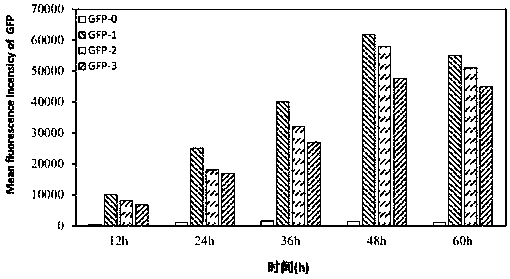
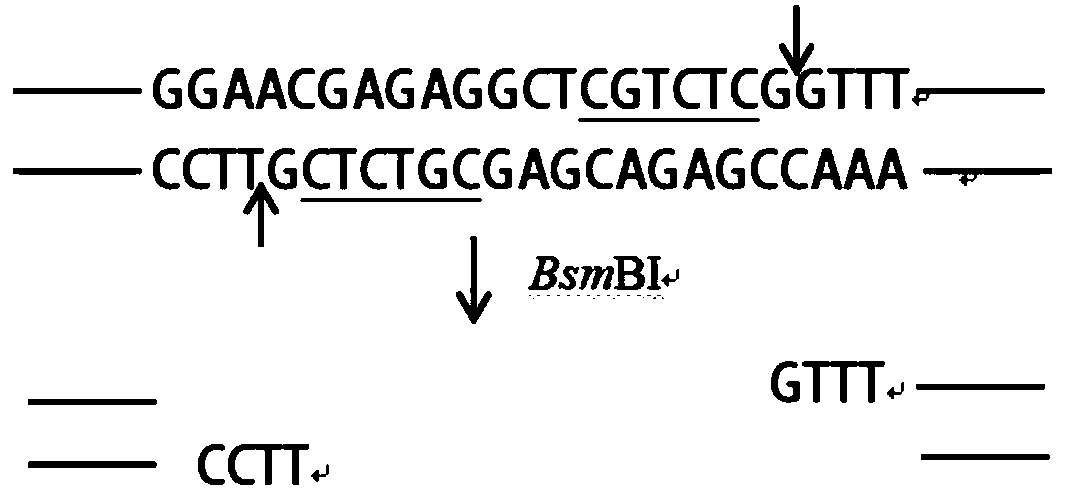
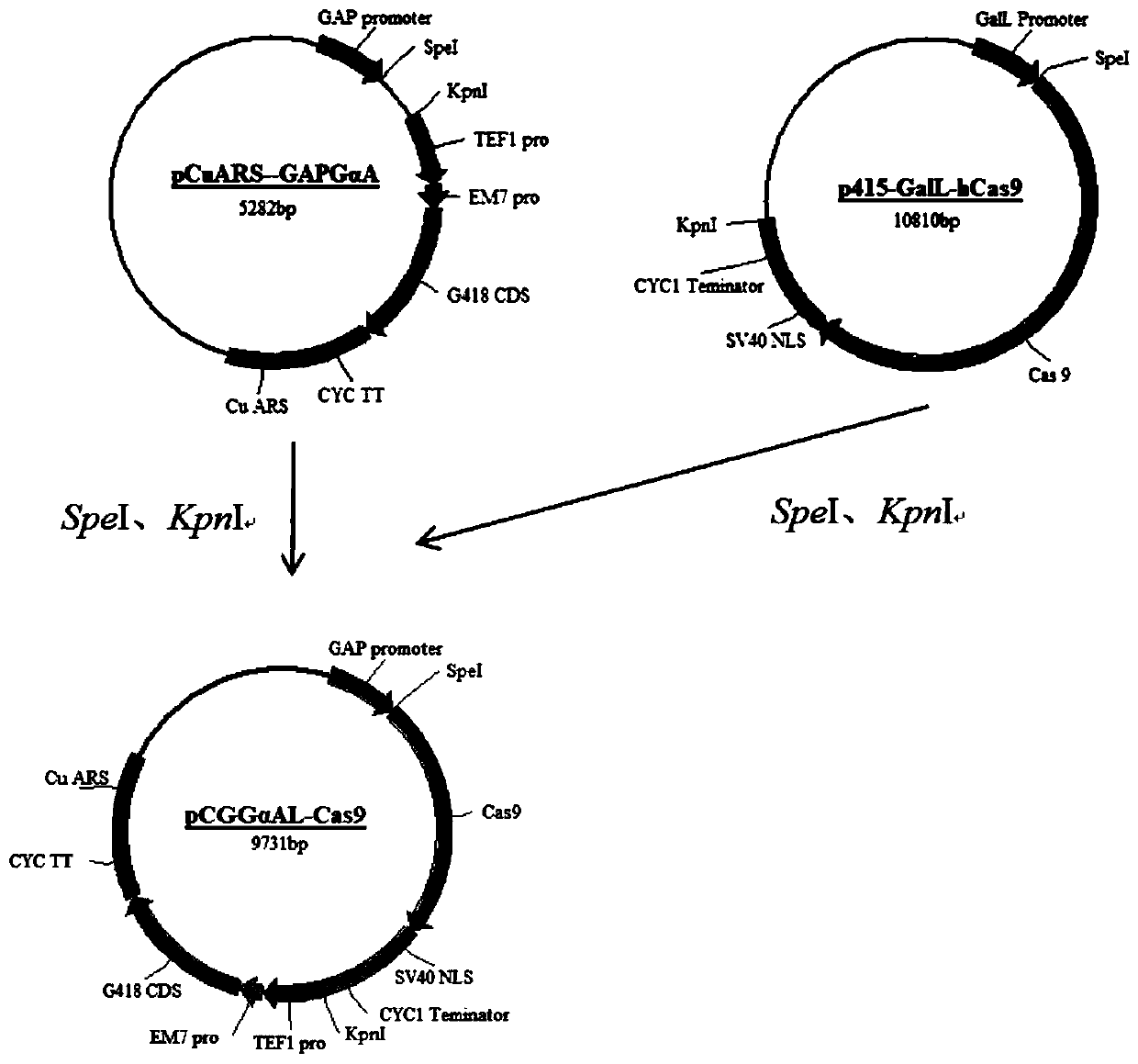
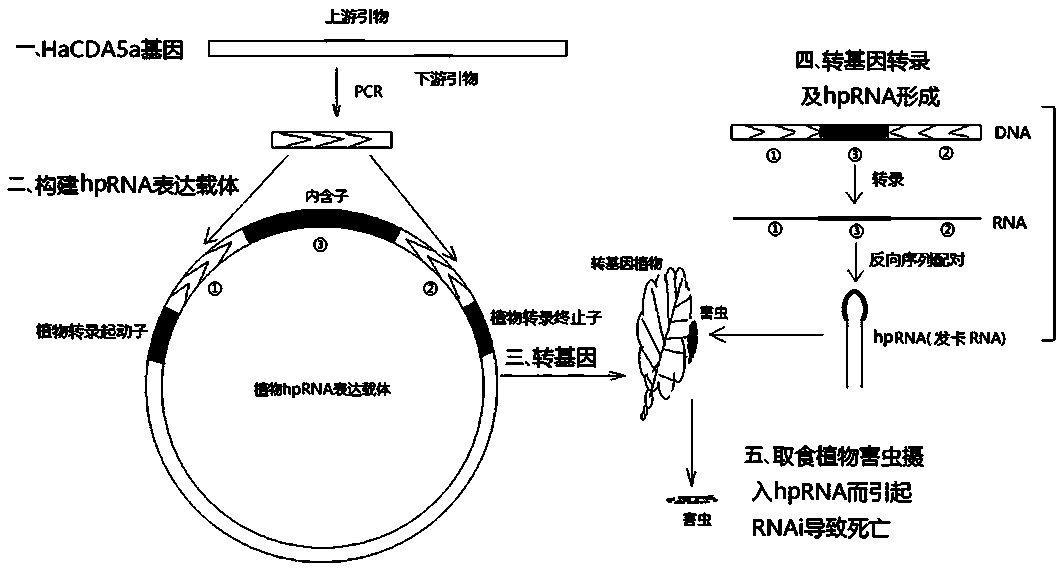
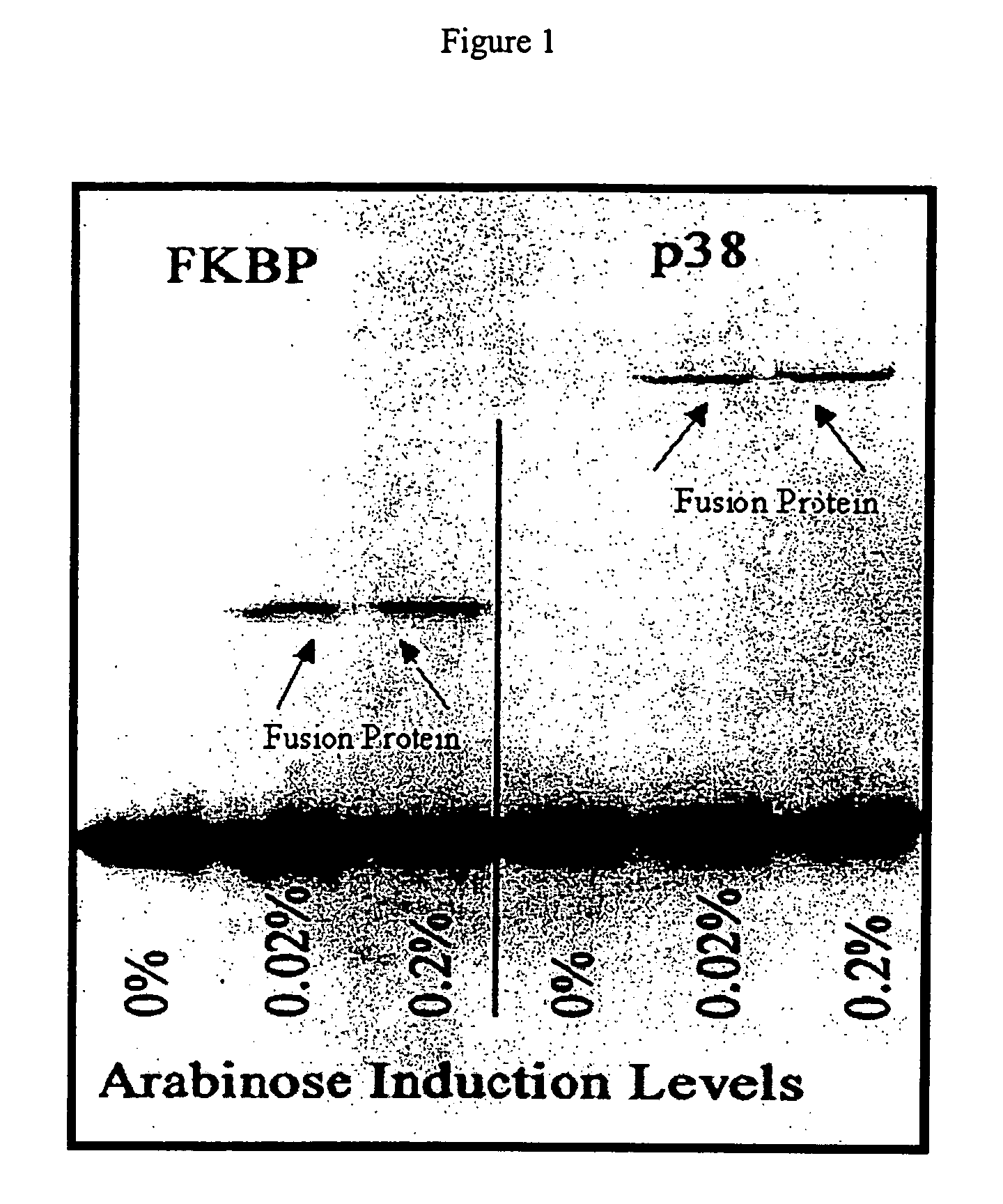
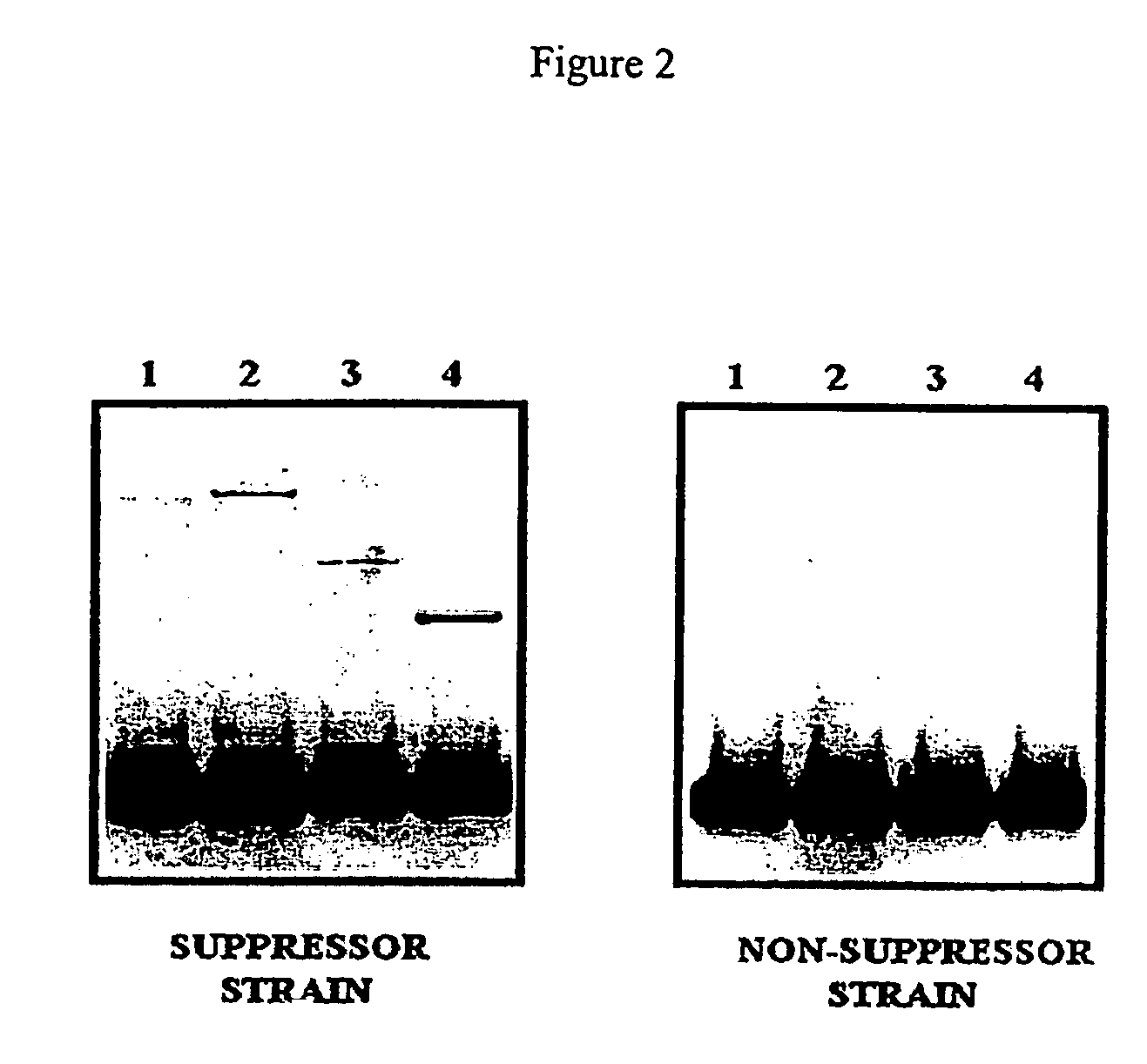
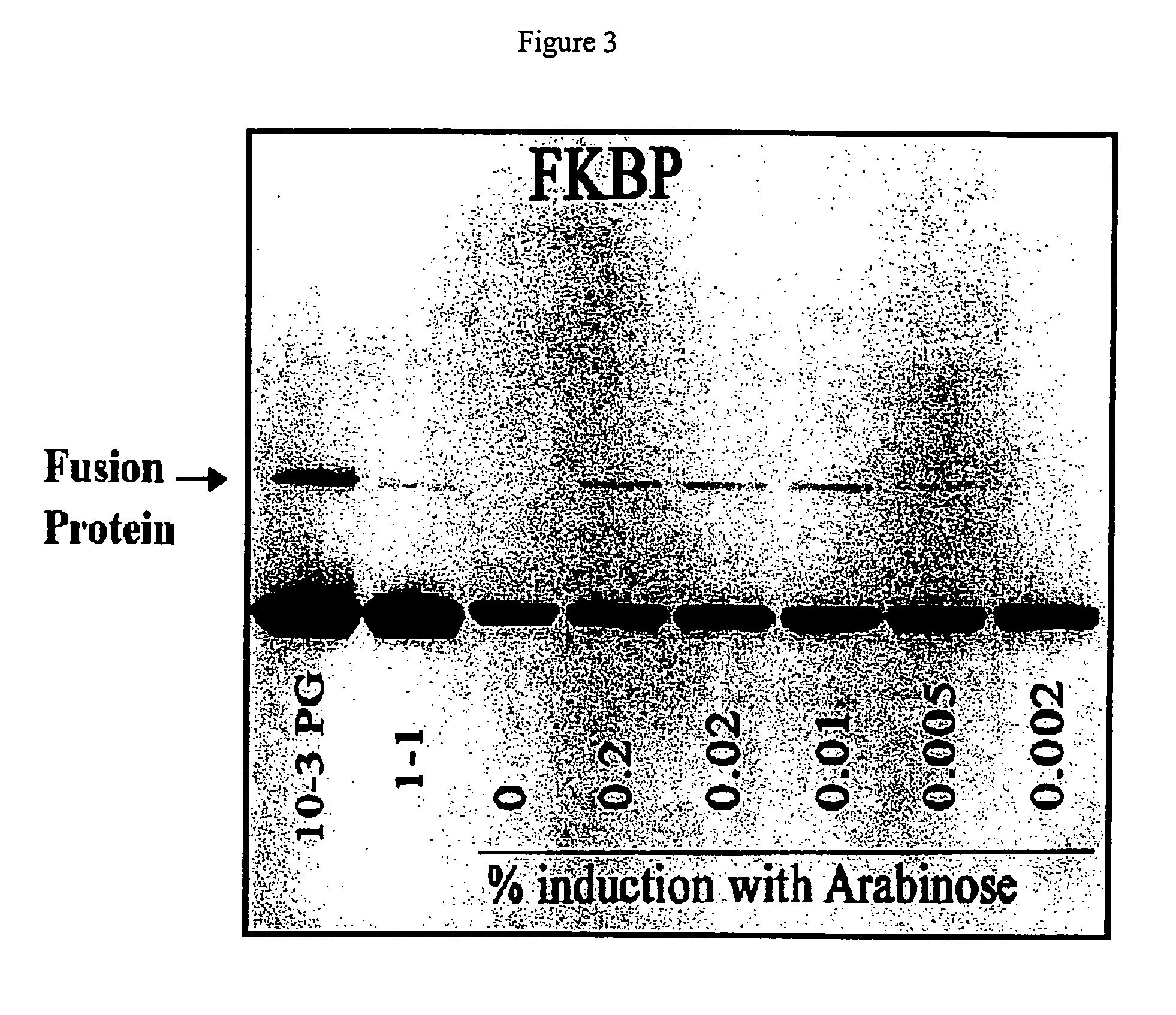
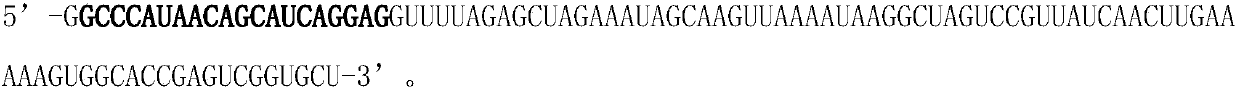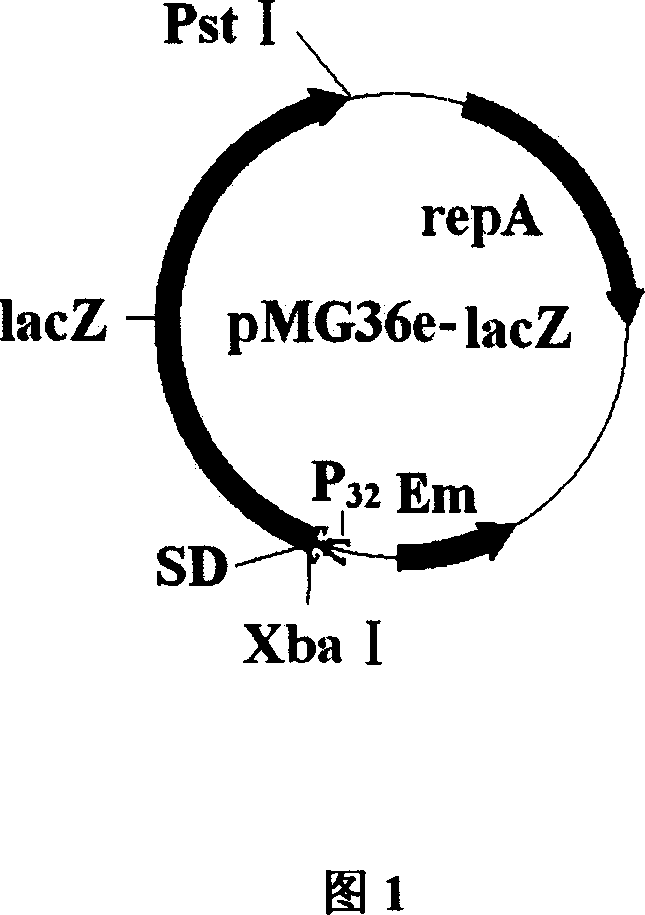Patents
Literature
50 results about "Intervening Sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Intervening sequence: Part of a gene that is initially transcribed from the DNA into the primary RNA transcript but then is excised (removed) from it when the so-called exons sequences on either side of it are spliced together. Intervening sequences, which are also called introns, are genetic sequences that intervene between the exons. The DNA ...
