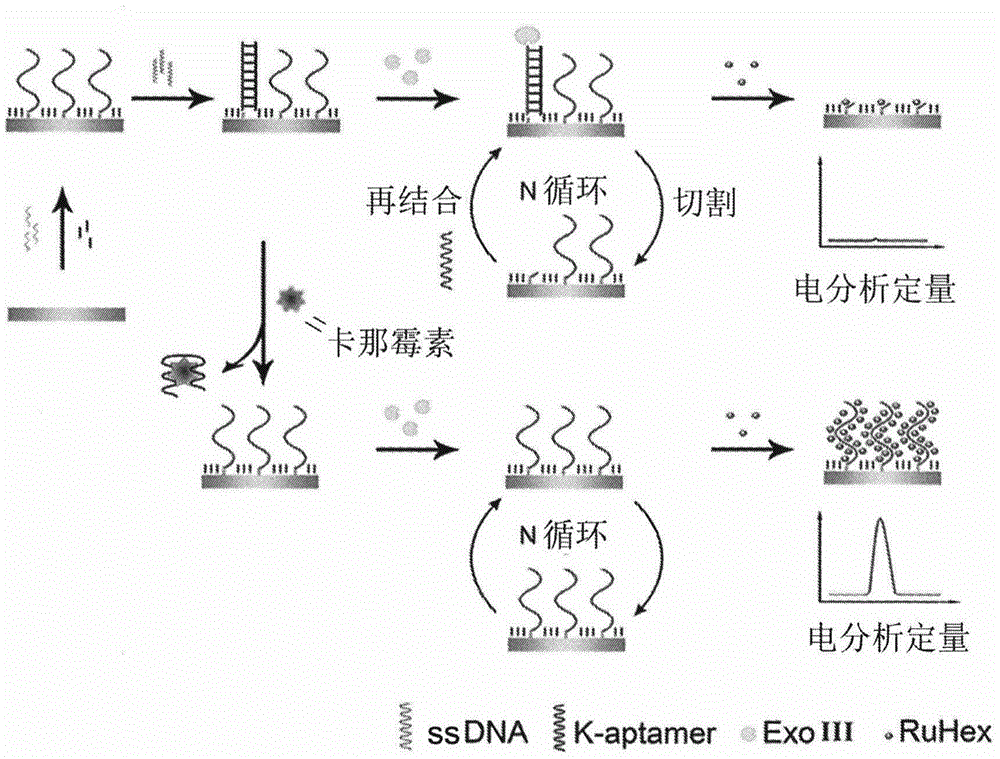
Method for detecting residual kanamycin
A kanamycin and detection method technology, applied in the field of analytical chemistry, can solve problems such as toxicity and ingestion allergy, and achieve the effect of sensitive detection and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
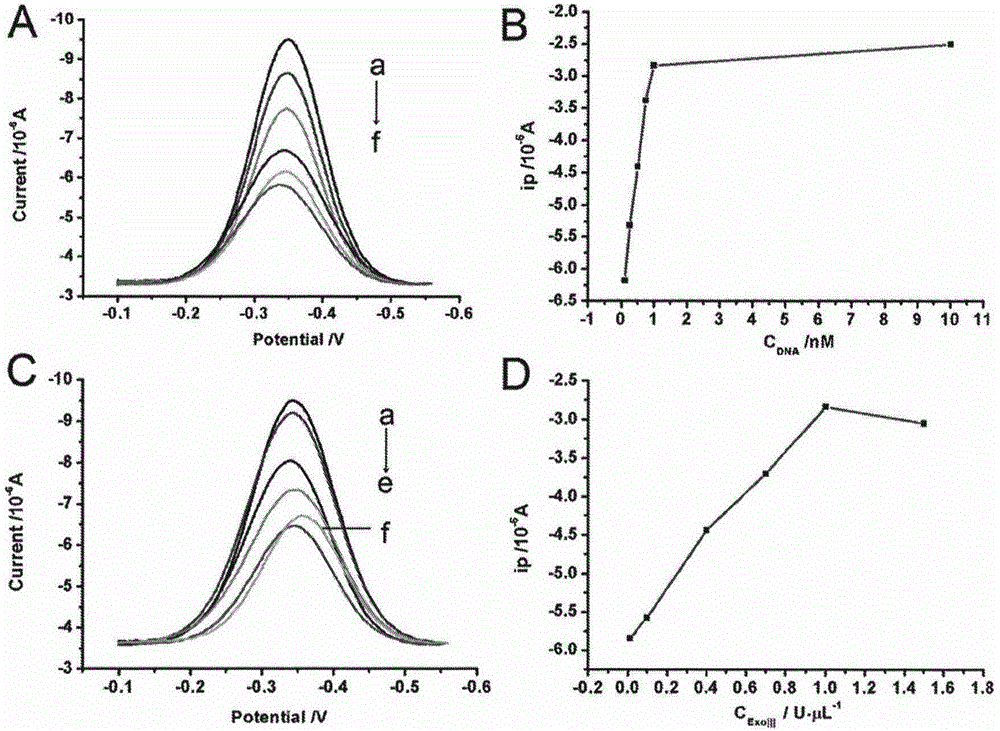
[0028] Example 1. Optimization of detection conditions for kanamycin residues based on aptamer-triggered ExoIII cycle digestion
[0029] In order to detect kanamycin more sensitively, we optimized the detection conditions and studied the influence of K-aptamer concentration and ExoIII concentration on the detection of kanamycin.
