled Nanotubes(SWCNT)
InactiveUS20100219383A1Improve electricityImprove thermal conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsFiberElectric power transmission
The present invention generally relates to methods and apparatus for the synthesis or preparation of boron-doped single-walled carbon nanotubes (B-SWCNTs). The invention provides a high yield, single step method for producing large quantities of continuous macroscopic carbon fiber from single-wall carbon nanotubes using inexpensive carbon feedstocks wherein the carbon nanotubes are produced by in situ boron substitutional doping. In one embodiment, the nanotubes disclosed are used, singularly or in multiples, in power transmission cables, in solar cells, in batteries, as antennas, as molecular electronics, as probes and manipulators, and in composites. It is another object of this invention to provide macroscopic carbon fiber made by such a method.
Owner:EKLUND PETER C
Semiconductor light emitting devices and methods
InactiveUS7354780B2Increase speedImprove mobilityLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical communicationOptical coupling
A method for producing an optical output, including the following steps: providing first and second electrical signals; providing a bipolar light-emitting transistor device that includes collector, base, and emitter regions; providing a collector electrode coupled with the collector region and an emitter electrode coupled with the emitter region, and coupling electrical potentials with respect to the collector and emitter electrodes; providing an optical coupling in optical communication with the base region; providing first and second base electrodes coupled with the base region; and coupling the first and second electrical signals with the first and second base electrodes, respectively, to produce an optical output emitted from the base region and coupled into the optical coupling, the optical output being a function of the first and second electrical signals.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
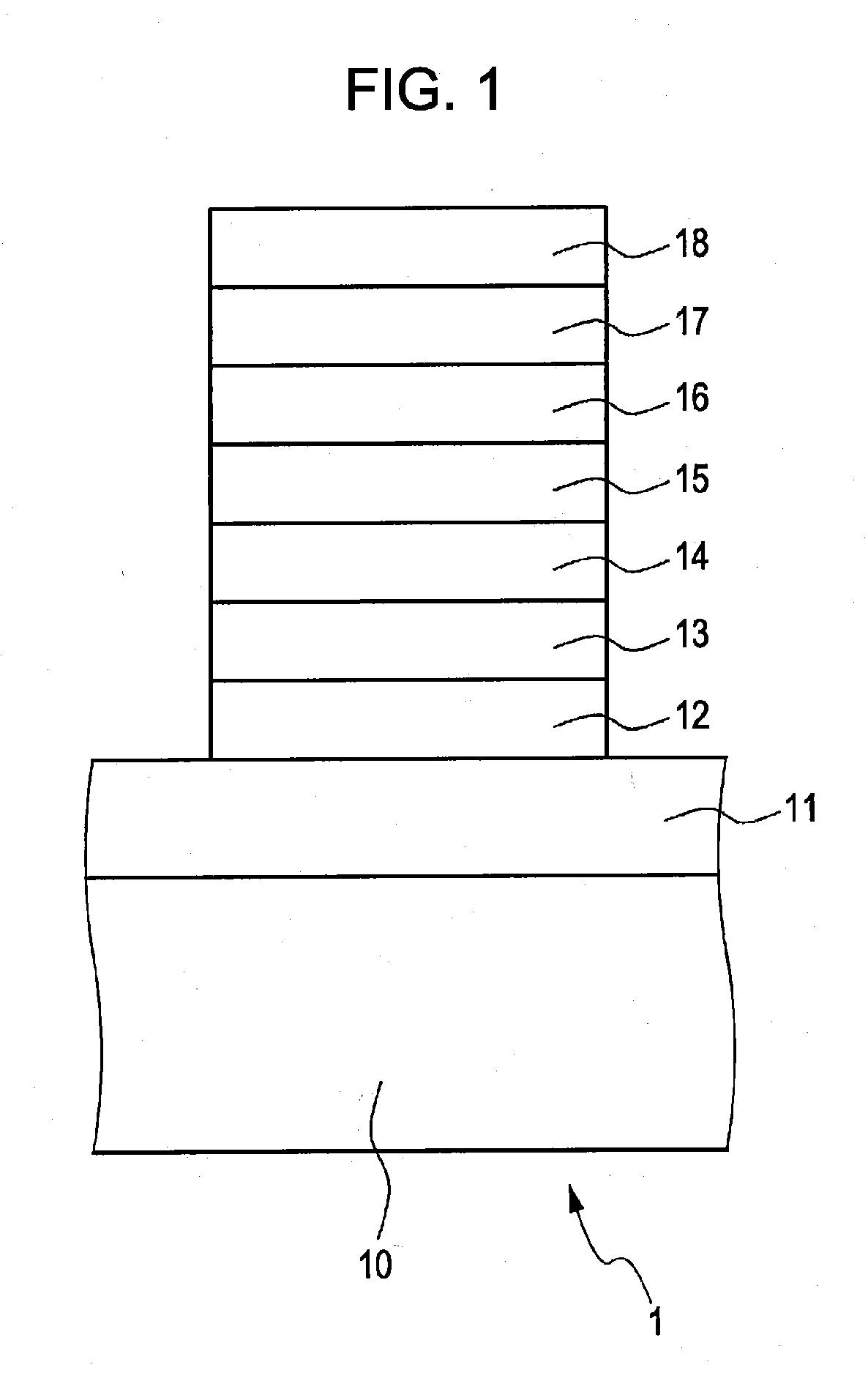
Gan-Based Semiconductor Light-Emitting Device, Light Illuminator, Image Display Planar Light Source Device, and Liquid Crystal Display Assembly
ActiveUS20070284564A1Suppress large shift of emission wavelengthIncrease in operating current densitySolid-state devicesNanoopticsLiquid-crystal displayQuantum well
