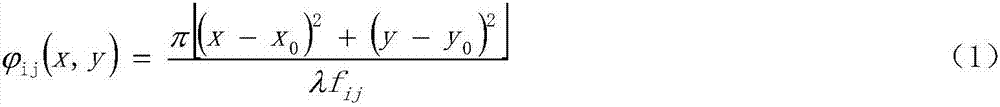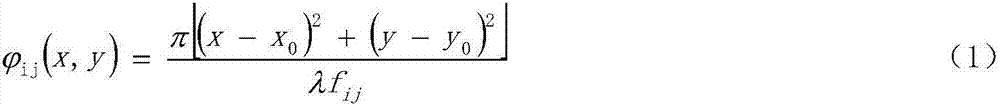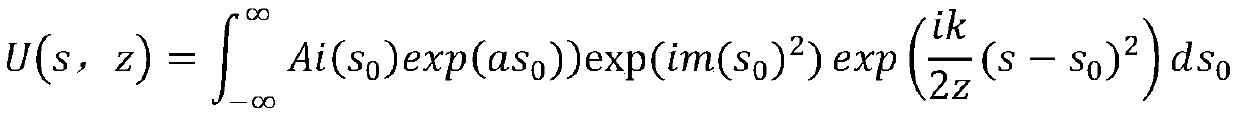Patents
Literature
79 results about "Quadratic phase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
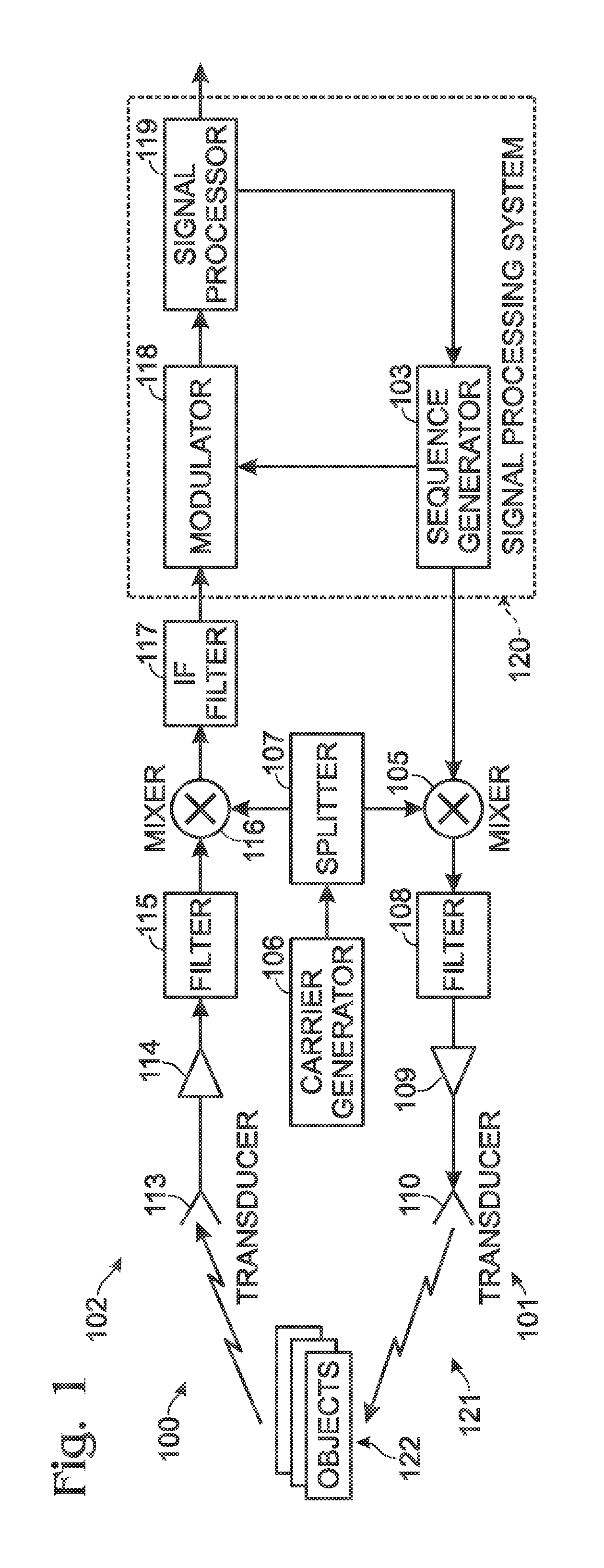
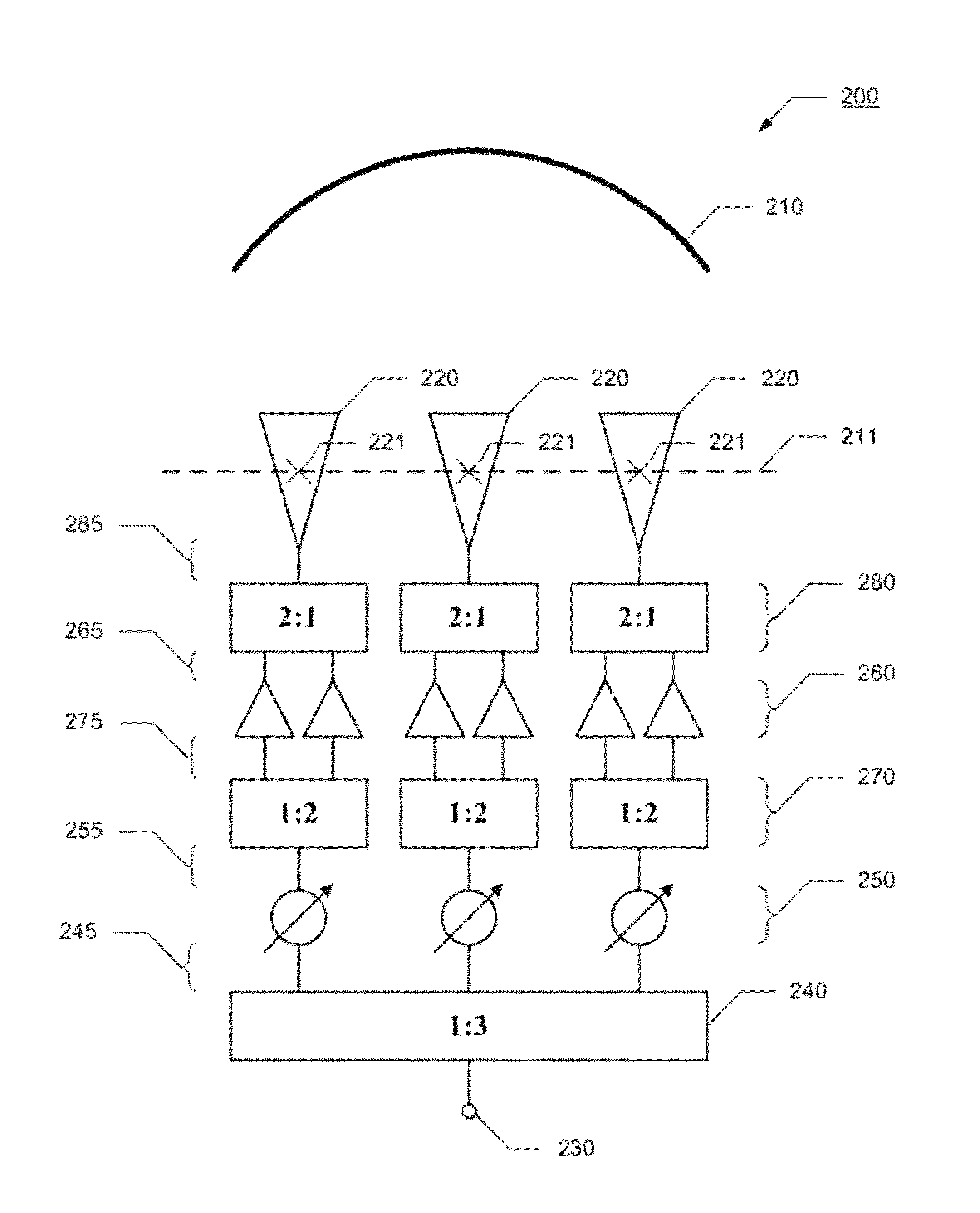
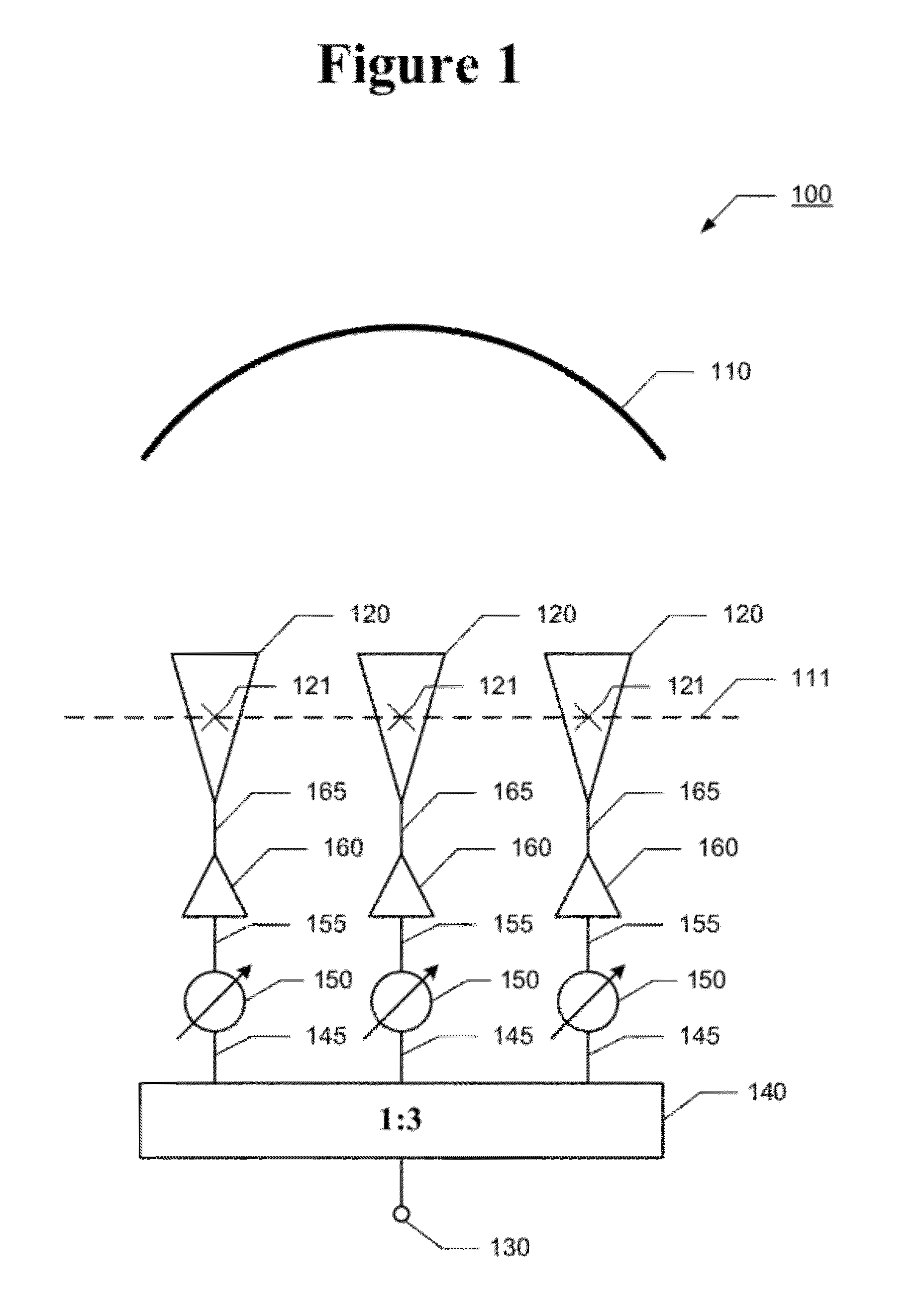
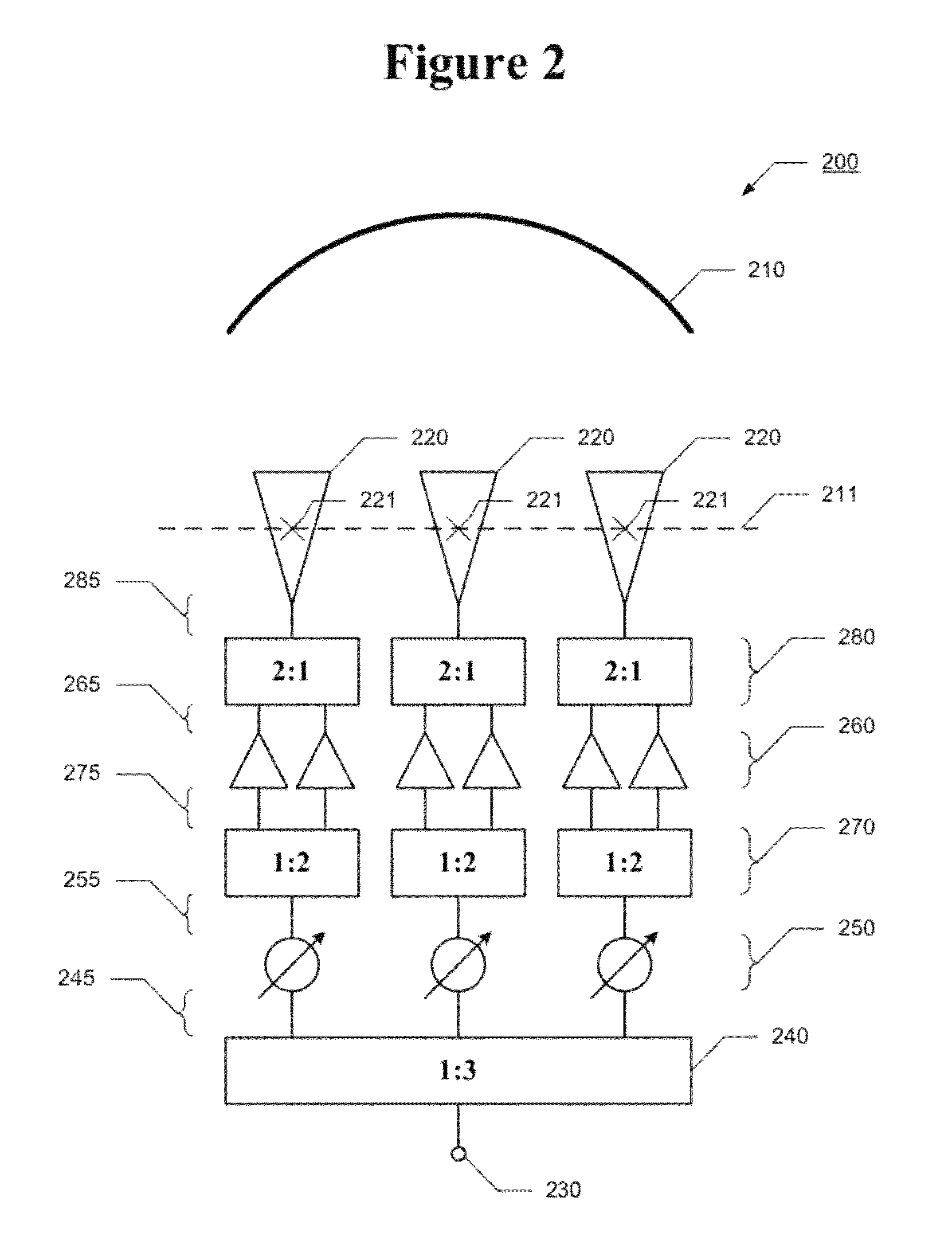
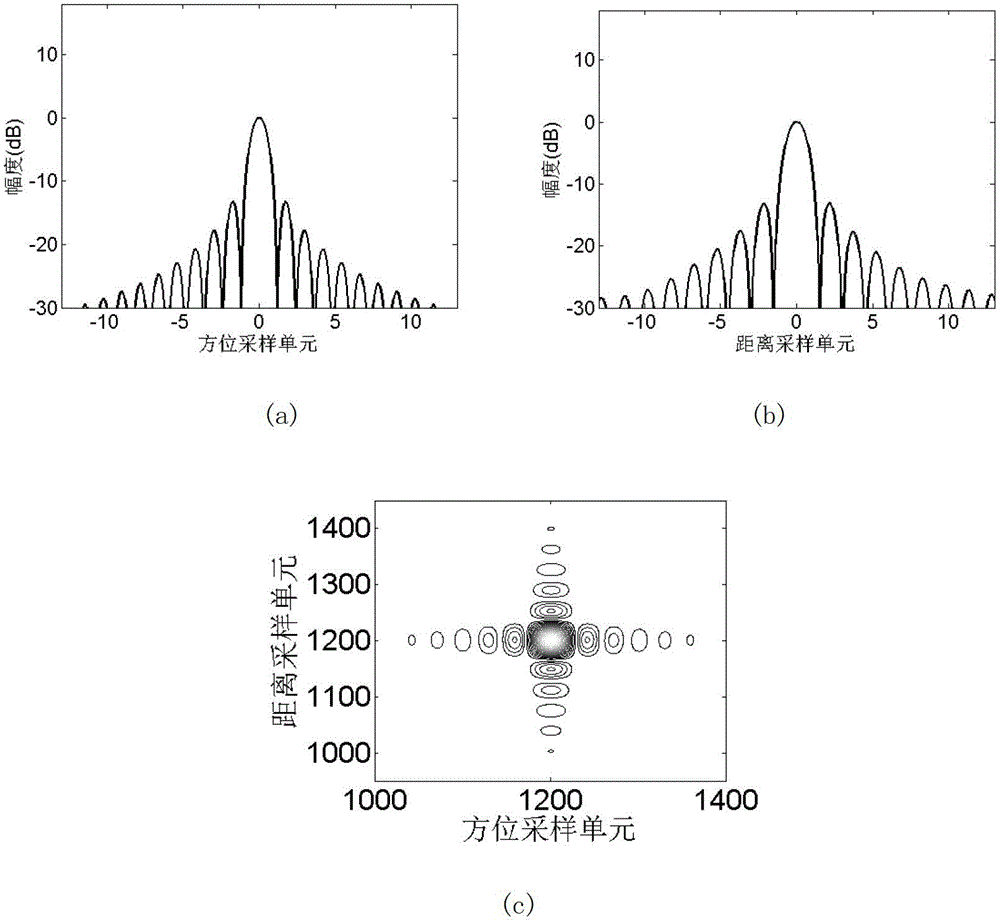
Quadratic Phase Array. A method to obtain a signal with a flat spectrum (such as a pulse), but having a smaller amplitude than the pulse. with . Thus and are a Fourier pair, and since , it is guaranteed that the sequence has a flat spectrum. The sequence is called the "quadratic phase array.".
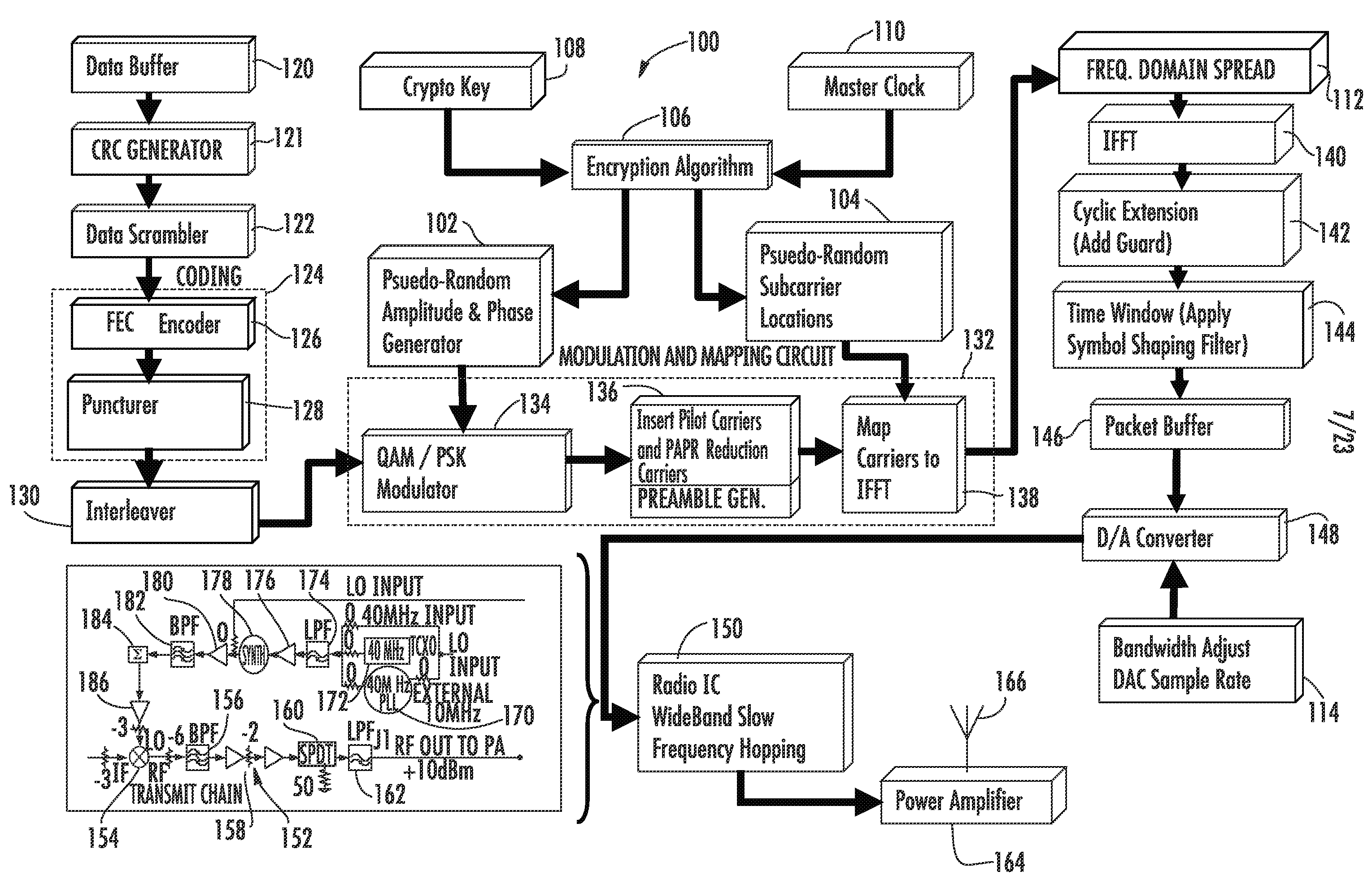
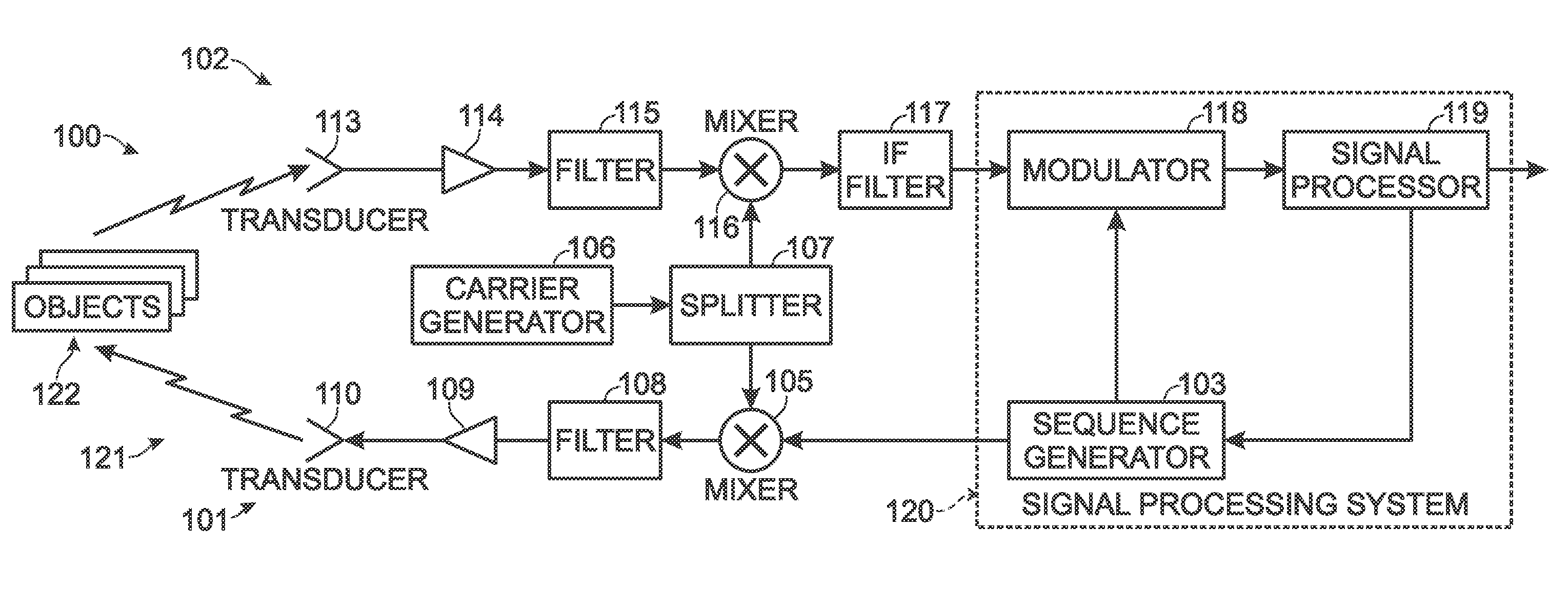
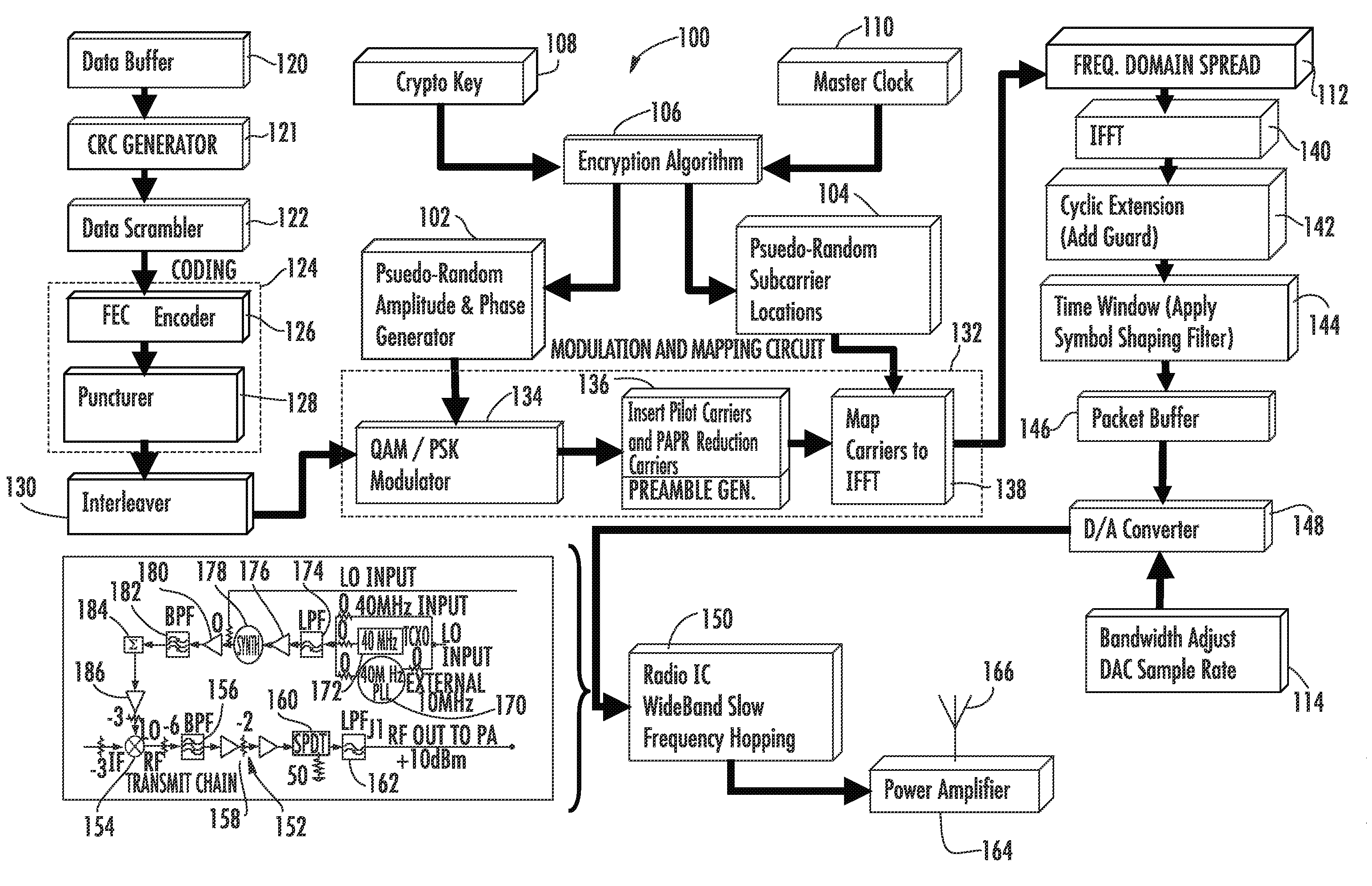
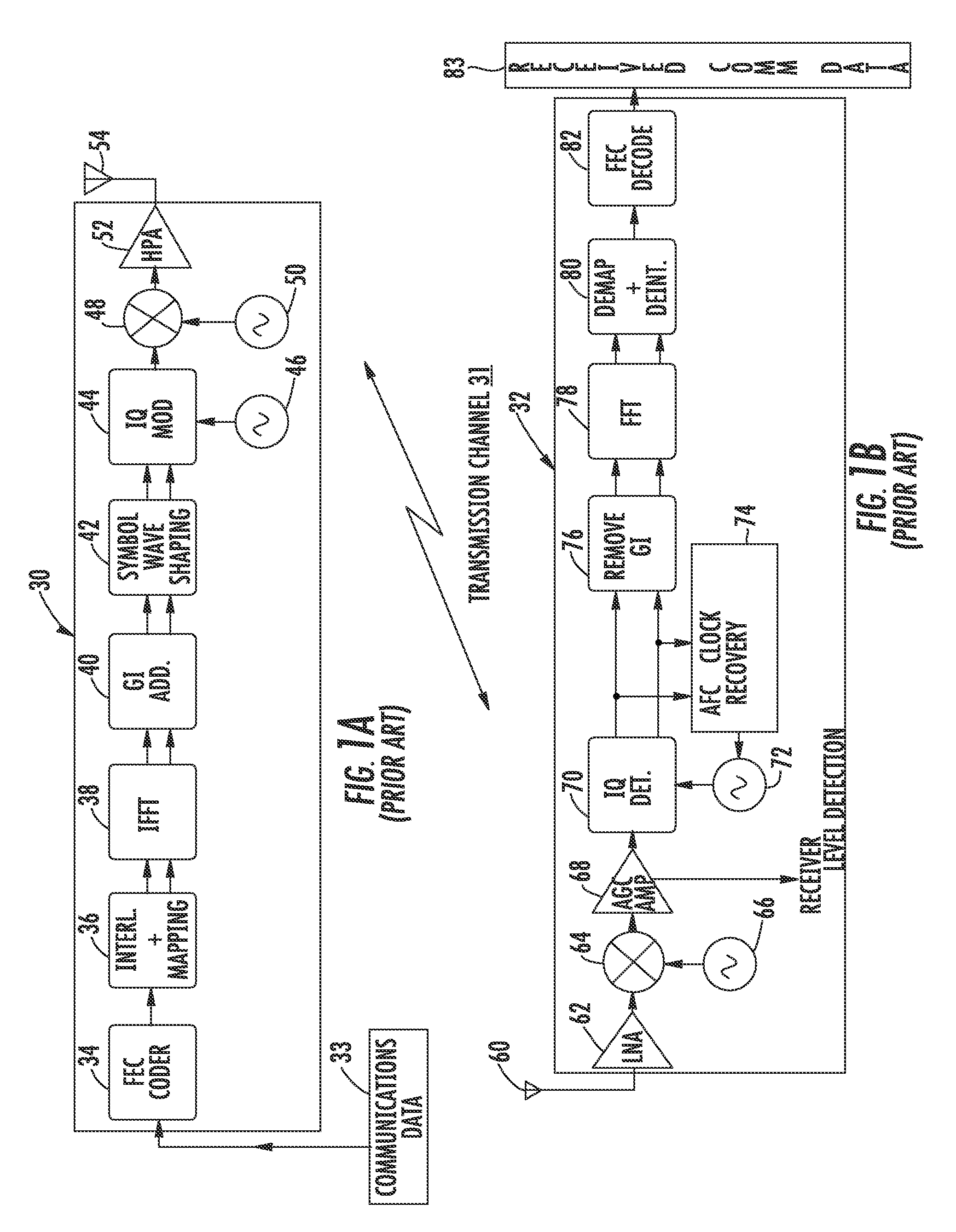
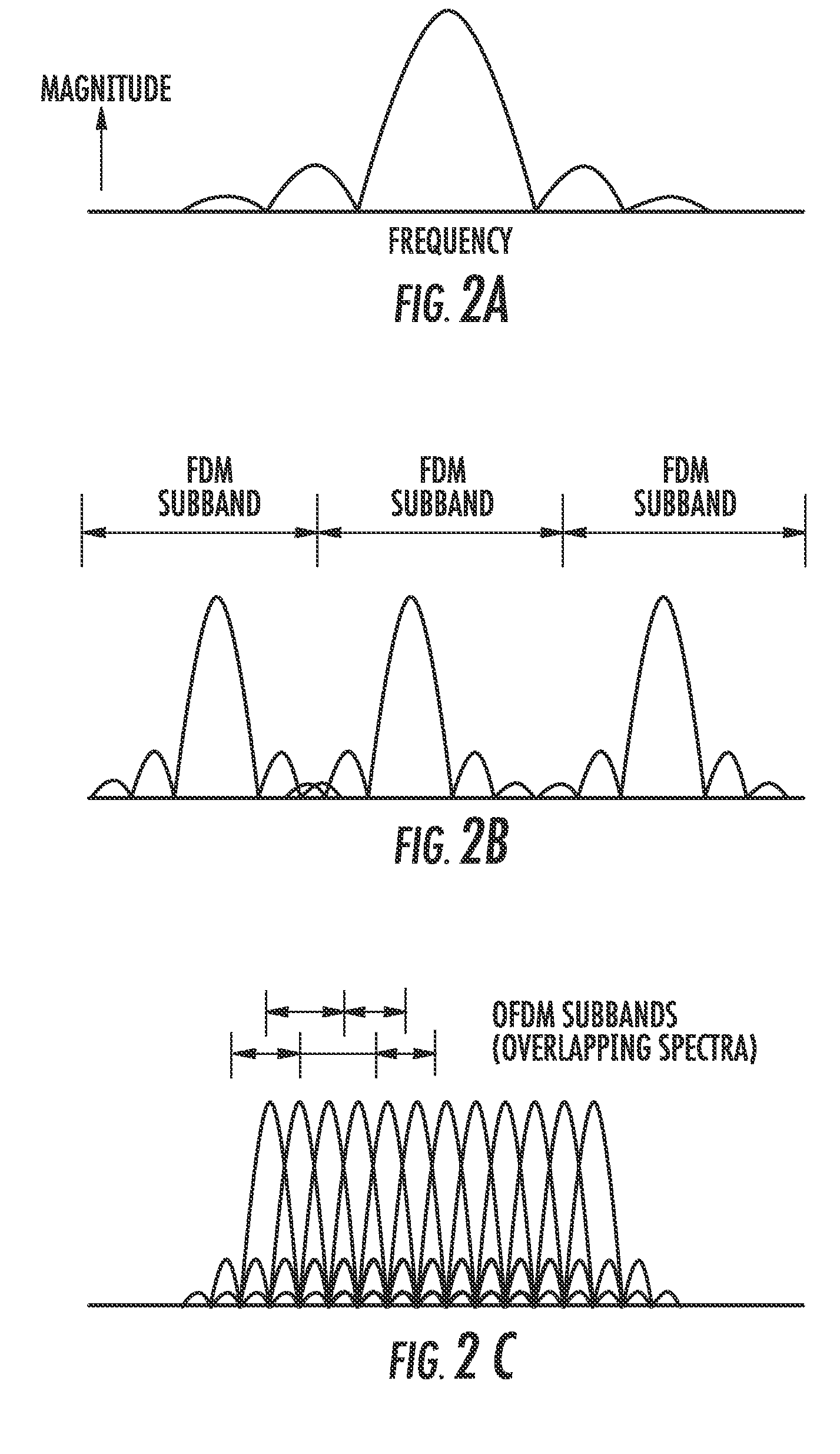
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) communications device and method that incorporates low papr preamble with circuit for measuring frequency response of the communications channel
ActiveUS20100080312A1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationFrequency spectrumFrequency-division multiplexing
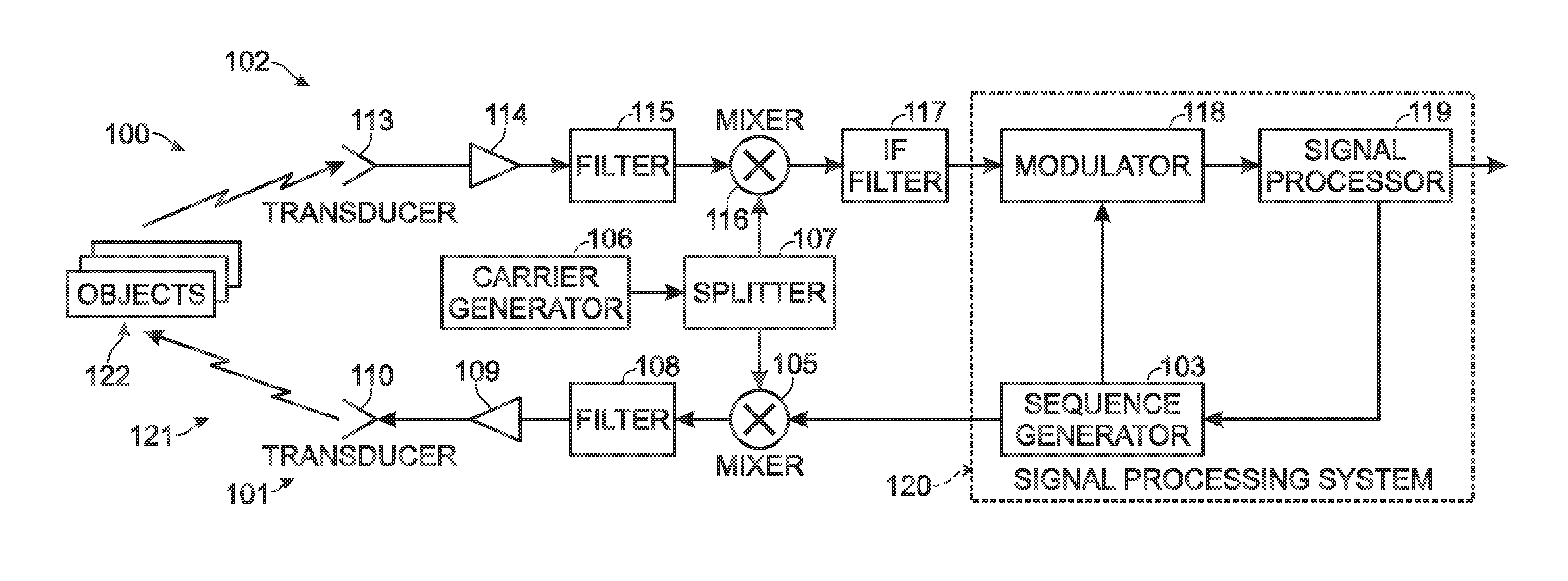
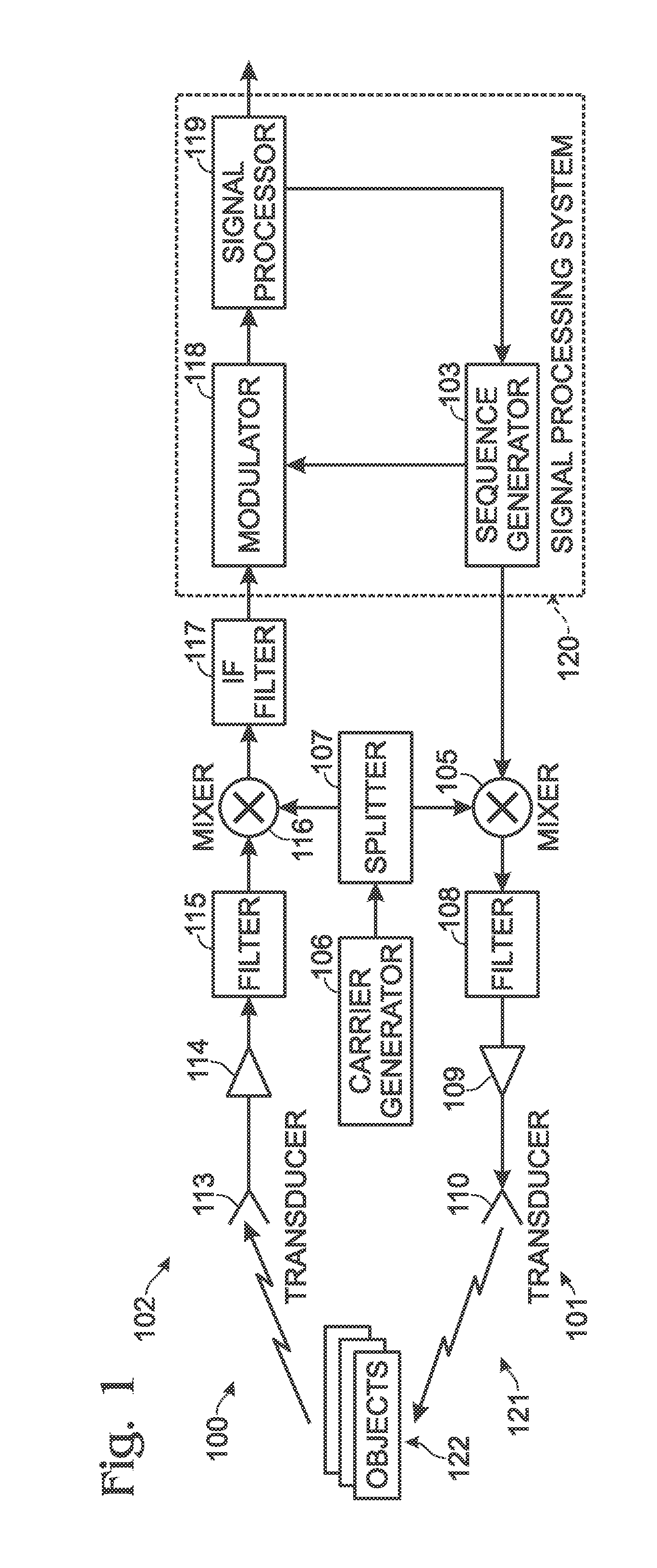
A communications device includes a demapping and demodulation circuit and processes an OFDM communications signal that includes modulated subcarriers carrying communications data forming a data payload and modulated subcarriers carrying a training sequence forming a preamble. Those OFDM subcarriers carrying the training sequence have a sample for each subcarrier at a frequency bin using evenly spaced, equal amplitude subcarriers that have a set