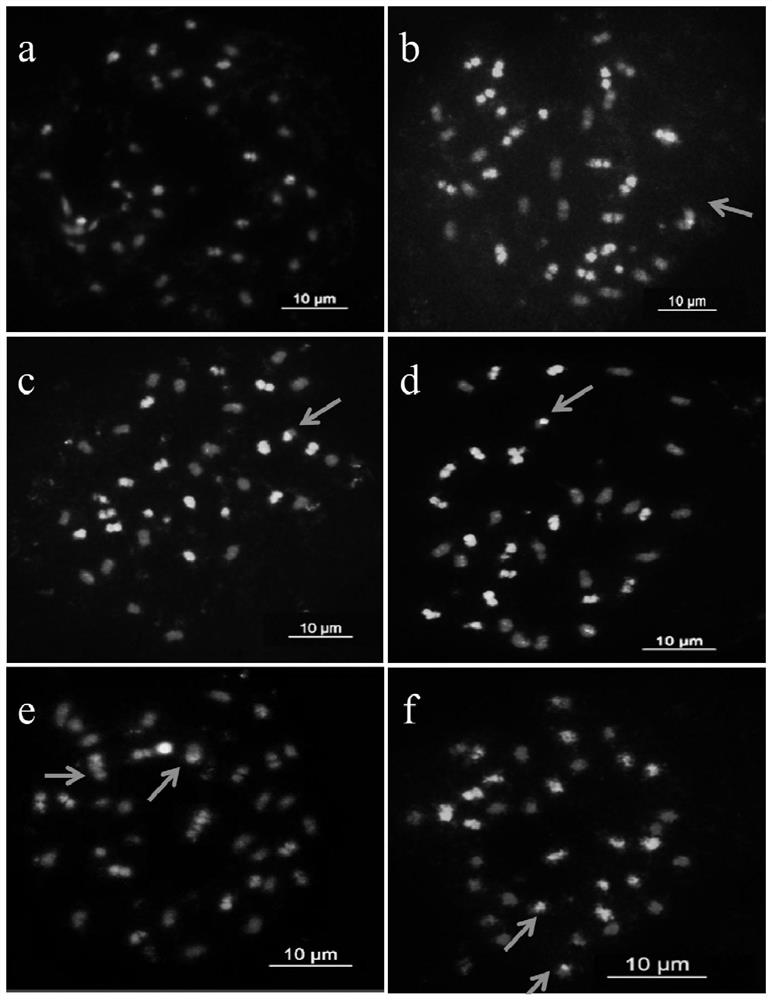
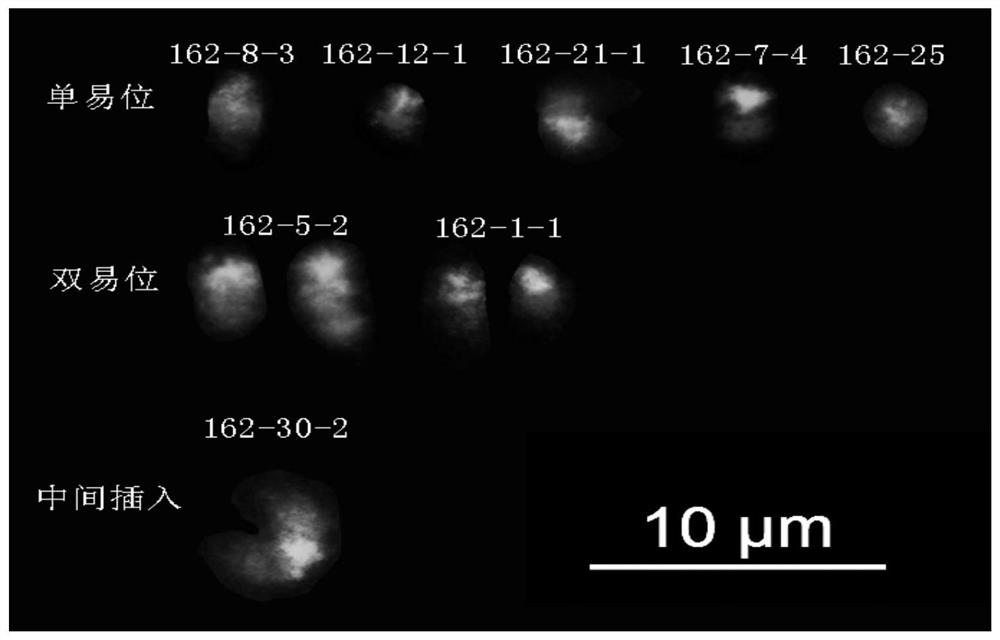
Patents
Literature
32 results about "Molecular cytogenetics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
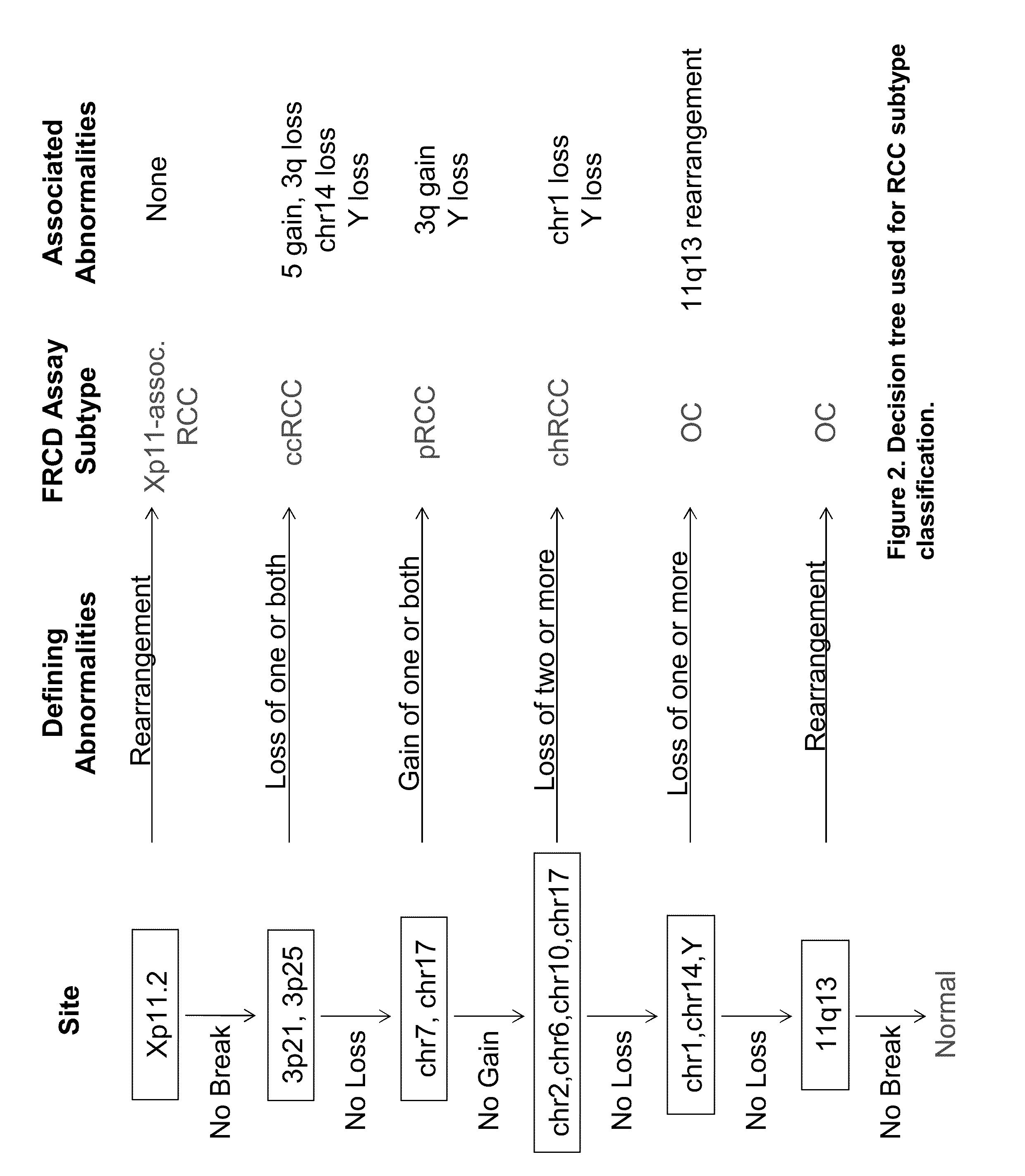
Molecular cytogenetics involves the combination of molecular biology and cytogenetics; using various reagents, molecular cytogenetics seeks to properly distinguish normal and cancer-causing cells. Molecular cytogenetics is a useful tool for the diagnosing and treatment of various malignancies such as brain tumors, haematological malignancies, etc. It includes a series of techniques referred to as fluorescence in situ hybridization, or FISH, in which DNA probes are labeled with different colored fluorescent tags to visualize one or more specific regions of the genome. FISH can either be performed as a direct approach to metaphase chromosomes or interphase nuclei. Alternatively, an indirect approach can be taken in which the entire genome can be assessed for copy number changes using virtual karyotyping. Virtual karyotypes are generated from arrays made of thousands to millions of probes, and computational tools are used to recreate the genome in silico.