A GaN-based semiconductor light-emitting device includes (A) a first GaN-based compound semiconductor layer 13 having n-type conductivity, (B) an active layer 15 having a multi-quantum well structure including well layers and barrier layers for separating between the well layers, and (C) a second GaN-based compound semiconductor layer 17 having p-type conductivity. The well layers are disposed in the active layer 15 so as to satisfy the relation d1<d2 wherein d1 is the well layer density on the first GaN-based compound semiconductor layer side in the active layer and d2 is the well layer density on the second GaN-based compound semiconductor layer side.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Method and device for the removal of partially protein bound substances
ActiveUS20050115898A1Large clearanceHigh ratioLiquid separation auxillary apparatusOther blood circulation devicesDialysis fluidMembrane configuration
A method and a device to increase the efficiency of dialysis for the removal from blood of substances that are more or less tightly bound to carriers such as albumin. According to the invention this is accomplished by a simultaneous significant increase of the flow rate of the dialysis fluid and of the area of the membrane that separates the blood from the dialysis fluid, compared to conventional dialysis.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
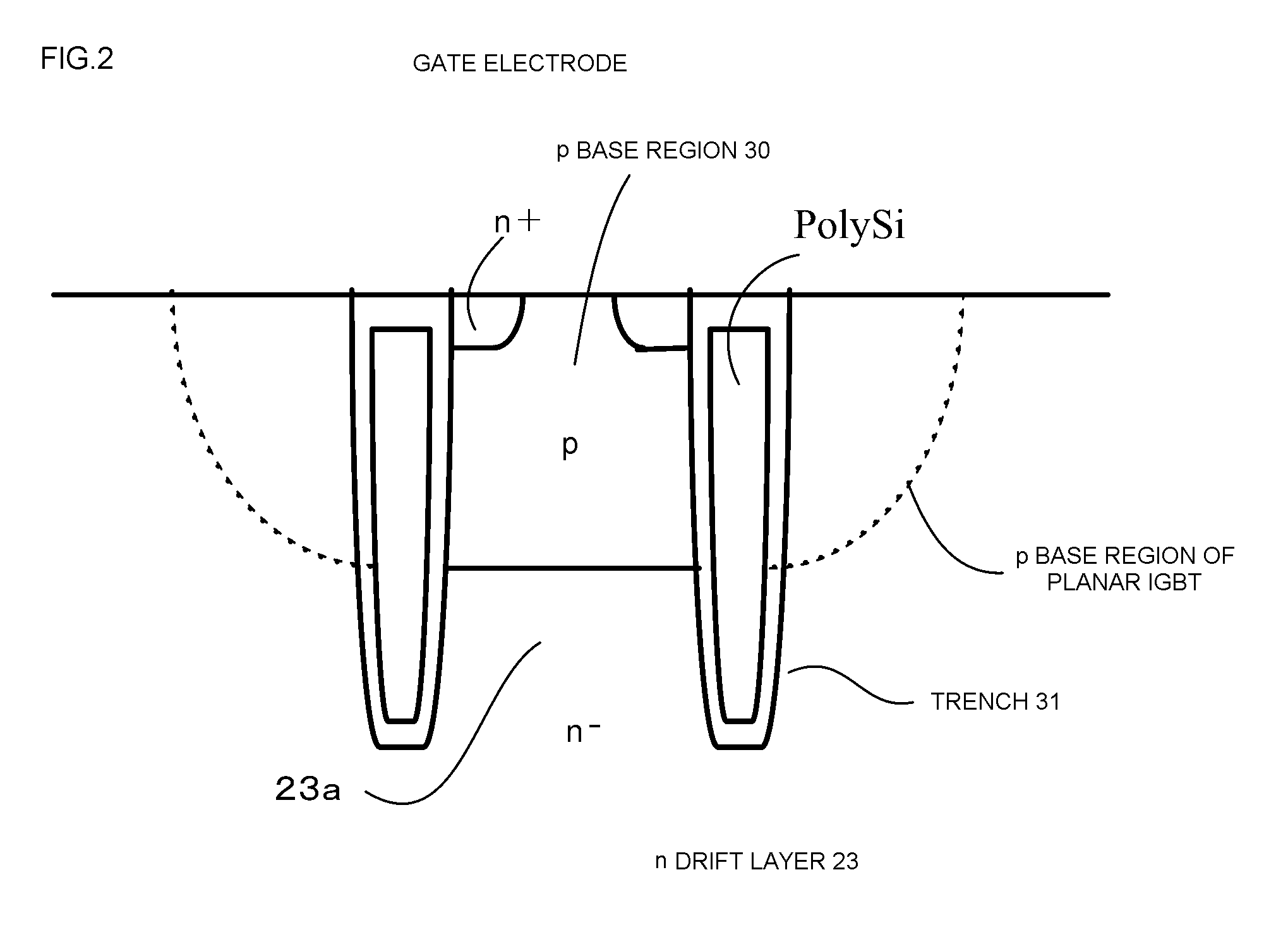
Reverse conducting IGBT
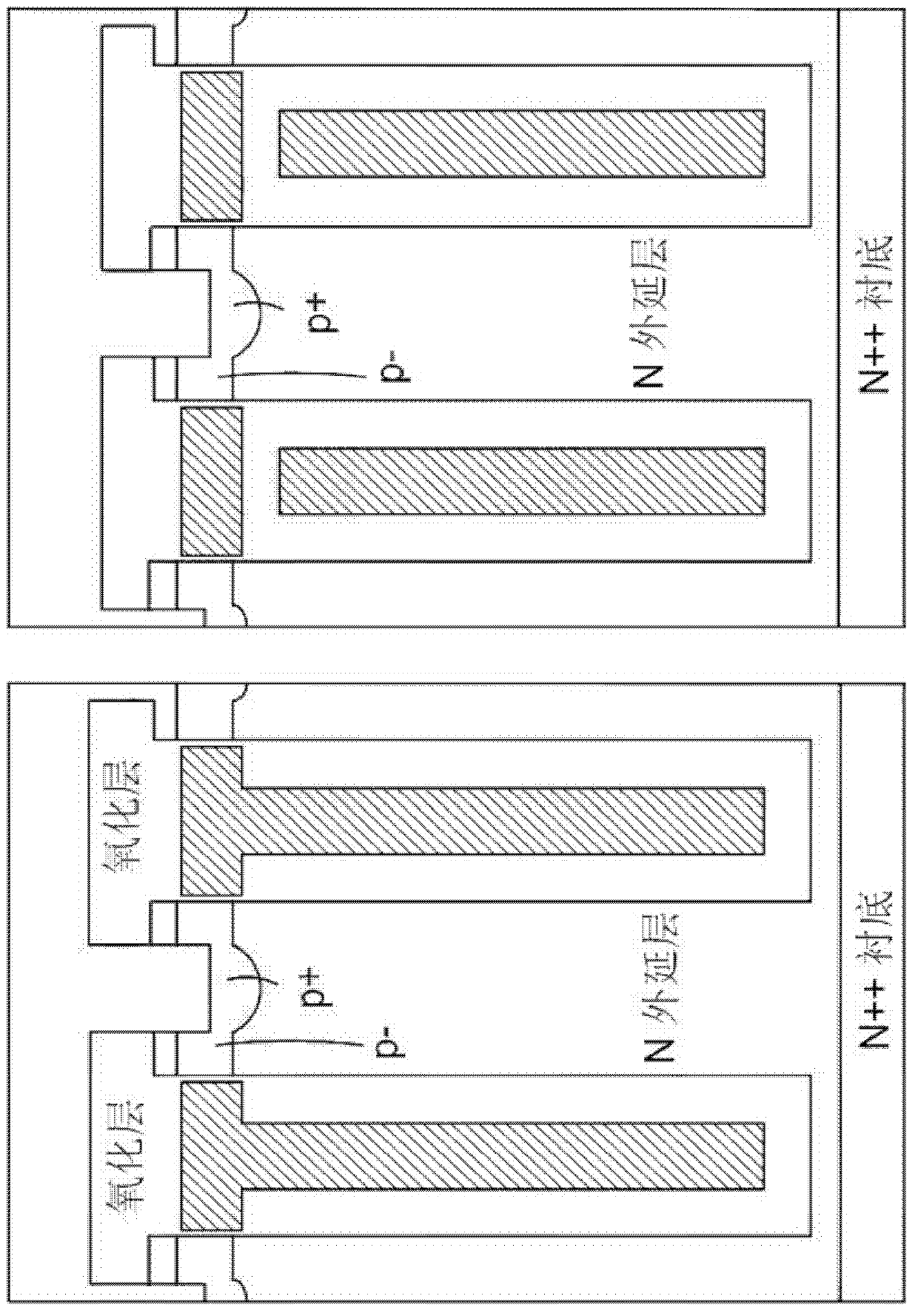
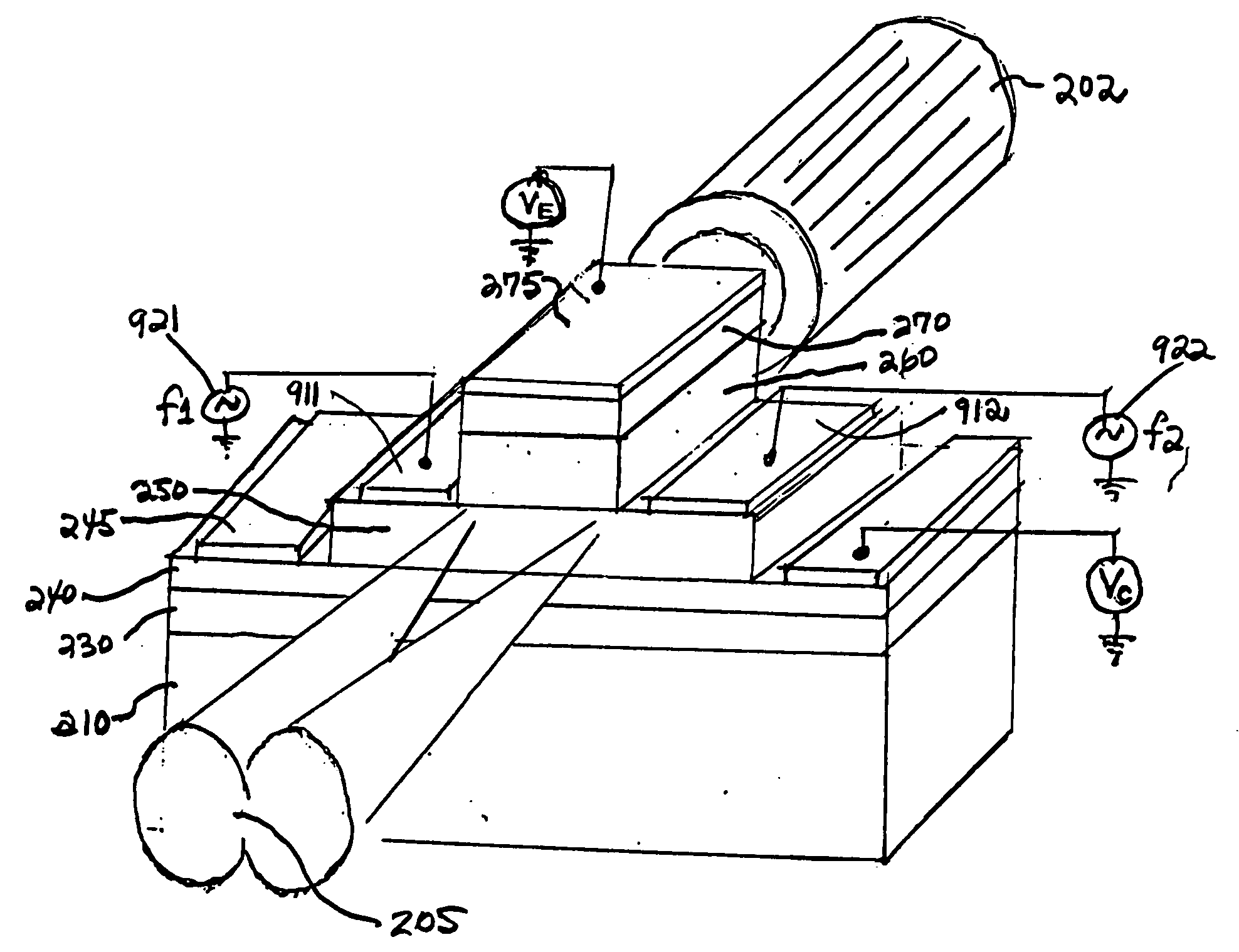
ActiveUS20160351561A1Increase the carrier concentrationReduce power lossTransistorSolid-state devicesTrench gateSemiconductor
A reverse conducting IGBT is provided with a trench gate member that is provided in an IGBT region and has a lattice-pattern layout, and a trench member that is provided in a diode region and has a stripe-pattern layout. The diode region of the semiconductor substrate includes an anode region of a first conductive type, a drift region of a second conductive type and a barrier region of the second conductive type. The barrier region is electrically connected to a top surface electrode via a pillar member that extends from a top surface of the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Mosfet and the method to make the same
ActiveCN103137698AImprove performanceLow balanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETEngineering
The invention discloses a MOSFET of a super-junction trench having a function of reducing surface electric-field stepped oxide and a split grid structure. The inventive structure can apply additional freedom for better optimization and manufacturing capability by tuning thick oxide thickness to minimize influence of charge imbalance, trapped charges, etc. . . . . Furthermore, the fabrication method can be implemented more reliably with lower cost.