phase of each sinusoid to a specific angle with quadratic phase to form a low peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) preamble with about a PAPR value of 2.6 decibels (dB). A channel estimate circuit is operative for measuring fluctuations within a flat-top spectrum of the received OFDM communications signal corresponding to the preamble to reflect the frequency response of the communications channel.
Owner:SMARTSKY NETWORKS
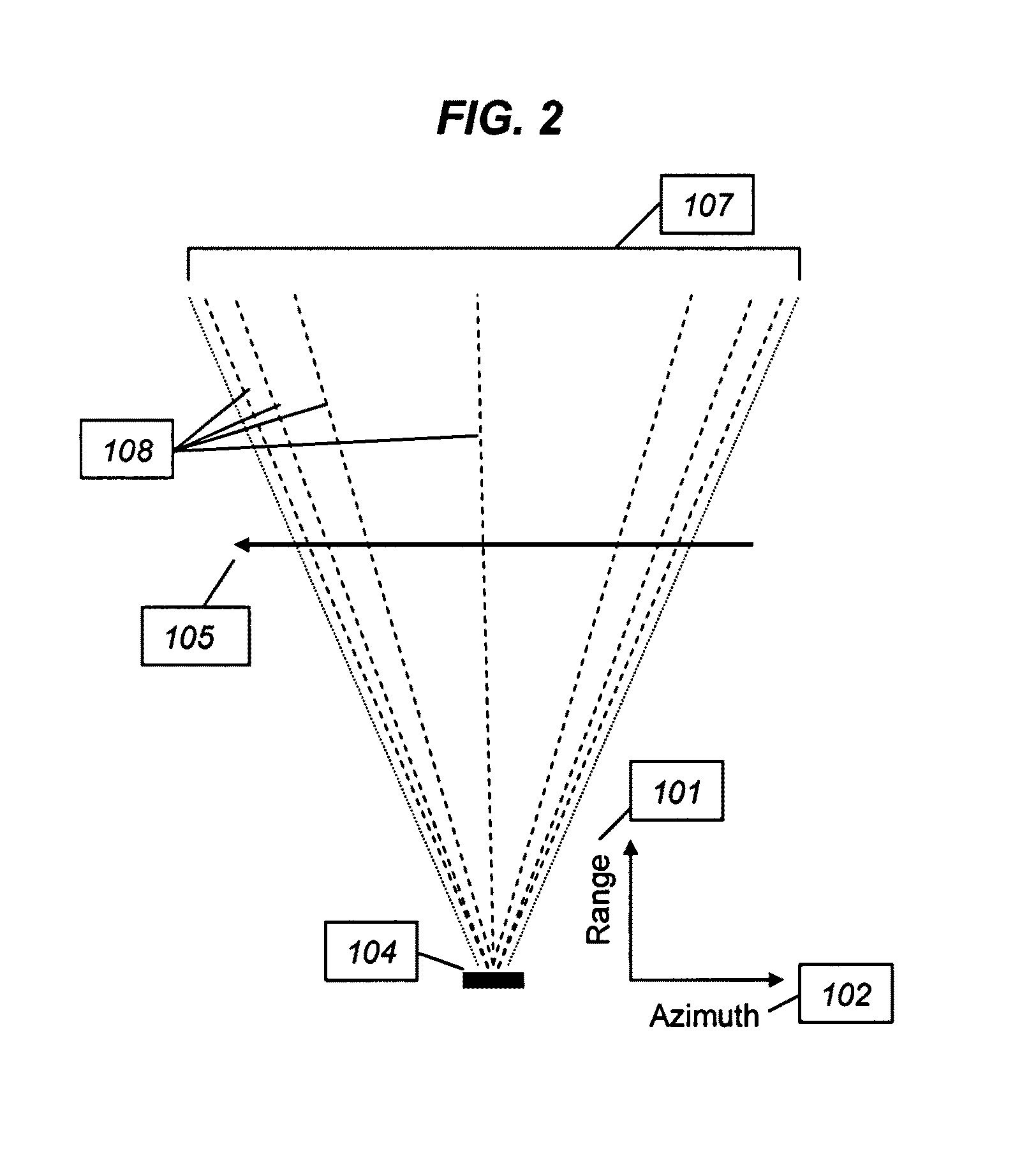
Beam phase modulation for improved synthetic aperture detection and estimation
InactiveUS20090066562A1Improve performanceSuppress ambiguityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSonificationSynthetic aperture sonar
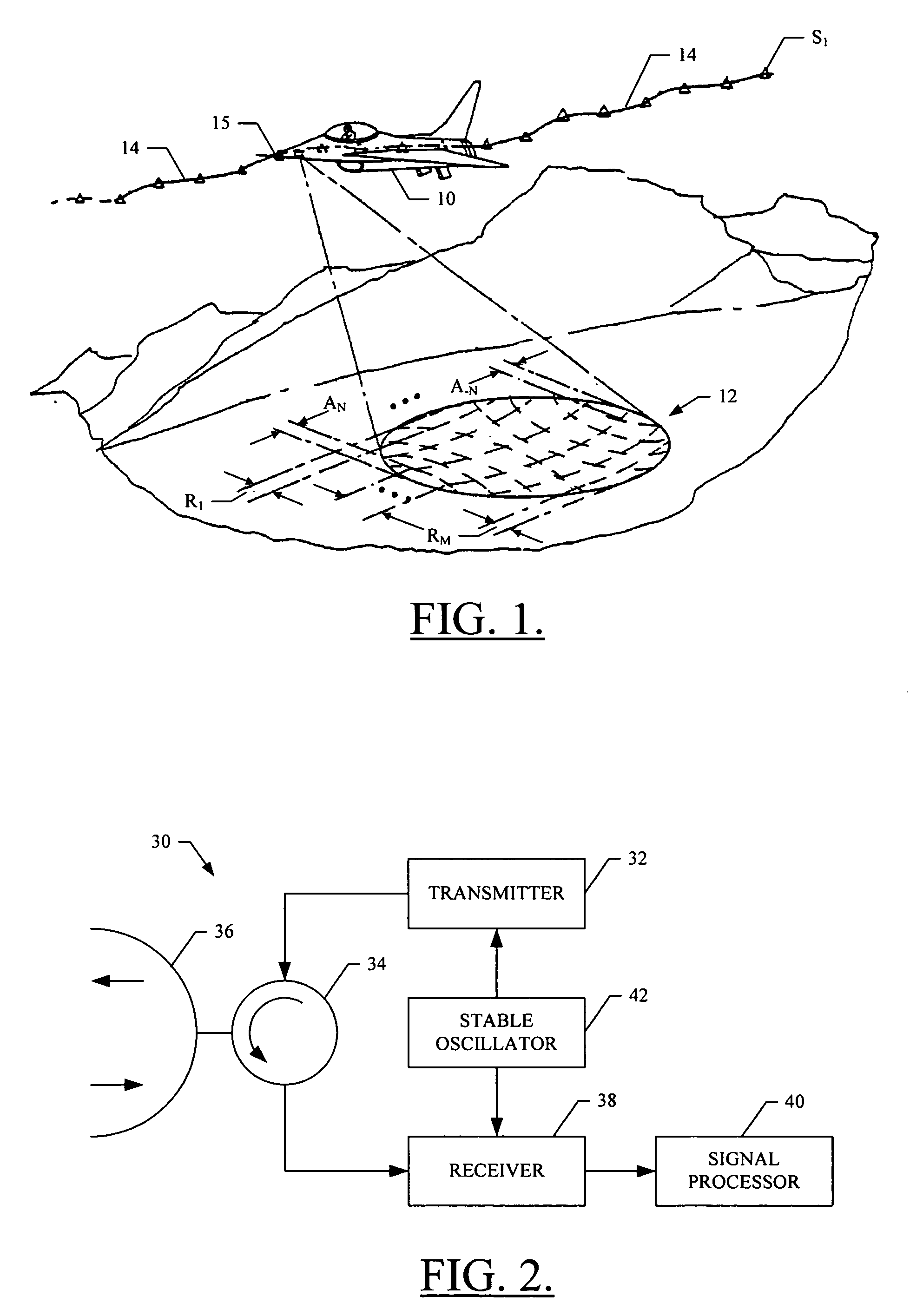
Phase modulated beam patterns are substituted for the constant-phase versions that have been used in prior synthetic aperture systems. Relative movement between a radar / sonar / ultrasound platform and a point target causes a sequence of echoes from the point target to be phase and amplitude modulated by the beam pattern, as well as by the usual quadratic phase variation caused by range changes. Azimuth, range rate, and azimuth rate estimation, as well as detection in clutter, are substantially improved by appropriate beam pattern phase modulation, which is applied to the transmitter and / or receiver beam patterns. Phase modulated beam patterns are synthesized with array element weighting functions that are designed for high ambiguity function peak-to-sidelobe level, reduction of unwanted ambiguity ridge lines, and adequate spatial sampling. Two dimensional beam pattern phase modulation is useful when the relative motion between a transmit-receive array and multiple targets has both azimuth and elevation components.