Method for separating cotton chromosomes
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular cytogenetics and particularly relates to a method for separating cotton chromosomes, which comprises the following steps: preparing material, preprocessing the material, performing primary hypotonic treatment, performing enzymolysis, performing secondary hypotonic treatment, drying and covering a plate, removing the cover plate, performing chromosome microisolation and collecting the chromosomes. In the method of the invention, the primary hypotonic treatment, emzymolysis, secondary hypotonic treatment and plate covering method are combined to prepare for making a chromosome membrane sheet; cell walls are completely removed; the chromosomes well disperse after being compressed slightly; and the shapes of the chromosomes are so clear as to facilitate the recognition of target chromosomes.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
FISH method of one piece and multiple target of cotton
InactiveCN101818206AGuarantee authenticityEnsure consistencyMicrobiological testing/measurementVisual field lossAgricultural science
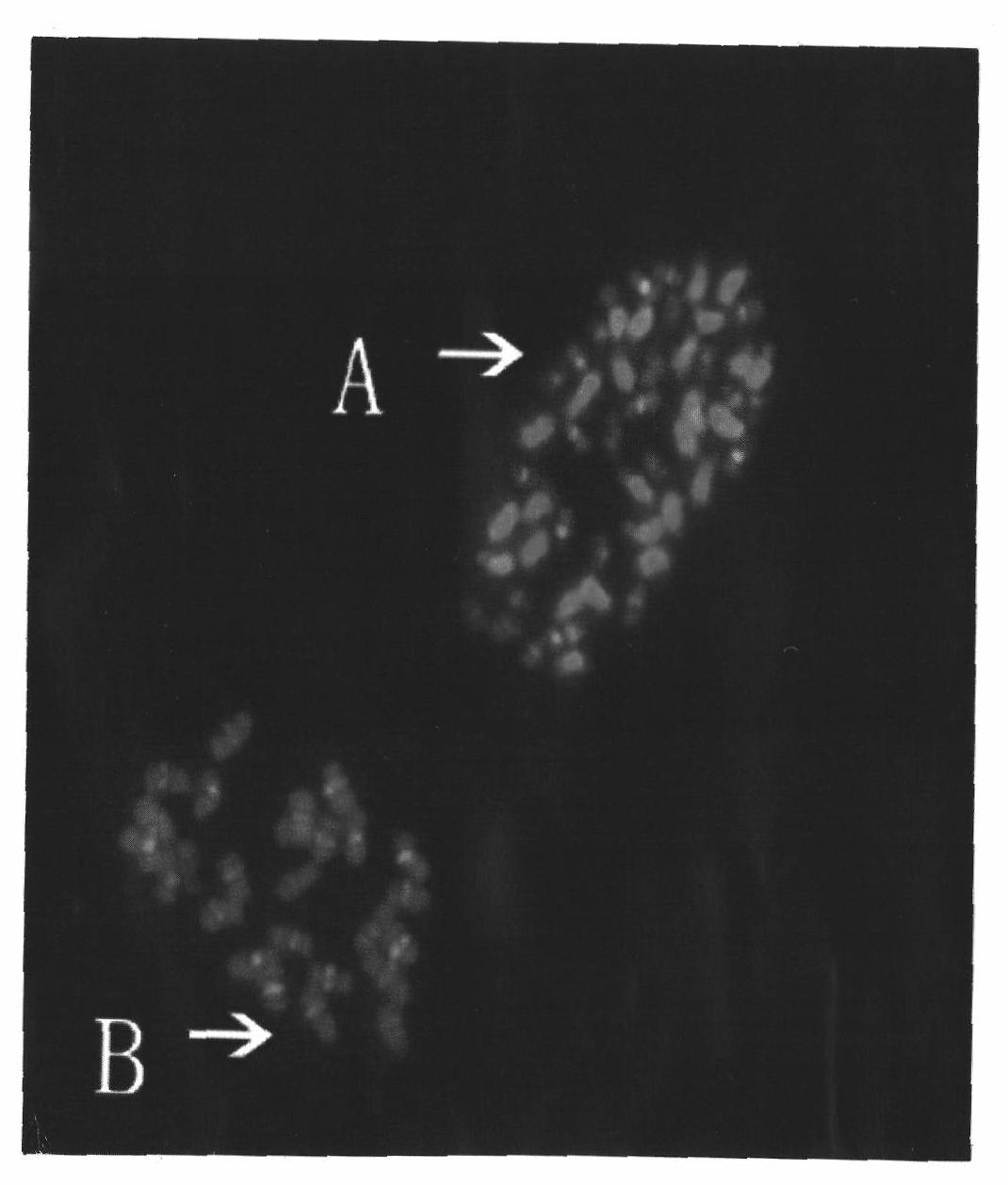
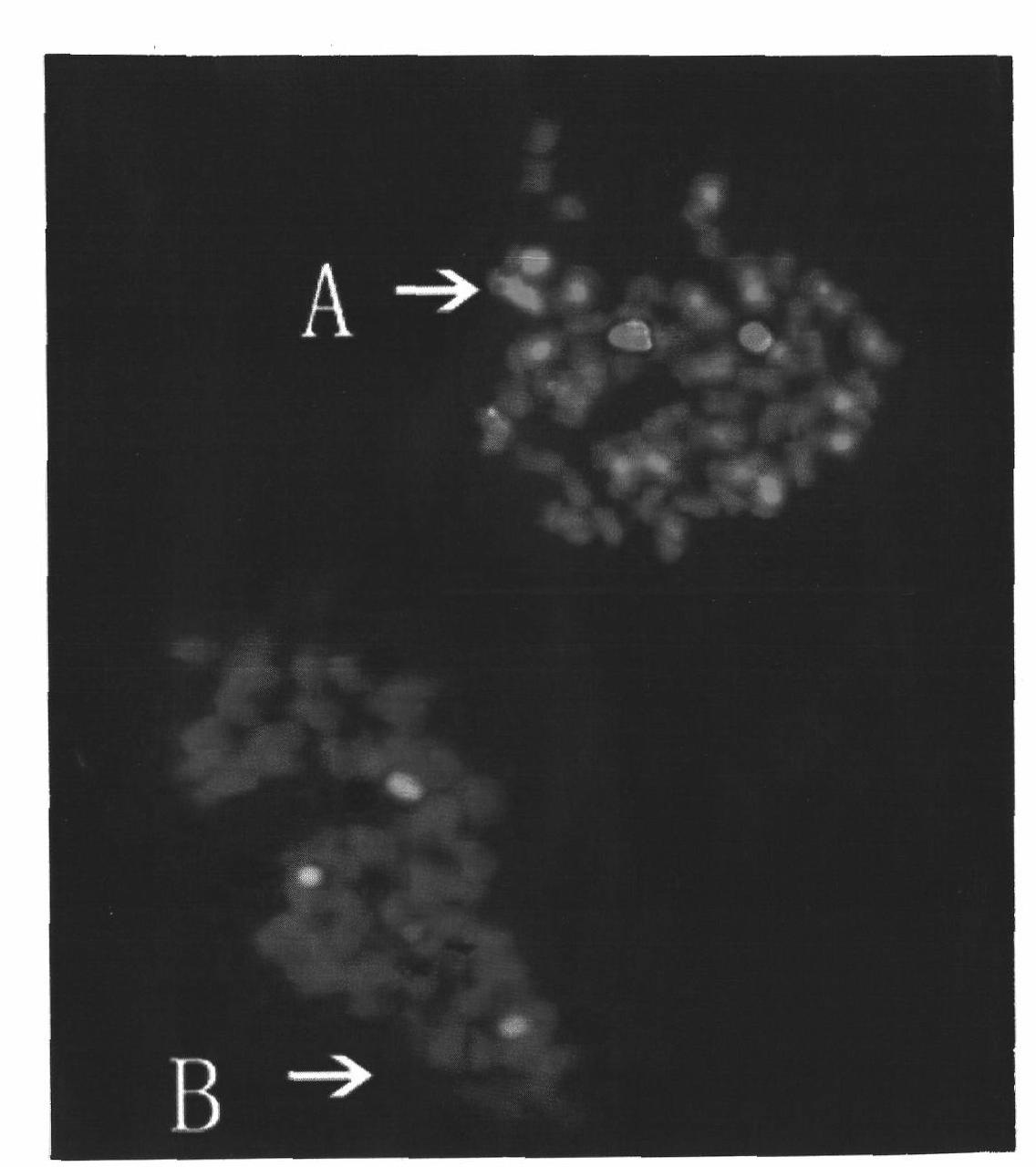
The invention belongs to the field of cytogenetics, specifically relating to a FISH method of the one piece and multiple target of the cotton, which comprises the following steps of: 1) putting chromosome samples of different cotton types on one carry sheet glass to produce a piece in a mixing way; and 2) simultaneously performing fluorescence in situ hybridization with the same probe, selecting and photographing the division phases of the chromosomes of the different cotton types under the same visual field when acquiring a fluorescence in situ hybridization result image. The method guarantees the consistency of external environment (the hybridizing or eluting temperature, humidity and time, and the content of each ion in solution, etc.), a manual operation step and the like, in the hybridization step of the target chromosomes of the different cotton types, and avoids the experimental error caused by the manual operation or the external condition when respectively performing the fluorescence in situ hybridization, therefore, the FISH experimental result obtained by the method is relatively true.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for creating and authenticating chromosome translocation line between peanut genomes A and B
ActiveCN107604088AEnables chromatin exchangeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGamma ray
