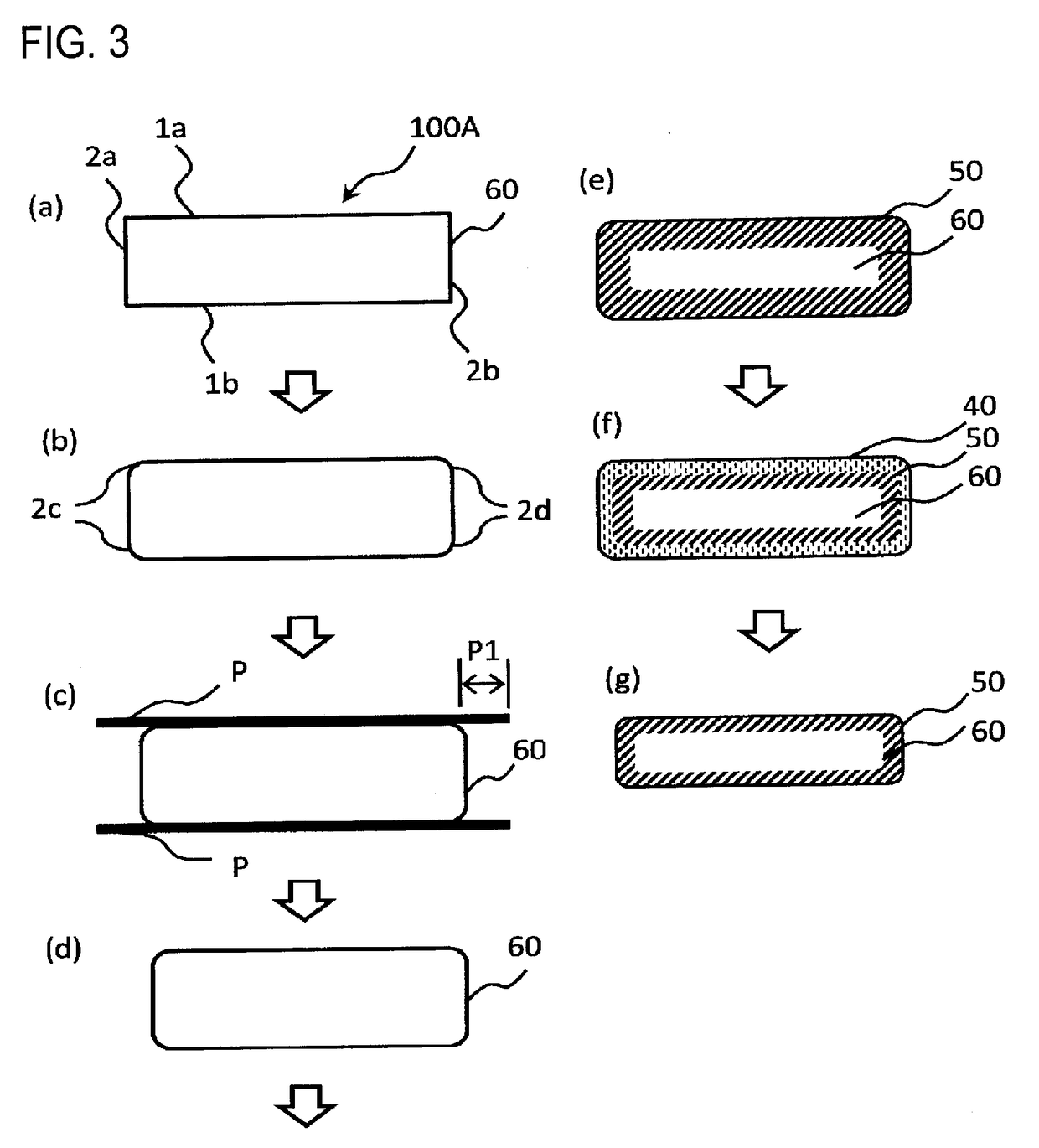
Patents
Literature
82 results about "Relational equation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
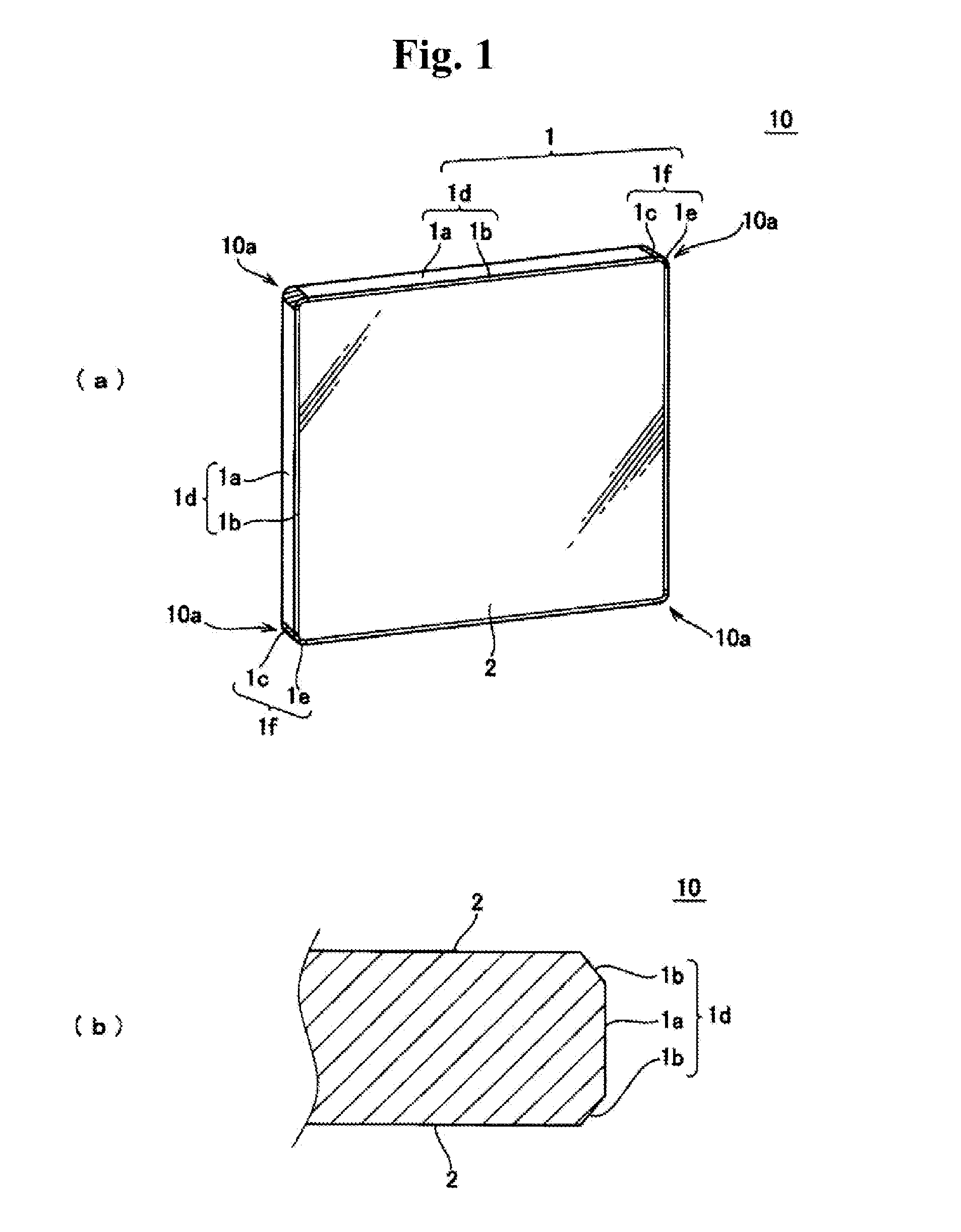
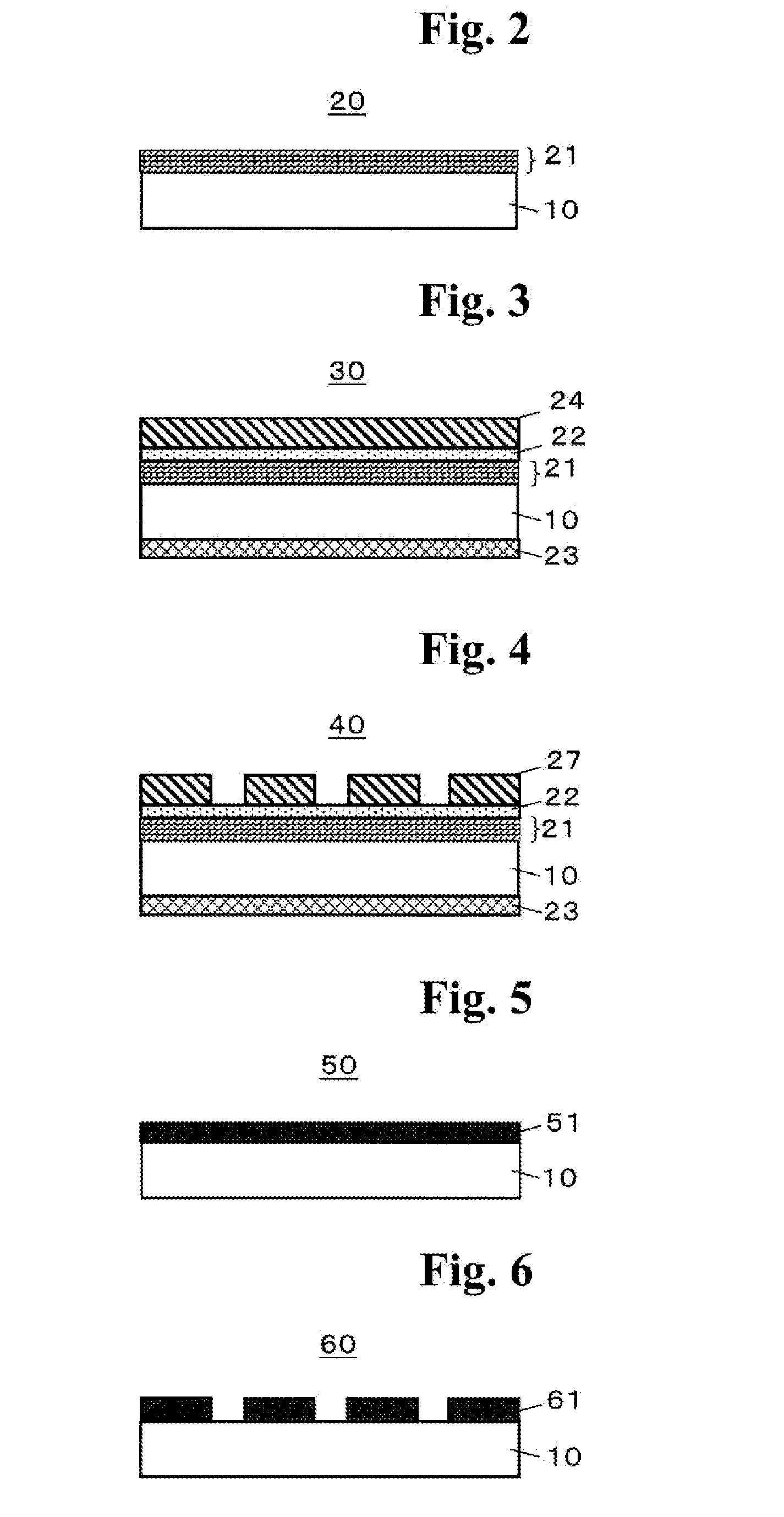
Mask blank substrate, substrate with multilayer reflection film, transmissive mask blank, reflective mask blank, transmissive mask, reflective mask, and semiconductor device fabrication method
ActiveUS20140329174A1Easy to detectSuppressing false defectPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLithographic artistRelational equation
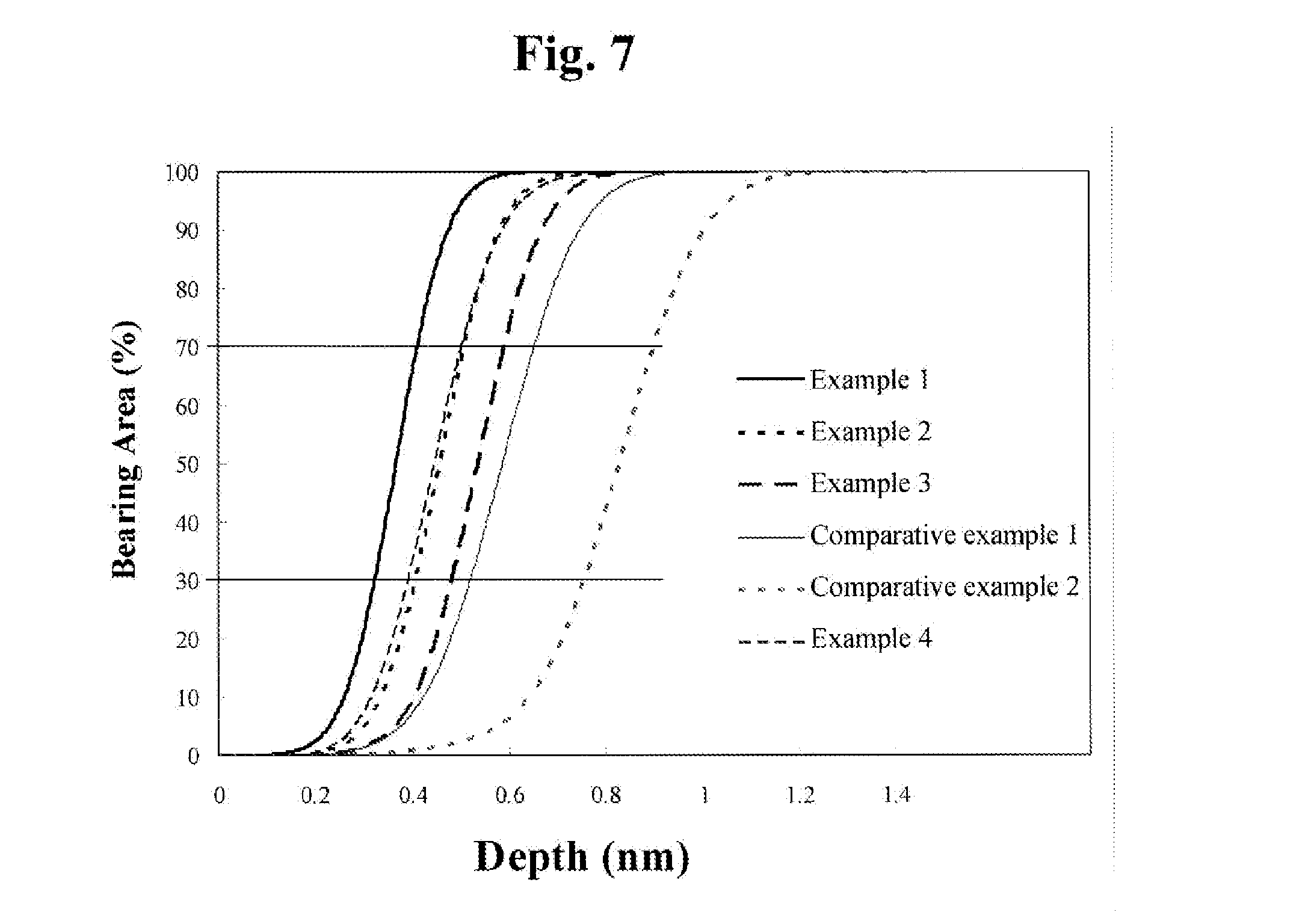
Disclosed is a mask blank substrate for use in lithography, wherein a main surface of the substrate satisfies a relational equation of (BA70−BA30) / (BD70−BD30)≧350 (% / nm), and has a maximum height (Rmax)≦1.2 nm in a relation between a bearing area (%) and a bearing depth (nm) obtained by measuring, with an atomic force microscope, an area of 1 μm×1 μm in the main surface on the side of the substrate where a transfer pattern is formed, wherein BA30 is defined as a bearing area of 30%, BA70 is defined as a bearing area of 70%, and BD70 and BD30 are defined to respectively represent bearing depths for the bearing area of 30% and the bearing area of 70%.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Bi-aspherical type progressive-power lens
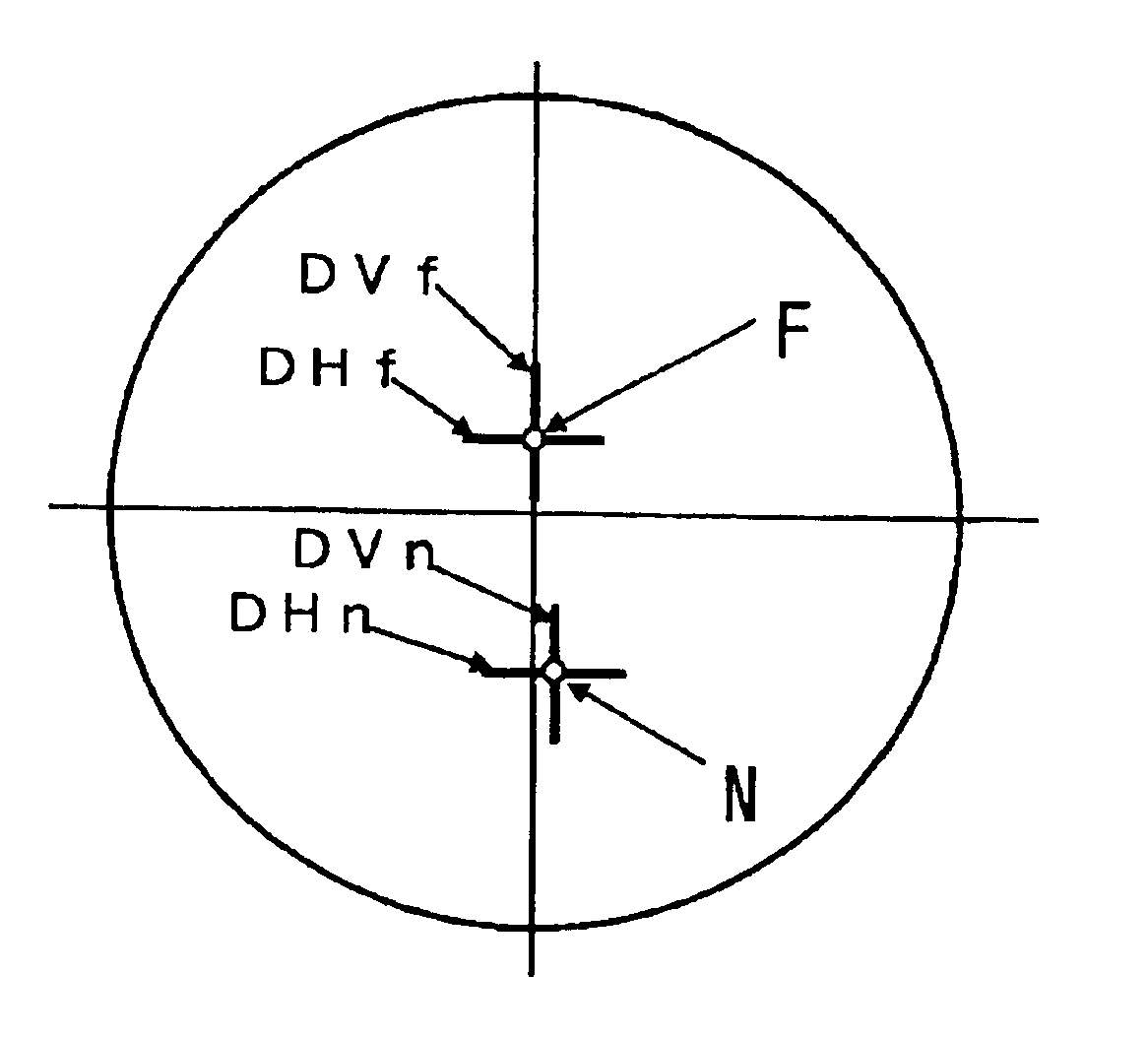
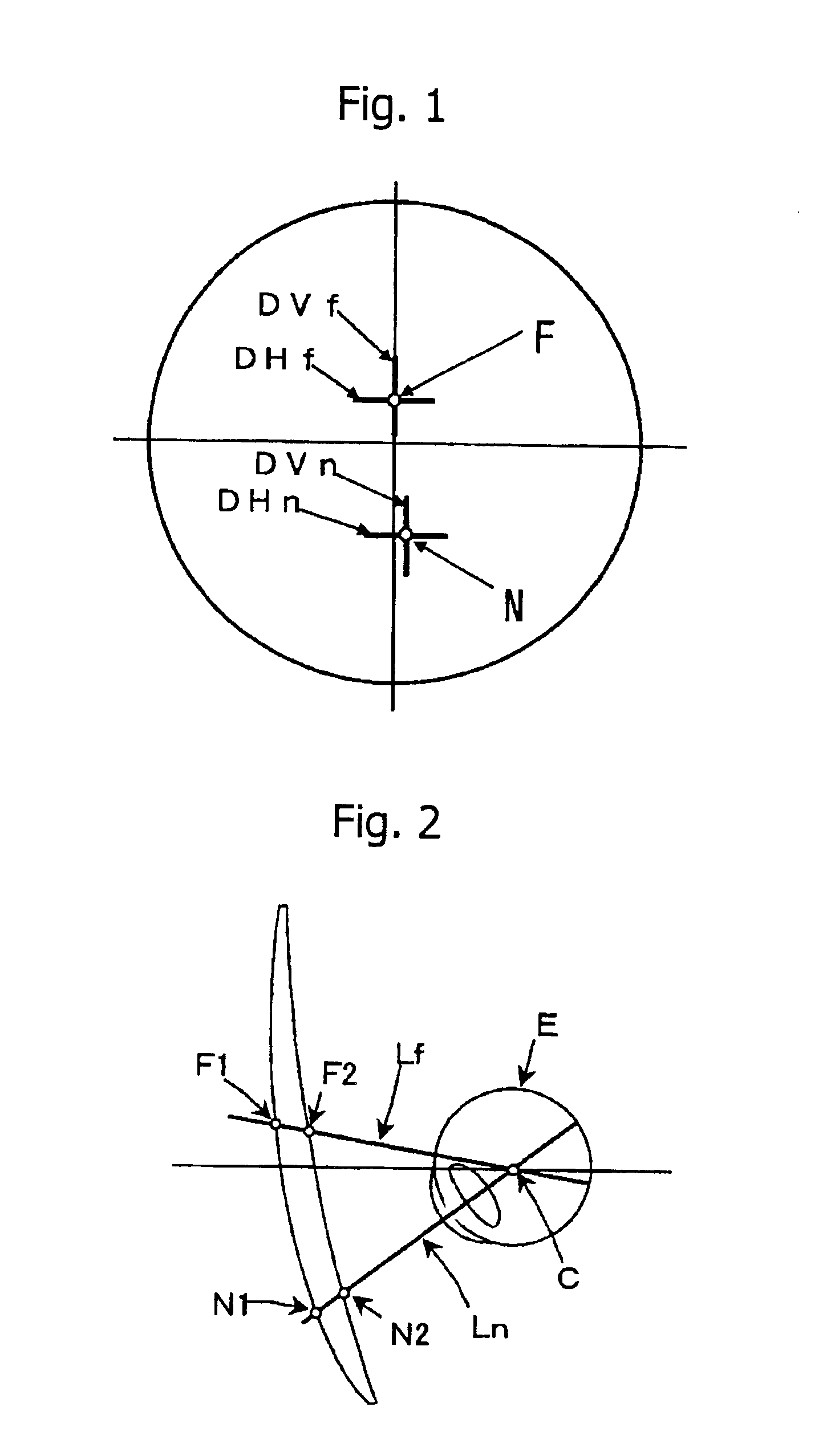
InactiveUS6935744B2Increase workforcePromote resultsEye diagnosticsOptical partsVisual field lossRefractive measurements
To provide a bi-aspherical type progressive-power lens which provides an excellent visual acuity correction for prescription values and a wide effective visual field with less distortion in wearing, by reducing a magnification difference of an image between a distance portion and a near portion. The lens is characterized in that when on a first refractive surface being an object side surface, a surface refractive power in a horizontal direction and a surface refractive power in a vertical direction, at a far vision diopter measurement position F1, are DHf and DVf respectively, and on the first refractive surface, a surface refractive power in a horizontal direction and a surface refractive power in a vertical direction, at a near vision diopter measurement position N1, are DHn and DVn respectively, relational equations,DHf+DHn<Dvf+DVn, and DHn<DVnare satisfied, and surface astigmatism components at F1 and N1 of the first refractive surface are cancelled by the second refractive surface being an eyeball side surface so that the first and second refractive surfaces together provide a far vision diopter (Df) and an addition diopter (ADD) based on prescription values.
Owner:HOYA CORP
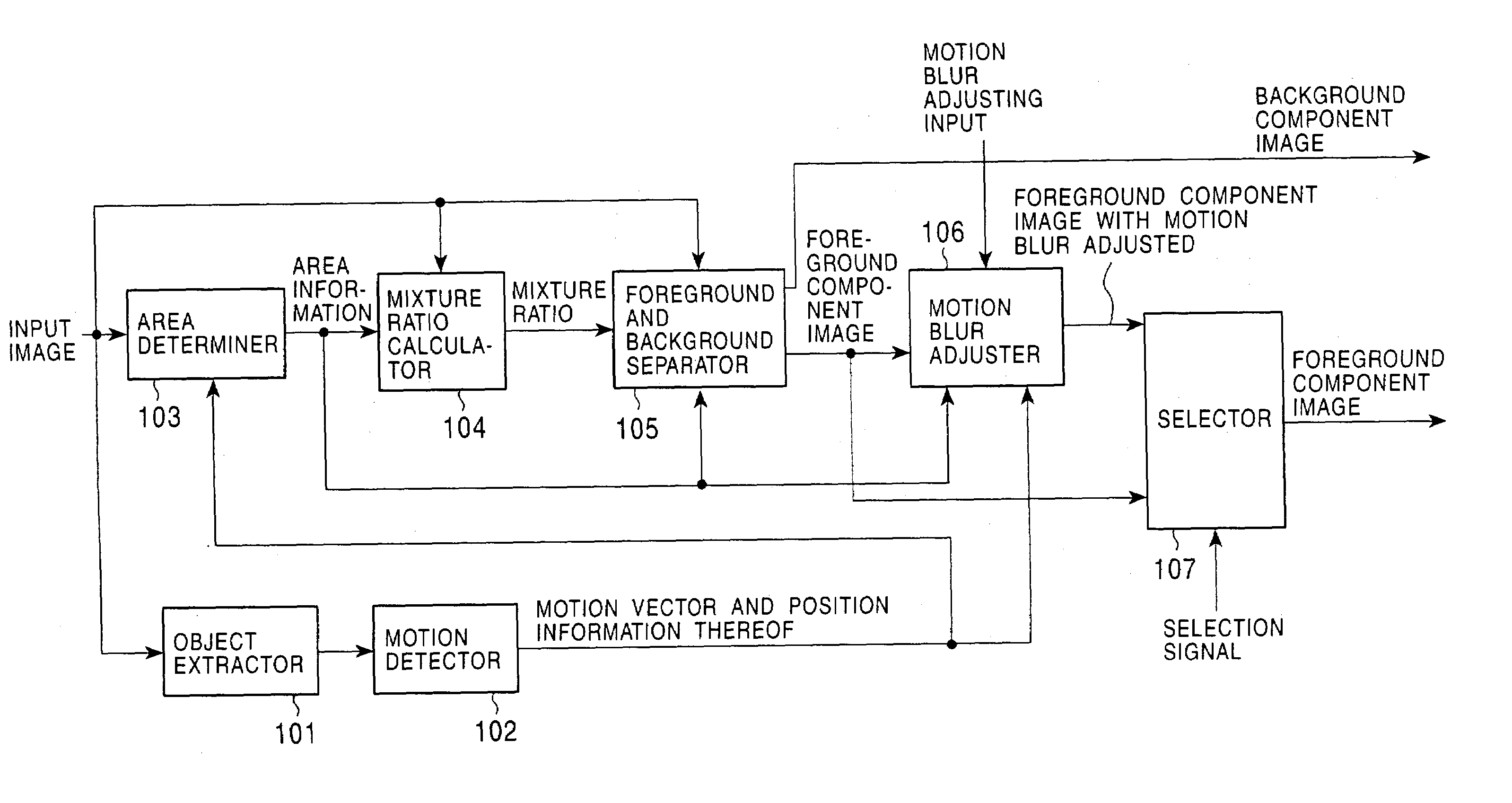
Image processing device
In accordance with the present invention, a mixture ratio indicating the state of mixture of a plurality of objects such as a background image and the image of an object is detected. A pixel value setter 502 extracts background pixel data while also extracting the date of a target pixel and a pixel in the vicinity of the target pixel. The pixel value setter 502 generates a plurality of relational equations indicating data of the target pixel and the pixel in the vicinity of the target pixel and the background pixel data. An arithmetic unit 503 calculates a mixture ratio indicating a mixed state of the plurality of objects in the real world with respect to the target pixel based on the relational equations. The present invention is applicable to an image processing apparatus that accounts for a difference between a signal detected by a sensor and the real world.