Owner:CHIRP
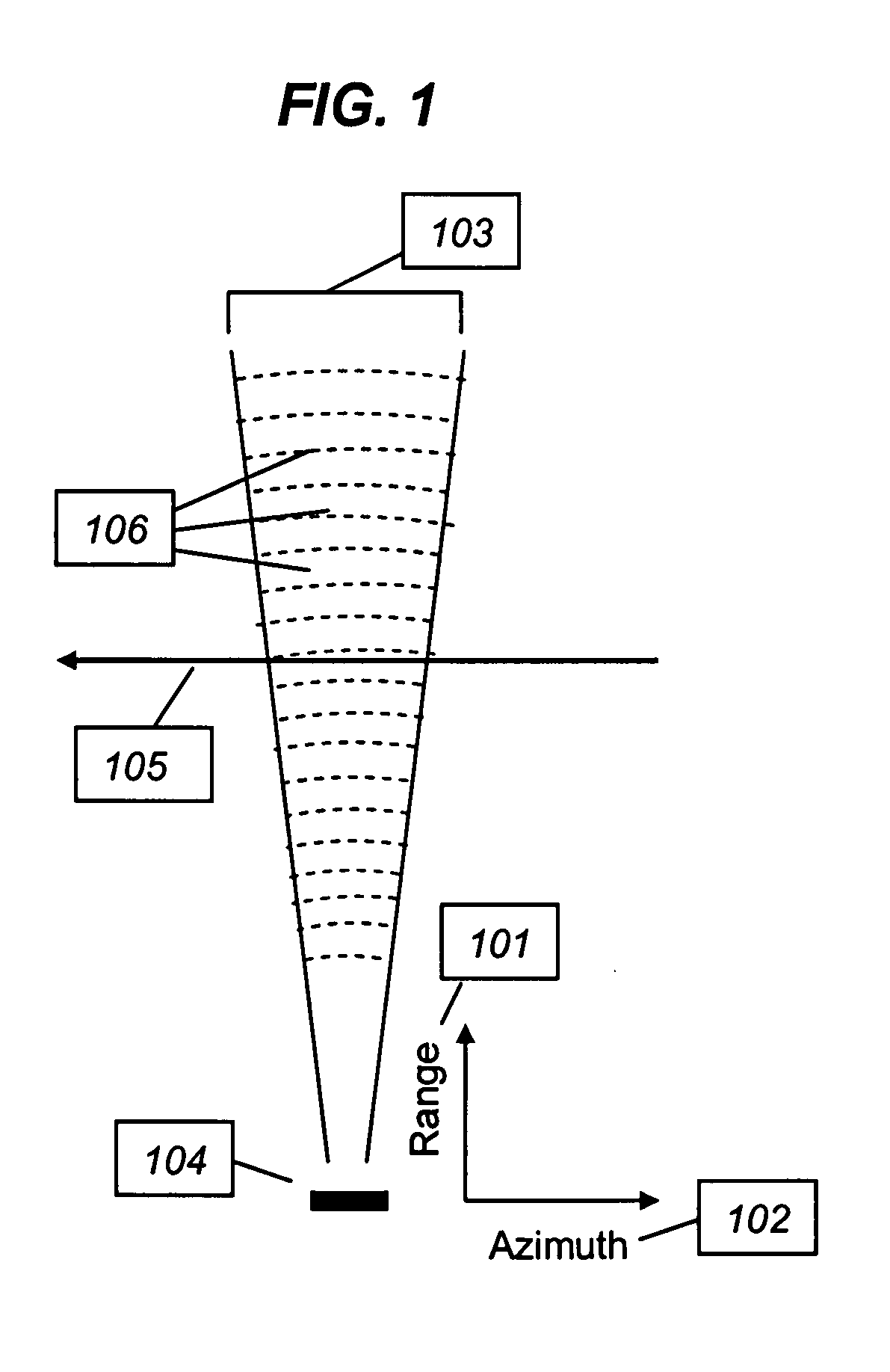
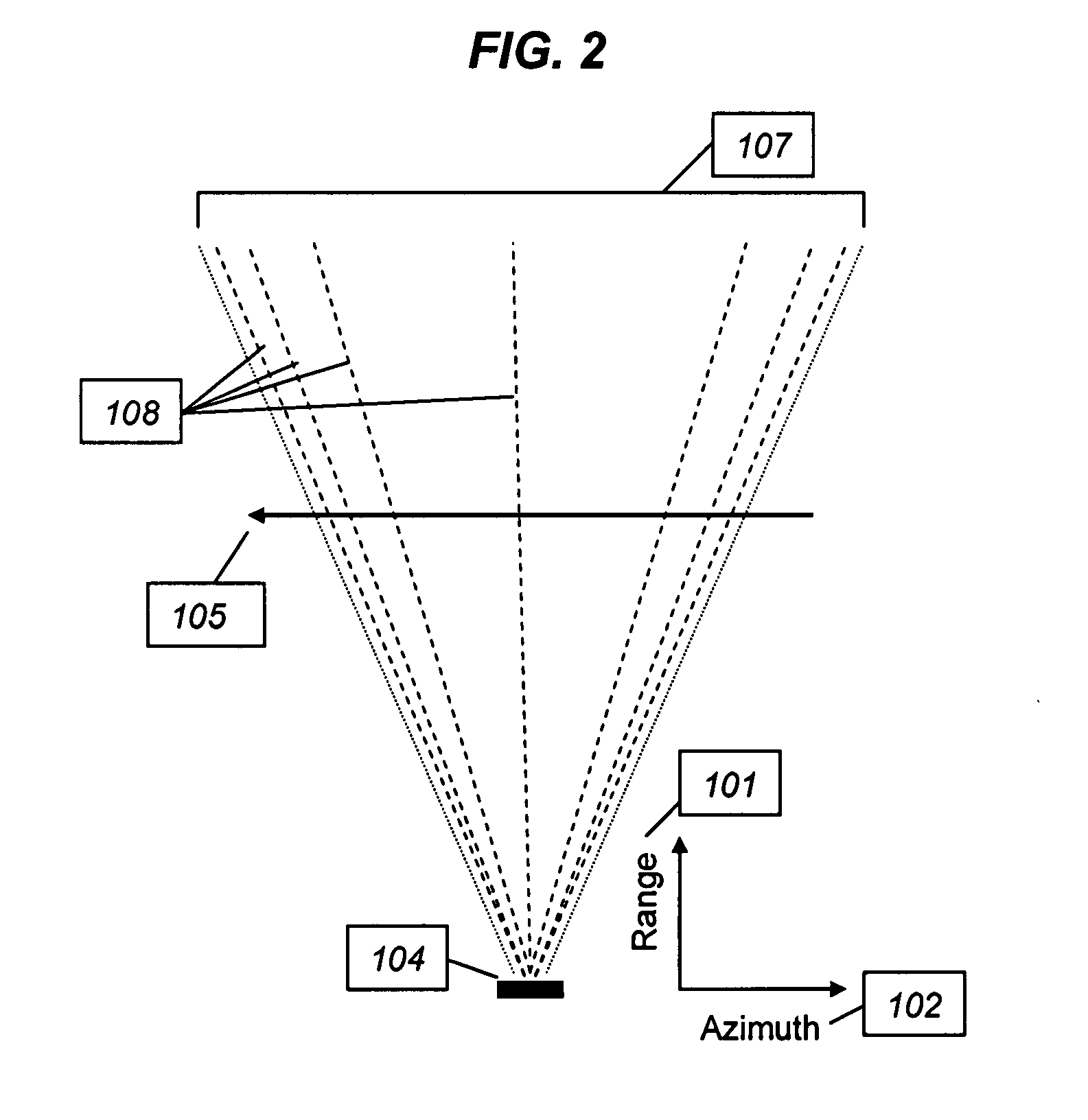
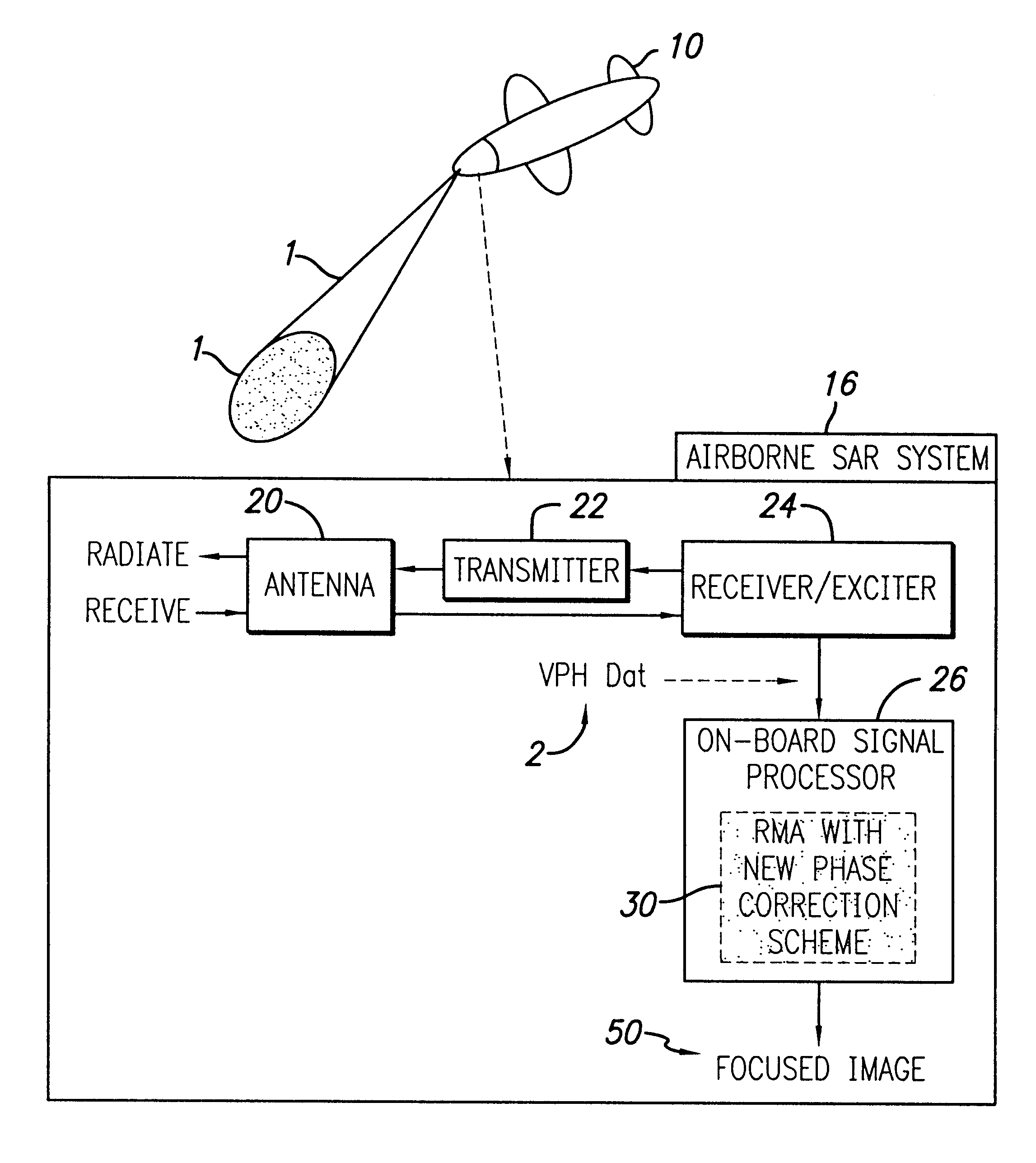
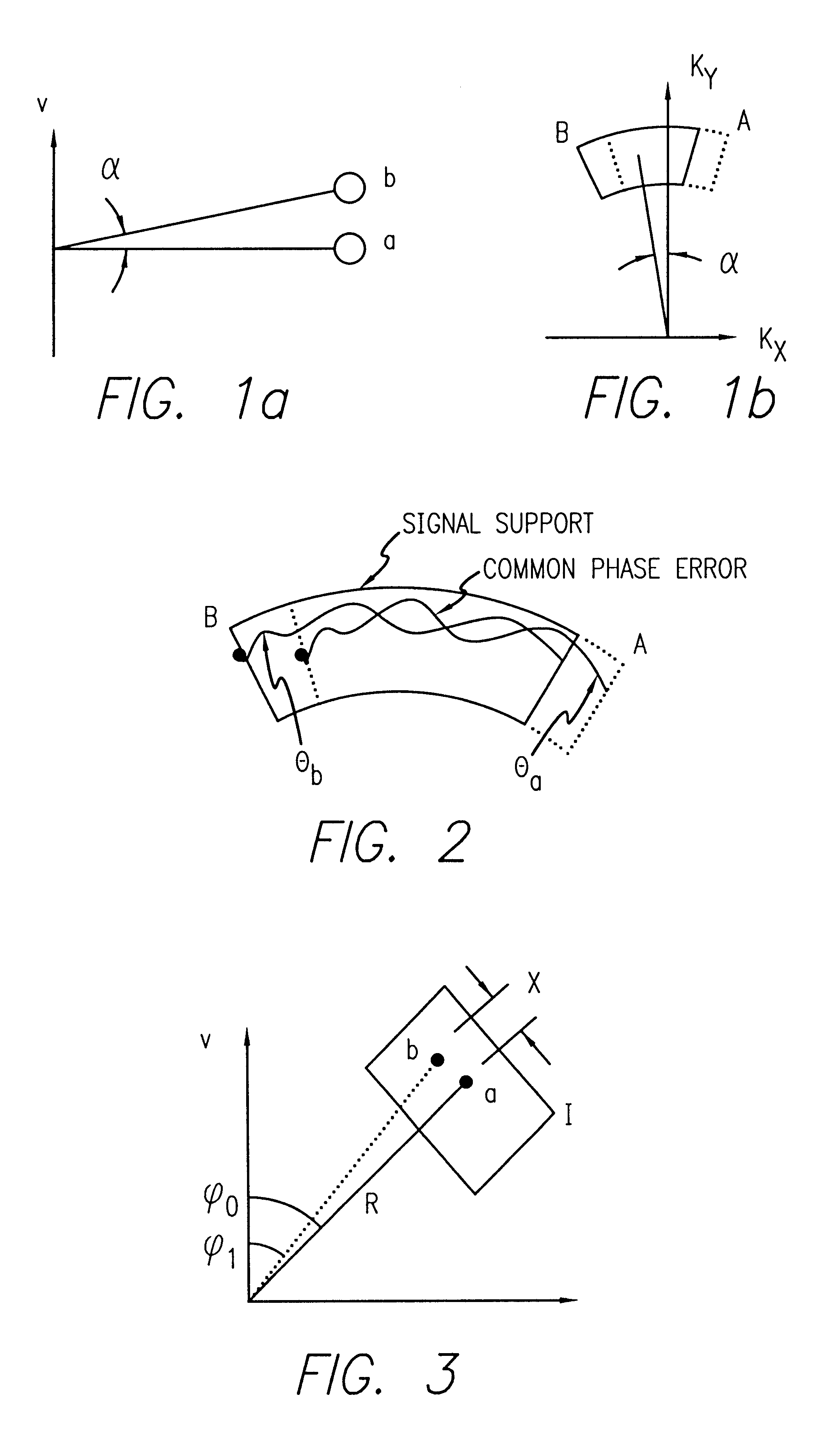
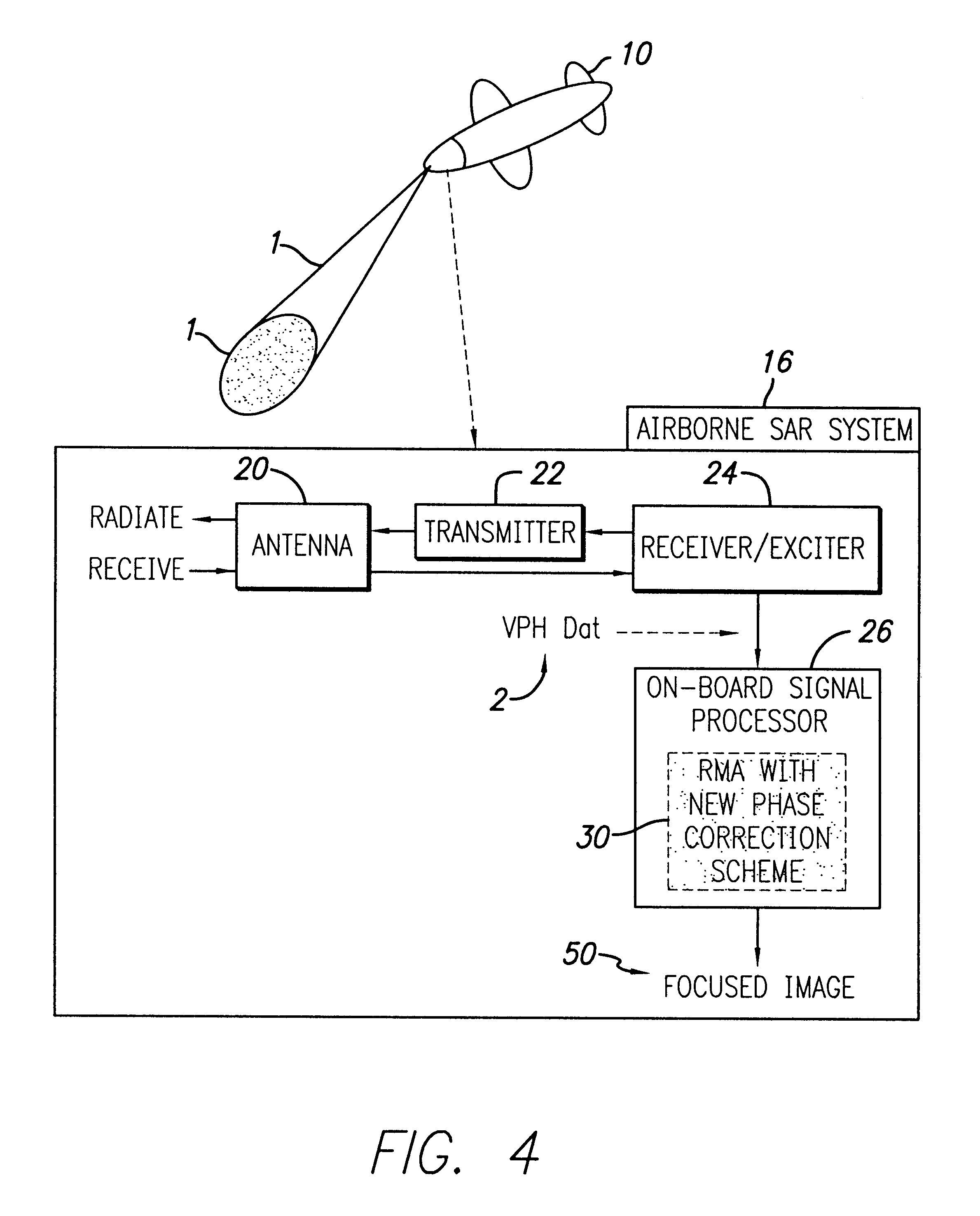
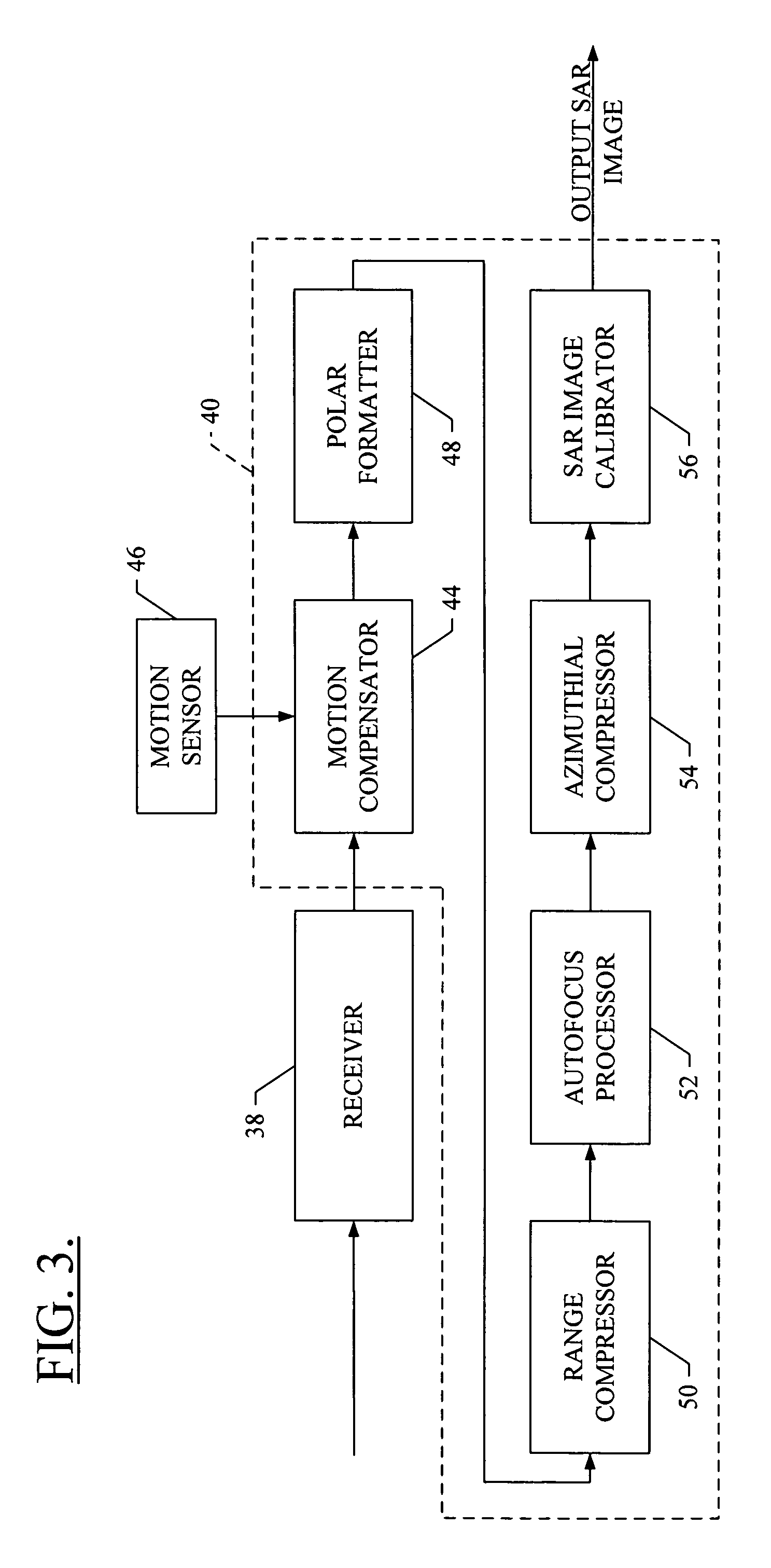
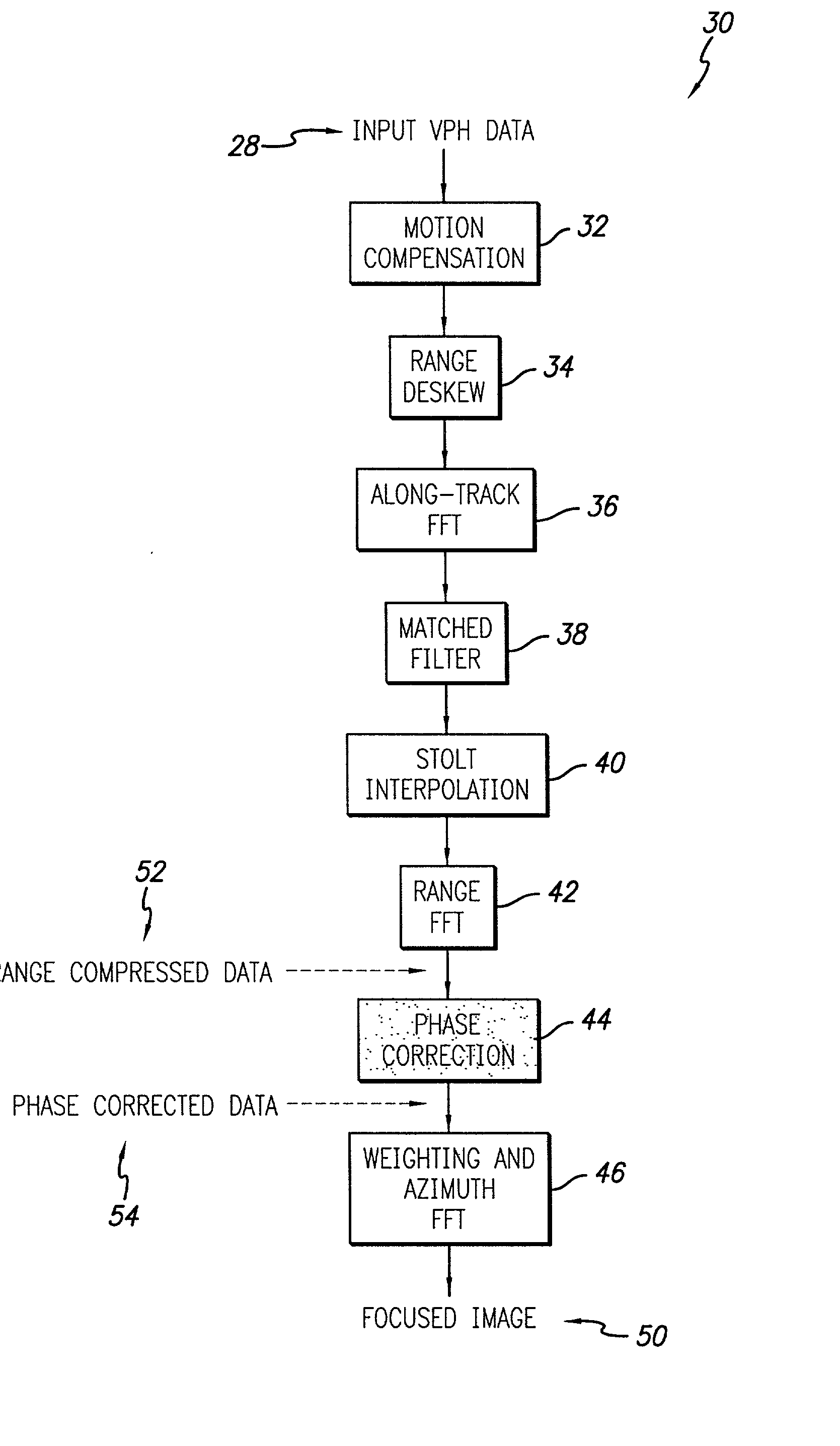
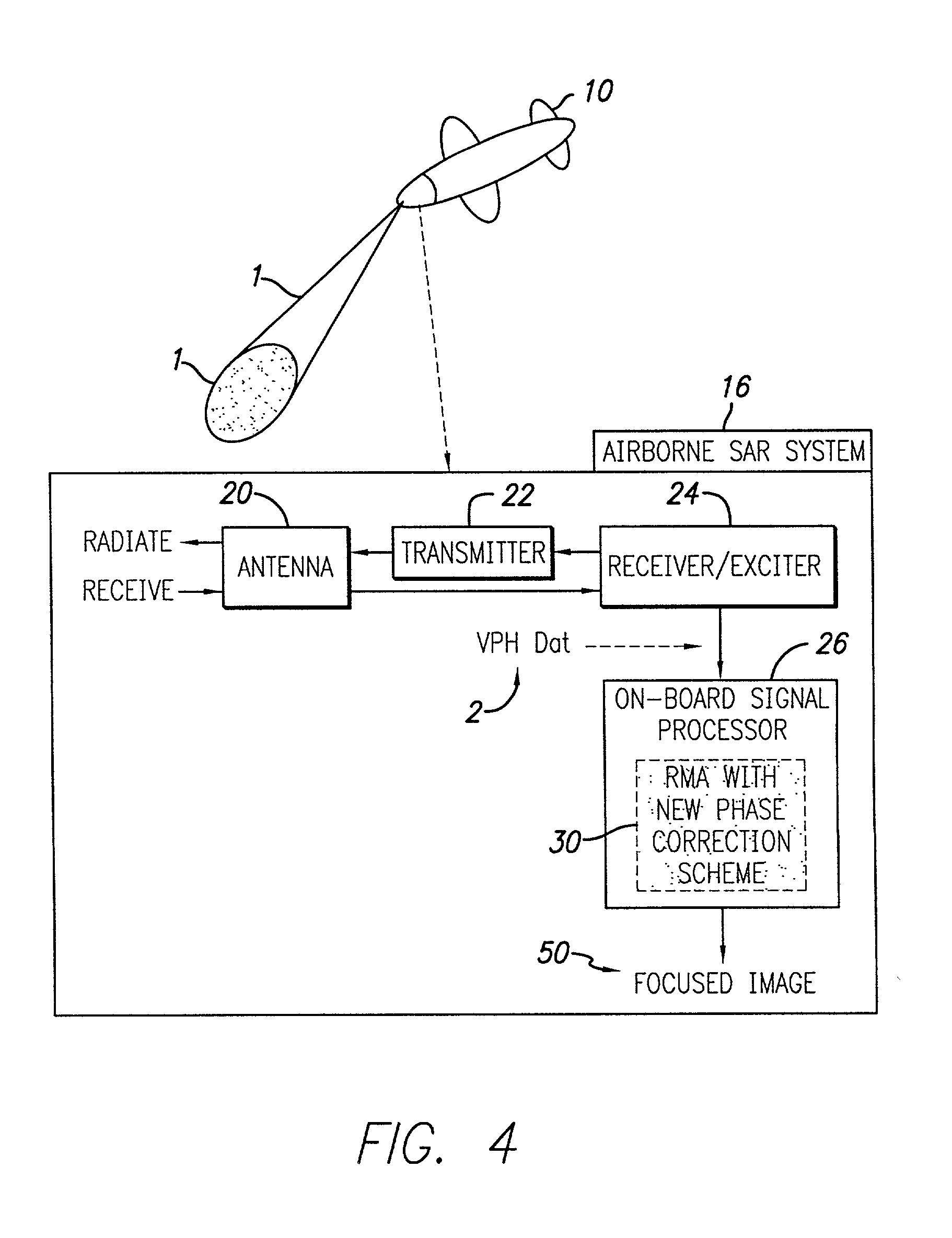
Efficient phase correction scheme for range migration algorithm
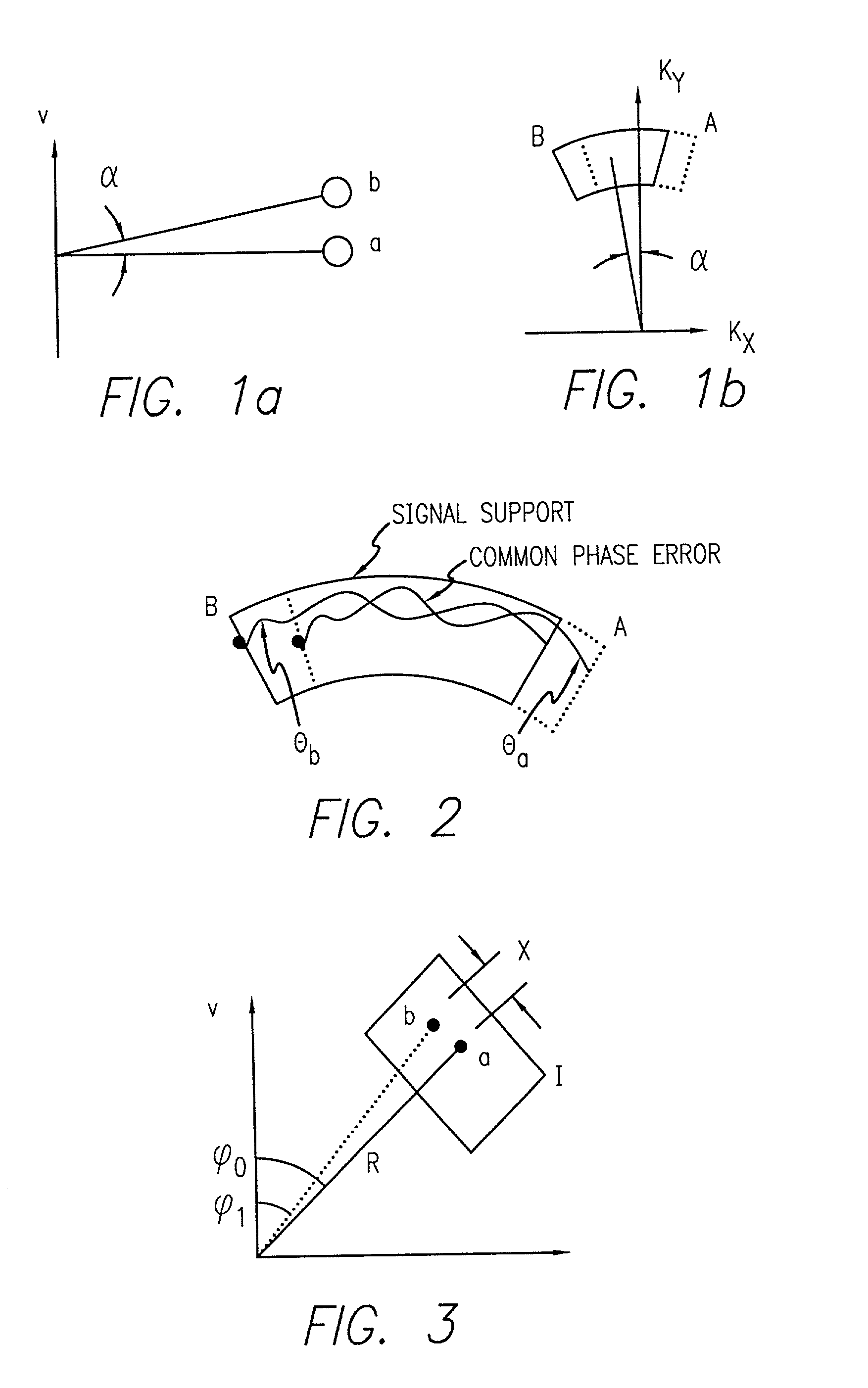
InactiveUS6670907B2Convenient lengthExemption stepsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBatch processingCommon phase error
A system and method for efficient phase error correction in range migration algorithm (RMA) for synthetic aperture radar (SAR) systems implemented by making proper shifts for each position dependent phase history so that phase correction can readily be performed using the aligned phase history data during batch processing. In its simplest form, the invention (44) is comprised of two main parts. First (60), alignment of the phase error profile is achieved by proper phase adjustment in the spatial (or image) domain using a quadratic phase function. Second (62), the common phase error can be corrected using autofocus algorithms. Two alternative embodiments of the invention are described. The first embodiment (44a) adds padded zeros to the range compressed data in order to avoid the wrap around effect introduced by the FFT (Fast Fourier Transform). This embodiment requires a third step (64): the target dependent signal support needs to be shifted back to the initial position after phase correction. The second embodiment (44b) uses the range compressed data without padded zeros. Instead, an aperture of greater length needs to be generated by the Stolt interpolation. In this embodiment, the third step (64) of shifting the signal support back can be eliminated.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
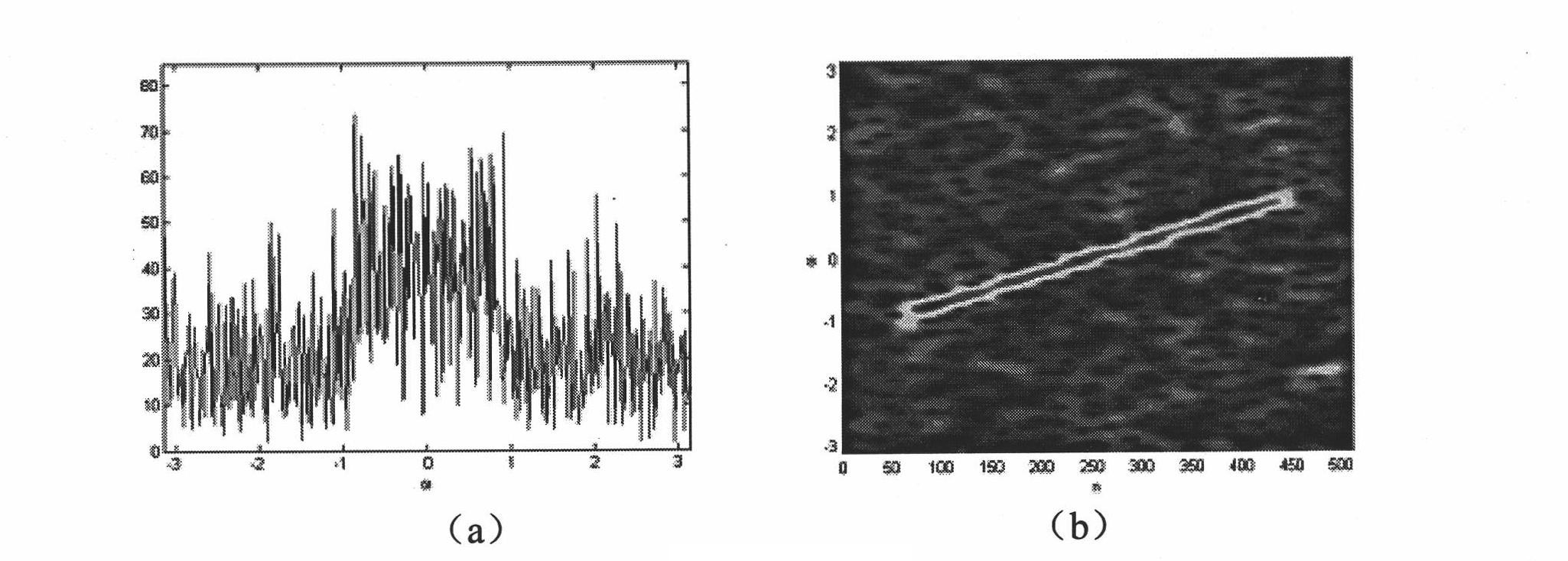
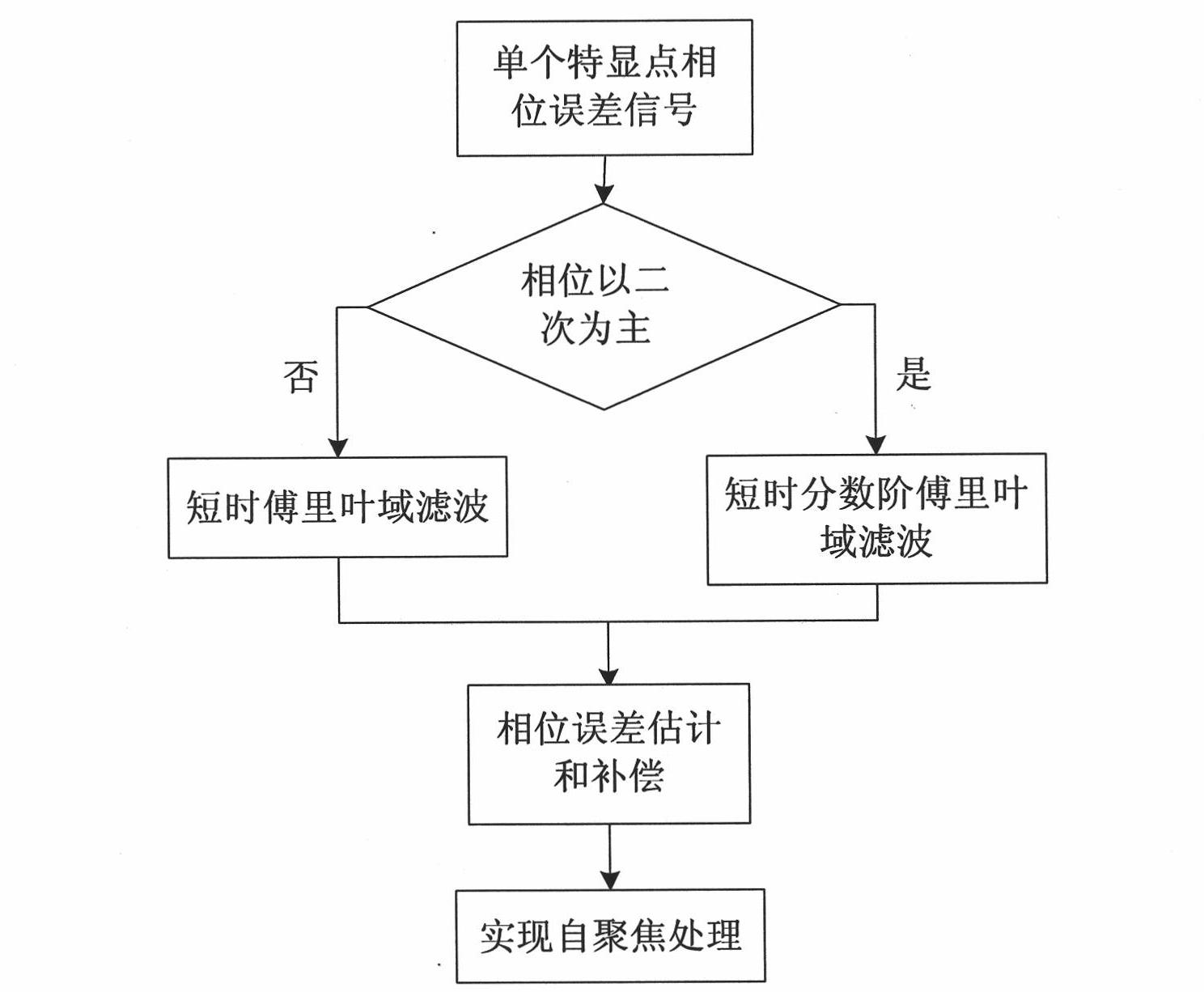
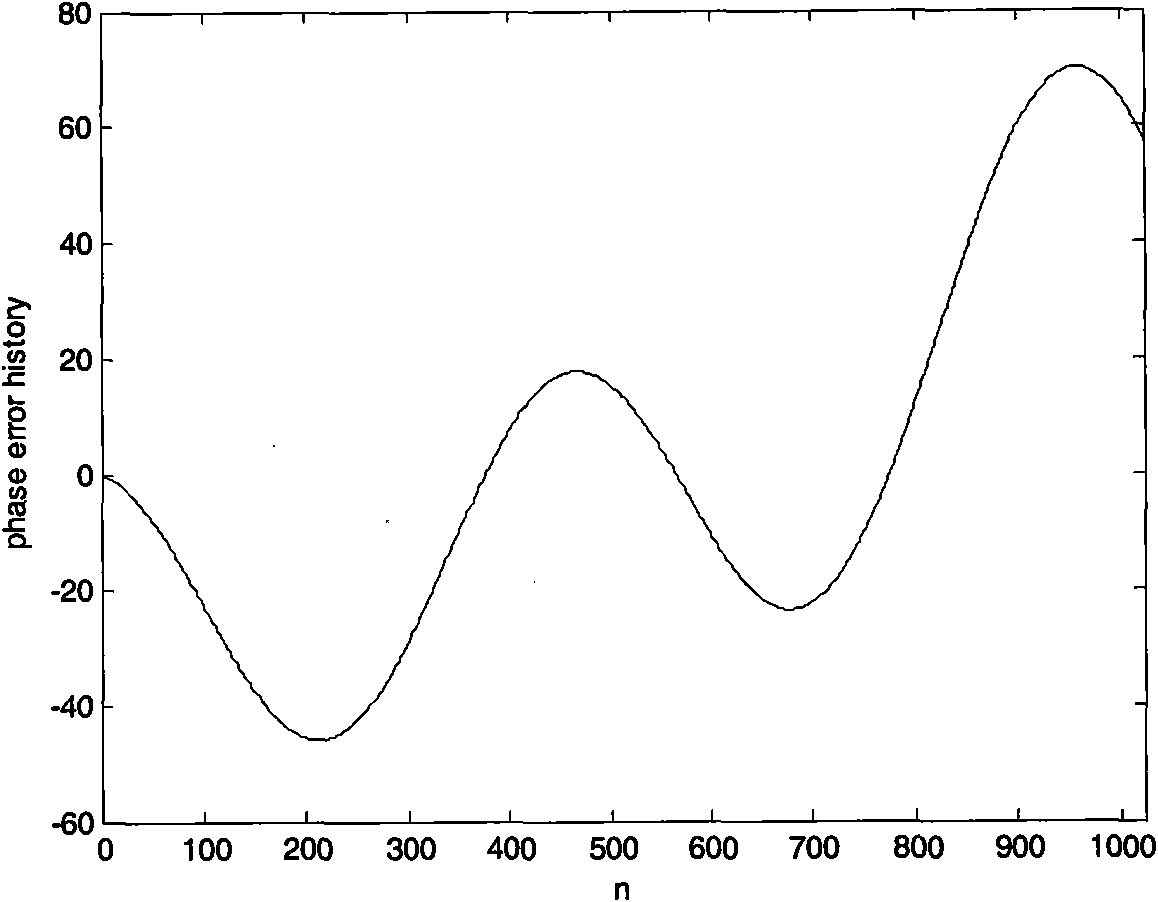
Self-focusing preprocessing method based on short-time fractional order Fourier domain filter
InactiveCN101963662AImprove matchHigh two-dimensional aggregationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime domainSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention relates to a self-focusing preprocessing method based on a short-time fractional order Fourier domain filter, which belongs to the field of synthetic aperture radar (SAR) signal processing. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) extracting a phase error signal of a single special showing point; (2) judging whether the phases of the phase error signal mainly are quadratic phase or not; (3) filtering noise in a transform domain: if the phases mainly are quadratic phases, using short-time fractional order Fourier domain filter; otherwise, using short-time Fourier domain filter; and (4) inversely transforming result time frequency to a time domain, estimating and compensating the phase error and realizing self-focusing preprocessing. The method effectively solves the problems of estimation and compensation of the phase error in a low-signal-to-noise ratio environment, especially the estimation and compensation of the quadratic phase error, and can obtain the main part of a phase error course and greatly improve the imaging quality after removing the phase error course from an original signal, thereby improving the signal-to-noise ratio of a special showing point signal.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Improved algorithm based on parameter estimation and compensation of quadratic phase function
ActiveCN108761404ARich spatial informationEasy accessRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInformation processingImproved algorithm
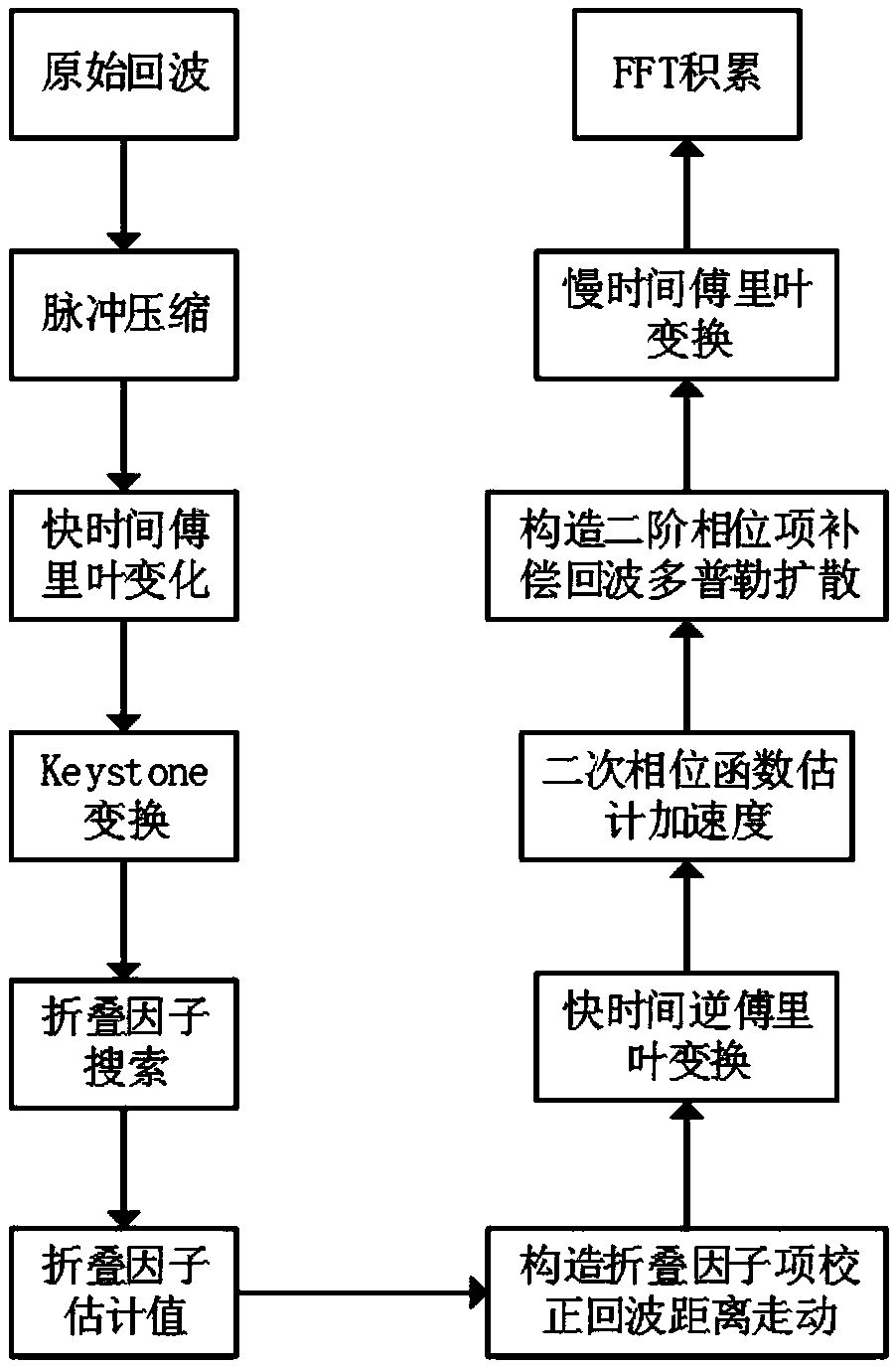
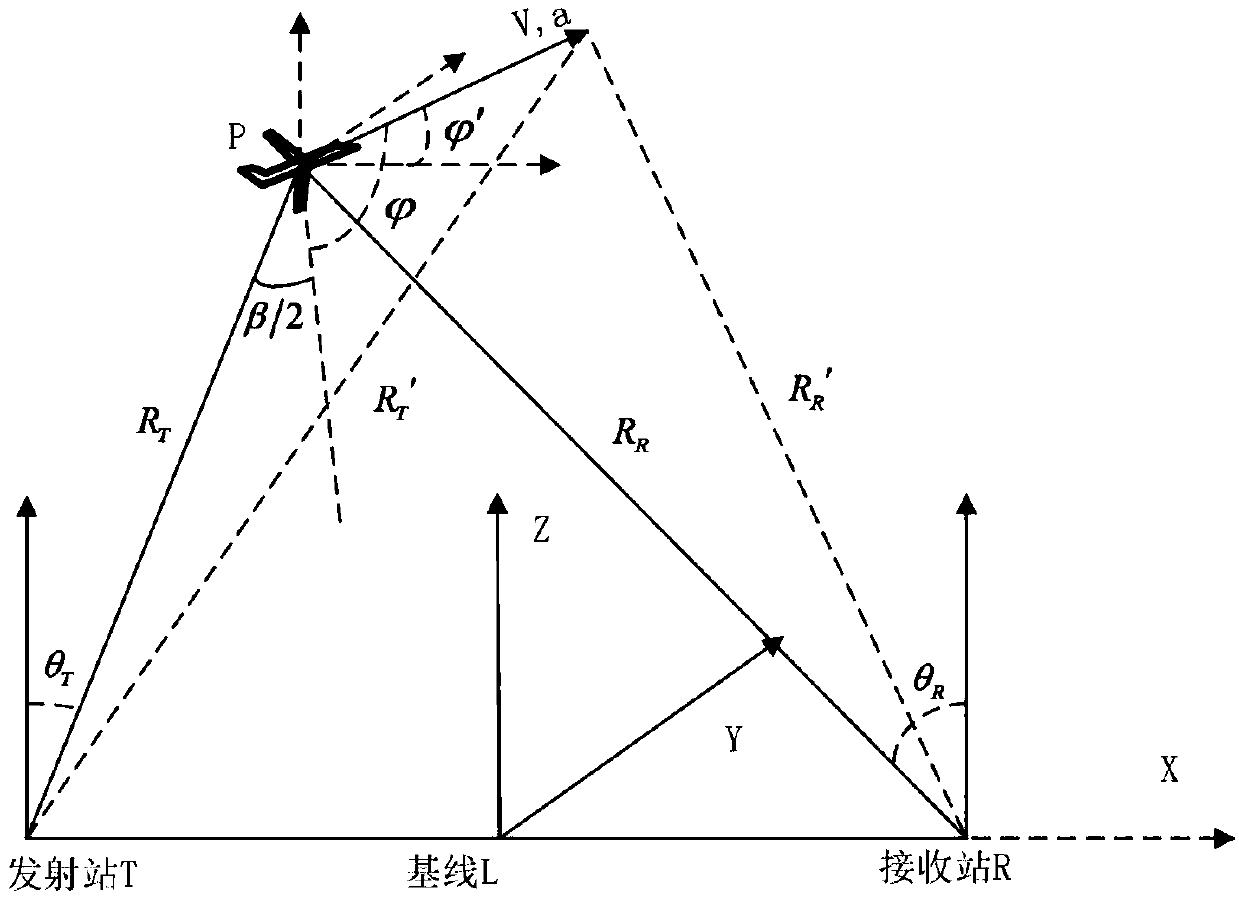
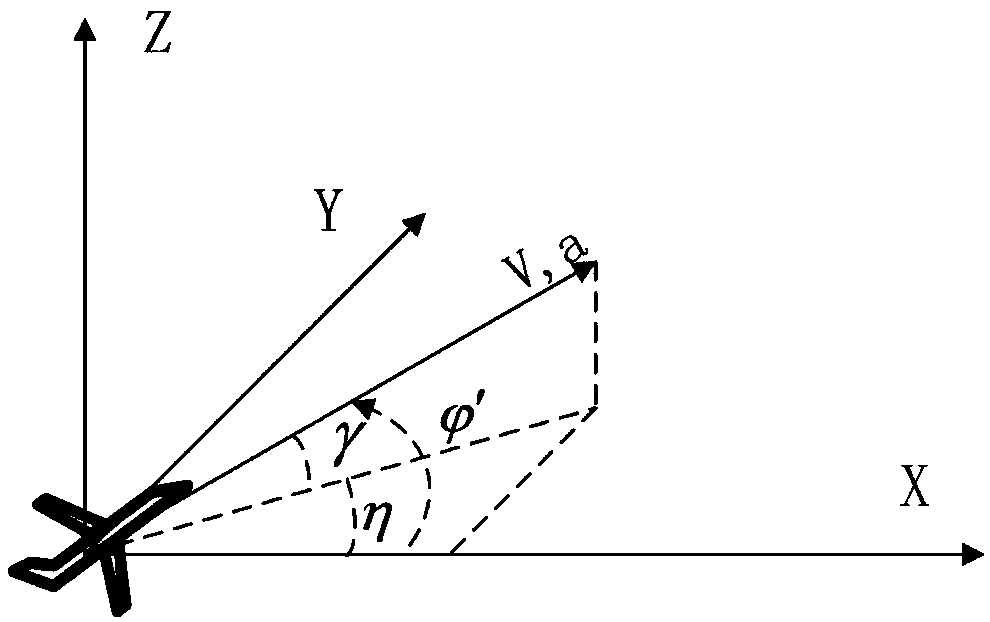