The invention discloses a method for creating and authenticating chromosome translocation line between peanut genomes A and B. The creating method comprises the steps of taking a peanut cultivation variety four-grain red as a material and irradiating the peanut plant by Co60-gamma rays at full-blossom period to obtain the peanut plant with the chromosome translocation between genomes A and B. Flowering phase Co60-gamma radiation induction is adopted, so that a large amount of chromosome translocation between the genomes A and B is generated, chromatin communication between the genomes A and Bis realized, a new resource material is provided for peanut breeding and molecular cytogenetic research, and an approach is provided for an artificially created exogenous chromosome (fragment) introgression line in a distant hybridization progeny material. The chromosome translocation line between peanut the peanut genomes A and B is authenticated by a genome fluorescent in-situ hybridization technology, a peanut cultivation variety genome A and B chromosome translocation line new material is created and authenticated for the first time, and an effective means is provided for authenticating peanut chromosome translocation.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
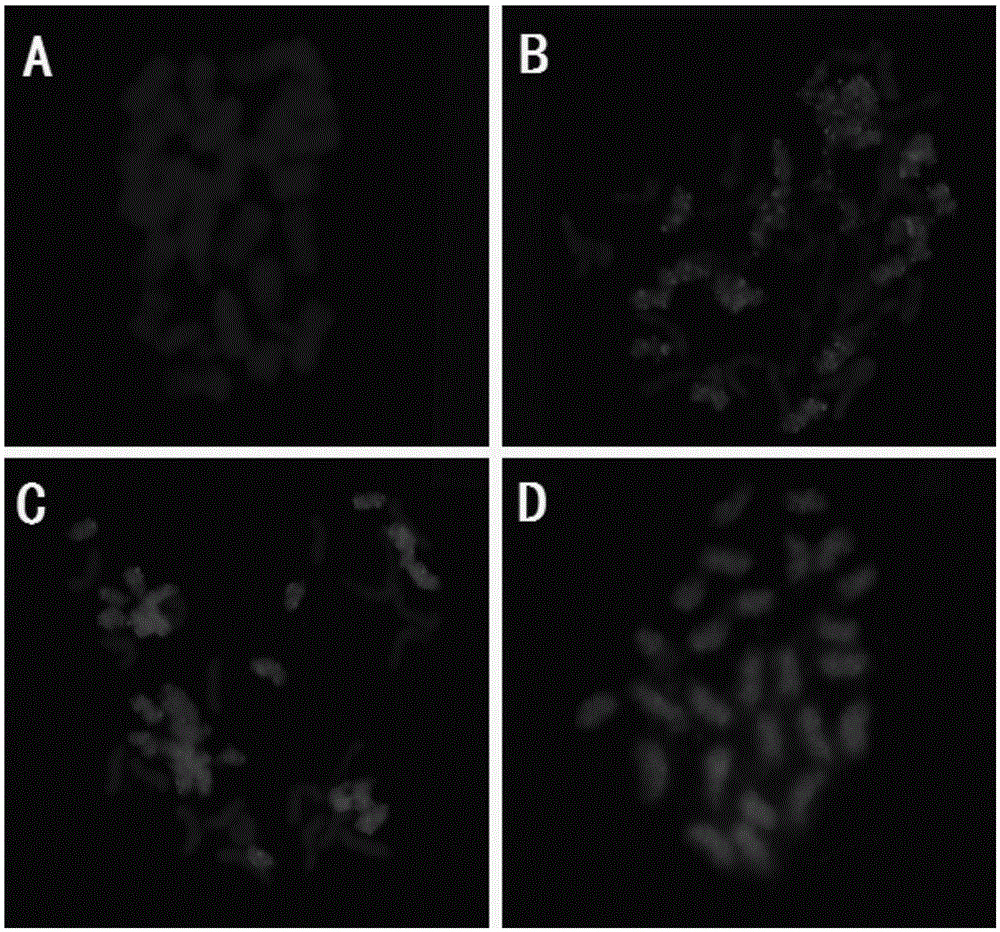
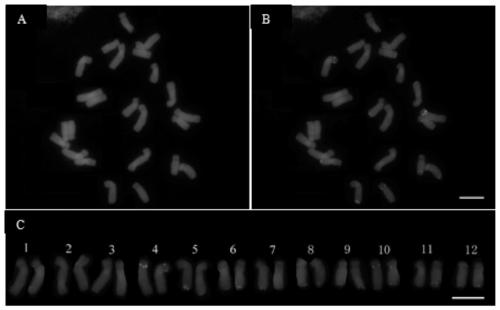
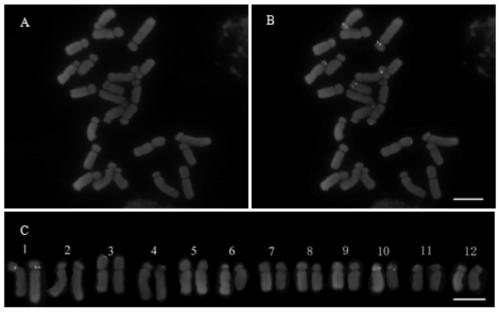
Method for identifying all chromosomes of poplar by using oligonucleotide probe
ActiveCN109825553ARealize identificationEfficient identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceBiotin
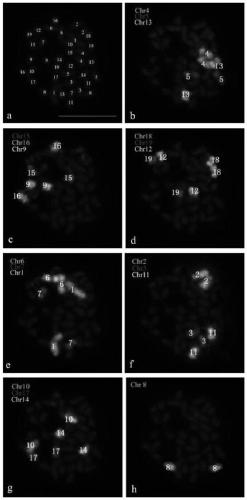
The invention discloses a method for identifying all chromosomes of poplar by using oligonucleotide probes. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a specific oligonucleotide sequence of each chromosome through bioinformatics analysis according to genome information of poplar tomentosa; synthesizing an oligonucleotide library corresponding to chromosome 1-19 of poplar; marking the oligonucleotide probes by using biotin or digoxin; identifying the chromosomes of the poplar by using a fluorescence in-situ hybridization technology; and repeatedly carrying out fluorescence in-situ hybridization for 7 times on the same metaphase splitting phase by using the oligonucleotide probes of up to three chromosomes simultaneously in each cycle of hybridization, so that 19 pairs of chromosomes of poplar species can be accurately identified.The method has the advantages of good universality in poplar species, good experimental repeatability and high resolution.The methoddisclosed by the invention provides a novel method for accurately identifying each chromosome of the poplar species, and lays a solid working foundation for molecular cytogenetics research of poplar.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method for displaying centromeres and short arms of Larimichthys crocea