Owner:SONY CORP
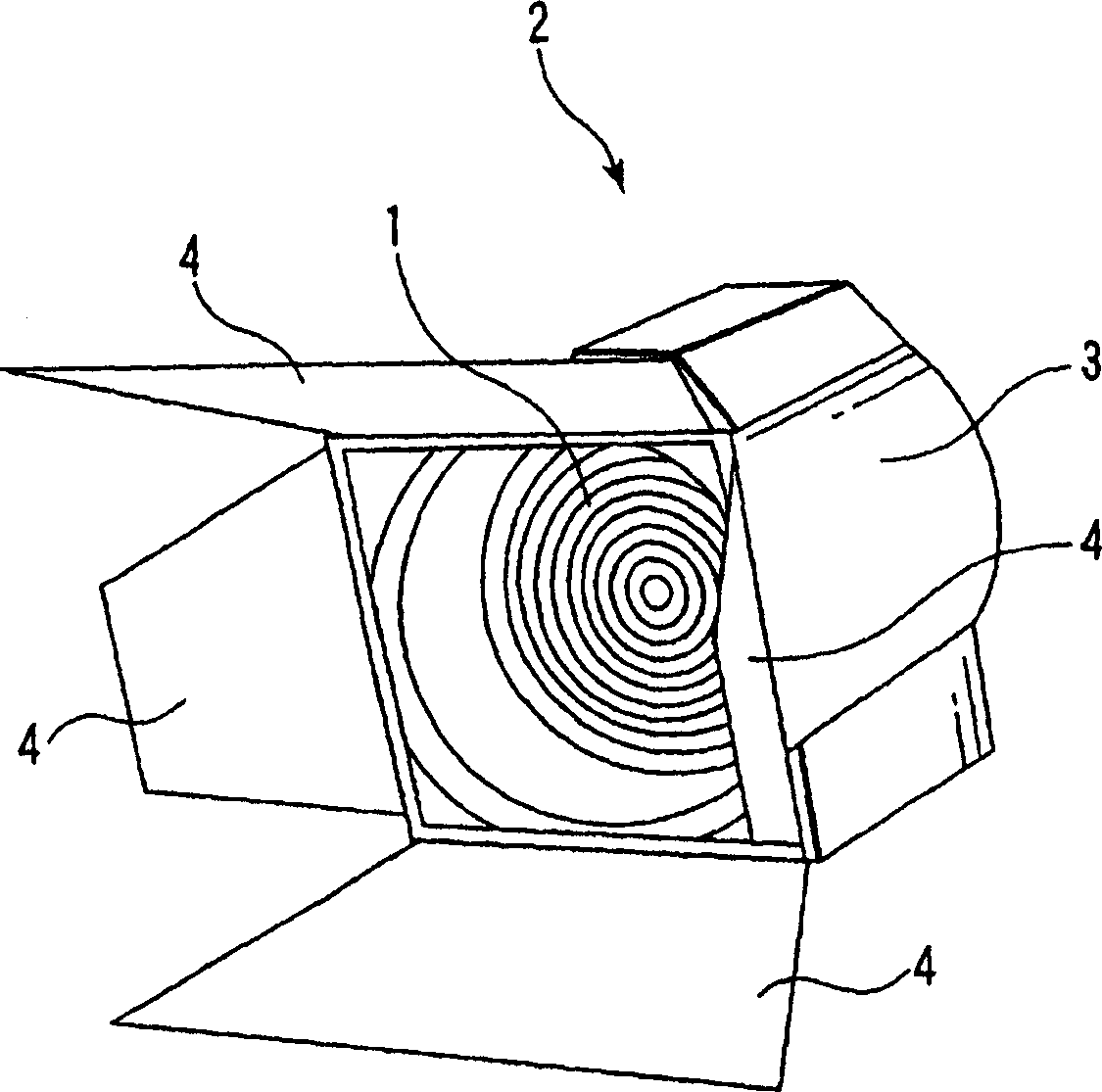
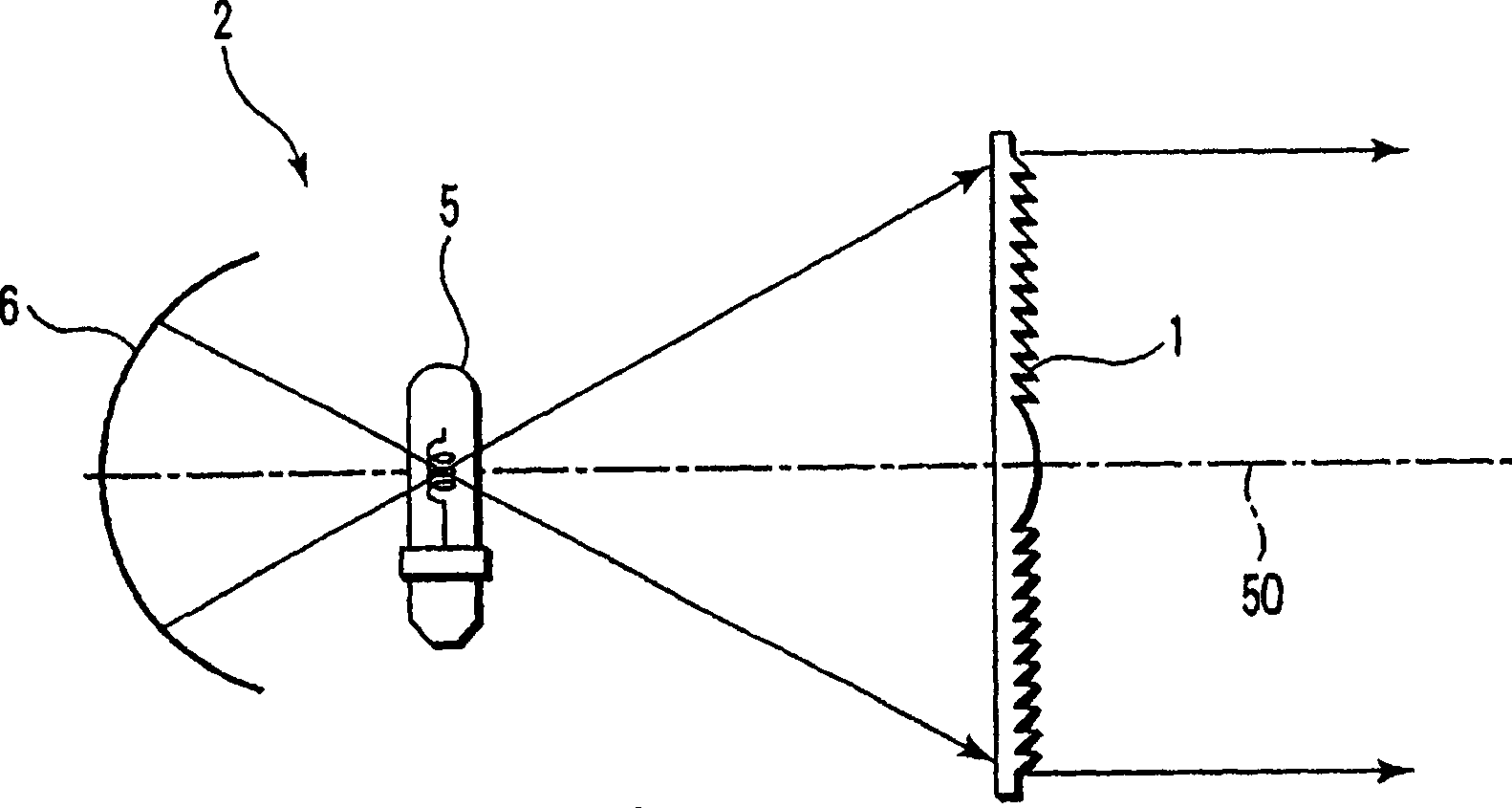
Fresnel lens and lighting apparatus provided with the fresnel lens
InactiveUS20060056185A1Enhance the stage effectReduce uneven brightnessLighting applicationsMechanical apparatusFresnel lensOptical axis
In a Fresnel lens which is made of a lens material whose refraction index is n, and focuses light beam from a light source at a specified radiation view angle φ, and has plural N pieces of circular lens surfaces arranged concentrically around a common optical axis, and plural circular rise surfaces arranged adjacent alternately between these lens surfaces, and two lens surfaces adjacent via at least one of the rise surfaces are concave surfaces, and tangent lines and at the intersecting point with the rise surfaces of the shape of a cross section passing through the optical axis of those lens surfaces intersect at the outside with respect to the optical axis, and when the angle formed between these tangent lines is defined as θ, a relational equation θ≧φ / (2 n N) stands.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
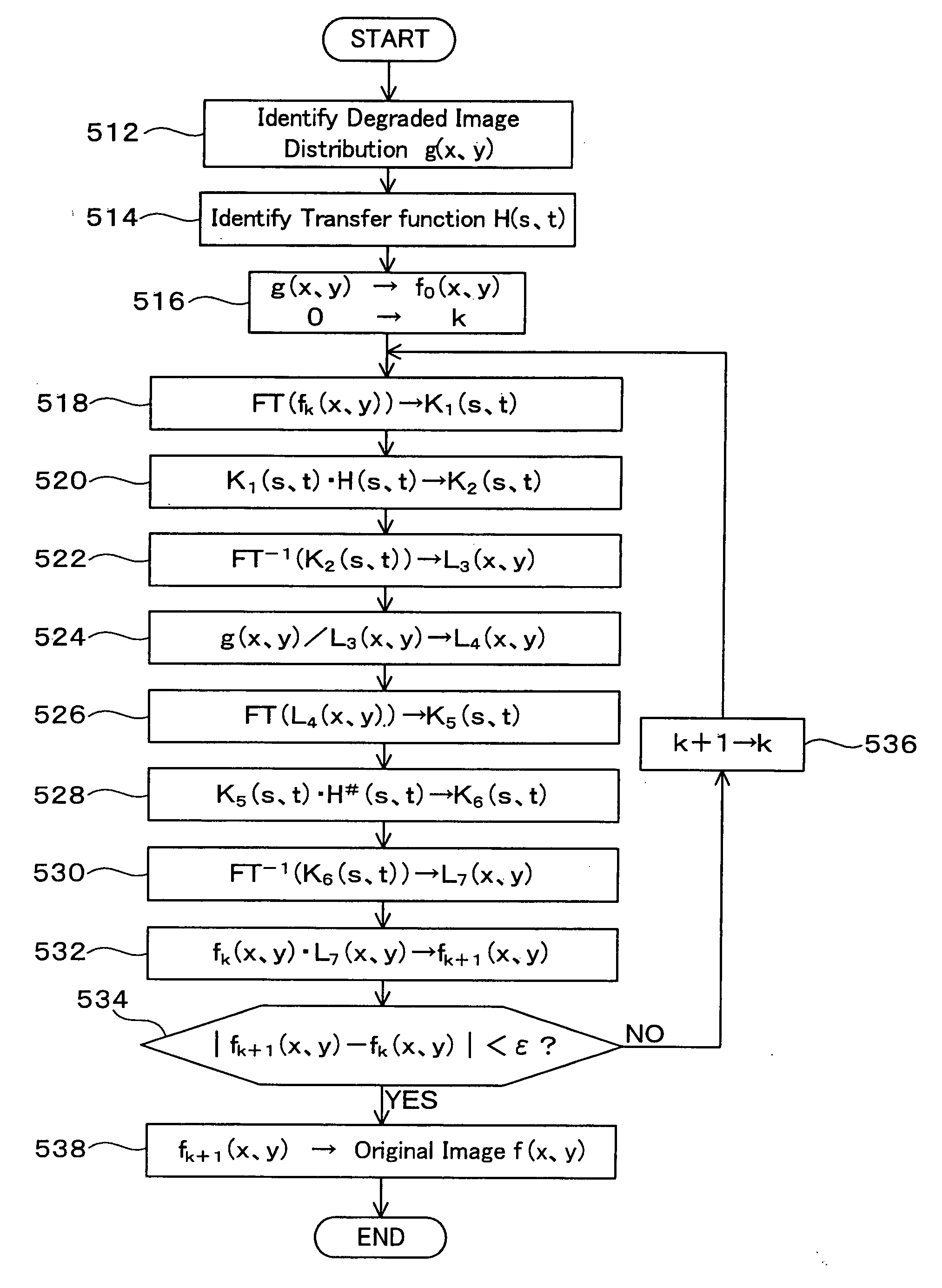
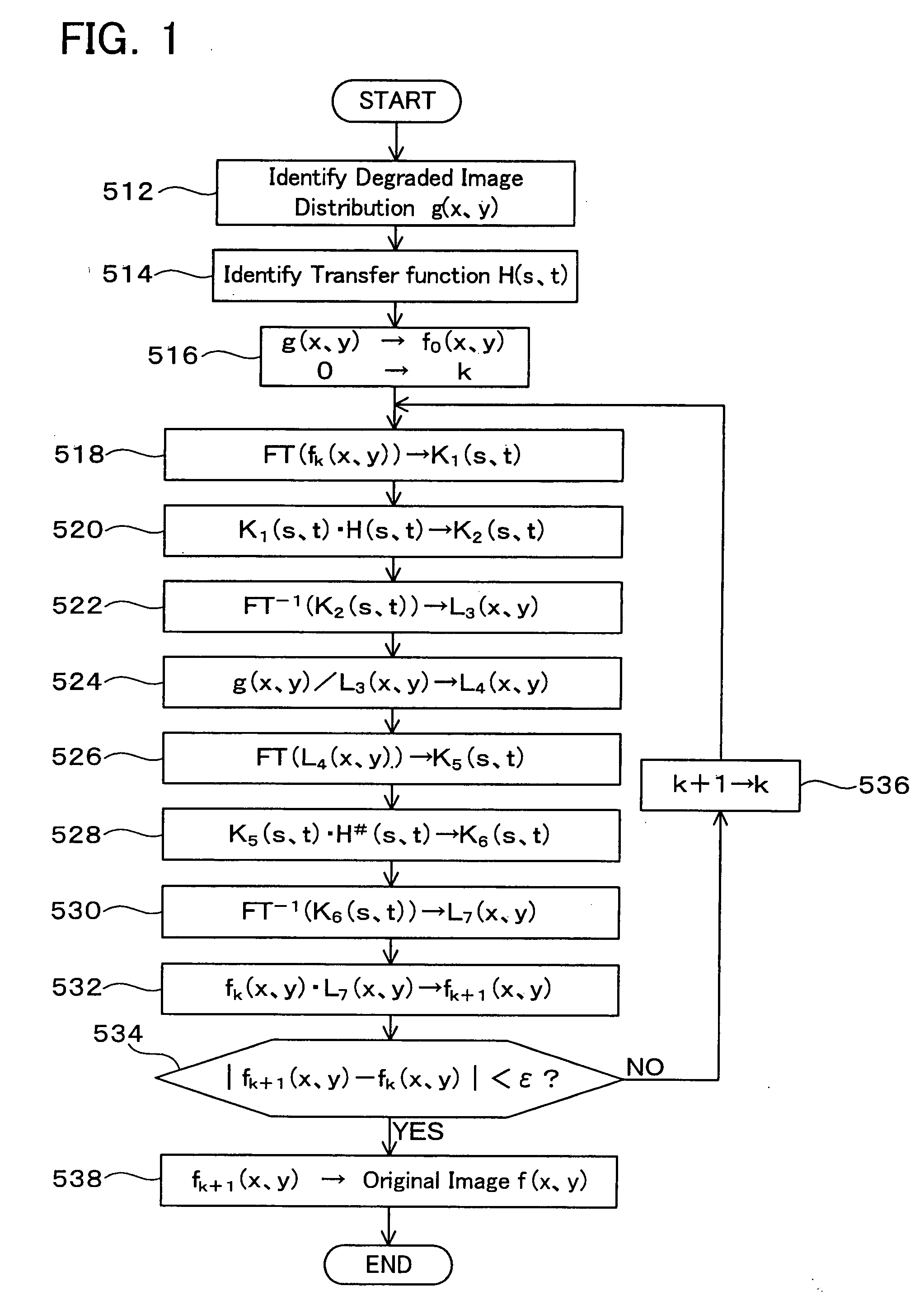
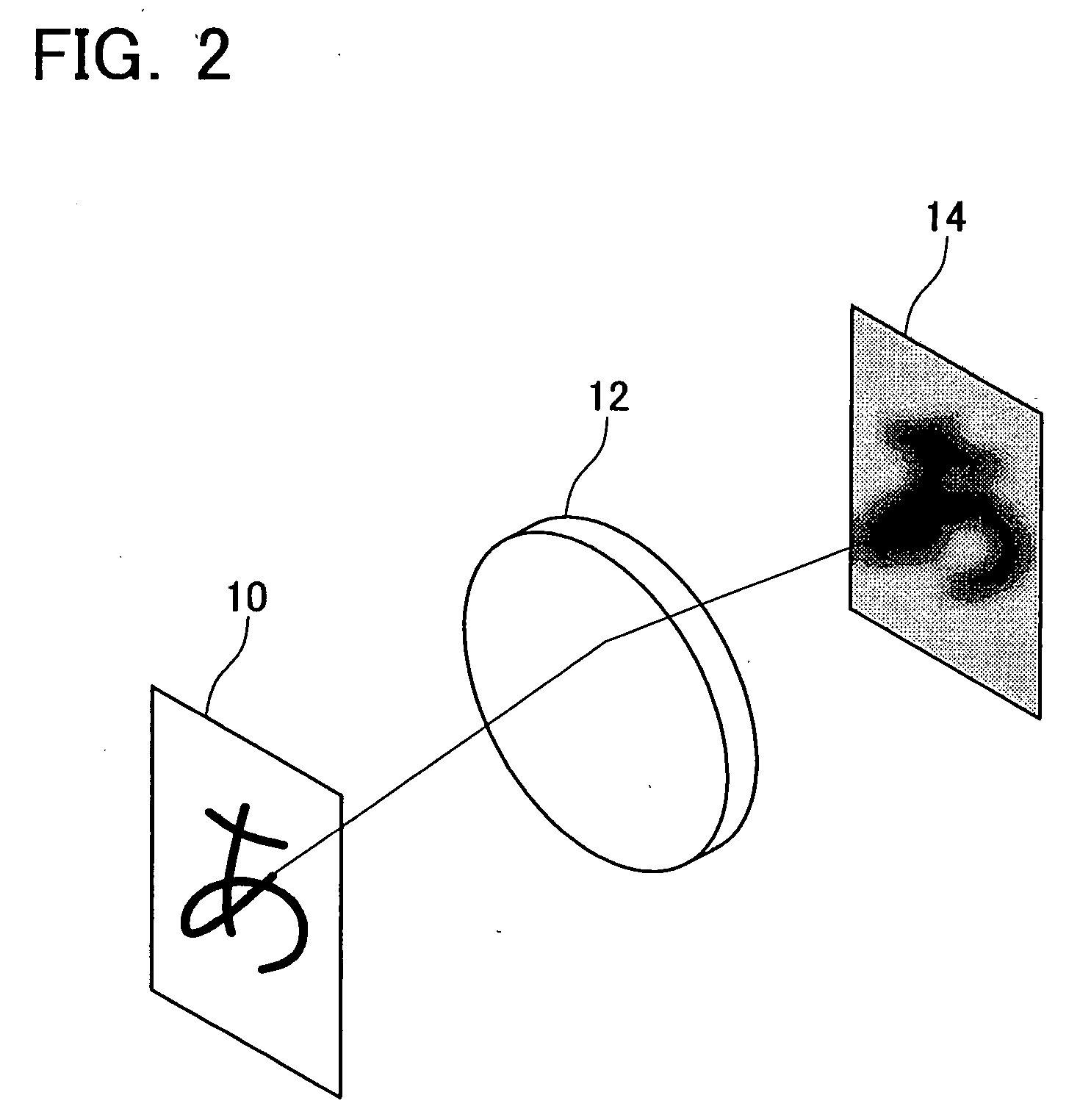
Method and Device for Restoring Degraded Information
The present invention provides a technology which precisely restores a distribution of original information by carrying out an iterative calculation based on a distribution of degraded information and a transfer function including a phase characteristic of a transfer system. A method according to the present invention restores the original information using the degraded information and the transfer function in the frequency space. The method according to the present invention considers a distribution of the degraded information and a distribution of the original information as distributions of probability density functions, and considers the transfer function as a probability density function of a conditional probability. The most probable distribution of the original information according to the distribution of the degraded information is acquired by the iterative calculation by means of relational equations based on the Bayes' theorem relating to the probability density functions.
