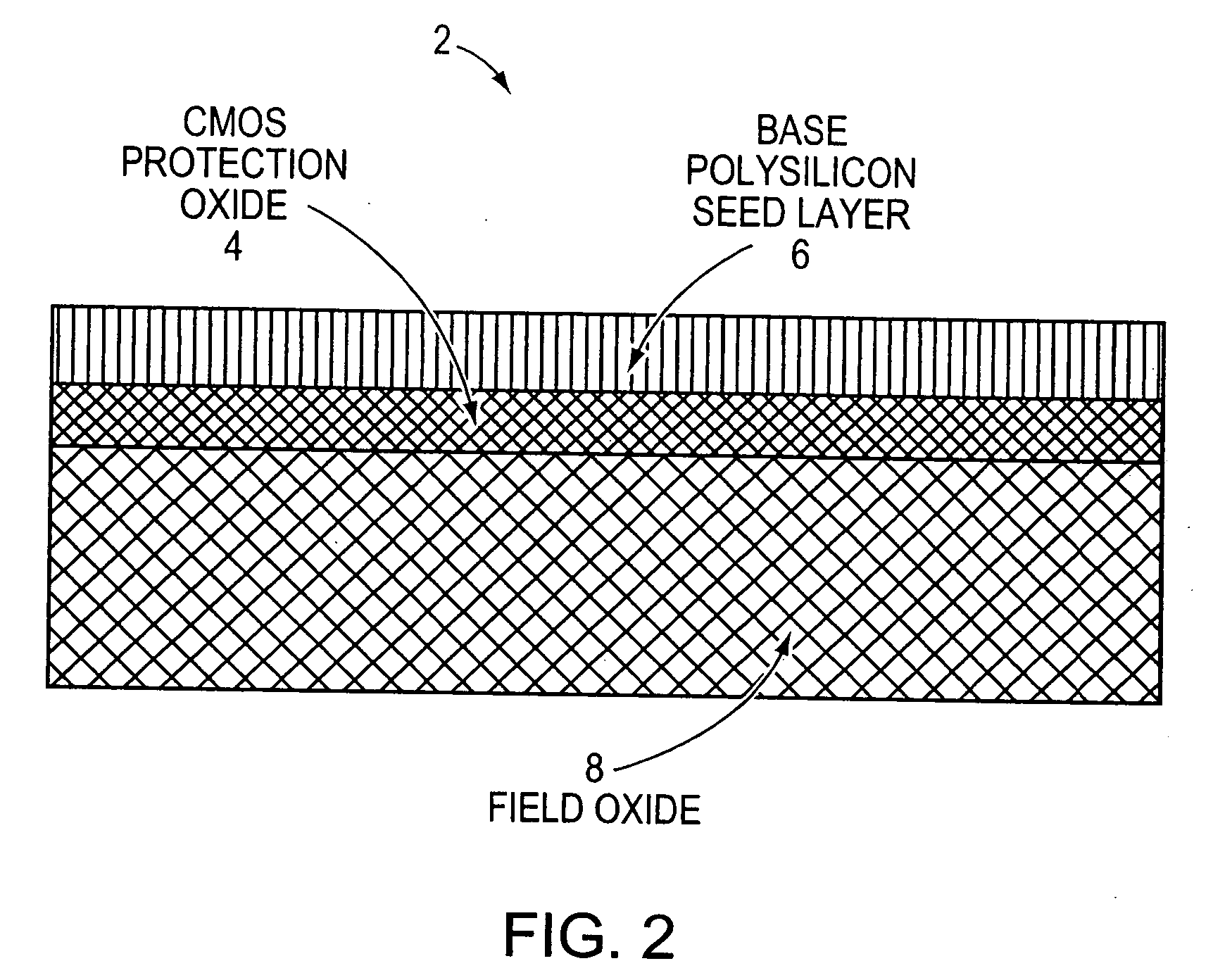
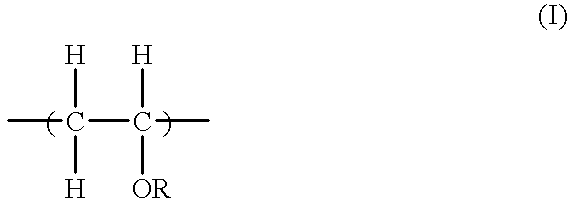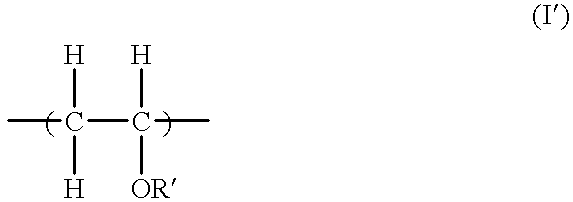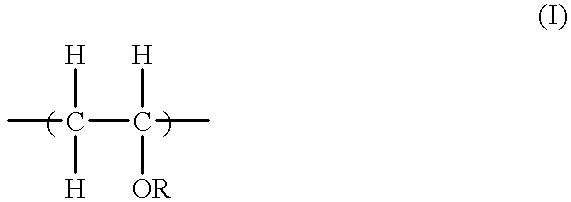Patents
Literature
37 results about "Intrinsic resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Intrinsic Resistance. Intrinsic resistance is the innate ability of a bacterial species to resist activity of a particular antimicrobial agent through its inherent structural or functional characteristics, which allow tolerance of a particular drug or antimicrobial class.
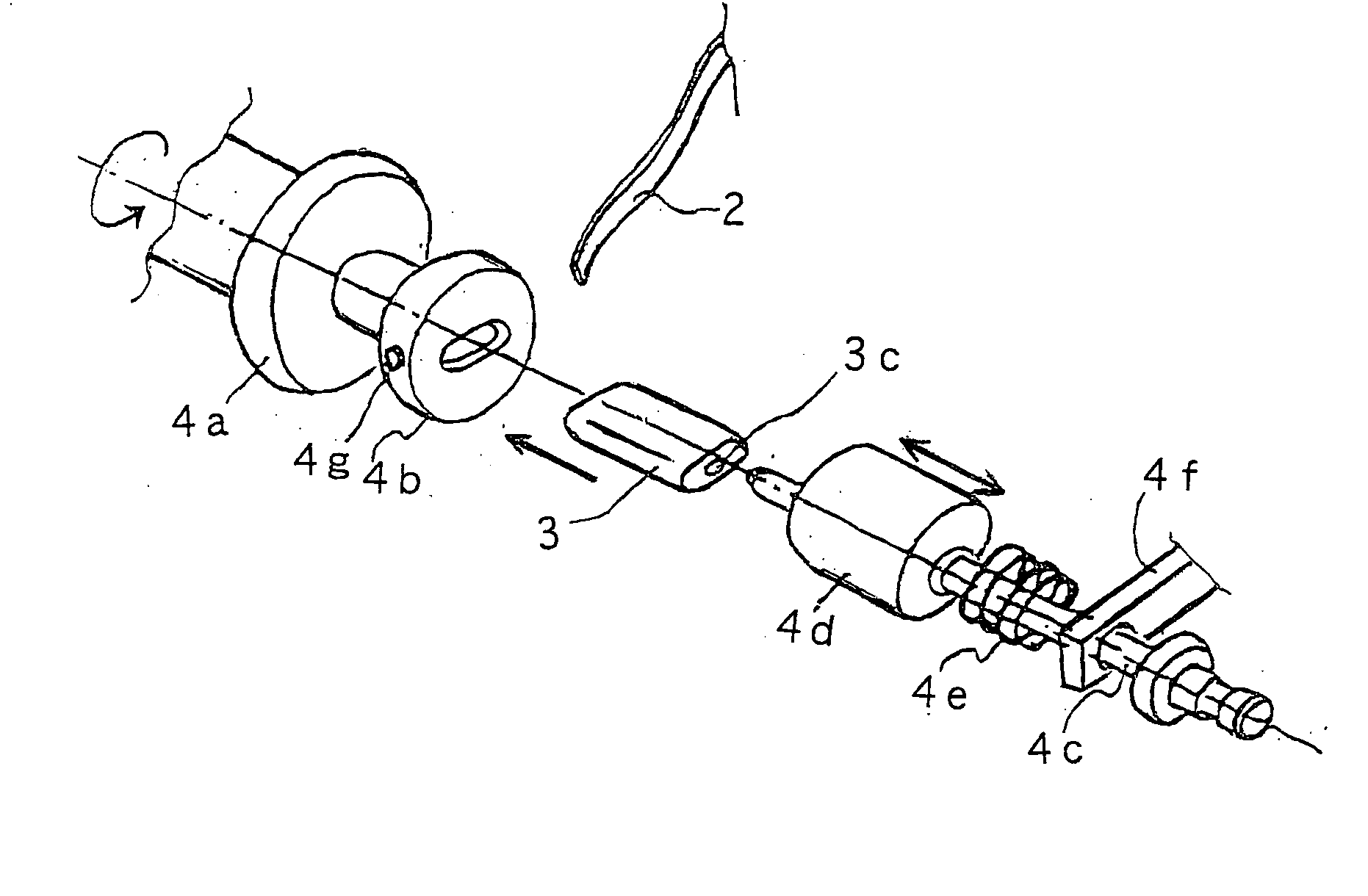
Semiconductor device, manufacturing method, and electronic device
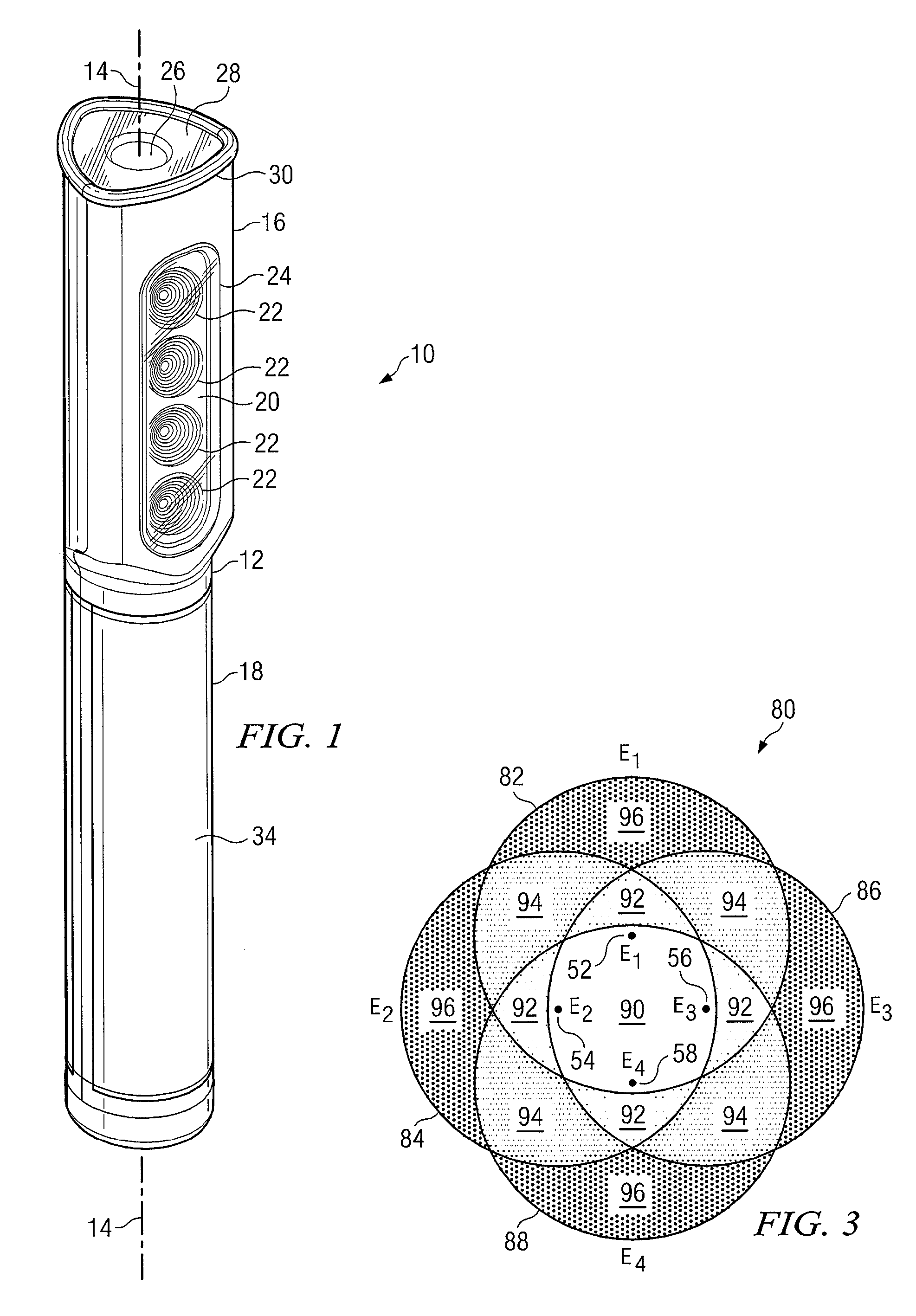
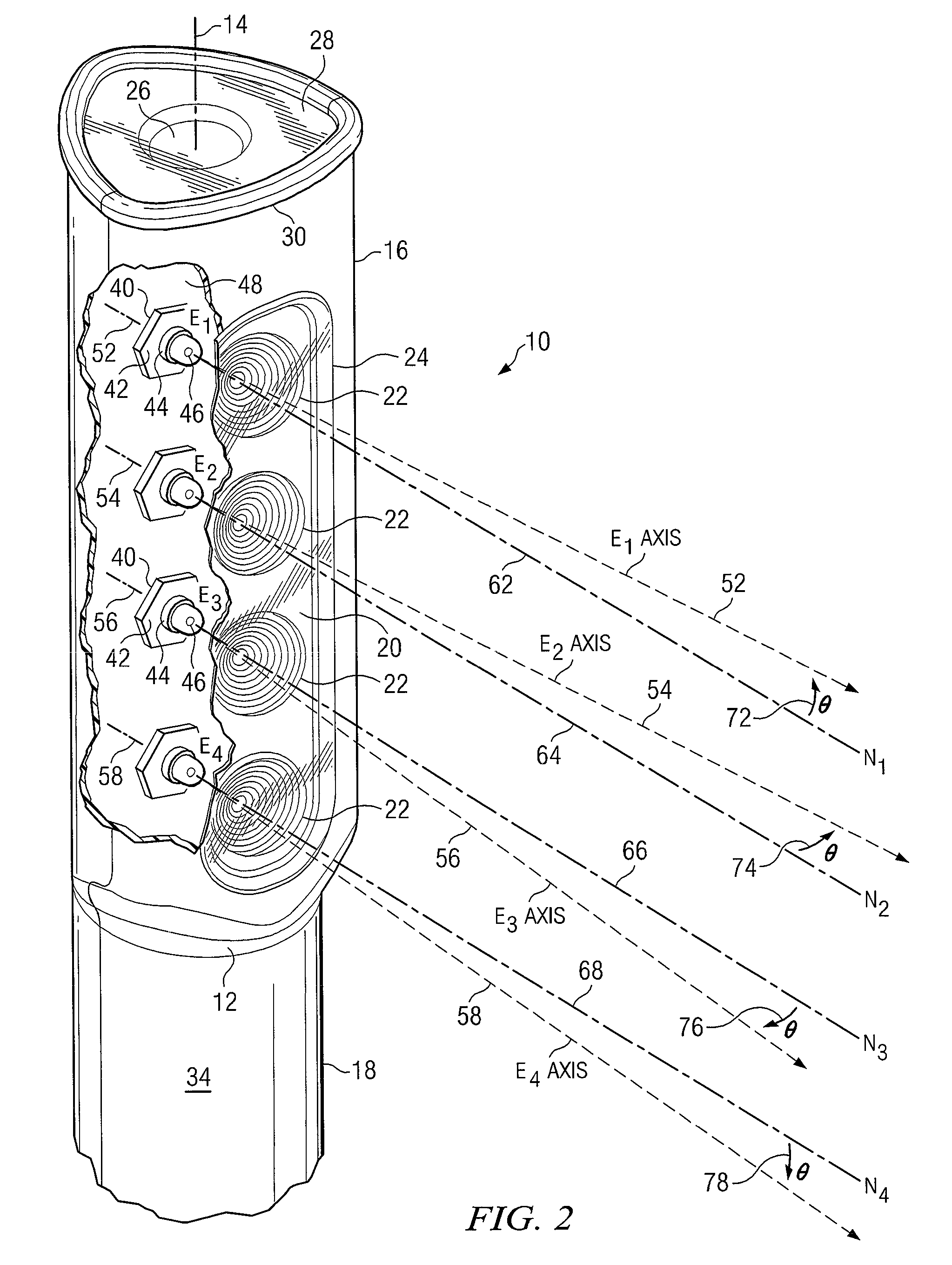
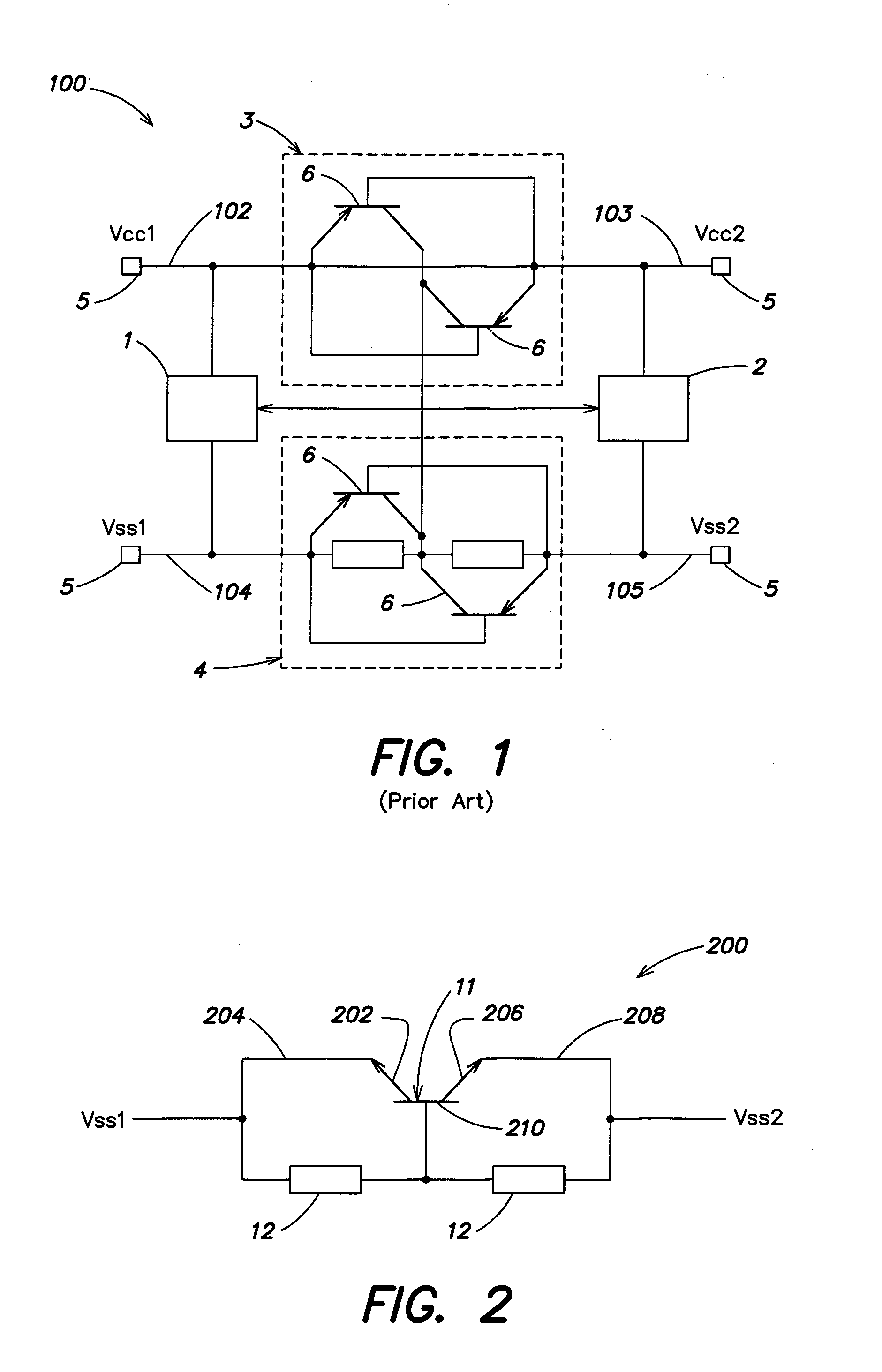
ActiveUS20060244107A1Stabilize element propertyEasy to manufactureTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSurface levelIntrinsic resistance
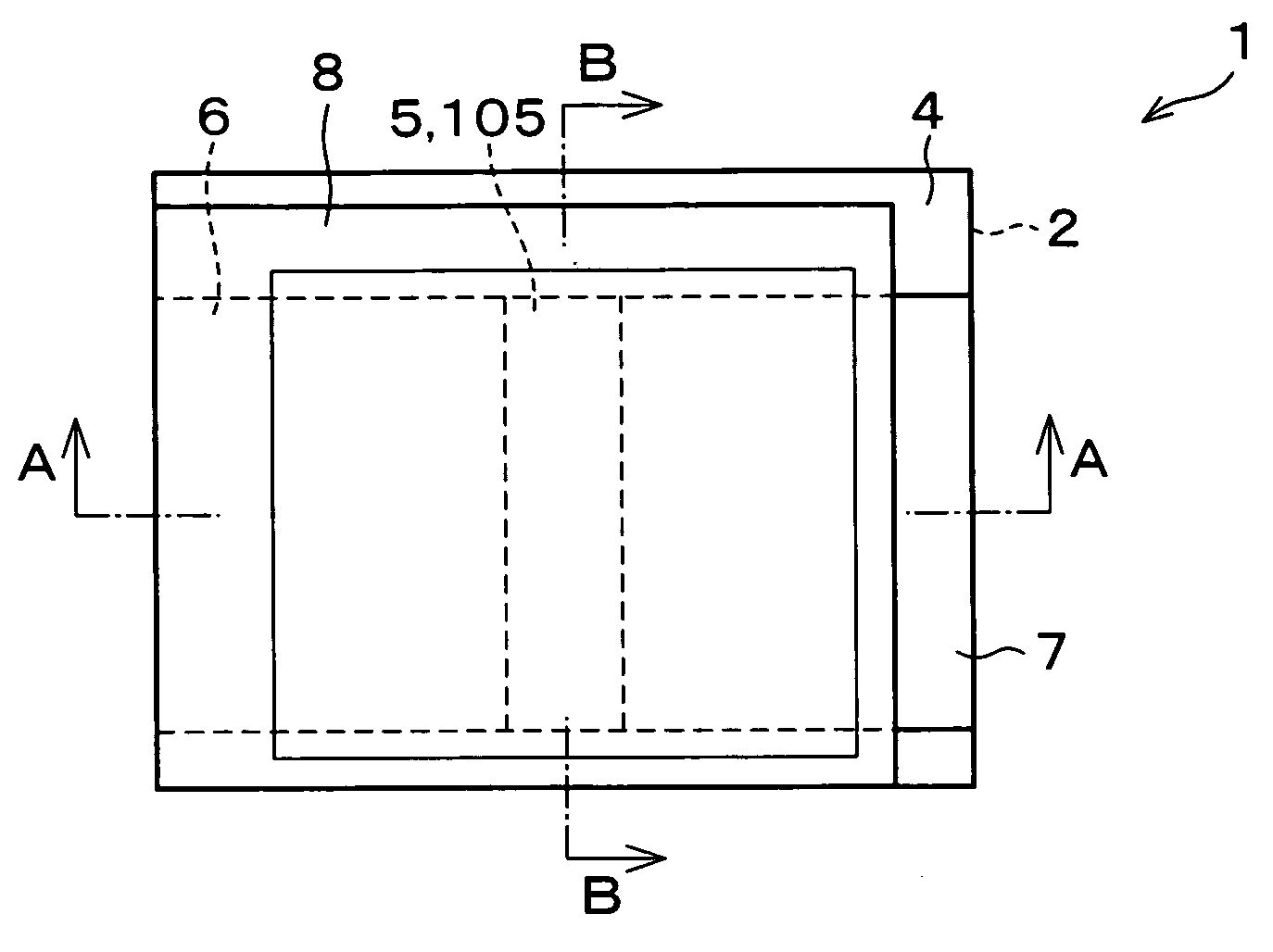
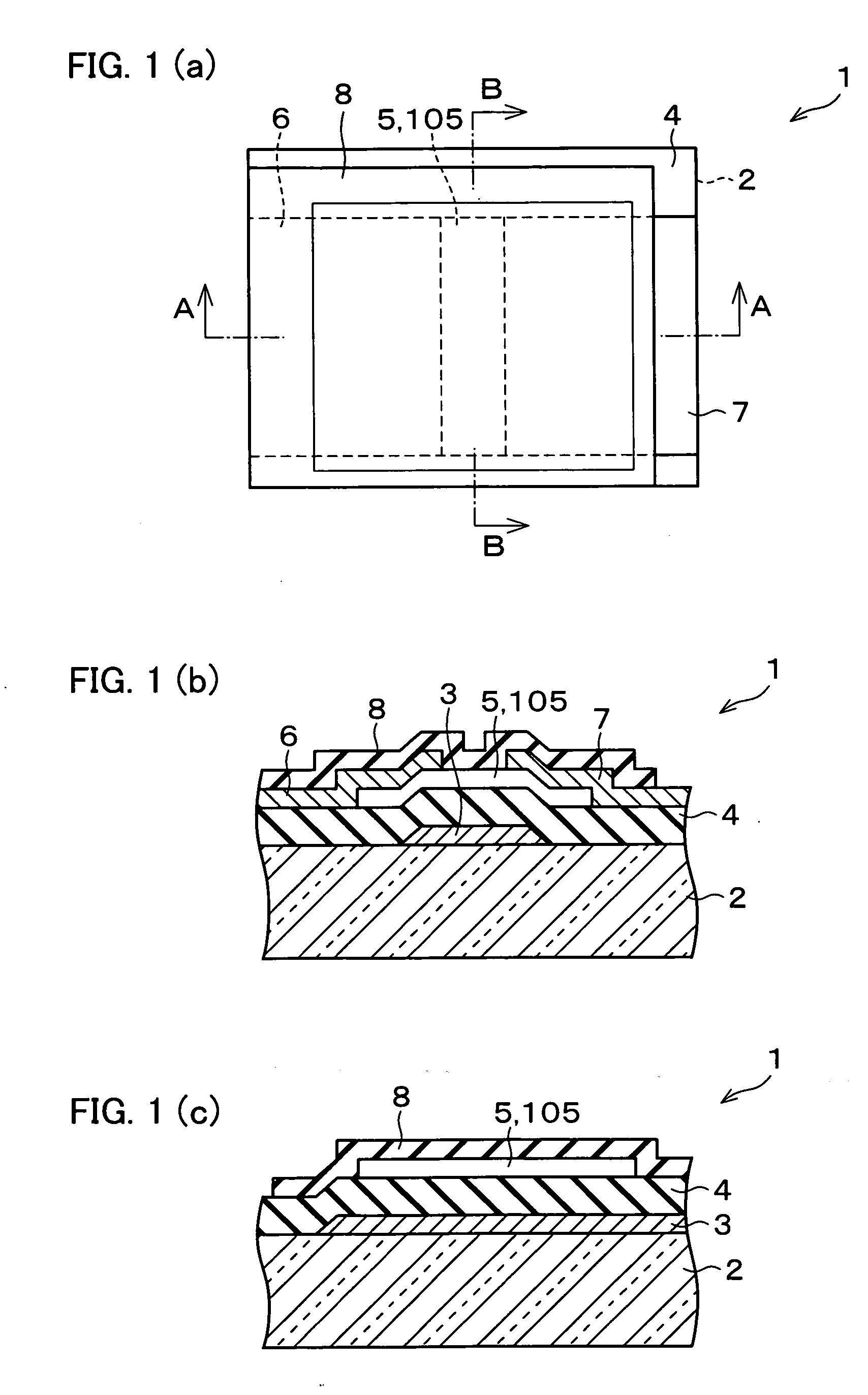
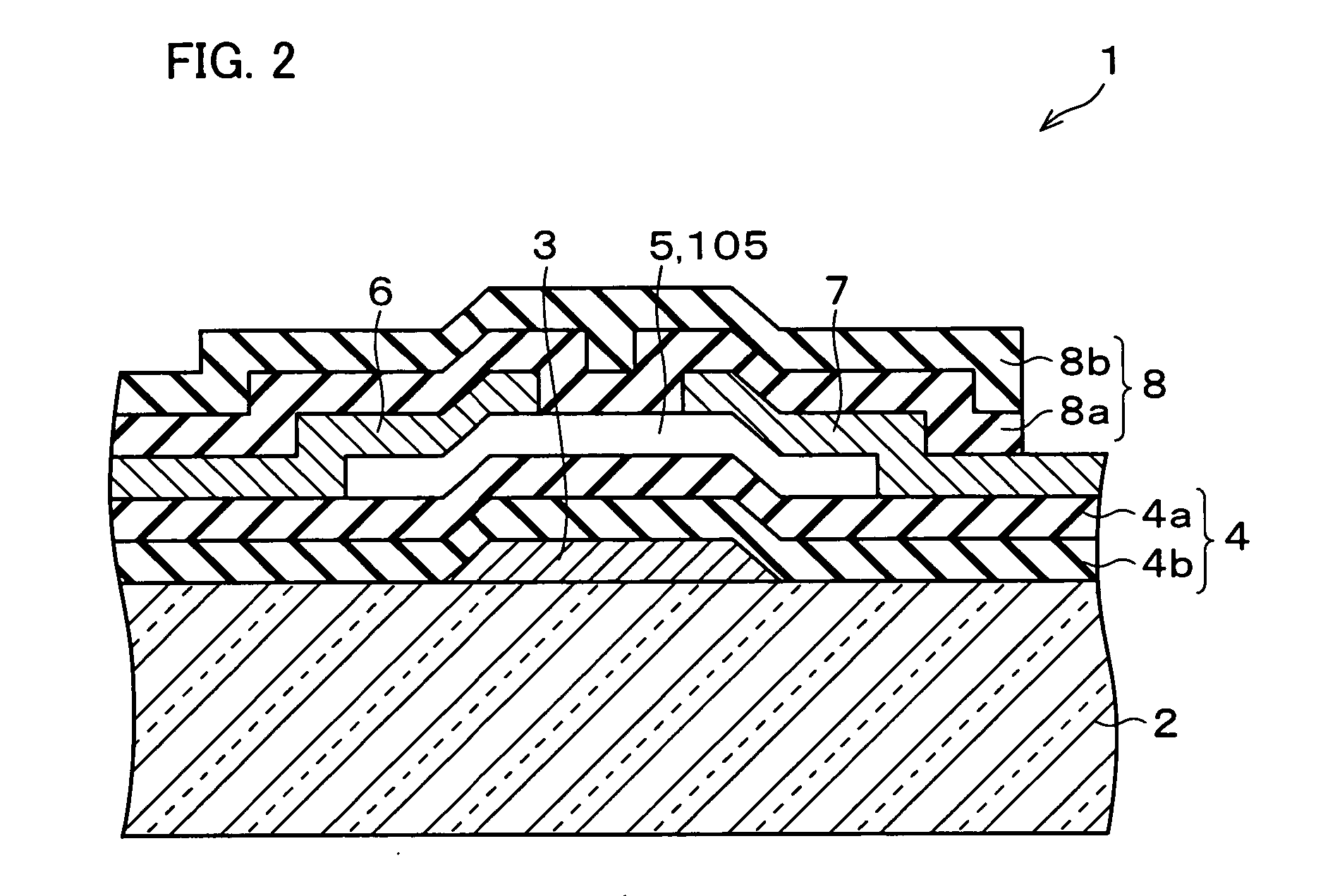
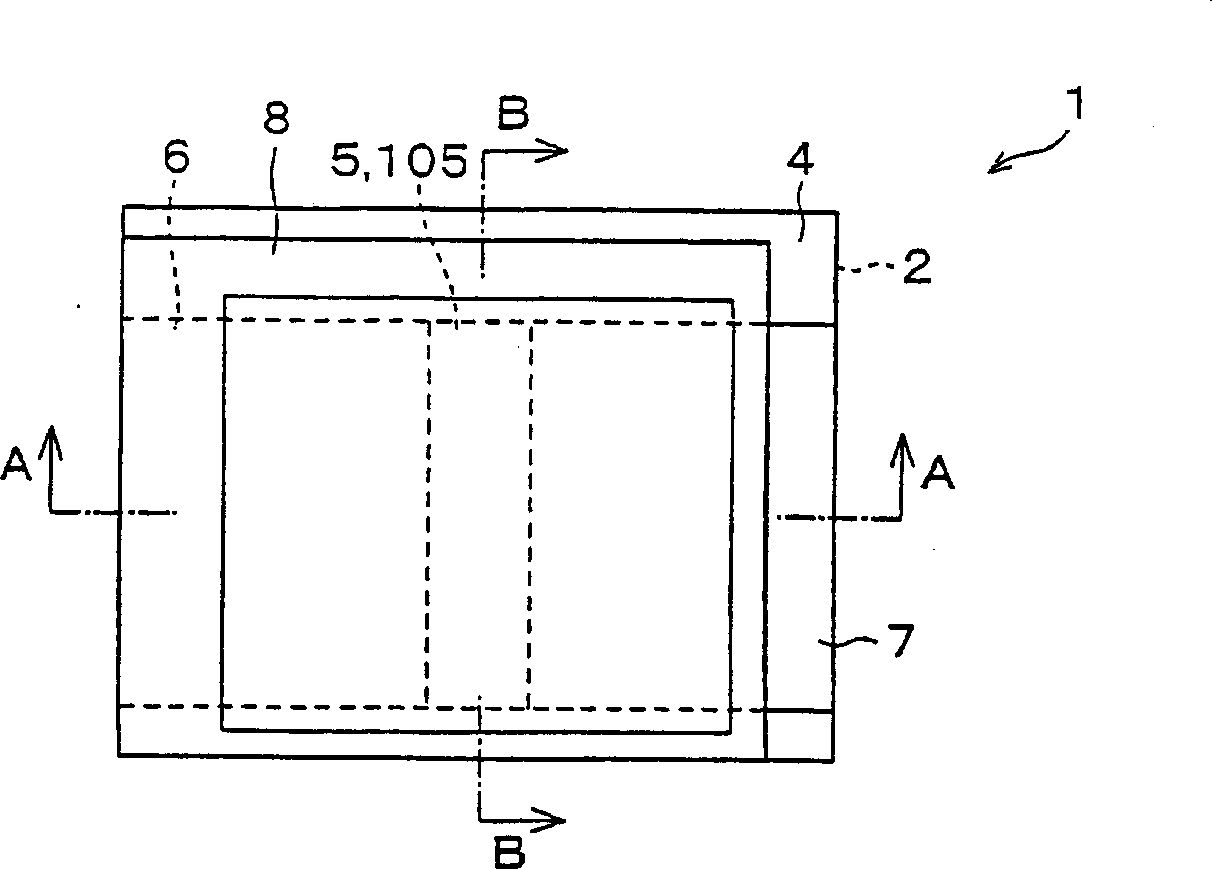
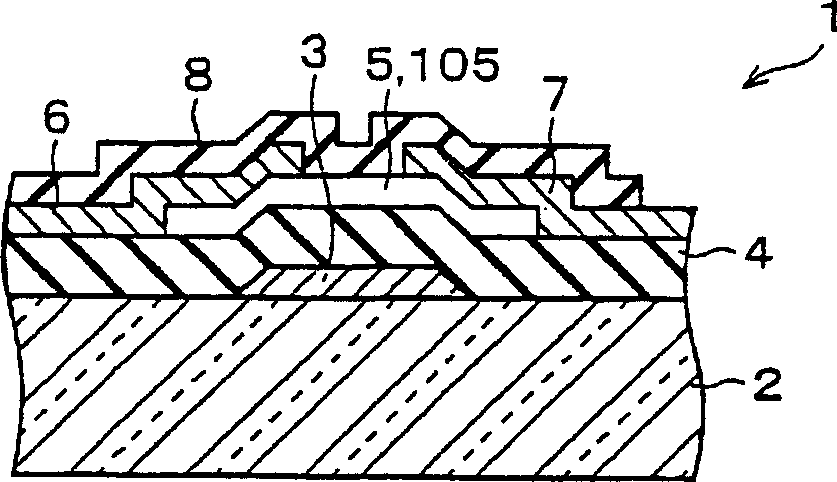
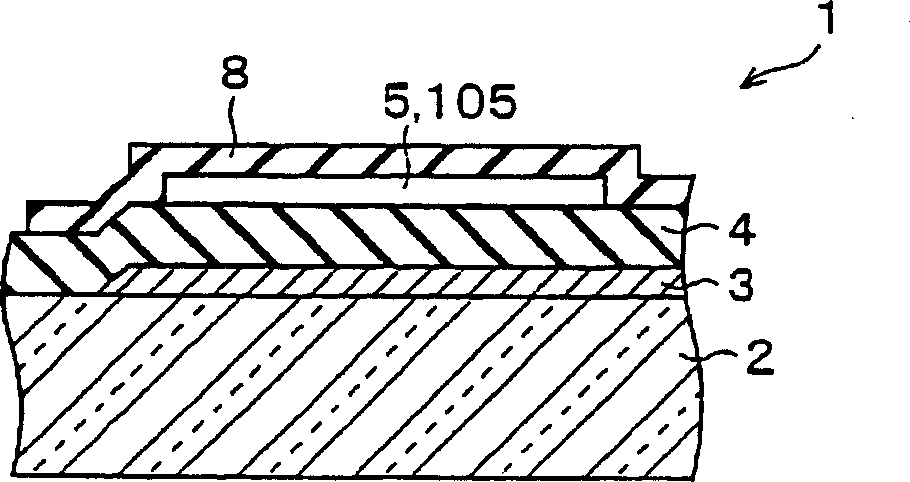
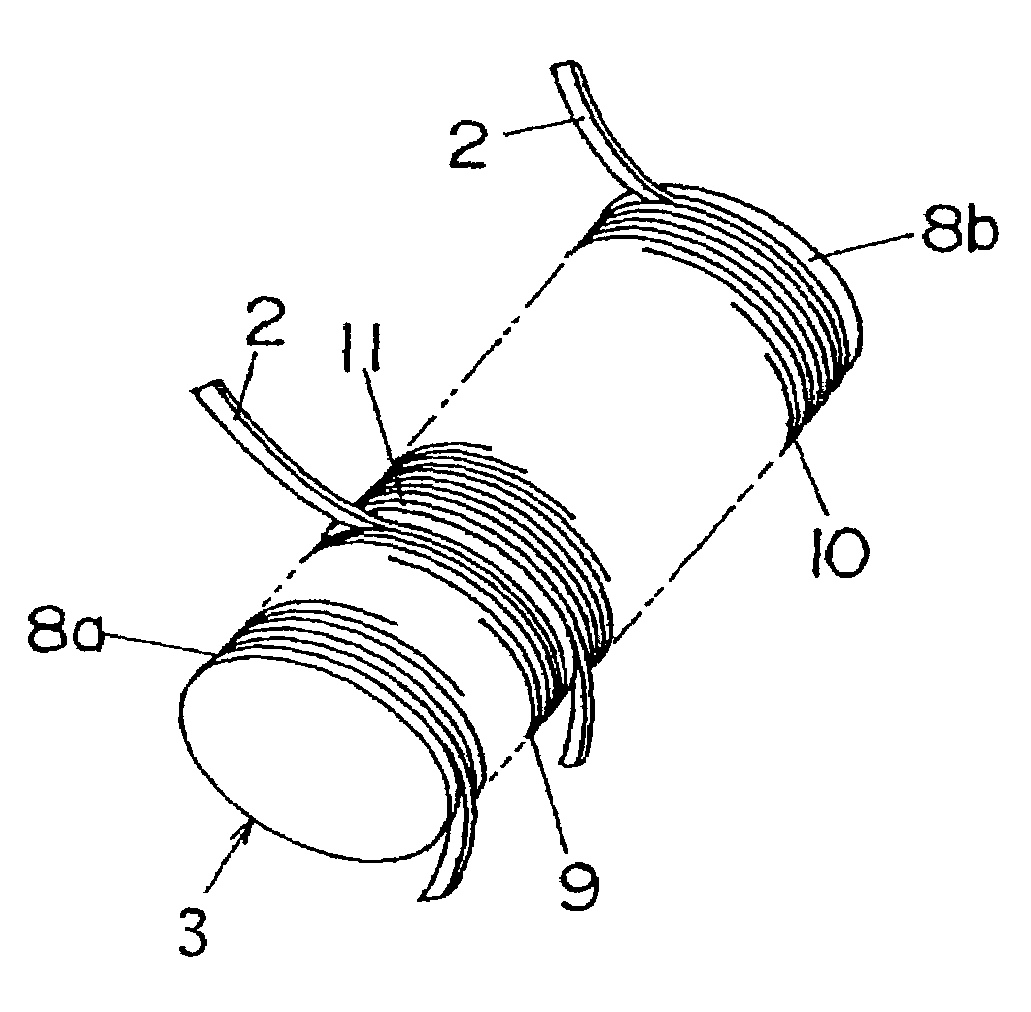
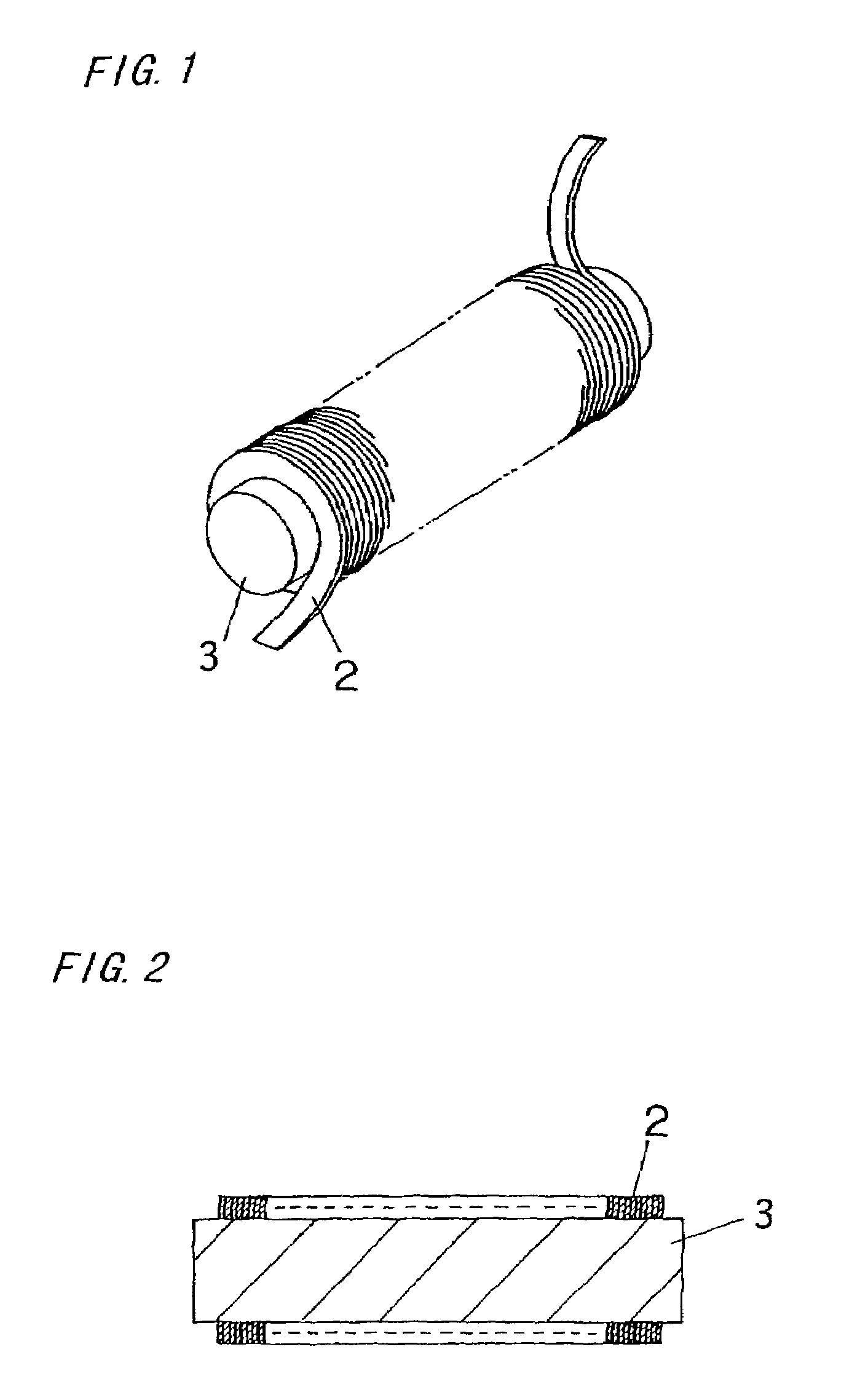
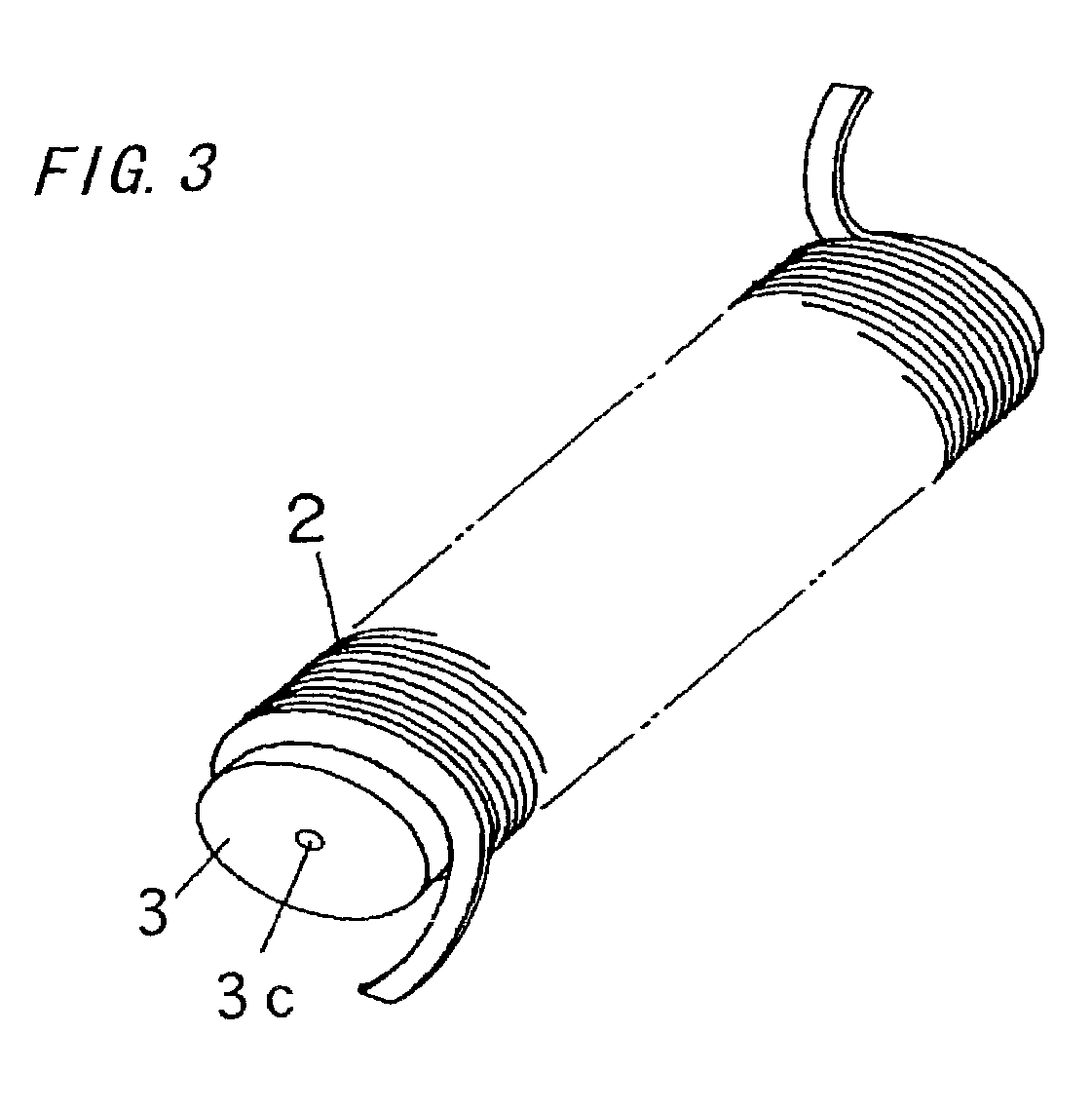
In a thin film transistor (1), a gate insulating layer (4) is formed on a gate electrode (3) formed on an insulating substrate (2). Formed on the gate insulating layer (4) is a semiconductor layer (5). Formed on the semiconductor layer (5) are a source electrode (6) and a drain electrode (7). A protective layer (8) covers them, so that the semiconductor layer (5) is blocked from an atmosphere. The semiconductor layer (5) (active layer) is made of, e.g., a semiconductor containing polycrystalline ZnO to which, e.g., a group V element is added. The protective layer (8) thus formed causes decrease of a surface level of the semiconductor layer (5). This eliminates a depletion layer spreading therewithin. Accordingly, the ZnO becomes an n-type semiconductor indicating an intrinsic resistance, with the result that too many free electrons are generated. However, the added element works on the ZnO as an accepter impurity, so that the free electrons are reduced. This decreases a gate voltage required for removal of the free electrons, so that the threshold voltage of the thin film transistor (1) becomes on the order of 0V. This allows practical use of a semiconductor device which has an active layer made of zinc oxide and which includes an protective layer for blocking the active layer from an atmosphere.
