Virus identification method and device
An identification method and virus technology, which are applied in the field of virus identification methods and virus identification devices, can solve problems such as large database dependence, and achieve the effect of improving detection rate and accuracy rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
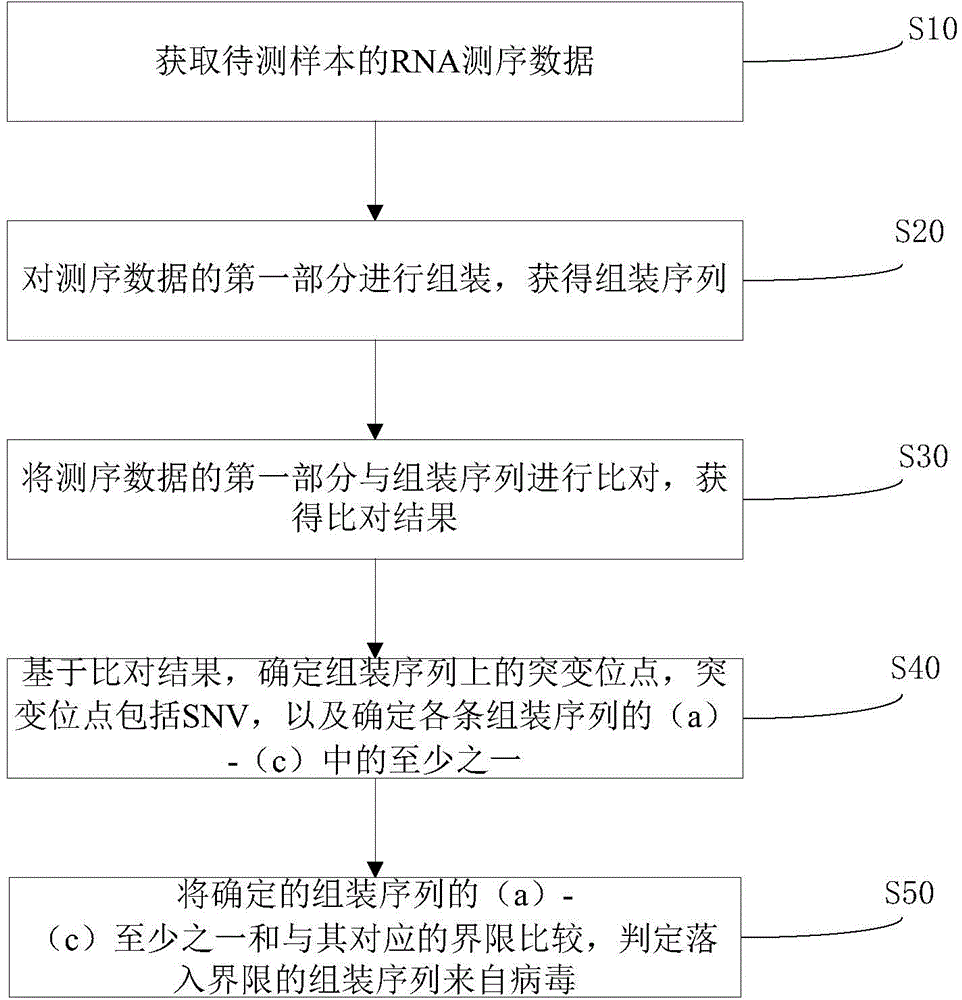
[0041] figure 2 Indicates the virus identification process and the determination process of the boundary, mainly including:
[0042] 1. Sample selection
[0043] This embodiment selects 16 plant samples, and the sample names are: Cooks_footf, Grass100f, Poplar100f, TCV_add, TCV, TCV-TYMV_add, TCV-TYMV, TGM-CK, TYMV-2, TYMV, Willow100f, GSM548932, GSM548933, peach_flower, peach_fruit, peach_leaf. Among them, TGM-CK is a sterile seedling purely cultured in the laboratory, TCV, TCV-TYMV, and TYMV are artificially actively infected with viruses on the basis of purely cultured seedlings, TCV (Turnip crinkle virus) is turnip crinkle virus, TYMV (Turnip yellow mosaic virus) is turnip yellow mosaic virus, sample TCV is infected with TCV virus, sample TCV-TYMV is infected with two kinds of viruses, TCV and TYMV, sample TYMV is infected with TYMV virus, sample TYMV-2 is the experimental repetition, sample TCV_add and TCV- TYMV_add is the duplication of sequencing data (technical dup...
