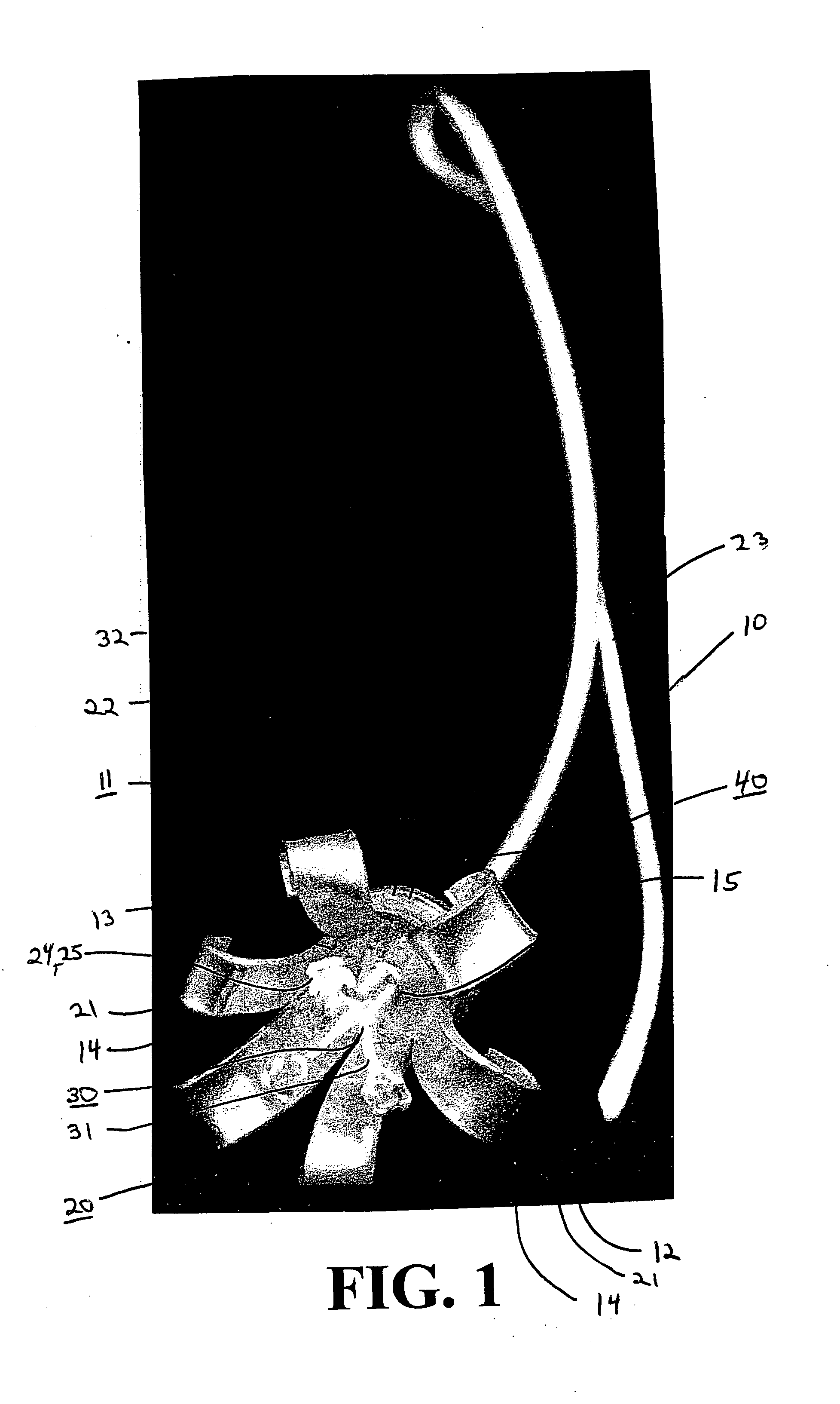
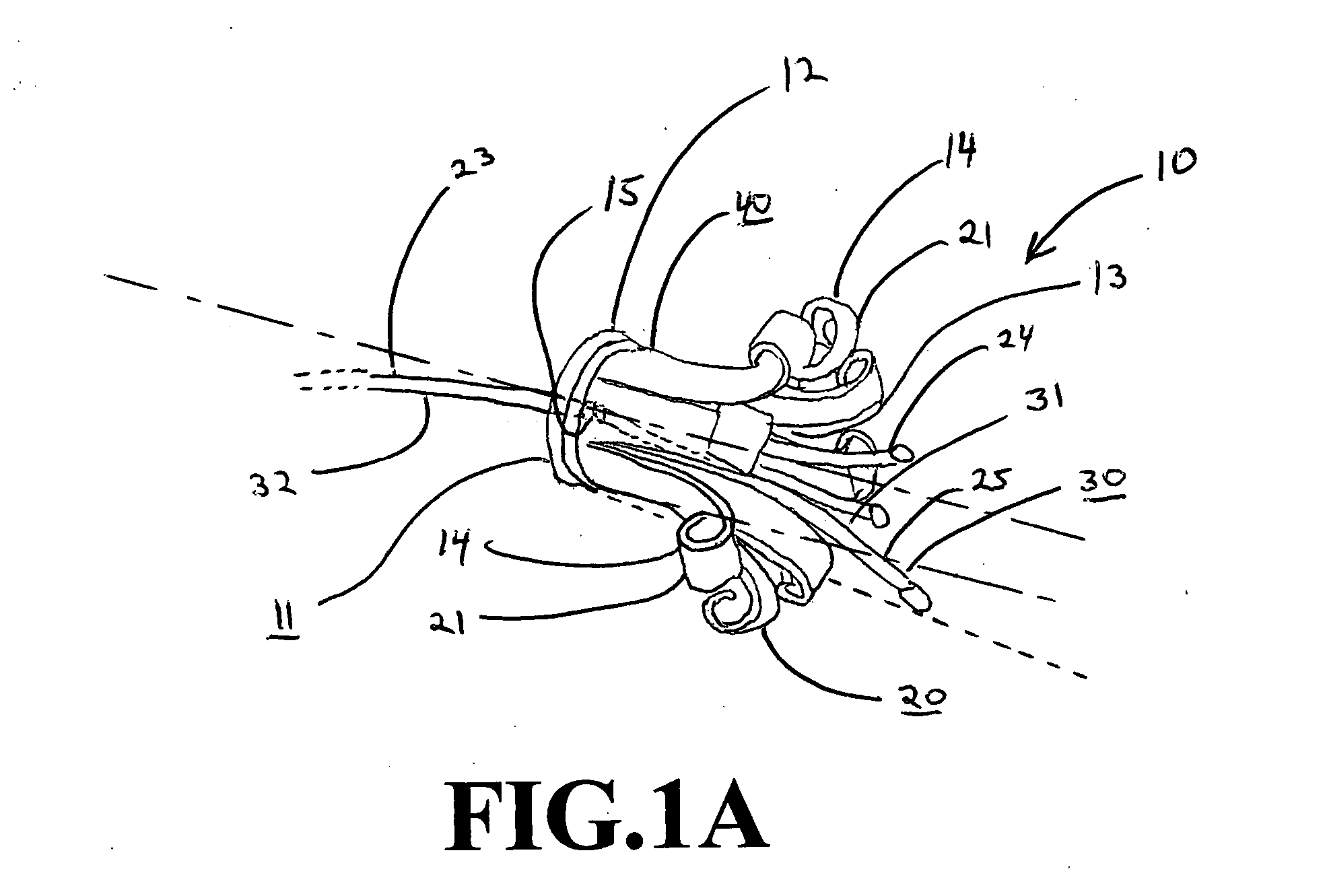
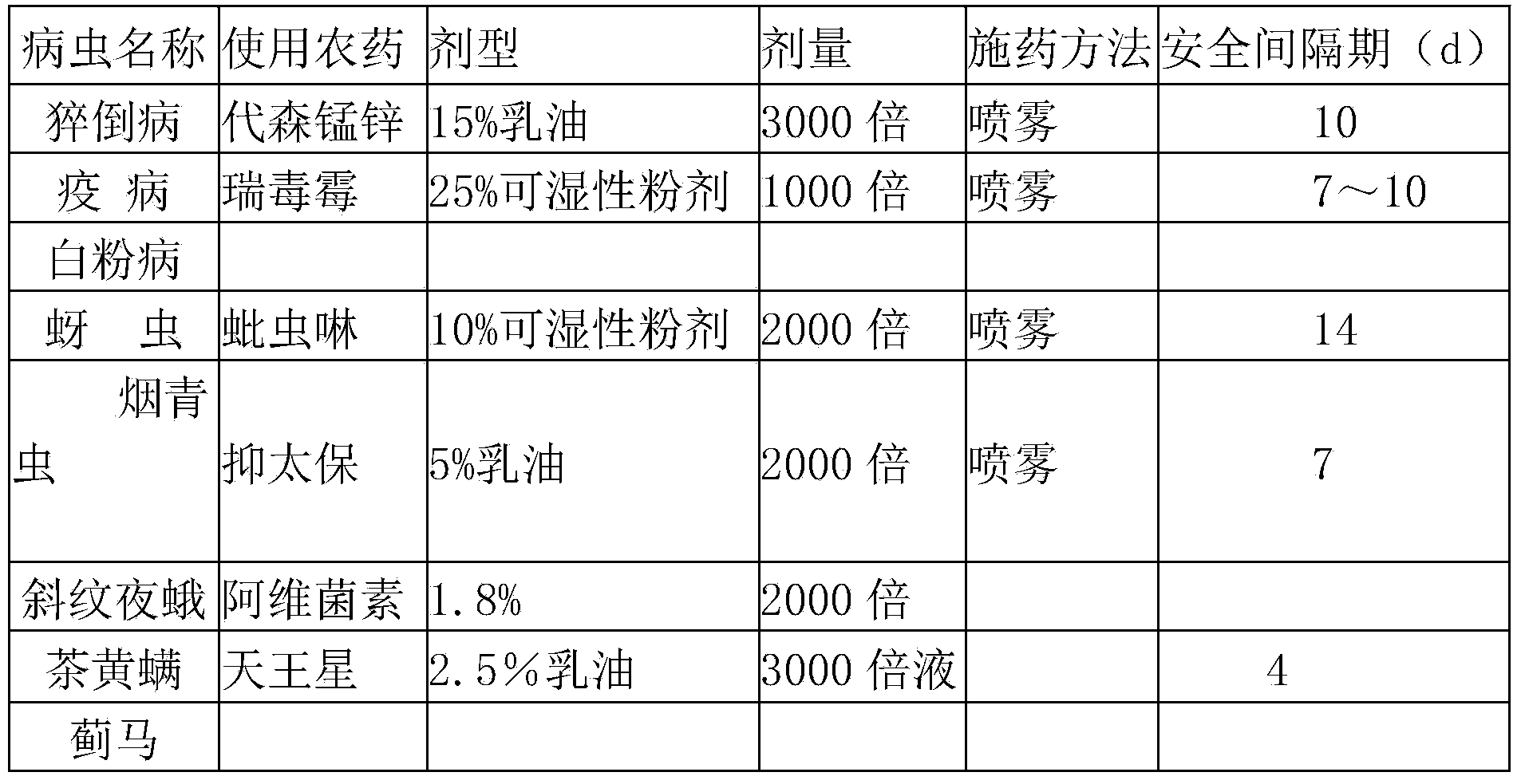
Patents
Literature
178 results about "Sepal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
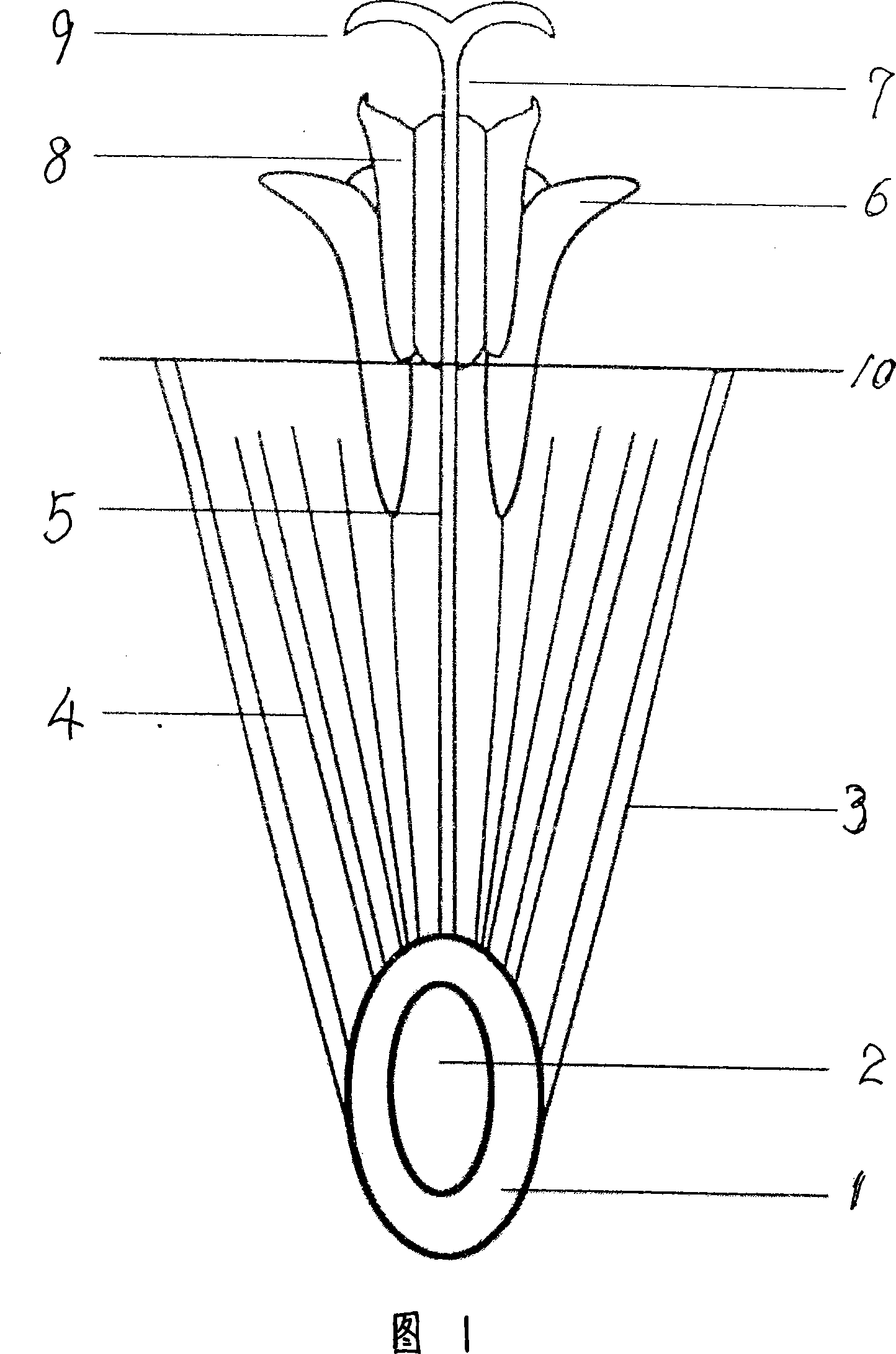
A sepal (/ˈsɛpəl/ or /ˈsiːpəl/) is a part of the flower of angiosperms (flowering plants). Usually green, sepals typically function as protection for the flower in bud, and often as support for the petals when in bloom. The term sepalum was coined by Noël Martin Joseph de Necker in 1790, and derived from the Greek σκέπη (skepē), a covering.
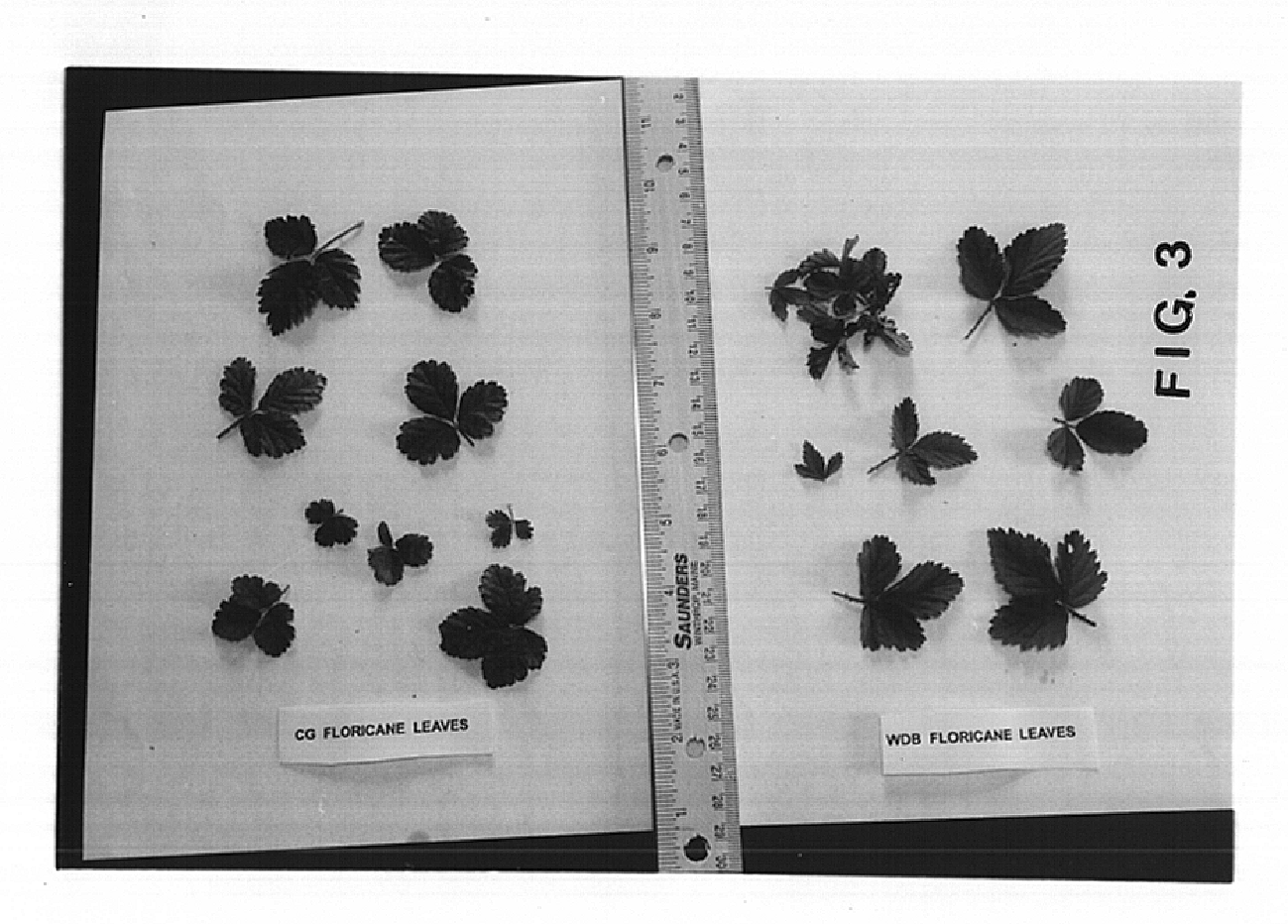
Strawberry plant named `Ventura`
This invention relates to a new and distinct variety of strawberry named `Ventura`. The variety is similar to the varieties `E26`, `Montalvo`, and `Baeza`. The variety is distinguished from `E26`, `Montalvo`, and `Baeza`, in particular, by its globose to flat globose habit, medium density, weak to medium vigor, medium leaf glossiness, calyx diameter that is smaller relative to the corolla, semi-erect attitude at first picking, conical to cordate fruit shape, slight differences in shape between the primary and secondary fruit, narrow band without achenes, insertion of the calyx that is in a basin to level, weak to medium adherence of the calyx, and fruit with firm flesh and a small hollow center.
Owner:DRISCOLLS INC
Strawberry plant named `San Juan`
This invention relates to a new and distinct variety of strawberry named `San Juan`. The variety is similar to the varieties `Commander` and `Lido`. The variety is distinguished from `Commander` and `Lido`, in particular, by its globose to flat globose habit, medium to strong interveinal blistering, weak to medium weak leaf glossiness, medium dense stipule pubescence, larger calyx diameter relative to the corolla, conical to almost cylindrical fruit, moderate differences in shapes of primary and secondary fruits, narrow band without achenes, and fruit with firm flesh and medium acidity.
Owner:DRISCOLLS INC
Artificial three-segment cultivating Paris Chinensis method
InactiveCN101248727AMajor risks can be mitigatedSeedlings grow fastSeed and root treatmentFertilising methodsInsect pestFarmyard manure