Owner:SHARP KK +2
Semiconductor device, its manufacturing method, and electronic device
InactiveCN1806322ATransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIntrinsic resistanceGate voltage
A thin film transistor (1) wherein a gate electrode (3) is formed on an insulative substrate (2), a gate insulating layer (4) is formed on the gate electrode (3), a semiconductor layer (5) is formed on the gate insulating layer (4), a source electrode (6) and a drain electrode (7) are formed on the semiconductor layer (5), and a protective layer (8) covering them are formed. The semiconductor layer (5) is isolated from the atmosphere. The semiconductor layer (5) (active layer) is formed of a ZnO polycrystalline semiconductor doped with, for example, a group V element. Since the surface state of the ZnO semiconductor is reduced thanks to the protective layer (8) and inward expansion of the depletion layer is prevented, the ZnO semiconductor is of an n-type showing its intrinsic resistance value and contains excessive free electrons. The added element acts as acceptor impurities in the ZnO semiconductor, decreasing the excessive electrons. Thus the gate voltage to eliminate the excessive free electrons lowers, thereby making the threshold voltage around 0 V. A semiconductor device using a zinc oxide for an active layer and having a protective layer for isolating the active layer from the atmosphere can be actually used.
Owner:SHARP KK +2
Lubricating oil for compression-type refrigerators containing pentafluoroethane and a polyvinyl ether
A lubricating oil for compression-type refrigerators using a refrigerant containing pentafluoroethane which lubricating oil comprises a polyvinyl ether compound having (a) a constituting unit represented by general formula (I):or a polyvinyl ether compound having constituting unit (a) and (b) a constituting unit represented by general formula (I'):(wherein R represents a hydrocarbon group which has 1 to 3 carbon atoms and may have ether bond in the group, and R' represents a hydrocarbon group which has 3 to 20 carbon atoms and may have ether bond in the group) as the main component. The above lubricating oil shows excellent compatibility with hydrofluorocarbon refrigerants containing pentafluoroethane which can replace chlorofluorocarbons causing environmental pollution, has a high volume intrinsic resistance, and exhibits excellent stability and lubricating property.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Fault detection apparatus of solenoid valve
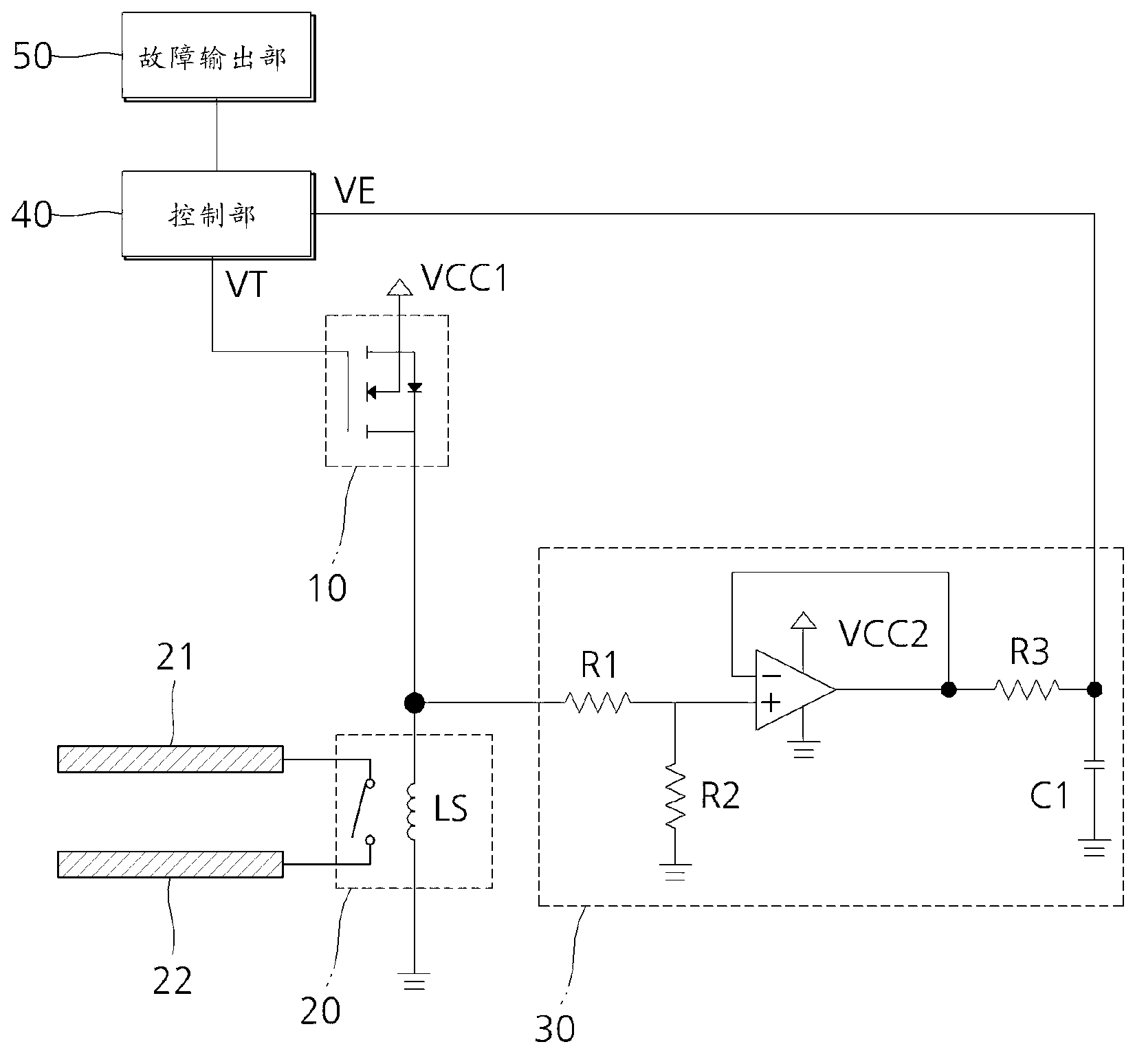
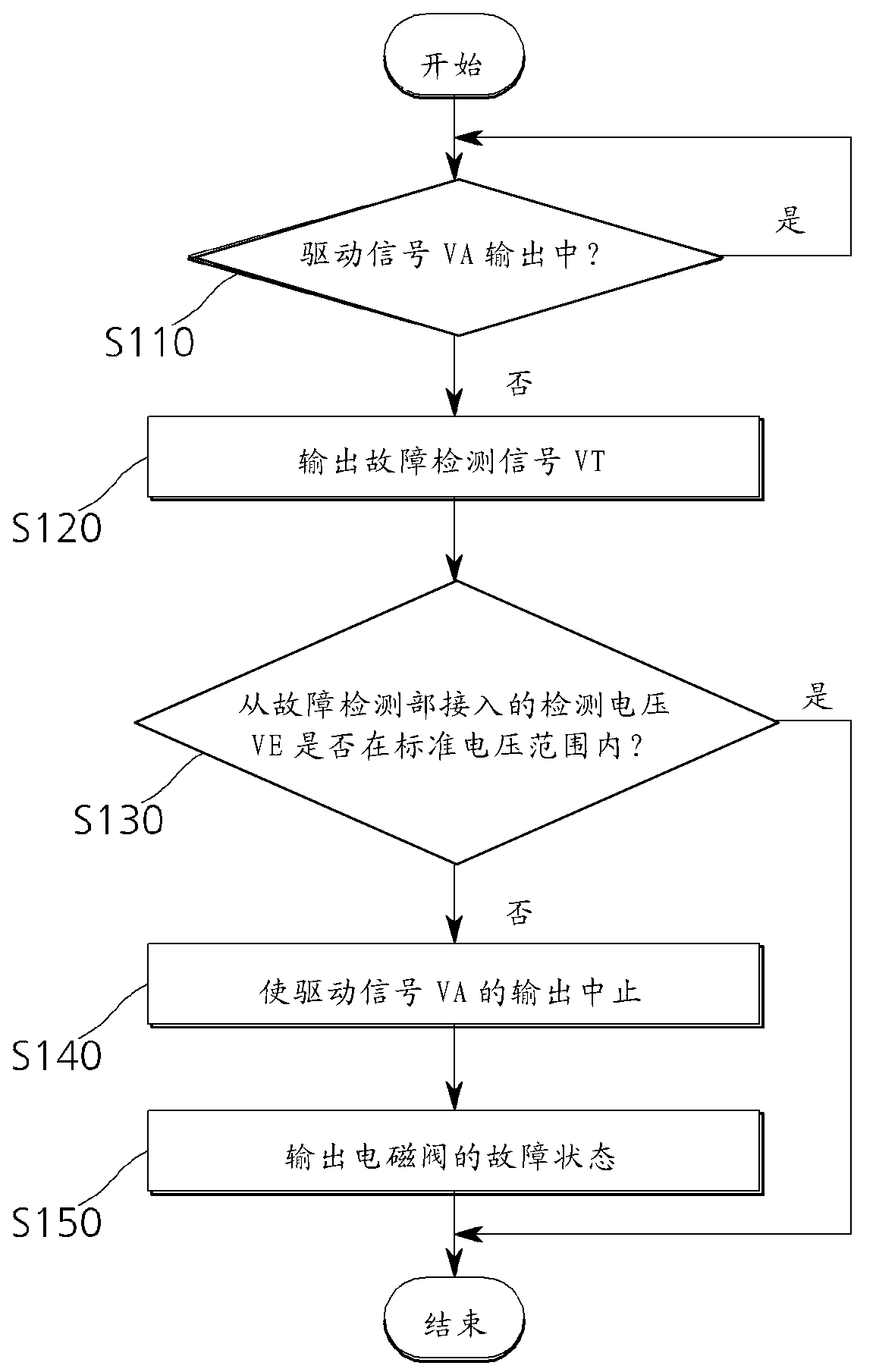
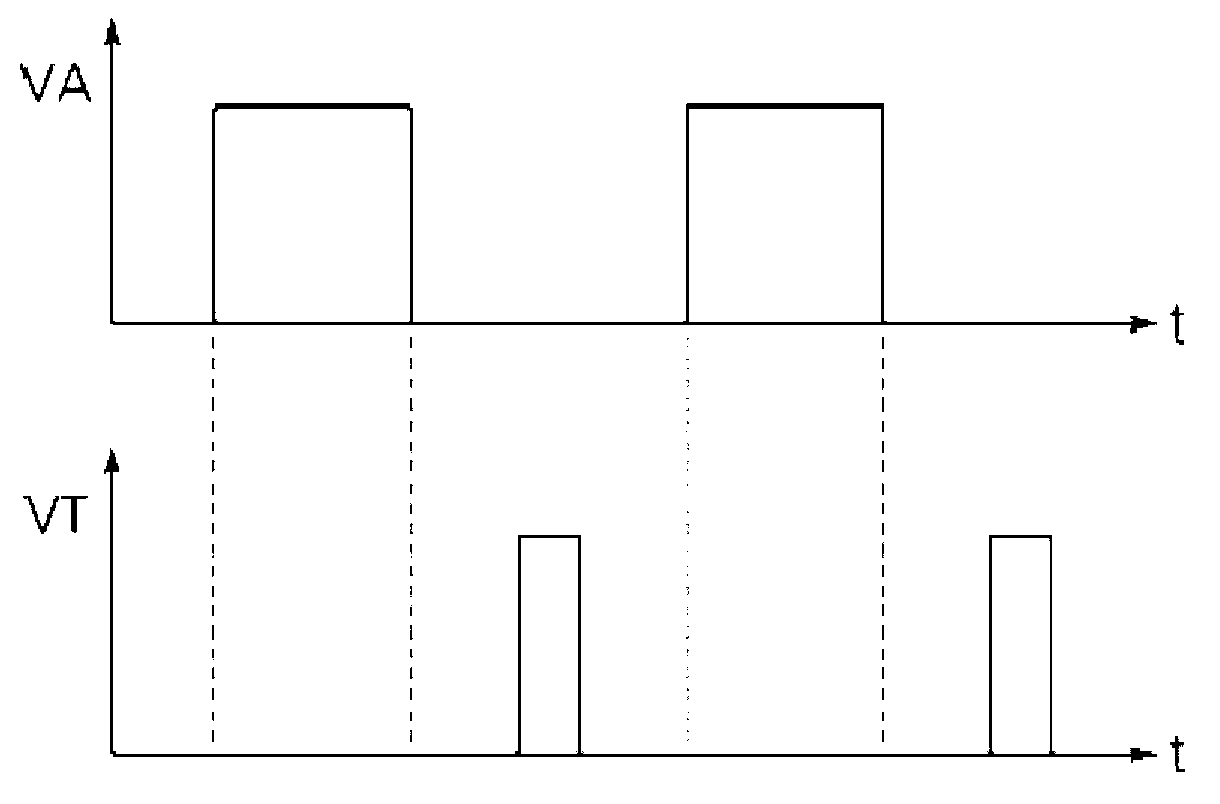
InactiveCN103207326AReduce the number of partsDoes not affect workElectrical testingVehicle sub-unit featuresElectrical resistance and conductanceSolenoid valve
The invention provides a fault detection apparatus of a solenoid valve. The fault detection apparatus comprises a switch which switches to a power supply for an electromagnetic coil according to a fault detection signal which has specific energy smaller than a critical value of driving the solenoid valve, a fault detection portion which measures voltage across two ends of the electromagnetic coil and outputs detection voltage, a control portion which outputs the fault detection signal to the switch and based on the detection voltage input by the fault detection portion determines whether a fault of the solenoid valve occurs, and a fault output portion which outputs a fault state of the solenoid valve. According to the fault detection apparatus, the fault of the solenoid valve is detected by using a distribution voltage determined by resistance of the switch and intrinsic resistance of the electromagnetic coil, and thus a shunt resistor for monitoring current and a complicated amplifier circuit can be replaced, and the number of used accessories can be reduced.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOBIS CO LTD
Electromagnetic device and high-voltage generating device and method of producing electromagnetic device
InactiveUS7142082B2Improve featuresSmall sizeMicrobiological testing/measurementTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical conductor
An electromagnetic device and a high-voltage generating device which are thin with improved characteristics includes a magnetic core of a cylindrical form of a ferrite material having a high intrinsic resistance. A winding is provided by winding a flat rectangular wire conductor in an edge-wise winding directly on substantially the entire length of the magnetic core. As an insulator, such as a coil bobbin, is not needed between the flat rectangular wire conductor and the magnetic core, the winding can be decreased in the overall size or thickness thus contributing to the reduction in dimension of the electromagnetic device. Also, as its flat rectangular wire conductor is wound directly on the magnetic core, the winding can be minimized in the length and thus the overall resistance.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Microprocessor-controlled multifunction light with intrinsically safe energy limiting
ActiveUS7738229B2Reduce total powerPoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsIntrinsic safetyElectrical resistance and conductance
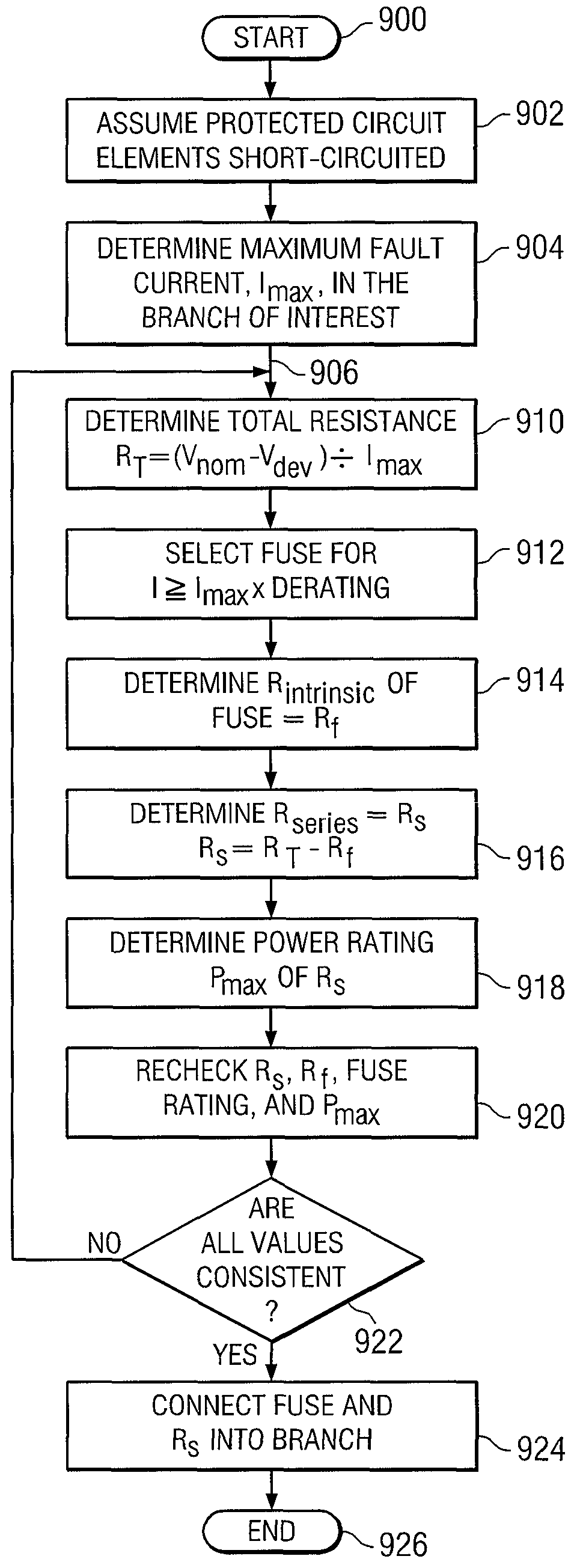
A method is provided for reducing the power rating of a current limiting resistor (R) in a branch circuit having at least one protected element and the current limiting resistor connected between first and second nodes. The method includes the steps of: determining a maximum fault current in the branch circuit; determining a total current limiting resistance to limit the current in the branch circuit having the short-circuited elements to the maximum fault current; inserting a fuse having an intrinsic resistance in the branch circuit; and dividing the determined total current limiting resistance between the resistor (R) and the intrinsic resistance of the fuse.