The invention discloses a method for displaying centromeres and short arms of large yellow croaker, and belongs to the field of molecular cytogenetics. A molecular marker is a segment of a 28S rDNA sequence cloned from human saliva, and is processed to prepare a probe (named as H-P3K), and the probe is crossed with metaphase chromosomes of Larimichthys crocea to obtain a positive signal. The positive signal in the centromeres and the short arms of every metaphase chromosome can be detected when FISH of the Larimichthys crocea chromosomes is carried out by the probe, the short arm signal intensity of one chromosome is weaker than the centromere signal intensity of the same chromosome, and the centromere signal intensities of different chromosomes are different. The method is used for determining the position of the centromere, analyzing the chromosome karyotype and researching the chromosome structure; and the positive signal can be used as a chromosome identifying and pairing marker.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
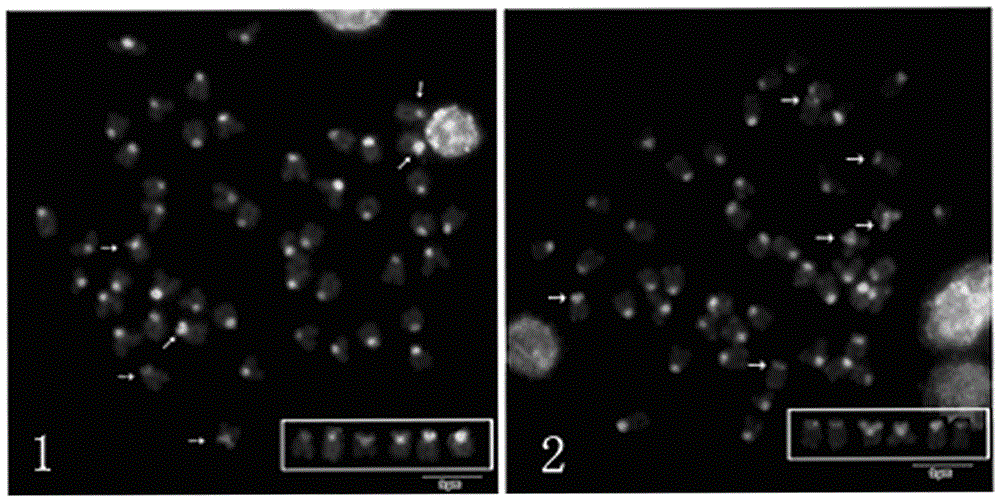
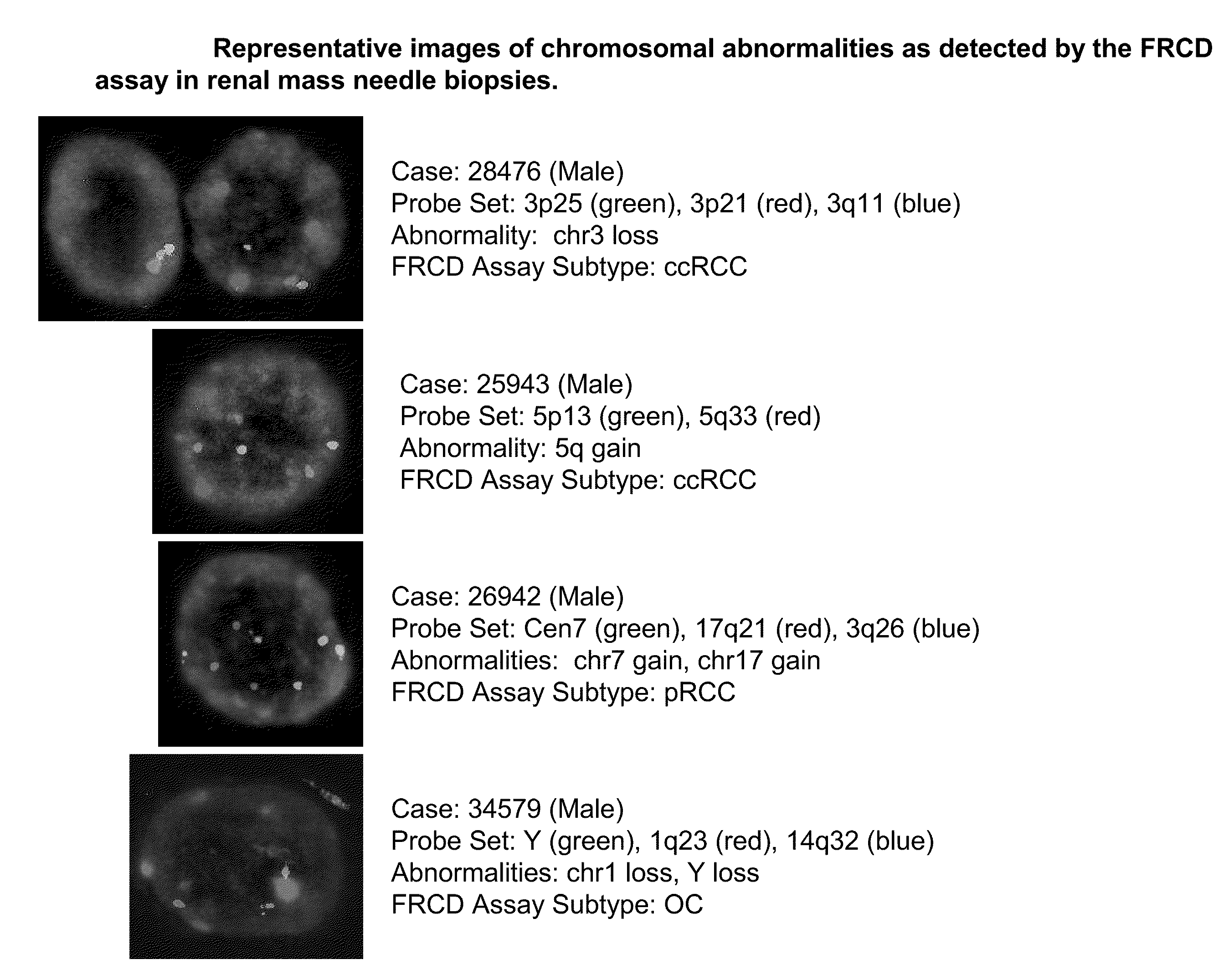
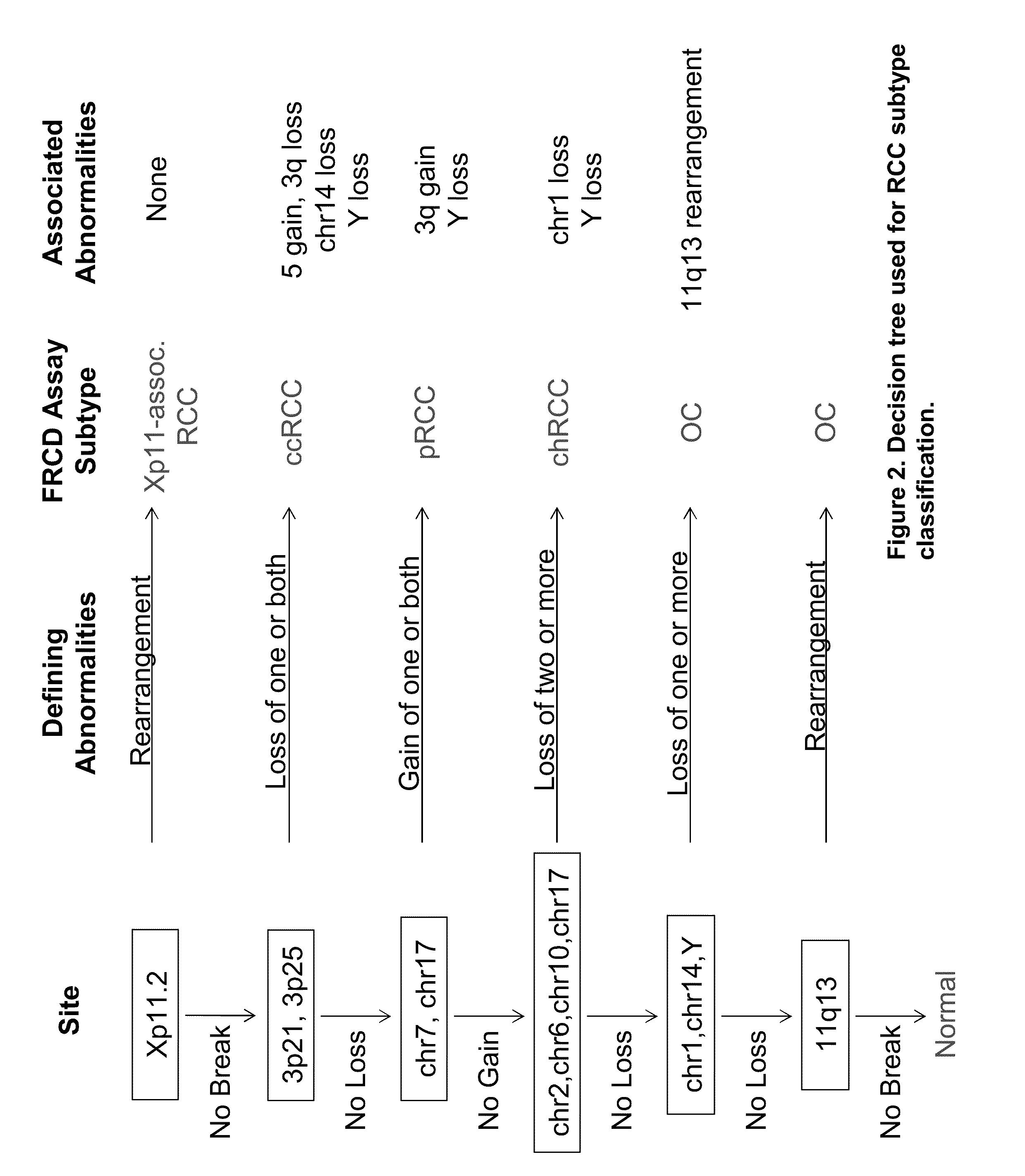
Panel for the detection and differentiation of renal cortical neoplasms
InactiveUS20090111704A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementRenal biopsy sampleNeoplasm present
The present invention provides a novel, highly sensitive and specific probe panel which detects the type of renal cortical neoplasm present in a biopsy sample. As such, the invention permits diagnosis of the predominant subtypes of renal cortical neoplasms without the use of invasive methods. The present invention further provides a molecular cytogenetic method for detecting and analyzing the type of renal cortical neoplasm present in a renal biopsy sample.
Owner:CANCER GENETICS
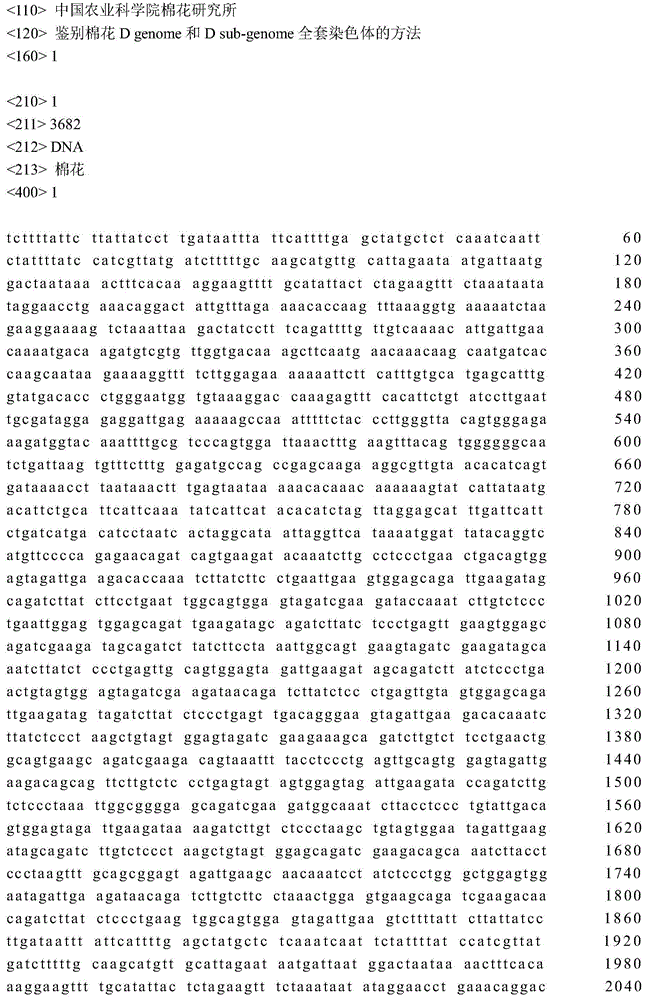
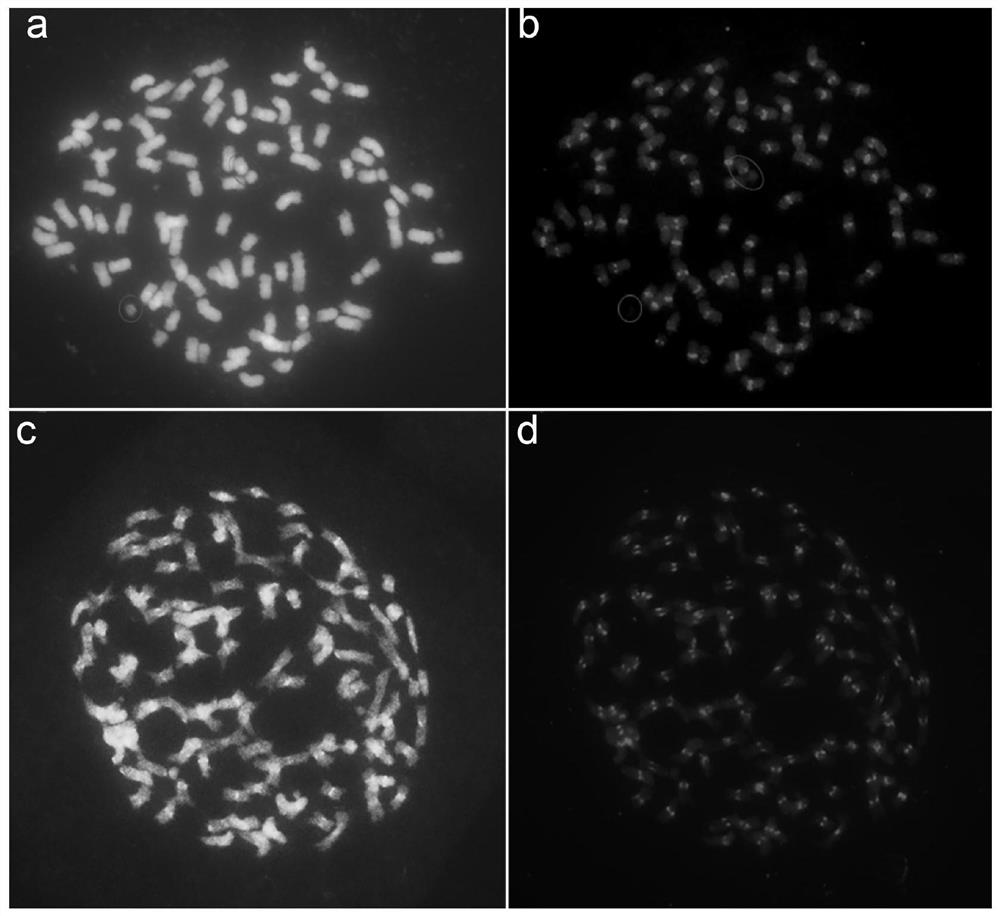
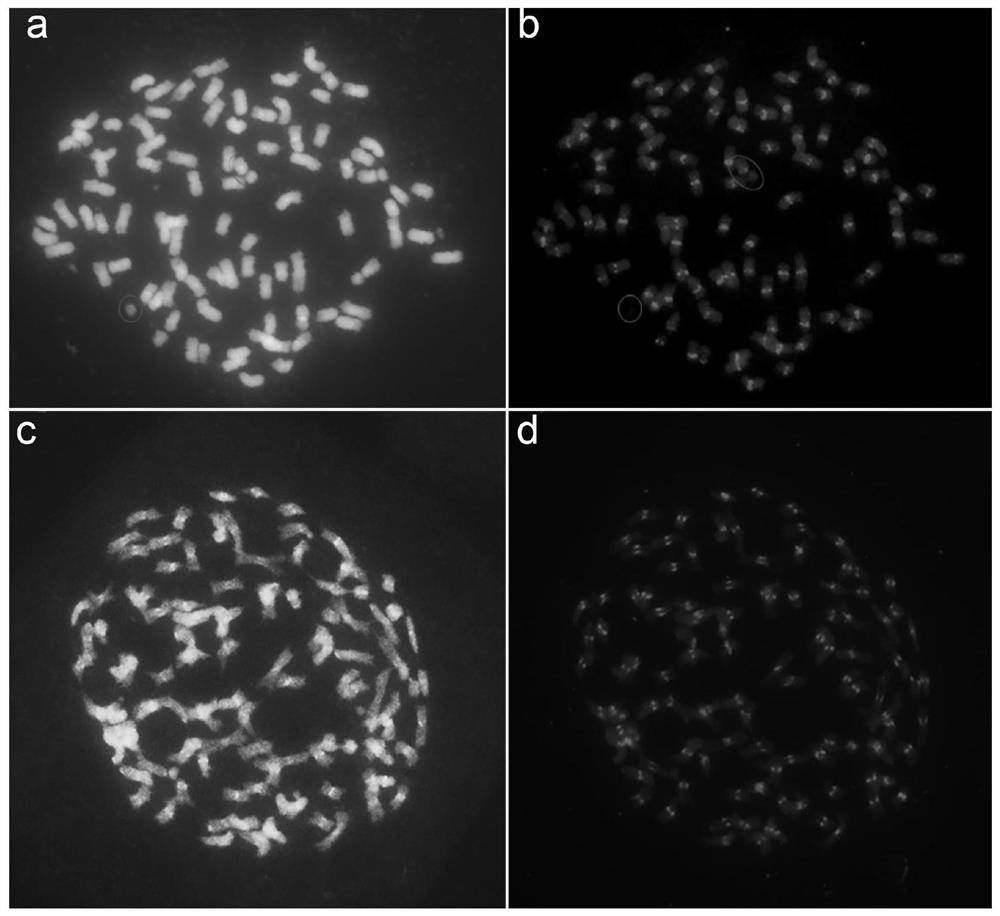
Method for identifying cotton D genome and D sub-genome complete chromosome
The invention belongs to the field of molecular cytogenetics and particularly relates to a method for identifying D genome and D sub-genome complete chromosome. The method comprises the following step: by taking a sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 as a probe to perform fluorescence in-situ hybridization on the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of a cotton genome. The sequence is taken as the probe, and chromosomes in the mitosis metaphase of the upland cotton, the asiatic cotton and the Raymond's cotton are taken as target DNA to perform fluorescence in-situ hybridization, and the results indicate that obvious hybrid signals are shown on the D subgenome chromosome of the upland cotton and the D genome chromosome of the Raymond's cotton, the signals are distributed on all chromosomes, and no obvious signals are shown in the A subgenome chromosome of the upland cotton and the A genome chromosome of the asiatic cotton. The sequence adopted by the method disclosed by the invention can be used for quickly identifying the cotton D genome and D sub-genome complete chromosome by virtue of a FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) method.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