The invention discloses an improved algorithm based on parameter estimation and compensation of a quadratic phase function, and belongs to the technical field of signal and information processing. Thealgorithm performs range walk correction on slow time-range frequency domain echo signal considering range walk and Doppler diffusion through Keystone transform, and then eliminates a coupling relation between the range frequency f and the slow time tn in a second-order phase item corresponding to the acceleration in a narrow-band condition; meanwhile, a folding factor corresponding to the blindspeed is searched, a folding factor compensation item is constructed to correct the range walk caused by the blind speed; then the target acceleration is estimated by using the quadratic phase function, and a second-order phase item corresponding to the acceleration is constructed to compensate Doppler diffusion of the echo signal; and finally, long-term phase-coherent accumulation is performed soas to realize high-speed weak target detection of bistatic radar. The method disclosed by the invention is high in operation speed, stable in performance and applicable to detection of weak targets with a low signal-to-noise ratio and difficultly estimated target parameters.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Radar operation with increased doppler capability
ActiveUS9057785B1Radio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationConstant frequencyFrequency spectrum
Owner:LASSEN RES CORP
System, method and computer program product for reducing quadratic phase errors in synthetic aperture radar signals
InactiveUS7064702B1Reducing quadratic phase errorReduce errorsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture sonarEnvironmental geology
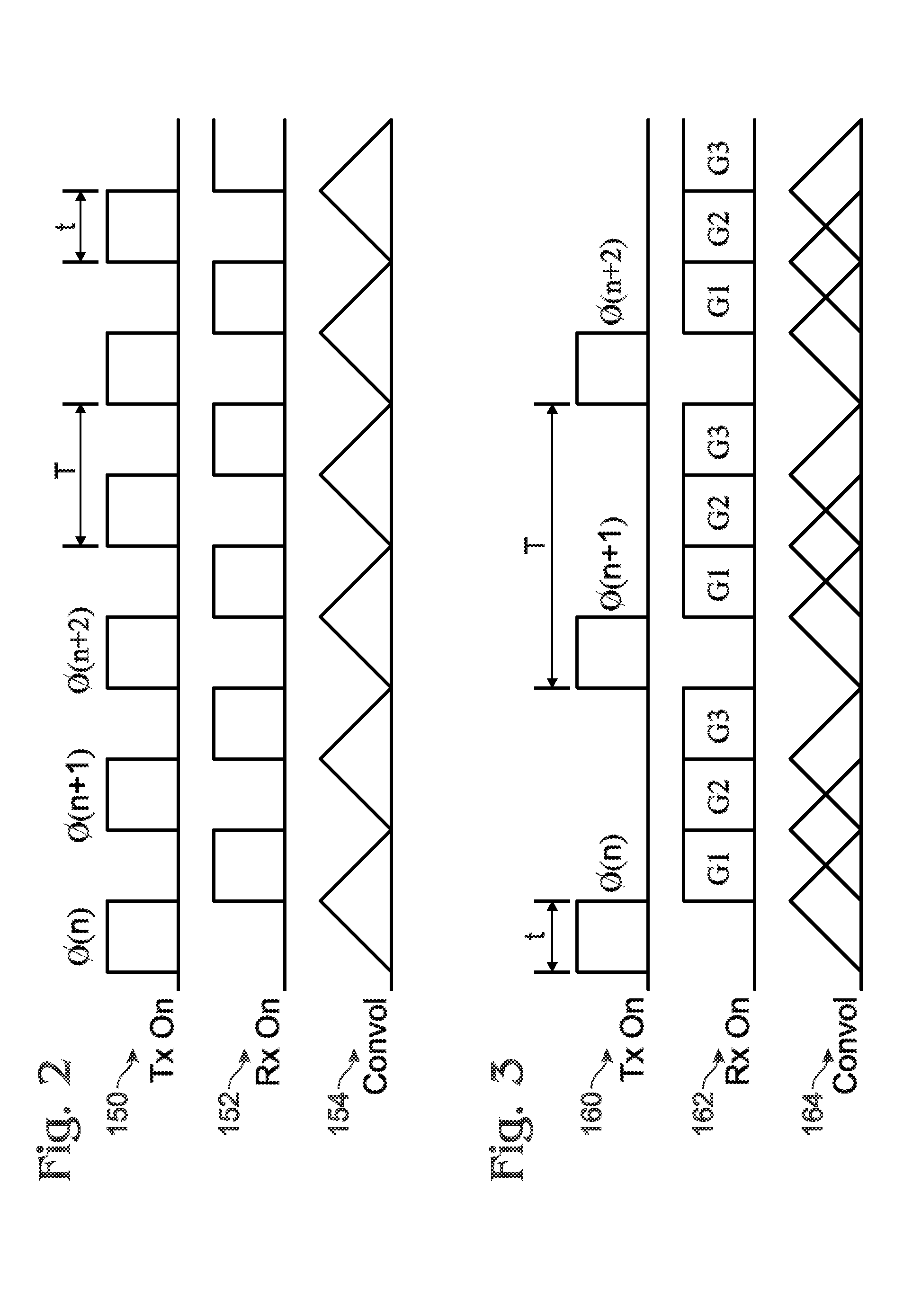
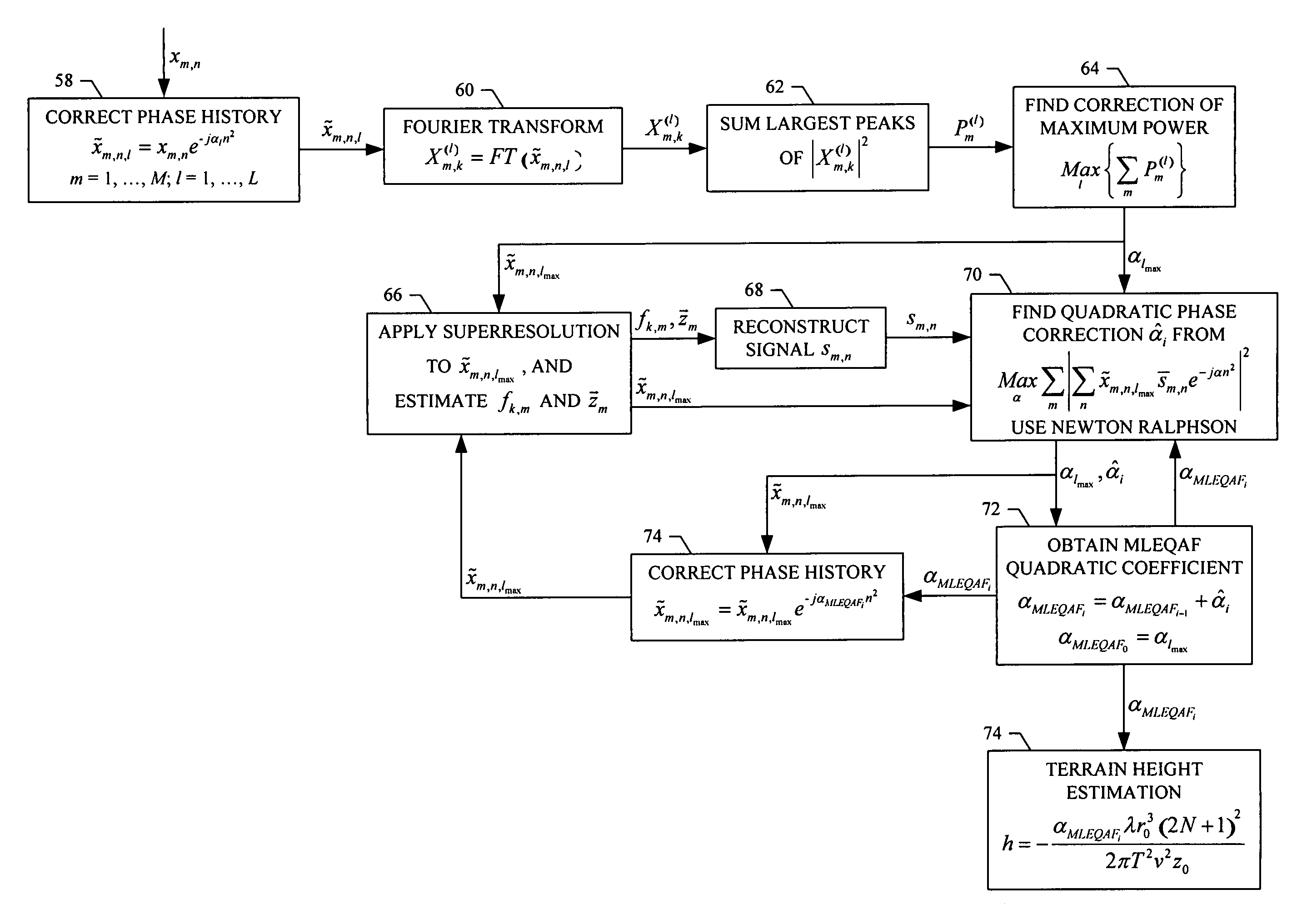
A method is provided for reducing quadratic phase errors in synthetic aperture radar signals from a plurality of range lines where each range line includes a plurality of azimuth positions. The method includes receiving a plurality of slow-time samples representing radar signals for a plurality of azimuth positions for a plurality of range lines. A plurality of corrected samples and an initial quadratic phase error coefficient are identified based upon the slow-time samples. The corrected samples are processed according to a superresolution signal processing technique to thereby obtain a plurality of estimated Doppler frequencies for a plurality of point scatterers at each range line, after which a true signal for each range line is reconstructed based upon the plurality of estimated Doppler frequencies. A correction to the initial quadratic phase error coefficient is then obtained based upon the corrected samples, the true signals and the initial quadratic phase error coefficient.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
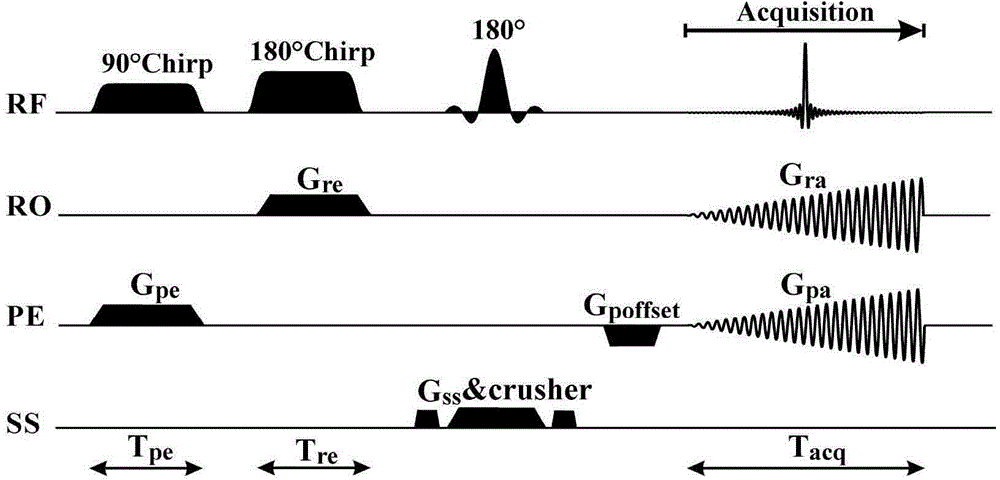
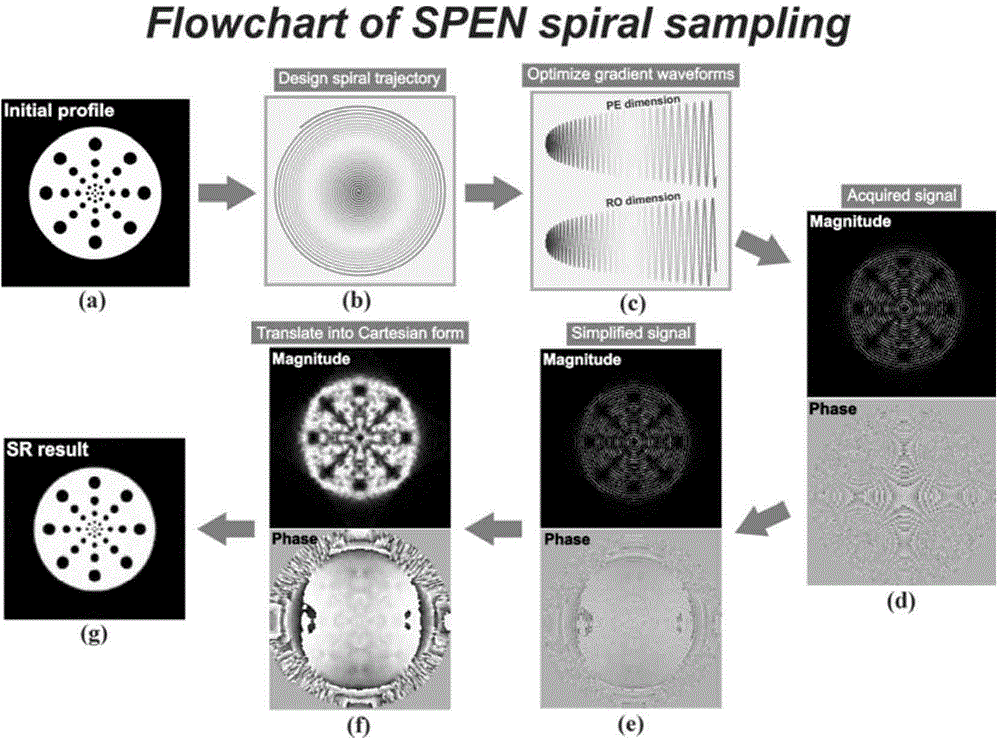
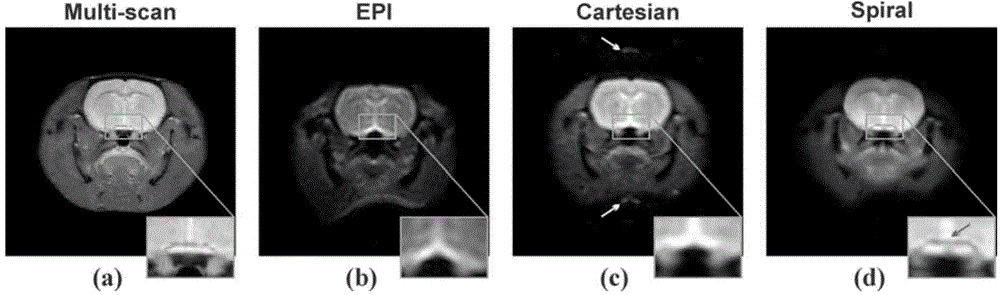
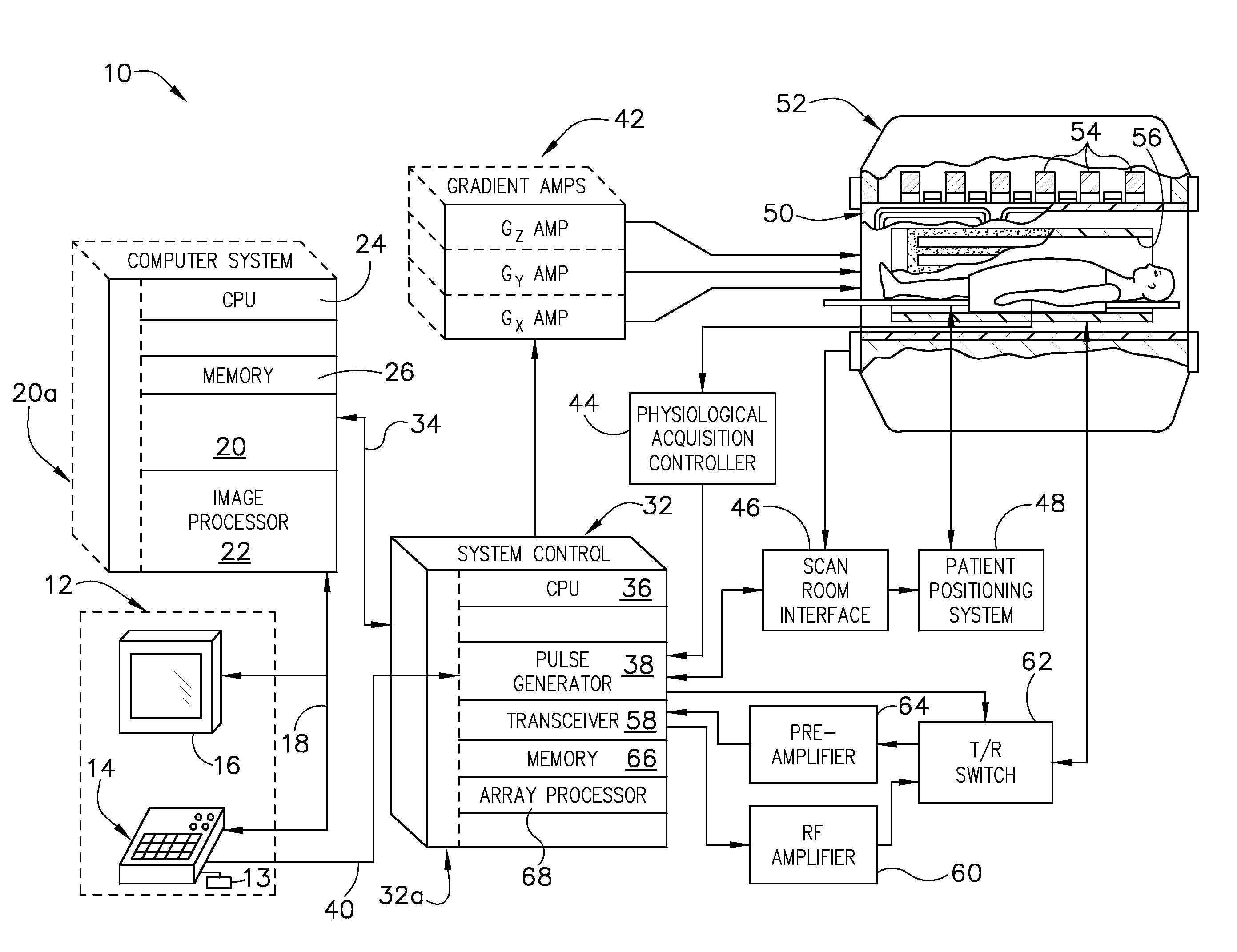
SPEN single-scanning magnetic resonance imaging spiral sampling and reconstructing method
ActiveCN104965184AHigh resolutionIncrease sampling densityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsImaging qualityData acquisition
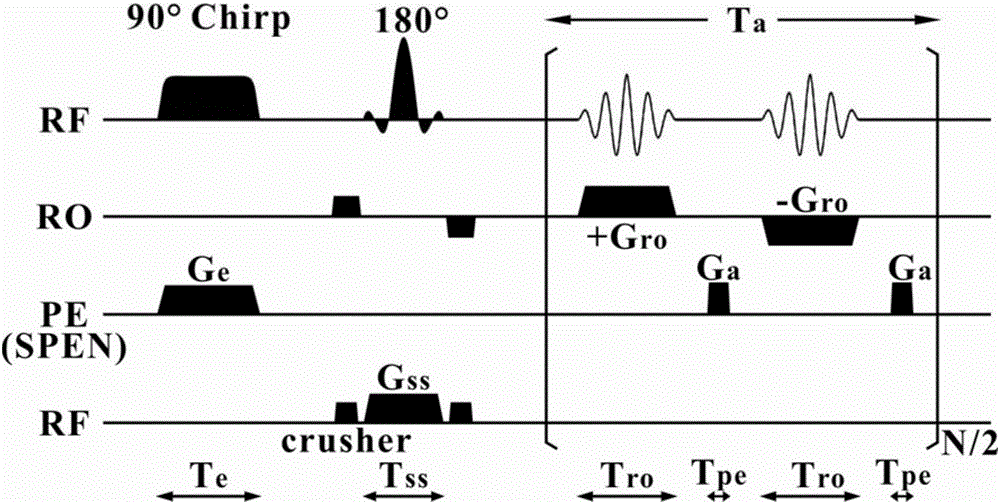
Provided is an SPEN (spatiotemporally-encoded) single-scanning magnetic resonance imaging spiral sampling and reconstructing method, relating to a magnetic resonance imaging method. 90 DEG linear scanning pulses and 180 DEG linear scanning pulses combine with corresponding SPEN gradients, and in a trigger period, protons in a space spin to obtain a quadratic phase relevant with a spatial position; in a sampling period, a spiral sampling gradient after optimization collets data, and obtains spatial domain magnetic resonance imaging data with T2*weighting in a superfast speed; and finally, spiral sampling data are reconstructed through a specific grid algorithm and a super-resolution reconstructing method based on compression perception, so as to obtain super-resolution high quality magnetic resonance images. The method greatly improves the image quality of SPEN single-scanning imaging, and provides a great imaging tool for the fields requiring superfast imaging.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Efficient phase correction scheme for range migration algorithm