Owner:BAYCO PRODS
Ion implantation monitoring method
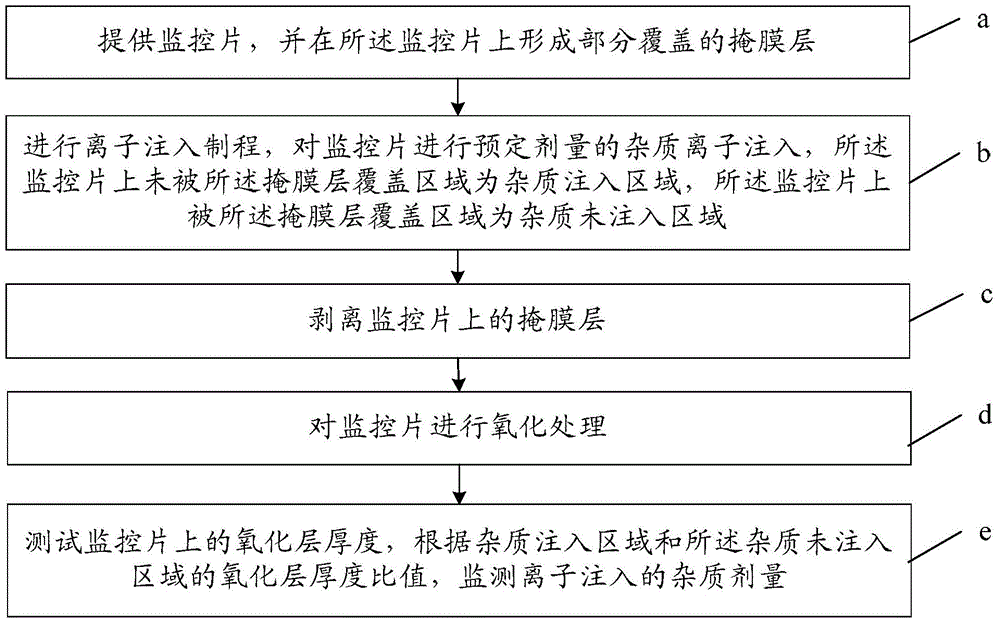
ActiveCN104091767AAvoid the defect that the monitoring result exceeds the limitImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesElectrical resistance and conductanceMedicine
The invention discloses an ion implantation monitoring method and relates to the field of semiconductors. The ion implantation monitoring method can accurately monitor whether the ion implantation amount reaches to the preset requirement, the defect that intrinsic resistance fluctuation of a substrate causes a monitoring result ultra-limit is effectively overcome, the monitoring accuracy is improved, and the device performance and yield are improved. The ion implantation monitoring method comprises the steps of (a) providing a monitoring piece and forming a partially-covered mask layer on the monitoring piece; (b) performing ion implantation processing, and implanting a preset amount of impurity ions into the monitoring piece, wherein a region which is not covered by the mask layer on the monitoring piece is an impurity implantation region, and a region which is covered by the mask layer is an impurity non-implantation region; (c) stripping the mask layer on the monitoring piece; (d) performing oxidation treatment on the monitoring piece; (e) respectively resting the oxide layer thicknesses of the impurity implantation region and the impurity non-implantation region, and monitoring the impurity amount in ion implantation according to oxide layer thickness values of the impurity implantation region and the impurity non-implantation region.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
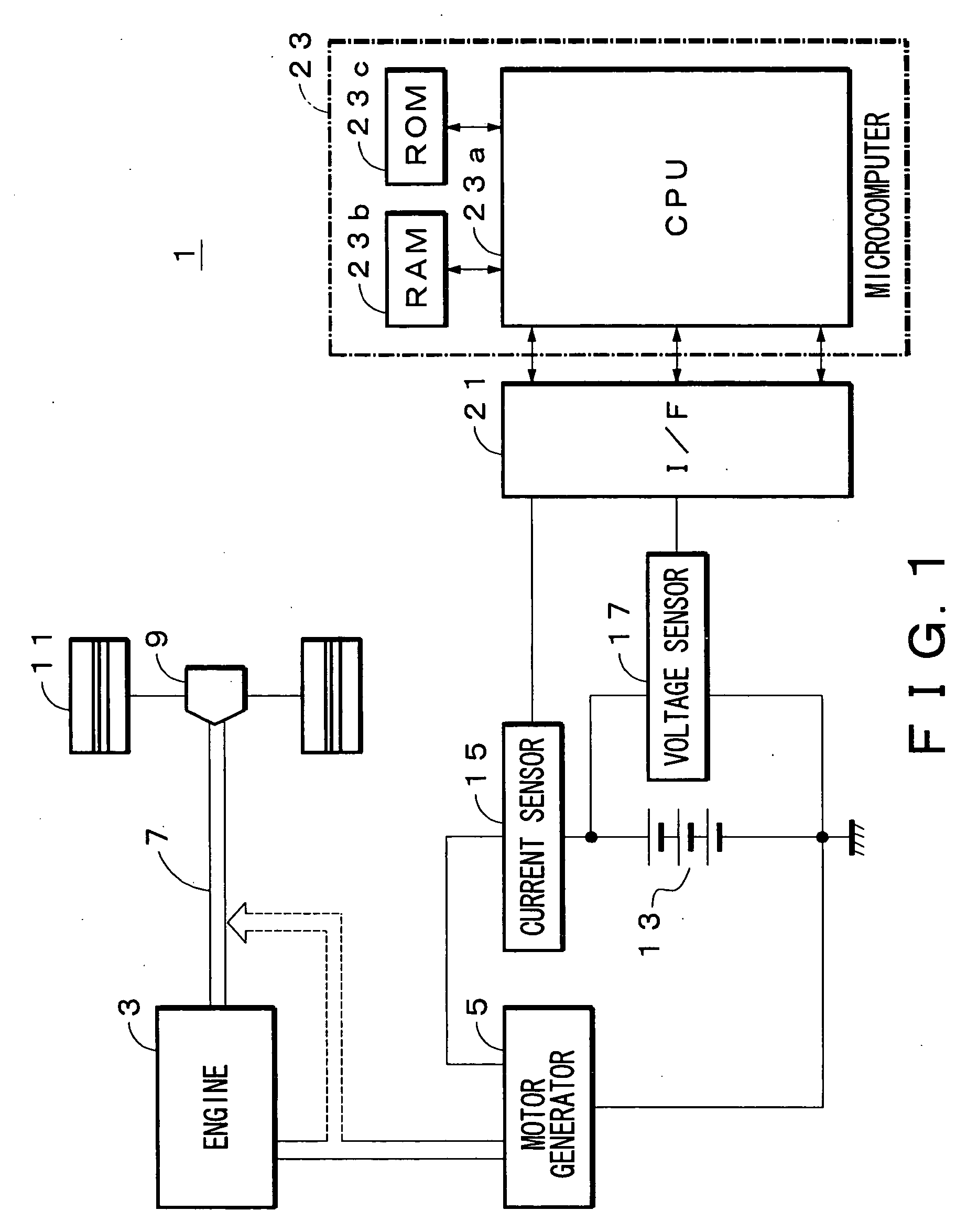
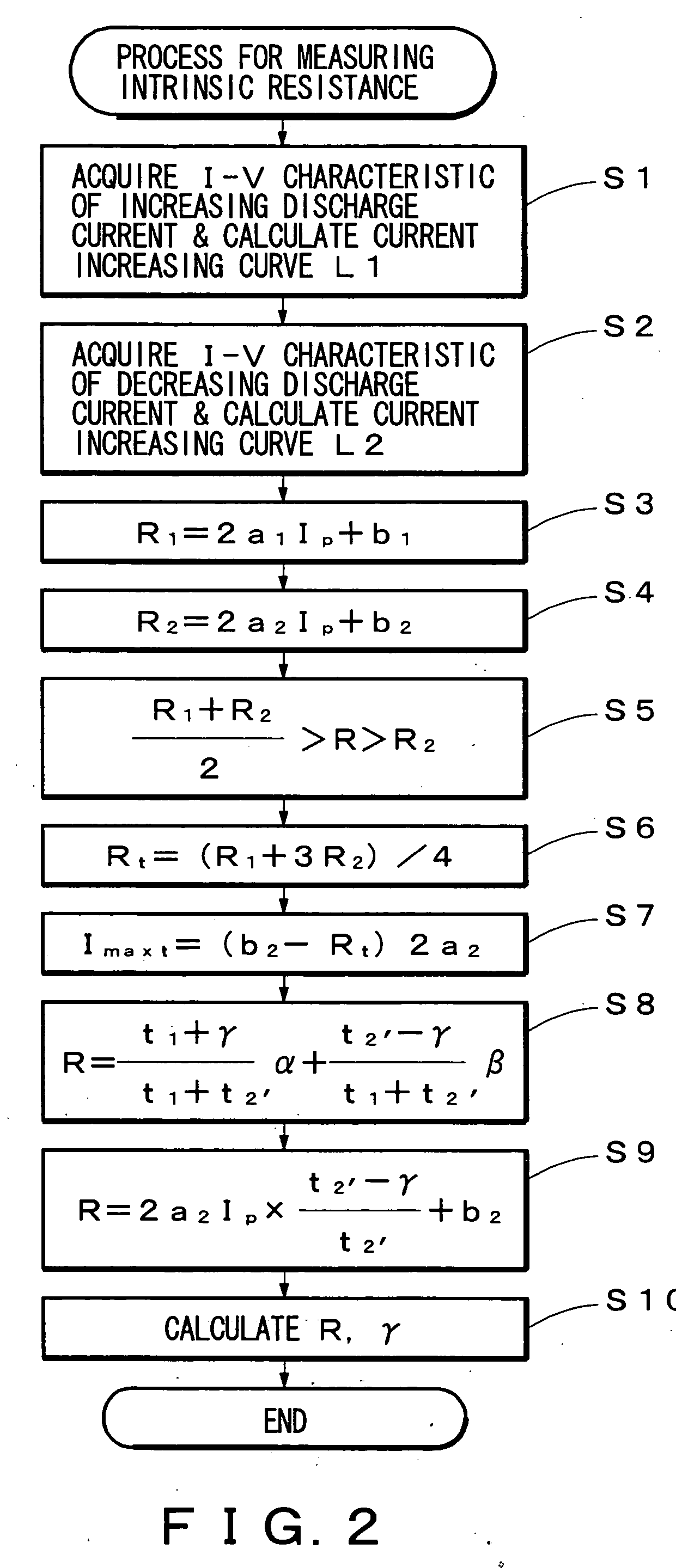
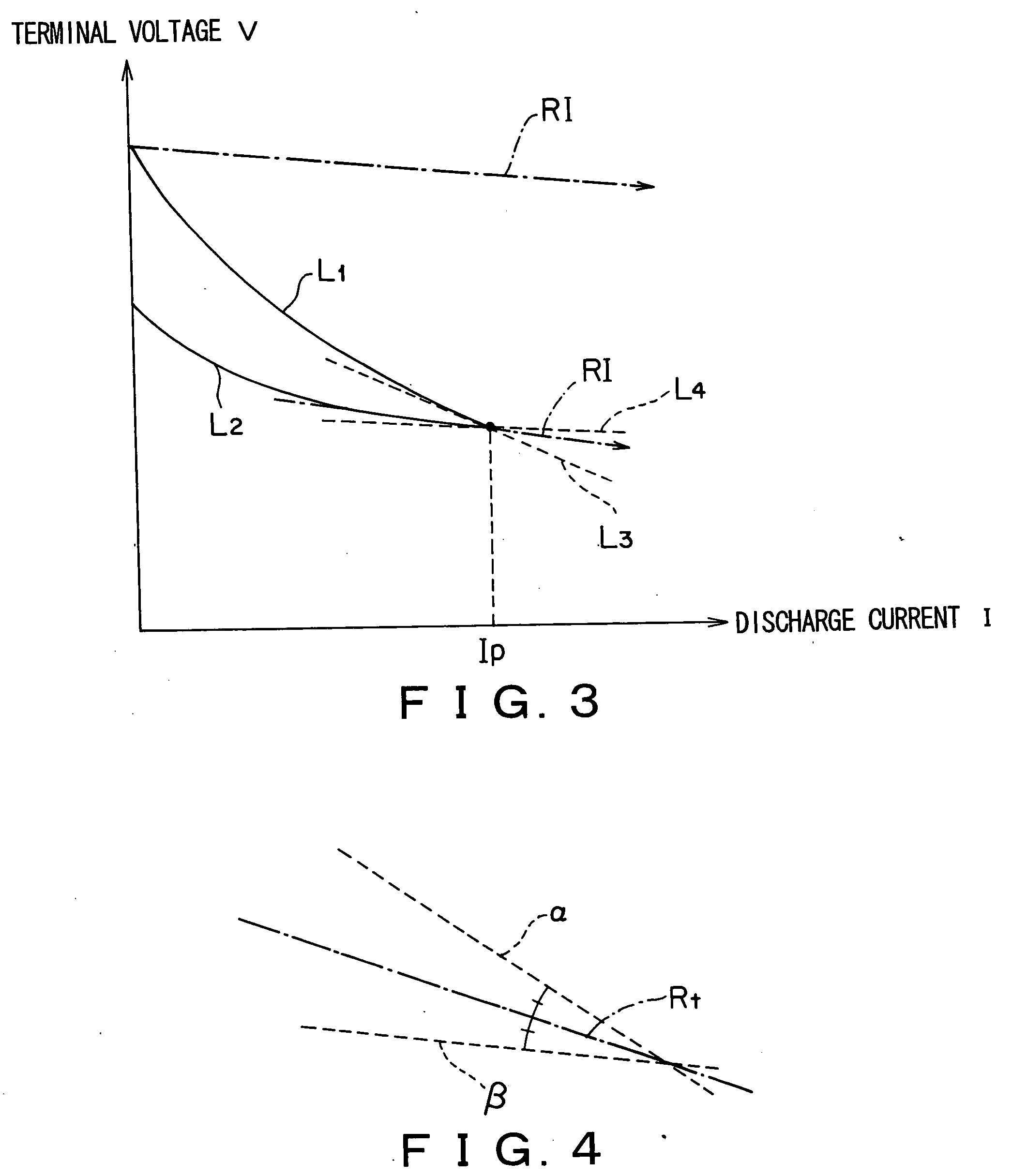
Method of measuring intrinsic resistance of battery and apparatus of same
InactiveUS20070120534A1Accurate acquisitionSmall differenceBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrical testingElectrical resistance and conductanceTerminal voltage
The present invention provides a method of measuring an intrinsic resistance of a battery at a low rate discharge and an apparatus of the same. A method of measuring an intrinsic resistance of a battery includes the steps of: measuring periodically a discharge current and a terminal voltage responding to the discharge current at a low rate discharge of the battery; determining a first approximate expression of the terminal voltage with respect to the increasing discharge current and a second approximate expression of the terminal voltage with respect to the decreasing discharge current based on the measured discharge current and terminal voltage; defining a range of the intrinsic resistance based on the first and second approximate expressions; assuming a resistance in the range of the intrinsic resistance as a tentative intrinsic resistance; determining a tentative maximum polarization time from the second approximate expression and the tentative intrinsic resistance; and determining the intrinsic resistance from two relational expressions including the intrinsic resistance, an intrinsic maximum polarization time and the tentative maximum polarization time.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
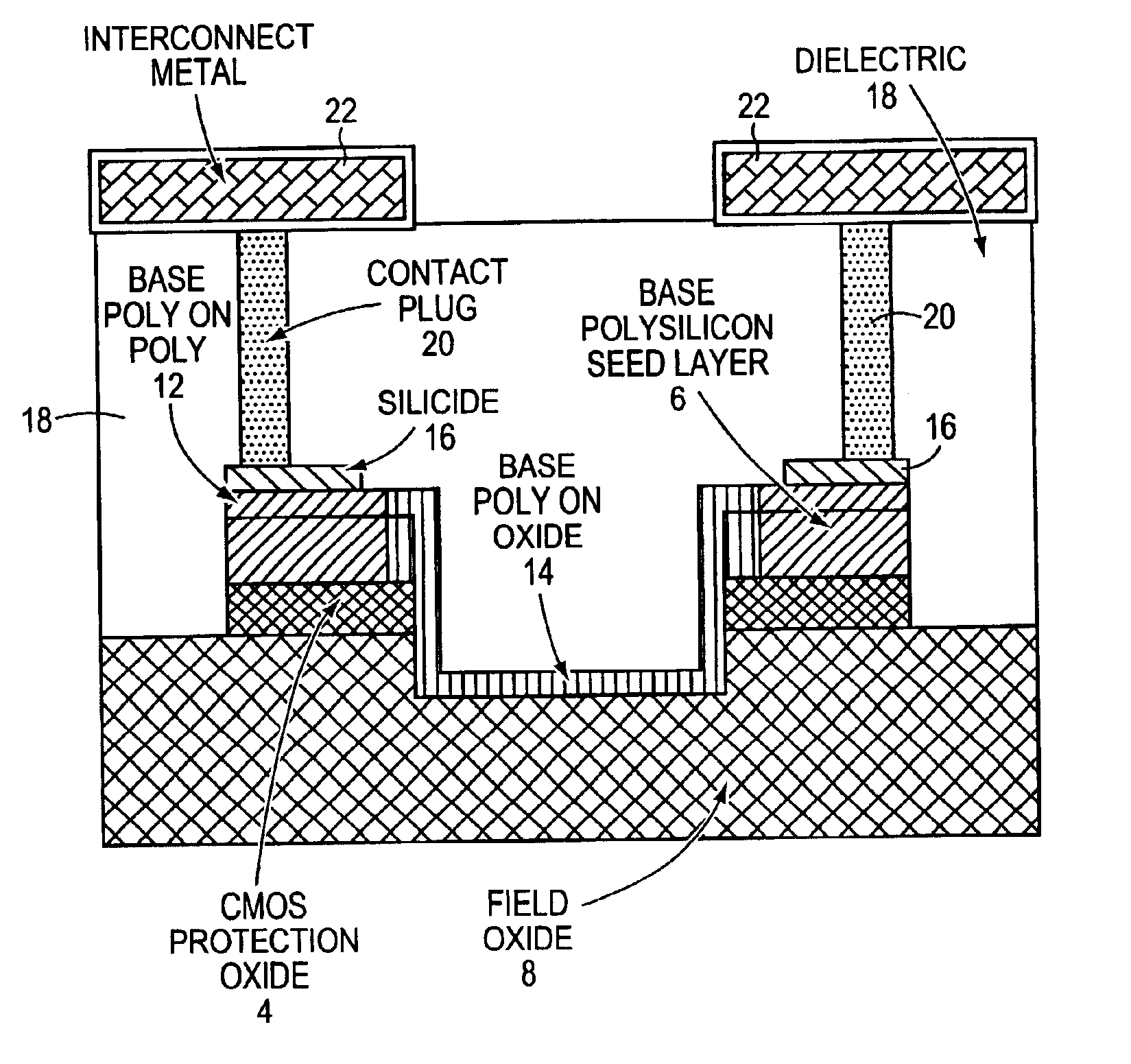
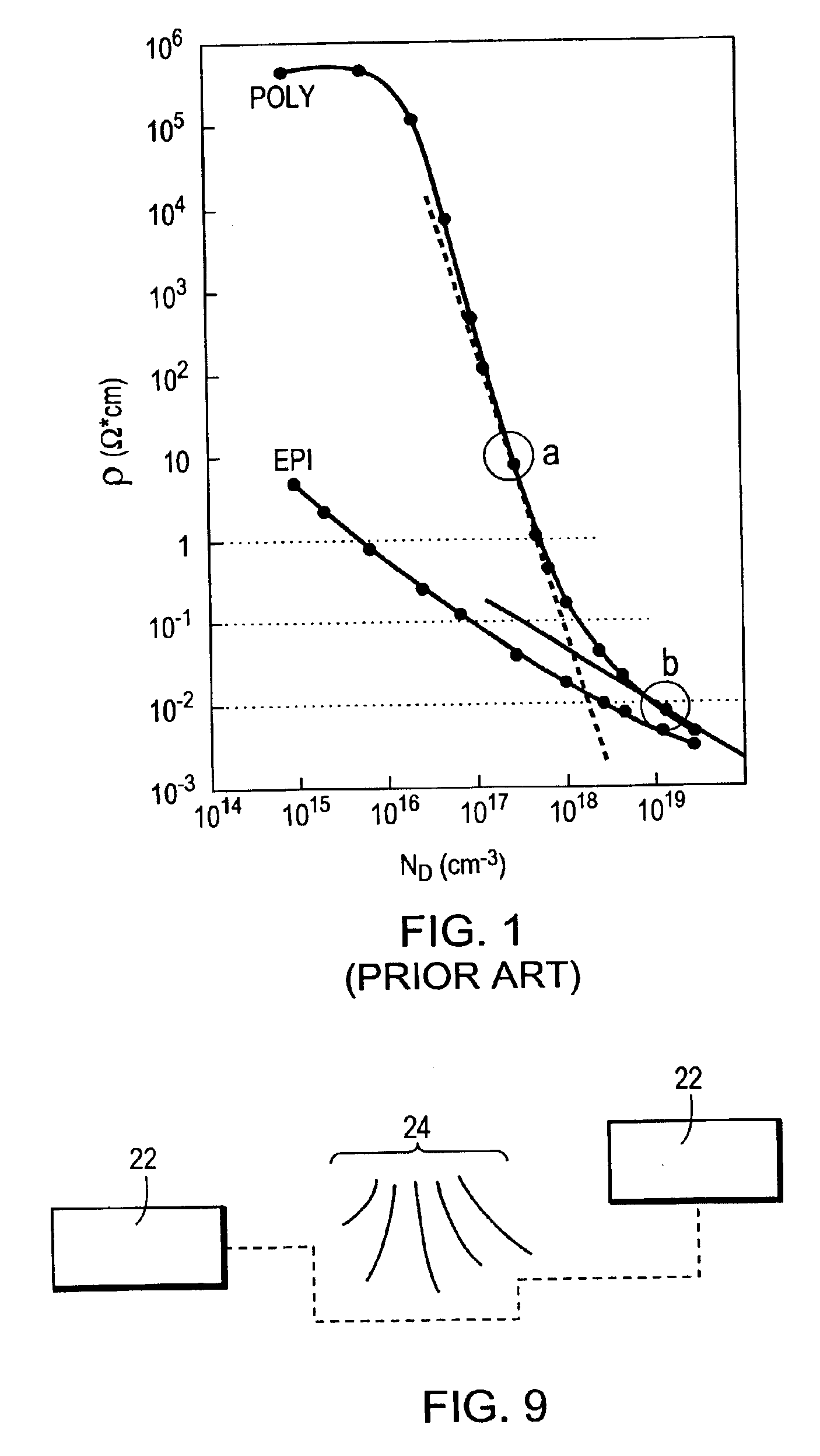
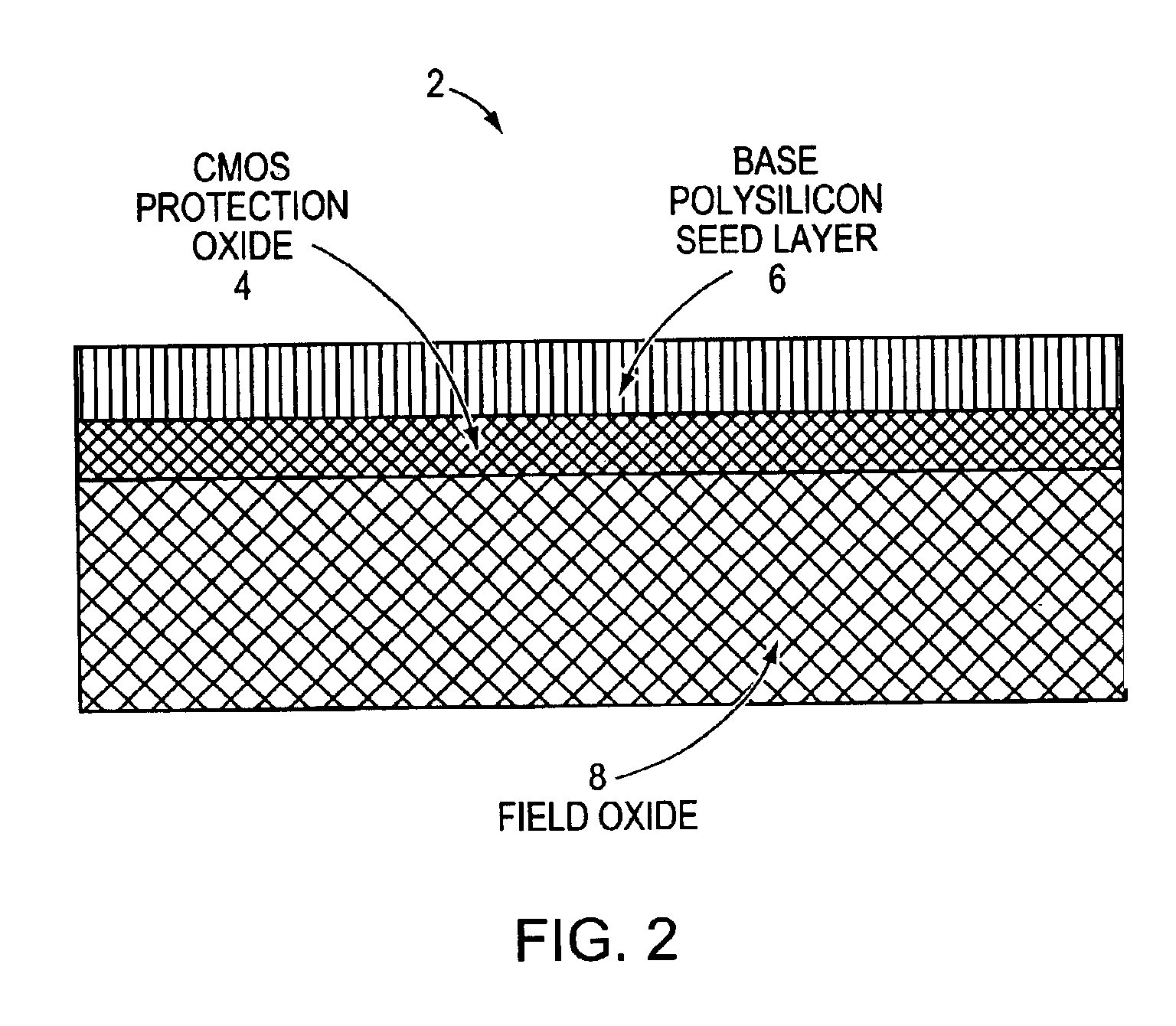
High value split poly P-resistor with low standard deviation
InactiveUS20050106805A1Easy to controlIncrease resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesIntrinsic resistanceMechanical engineering
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Electrostatic discharge protection with input impedance
InactiveUS6967826B2Solid-state devicesEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentCapacitanceRC time constant
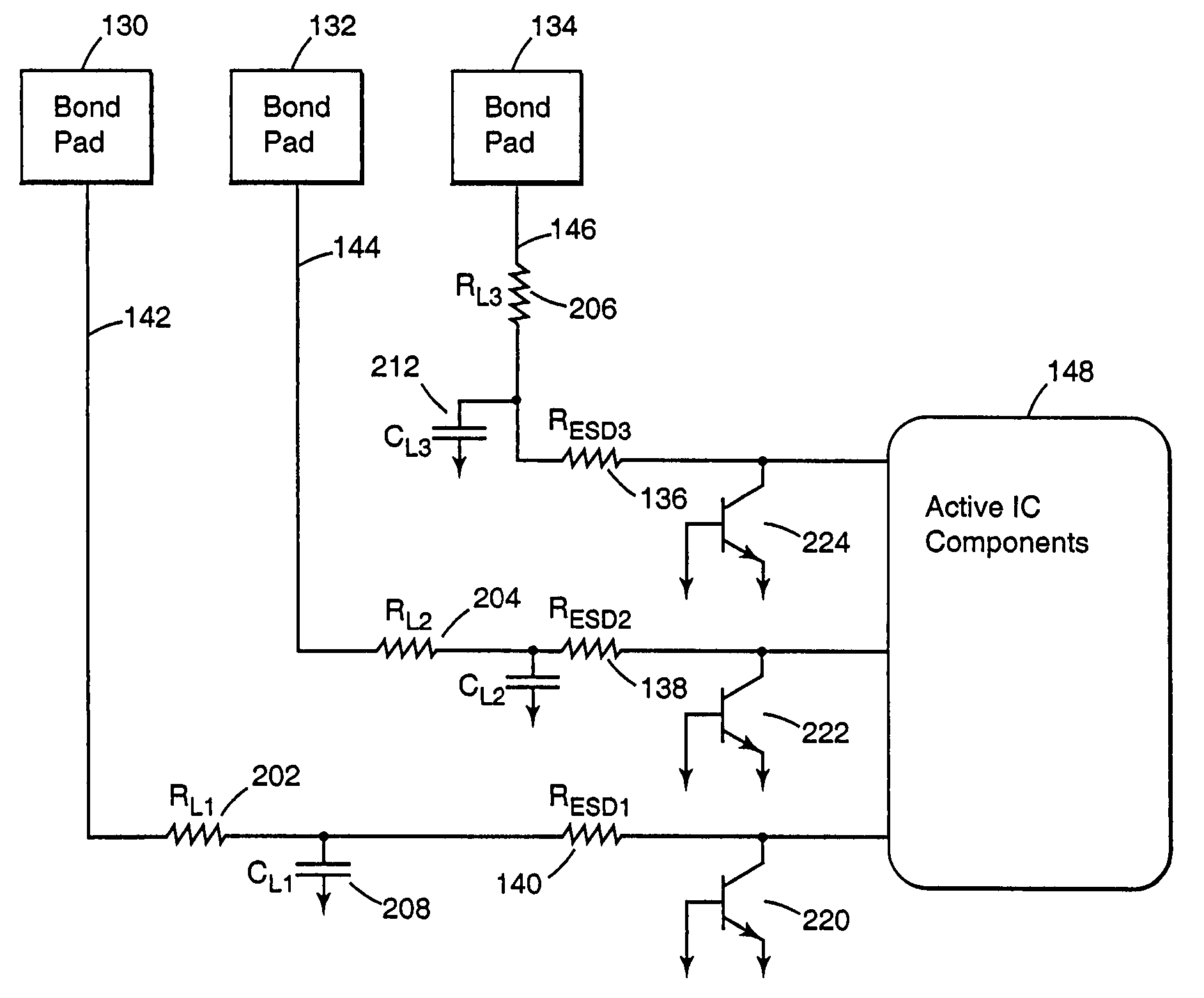
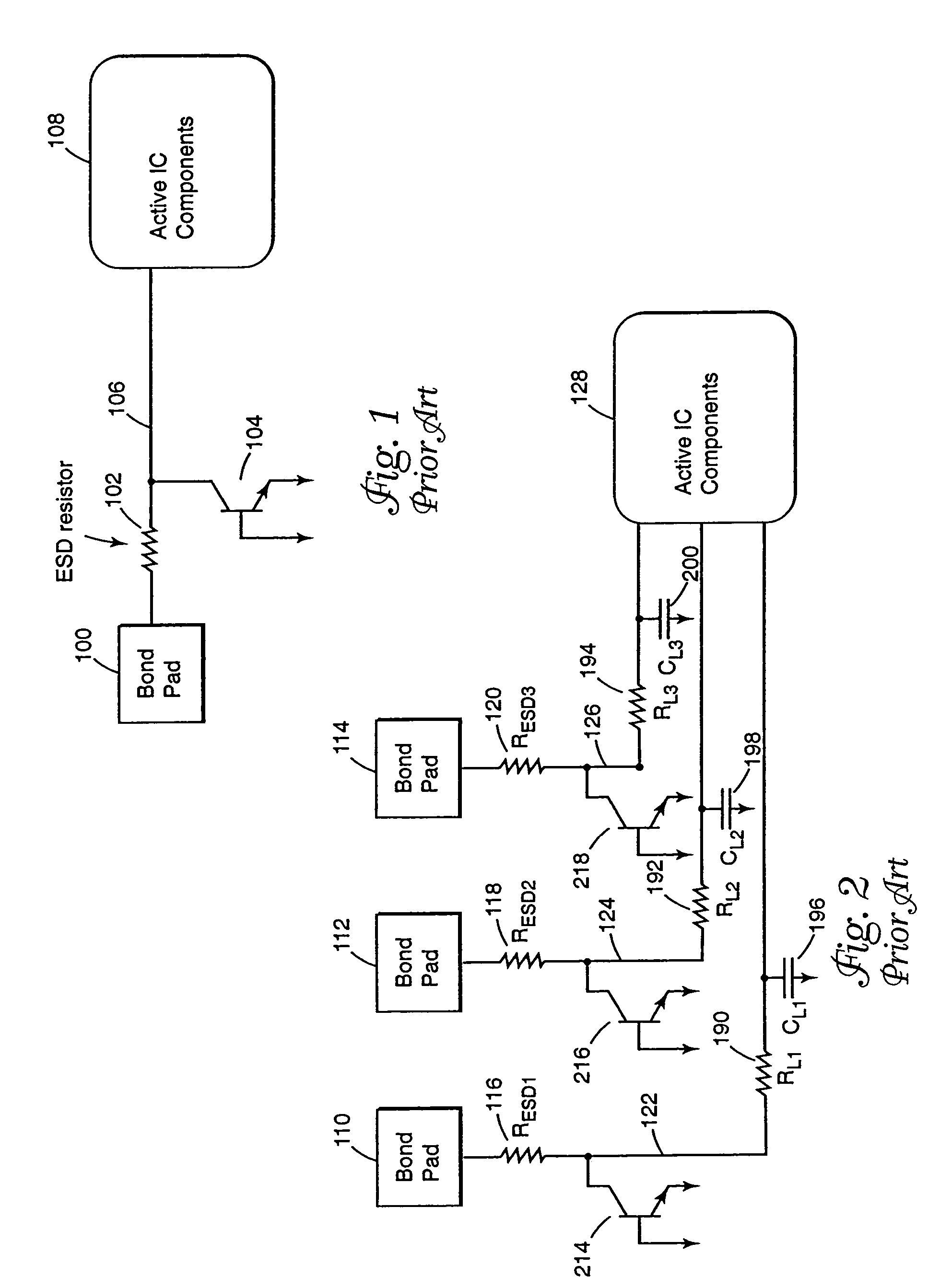