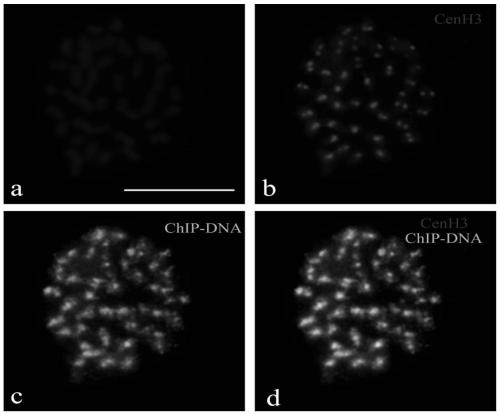
Antigenic polypeptide of poplar functional centromere histone CENH3 and application thereof
ActiveCN111410683AAccurate identificationSerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against plantsGenomicsPopulus trichocarpa
The invention discloses an antigenic polypeptide of poplar functional centromere histone CENH3 and application thereof, belonging to the fields of bioinformatics and molecular cytogenetics. The invention mainly comprises the following steps: screening a specific amino acid sequence of populus tomentosa CENH3 protein and artificially synthesizing a polypeptide; immunizing New Zealand rabbits with the polypeptide to prepare antiserum; and carrying out affinity purification to obtain a CENH3 protein antibody. Immunofluorescence detection and ChIP-FISH are carried out on the antibody to verify thespecificity, thereby proving that the antibody can accurately identify the functional centromere. The antibody can be universally used in poplar species, can accurately mark the position of the poplar functional centromere, and lays a foundation for developing the research on the structure, function and evolution of the poplar functional centromere. The invention has wide application prospects inthe research fields of poplar molecular cytogenetics, genomics, epigenomics and the like.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method for marking chromosome terminals of cotton A genome and A sub-genome
The invention belongs to the field of molecular cytogenetic, and concretely relates to a method for marking chromosome terminals of cotton A genome and A sub-genome. The method comprises: using BAC coming from gossypium barbadense pima-90BAC library to clone 350B21, performing BAC-FISH on mitosis mid-term chromosomes of different cotton species, and discovering the phenomena that the terminals of all chromosomes of A genome and A sub-genome generate strong hybridization signals, while the hybridization signals of all chromosomes of D genome and D sub-genome are not obvious. By utilizing the BAC-FISH method for BAC cloning, the chromosome terminals of cotton A genome and A sub-genome can be rapidly effectively marked.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +2
Panel for the detection and differentiation of renal cortical neoplasms
InactiveUS8603948B2Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementRenal biopsy sampleNeoplasm present
The present invention provides a novel, highly sensitive and specific probe panel which detects the type of renal cortical neoplasm present in a biopsy sample. As such, the invention permits diagnosis of the predominant subtypes of renal cortical neoplasms without the use of invasive methods. The present invention further provides a molecular cytogenetic method for detecting and analyzing the type of renal cortical neoplasm present in a renal biopsy sample.