InactiveUS20030142000A1Convenient lengthExemption stepsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBatch processingCommon phase error
A system and method for efficient phase error correction in range migration algorithm (RMA) for synthetic aperture radar (SAR) systems implemented by making proper shifts for each position dependent phase history so that phase correction can readily be performed using the aligned phase history data during batch processing. In its simplest form, the invention (44) is comprised of two main parts. First (60), alignment of the phase error profile is achieved by proper phase adjustment in the spatial (or image) domain using a quadratic phase function. Second (62), the common phase error can be corrected using autofocus algorithms. Two alternative embodiments of the invention are described. The first embodiment (44a) adds padded zeros to the range compressed data in order to avoid the wrap around effect introduced by the FFT (Fast Fourier Transform). This embodiment requires a third step (64): the target dependent signal support needs to be shifted back to the initial position after phase correction. The second embodiment (44b) uses the range compressed data without padded zeros. Instead, an aperture of greater length needs to be generated by the Stolt interpolation. In this embodiment, the third step (64) of shifting the signal support back can be eliminated.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Apparatus and method for acquisition and reconstruction of non-cpmg propeller sequences
ActiveUS20110025325A1Electrical measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsPropellerEngineering
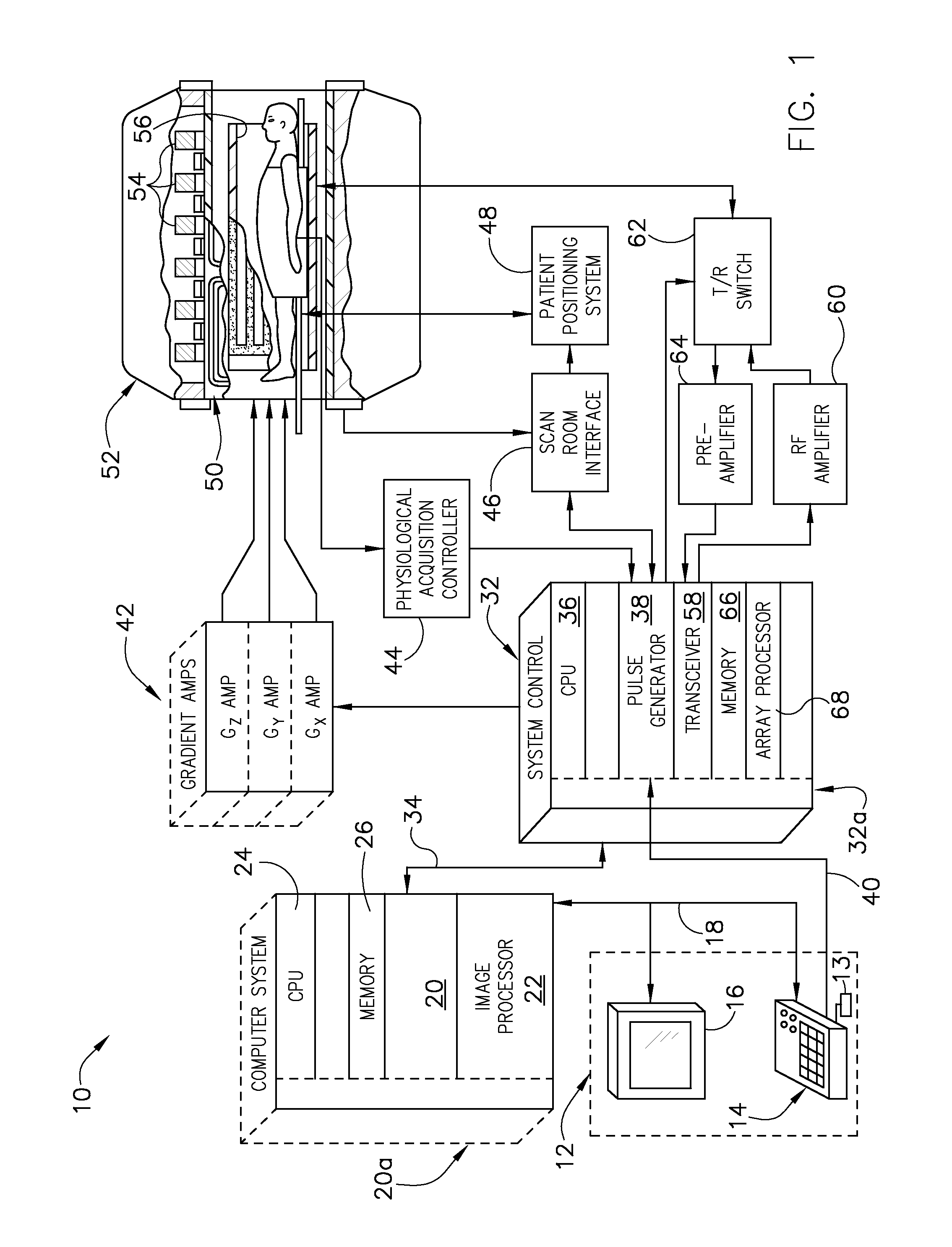
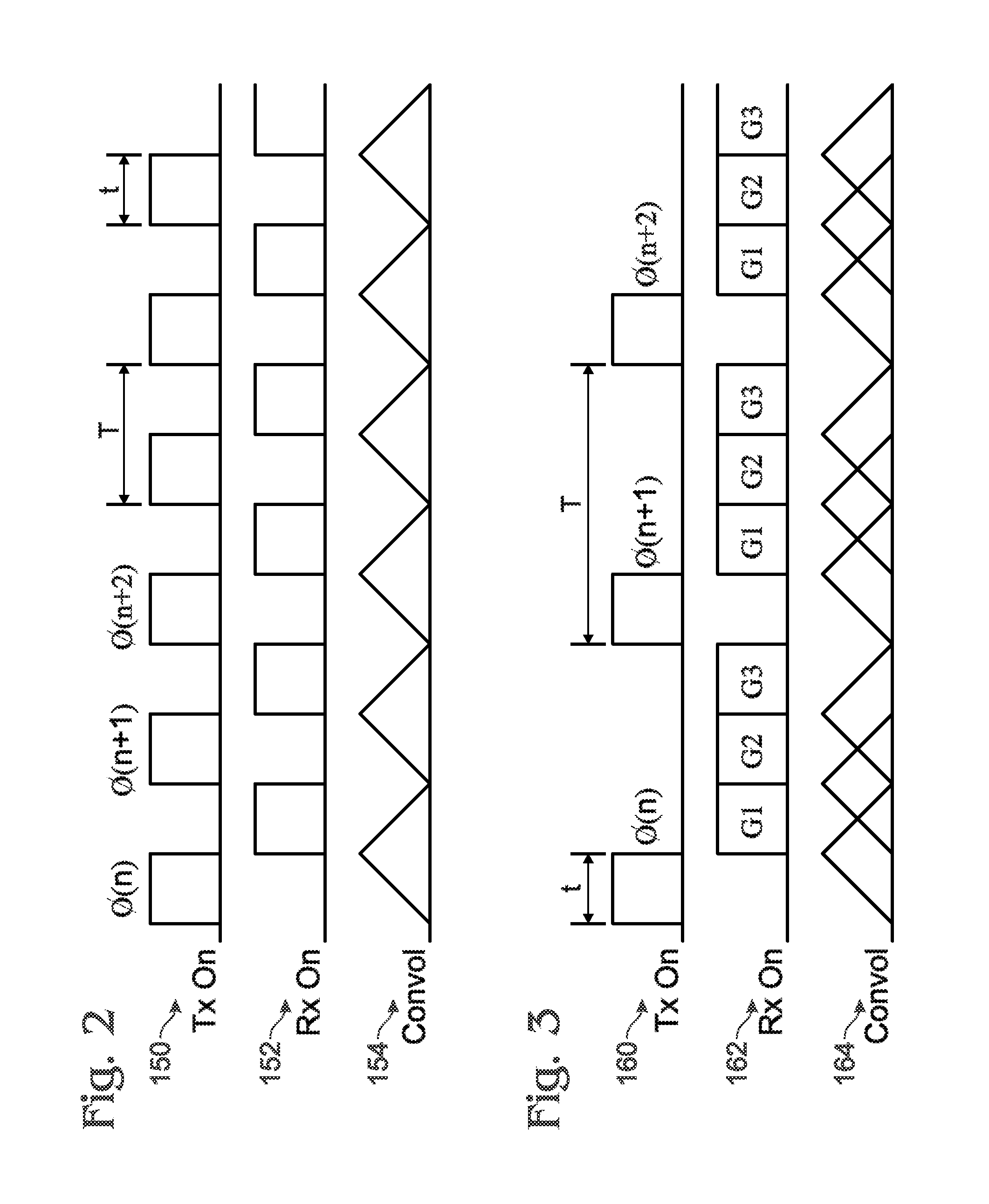
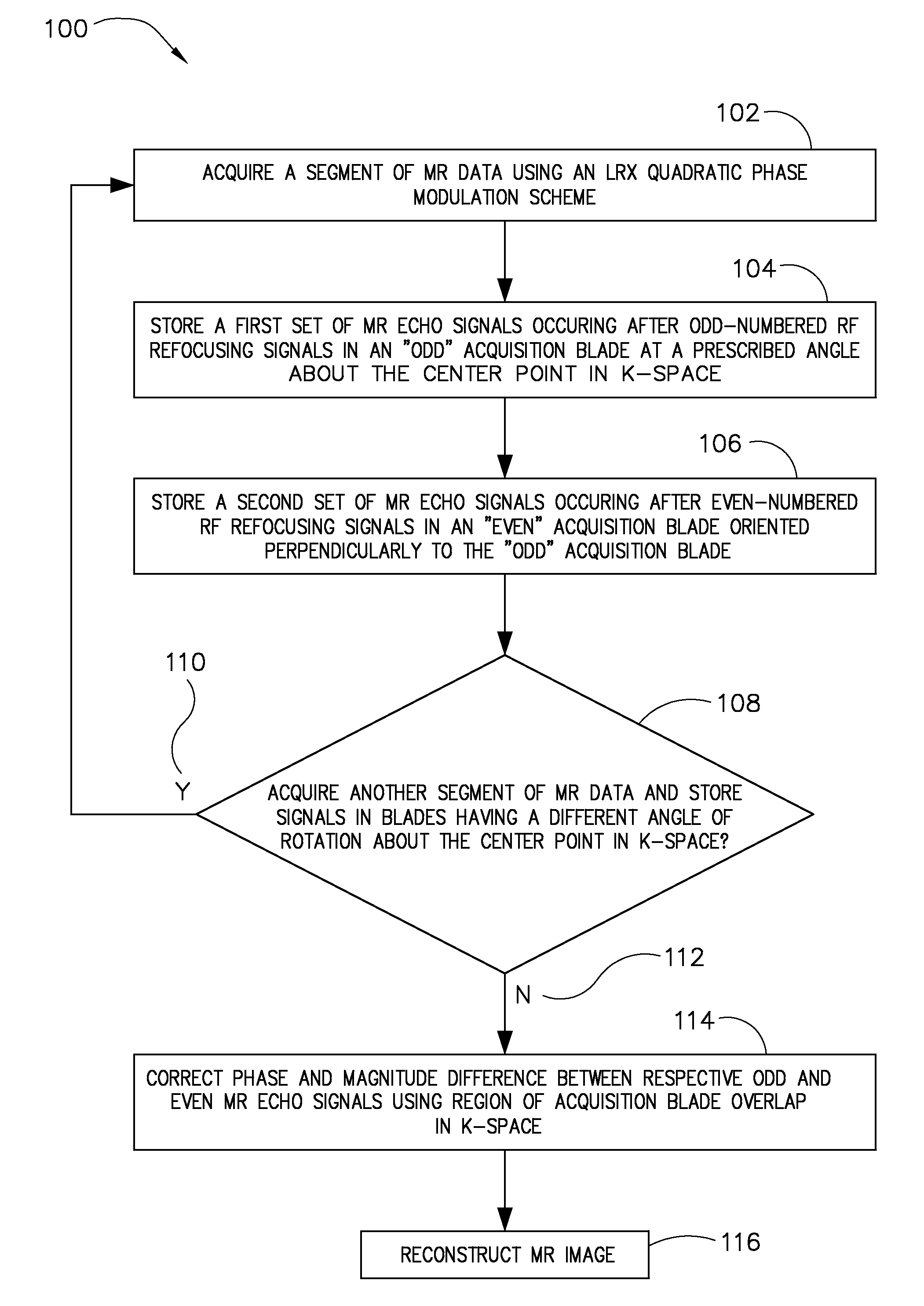
An apparatus and method of MR imaging is disclosed. The apparatus and method comprises segmenting acquisition of an echo train into separate odd and even acquisition blades in k-space, wherein the odd and even acquisition blades extend orthogonally through a common reference point in a central region of k-space. A segment of MR data is acquired using a quadratic phase modulation scheme, wherein a first set of MR echo signals occurring after odd-numbered RF refocusing pulses are stored in the odd acquisition blade, and a second set of MR echo signals occurring after even-numbered RF refocusing pulses are stored in the even acquisition blade. This acquisition and segmentation is repeated until a sufficient number of blades are acquired to fill k-space. Finally, an image is reconstructed from the acquisition blades.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Beam phase modulation for improved synthetic aperture detection and estimation
InactiveUS7701380B2Improve performanceSuppress ambiguityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSonificationAmbiguity
Owner:CHIRP
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) communications device and method that incorporates low PAPR preamble with circuit for measuring frequency response of the communications channel
A communications device includes a demapping and demodulation circuit and processes an OFDM communications signal that includes modulated subcarriers carrying communications data forming a data payload and modulated subcarriers carrying a training sequence forming a preamble. Those OFDM subcarriers carrying the training sequence have a sample for each subcarrier at a frequency bin using evenly spaced, equal amplitude subcarriers that have a set phase of each sinusoid to a specific angle with quadratic phase to form a low peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) preamble with about a PAPR value of 2.6 decibels (dB). A channel estimate circuit is operative for measuring fluctuations within a flat-top spectrum of the received OFDM communications signal corresponding to the preamble to reflect the frequency response of the communications channel.