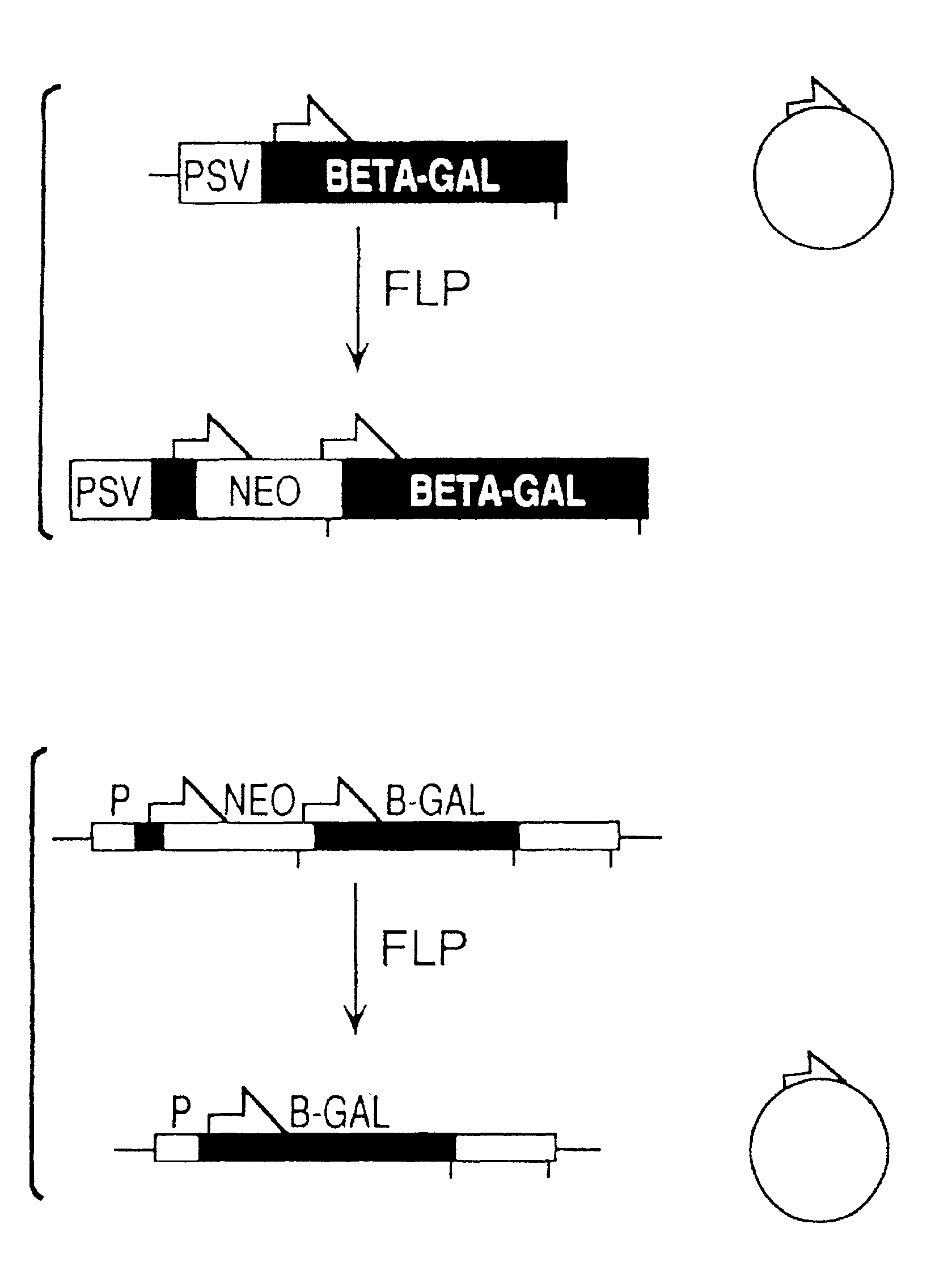
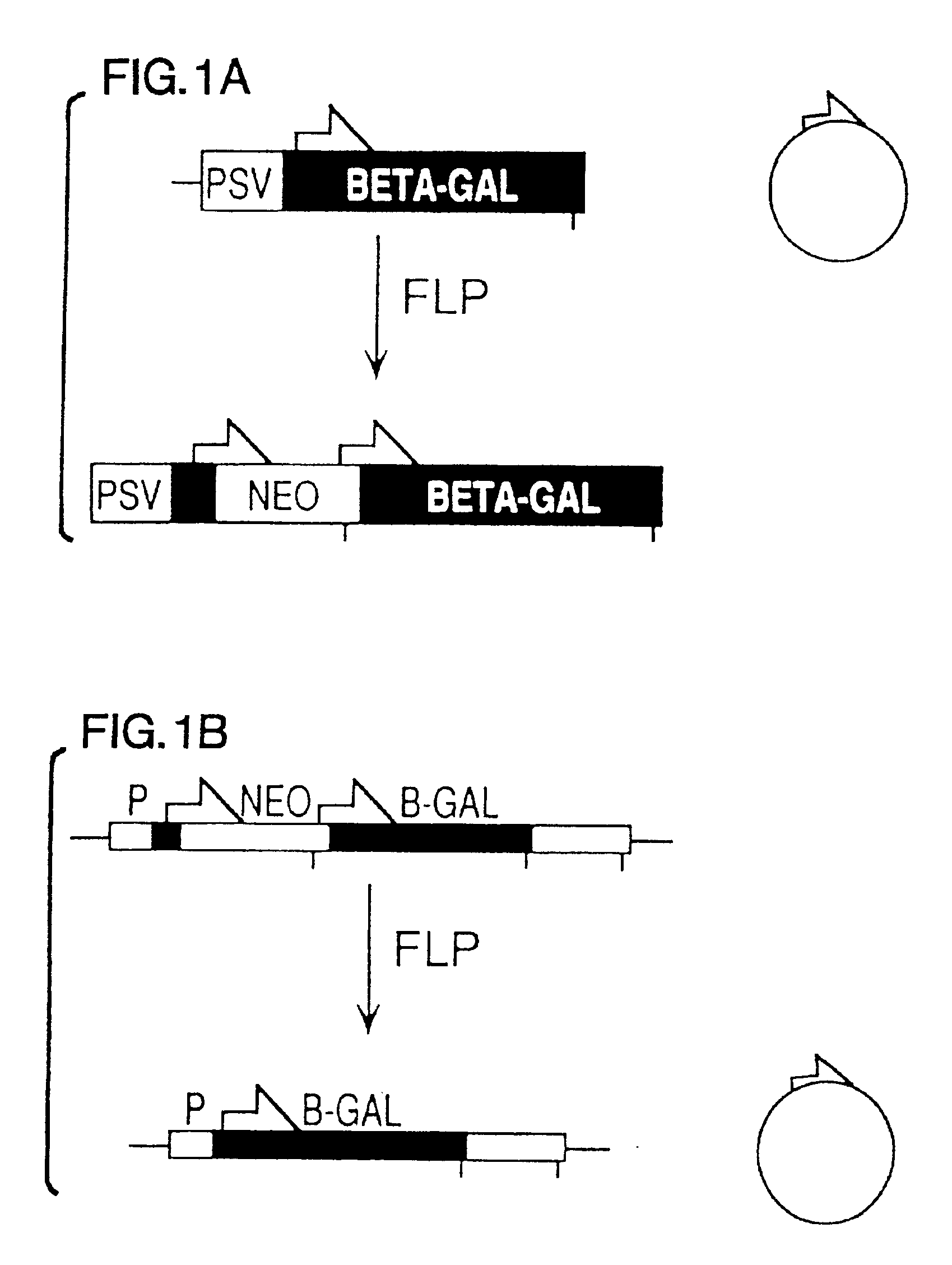
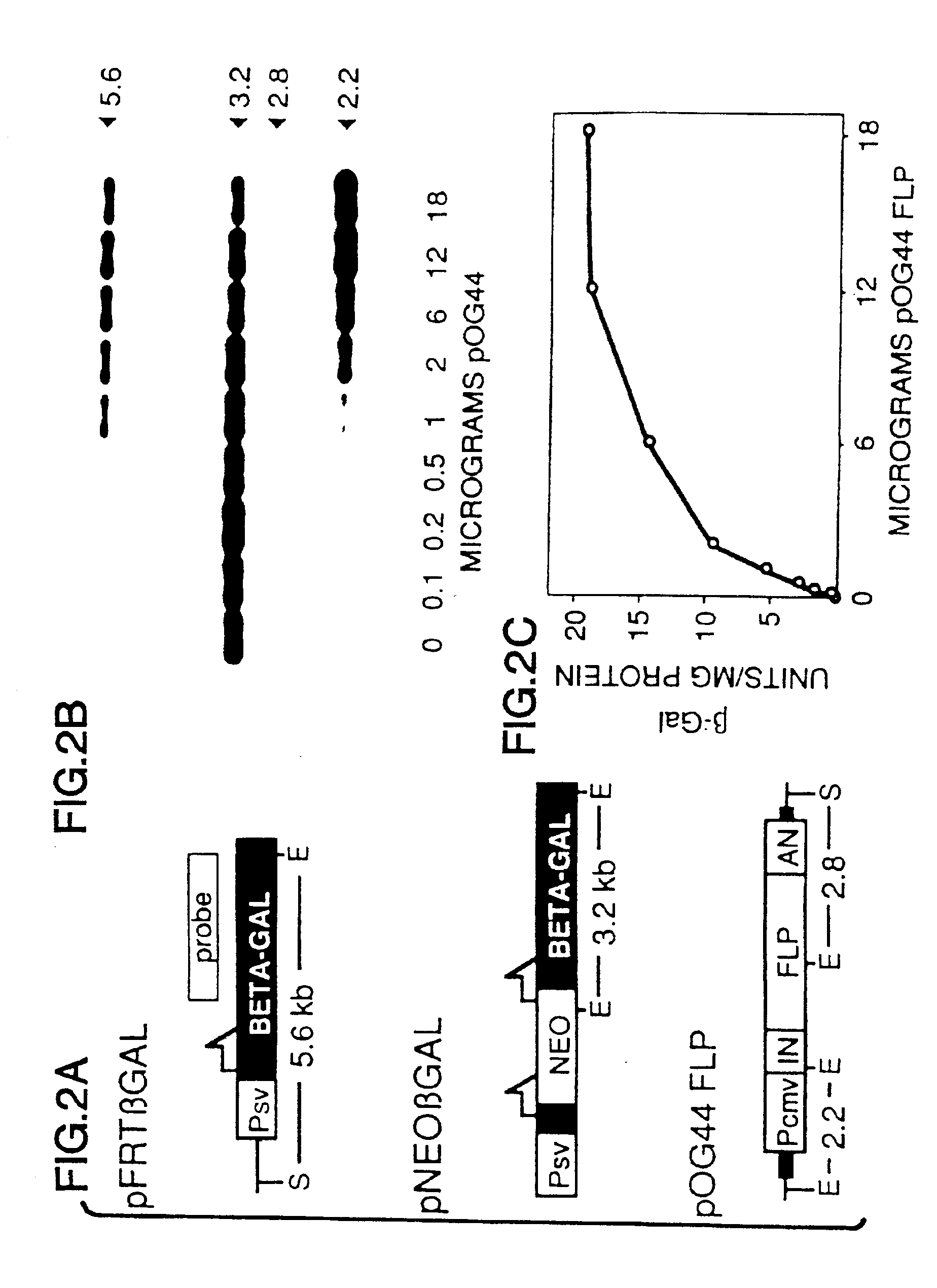
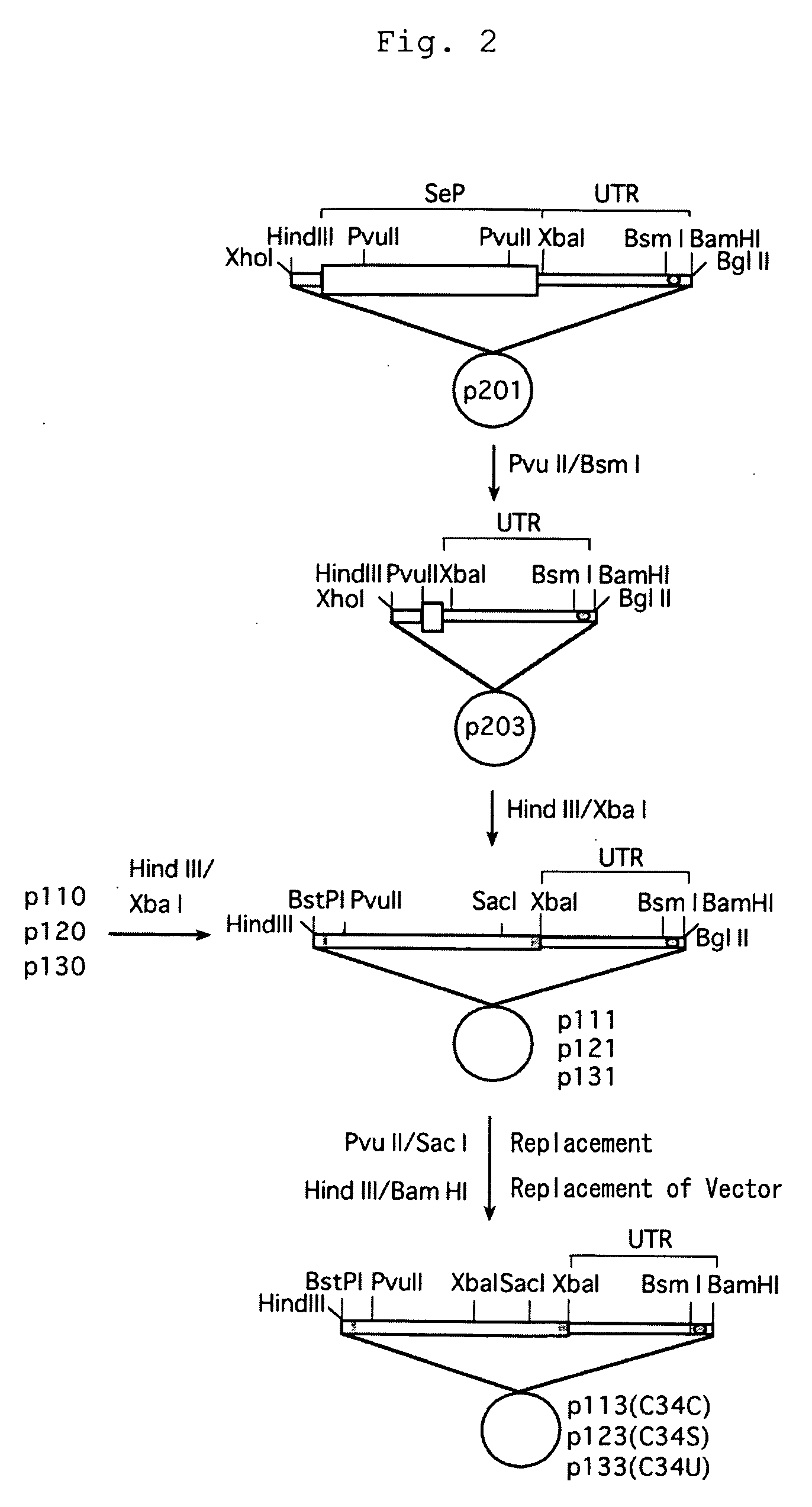
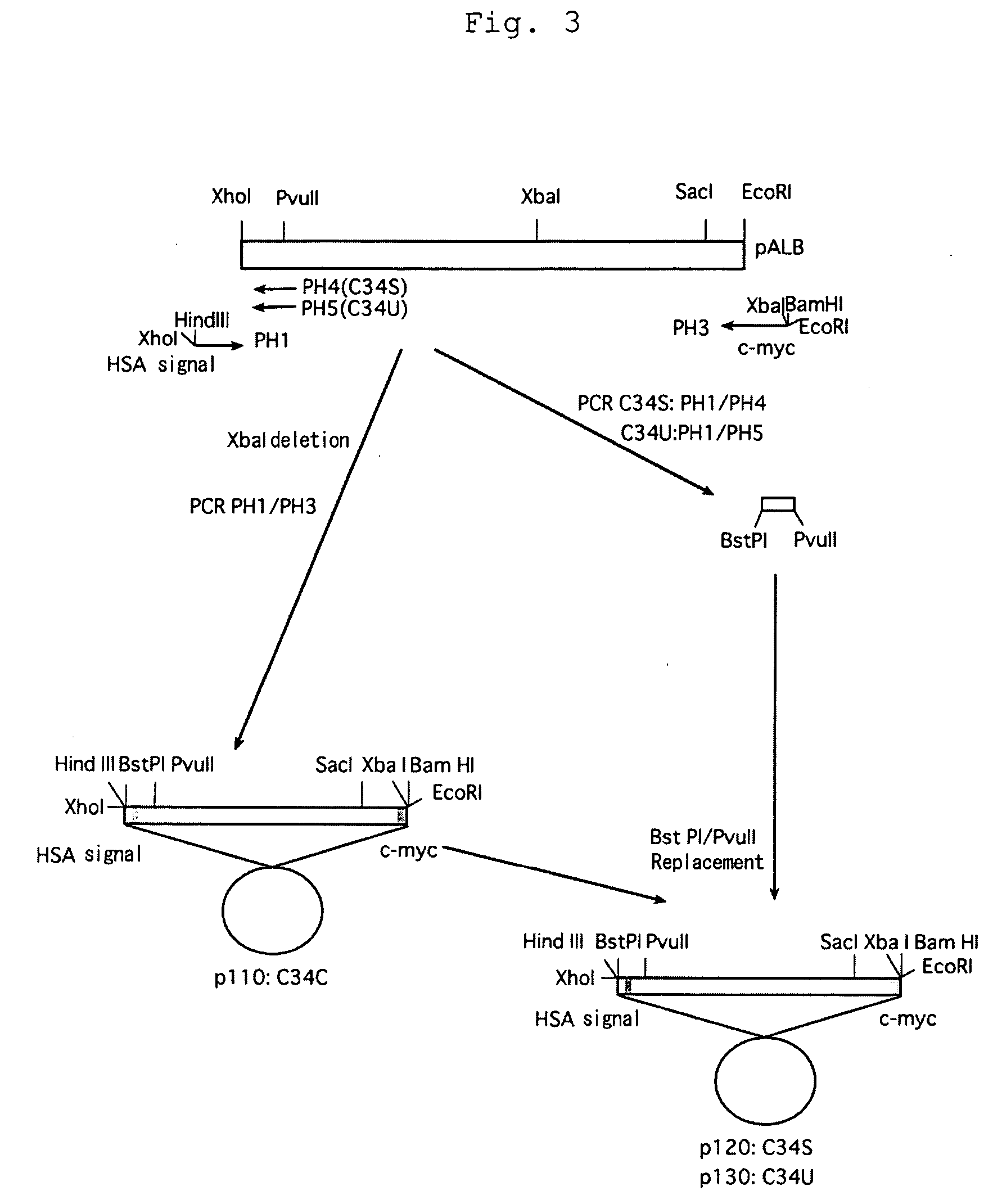
FLP-mediated gene modification in mammalian cells, and compositions and cells useful therefor
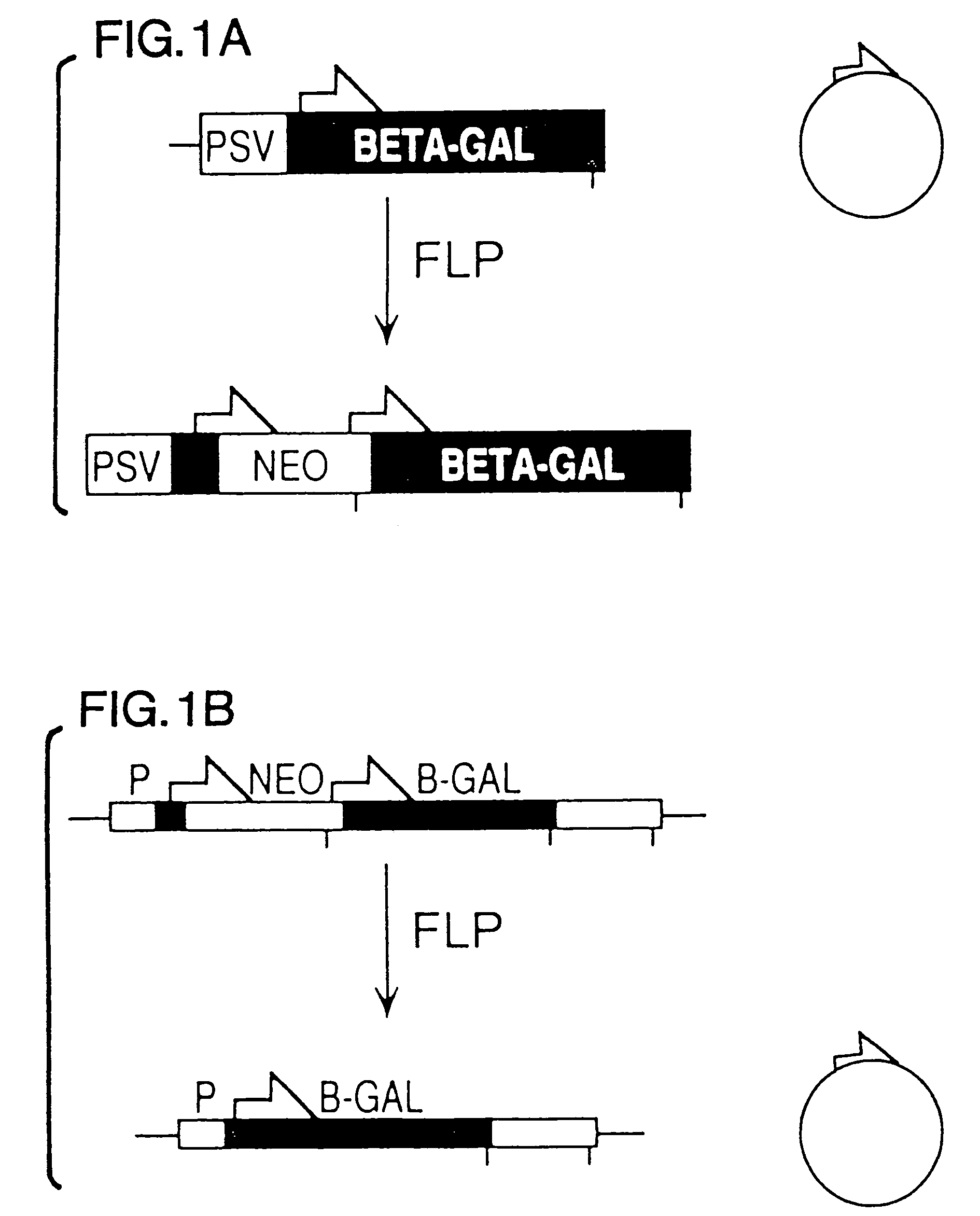
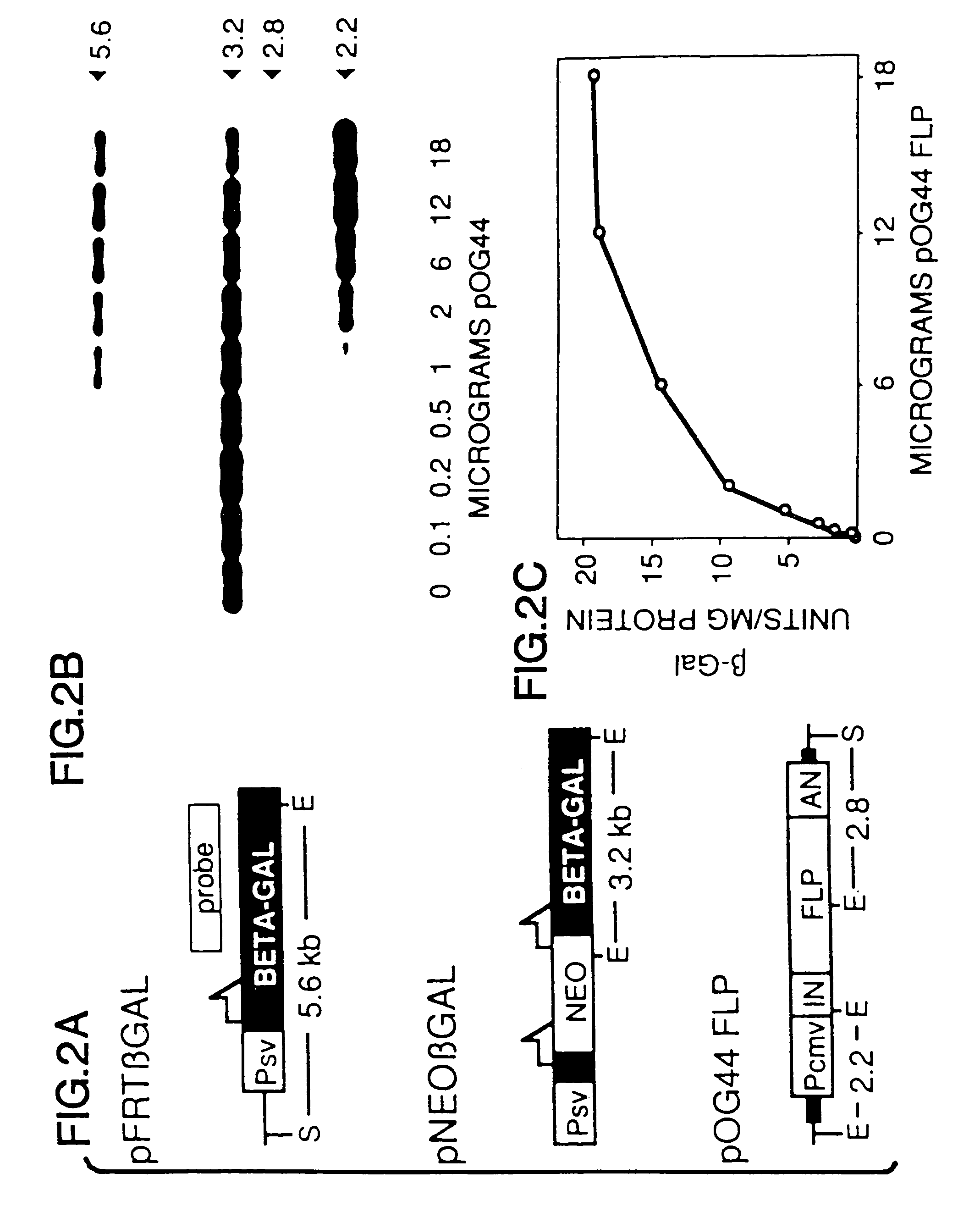
A gene activation / inactivation and site-specific integration system has been developed for mammalian cells. The invention system is based on the recombination of transfected sequences by FLP, a recombinase derived from Saccharomyces. In several cell lines, FLP has been shown to rapidly and precisely recombine copies of its specific target sequence. For example, a chromosomally integrated, silent β-galactosidase reporter gene was activated for expression by FLP-mediated removal of intervening sequences to generate clones of marked cells. Alternatively, the reverse reaction can be used to target transfected DNA to specific chromosomal sites. These results demonstrate that FLP can be used, for example, to mosaically activate or inactivate transgenes for a variety of therapeutic purposes, as well as for analysis of vertebrate development. The FLP recombination system of the present invention can be incorporated in transgenic, non-human mammals to achieve site-specific integration of transgenes, to construct functional genes or to disrupt existing genes.
