Modificatory DNA incision enzyme and its application method
A cleavage enzyme, unmodified technology, applied to modified DNA cleavage enzymes and their application fields, can solve problems such as difficulty in identifying common structural features, dissociation enzyme toxicity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0120] Example 1: Mutations at bridge sites and overexpression of the modified enzyme
[0121] Materials and methods
[0122] Restriction enzyme, nickase N.BstNB I, DNA polymerase, T4 ligase, T4 DNA kinase, β-agarase, λ exonuclease, maltose binding protein including plasmid pMAL-c2x (MBP) protein fusion expression and purification system, host Escherichia coli strains TB1 and ER2566, factor Xa protease, plasmid pUC(AT) containing a cruciform structure, and plasmid LITMUS28 were obtained from New England Biolabs Inc., Beverly , MA). Synthetic oligonucleotides were synthesized using standard techniques. T7 phage DNA encoding T7Endo I has a sequence corresponding to SEQ ID NO:1.
[0123] Recombinant DNA and Mutagenesis Methods
[0124] DNA manipulation and site-directed mutagenesis (Kunkel, Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA.82 (2): 488-92 (1985Jan)) or PCR method according to Sambrook et al. Molecular Cloning (Sambrook, J. and Russell, D.W. (2001) Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Man...
Embodiment 2
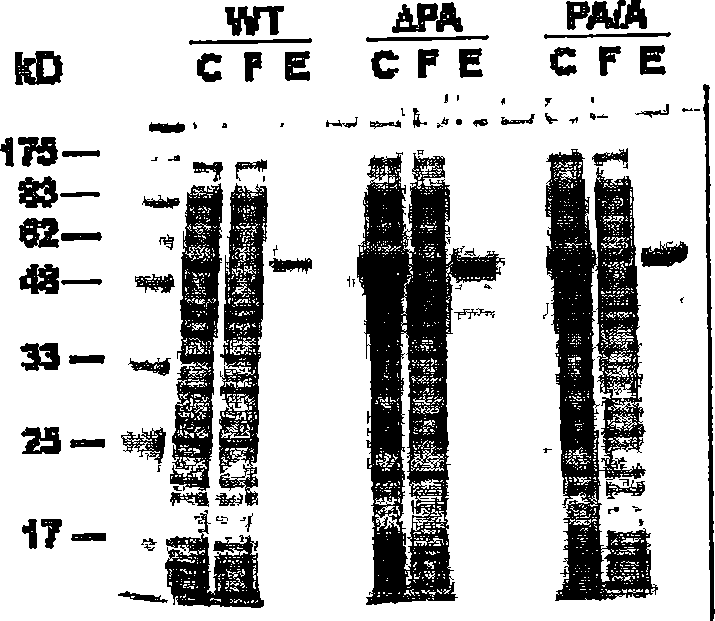
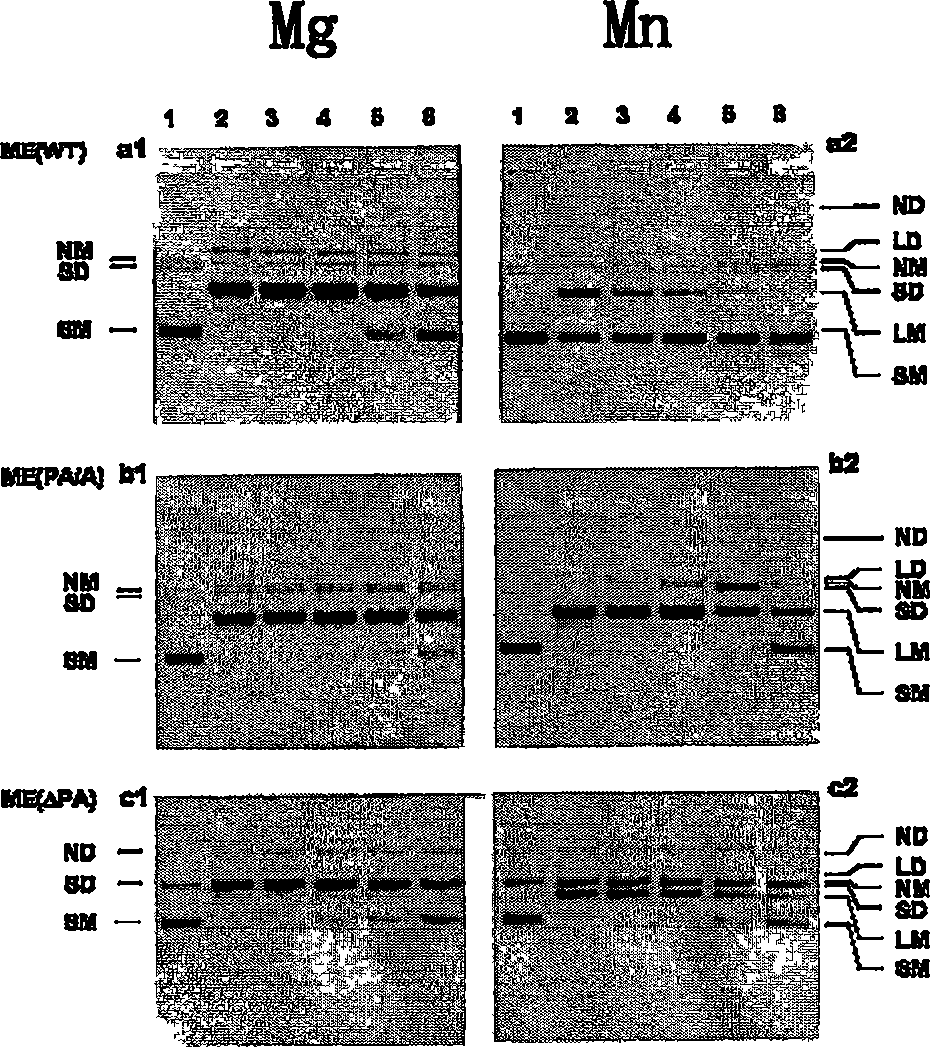
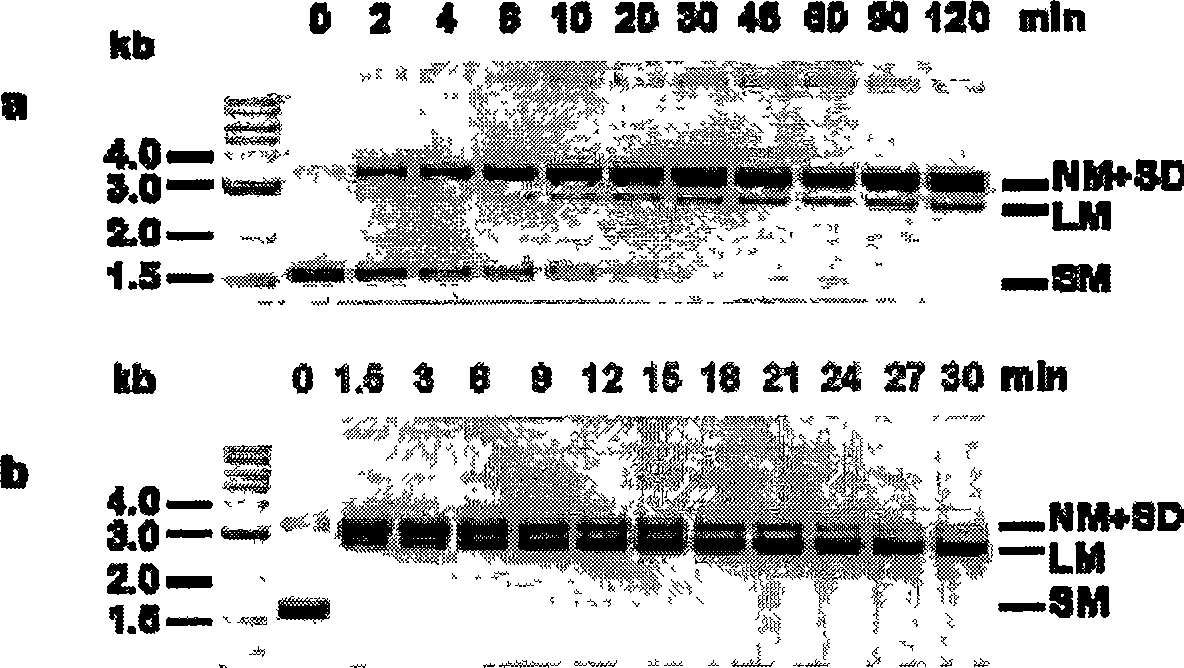
[0154] Example 2: Characterization of two deletion mutants ME(PA / A) and ME(ΔPA)
[0155] 1. Cutting of cruciform DNA
[0156] [104] The stable cruciform structure on negatively supercoiled plasmids is structurally similar to the four-way linker of DNA. T7 Endo I decomposes both DNA structures with high efficiency (Parkinson, M.J. and Lilley, D.M.J.J. Mol. Biol. 270:169-178 (1997)). To compare the enzymatic activity between the different T7 Endo I mutants, we used cleavage of the cruciform-containing plasmid pUC(AT) as substrate to define the specific activity. One unit of activity is defined as the conversion of 1 μg of supercoiled pUC(AT) to a linear form (two-strand cleavage) or a nicked form (single-strand cleavage) within 30 minutes at 37°C in a 20 ml reaction. ) the amount of enzyme required. We measure specific activity by enzyme titration assay. result in figure 2 given in.
[0157] [105] in Mg 2+ Buffer, ME and ME(PA / A) have roughly the same specific activity, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com