Owner:SMARTSKY NETWORKS
Space segment payload architecture for mobile satellite services (MSS) systems
ActiveUS8354956B2Not adversely impactedReduce complexityRadio transmissionAntennasAudio power amplifierLight beam
A antenna system for generating and distributing power among a plurality of non-focused beams is provided The system comprises a reflector having a focal plane and a non-parabolic curvature configured to form the defocused beams. The curvature is configured to create a symmetrical quadratic phase-front in an aperture plane of the reflector. The system further comprises a plurality of feed antennas disposed in the focal plane of the reflector and configured to illuminate the reflector. Each feed antenna is configured to contribute power toward each of the defocused beams. The system further comprises a plurality of fixed-amplitude amplifiers, at least one of which corresponds to each feed antenna.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Method for preparing partial stabilization zirconium oxide ceramic capable of increasing thermal shock resistance
The present invention is the preparation process of partially stable zirconia ceramic with high heat shock resistance, and belongs to the field of functional ceramic and inorganic material preparing technology. The partially stable zirconia ceramic material is prepared through mixing zirconia with stabilizer yttria or magnesia, adding adhesive and tabletting, pre-sintering at 500-900 deg.c, and ball milling into powder of size below 20 microns. Compared with available technological process, the preparation process of the present invention has the advantages including precise control on stabilizer content, improved quadratic phase distribution homogeneity, obviously raised heat shock resistance, simple process, high repeatability and low cost in equipment.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
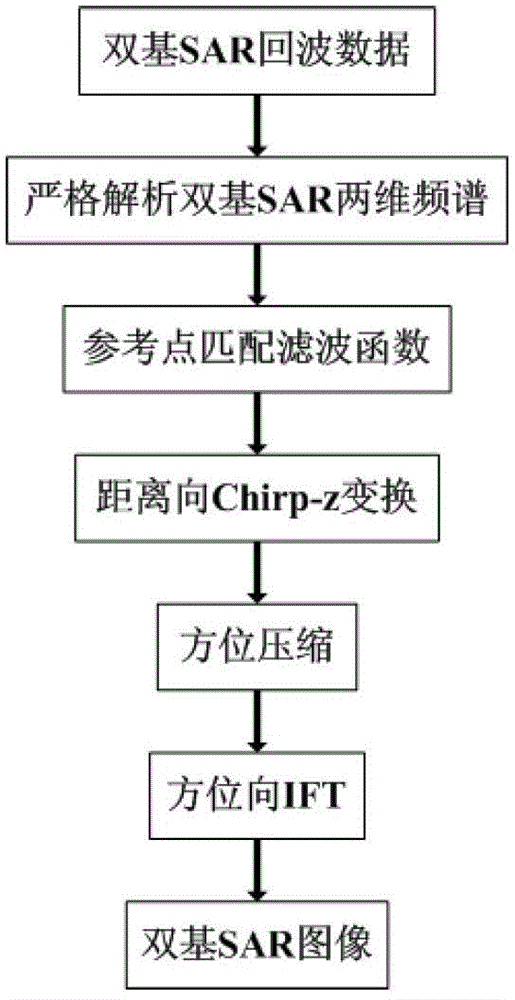
Scaling inverse Fourier transformation imaging method of bistatic synthetic aperture radar (SAR)
InactiveCN103149554ALarge drawing widthHigh precision spectrum accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFourier transformFundamental frequency
The invention discloses a scaling inverse Fourier transformation Chirp-Z imaging algorithm suitable for bistatic synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and mainly solving the problem of unsatisfactory imaging effect under a long baseline situation in the prior art. The method comprises a first step of adopting geometrical relation formula method GBF to obtain a two dimensional spectrum expression of signal strict parsing, a second step of taylor expression of the two dimensional spectrum expression at distance wave number fundamental frequency and keeping to a quadratic term, a third step of phase compensation of the distance frequency quadratic term by using a parameter of a reference point, a fourth step of space-variant range cell migration correction to signals after twice phase compensation through Chirp-Z scaling algorithm, a fifth step of azimuth compression to the signals after cell migration correction, and a sixth step of obtaining a final imaging result through one inverse Fourier transformation. The scaling inverse Fourier transformation imaging method of the bistatic SAR can achieve fast imaging treatment of bistatic SAR signal under the long baseline situation, an imaging process only needs fast Fourier transformation and phase complex multiplication operation, and the method is high in efficiency and suitable for real-time imaging.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Universal optical antenna of synthetic aperture laser imaging radar
ActiveCN101477198AAdjust receiving directivityAperture Synthetic ImagingTelescopesElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadar systemsPhotovoltaic detectors
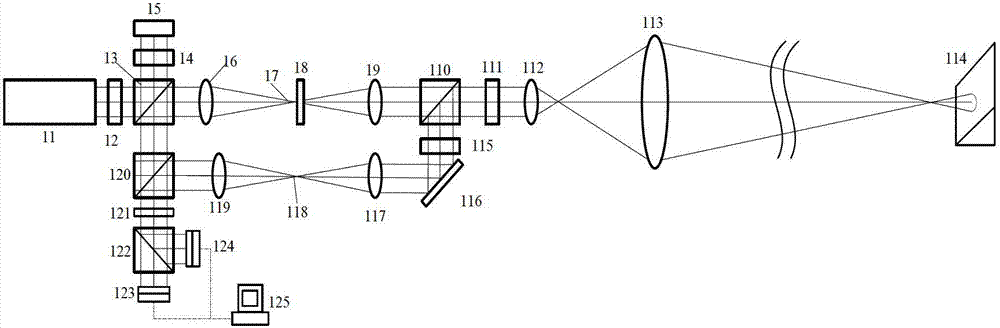
The invention provides a universal synthetic aperture laser imaging radar optical antenna for transmitting and receiving a distant-field or near-field optical signal for the same synthetic aperture laser imaging radar system. The antenna transmits and receives a primary telescope by a bidirectional loop, wherein the bidirectional loop consists of a transmitting channel of an adjustable secondary telescope structure and a receiving channel of an erecting telescope structure, and is connected with a laser light source, a photoelectric detector and the primary telescope; the position of a primary mirror of the secondary telescope in the transmitting channel can be moved; erecting system defocusing is arranged in the receiving channel; and a variable aperture light diaphragm is arranged in front of the photoelectric detector. The universal synthetic aperture laser imaging radar optical antenna can realize a laser transmitting wave surface with different curvature radiuses additively offset through special quadratic phase by controlling the moving distance of transmitting the secondary telescope, and can realize adjustment of receiving directivity of the optical antenna by controlling defocusing amount of the receiving channel and size of the aperture light diaphragm while eliminating target echo received wave surface aberration.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
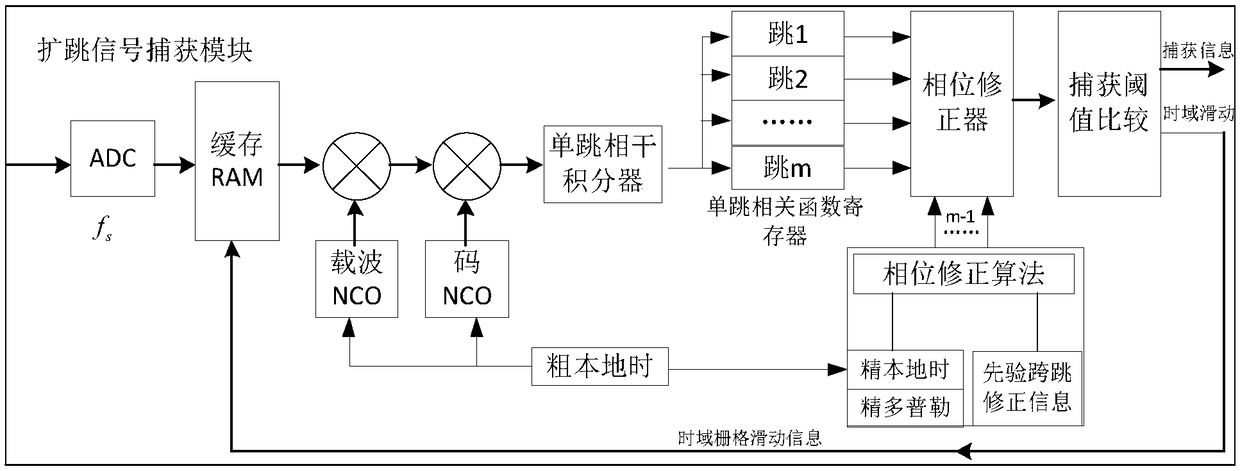
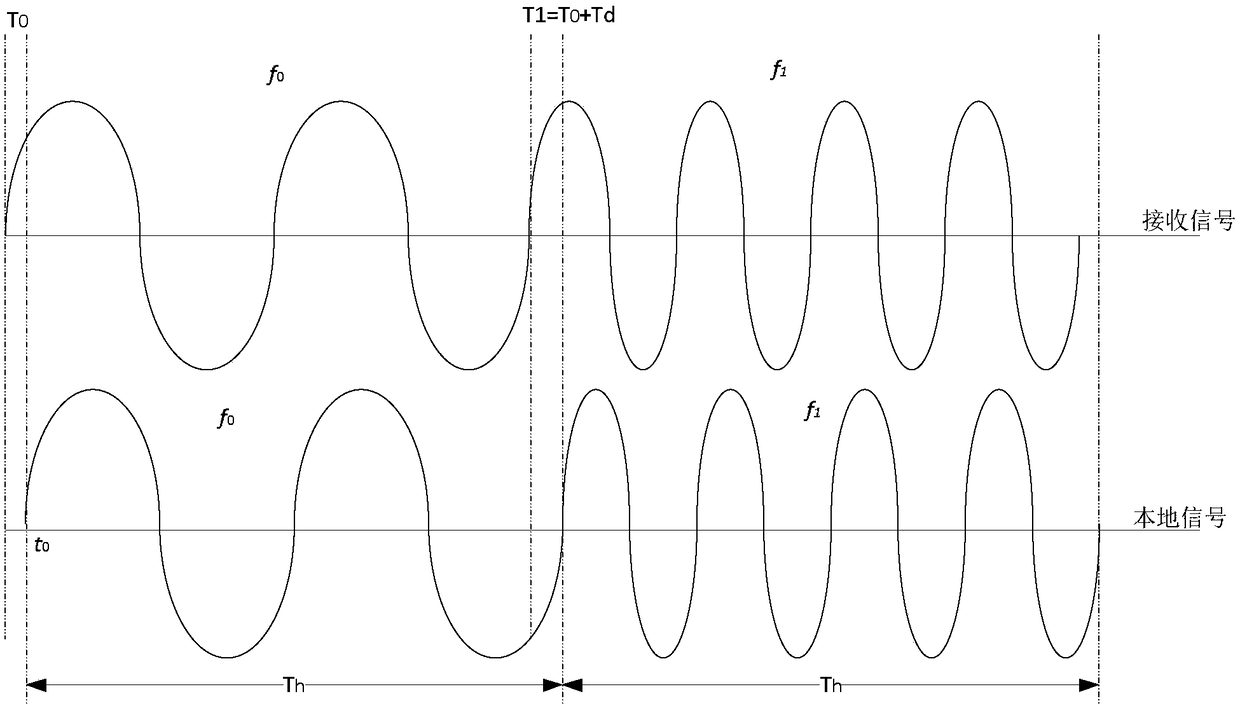
Modified broadband hopping spread signal cross-hop coherent integration method
ActiveCN109217898AEliminate the effects ofSmall amount of calculationRadio transmissionPhase correctionCorrelation function
The invention provides a modified broadband hopping spread signal cross-hop coherent integration method, aiming at solving the problem of long-time coherent integration of high-hop speed broadband hopping spread signal. The invention is realized by the following technical scheme: based on the carrier phase, the spread hopping signal acquisition module obtains the carrier initial phase difference correction amount between frequency hopping points of the spread hopping system introduced by the equipment channel through a priori information, and takes the correction amount as the initial phase correction amount of the subsequent cross-hop coherent integration; the carrier initial phase difference correction amount of the spread hopping system introduced by the equipment channel is used as theinitial phase correction amount. The A / D converter ADC divides the local time into coarse local time and fine local time. First Phase Correction of Cross-Hopping Coherent Integration Carrier Using Prior Initial Phase Correction; calculating a quadratic phase correction amount of a correlation function of each single-hop signal; the results of m-hop coherent integration are modified and accumulated across hops to realize the cross-hop coherent integration. If the results of m-hop coherent integration are larger than the acquisition threshold, the accurate estimation information of time delay and Doppler of the received signal is output.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Near-eye holographic three-dimensional display system and display method
ActiveCN107390379AQuality improvementReduce the number of operationsOptical elementsSpatial light modulatorImaging quality
The invention provides a near-eye holographic three-dimensional display system and a display method. The near-eye holographic three-dimensional display system comprises a first lens, a spatial light modulator, a 4f system and a display screen. The near-eye holographic three-dimensional display system and the display method have the advantages that three-dimensional scene reconstruction can be achieved by using the simple display system; when the phase hologram corresponding to a three-dimensional field depth image is calculated, the depth information of each pixel point in the field depth image is encoded into quadratic phase information, and the quadratic phase information is loaded to the phase type spatial light modulator; device operation times and data storage are lowered as compared with those of a traditional phase hologram calculation algorithm using a point-element method and chromatography, and operation speed is increased; meanwhile, a two-dimensional image loaded by the display screen is projected to the phase type spatial light modulator through the 4f system, so that each pixel point of the two-dimensional image is modulated by the corresponding quadratic phase factor on the spatial light modulator, the original depth information is given to each pixel point of the two-dimensional image, and image quality is increased greatly.
Owner:南京芯视半导体有限公司
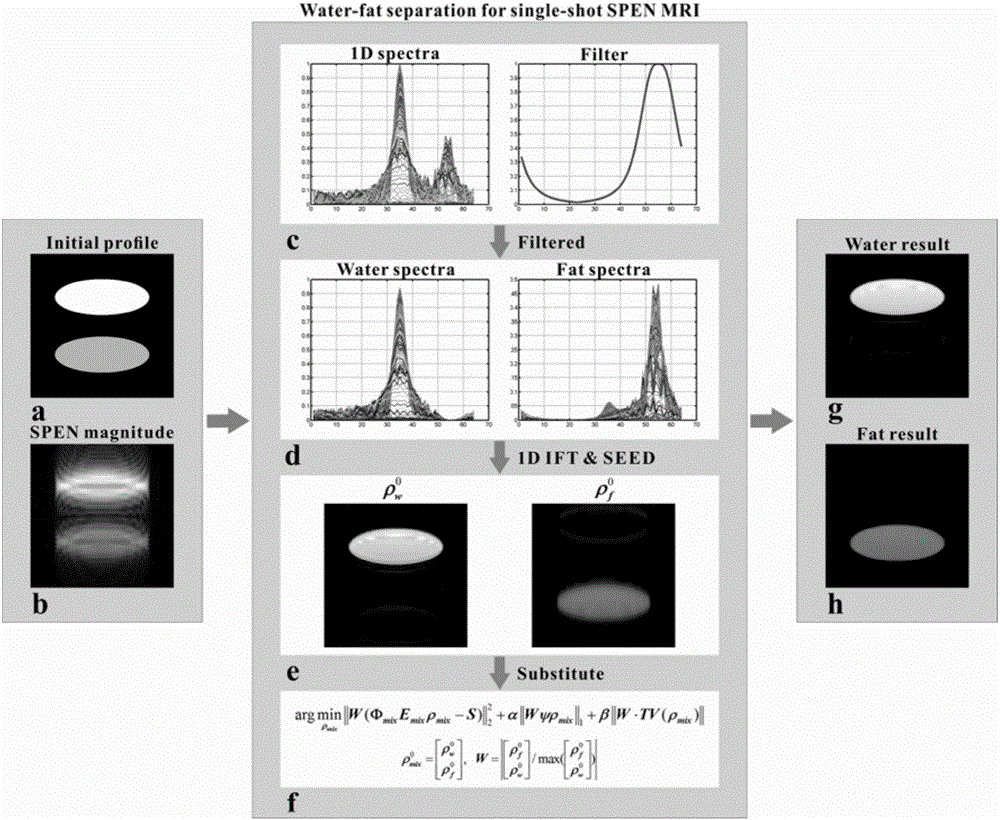
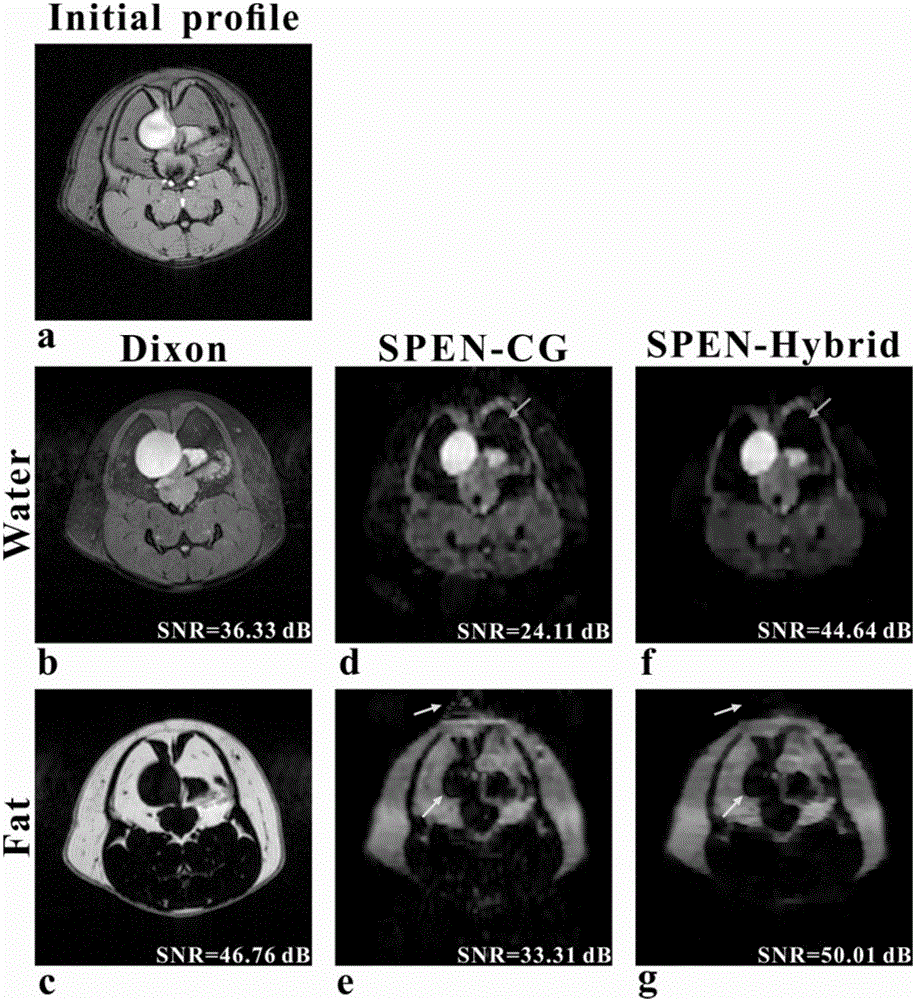
Water-fat separation rebuilding method based on single-scanning space-time coding magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveCN106841273AHigh resolutionImprove signal-to-noise ratioAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceWater resource assessmentSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Imaging quality
The invention provides a water-fat separation and rebuilding method based on single-scanning space-time coding magnetic resonance imaging, and relates to a magnetic resonance imaging method. The method comprises the steps of utilizing a single-scanning space-time coding and imaging sequence to encode and collect a water-fat signal, wherein a 90-degree linear frequency sweep pulse is combined with a space-time coding gradient to give one quadratic phase to the water-fat signal in an exciting stage; based on the characteristic, obtaining priori knowledge images of water and fat used for guiding water-fat separation and rebuilding by selecting an appropriate filter to preprocess collected data; in a water-fat separation stage, utilizing the priori knowledge images as an initial value and weighted information, and obtaining a high-resolution and high-signal-to-noise ratio water image and fat image by solving a super-resolution lifting and edge artifact removing algorithm equation in a water-fat environment. According to the water-fat separation and rebuilding method based on single-scanning space-time coding magnetic resonance imaging, the water-fat separation of single-scanning space-time coding magnetic resonance imaging can be effectively achieved, meanwhile the image quality of separated images is improved, and the clinical application progress is promoted.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