[0030] Incubate the ssDNA-modified electrodes obtained in step (2) of the above method with 100 μL of K-aptamer hybridization solutions containing 0.1 nM, 0.25 nM, 0.5 nM, 0.75 nM, 1 nM, and 10 nM, respectively, at 90° C. for 5 minutes, and then slowly cool to room temperature. Then soak it in 50 μL of binding solution and incubate for 10 minutes, then rinse with washing solution. Finally, soak the electrode in 50μL containing 1U·μL -1 ExoIII was reacted in 1×NEB solution at 37°C for 1 hour, washed again with washing solution, and then scanned by square wave voltammetry. The measured scan results are as figure 2 As shown in A and 2B, with the inc...
Embodiment 2
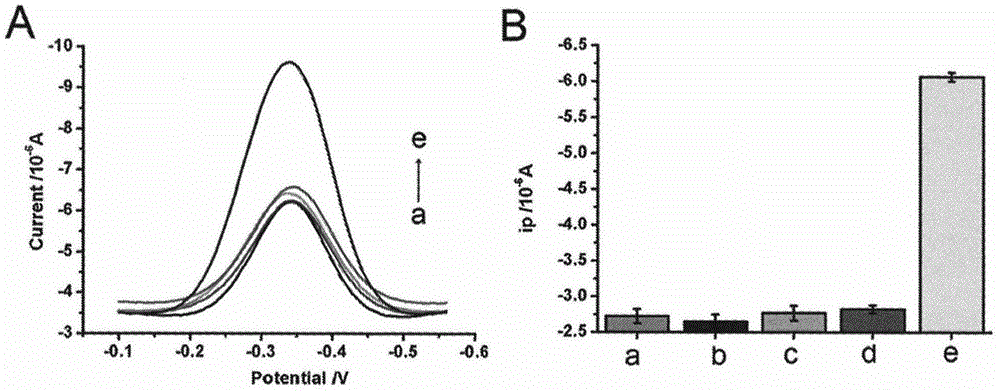
[0032] Example 2. Kanamycin residue detection specificity map based on aptamer-triggered ExoIII cycle digestion
[0033]Incubate the modified electrodes obtained in step (3) of the above method with 50 μL of binding solutions containing 500 pM of different antibiotics for 10 minutes, then wash with washing solution, and then soak the electrodes in 50 μL of 1U·μL -1 ExoIII was reacted in 1×NEB solution at 37°C for 1 hour, washed again with washing solution, and scanned by square wave voltammetry. The measured scan results are as image 3 A, As shown in 3B, the assay has good selectivity for kanamycin.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3. The mensuration of electrochemical signal-concentration standard curve of different concentration kanamycin standard solution
[0035] Incubate the modified electrodes obtained in step (3) of the above method with 50 μL of kanamycin standard solutions of different concentrations for 10 minutes, and then wash them with washing solution, and then soak the electrodes in 50 μL of 1U·μL -1 ExoIII was reacted in 1×NEB solution at 37°C for 1 hour, washed again with washing solution, and scanned by square wave voltammetry. The measured scan results are as Figure 4 As shown in A and 4B, in the range of 1-500pM kanamycin concentration, the peak value of the electrochemical signal increases with the increase of the kanamycin concentration, and both meet y=-2.7163-1.2117×lgx(R 2 =0.996), where y is the peak value of the electrochemical signal (μA), and x is the concentration of kanamycin (pM).
[0036] Add standard concentration kanamycin to milk to prepare artific...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com