Owner:CORN PROD DEV INC
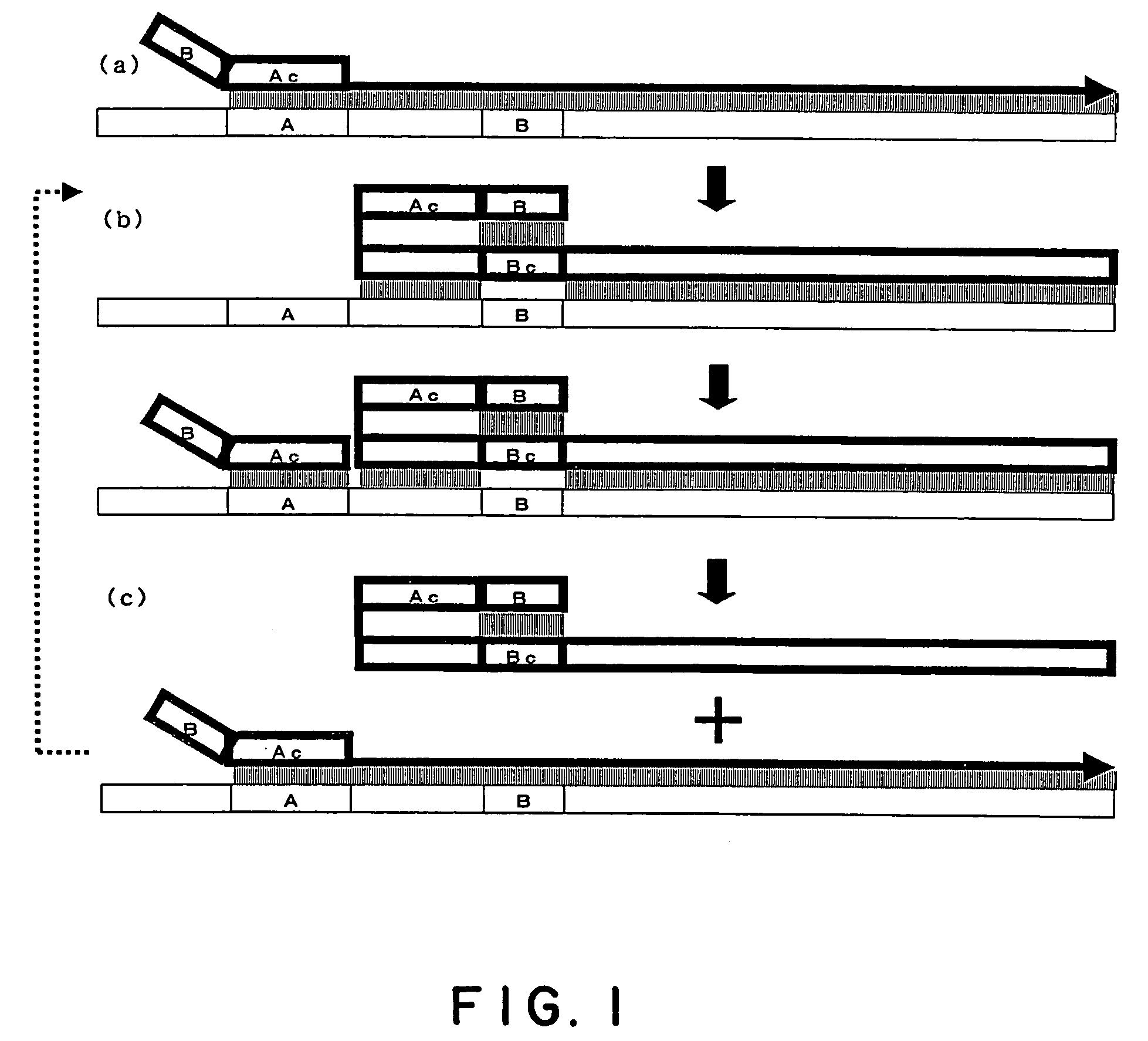
Process for amplifying nucleic acid
InactiveUS20060160084A1Meet growth requirementsEfficient amplificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingInsertion sequence
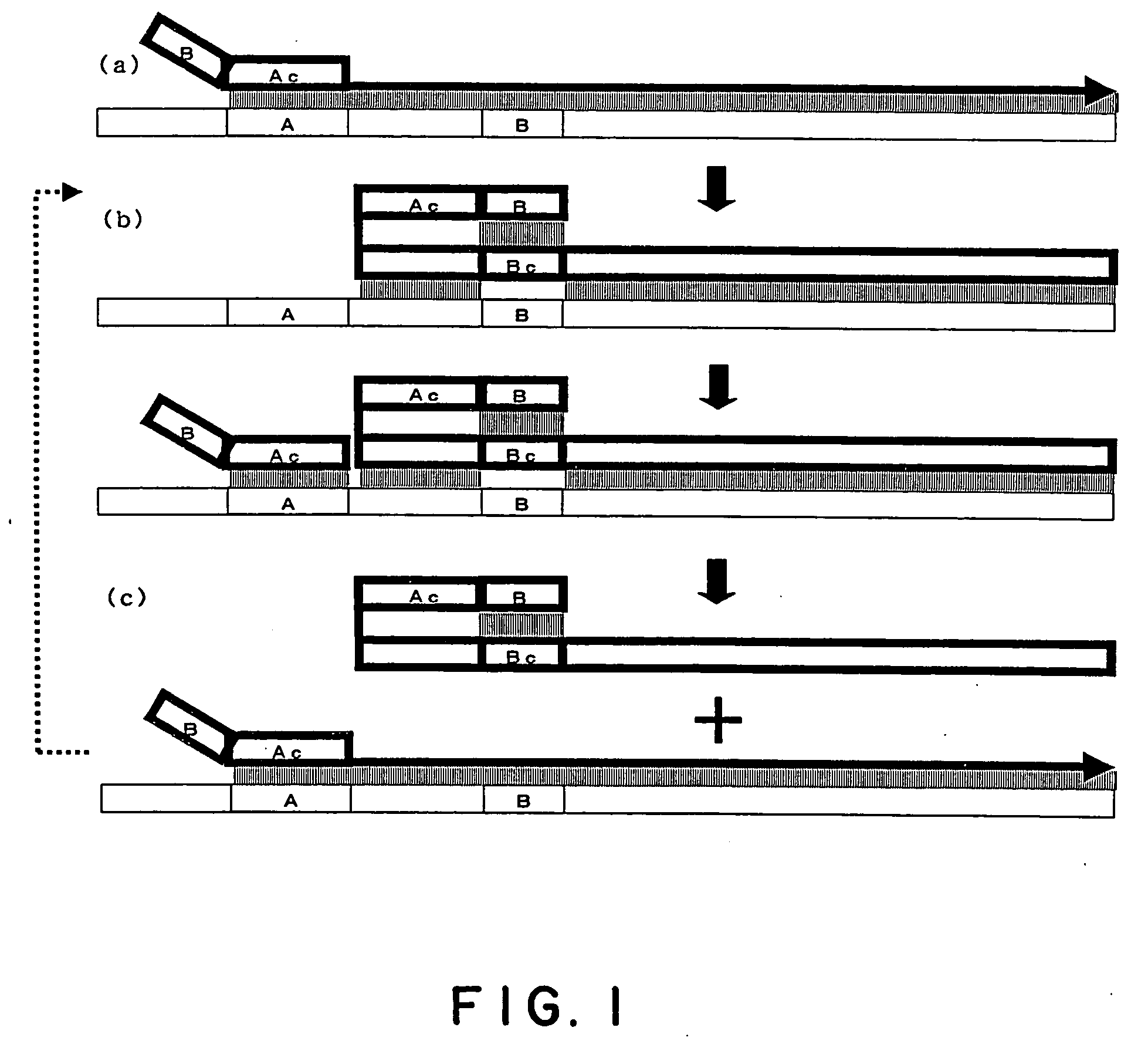
The present invention relates to a process for synthesizing or amplifying efficiently a nucleic acid comprising a target nucleic acid sequence. In the process according to the present invention, a primer comprising in its 3′-end portion a sequence (Ac′) which hybridizes a sequence (A) in the 3′-end portion of the target nucleic acid sequence, and in the 5′-side of said sequence (Ac′) a sequence (B′) which hybridizes the complementary sequence (Bc) of a sequence (B) positioned in the 5′-side of said sequence (A) on the target nucleic acid sequence, wherein {X−(Y−Y′)} / X is in the range of −1.00 to 1.00, in which X denotes the number of bases in said sequence (Ac′), Y denotes the number of bases in the region flanked by said sequences (A) and (B) in the target nucleic acid sequence, and Y′ denotes the number of bases in an intervening sequence between said sequences (Ac′) and (B′) (Y′ may be zero).
