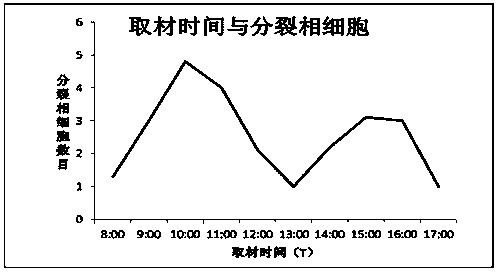
Method for quickly identifying chromosome number of rosa plant
A technology of chromosome number and rose genus, which is applied in the field of plant cell biology and cytogenetics, can solve the problems of limited number of mitotic cells, difficulty in seed germination, inability to count, etc., to achieve accurate size and position of the sample, and shorten the pretreatment time , Time is easy to control the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] The diploid young flower buds of R. chinensis 'Old Pink Daily'. are used as materials.
[0076] A. At 9:00 in the morning, take the tops of the branches in the flowering stage cultivated in the open field, and the young flower buds with a round and compact external shape, and quickly strip the materials with a height of about 2.0mm under the stereoscope.
[0077] B. Use p-dichlorobenzene at 25°C for 3 hours. The top of the young flower buds is the unexpanded sepal, which is densely covered with fluff. Before processing, use a scalpel to cut off the top 0.5mm under the stereoscope, put it into 20ml of saturated p-dichlorobenzene solution, and use a needle The syringe was vacuumed until the material sank to the bottom of the pretreatment solution, and then washed 5 times with deionized water.
[0078] C. Use Carnot's fixative solution to fix in an ice box for 5 hours, and then wash with deionized water for 5 times.
[0079] D. Dissociate with 1M hydrochloric acid at 60°...
Embodiment 2
[0084] The stem tip of diploid R. chinensis 'Old Pink Daily'. is used as the material.
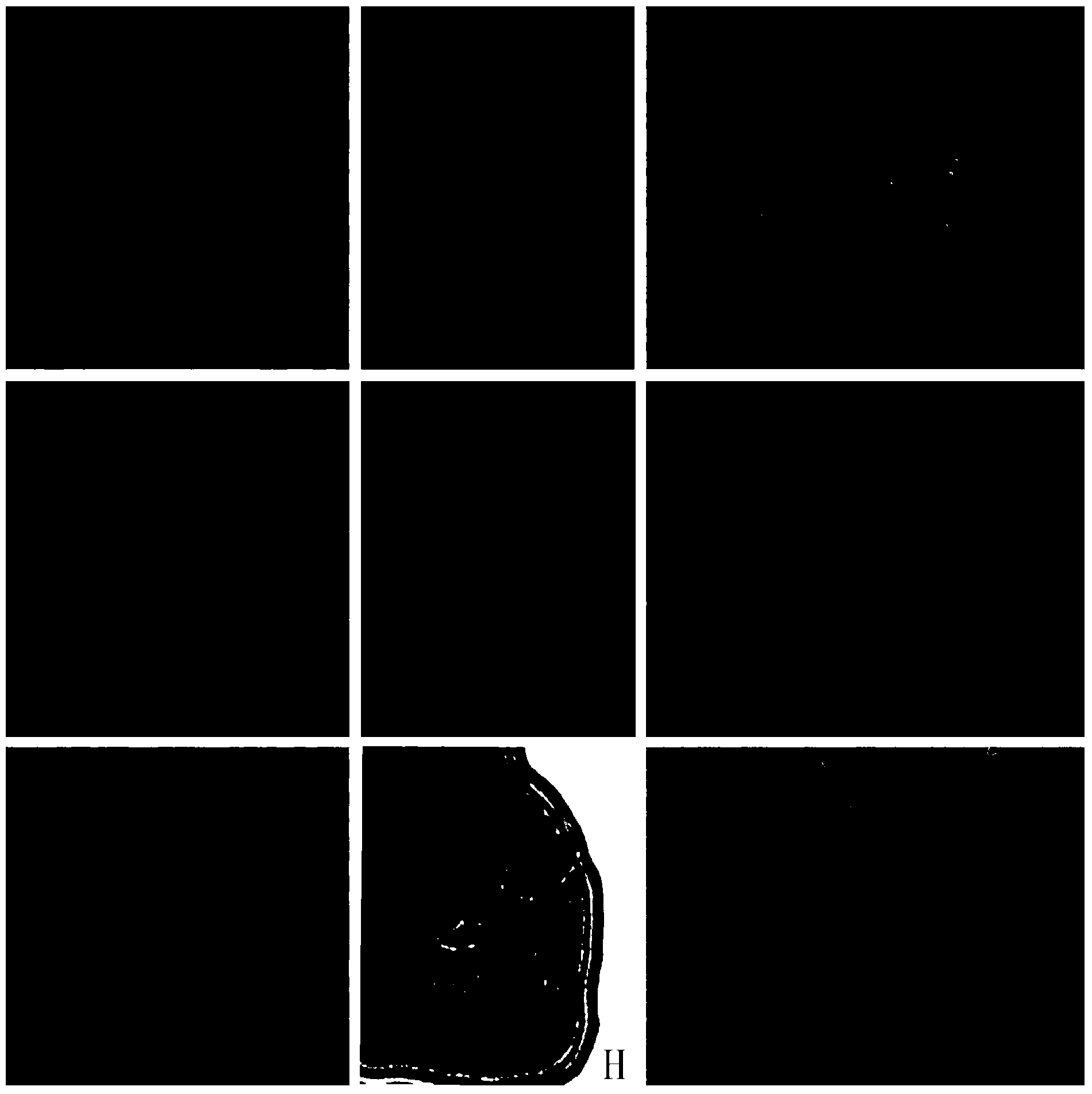
[0085] At 9:00 in the morning, take the tops of vigorously growing annual branches cultivated in the open field, and quickly strip off stems with a length of about 1.5 mm under a stereoscope. Treat in a saturated solution of p-dichlorobenzene at 25°C for 2.5 hours, wash with deionized water 5 times; dissociate with 1M hydrochloric acid for 8 minutes. Both the first and second strokes are carried out with a force of 28N and a frequency of 80; the rest of the steps are the same as those described in case (1). For the results, please refer to image 3 b.
Embodiment 3
[0087] The shoot tip of diploid Baiyutang (R.multiflora var.albo-plena) was used as material.
[0088]At 9:00 in the morning, take the top 2cm of the annual young shoots cultivated in the open field, peel off the surrounding leaves layer by layer under the stereoscope to expose the top of the stem, and use a scalpel to cut off the top growth point with a length of about 2.5mm at the front . The saturated solution of p-dichlorobenzene was treated at 25°C for 3.0h. The leaves of the newly grown young terminal buds of this material are densely covered with white hairs. Carnot's fixative was fixed for 4 hours, and 1M hydrochloric acid aqueous solution was dissociated for 9 minutes. Both the first and second percussions were performed with a force of 34N and a number of times of 100. The remaining steps are the same as those described in case (1), and the results can be found in image 3 E and 3H. It can be seen from the results that there is a deletion problem in the diploid ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com