Soybean MADS-box gene and applications thereof in floral organ modification
A soybean and gene technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, can solve the problems of flower development research lag
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Embodiment 1, cDNA cloning and identification of soybean MADS-box gene GmMADS1
[0037] Primers were designed according to the full-length sequence of GmMADS1,
[0038] Upstream primer: 5′-GAGATGGGAAGGGGAAGAGT-3′
[0039] Downstream primer: 5′-CAAGGAAGAGGCTAGCTAGG-3′
[0040]Using the RT-PCR method, the GmM Shuchang ADS1 gene was cloned from the soybean variety Jackson (publicly known and available for purchase from the National Soybean Improvement Center). Take the mixture of soybean flowers and flower buds, grind it with a mortar, add it to a 1.5mL EP tube filled with lysate, shake it fully, and then transfer it into a glass homogenizer. After homogenization, transfer to 1.5mL EP tube, and extract total RNA (TRIzol Reagents, Invitrogen, USA). The quality of total RNA was identified by formaldehyde denaturing gel electrophoresis, and then the RNA content was determined on a spectrophotometer. The obtained total RNA was used as a template, and reverse transcription ...
Embodiment 2
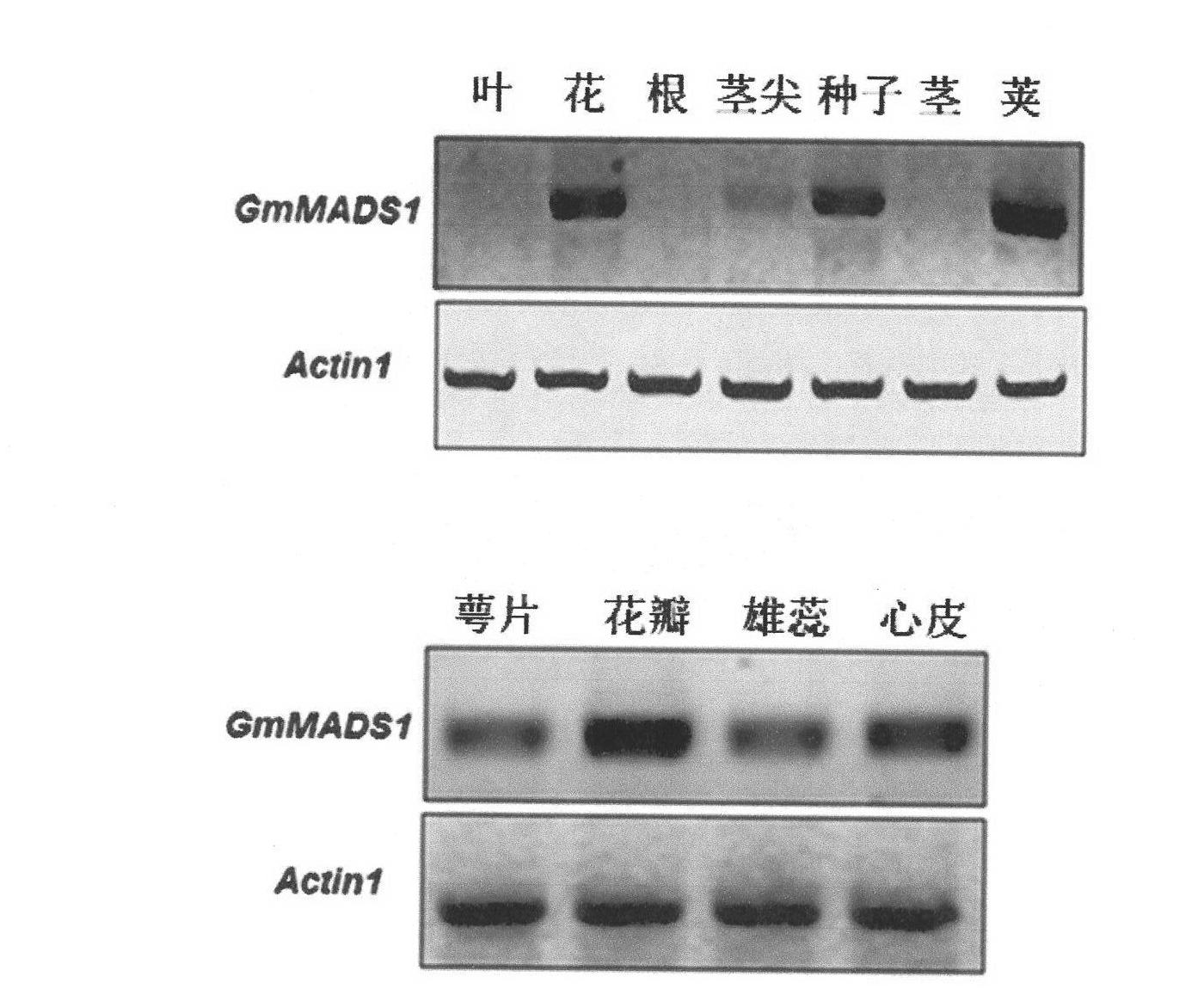
[0041] Embodiment 2, expression characteristics of soybean GmMADS1 gene in different tissues
[0042] The soybean variety Jackson was planted in the net room of Nanjing Agricultural University in normal season. Take the roots, stems and leaves of soybean at the six compound leaf stage, the mixture of flowers and flower buds at the full flowering stage (R1), the pods at the initial pod stage (R3), and the tender seeds 20 days after flowering, and store them in liquid nitrogen. Standby at -80°C. The whole soybean flower was aseptically divided into sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils at the full flowering stage, and was quickly frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80°C for later use.
