A method for improving the efficiency of sexual hybridization of sweet potato
A sexual and efficient technology, applied in the field of crop breeding, can solve the problems of affecting the survival rate of sweet potato, prolonging the hybridization process time, withering and dying, etc., and achieving the effect of avoiding the death of hybrid sweet potato resources, reducing the workload of hybridization, and improving the success rate of hybridization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1, a kind of method that improves sweet potato sexual hybridization efficiency, this method adopts directional hybridization, comprises the following steps:
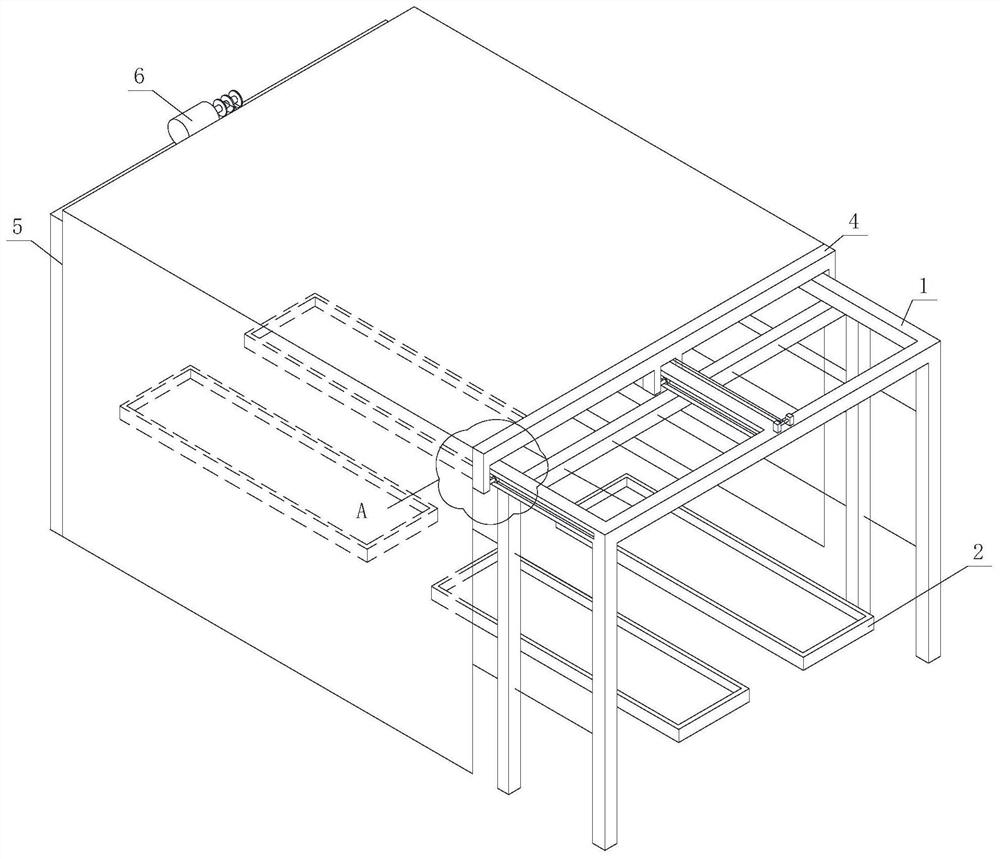
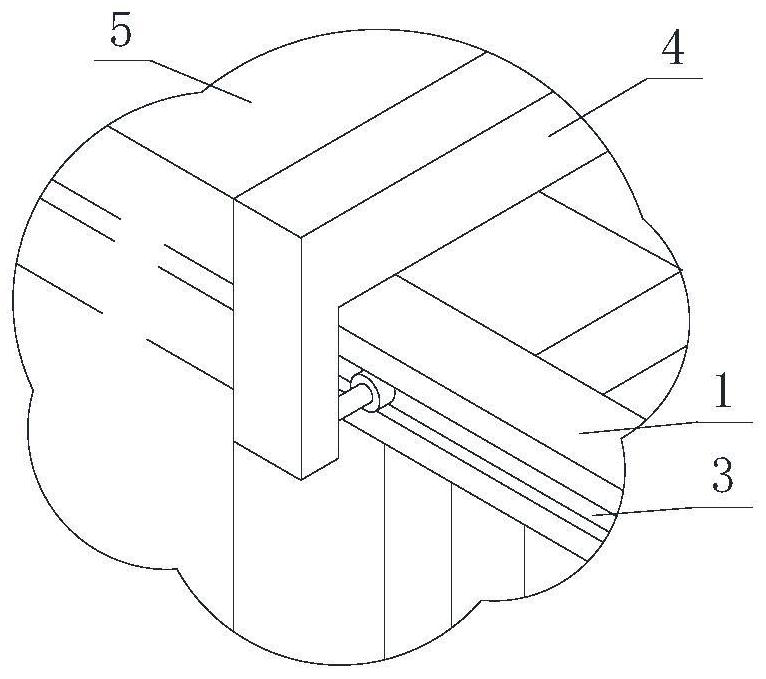
[0031] A, build hybrid shed 1 outdoors, as Figure 1-2 As shown, the length of the hybridization shed 1 is 23-24m, the width is 5.5-6.0m, and the height is 2.3-2.5m. The hybridization shed 1 is provided with an automatic opening and closing sunshade mechanism; Track 3, the walking trolley 4 and the sunshade net 5 that are arranged on the track 3, the sunshade net 5 covers the upper end of the hybridization shed 1, and the two sides of the sunshade net 5 fall along the left and right sides of the hybridization shed 1 to the two sides of the hybridization shed 1. The sides are covered; the two ends of the sunshade net 5 are respectively fixedly connected with the hybridization shed 1 and the walking trolley 4, and the driving unit drives the walking trolley 4 to reciprocate on the hybridization shed 1, an...
Embodiment 2
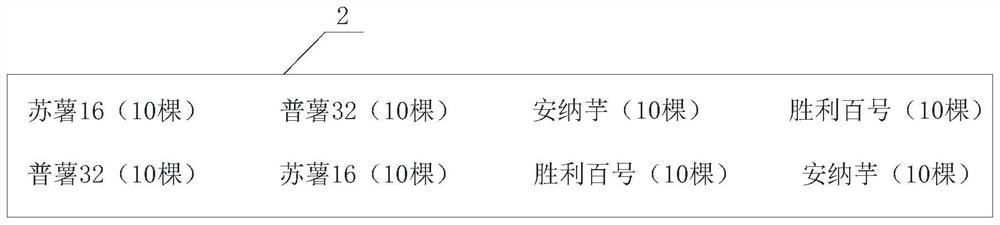