Owner:LIGHTRON INT +1
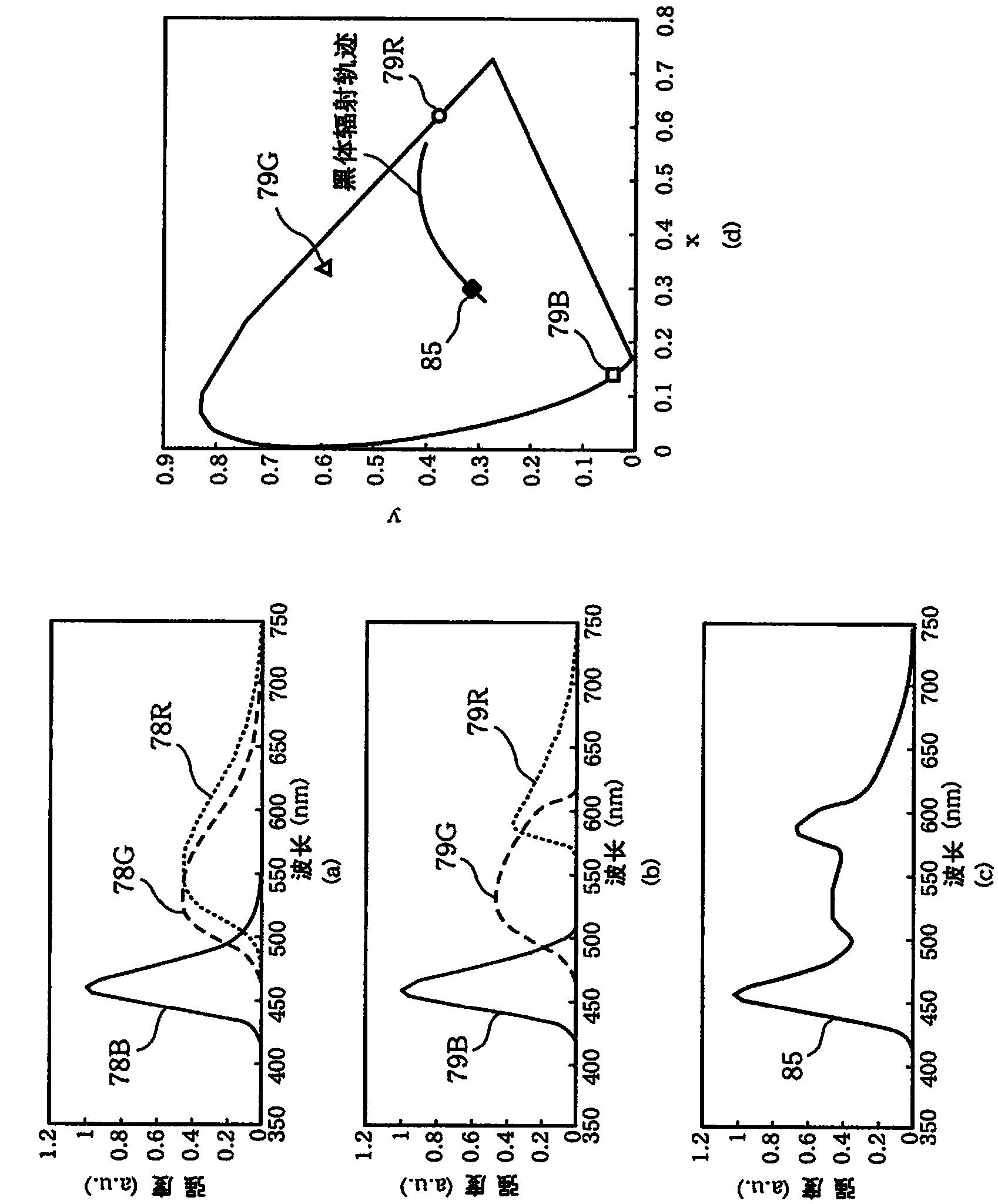
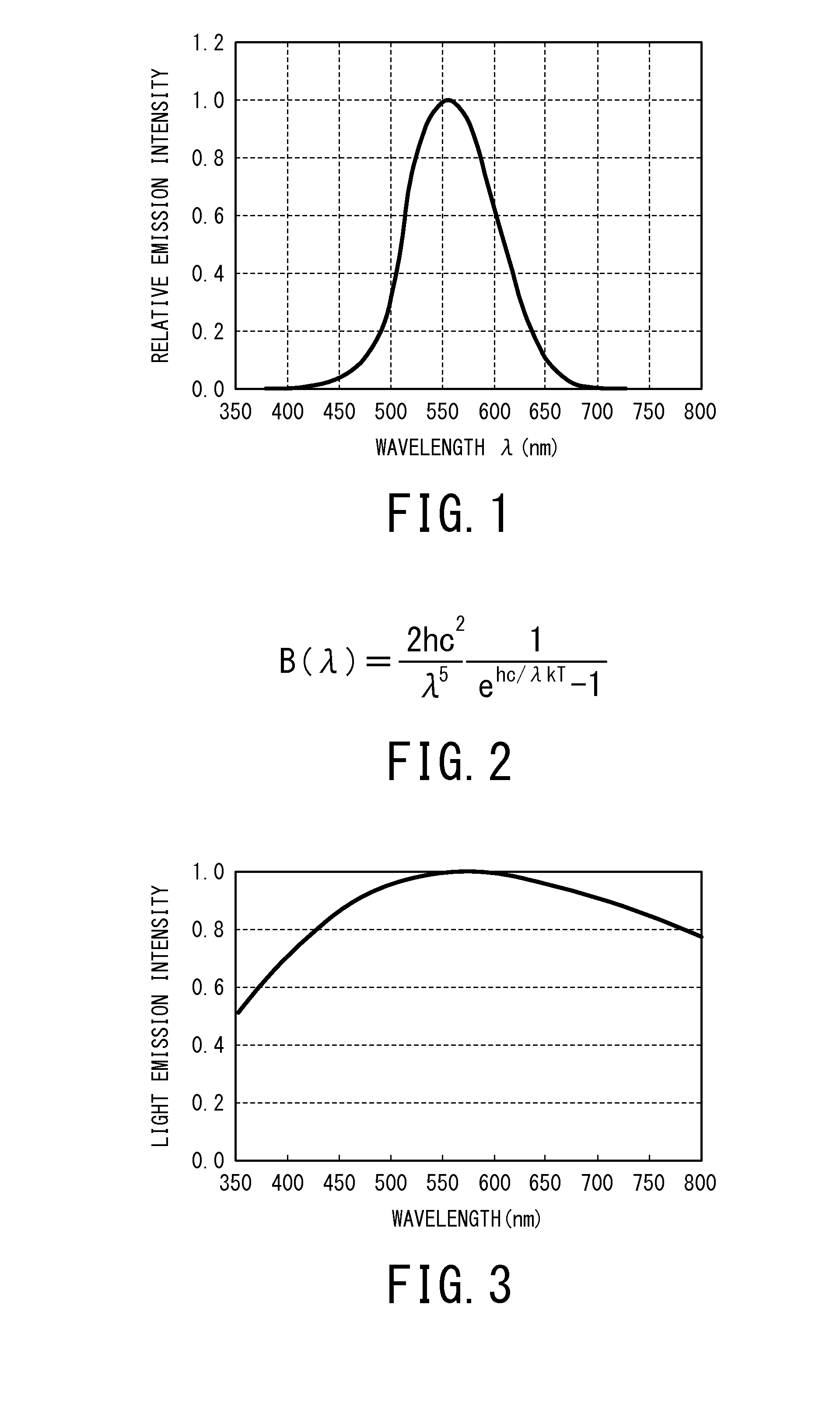
White light source and white light source system including the same
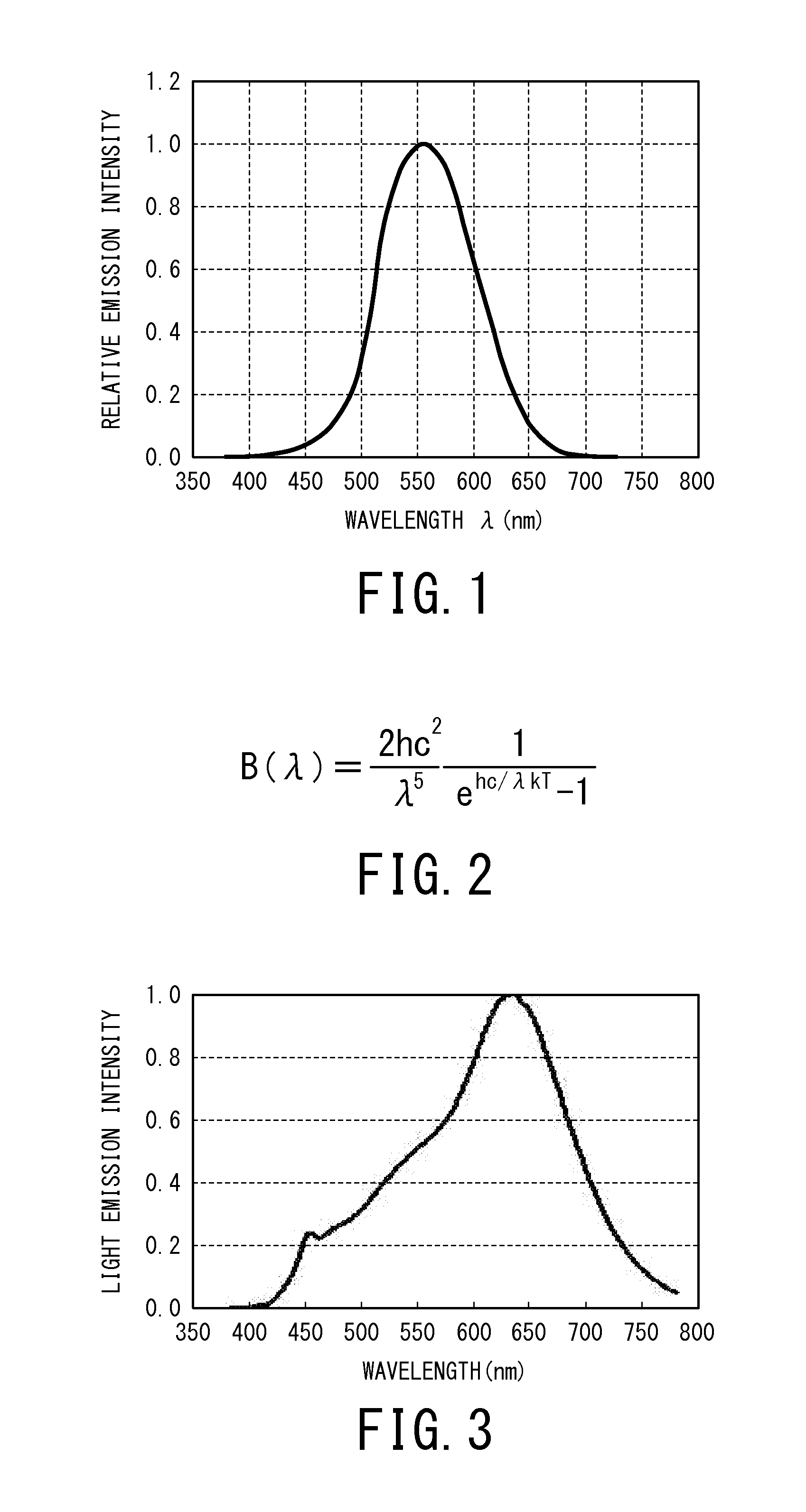
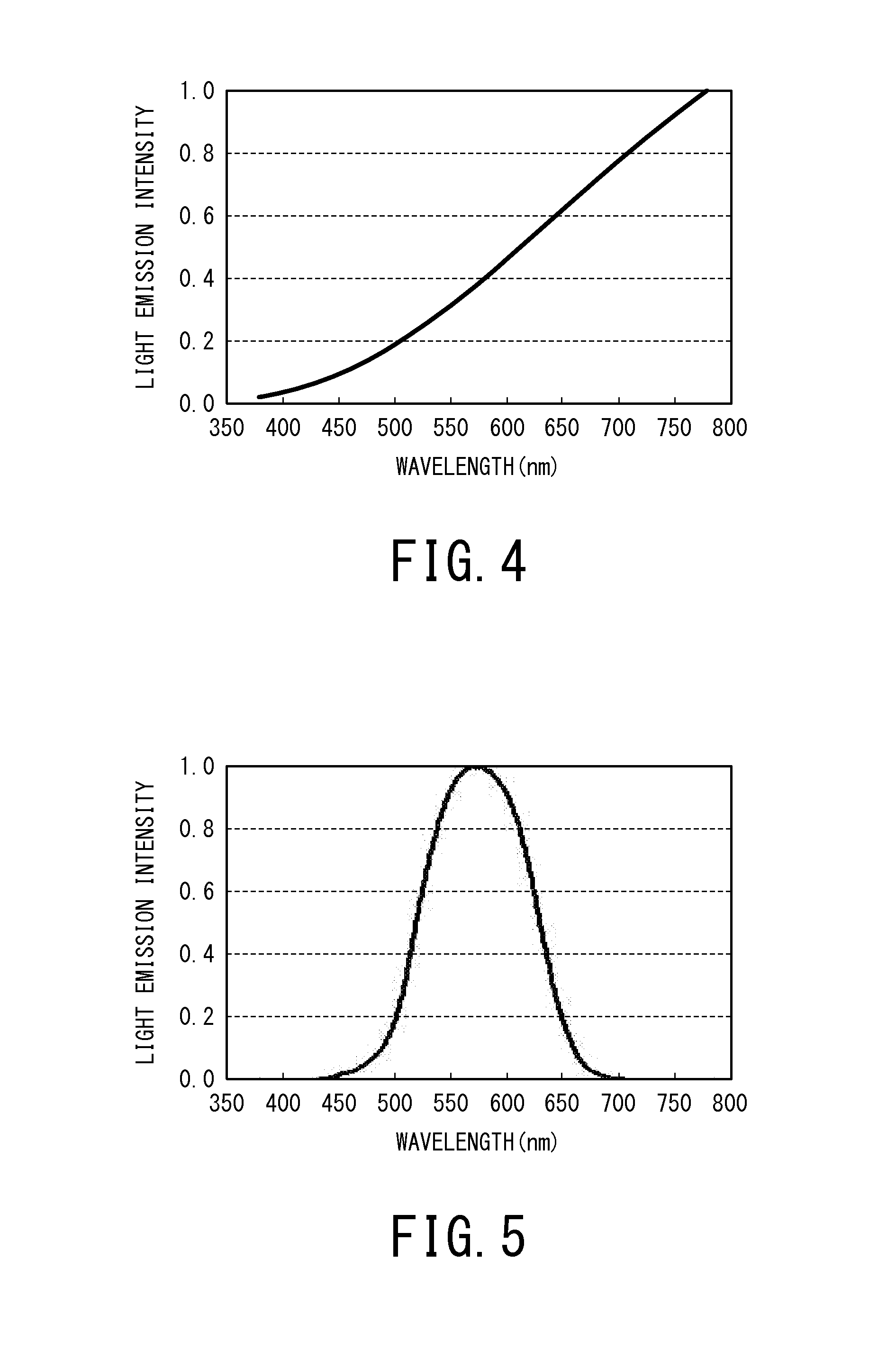
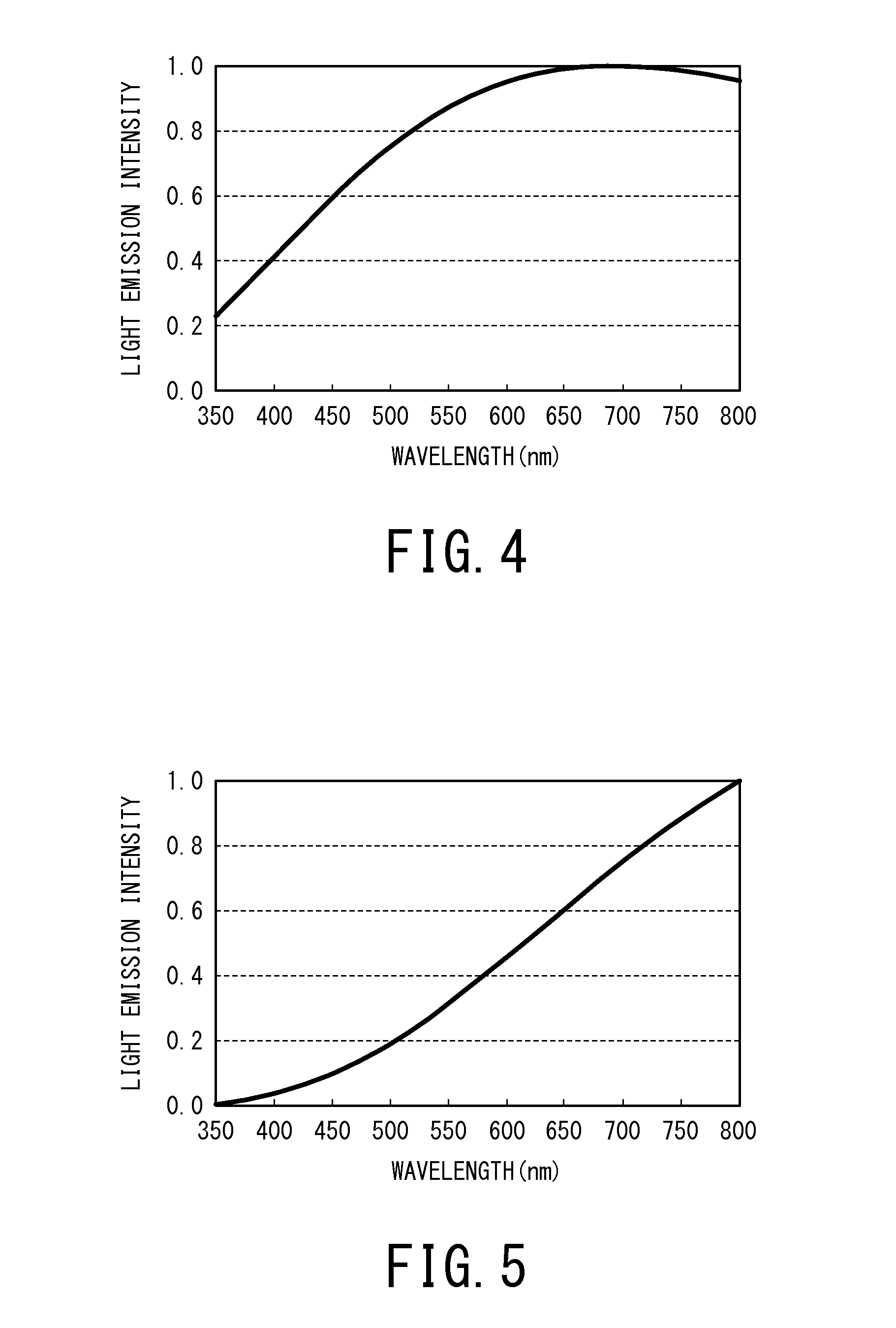
The present invention provides a white light source comprising a blue light emitting LED having a light emission peak of 421 to 490 nm and satisfying a relational equation of−0.2≦[(P(λ)×V(λ)) / (P(λmax1)×V(λmax1))−(B(λ)×V(λ)) / (B(λmax2)×V(λmax2))]≦+0.2,assuming that: a light emission spectrum of the white light source is P(λ); a light emission spectrum of black-body radiation having a same color temperature as that of the white light source is B(λ); a spectrum of a spectral luminous efficiency is V(λ); a wavelength at which P(λ)×V(λ) becomes largest is λmax1; and a wavelength at which B(λ)×V(λ) becomes largest is λmax2. According to the above white light source, there can be provided a white light source capable of reproducing the same light emission spectrum as that of natural light.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
Thermoplastic resin composition for sealing solar cell, sheet for sealing solar cell and solar cell
InactiveUS20100000600A1Improve heat resistanceIncrease flexibilityPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesCross-linkSolar cell
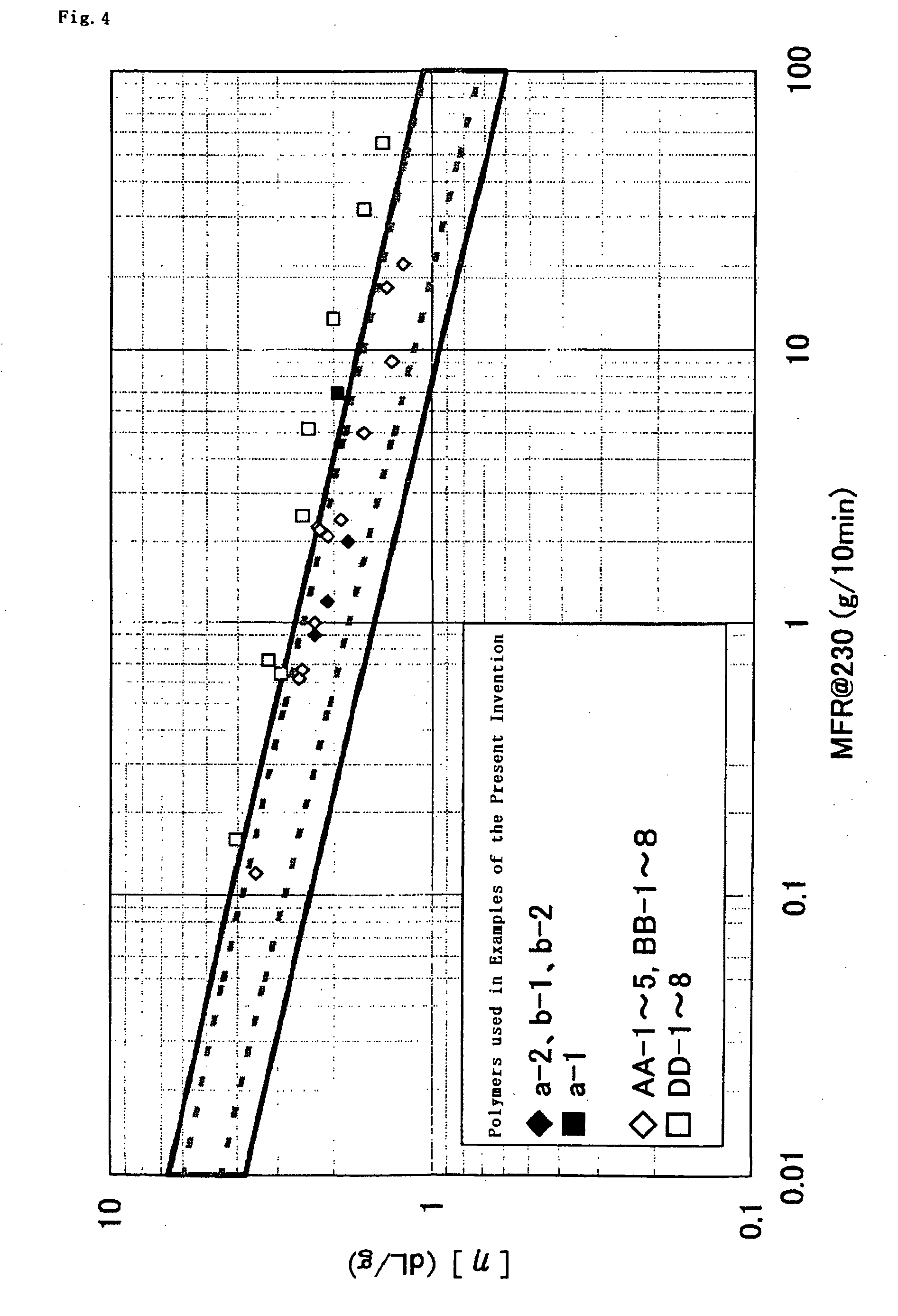
An object of the present invention is to provide a material used for producing a sheet for sealing a solar cell which is excellent in mechanical strength, solar cell sealing property and transparency if the material is not cross-linked.The thermoplastic resin composition of the present invention for sealing a solar cell is characterized by comprising:(A) 0 to 70 parts by weight of a propylene-based polymer having a melting point of 100° C. or higher and(B) 30 to 100 parts by weight of a propylene-based copolymer satisfying the following requisite (b);(b): MFR (230° C., load: 2.16 kg) falls in a range of 0.01 to 100 g / 10 minutes, and at least one of the following requisites (b-1) and (b-2) is satisfied;(b-1): an rr fraction is 60% or more and(b-2): a structural unit derived from propylene is contained in an amount of 55 to 90 mole %, and a structural unit derived from α-olefin having 2 to 20 carbon atoms (excluding propylene) is contained in an amount of 10 to 45 mole %; and an intrinsic viscosity [η] (dL / g) measured in decalin at 135° C. and MFR described above satisfy a specific relational equation.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
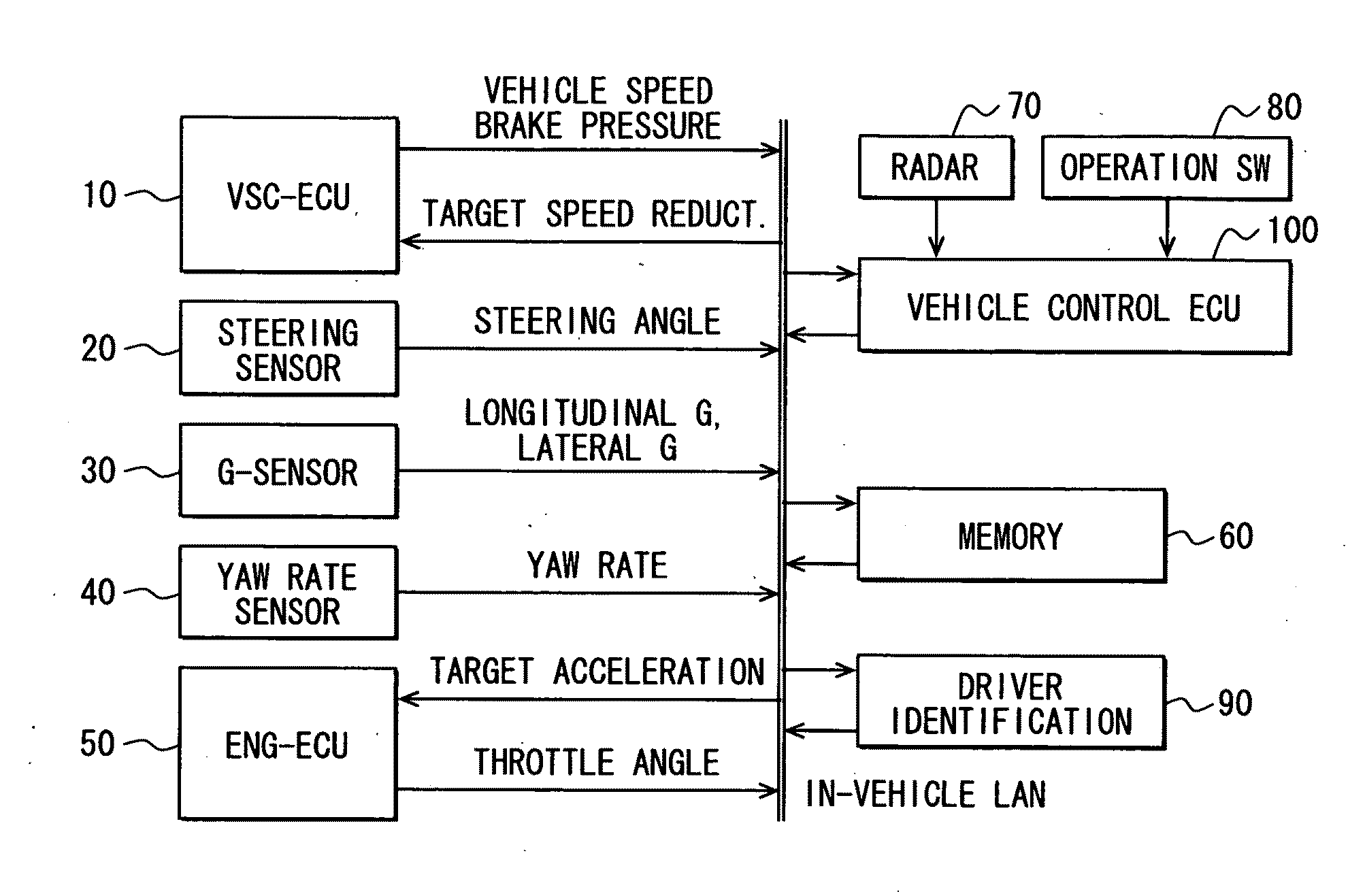
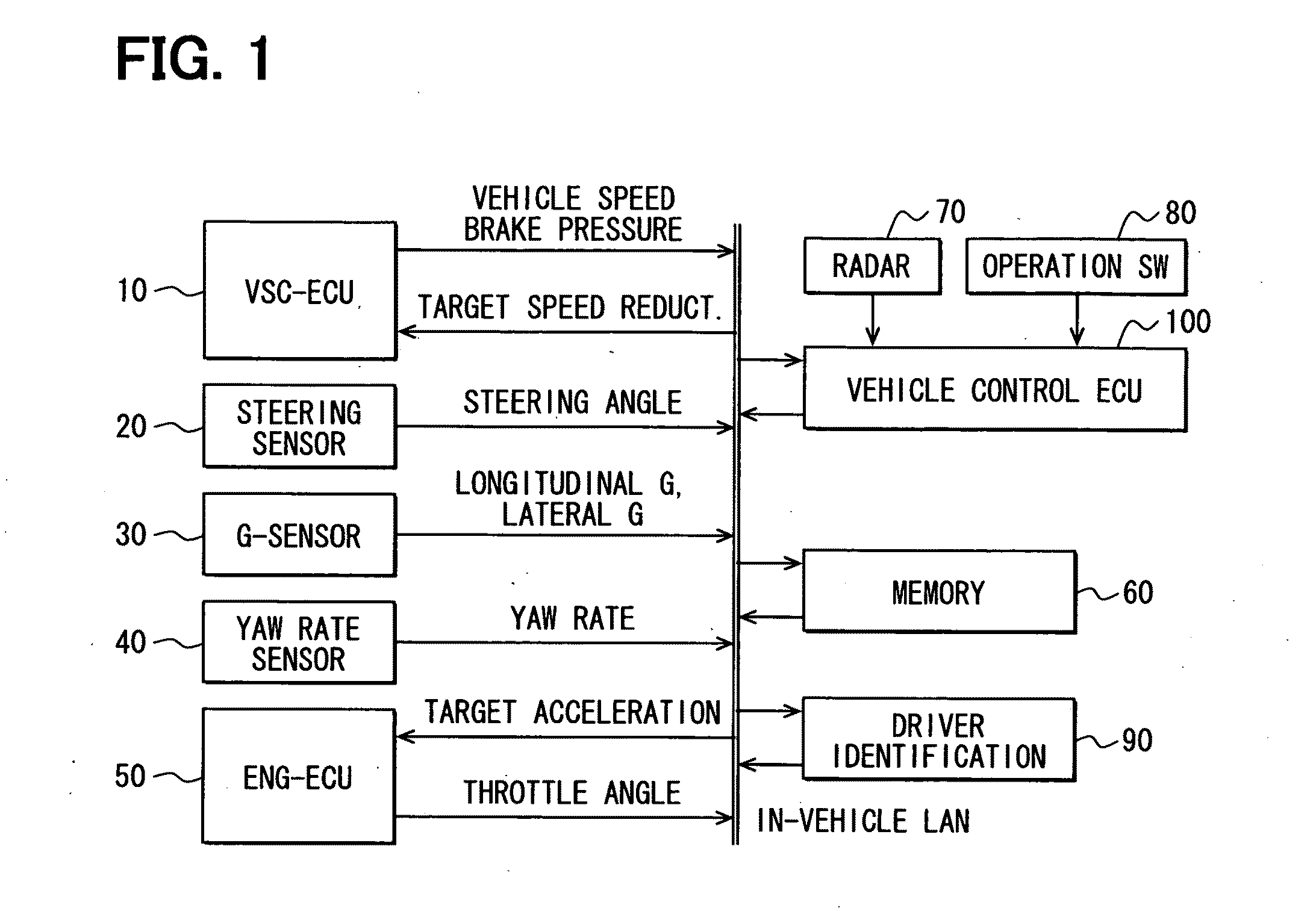
Vehicle control system
InactiveUS20090265071A1Analogue computers for trafficAnti-collision systemsDriver/operatorControl system
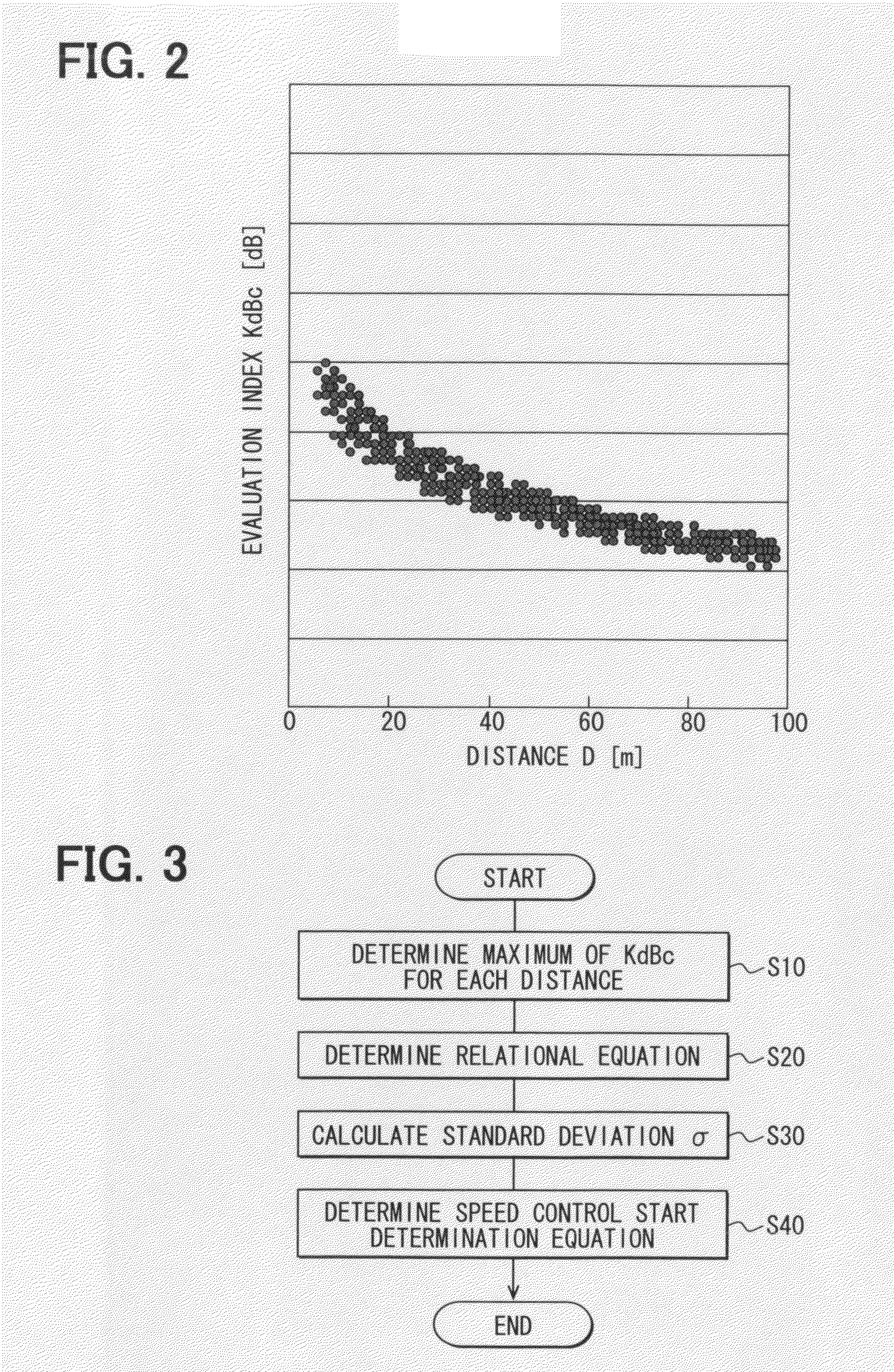
In a vehicle drive control system, a control unit calculates an evaluation index indicating an approach / separation condition of a subject vehicle during a travel and stores this evaluation index together with an inter-vehicle distance with respect to each driver in a memory device. The control unit further calculates a maximum value of the stored evaluation index for each distance, and calculates a relational equation between the distance and the calculated maximum evaluation index. The control unit determines, by correcting the relational equation, a speed control start determination equation, which determines the start timing of the automatic acceleration and / or deceleration control.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Electronic apparatus and method of controlling electronic apparatus
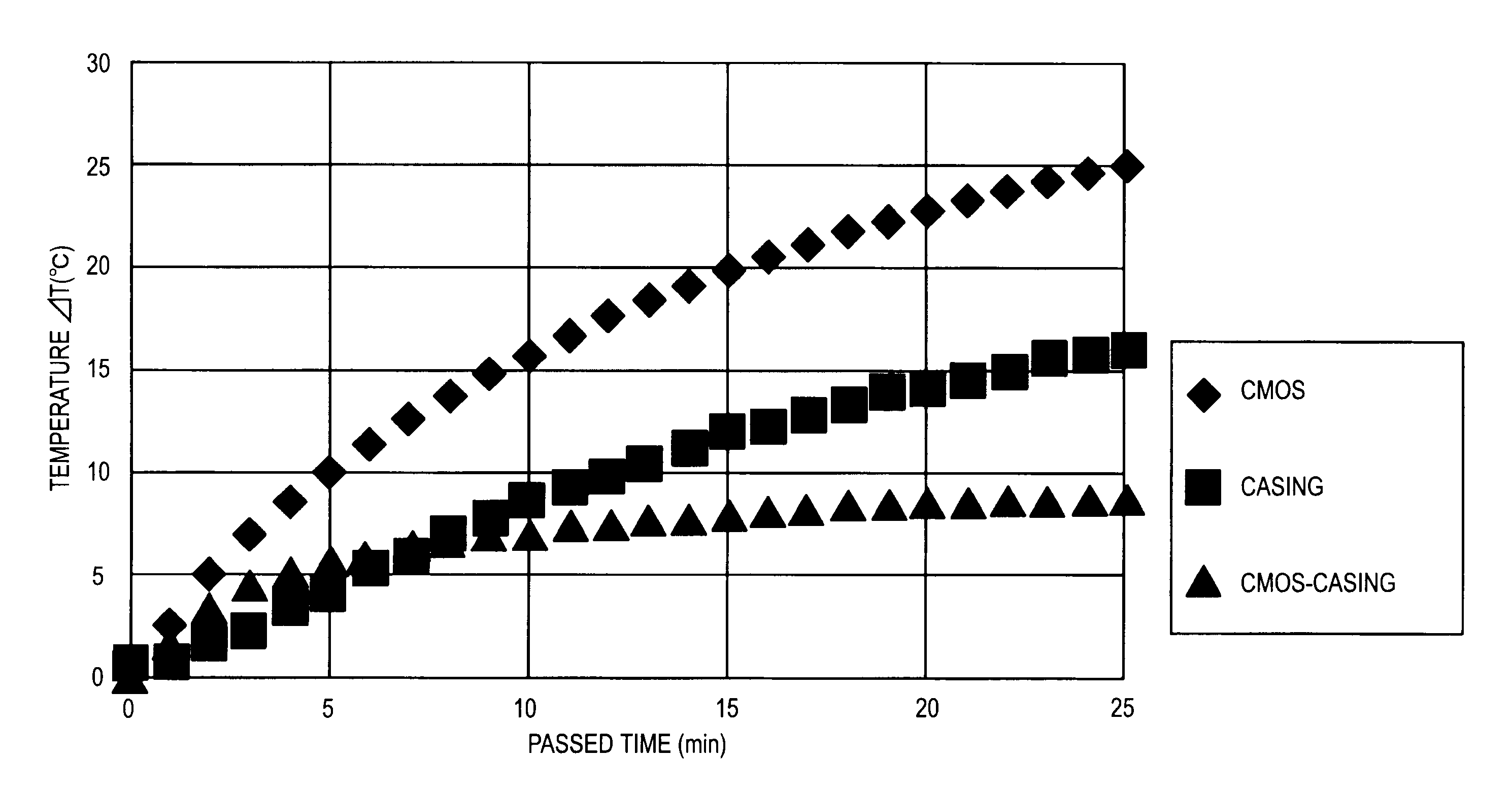
An electronic apparatus includes: a temperature measurement section that measures a temperature of a heat generation source generating heat by consuming power or a temperature of an inner position of a casing of which the temperature changes due to the heat generation of the heat generation source; and an environmental temperature calculation section that calculates a temperature which is calculated using a predetermined relational equation that is different in accordance with a model from a difference between a first temperature measured by the temperature measurement section at a point in time when the heat generation source starts consuming a predetermined amount of power and a second temperature measured by the temperature measurement section at a point in time after the passage of a predetermined period from the start of consumption of a predetermined amount of power by the heat generation source as an environmental temperature in an environment where the casing is placed.
