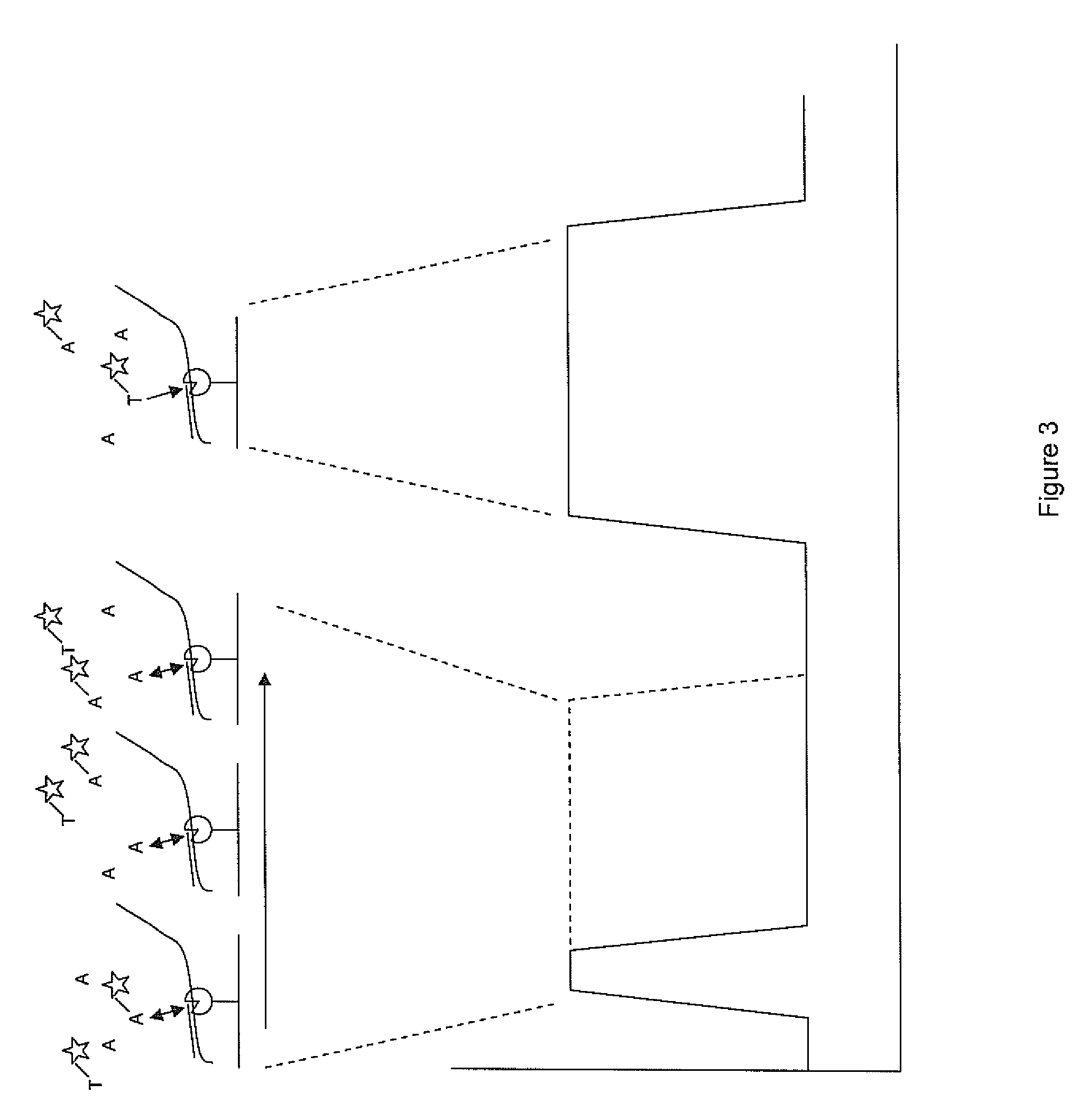
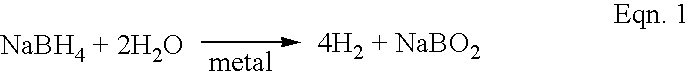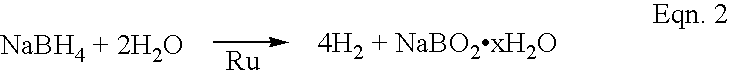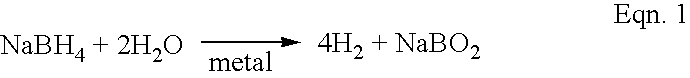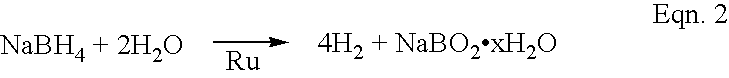Patents
Literature
46results about How to "Rate of reaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
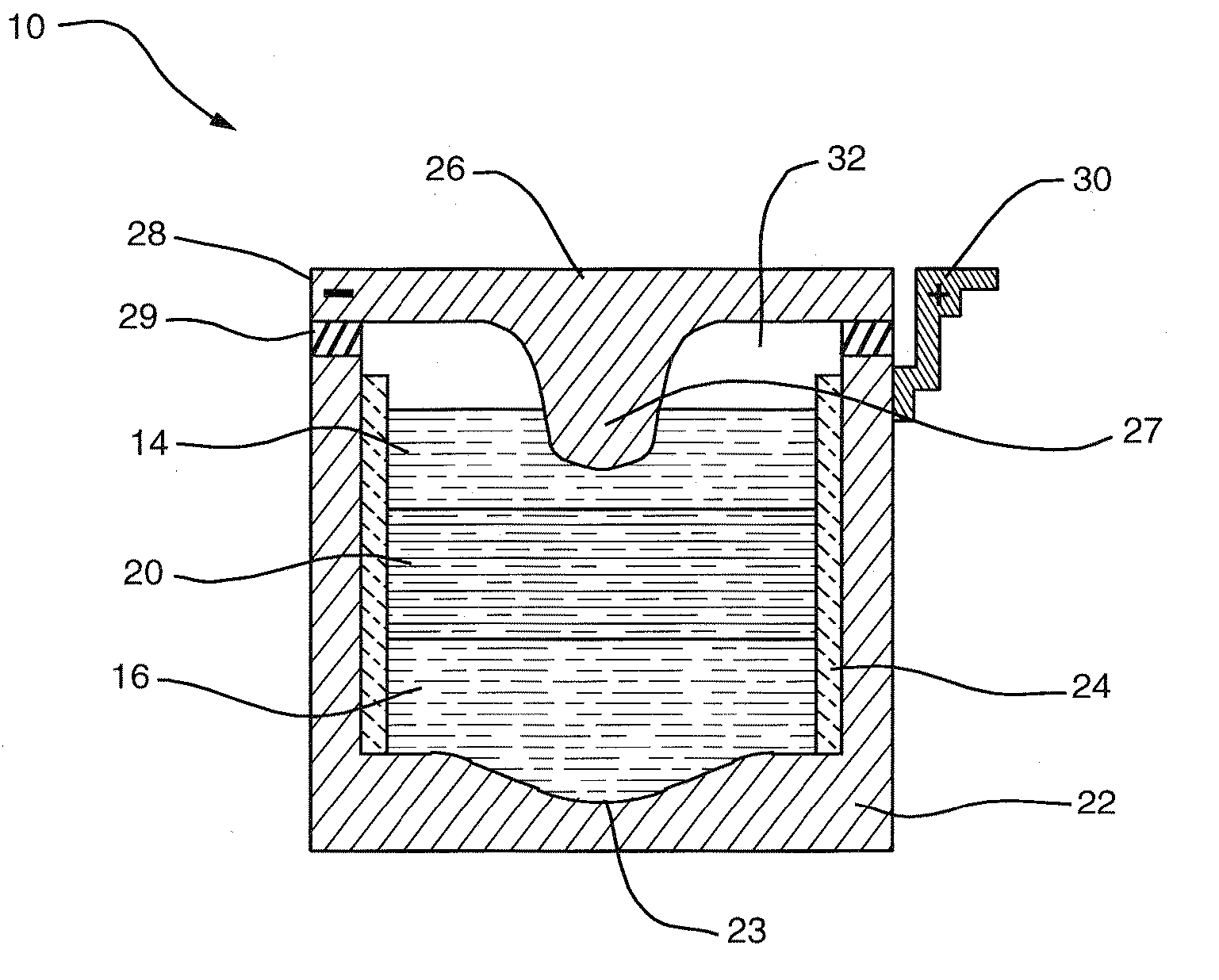
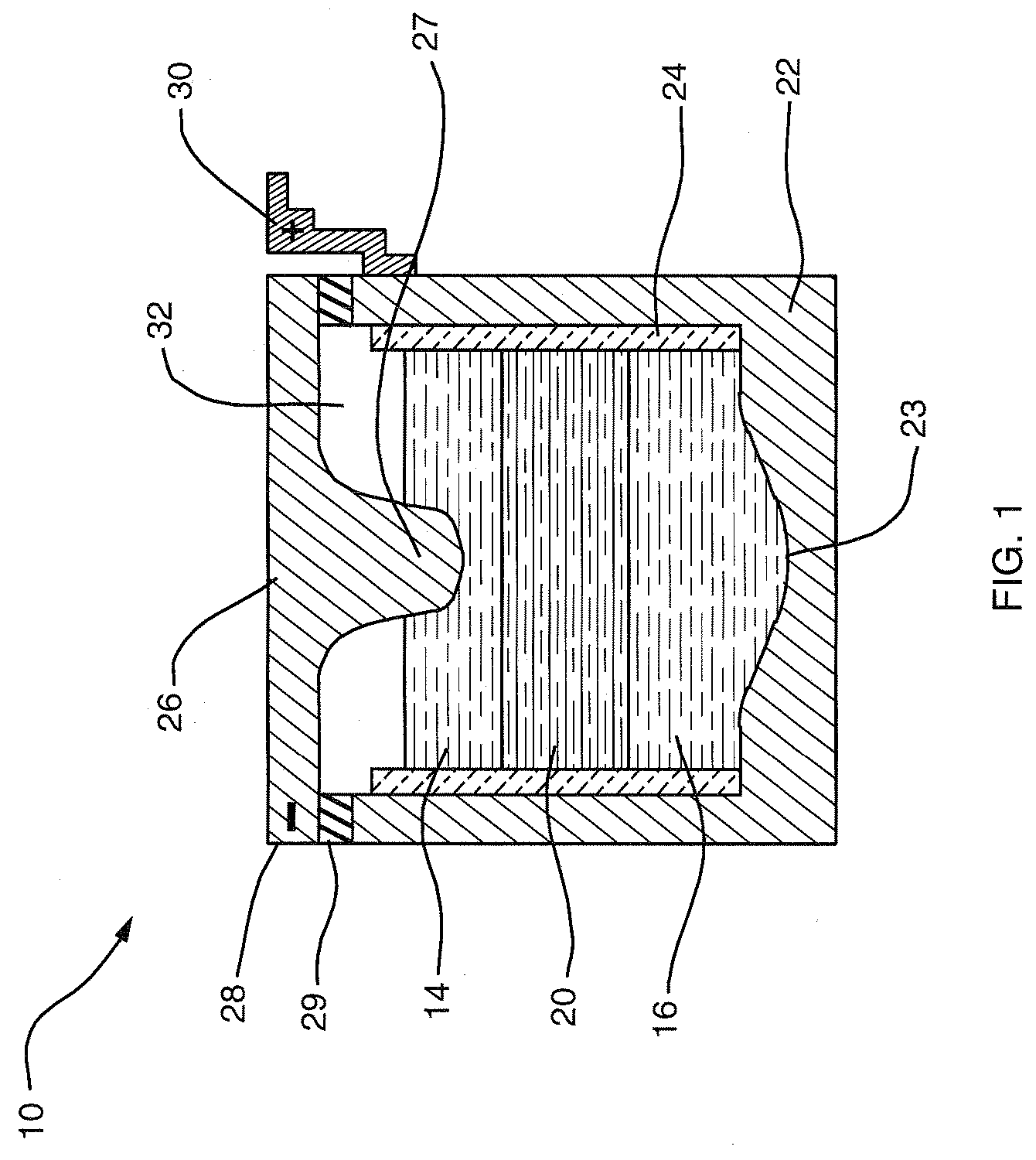
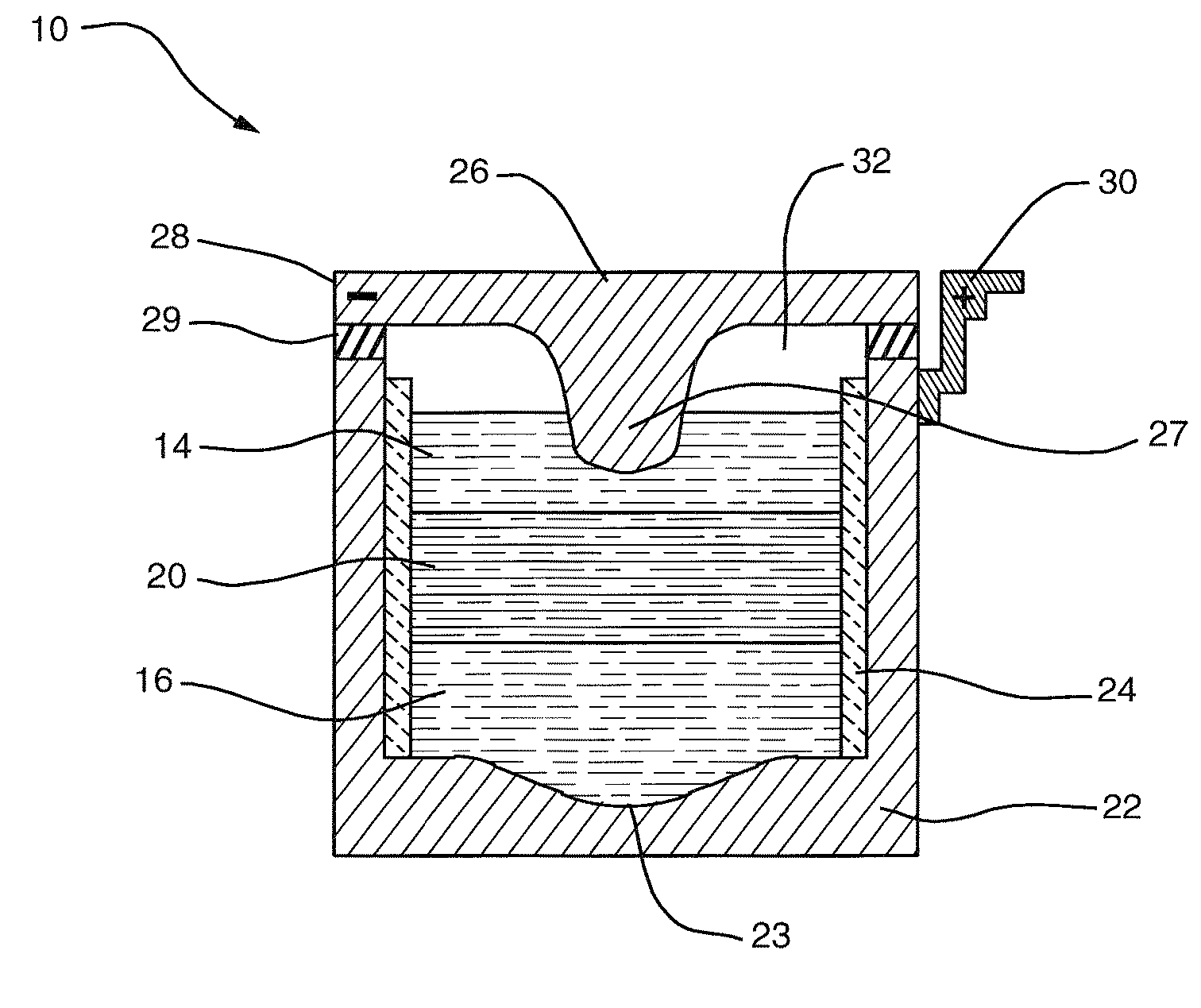
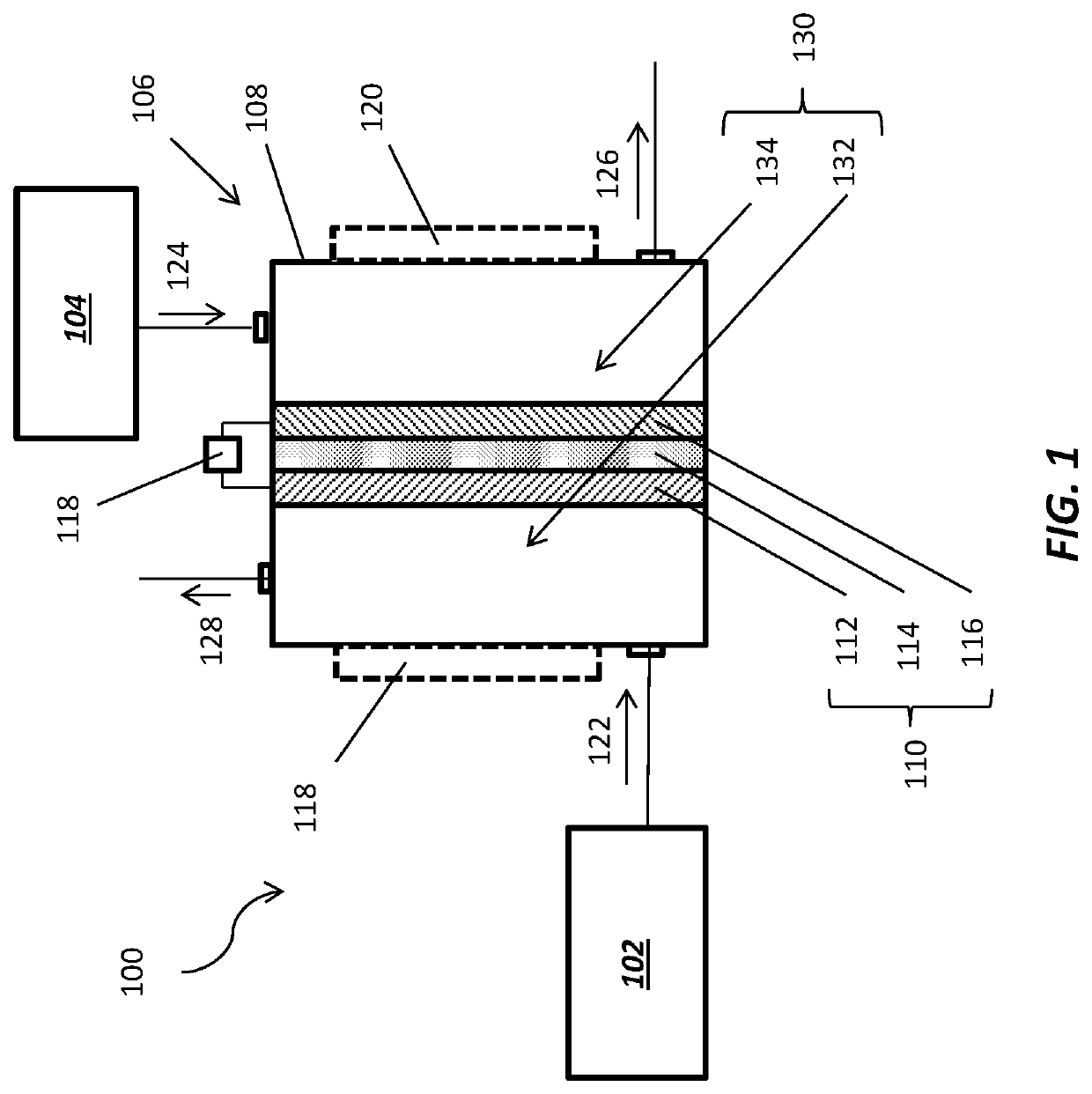
High-amperage energy storage device and method
ActiveUS20080044725A1Power capacity is large and scalableImprove ionic conductivityPrimary cell to battery groupingCell electrodesElectrical energy storageElectric energy
An electrochemical method and apparatus for high-amperage electrical energy storage features a high-temperature, all-liquid chemistry. The reaction products created during charging remain part of the electrodes during storage for discharge on demand. In a simultaneous ambipolar electrodeposition cell, a reaction compound is electrolyzed to effect transfer from an external power source; the electrode elements are electrodissolved during discharge.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
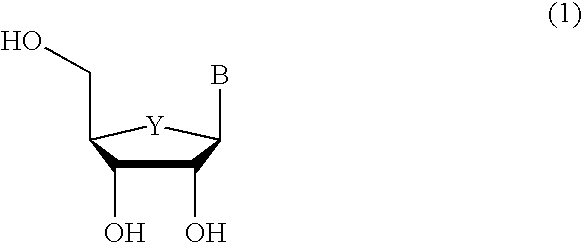
Method for the synthesis of 2′,3′-dideoxy-2′,3′-didehydronucleosides
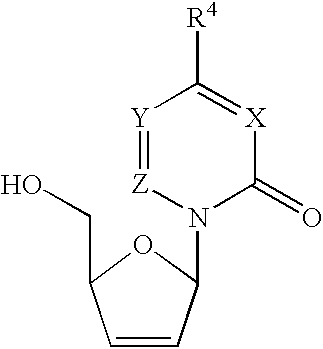
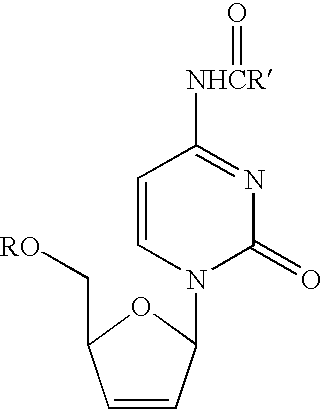
An efficient synthetic route to antiviral 2′,3′-dideoxy-2′,3′-didehydro-nucleosides, such as 2′,3′-dideoxy and 2′- or 3′-deoxyribo-nucleoside analogs, from available precursors is disclosed, with the option of introducing functionality as needed. In one embodiment, a method for the preparation of β-D and β-L-2′,3′-dideoxy-2′,3′-didehydro-nucleosides is described that includes: activating a compound of structure (1) wherein B is a pyrimidine or purine base and Y is O, S or CH2 with an acyl halide of the formula X—C(═O)R1, X—C(═O)C(R1)2OC(═O)R1 or X—C(═O)OR1 (wherein X is a halogen, and each R1 is independently hydrogen, lower alkyl, alkyl, aryl or phenyl); reducing the resulting compound with a reducing agent to form a 2′,3′-dideoxy-2′,3′-didehydro-nucleoside; and optionally deprotecting the nucleoside. The haloacylation of the first step can form the 2′-acyl-3′-halonucleoside, the 3′-acyl-2′-halonucleoside, or a mixture thereof.