A method for manually-cultivating three-stage Rhizoma Paridis belonging to the technical field of agriculture includes primary seedling planting and raising, secondary seedling planting and raising, Rhizoma Paridis cultivation and field management, wherein, the primary seedling planting and raising includes the steps of presprouting of seeds and seed seedling raising, when tubers weigh 2g after 3 years, transplantation can be carried out. The secondary seedling planting and raising includes the steps that: the primary seedlings with 2g of tubers are transplanted in October and last third of November and transplantation can be carried out when the tubers are 15g after 3 years. The steps of Rhizoma Paridis cultivation and field management are that: the secondary seedlings are transplanted according to the proportion of 21,000 seedlings in per acre in October and last third of November, and mature Rhizoma Paridis can be dug after 3 years; farmyard manure is fertilized once or twice every May and last third of August with the amount of 3000kg per acre every time, or carbamide is fertilized or foliar fertilizer is sprayed for three times in the vigorous growth period; in the non-seed-collecting filed, ovaries are picked off after sepals unfold; commercial pesticide is used for preventing plant diseases and insect pests in the growth period of the Rhizoma Paridis. The method for manually-cultivating Rhizoma Paridis is characterized by less investment, early effect, good harvest, high efficient, etc., which can realize major production.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A kind of capsicum self-isolation method
InactiveCN102273402AEasy to operateReduce labor costsPlant genotype modificationGeitonogamyAfter treatment
Belonging to the technical field of plant breeding, the invention relates to a pepper inbred isolation method, which comprises the steps of: 1) plant selection: obsoleting substandard heterologous strains; 2) blend solution preparation: preparing a blend solution with a sodium alginate concentration of 5-10% and a carboxymethylcellulose sodium concentration of 0.5-2% with deionized water; 3) petal selection: selecting petals about 6-12h before flowering; 4) petal treatment: taking the petals to be treated on one hand lightly and taking the blend solution on the other hand, and soaking the petals in the blend solution till the joint of a calyx and a flower stalk, and making a mark with a color line; 5) management after treatment: identical with the routine field management method of pepperproduction. The pepper inbred isolation method of the invention isolates petals through a flexible film generated by the blend solution, and conducts geitonogamy to a gynoecium and a stamen of a sameflower. Being simple and rapid, the method of the invention can save the labor cost and has high?fruiting rate. Besides, the method in the invention causes no pollution to the environment and agricultural products, and can realize good application effect.