Owner:SONY CORP
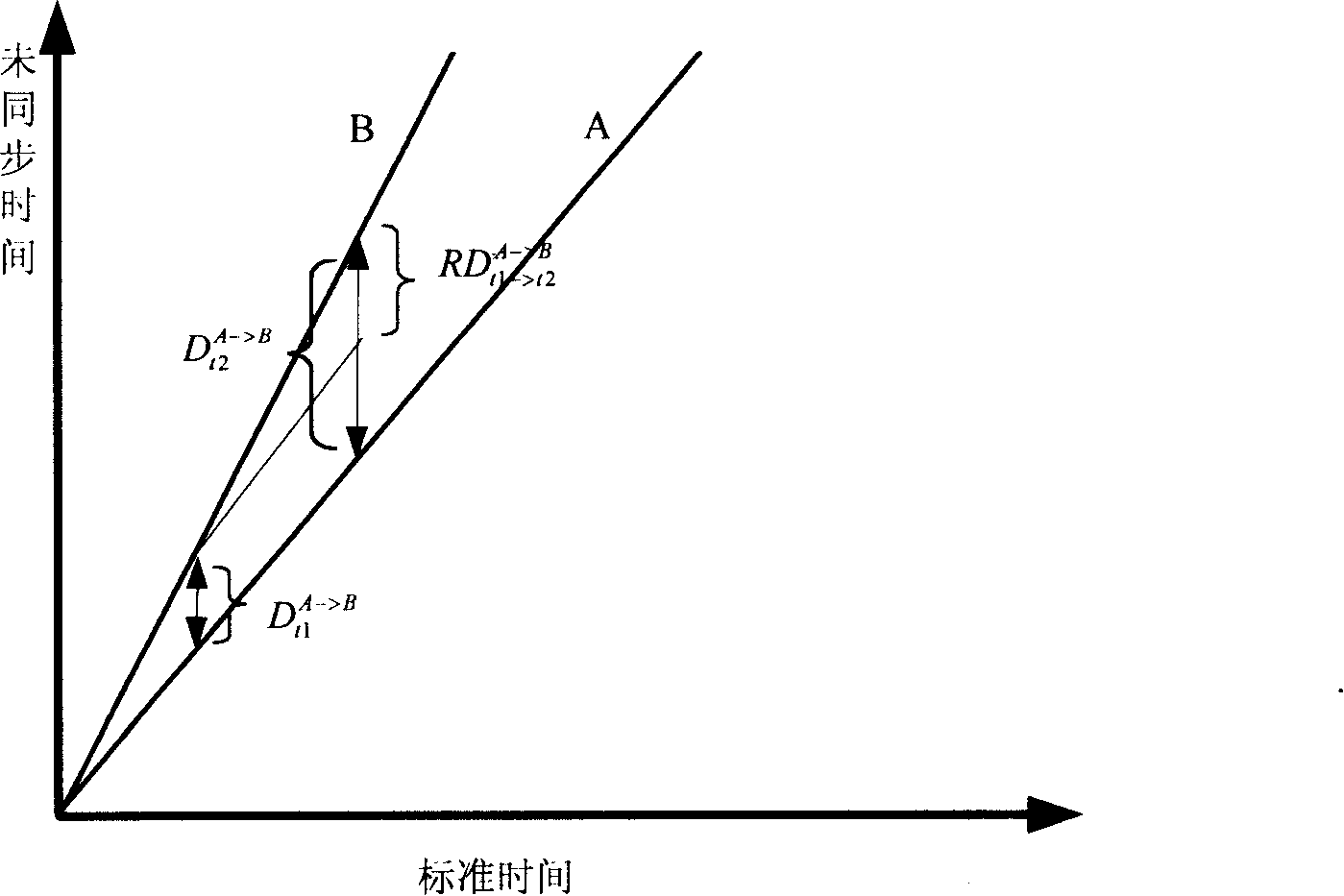
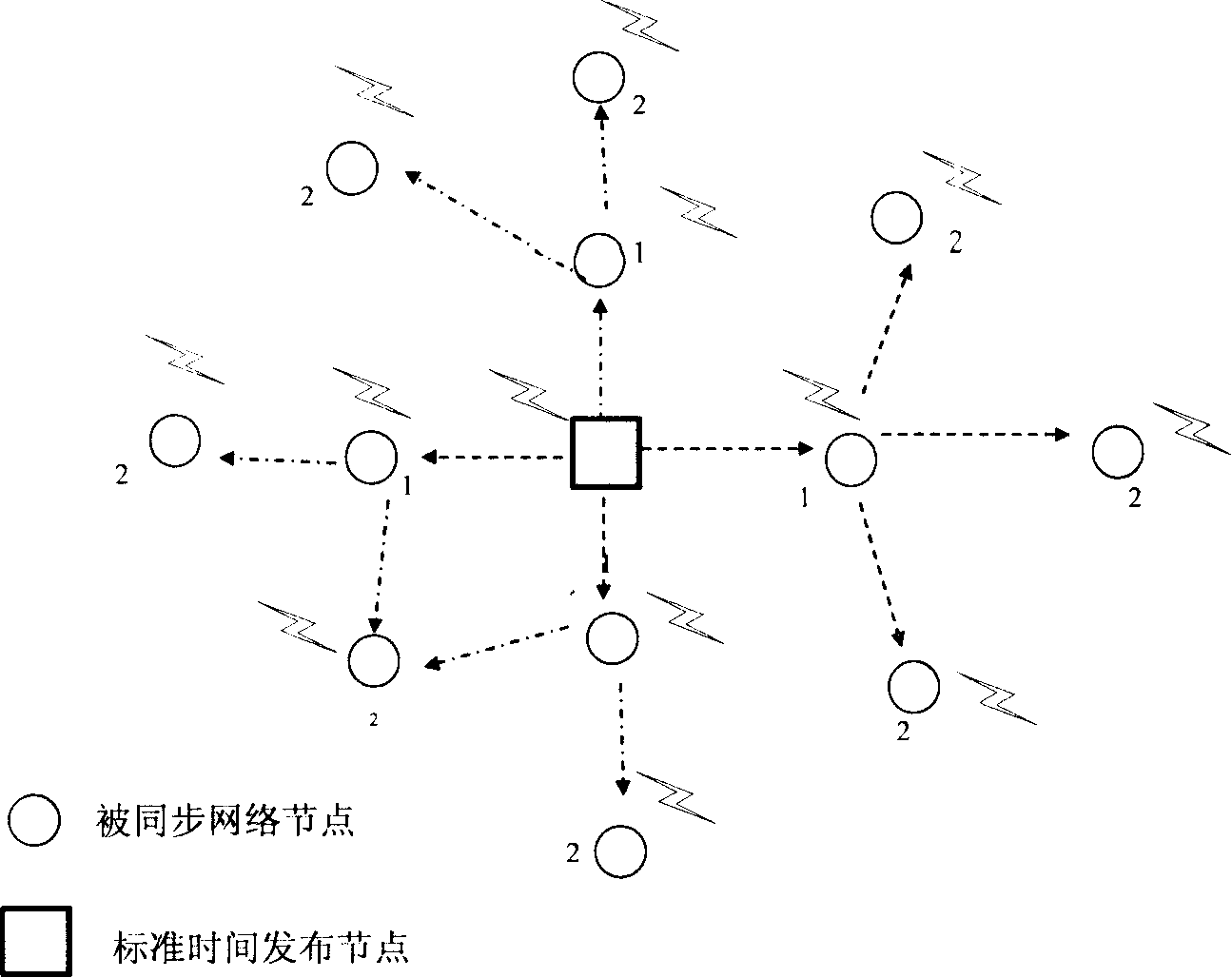
Wireless meshed network low-spending high-precision time synchronization process for industry monitoring
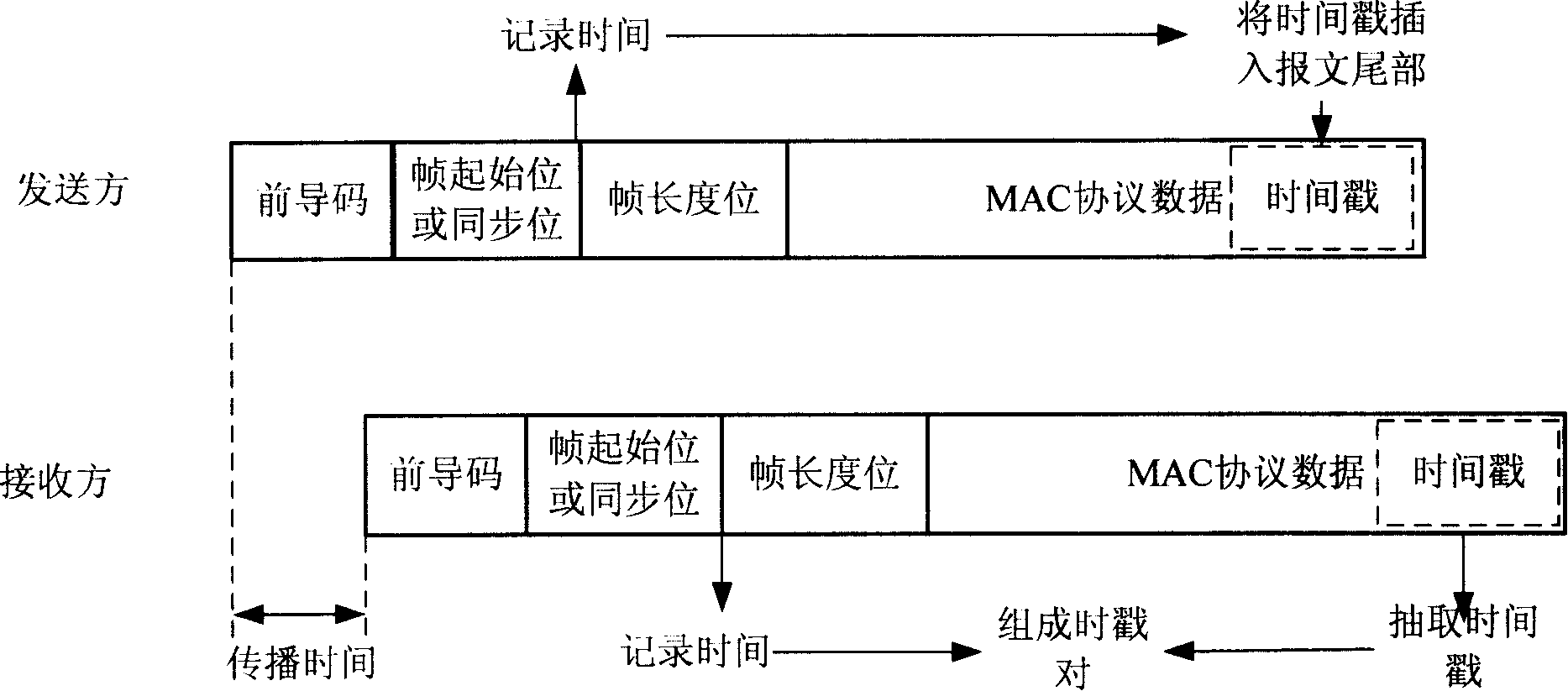
ActiveCN101174939AReduce overheadHigh precisionRadio transmission for post communicationData switching networksTimestampWireless mesh network
The invention belongs to the field of wireless network communication, in particular to a high-precision time synchronization method for realizing a node and a time reference source in a wireless mesh network. The main technical points are: record the precise time stamp of message sending and receiving at the MAC layer; the receiving node that needs to be synchronized collects the time synchronization beacons periodically released by the time source, and after receiving several time synchronization beacons, uses statistical methods to establish The relational equation of the local time and the global time at the time synchronization beacon sending node eliminates the influence of the clock crystal frequency offset on the time synchronization accuracy; during the operation of the network, the parameters of the relational equation are updated online. By adopting the method of the invention, the time uncertainty in the synchronization process can be eliminated to the greatest extent, and the synchronization overhead can be reduced.
Owner:SHENYANG ZHONGKE AOWEI SCI & TECH CO LTD
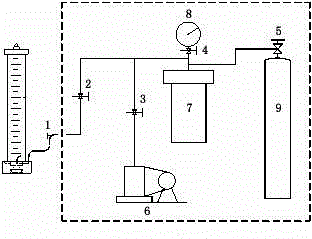
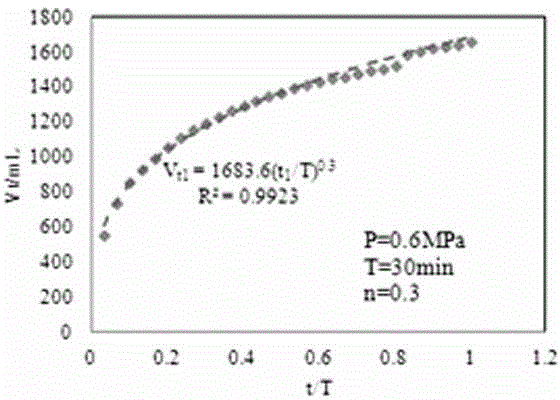
Gas loss calculation method
InactiveCN103983534AThe calculation result is accurateMaterial analysisExperimental laboratoryThermodynamics
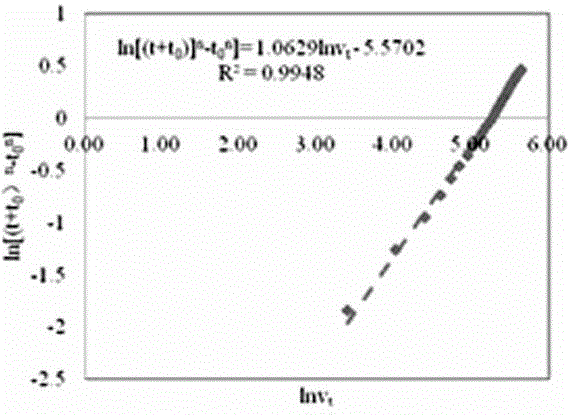
The invention relates to a method for calculating gas loss according to a relation between an accumulated desoprtion value and the time. A large quantity of experiments show that the relational equation between the accumulated desorption value in the initial stage after pressure of coal cuttings is released is V=A(t / T)<n>, but the power exponent n is not a constant, is related to the gas pressure and is changed along with the time; accurate determination of the power exponent n of the accumulated desorption value is a key for calculation of the gas loss. In order to accurately calculate the gas loss, the method comprises the steps of 1, firstly evaluating the gas pressure of a coal seam through on-site measurement; 2, recording the observation time t, the accumulated desorption value Vt with the time t, the total desorption time T and the loss time t0 during the on-site measurement of the gas content; 3, measuring the value of n in a lab under a condition of the gas pressure of the coal seam to be measured: obtaining a unitary regression relational equation between lnVt and ln[(t+t0)n-t0n] through Excel by a least square method, wherein an intercept is ln(A / Tn), and substituting the n value and the T value to obtain an A value; and 4, substituting the A value, the T value the n value into V=A(t0 / T)<n> to obtain the gas loss V.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Method and apparatus for generating check matrix
InactiveUS7272770B2Error correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionEssential matrixTheoretical computer science
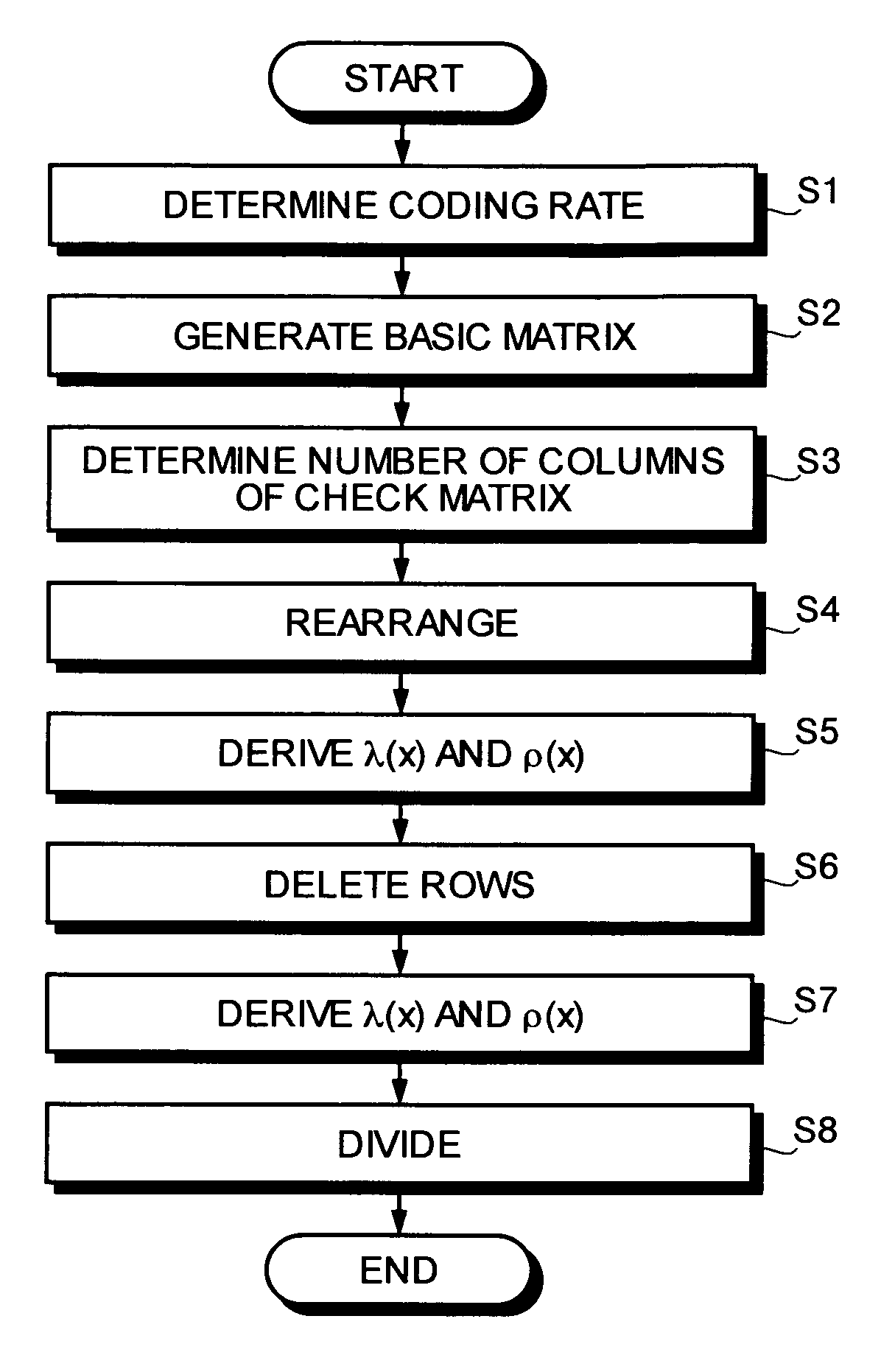
A method of generating a check matrix for an LDPC code includes determining a coding rate, generating a basic matrix that satisfies predetermined conditions, determining a number of columns of a check matrix, substituting rows of the basic matrix based on a specific relational equation, provisionally searching an ensemble of weights by executing Gaussian approximation, deleting rows of the basic matrix after the permutation in order from the bottom by considering the number of rows after a division, searching an optimal ensemble of weights by executing Gaussian approximation based on a predetermined condition after row deletion, and dividing at random the weights of the basic matrix after the row deletion based on the optimal ensemble.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
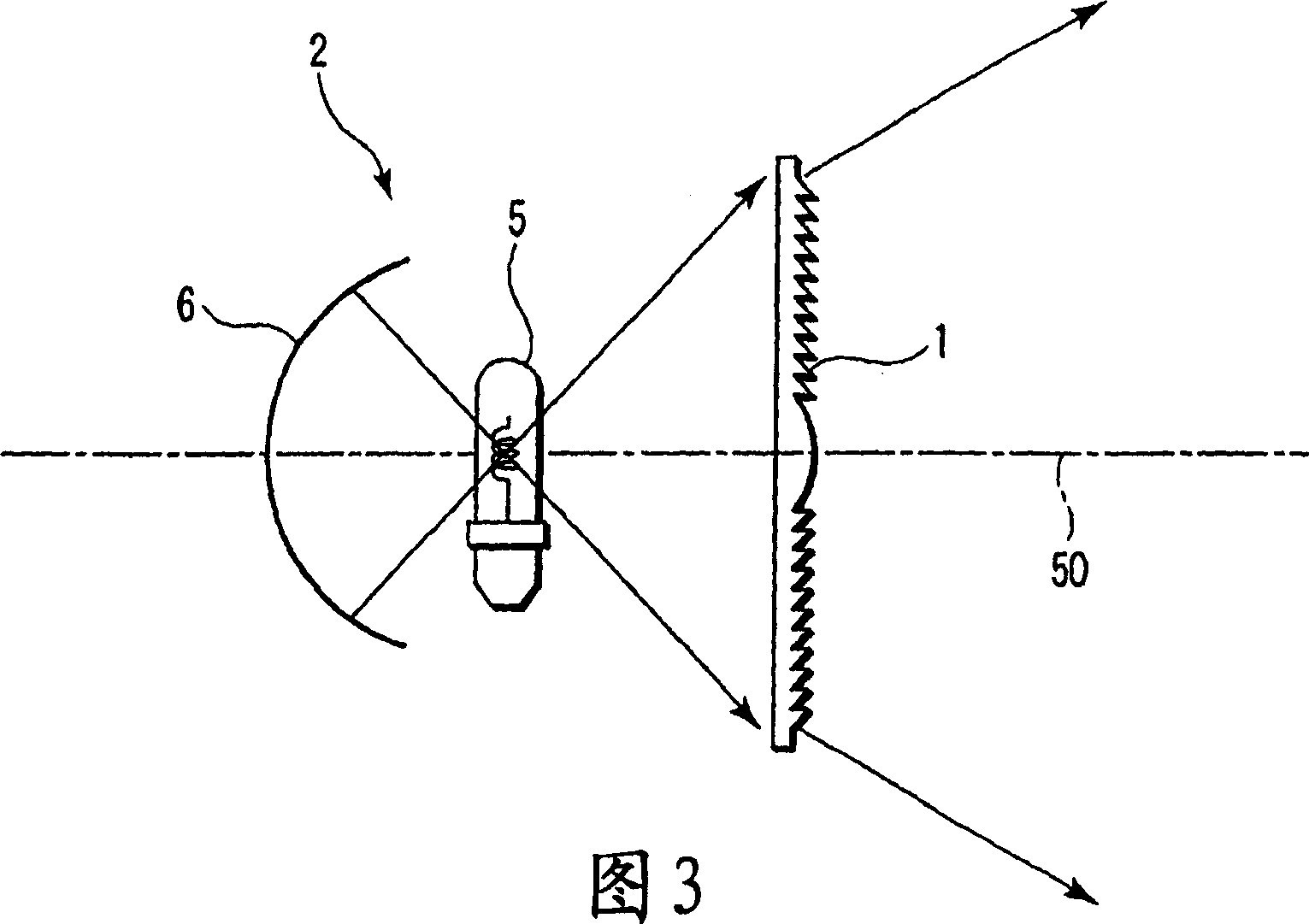
Fresnel lens and lighting apparatus provided with the fresnel lens
InactiveCN1828339AReduce Illumination Non-UniformityLighting applicationsMechanical apparatusLight equipmentEffect light
In a Fresnel lens which is made of a lens material whose refraction index is n, and focuses light beam from a light source at a specified radiation view angle phi, and has plural N pieces of circular lens surfaces arranged concentrically around a common optical axis, and plural circular rise surfaces arranged adjacent alternately between these lens surfaces, and two lens surfaces adjacent via at least one of the rise surfaces are concave surfaces, and tangent lines and at the intersecting point with the rise surfaces of the shape of a cross section passing through the optical axis of those lens surfaces intersect at the outside with respect to the optical axis, and when the angle formed between these tangent lines is defined as theta, a relational equation theta>=phi / (2 n N) stands.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