Embodiment 2
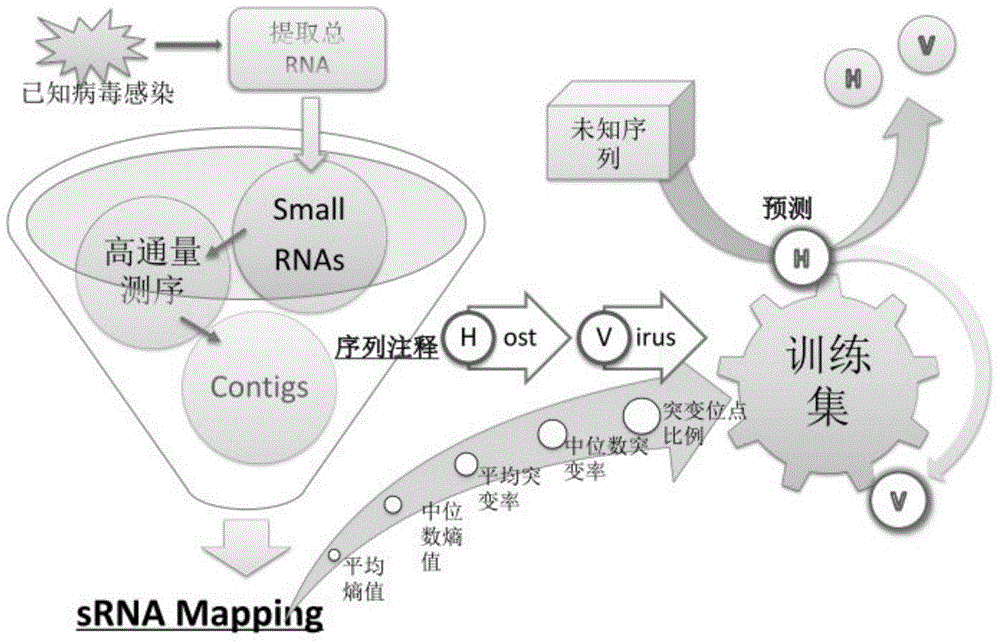
[0063] Consideration and determination of factors related to virus identification, including the amount of sequencing data, assembly method, five-element judgment criteria, suggestion and evaluation of prediction models.
[0064] 1. Determine the amount of sequencing data
[0065] In order to find the virus in the sample as much as possible, we expect to measure more data, but the cost of sequencing will also increase as the amount of sequencing increases. Moreover, if the amount of sequencing can already cover all the sequences in the sample, it is also necessary to measure more data. It is a waste, therefore, it is necessary to roughly determine the amount of sequencing data for small RNA.
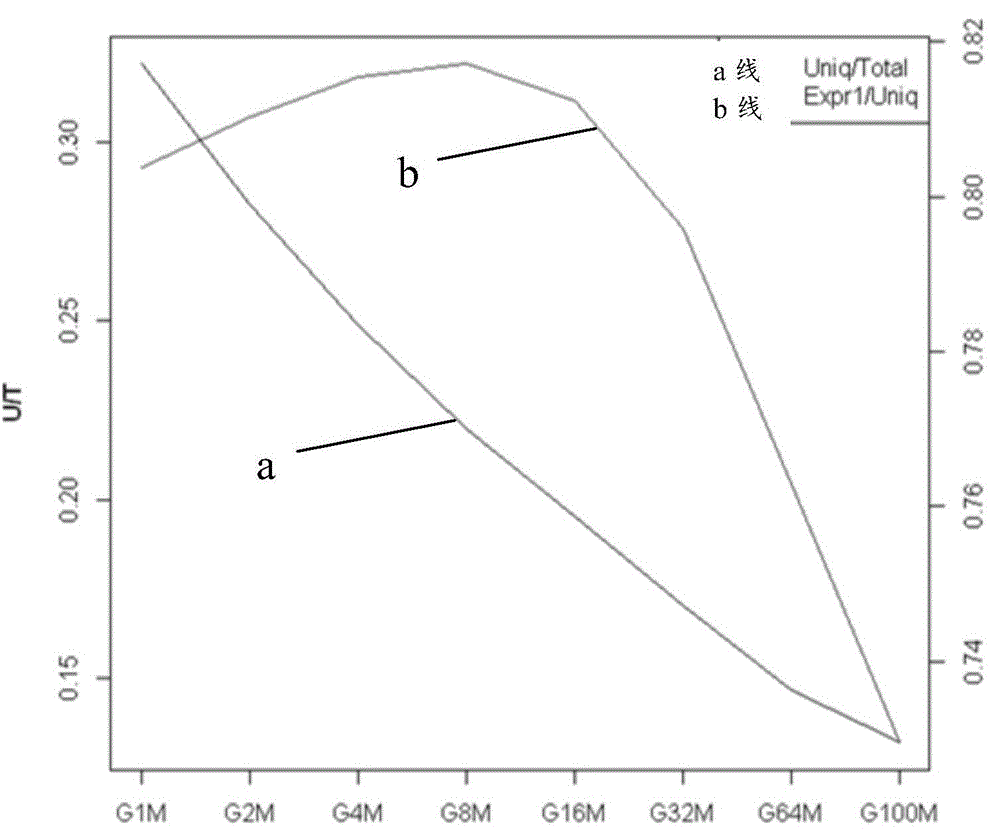
[0066] In order to evaluate this amount, we measured 100M sequences, and took the ratio of the number of non-redundant sequences in different data volumes to the number of non-redundant sequences as a reference for evaluating the saturation of sequencing data.
[0067] image 3 Display...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Prediction and validation of whether an unknown sequence is from a virus.
[0085] 1) Low-quality data filtering. The fq file obtained by sequencing is dejoined and low-quality, and the fasta format file is generated, and the number of redundancy is counted, that is, the ID of each sequence includes the number of repetitions of the sequence, such as: t00001200. Where t00001 is the ID, and 200 is the repeat number of the sequence.
[0086] 2) Known ncRNA filtering. Comparing the fasta files completed by preliminary filtering with known ncRNA databases, including: http: / / www.sanger.ac.uk / software / Rfam, GenBank's noncoding RNA database (noncoding RNAdatabase) ( http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / ), using BLAST 2.2.23 software, requiring an e value <0.01. Then compare it with the miRBase (release 18) database, which requires exactly the same comparison. Get further filtered fasta format files.
[0087] 3) Data assembly. If the species already has a genome sequence, then th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com