Owner:HANGZHOU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
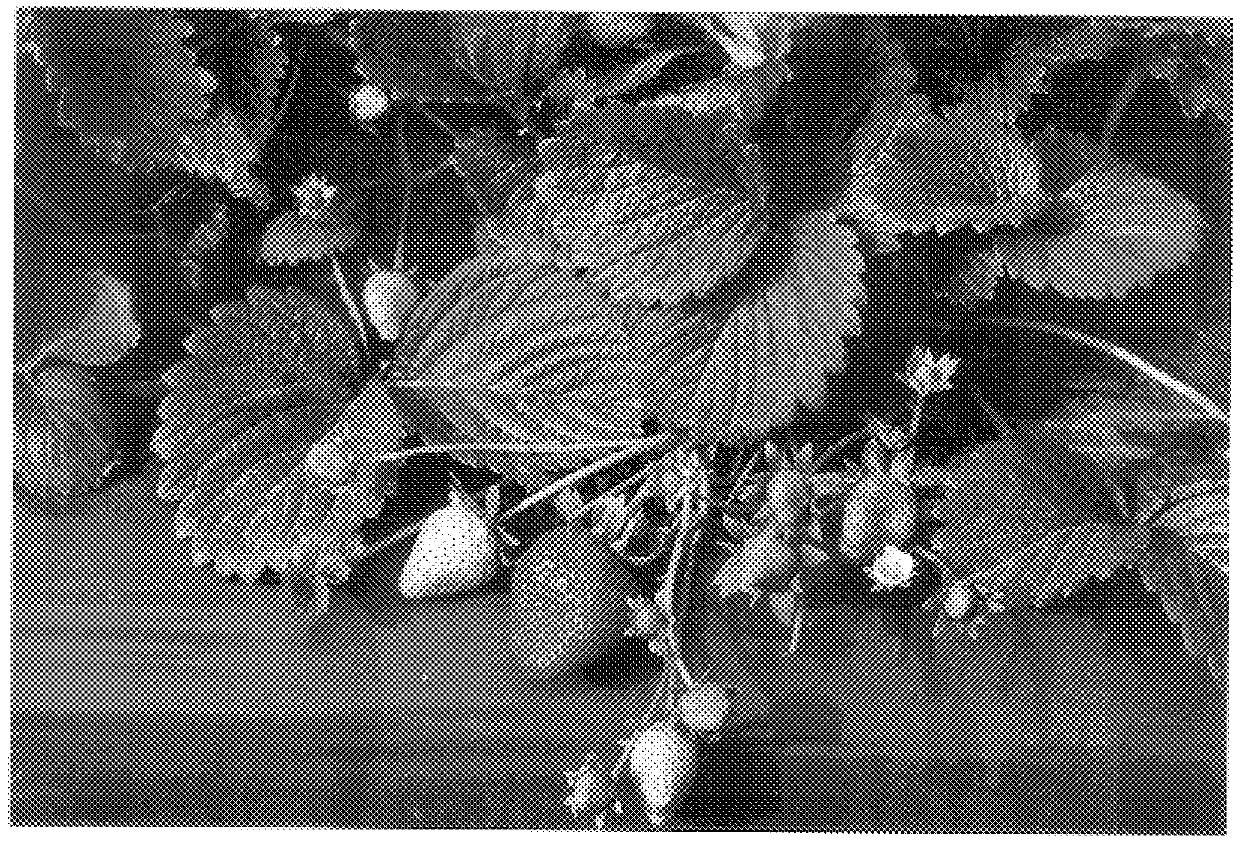
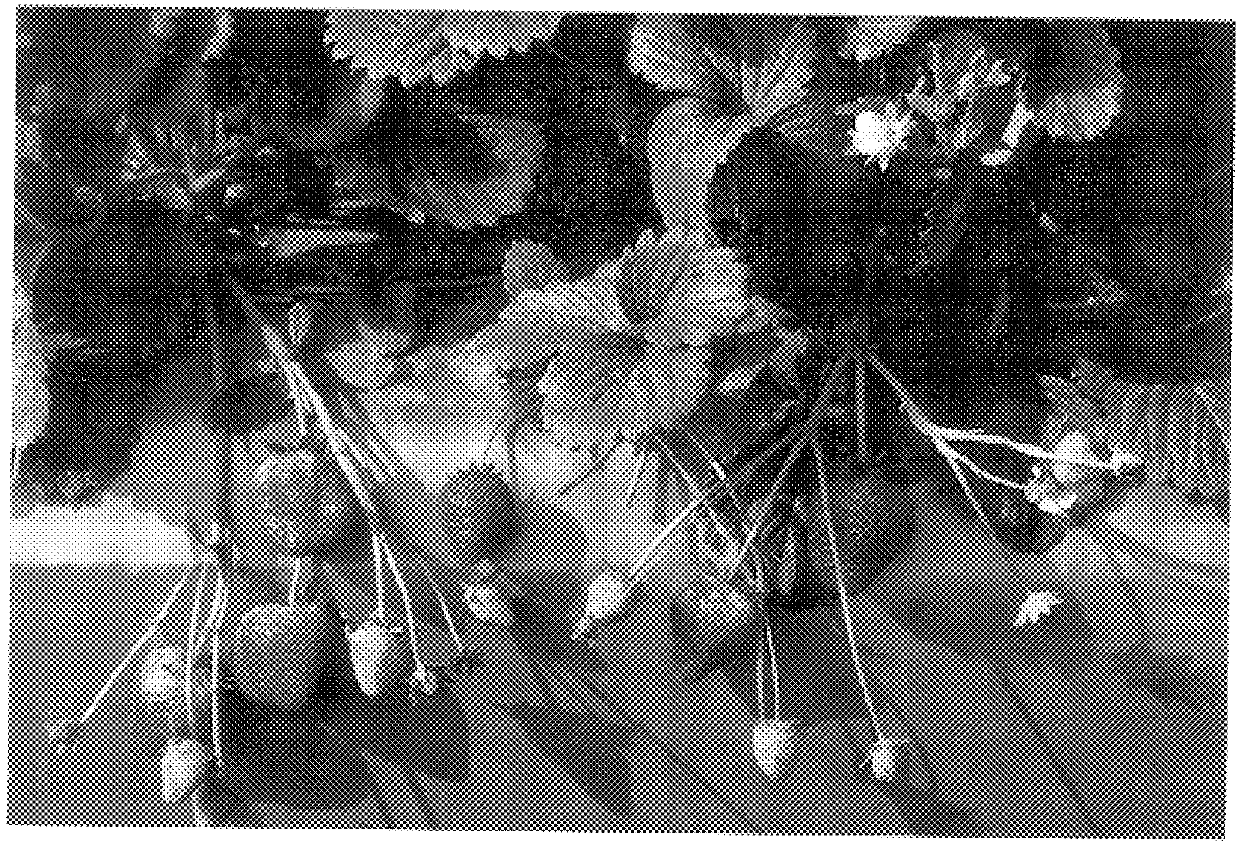
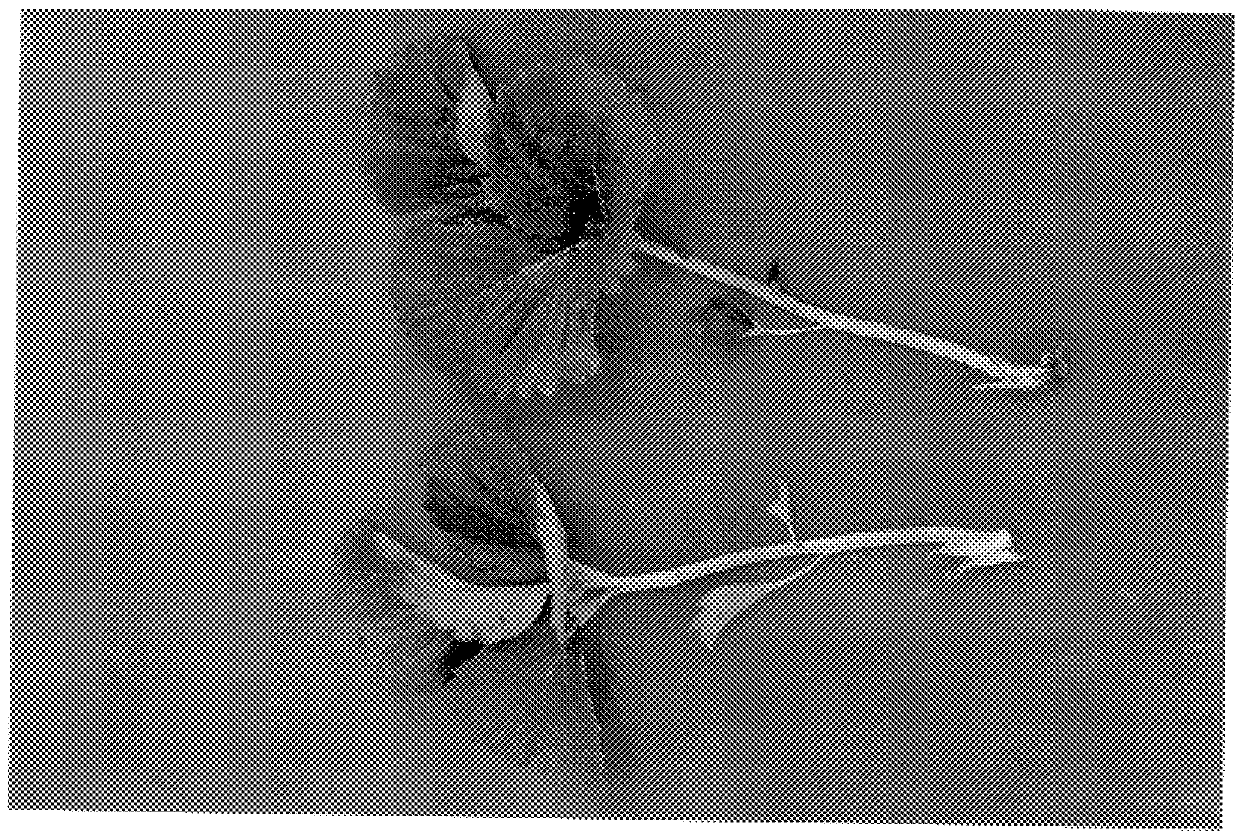
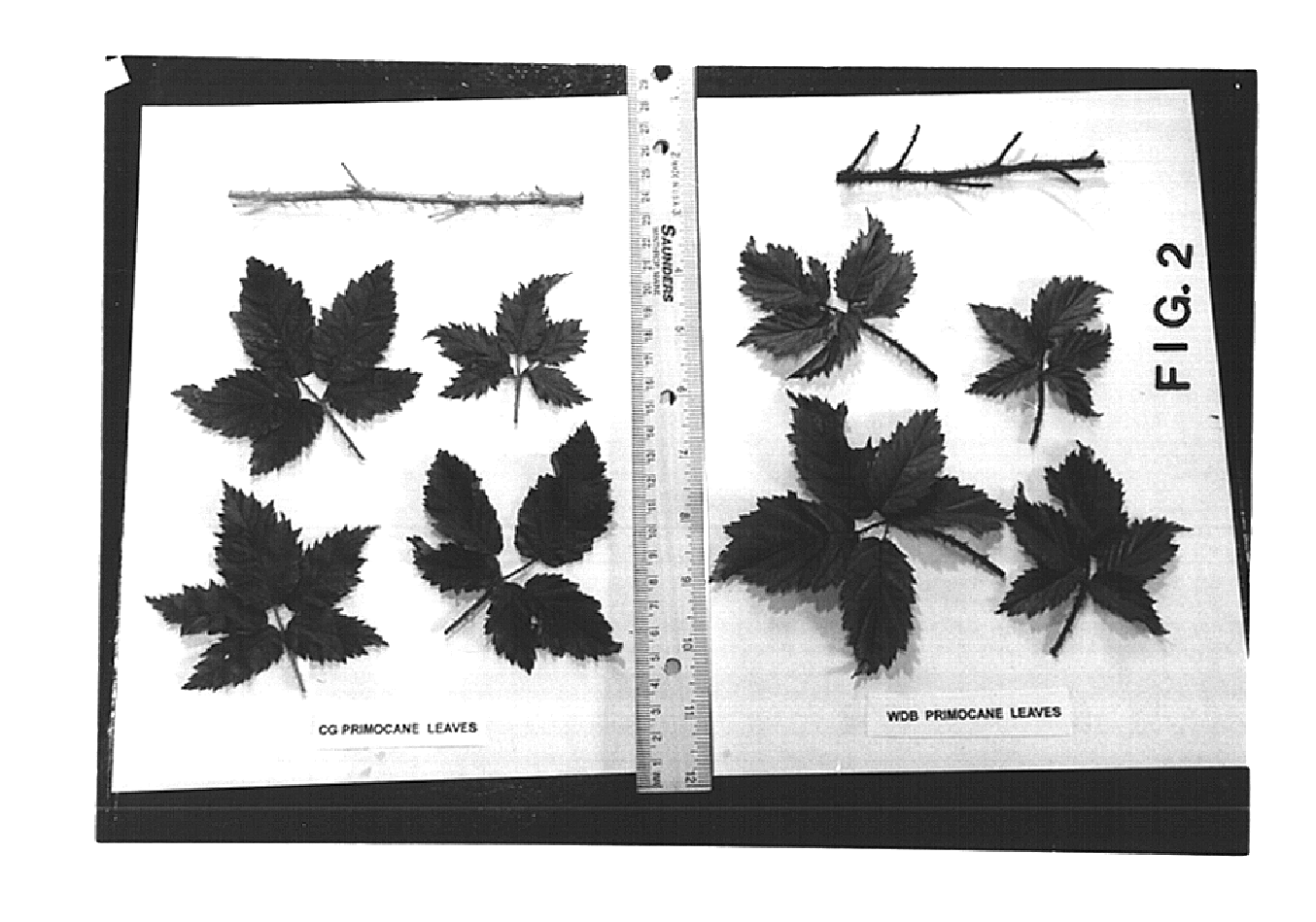
Blackberry plant named 'Clark Gold'
A new and distinct variety of blackberry plant lacking anthocyanin coloration in it's various plant parts and having yellow fruit is described. The new variety named 'Clark Gold' also has double flowers and enlarged sepals. 'Clark Gold' is a sport of the southern dewberry, Rubus trivalis, and is a biennial, thorny, trailing-vine plant type. The yellow fruit is of medium size and has the sweetness of its wild blackberry relative. It is also a very early variety with low chill requirements.
Owner:CLARK JOHN WILLIAM
Method for obtaining dihaploid plants of sweet peppers
InactiveCN102047843AImprove cultivation efficiencyIncrease DH Strain RatioPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGenotypeCapsicum baccatum
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Mulberry kidney-nourishing noodles
The invention discloses mulberry kidney-nourishing noodles, which are prepared from the following raw materials in part by weight: 100 to 140 parts of flour, 5 to 8 parts of buckwheat, 3 to 5 parts of konjac flour, 5 to 8 parts of black bean powder, 2 to 4 parts of coix seed extract, 6 to 8 parts of mulberry fruit, 3 to 4 parts of purple grape, 2 to 5 parts of corn stigma, 2 to 4 parts of tuckahoe, 1 to 2 parts of cassia seed, 5 to 6 parts of pumpkin seed, 4 to 8 parts of roselle calyx, 3 to 5 parts of dried rose hip, 0.1 to 0.3 part of grape seed oil and 1 to 4 parts of salt. The mulberry kidney-nourishing noodles are good in mouthfeel, delicious and rich in nutrition and simultaneously have a health-care effect of nourishing kidney; and substances which are harmful to human bodies such as any pigment, essence and preservative are not added during preparation.
Owner:ANHUI SIHAI FOOD
Lotus young-keeping noodles
The invention discloses lotus young-keeping noodles, which are prepared from the following raw materials in part by weight: 100 to 150 parts of flour, 5 to 8 parts of buckwheat, 4 to 8 parts of konjac flour, 3 to 5 parts of lotus pollen, 5 to 8 parts of needle mushroom powder, 3 to 5 parts of acerola cherry freeze-dried powder, 5 to 8 parts of kiwi fruit freeze-dried powder, 1 to 2 parts of roselle calyx, 3 to 5 parts of cassia seed, 1 to 2 parts of osmanthus fragrans, 3 to 5 parts of Lecai, 2 to 4 parts of Chinese wolfberry, 2 to 4 parts of Chinese angelica, 5 to 7 parts of common lophatherum herb, 3 to 5 parts of lotus leaf, 2 to 4 parts of lotus, 1 to 3 parts of salt and 0.1 to 0.3 part of grape seed oil. The lotus young-keeping noodles are good in mouthfeel, delicious and rich in nutrition and simultaneously have dietetic and health-care effects of maintaining beauty and keeping young.
Owner:ANHUI SIHAI FOOD
Extraction method of Flos chrysanthemi indici volatile oil