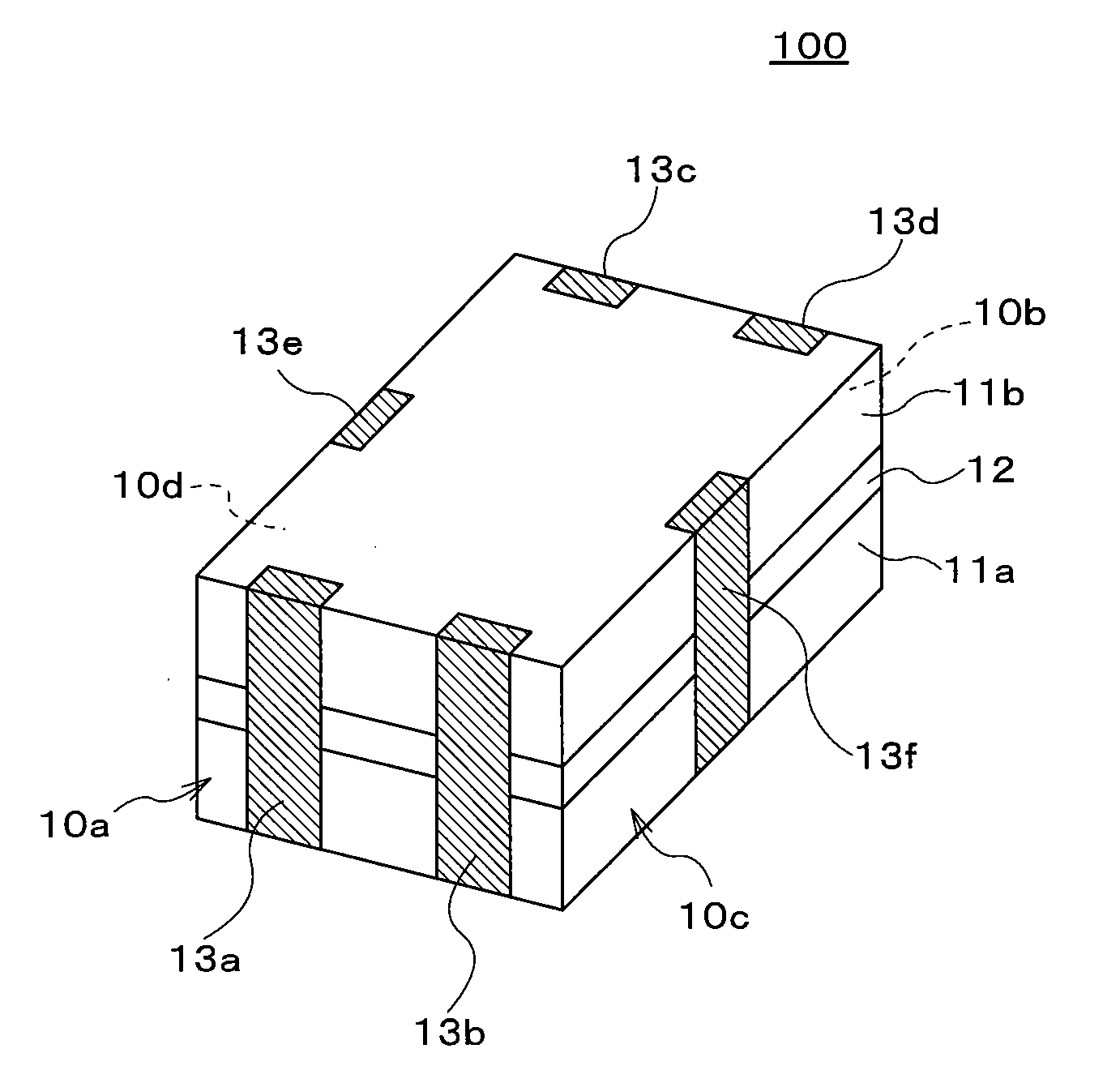
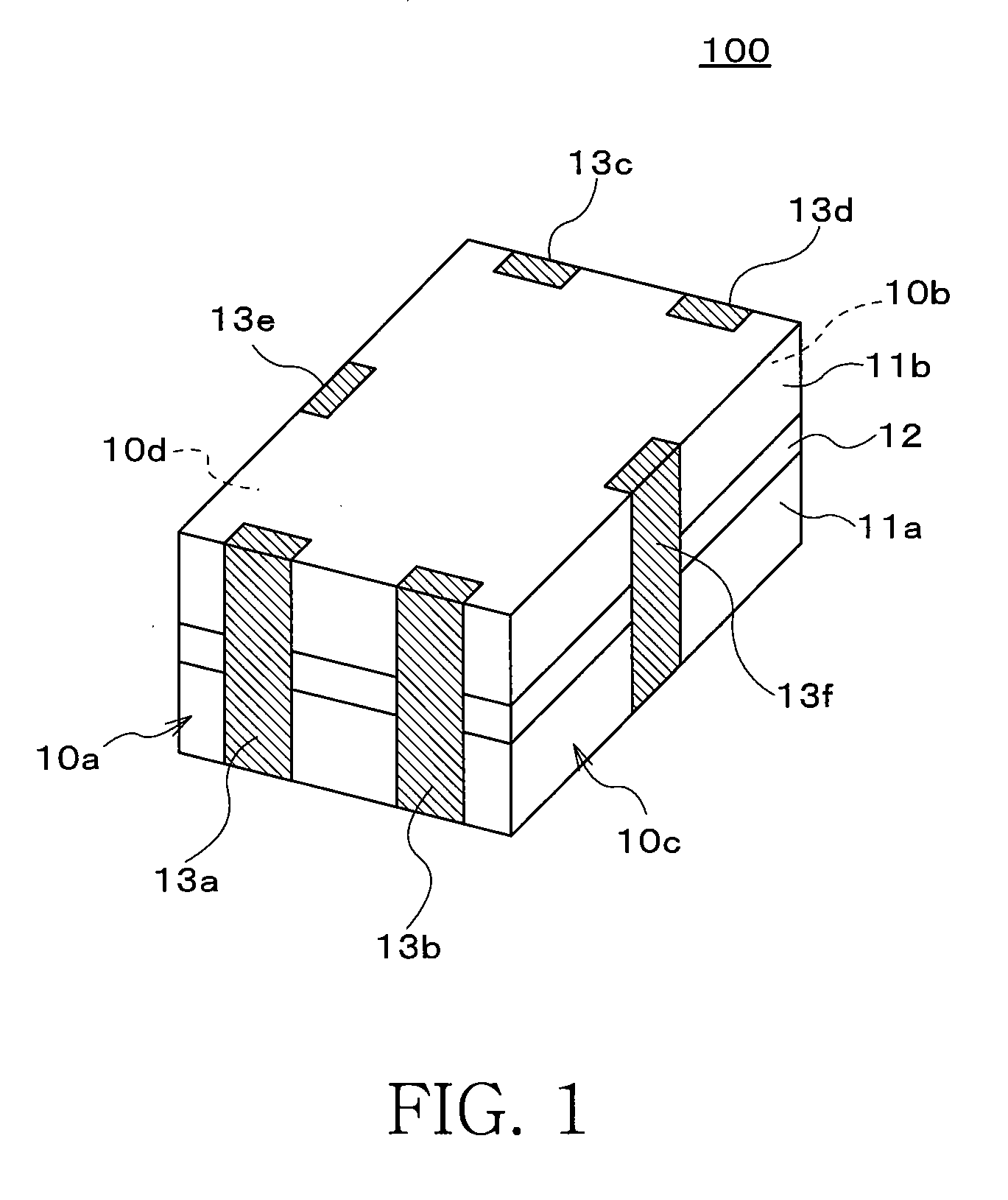
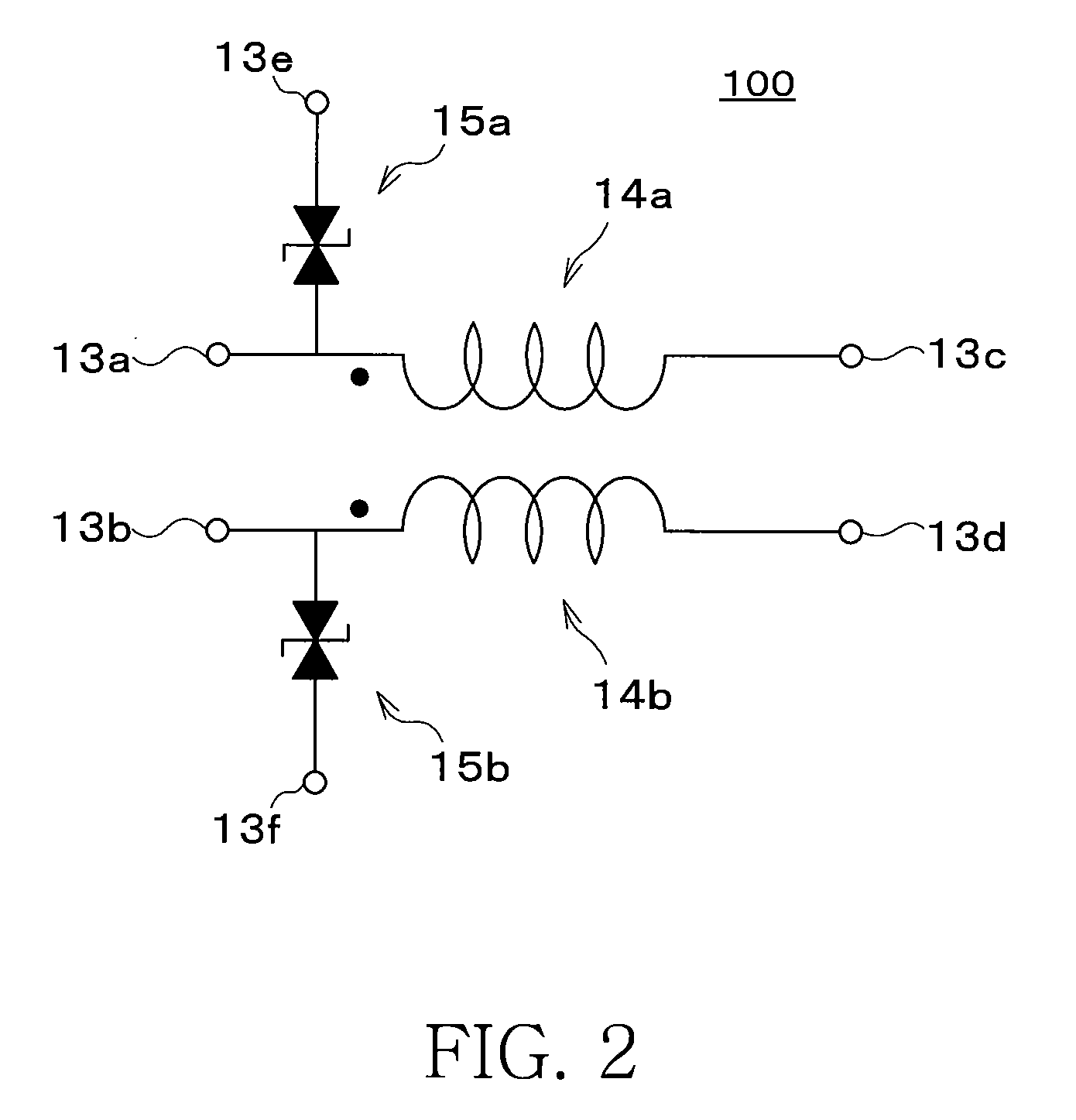
Composite electronic device and digital transmission circuit using thereof
ActiveUS20100182724A1Small electrostatic capacitanceImprove discharge characteristicsMultiple-port networksEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
A composite electronic device includes first and second magnetic substrates, and a functional layer sandwiched between these magnetic substrates, and the functional layer is configured by a common-mode filter layer and a ESD protection element layer. An electrostatic capacitance of the ESD protection elements is equal to or lower than 0.35 pF. The common-mode filter layer includes a first spiral conductor formed on an insulation layer, and a second spiral conductor formed on an insulation layer. DC resistance of a common mode filter is equal to or higher than 0.5Ω and equal to or lower than 5Ω, and an electrostatic capacitance of the ESD protection elements is equal to or lower than 0.35 pF. A width W and a length L of the first and second spiral conductors satisfy a relational equation expressed by √(L / W)<(7.6651−fc) / 0.1385.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
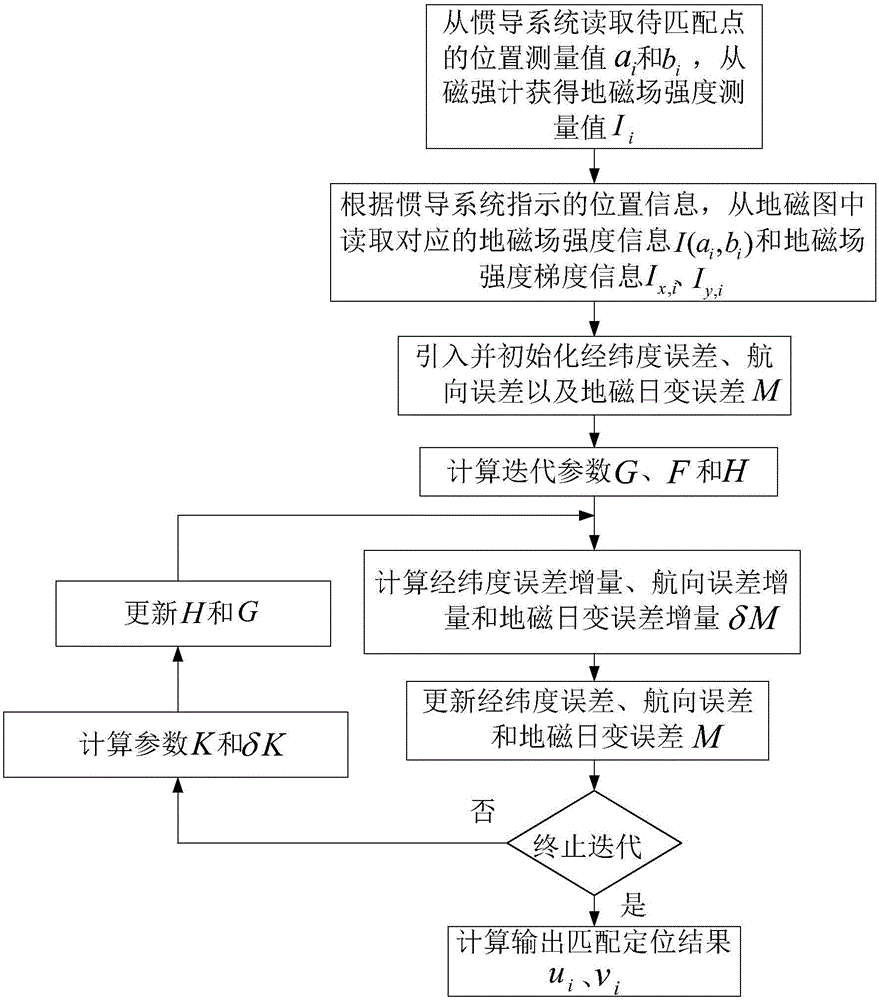
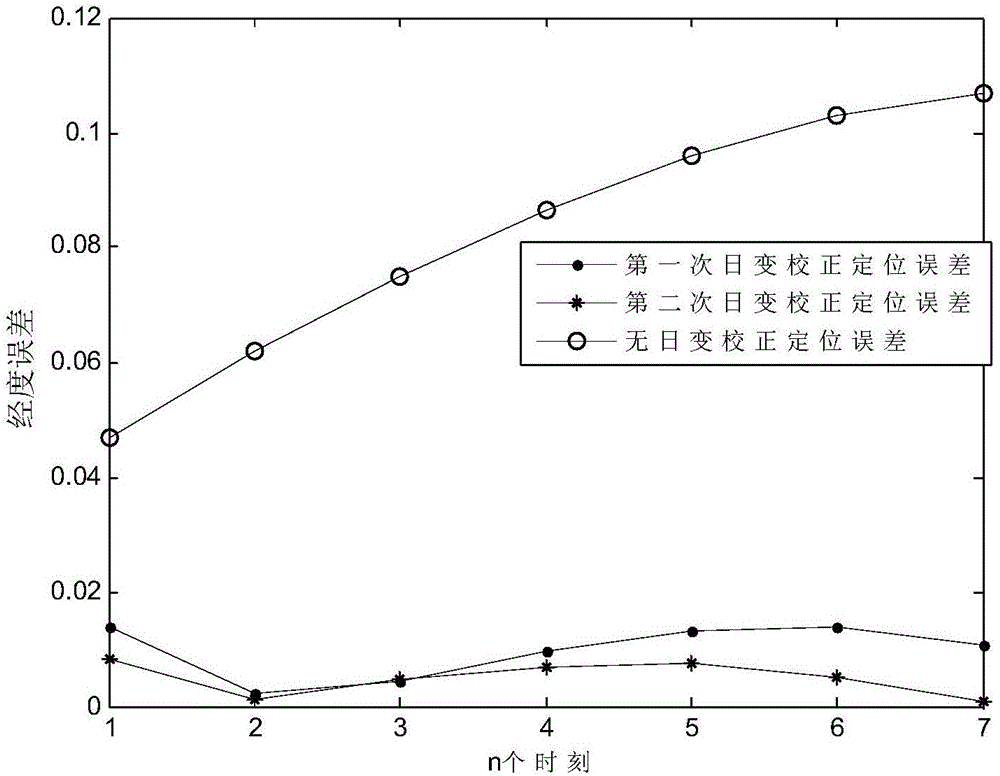
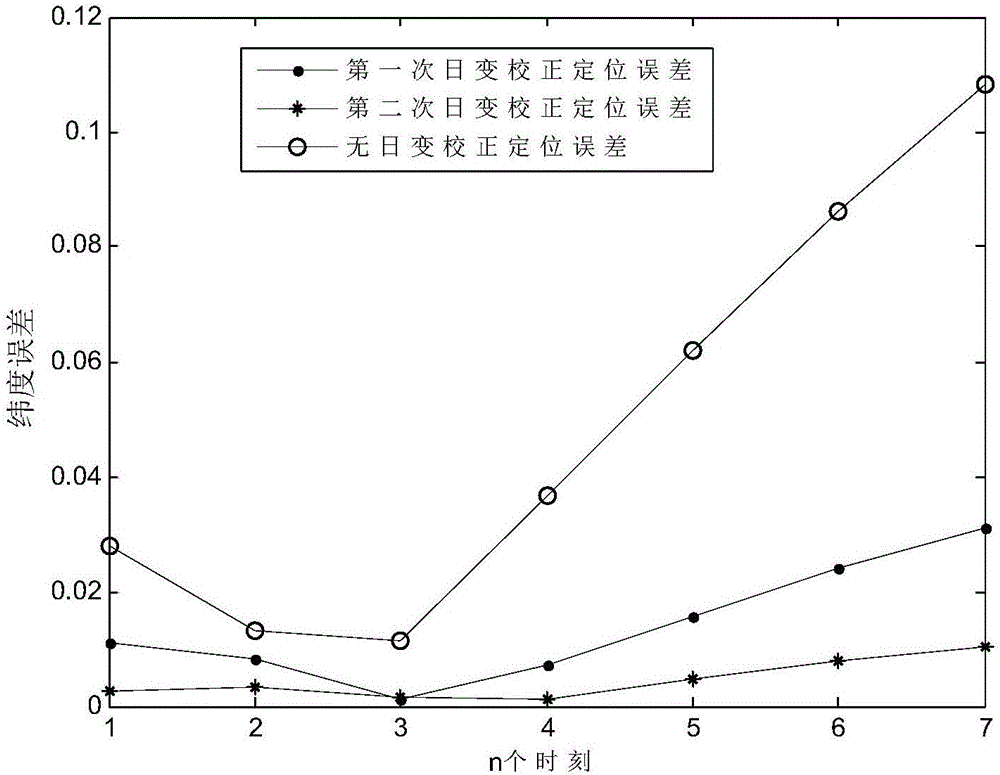
Inertial geomagnetic matching location method under influence of geomagnetic daily variation
ActiveCN106197405AHigh positioning accuracyNavigation by terrestrial meansNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsLongitudeRelational equation
The invention provides an inertial geomagnetic matching location method under the influence of geomagnetic daily variation. The inertial geomagnetic matching location method comprises the following steps: reading position measurement values ai and bi of a to-be-matched point at N moments from an inertial navigation system, and obtaining geomagnetic field strength information Ii from a magnetometer; respectively reading corresponding reference values I (ai, bi) of geomagnetic field strength and corresponding gradient reference values Ix, i and Iy, i of the geomagnetic field strength from a pre-stored geomagnetic database according to positions of N to-be-matched points indicated by the inertial navigation system; bringing in and initializing longitude and latitude error, course error and geomagnetic daily variation error; calculating delta M of increment of the longitude and latitude error, increment of the course error and increment of the geomagnetic daily variation error; updating M of the longitude and latitude error, the course error and the geomagnetic daily variation error; judging whether a termination iteration condition is met or not, and calculating parameters K and delta K according to updated M; obtaining the longitude and latitude error, the course error and the geomagnetic daily variation error according to iteration calculation, and substituting an obtained result into a relational equation of a matching track and a reference track, thus obtaining the matching track.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
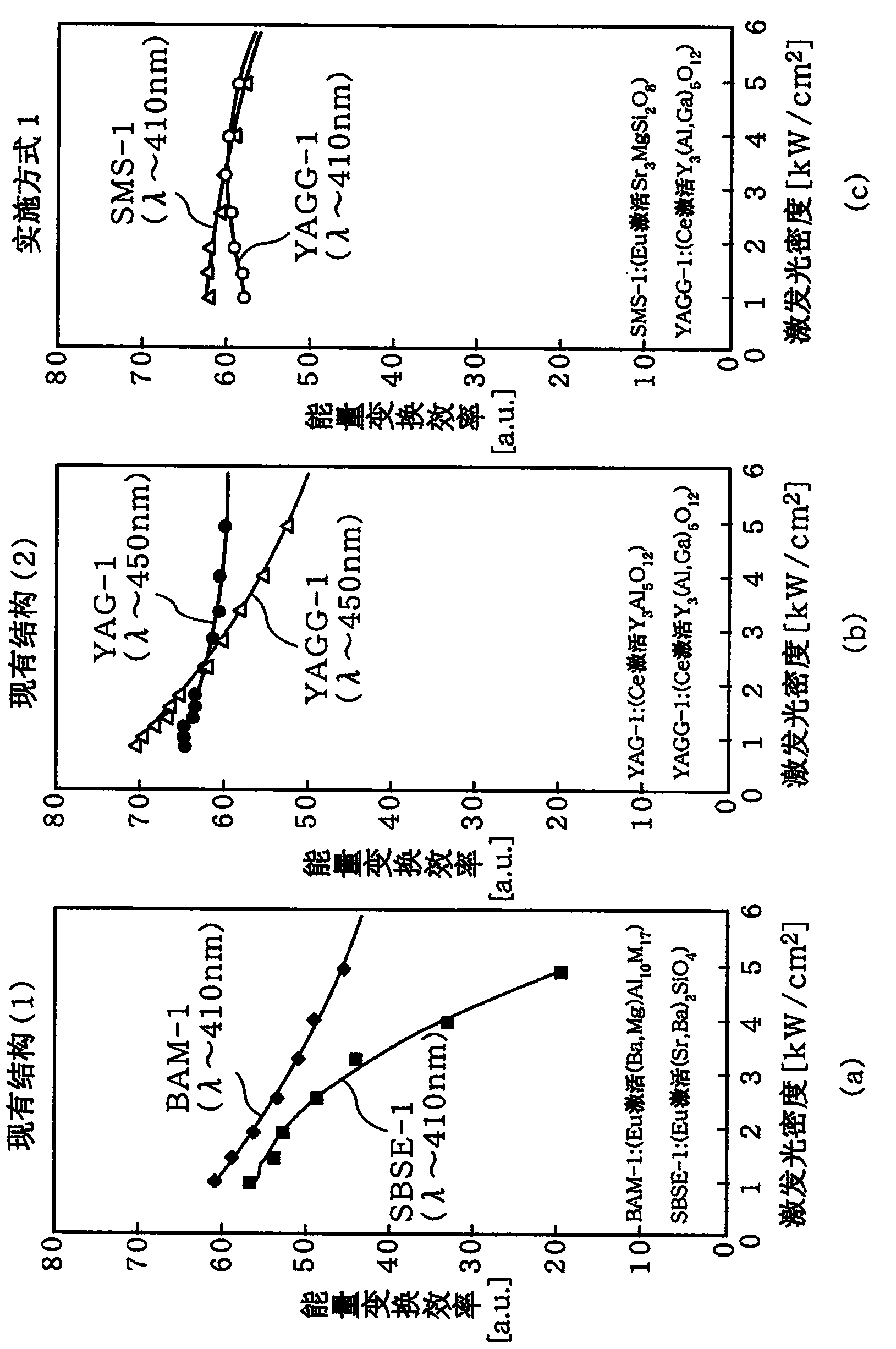
Light emitting device and projection device
ActiveCN104169637AImprove conversion efficiencyLittle variation in color reproducibilityPoint-like light sourceProjectorsPhosphorLength wave
A light emitting device in this disclosure is provided with a semiconductor light emitting element that radiates light of a first wavelength and a first wavelength conversion unit that includes at least one type of first phosphor, is excited by light of the first wavelength, and radiates light of a second wavelength, which is different from the light of the first wavelength. The phosphor includes europium (Eu) as an activator, and the light of the first wavelength is irradiated onto the first wavelength conversion unit at a light density of 1 kW / cm2 or greater. Letting eta1 be the light output ratio for the light of the first wavelength incident to the first wavelength conversion unit and the light of the second wavelength radiated from the first wavelength conversion unit, the light output ratio eta11 when the light of the first wavelength is irradiated onto the first wavelength conversion unit at a light density of 5 kW / cm2 and the light output ratio eta12 when the light of the first wavelength is irradiated onto the first wavelength conversion unit at a light density of 2.5 kW / cm2 satisfies the relational equation 1 <= eta12 / eta11 <= 1.17.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Antiglare film, method for producing same, polarizing plate, image display device, member for touch panel
ActiveCN103582829AImprove visibilityReduce moiréDiffusing elementsPolarising elementsDisplay deviceRelational equation
One embodiment of the present invention is an antiglare film having an antiglare film disposed on top of a substrate film, the antiglare film being characterized in that the arithmetic average roughness Ra (nm) of the surface of the antiglare layer and the correlation length Ic (µm) as defined by the following definitional equation satisfy the following relational equation (1). Relational equation (1): 0 = Ic = 21-8×exp((215-Ra) / 40)-13×exp((215-Ra) / 400) Definitional equation: Correlation length Ic = root mean square roughness Rq (µm) / root mean square gradient ?q × 21 / 2