[0044] Embodiment 2, a method for improving the efficiency of sexual hybridization of sweet potatoes, the difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is that the method adopts non-directional hybridization, adopts a plurality of fresh-eating sweet potato varieties to plant together, and the parent varieties are respectively selected Sushu 16, Pushu 32, Shengli 100, Anna taro, in step B hybridization pool 2, each row is planted with Sushu 16, Pushu 32, Shengli 100, Anna taro, 10 plants of each variety, two rows staggered planting, such as image 3 shown;
[0045] The pollination method of step D in Example 2 adopts honeybee pollination, and finally 1340 seeds are harvested with Sushu 16 as the female parent, 960 seeds are harvested with Pushu 32 as the female parent, and 880 seeds are harvested with Anna taro as the female parent. Shengli 100 harvested 640 seeds for the female parent.
[0046] Count the survival rate, flowering number, hybridization number, and seed sett...
Embodiment 3
[0054] The difference between Example 3 and Example 1 is that Sushu 16 and Mingmen Jinshi are used as parents, and insects such as bees are used to carry out natural hybridization. On May 5, two rows of potato seedlings were planted in the hybridization pool 2. The potato seedlings were Sushu 16 and Mingmen Jinshi, and 20 plants of Sushu 16 and Mingmen Jinshi were planted respectively. A total of 3 groups Ⅰ, Ⅱ, and Ⅲ were set up. The survival rate of Sushu 16 and Mingmen Jinshi was counted, and the short-day treatment was carried out. Sushu 16 and Mingmen Jinshi were induced to flower, and the flowering numbers were counted until August 15. The statistical results are shown in Table 5.
[0055] The non-grafting hybridization test statistical result of table 5 embodiment 3
[0056]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com