InactiveCN105802738AImprove crushing efficiencyHigh purityEssential-oils/perfumesOrganic solventDistillation
The invention provides an extraction method of Flos chrysanthemi indici volatile oil.The extraction method includes: removing receptacles, sepals and flower stalks of dry Flos chrysanthemi indici; smashing petals of the dry Flos chrysanthemi indici into Flos chrysanthemi indici powder, and repeatedly freezing and thawing for 2-3 times; adding into water of 60-70 DEG C for soaking for 1-2 h, and ultrasonically treating the Flos chrysanthemi indici powder after being soaked and extract; performing distillation extraction on the Flos chrysanthemi indici powder after being ultrasonically treated and the extract at 100-120 DEG C for 3-5 h, and collecting upper-layer oily substance in distillation condensate to obtain Flos chrysanthemi indici volatile oil crude extract; using macroporous resin to adsorb and desorb the Flos chrysanthemi indici volatile oil crude extract to obtain pure Flos chrysanthemi indici volatile oil.No additive or organic solvent is used in the method, so that original fragrance of volatile oil is retained; no organic solvent is left in the Flos chrysanthemi indici volatile oil, so that the extraction method is safer and pollution-free.The extraction method has the advantages that extraction rate is up to 7.5%, extraction time is short, and extracted volatile oil is higher in purity.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Cultivation method of peas
InactiveCN102113463AImprove germination rateEarly maturitySeed and root treatmentSowingEarly maturationPetal
The invention relates to a cultivation method of peas. The cultivation method is characterized in that ordinary pea flowers are selected as female bodies, and wild pea flowers are selected as male bodies; calyces and pedals of the ordinary pea flowers used as the female bodies and stamina of the wild pea flowers used as the male bodies are removed together during the initial bloom stage; the calyces and the pedals of the wild pea flowers are removed during the full-bloom stage, the stamina of the wild pea flowers are used for performing pollination on pistil stigmas of the ordinary pea flowers twice, and carefully selecting pea fruits bred by the method as the first generation of hybrid pea seeds; then further selecting the ordinary pea flower as the female bodies, using the first generation of the hybrid pea seeds as the male bodies in the same method, and carefully selecting the pea fruits obtained by pollination of the female bodies and the male bodies as the second generation of the hybrid pea seeds; and directly planting the second generation of the hybrid pea seeds, which are carefully selected, pollinating naturally, and carefully selecting the fruits as domesticated pea original seeds for large-area popularization and planting. The hybrid peas have high emergence rate, early maturation period and high yield, and the quality of the hybrid peas is higher than that of the ordinary peas.