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
White light source and white light source system including the same
The present invention provides a white light source satisfying a relational equation of−0.2≦[(P(λ)×V(λ)) / (P(λmax1)×V(λmax1))−(B(λ)×V(λ)) / (B(λmax2)×V(λmax2))]≦+0.2,assuming that: a light emission spectrum of the white light source is P(λ); a light emission spectrum of black-body radiation having a same color temperature as that of the white light source is B(λ); a spectrum of a spectral luminous efficiency is V(λ); a wavelength at which P(λ)×V(λ) becomes largest is λmax1; and a wavelength at which B(λ)×V(λ) becomes largest is λmax2. According to the above white light source, there can be provided a white light source capable of reproducing the same light emission spectrum as that of natural light.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
Exposure mask and method of forming pattern
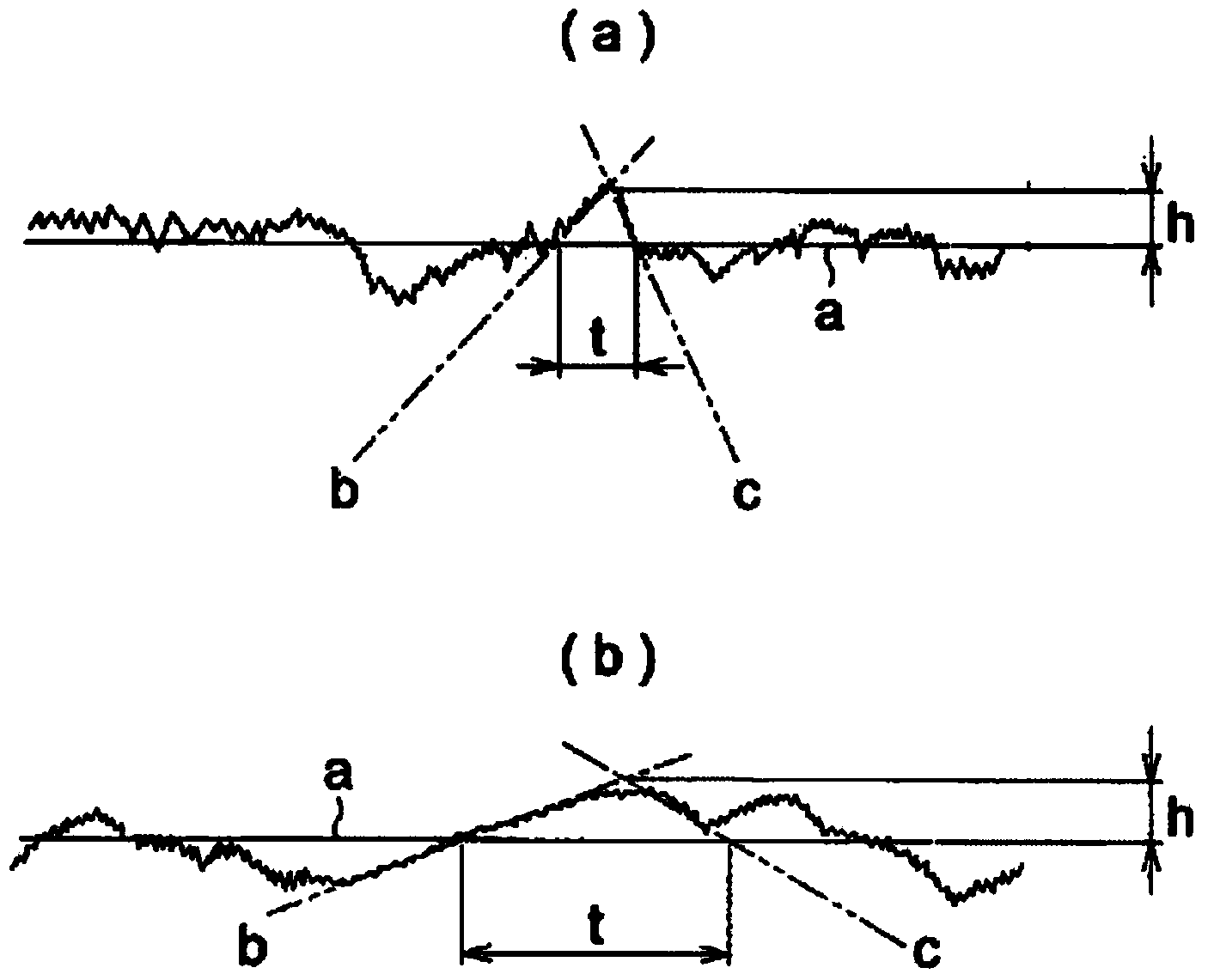
InactiveUS20080176150A1High resolutionImprove processing yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingRelational equationLength wave
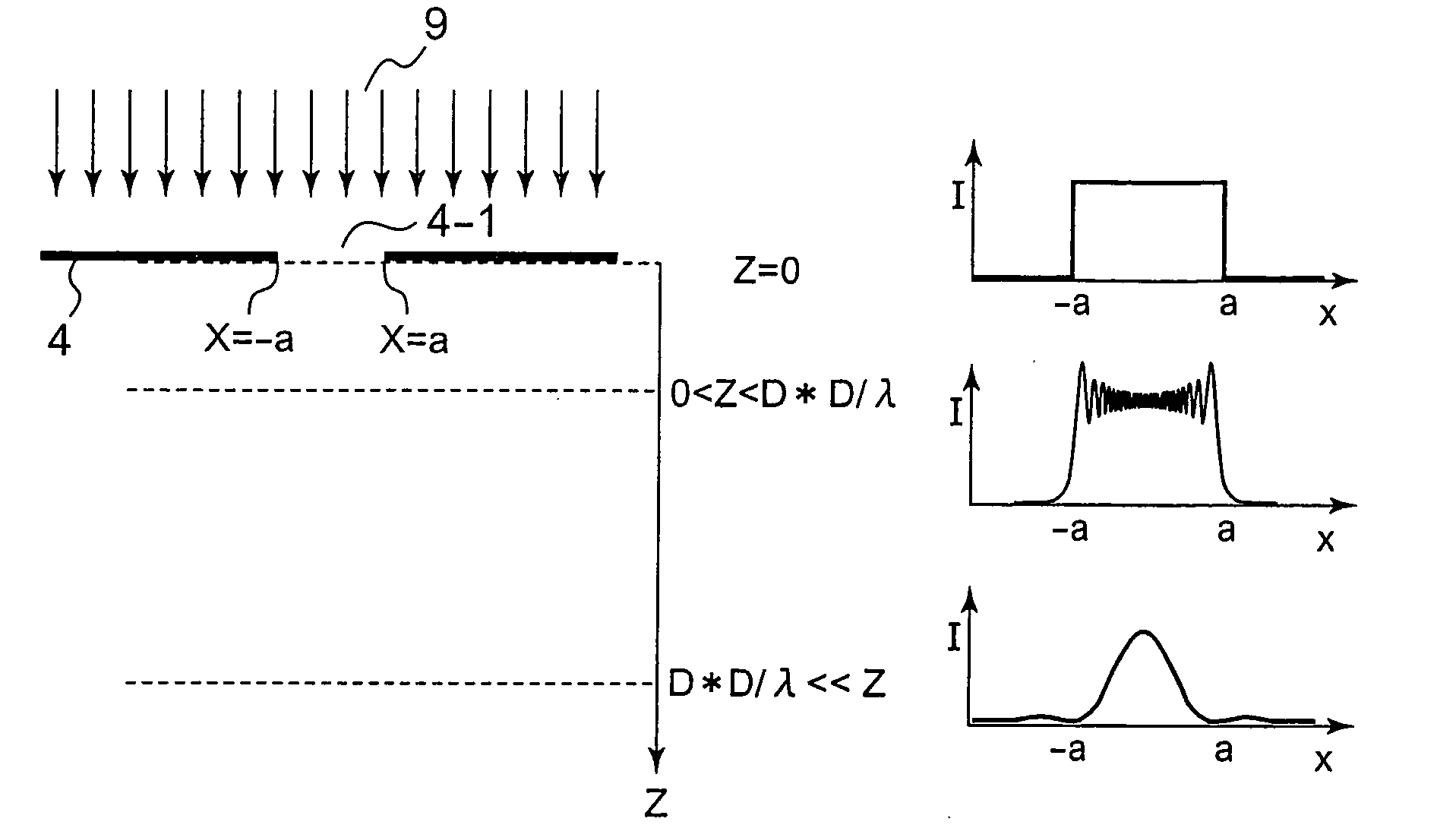
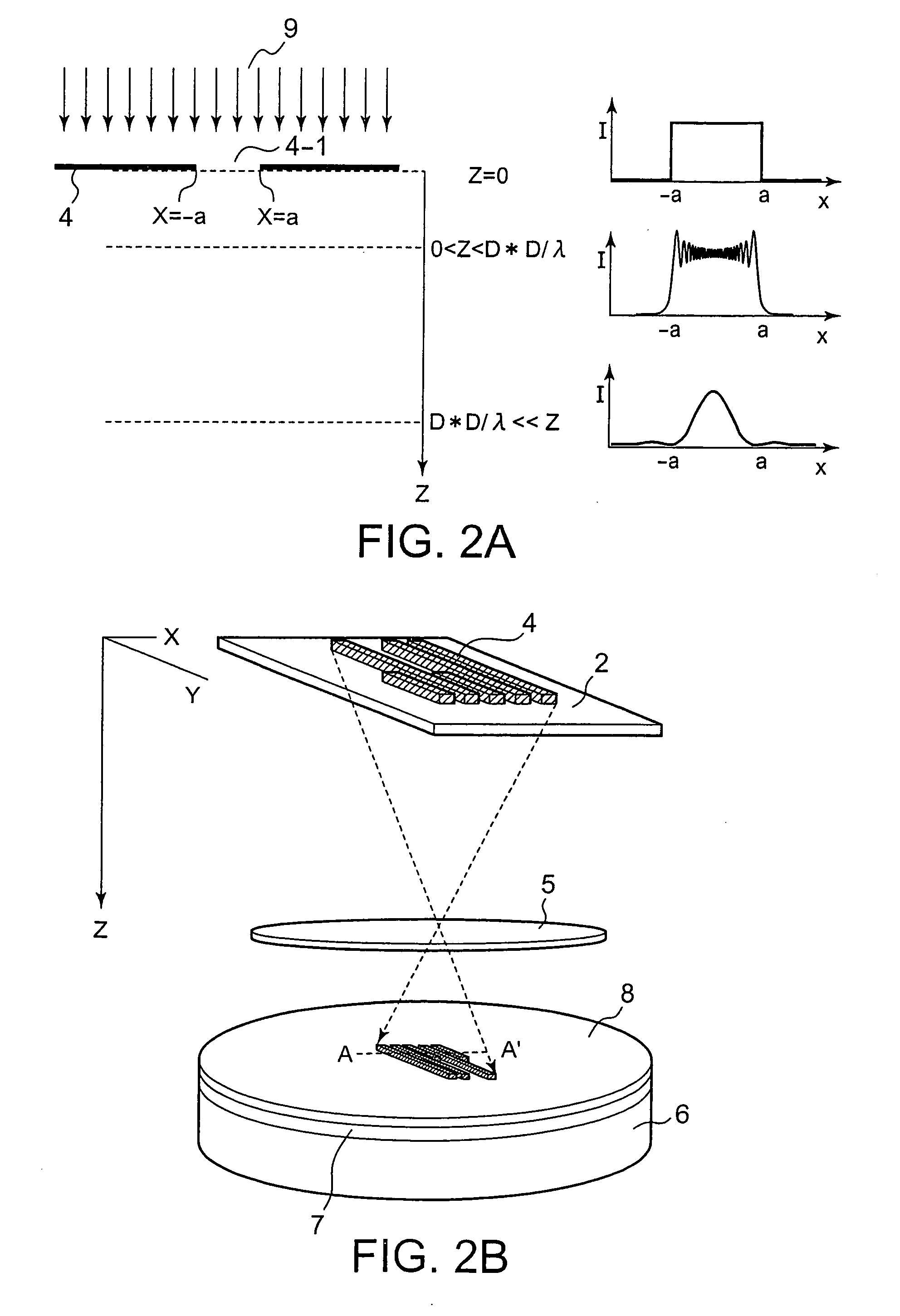
A method of forming a pattern according to the present invention comprising preparing a reduced projection exposure apparatus having a reduced projection ratio 1 / m and a wavelength λ (nm) of exposing light and patterning a light shielding element pattern of a reticle mask on a resist film having a thickness tr (nm). The light shielding element pattern has a pattern opening portion having a minimum opening dimension D (nm). A thickness t0 of the light shielding element pattern is set so as to meet a relational equation of m*tr≦t0+5*D*D / λ. Preferably, the thickness t0 of the light shielding element pattern is set so as to meet a relational equation of m*tr≦t0+D*D / λ.
Owner:ELPIDA MEMORY INC
Two-dimensional lattice calibrating device, two-dimensional lattice calibrating method, two-dimensional lattice calibrating program and recording medium
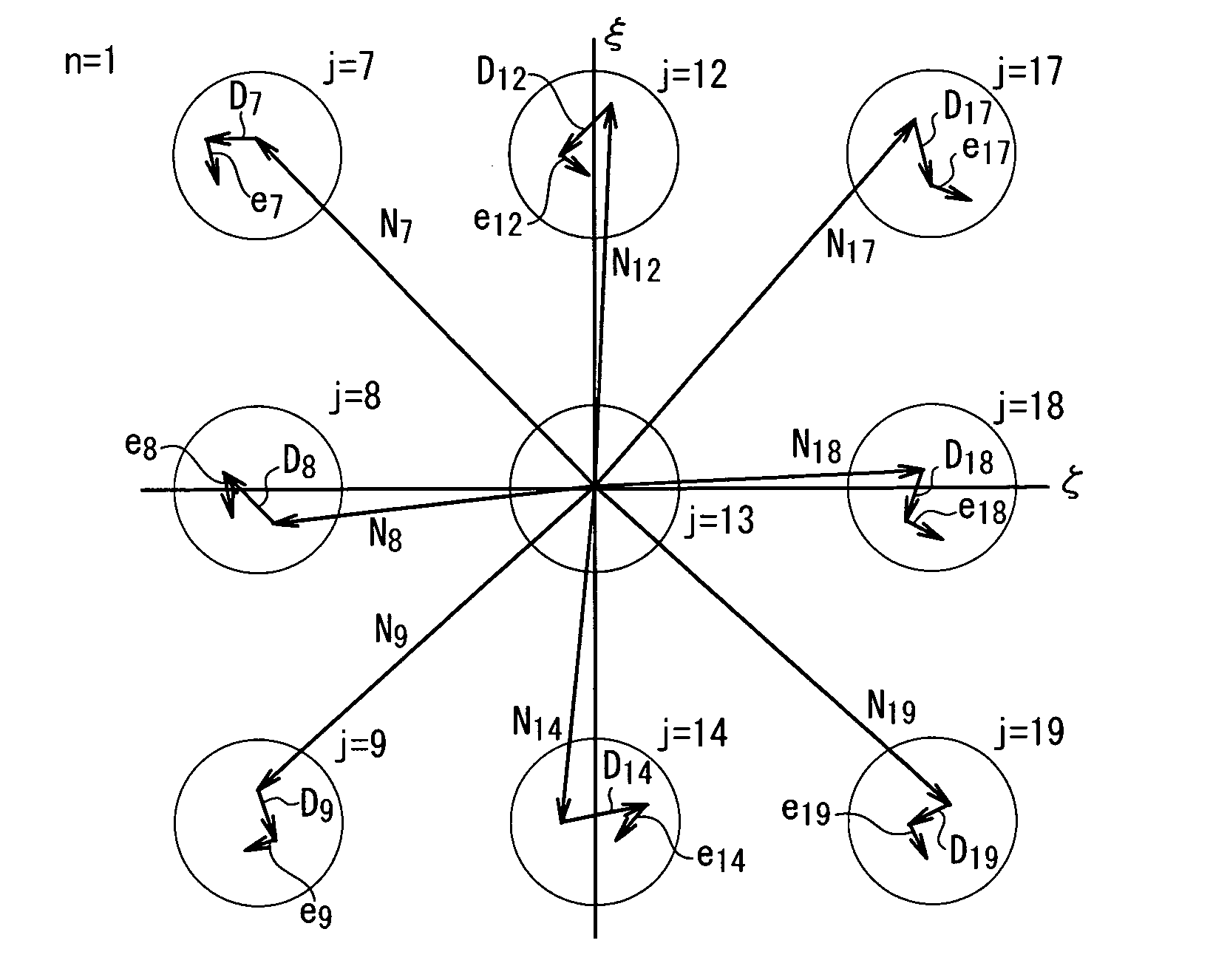
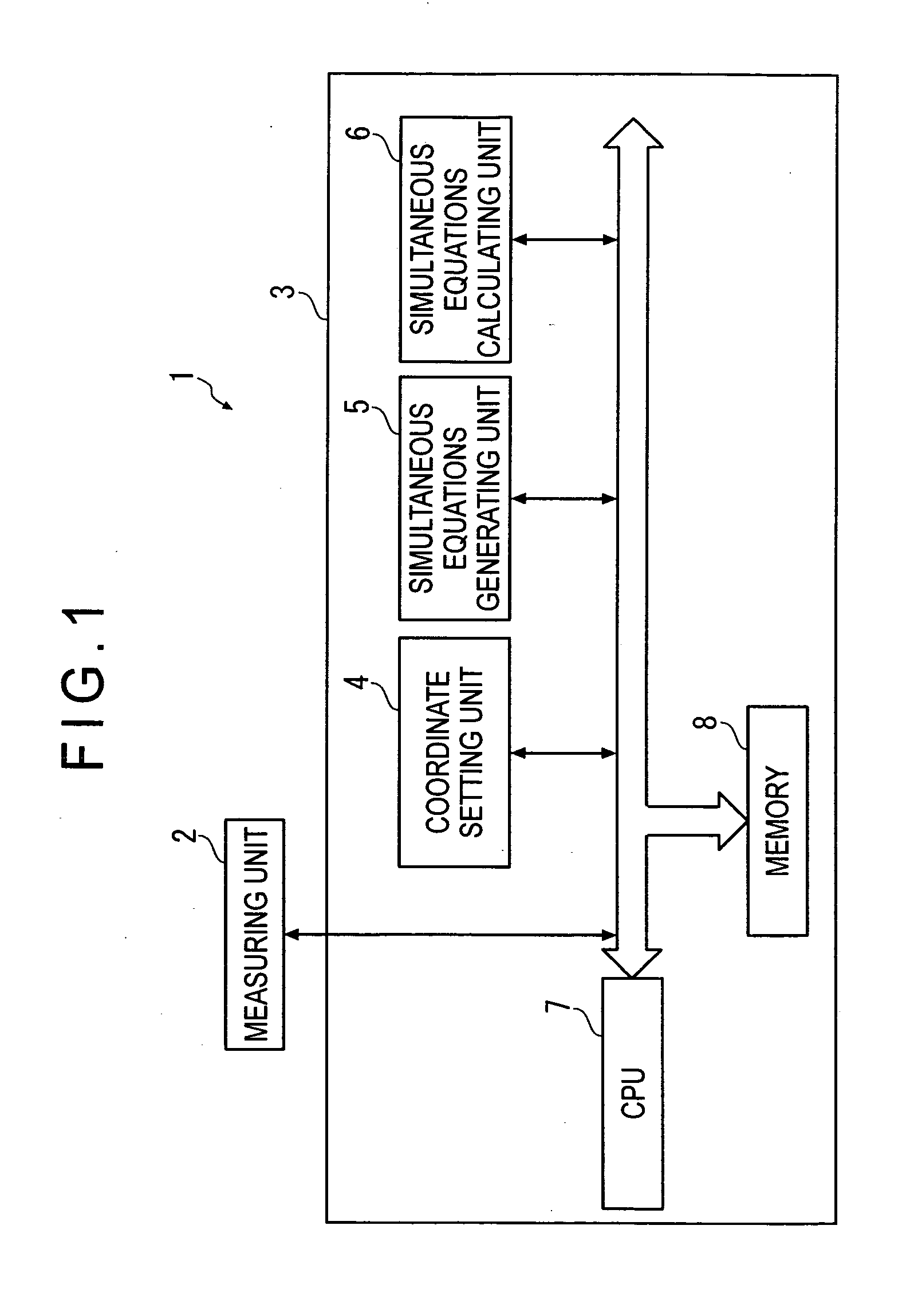
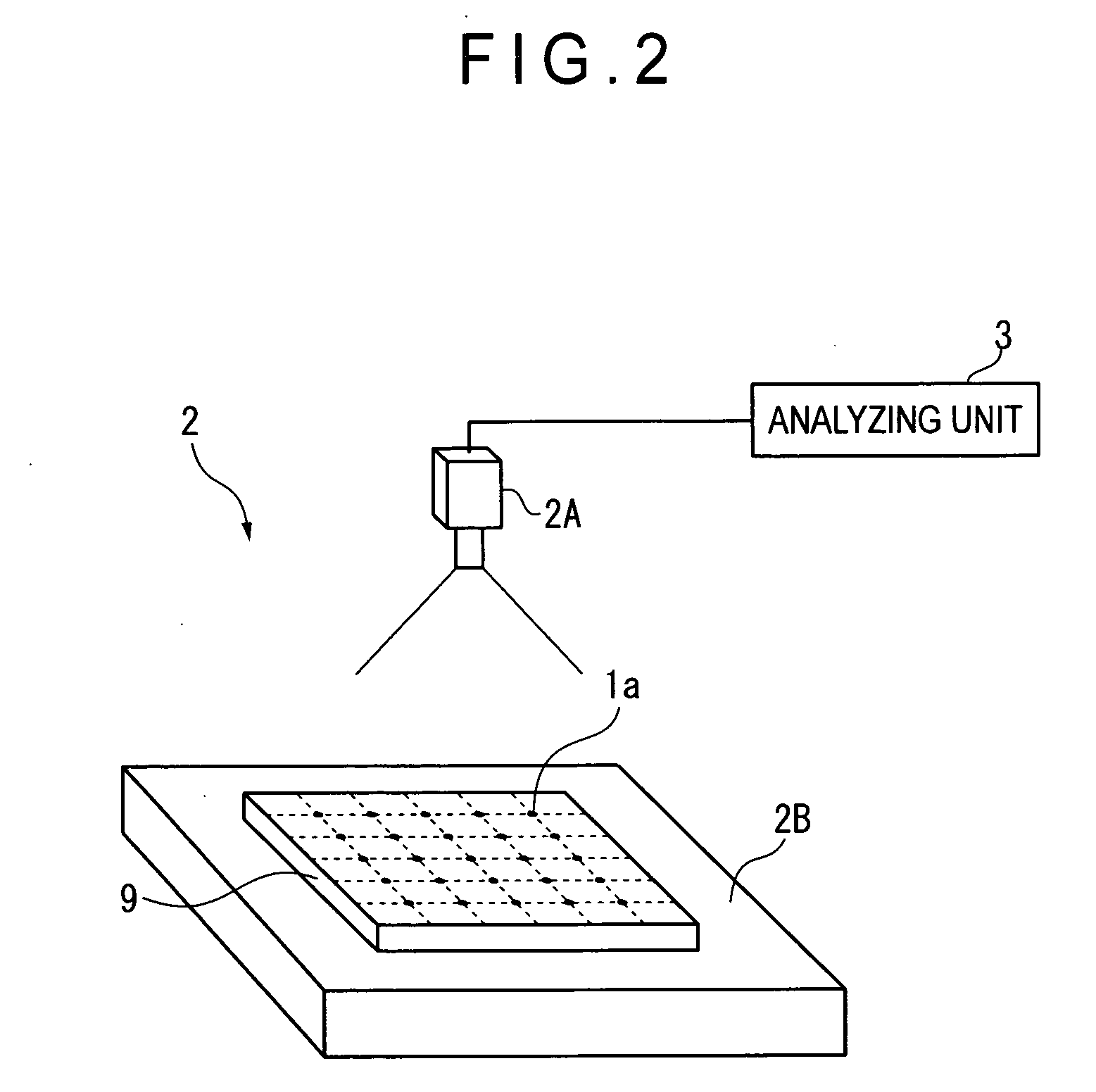
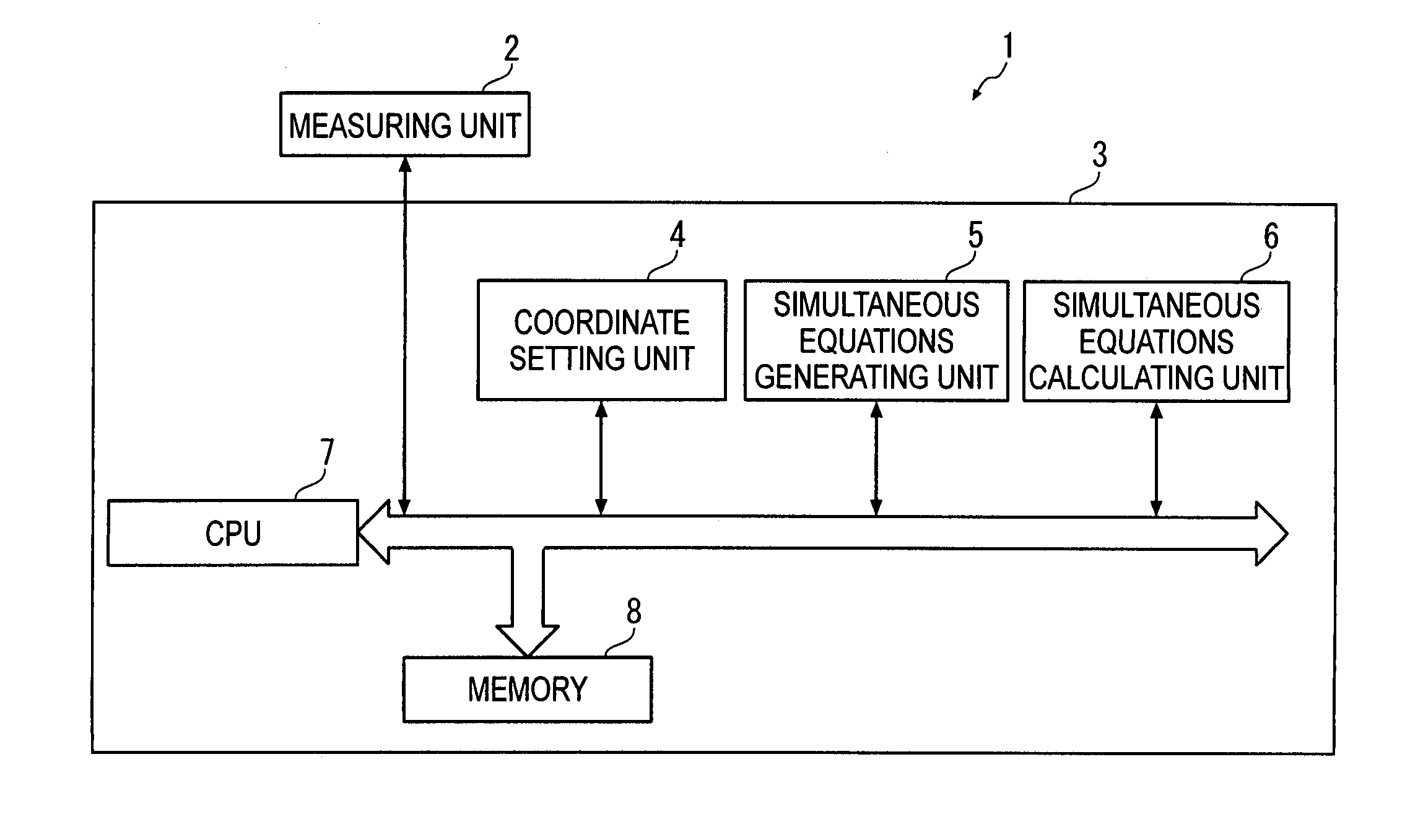
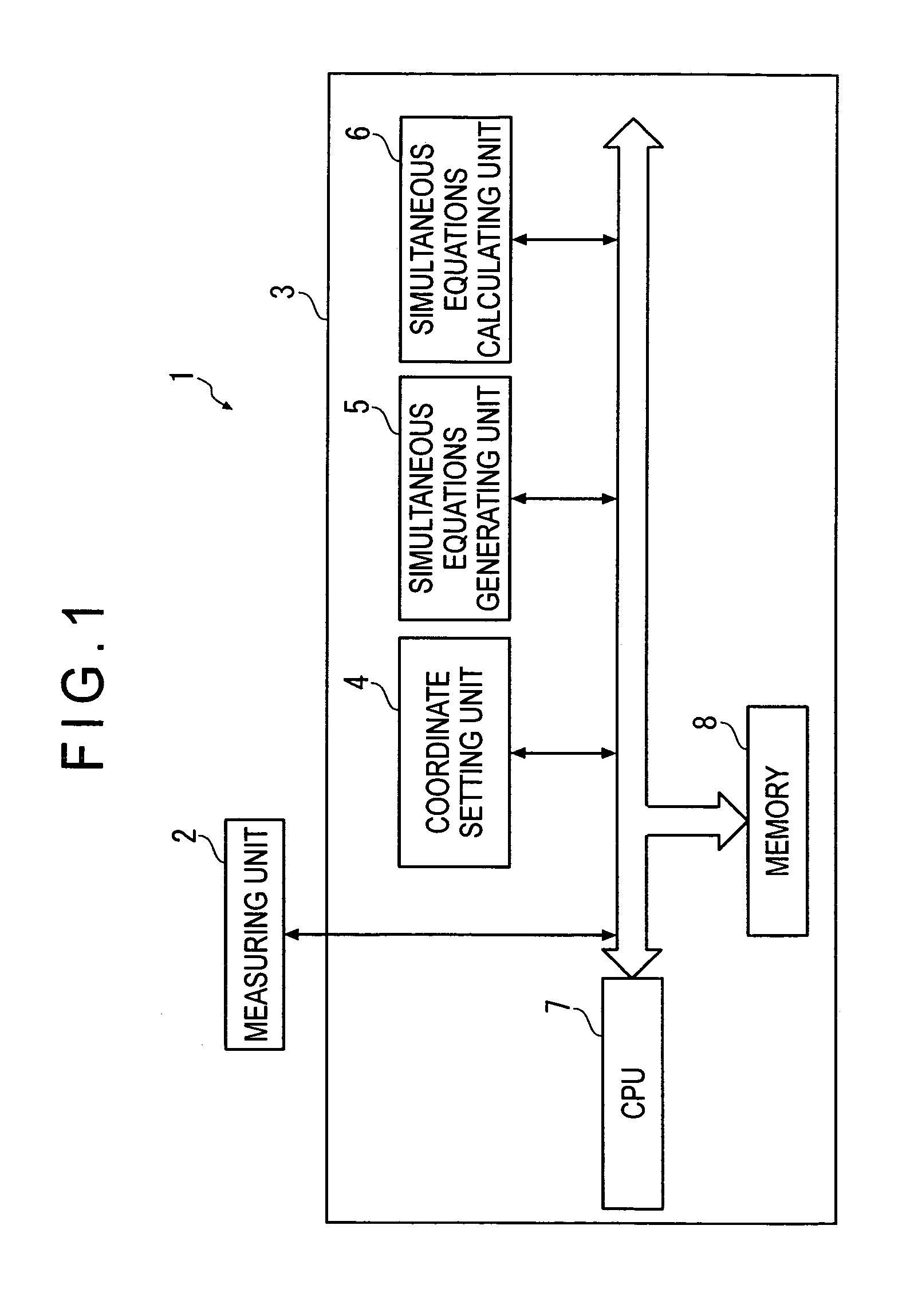
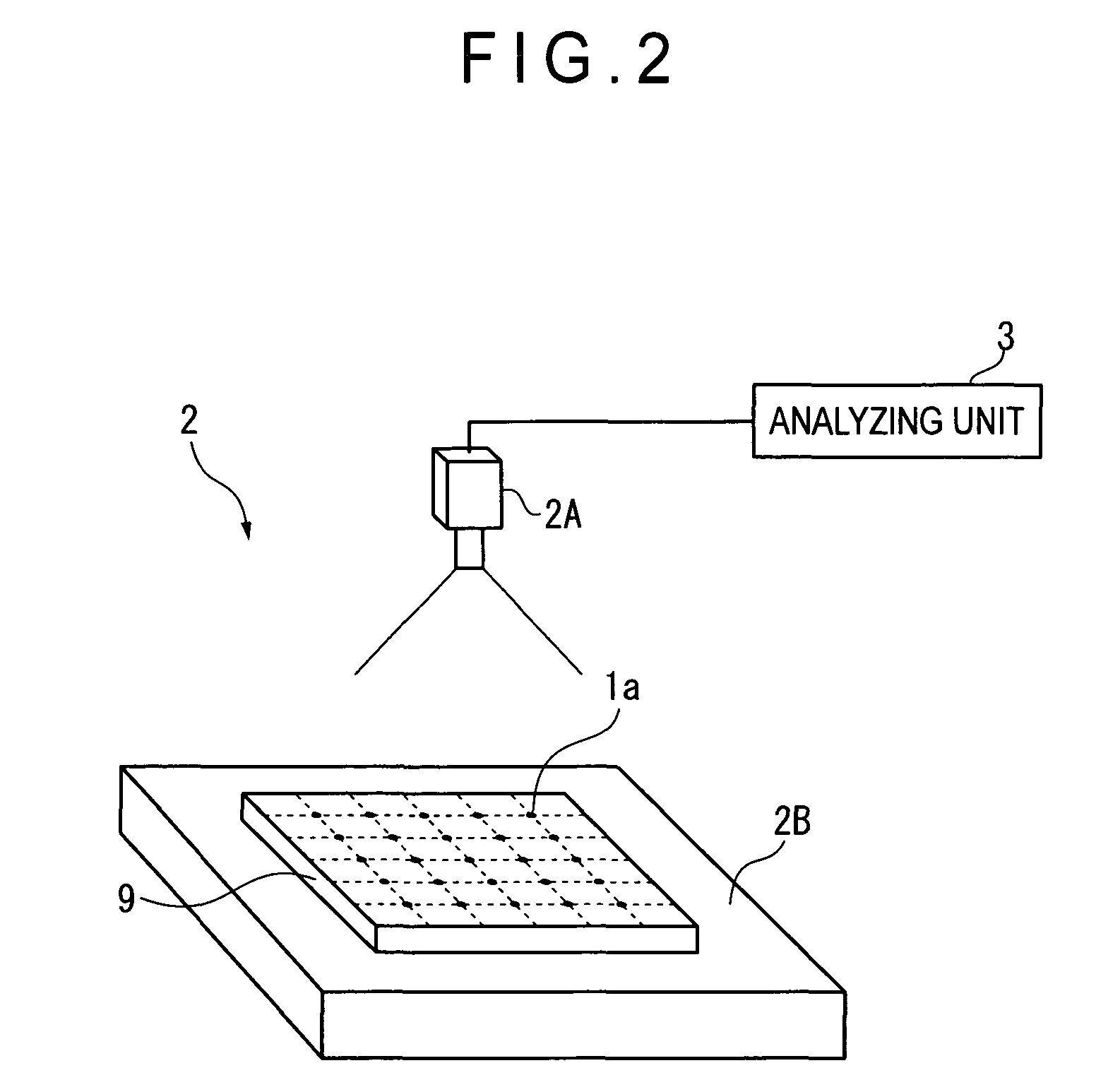
ActiveUS20080294364A1Accurate calculationImprove accuracyTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesSpecial data processing applicationsDot matrixSimultaneous equations
A two-dimensional lattice calibrating device includes: a measuring unit that measures respective positions of marks for each of a plurality of measurement dispositions; a simultaneous-equations generating unit that generates simultaneous equations for acquiring deviations of the plurality of marks using a coordinate relational equation and a least-squares conditional equation that sets least-squares lines that minimize the deviation of actual position of the marks based on measurement values as coordinate axes of artifact coordinates; and a simultaneous-equations calculating unit that solves the derived simultaneous equations.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Method of estimating dynamic elastic modulus of subgrade soil based on state variable and stress variable
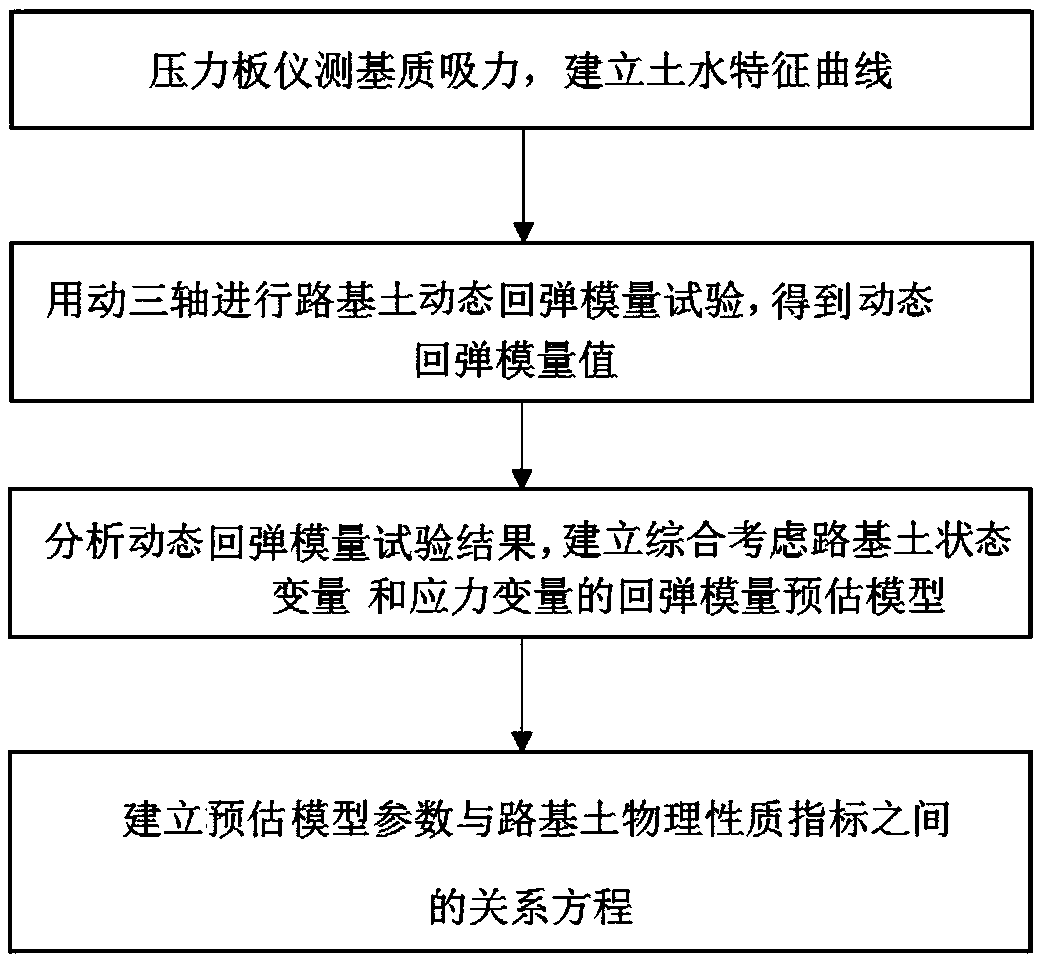
ActiveCN109142118ASolve incomplete problemsImprove accuracyInvestigating material hardnessState variableModel parameters
The invention discloses a method of estimating dynamic elastic modulus of subgrade soil based on state variable and stress variable. The method includes: using a pressure plate instrument to measure matrix suction of the subgrade soil, and establishing a soil-water characteristic curve to obtain model parameters under different compactness degrees; using a dynamic triaxial instrument to perform dynamic elastic modulus test of subgrade soil to obtain dynamic elastic modulus value of the subgrade soil; establishing a subgrade soil dynamic elastic modulus estimation model based on a state variable and a strain variable; establishing a relational equation between estimation model parameters and subgrade soil physical property indexes. The problem is solved that existing methods of estimating elastic modulus give no consideration to subgrade soil state variable, strain variable, and subgrade soil physical properties.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Chemically strengthened glass and production method for same
ActiveUS20170313620A1Improve glass strengthImprove surface strengthCoatingsHydrogen concentrationSurface layer