Owner:GILEAD PHARMASSET LLC
Compositions and methods for use in analytical reactions
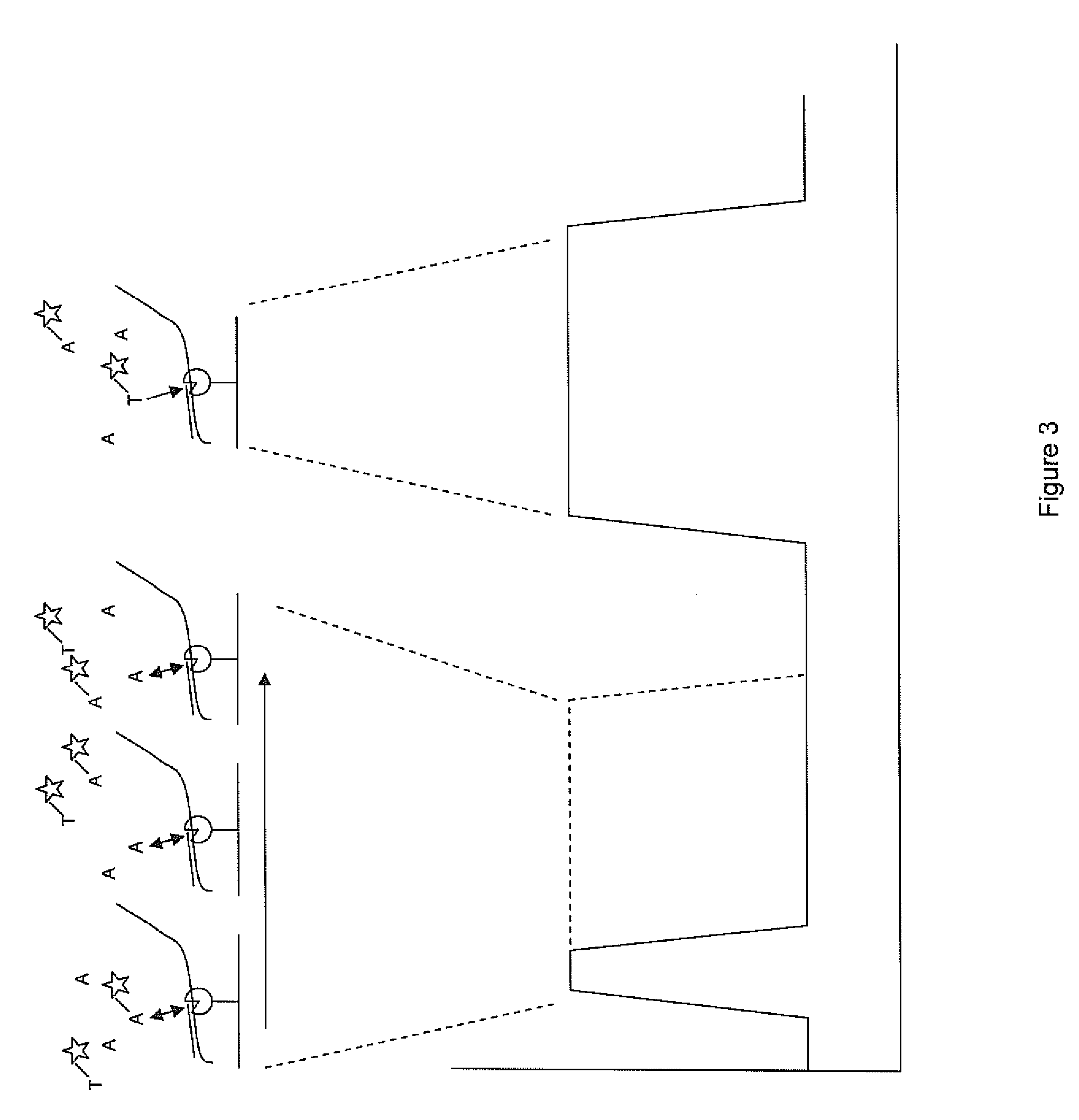
ActiveUS8252911B2Rate of reactionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisPolyphosphate
Compositions, methods, substrates and systems for use in analysis of single molecule reactions and particularly single molecule nucleic acid sequence analysis. Compositions that include non-reactive, distinguishable or undetectable competitive substrates for the reaction system of interest are provided, as well as their use in systems and substrates for such applications, such compounds typically preferably polyphosphate chains or analogous structures.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Accelerated hydrogen generation through reactive mixing of two or more fluids
InactiveUS6818334B2Reactivity issueStability issueCell electrodesFuel cell auxillariesPtru catalystProton exchange membrane fuel cell
Owner:INTELLIGENT ENERGY LTD
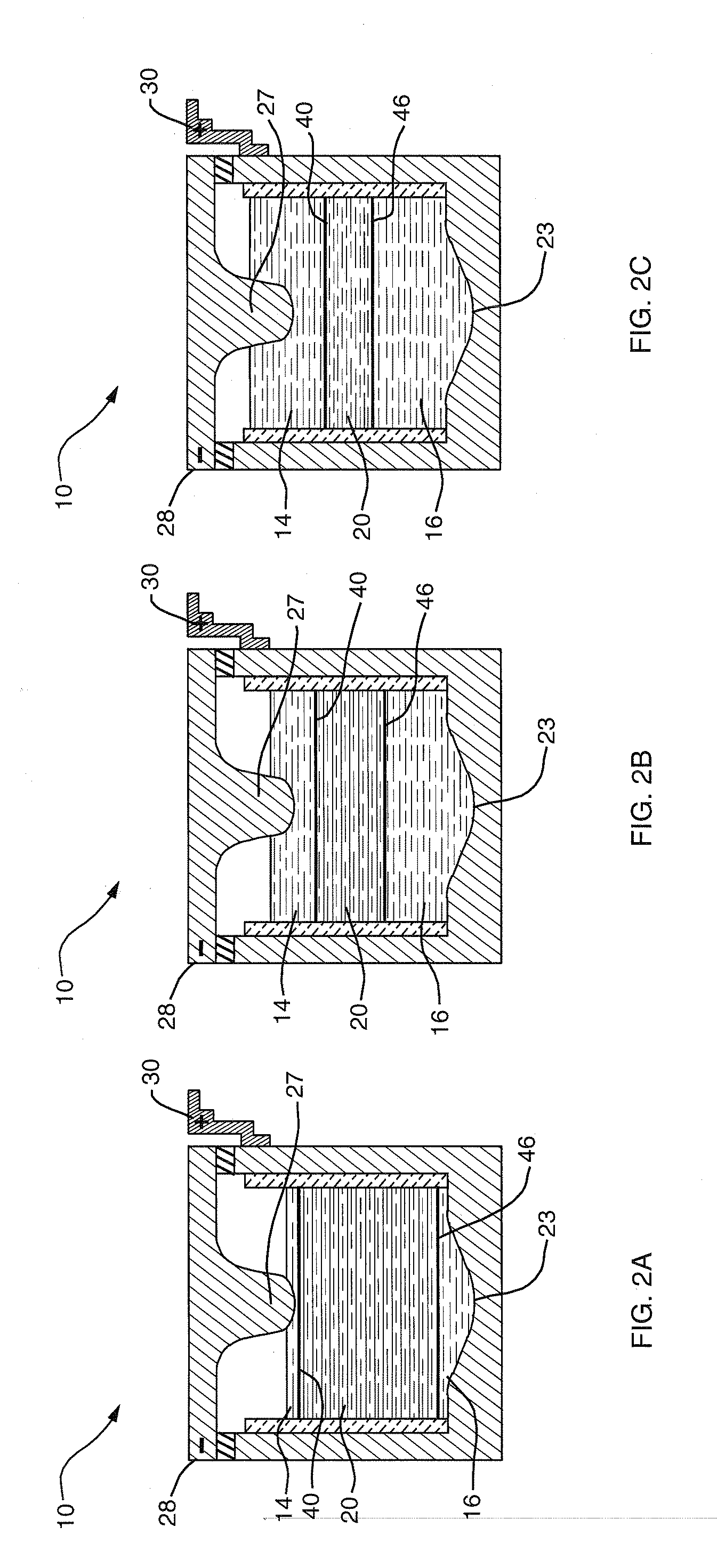
High-amperage energy storage device with liquid metal negative electrode and methods
ActiveUS8268471B2Improve ionic conductivityIncrease response ratePrimary cell to battery groupingCell electrodesElectrolysisEngineering
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Compositions and methods for use in analytical reactions
ActiveUS20090208961A1Modulation rateRate of reactionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisPhosphoric acid
Compositions, methods, substrates and systems for use in analysis of single molecule reactions and particularly single molecule nucleic acid sequence analysis. Compositions that include non-reactive, distinguishable or undetectable competitive substrates for the reaction system of interest are provided, as well as their use in systems and substrates for such applications, such compounds typically preferably polyphosphate chains or analogous structures.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Accelerated hydrogen generation through reactive mixing of two or more fluids
InactiveUS20030228505A1Reactivity issueStability issueCell electrodesFuel cell auxillariesFuel cellsHydrogen
The rate of hydrogen generation in proton-exchange-membrane (PEM) fuel cells is greatly accelerated by mixing a first aqueous alkali borohydride solution with a second aqueous solution in the presence of one or more transition metal catalysts: wherein the first solution comprises (a) 5 to 50 wt % MBH4, where M is an alkali metal, (b) 5 to 40 wt % alkali hydroxide or alkaline metal hydroxide, and (c) the balance water, and wherein the second solution comprises (a) 51 to 100% water, and (b) the balance, if any, comprising at least one water-soluble additive.
Owner:INTELLIGENT ENERGY LTD
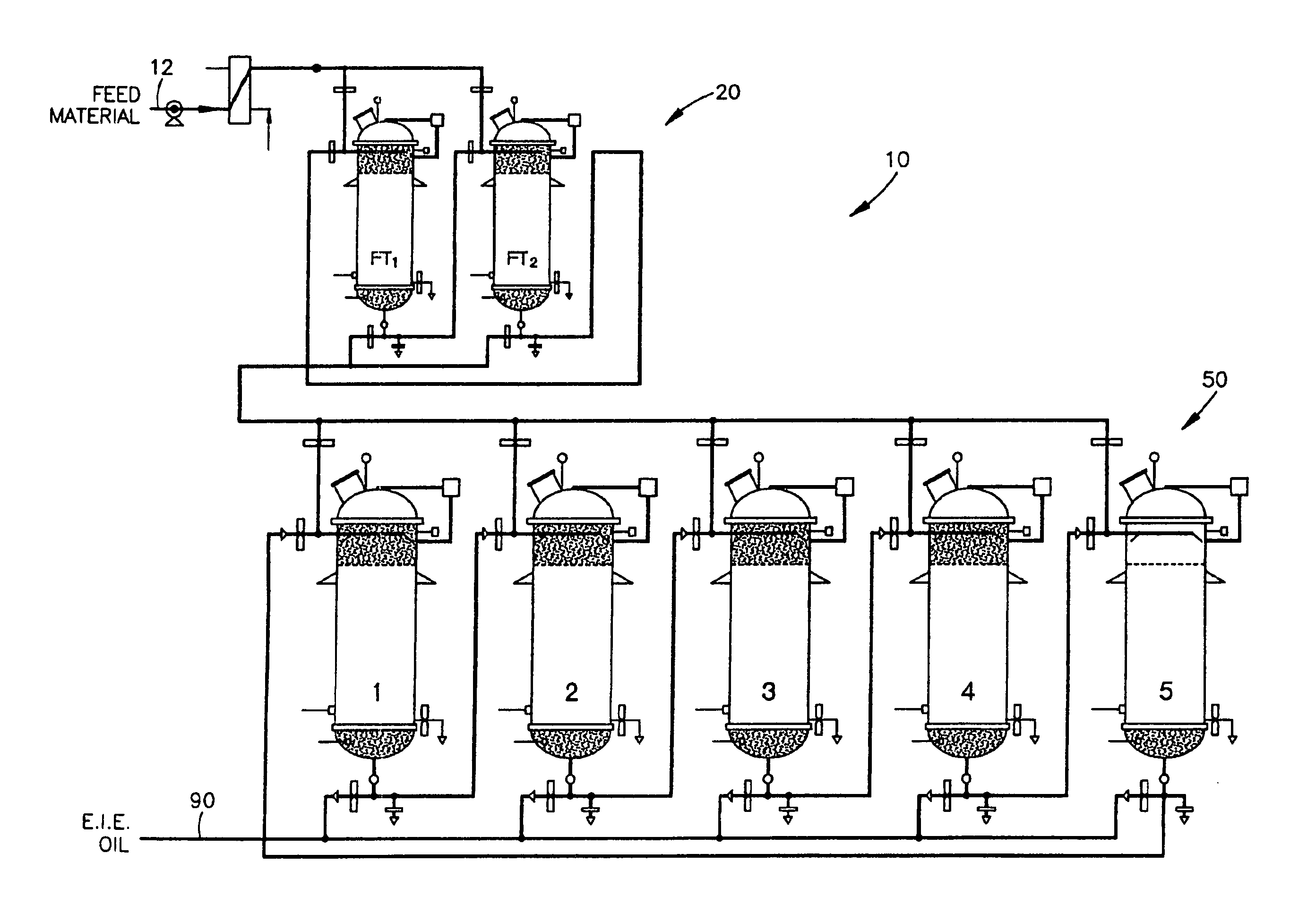
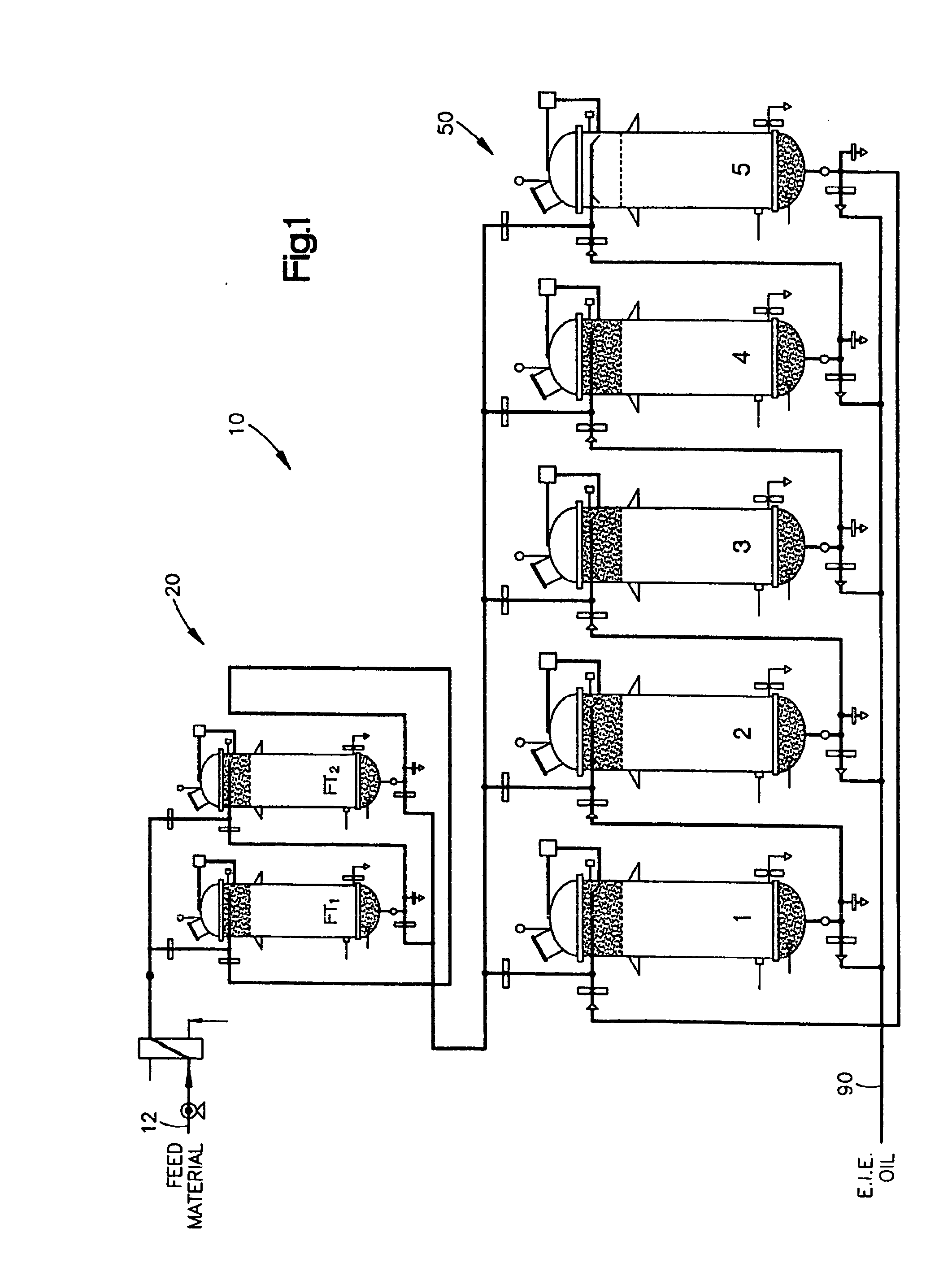
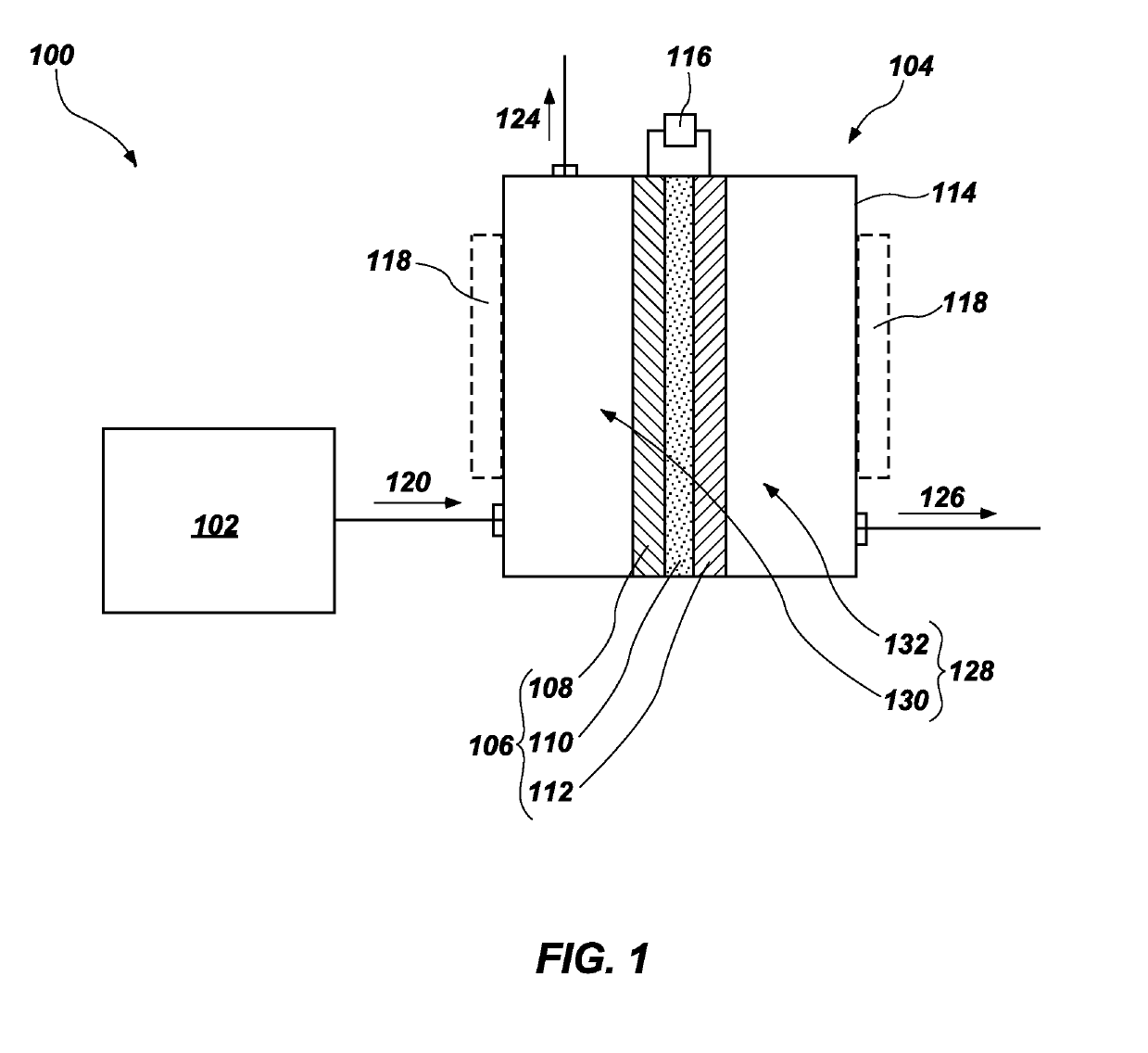
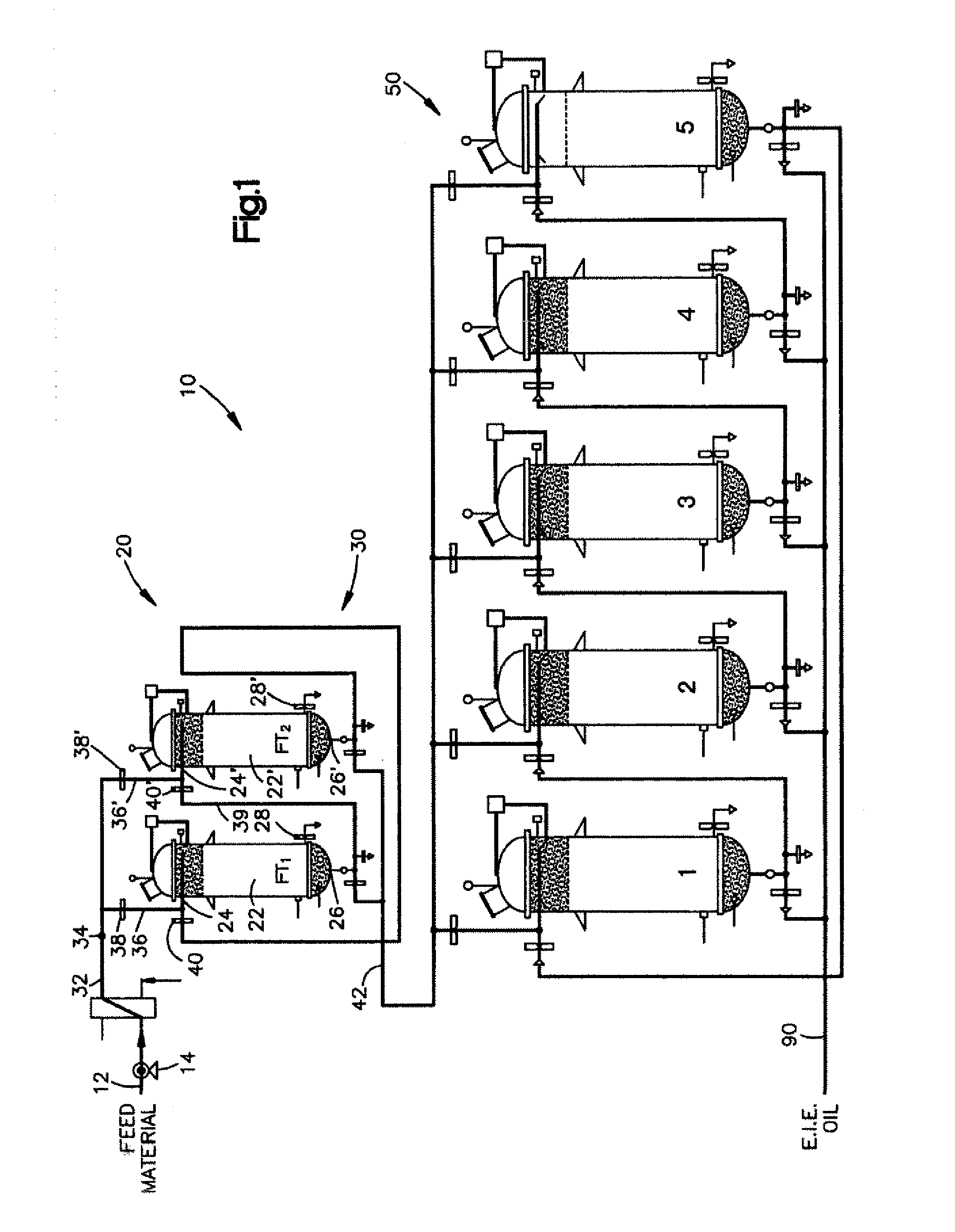
Continuous Process and Apparatus for Enzymatic Treatment of Lipids
ActiveUS20080138867A1Constant flowLess operator monitoringBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLipid formationFixed bed
A method and system for the enzymatic treatment of a lipid containing feedstock comprises contacting the feedstock with a processing aid, then causing the feedstock to pass at a substantially constant flow rate through a treatment system comprising a plurality of enzyme-containing fixed bed reactors connected to one another in series. The fixed bed reactors can be individually serviceable, the flow rate of the feedstock remaining substantially constant through the system when one of the fixed bed reactors is taken off line for servicing. In the most preferred embodiment, the processing aid is a substantially moisture-free silica. The processing aid can be placed in one or more of the fixed bed reactors, disposed above the enzyme in the reactor, or it can be in a pre-treatment system which can comprise one or more reactors.