Owner:章晓文
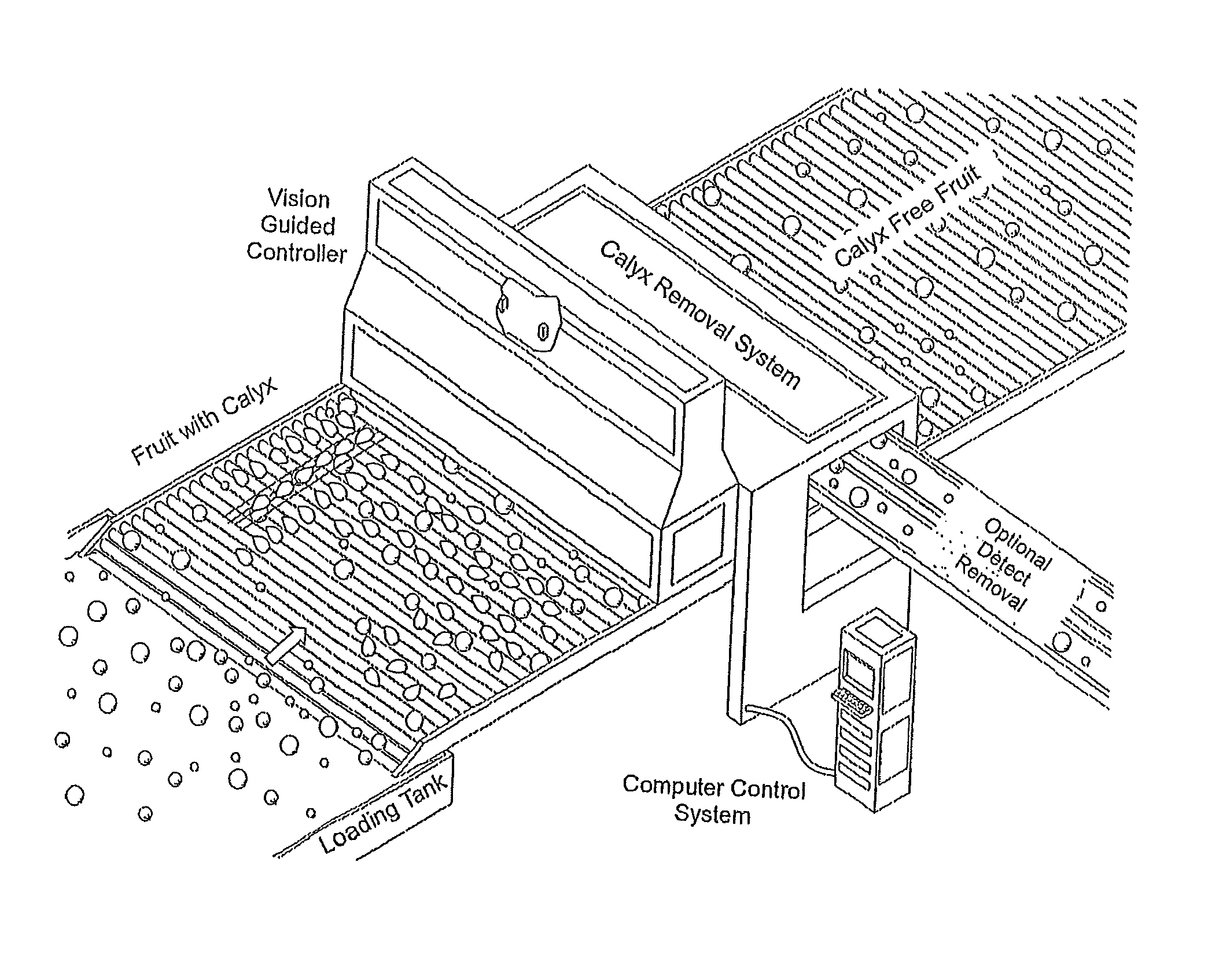
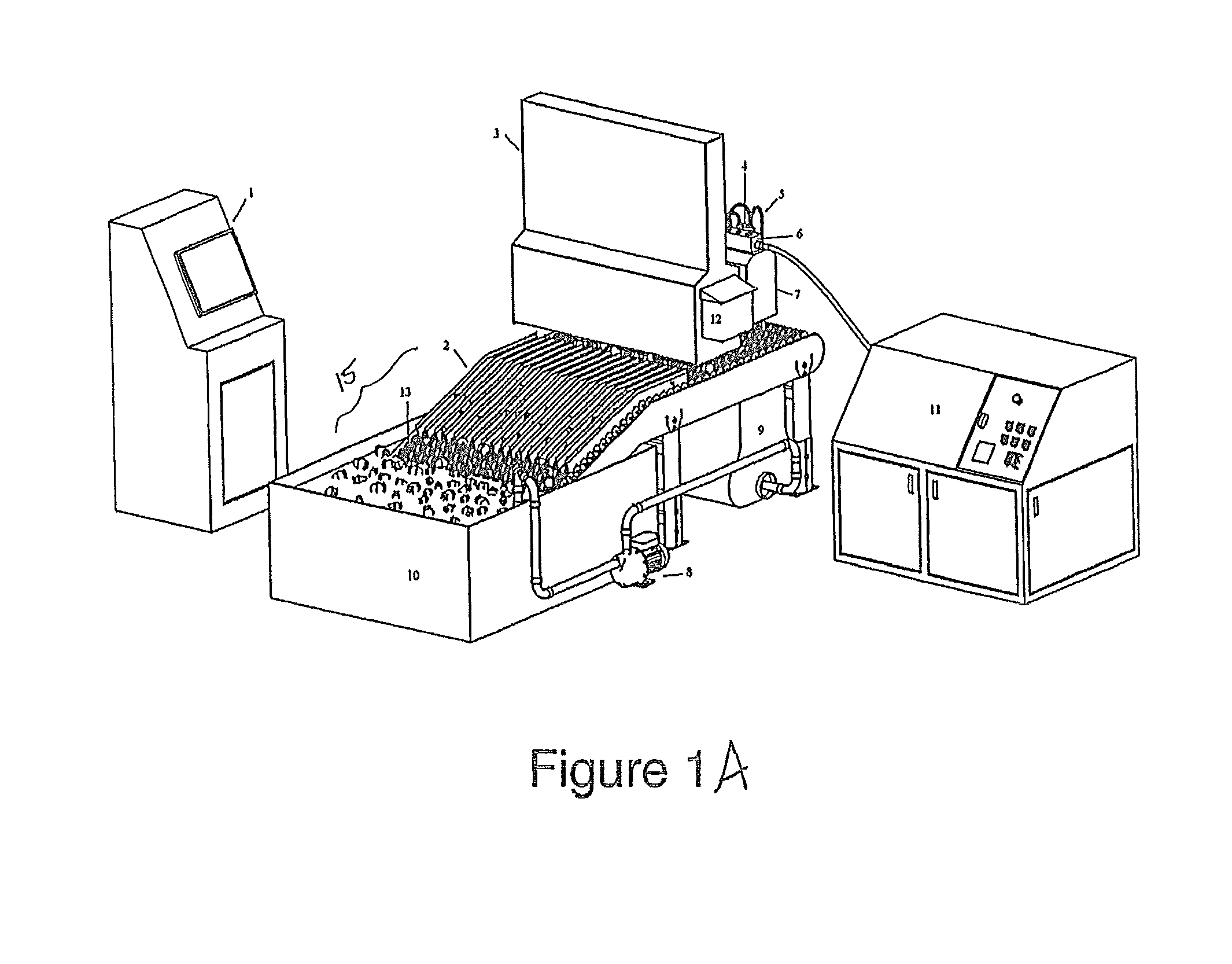
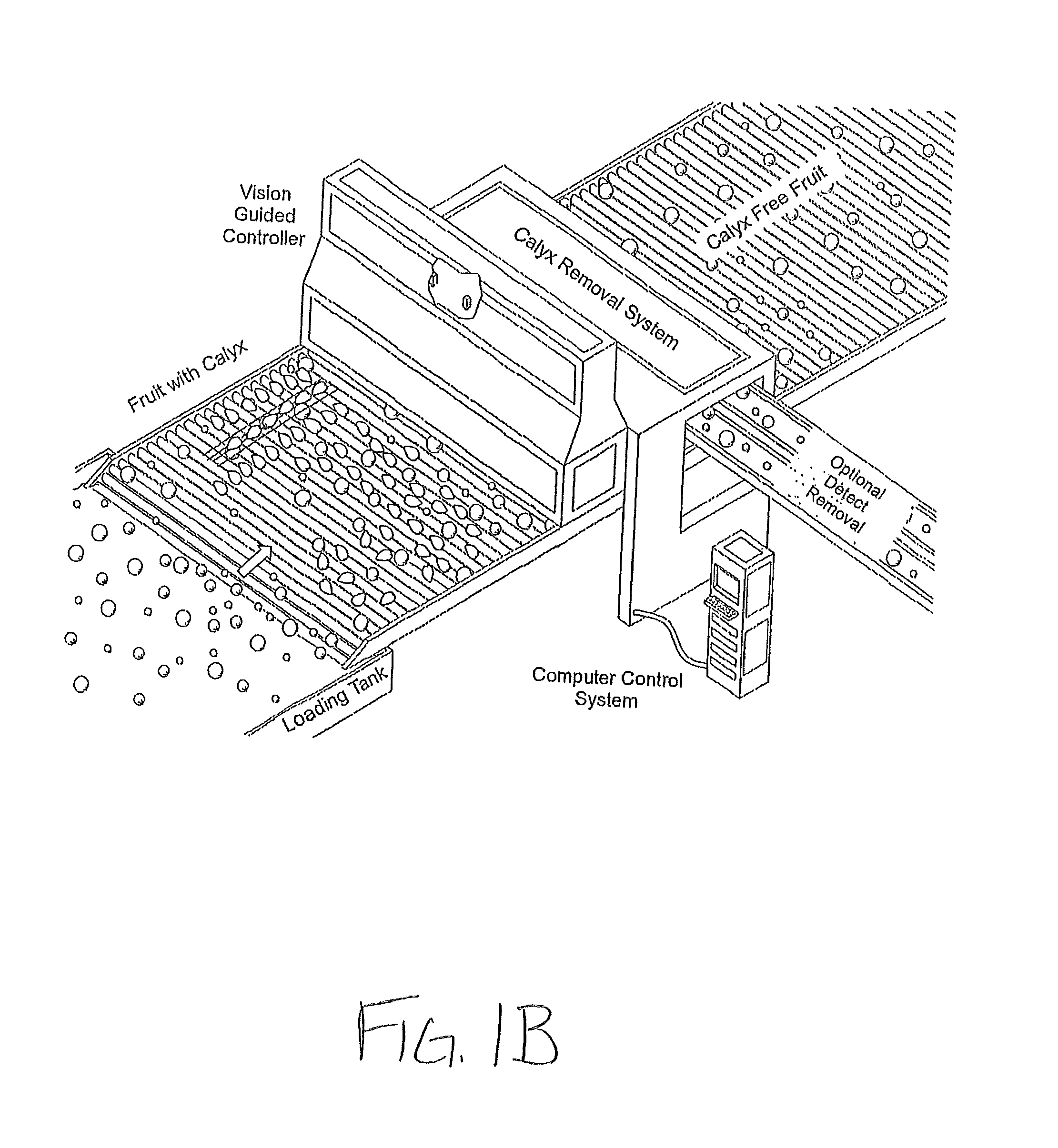
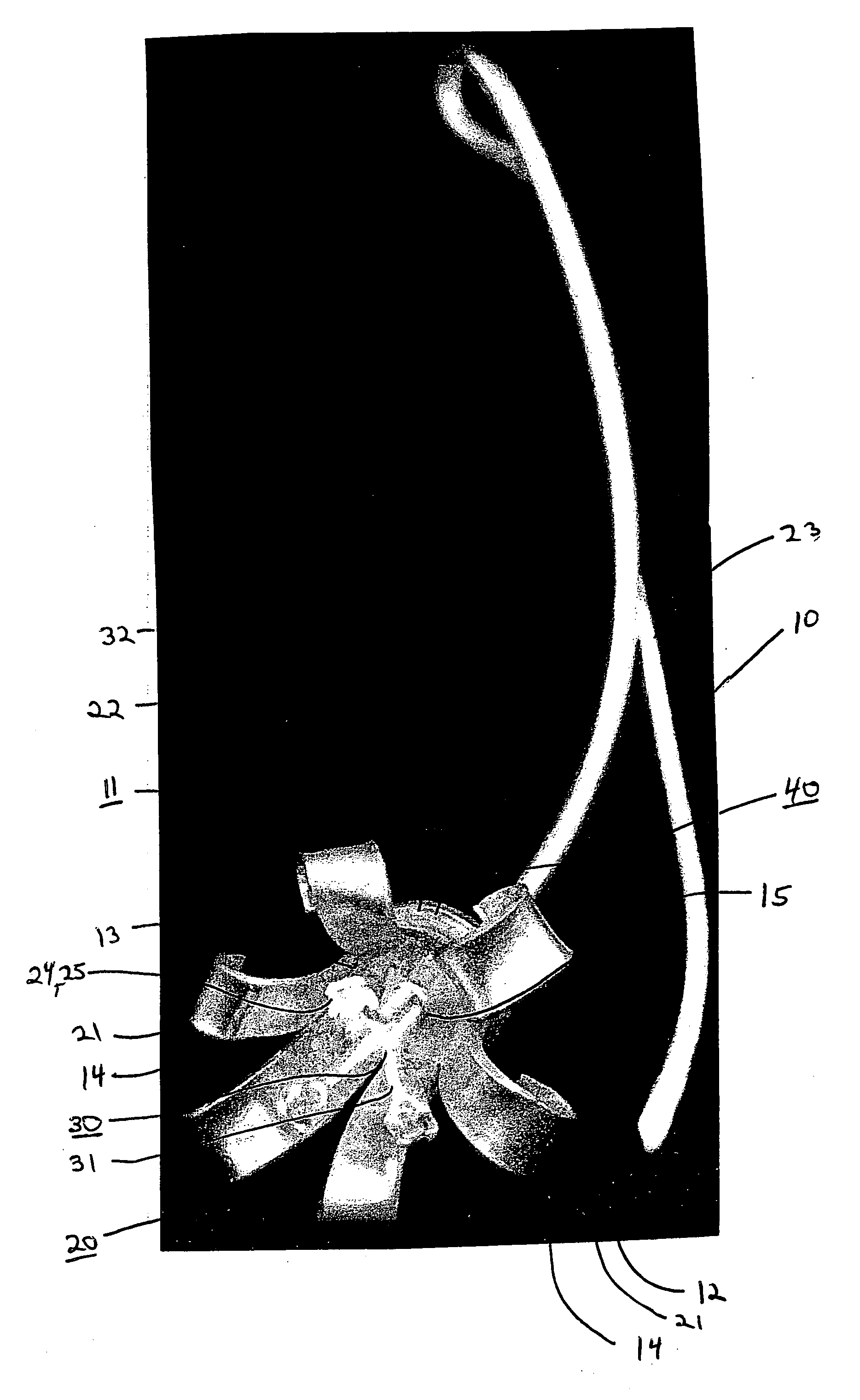
Automated fruit and vegetable calyx or stem removal machine
A process for automated high-throughput fruit or vegetable calyx removal includes a material handling system, a vision system, and a cutting system. The material handling system is capable of transporting the fruit or vegetable through the automated process. The material handling system may also orient the fruits or vegetables along an axis of the fruit and or align the fruit or vegetables in a desired pattern, orientation, and / or configuration. The vision system identifies the calyx and determines calyx position data and optimal cutting angle for individual fruit. The cutting system uses data received from the vision system to automatically remove the calyx from the fruit or vegetables.
