Patents
Literature
34 results about "Resource poor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
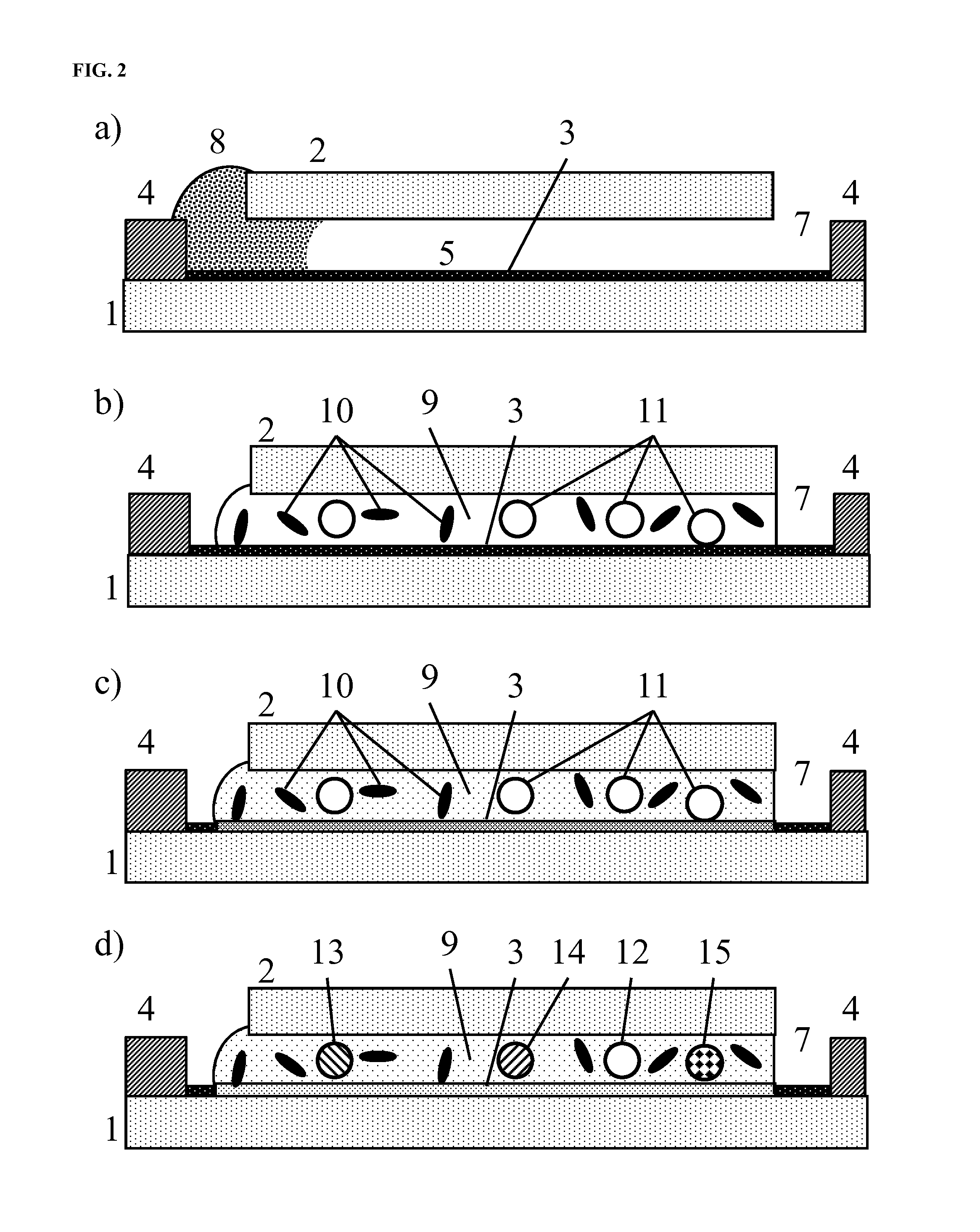
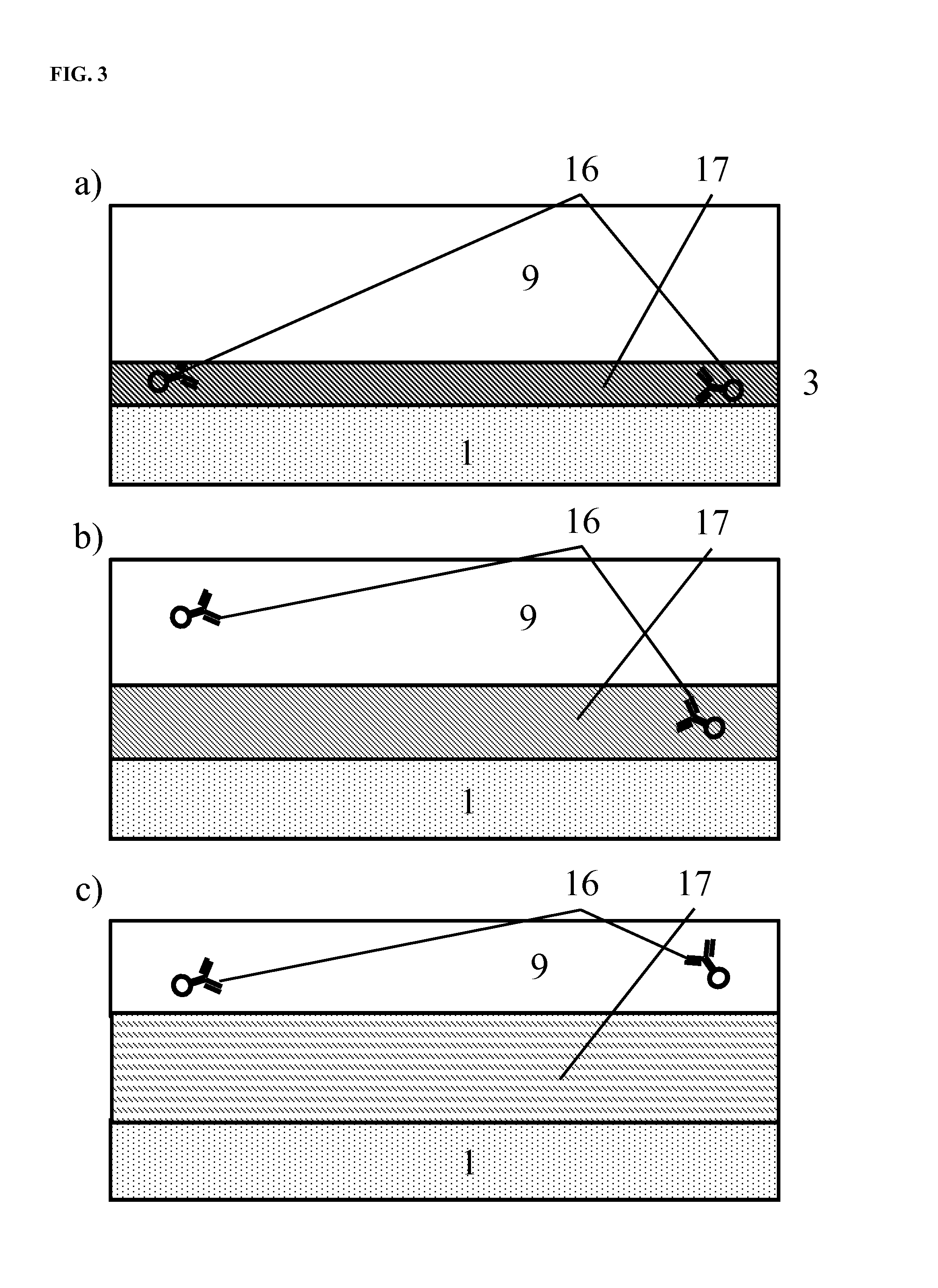
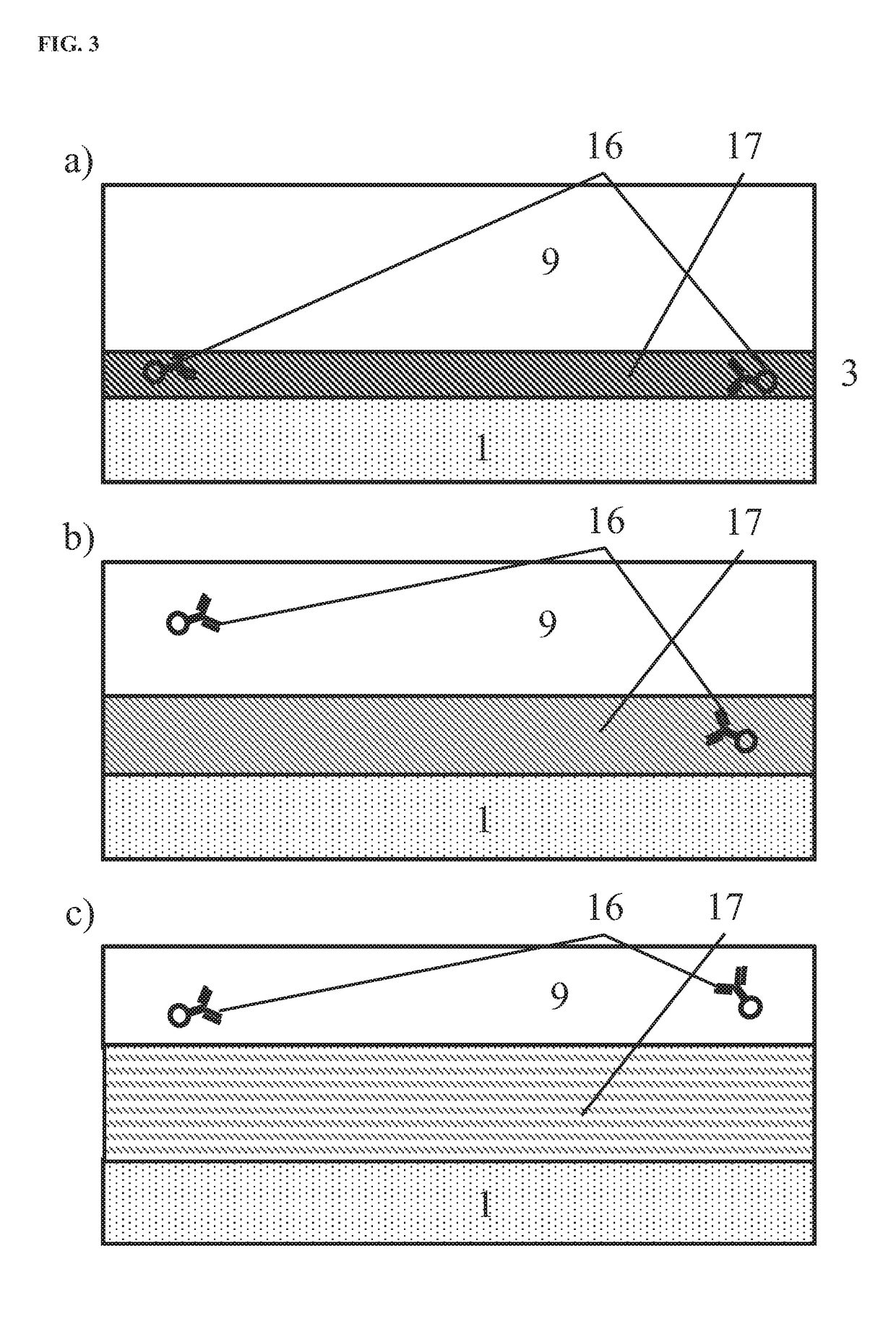
Methods and algorithms for cell enumeration in low-cost cytometer
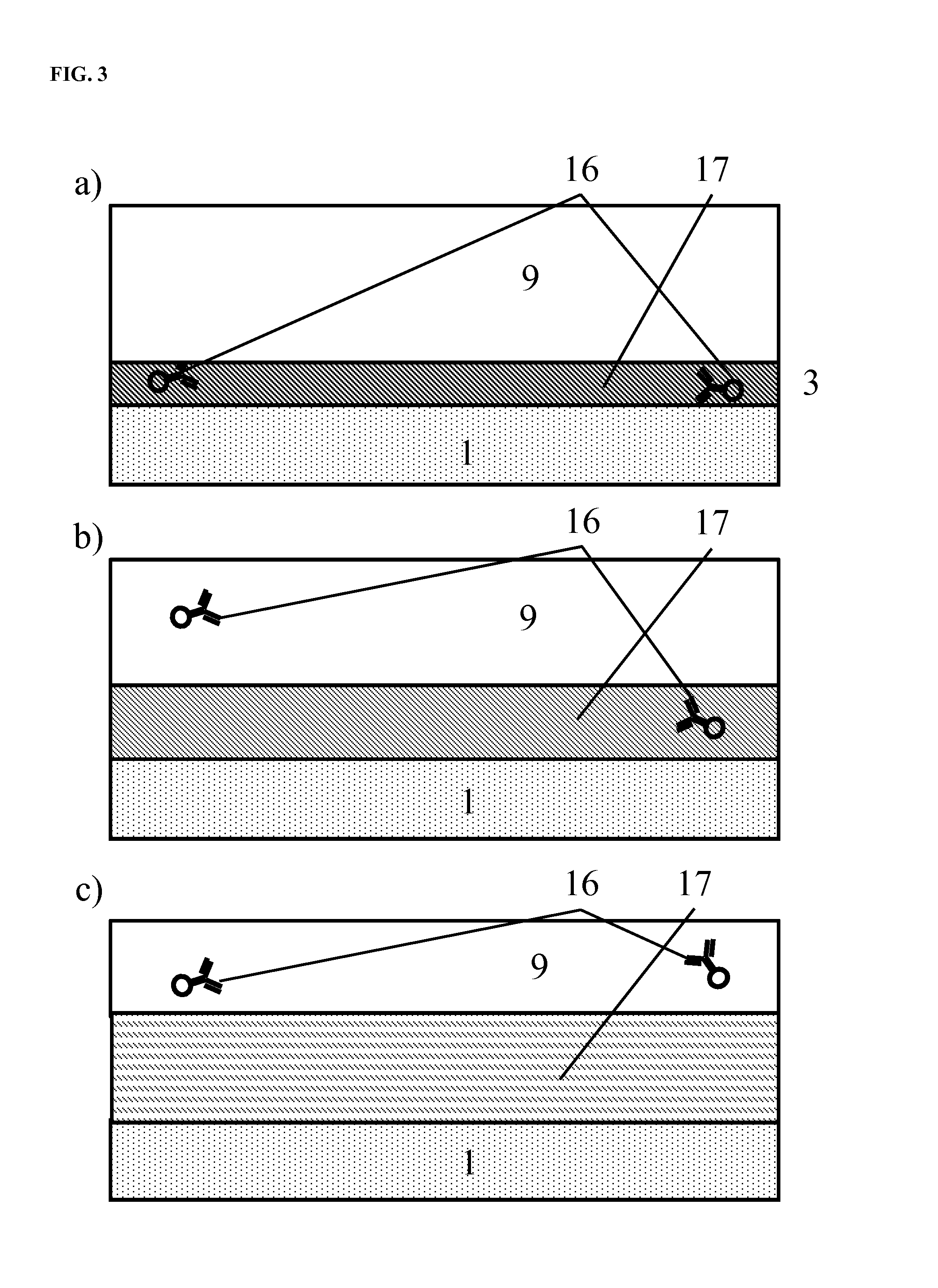
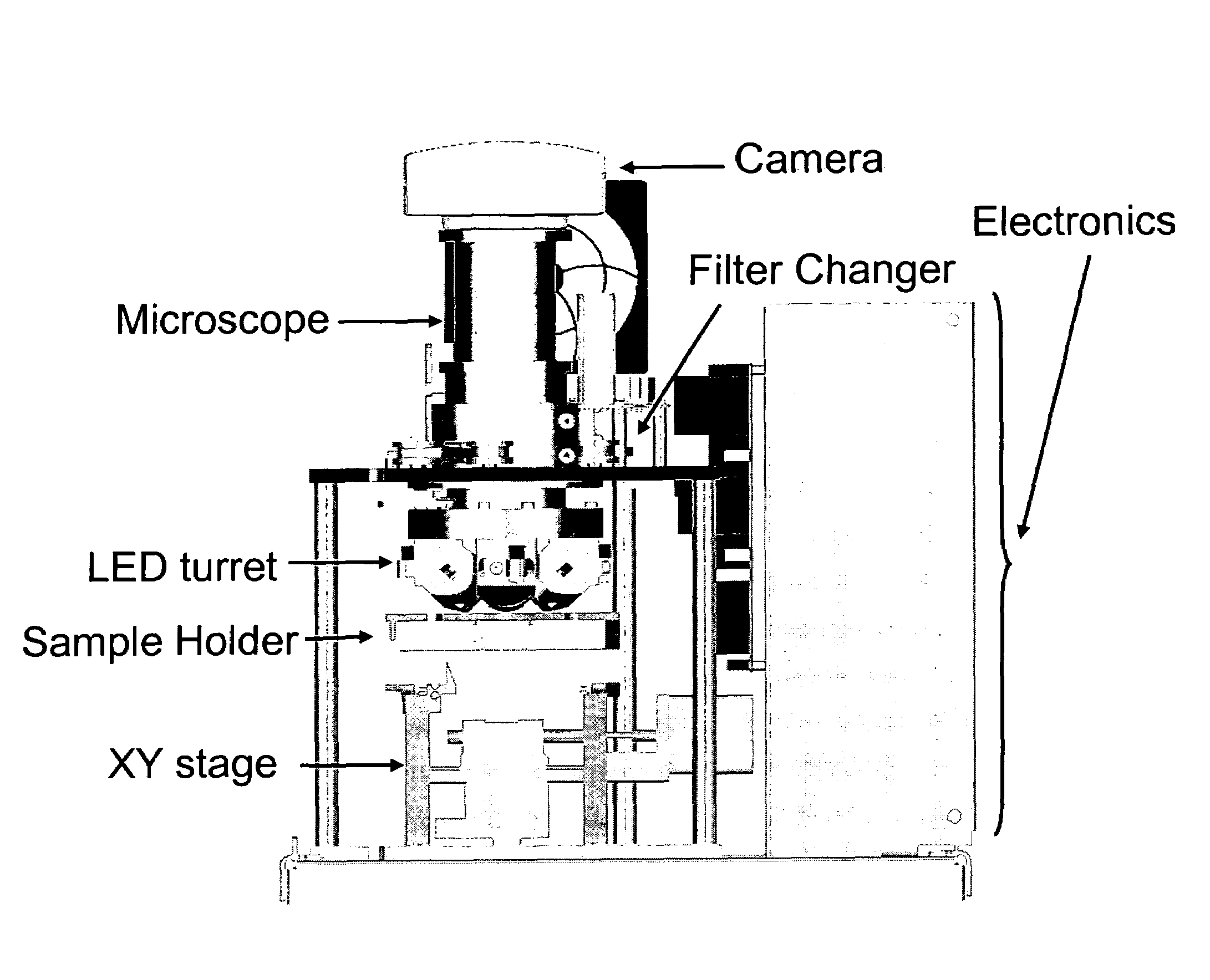
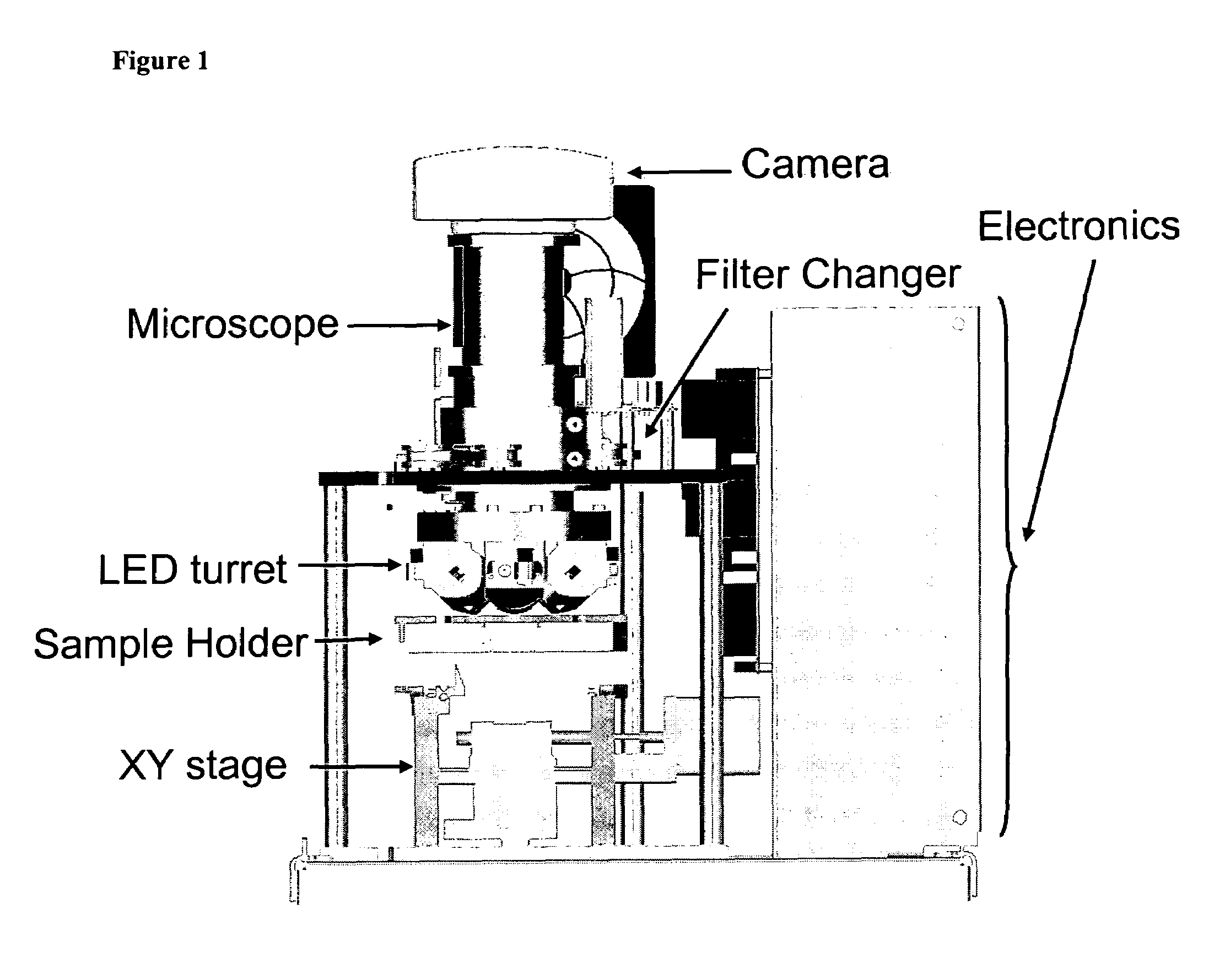
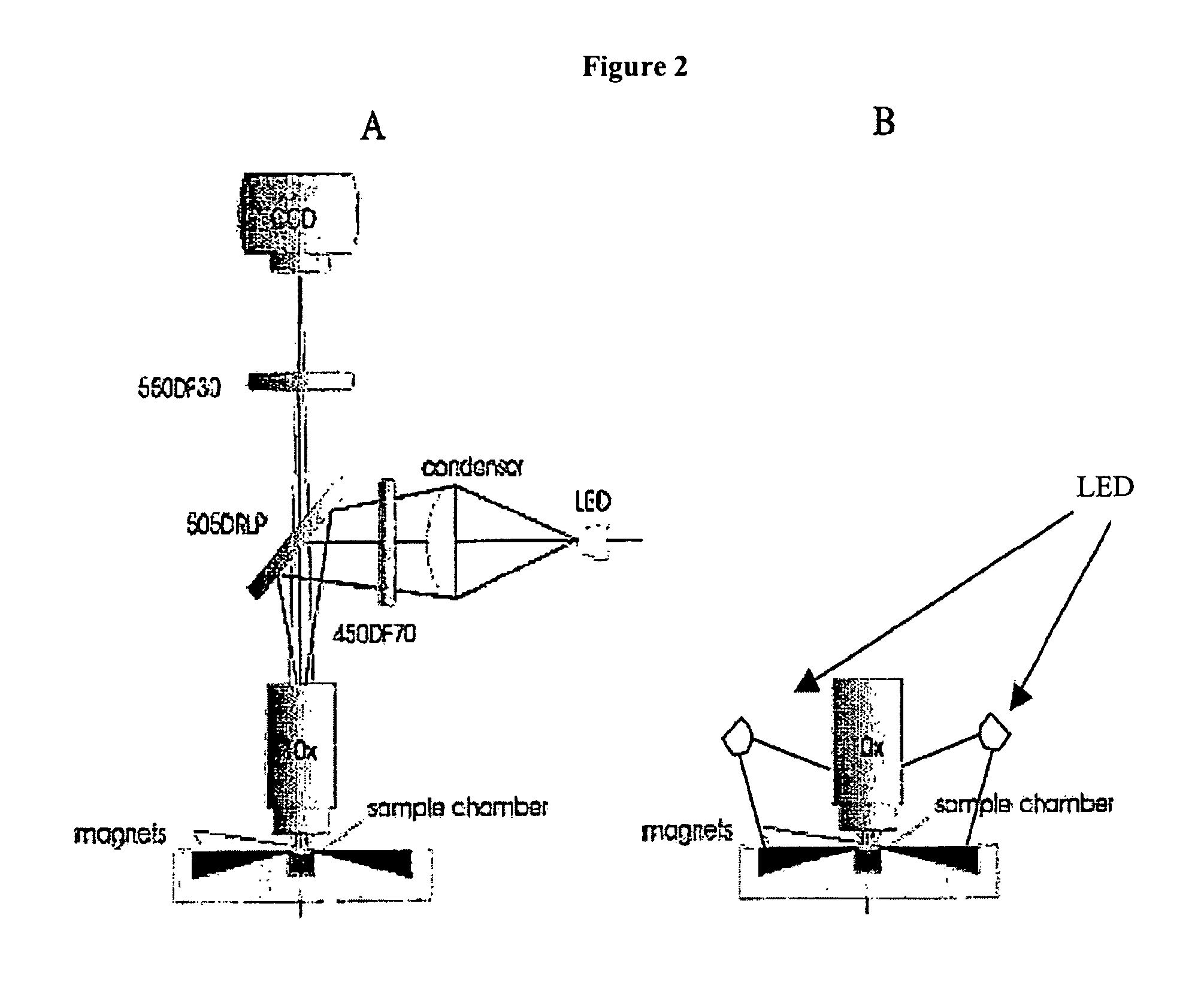