Owner:CANCER GENETICS INC
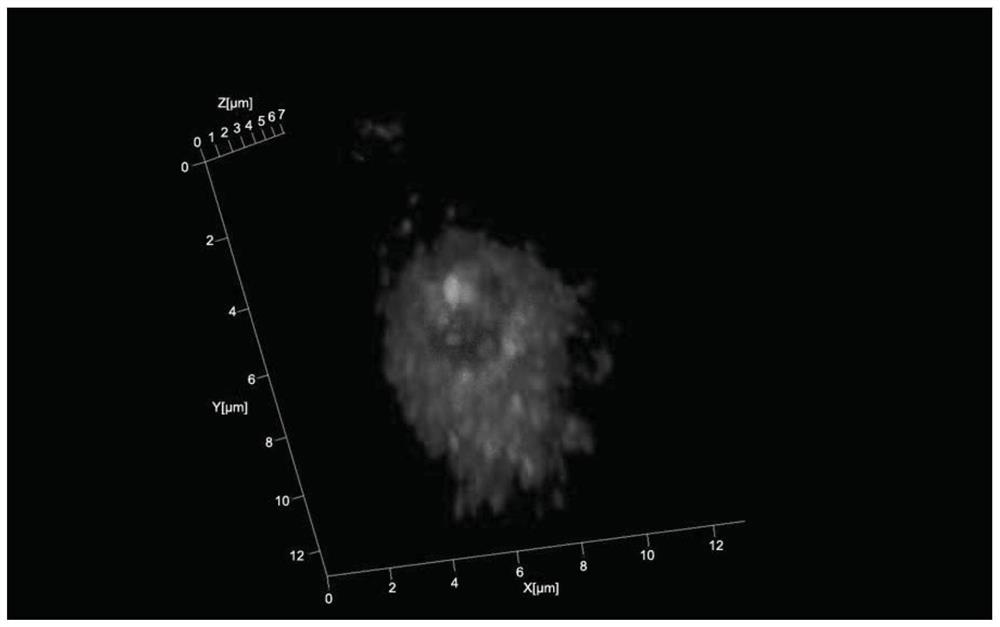
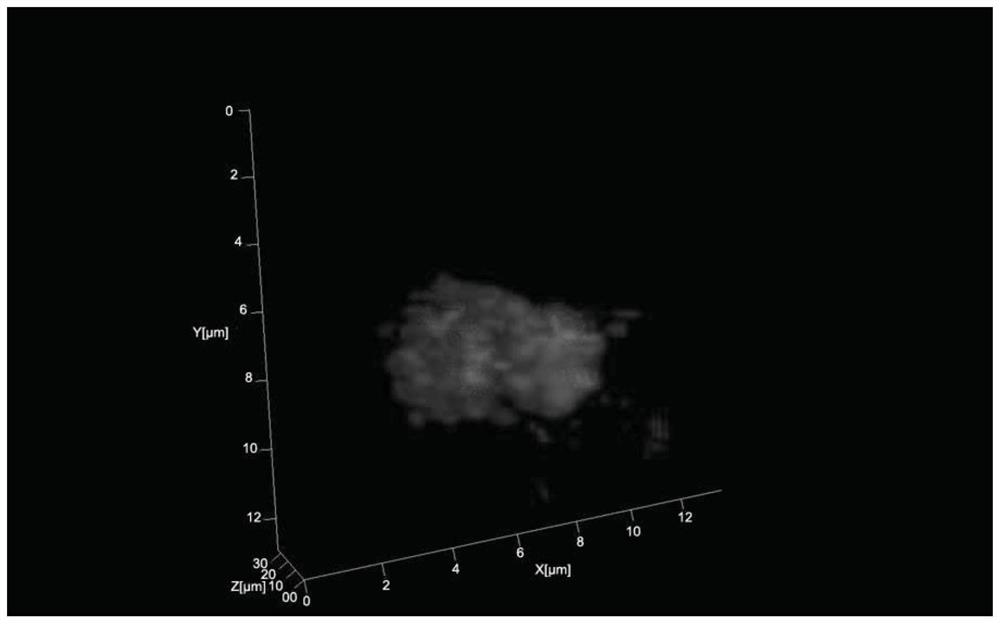
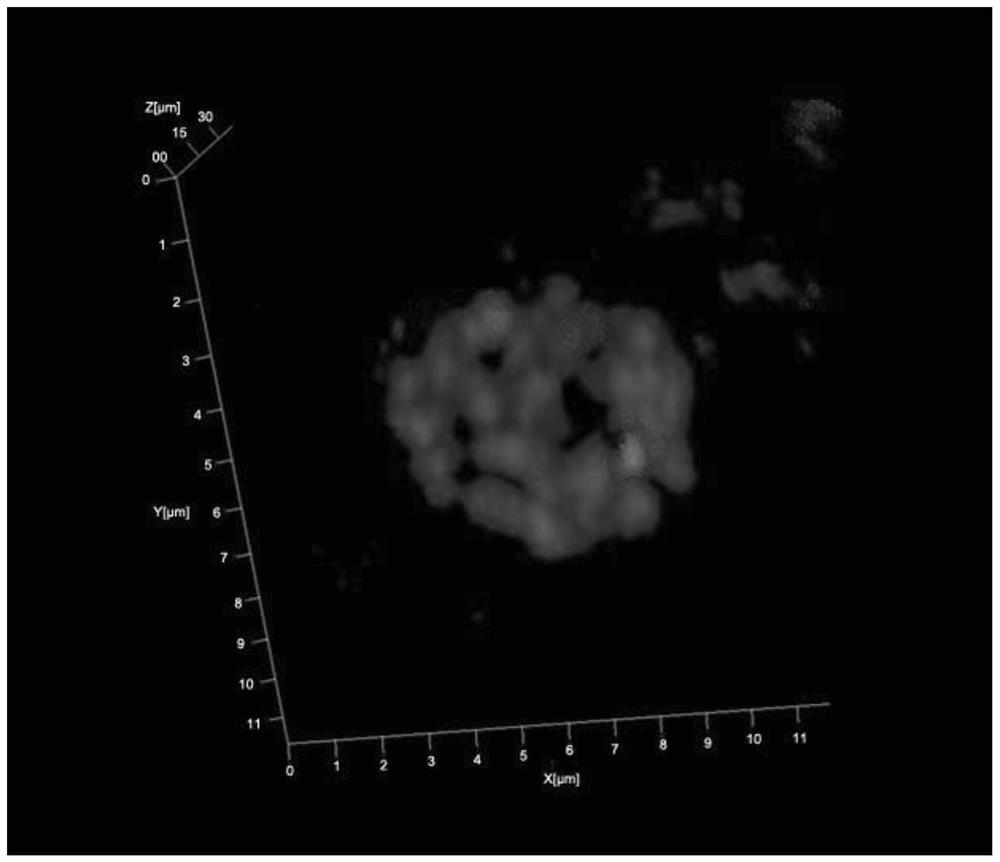
A 3D fluorescence in situ hybridization method of poplar root tips based on paraffin sections
ActiveCN111235231BClear organizational structureFISH signal is clearMicrobiological testing/measurementPectinaseIn situ hybridisation
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
A method for identifying the complete set of chromosomes of cotton d genome and D sub-genome
The invention belongs to the field of molecular cytogenetics and particularly relates to a method for identifying D genome and D sub-genome complete chromosome. The method comprises the following step: by taking a sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 as a probe to perform fluorescence in-situ hybridization on the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of a cotton genome. The sequence is taken as the probe, and chromosomes in the mitosis metaphase of the upland cotton, the asiatic cotton and the Raymond's cotton are taken as target DNA to perform fluorescence in-situ hybridization, and the results indicate that obvious hybrid signals are shown on the D subgenome chromosome of the upland cotton and the D genome chromosome of the Raymond's cotton, the signals are distributed on all chromosomes, and no obvious signals are shown in the A subgenome chromosome of the upland cotton and the A genome chromosome of the asiatic cotton. The sequence adopted by the method disclosed by the invention can be used for quickly identifying the cotton D genome and D sub-genome complete chromosome by virtue of a FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) method.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Novel method for carrying out accurate chromosome counting by applying saccharum centromere specific repetitive sequence
ActiveCN113073134ALower requirementAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementRepetitive SequencesSaccharum
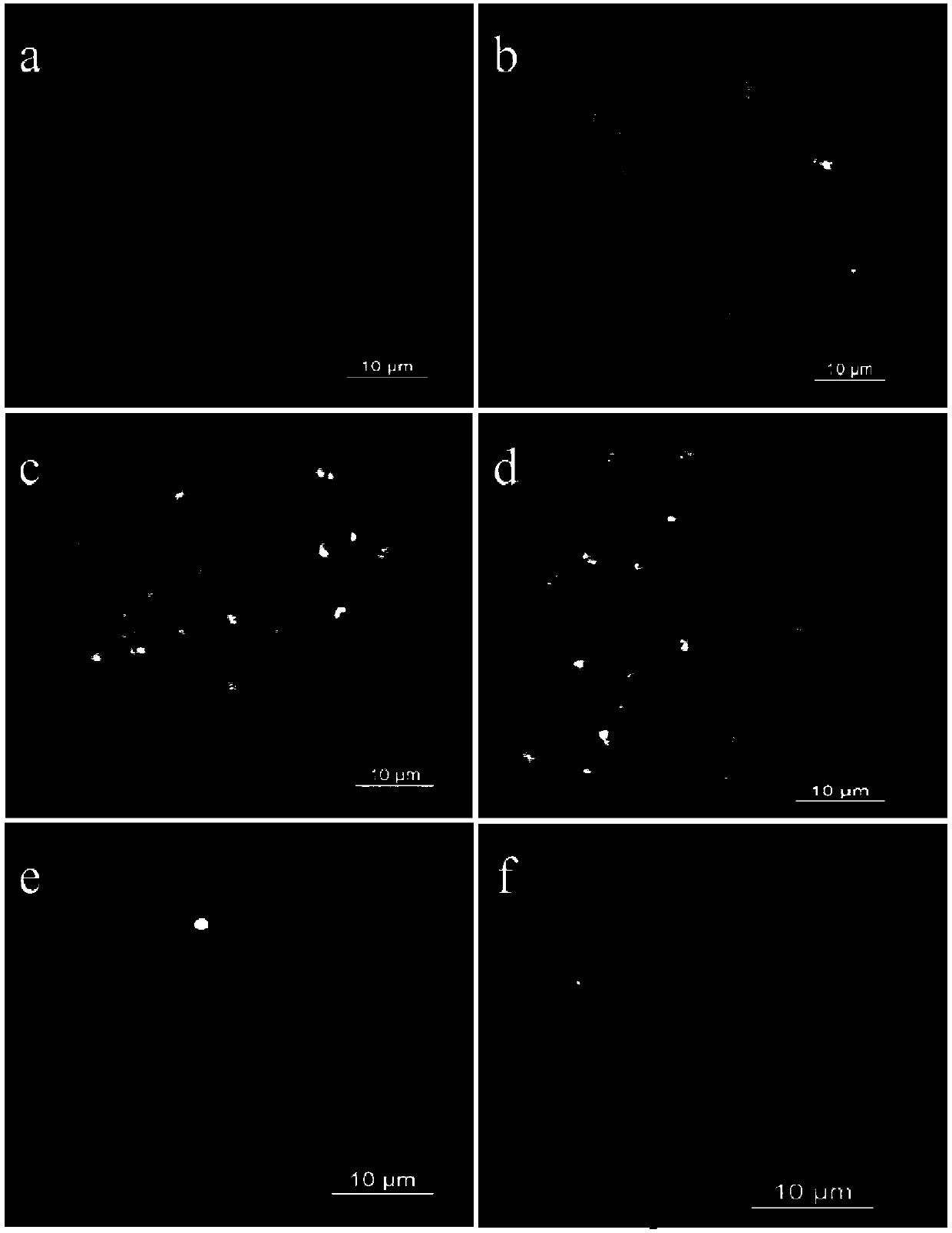
The invention relates to the technical field of bioinformatics and molecular cytogenetics, in particular to a novel method for carrying out accurate chromosome counting by applying a saccharum centromere specific repetitive sequence. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, acquiring the saccharum centromere specific repetitive sequence; and step 2, separating the saccharum centromere repetitive sequence and carrying out counting analysis. According to the invention, a method of combining chromatin immunoprecipitationassay with a high-throughput sequencing technology (ChIP-Seq) for a saccharum centromere specific histone is utilized to obtain a DNA sequence of a saccharum centromere region; and through comparative analysis, repetitive sequences in centromere regions of different saccharum species are screened out. Primers are designed according to the sequence, amplified and marked to be used for mitosis metaphase fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and chromosome counting is carried out. Result shows that the sequence generates specific, clear and bright signals in centromere regions of all chromosomes of different saccharum species. The number of chromosomes of different materials can be rapidly and accurately obtained by counting the number of the centromere signals.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
A new method for accurate chromosome counting using sugarcane centromere-specific repeat sequences
ActiveCN113073134BLower requirementAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyBio informatics
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
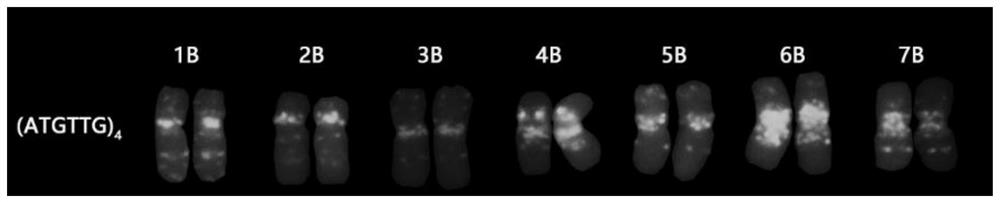
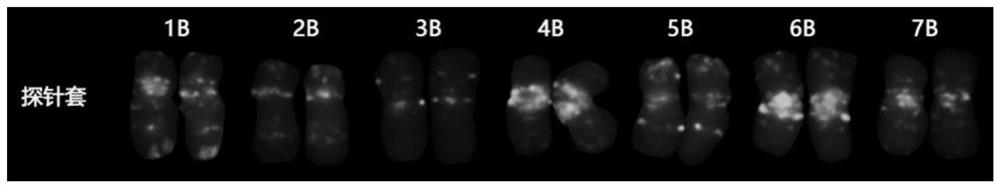
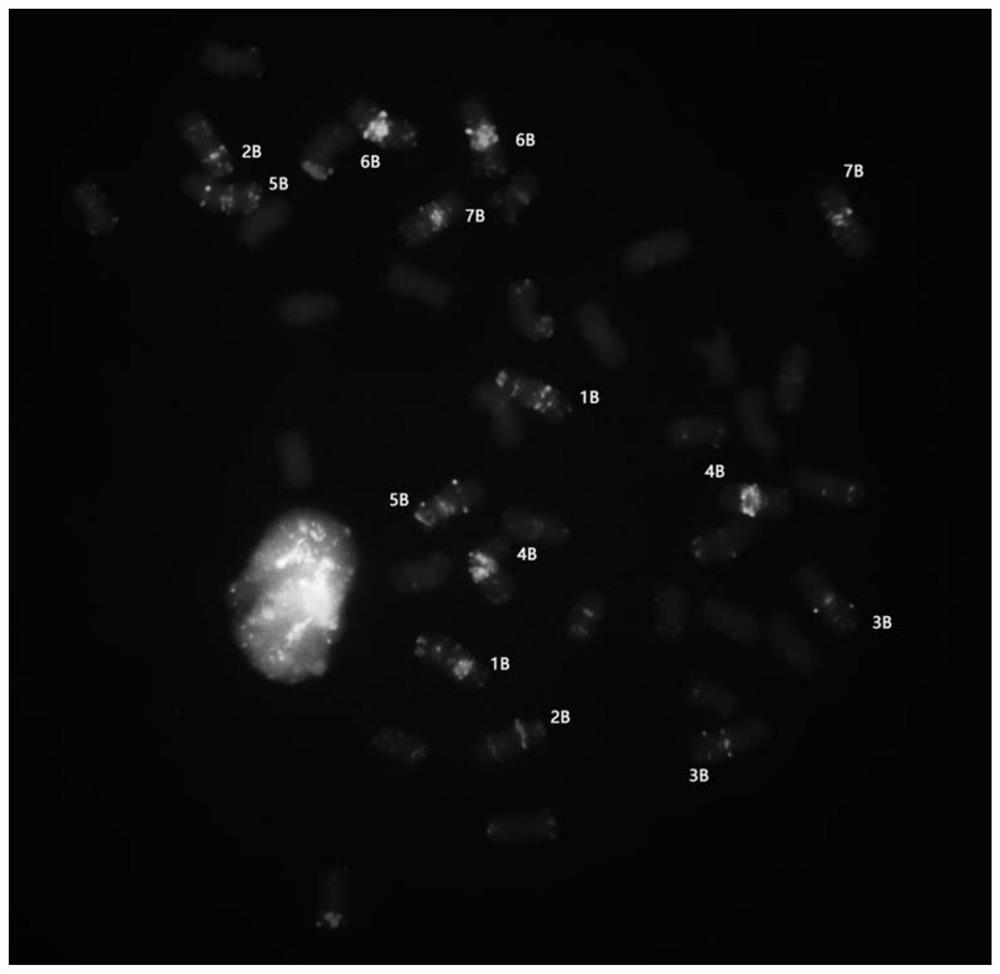
Fluorescence in-situ hybridization probe for identifying group B chromosomes of triticum aestivum as well as design method and application of fluorescence in-situ hybridization probe
ActiveCN113699264ARapid identificationAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementAgriculture gas emission reductionIn situ hybridisationHybridization probe
The invention belongs to the field of molecular cell genetics, and particularly relates to a fluorescence in-situ hybridization probe for identifying group B chromosomes of triticum aestivum as well as a design method and application of the fluorescence in-situ hybridization probe. An oligonucleotide probe is designed on the basis of a genome SSR sequence of the triticum aestivum, and compared with a probe set consisting of multiple probes, clear karyotypes of group B chromosomes can be obtained by using the probe to perform fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH), so that not only is the experiment input cost reduced, but also the time is saved, and the experiment efficiency is improved. The probe disclosed by the invention can be used for rapidly and accurately identifying the group B chromosome in the wheat genetic background, and has a good application prospect in the field of wheat genetic breeding.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Poplar root tip 3D fluorescence in-situ hybridization method based on paraffin sections
ActiveCN111235231AClear organizational structureClear FISH signalMicrobiological testing/measurementPectinaseLaser scanning
The invention discloses a poplar root tip 3D fluorescence in-situ hybridization method based on paraffin sections, and belongs to the field of molecular cytogenetics. The poplar root tip 3D fluorescence in-situ hybridization method mainly includes the steps that tender root tips of poplar are obtained and fixed with Carnoy fluid; n-butanol gradient solution dehydrating, dipping wax and embedding are carried out; section slicing, section spreading, section baking and dewaxing are carried out; section preparation adopts pectinase, cellulase, pepsin and RNase for treatment; section preparation, probe denaturation and hybridization overnight are carried out; and hybridization signals are detected after incubation with secondary antibodies is carried out. The poplar root tip 3D fluorescence in-situ hybridization method can obtain clear FISH signals of the poplar root tip paraffin sections, and 3D images captured by a laser scanning confocal microscope can accurately reflect the three-dimensional level spatial distribution of a target sequence in cells. The poplar root tip 3D fluorescence in-situ hybridization method can be used in research fields such as chromosomal space occupation ofpoplar, gene expression and analysis of Hi-C sequencing results, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
A method for creating and identifying a chromosomal translocation line between a and b genomes of peanut
ActiveCN107604088BEnables chromatin exchangeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyChromosome translocations