Owner:BUNGE OILS INC
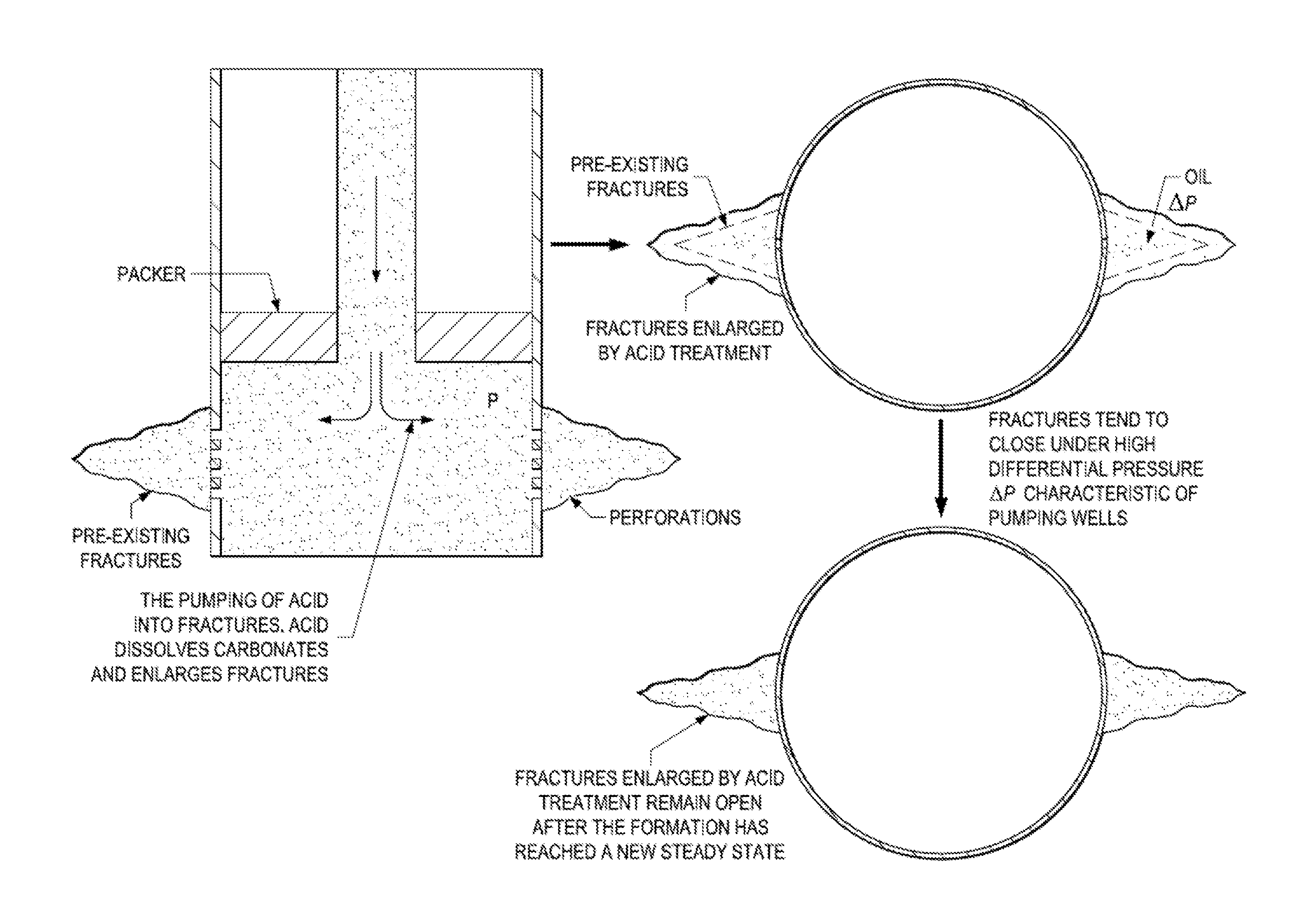
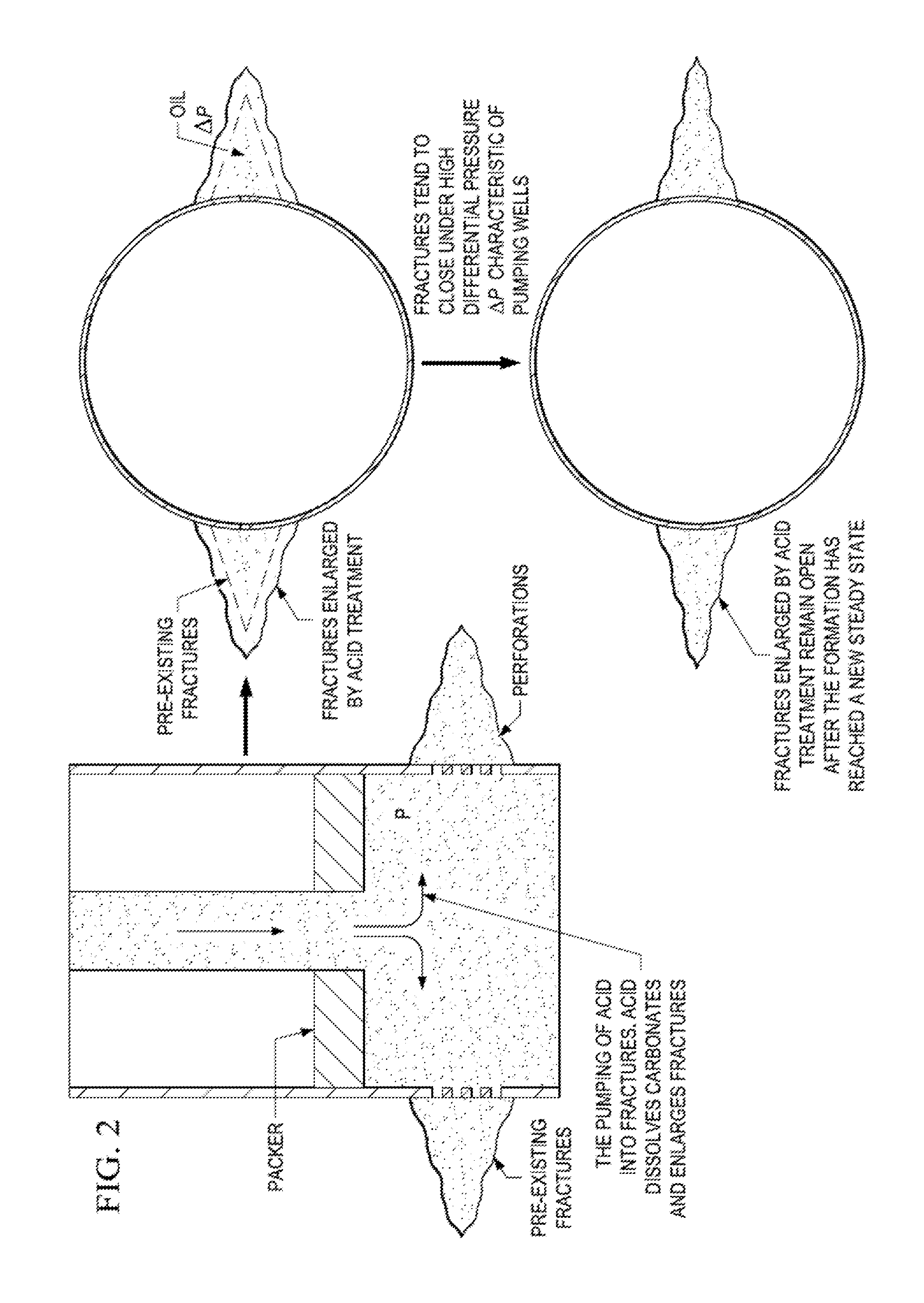
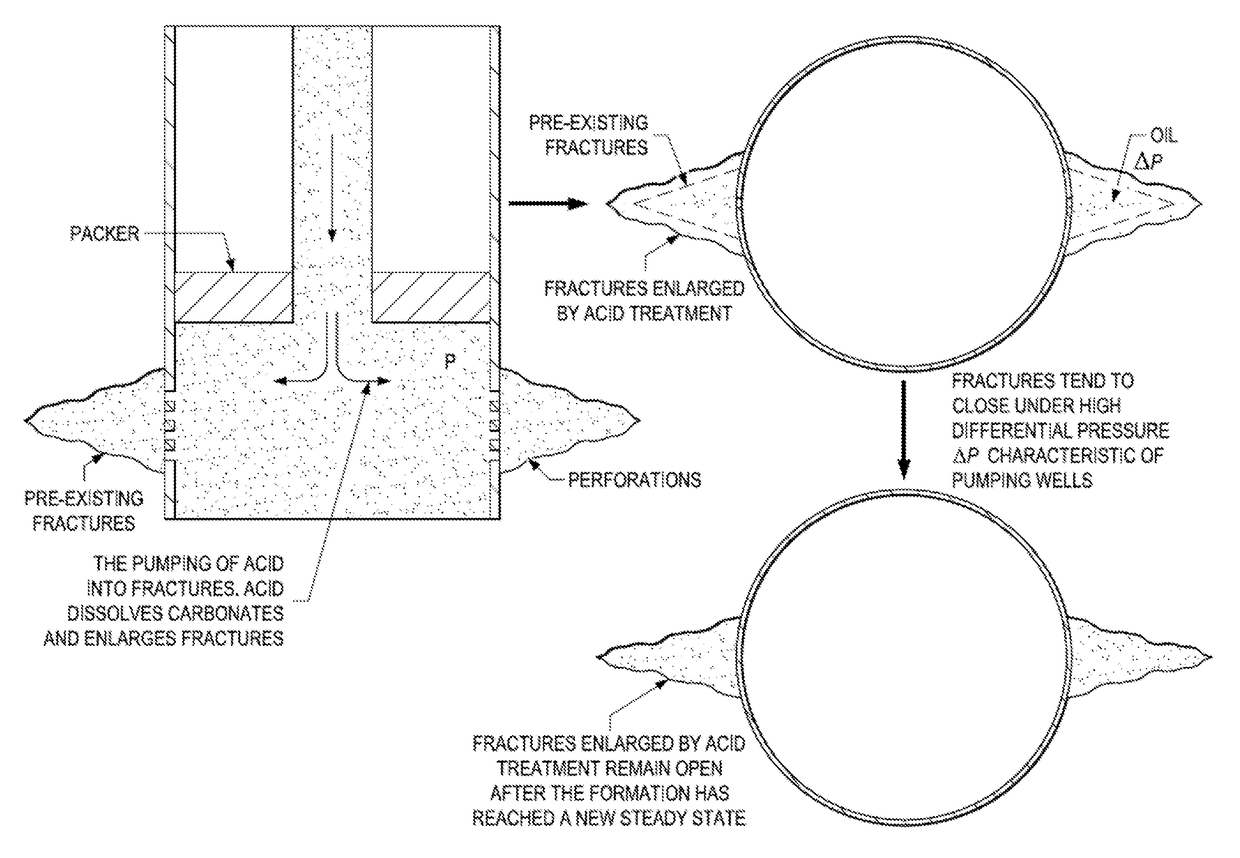
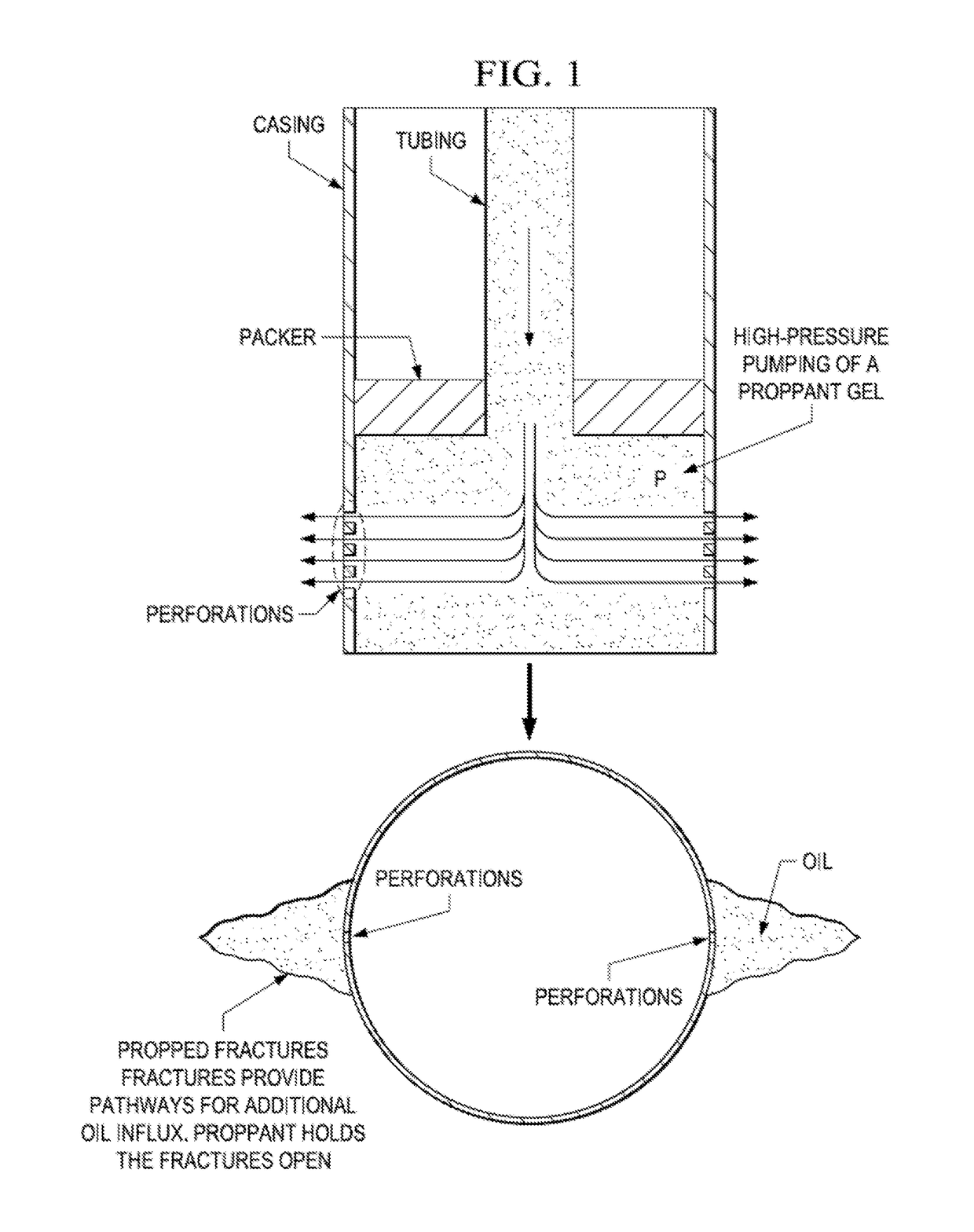
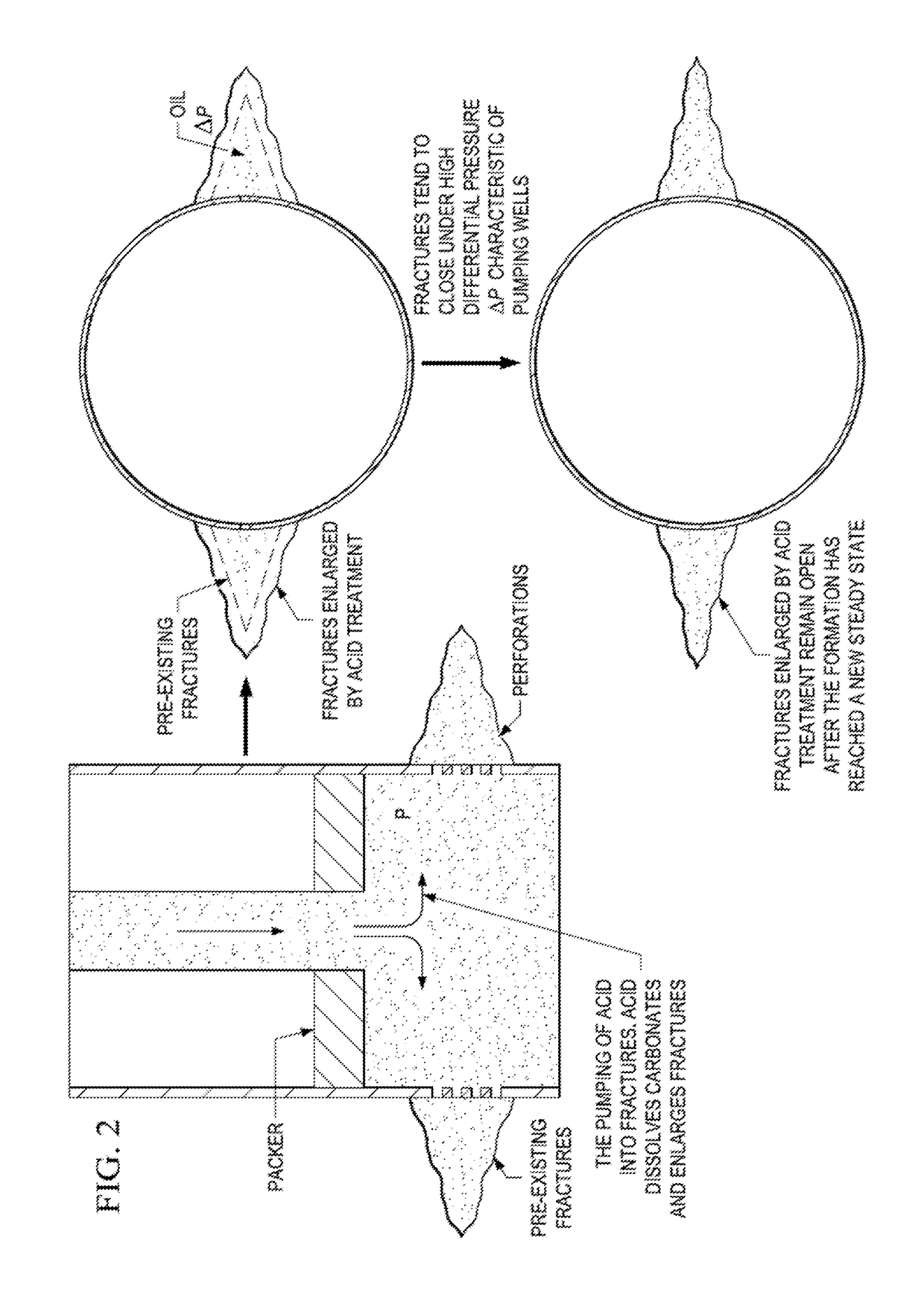
Cryogenic acid frack
ActiveUS20150218439A1Extended reaction timeIncreased penetration distanceFluid removalDrilling compositionOrganic chemistry
A method of fracking carbonate-rich reservoirs, comprising injecting a cryogenic or chilled fluid followed by an acid into said reservoir, allowing the acid to etch said reservoir, and thereby increasing production of a fluid, such as water, oil or gas, from said reservoir.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
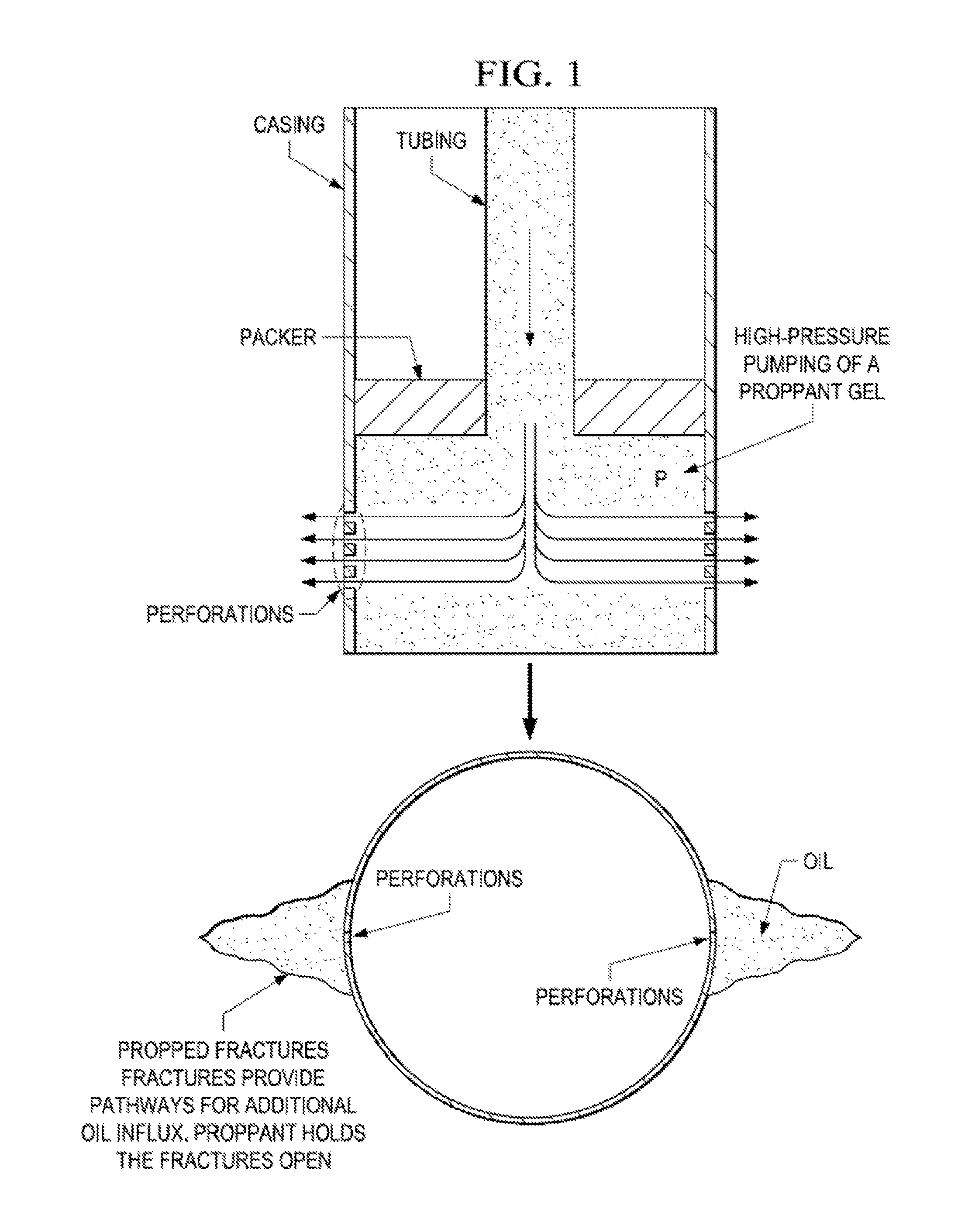
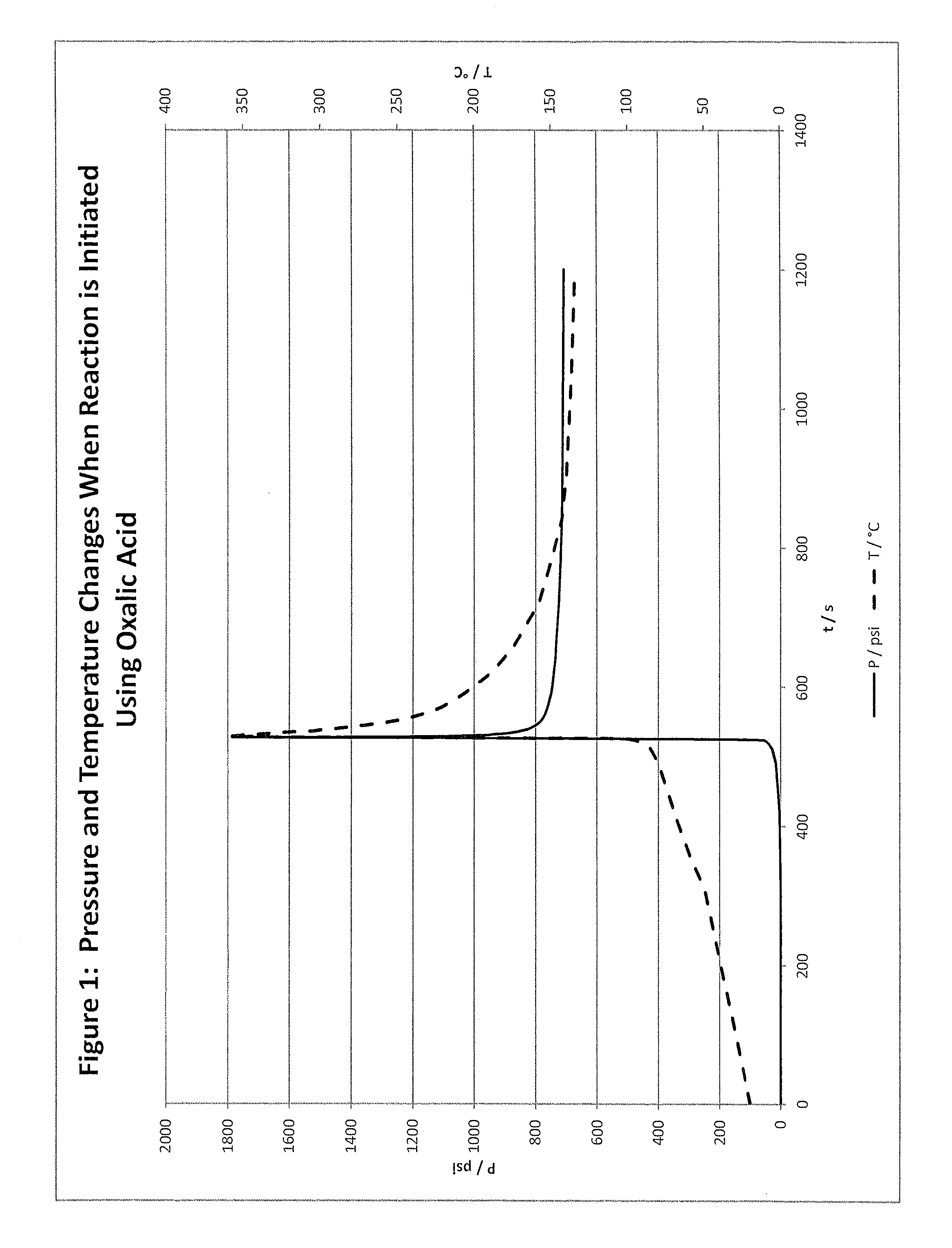
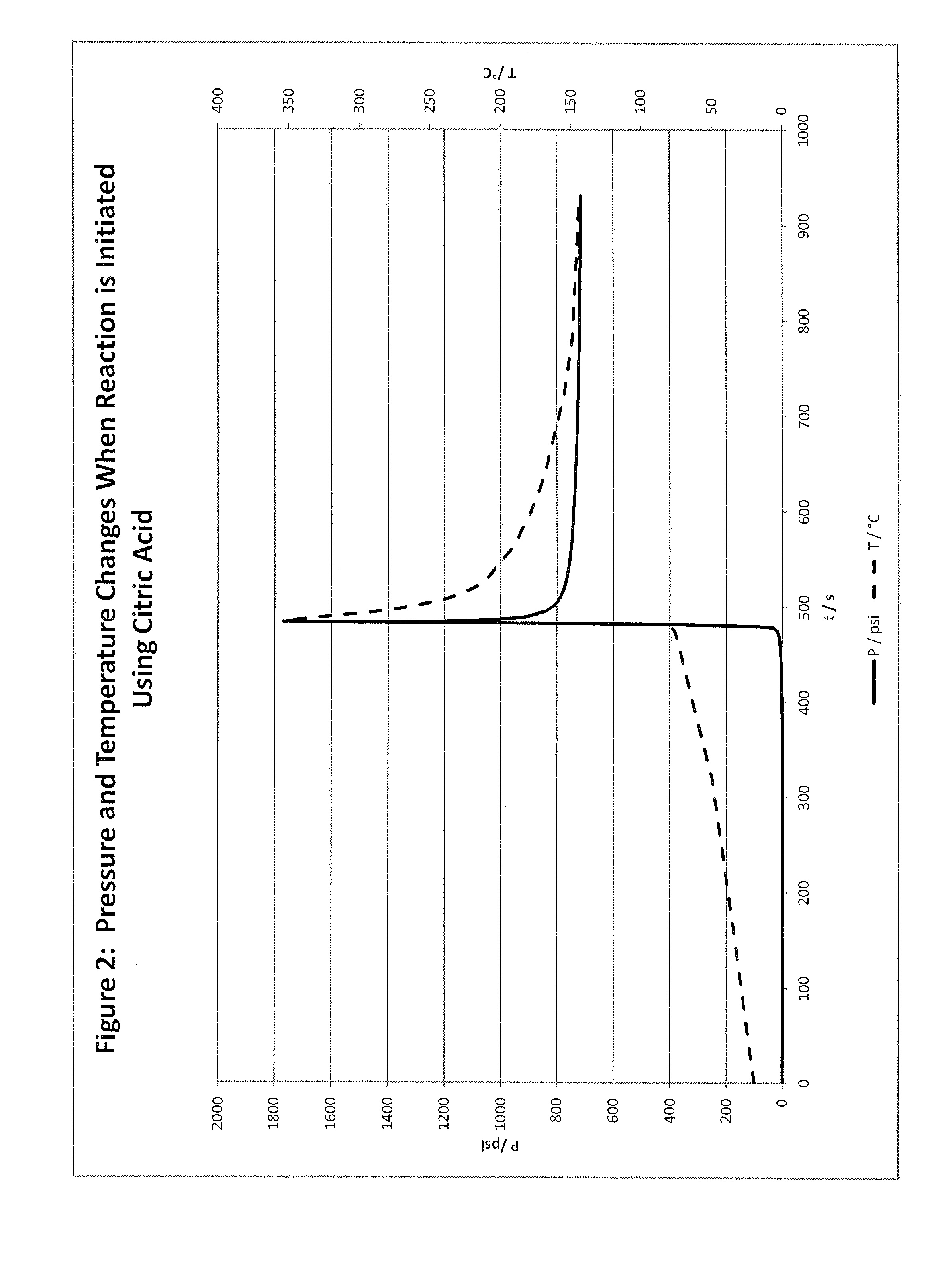
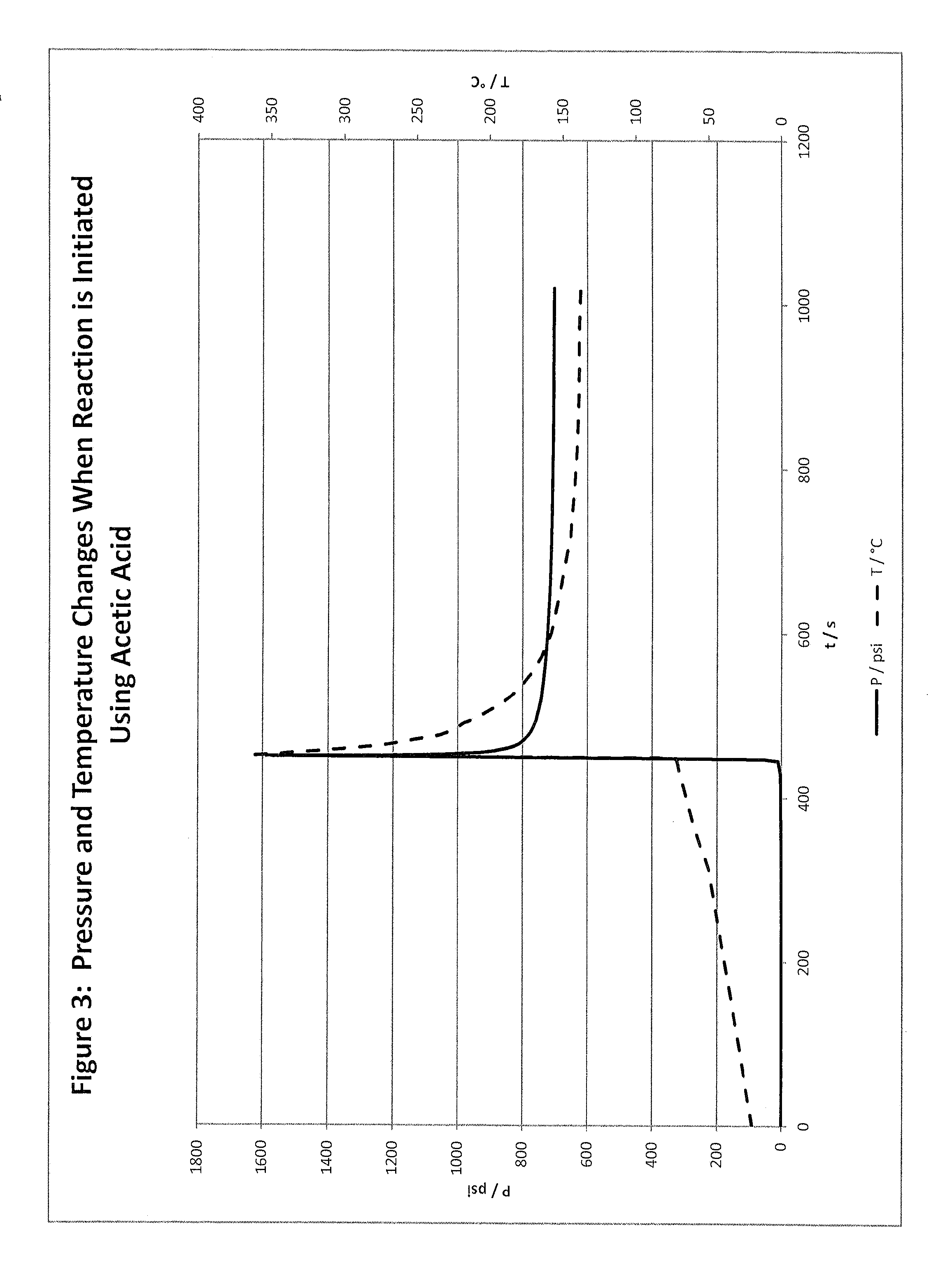
Hydrocarbon stimulation by energetic chemistry
InactiveUS20150337638A1Reduce viscosityIncrease mobilityFluid removalDrilling compositionChemical substanceFuel oil
Disclosed are methods and compositions for stimulating a hydrocarbon formation by generating heat and / or pressure in the formation, in either a fracturing or matrix treatment. This invention utilizes reactive fluids which comprise energetic chemistry that reacts in the formation to create heat and / or pressure. The heat may reduce the viscosity and increase the mobility of heavy oil, and / or the pressure may initiate or extend fractures in the hydrocarbon bearing formation. The reactive fluid may be buffered to slow the reaction and include an encapsulated activator to accelerate the reaction after suitable delay or when the fluid is placed in a zone of interest. Reactive fluids may be sequentially used, wherein each reactive fluid is successively less energetic than the preceding reactive fluid.
