Centromere mark realizing fluorescence in situ hybridization with asparagus chromosome and applications of centromere mark
A technique of fluorescence in situ hybridization and chromosomes, applied in the field of molecular cytogenetics, can solve the problems of small chromosomes, difficulties in handling cells, and difficulty in obtaining division equality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
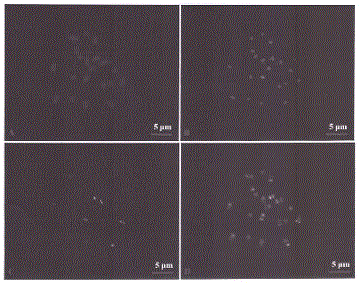
[0022] Such as figure 1 As shown, the acquisition of the centromere marker sequence of A. chinensis, specifically:
[0023] 1. The source of the centromere marker sequence of A. chinensis, which was discovered when the sequence assembled by high-throughput sequencing was verified. Illumina HiSeq2000 sequencing technology was used to sequence the genomes of male and female A. chinensis. The sequencing results obtained a total of 17 Gb sequences (12 times coverage). After assembly, a total of 163,406 scaffolds were obtained, with a length of 400 Mbp. 30% of the Diabolic genome. 20 scaffolds were randomly selected, and sequence-specific primers were designed to amplify the sequence from the genome of A. chinensis and sequenced to verify the reliability of the sequencing and assembly data. The centromere marker sequence used in the present invention is amplified by designing primers for the scaffold5783 sequence.
[0024] 2. The PCR amplification of the centromere marker sequen...
Embodiment 2
[0027] The centromere marker of Chromosome fluorescence in situ hybridization of A. chinensis, the centromere marker is Texas red marker, and its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.1,
[0028] Among them, the primer pair F: 5'-CAACCCCCACTTATCCT, R: 5'-CGGCAATATACACAGATAC was used to carry out PCR amplification with Genomic DNA of A. dNTP, 100-200 ng of genomic DNA, including 0.1 μmol / L of upstream and downstream primers.
Embodiment 3
[0030] A method for centromere marking of Chromosome fluorescent in situ hybridization comprising the following steps:
[0031] Step S1: Preparation of root apical metaphase chromosomes, specifically laying 2-3 layers of filter paper in a petri dish, soaking it in water, putting the seeds of Cypress chinensis, and culturing at 25°C for 5-7 days until the root length is 1.5-2 cm. Cut the root tip into N 2 Treat in an O gas chamber for 1-3 h with a pressure of 10 atm (1.01 Mpa). The root tips were then fixed on ice with 90% acetic acid for 10 min. After the root tip was washed with water, the 2 mm-long part of the root tip growth point was cut and transferred to 20 μL of ice-cold enzyme solution (1% pectolyase Y-23 and 2% Onozuka R-10), and placed in a water bath at 37 °C for 2 h . After the enzymatic hydrolysis, resuspend twice with 70% ethanol, pour off the ethanol, keep 40 μL of ethanol, smash the root tip with a dissecting needle, vortex for a few seconds or flick the tub...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com