Owner:RIKEN +1
Oligonucleotide modulation of cell adhesion
InactiveUS6015894AHigh expressionAvoid inhibitionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseTranscription initiation site
Compositions and methods are provided for the treatment and diagnosis of diseases amenable to treatment through modulation of the synthesis or metabolism of intercellular adhesion molecules. In accordance with preferred embodiments, oligonucleotides are provided which are specifically hybridizable with nucleic acids encoding intercellular adhesion molecule-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, and endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1. The oligonucleotide comprises nucleotide units sufficient in identity and number to effect said specific hybridization. In other preferred embodiments, the oligonucleotides are specifically hybridizable with a transcription initiation site, a translation initiation site, 5'-untranslated sequences, 3'-untranslated sequences, and intervening sequences. Methods of treating animals suffering from disease amenable to therapeutic intervention by modulating cell adhesion proteins with an oligonucleotide specifically hybridizable with RNA or DNA corresponding to one of the foregoing proteins are disclosed. Methods for treatment of diseases responding to modulation cell adhesion molecules are disclosed.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
FLP-mediated gene modification in mammalian cells, and compositions and cells useful therefor
A gene activation / inactivation and site-specific integration system has been developed for mammalian cells. The invention system is based on the recombination of transfected sequences by FLP, a recombinase derived from Saccharomyces. In several cell lines, FLP has been shown to rapidly and precisely recombine copies of its specific target sequence. For example, a chromosomally integrated, silent β-galactosidase reporter gene was activated for expression by FLP-mediated removal of intervening sequences to generate clones of marked cells. Alternatively, the reverse reaction can be used to target transfected DNA to specific chromosomal sites. These results demonstrate that FLP can be used, for example, to mosaically activate or inactivate transgenes for a variety of therapeutic purposes, as well as for analysis of vertebrate development. The FLP recombination system of the present invention can be incorporated in transgenic, non-human mammals to achieve site-specific integration of transgenes, to construct functional genes or to disrupt existing genes.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Primer composition for discriminating green-shelled-egg chicken genotype and use thereof
InactiveCN104830843AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGallus gallus gallusGenotype
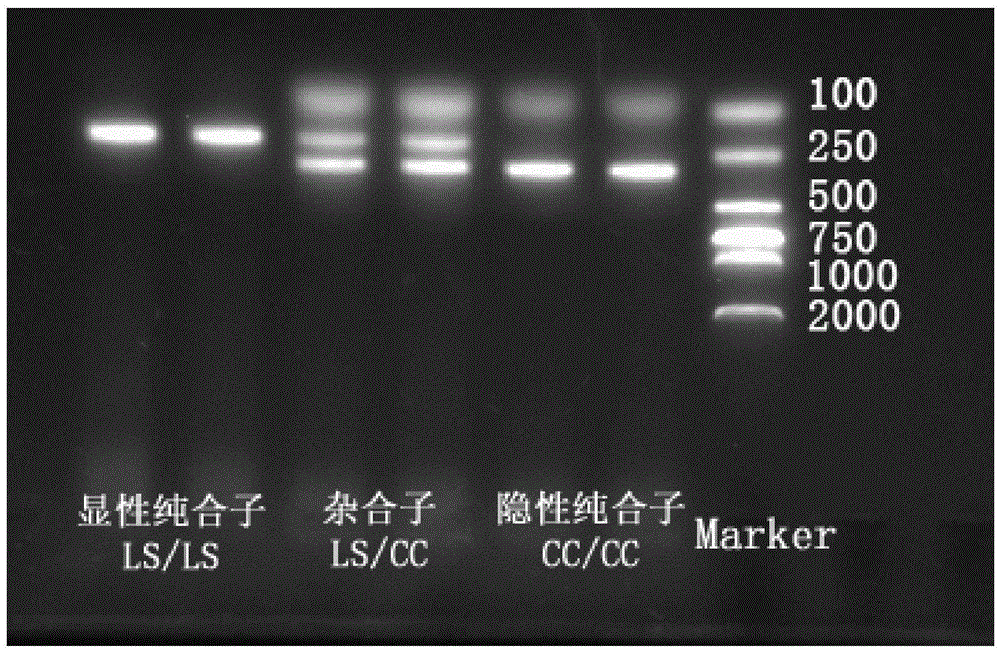
The invention discloses a primer composition for discriminating a green-shelled-egg chicken genotype and a use thereof. The primer composition comprises two primer pairs, one primer pair comprises SLCO1B3 gene inserted EAV-HP sequence primers respectively shown in the formulas of SEQ ID NO. 1 and 2, and the other primer pair comprises SLCO1B3 gene non-inserted sequence primers respectively shown in the formulas of SEQ ID NO. 1 and 3. A DNA genome of a chicken to be detected is used as a template and is subjected to PCR amplification under the action of the primer pairs so that a PCR amplification product is obtained. Through detection of the amplified 209bp and 312bp bands, it is determined if the chicken to be detected can produce green-shelled eggs. The primer composition can discriminate the green-shelled-egg chicken genotype.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
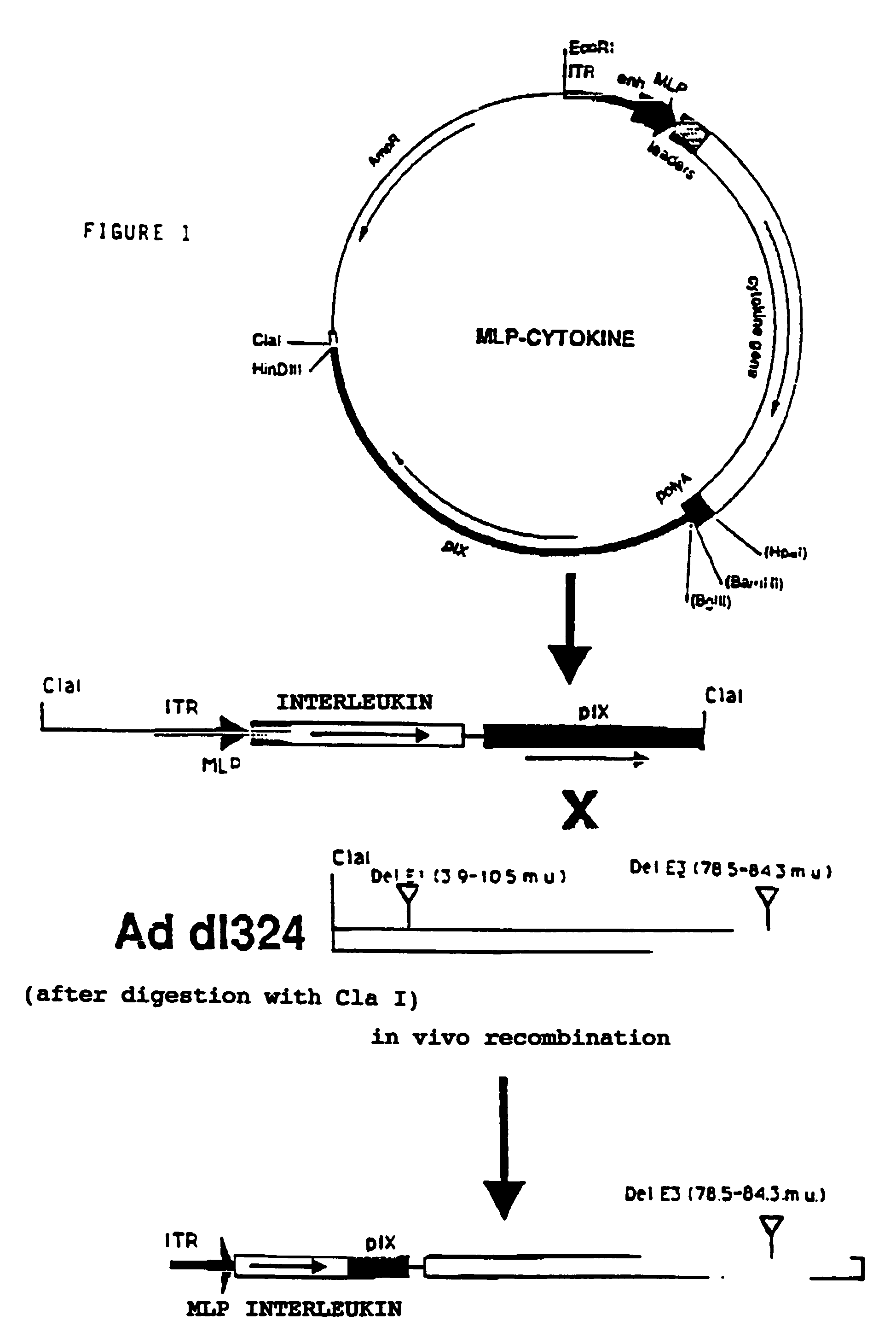
Defective recombinant adenoviruses expressing cytokines for antitumor treatment
A recombinant nucleic acid used for the production of a defective adenovirus containing an inserted sequence coding for a cytokine under the control of a promoter in the genomic sequence of the recombinant adenovirus. This recombinant adenovirus is useful in the preparation of anti-tumoral drugs which can be directly injected into the tumor of the host.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Insertion sequence element derived from ralstonia solanacearum
InactiveUS20030009026A1Useful industriallyReduce pathogenicitySugar derivativesHydrolasesRalstonia solanacearumInsertion sequence
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI
Process for amplifying nucleic acid
InactiveUS7803579B2Efficient amplificationMeet growth requirementsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
The present invention relates to a process for synthesizing or amplifying efficiently a nucleic acid comprising a target nucleic acid sequence. The process involves providing a primer comprising in its 3′-end portion a sequence (Ac′) which hybridizes a sequence (A) in the 3′-end portion of the target nucleic acid sequence, and in the 5′-side of the sequence (Ac′) a sequence (B′) which hybridizes the complementary sequence (Bc) of a sequence (B) positioned in the 5′-side of the sequence (A) on the target nucleic acid sequence, wherein {X−(Y−Y′)} / X is in the range of −1.00 to 1.00, in which X denotes the number of bases in the sequence (Ac′), Y denotes the number of bases in the region flanked by the sequences (A) and (B) in the target nucleic acid sequence, and Y′ denotes the number of bases in an intervening sequence between the sequences (Ac′) and (B′) (Y′ may be zero).
Owner:RIKEN +1
Escherichia coli t7 expression vector, vectors for the co-expression and co-purification of recombinant peptides in/with carrier proteins, use of expression vectors for obtaining complexes with multiple antigens and immonomodulators
InactiveUS20180135060A1Increase productionAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEscherichia coliAmpicillin
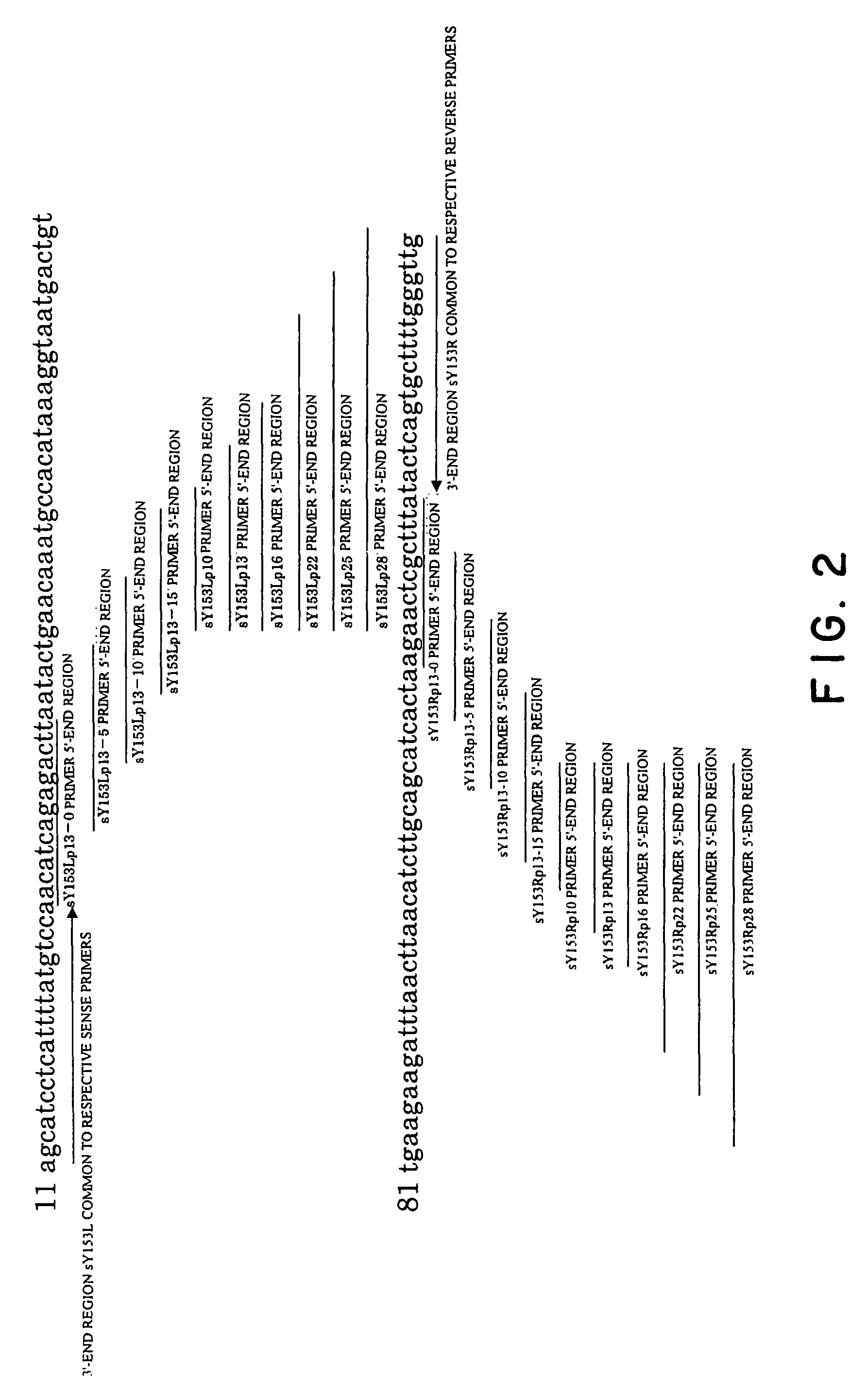
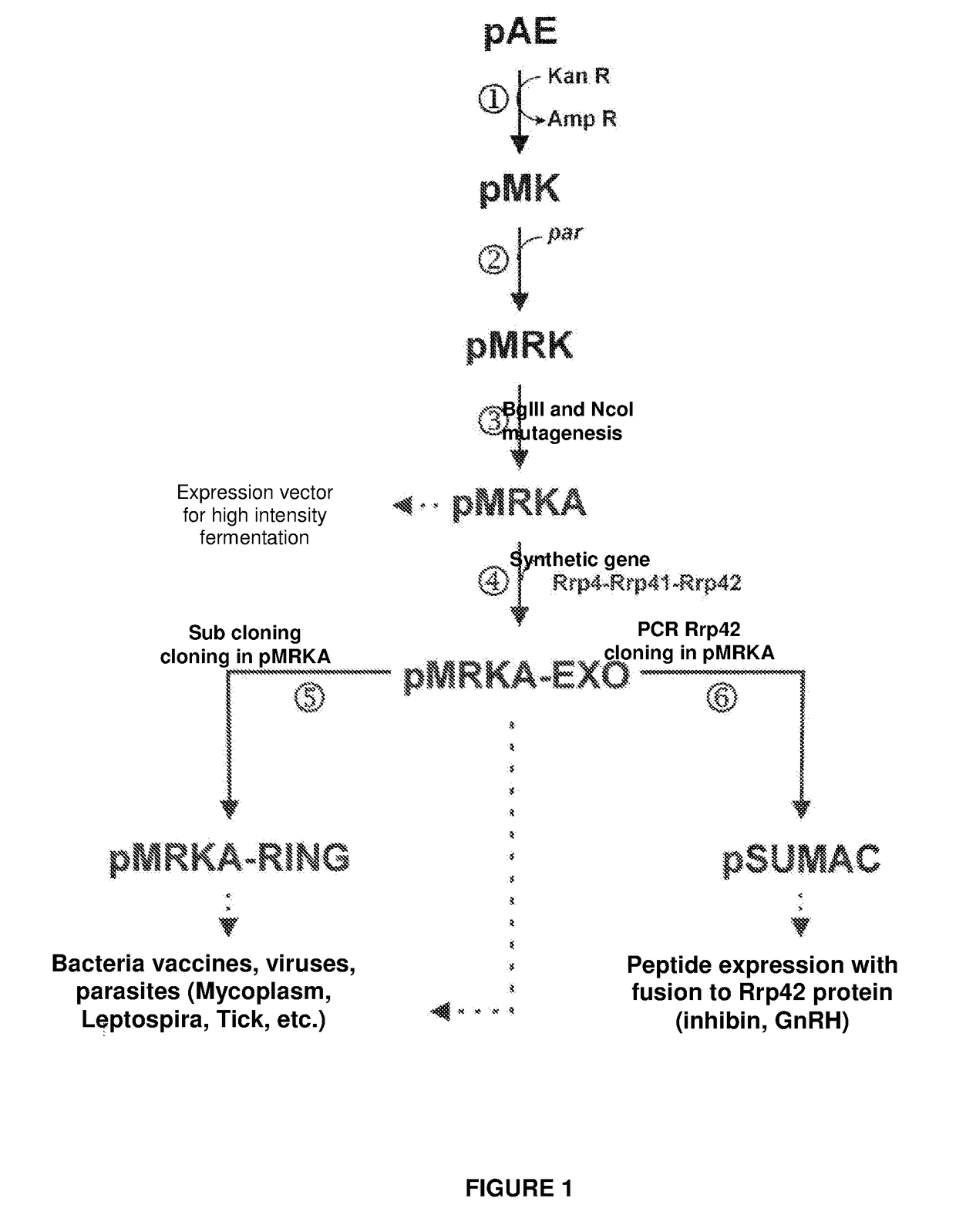
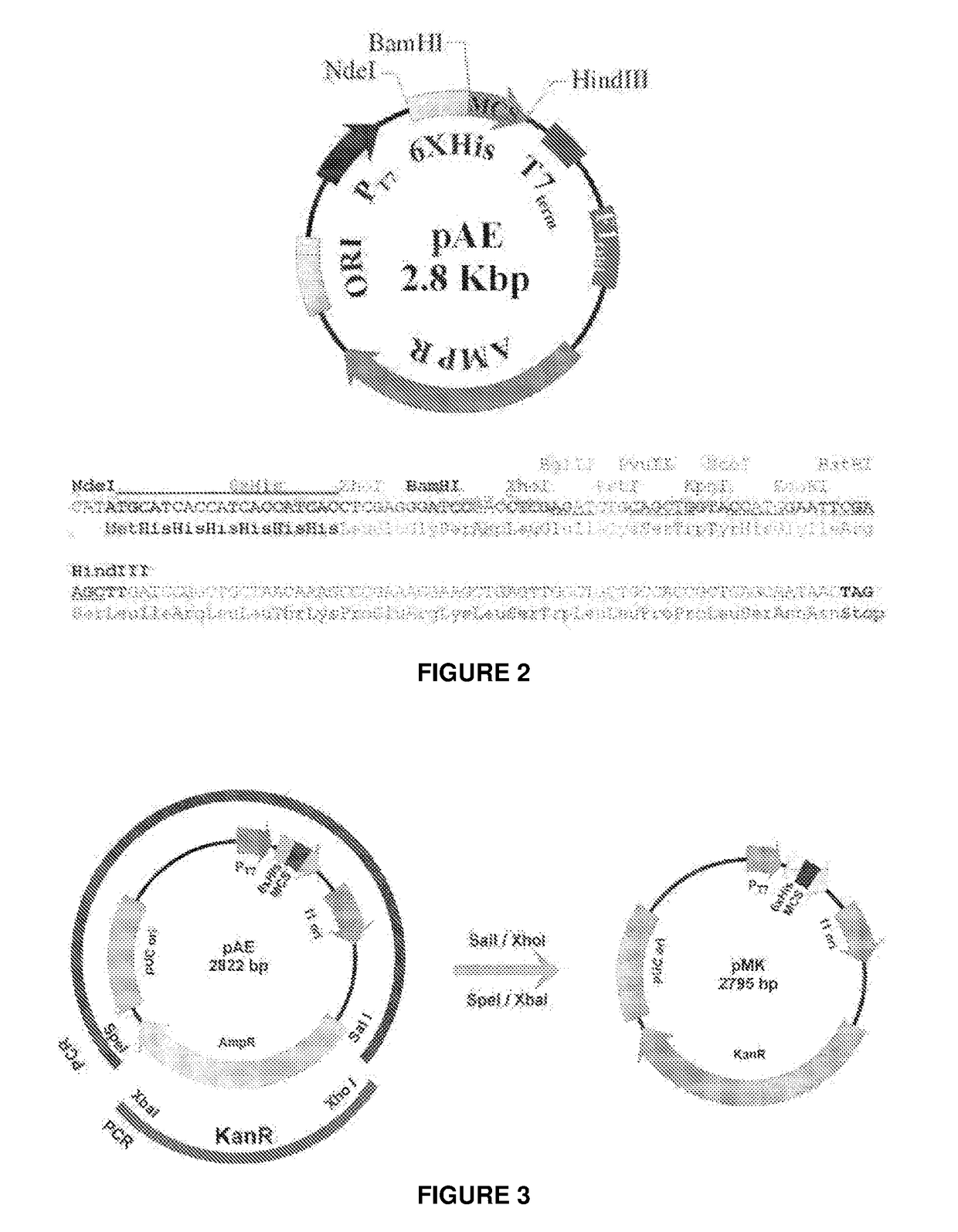
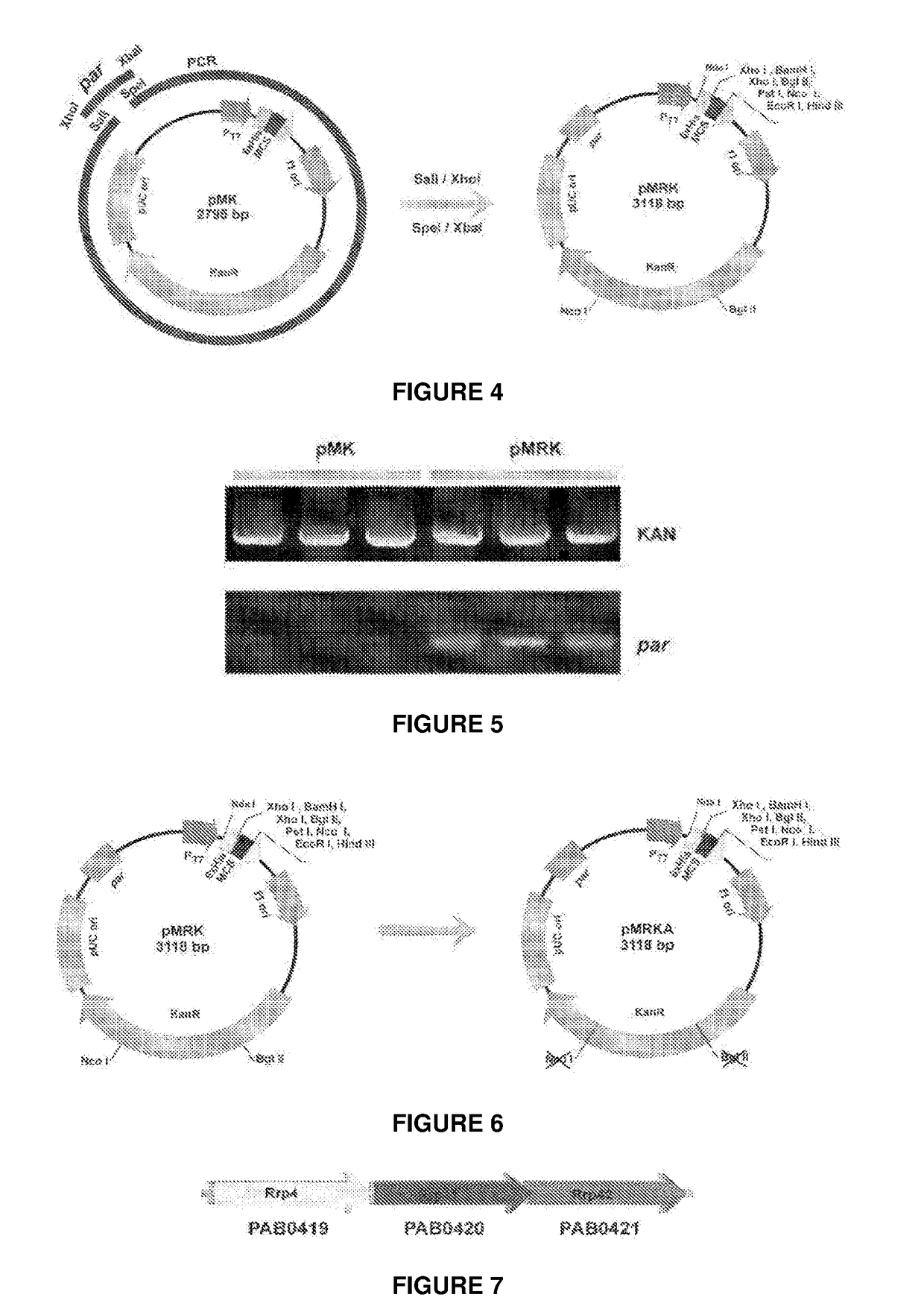
The present invention relates to a vector for the expression of recombinant proteins, antigens, pathogen-like particles and immunogenic complexes, said vector (pMRKA vector) being produced by modifying the plasmids containing the gene sequence of the T7 promoter of E. coli, this modification being mainly characterized by the substitution of the ampicillin-resistance gene by the kanamycin-resistance gene, and by the insertion of the par sequence (partition sequence which determines the efficient segregation of the plasmids in daughter cells during cell division). Also provided are expression vectors based on the pMRKA plasmid, which additionally comprise at least one of the gene sequences of the exosome of P. abyssi, which vectors are designated pMRKA-EXO, pMRKA-RING and pSUMAC. The invention also provides the vectors additionally comprising gene sequences with immunomodulatory or immunoregulatory activity, preferably the pMRKA-Z-Z-EXO and pMRKA-Z-Z-RING vectors. Other aspects of the invention include the method for producing said expression vectors and the use of the obtained vectors.