Owner:LIBERTY OILFIELD SERVICES LLC
Method of cryogenic acid fracking
ActiveUS9644137B2Improve reaction speedReduce distanceFluid removalDrilling compositionChemistryThermodynamics
A method of fracking carbonate-rich reservoirs, comprising injecting a cryogenic or chilled fluid followed by an acid into the reservoir, allowing the acid to etch the reservoir, and thereby increasing production of a fluid, such as water, oil or gas, from the reservoir. Further, injecting a preflush into the reservoir and later injecting a postflush into the reservoir to displace the acid from the tubulars into the reservoir.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
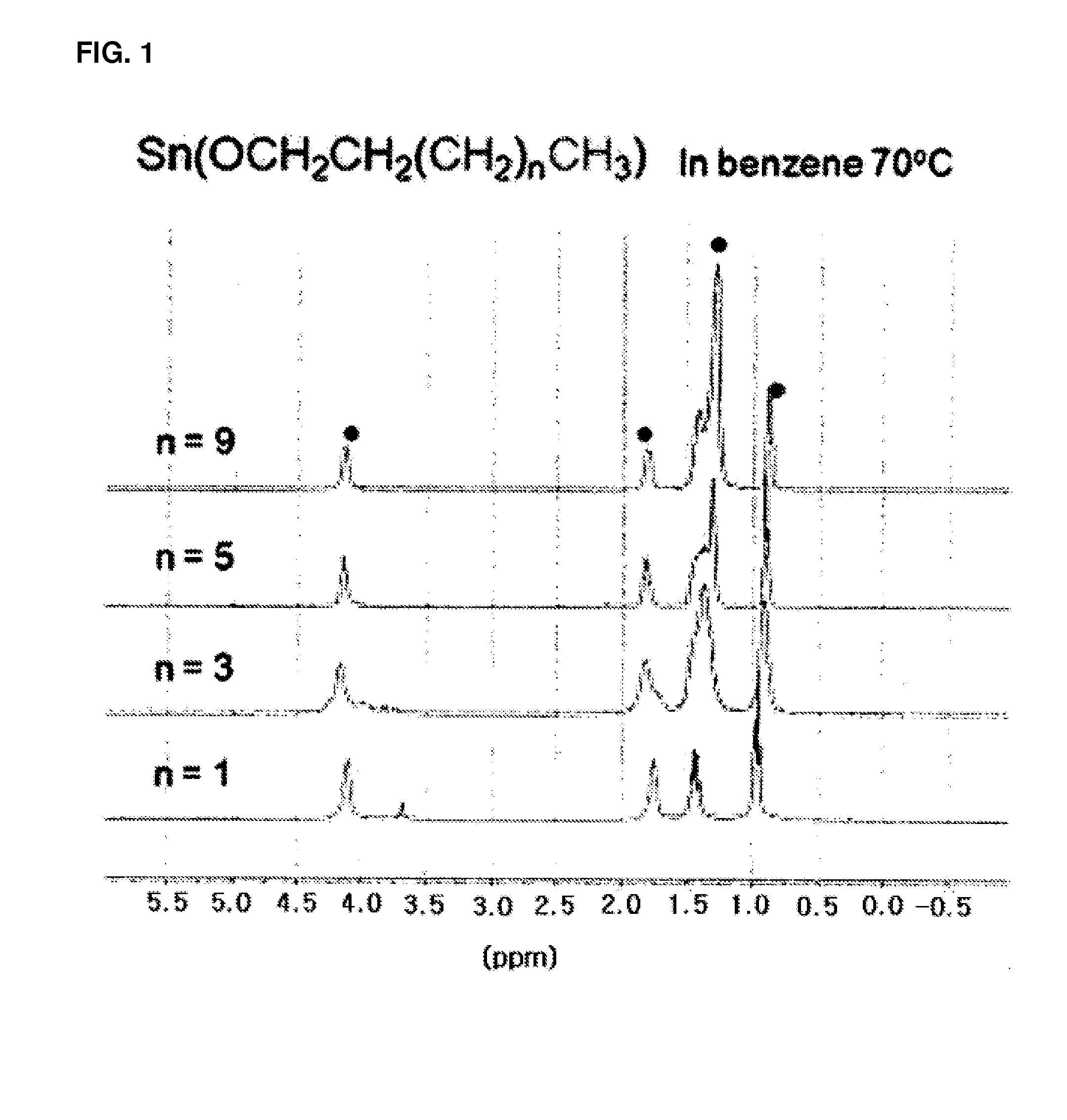
Organotin compounds, preparation method thereof, and preparation of polylactide resin using the same
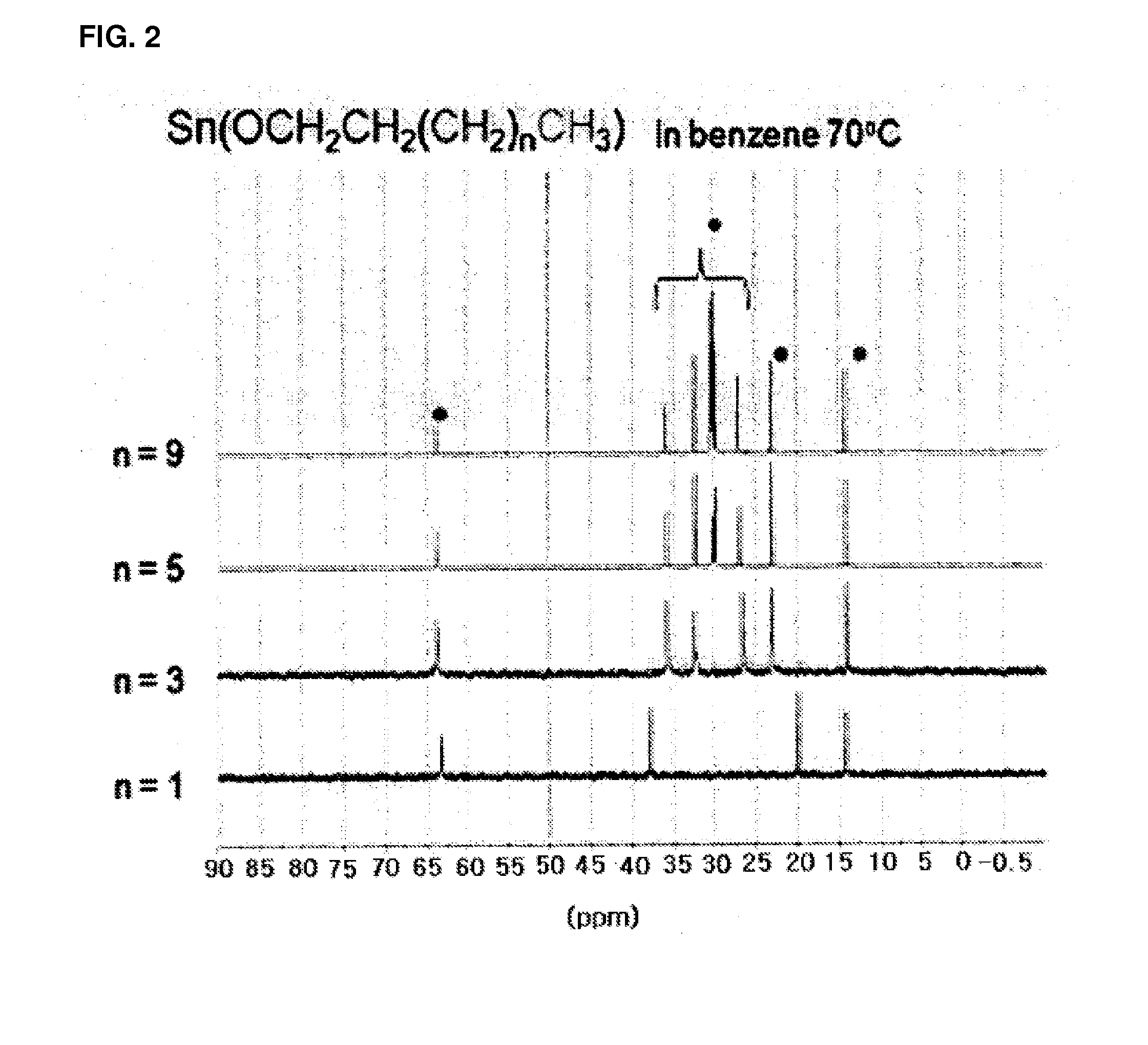
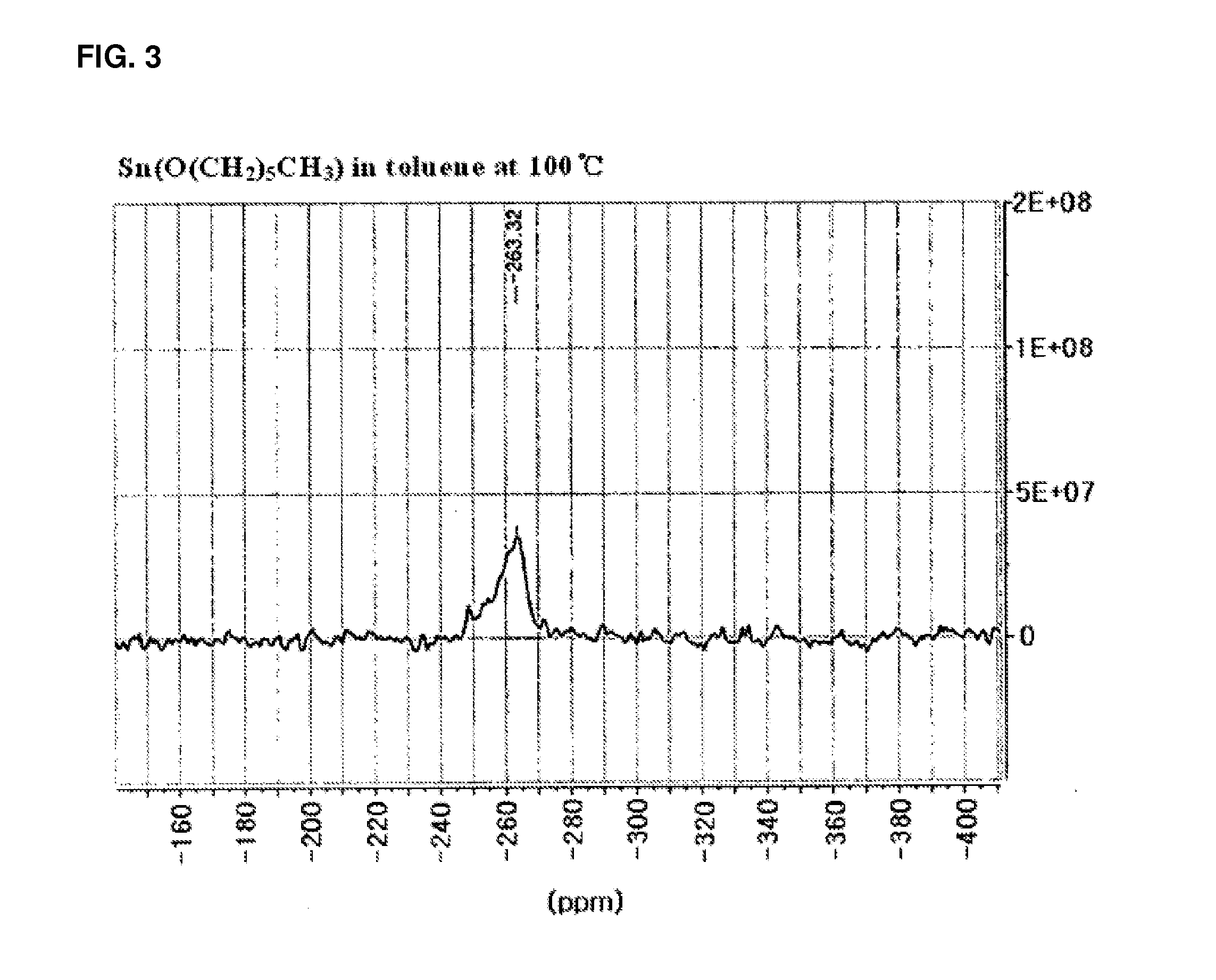
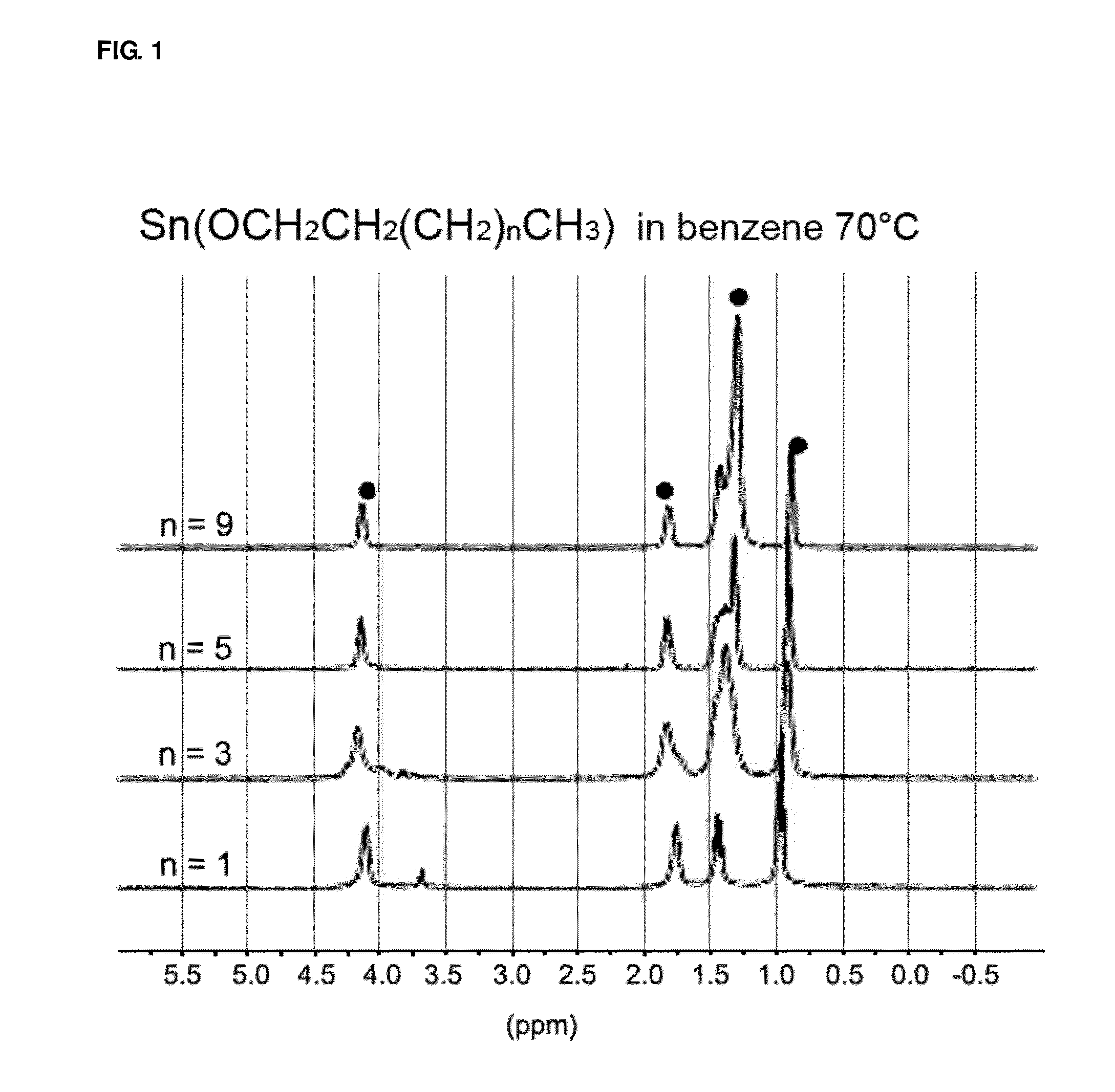
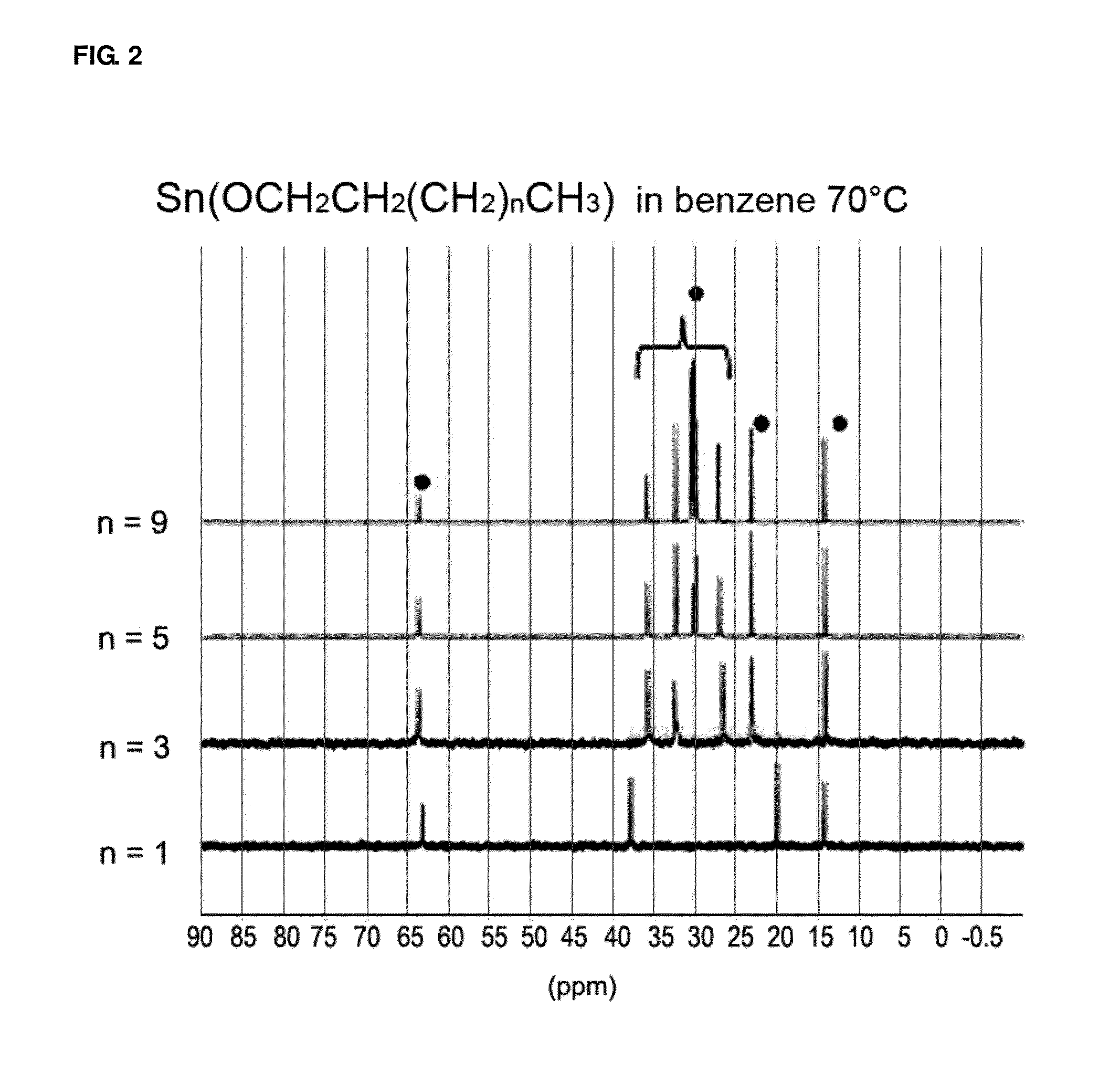
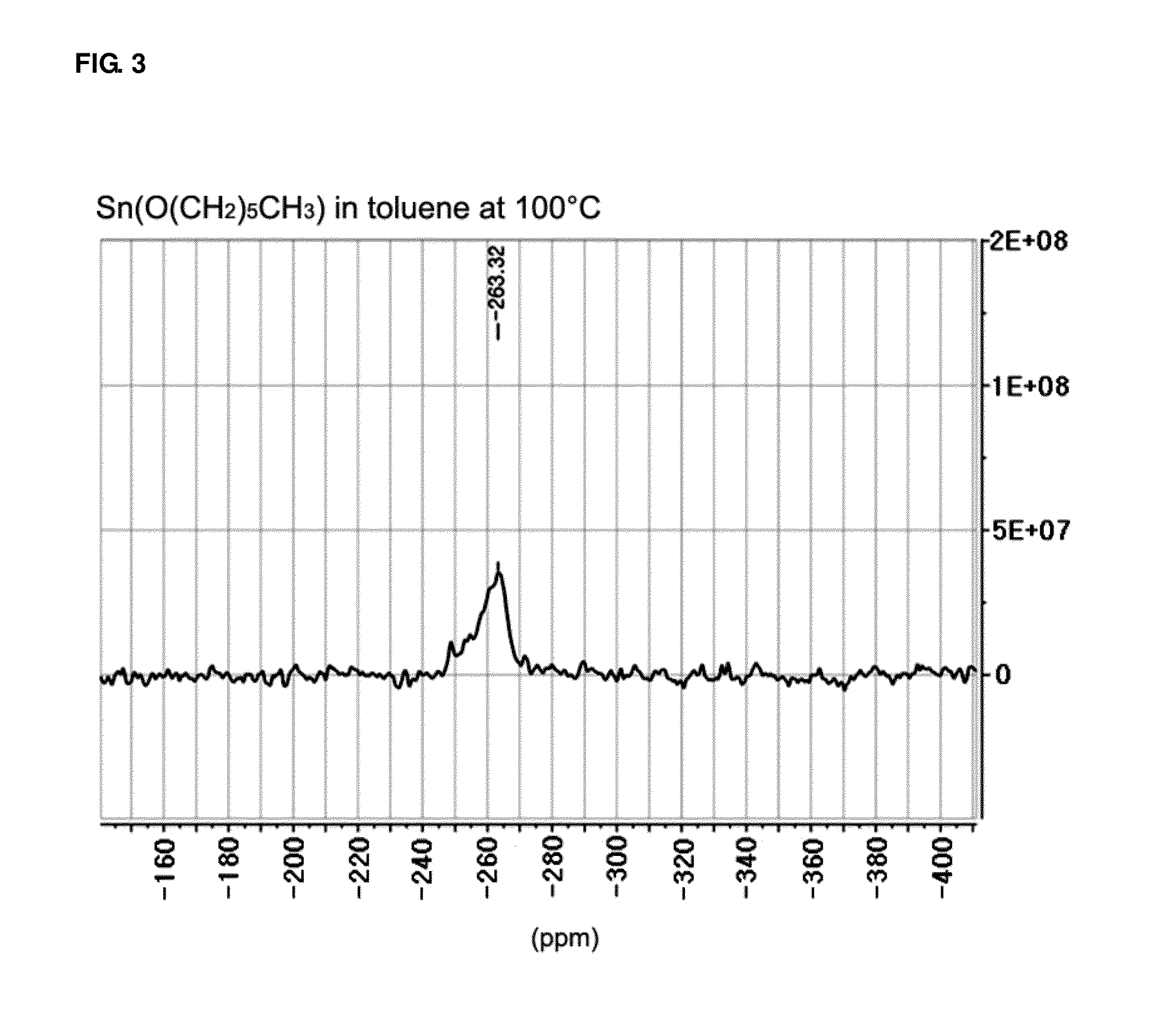
InactiveUS20120214959A1Rate of reactionIncrease polymerization rateTin organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCarbon atomOrganic tin compound
The present invention relates to an organotin compound represented by R1O—Sn—OR2 (where R1 and R2 are independently a primary, secondary, or tertiary alkyl group having 5 to 30 carbon atoms), a preparation method thereof, and a preparation method for polylactide using the organotin compound. The organotin compound of the present invention is easy to prepare and is used to prepare a polylactide resin having a high molecular weight at a high yield without using a separate initiator.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