Owner:FORCE MOS TECH CO LTD
Longitudinal power device for low-ratio on-resistance employing groove structure with high dielectric constant
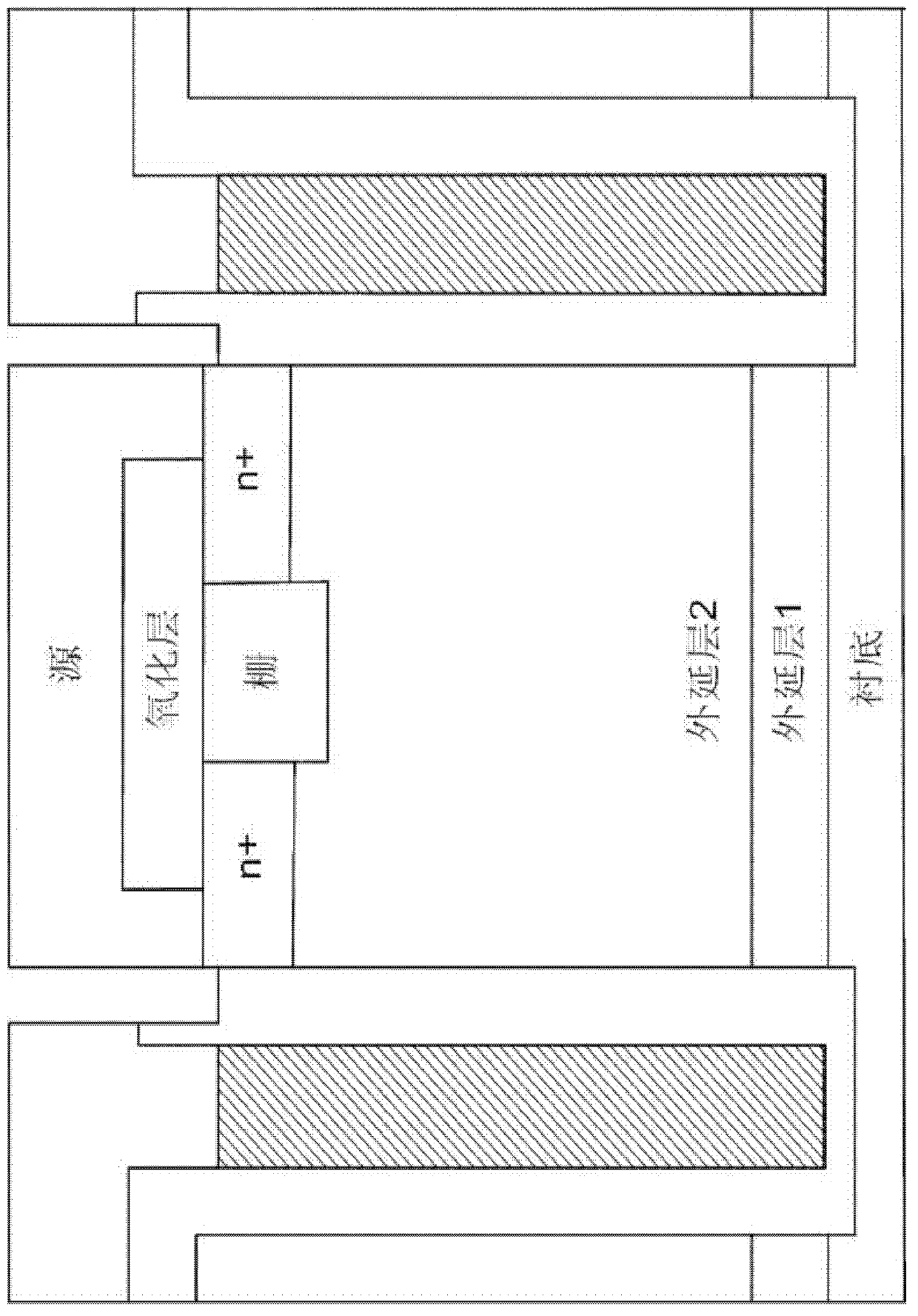
ActiveCN102779836ARealize super cumulative effectIncrease the carrier concentrationSemiconductor devicesThree levelDielectric
The invention discloses a longitudinal power device for low-ratio on-resistance employing a groove structure with a high dielectric constant and relates to semiconductor power devices. The longitudinal power device comprises a drift region, a silicon substrate, a gate, a channel region, an ohmic contact heavily-doped region, a source and an insulated gate medium. The longitudinal power device is characterized in that the drift region, the silicon substrate and the source form a first conductive type; the channel region and the ohmic contact heavily-doped region form a second conductive type; a material column with a high dielectric constant is arranged between the gate and the silicon substrate; the gate is directly contacted with the material column with the high dielectric constant; and the drift region surrounds the material column with the high dielectric constant. Compared with a longitudinal Super Junction power device, the low-ratio on-resistance for the high dielectric material power device has the advantage that the reduction in three levels of magnitude exists.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
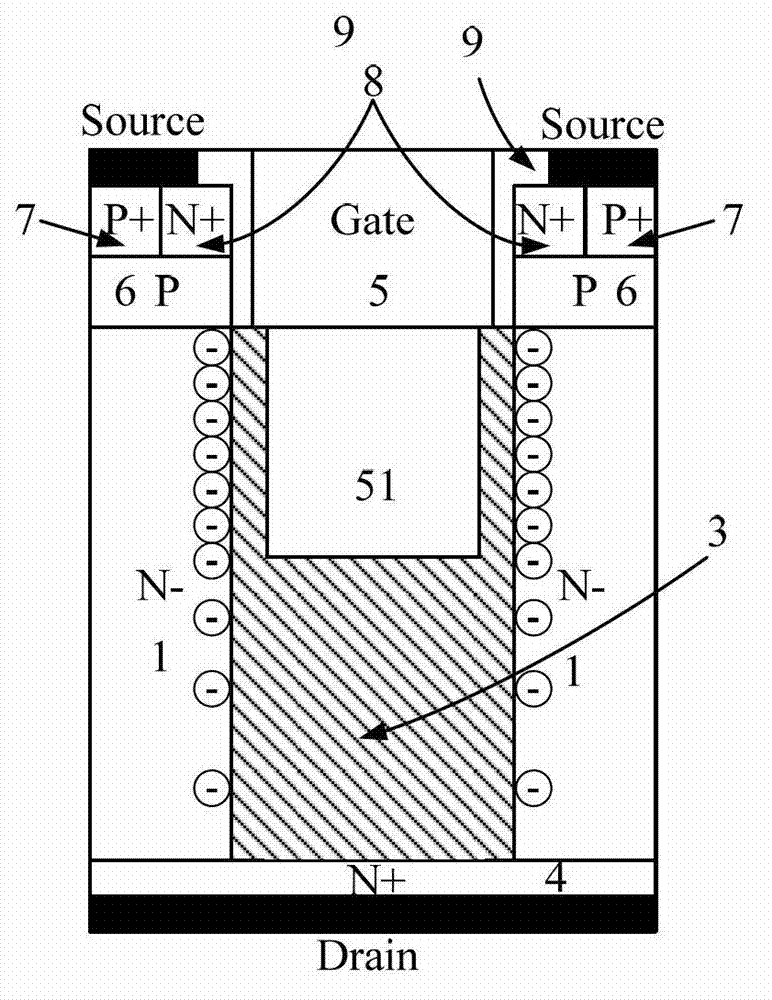
Nitride semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS8129748B2Large operating currentImprove switching characteristicsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceHigh resistance
A nitride semiconductor device includes: a first nitride semiconductor layer; a second nitride semiconductor layer formed on the first nitride semiconductor layer and having a wider band gap than the first nitride semiconductor layer; and a third nitride semiconductor layer formed on the second nitride semiconductor layer. A region of the third nitride semiconductor layer located below the gate electrode is formed with a control region having a p-type conductivity, and a region of the third nitride semiconductor layer located between the gate electrode and each of the source electrode and the drain electrode is formed with a high resistive region having a higher resistance than the that of the control region.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
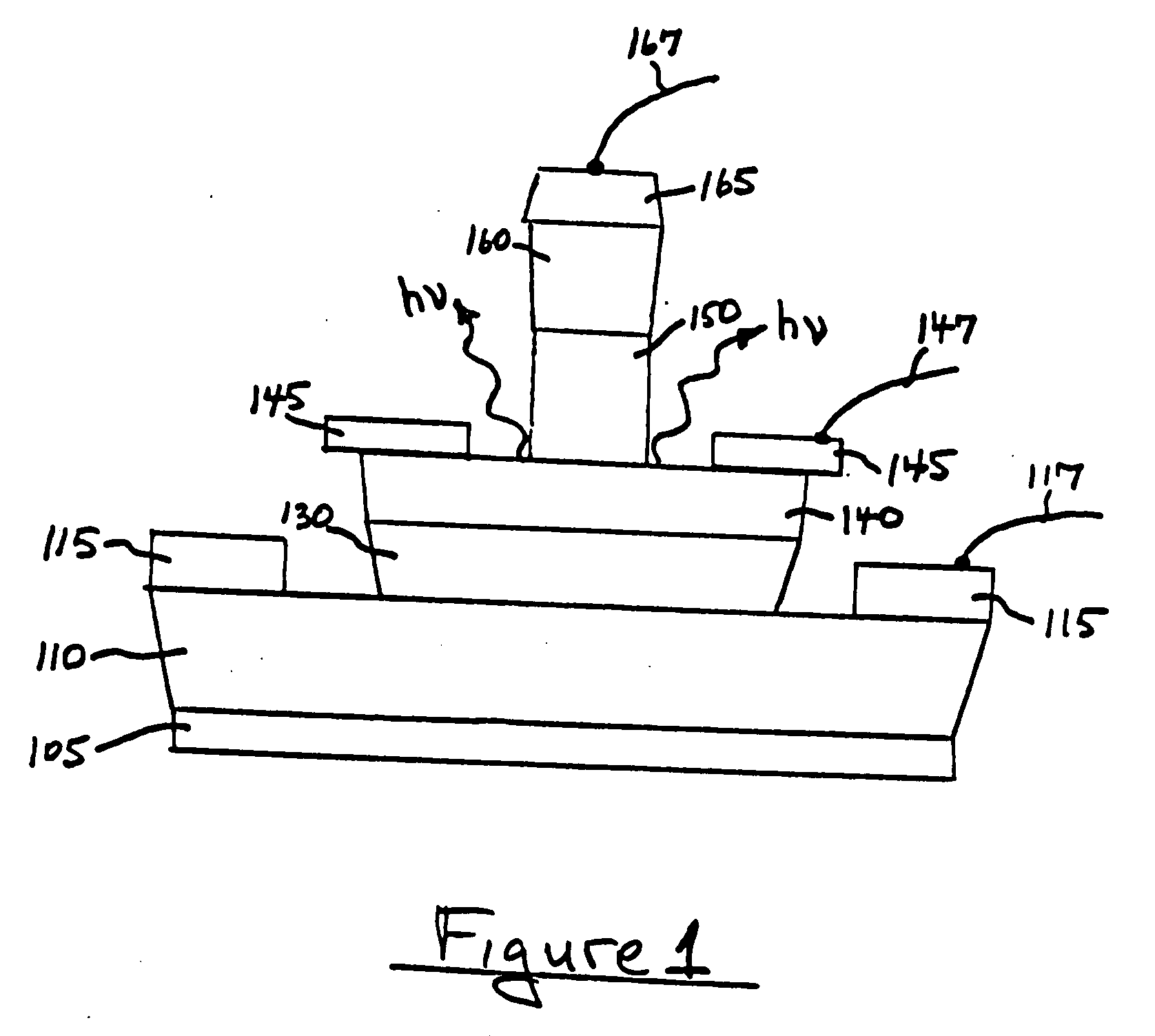
Method for increasing the speed of a light emitting biopolar transistor device
ActiveUS7998807B2Increase speedImprove mobilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStimulated emissionSpontaneous emission
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Semiconductor light emitting devices and methods
InactiveUS20060208290A1Increase speedImprove mobilityLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical communicationOptical coupling
A method for producing an optical output, including the following steps: providing first and second electrical signals; providing a bipolar light-emitting transistor device that includes collector, base, and emitter regions; providing a collector electrode coupled with the collector region and an emitter electrode coupled with the emitter region, and coupling electrical potentials with respect to the collector and emitter electrodes; providing an optical coupling in optical communication with the base region; providing first and second base electrodes coupled with the base region; and coupling the first and second electrical signals with the first and second base electrodes, respectively, to produce an optical output emitted from the base region and coupled into the optical coupling, the optical output being a function of the first and second electrical signals.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Method for forming shallow groove separation structure and shallow groove separation structure
