Method for flexibly detecting DNA through exonuclease III assisted multiple circulation amplification
An exonuclease and multiple cycle technology, applied in the field of biological analysis, can solve problems such as limited sensitivity, high background noise of a single cycle signal, and achieve high sensitivity, reduced experimental cost, and good specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0055] In one or some specific embodiments of the present disclosure, the preparation method of the single-stranded DNA binding protein-probe 1 complex and / or the single-stranded DNA binding protein-probe 2 complex comprises the following steps: probe 1 and / or probe 2 and single-stranded DNA binding protein (SSB) in 1 × NEB buffer 4 (the buffer solution is: 50 mmol per liter of potassium acetate, 20 mmol per liter of trimethylol at pH 7.9 aminomethane-acetic acid, 10 mmol / L magnesium acetate and 1 mmol / L dithiothreitol), and incubated at 37°C.
[0056] In one or some specific embodiments of the present disclosure, a method for sensitively detecting DNA by exonuclease III-assisted multiple cycle amplification is provided, and the reaction system of the method includes:
[0057] Exonuclease III (Exo III)-assisted signal amplification is performed in a 20 µl reaction containing target DNA, ssDNA-binding protein-probe 1 complex, and ssDNA-binding protein-probe 2 Complex (a total...
Embodiment 1
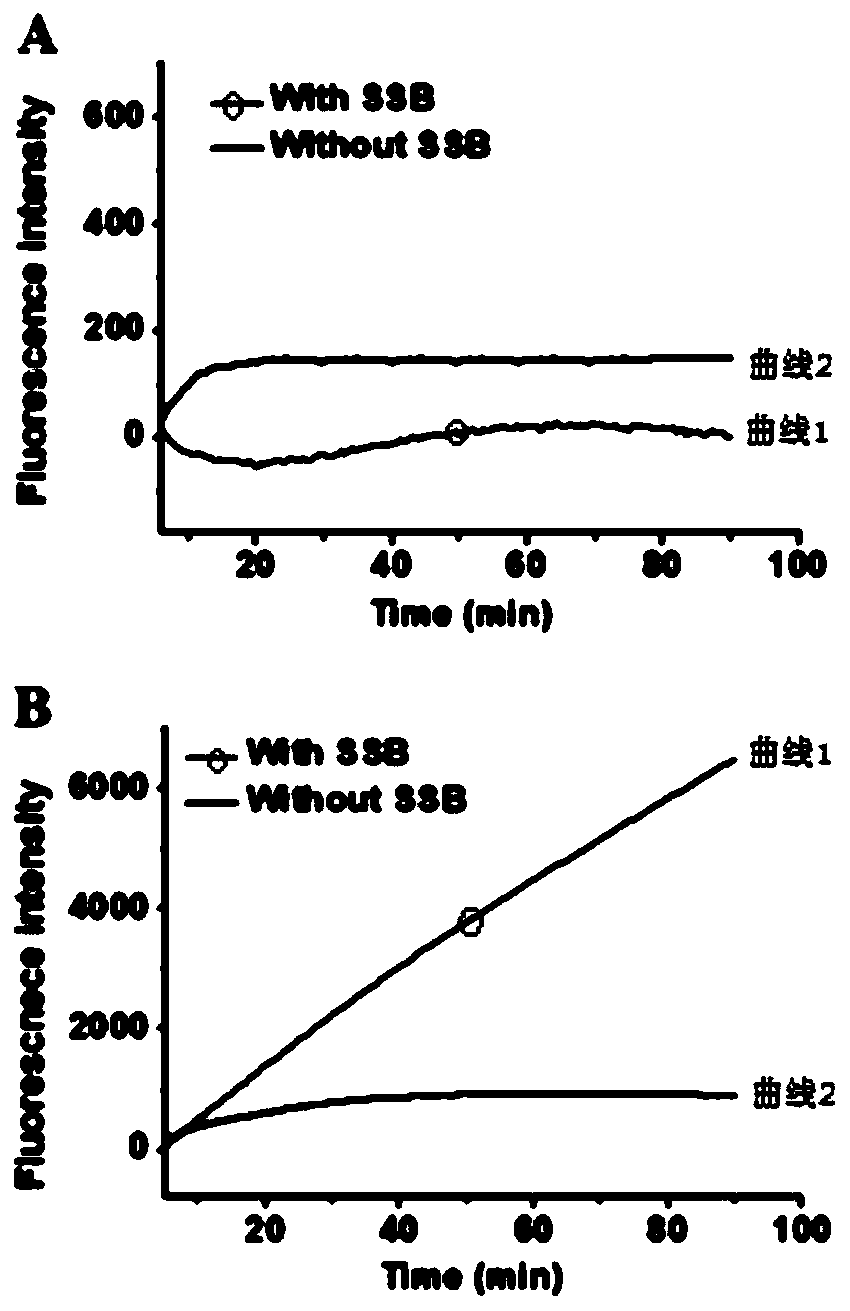
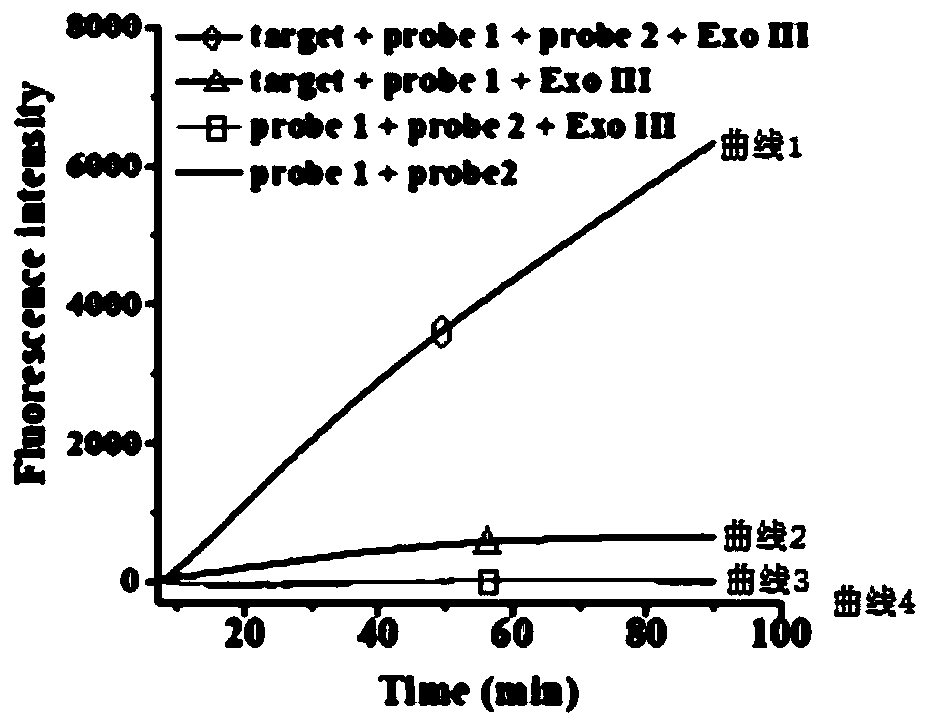
[0081] Fluorescence detection: All oligonucleotides were diluted with 10× Tris-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (Tris-EDTA) buffer to prepare stock solutions. 1 micromole per liter of hairpin probe (including probe 1 and probe 2 in a molar ratio of 1:1) in annealing buffer (5 mmol per liter of tris-hydrochloric acid at pH 8.0 ( Tris-HCl), 50 mmol per liter of NaCl), incubated at 95°C for 5 minutes, then slowly cooled to room temperature, and stored at 4°C for use. To prepare ssDNA-binding protein (SSB)-probe complexes, two different hairpin probes were mixed with ssDNA-binding protein (SSB) in 1×NEB buffer 4 (50 mmol / L potassium acetate, 20 mmol / L tris-acetic acid pH 7.9, 10 mmol / L magnesium acetate, 1 mmol / L dithiothreitol), incubated at 37°C. Exonuclease III (Exo III)-assisted signal amplification was performed in 20 µl reactions containing different concentrations of DNA, two different ssDNA-binding protein-probe complexes (200 nmol total per liter, the molar ratio is 1:1)...