Owner:OURO FINO SAUDE ANIMAL
Method for enhancing aphid resistance of plant
ActiveCN102206668AIncrease resistanceBreak through subspecies restrictionsVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsSense strandDouble stranded
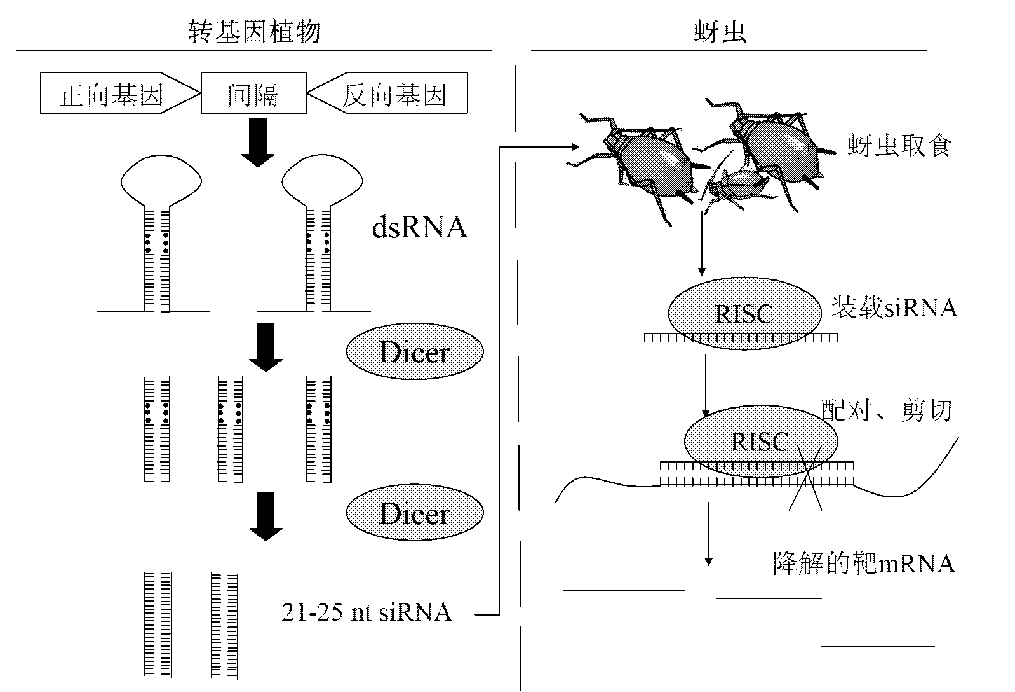
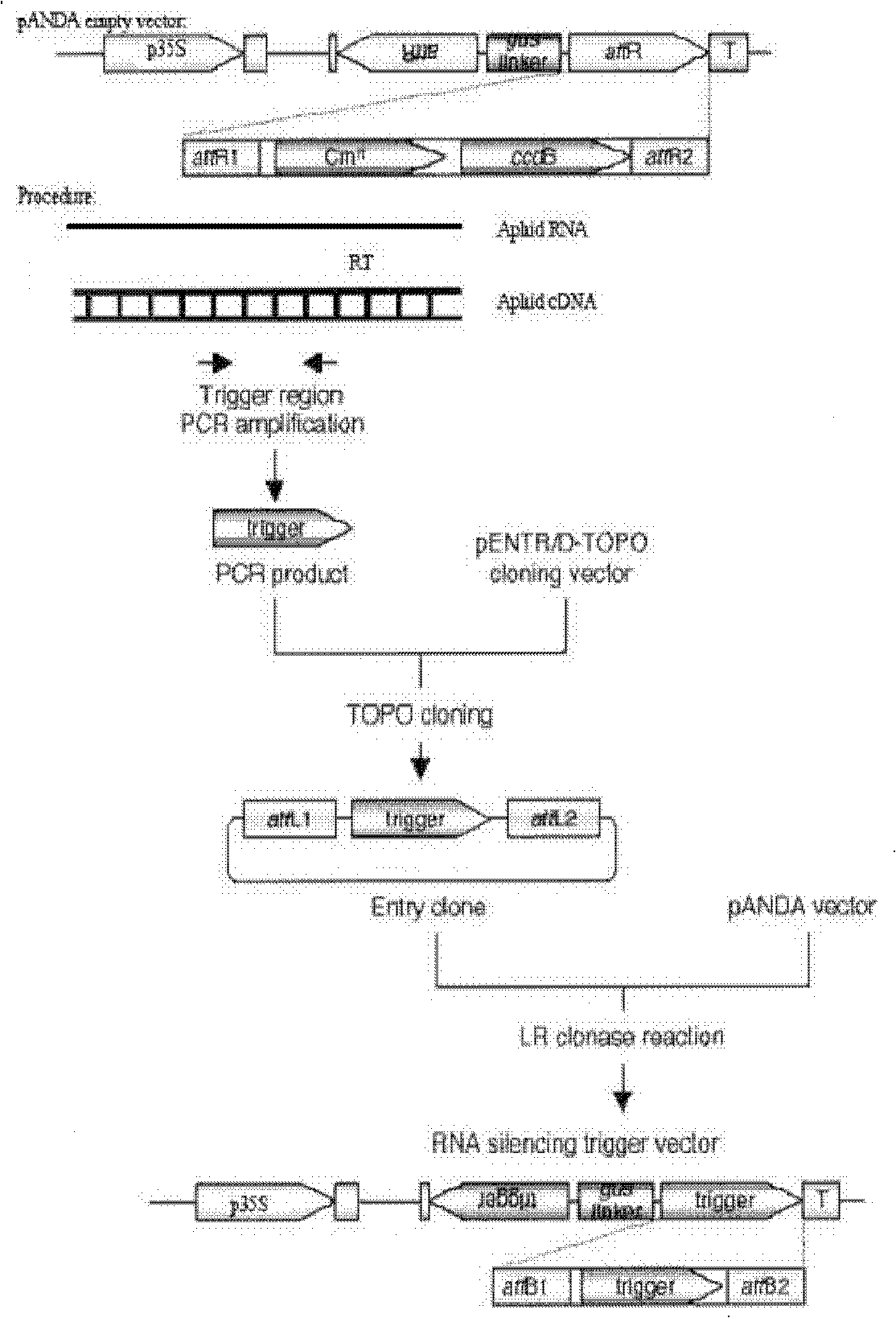
The invention relates to a method for enhancing the aphid resistance of a plant, belonging to the technical field of biology. With the method, a construct expressing the dsRNA (Double-Stranded RNA) of an aphid gene is transferred into the plant; the construct expressing the dsRNA of the aphid gene is double-stranded, a positive-sense strand and a negative-sense strand of the aphid gene contain the following structures: Ap forward direction-X-Ap reverse direction, wherein the Ap forward direction is a forward sequence or fragment of the aphid gene, the Ap reverse direction is a reverse complementary sequence or fragment of the same aphid gene, and X is an intervening sequence positioned between the Ap forward direction and the Ap reverse direction; and the dsRNA shown in the description is formed after a constructed vector is transcribed in the plant, wherein ll expresses a hydrogen bond formed between the Ap forward direction and the Ap reverse direction.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Gene mutation multi-detecting method based on signal amplification DNA logic gate
ActiveCN107523630AHigh detection sensitivityHigh detection specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)A-DNA
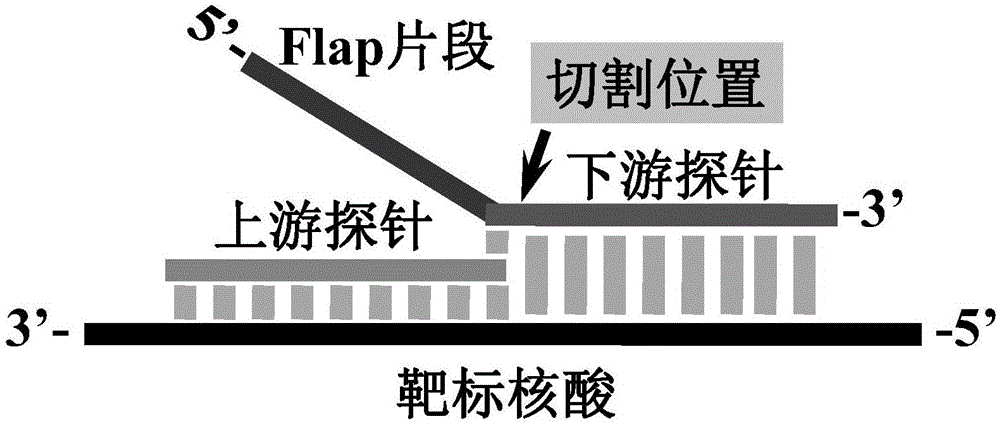
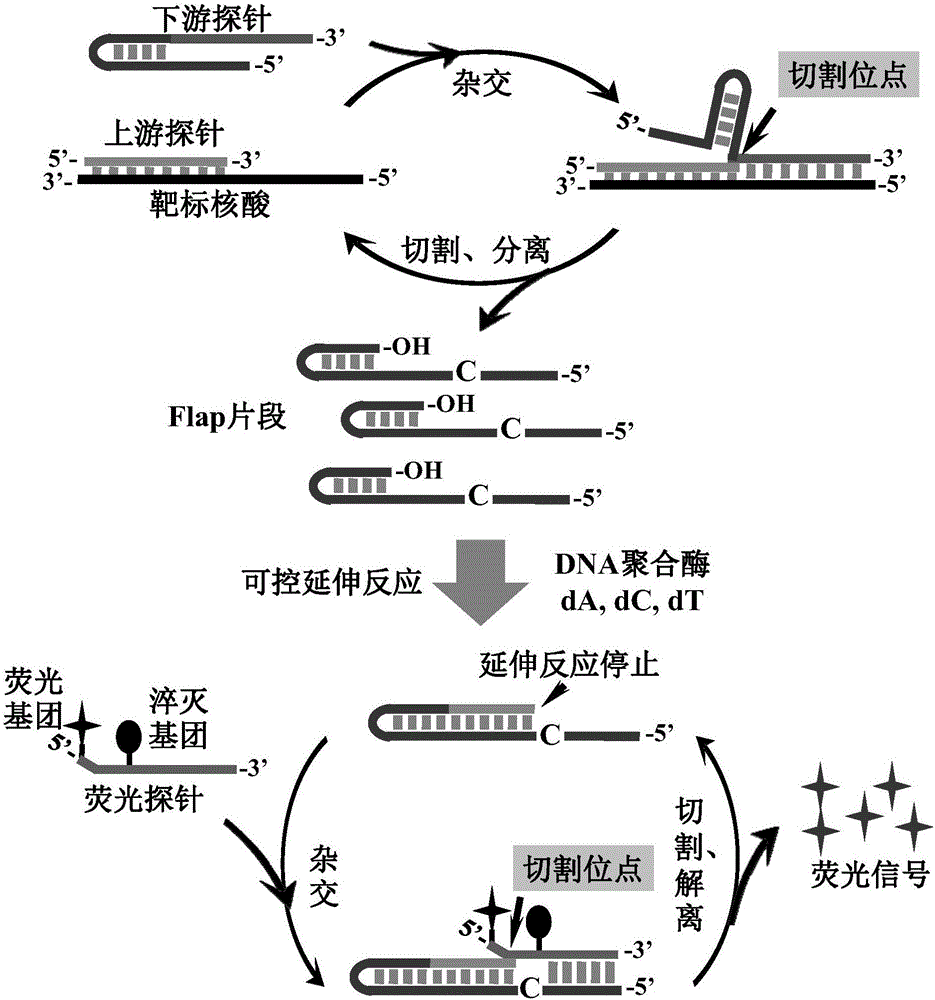
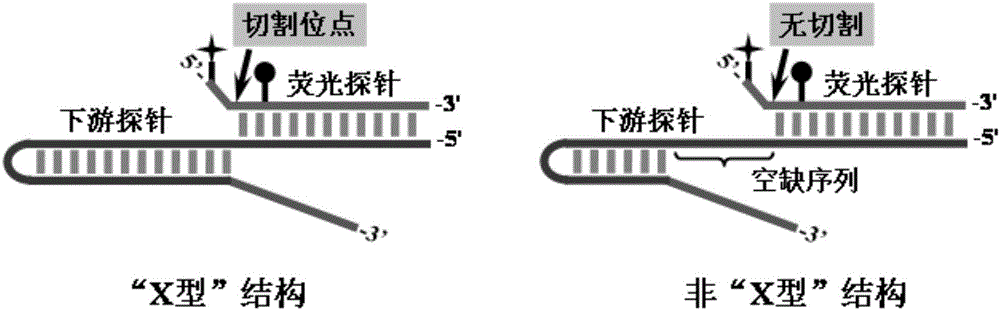
The invention discloses a gene mutation multi-detecting method based on a signal amplification DNA logic gate. The method comprises the following steps: performing high specificity recognition on a detecting target by invading into a signal amplification reaction by utilizing nucleic acid, and simultaneously, invading into the signal amplification reaction by utilizing a controllable DNA polymerase extension reaction bridging two-step nucleic acid to form signal amplification. The method disclosed by the invention has high detecting sensitivity and high detecting specificity to a nucleic acid target. A DNA logic gate is constructed by invading into the signal amplification reaction by adopting the controllable DNA polymerase extension reaction bridging two-step nucleic acid disclosed by the invention, a background signal is inhibited by introducing an intervening sequence, and meanwhile, a two-step signal amplification reaction exists, so that the defecting sensitivity is improved, and high signal-to-noise ratio output can be realized under the conditions of trace amount of DNA input and short reaction time. Moreover, through the method established by the invention, a plurality of gene mutation points can be detected simultaneously and results can be subjected to logical judgment, and an analyzing process of gene mutation detection in a clinically individualized medicating process is simplified.
Owner:NANJING GENERAL HOSPITAL NANJING MILLITARY COMMAND P L A
Oligonucleotide inhibition of cell adhesion
Compositions and methods are provided for the treatment and diagnosis of diseases amenable to treatment through modulation of the synthesis or metabolism of intercellular adhesion molecules. In accordance with preferred embodiments, oligonucleotides are provided which are specifically hybridizable with nucleic acids encoding intercellular adhesion molecule-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, and endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1. The oligonucleotide comprises nucleotide units sufficient in identity and number to effect said specific hybridization. In other preferred embodiments, the oligonucleotides are specifically hybridizable with a transcription initiation site, a translation initiation site, 5'-untranslated sequences, 3'-untranslated sequences, and intervening sequences. Methods of treating animals suffering from disease amenable to therapeutic intervention by modulating cell adhesion proteins with an oligonucleotide specifically hybridizable with RNA or DNA corresponding to one of the foregoing proteins are disclosed. Methods for treatment of diseases responding to inhibition of cell adhesion molecules are disclosed.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Hematopoietic stem cell gene modification method for targeting hemoglobin HBB mutant gene
The invention discloses a hematopoietic stem cell gene modification method for targeting a hemoglobin HBB mutant gene. The method 1 comprises the following steps: electro-transforming gRNA1, gRNA2 andthe mRNA of spCas9-2.0 into CD34+ cells containing the hemoglobin HBB mutant gene; and culturing the cells for one day, and transferring rAAV-HBB into the CD34+ cells, and harvesting the cells. The method 2 comprises the following steps: mixing and recombining a Cas9 protein with the gRNA1 and the gRNA2, and electro-transforming the recombinant Cas9 protein into the CD34+ cells; and culturing thecells for one day, and transferring the rAAV-HBB into the CD34+ cells, and harvesting the cells. The CD41 / 42 (-CTTT) in the most common HBB mutation in Guangxi province and Guangdong province in China is targeted, no other mutation or insertion sequences are left in chromosomes after gene editing is completed, and the gene editing efficiency can reach 15-20%.