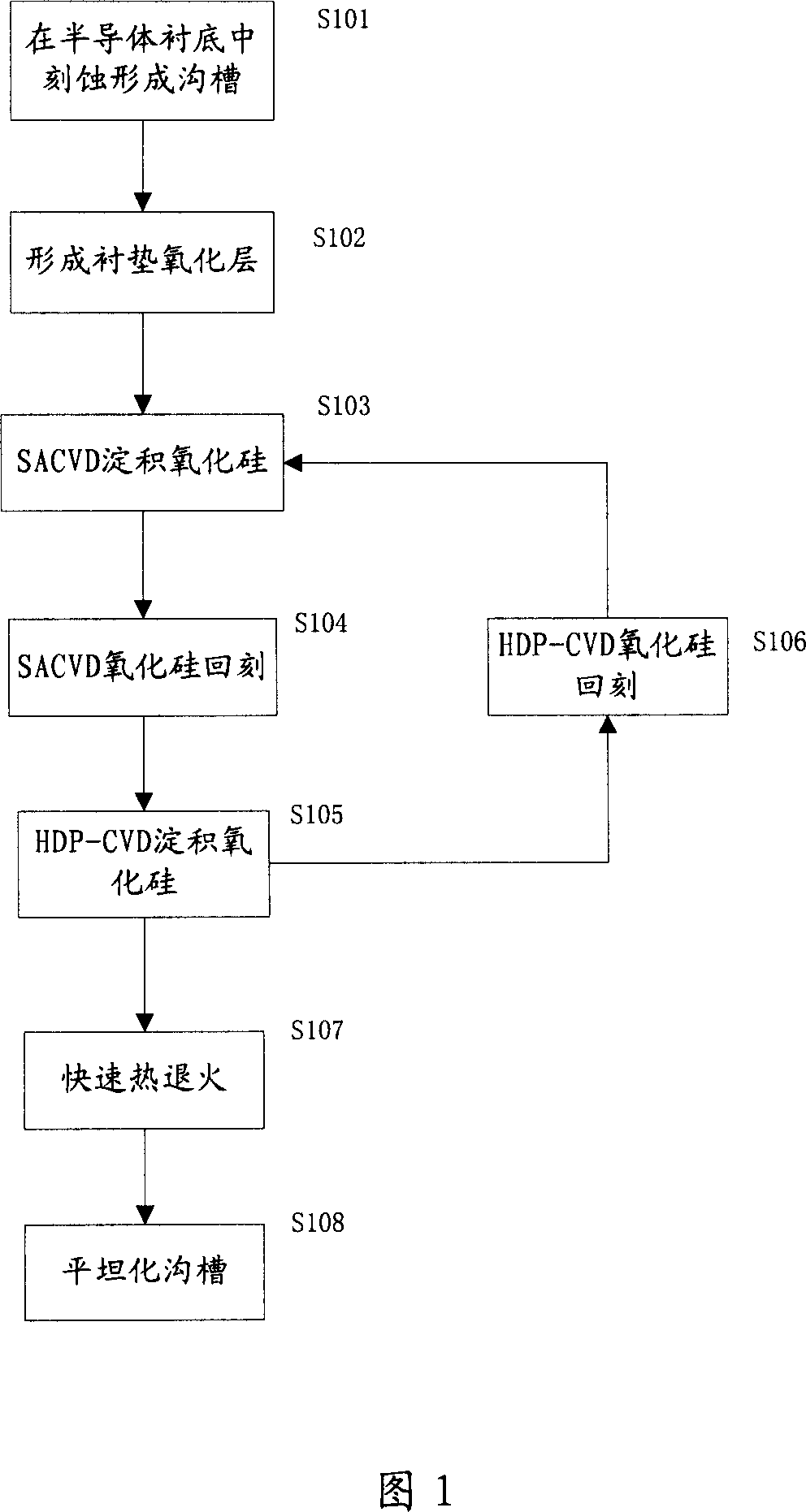
ActiveCN101123204AIncrease the carrier concentrationImprove mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRapid thermal annealingSemiconductor
A method for forming shallow groove isolation in semi-conductor device comprises that: a mask film layer is formed on the underlayer of the semi-conductor; the mask film layer is made into a design to expose the underlayer of semi-conductor opposite to the position of the groove; the underlayer is corroded to form a groove and a padding oxidizing layer in the groove; a first insulating medium and a second insulating medium are deposited in turn until the groove is filled fully; a quick flash annealing process is carried out onto the underlayer of the semi-conductor; the insulating mediums are made flat to form a shallow groove isolation structure. The shallow groove isolation structure of the invention comprises the underlayer of the semi-conductor and the grooved formed in the underlayer. The groove is filled with insulating mediums, comprising the first insulating medium and the second insulating medium. The first insulating medium and the second insulating medium are piled against each other, forming a stack structure. The invention effectively controls the stress of the shallow groove isolation structure, thus improving the properties of semi-conductor devices.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
Preparation method of (doped amorphous) p-type transparent conductive oxide films
InactiveCN103173732AThe principle is simpleLow deposition temperatureVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingCrystalline oxideDeposition temperature
The invention discloses a preparation method of films of (doped amorphous) p-type transparent conductive oxide films, and relates to the technical field of semiconductor films. The amorphous films having a higher hole carrier concentration and a higher mobility than crystallized oxide films are prepared through adopting a reaction magnetron sputtering process and controlling technological parameters. The preparation method has the advantages of simple principle, low deposition temperature, strong controllability of the technological parameters, low preparation cost, and huge scale production potential.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Surface treatment method of metal oxide and preparation method of thin film transistor
InactiveCN102651317AIncrease concentrationReduce contact resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOxide semiconductorOxygen vacancy
The invention provides a surface treatment method of metal oxide semiconductor and a preparation method of a thin film transistor, wherein the surface treatment method of the metal oxide comprises the following steps that: plasmas are utilized for carrying out surface treatment on a device to be treated; and the plasmas comprise mixed gas of F-base gas and O2, and the device to be treated is a metal oxide semiconductor product or a product plated with the metal oxide semiconductor. In the embodiment provided by the invention, the plasmas obtained by using the mixed gas of F base gas and O2 are used for treating the metal oxide for enhancing the oxygen vacancy concentration in the metal oxide, reducing the contact resistance between the metal oxide and other electrodes and improving the ohm contact effect of the metal oxide.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Realizing N-Face III-Nitride Semiconductors by Nitridation Treatment