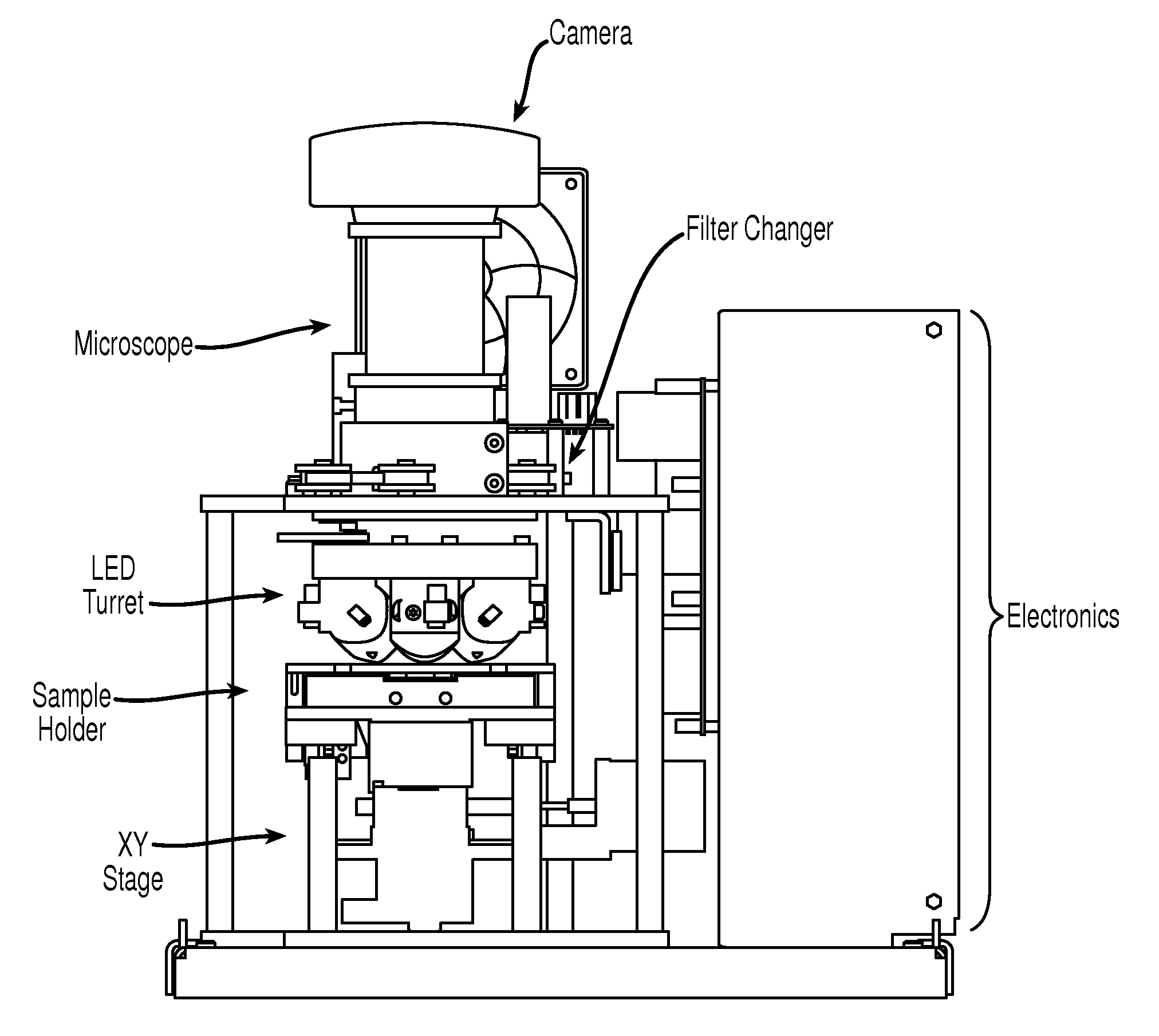
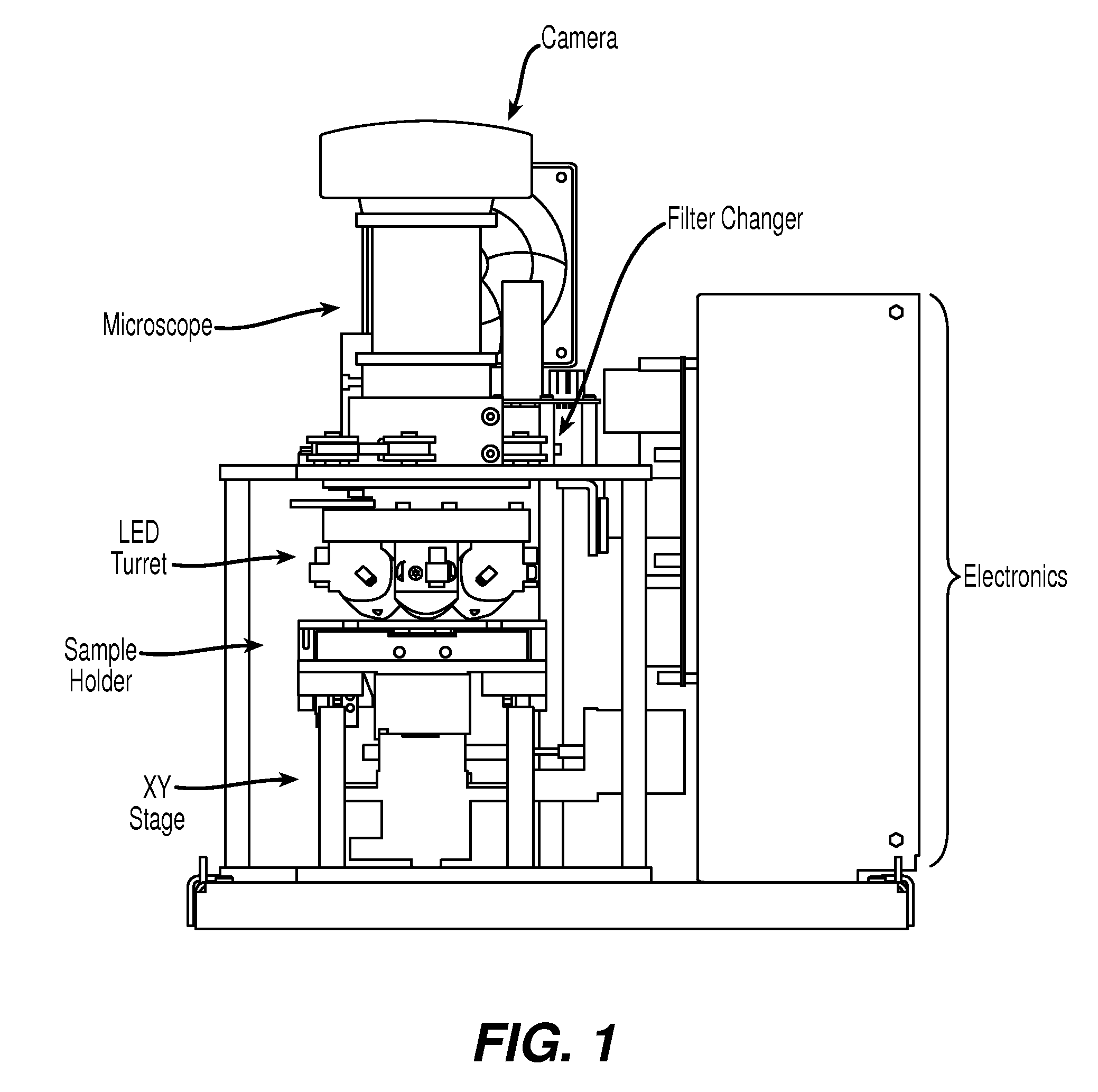
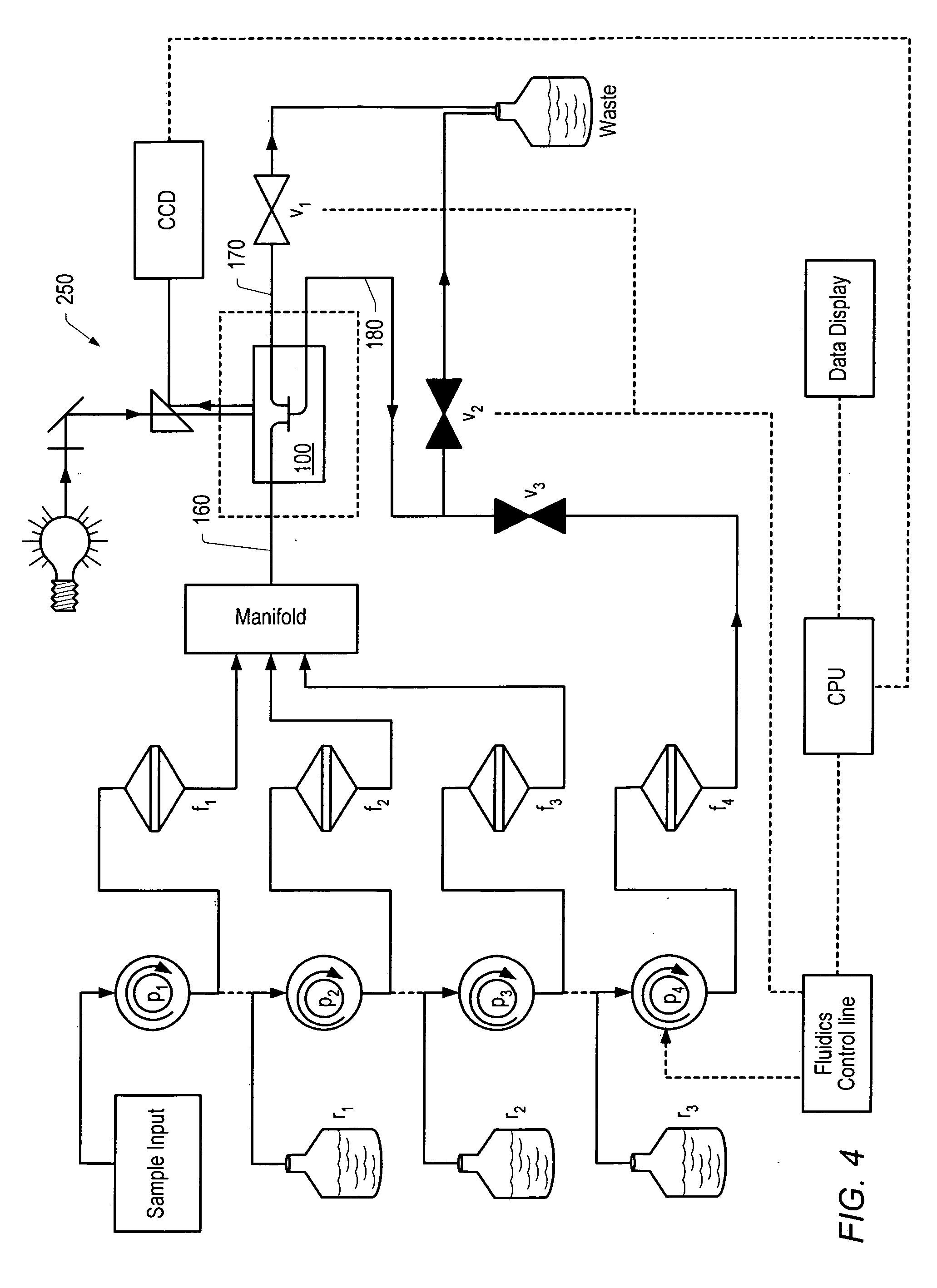
InactiveUS20060024756A1Simple designReduce operating costsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWhite blood cellCcd camera
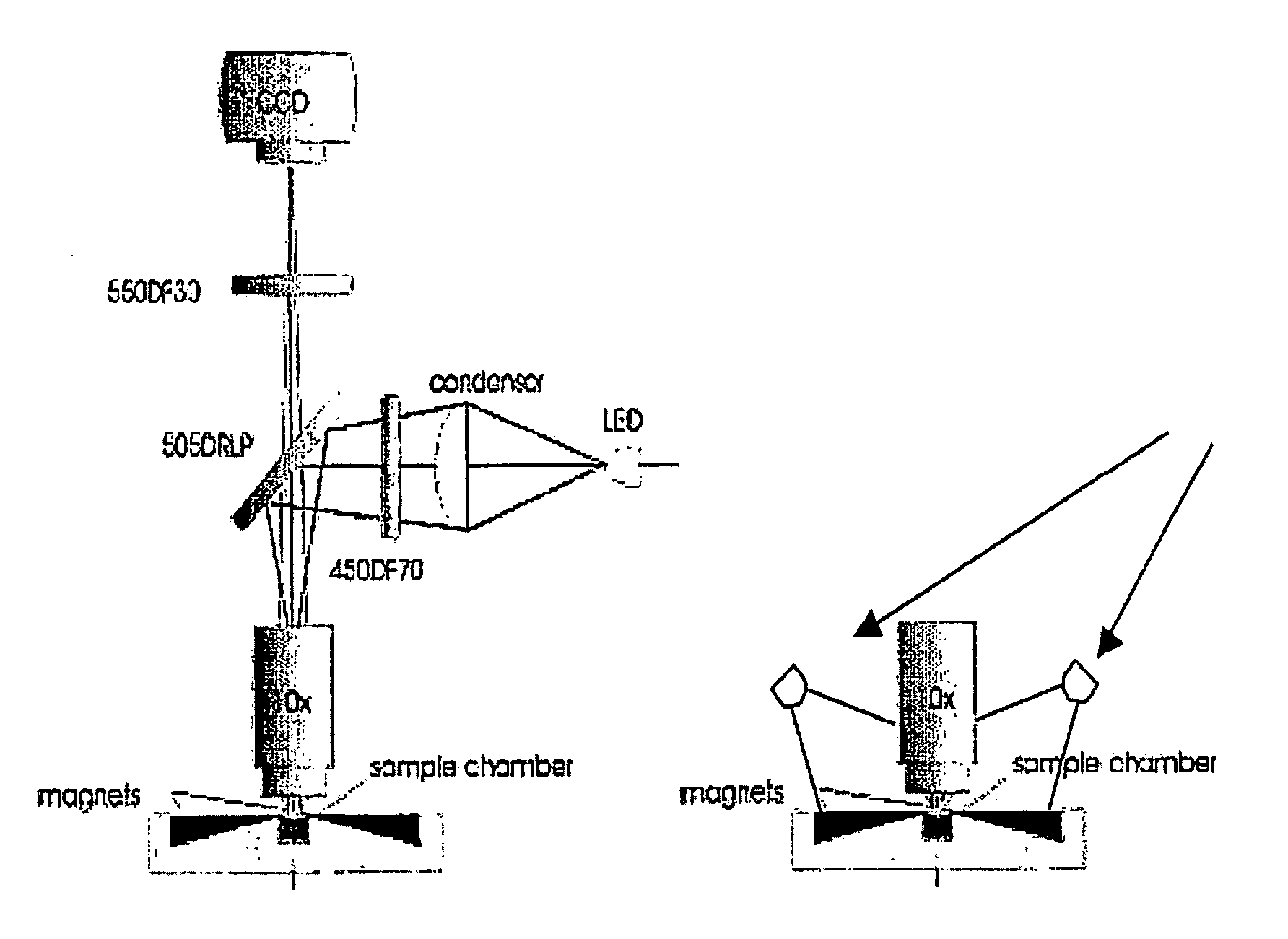
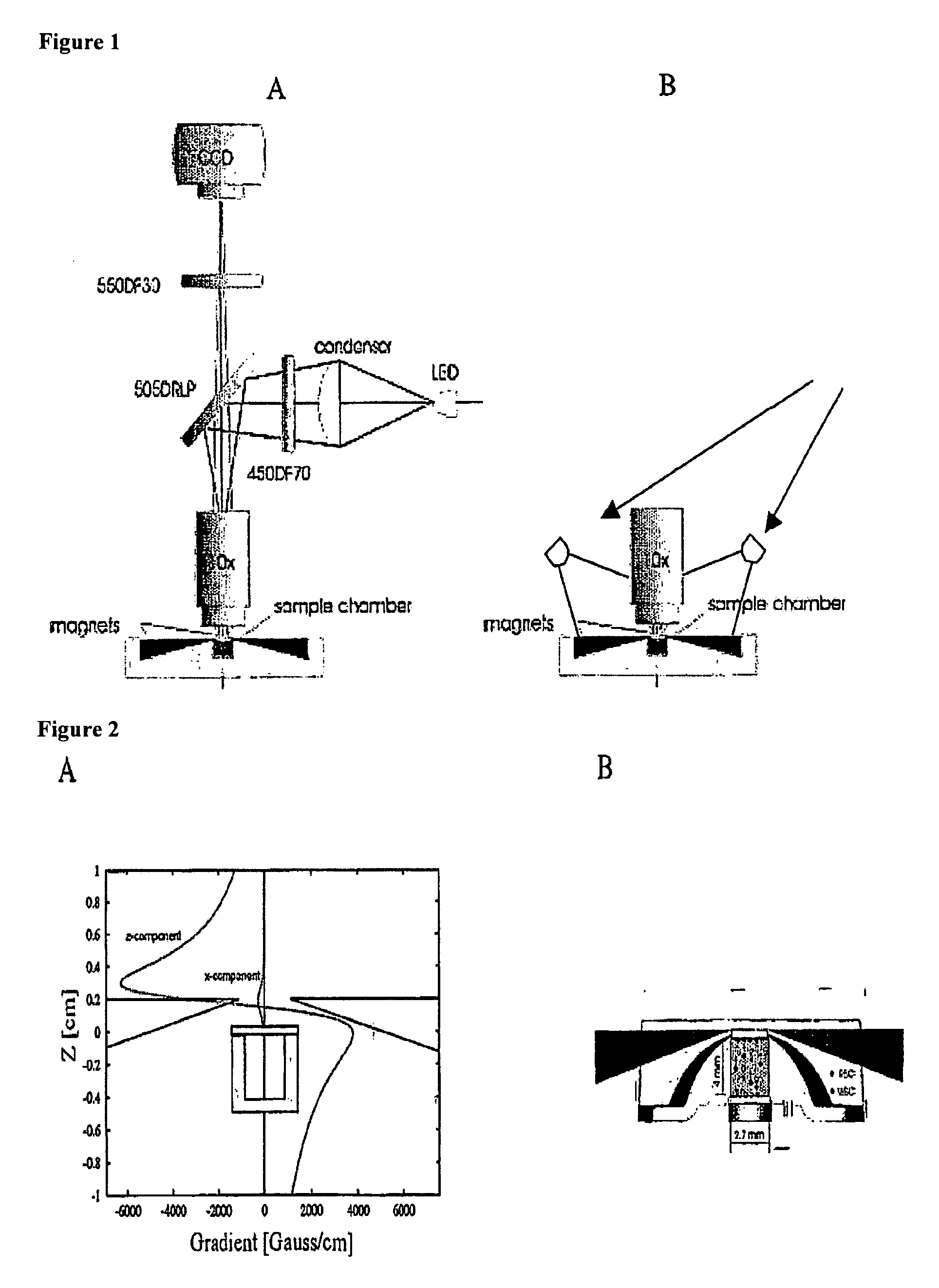
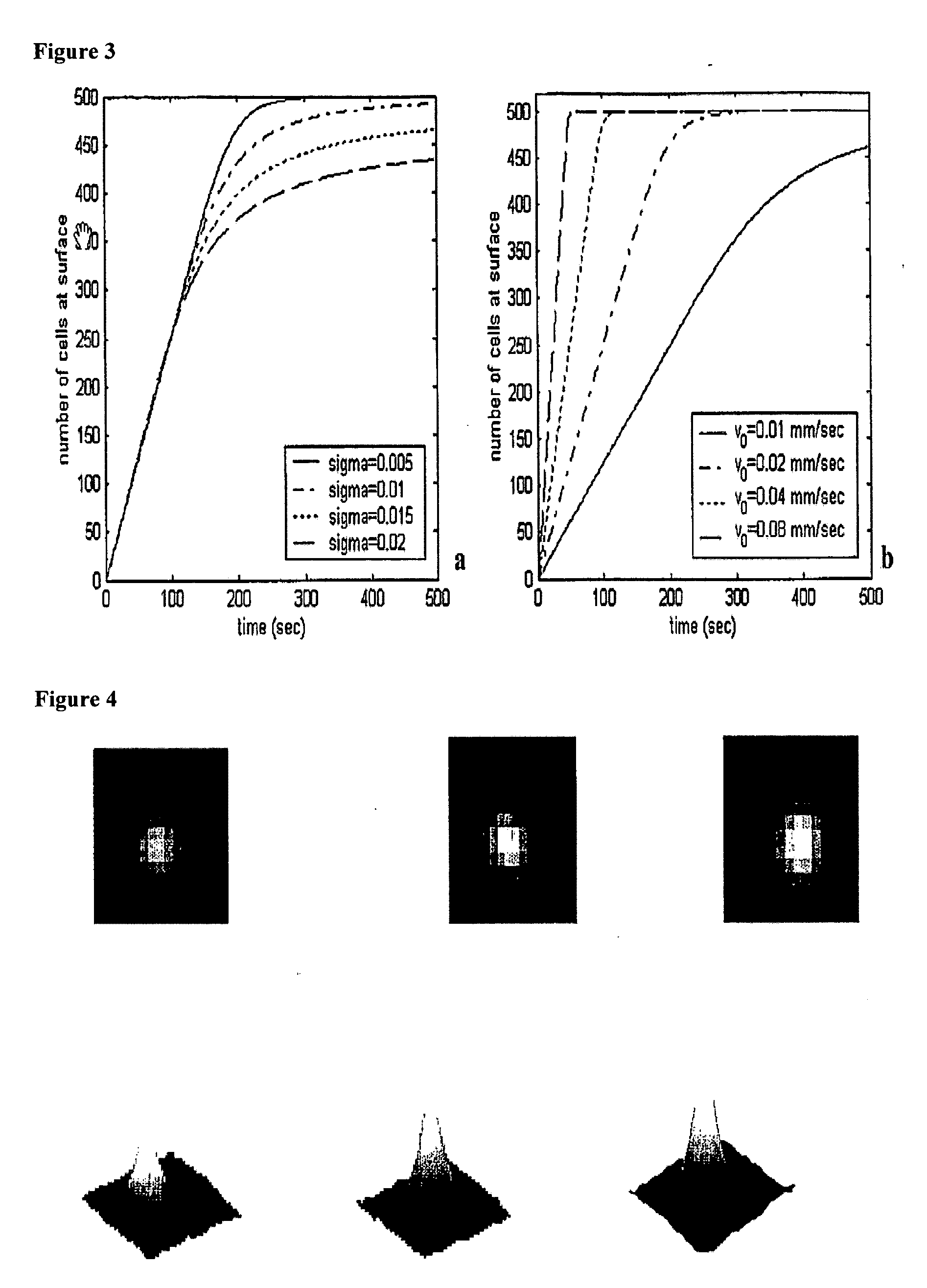
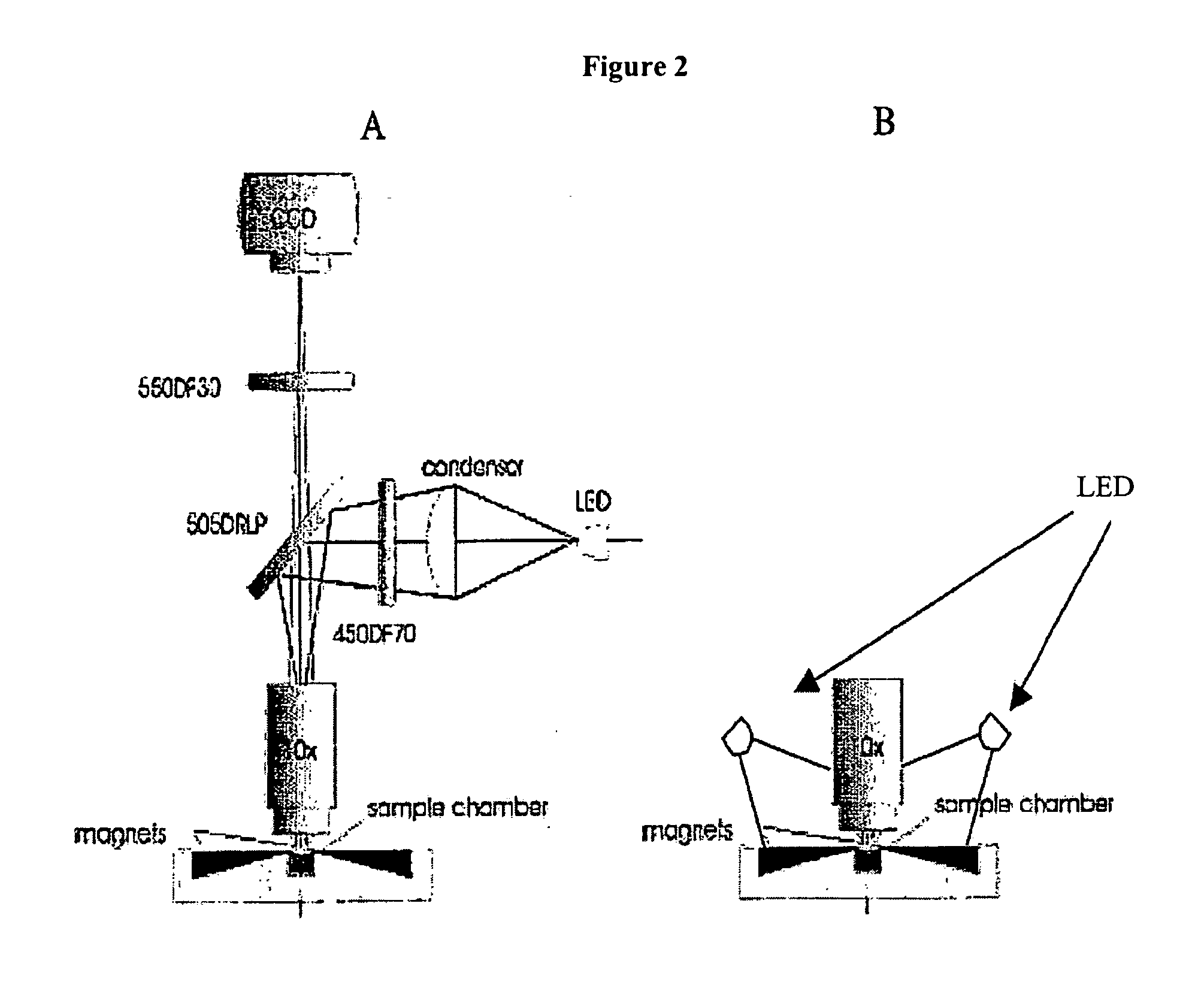
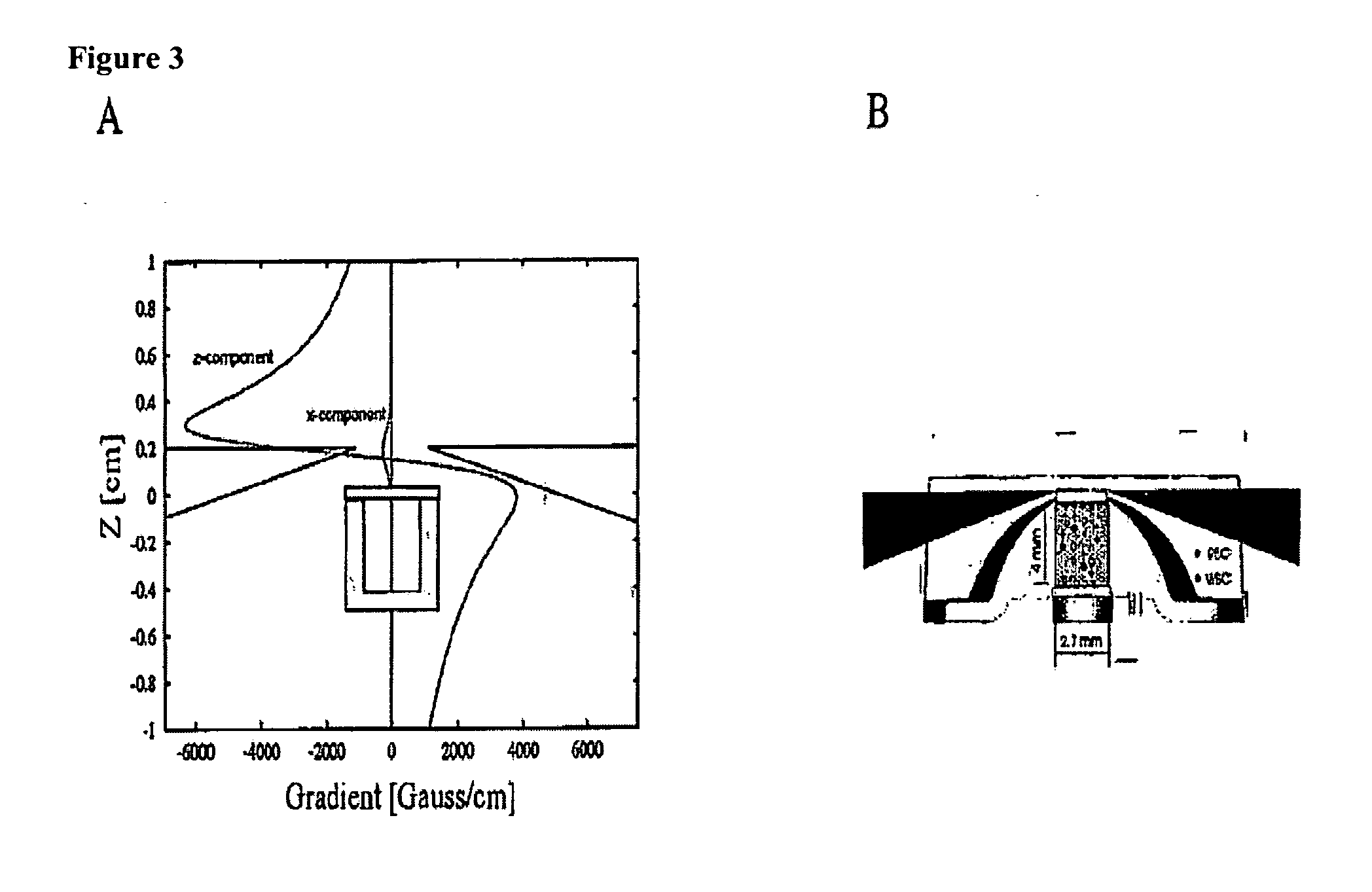
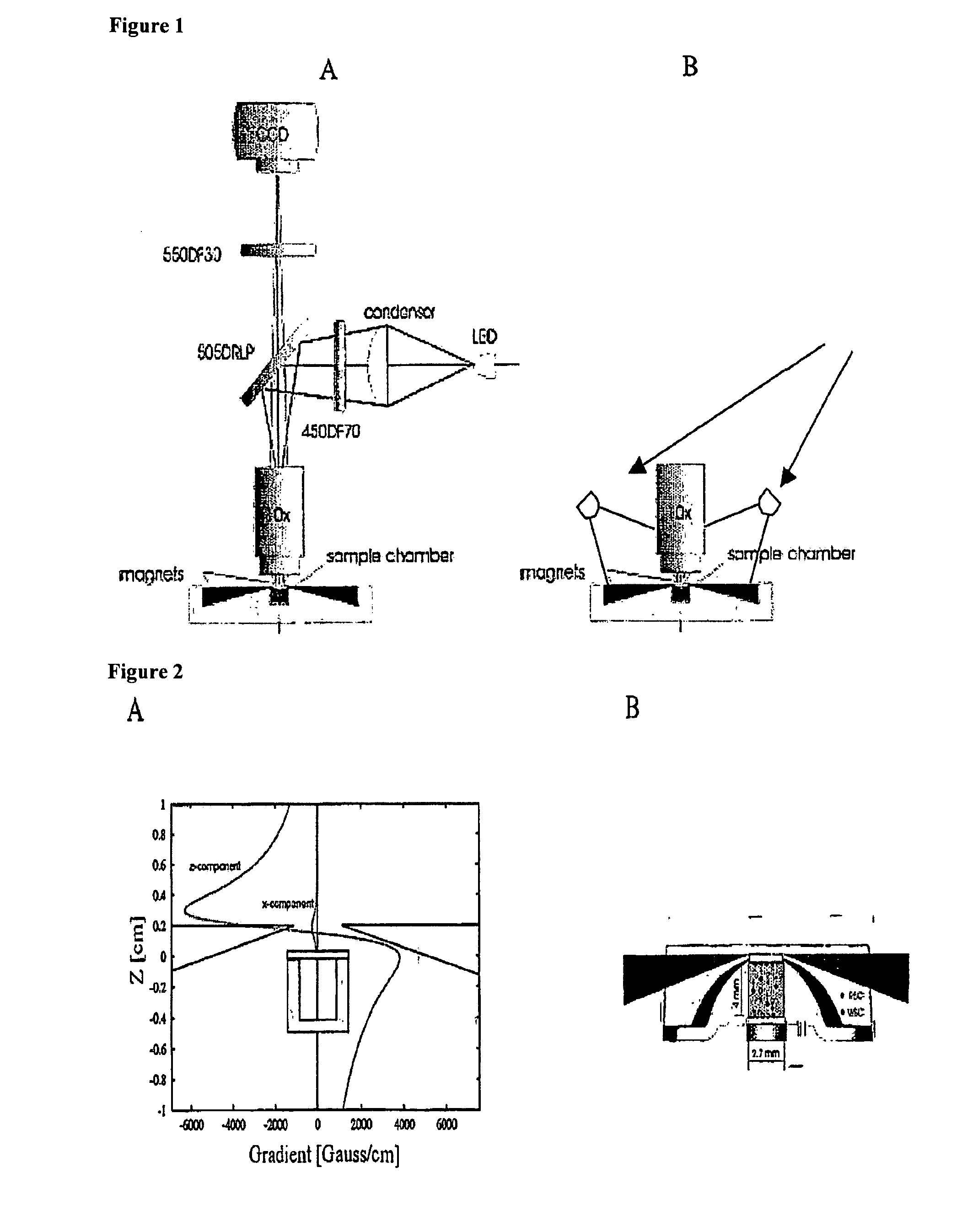
