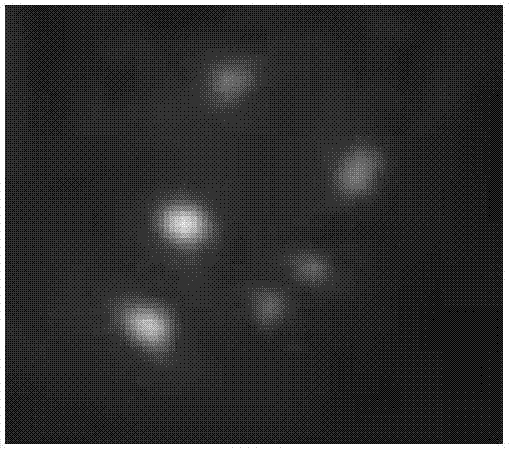
Fluorescence in situ hybridization method of prunus mume chromosome
A fluorescence in situ hybridization and chromosome technology, which is applied in the field of fluorescence in situ hybridization of plum blossom chromosomes, can solve problems such as the application of FISH technology that has not been reported, and achieve the effect of improving the success rate of hybridization and high hybridization specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] 1. Preparation of chromosome slide specimens
[0058] The stem tip of plum blossom 'Longyou' (Prunus mume 'Longyou') germinated in spring is used as the material, and its length is preferably 0.5-1cm. Chromosomal slide specimens were prepared by the wall-removing hypotonic flame-drying method, followed by Carnot’s fixative at -20°C for more than 24 hours, 0.075mol / L KCl solution before hypotonic treatment for 30 minutes, and 2.5% cellulase and pectinase enzymes Solution 110min, ddH 2 After O, hypotonic treatment was performed for 30 minutes. Perform microscopic examination under an optical microscope, and select metaphase cleavage specimens with clear images and a high degree of dispersion and store them in a -20°C refrigerator for later use.
[0059] 2. Pretreatment of chromosome slide specimens
[0060] 1) Operate in groups of 4 slides, place the chromosome slide specimen in an oven at 65°C for 1 hour, add 100 μl of 0.1 mg / ml RNaseA solution on the chromosome slide...
Embodiment 2
[0080] The difference from Example 1 is that the plum blossom variety is 'Xiaogongfen'. The steps and signal observation are the same as in Example 1.
[0081] Analysis of results: from Figure 4 and Figure 8 It can be seen that there are 6 hybridization signals when the Dig-labeled 45SrDNA probe hybridizes with the Meihua chromosome preparation, and the signal points are located on the 1st, 3rd, and 7th pairs of homologous chromosomes. Among them, the signal of homologous chromosome 1 was the strongest, the signal of homologous chromosome 7 was the weakest, and the signal intensity of homologous chromosome 3 was in the middle, with slight differences among different varieties. The karyotype formula is 2n=2x=16=10m(2SAT)+6sm. The signal points are all located at the end of the short arm of the chromosome, which can well distinguish non-homologous chromosomes with similar shapes, assist karyotype analysis to a large extent, and improve the accuracy of karyotype.
[0082] P...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com