An object of the present invention is to provide a chemically strengthened glass having enhanced surface strength and bending strength. The present invention relates to a chemically strengthened glass having a compressive stress layer formed on a surface layer thereof by an ion exchange method, in which a straight line obtained by a linear approximation of a hydrogen concentration Y in a region of a depth X from an outermost surface of the glass satisfies a specific relational equation (I) in X=0.1 to 0.4 (μm), and an edge surface connecting main surfaces on a front side and a back side of the glass has a skewness (Rsk) measured based on JIS B0601 (2001) being −1.3 or more.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Electronic apparatus and method of controlling electronic apparatus
An electronic apparatus includes: a temperature measurement section that measures a temperature of a heat generation source generating heat by consuming power or a temperature of an inner position of a casing of which the temperature changes due to the heat generation of the heat generation source; and an environmental temperature calculation section that calculates a temperature which is calculated using a predetermined relational equation that is different in accordance with a model from a difference between a first temperature measured by the temperature measurement section at a point in time when the heat generation source starts consuming a predetermined amount of power and a second temperature measured by the temperature measurement section at a point in time after the passage of a predetermined period from the start of consumption of a predetermined amount of power by the heat generation source as an environmental temperature in an environment where the casing is placed.
Owner:SONY CORP
Two-dimensional lattice calibrating device, two-dimensional lattice calibrating method, two-dimensional lattice calibrating program and recording medium
ActiveUS7765079B2Accurate calculationImprove accuracyTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesSpecial data processing applicationsSimultaneous equationsRelational equation
A two-dimensional lattice calibrating device includes: a measuring unit that measures respective positions of marks for each of a plurality of measurement dispositions; a simultaneous-equations generating unit that generates simultaneous equations for acquiring deviations of the plurality of marks using a coordinate relational equation and a least-squares conditional equation that sets least-squares lines that minimize the deviation of actual position of the marks based on measurement values as coordinate axes of artifact coordinates; and a simultaneous-equations calculating unit that solves the derived simultaneous equations.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
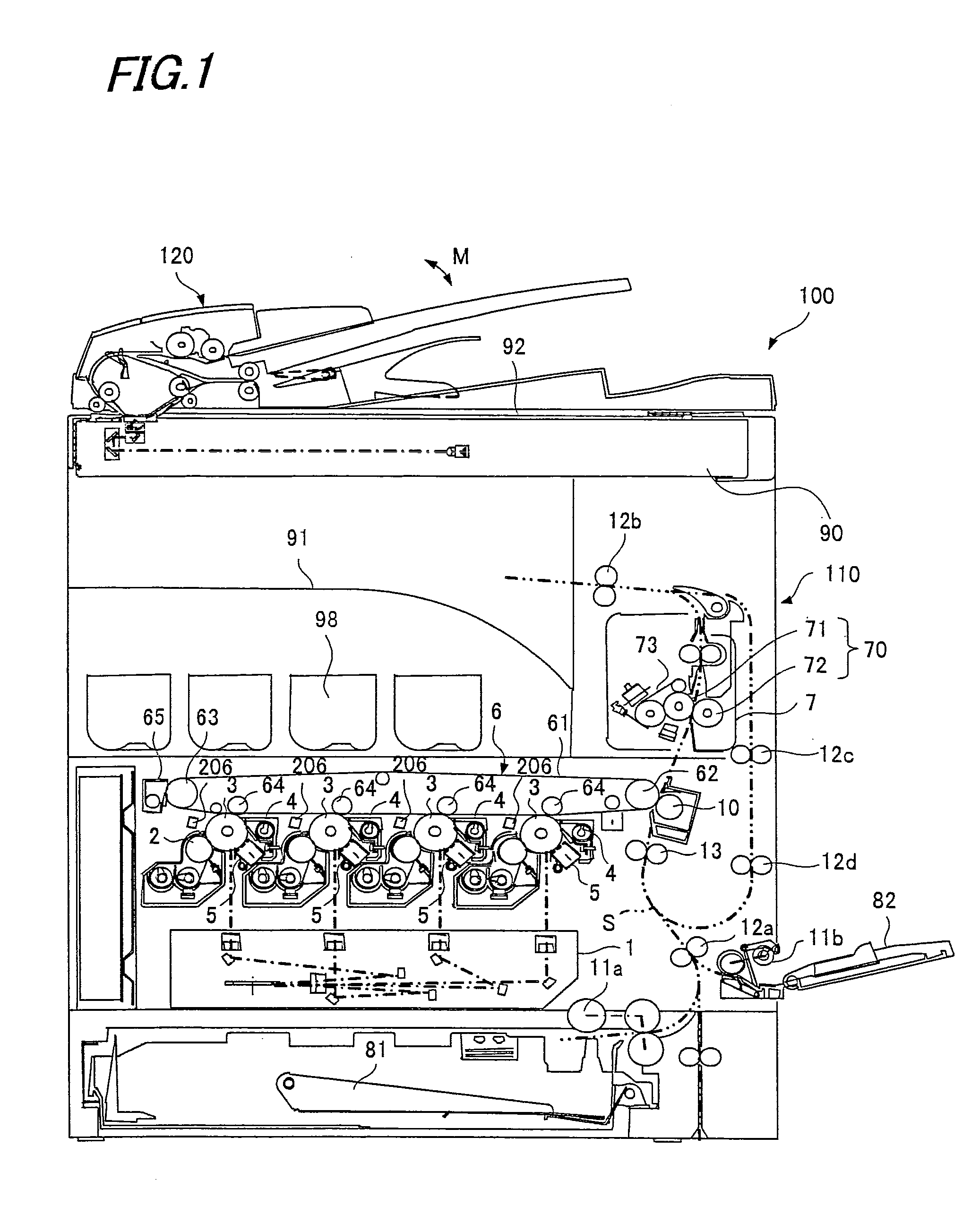
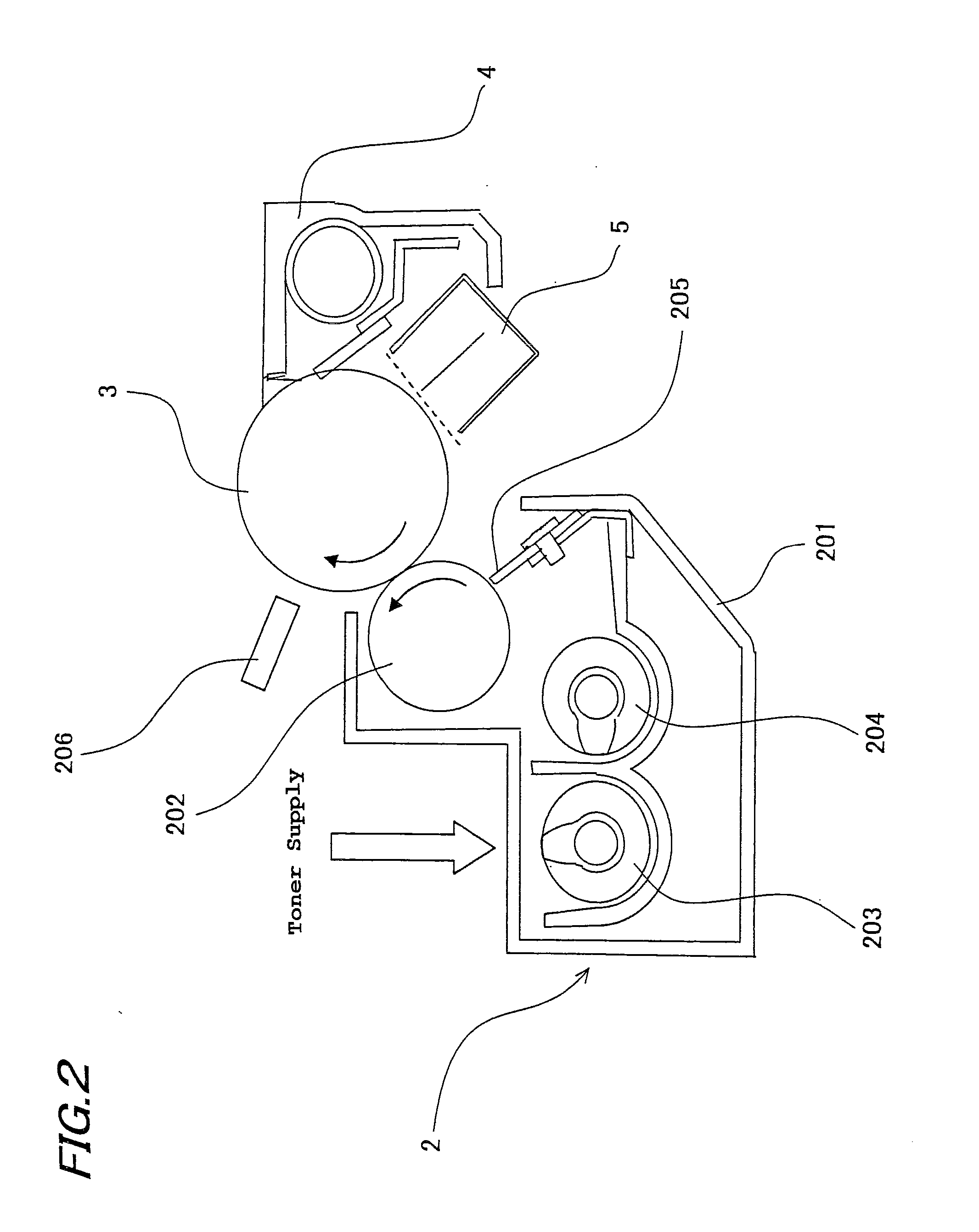
Image forming apparatus, image density control method, control program and recording medium
InactiveUS20110182604A1Improve accuracyEfficient implementationElectrographic process apparatusPictoral communicationHigh densityImage formation
An image forming apparatus includes: a developing unit forming a toner image on a photoreceptor drum; a photo sensor detecting the image density of the toner image; an operation unit calculating a relational equation between the measurement detected by the photo sensor and the development potential; a storage unit storing the relational equation; and a control unit setting up a corrected development potential to obtain a target image density for the developing unit, based on the image density of toner image patches. When high-density correction is performed, the control unit forms a multiple number of toner image patches on the photoreceptor drum based on the corrected development potential that was obtained at the time of the previous high-density correction, and sets up a corrected development potential for obtaining the target image density, based on the multiple image densities of the multiple toner image patches.
Owner:SHARP KK
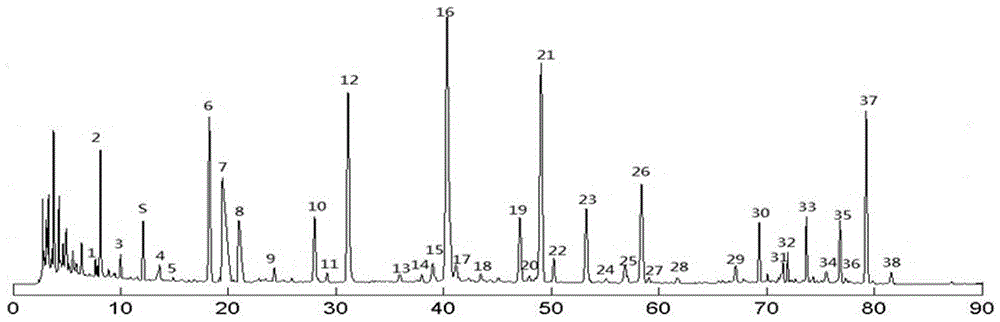
Quality control method of gastrointestinal motility promoting power of qi-stagnation and stomachache granules based on dose-effect color card
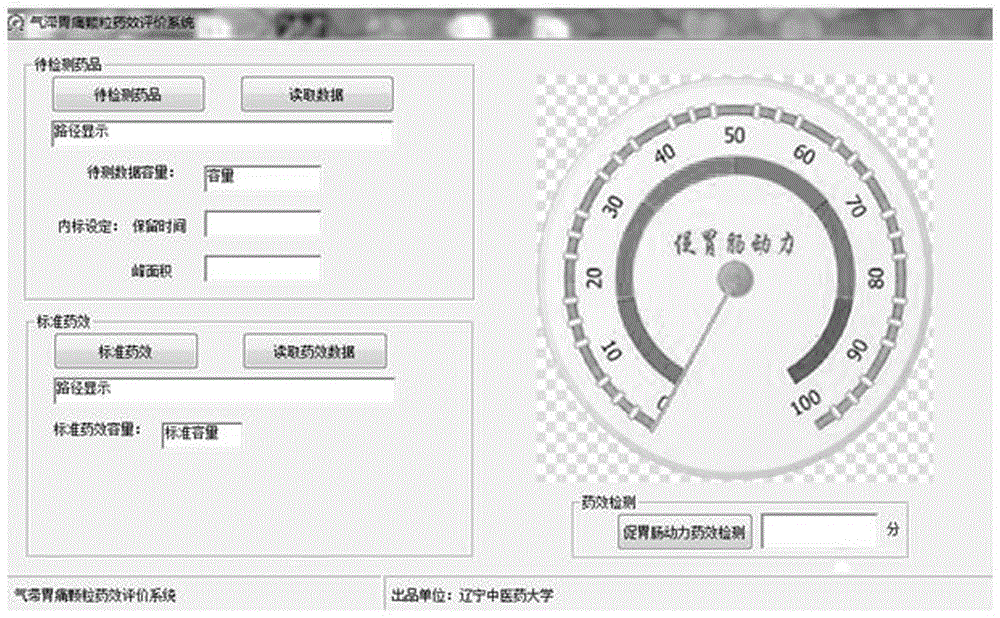
ActiveCN105758949AQuality improvementRealize "visual" predictionComponent separationMedicineMotility
The invention provides a quality control method of gastrointestinal motility promoting power of qi-stagnation and stomachache granules based on a dose-effect color card. The quality control method comprises the following steps of: establishing a qi-stagnation and stomachache granule fingerprint spectrum and evaluating the acting drug effect of the gastrointestinal motility promoting power of the qi-stagnation and stomachache granules; and evaluating the relevance of the mass of the qi-stagnation and stomachache granules and the drug effect and establishing a dose-effect relational equation, so as to successfully construct an acting dose-effect color card of the gastrointestinal motility promoting power of the qi-stagnation and stomachache granules. Therefore, a gastrointestinal motility promoting power drug effect can be directly reflected in a color card manner through detecting a specific component relative peak area in the qi-stagnation and stomachache granule; the quality control method can be used for evaluating the acting degree and quality of expressing the gastrointestinal motility promoting power of the qi-stagnation and stomachache granules.