The invention discloses a method for creating and identifying a chromosomal translocation line between the genomes of peanut A and B. The method for creating is to use the cultivar Silihong as the material, and use Co 60 ‑γ-ray irradiated peanut plants to obtain peanut plants with chromosomal translocation between A and B genomes. The present invention adopts florescence Co 60 ‑γ-irradiation induced a large number of translocations between genomes A and B, realizing chromatin exchange between genomes A and B, providing new resource materials for peanut breeding and molecular cytogenetic research, and also for distant hybridization Artificial creation of exogenous chromosome (segment) introgression lines in progeny materials provides a way. The present invention uses genome fluorescence in situ hybridization technology to identify chromosome translocation lines between peanut A and B genomes, creates and identifies a batch of peanut cultivars A and B genome chromosome translocation lines new materials for the first time, and provides a basis for identifying peanut chromosome translocations effective means.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A method for displaying the centromere and short arm of large yellow croaker
The invention discloses a method for displaying centromeres and short arms of large yellow croaker, and belongs to the field of molecular cytogenetics. A molecular marker is a segment of a 28S rDNA sequence cloned from human saliva, and is processed to prepare a probe (named as H-P3K), and the probe is crossed with metaphase chromosomes of Larimichthys crocea to obtain a positive signal. The positive signal in the centromeres and the short arms of every metaphase chromosome can be detected when FISH of the Larimichthys crocea chromosomes is carried out by the probe, the short arm signal intensity of one chromosome is weaker than the centromere signal intensity of the same chromosome, and the centromere signal intensities of different chromosomes are different. The method is used for determining the position of the centromere, analyzing the chromosome karyotype and researching the chromosome structure; and the positive signal can be used as a chromosome identifying and pairing marker.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Method for re-hybridizing FISH film
InactiveCN104313138AReduce pollutionReduce experiment costMicrobiological testing/measurementAlcoholFluorescence
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A bac-fish method for simultaneous identification of complete sets of chromosomes in each subgroup in the background of ad or ade in cotton
The invention belongs to the field of molecular cytogenetics and particularly relates to a BAC-FISH method for simultaneously identifying whole sets of chromosomes of subgroups under a gossypium AD / ADE background. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out BAC-FISH on different cotton seeds by using BAC cloned 57I23 originated from an Africanum BAC library, and simultaneously identifying chromosomes of an AD genome and AD sub genome of cotton obviously; by using BAC-DNA as a probe, covering most regions out of ends of all chromosomes of the subgroup A in five gossypium tetraploids as well as a small region near the middle part of the all chromosomes of the subgroup D by a hybrid signal; and in allohexaploid hybrids AADDEE hybridized by upland cotton and G.stocksii (E1) in the group E, as the hybrid signal is similar to the tetraploid, obviously differentiating the hybrid signal from the subgroup E (without a signal) so as to simultaneously identify three sets of chromosomes of subgroups (A,D,E). By adopting the BAC-FISH method through BAC cloning, the whole sets of chromosomes of subgroups under the gossypium AD / ADE background can be simultaneously identified.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A Method for Identifying All Chromosomes of Poplar Using Oligonucleotide Probes
ActiveCN109825553BRealize identificationEfficient identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementPopulus trichocarpaGenetics
The invention discloses a method for identifying all the chromosomes of poplar by using oligonucleotide probes. According to the genome information of Populus trichocarpa, the specific oligonucleotide sequence of each chromosome is obtained through bioinformatics analysis, and the synthetic poplar 1 The oligonucleotide library corresponding to chromosome 19 is then labeled with biotin or digoxin into oligonucleotide probes, and then the chromosomes of poplar are identified by fluorescence in situ hybridization technology. Each round of hybridization can be used at most at the same time The oligonucleotide probes of the three chromosomes were repeated 7 times on the same metaphase division phase, and the 19 pairs of chromosomes of Populus species could be accurately identified. It has the advantages of common use in Populus species, good experimental repeatability, and high resolution; the invention provides a new method for accurately identifying each chromosome of Populus species, and has laid a solid foundation for the molecular cytogenetics research of Populus Base.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
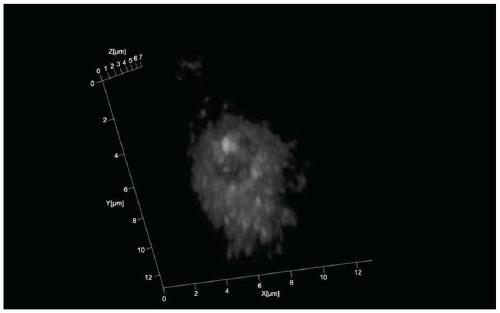
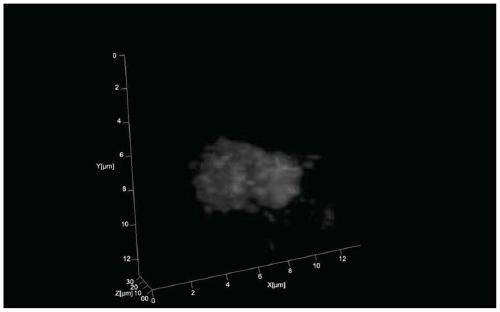
A method for 3D fluorescence in situ hybridization of poplar root tips based on frozen sections
ActiveCN111218499BOrganizational structure is completeFISH signal is clearMicrobiological testing/measurement3d imageHybrid antibody
The invention discloses a 3D fluorescence in-situ hybridization method for a poplar root tip based on a frozen section, belonging to the field of molecular cytogenetics. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a poplar root tip, fixing the poplar root tip with a Carnoy's fixative, then performing washing with water, embedding the poplar root tip with an embedding agent, carrying out freezing, conducting slicing, adhering an obtained section onto a glass slide, carrying out FISH steps such as section baking, denaturation, hybridization, antibody detection and the like, and finally carrying out observing under a laser confocal microscope and capturing a 3D image. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the complete tissue structure of the root tip can be obtained and a FISH signal is clear. Compared with a 2D FISH result obtained by a traditional section preparation method, the method of the invention has the advantages that the method can visually display real space occupation of chromosomes in cells at a three-dimensional level and accurately locate the space distribution of target sequences in the cells at the three-dimensional level, is applicableto the fields of chromosome space occupation and gene expression of poplars, analysis of Hi-C sequencing results and the like, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
A probe combination and method suitable for physical location of rDNA in plant chromosomes
ActiveCN108977565BClear fluorescent signalEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyIn situ hybridisation