Owner:YINFENG BIOLOGICAL GRP +1
Colibacillus-lactic acid bacteria shuttle plasmid capable of expressing and excreting beta-galactosidase and its construction method and application
InactiveCN101033471AAchieve separationImmediate and broad application valueBacteriaFermentationPhosphorylationGenomic DNA
Gene of an E.coli-Lactobacillus shuttle plasmid expressing and secreting beta-galactosidase is composed of the gene encoding beta-galactosidase and its upstream regulatory sequence containing SD sites. Experiments proves that the recombinant plasmid can be transformed into Lactococcus lactis, and highly express the non-fused beta-galactosidase in E.coli and Lactococcus lactis, which is applicable in the lactic acid bacteria strain expressing beta-galactosidaseion. The construction method includes the following steps: taking Lactobacillus Bulgaria subspecies genomic DNA as template to amplify and obtain the beta-galactosidase gene containing the upstream regulatory sequence, digesting the gene to conjugate with the dephosphorylated vector digested with the same two enzymes and transform E.coli, then screening the positive one to extract the recombinant for enzyme identification and sequencing the inserted sequence.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
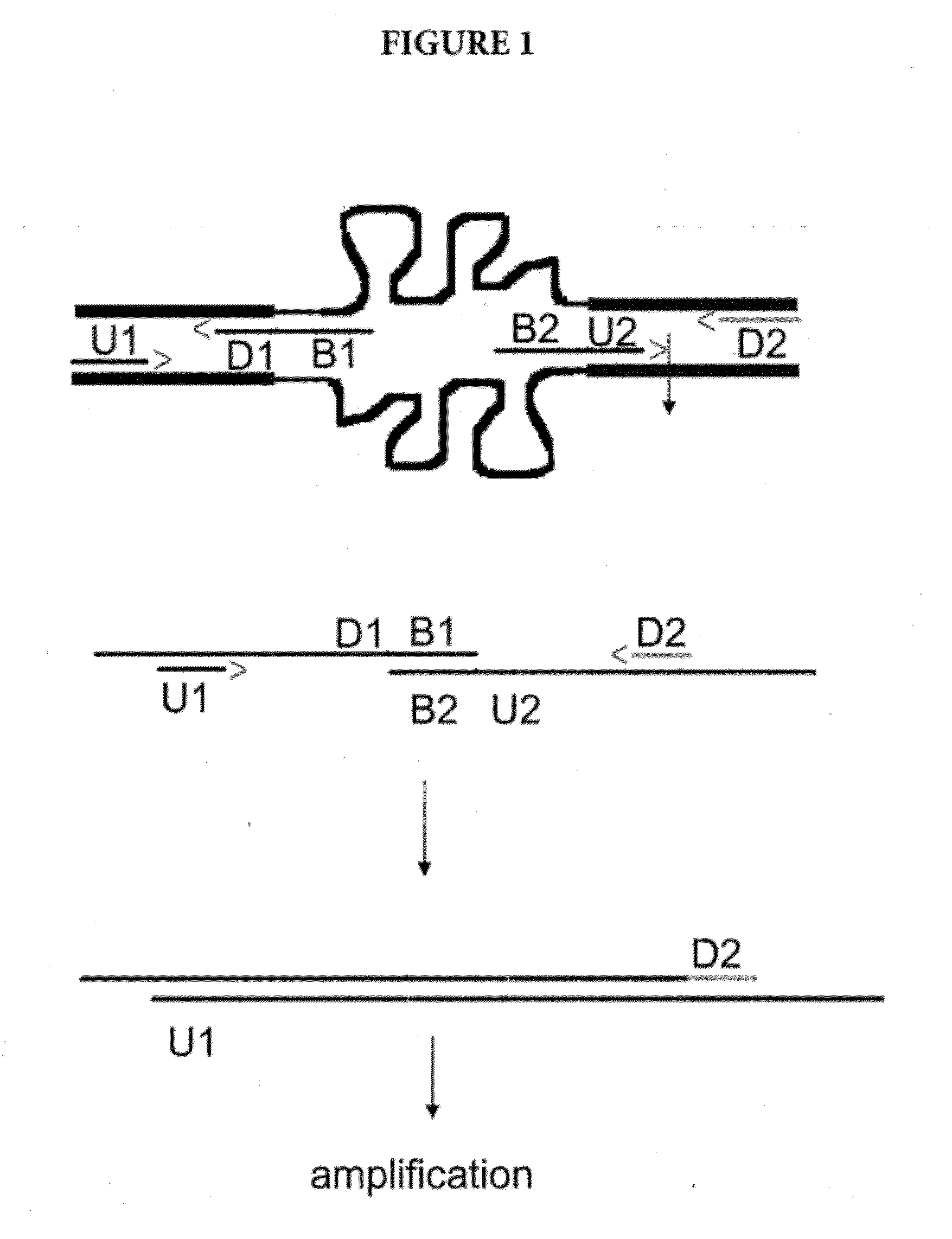
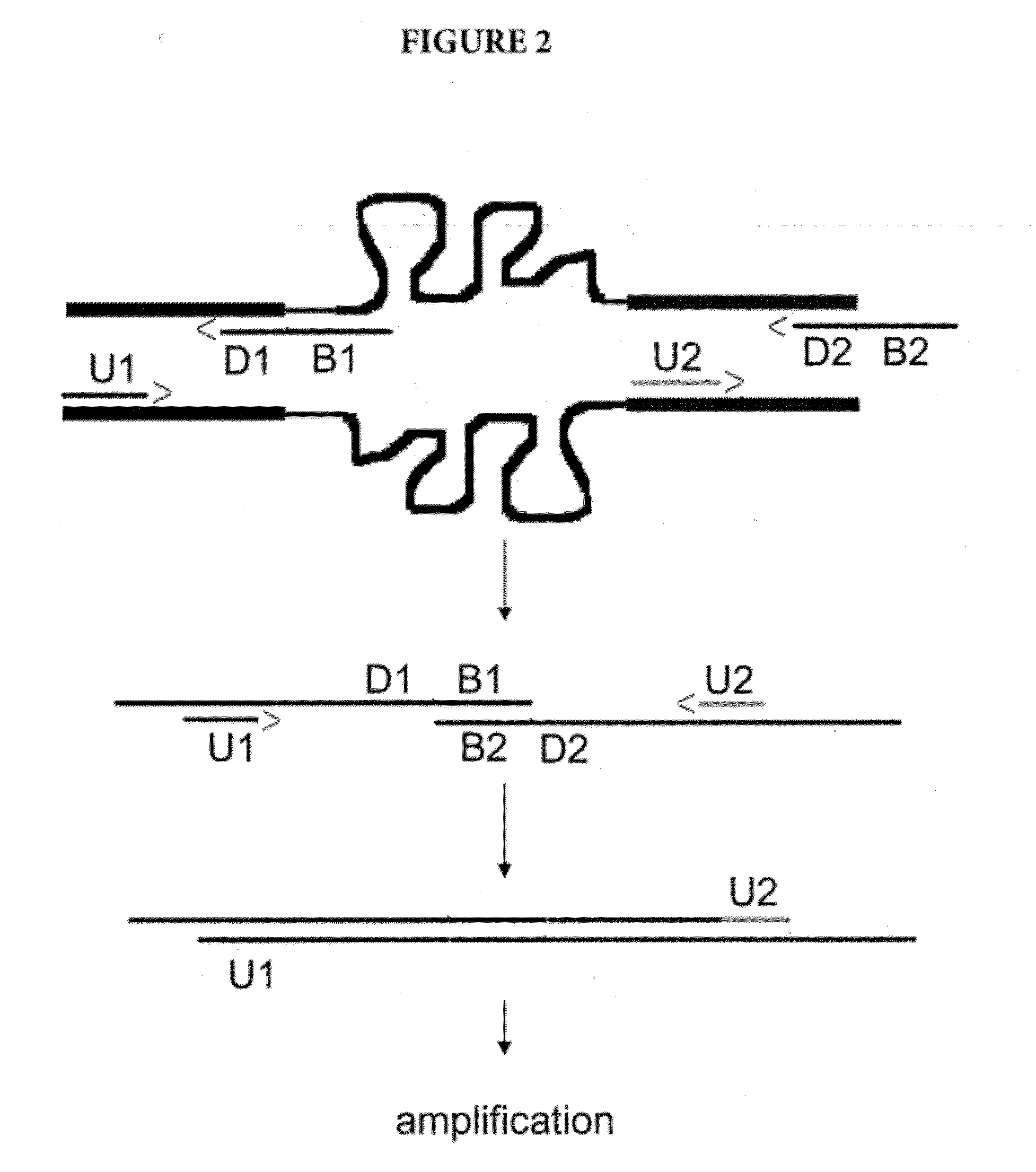
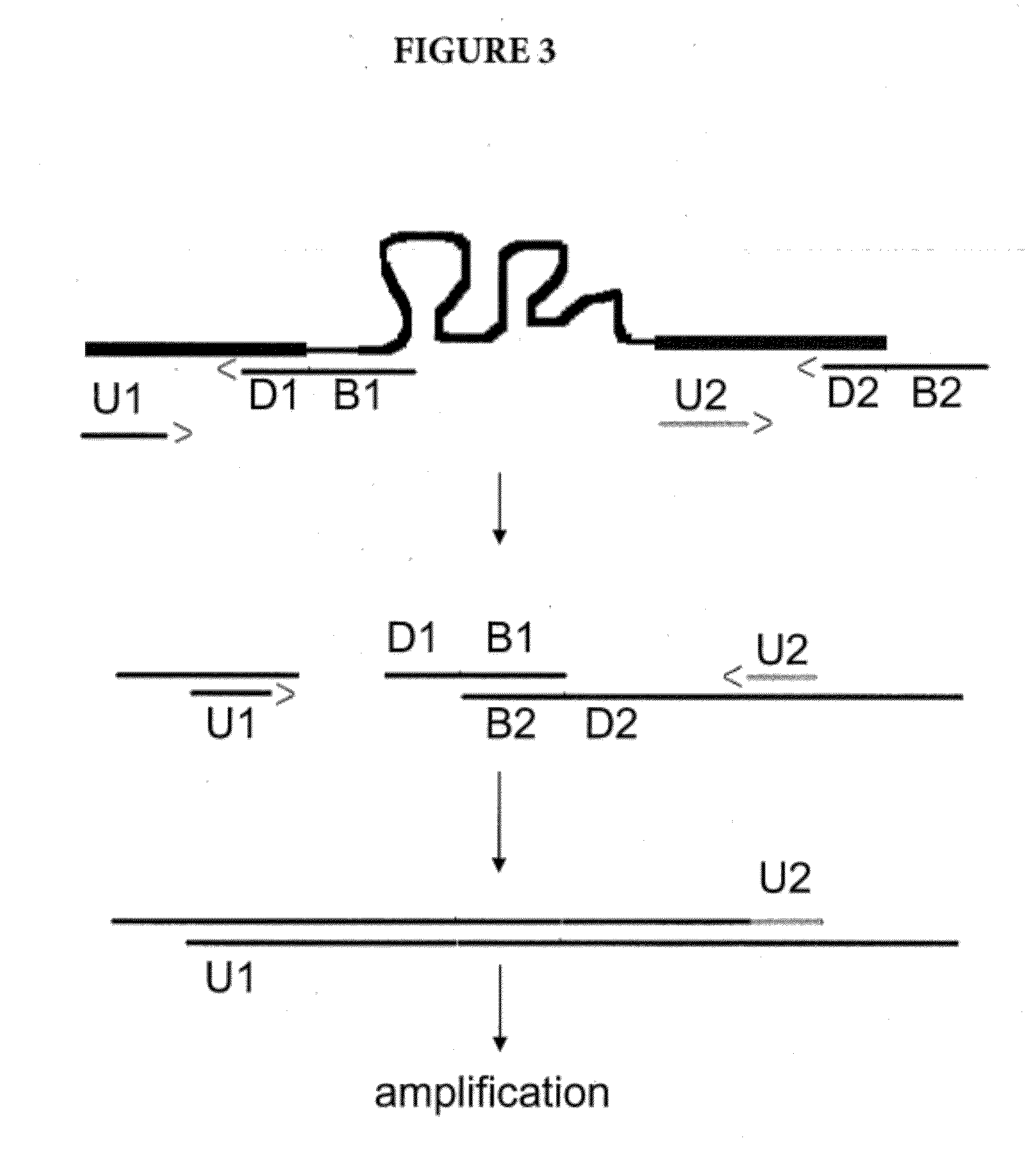
Amplification of Distant Nucleic Acid Targets Using Engineered Primers
InactiveUS20120070831A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyIntervening Sequence
The invention is a method of amplifying nucleic acids by synthesizing an engineered amplicon containing the sequence of interest, but omitting intervening sequences present in the template molecule. The method utilizes an “amplicon bridge” incorporated into the amplification primers. The length and content of the desired amplicon can be chosen by the operator and can contain unique regions for probe binding.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
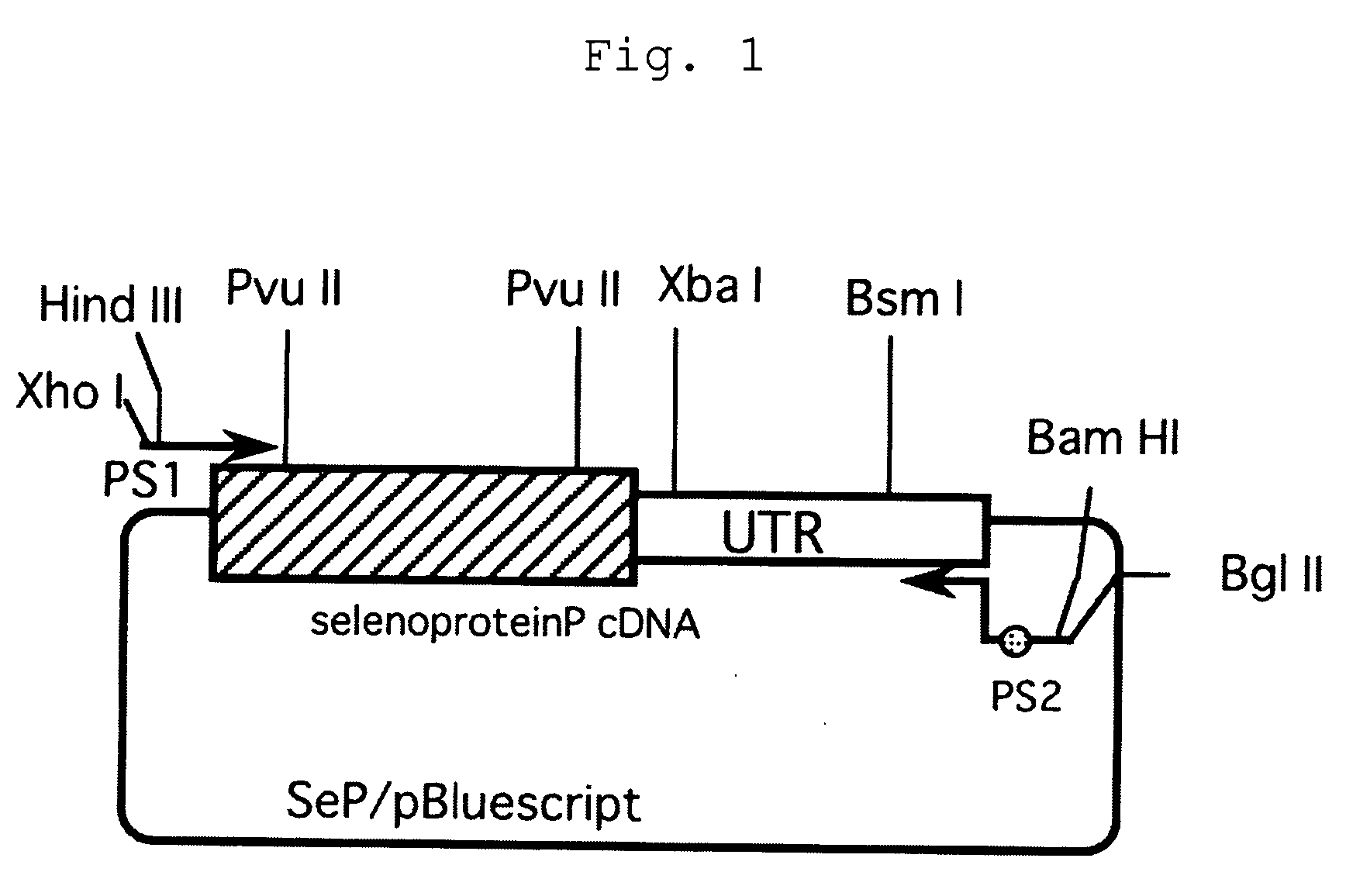
Novel selenocysteine-containing protein
InactiveUS20060051851A1High activityImproves antioxidant activityNervous disorderAntipyreticDiseasePhospholipid
A novel selenocysteine-containing protein is provided which is a substantial entity having an enzymatic activity, typically an activity to reduce peroxide phospholipids. There are provided a gene consisting of a coding sequence for a protein not containing selenocysteine in which the codon for selenocysteine is introduced at a desired position and a selenocysteine insertion sequence resided at the 3′-end of said coding sequence and a protein expressed therefrom, typically a selenocysteine-containing protein having an activity to reduce peroxide phospholipids which is prepared by introducing selenocysteine into albumin and as well as a gene encoding said protein. A novel anti-oxidative substance is provided which can be applied for prevention of worsening, prophylaxis or treatment of various diseases associated with oxidative stress.
Owner:JURIDICAL FOUND THE CHEMO SERO THERAPEUTIC RES INST
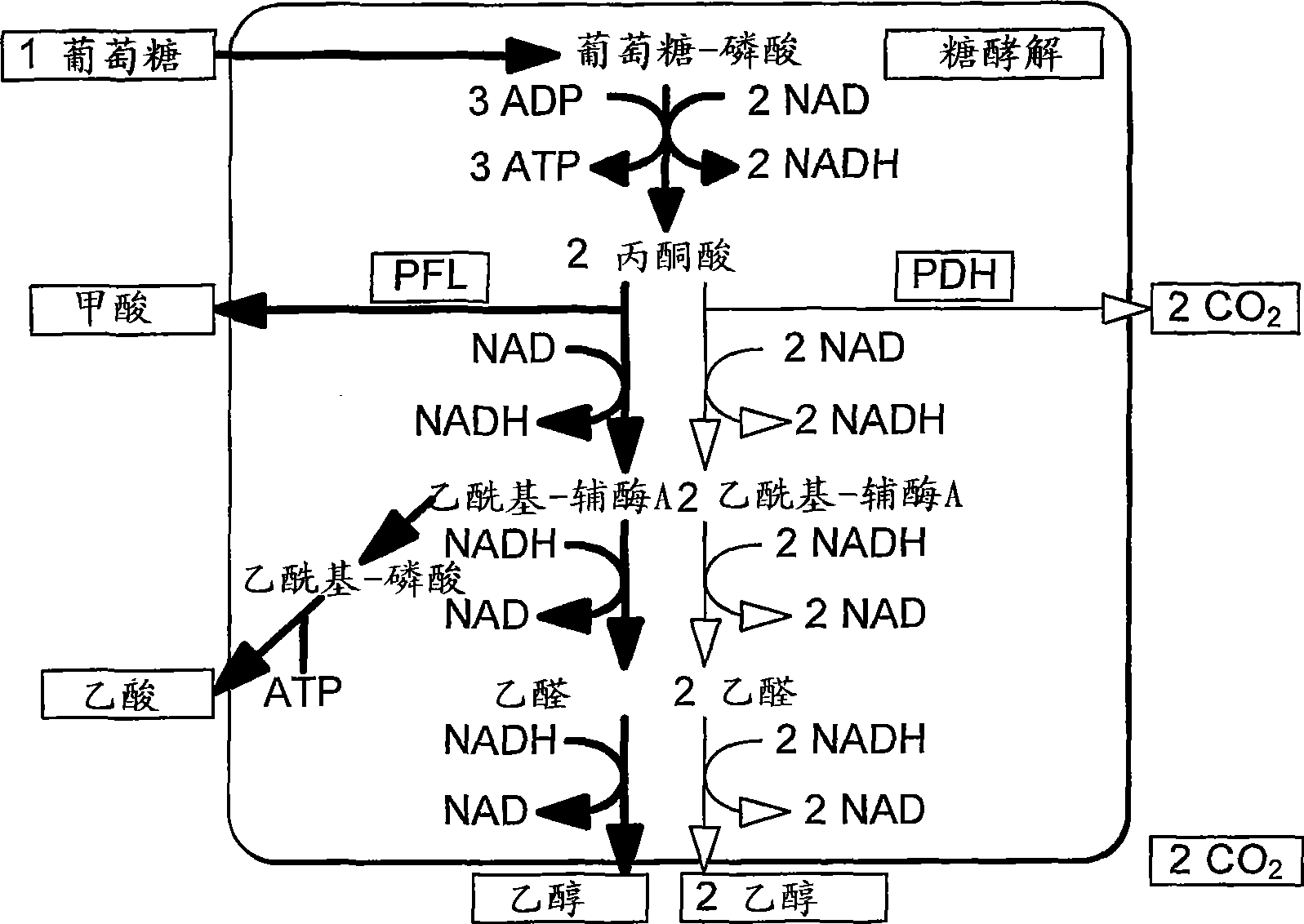
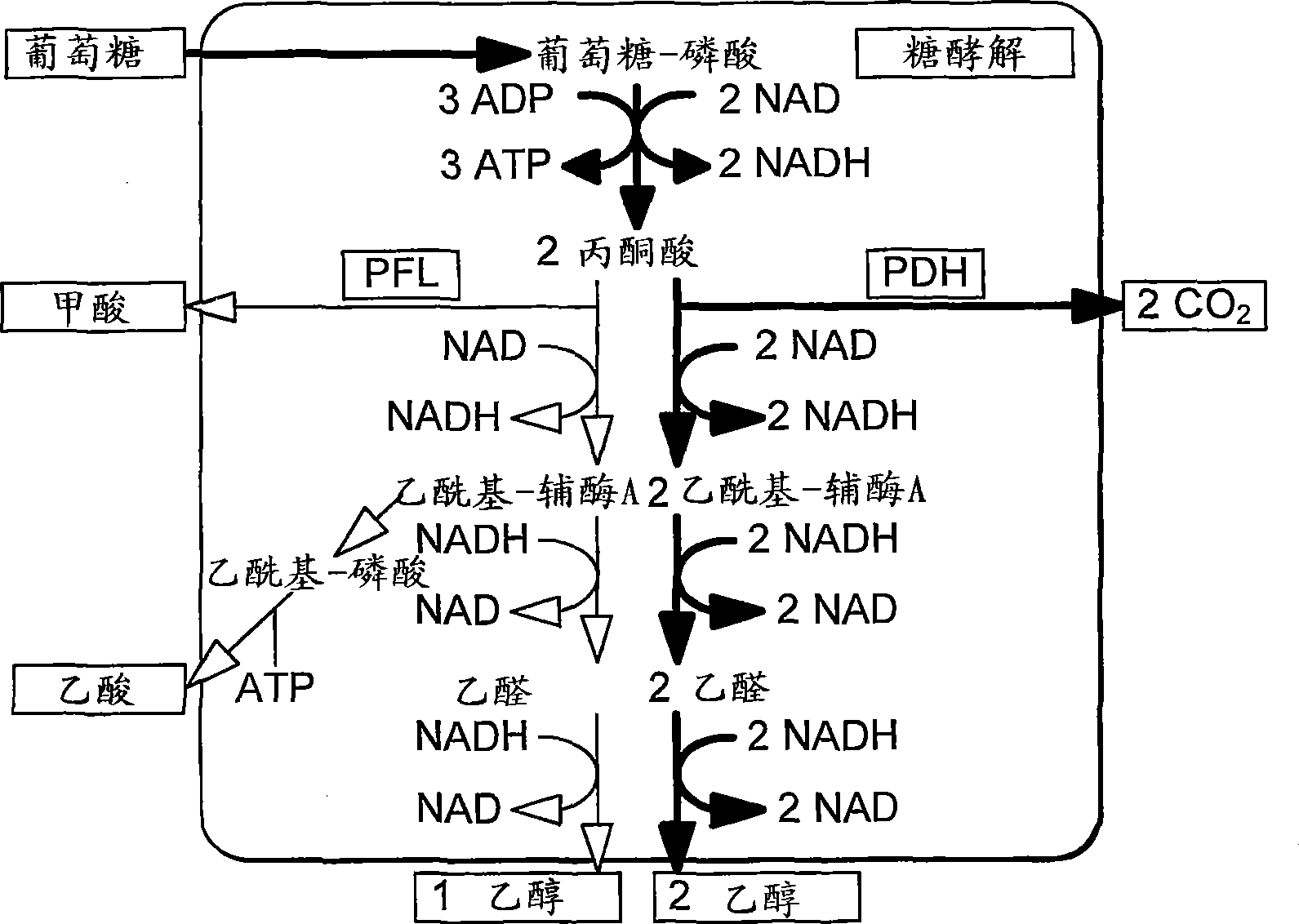
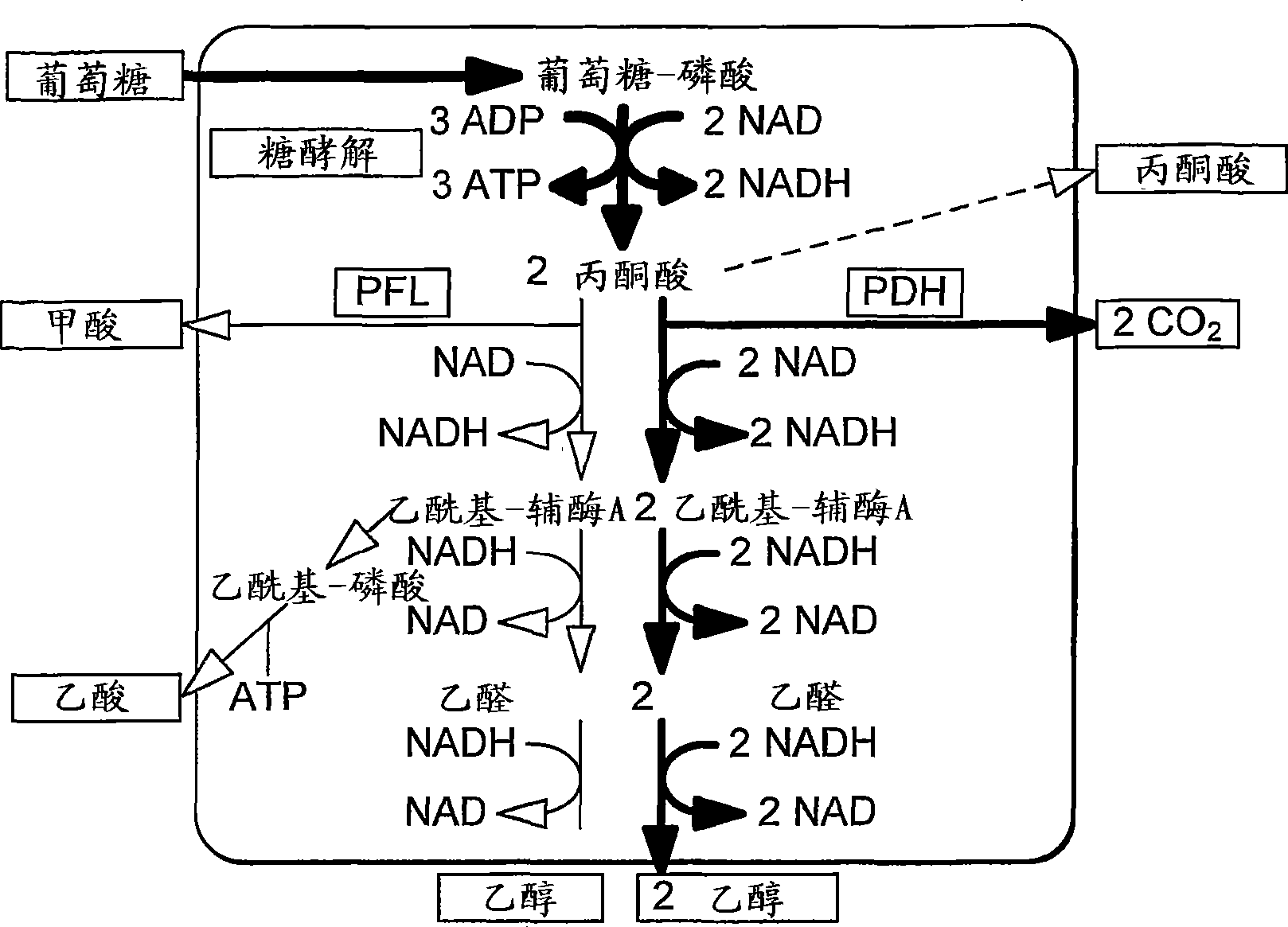
Enhancement of microbial ethanol production
Owner:BIOCONVERSION TECH INC
Fusion anticaries DNA vaccine and prepring method thereof
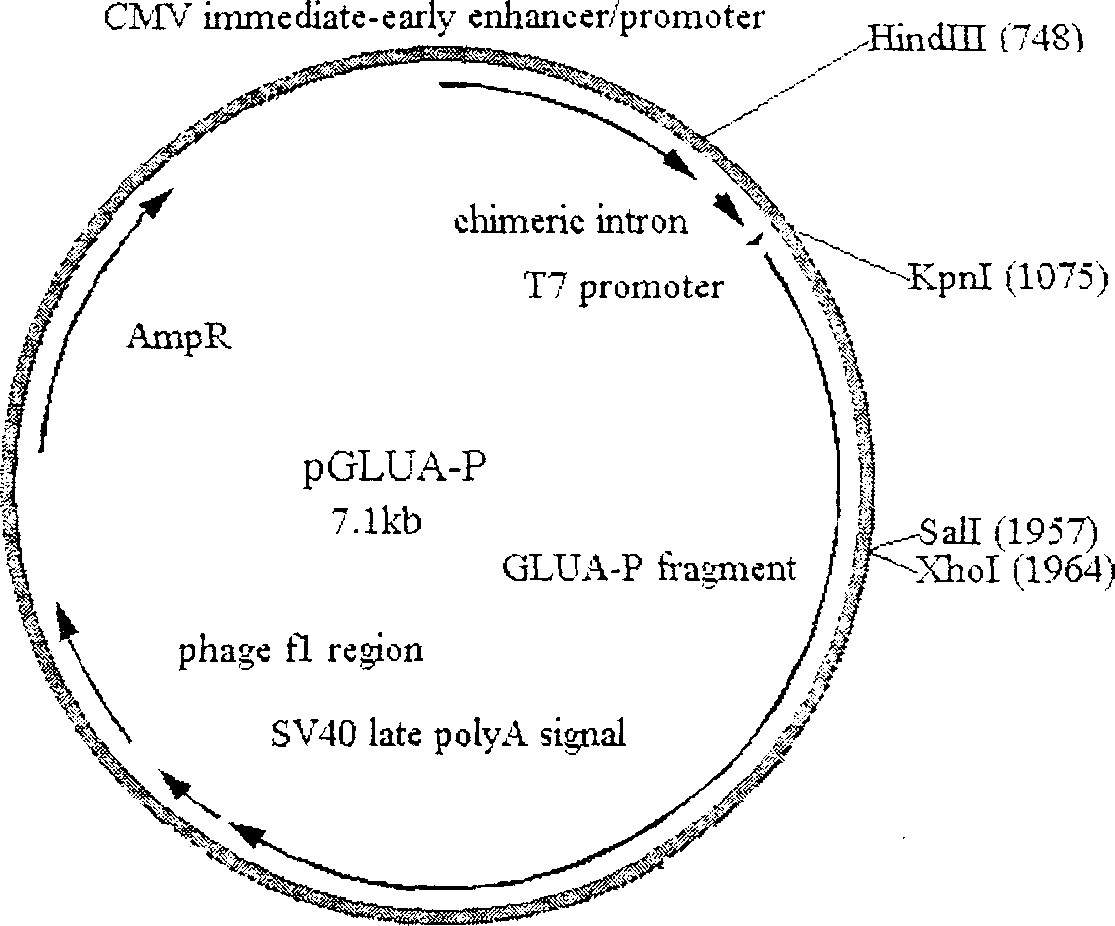
A DNA vaccine for fusional decayed tooth prevention is prepared from Esherichia coli JM109 / pGLUA-P CCTCC No.M201042 through PCR amplification of the plasmid pYNB13 carrying the gene gtfB of deformed streptococci GS-5 glucosyl transferase GTT-1 to obtain sequence GLU in glucosan binding region, cloning it to eukaryotic vector pCI to obtain eukaryotic expression plasmid pGLU, and linking it with the A-P fragment sequence in regions A and P of the surface protein PAc of deformed streptococci in pCIA-P plasmid. Its advantages are simple method, high safety, low cost, durable immune response and high effect.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
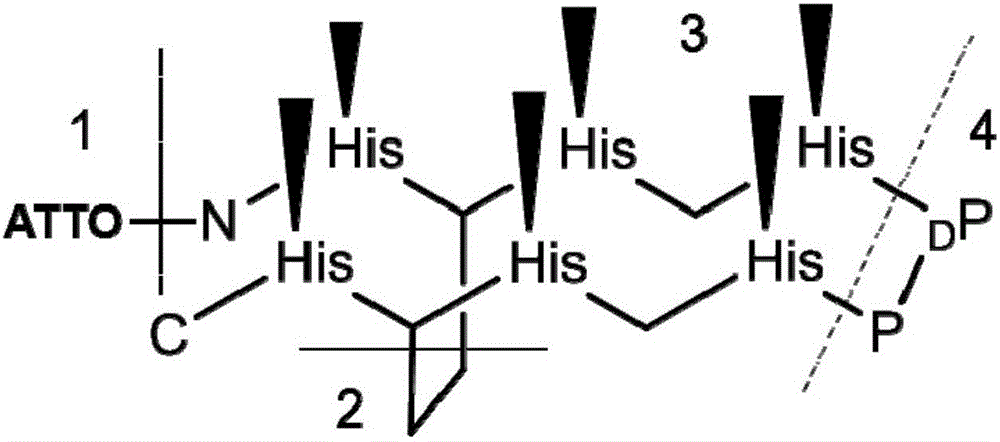
Novel annular polypeptide ligand used for modifying quantum dots
The invention discloses a novel annular polypeptide ligand (ATTO-H6) used for modifying quantum dots, and belongs to the technical field of nano-biology. The novel annular polypeptide ligand comprises a dye ATTO 590 (1) used for undergoing FRET together with quantum dots, a sequence (2) used for polypeptide cyclization, histidine intervening sequences (3) used for combining the quantum dots, and sequences (4) used for polypeptide folding, and all sequences are combined through peptide bonds. The ligand is simple to synthesize, and the combination of six histidine intervening sequences and the quantum dots greatly improves the combination rate and stability of the ligand and the quantum dots, so the ligand can be widely used in biological marking as a fluorescence nano-probe.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Uncoupling of DNA insert propagation and expression of protein for phage display