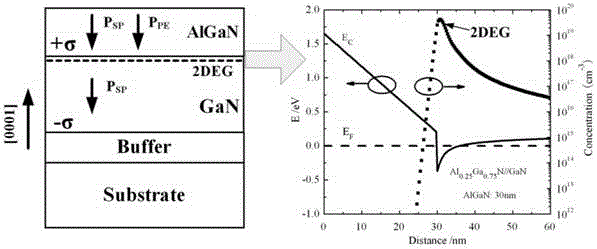
InactiveUS20100015787A1Increase the carrier concentrationReduce layeringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor structureNucleation
A method of forming a semiconductor structure includes providing a substrate; forming a buffer / nucleation layer over the substrate; forming a group-III nitride (III-nitride) layer over the buffer / nucleation layer; and subjecting the III-nitride layer to a nitridation. The step of forming the III-nitride layer comprises metal organic chemical vapor deposition.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method and device for the removal of partially protein bound substances
ActiveUS7615158B2Reduce concentrationEasy to fallLiquid separation auxillary apparatusOther blood circulation devicesDialysis fluidIntensive care medicine
A method and a device to increase the efficiency of dialysis for the removal from blood of substances that are more or less tightly bound to carriers such as albumin. According to the invention this is accomplished by a simultaneous significant increase of the flow rate of the dialysis fluid and of the area of the membrane that separates the blood from the dialysis fluid, compared to conventional dialysis.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Co-Ga co-blended ZnO based diluted semi-conductor thin-film and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101483219AMature technologyEasy to operateVacuum evaporation coatingGalvano-magnetic material selectionMagnetic semiconductorRoom temperature
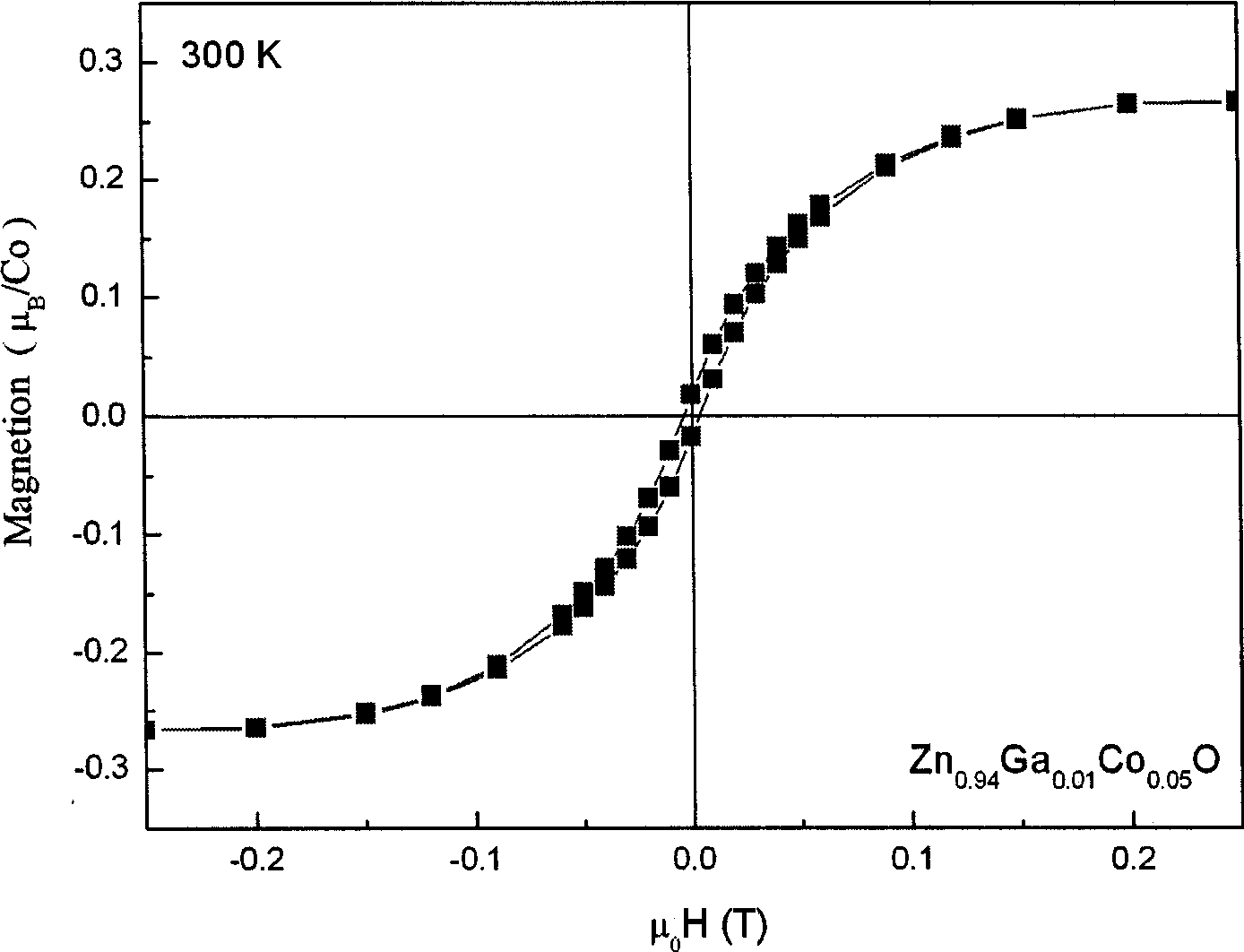
The invention discloses a Co-Ga codoped Zno base diluted magnetic semiconductor film, wherein a Co molar content is more or equal than 2and less or equal to 10, a Ga molar content is more or equal to 1and less or equal to 3 The diluted magnetic semiconductor film is prepared by a pulsed laser deposition method and a pure ZnO, Co2O3, a Ga2O3 powder mixed sintered ceramic chip is employed as a target material. A substrate is placed in a growth chamber of a pulsed laser deposition device after cleaning the substrate, and the growth chamber is vacuumized to a background vacuum less than 8.0 *10 Pa. The mixture is grown under an O2 atmosphere with a pressure of 2-15Pa and a temperature of 350-700 DEG C. The preparation method of the invention is simple, an n type doping carrier concentration can reach 5.0*10-5.0*10 cm and simultaneously have a room temperature iron magnetic property.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
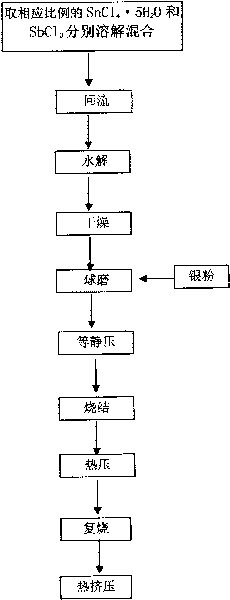
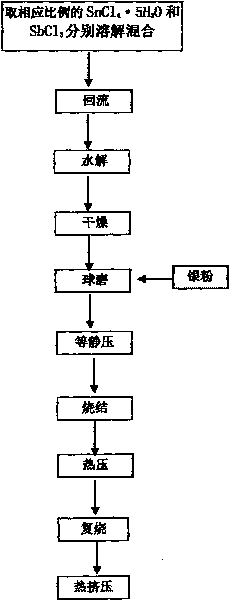
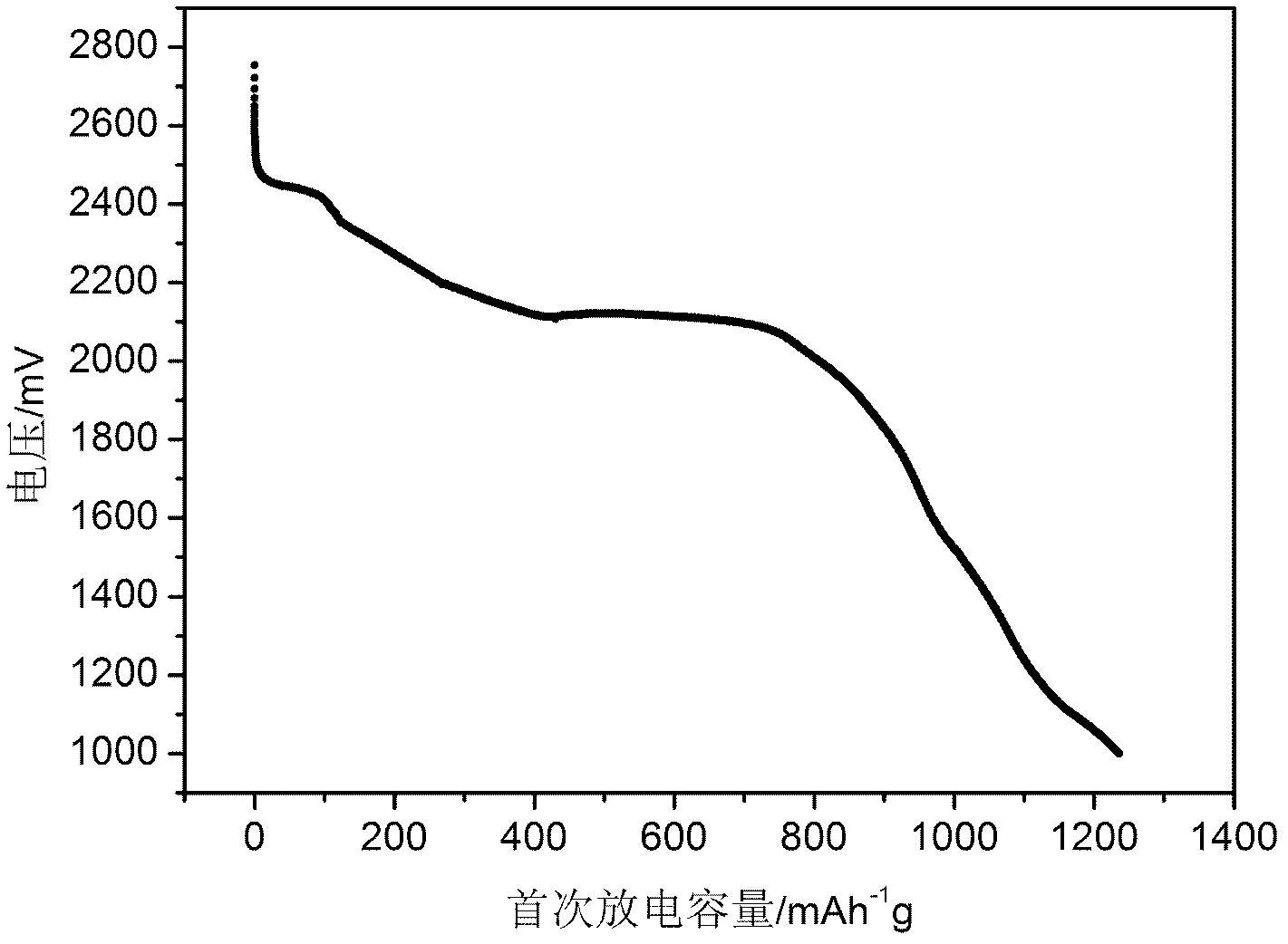
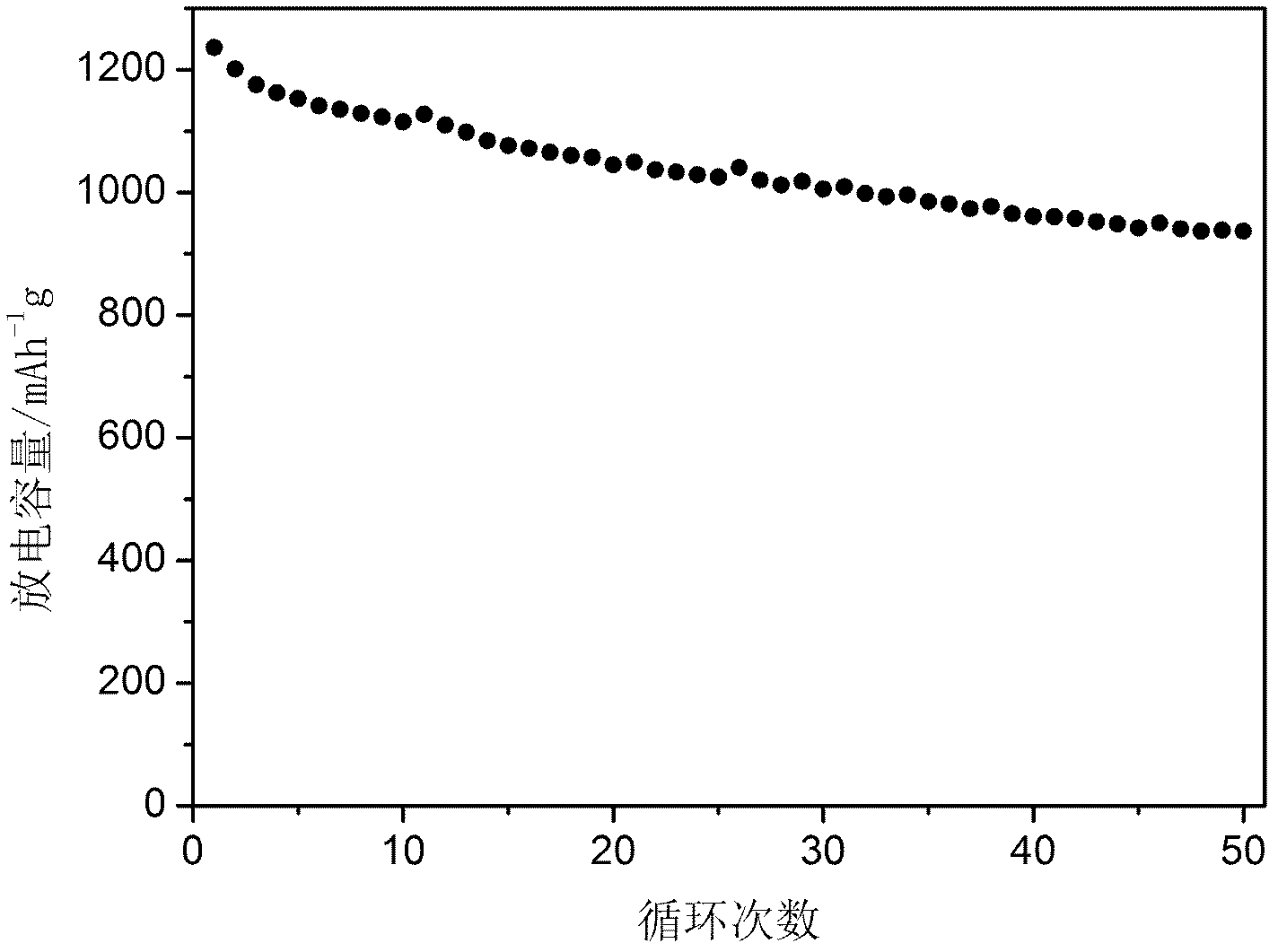
Method for preparing Ag-SnO2-doped electrical contact material
ActiveCN101707157AEvenly dispersedImprove organizational structureElectric switchesElectrical resistance and conductanceContact resistance
The invention discloses a method for preparing an Ag-SnO2-doped electrical contact material, comprising the following steps: obtaining modified SnO2 particles by adopting a sol-gel method, improving the electrical conductivity of the SnO2 particles, and then preparing a dispersed composite material with compact distribution from modified SnO2 used as raw material and Ag powder by the process flow of ball milling, pressing, sintering, hot extrusion and the like. Since the electrical conductivity of the SnO2 particles is improved, the problem that contact resistance and overhigh temperature rise of the material in the use process can be solved, thereby widening the use range of the Ag-SnO2 material and improving the electrical contact performance of the material.