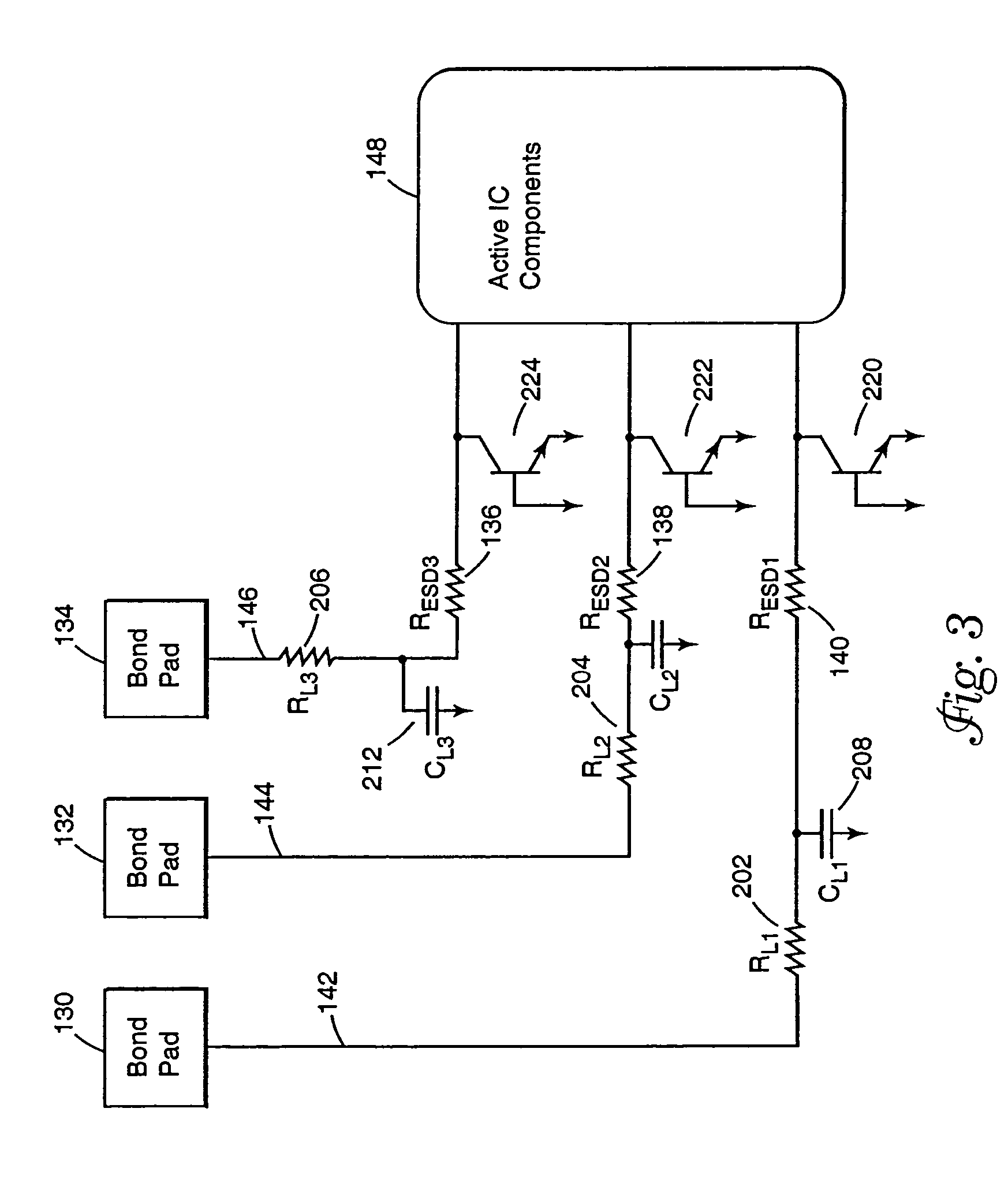
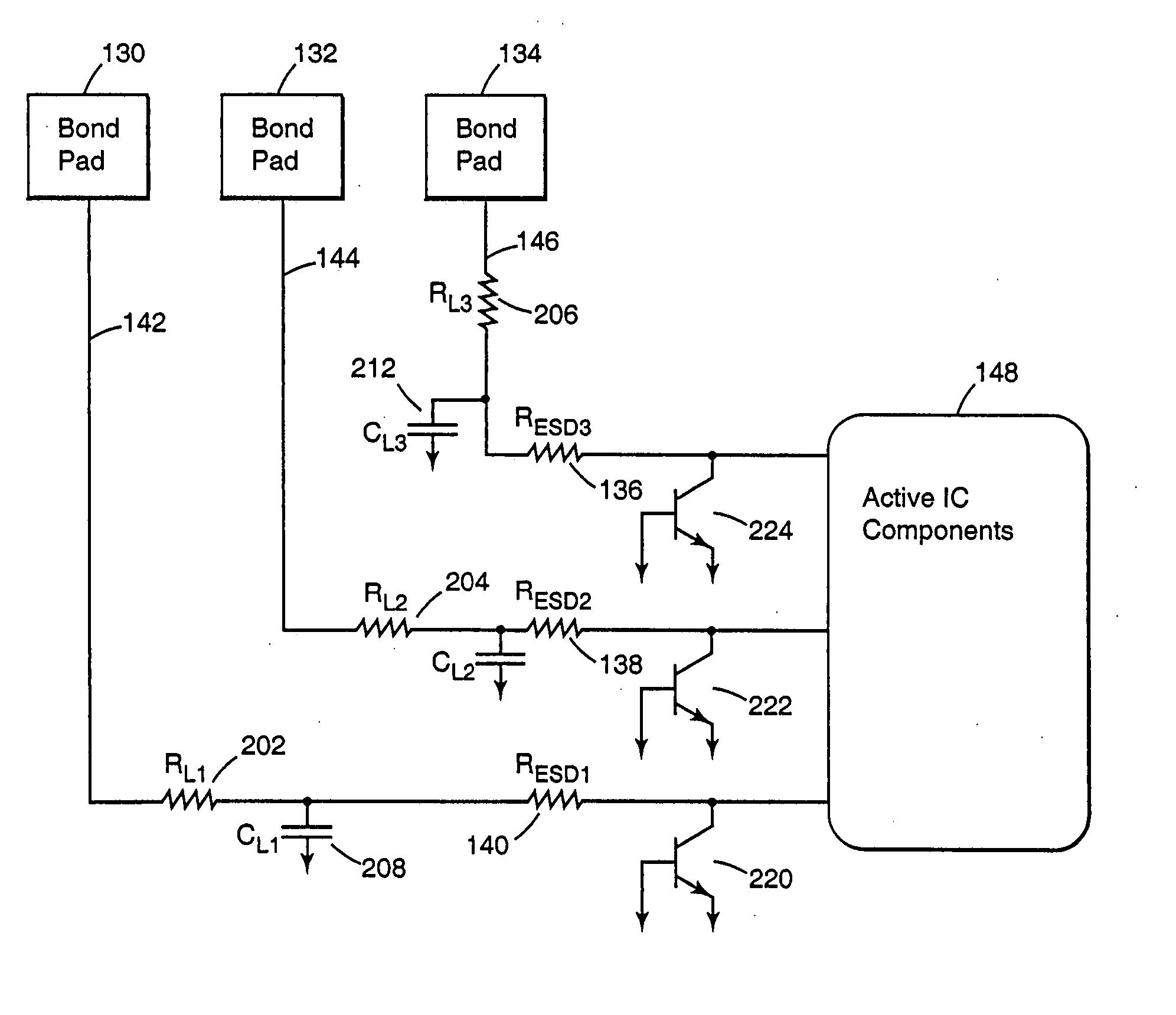
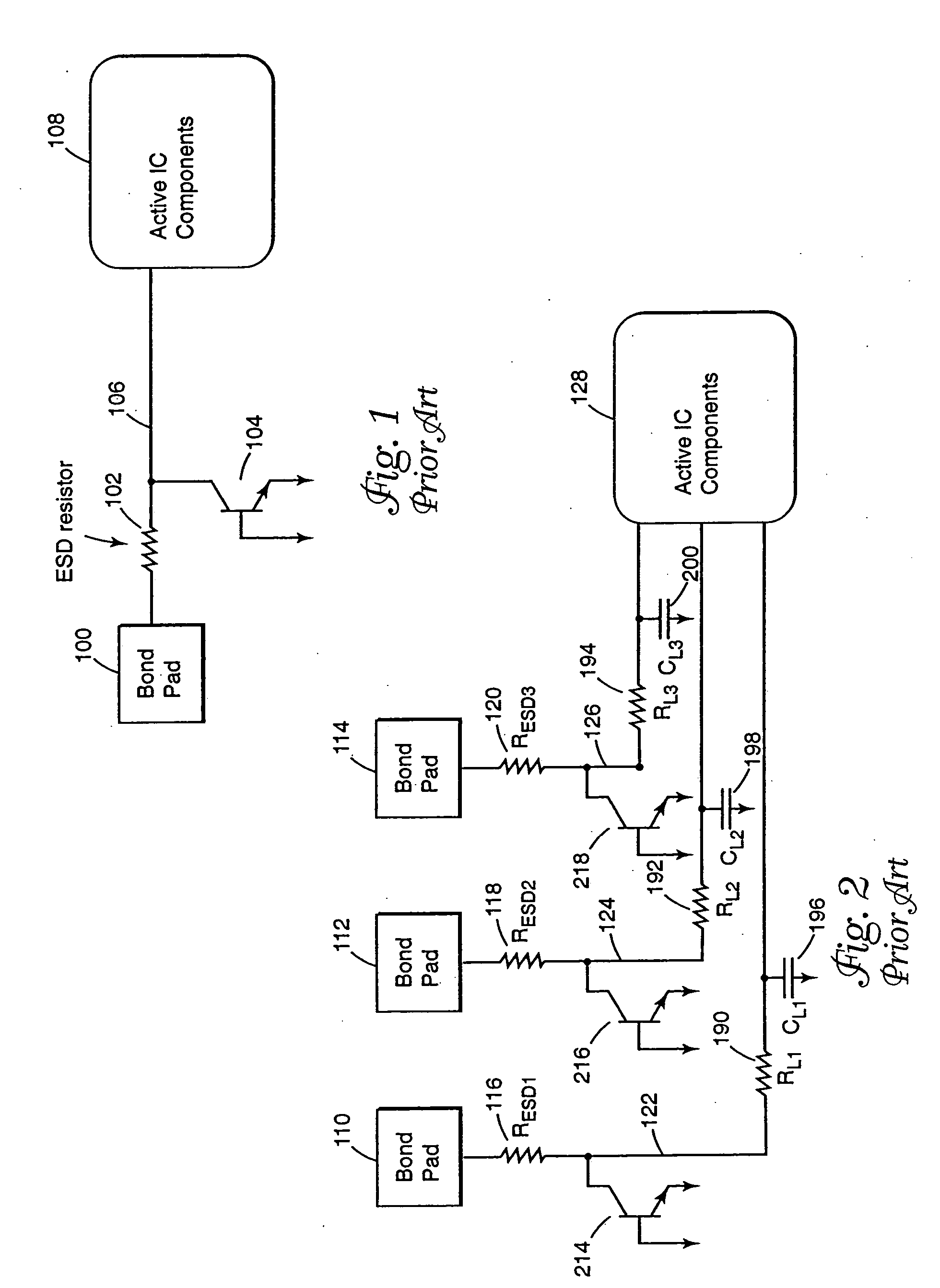
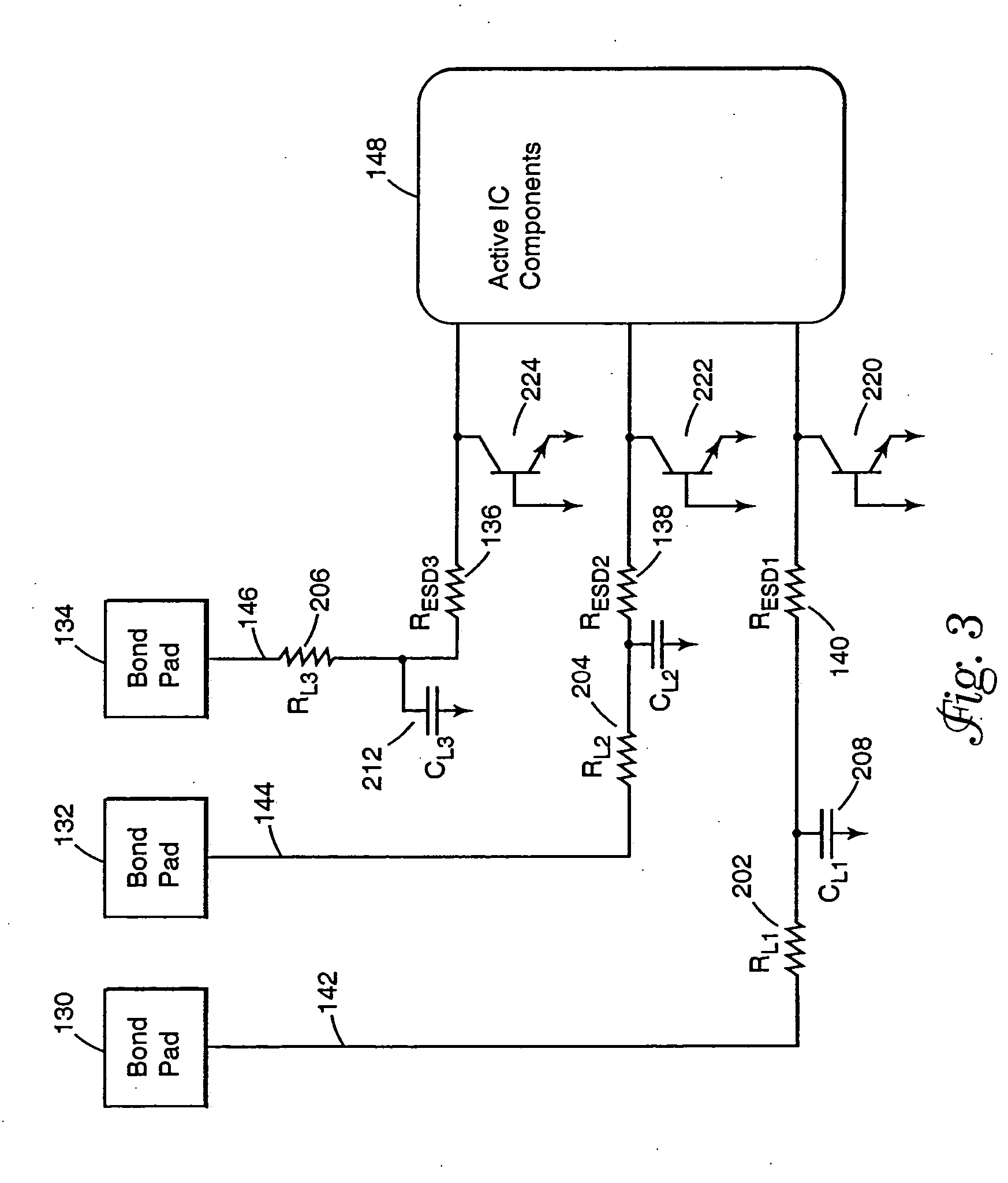
An input circuit for an integrated circuit includes an electrostatic discharge circuit. The input circuit incorporates an interconnect pad, an ESD protection resistor, and an interconnect line that are coupled to the active internal components of the integrated circuit. The interconnect pad is coupled to the interconnect line, and the interconnect line is coupled to the ESD protection resistor which is coupled to the active internal components of the integrated circuit. The ESD protection resistor is positioned physically proximate to the active internal components of the integrated circuit and adjusted in value to compensate for the intrinsic resistance or RC time constant of the interconnect line. The circuitry provides for a lower signal propagation delay through the external connection because of lower RC time constants to drive the capacitance of the interconnect.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Electrostatic discharge protection with input impedance
InactiveUS20050128665A1Solid-state devicesEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentCapacitanceRC time constant
An input circuit for an integrated circuit includes an electrostatic discharge circuit. The input circuit incorporates an interconnect pad, an ESD protection resistor, and an interconnect line that are coupled to the active internal components of the integrated circuit. The interconnect pad is coupled to the interconnect line, and the interconnect line is coupled to the ESD protection resistor which is coupled to the active internal components of the integrated circuit. The ESD protection resistor is positioned physically proximate to the active internal components of the integrated circuit and adjusted in value to compensate for the intrinsic resistance or RC time constant of the interconnect line. The circuitry provides for a lower signal propagation delay through the external connection because of lower RC time constants to drive the capacitance of the interconnect.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Integrated circuit
InactiveUS7202532B2Route length effectiveEffective resistance of substrateTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical resistance and conductanceCoupling
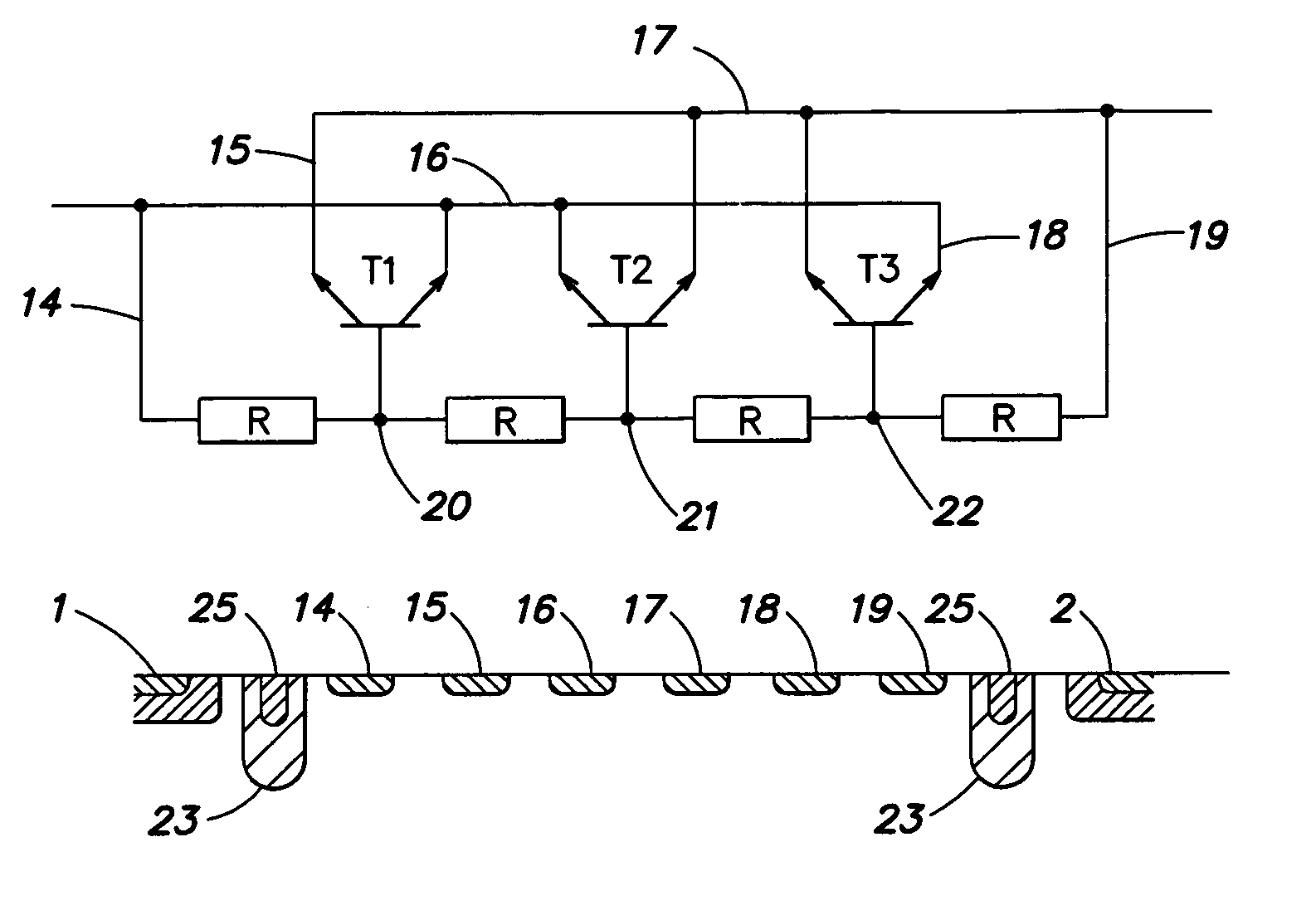
An integrated circuit includes at least two circuit components formed on a common semiconductor substrate. Each circuit component has a self-contained supply voltage system. Coupling circuits couple the supply voltage systems for the at least two circuit components. Each coupling circuit includes at least one transistor having a base formed by or within the substrate itself; more specifically, by or within a region of the substrate contiguous with collector doping zones and emitter doping zones of the transistor. The resistance between the transistor base and the potentials of the two supply voltage systems coupled by each of the coupling circuits is the intrinsic resistance of the substrate between the region forming the base and one of each contact doping zone conductively connected to the collector or emitter through a metallization applied to the substrate. To obtain an identical coupling behavior for the transistor in both directions, the collector and emitter of the transistor are preferably symmetrical, i.e., a transistor with a double emitter. The coupling circuit may be implemented with a single transistor, the dimensions of which are fixed by the desired volume resistivity. Greater flexibility of design with respect to accommodating the coupling circuit on one substrate surface without an increased area requirement is provided by employing multiple transistors as the coupling circuit. These transistors may be distributed independently of each other on the substrate surface.