ActiveUS7112435B1High levelHigh expressionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousADAMTS Proteins
The present invention provides an advance in phage display technology by permitting the uncoupling of the propagation of phages containing inserted sequences encoding heterologous polypeptides from the expression of said polypeptides. The invention provides phage constructs and methods for their use to permit phage coat protein expression, and thus phage propagation, in the absence of display of heterologous polypeptides, which may be expressed as a fusion with said coat protein in a regulated manner.
Owner:DISCOVERYX CORP
Method for verifying feasibility of inserting CRISPR-Cas9 system mediated target gene into candida utilis
ActiveCN110305892AImprove gene editing efficiencyEnable overlapping PCR ligationVectorsStable introduction of DNAEnzyme digestionInsertion sequence
The invention discloses a method for verifying the feasibility of inserting a CRISPR-Cas9 system mediated target gene into candida utilis. The method includes the following steps that S1, an expression vector of the candida utilis containing Cas9 segments is constructed; S2, tRNAGlu genes and downstream expression units of sgRNA are amplified, PCR link is overlapped and a restriction enzyme cutting site is introduced, and after connection, the amplified tRNAGlu genes and downstream expression units of the sgRNA are combined with the vector of the candida utilis to obtain sgRNA initial recombinant plasmid; S3, pre-insertion and target sequences are selected, a sticky tail end is added to the 5' end of a target and complementary sequence, and double chain segments are formed by annealing andthen connected with the initial recombinant plasmid after enzyme digestion to obtain sgRNA mature recombinant plasmid; S4, a recombinant donor segment containing a left homologous arm and a right homologous arm of a pre-insertion sequence is constructed; and S5, the sgRNA recombinant plasmid and the recombinant donor segment are used for transforming the candida utilis carrying Cas9. The feasibility of inserting the CRISPR-Cas9 system mediated target gene into the candida utilis is verified by identifying the expression of the donor segment.
Owner:GUANGDONG QIZHI BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +2
Method for improving insect resistance of plants by using RNA interference technique and special DNA fragment of method
ActiveCN109837291AReduce harmStrong food refusalFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionNicotiana tabacumWild type
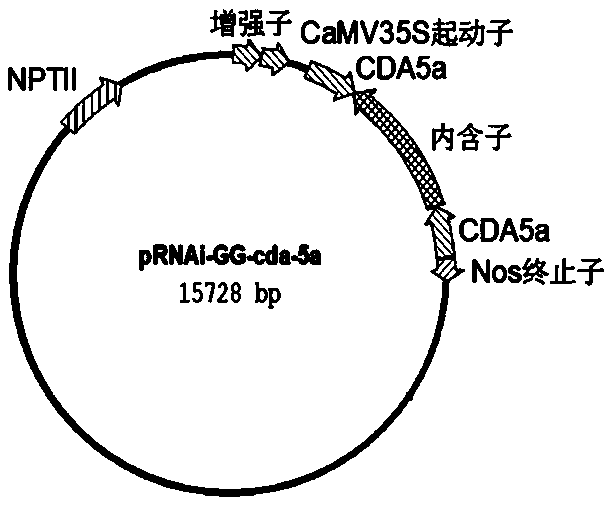
The invention provides a method for improving insect resistance of plants by using an RNA interference technique and a special DNA fragment of the method. The DNA fragment is shown as formula (I), andSEQ forward -X-SEQ backward (I), wherein the SEQ forward is any one fragment at least comprising 21bp in the overall length cDNA fragment of bollworm chitin deacetylase 5a genes; SEQ backward is in backward complementary with the SEQ forward; the X is an intervening sequence between the SEQ forward and SEQ backward, and is not complementary with the SEQ forward and SEQ backward, and the overall length cDNA of the bollworm chitin deacetylase 5a gene is shown as the sequence 1 in a sequence table. For the first time, the bollworm chitin deacetylase 5a gene is used as the RNA interference targetgene, and is applied to breeding of genetically-modified plants. Insect test results prove that after switching for 2-5 days, the body weight of young bollworms is 1 / 10 smaller than that of the control group, and the mortality rate of the young insects of 5 days on genetically modified tobacco leaves achieves 68%, and the mortality rate of wild type tobacco is only 21%.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
Uncoupling of DNA insert propagation and expression of protein for phage display
ActiveUS20080318298A1High levelHigh expressionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousInsertion sequence
The present invention provides an advance in phage display technology by permitting the uncoupling of the propagation of phages containing inserted sequences encoding heterologous polypeptides from the expression of said polypeptides. The invention provides phage constructs and methods for their use to permit phage coat protein expression, and thus phage propagation, in the absence of display of heterologous polypeptides, which may be expressed as a fusion with said coat protein in a regulated manner.