Owner:WENZHOU HONGFENG ELECTRICAL ALLOY
All-solid-state polymer electrolyte used for lithium-sulfur secondary battery and its preparation method
InactiveCN102496736ALow costShort production processSecondary cellsCell component detailsPolymer electrolytesAll solid state
Belonging to the technical field of lithium-sulfur secondary battery preparation, the invention relates to an all-solid-state polymer electrolyte used for a lithium-sulfur secondary battery and its preparation method. Directed at the current situation that a metal lithium negative electrode is likely to generate a dendrite which can break a diaphragm so as to cause a short circuit when the liquid electrolyte or gel polymer electrolyte of a lithium-sulfur secondary battery matches with metal lithium, the invention provides an all-solid-state polymer electrolyte used for a lithium-sulfur secondary battery. The electrolyte comprises PEO (polyethylene oxide), a Li4Ti5O12 particle and a lithium salt, which can be LiClO4, LiPF6, LiBF4, LiCF3SO3 or LiTFSI. At a temperature of 30DEG C, the electrolyte has electric conductivity greater than 10<-4>S / cm, which is far higher than the electric conductivity of 10<-6>-10<-7>S / cm of PEO / a lithium salt at a temperature of 30DEG C. In a lithium-sulfur secondary battery, the electrolyte can serve both as an electrolyte and a diaphragm, and the double functions can substantially enhance the utilization rate and circulation stability of a positive active material.
Owner:RUISHENG NEW ENERGY DEV CHANGZHOU
Method for preparing transparent conducting film made from multi-element oxides with antimony being doped into
InactiveCN1600895AImprove stabilityImprove electrical stabilityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingIndiumSesquioxide
This invention relates to antimony-doped multi-elements oxide transparent conductive membrane. On the Zn-Sn-O membrance, antimony doping is proceeded, by using radio-frequency magnetic-control technique, under vacuum condition, to produce Zn-Sn-O:Sb transparent conductive membrane having multi-crystal structure. The ceramic target for sputtering use is composed of zinc oxide stannic oxide, antimony sesquioxide, the prepn. conditions are: argon pressure=0.5-5 Pa, oxygen pressure=0-6 mPa, sputtering power=50-200w, temp.=150-450 deg.C. This inventive complex transparent conductive membrane material has the property of stability in hydrogen plasma like ZnO, and has high electrical stability like SnO2. It has advantages of: no toxicity, broad application field, being substituted for ITO membrane, saving noble metal indium.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
P-type conductive zinc oxide film material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102386246AIncrease the doping concentrationIncrease the carrier concentrationFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFilm materialInstability
The invention discloses a p-type conductive zinc oxide film material, which comprises a substrate and an epitaxial layer growing on the substrate, wherein a metal magnesium layer, a magnesium oxide layer, a first zinc oxide layer and a second zinc oxide layer are arranged in sequence between the substrate and the epitaxial layer; the growth temperatures of the first and the second zinc oxide layers are gradually increased; and the epitaxial layer is a p-type AZnO:B layer formed by a zinc oxide alloy doped with acceptor element B and A atoms. The p-type conductive zinc oxide film material and the preparation method thereof have the advantages that the stable hole conduction with high-carrier concentration is achieved by introducing A atoms into ZnO to form AZnO alloy and then doping acceptor element B in the alloy. In the invention, the Zn atoms are replaced by the introduced A atoms, and after the A atoms bond with the acceptor atoms B, since the energy of A-B bonds is very strong as compared with that of the Zn-B bonds, the A atoms can effectively trap the acceptor B atoms to prevent instability due to the Zn-B bond rupture during the process of directly doping the acceptor B atoms in ZnO. Besides, the introduction of A atoms increases the doping concentration of acceptor B atoms, so as to ensure high-concentration and stable hole conduction.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
MOS type semiconductor device
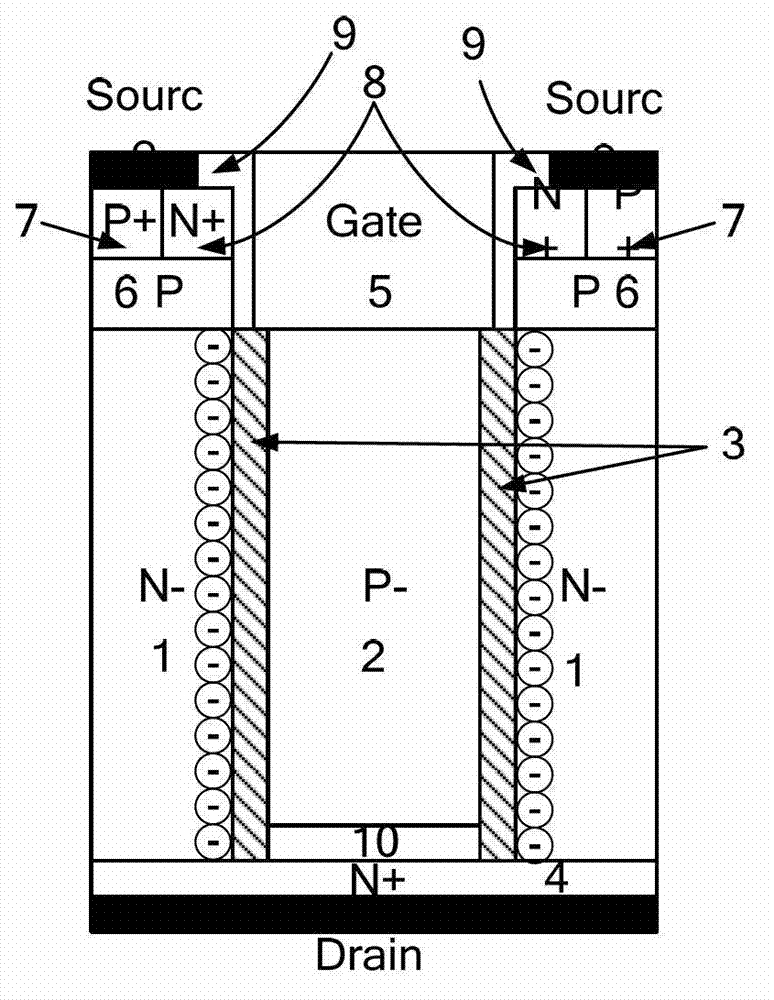
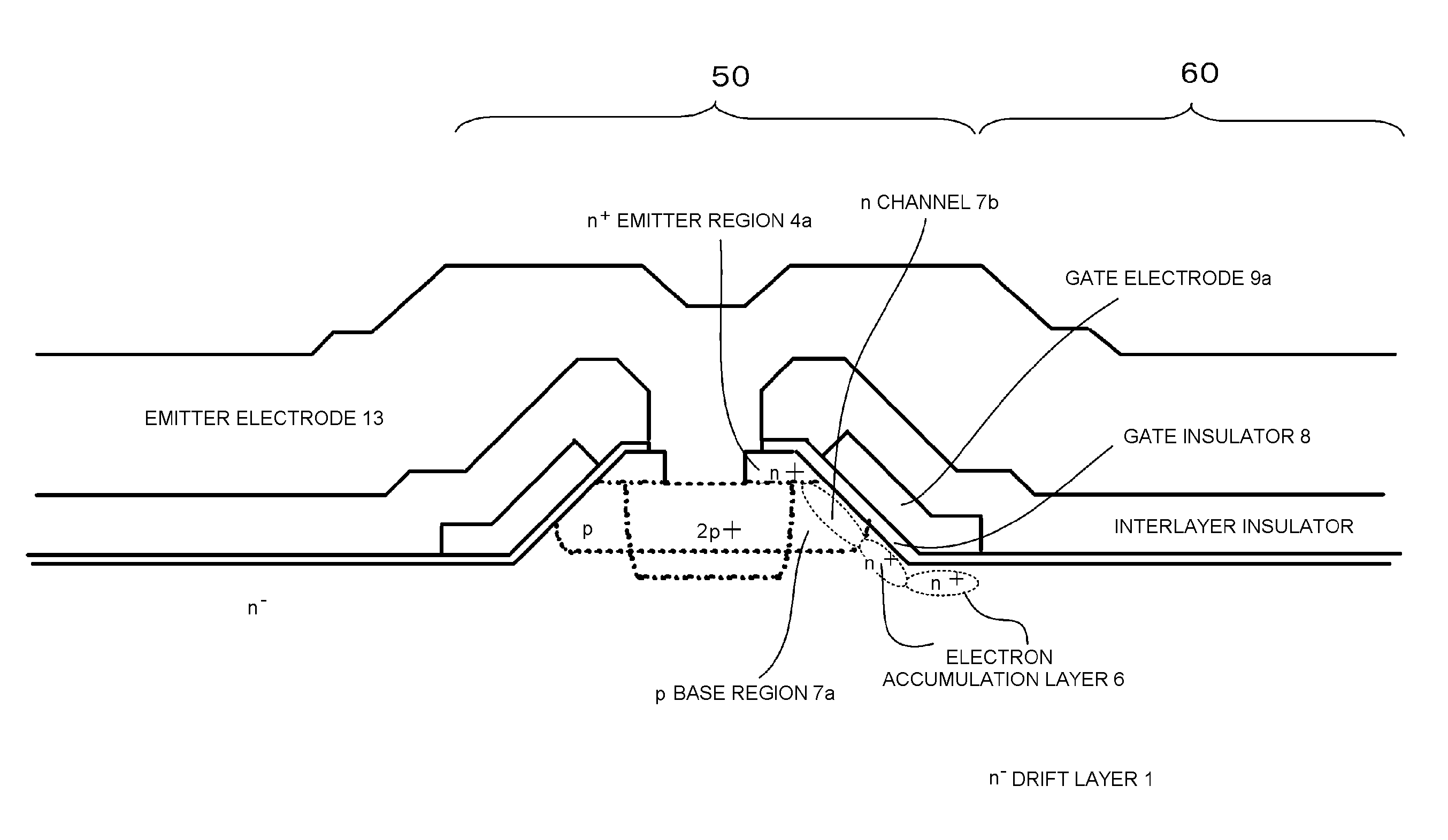
InactiveUS20140061719A1Reduce radiated noiseSuppress DiffuseSemiconductor devicesEngineeringTurn on time
