Semiconductor device, its manufacturing method, and electronic device
A technology of electronic equipment and semiconductors, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, circuits, transistors, etc., can solve problems that cannot be used in practice
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
[0081] Regarding the first embodiment of the present invention, based on FIGS. Figure 5 It will be explained as follows.
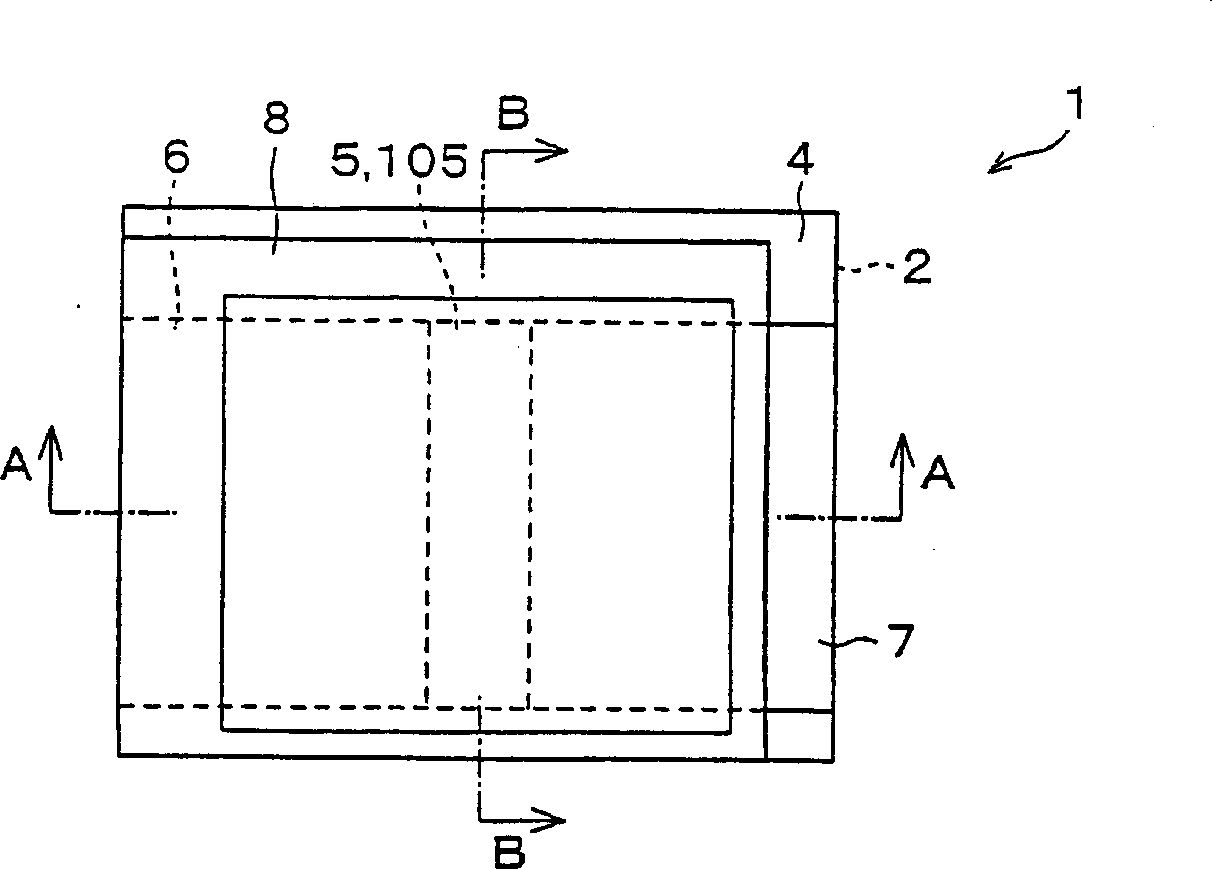
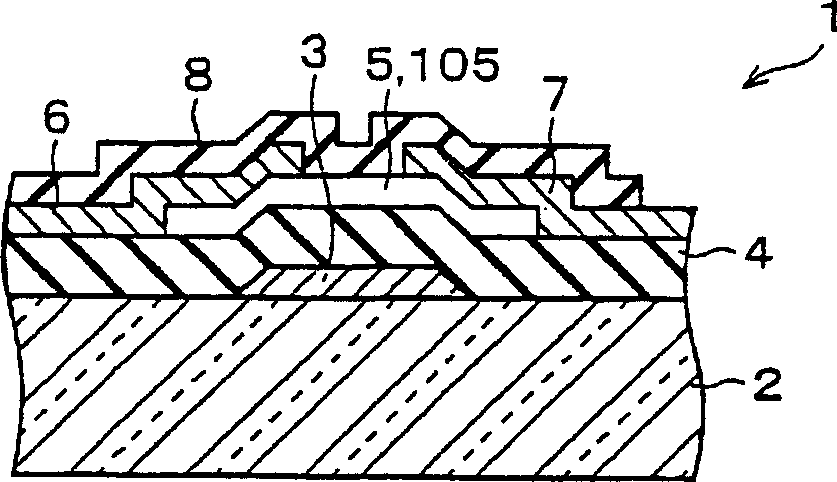
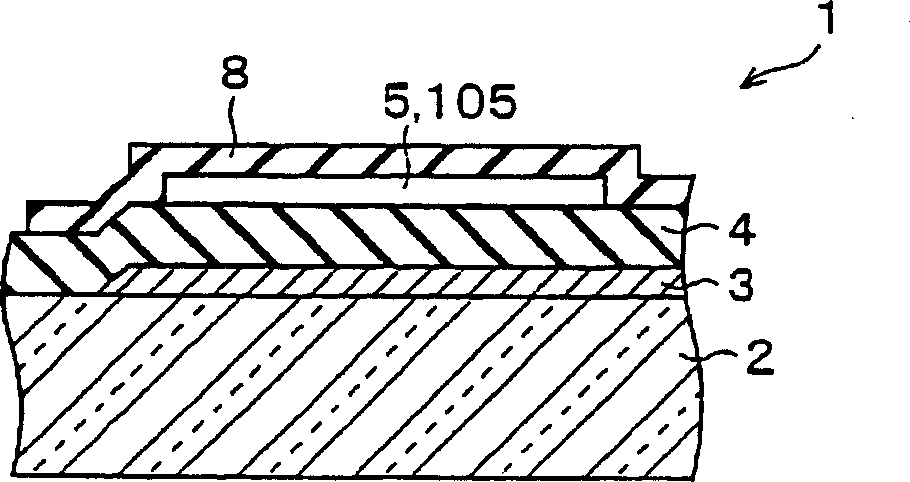
[0082] FIG. 1( a ) shows a plan view of a thin film transistor 1 of this embodiment. Moreover, FIG. 1( b ) shows a sectional view taken along the line A-A of FIG. 1( a ), and FIG. 1( c ) shows a sectional view taken along the line B-B of FIG. 1( a ). In addition, in FIG. 1( a ), for the sake of simplification of the drawing, the description of the unevenness in the central part of the surface of the protective layer 8 shown in FIG. 1( b ) and FIG. 1( c ) is omitted.
[0083] Such as Figure 1(a) ~ Figure 1(c) As shown, in a thin film transistor 1 as a semiconductor device, a gate electrode 3 is formed on an insulating substrate 2, a semiconductor layer 5 is laminated on the gate electrode 3 via a gate insulating layer 4, and an electrode part is formed on the semiconductor layer 5. The source electrode 6 and the drain electrode 7 are formed, and the pr...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0104] The second embodiment of the present invention will be described as follows based on FIGS. 6 to 8 .