Owner:辽宁华润本溪三药有限公司
Method and device for solving static thermoelasticity problem of isotropic solid material
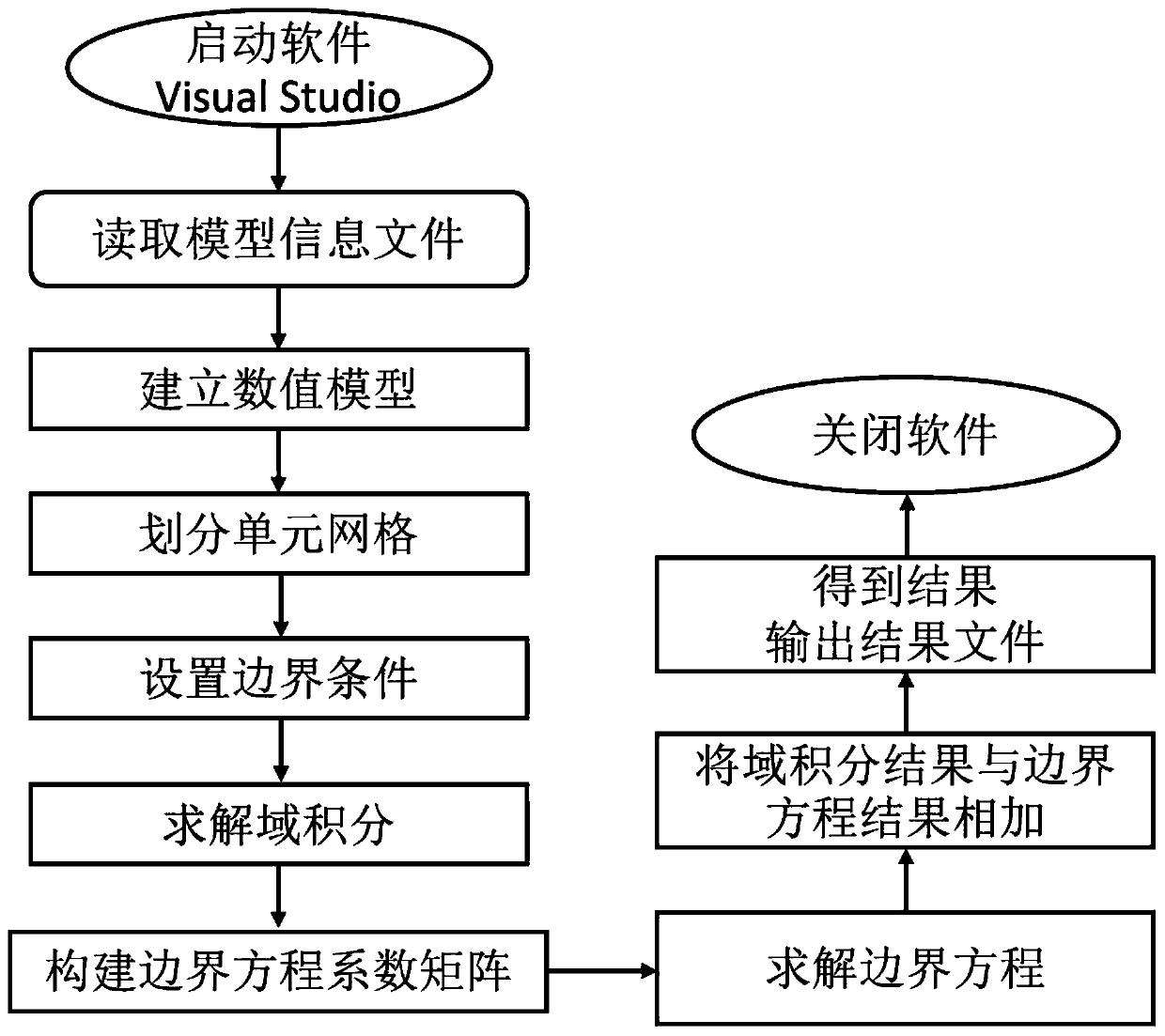
ActiveCN110705057AImprove accuracyImprove effectivenessDesign optimisation/simulationElastomerTypes of mesh
The invention provides a method and device for solving a static thermoelasticity problem of an isotropic solid material. The method comprises the steps of establishing a numerical model of a to-be-solved structure based on material parameters, gridding scores, grid types and boundary condition information of the actual to-be-solved structure, and adding the material parameters and the boundary condition information to nodes on each unit of the numerical model; establishing strain and stress equations including a relation equation between the total strain and stress of the isotropic elastomer material and a stress equation; further, establishing a displacement integral equation; establishing an internal stress integral equation; converting domain integrals in the displacement integral equation and the internal stress integral equation into boundary integrals; establishing a solving matrix throughout the integral equation, and performing discretization and integration to obtain a matrixequation; and then, obtaining change data of the boundary and the internal point of the model by utilizing a Gaussian elimination solution method, and taking the change data as change data of the boundary and the internal point of the to-be-solved structure.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Chemically strengthened glass and production method for chemically strengthened glass
ActiveUS20170313621A1Improve surface strengthHigh light transmittanceNon-linear opticsHydrogen concentrationSurface layer
An object of the present invention is to provide a chemically strengthened glass that can effectively suppress strength of a glass from being deteriorated even though performing chemical strengthening and has high transmittance (that is, low reflectivity). The present invention relates to a chemically strengthened glass having a compressive stress layer formed on a surface layer thereof by an ion exchange method, in which the glass contains sodium and boron, and has a delta transmittance being +0.1% or more, and in which a straight line obtained by a linear approximation of a hydrogen concentration Y in a region of a depth X from an outermost surface of the glass satisfies a specific relational equation in X=0.1 to 0.4 (μm).
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
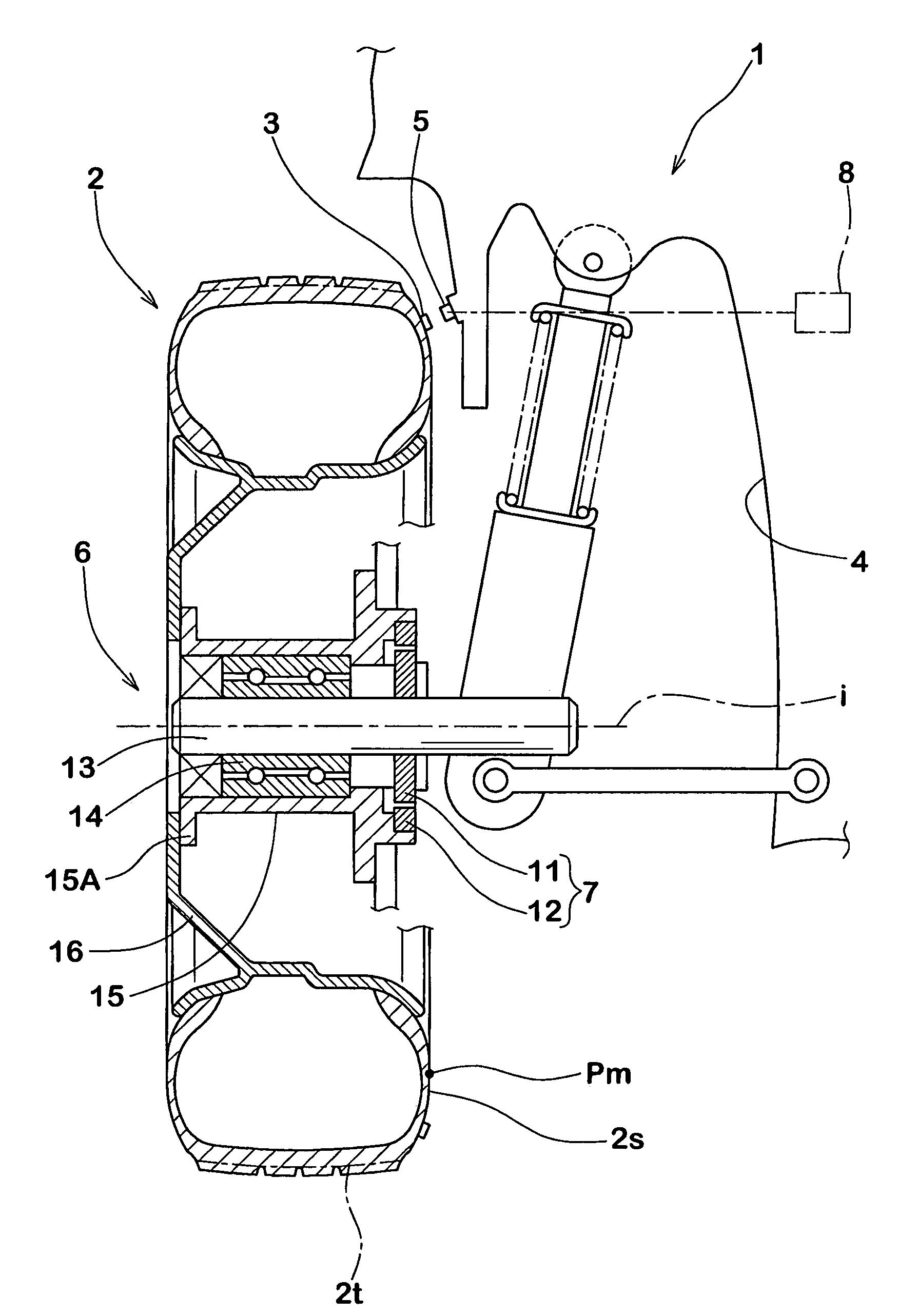
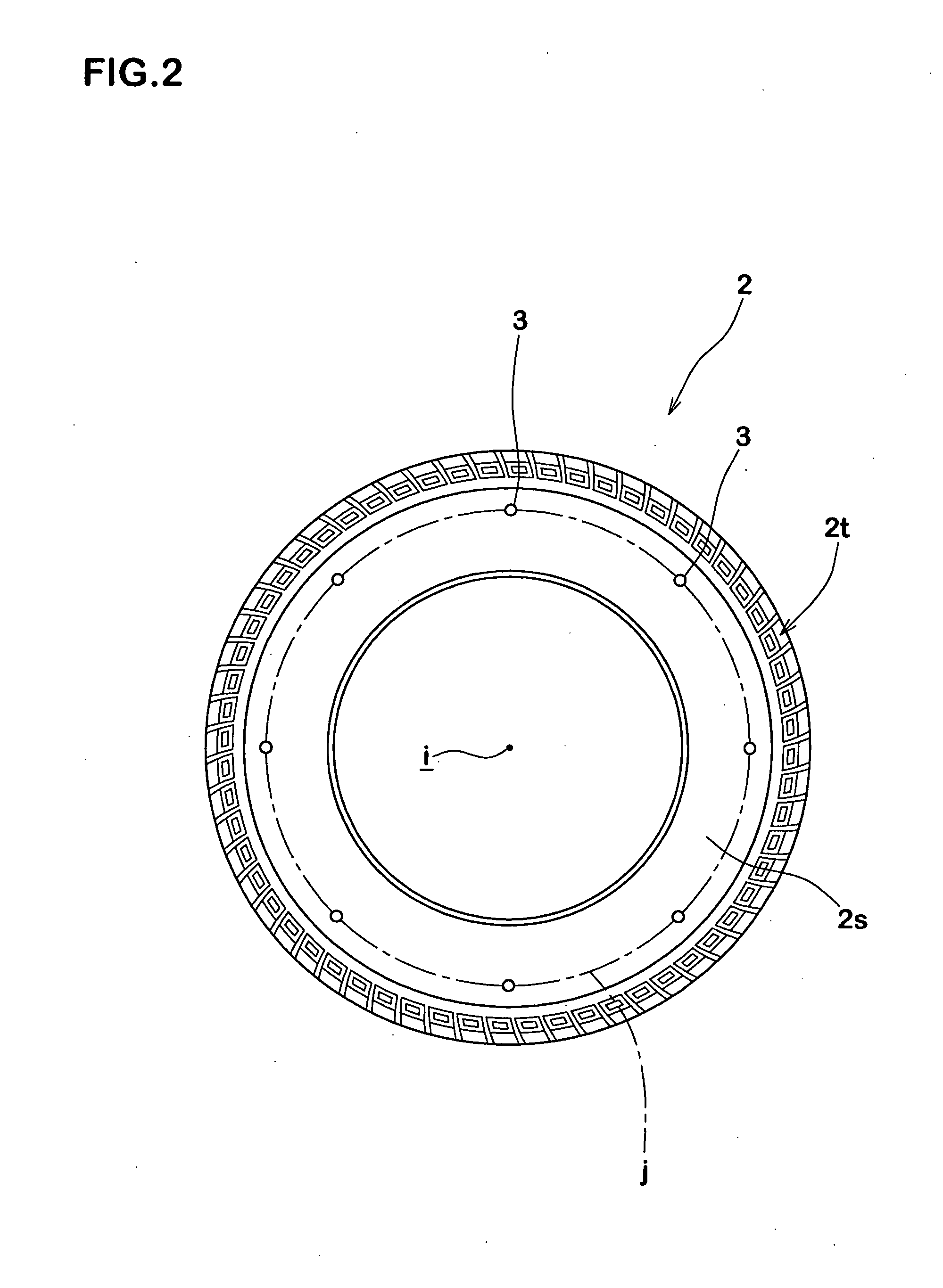
Method of detecting longitudinal force of tire and longitudinal force detecting apparatus used therein
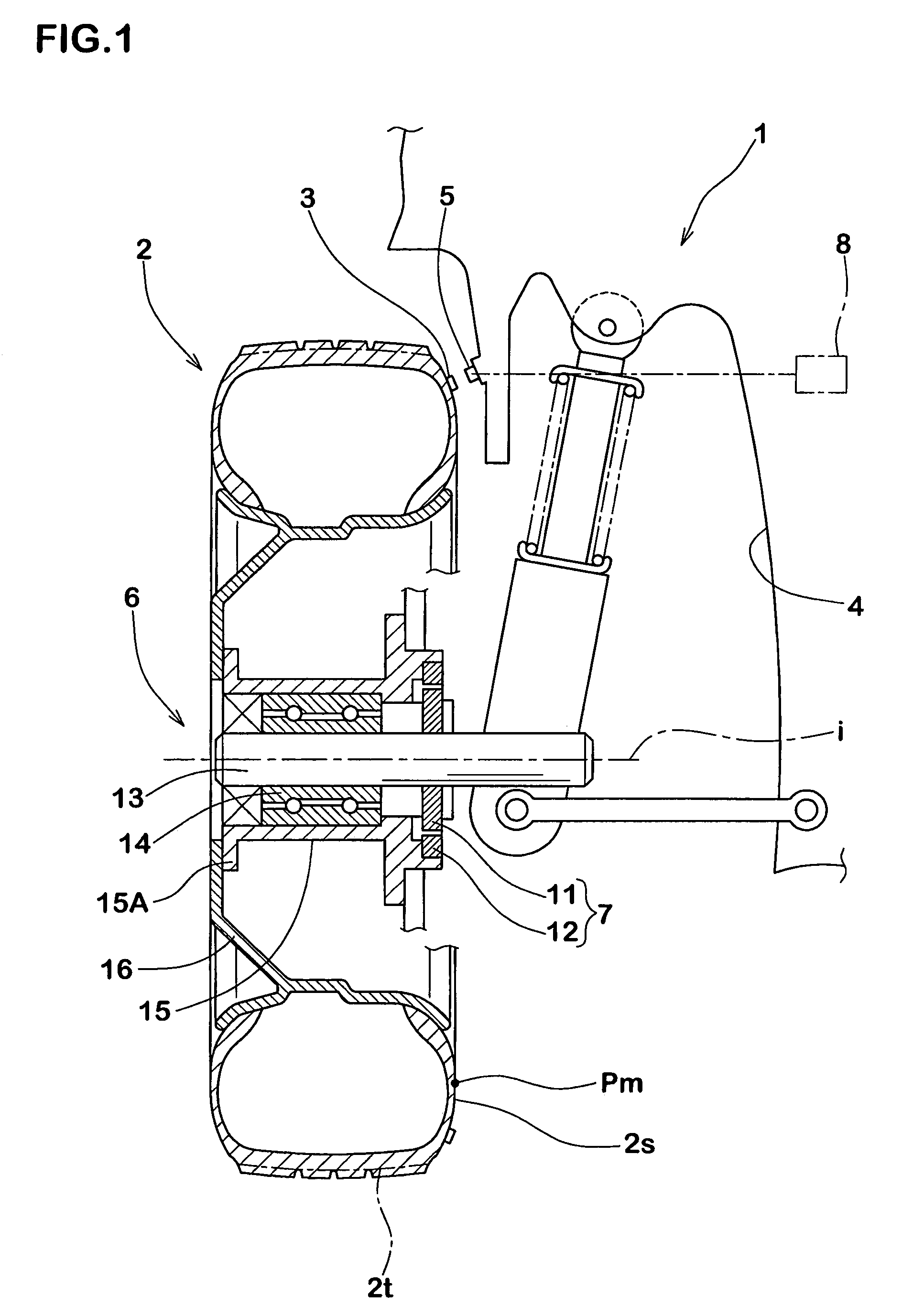
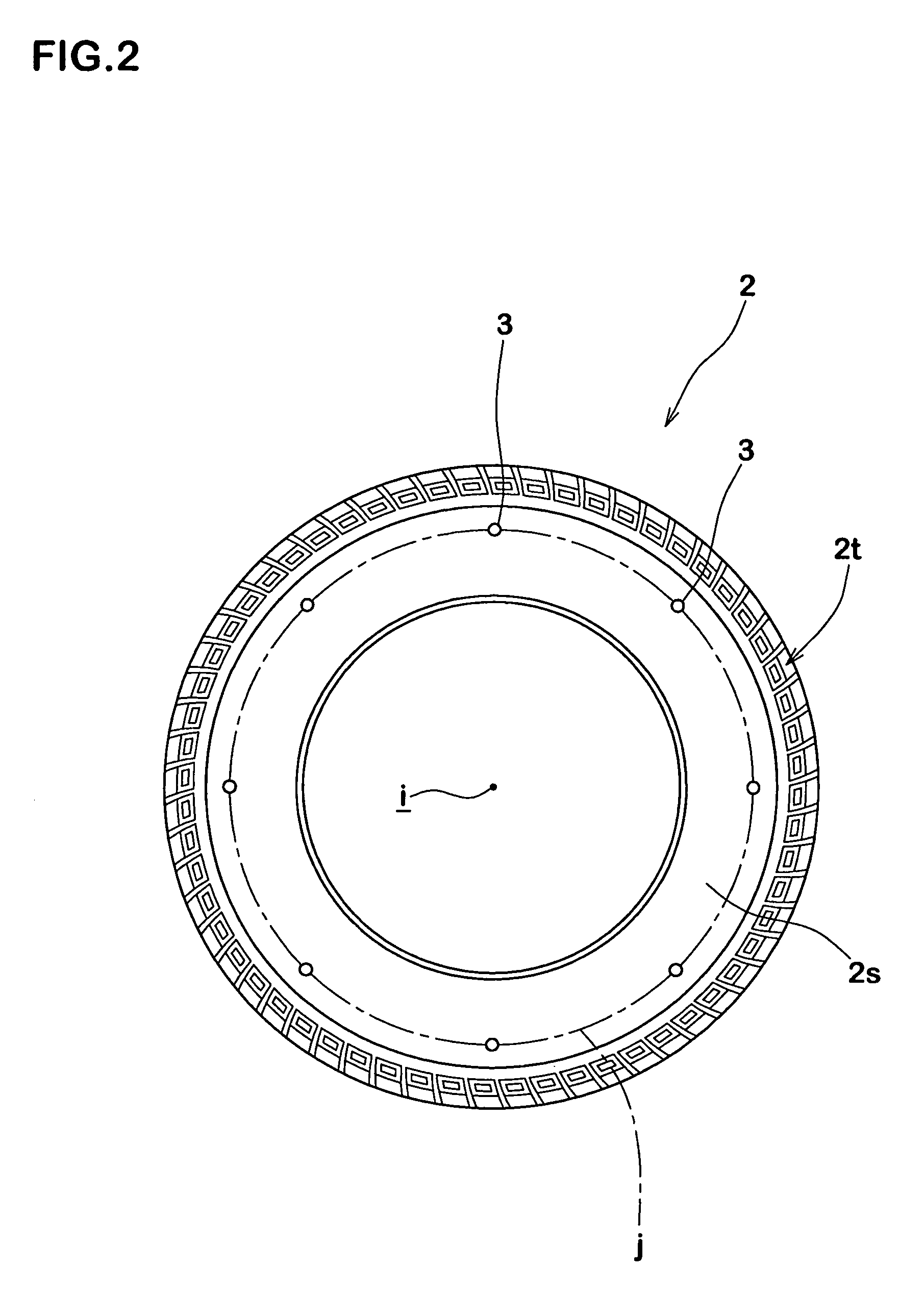
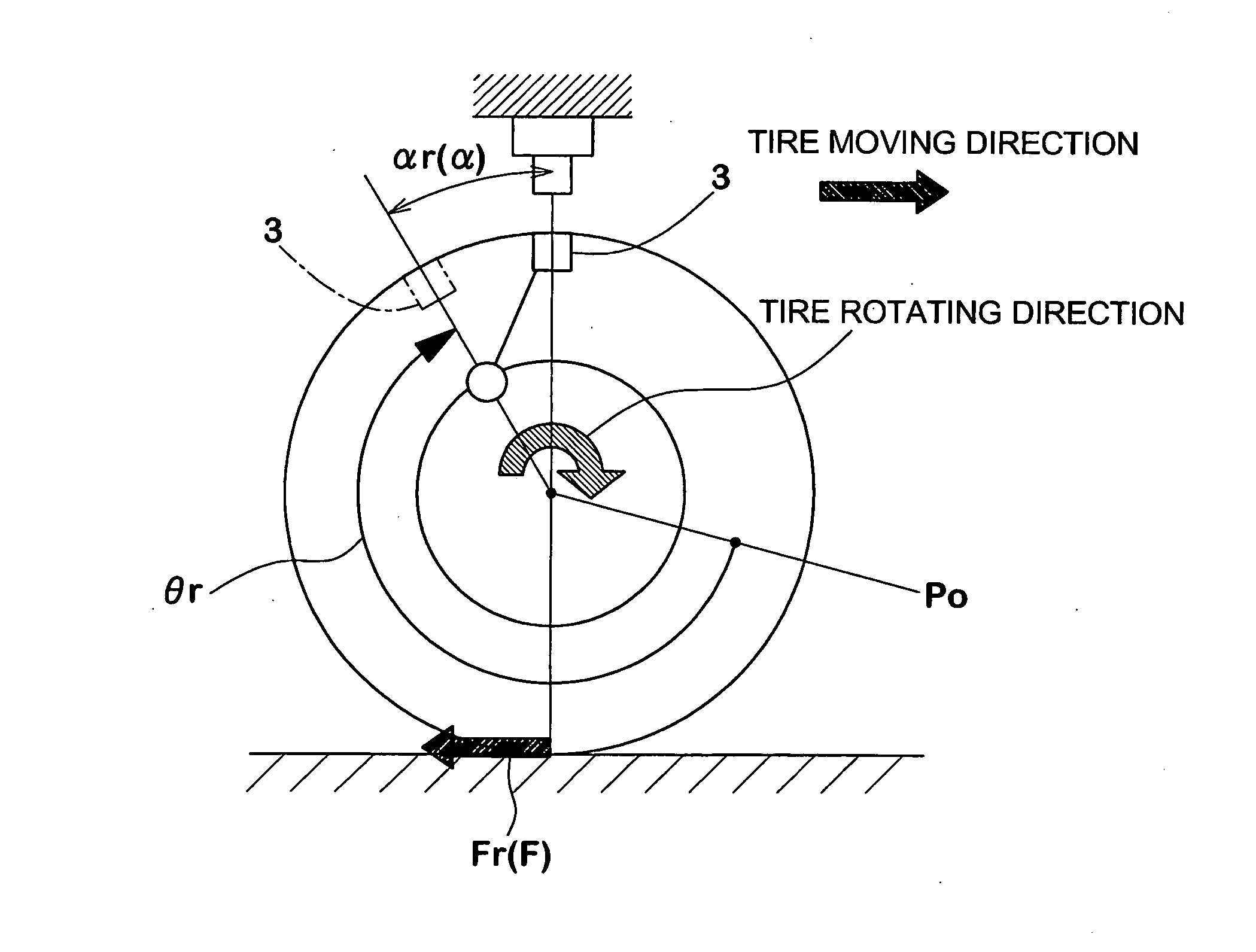
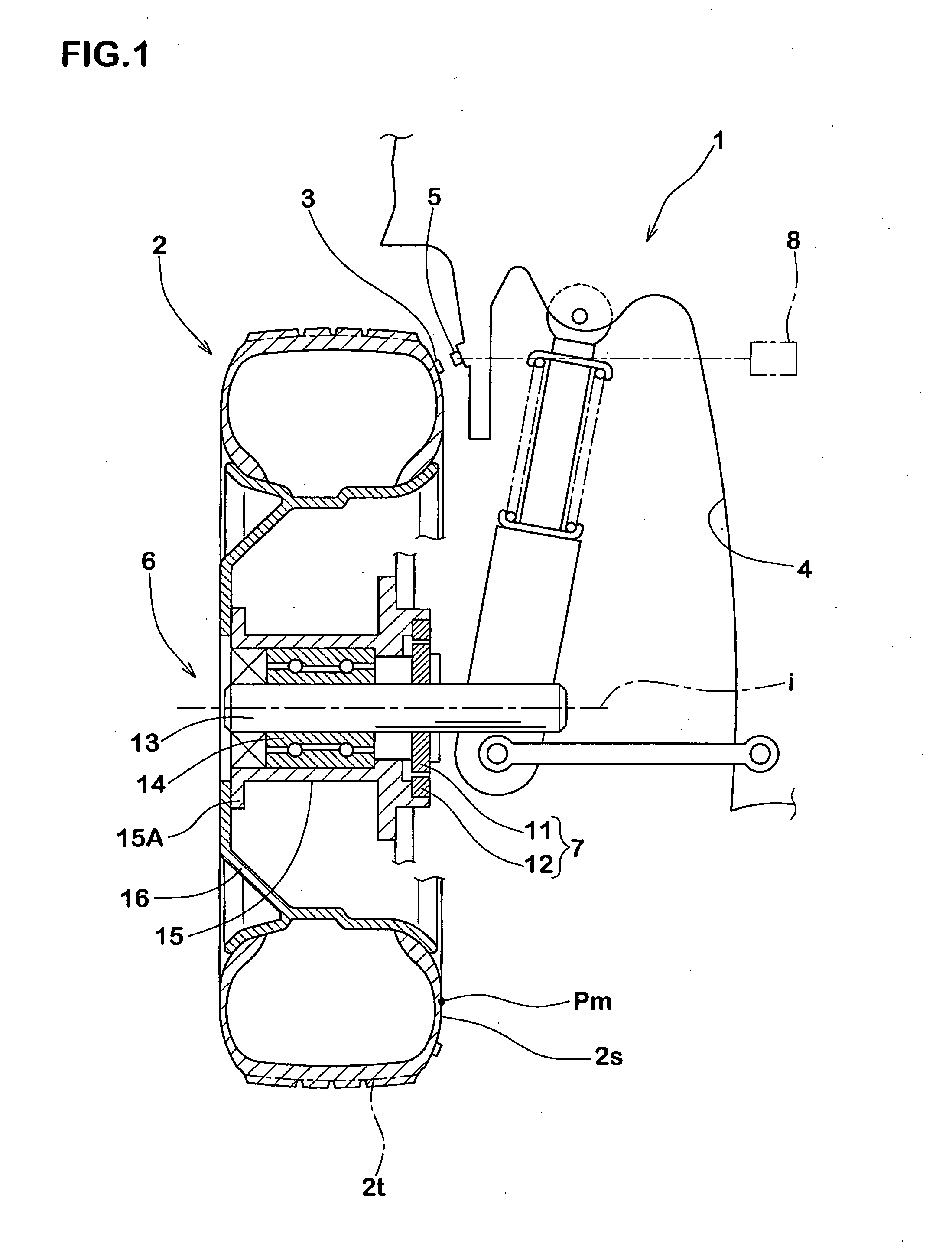
InactiveUS7257997B2Simple to executeGood precisionUsing mechanical meansTyre measurementsEngineeringRelational equation
An apparatus for detecting a longitudinal force of a tire is provided with at least one mark (3) provided in on one circumferential line (j) in a tire (2), a first sensor (5) disposed in a vehicle body side (4) and capable of detecting a passage of the mark (3), a second sensor (7) capable of detecting a rotation angle (θ) of an axle (6), and a computing device (8) for computing a longitudinal force (Fr) of the tire (2) on the basis of an information of the first and second sensors (5, 7). The computing device (8) sequentially stores a rotation angle (θr) of the axle (6) when the mark (3) passes through the first sensor (5). Further, the computing device (8) computes a tire warp angle (αr) corresponding to a difference (θo−θr) between a no-load rotation angle θo (a rotation angle of the axle (6) in a no-load state) stored in advance and the rotation angle θr, and sequentially computes a tire longitudinal force (Fr) of a tire applied during the running from the warp angle (αr), using a previously determined relational equation F=f(α) between the warp angle (α) and the tire longitudinal force (F).
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD +1
Method of detecting longitudinal force of tire and longitudinal force detecting apparatus used therein
InactiveUS20060219000A1Simple to executeGood precisionUsing mechanical meansTyre measurementsEngineeringRelational equation
An apparatus for detecting a longitudinal force of a tire is provided with at least one mark (3) provided in on one circumferential line (j) in a tire (2), a first sensor (5) disposed in a vehicle body side (4) and capable of detecting a passage of the mark (3), a second sensor (7) capable of detecting a rotation angle (θ) of an axle (6), and a computing means (8) for computing a longitudinal force (Fr) of the tire (2) on the basis of an information of the first and second sensors (5, 7). The computing means (8) sequentially stores a rotation angle (θr) of the axle (6) when the mark (3) passes through the first sensor (5). Further, the computing means (8) computes a tire warp angle (ar) corresponding to a difference (θo−θr) between a no-load rotation angle θo (a rotation angle of the axle (6) in a no-load state) stored in advance and the rotation angle θr, and sequentially computes a tire longitudinal force (Fr) of a tire applied during the running from the warp angle (αr), using a previously determined relational equation F=f(α) between the warp angle (α) and the tire longitudinal force (F).
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com