Owner:CALIFORNIA STRAWBERRY COMMISSION +1
Raspberry planting method
The invention discloses a raspberry planting method. The raspberry planting method includes the following steps that (1) seeds are selected; (2) culture of seedlings is conducted; (3) land is selected; (4) base fertilizer is applied before transplantation; (5) transplantation is conducted in May in the next year; (6) topdressing is conducted in the next year; (7) after lateral branches grow from shoots, terminal buds are picked off, and pinching is conducted on the lateral branches; (8) a frame is erected to lead the branches; (9) soil is loosened, and weeding and watering are conducted; (10) insect pests and diseases are prevented; (11) branch trimming is conducted, wherein weak branches, damaged branches and more sub-branches are trimmed; (12) fruits are picked together with calyxes when the fruits are mature in 80% in the middle of May in the third year. According to the raspberry planting method, sterilization is conducted before planting, diseases and insect pests are reduced, the survival rate is increased, through reasonable applying of the base fertilizer and additional fertilizer, reasonable field management, in-time soil loosening, in-time weeding and in-time deinsectization, the survival rate can reach above 98%, and raspberries obtained through the planting method are good in quality and herbal property, high in adaptability and suitable for large-area popularization due to the fact that the requirements for land are not strict.
Owner:NINGGUO THOUSAND SQUARE TCM DEV
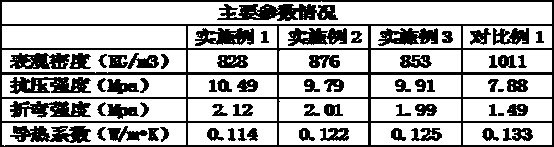
Concrete foamed insulating brick and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104261865AHigh compressive strengthImprove bending strengthSolid waste managementCeramicwareBrickRed mud
The invention discloses a concrete foamed insulating brick. The concrete foamed insulating brick is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 134-156 parts of Portland cement, 96-125 parts of base material, 8-13 parts of an additive, 7-12 parts of a foaming complexing agent and 64-76 parts of water, wherein the base material is composed of alkaline phenolic waste sand, red mud, silicon carbide and basalt fibers; the foaming complexing agent is composed of a protein foaming agent, sodium lauroyl sarcosine, fosetyl aluminum and gum acacia powder; the additive is composed of polycarboxylate superplasticizer and potassium sodium tartrate; the polycarboxylate superplasticizer is UXP-type liquid polycarboxylate superplasticizer produced by Shanghai Sepal Chemical Factory Co.,Ltd.; the foaming agent is a YJ-25-type protein foaming agent produced by Tianjin Yuchuan Microbial Product Co.,Ltd.; the basalt fibers are Anjie BCS3-12 type basalt chopped swelled fibers which is produced by Haining Anjie Composite Materials Co., Ltd., and the specification of the fibers is 3-9 mm.
Owner:合肥候鸟新型材料有限公司
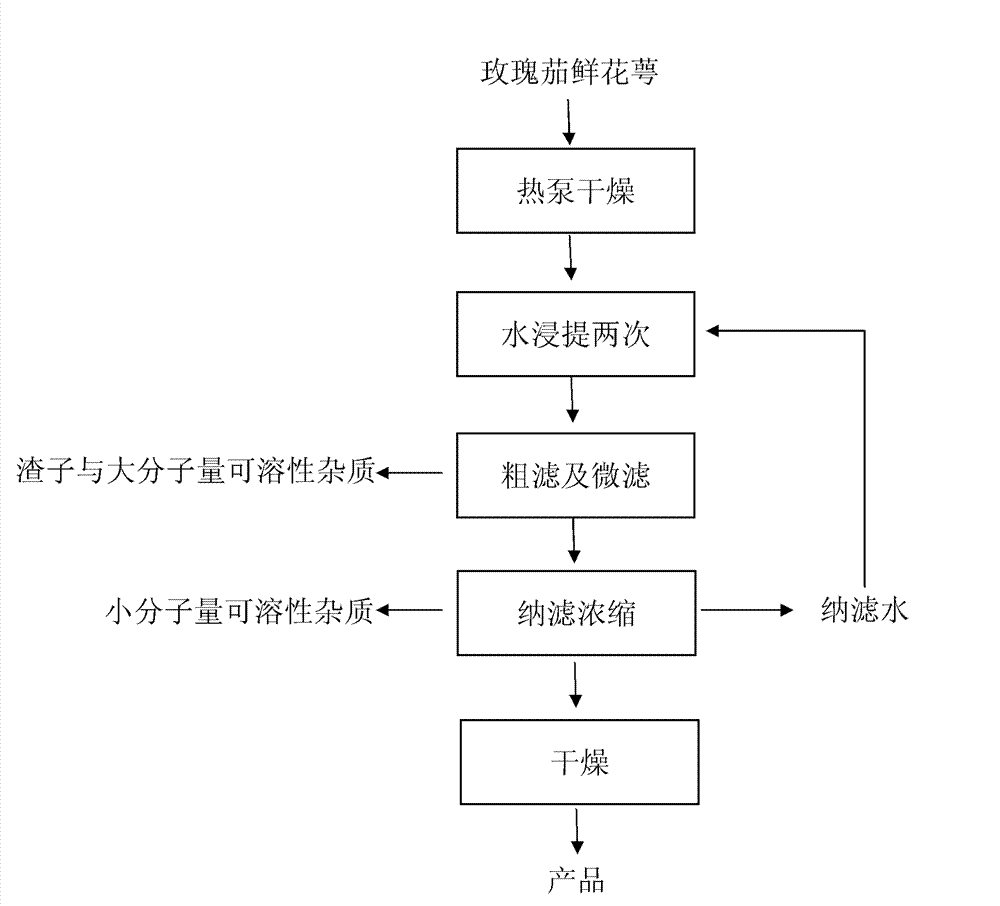
Method for extracting roselle calyx red pigment
The invention relates to a method for extracting a roselle calyx red pigment, which relates to a method for extracting a roselle calyx red pigment, the method comprises the following steps: 1) dehydrating and preserving a fresh roselle calyx raw material through a heat pump; 2) extracting the dehydrated raw material through water; 3) extracting the pigment, through rough filtering and filter membrane fine filtering, separating and purifying a pigment extract,4) concentrating the pigment extract through a nanofiltration membrane, circularly using the nanofiltrated water for extracting the raw material; and 5) spraying and drying a pigment concentrated solution to obtain the products. Compared with the prior art, the method for extracting the roselle calyx red pigment has the advantages of energy conservation and environmental protection, and the obtained product has high quality and reasonable price.