Owner:DISCOVERYX CORP
Escherichia coli pressure response type promoter and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108866057AEfficient startBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliConserved sequence
The invention discloses an escherichia coli pressure response type promoter and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the field of promoter engineering. According to the escherichia coli pressure response type promoter, a pColaDuet-GFP plasmid is used as a template, and a degenerate primer is designed to connect conserved sequences of promoters identified by different sigma factors in series; intervening sequences are randomly mutated; green fluorescent protein GFP is used as a reporter gene to screen a plurality of promoters which have relatively high expression strength under low temperature, high osmotic pressure and low PH (Potential of Hydrogen) conditions.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Flanking sequence of genetically modified insecticidal maize HKG60 exogenous insert fragment and detecting method of flanking sequence
ActiveCN105779610AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetically modified maizeGenome
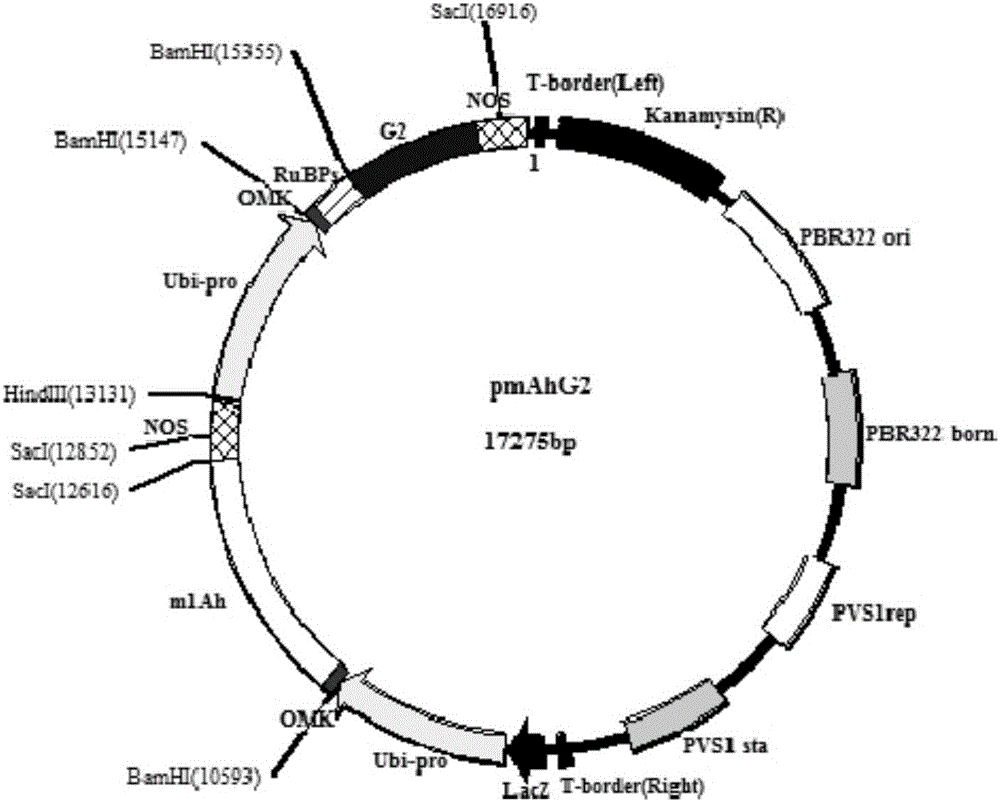
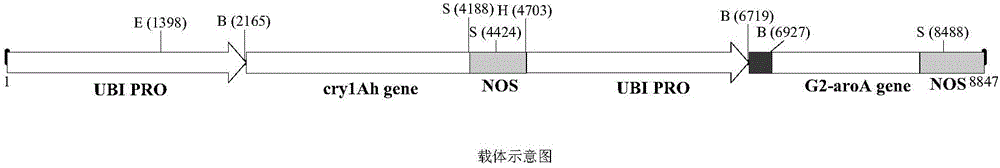
The invention relates to a flanking sequence of a genetically modified insecticidal maize HKG60 exogenous insert fragment and a detecting method of the flanking sequence, and belongs to the technical field of biology.A plant expression carrier pmAhG2 containing a Bt cry1Ah gene is established, a genetically modified maize plant genetically modified by the Bt cry1Ah gene is obtained, and a genetic modification event HGK60 with a remarkable ostrinia nubilalis resistant effect is screened out; the maize event HGK60 contains an insert gene sequence on a first chromosome of a maize genome, and the 5' flanking sequence and the 3' flanking sequence of the maize genome are as shown in SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2 respectively.A primer can be designed according to the DNA of a combination area where the insert sequence and the flanking sequences of maize are introduced, and the event HGK60 is specifically, qualitatively and quantitatively detected.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
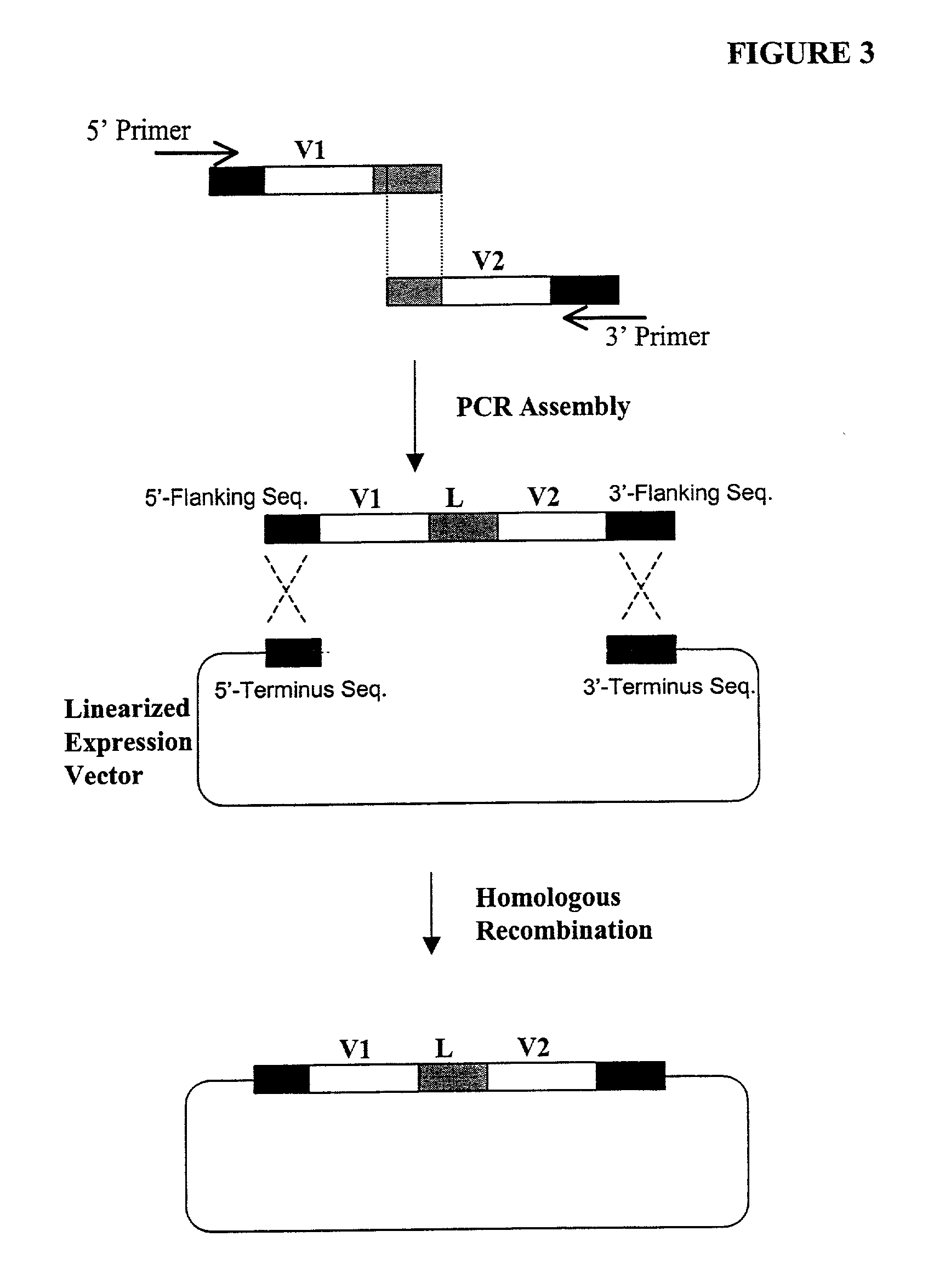
Generation of highly diverse library of expression vectors via homologous recombination in yeast
InactiveUS20030165990A1High affinityEasy to assembleFungiFusion with DNA-binding domainSingle-Chain AntibodiesNucleotide
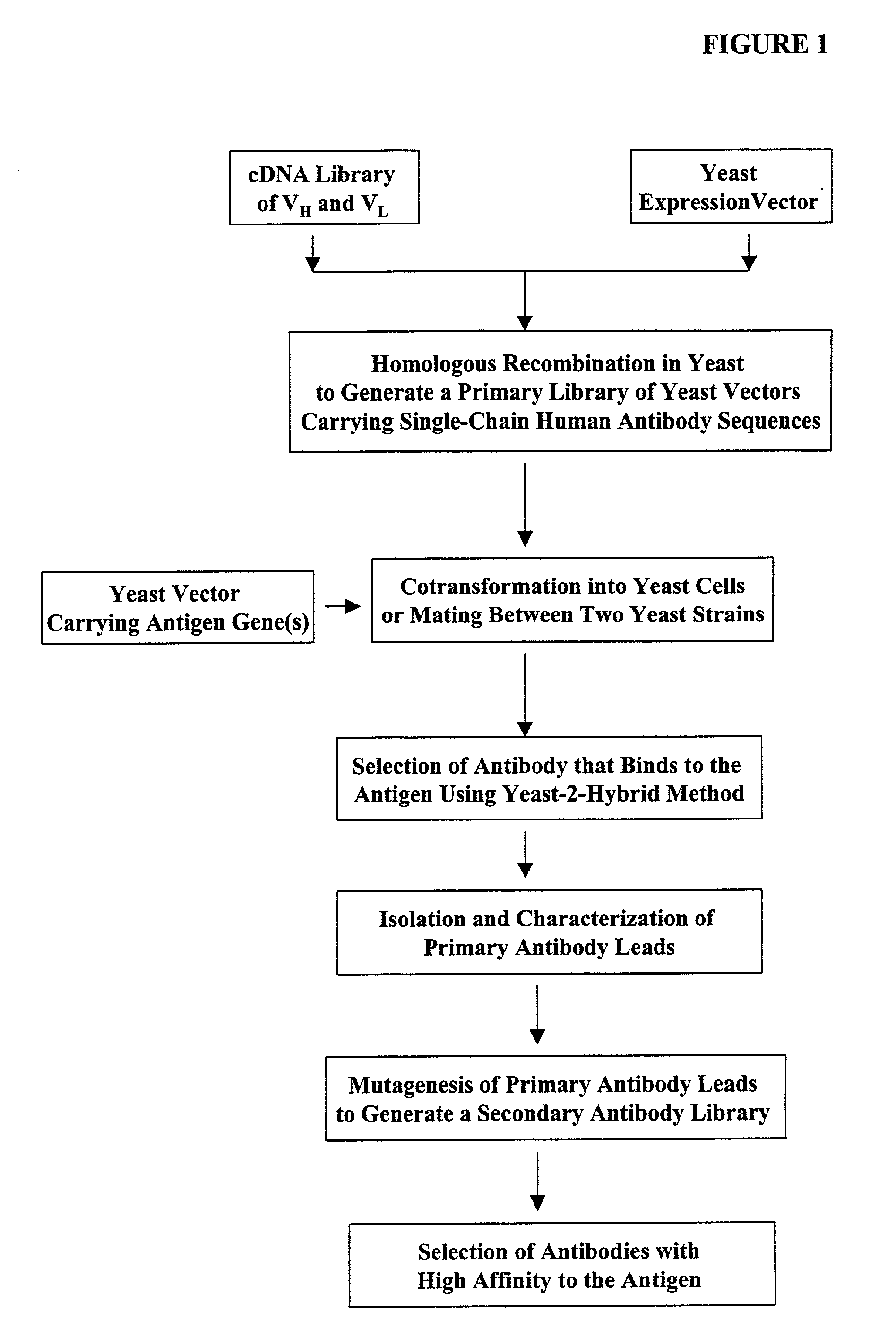
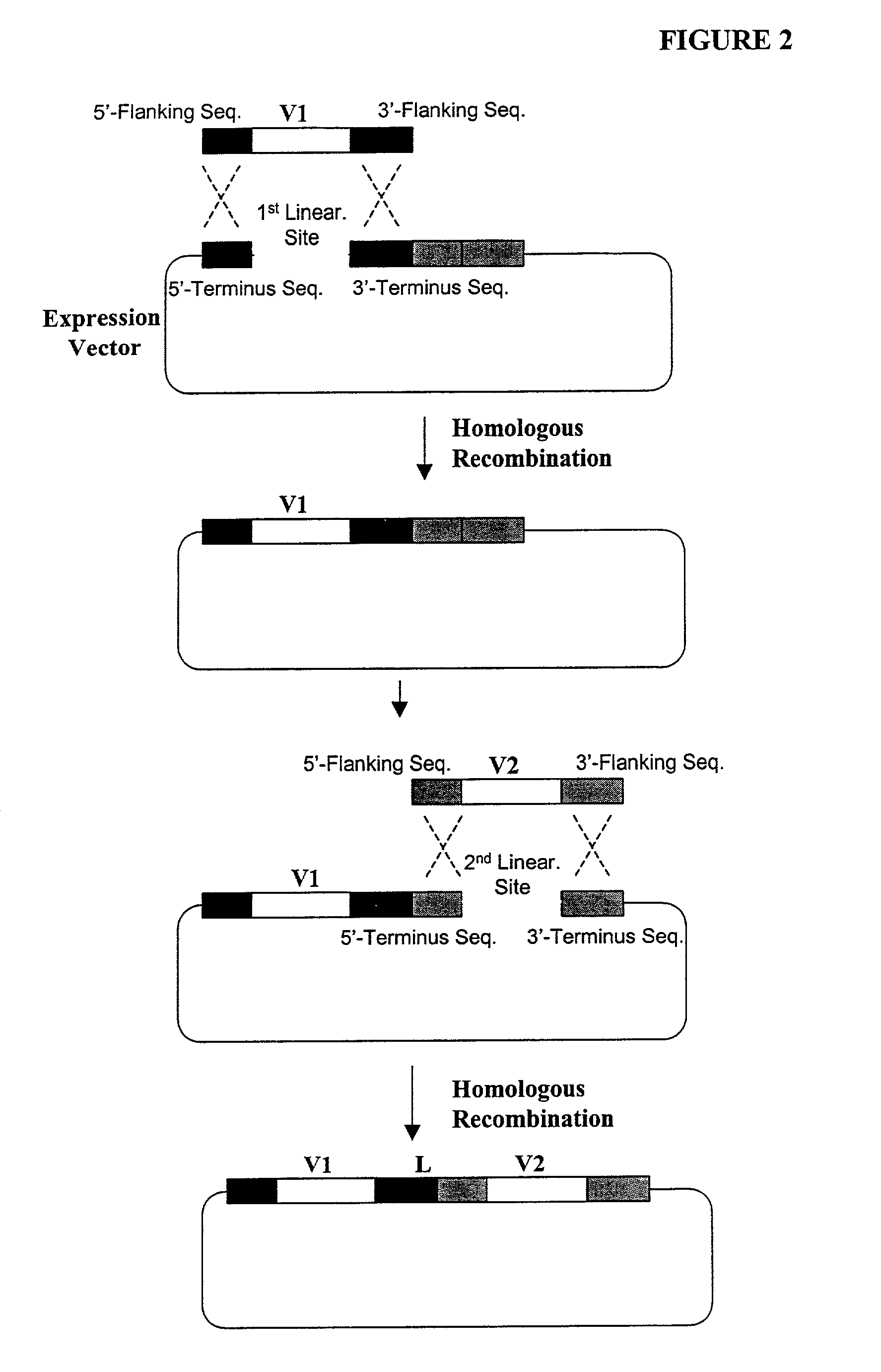
Methods are provided for generating highly diverse libraries of expression vectors encoding fusion proteins such as single-chain antibodies via homologous recombination in yeast. The method comprises: transforming into yeast cells a linearized yeast expression vector having a 5'- and 3'-terminus sequence at the site of linearization and a library of insert nucleotide sequences that are linear and double-stranded; and having homologous recombination occur between the vector and the insert sequence such that the insert sequence is included in the vector in the transformed yeast cells. The insert sequence comprises a first nucleotide sequence encoding a first polypeptide subunit, a second nucleotide sequence encoding a second polypeptide subunit, a linker sequence encoding a linker peptide that links the first and second polypeptide subunits, and a 5'- and 3'-flanking sequence at the ends of the insert sequence which are sufficiently homologous to the 5'- and 3'-terminus sequences of the linearized yeast expression vector, respectively, to enable homologous recombination to occur. The first polypeptide subunit, the second polypeptide subunit, and the linker polypeptide are expressed as a single fusion protein; and the first and second nucleotide sequences each independently varies within the library of expression vectors.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
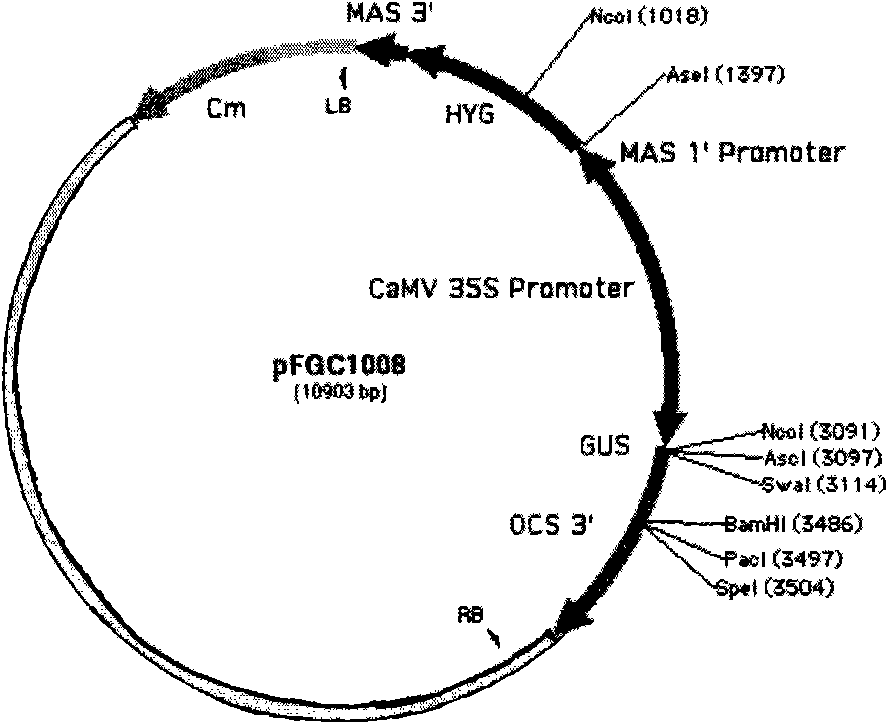
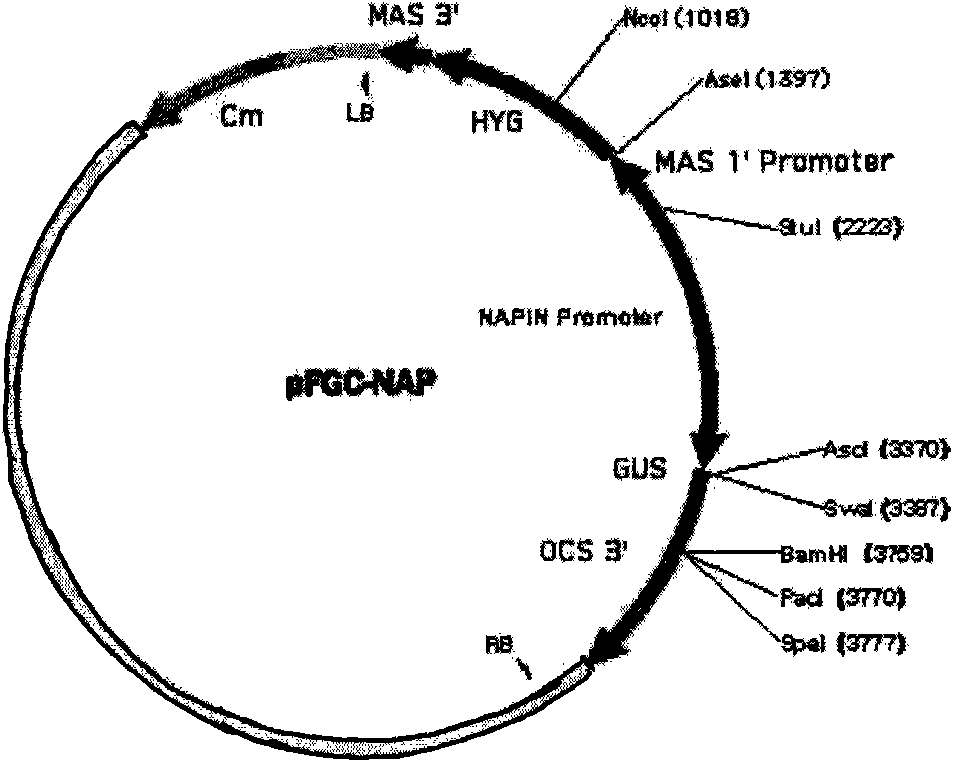
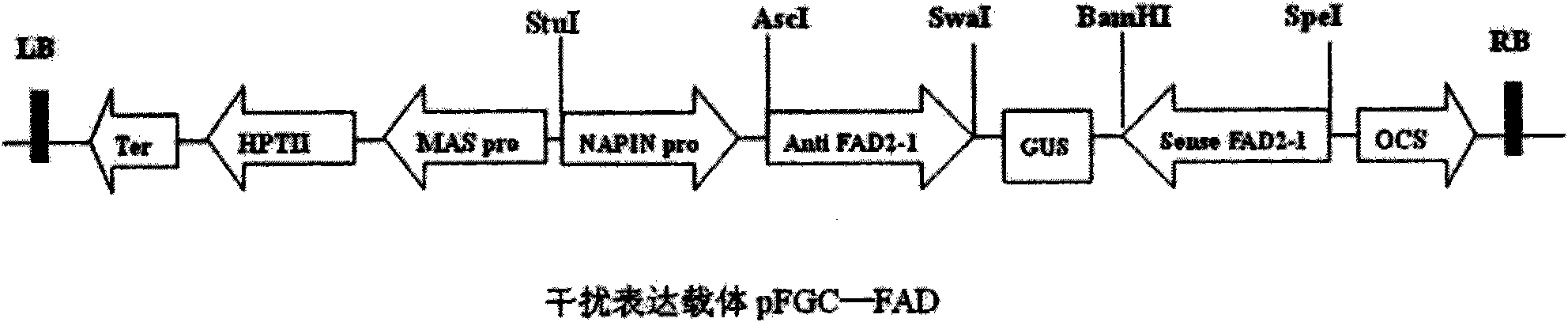
Plasmid for constructing interference vector and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN101880683AImprove qualityHigh interference efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsInverted Repeat SequencesA-DNA
The invention discloses a plasmid for constructing an interference vector, a construction method thereof and application thereof. The invention provides a plasmid pFGC-NAP obtained by inserting a DNA presented by sequence 1 in a sequence list between an Stu I enzyme cutting site and an Asc I enzyme cutting site of a plasmid pFGC1008. The interference vector can be obtained by respectively inserting a plus-sense DNA fragment and an anti-sense DNA fragment into a multiple cloning site of the plasmid pFGC-NAP, wherein the plus-sense DNA fragment and the anti-sense DNA fragment are inverted repeat sequences designed for a target gene to be interfered and expressed. The plasmid constructs the interference vector capable of specially expressing a promoter during a seed development period, has high interference efficiency, can control a spatial temporal specificity expression, can be used for a specific gene expressed in silent plant seeds, and improves quality of oil crop seeds or other plant seeds.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Uncoupling of DNA insert propagation and expression of protein for phage display
InactiveUS7833741B2High levelHigh expressionBacteriaMicroorganism separationHeterologousADAMTS Proteins
The present invention provides an advance in phage display technology by permitting the uncoupling of the propagation of phages containing inserted sequences encoding heterologous polypeptides from the expression of said polypeptides. The invention provides phage constructs and methods for their use to permit phage coat protein expression, and thus phage propagation, in the absence of display of heterologous polypeptides, which may be expressed as a fusion with said coat protein in a regulated manner.
Owner:DISCOVERYX CORP
Method for transferring exogenous genes into spiral seaweeds with transposons as medium
InactiveCN104480133AChange qualityMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionBlue green algaeGenetic engineering
The invention relates to genetic engineering, in particular to a method for transferring exogenous genes into spiral seaweeds with transposons as a medium. Multiple sets of primers IS1-IS4 are designed according to sequences of known blue-green algae of the NCBI, and transposons elements are cloned from the blue-green algae and implanted into the sequences; ultrasonic transformation and screening of donor plasmids pEGFP-IS-IS-Km are conducted; EcoR I is utilized for digesting pEGFP-IS-IS-Km to obtain linear plasmids, the two ends each have an IS sequence, spiral seaweeds 869s are transformed, and GFP and G418 (npt II) are utilized for screening out mutation-inserted spiral seaweed plants. An integrated spiral seaweed screening system including gfp genes, npt II mark genes and transposons sequences is built, and the gene structure of spiral seaweeds is influenced by random insertion mutation of transposons, so that the quality of spiral seaweeds is changed. The method can be applied to building of a spiral seaweed mutation library, and can also realize introduction and expression of exogenous genes and antisense inhibition regulation of endogenous genes of spiral seaweeds.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Oligonucleotide modulation of cell adhesion
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com