A MOS type semiconductor device wherein on voltage is low, the rate of rise of current at turn-on time is low, and it is possible to hold down the rate of rise of collector current at turn-on time, and reduce radiation noise. The device includes a stripe-shaped plan-view pattern of protruding semiconductor region on an n-type substrate and having a p-type region sandwiched between an upper side n-type first region and a lower side n-type second region, a top flat portion including a depression region with a depth reaching the p-type region, and an inclined portion between the top flat portion and a bottom flat portion around the protruding semiconductor region; and a gate electrode with one end portion of the gate electrode on a surface within the inclined portion, and another end portion on a surface of the lower side n-type second region in the p-type region side vicinity.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Organic electroluminescent display device, method for manufacturing the same and display apparatus
ActiveUS20160013415A1Shorten production timeSimple processTransistorSolid-state devicesElectricitySemiconductor materials
Disclosed is an organic electroluminescent display device, a method for manufacturing the same and a display apparatus. The organic electroluminescent display device comprises: a substrate; a thin film transistor disposed on the substrate and including a gate electrode and an active layer insulated with each other, and a source electrode and a drain electrode connected with the active layer; and an organic electroluminescent structure disposed on the substrate and including an anode, a luminescent layer and a cathode stacked sequentially, the anode and the drain electrode being electrically connected with each other. The anode and the active layer are disposed in the same layer. The active layer is made of a transparent oxide semiconductor material. The anode is made of the transparent oxide semiconductor material undergone a plasma treatment. When producing the OLED device, the active layer and the anode may be simultaneously produced only by changing the pattern of the corresponding mask without additional patterning processes for producing the anodes, thereby simplifying process steps and saving production costs.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Schottky diode and manufacturing method thereof
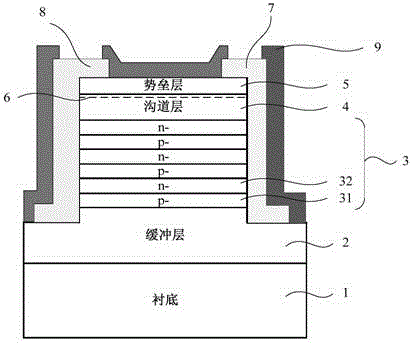
ActiveCN104617160AIncrease concentrationImprove mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower flowOhmic contact
The invention discloses a Schottky diode and a manufacturing method thereof. The Schottky diode comprises a substrate, a buffer layer, an extension structure, a Schottky contact metal and an Ohmic contact metal, wherein the substrate the buffer layer and the extension structure are sequentially arranged in an overlapped structure; the extension structure comprises a super bonding layer, a GaN channel layer and a barrier layer which are sequentially stacked, and the super bonding layer is composed of a plurality of p-type GaN layer and a plurality of n-type GaN layer which are alternately stacked each other; the Schottky contact metal and the Ohmic contact metal are symmetrically arranged on the opposite two side surfaces of the extension structure, one ends of the Schottky contact metal and the Ohmic contact metal extend to the upper surface of the extension structure, and the other ends of the Schottky contact metal and the Ohmic contact metal extend to the buffer layer. The Schottky diode has relatively high pressure resistance, ensures current transmission capacity and stability and avoids a traditional field plate structure or protecting ring structure, thereby simplifying the manufacturing process and reducing the cost.
Owner:FIFTH ELECTRONICS RES INST OF MINIST OF IND & INFORMATION TECH
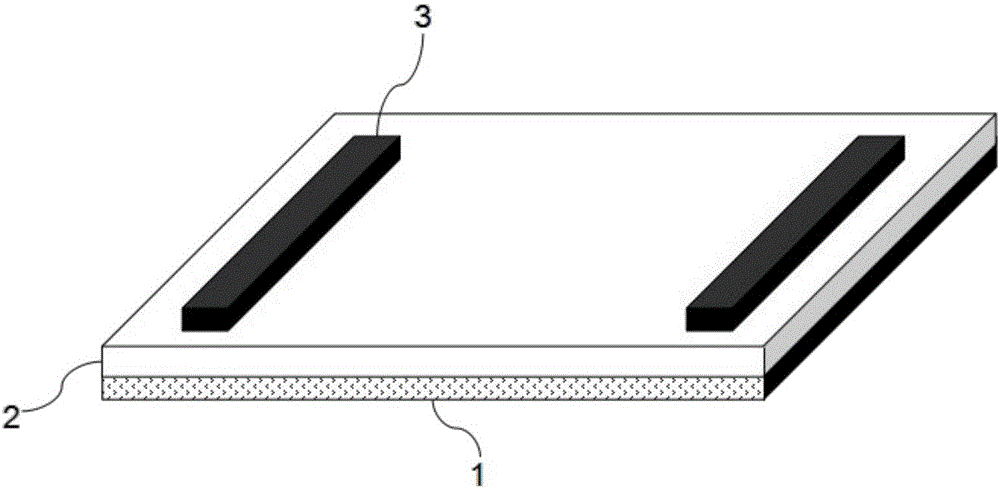
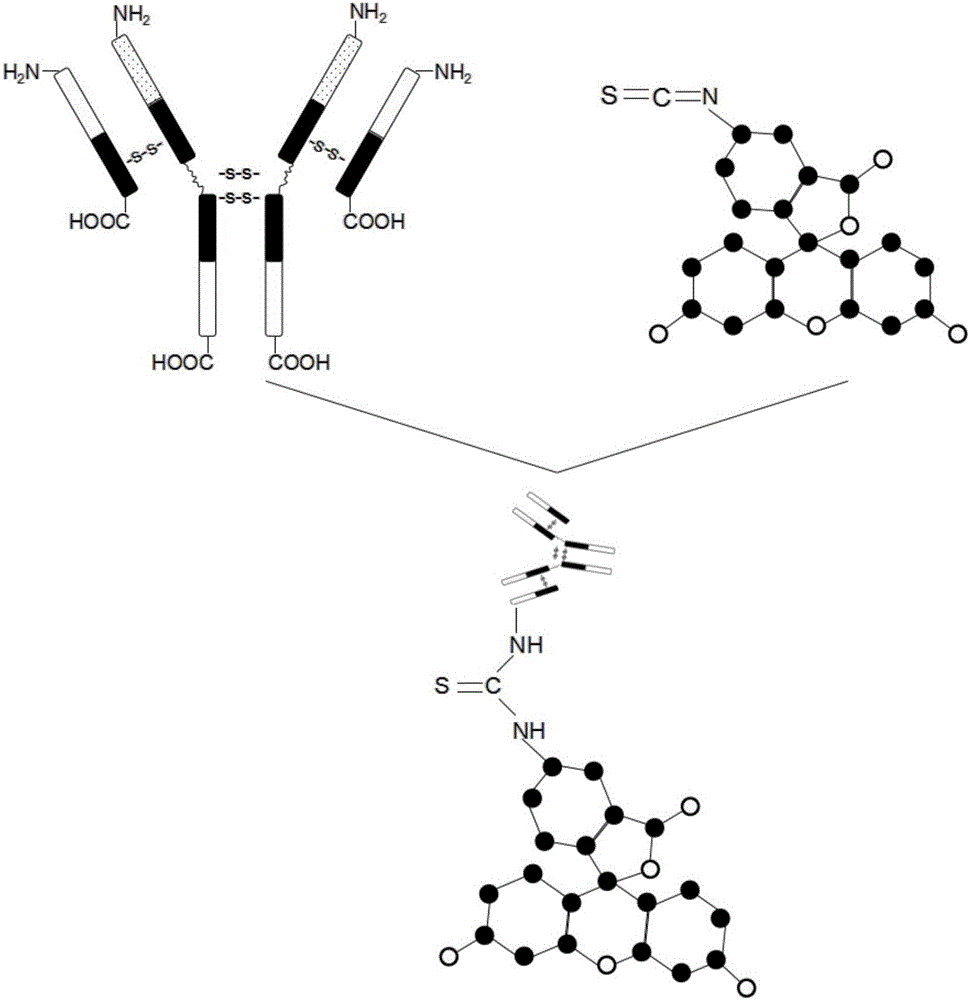
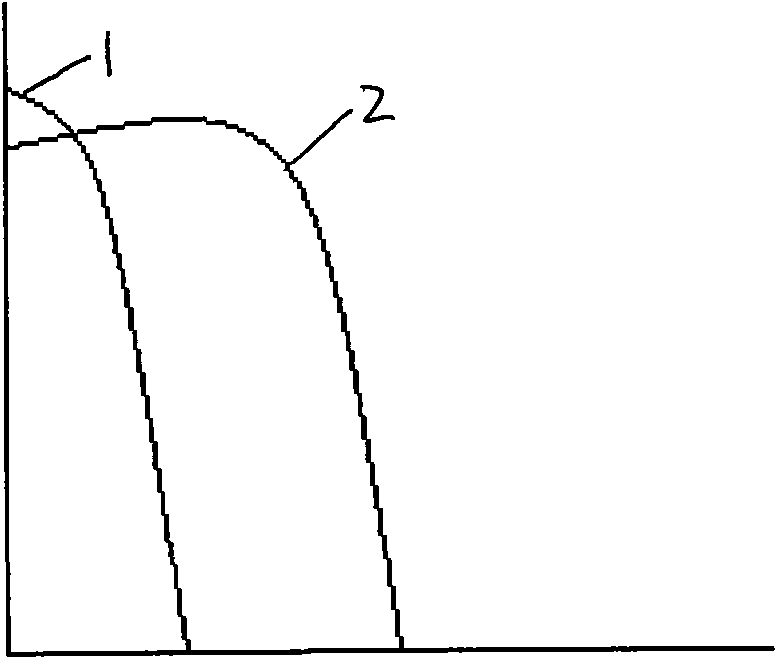
Method for detecting protein based on graphene sensor
ActiveCN105044072AIncrease the carrier concentrationLow resistivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceUltraviolet lights
The invention discloses a method for detecting protein based on graphene sensor. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a graphene sensor, namely arranging a graphene thin film on a substrate, and arranging electrodes at the two ends of the graphene thin film; (2) pretreating a sample to be detected, namely adding fluorescent dyes which are used for labeling protein in the sample into the sample to be detected, thus obtaining a fluorescent dye-protein compound; and (3) detecting the content of protein in the sample, namely dropwise adding pretreated sample to be detected to the surface of the graphene thin film, and quenching fluorescence under the irradiation of ultraviolet light, wherein the graphene thin film resistance is changed, the variable quantity of the resistance is in direct proportion to the content of the fluorescent dye-protein compound, so that the content of protein in the sample is detected. According to the method, the protein can be detected with high sensitivity and high precision, and compared with the conventional fluorescence excitation detection method, the method has the advantages of simplicity and rapid measurement speed.