Owner:漳州金三角生物科技有限公司
Method for quickly identifying differential protein during interaction of chrysanthemum pollen and stigma
InactiveCN102841126AOvercoming incompatibilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansWild speciesPetal
The invention discloses a method for quickly identifying differential protein during interaction of chrysanthemum pollen and stigma, belonging to the field of chrysanthemum proteomics. The method comprises the following steps of: performing distant hybridization work of chrysanthemum by taking cultured chrysanthemum as a female parent and wild chrysanthemum as a male parent; cutting off pollinated inflorescences in 1 h and 24 h after pollination; removing petals and sepals of ligulate flowers in the obtained inflorescences to obtain pistils; extracting a protein sample from the obtained pistils by using a TCA (Trichloroacetic Acid) / acetone precipitation method; and quickly identifying the differential protein by applying iTRAQ (Isobaric Tags For Relative And Absolute Quantitation) and a mass spectrum technology and performing bioinformatic analysis. Aiming at the chrysanthemum and wild species of related genera thereof, the invention provides a method for quickly and accurately identifying key differential protein during the interaction of the chrysanthemum pollen and the stigma for providing research foundation for solving the problem of distant hybridization incompatibility of the chrysanthemum.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Colored cotton ovule in vitro culture method
InactiveCN103931494AGuaranteed nutrition supplyKeep aliveHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureFiberContamination rate
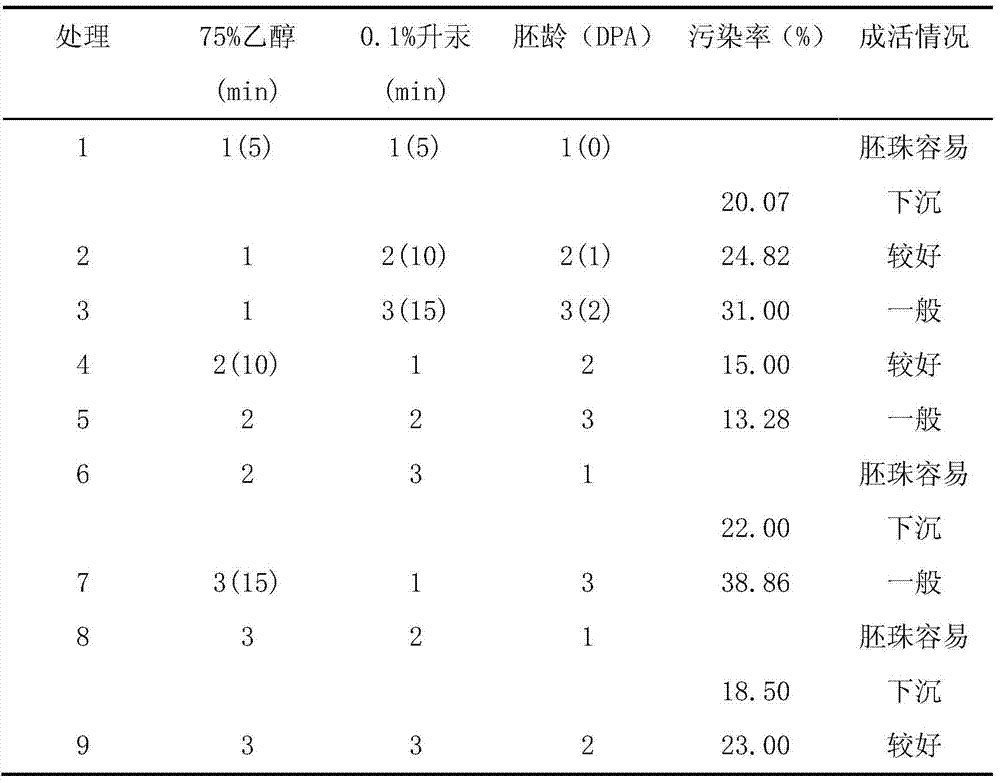
The invention discloses a colored cotton ovule in vitro culture method, which comprises the steps of: collecting 0-2 days old young bolls of green cotton or brown cotton of the day, pulling off the corolla, stripping calyxes, and retaining flower stalks; washing the young bolls with distilled water twice, conducting disinfection with 75% alcohol for 5-15min under a sterile condition, then performing soaking with 0.1% mercury chloride for 5-15min, and conducting washing with sterile water 5-8 times, and stripping ovules; inoculating the ovules under a sterile condition into a BT medium containing hormone ZR, GA3 and IAA, inoculating 15-25 ovules of one ovary into each bottle, and carrying out dark culture for 30-40d at 30-32DEG C. Preferably, during inoculation of green cotton ovules, the hormone ratio wais GA31.0micromol / L+IAA5.0micromol / L+ZR2.5micromol / L, and during inoculation of brown cotton ovules, the hormone ratio is GA31.0micromol / L+IAA1.0micromol / L+ZR1.0micromol / L. The method provided by the invention can reduce the contamination rate, improve the survival rate, and promote cotton fiber growth and pigment synthesis.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Jewelrey article and method of making the same
InactiveUS20080053149A1Superior aesthetic appealSuperior aesthetic appeal to the wearerJewelleryEngineeringMaterial Perforation
A floral-like jewelry article and method for making the same, the article having a cylindrically cupped body with a closed or base end and an open end, the open end including a plurality of edge portions sectioned and shaped such that the body takes the form of a flower. Each edge portion corresponds to a petal and the body corresponds to a sepal. The base end of the body has a piercing, perforation or hole for receiving a curvilinear strand therethrough with a first strand end extending generally from the base end toward the edge portions and a second strand end extending from the base end, the second strand end corresponding to the flower stem. The first strand end is formed into or mounts one or more pistil-like and / or stamen-like shapes, wherein the body comprises, or is formed from, an empty ammunition cartridge casing or shell, or a shape resembling the same.
Owner:JENUINELY JENI
Culturing method for early spring pollution-free white eggplants
A culturing method for early spring pollution-free white eggplants relates to the technical field of vegetable planting and is characterized by comprising the following steps of 1, producing area selecting; 2, variety selecting; 3, seedbed preparing; 4, nutrition soil preparing; 5, sowing; 6, seedbed managing after seedling transplanting; 7, field planting; 8, large field managing and petal picking, wherein after eggplant fruits are formed and grown to the state that petals are obviously exposed, the petals are timely picked and sepals are left on the fruits during picking; 9, insect controlling; 10, harvesting. The white eggplants planted according to the method are large in size, high in yield, high in quality and good in economic benefits and the generated irregular fruits are few.
Owner:LANGXI SHENGCHUAN VEGETABLES COOP
Method for in vitro inducing winter date anther callus
InactiveCN1934932AAchieve multiplicationOvercoming the major technical problem of difficult access to callusPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsZiziphus jujubaEnrichment culture
The present invention relates to a method capable of adopting isolated induction process to obtain winter jujube anther callus. It is characterized by that said invention utilizes tissue culture of winter jujube anther to obtain its callus. Said method includes the following several steps: explant collection, disinfection, in initial induction and enrichment culture. Besides, said invention also provides the concrete requirements of the above-mentioned every step and its concrete operation method.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Method for obtaining regeneration plants of petunia hybrida by anther culture
The invention discloses a method for obtaining regeneration plants of petunia hybrida by anther culture. The method comprises the following steps of: A) performing pretreatment and disinfecting petunia hybrida buds at low temperature; B) peeling calyx and petals of the buds obtained in the step A) by using tweezers, extracting anther, and after removing capillament of the anther completely, inoculating the anther to an inducing callus culture medium; C) transferring callus obtained by subculture in the step B) to a differential culture medium to differentiate adventitious buds, and when the adventitious buds are between 3 and 5 centimeters, stopping differential culture; and D) transferring the adventitious buds which are obtained in the step C) and are used as plantlets to a rooting culture medium to perform rooting culture until at least three adventitious roots of which the lengths are more than or equal to 2 centimeters grow on the plantlets to obtain seedlings which can be planted outside a bottle, wherein the steps A), B), C) and D) are performed in sterile environment.
Owner:HANGZHOU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for preparing honey strawberries
The invention relates to a method for preparing honey strawberries, which belongs to the field of food processing. The method for making the honey strawberries comprises the following steps: a, selecting ripe and fresh strawberries, removing foreign matters and impurities, picking off sepals, roots and pedicles, cleaning the strawberries with clear water, and then drying the strawberries for standby; b, mixing 50 portions of water, 80 portions of white granulated sugar and 35 portions of starch syrup in portion by weight, heating and sterilizing the mixture, fully melting the white granulated sugar and the starch syrup to obtain clear and transparent honey solution, and then cooling the honey solution to 30 DEG C for standby; c, adding the strawberries to the honey solution until the strawberries are completely immersed in the honey solution, and keeping the temperature of 30+ / -2 DEG C for processing the mixture with honey for 12 hours; and d, drying the honey solution and rapidly freezing the same hard at a temperature of between 35 and 37 DEG C below zero to obtain the honey strawberries. The method has advantages of advanced method of processing with the honey, reasonable raw material formulation and natural mouthfeel of products in a low-temperature frozen state.
Owner:杭州源淇食品科技有限公司
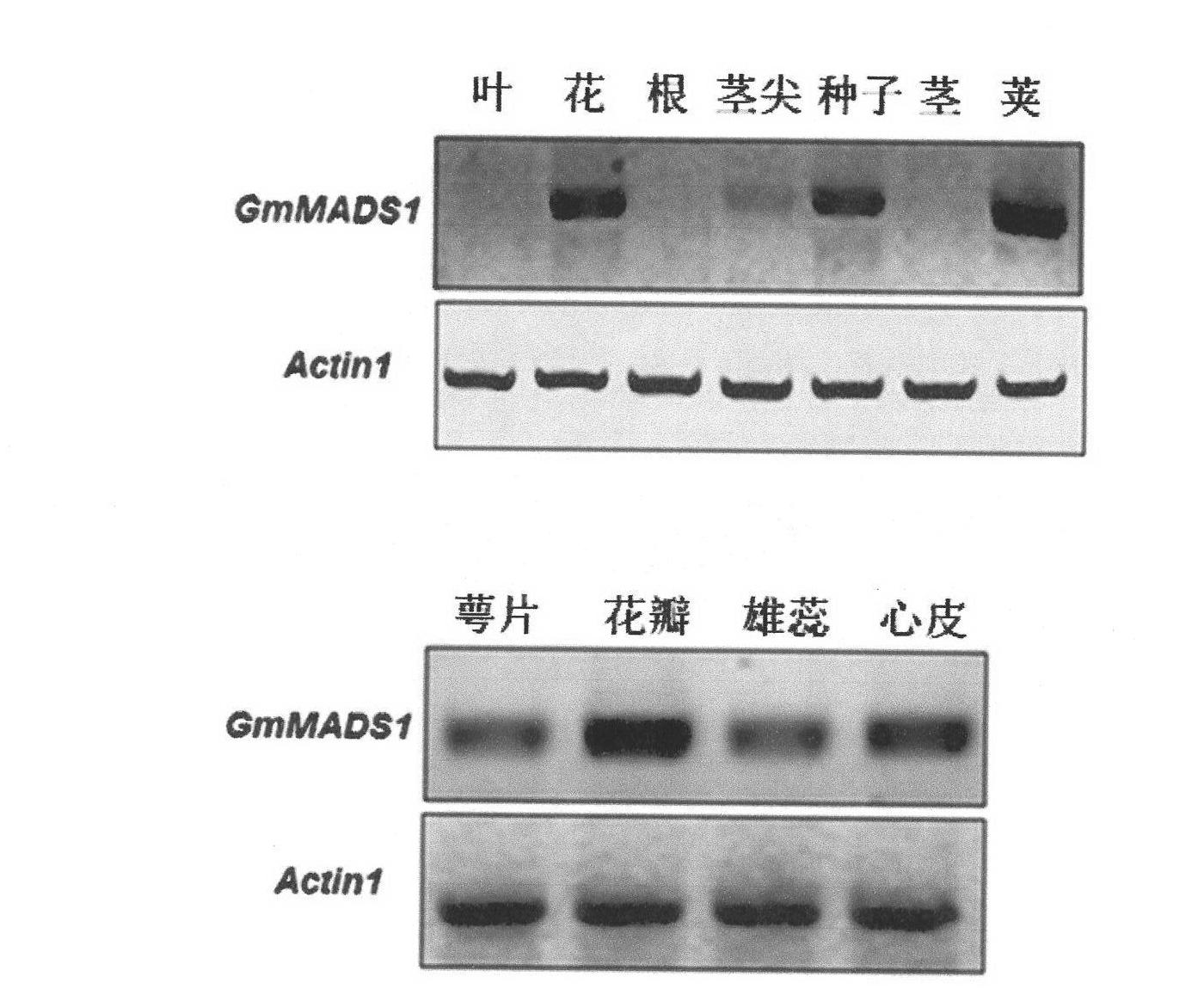
Soybean MADS-box gene and applications thereof in floral organ modification
InactiveCN101805740AYield-enhancing servicesFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPetalAnther dehiscence
The invention discloses a soybean MADS-box gene and applications thereof in floral organ modification, belonging to the field of biotechnology. GmMADS1, transcription factor in nucleus, is expressed in all the floral organs of four circles and, however, expressed in large quantity in petals and stamens, tobacco expressing excessive GmMADS1 increases the number of sepals, stamens and petals, a transformation from the sepals and the stamens to the petals is formed, as a result, the occurrence of cracking petals and bending stamens etc. causes the stamens to fail to come into contact with pistils, thus normal pollination and normal anther dehiscence cannot be realized and pollen activity is lowered. The above results represent that GmMADS1 plays an important regulation and control role in determining the position and the number of the petals and the development of male organs. New floral organ-variant material, resulted from the GmMADS1 gene, can be used for the breeding of crops and ornamental horticulture plants.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Soybean sexual hybridization method
The invention relates to the field of hybridization breeding, and specifically relates to a soybean sexual hybridization method. The soybean sexual hybridization method comprises the following nine links: (1) fixing flower buds; (2) removing sprout for the first time, namely only reserving quasi-hybrid flower buds in the whole inflorescence, and completely removing the rest of flower buds; (3) removing calyx, namely removing calyx lobus at the upper half part of the calyx while reserving the basic cylindrical structure of the calyx; (4) castrating; (5) belaying, namely coiling a short wire into an annular slipknot to gently tie a flower stalk after passing through the flower; (6) taking flowers, namely before 6 a.m. the next day after castrating, picking flowers with unopened petals and uncracked carina on a plant with typical male parent variety characters as a pollen taking object; (7) pollinating at 6-8 a.m. the next day after castrating; (8) putting up brass plates; and (9) managing in the later period. The hybrid survival rate and hybrid efficiency are greatly improved according to the soybean sexual hybridization method provided by the invention.