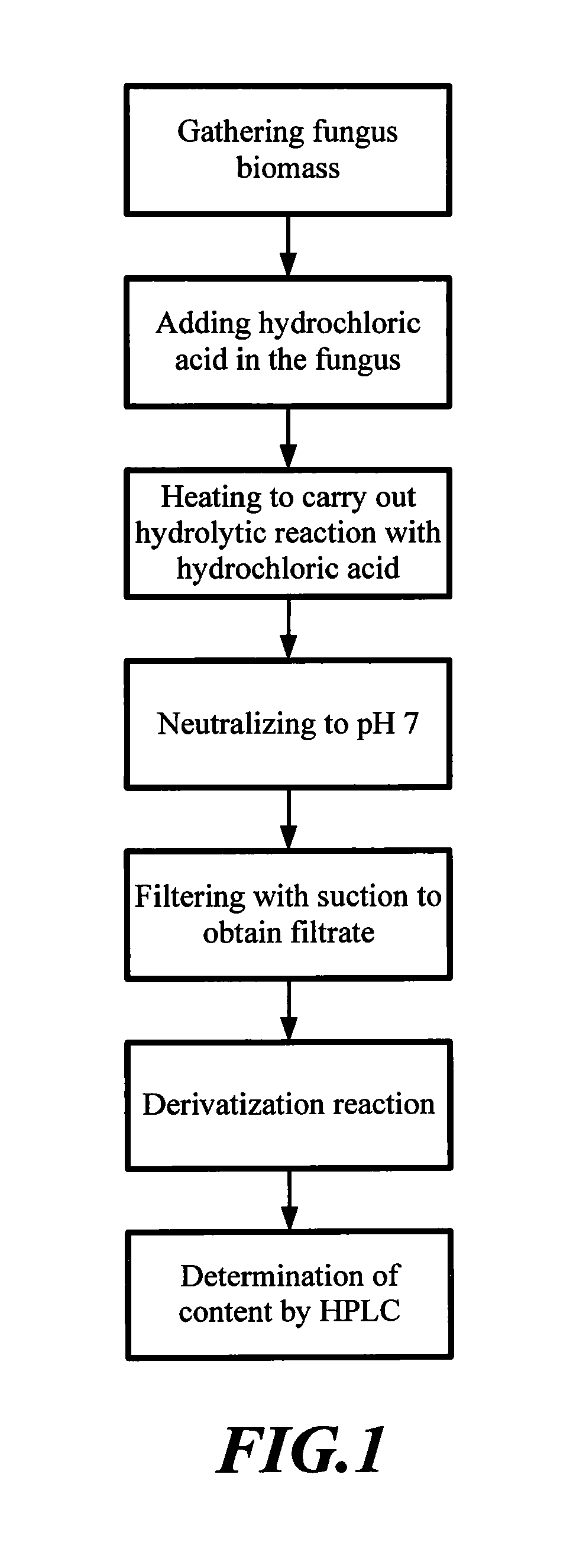
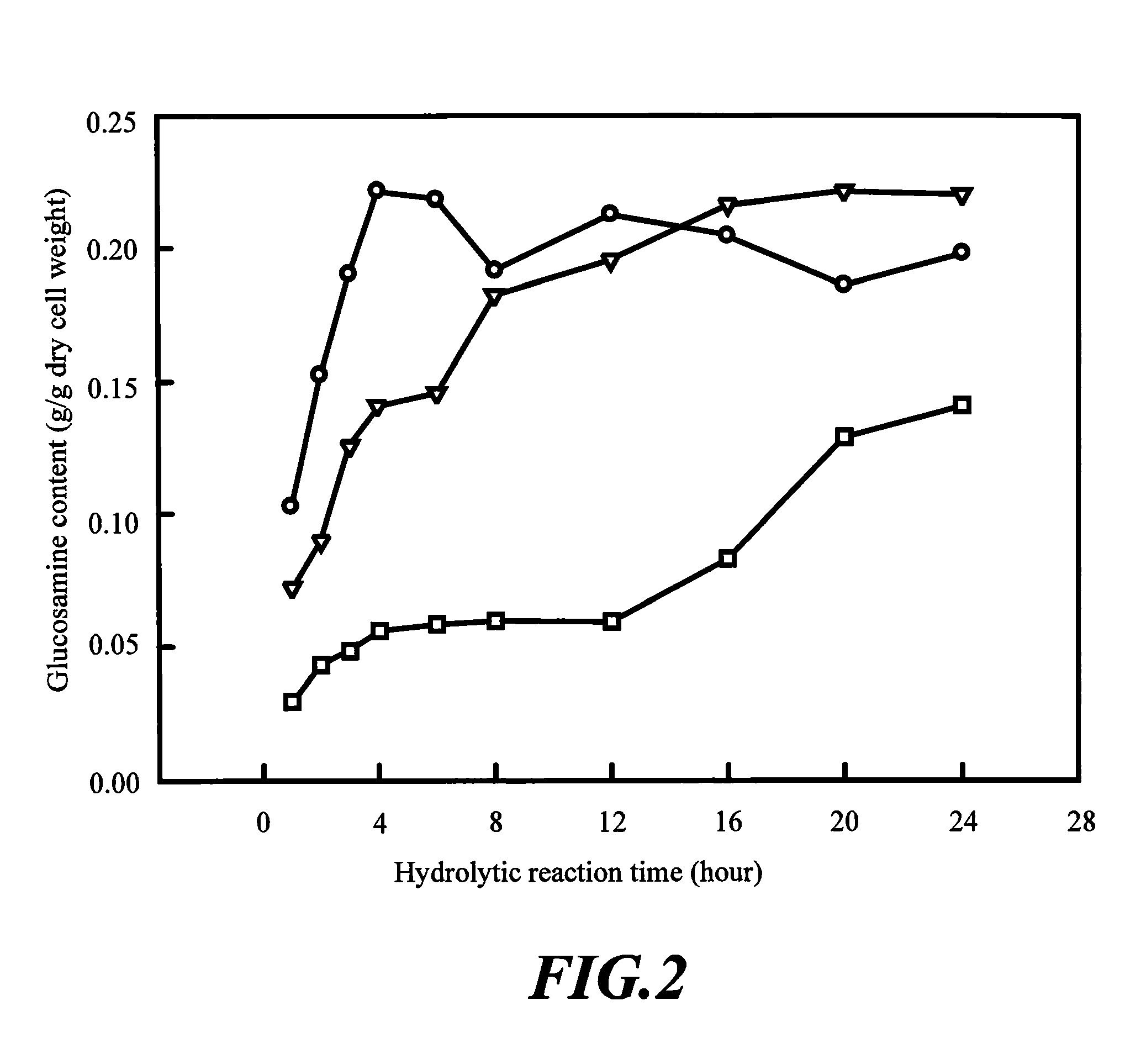
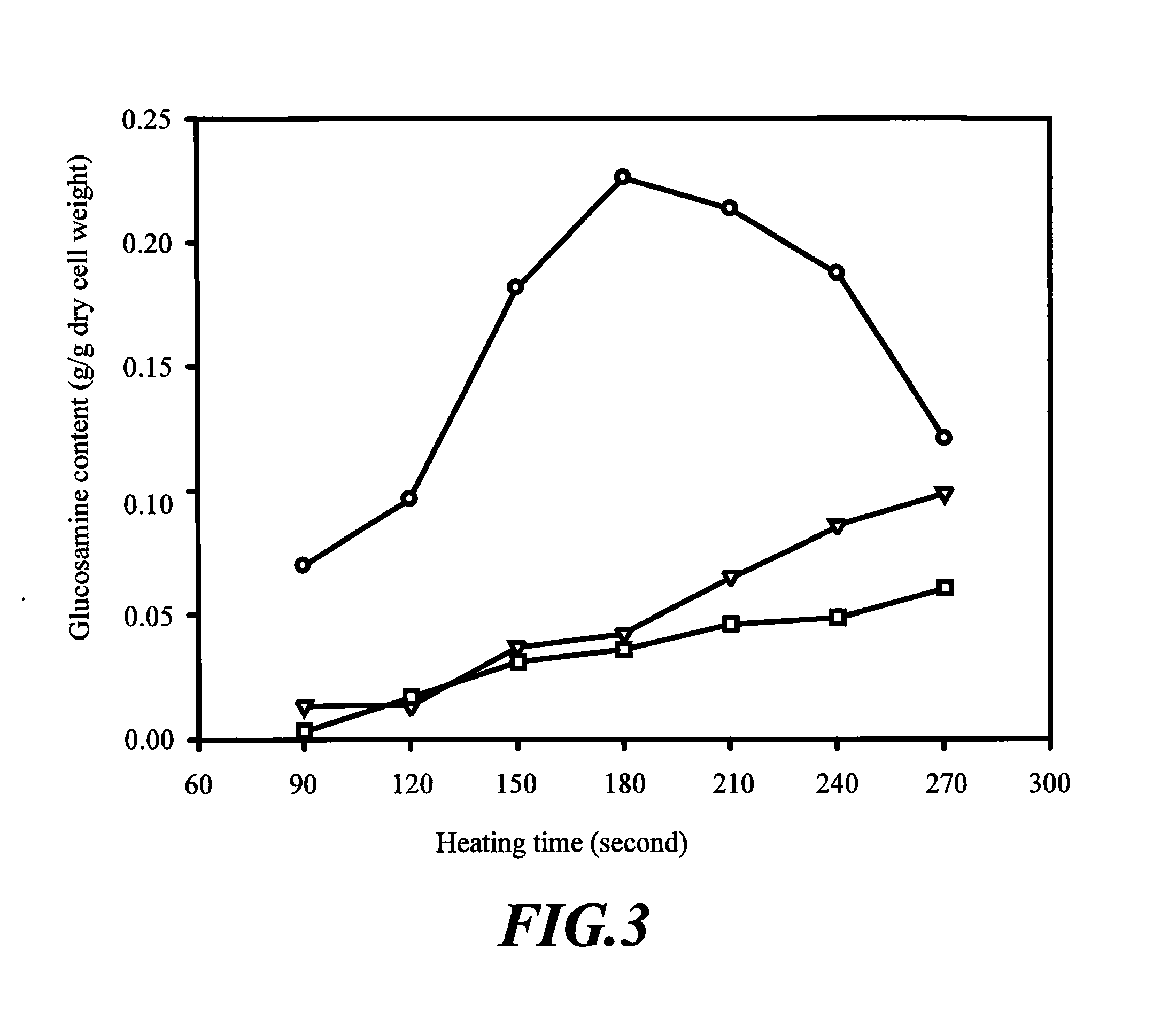
Process for producing glucosamine and acetyl glucosamine by microwave technique
InactiveUS20110114472A1Waste of energySave energySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationChitinMicrowave
A process for producing glucosamine and acetyl glucosamine by using microwave technique, comprising following steps: (1) providing a chitin or chitosan source formed by a microorganism; (2) adding hydrochloric acid solution having concentration of 2N˜6N into said chitin or chitosan source to form a reaction solution; (3) placing said reaction solution in a microwave device and heating therein at power of 700˜2100 watt to carry out hydrolytic reaction such that chitin or chitosan is hydrolyzed into glucosamine or acetyl glucosamine.
Owner:YUAN ZE UNIV
Process of making synthetic absorbable autoclaveable monofilament fibers and brachytherapy seed spacers
InactiveUS6419866B1Reduce usageRate of reactionArtificial filament heat treatmentMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentBrachytherapyHigh pressure
The present invention is directed to absorbable, autoclaveable, monofilament fibers prepared from absorbable glycolide-rich polymers, in which the fibers are oriented in the total draw ratio range 4.1 to 5.6x, and are annealed at a temperature between about 165° C. and about 185° C.; to brachytherapy seed spacers manufactured from the absorbable, autoclaveable, glycolide-rich polymers, monofilament fibers; and to methods of manufacturing such fibers and brachytherapy seed spacers.
