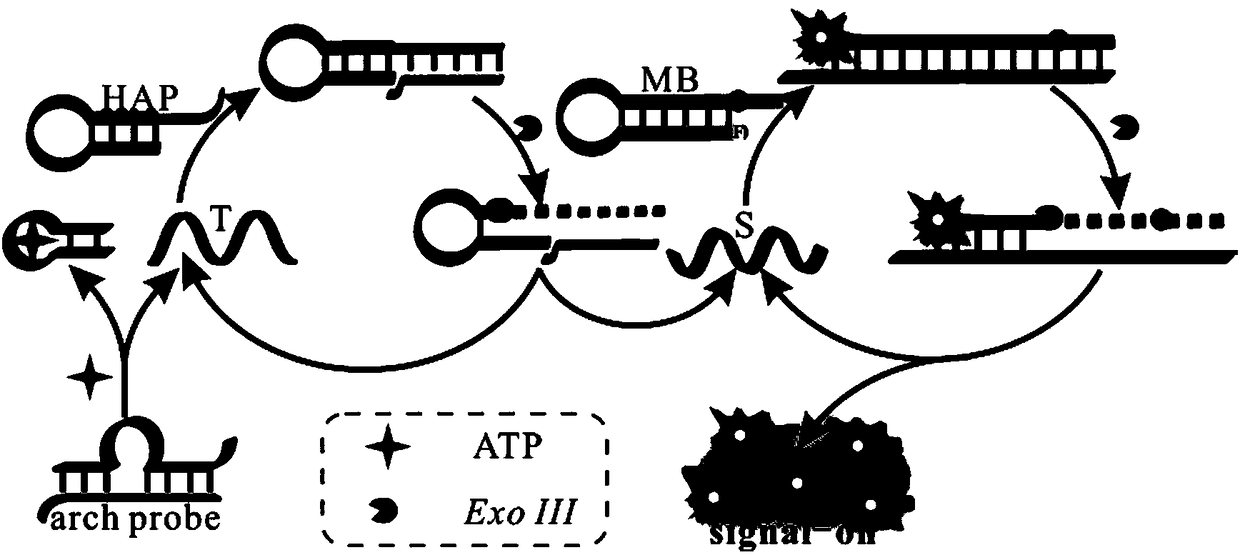
Biosensor for detecting adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
A technology of biosensor and adenosine triphosphate, which is applied in the direction of instruments, measuring devices, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of long detection cycle, low specificity and