Owner:MICRONAS
Liquid crystal display and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6949417B1Reduce contact resistanceQuality improvementSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid-crystal displaySilicon oxide
In manufacturing an active panel of a liquid crystal display, when a pad portion to which outer driving signals are applied is formed, oxide or nitride layer is generated on the surface of the pads. Since these oxide and nitride layers have a high intrinsic resistance, they cause a reliability of the signal transmission in the pad portion to be decreased. The present invention provides a method for enhancing the reliability of the signal transmission in the pad portion by removing contaminants such as oxide layer and nitride layer and reducing the contact resistance of the pad portion. The present inversion also provides a method for maintaining a good adhesion by forming a surface of the pad portion in an uneven shape and by increasing the contact area. The pad is formed from dual metal layer made by depositing sequentially a first metal layer and a second metal layer. A protection layer is formed by depositing an insulation material such a silicon oxide or silicon nitride on the entire surface of the substrate on which the pad is formed. By etching the protection layer using dry etching method, a pad contact hole is formed on the pad. The second metal of the pad is removed by wet etching method, using the pad contact hole as mask. By doing so, the contaminants between the metal layer and the protection layer can be completely removed. Further, the present invention can have a plurality of pad contact holes to enlarge the contact area between the pad and the pad terminal, and thereby enhancing adhesion between the pad and the pad terminal.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
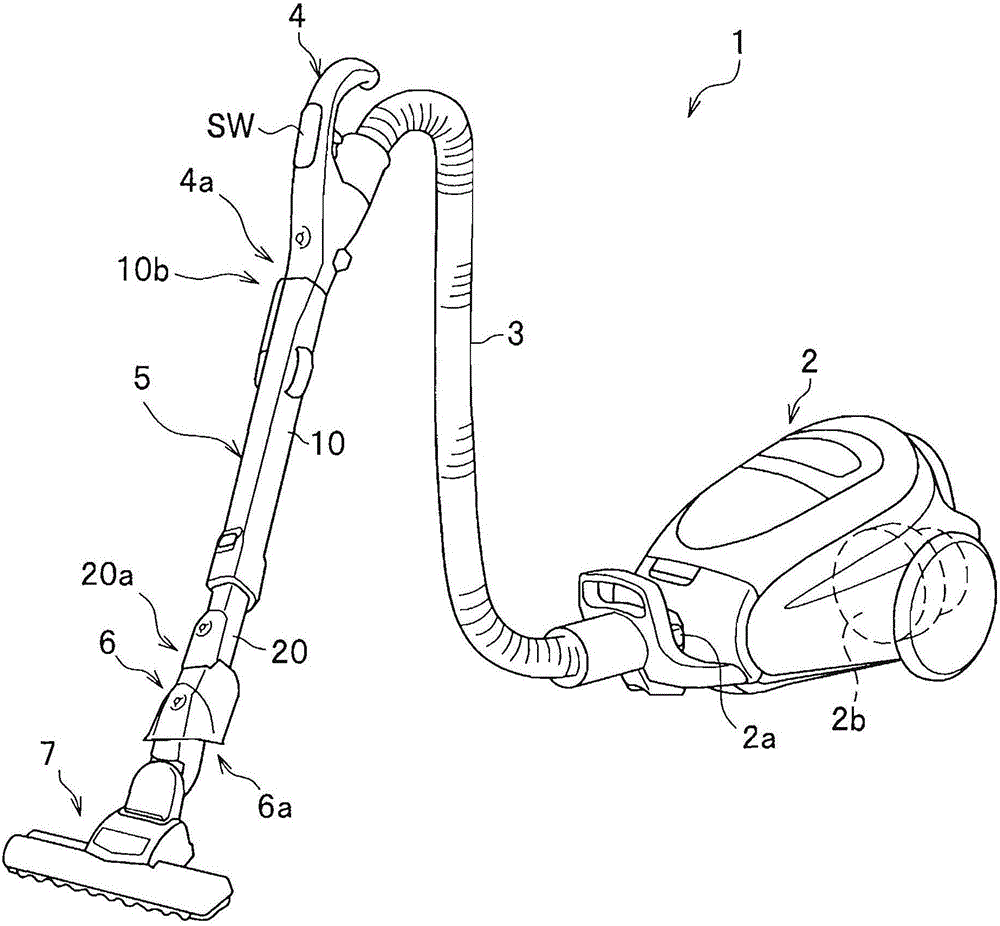
Electric dust collector
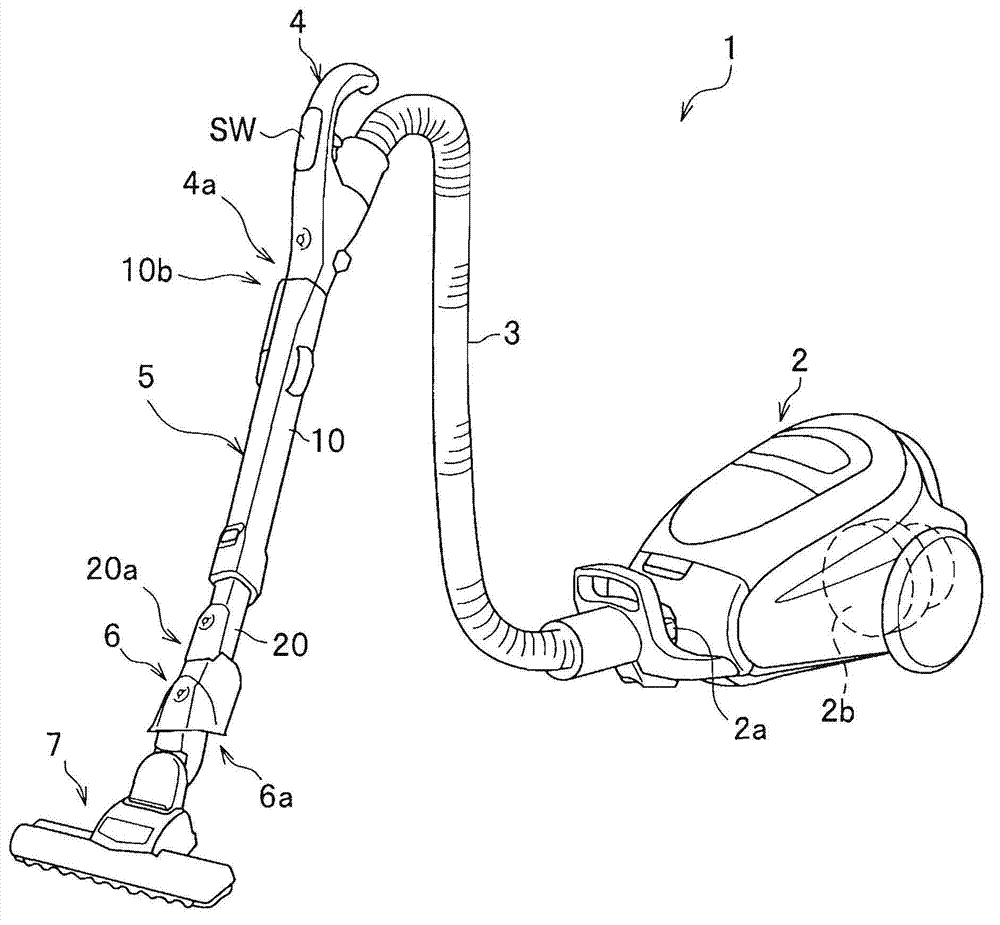
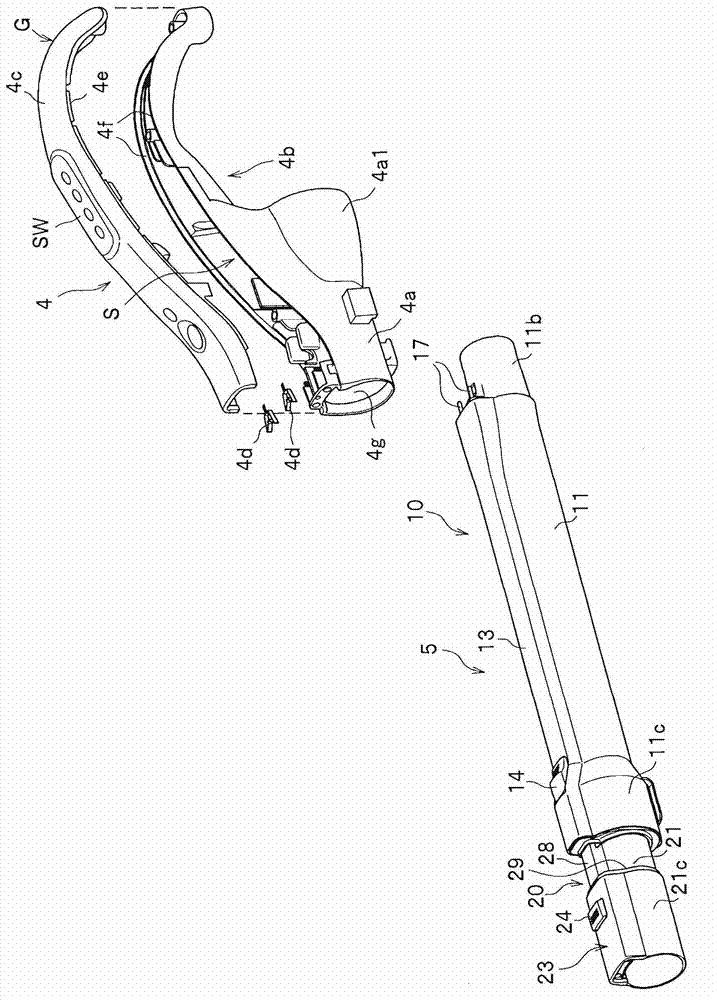
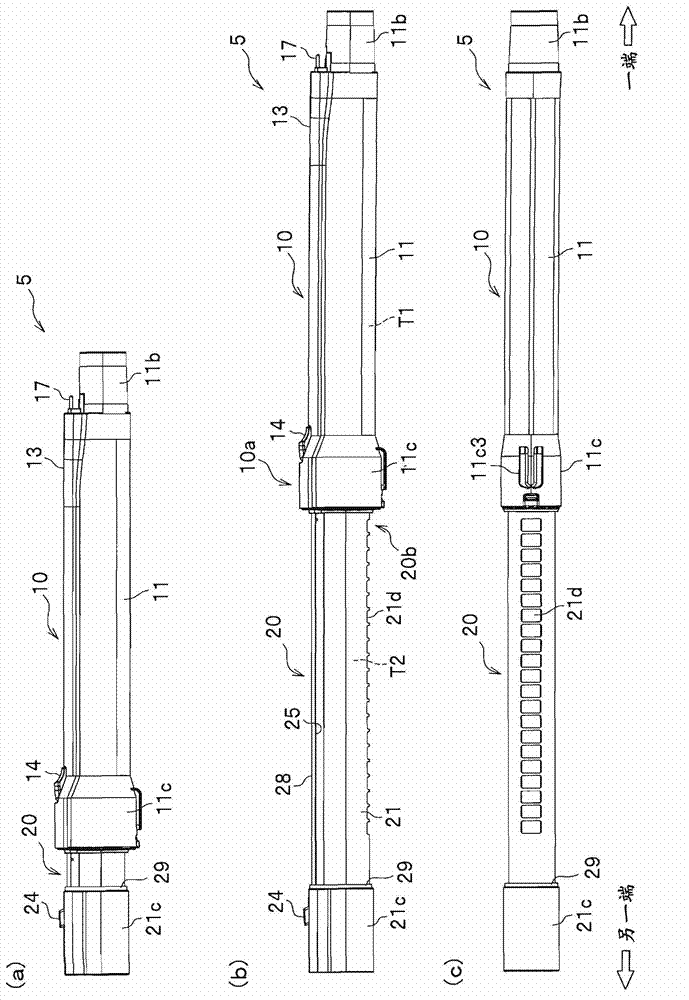
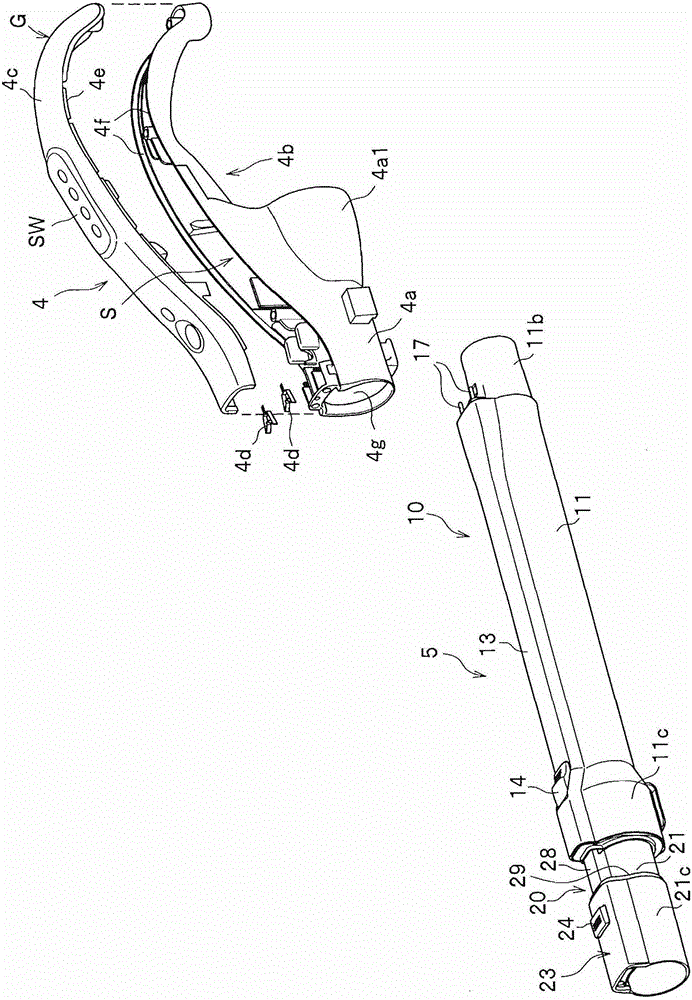
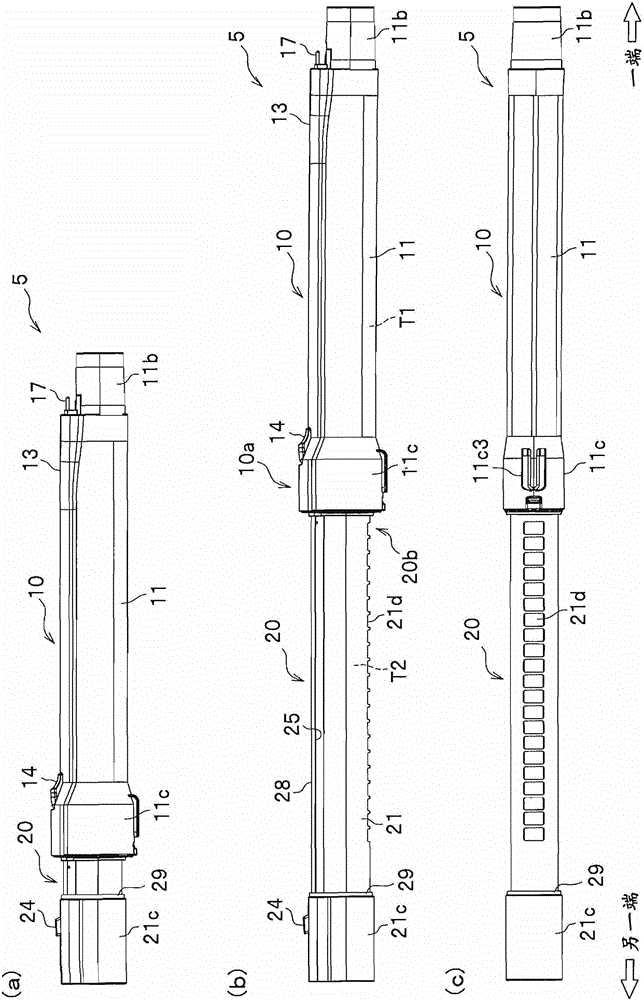
ActiveCN103356134ASurface intrinsic resistance is smallExcellent static electricity removalSuction hosesSuction handlesIntrinsic resistanceEngineering
The invention provides an electric dust collector that has excellent antistatic performance. The electric dust collector has a suction member (7), an extension pipe (5) which is connected with the suction member (7) and is made of conductive material, an operation pipe (4) which is connected with the extension pipe (5) and a soft pipe portion (3), and further has a power supply mechanism which supplies power to the suction member (7) from a vacuum cleaner main body (2). The extension pipe (5) has an insulating resin part and a conductive part of the power supply mechanism, which is insulated from the extension pipe (5) and is configured on the insulating resin part. The insulating resin part is covered within a range less than a whole circle of an outer periphery of an end portion in the length direction of the extension pipe (5). The insulating resin part which forms the part of the extension pipe (5) is made of a material containing a charged prevention agent, and compared with a part made of a general resin not containing the charged prevention agent, the insulating resin part is smaller has a smaller surface intrinsic resistance value.
Owner:日立グローバルライフソリューションズ株式会社
Electromagnetic device, high-voltage generating device, and method for making the electromagnetic device
InactiveUS20050104698A1Improve featuresSmall sizeMicrobiological testing/measurementElectric lighting sourcesElectrical conductorBobbin
An electromagnetic device and a high-voltage generating device which are thin and improved in the characteristics are provided in which a magnetic core 3 is made of a cylindrical form of a ferrite material having a higher intrinsic resistance. A winding is provided by winding a flat rectangular wire conductor 2 in an edge-wise winding form directly on substantially the entire length of the magnetic core 3. As any insulator such as a coil bobbin is not needed between the flat rectangular wire conductor 2 and the magnetic core 3, the winding can be decreased in the overall size or thickness thus contributing to the dimensional reduction of the electromagnetic device. Also, as its flat rectangular wire conductor 2 is wound directly on the magnetic core 3, the winding can be minimized in the length and thus the overall resistance. Moreover, as there is no gap between the winding and the magnetic core 3, the self-inductance can be reduced while the size and the number of turns of the winding remain unchanged.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Measurement method of base resistance of bipolar transistor
ActiveCN101696992AThe resistance reachesAccurate measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical resistance and conductanceDelta-v
The invention provides measurement structure and method of a base resistance of a bipolar transistor. The measurement method comprises the steps of: designing a plurality of bipolar transistor measurement structures with different emitter region widths b; in measurement, zero-offsetting an emitter electrode and a collector electrode of each measurement structure, connecting four metal leading outterminals of a base by using a testing Kelvin resistance mode, applying an excitation current I and measuring a voltage drop Vbb; fitting a curve by using Delta Vbb / I as ordinates and Delat b / L as abscissas according to the formula of Delta Vbb / I=Rsh*Delta b / L+Rlink, wherein L is the effective length of an emitter region, slope of the curve is an intrinsic square resistance Rsh of a base and intercept is a connecting resistance Rlink of the base; zero-offsetting the emitter region and a collector region of each measurement structure, respectively applying voltages of Vbe+Delta V and Vbe-DeltaV to the two metal leading out terminals closest to the emitter region, measuring the current I flowing through the base; and fitting a curve according to the formula of 2Delta V / Delta I=Rsh*Delta b / L+Rx, wherein the intercept is a non-intrinsic resistance Rx of the base. The base contact resistance is Rx-Rlink.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