Owner:ETHICON INC
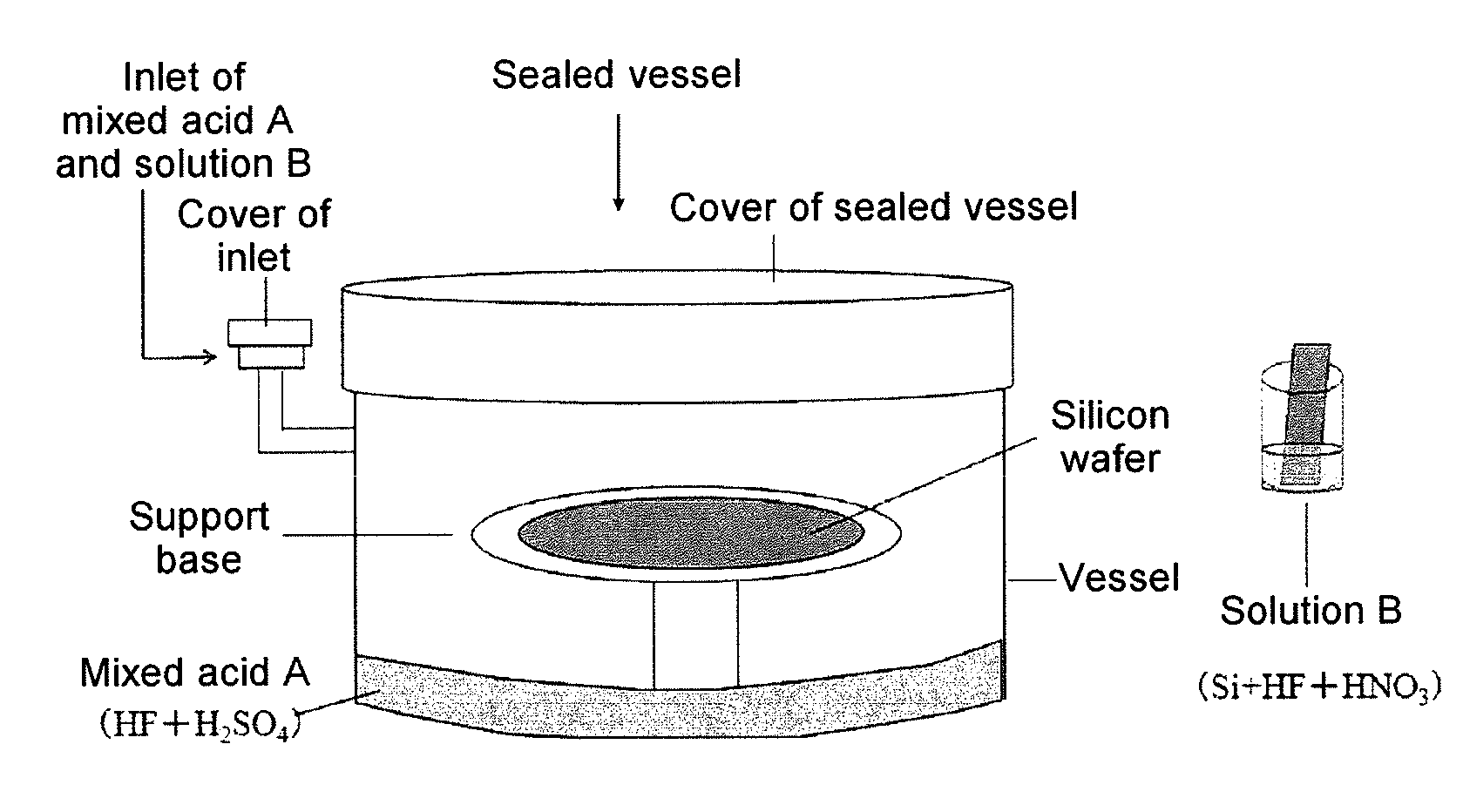
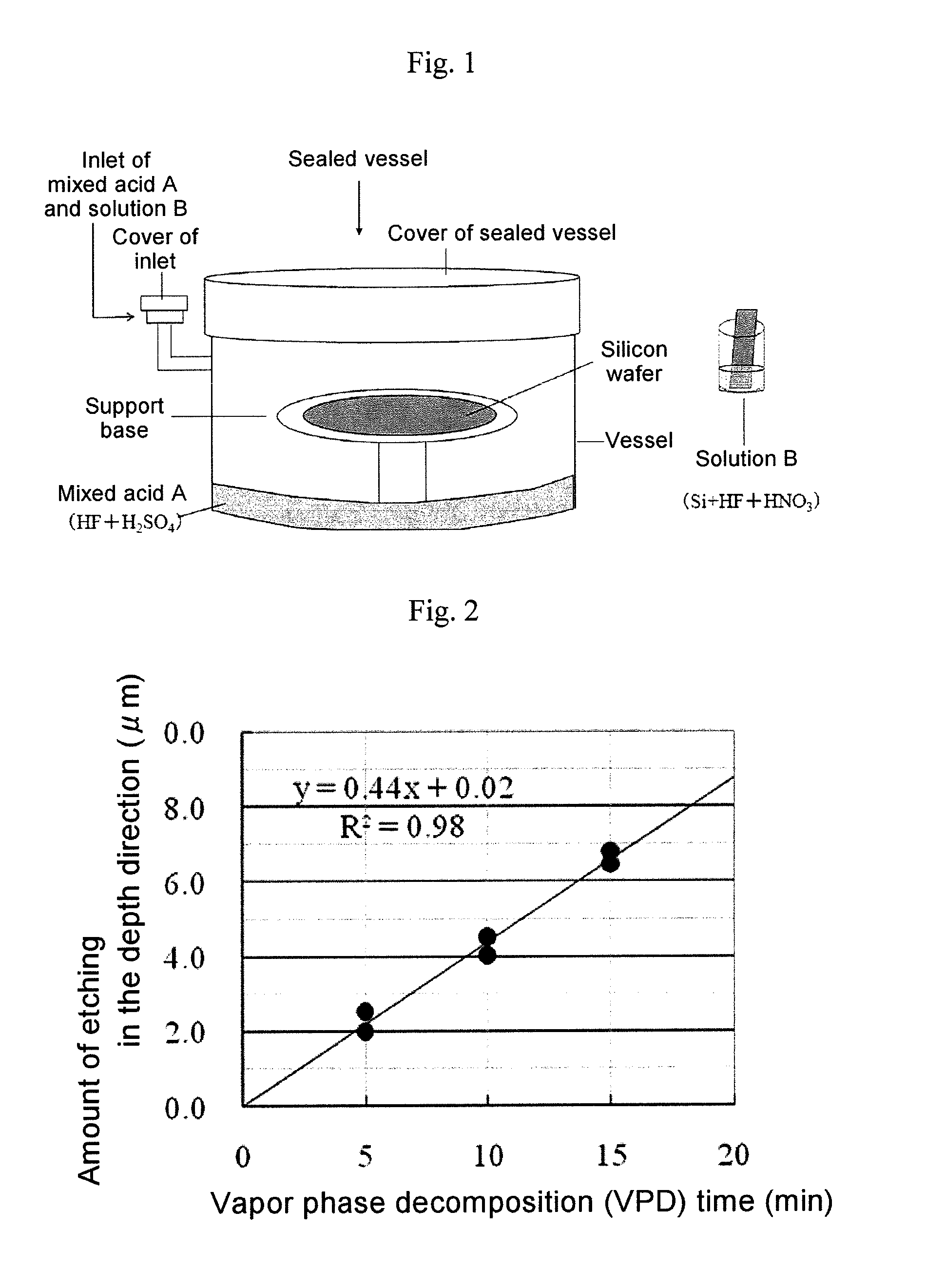
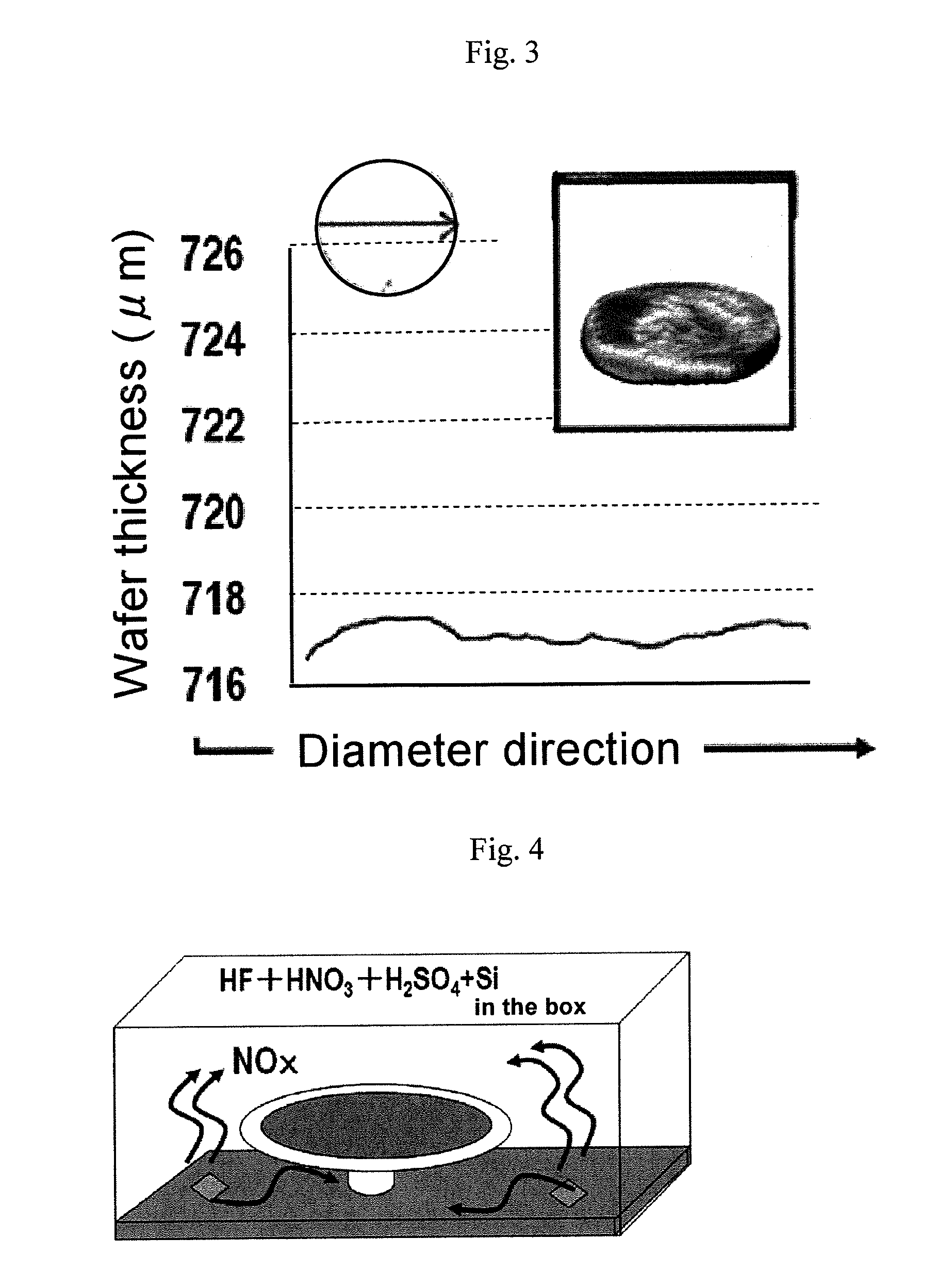
Method of etching surface layer portion of silicon wafer and method of analyzing metal contamination of silicon wafer
ActiveUS20120077290A1Rapidly and uniformly etchRate of reactionSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationMetal contaminationVapor phase
An aspect of the present invention relates to a method of etching a surface layer portion of a silicon wafer comprising: positioning the silicon wafer within a sealed vessel containing a mixed acid A of hydrofluoric acid and sulfuric acid so that the silicon wafer is not in contact with mixed acid A; introducing a solution B in the form of nitric acid containing nitrogen oxides into the sealed vessel and causing solution B to mix with mixed acid A; and vapor phase decomposing the surface layer portion of the silicon wafer within the sealed vessel within which mixed acid A and solution B have been mixed.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Bioreactive allosteric polynucleotides
InactiveUS20050176017A1Enhance and inhibit catalytic rateMaximally inhibitedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical effectsSteroid Compound
Owner:YALE UNIV
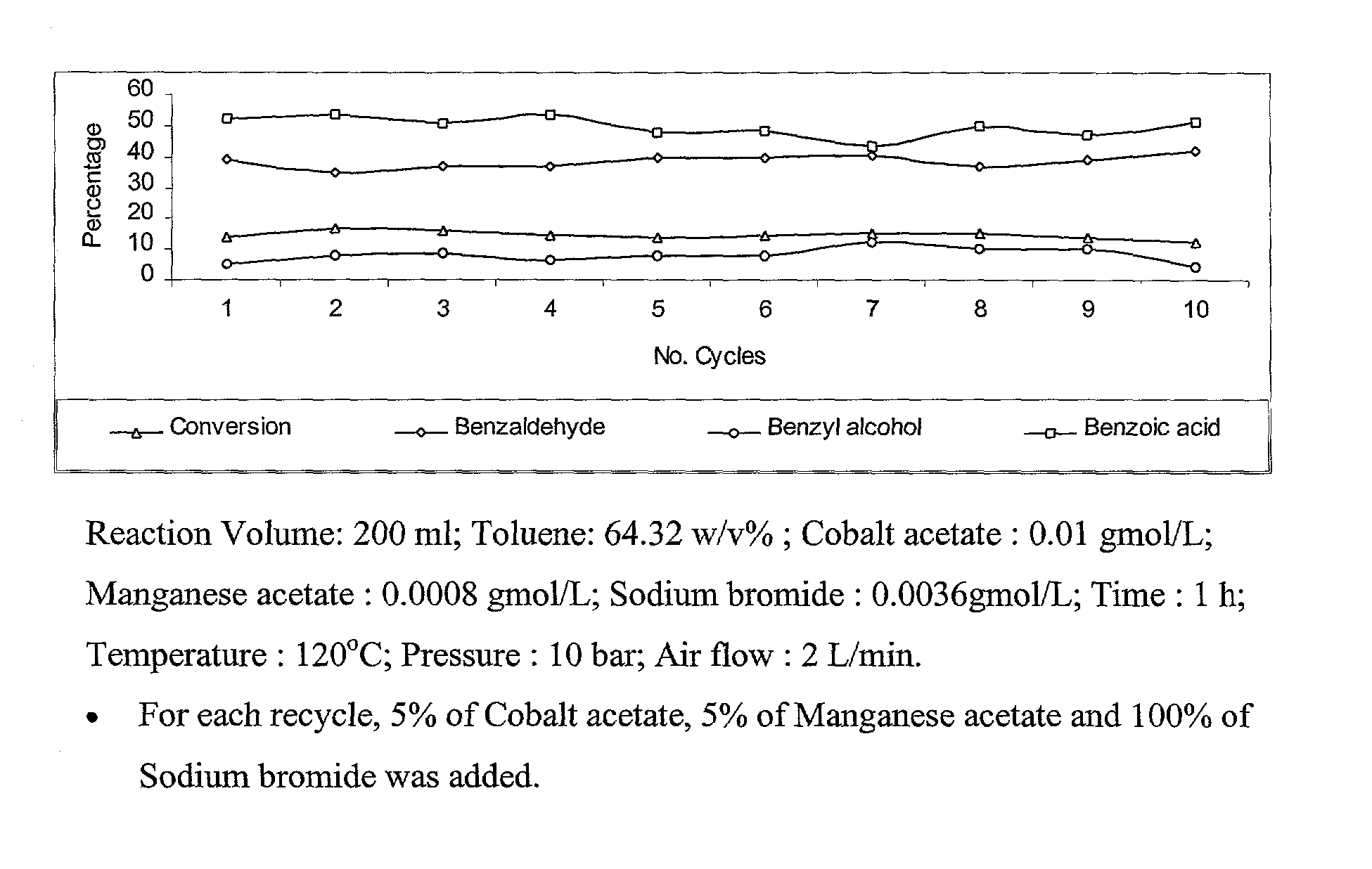
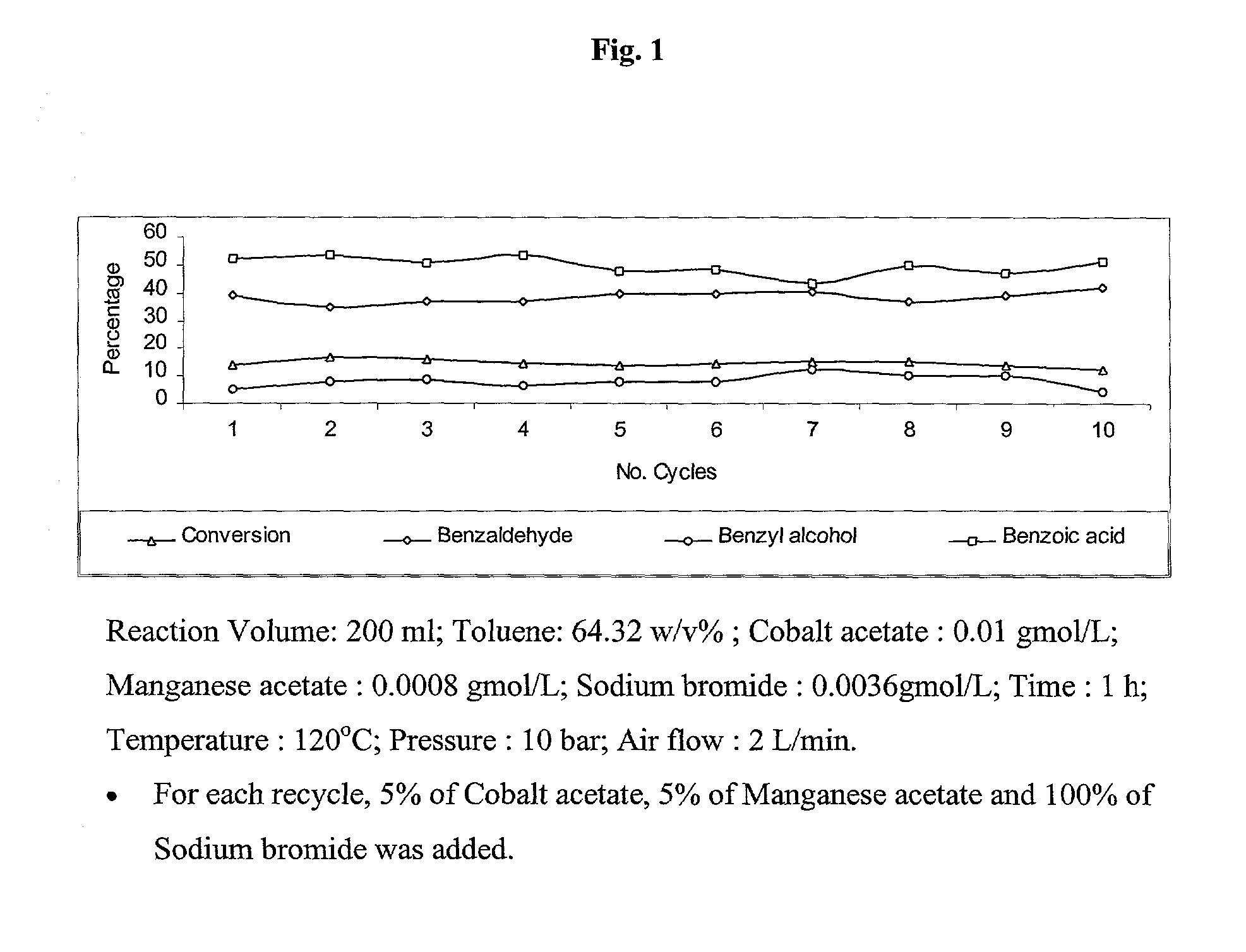
Selective liquid phase air oxidation of toluene catalysed by composite catalytic system
InactiveUS20030187304A1High selectivityMinimise the loss of expensive brominePreparation by oxidation reactionsOrganic compound preparationRecyclable catalystZinc bromide
The present invention provides an improved process for the production of benzaldehyde with 40-50% selectivity by the catalytic liquid phase air oxidation of toluene using a composite catalytic system comprising salts of iron, cobalt, manganese, molybdenum or nickel as recyclable catalyst, salts of manganese or copper as recyclable co-catalyst and cobalt bromide, sodium bromide, sodium chloride and zinc bromide as promoter.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
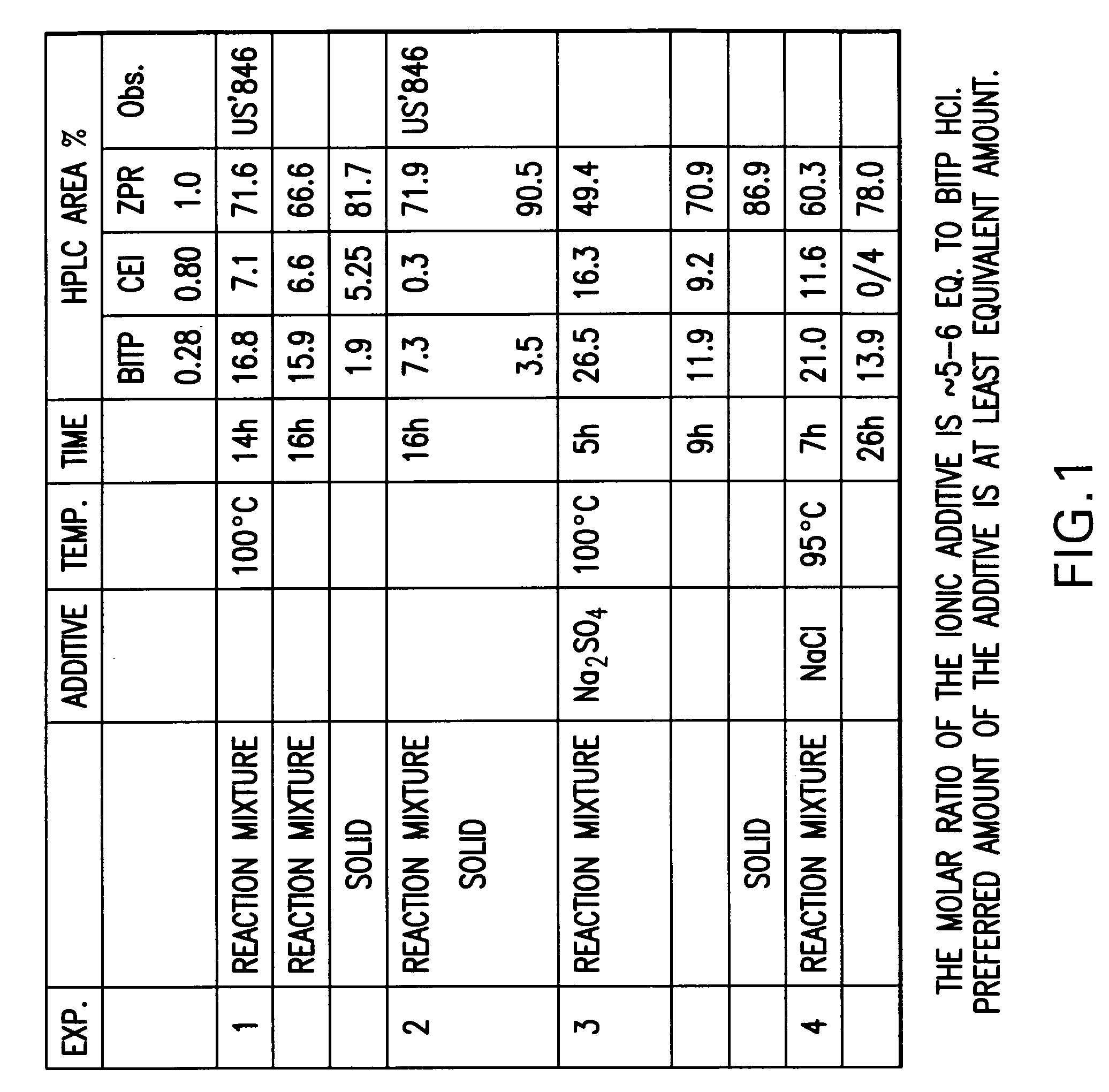
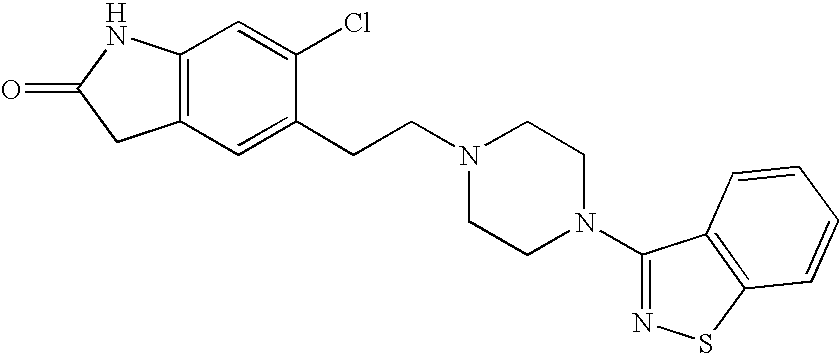
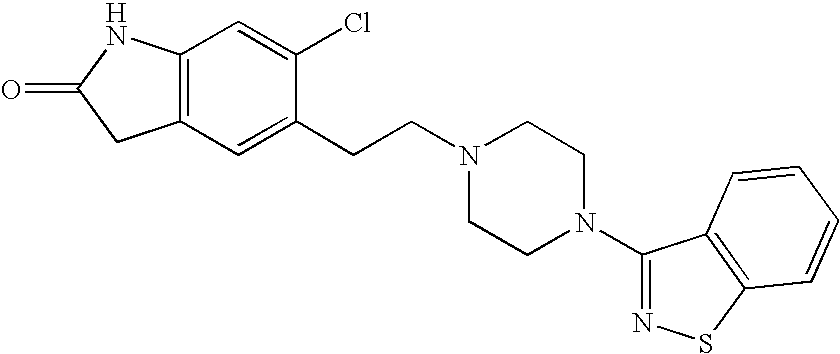
Processes for preparation of ziprasidone
InactiveUS20050143397A1Improve reaction speedImproved purity profileBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCombinatorial chemistryZiprasidone
Owner:TEVA PHARM USA INC
Methods for producing hydrocarbon products and hydrogen gas through electrochemical activation of methane, and related systems and electrochemical cells
ActiveUS20190177861A1Improve reaction speedRate of reactionCellsNoble metal coatingsHydrogenPotential difference
A method of forming a hydrocarbon product and hydrogen gas comprises introducing CH4 to a positive electrode of an electrochemical cell comprising the positive electrode, a negative electrode, and a proton-conducting membrane between the positive electrode and the negative electrode. The proton-conducting membrane comprises an electrolyte material having an ionic conductivity greater than or equal to about 10−2 S / cm at one or more temperatures within a range of from about 150° C. to about 600° C. A potential difference is applied between the positive electrode and the negative electrode of the electrochemical cell to produce the hydrocarbon product and the hydrogen gas. A CH4 activation system and an electrochemical cell are also described.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Thermal Barrier Coating and An Ultra-High-Temperature Cold-Wall Suspension Bed Hydrogenation Reactor Comprising the Same
ActiveUS20180085729A1Easily damagedIncrease productionFilm/foil adhesivesInorganic adhesivesStress concentrationHydrogen
A thermal barrier coating and a cold-wall reactor including the coating are provided. A second ceramic layer is sandwiched between the conventional two-layer structures of the thermal barrier coating. The second ceramic layer is made of aluminum oxide stabilized zirconium oxide and the content of aluminum oxide does not exceed 30 wt %. The zirconium oxide in the first and second ceramic layer has a tetragonal crystal structure. A cold-wall reactor formed by applying the thermal barrier coating provides advantageous steel hydrogen corrosion resistance in ultra-high temperature. The effective volume of the hydrogenation reactor is fully used, overcoming the problem that the thermal insulation liner is easily damaged and causes local overheating of the reactor wall, as well as eliminating potential safety hazards of reactor wall local stress concentration caused by expansion and contraction of the liner cylinder attachment member.