The invention discloses a probe combination and method suitable for the physical location of plant chromosome rDNA, and relates to the technical field of molecular cytogenetics. The probe combination includes the probes of SEQ ID NO.1-4, which are respectively 5S rDNA probe, 5.8S rDNA probe, 18S rDNA probe and 25S rDNA probe; the probe combination and method are used to carry out plant chromosome priming In situ hybridization, which can capture higher resolution chromosome and fluorescence in situ hybridization signals, and is suitable for chromosome in situ hybridization of various plants; and the probe combination is an oligonucleotide probe, which has the advantages of low production cost and convenient use , Simple operation and so on.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Triploid oyster ploidy identification and genetic material source analysis method
ActiveCN114214427ASimple preparation stepsShorten production timeMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationMolecular identificationOyster
The invention relates to a triploid oyster ploidy identification and genetic material source analysis method, and belongs to the field of molecular cell genetics, and the method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a metaphase chromosome specimen of a single individual triploid oyster; 2) performing mode analysis on somatic cell chromosomes; 3) carrying out multiple specific PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction); 4) analyzing genetic material sources of triploid oysters; the preparation steps of the oyster somatic cell chromosome are simplified, the analysis time is shortened, and the whole process only needs 2-3 hours. The prepared chromosome slice is clean and clear; through molecular identification of multiple specific PCR, a tetraploid male parent and a diploid female parent of triploid oysters can be further determined, analysis of genetic material composition, chromosome ploidy, parent oyster identification and the like is carried out on the triploid oysters on chromosome and molecular levels, chromosome preparation and analysis can be combined with molecular identification of multiple specific PCR for use, and the method is simple and convenient to operate. The method is helpful for identifying the source of the triploid parent, so that the quality of the triploid offspring seeds
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
The method of re-hybridization of fish production
InactiveCN104313138BReduce pollutionReduce experiment costMicrobiological testing/measurementAlcoholFluorescence
The invention belongs to the field of molecular cytogenetics, and in particular relates to a method for re-hybridizing a FISH film. The method mainly comprises the following steps: soaking the film into 2*SSC to wash away a cover plate after first fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and then soaking the treated film in 2*SSC for 3*5min; putting the film into 2*SSC of 90 DEG C for 10min while shaking continuously; putting the film into 70% deionized formamide of 78 DEG C for 4min while shaking continuously; and quickly putting into 70% alcohol of -20 DEG C. A hybridization signal can be washed away by adopting the method, and then the hybridization signal cannot be detected by observing the film. When the treated film is reused for a FISH experiment by adopting the same probe, the hybridization signal can be detected again at the same position of a chromosome. By adopting the method, the film subjected to in situ hybridization can be reused, so that resources are effectively saved, the cost is reduced and the environmental pollution is reduced.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A Method for Marking Cotton A Genome and A Sub-genome Chromosome Ends
The invention belongs to the field of molecular cytogenetic, and concretely relates to a method for marking chromosome terminals of cotton A genome and A sub-genome. The method comprises: using BAC coming from gossypium barbadense pima-90BAC library to clone 350B21, performing BAC-FISH on mitosis mid-term chromosomes of different cotton species, and discovering the phenomena that the terminals of all chromosomes of A genome and A sub-genome generate strong hybridization signals, while the hybridization signals of all chromosomes of D genome and D sub-genome are not obvious. By utilizing the BAC-FISH method for BAC cloning, the chromosome terminals of cotton A genome and A sub-genome can be rapidly effectively marked.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +2
A method for fluorescence in situ hybridization of mature pollen cells of Chinese cabbage
InactiveCN106636320BClear and distinct hybridization signalsSimple technologyMicrobiological testing/measurementBrassicaceaeCell sheet
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Antigenic polypeptide of poplar functional centromere histone cenh3 and its application
ActiveCN111410683BAccurate identificationSerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against plantsPopulus trichocarpaGenomics
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
3D fluorescence in-situ hybridization method for poplar root tip based on frozen section
ActiveCN111218499AOrganizational structure is completeFISH signal is clearMicrobiological testing/measurement3d imageHybrid antibody
The invention discloses a 3D fluorescence in-situ hybridization method for a poplar root tip based on a frozen section, belonging to the field of molecular cytogenetics. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a poplar root tip, fixing the poplar root tip with a Carnoy's fixative, then performing washing with water, embedding the poplar root tip with an embedding agent, carrying out freezing, conducting slicing, adhering an obtained section onto a glass slide, carrying out FISH steps such as section baking, denaturation, hybridization, antibody detection and the like, and finally carrying out observing under a laser confocal microscope and capturing a 3D image. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the complete tissue structure of the root tip can be obtained and a FISH signal is clear. Compared with a 2D FISH result obtained by a traditional section preparation method, the method of the invention has the advantages that the method can visually display real space occupation of chromosomes in cells at a three-dimensional level and accurately locate the space distribution of target sequences in the cells at the three-dimensional level, is applicableto the fields of chromosome space occupation and gene expression of poplars, analysis of Hi-C sequencing results and the like, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method for separating cotton chromosomes
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular cytogenetics and particularly relates to a method for separating cotton chromosomes, which comprises the following steps: preparing material, preprocessing the material, performing primary hypotonic treatment, performing enzymolysis, performing secondary hypotonic treatment, drying and covering a plate, removing the cover plate, performingchromosome microisolation and collecting the chromosomes. In the method of the invention, the primary hypotonic treatment, emzymolysis, secondary hypotonic treatment and plate covering method are combined to prepare for making a chromosome membrane sheet; cell walls are completely removed; the chromosomes well disperse after being compressed slightly; and the shapes of the chromosomes are so clear as to facilitate the recognition of target chromosomes.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com