[0105] FIG. 6( a ) shows a plan view of the thin film transistor 11 of this embodiment. And Fig. 6 (b) shows the sectional view of the C-C line arrow direction of Fig. 6 (a), and Fig. 6 (c) shows the sectional view of the D-D line arrow direction of Fig. 6 (a). In addition, in FIG. 6( a ), for the sake of simplification of the drawing, the description of the irregularities in the central portion of the surface of the protective layer 19 shown in FIGS. 6( b ) and 6( c ) is omitted.
[0106] Such as Figure 6(a) ~ Figure 6(c) As shown, in a thin film transistor 11 as a semiconductor device, a source electrode 14 and a drain electrode 15 are formed on an insulating base layer 13 formed on an insulating substrate 12 except for intervals, and a semiconductor layer 16 and a gate insulating layer 17 are sequentially stacked on them. and the gate electrode 18 , and further fo...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0130] About 3rd Embodiment of this invention, if it demonstrates based on FIGS. 9-11, it will be as follows.
[0131] FIG. 9( a ) shows a plan view of the thin film transistor 21 of this embodiment. Moreover, FIG. 9( b ) shows a cross-sectional view in the arrow direction of E-E line in FIG. 9( a ), and FIG. 9( c ) shows a cross-sectional view in the arrow direction of line F-F in FIG. 9( a ).
[0132] Figure 9(a) ~ Figure 9(c) As shown, in a thin film transistor 21 as a semiconductor device, a source electrode 24 and a drain electrode 25 are formed on an insulating base layer 23 formed on an insulating substrate 22 , and a semiconductor layer 26 and a first gate insulating layer 27 are formed thereon. The semiconductor layer 26 and the first gate insulating layer 27 are covered with the second gate insulating layer 28 , and the second gate insulating layer 28 also serves as a protective layer for the semiconductor layer 26 . A gate electrode 29 is formed on the second gat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com