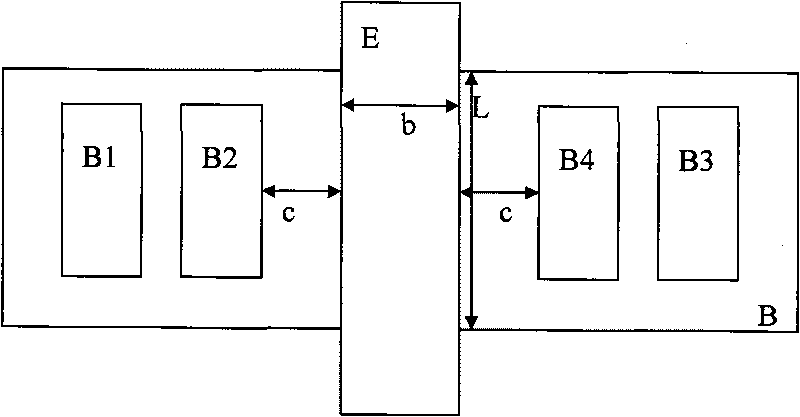
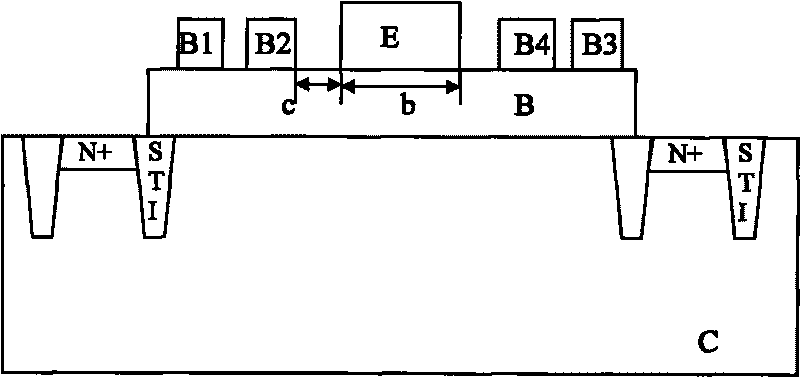
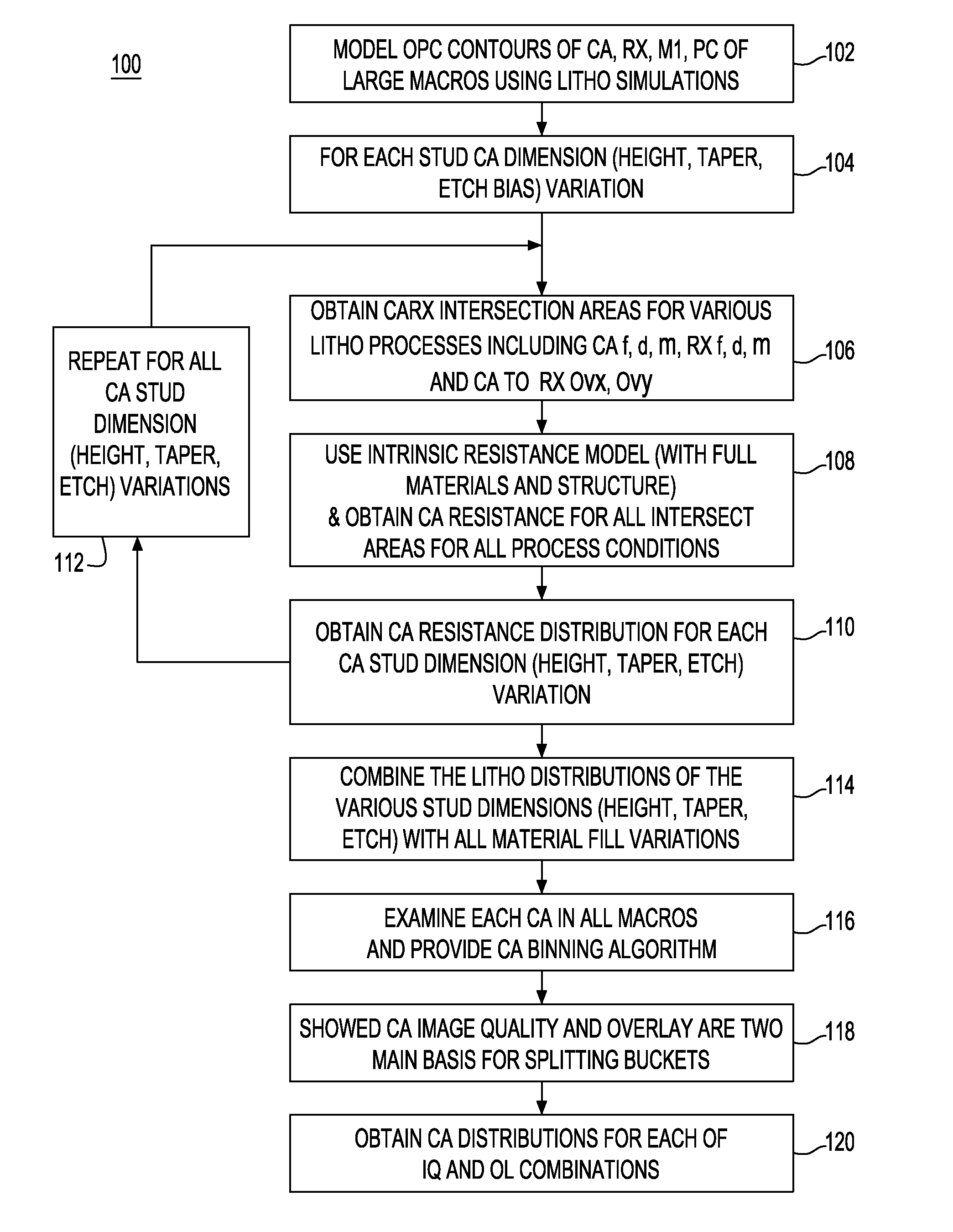
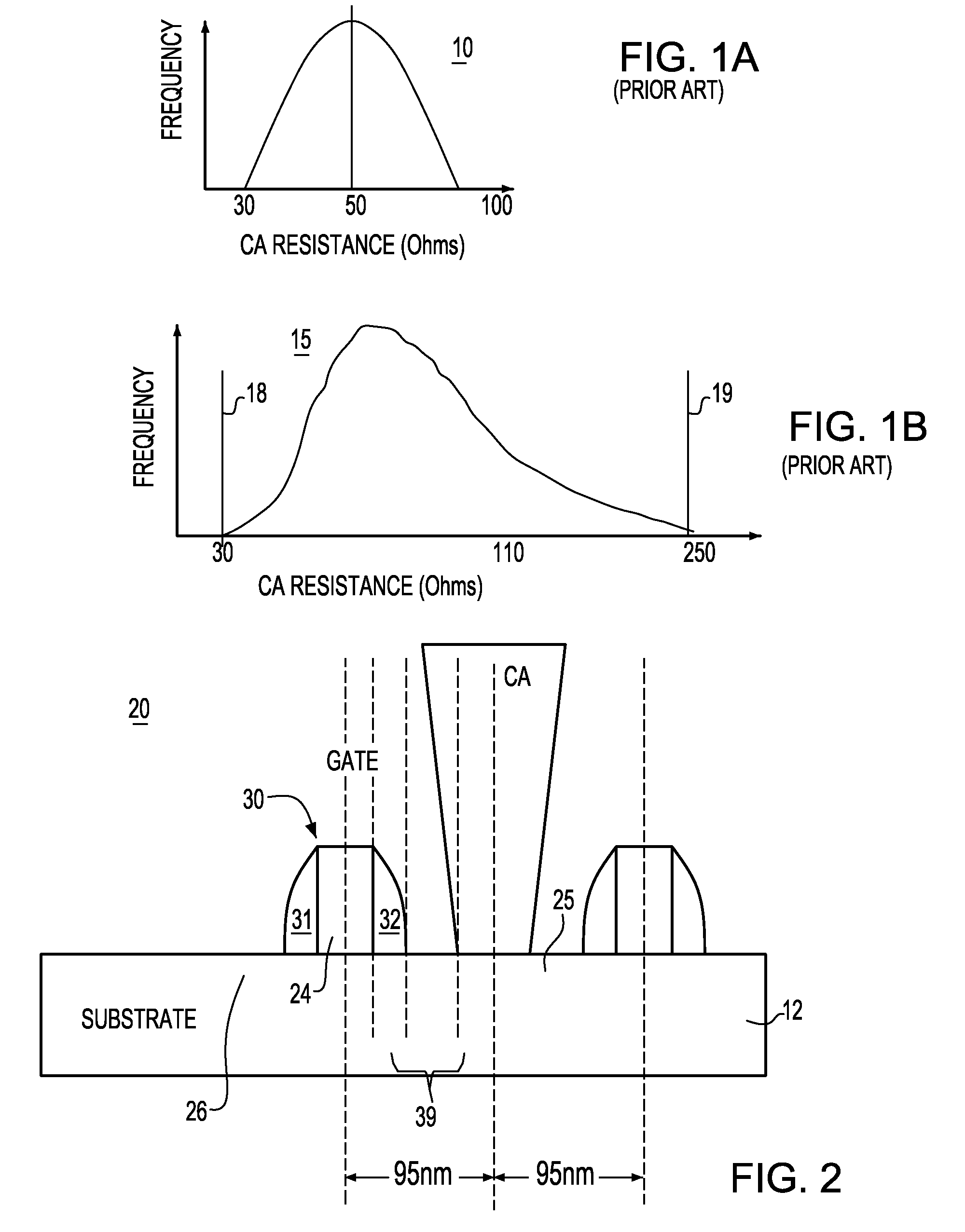
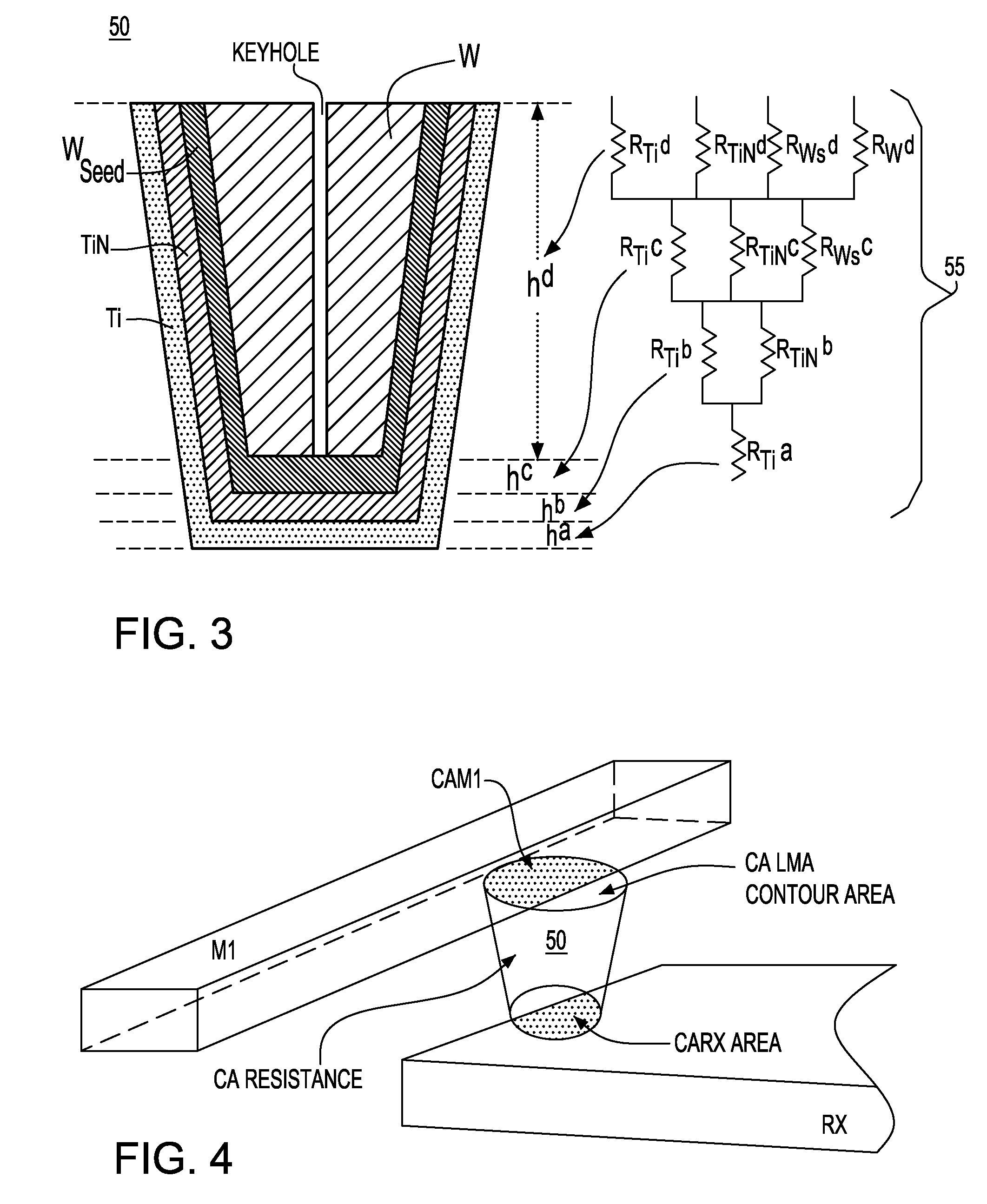
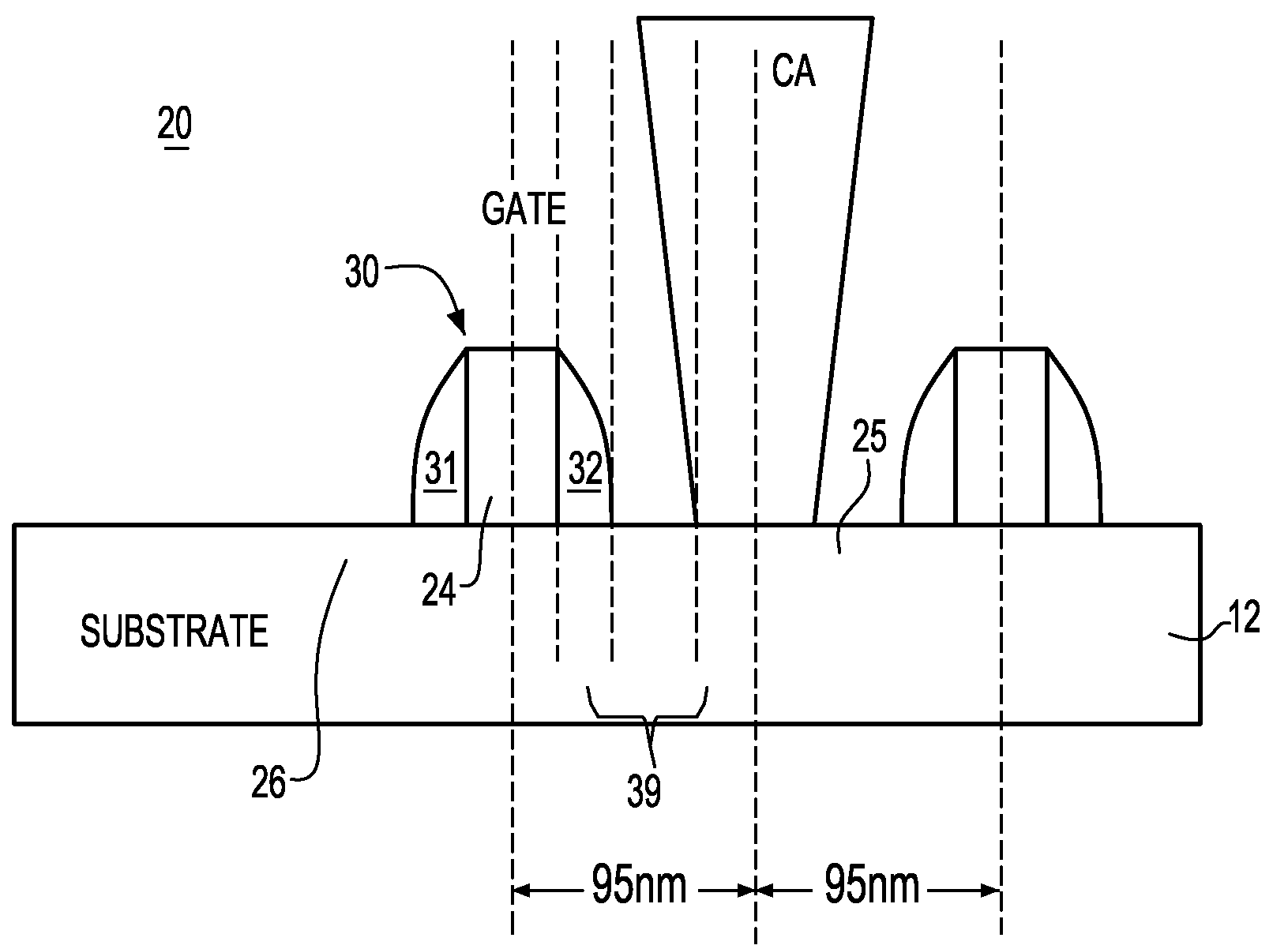
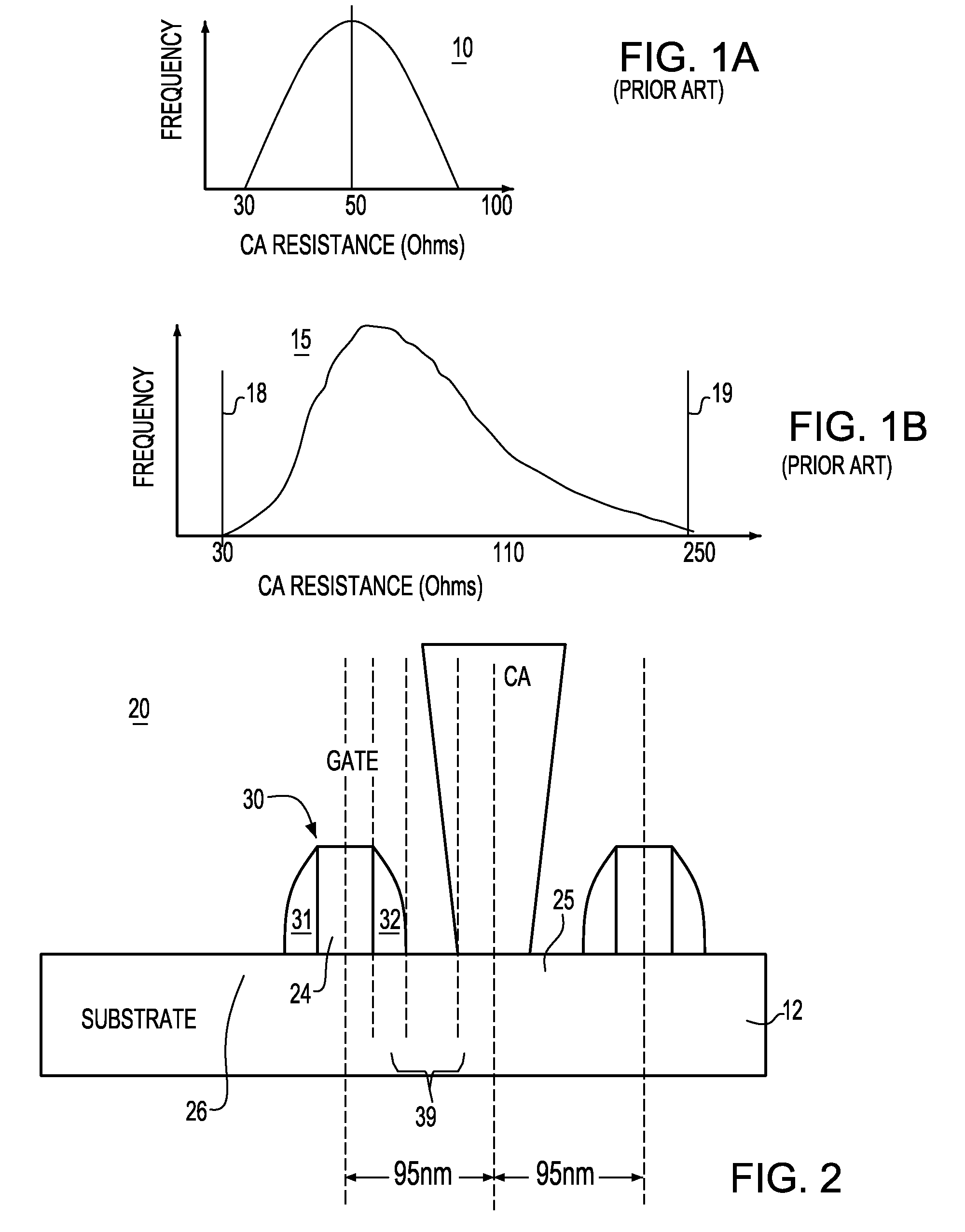
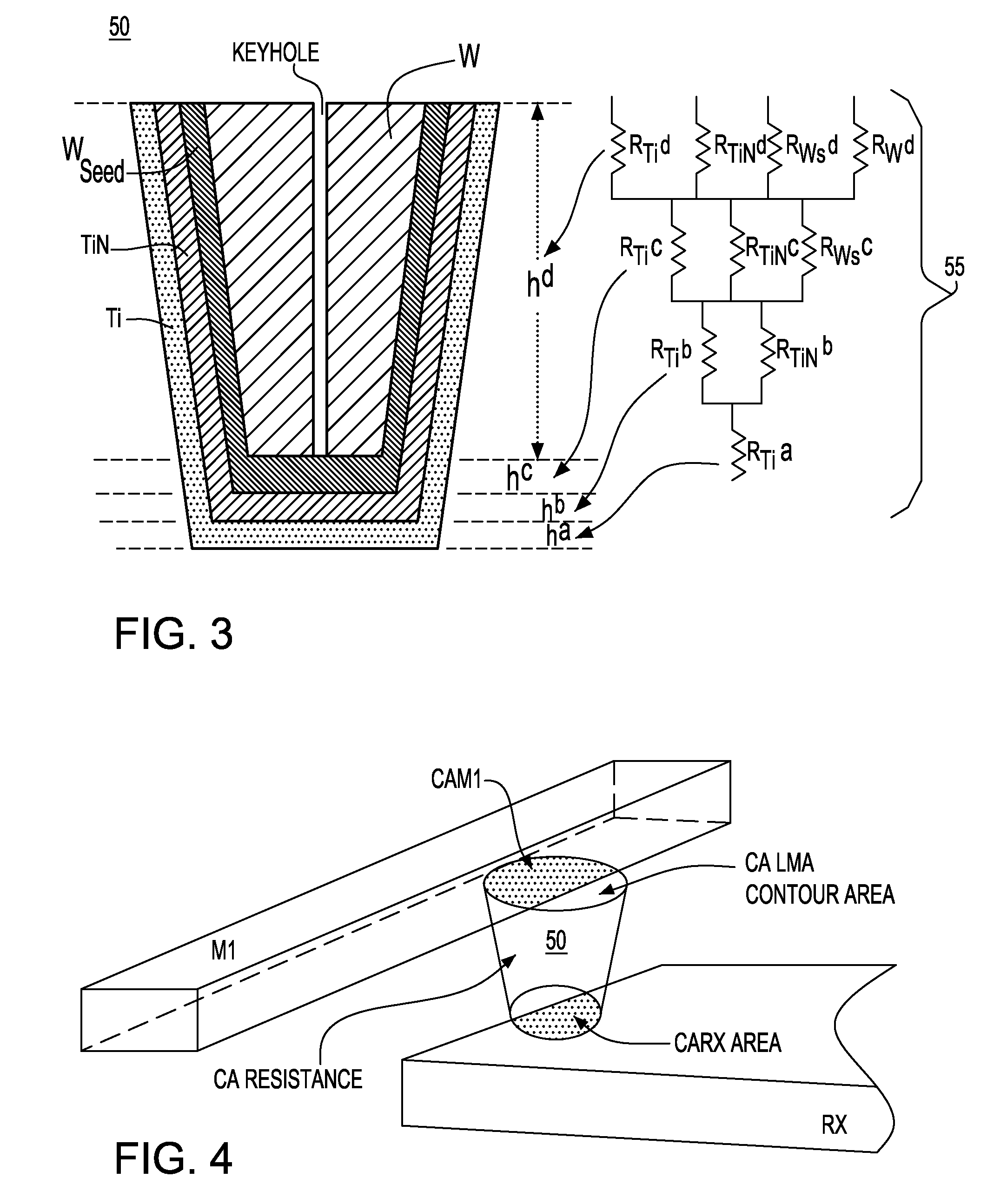
CA resistance variability prediction methodology
ActiveUS7831941B2Simple designAccurate circuit behavior modelingComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationElectrical resistance and conductancePredictive methods
A methodology for obtaining improved prediction of CA resistance in electronic circuits and, particularly, an improved CA resistance model adapted to capture larger than anticipated “out of spec” regime. In one embodiment, a novel bucketization scheme is implemented that is codified to provide a circuit designer with considerably better design options for handling large CA variability as seen through the design manual. The tools developed for modeling the impact of CA variable resistance phenomena provide developers with a resistance model, such as conventionally known, modified with a new CA model Basis including a novel CA intrinsic resistance model, and, a novel CA layout bucketization model.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Ca resistance variability prediction methodology
ActiveUS20090171644A1Simple designAccurate circuit behavior modelingComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
A methodology for obtaining improved prediction of CA resistance in electronic circuits and, particularly, an improved CA resistance model adapted to capture larger than anticipated “out of spec” regime. In one embodiment, a novel bucketization scheme is implemented that is codified to provide a circuit designer with considerably better design options for handling large CA variability as seen through the design manual. The tools developed for modeling the impact of CA variable resistance phenomena provide developers with a resistance model, such as conventionally known, modified with a new CA model Basis including a novel CA intrinsic resistance model, and, a novel CA layout bucketization model.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
High value split poly p-resistor with low standard deviation
InactiveUS6885280B2Easy to controlIncreasing polysilicon resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesIntrinsic resistanceMechanical engineering
A resistor structure is disclosed that is constructed out of two layers of polysilicon. The intrinsic device is made using the top layer which is either a dedicated deposition, or formed as part of an existing process step such as a base epi growth in a BiCMOS flow. This poly layer can be made with a relatively high (greater than 2000 ohms per square) sheet resistance by appropriate scaling of the implant dose or by insitu doping methods. In this invention this layer is arranged to be about 1000 A or less thick. Such a resistor form with this thickness has been shown to demonstrate a better standard; deviation of resistance compared to resistors made with a thicker layer. Additionally, practical resistors made in elongated forms demonstrate better standard deviations of resistance when five bends were incorporated into the form. The resistor ends are formed by the addition of a bottom poly layer in a self aligned manner with a deposition that may already be part of the process sequence. The end result is that the intrinsic resistor body is formed of a single poly layer, while the ends are created out of two layers. These ends are thick enough so that standard silicide and contact etch processing may be added to the structure without special care. In addition, dedicated or already available implants may be incorporated into the resistor ends to ensure ohmic contacts from polysilicon to the silicide or the contact metal are achieved. These steps can produce an easily fabricated resistor structure with consistent, low resistance, ohmic end contacts, and intrinsic resistance of greater than 2000 ohms per square.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
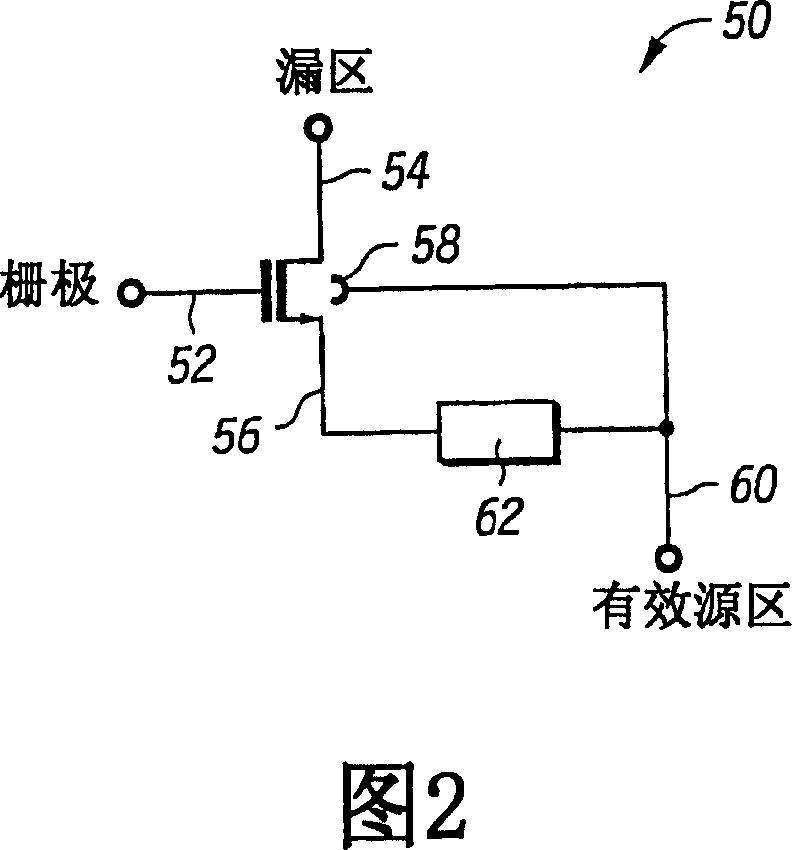
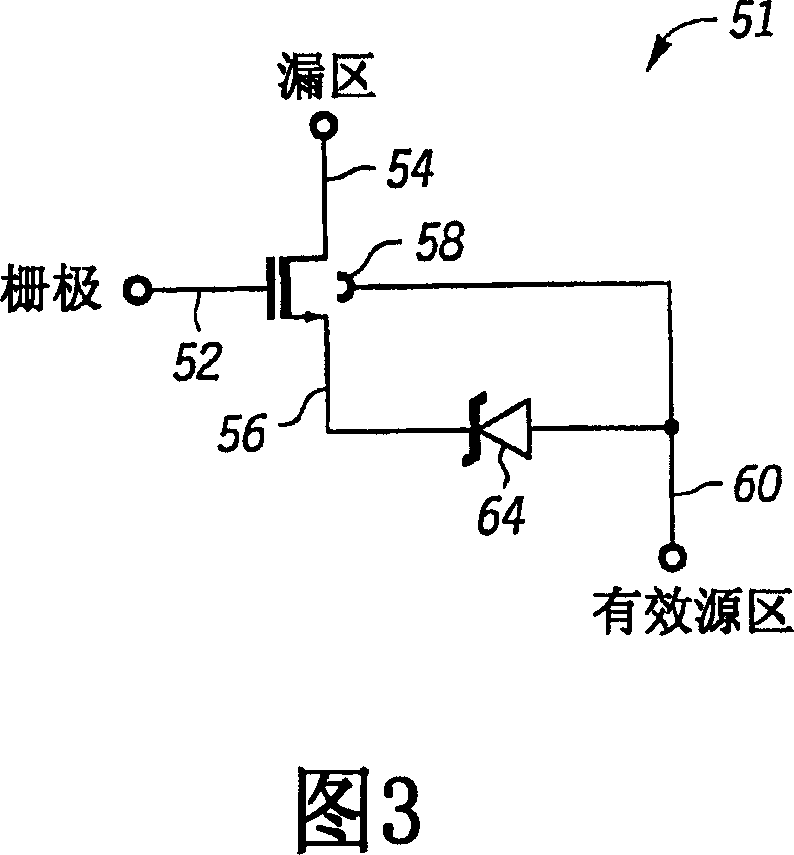
High current MOS device with avalanche protection and method of operation
Particularly in high current applications, impact ionization induced electron-hole pairs are generated in the drain (74) of an MOS transistor (51) that can cause a parasitic bipolar transistor (38) to become destructively conductive. The holes pass through the body region (76) of the MOS transistor (51), which has intrinsic resistance, to the source (80), which is typically held at a relatively low voltage, such as ground. The hole current causes a voltage to develop in the body region (76), which acts as the base (42). This increased base voltage is what can cause the parasitic bipolar transistor (38) to become conductive. The likelihood of this is greatly reduced by developing a voltage between the source (80), which acts as the emitter (44), and the body region (76) by passing the channel current through an impedance (62) between the source (80) and the body region (76). This causes the emitter voltage to increase as the base voltage is increased and thereby prevent the parasitic bipolar transistor (38) from becoming conductive.