[0043] The extraction of total RNA was the same as in Example 1. Using soybean constitutively expressed Actin gene (GenBank accession No. V00450) as an internal reference, and using total RNA from different soybean tissues as templates, RT-PCR analysis was performed. RT-PCR analysis showed...
Embodiment 3
[0044] The genetic engineering application of embodiment 3, GmMADS1
[0045] According to the cDNA sequence of GmMADS1, primers were designed to amplify the complete coding reading frame, and a BamH I restriction endonuclease site was introduced on the upstream primer, and a SacI restriction endonuclease site was introduced on the downstream primer:
[0046] Upstream primer: 5-A GGATCC GAGATGGGAAGGGGAAGAGT-3
[0047] Downstream primer: 5-A GAGCTC CAAGGAAGAGGCTAGCTAGG-3
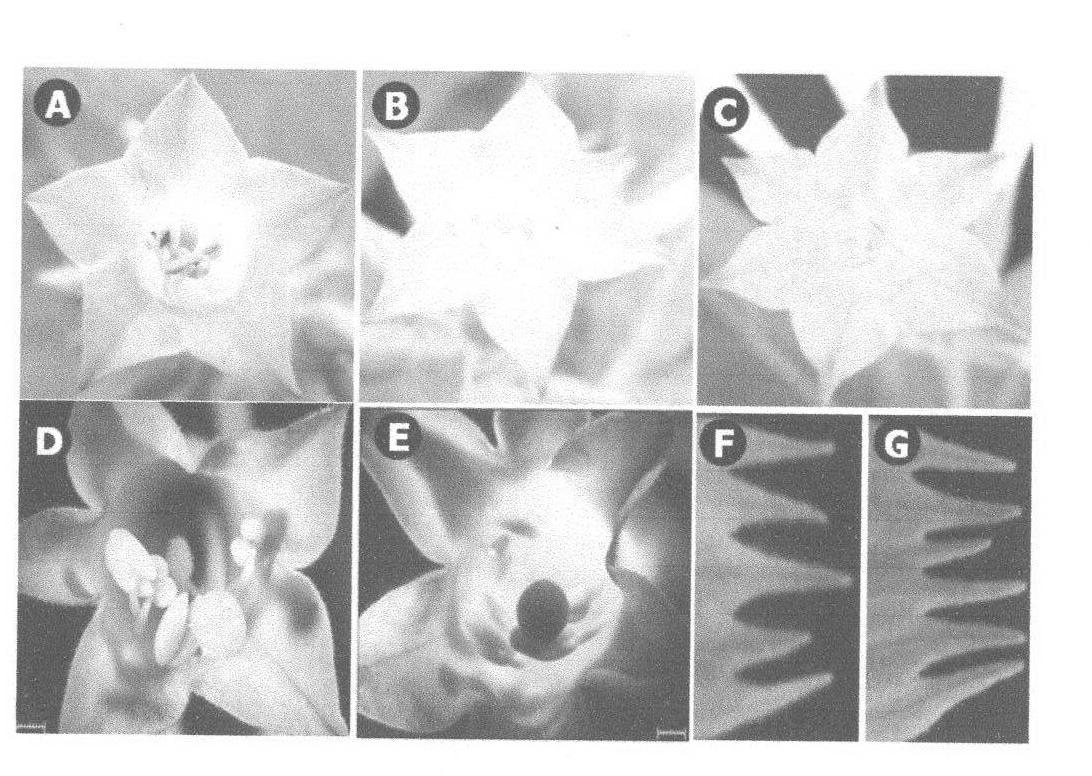
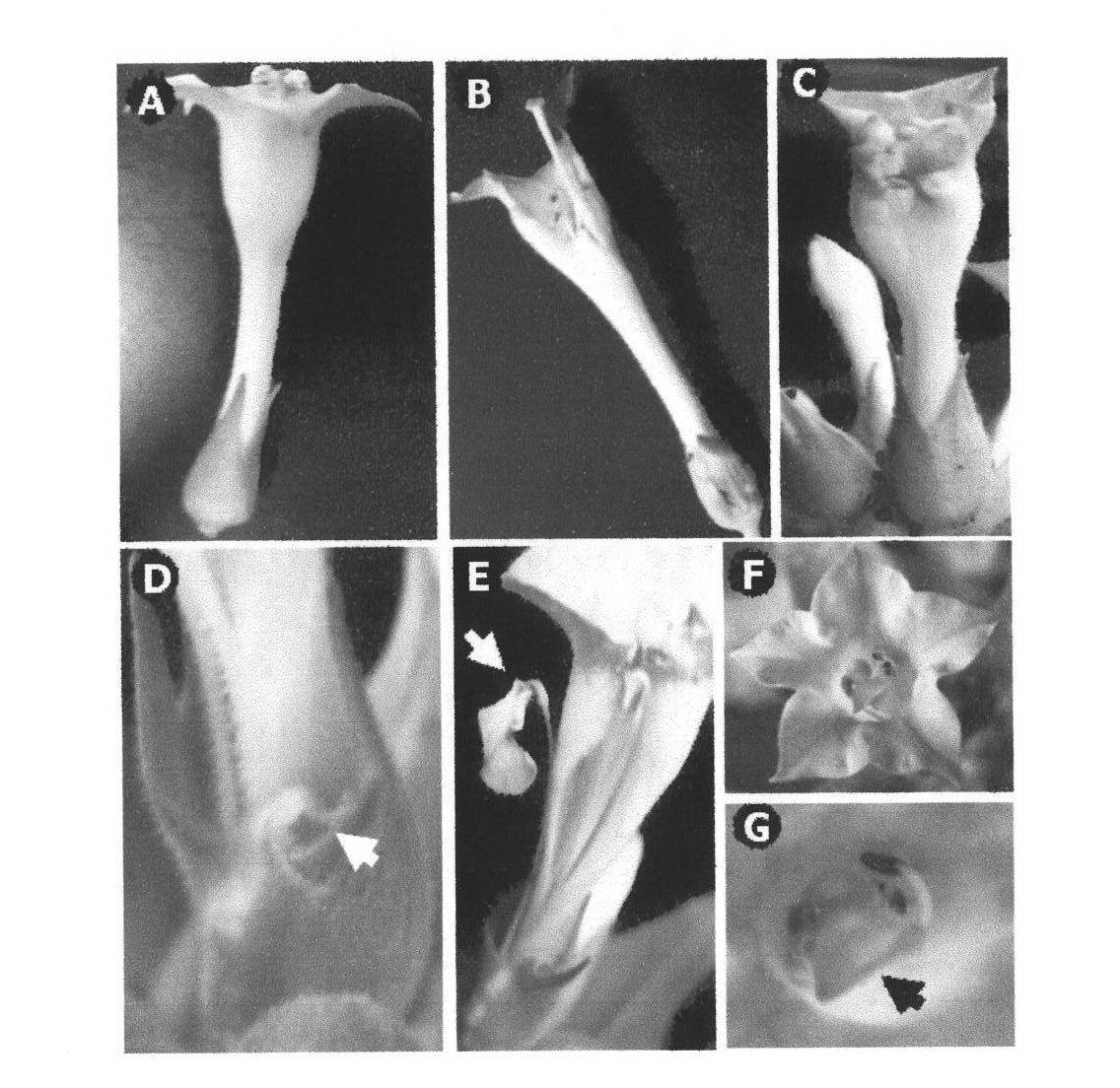
[0048] Using the PCR amplification product obtained in 1) as a template, after PCR amplification, the cDNA of GmMADS1 was cloned into the intermediate vector pMD18-T, and further cloned into the binary expression vector pBI121; the obtained expression vector was transformed into Agrobacterium strain LBA4404 was introduced into tobacco, and tobacco was transformed by Agrobacterium-mediated method. The obtained transgenic plants were analyzed by phenotype and cytology. It was found that the ectopic expressio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com