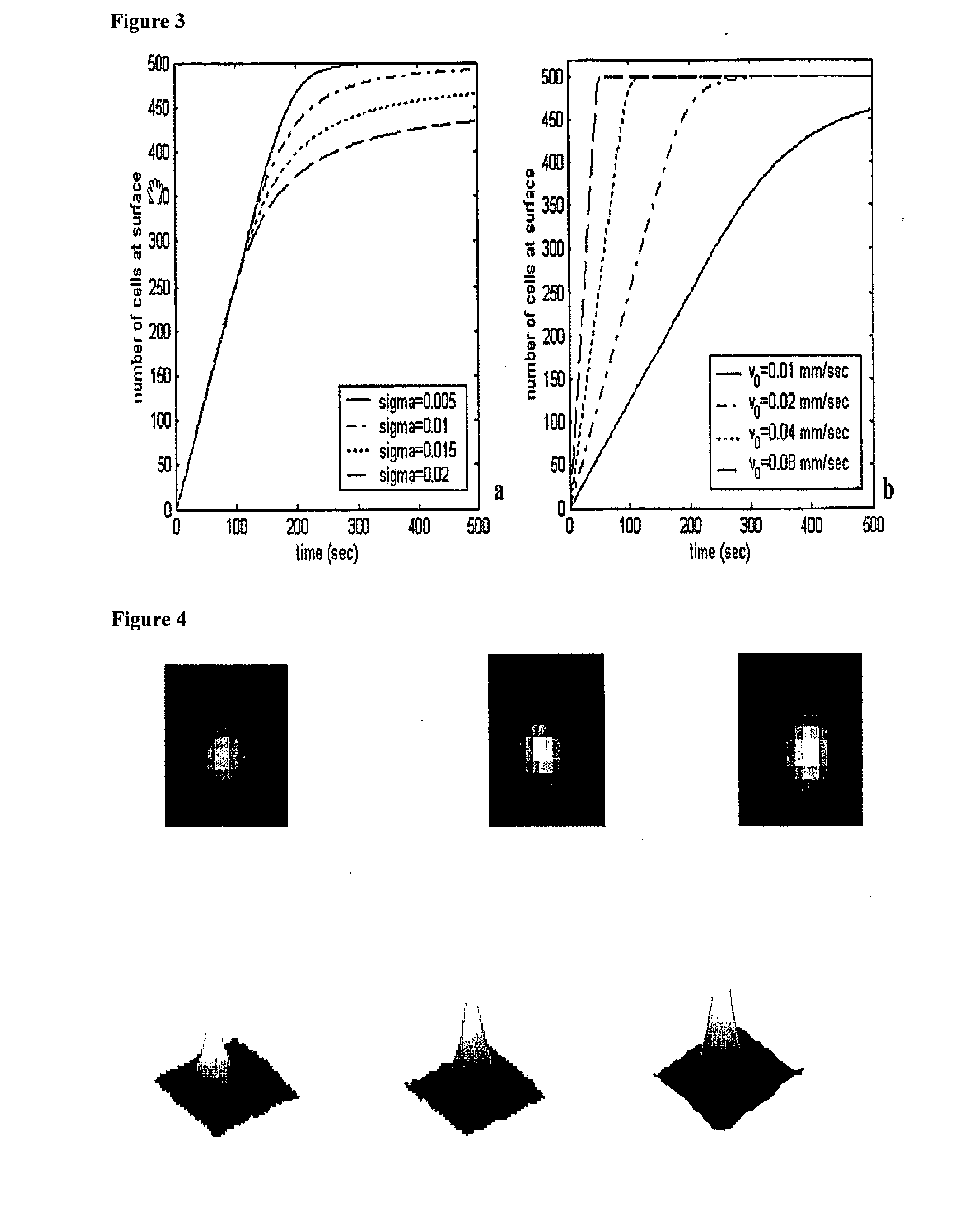
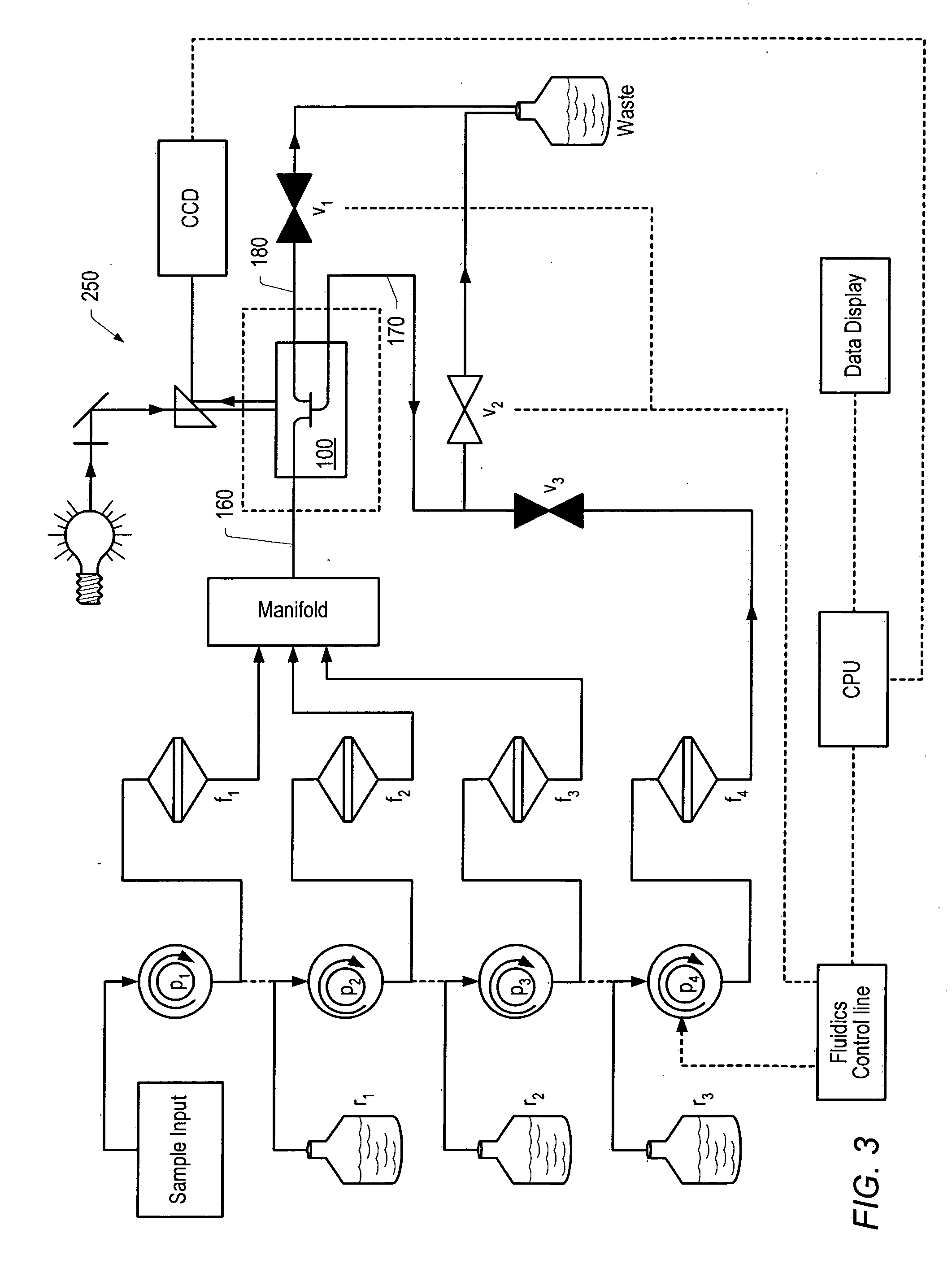
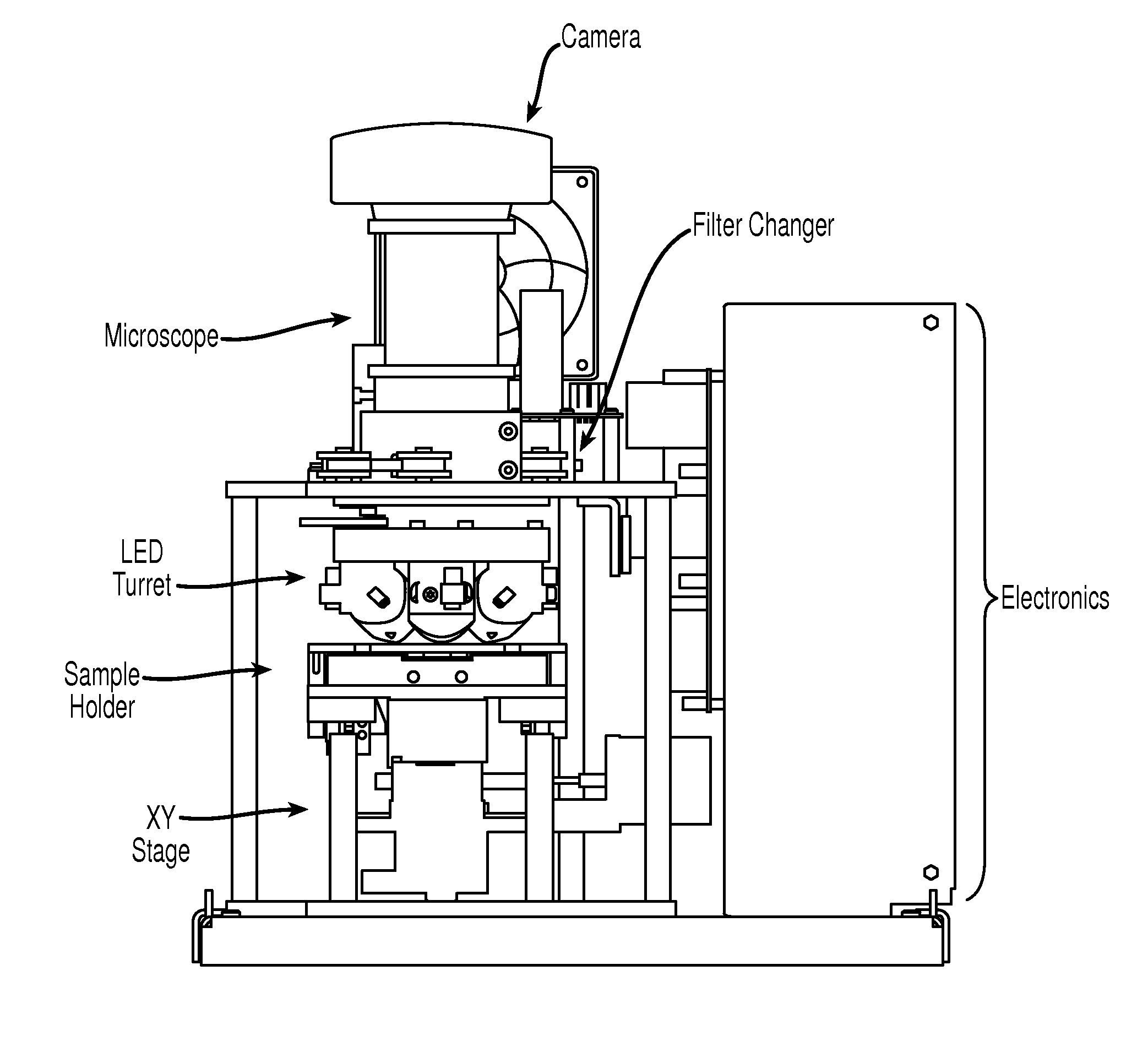
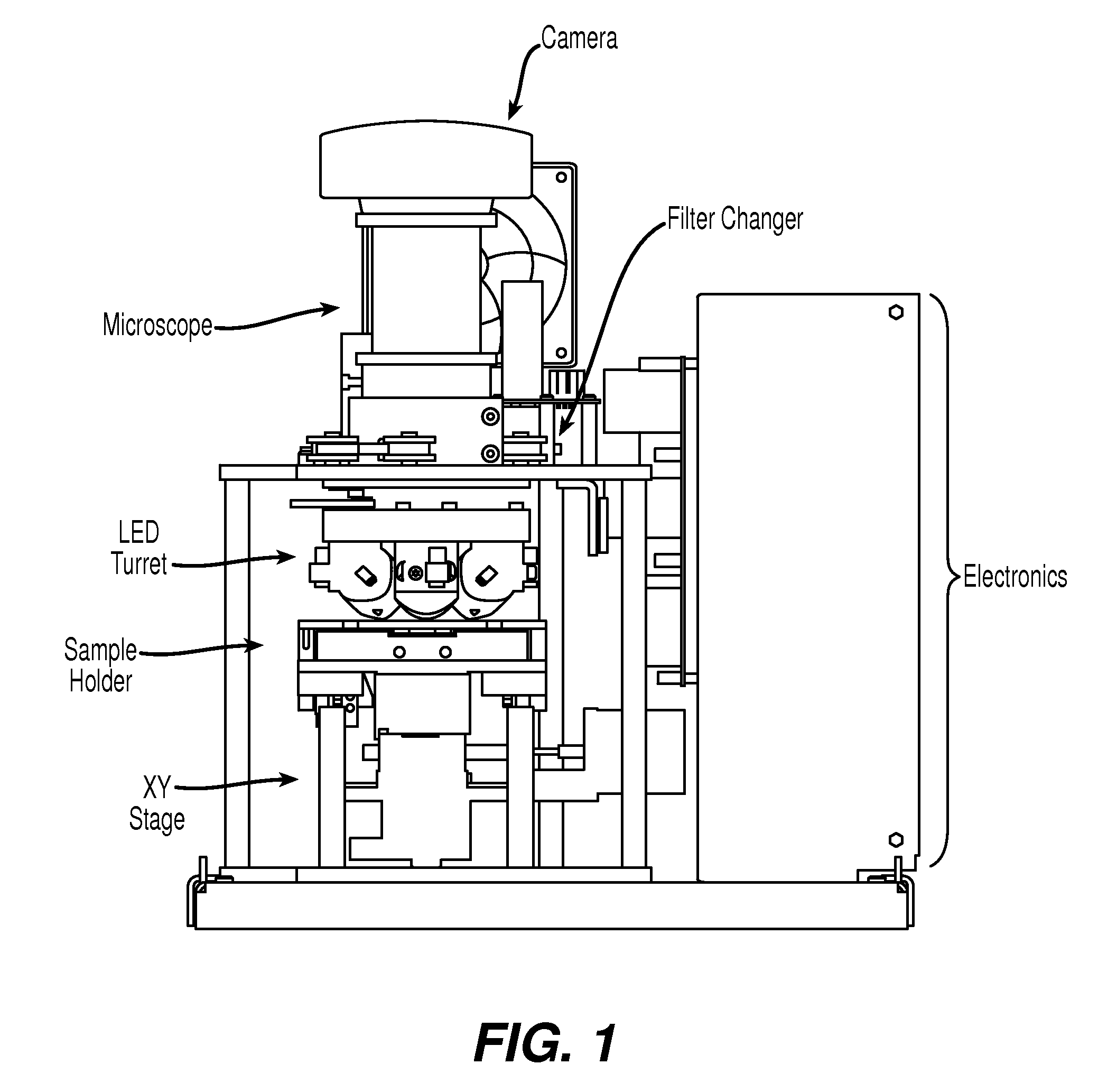
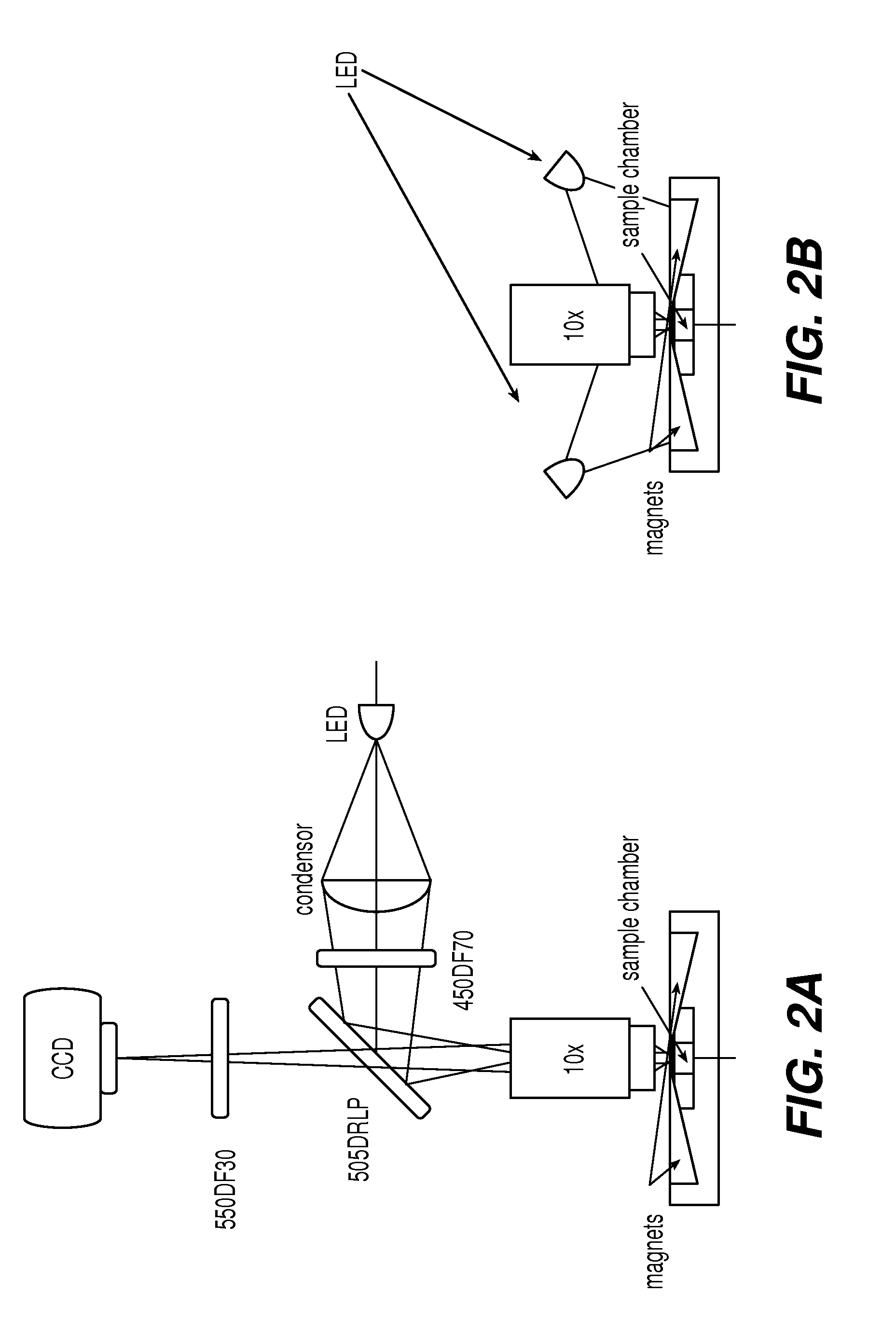
The enumeration of cells in fluids by flow cytometry is widely used across many disciplines such as assessment of leukocyte subsets in different bodily fluids or of bacterial contamination in environmental samples, food products and bodily fluids. For