sensitivity, etc., and achieve the effect of short detection cycle, good specificity and low process cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
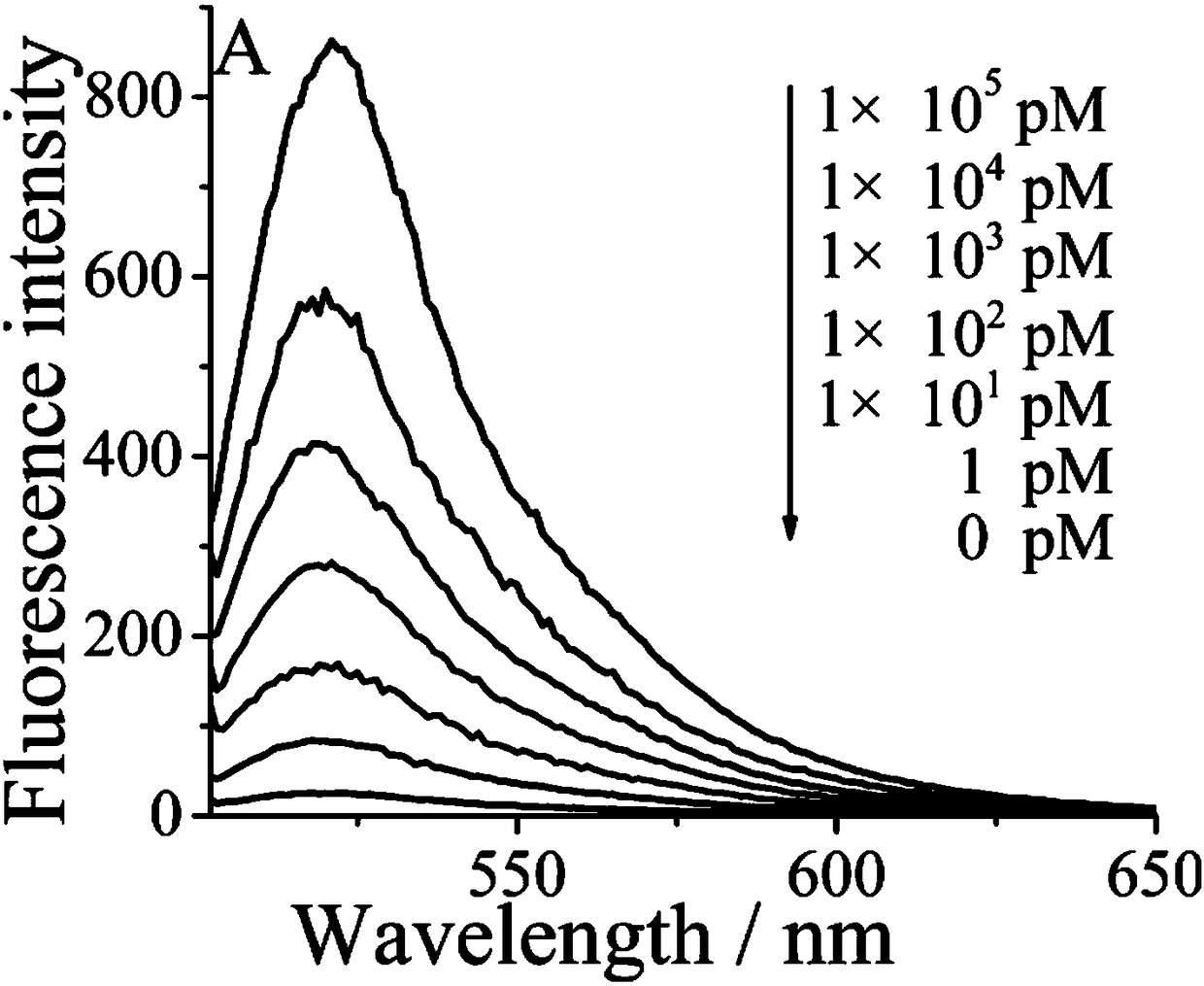
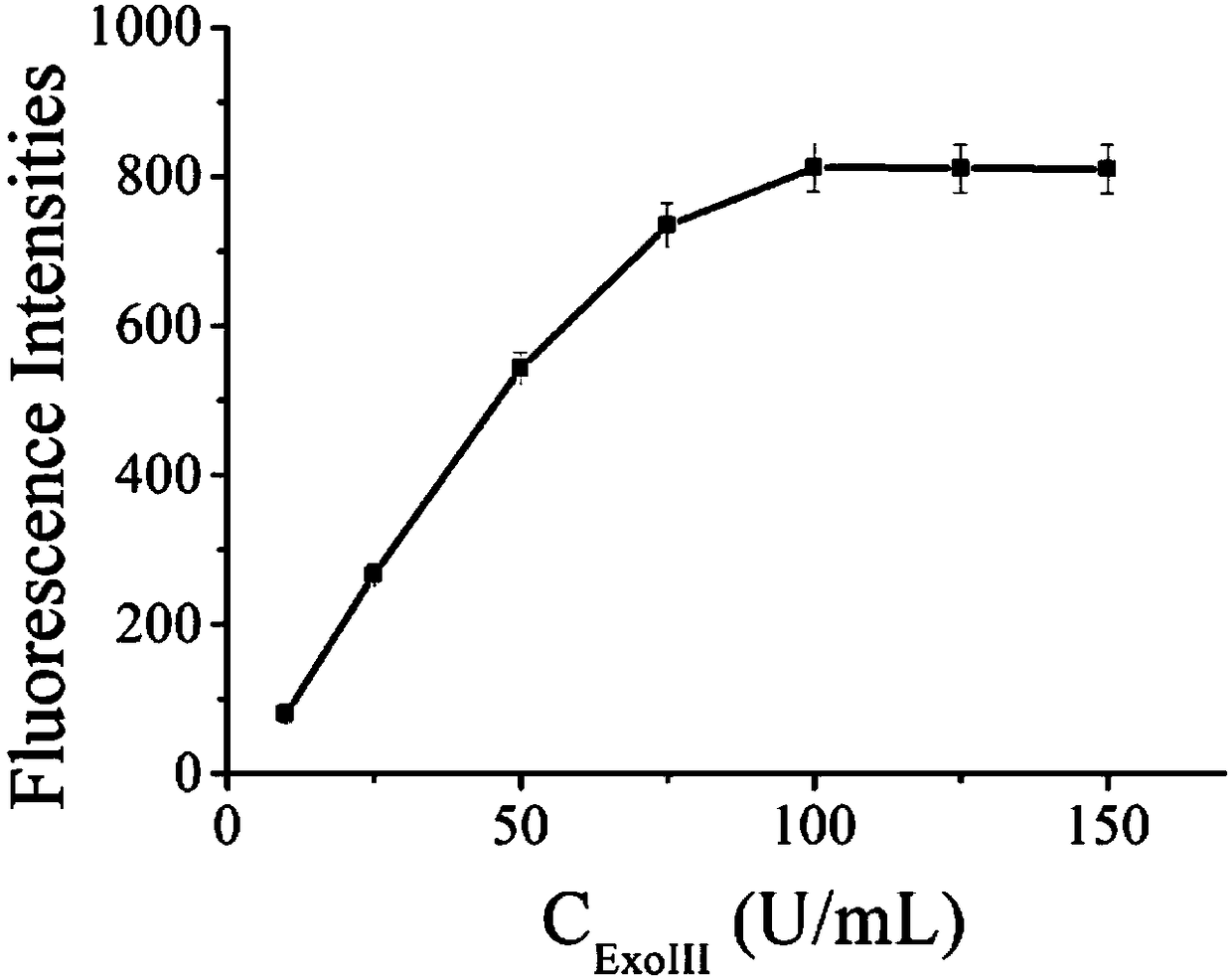
[0035] Example 1 The effect of different concentrations of Exo III on the detection of ATP fluorescence intensity.