Owner:BEIJING HUASHI UNITED ENERGY TECH & DEV
Process for preparation of cyclododecanone
InactiveUS6861563B2Improve efficiencyIncrease response rateOrganic compound preparationPreparation from heterocyclic compoundsIsomerizationDodecane
In the process for producing a cyclododecanone by isomerizing an epoxycyclododecane-containing starting material in the presence of an isomerization reaction catalyst containing lithium bromide and / or lithium iodide, in order to perform the reaction with high efficiency (high reaction rate) and high selectivity and stably produce a high-purity cyclododecanone in industry while maintaining a high-level reaction rate, the epoxycyclododecane-containing starting material is produced by contacting an epoxycyclododecadiene with hydrogen in the presence of a hydrogen-reduction catalyst and has a content of the hydroxyl group-containing cyclododecane compounds contained in the epoxycyclododecane-containing starting material controlled to 5 mol % or less.
Owner:UBE IND LTD +1
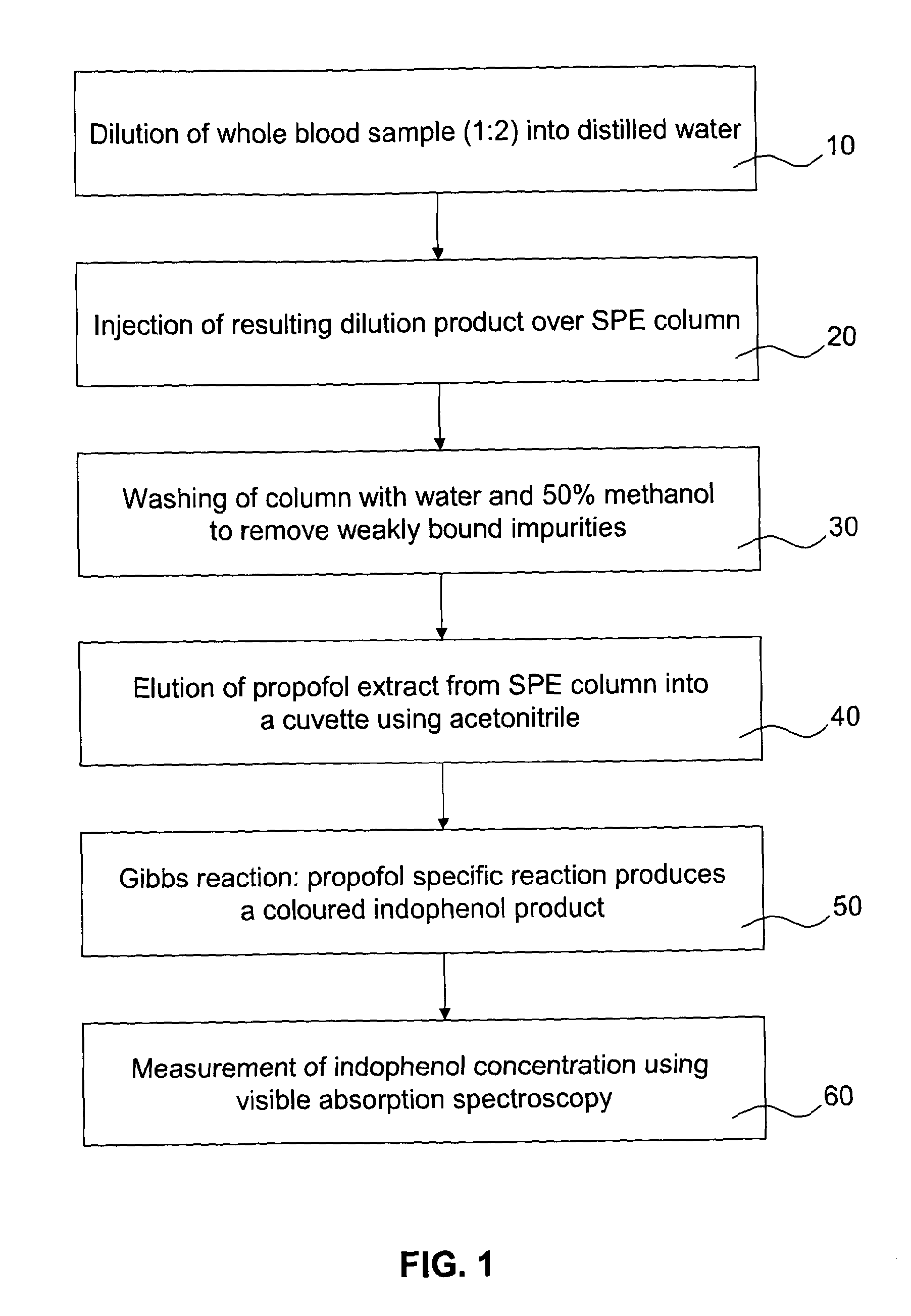
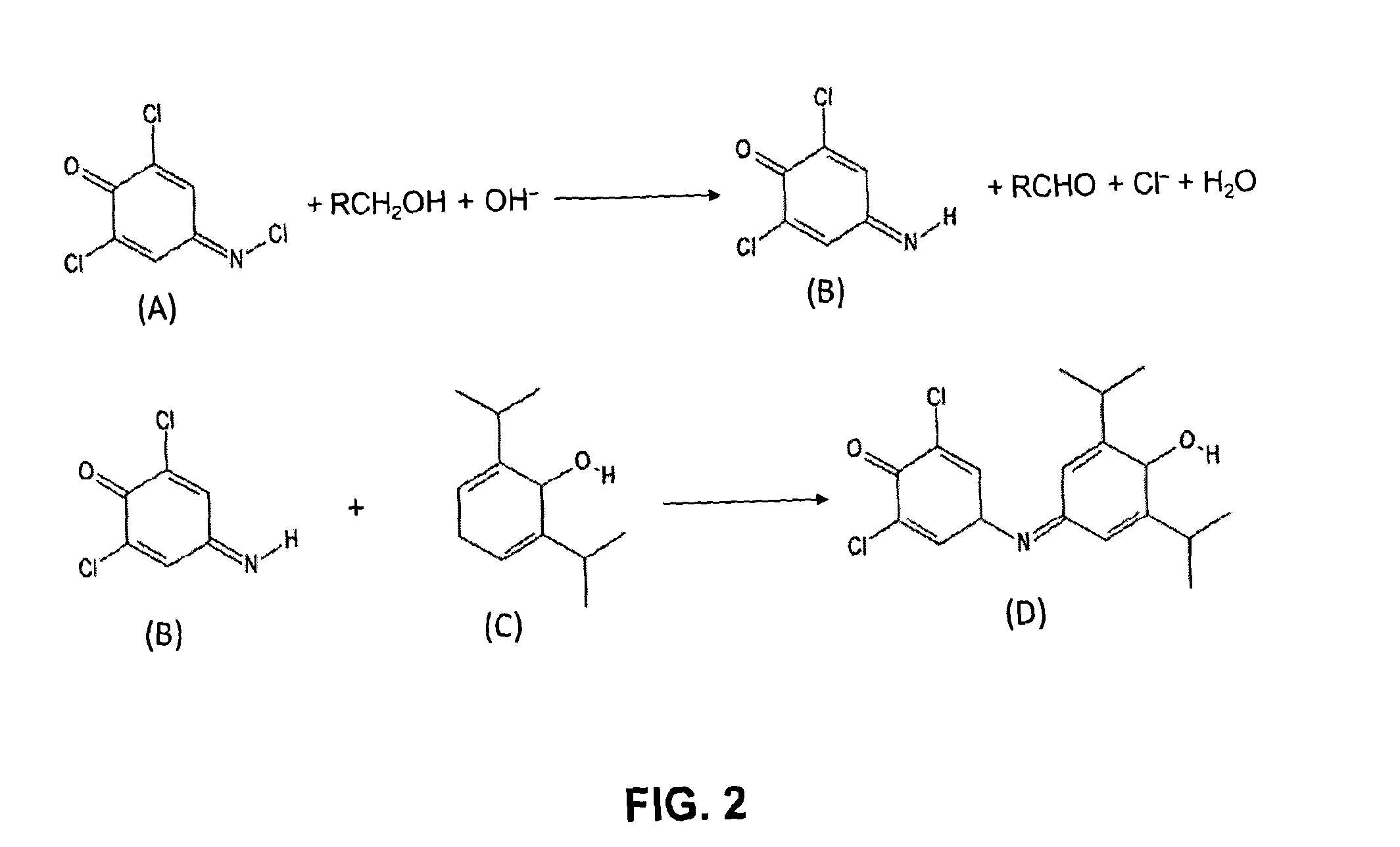
Analyte detection method
ActiveUS20130302781A1Improving limit of detection and concentration measurementReduce rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingTarget analysisGibbs Reagent
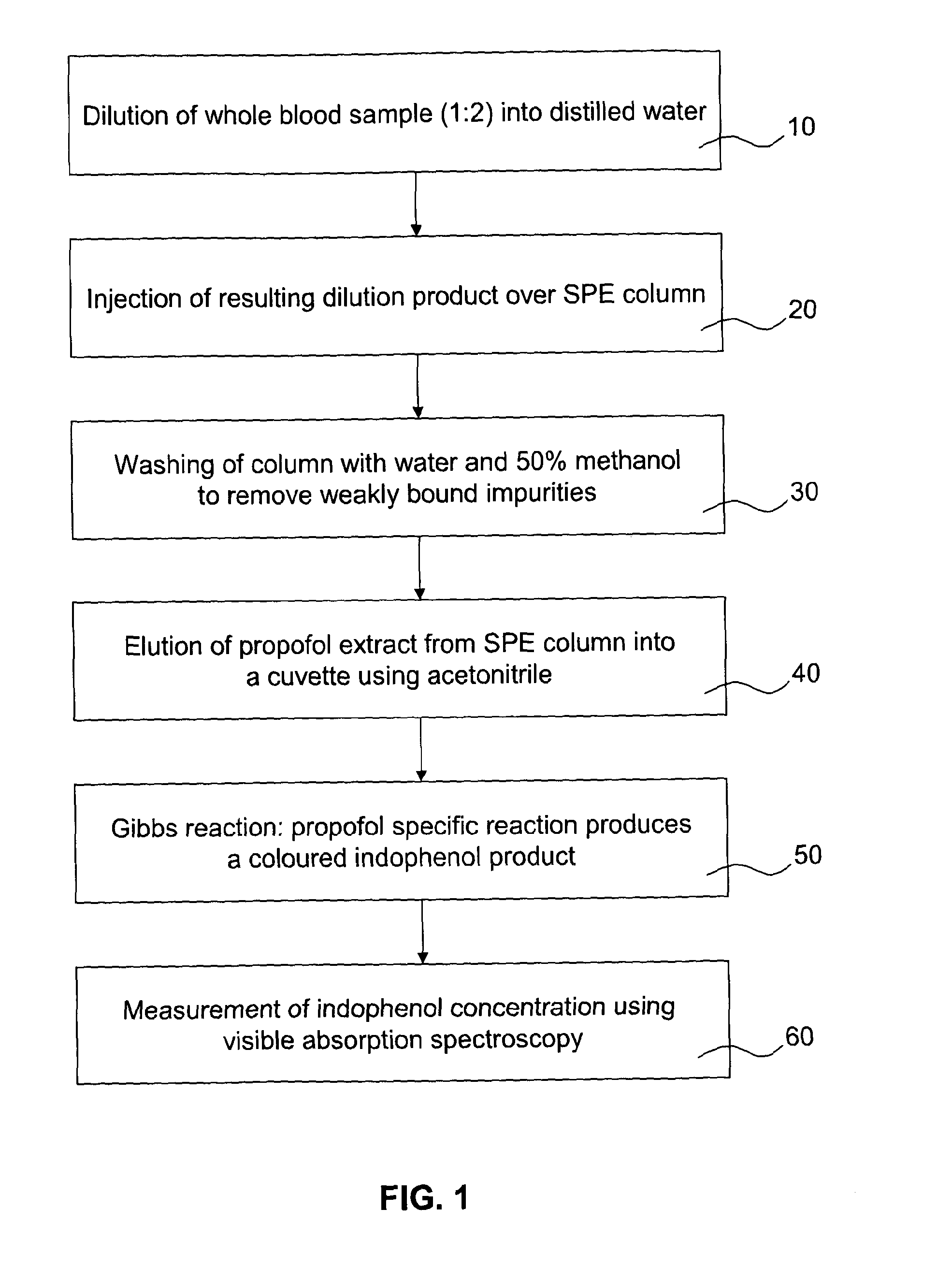
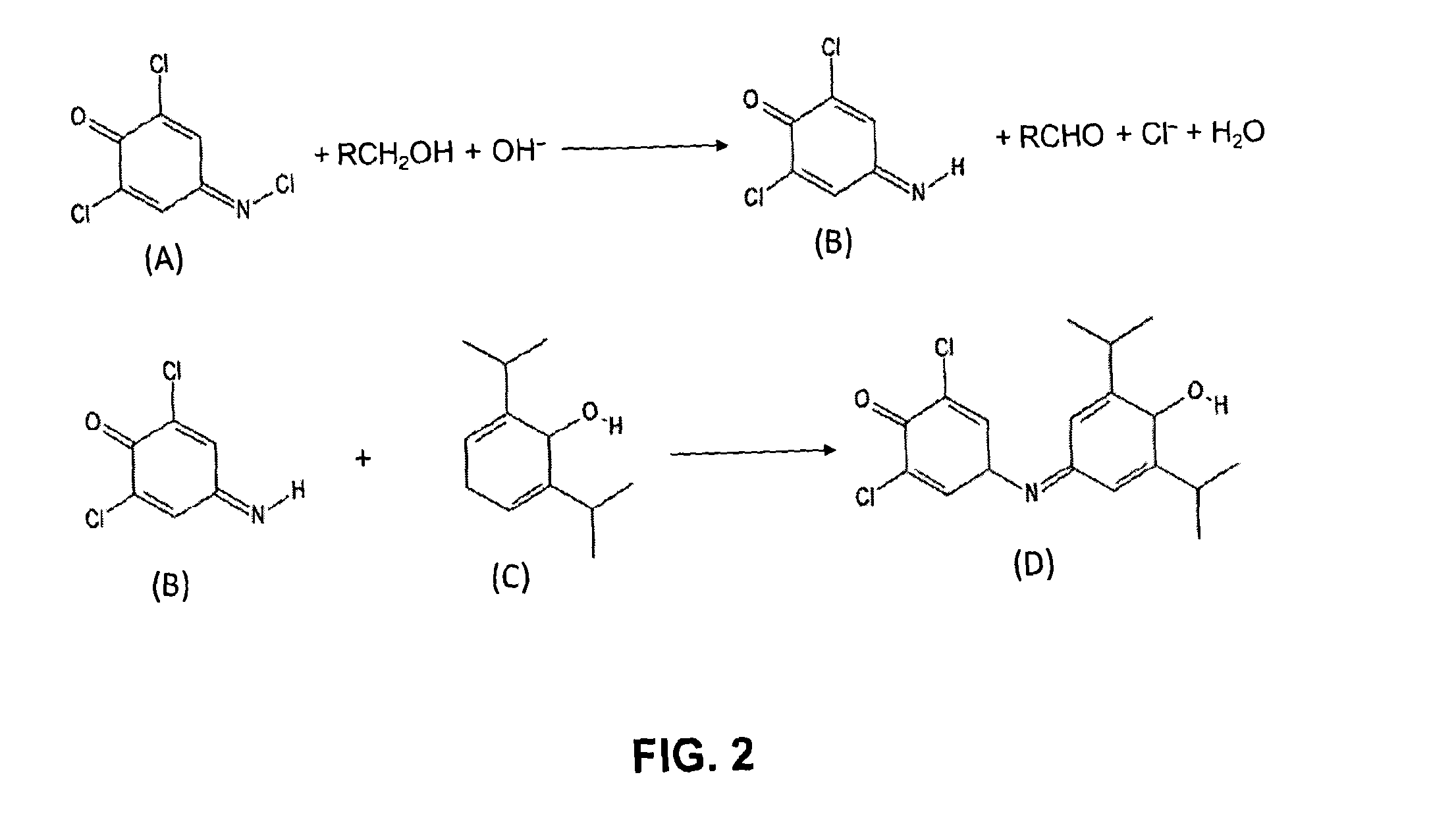
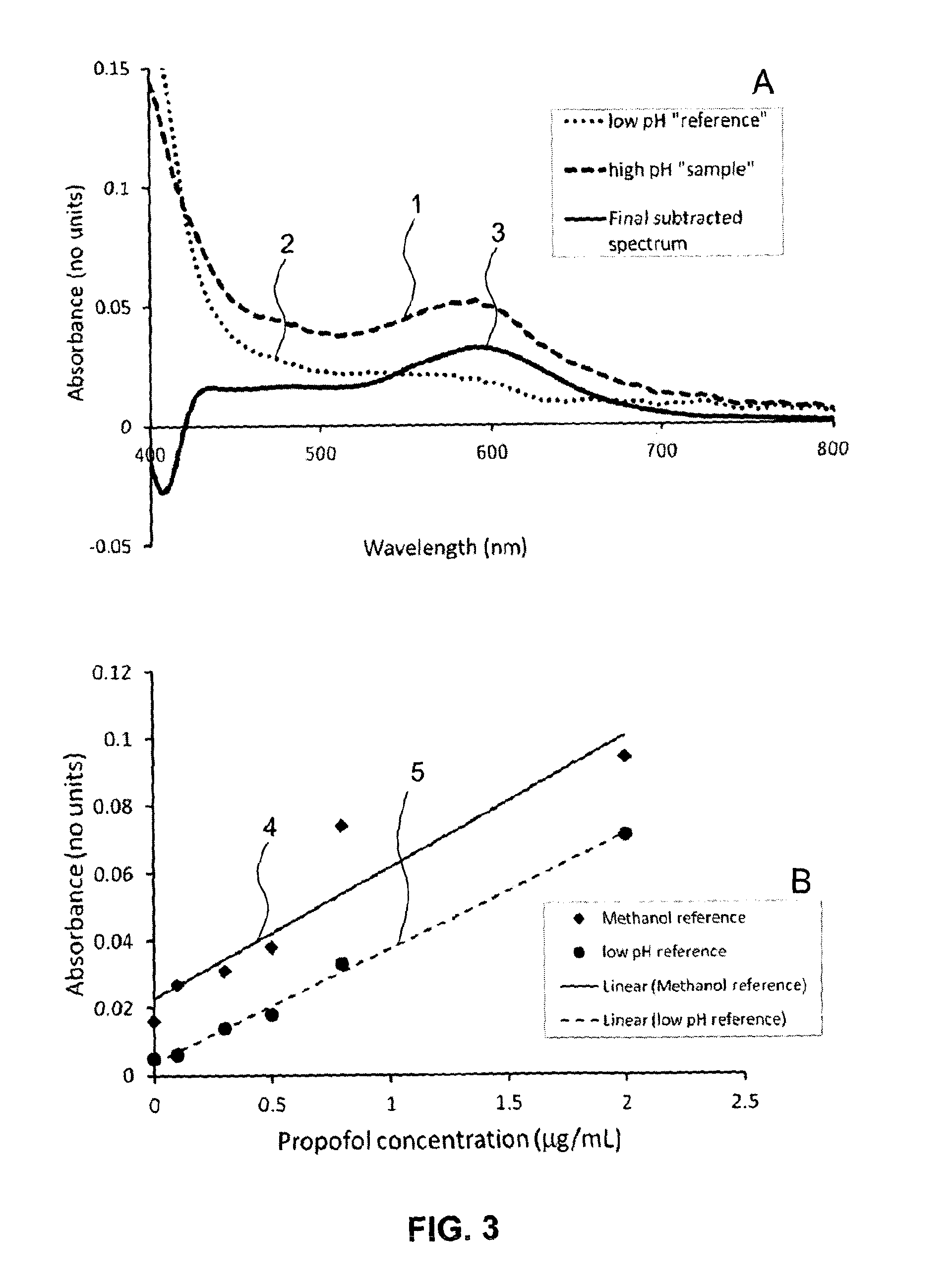
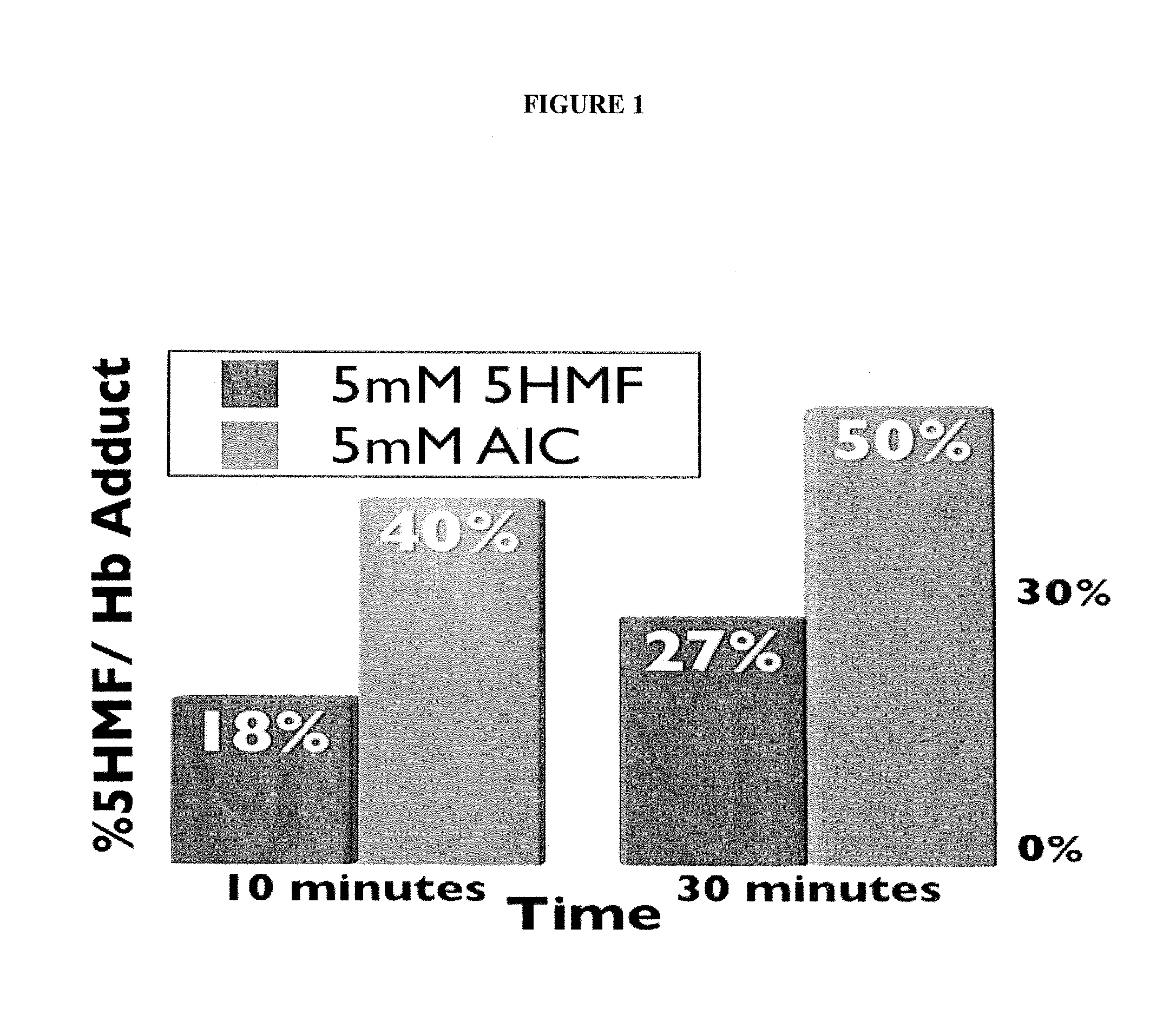
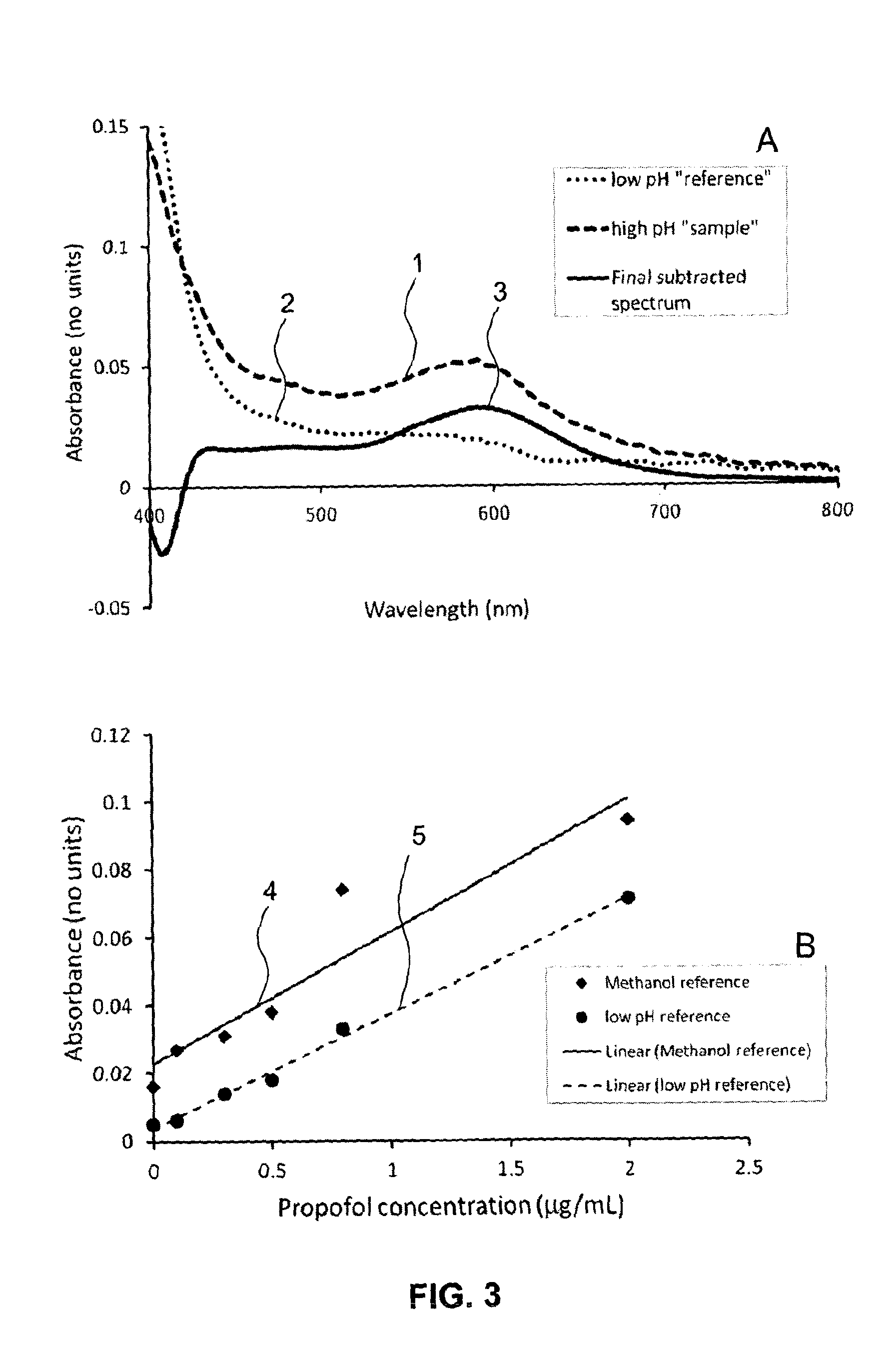
Disclosed is a method of determining the presence of an analyte of interest by means of a detection of a reaction product between the analyte of interest and a reactant, the method comprising extracting the analyte of interest from a complex sample matrix; transferring the analyte of interest to an initial reaction mixture; performing a background measurement on the initial reaction mixture comprising at most a negligible concentration of the reaction product, wherein the reaction conditions present in said initial reaction mixture at least reduce the reaction rate of the formation of the reaction product such that the background measurement can be performed without a measurable change in said negligible concentration; altering the reaction conditions in the initial reaction mixture to accelerate said reaction rate; continuing said reaction until the concentration of the reaction product has stabilized; performing a second measurement on the resultant reaction mixture to obtain a signal correlated to said concentration; and determining the presence of the analyte of interest from a difference between the background measurement and the second measurement. In a preferred embodiment, the analyte of interest is Propofol (2,6-di-isopropylphenol), and the reactant is the activated Gibbs reagent (2,6-dichloroquinoneimine).
Owner:SPHERE MEDICAL
Synthesis, composition and use of novel therapeutic and cosmetic Schiff base products formed by reaction of a carbonyl containing moeity with a transimination nucleophilic catalyst and the use of transimination nucleophilic catalysts to increase the rate at which carbonyl containing therapeutic and cosmetic actives form Schiff base products with biological amines
The present invention relates to the synthesis, composition and use of novel moieties formed by reacting a transimination nucleophilic catalyst, molecular or polymeric, with carbonyl-containing therapeutic or cosmetic moieties. The resultant Schiff base product is highly reactive towards transimination with a biological amine. The catalyst and carbonyl-containing moiety can be molecular or polymeric, and the resultant chemical and physical properties of the Schiff base products can be engineered by appropriate selection of said catalyst. The present invention also relates to the synthesis, composition and use of novel moieties that are used as actives in sunless tanning preparations. The present invention also relates to the use of transimination nucleophilic catalysts to increase the rate at which a carbonyl-containing moiety reacts with a biological amine. The present invention also relates to the use of transimination nucleophilic catalysts to increase the rate and efficacy of commercial sunless tanning preparations. Improvements on stability and efficacy of said preparations are disclosed. While the invention has been described in terms of its preferred embodiments, those skilled in the art will recognize that the invention can be practiced with modification within the spirit and scope of the appended claims. Accordingly, the present invention should not be limited to the embodiments as described above, but should further include all modifications and equivalents thereof within the spirit and scope of the description provided herein.