Embodiment 2
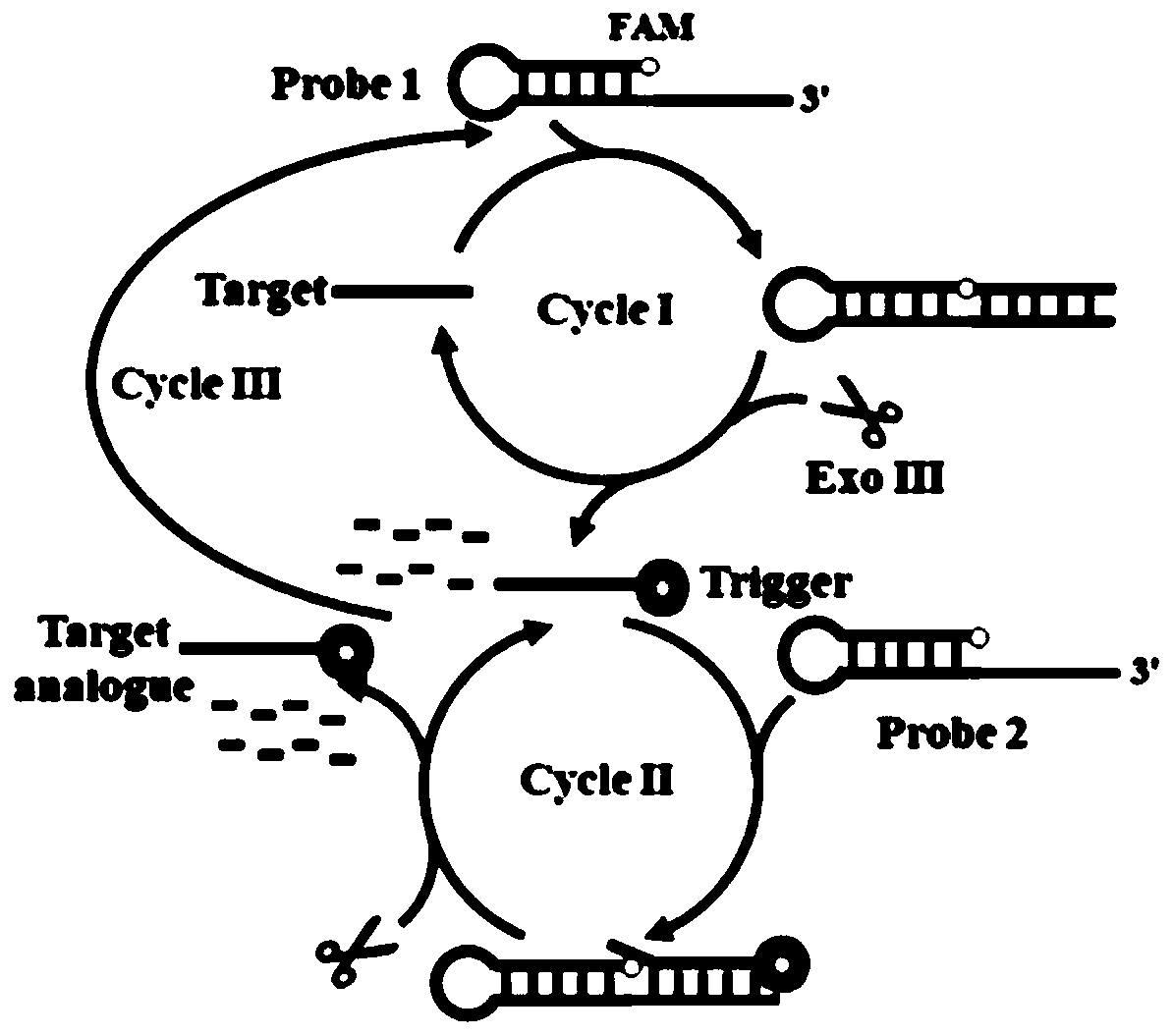
[0083] The principle of the experiment (such as figure 1 ): In this technical scheme, two kinds of hairpin probes (probe 1 and probe 2) with 3′-protruding ends are designed, and the two kinds of probes are modified with the fluorescent group aminofluorescein (FAM) at their 5′-ends. ), the fluorescence of aminofluorescein (FAM) can be efficiently quenched by the consecutive guanine bases opposite it through photoinduced electron transfer (PIET). In the absence of target DNA, since the 3'-protruding end of the probe is resistant to cleavage by Exo III, it cannot be digested by Exo III and detects Very low fluorescence signal. When the target DNA ( figure 1 ), binding to the 3'-overhanging end of probe 1 ( figure 1 ) form a target-probe 1 duplex with a 3'-blunt end that can be recognized and progressively digested by Exonuclease III (Exo III). Thus, the target DNA and trigger primer are released from the duplex. Subsequently, the released target DNA can bind new probe 1 to i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com