Owner:CANGZHOU ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Preparation method of paraffin section of pear flower tissue
InactiveCN109060468AImprove post-embedding qualityImprove embedded qualityPreparing sample for investigationParaffin waxPetal
The invention relates to the technical field of biological histology, in particular to a preparation method of paraffin section of pear flower tissue, which comprises the following steps: taking out the pear flowers preserved in a 4-5 degree Celsius refrigerator and washing them with distilled water, removing the center of the flower, stamen, calyx, petals, and the 3 mm portion below the base of the stalk to obtain the treated pear flower tissue; putting the obtained pear flower tissue into a FAA fixing solution of a fixing container, and evacuating the fixing container until the FAA fixing solution no longer appears bubbles, fixing 1-2days after evacuating; placing the pear flower tissue obtained after evacuating on a gauze to absorb the FAA fixing solution, and carrying out dehydration,transparency, waxing, embedding, slicing, sticking, dewaxing, dyeing and de-floating treatment in turn. According to the preparation method of paraffin section of pear flower tissue, the problem thatthe traditional paraffin section has no strict requirements on material processing, which causes the tissue to be too large when slicing, thereby having a great influence on the experimental result issolved, and the quality of the paraffin section obtained is high.
Owner:TARIM UNIV
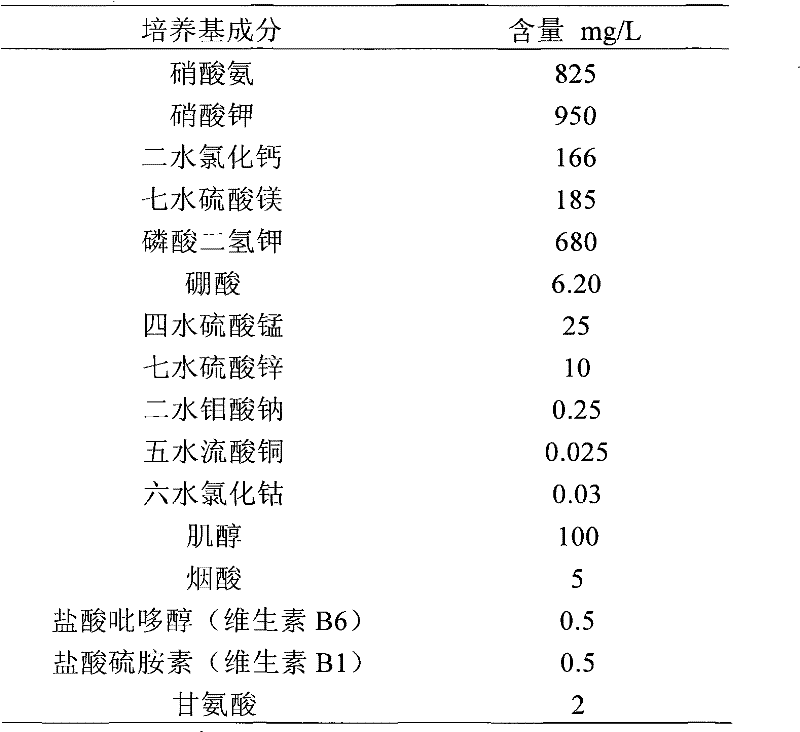
Strawberry tissue culture fast propagation method
InactiveCN105638465AGood regulationPromote growthHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureCulture mediumsPlant management
The invention discloses a strawberry tissue culture fast propagation method. The strawberry tissue culture fast propagation method comprises the following steps of (1) selection and sterilization of an explant: cutting a strawberry leaf or sepal, cleaning, and sterilizing, so as to obtain the explant; (2) induced culture of a callus: inoculating the explant obtained in step (1) into an induced culture medium of the callus to culture for 2-3 weeks, so as to obtain the callus; (3) differentiation and proliferation culture: inoculating the callus obtained in step (2) into a differentiation culture medium to culture for 5-6 weeks, so as to obtain a differentiation bud; inoculating the differentiation bud onto a proliferation culture medium to culture for 8-9 weeks, so as to obtain a proliferation seedling; (4) rooting culture: separating the proliferation seedling obtained in step (3) into single strains, and inoculating into a rooting culture medium to culture for 2-4 weeks, so as to obtain a strawberry sterile plant. The strawberry tissue culture fast propagation method has the advantages that the tissue culture process is simple and convenient, the culture time is short, the proliferation efficiency is high, the seedlings are regular, the subsequent uniform transplanting and planting management is convenient, the operation is easy, and the industrialized production is realized.
Owner:成都贝瑞生态农业开发有限公司
Eucalyptus floral product
A eucalyptus floral product and a method for producing the same is provided. The floral product is non-perishable and permanent, while appearing to be naturally grown as opposed to artificially manufactured. The eucalyptus leaf floral product comprises a plurality of eucalyptus leaves attached to a central stem to substantially resemble a corolla. Additionally, the corolla preferably resembles a rosette. The central stem is preferably a length of wire, and the eucalyptus leaves are preferably preserved eucalyptus leaves. The corolla includes an underside, and a plurality of smaller eucalyptus leaves attached to the underside of the corolla form to substantially resemble a calyx. Additionally, the leaves can be soaked in a mildly acidic solution, such as vinegar, before the leaves are formed into the floral product.
Owner:MINEAR MELAINE
Development and application method of solanum melongena L. EST-SSR marker
The invention relates to a development and application method of a solanum melongena L. EST-SSR marker. The development and application method comprises the following steps of: (1) obtaining an EST sequence from a NCBI database, processing and detecting the SSR; (2) designing the sequences of the primers of an SSR marker; (3) obtaining the data of the solanum melongena L. No.1-48 in a table 1 and the light green leaves of the solanum melongena L. in an solanum melongena L. group F2, and extracting the total DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid); (4) amplifying the data of the solanum melongena L. No.1-12 in the table 1 by using the designed sequences of the primers of the SSR marker; (5) obtaining a different EST-SSR marker in the data of the solanum melongena L. No.7-12 in the table 1, wherein the sequence of the EST-SSR marker is showed in a sequence table; (6) amplifying the data of the solanum melongena L. No.7-12 in the table 1 and the solanum melongena L. group F2 by using the obtained EST-SSR marker; (7) calculating the content of the polymorphism information of each pair of primers, and analyzing the genetic diversity of the data of the solanum melongena L. No13-48 in the table 1 in a clustering way; and (8) carrying out linkage mapping and QTL positioning to the solanum melongena L. group F2 obtained in the step (6). The results show that the G249 primer is linked to the solanum melongena L. fruit length and the fruit solanum melongena L. fruit character to explain 4% and 5.1% of phenotypic variation, and the G192 primer is linked to the solanum melongena L. calyx size and the solanum melongena L. calyx character to explain 5.3% of phenotypic variation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Gerbera jamesonii receptacle induction method
InactiveCN102499081ADifferences in Subtractive Induction RatesHigh induction ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBudInflorescence
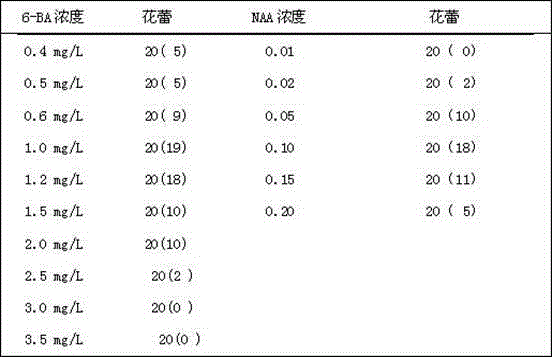
The invention provides a gerbera jamesonii receptacle induction method and relates to a flower culture method. The gerbera jamesonii receptacle induction method comprises the following steps of: selecting explants, disinfecting the explants, selecting receptacle induction media and selecting culture conditions and modes. Tender gerbera jamesonii buds are vertically cut into four blocks after calyx and small inflorescence peeling and are then inoculated into the induction culture medium for normal light illumination culture. The method is characterized in that in the step of selecting the explants, explants with the bud diameter being 0.5 to 0.8cm are used as selection objects, and in addition, the cold storage pre-treatment on the selected objects for 48 hours at 4 DEG C is added; in the step of selecting receptacle induction media, the selected culture medium has a recipe consisting of 10mg / L 1 / 2MS+6-BA, 0.5mg / L of NAA, 30g / L of cane sugar and 7g / L of agar, and the pH value is controlled to be about 5.8; and the culture conditions and modes are as follows: 7-day dark pre-culture is firstly carried out, then, the normal light illumination culture is adopted, the light illumination intensity is 1500 to 2000lx, the light illumination time is 14hours / day, and the temperature is 23 to 25 DEG C until annual seedlings are obtained through culture. The induction rate of the receptacle callus and the differentiation rate of adventitious buds are improved.
Owner:福建宏翔农科农业发展有限公司
Emasculation method for compositae plants
A method for detasseling Compositae plants is characterized in adopting artificial detasseling through cutting corolla in plant breeding of Lactuca, Sonchus, and Taraxacum of Compositae. the method comprises cutting maternal calyces to remove corolla in early morning before florescence without injuring calyces, after 1 h, pistil grows out new thrumb, chapiter and petal, when the chapiter grows to Y shape, pollinating with male parent through cap bag at once to perform intergeneric crossing. Compared with present technology, the invention creates conditions for hybridization breeding of Lactuca, Sonchus, and taraxacum of Compositae due to the regrowth vigor and recuperability of their corolla, thrumb, and chapiter, and promotes the development of conventional breeding technology.
Owner:陈振志 +1
Method for acquiring virus-free strawberry seedlings
InactiveCN104429940AAvoid destructionEasy to peel offHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureFragariaBud
The invention provides a rapid propagation method for acquiring virus-free strawberry seedlings. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting a raw material and sterilizing the raw material; (2) bud culture: removing sepals of a sterilized bud, then inoculating the bud into a prepared culture medium of MS+6-BA1.0mg / L+NAA0.1mg / l for culture till clumpy buds grow out; (3) propagation culture: transferring the clumpy buds onto a culture medium of MS+6-BA0.1mg / L for propagation culture; (4) induced rooting: cutting off strawberry seedlings from the clumpy buds, transferring the strawberry seedlings to the culture medium of 1 / 2MS+NAA0.1mg / L culture medium, inducing the rooting, and transferring the rest of callus to the culture medium of MS+6-BA0.1mg / L for culture; (5) seedling hardening: transplanting the rooted strawberry seedlings into a culture plate from a culture bottle, and carrying out the seedling hardening growth in a greenhouse. By utilizing the method, the method for acquiring the virus-free seedlings is simple, the acquired seedlings are strong, stolon reproduce quickly, and the quality is good.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com