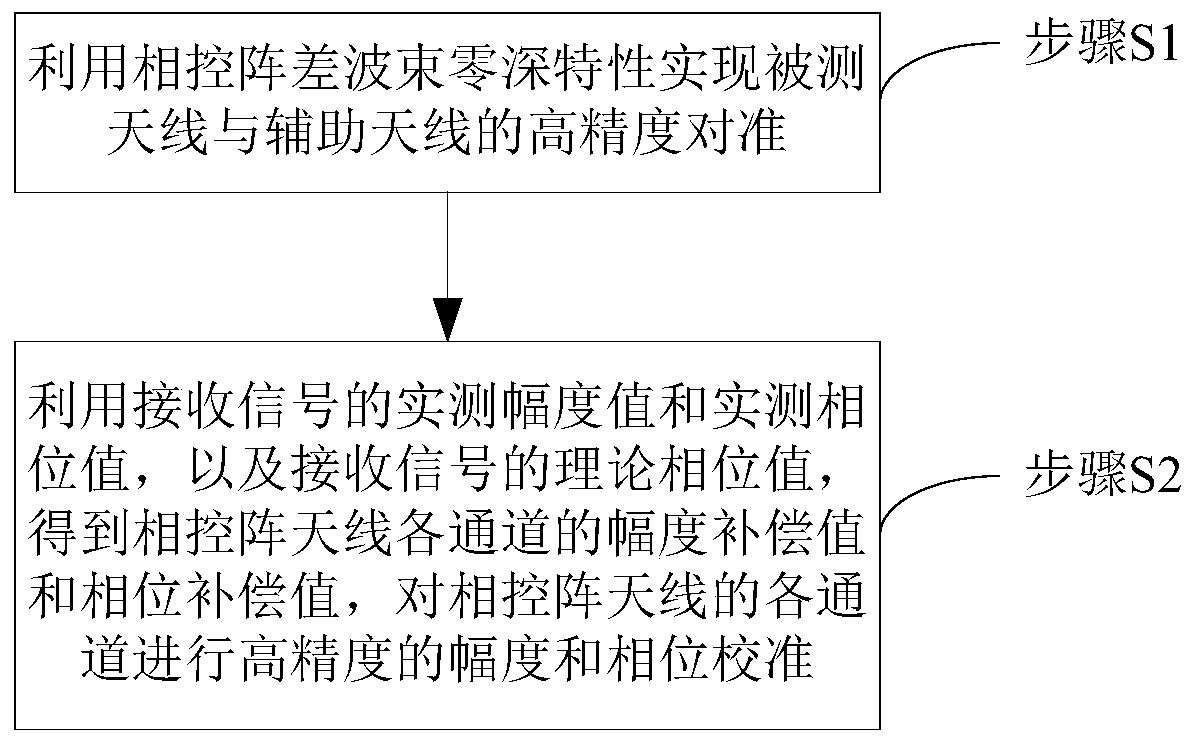
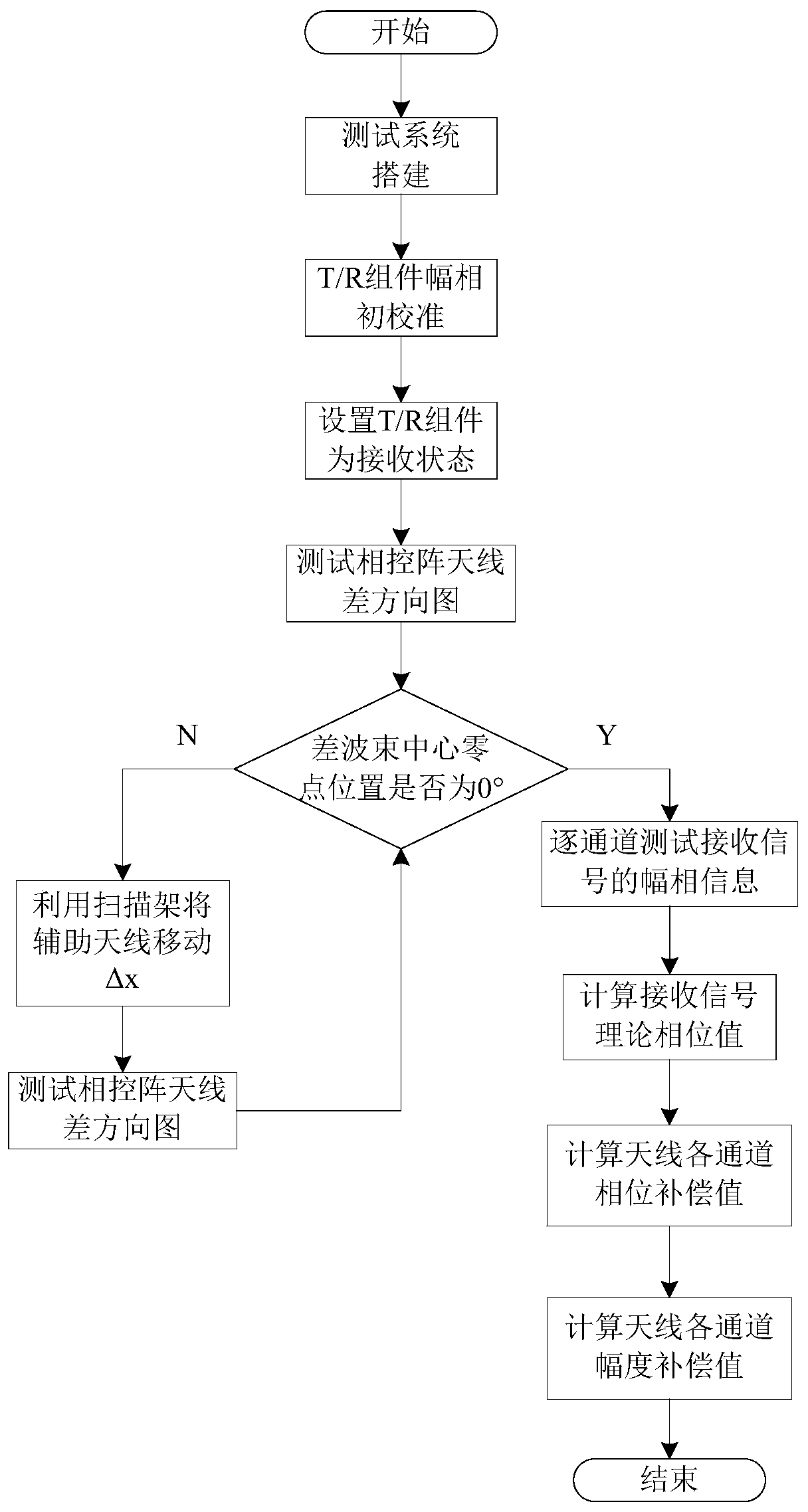
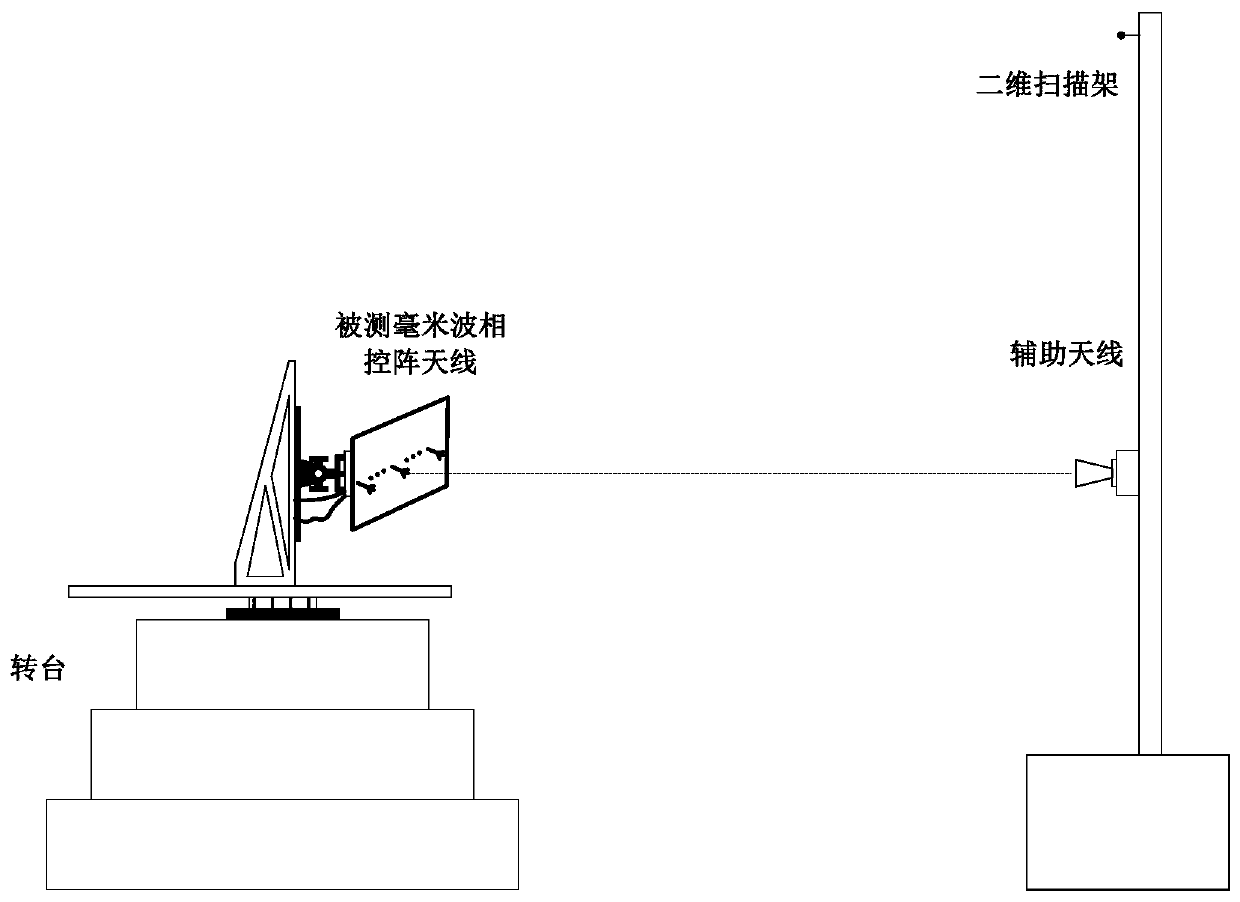
Phased-array antenna calibration method based on difference beam calibration
ActiveCN111490834AHigh precisionImprove calibration resultsTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringEngineeringCalibration result
The invention discloses a phased-array antenna calibration method based on difference beam calibration. High-precision alignment of the measured phased-array antenna and the auxiliary antenna is realized by utilizing the zero-depth characteristic of a phased-array difference beam to obtain the secondary amplitude compensation value and the secondary phase compensation value of each channel of thephased-array antenna by utilizing the actually measured amplitude value and the actually measured phase value of the received signal and the theoretical phase value of the received signal, and high-precision amplitude and phase calibration is performed on each channel of the phased-array antenna. According to the midfield test method for performing high-precision calibration on the phased-array antenna by utilizing the zero-depth characteristic of the difference beam, the high-precision alignment of the auxiliary antenna and the tested antenna can be realized, no fitting error exists, and a high-precision calibration result can be obtained. Besides, the method can be carried out in the dark room all day long without meeting far-field conditions, auxiliary test equipment such as a total station is not needed, and the method has very high operability and relatively high engineering value.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
Methods for differencing and self-focusing phases of synthetic aperture laser imaging radar
ActiveCN103163531AOptimizing the phase of the quadratic term in azimuthSuppress noise phaseElectromagnetic wave reradiationImaging qualityRadar
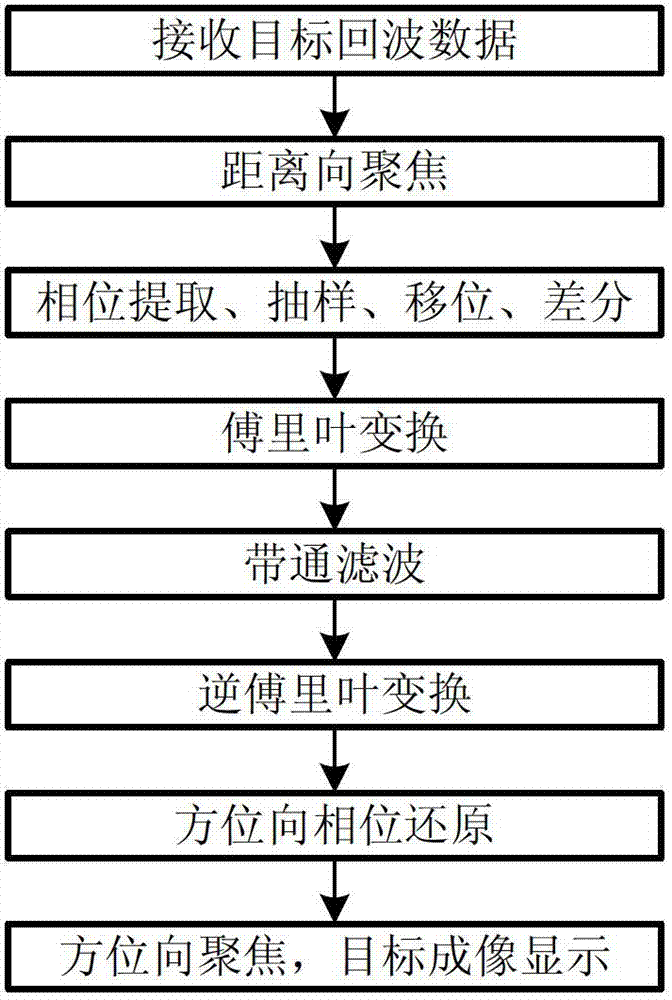
The invention discloses methods for differencing and self-focusing phases of a synthetic aperture laser imaging radar. According to a principal, an azimuth phase signal with a noise phase is extracted from a radar echo signal subjected to range focusing and shifted, the shifted phase signal and an unshifted phase signal are differenced, a signal obtained through differencing is sequentially subjected to Fourier transformation, band-pass filtering and inversion Fourier transformation to obtain signals, the obtained signals are sampled and accumulated at equal intervals to obtain an optimized azimuth quadratic phase, and the optimized azimuth quadratic phase is subjected to azimuth focusing to image a target. By the method, quadratic phase process crucial to target aperture synthesis is optimized, so that the imaging quality can be improved; and the method is important technological improvement of the synthetic aperture laser imaging radar.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Processing method for imaging two-dimensional missing data with high-resolution bunching SAR
ActiveCN106842204AReduce data transferReduce storage burdenRadio wave reradiation/reflectionComplete dataMissing data
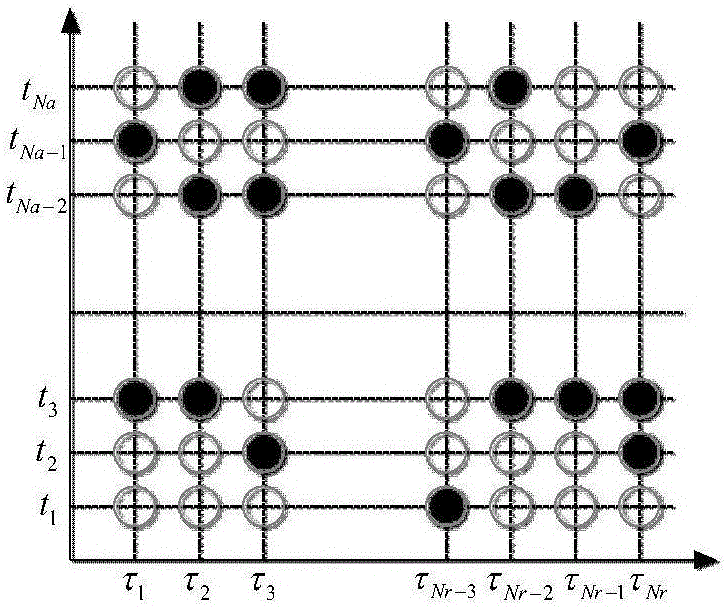
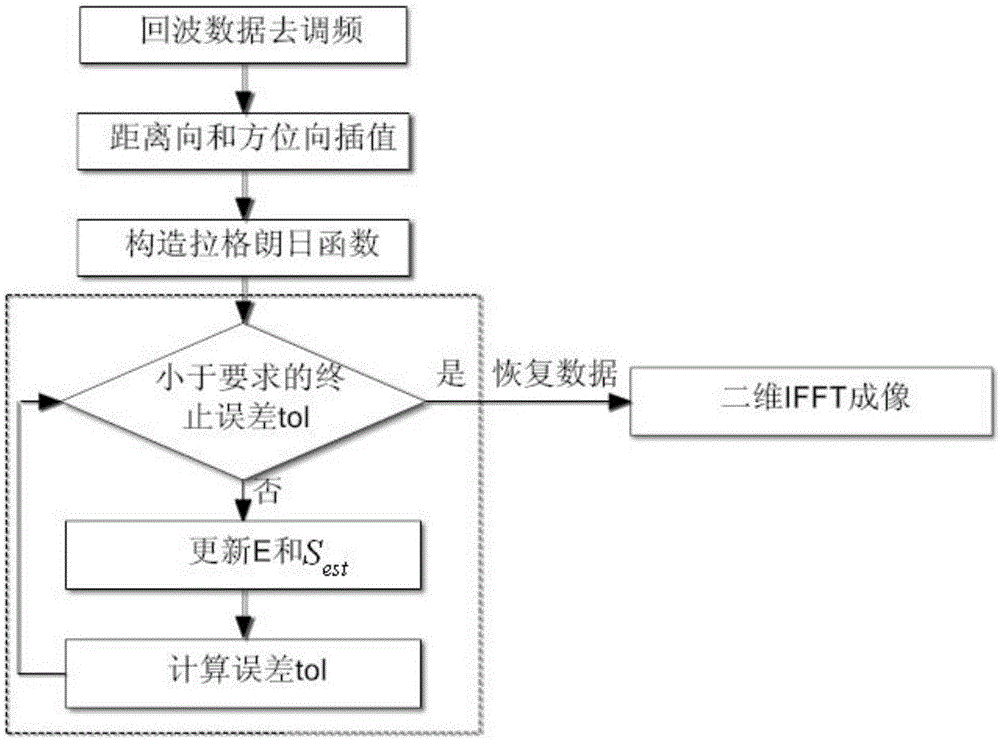
The invention discloses a processing method for imaging two-dimensional missing data with high-resolution bunching SAR. In an actual data collecting process, air turbulence, radio frequency band interference and other factors may cause data lost at a certain frequency point or certain position, at the moment, distortion, fuzziness, aliasing and other phenomena of a point target response function inevitably exist in a SAR image by adopting an FFT method, and the subsequent target identification and detection work are influenced. Regarding the problem, matrix complete theory-based bunching SAR missing data imaging is provided; missing-contained echoed data is demodulated to remove quadratic phase in an echo signal; then, complete data is recovered by utilizing the matrix complete theory, and imaging is realized by utilizing two-dimensional IFFT of the recovered complete data. Compared with an existing echo imaging algorithm by utilizing missing-contained data, the method has the advantages that the situation of two-dimensional data missing is taken into consideration, and the resolution the same as bunching SAR is realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Radar operation with enhanced doppler capability
ActiveUS20160011300A1ICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumConstant frequency
Owner:LASSEN RES CORP
Apparatus and method for acquisition and reconstruction of non-CPMG propeller sequences
An apparatus and method of MR imaging is disclosed. The apparatus and method comprises segmenting acquisition of an echo train into separate odd and even acquisition blades in k-space, wherein the odd and even acquisition blades extend orthogonally through a common reference point in a central region of k-space. A segment of MR data is acquired using a quadratic phase modulation scheme, wherein a first set of MR echo signals occurring after odd-numbered RF refocusing pulses are stored in the odd acquisition blade, and a second set of MR echo signals occurring after even-numbered RF refocusing pulses are stored in the even acquisition blade. This acquisition and segmentation is repeated until a sufficient number of blades are acquired to fill k-space. Finally, an image is reconstructed from the acquisition blades.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
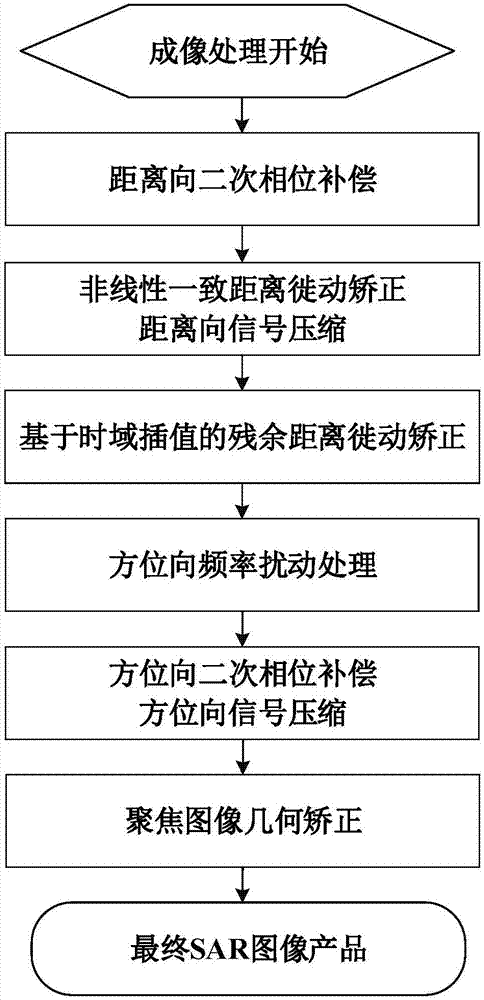
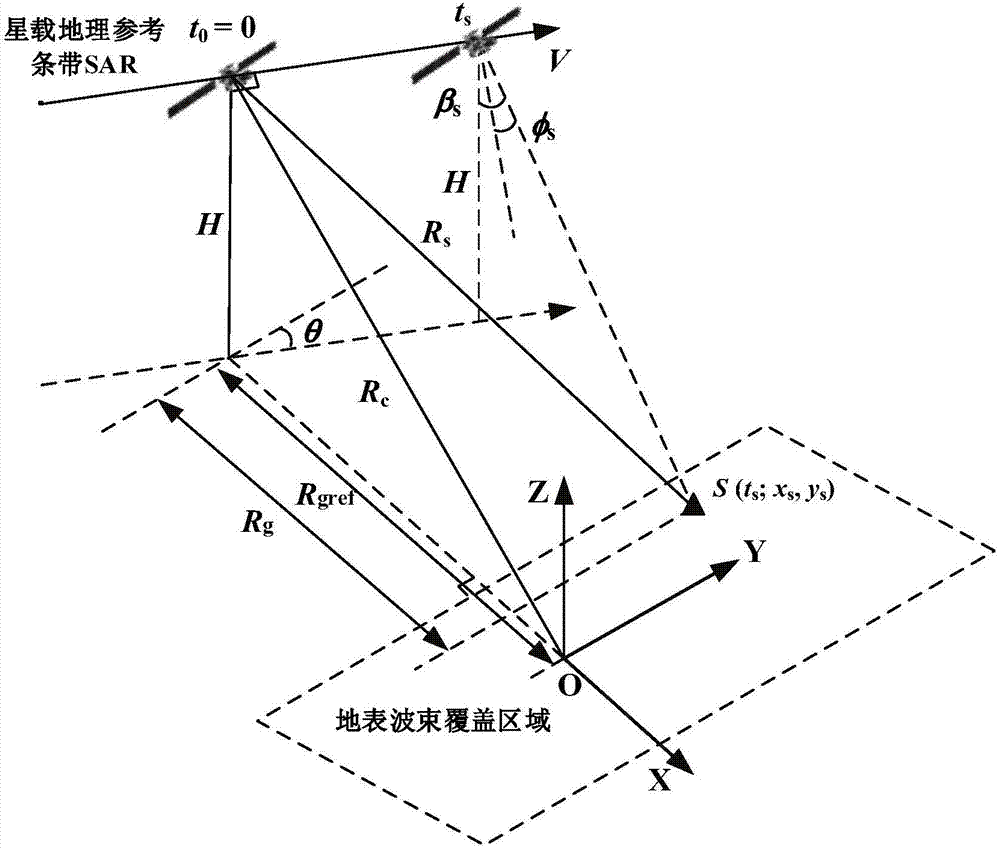
WNLCS imaging method facing satellite-borne geographic reference strip SAR
InactiveCN107102330ADistance Migration CorrectionResidual distance migration can be corrected in batchesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEarth observationSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a wide nonlinear chirp scaling imaging processing method (wide nonlinear chirp scaling, WNLCS) suitable for a satellite-borne geographic reference strip synthetic aperture radar (synthetic aperture radar, SAR). The WNLCS method mainly comprises six steps of step1, range-direction secondary phase compensation; step2, nonlinear uniform distance migration correction and range-direction signal compression; step3, residual distance migration correction based on a time-domain interpolation; step4, azimuth frequency disturbance processing; step5, azimuth secondary phase compensation and azimuth signal compression; and step6, focusing-image geometric correction. The WNLCS imaging processing method provided in the invention possesses a data processing capability of a full aperture and a data redundancy is low. The method is a high-efficient and accurate imaging processing method suitable for an earth observation demand of the satellite-borne geographic reference strip SAR.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for flexibly regulating and controlling self-focusing focal length of self-focusing light beam
The invention discloses a method for flexibly regulating and controlling the self-focusing focal length of a self-focusing light beam. According to the method, a phase hologram that has a secondary phase factor and is generated by using a computer holographic technology is loaded to a spatial light modulator; the self-focusing focal length of a round Airy beam is regulated and controlled by changing the coefficient of the secondary phase factor and the round Airy beam with the required self-focusing focal length is generated, so that the halo distribution is clear and the focusing effect is good. The cubic phase hologram is generated by utilizing a computer holographic technology, so that the cost is hardly required; focusing effects of lenses with different focal lengths on the round Airybeam can be reflected; and compared with the mode of generating the round Airy beam by using Fourier space, the disclosed method does not need a Fourier transform lens. Moreover, the regulation and control mode is convenient to operate; the self-focusing focal length can be regulated and controlled more flexibly; and a specific research task can be completed.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Secondary phase error compensation method and device for digital holographic microscopy
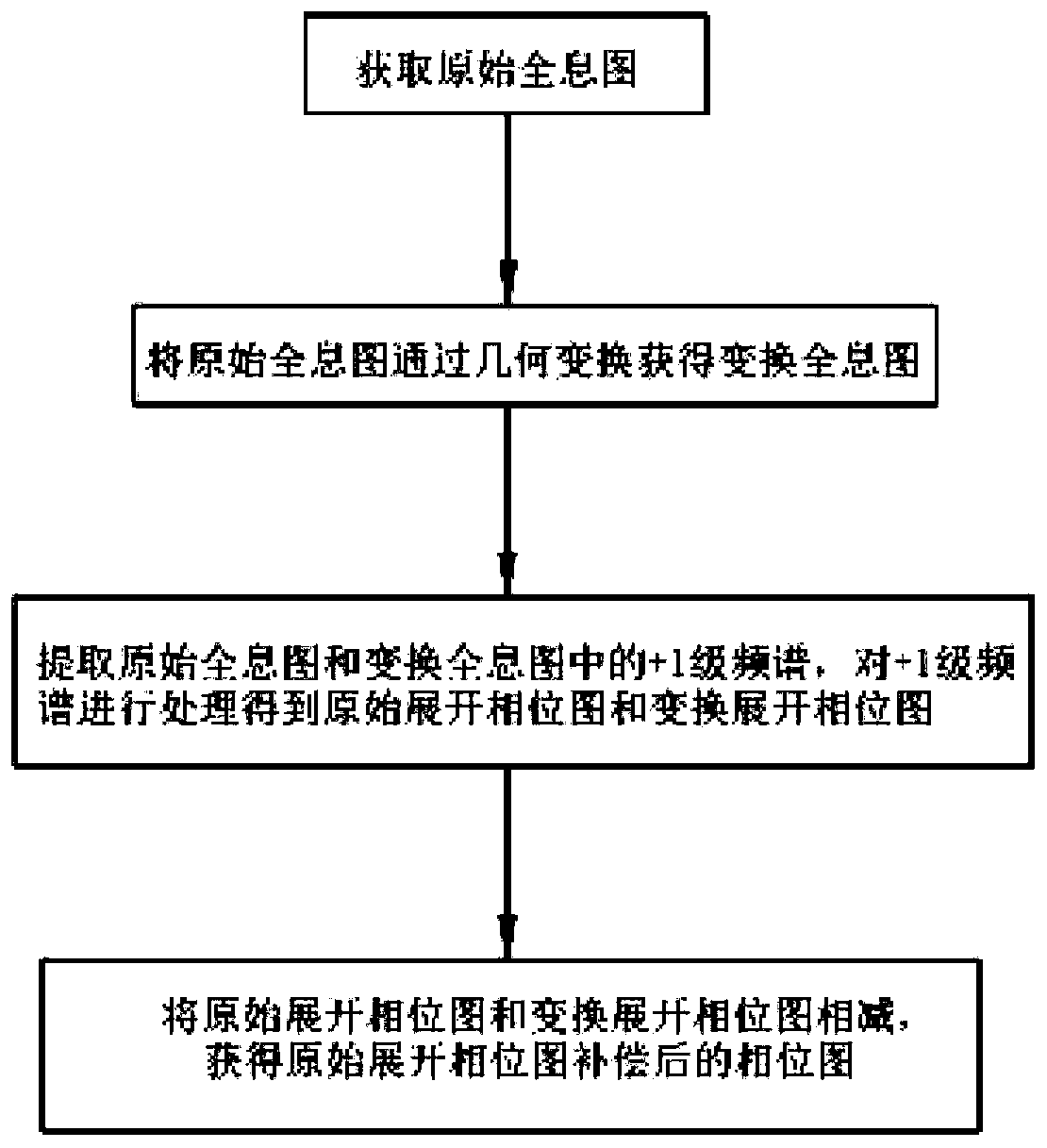
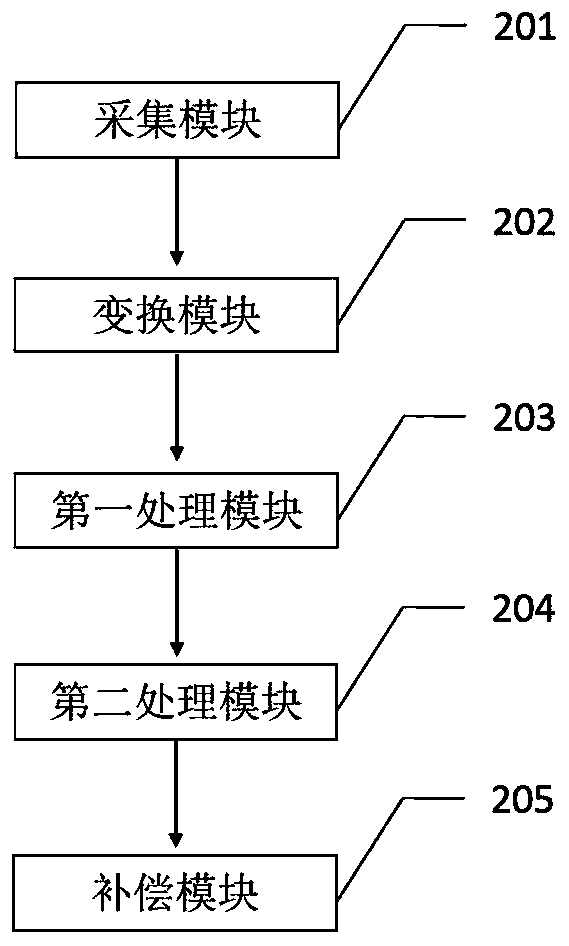
InactiveCN109724511AQuadratic Phase Error CancellationLow costUsing optical meansFrequency spectrumDigital holographic microscopy
The invention discloses a secondary phase error compensation method for digital holographic microscopy, comprising the steps of: collecting a hologram of an object to be tested as an original hologram; performing a geometric transformation operation on the original hologram to obtain a transformed hologram; extracting +1-level spectrum from the spectrum of the original hologram, removing the tiltphase error in the +1-level spectrum, then converting to obtain an original unwrapped phase diagram FORMULA referred; extracting +1-level spectrum from the spectrum of the transformed hologram, removing the tilt phase error in the +1-level spectrum, then converting to obtain a transformed unwrapped phase diagram FORMULA referred; and subtracting the original unwrapped phase diagram FORMULA referred and the transformed unwrapped phase diagram FORMULA referred to obtain a phase diagram after secondary phase error compensation of the original unwrapped phase diagram. A secondary phase error compensation device comprises an acquisition module, a transformation module, a first processing module, a second processing module, and a compensation module. The invention has the advantage of being possible to eliminate secondary phase errors simply and accurately by geometric transformation.