Owner:FREESCALE SEMICON INC
Fibre-optical device and method with intensified resitance to environment condition
A method for producing fiber optic devices having improved intrinsic resistance to external environmental conditions and a fiber optic device made my the method are disclosed. The fabrication method produces an optic device that is treated with deuterium. The method includes a step for treating and / or making optical devices in the presence of a flame produced by the combustion of deuterium gas or a mixture including deuterium.
Owner:GOULD FIBER OPTICS
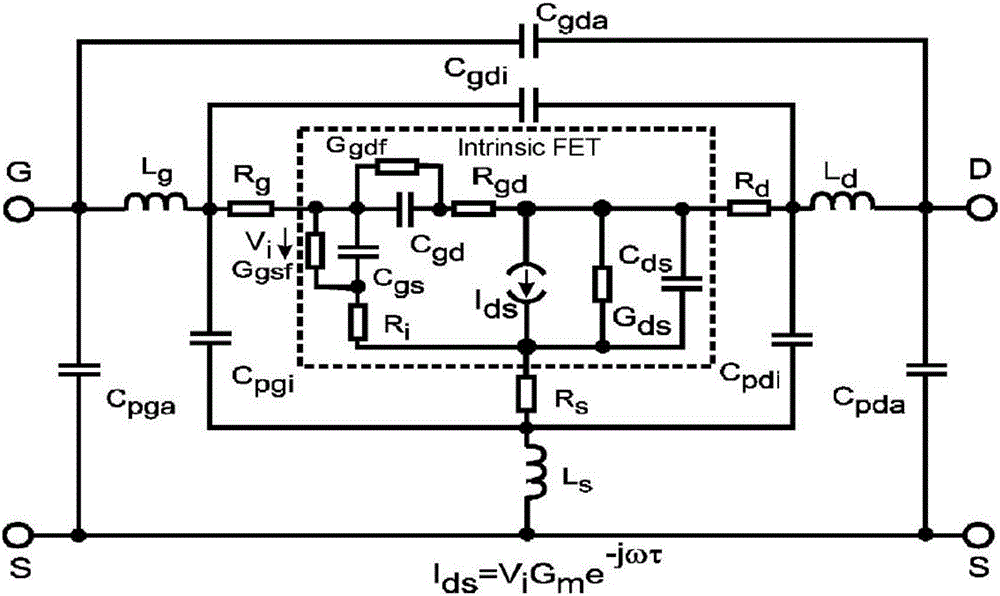
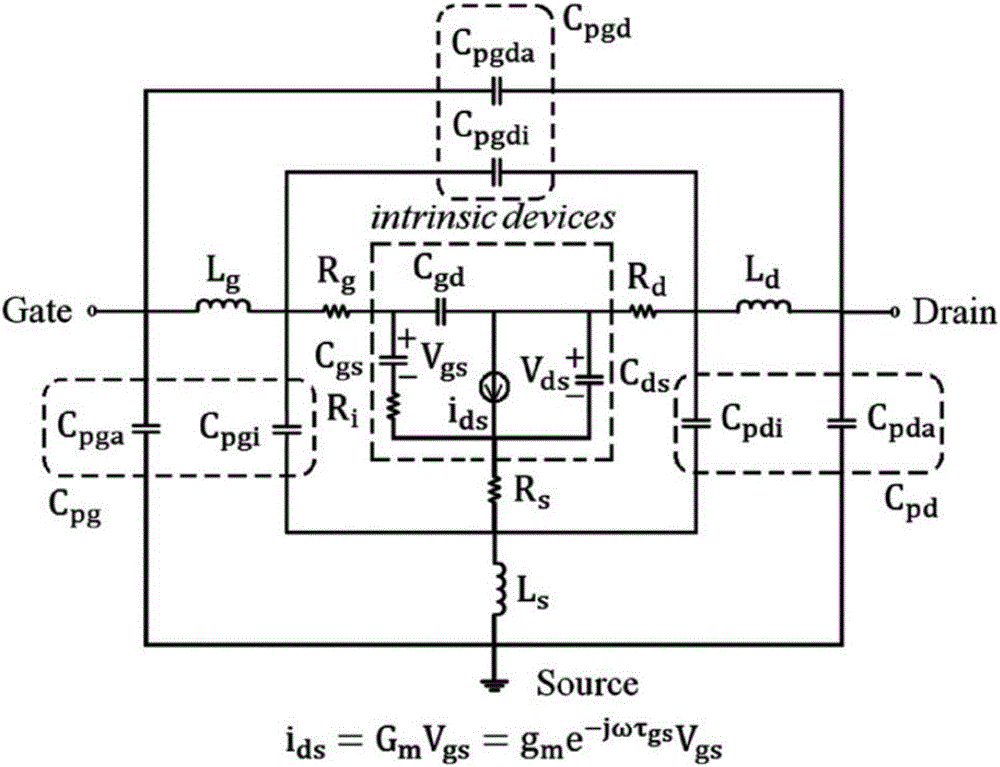
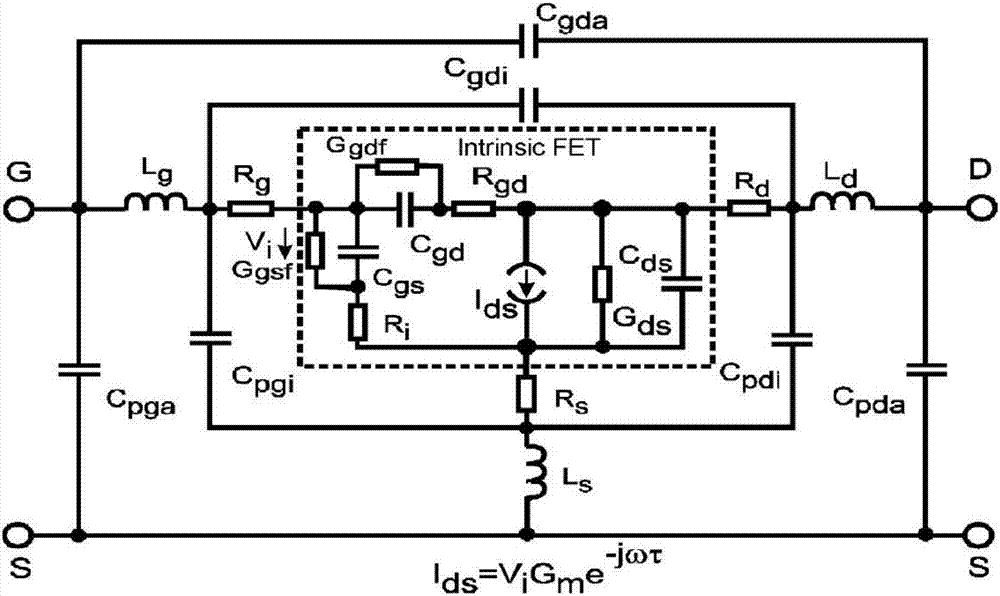
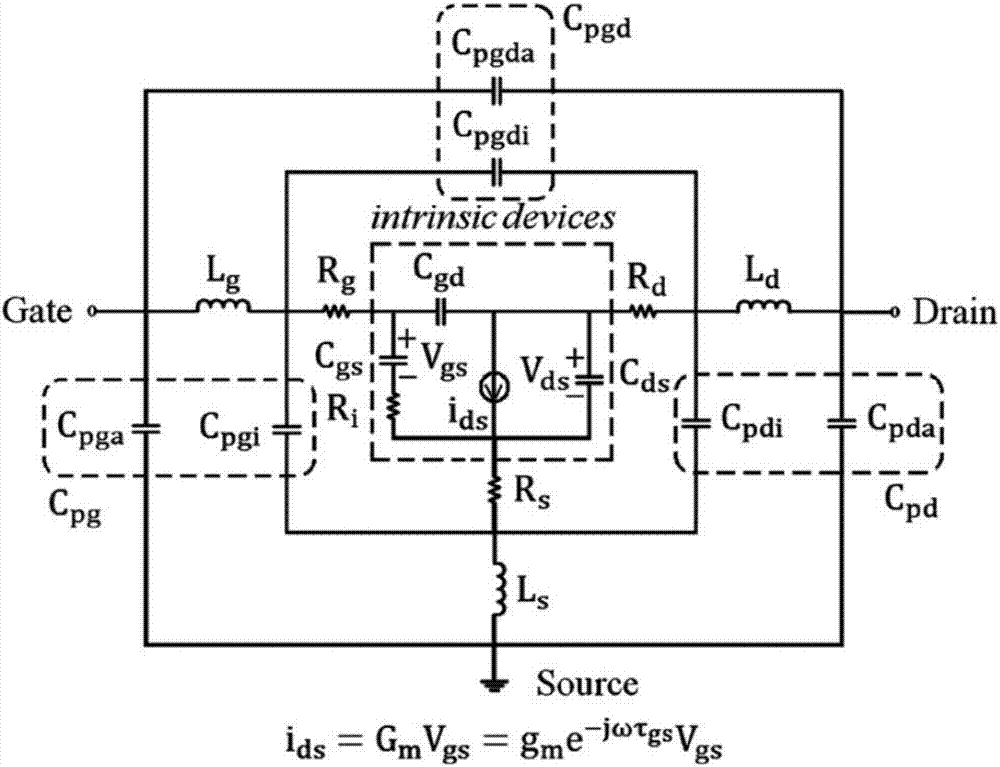
Ultra-wideband gallium nitride device small-signal model and parameter extracting method thereof
InactiveCN106354951AWide application frequency bandAccurate extractionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsUltra-widebandGrating
The invention discloses an ultra-wideband gallium nitride device small-signal model and a parameter extracting method thereof. Three interconnected capacitor and cascaded inductor network structure forms are adopted for the grating end, the source end and the drain end of the small-signal model respectively, and the small-signal model comprises 18 parasitic parameters and 10 intrinsic parameters; the parasitic parameters comprise outer layer parasitic capacitance Cpgi1, Cpdi1, Cgdi1 and others, parasitic inductance Lgi1, Ldi1, Lsi1 and others and parasitic resistance Rg, Rd and Rs; the intrinsic parameters comprise intrinsic capacitance Cgd, Cgs and Cds and intrinsic resistance Rgs, Rgd and Rds, wherein an intrinsic current source Ids is equal to Gm plus ta as parameters in ViGme-j omega ta. The model can accurately describe the characteristics of a high-frequency device, has wider application frequency band and can adapt to a W frequency band as the highest; by the utilization of the parameter extracting method, the model parameters can have good stability within the frequency range of 0.2-110 GHz.
Owner:徐跃杭 +1
Fiber optic device with enhanced resistance to environmental conditions and method
InactiveUS6865322B2No high excess lossGlass making apparatusCoupling light guidesFiberElectrical resistance and conductance
A method for producing fiber optic devices having improved intrinsic resistance to external environmental conditions and a fiber optic device made my the method are disclosed. The fabrication method produces an optic device that is treated with deuterium. The method includes a step for treating and / or making optical devices in the presence of a flame produced by the combustion of deuterium gas or a mixture including deuterium.
Owner:GOI ACQUISITION
Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Strains Suitable For The Production Of Baker's Yeasts Which Are Osmotolerant And Which Exhibit Intrinsic Resistance To Weak Organic Acids, Methods For The Preparation Thereof And Uses
The present invention relates to Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains suitable for the production of baker's yeasts which are osmotolerant and which exhibit intrinsic resistance to weak organic acids.The strains of the present invention are obtained by means of a process of hybridization or of mutation of the industrial S. cerevisiae strain deposited on Jul. 8, 2010 with the CNCM [French National Collection of Microorganism Cultures] under number 1-4341, or from an industrial strain related thereto via the Ty profile thereof and / or via quantitative trait locus mapping (QTL mapping).
Owner:LESAFFRE & CIE
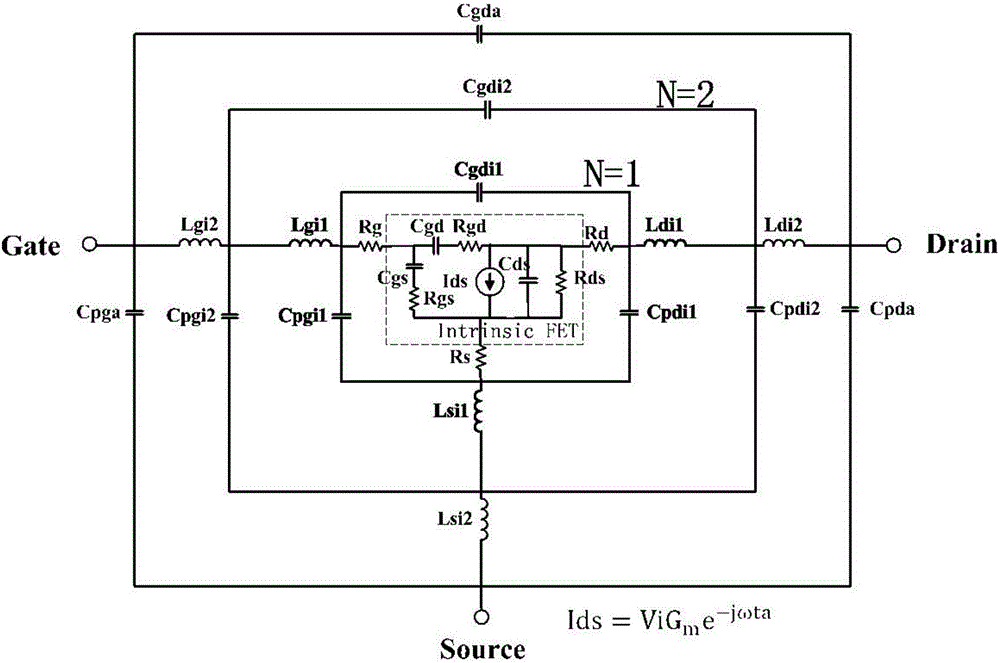
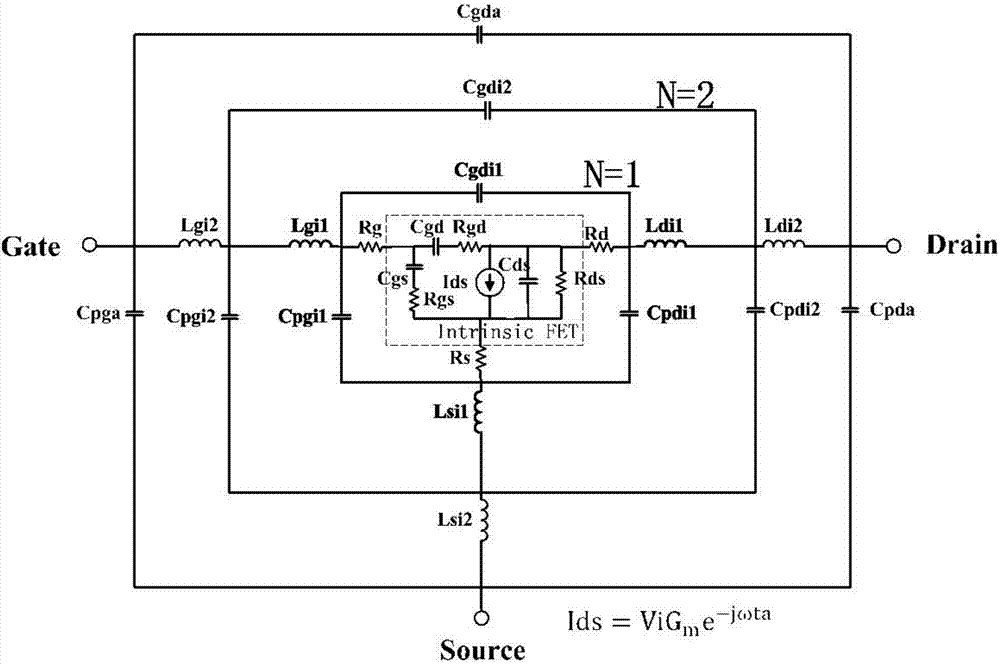
Small-signal model of super broadband gallium nitride device and parameter extraction method thereof
InactiveCN106886650AWide application frequency bandAccurate extractionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsParasitic capacitorCapacitance
The invention discloses a small signal model of the super broadband gallium nitride device and a parameter extraction method thereof. The small signal model in a bar, a source, and a leak end uses three interconnected capacitors and a cascadeinductance network structure formrespectively, and comprises 18 parasitic parameters and 10 intrinsic parameters; the parasitic parameterscomprise outer parasitic capacitors Cpgi1, Cpdi1, and Cgdi1 and the like, the parasitic inductancesLgi1, Ldi1, and Lsi1 and the like, andthe parasitic resistances Rg, Rd, and Rs; the intrinsic parameterscomprisethe intrinsic capacitors Cgd, Cgs and the Cds, the intrinsic resistances Rgs, Rgd, Rds, and the parameters Gm and ta in the intrinsic current source Ids=ViGme-jOmegata. The model can be used to accurately describe the characteristics of high-frequency devices, can makethe model to have a wider application band, the maximum can be applied to the w-frequency band; the parameter extraction method can achieve excellent stability in a 0.2-110GHz frequency range of the model parameters.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Sn-Bi base brazing filler metal used for producing crystal silicon heterojunction solar cell electrode
InactiveCN106505110AReduce intrinsic resistanceImprove power generation efficiencyPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesSlurryAlloy
The invention discloses a Sn-Bi base brazing filler metal used for producing a crystal silicon heterojunction solar cell electrode belonging to the solar cell material technology field. The components of the Sn-Bi base brazing filler metal are Sn and Bi. The weight percentage content of the Bi is in a range from 5% to 70%, and the residual is Sn. By adopting the above mentioned alloy to replace silver slurry to produce the crystal silicon heterojunction solar cell electrode, great consumption of silver resources is prevented, and costs are greatly reduced, and then the intrinsic resistance of the solar cell is reduced, and therefore great benefits are provided for the further improvement of the power generating efficiency of the battery.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Thermostable nuclease
InactiveUS20160053242A1Easy to produceEasy to prepareAnimal cellsOrganic active ingredientsEscherichia coliEnterobacter
A heat-stable nuclease found in Y. enterocolitica subsp. Palearctica, named Nucyep, is active in broad spectrum conditions. The gene for Nucyep was sequenced in a strain Y. enterocolitica subsp. palearctica, cloned, and expressed in E. coli, and then purified and characterized. The molecular weight of this enzyme is about 30 to 32 kDa. The translation product, Nucyep1, is biologically active. The purified Nucyep1 exhibits non-specific nuclease activity, being able to degrade various nucleic acids, including RNA, single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) and linear or circular double-stranded DNA (dsDNA). This enzyme is active in a wide range of temperatures, from 0 to 100° C. The enzyme is active in a wide range of pH values from 3.6 to 9.9, and keeps greater than 75% of the activity at pH 7.24. This enterobacterial nuclease has unique levels of intrinsic resistance to heat, and is active under a large spectrum of conditions.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
electric vacuum cleaner
ActiveCN103356134BExcellent static electricity removalSuction hosesSuction handlesElectrical resistance and conductanceConductive materials
The invention provides an electric dust collector that has excellent antistatic performance. The electric dust collector has a suction member (7), an extension pipe (5) which is connected with the suction member (7) and is made of conductive material, an operation pipe (4) which is connected with the extension pipe (5) and a soft pipe portion (3), and further has a power supply mechanism which supplies power to the suction member (7) from a vacuum cleaner main body (2). The extension pipe (5) has an insulating resin part and a conductive part of the power supply mechanism, which is insulated from the extension pipe (5) and is configured on the insulating resin part. The insulating resin part is covered within a range less than a whole circle of an outer periphery of an end portion in the length direction of the extension pipe (5). The insulating resin part which forms the part of the extension pipe (5) is made of a material containing a charged prevention agent, and compared with a part made of a general resin not containing the charged prevention agent, the insulating resin part is smaller has a smaller surface intrinsic resistance value.
Owner:HITACHI APPLIANCES INC
Lubricating oil composition for refrigerator
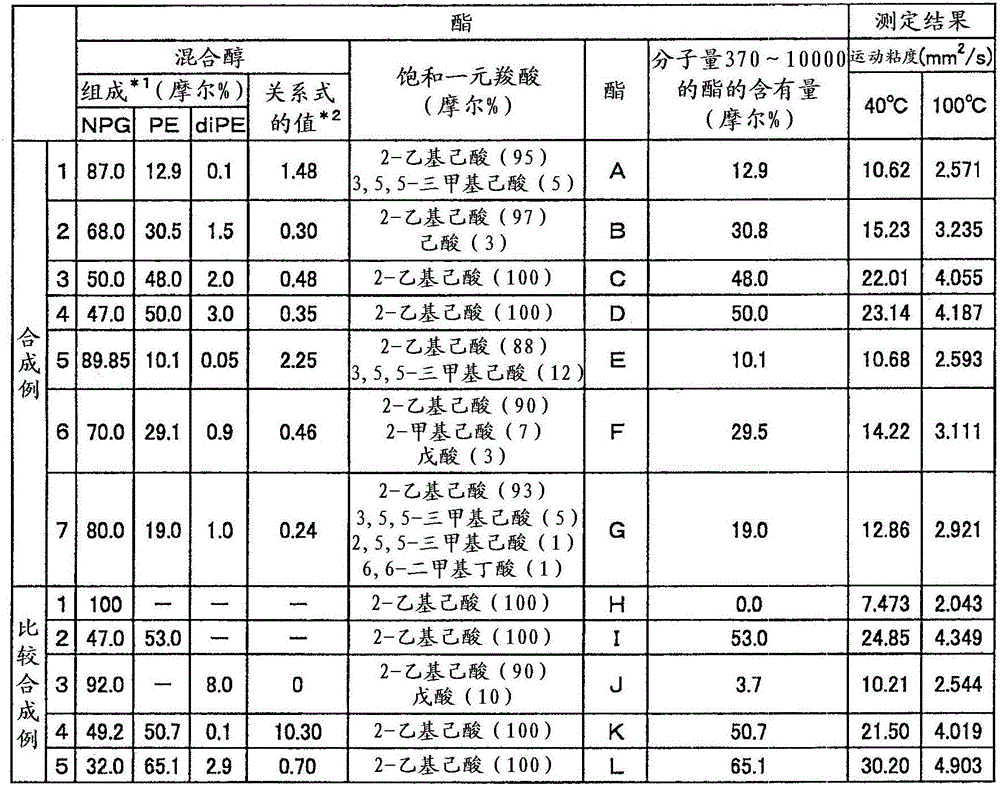
ActiveCN103013619BLow viscosityHigh volume intrinsic resistanceHeat-exchange elementsBase-materialsChemical compositionAlcohol
The invention provides a refrigeration lubricant composition which with low viscosity, high volume intrinsic resistance and good low-temperature stability. The lubricating oil composition for refrigerators is mainly composed of a mixed ester obtained from a mixed alcohol and a 5-10C saturated monocarboxylic acid, the mixed alcohol comprising 1-90 mol% of neopentyl glycol, 10-80 mol% of pentaerythritol and 0.01-20 mol% of dipentaerythritol and satisfying the relational equation: 0.2<=[(mol% of pentaerythritol) / (mol% of neopentyl glycol * mol% of dipentaerythritol)]<=7.0, and has a kinematic viscosity at 40[deg.]C of 6-28 mm<2> / s.
Owner:NOF CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com