Owner:NANOMETICS
Processes for preparation of ziprasidone
InactiveUS7667037B2Rate of reactionImproved profileOrganic active ingredientsBiocideMedicinal chemistryZiprasidone
Owner:TEVA PHARM USA INC
Organotin compounds, preparation method thereof, and preparation of polylactide resin using the same
InactiveUS20150005470A1Rate of reactionIncrease polymerization rateTin organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsChemistryCarbon atom
The present invention relates to an organotin compound represented by R1O—Sn—OR2 (where R1 and R2 are independently a primary, secondary, or tertiary alkyl group having 5 to 30 carbon atoms), a preparation method thereof, and a preparation method for polylactide using the organotin compound. The organotin compound of the present invention is easy to prepare and is used to prepare a polylactide resin having a high molecular weight at a high yield without using a separate initiator.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Methods and systems for co-producing hydrocarbon products and ammonia, and related electrochemical cells
ActiveUS20200039896A1Improve reaction speedRate of reactionCellsNon-noble metal oxide coatingsHydrocotyle bowlesioidesPotential difference
A method of a hydrocarbon product and ammonia comprises introducing C2H6 to a positive electrode of an electrochemical cell comprising the positive electrode, a negative electrode, and a proton-conducting membrane between the positive electrode and the negative electrode. The proton-conducting membrane comprising an electrolyte material having an ionic conductivity greater than or equal to about 10−2 S / cm at one or more temperatures within a range of from about 150° C. to about 600° C. N2 is introduced to the negative electrode of the electrochemical cell. A potential difference is applied between the positive electrode and the negative electrode of the electrochemical cell. A system for co-producing higher hydrocarbons and NH3, and an electrochemical cell are also described.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
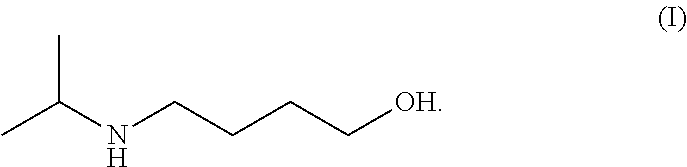
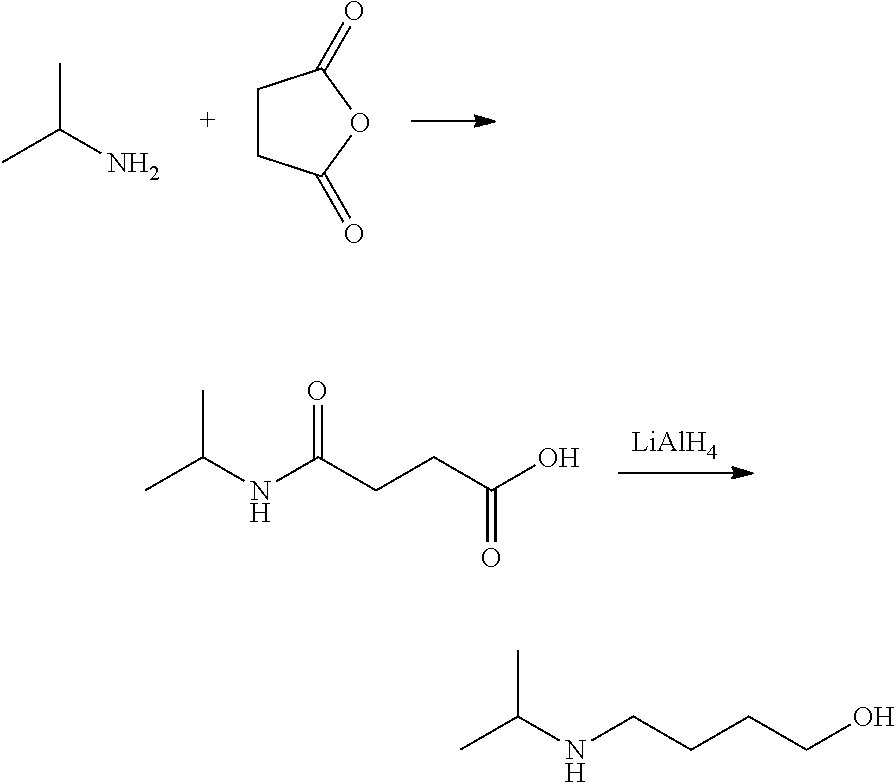
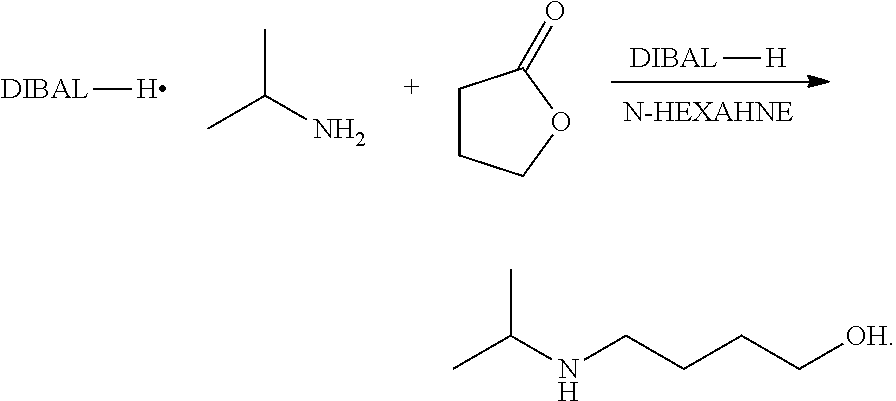
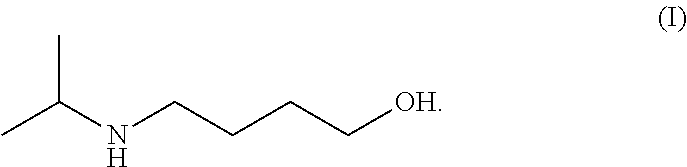
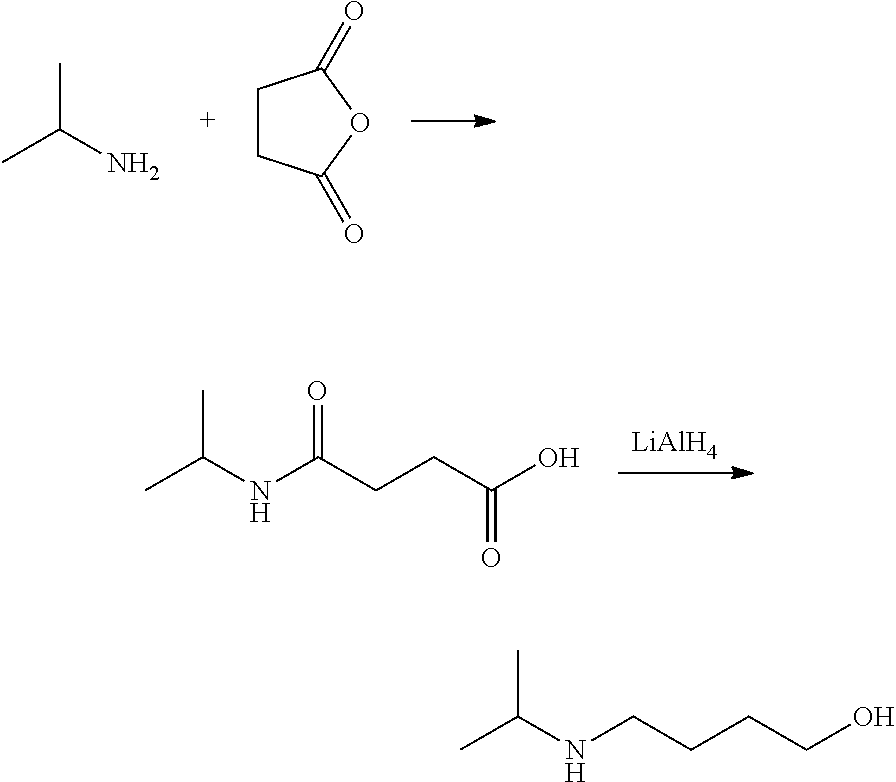
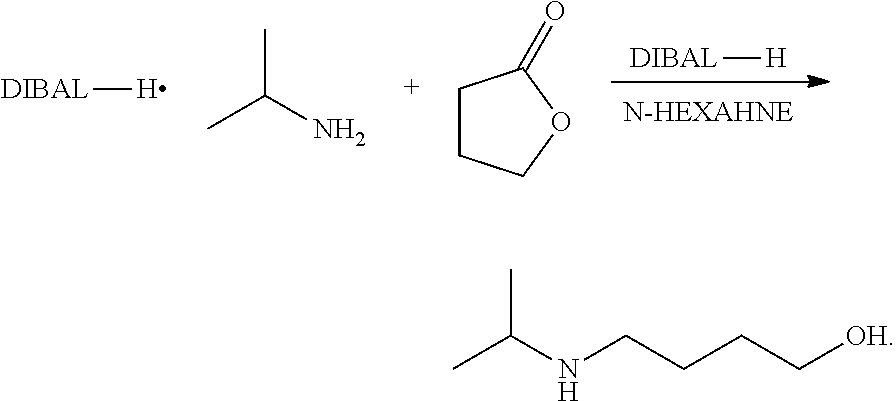
Method for preparing 4-isopropylamino-1-butanol
ActiveUS10144701B2Low costQuality improvementOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationN-ButanolAcetic acid solution
Owner:SEASONS BIOTECHNOLOGY (TAIZHOU) CO LTD
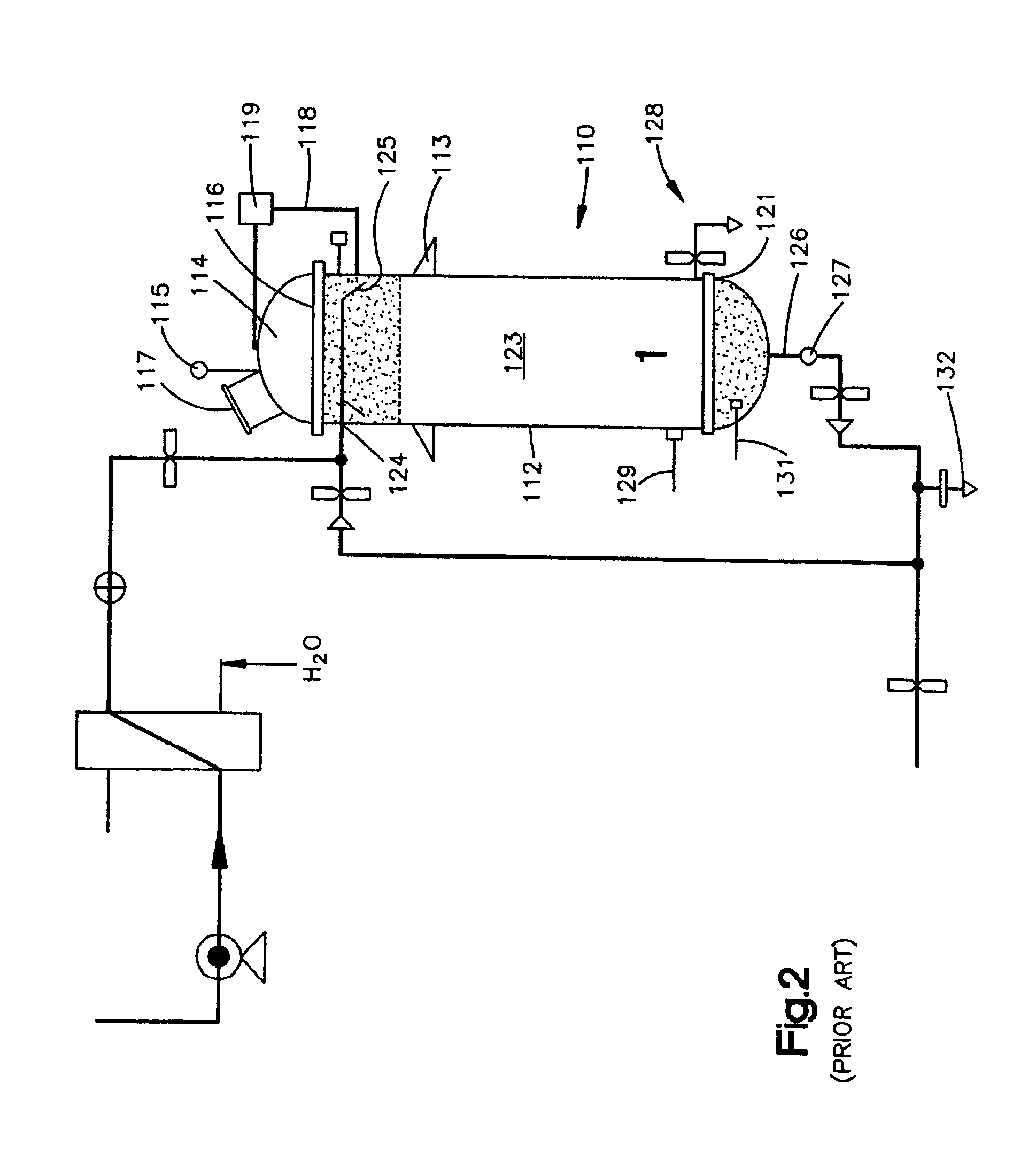
Continuous process and apparatus for enzymatic treatment of lipids
ActiveUS20090317902A1Constant flowLess operator monitoringBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLipid formationProcedure Agents
A method and system for the enzymatic treatment of a lipid containing feedstock comprises contacting the feedstock with a processing aid, then causing the feedstock to pass at a substantially constant flow rate through a treatment system comprising a plurality of enzyme-containing fixed bed reactors connected to one another in series. The fixed bed reactors can be individually serviceable, the flow rate of the feedstock remaining substantially constant through the system when one of the fixed bed reactors is taken offline for servicing. In the most preferred embodiment, the processing aid is a substantially moisture-free silica. The processing aid can be placed in one or more of the fixed bed reactors, disposed above the enzyme in the reactor, or it can be in a pre-treatment system which can comprise one or more reactors.
Owner:BUNGE OILS INC
Analyte detection method
ActiveUS9068996B2Improving limit of detection and concentration measurementReduce rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingTarget analysisGibbs Reagent
Owner:SPHERE MEDICAL
Method for preparing 4-isopropylamino-1-butanol
ActiveUS20180029973A1Improve reaction speedHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationN-ButanolAcetic acid solution
The present invention relates to a preparation method of 4-isopropylamino-1-butanol, in which using cheap and readily available tetrahydrofuran and acetic acid solution of hydrogen bromide as starting materials to prepare a novel intermediate of 4-isopropylamino-1-acetoxyl butane and further obtain the target product. The present invention has advantages of convenient process operations, mild reaction conditions, economical and environment-friendly benefits, and suitability for industrial production to obtain the product with high purity and high yield.
Owner:SEASONS BIOTECHNOLOGY (TAIZHOU) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com