Owner:JIAYING UNIV
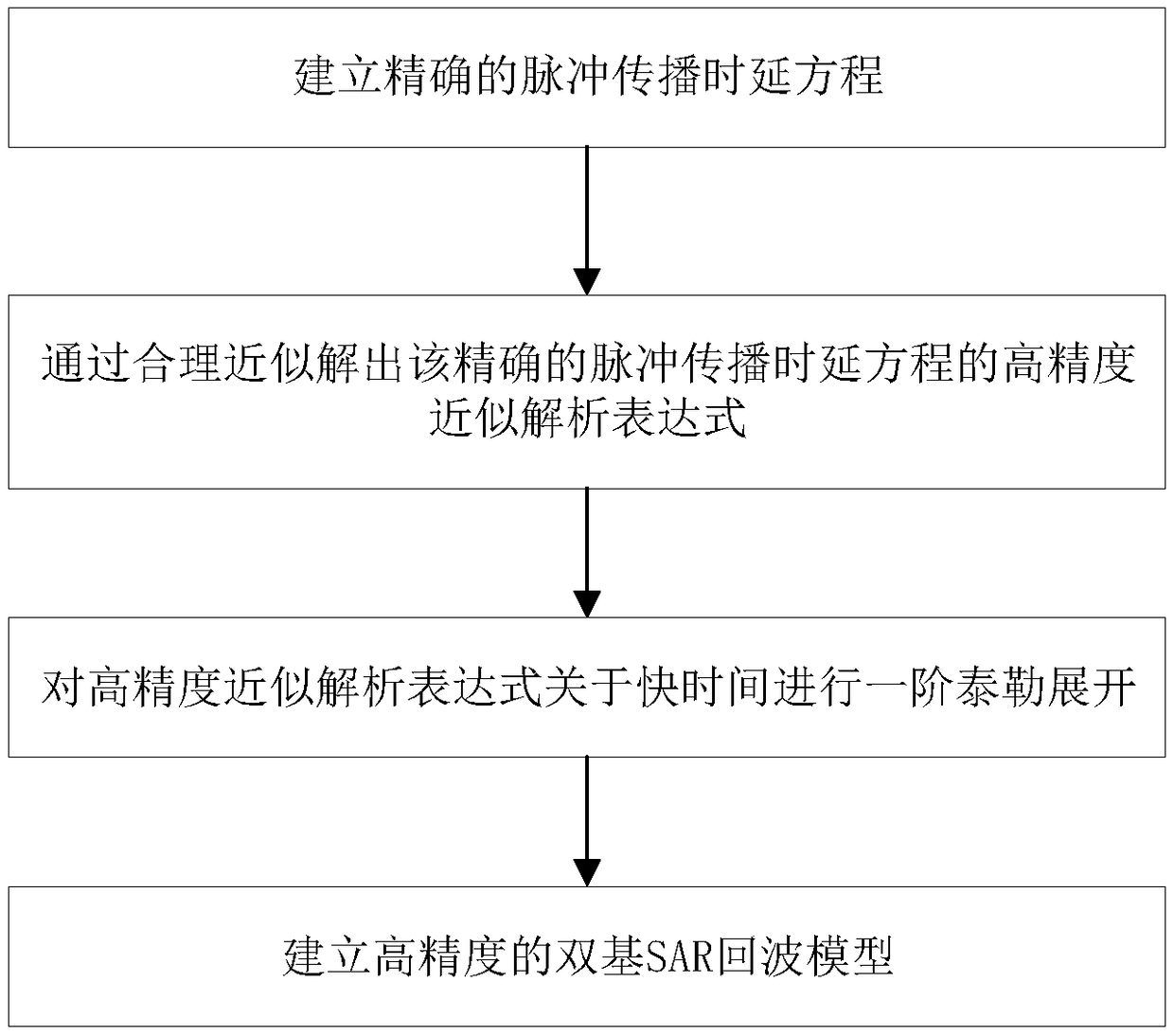
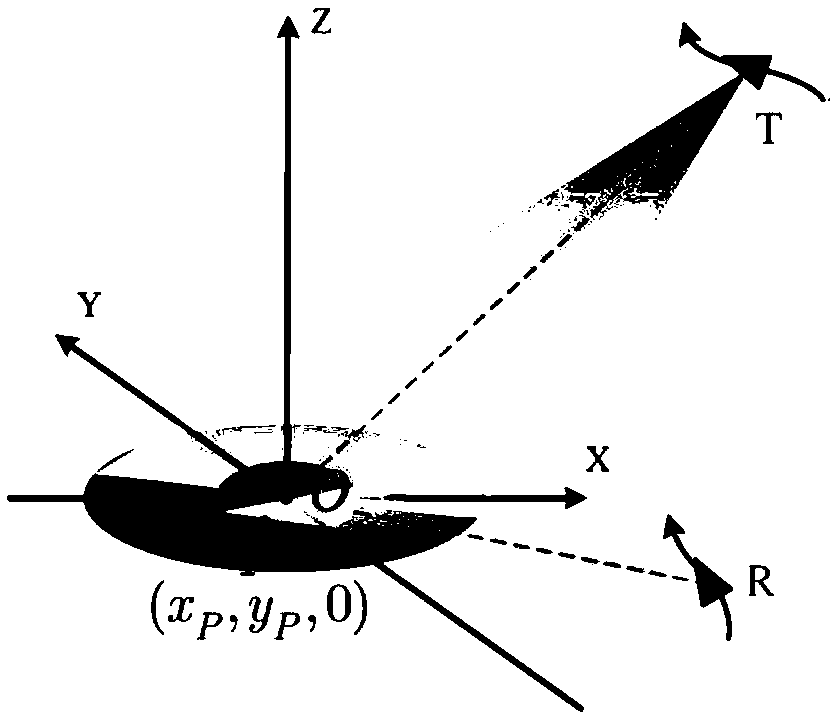
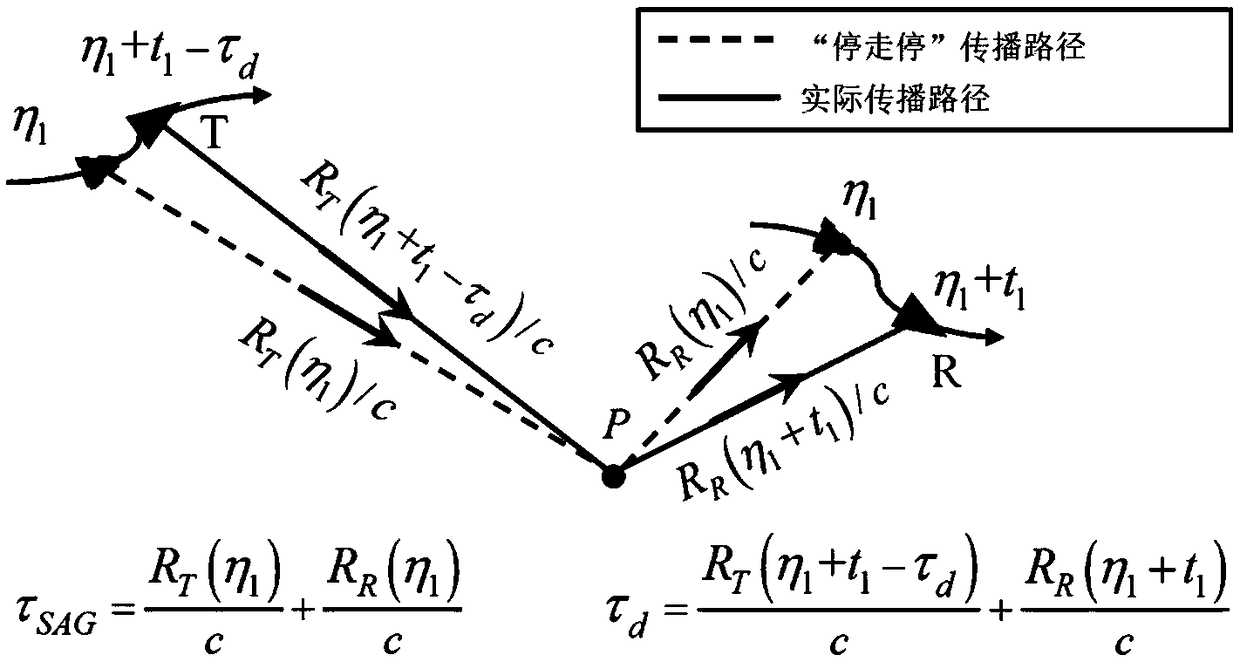
Method for establishing platform-based maneuvering bistatic SAR echo model in pulse propagation time
ActiveCN109358329AAvoid the Uniform Linear Motion AssumptionAvoid "stop-and-go" assumptionsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPropagation delayHypothesis
The invention discloses a method for establishing a platform-based maneuvering bistatic SAR echo model in the pulse propagation time, aiming at the problem that all current echo models for single-baseSAR and bistatic SARs of mobile platforms are based on the "stop-run-stop" hypothesis, which causes considerable propagation delay error and azimuth quadratic phase error. The invention considers themaneuverability of the platform during the pulse propagation process, and corrects a traditional pulse propagation delay equation based on the "stop-run-stop" hypothesis, thereby establishing an accurate pulse propagation delay equation. An approximate solution of the receiving station distance historical high-order term is found to solve the high-precision approximate analytical expression of the exact pulse propagation delay equation solution. Then, a first-order Taylor expansion is performed on a high-precision approximate analytical expression for fast time, and finally a high-precision bistatic SAR echo model can be established, which can be applied to various bistatic SAR cases.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
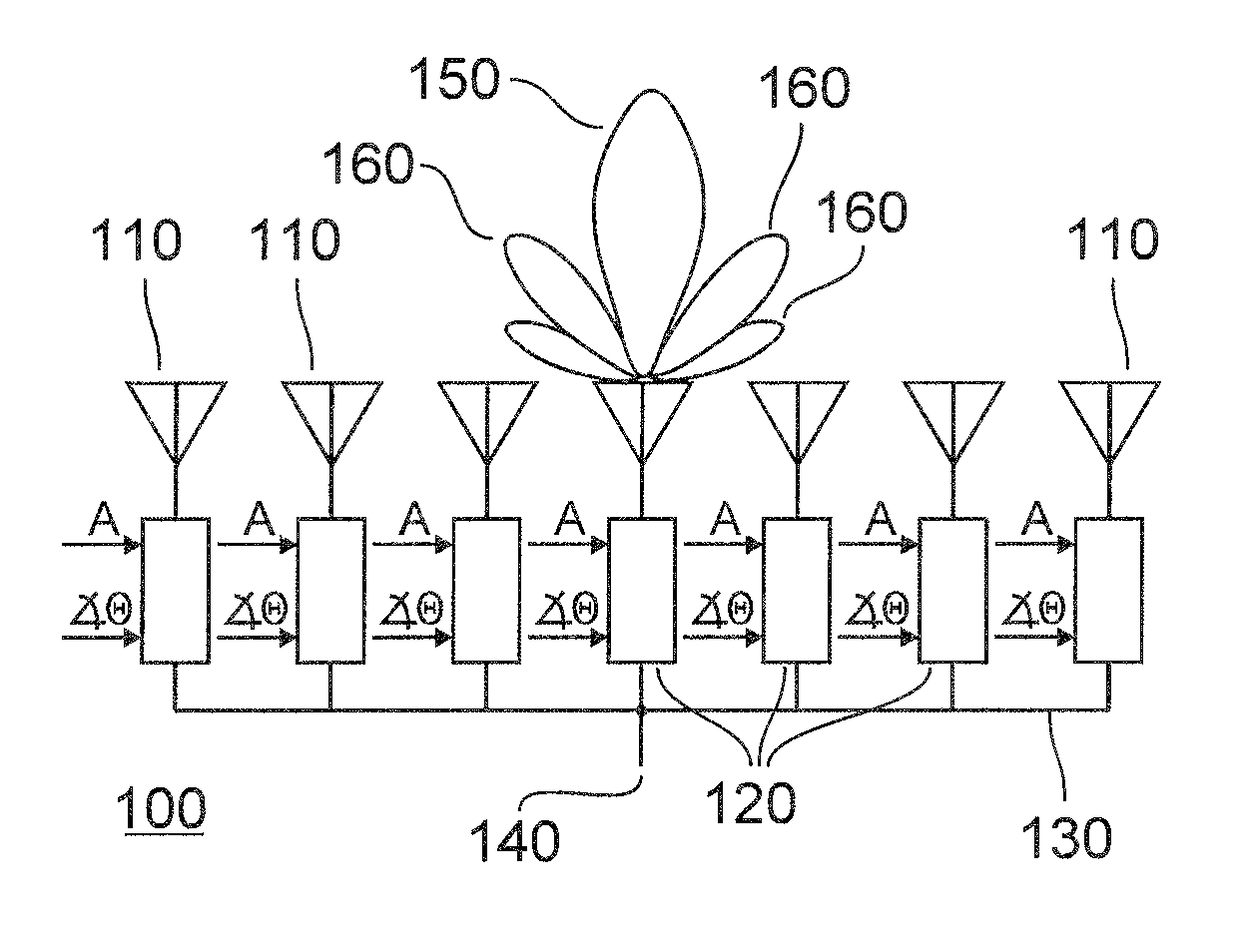
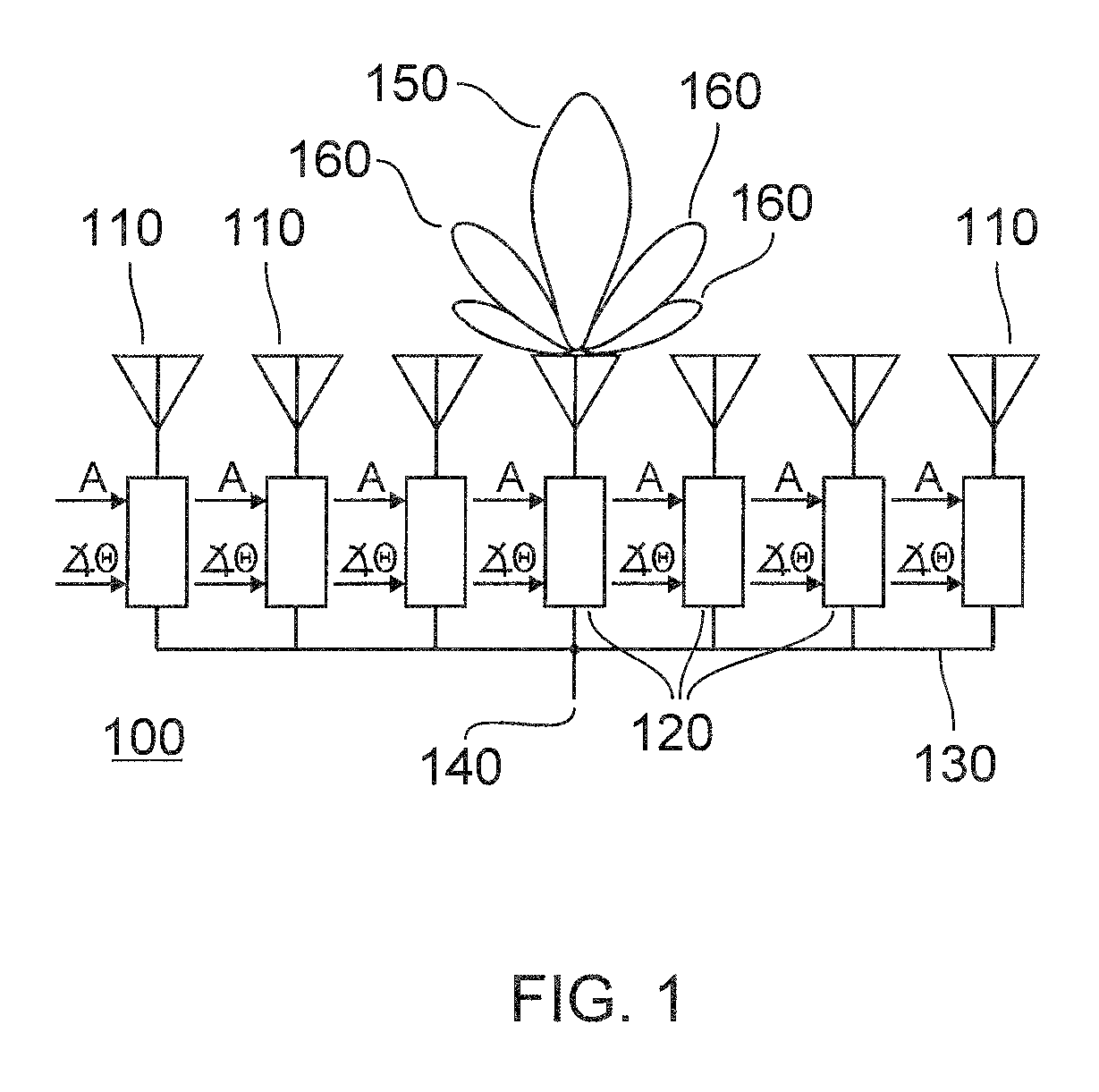
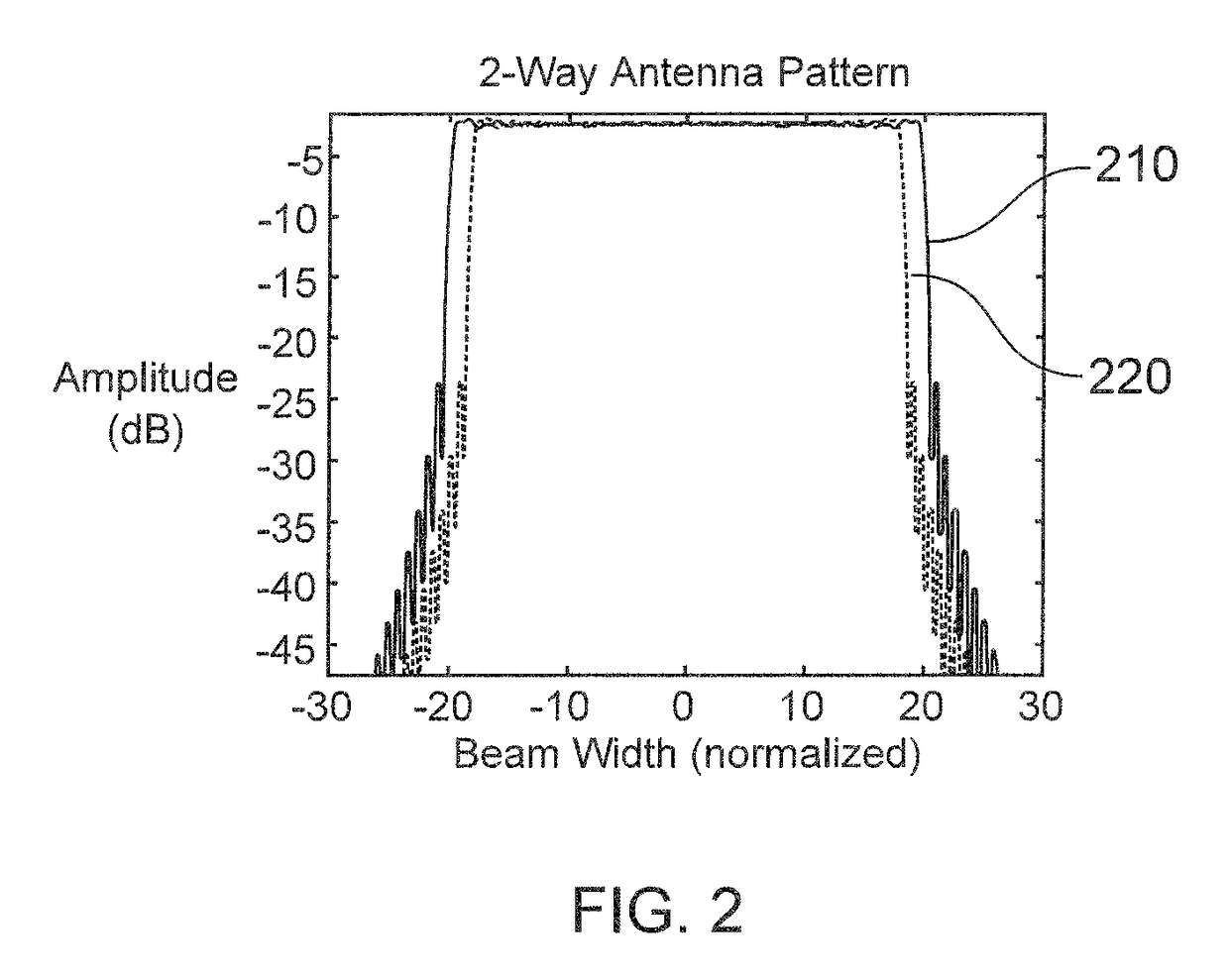
Beam broadening with large spoil factors
ActiveUS9620856B2Fast drop rateReduce power consumptionIndividually energised antenna arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBeam broadeningMain lobe
Methods for generating weights for the antenna elements (110) in an AESA antenna (100). In one embodiment, transmitting weights are selected to have unit amplitude and quadratic phase, and receiving weights are selected to provide a two-way antenna pattern which is uniform over a useful portion (300) of the main lobe, and decreases rapidly outside of the uniform portion. In another embodiment the transmitting weights have unit amplitude over a central portion of the array and the receiving weights are selected to provide a two-way antenna pattern which is uniform over a useful portion (300) of the main lobe.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
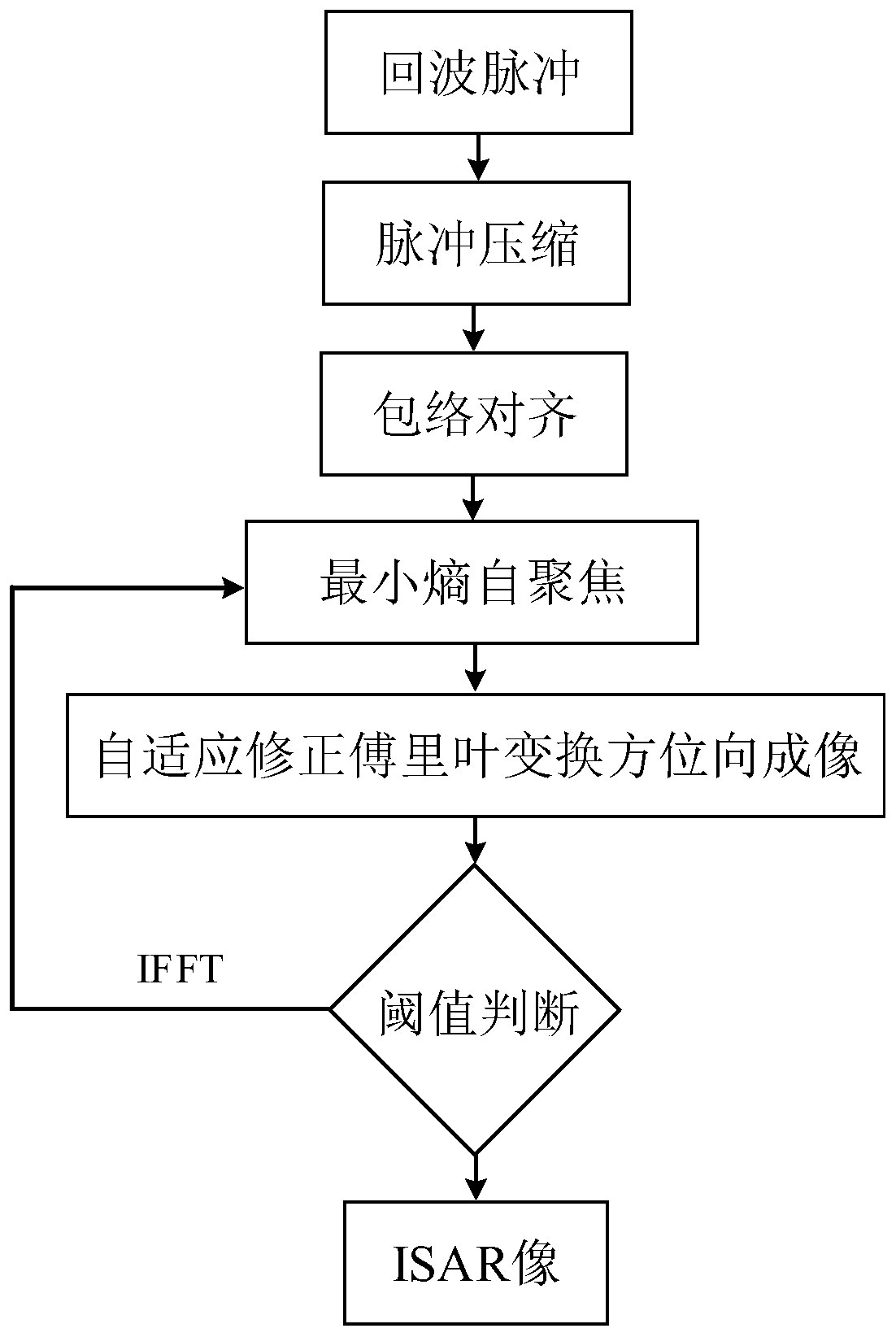
Maneuvering target ISAR imaging method based on iterative phase self-focusing
ActiveCN111157992AEliminate Phase ErrorHigh compensation accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency modulationFourier transform
The invention discloses a maneuvering target ISAR imaging method based on iterative phase self-focusing, and the method comprises the steps: step 1, receiving an echo pulse of a maneuvering target, carrying out the pulse compression and envelope alignment, and obtaining a one-dimensional range profile sequence after the envelope alignment of the maneuvering target; step 2, estimating a phase compensation amount of the one-dimensional range profile sequence by using a minimum entropy self-focusing method; step 3, completing azimuth compression by using adaptive correction Fourier transform, andrecording a corresponding relative modulation frequency at the moment; step 4, comparing the relative frequency modulation rate in the step 3 with a preset threshold value, and if the relative frequency modulation rate is greater than the preset threshold value, returning to the step 2 for iteration; and outputting the optimal ISAR image if the ISAR image is smaller than the preset threshold. According to the method, the minimum entropy self-focusing algorithm and the adaptive correction Fourier transform are used for alternately iteratively estimating the translation phase error of the maneuvering target and the secondary phase term caused by uniform acceleration rotation, the phase error caused by translation of the maneuvering target is effectively eliminated, the compensation precision is high, and the imaging effect is good.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com