Owner:厦门烯成石墨烯科技有限公司
Diffusion method used for crystalline silicon solar battery
InactiveCN102157606AHigh gettering capacityIncrease short circuit currentFinal product manufactureDiffusion/dopingDiffusion methodsSurface concentration
The invention discloses a diffusion method used for a crystalline silicon solar battery. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) placing a silicon wafer into a diffusion furnace; rising the temperature from 780-810 DEG C to 840-860 DEG C; and simultaneously introducing POCL3+O2+N2 for 12 to 14 minutes; (2) simultaneously introducing O2+N2 when rising the temperature in the diffusion furnace to 840-860 DEG C and keeping the constant temperature for 2 to 5 minutes; simultaneously introducing the POCL3+O2+N2 for 8 to 12 minutes when rising the temperature from 840-860 DEG C to 870-890 DEG C; reducing the temperature from 870-890 DEG C to 800 DEG C; introducing the O2+N2 in the process of reducing the temperature; stabilizing for 2 minutes at the temperature of 800 DEG C; and introducing the POCL3+O2+N2; and (3) taking the silicon wafer out of the diffusion furnace. In the method, both the requirements on the doping concentration of an emitting region and the surface concentration of the emitting region in diffusion can be met at the same time; a gettering effect is good; and the distribution of a doping curve is more reasonable.
Owner:BAODING GUANGWEI GREEN ENERGY TECH CO LTD
N-type antimony trimagnesium alloy thermoelectric material with high mobility and preparation method thereof
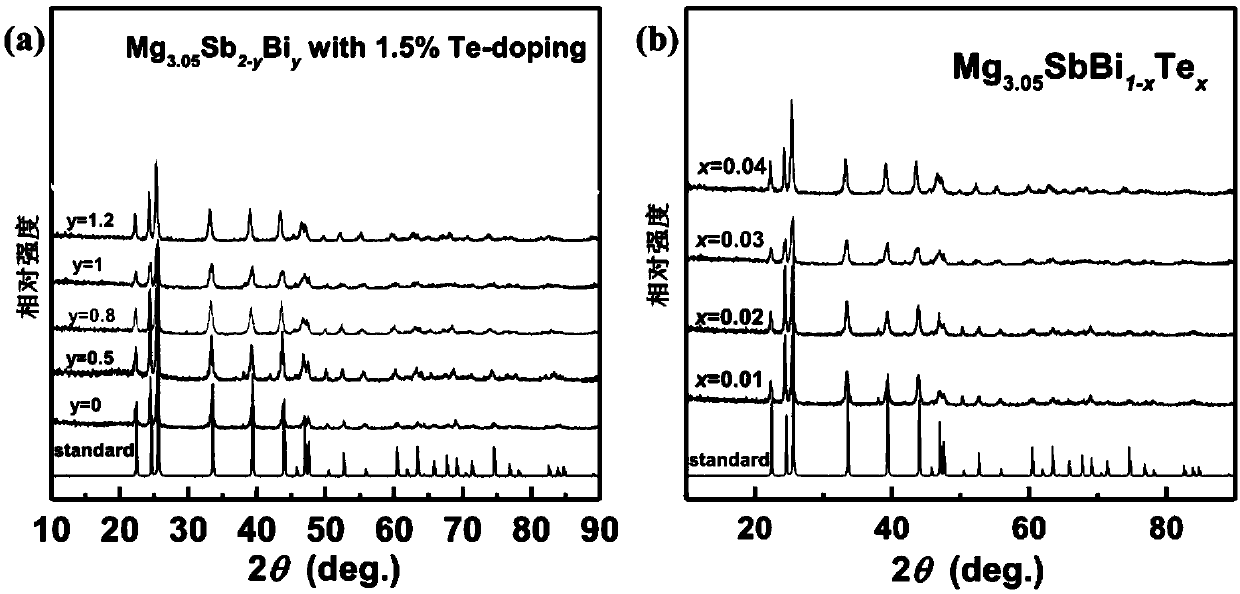
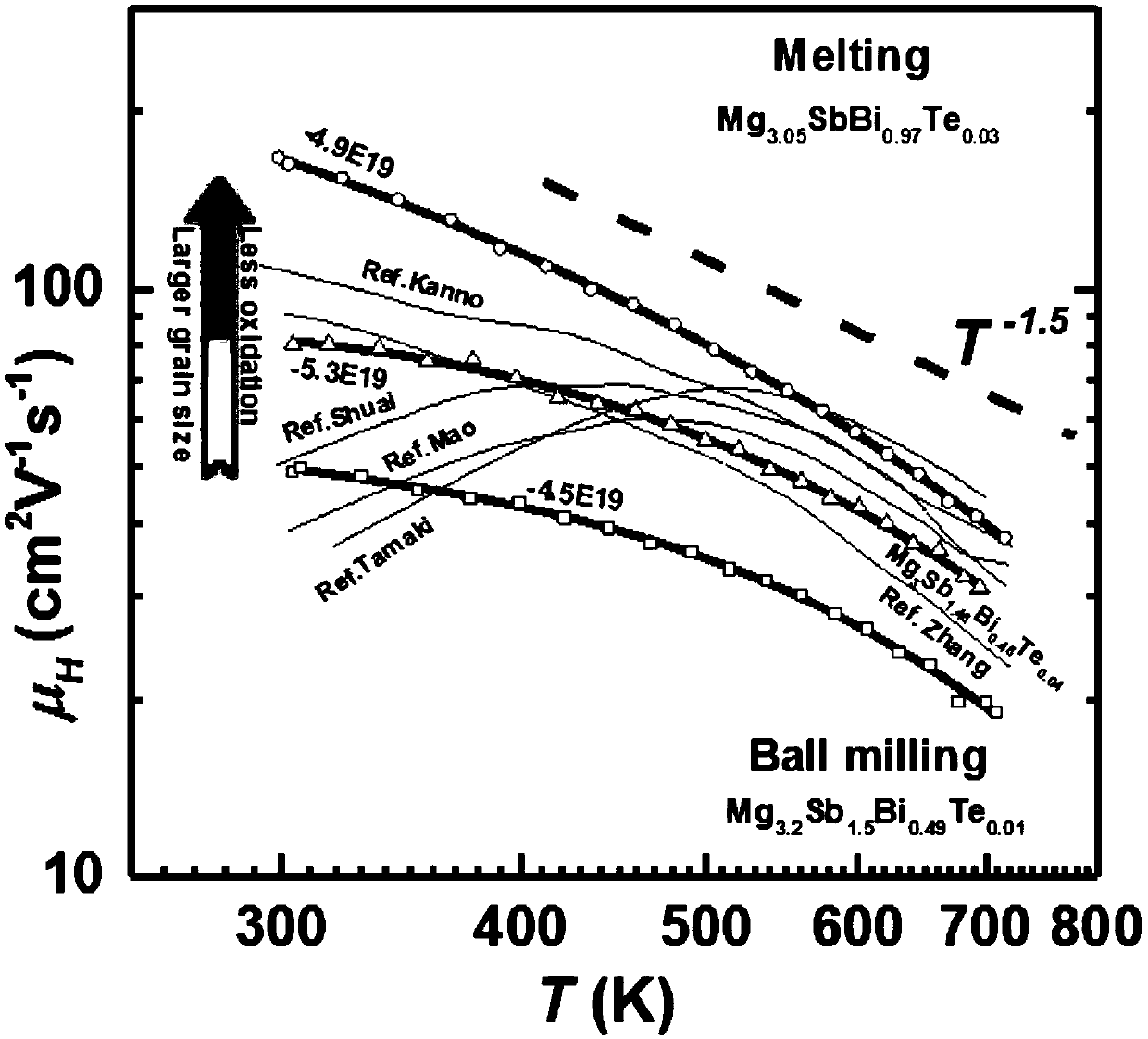
ActiveCN109616568AIncrease the carrier concentrationImprove mobilityThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsTe elementSlow cooling
The invention relates to an N-type antimony trimagnesium alloy thermoelectric material with high mobility and a preparation method thereof. The chemical formula of the thermoelectric material is Mg<3.05>Sb<2-x-y>Bi<y-x>Te<x>, wherein x is more than 0 but less than or equal to 0.04, and y is more than 0 but less than or equal to 1.5. The thermoelectric material takes a high-pure element as a raw material, material is prepared according to a stiochiometric ratio in the chemical formula, the raw material is grinded to form powder after vacuum package by a tantalum pipe, high-temperature melting and annealing thermal treatment, and the thermoelectric material is obtained after vacuum hot-press sintering and slow cooling. Compared with the prior art, the tellurium doping is improved by solid solution of antimony trimagnesium, negative ion electrons are introduced, and simultaneous control of carrier concentration and lattice thermal conductivity is achieved; and meanwhile, the content of magnesium oxide in an N-type Mg3Sb2 alloy crystal boundary is reduced by tantalum package melting, so that higher mobility than that of traditional document is shown. The simple and controllable technology can be widely applied to various thermoelectric materials, particularly materials with a large amount of intrinsic defects, and a new method is provided for improving the thermoelectric performance.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Rare earth doping Mg2Si based thermoelectric material
InactiveCN101197420AExcellent thermoelectric performanceImprove thermoelectric performanceThermoelectric device junction materialsThermoelectric materialsRare-earth element
The invention discloses a rare earth doping Mg2Si based thermoelectric material. The invention utilizes rare earth doping to improve thermoelectric properties of the material. Rare earth is directly added during melting, then the melted material is hot pressed after mechanical milling, and thermoelectric material blocks Mg2-xSiREx are obtained, in which RE represents rare earth element, and x equals to 0.002 to 0.01. The invention, the rare earth doping Mg2Si based thermoelectric material, has better thermoelectric properties than non-doping Mg2Si2 thermoelectric material; the doped rare earth elements comprises heavy rare earth and light rare earth; the mechanism is that rare earth elements have similar properties as alkaline earth metal; Mg is easily substituted after rare earth elements are added as donor doping, which increases carrier concentration and thus improves thermoelectric properties of the material.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com