[0036] (1) Add 14 μL sterilized water, 2 μL Exo III enzyme buffer, 2 μL 100 μM Aptamer chain and 2 μL 100 μM Trigger chain into the pre-prepared sterilized EP tube; shake for 30s, at 95°C Incubate for 5 minutes, cool slowly to room temperature, and store at -20°C for use.
[0037] (2) Add 6 μL of the solution in step (1) to the EP tube, followed by adding ATP (5 μL, 10 2 nM), HAP (3 μL, 5 μM), MB (6 μL, 10 μM), 3 μL Exo III (10 U / mL, 25 U / mL, 50 U / mL, 75 U / mL, 100 U / mL, respectively mL, 125 U / mL, 150 U / mL), 6 μL ExoIII enzyme buffer and 31 μL sterile water. Shake for 30 s and incubate for 2 h in a 37°C incubator.
[0038] (3) Dilute 60 μL of the solution after the reaction in the previous step to 70 μL, set the excitation wavelength of the fluorometer to 486 nm, the emission wavelength to 518 nm, and the detection range of 500 nm-650 nm to read the changes i...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2 Effects of different concentrations of HAP on detection of ATP fluorescence intensity.
[0041] (1) Add 14 μL sterilized water, 2 μL Exo III enzyme buffer, 2 μL 100 μM Aptamer chain and 2 μL 100 μM Trigger chain into the pre-prepared sterilized EP tube; shake for 30s, at 95°C Incubate for 5 minutes, slowly cool down to room temperature, and store at -20 °C for use;
[0042] (2) Add 6 μL of the solution in step (1) to the EP tube, followed by adding 3 μL of HAP (final concentrations are 1 μM, 2 μM, 3 μM, 4 μM, 5 μM, 6 μM), ATP (5 μL10 2 nM), MB (6 μL, 5 μM), exonuclease III (3 μL, 100U / mL), 6 μL ExoIII enzyme buffer and 31 μL sterilized water. Shake for 30 s and incubate in a 37°C incubator for 2 h;
[0043] (3) Dilute 60 μL of the solution after the reaction in the previous step to 70 μL, set the excitation wavelength of the fluorometer to 486nm, the emission wavelength to 518nm, and the detection range to 500 nm-650 nm, and read the change of the fluoresc...
Embodiment 3
[0045]Example 3 The effect of different concentrations of MB on the detection of ATP fluorescence intensity.
[0046] (1) Add 14 μL sterilized water, 2 μL Exo III enzyme buffer, 2 μL 100 μM Aptamer chain and 2 μL 100 μM Trigger chain into the pre-prepared sterilized EP tube; shake for 30s, at 95°C Incubate for 5 minutes, slowly cool down to room temperature, and store at -20 °C for use;
[0047] (2) Add 6 μL of the solution in step (1) into the EP tube, followed by adding 6 μL of MB (final concentrations are 2 μM, 4 μM, 6 μM, 8 μM, 10 μM, 12 μM), ATP (5 μL10 2 nM), HAP (3 μL, 5 μM), Exo III enzyme (3 μL, 100U / mL), 6 μL ExoIII enzyme buffer and 31 μL sterilized water. Shake for 30s, and incubate for 2 hours in a 37°C incubator;
[0048] (3) Dilute 60 μL of the solution after the reaction in the previous step to 70 μL, set the excitation wavelength of the fluorometer to 486 nm, the emission wavelength to 518 nm, and the detection range of 500 nm-650 nm to read the changes in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com