many applications the cost, size and complexity of the instruments prevents wider use, for example, CD4 analysis in HIV monitoring in resource-poor countries. The novel device, methods and algorithms disclosed herein largely overcome these limitations. Briefly, all cells in a biological sample are fluorescently labeled, but only the target cells are also magnetically labeled. The labeled sample, in a chamber or cuvet, is placed between two wedge-shaped magnets to selectively move the magnetically labeled cells to the observation surface of the cuvet. An LED illuminates the cells and a CCD camera captures the images of the fluorescent light emitted by the target cells. Image analysis performed with a novel algorithm provides a count of the cells on the surface that can be related to the target cell concentration of the original sample. The compact cytometer system provides a rugged, affordable and easy-to-use technique, which can be used in remote locations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TWENTE
Methods and algorithms for cell enumeration in a low-cost cytometer
InactiveUS20070117158A1Simple designReduce operating costsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsImage analysisWhite blood cellCcd camera
The enumeration of cells in fluids by flow cytometry is widely used across many disciplines such as assessment of leukocyte subsets in different bodily fluids or of bacterial contamination in environmental samples, food products and bodily fluids. For many applications the cost, size and complexity of the instruments prevents wider use, for example, CD4 analysis in HIV monitoring in resource-poor countries. The novel device, methods and algorithms disclosed herein largely overcome these limitations. Briefly, all cells in a biological sample are fluorescently labeled, but only the target cells are also magnetically labeled. In addition, non-magnetically labeled cells are imaged for viability in a modified slide configuration. The labeled sample, in a chamber or cuvet, is placed between two wedge-shaped magnets to selectively move the magnetically labeled cells to the observation surface of the cuvet. An LED illuminates the cells and a CCD camera captures the images of the fluorescent light emitted by the target cells. Image analysis performed with a novel algorithm provides a count of the cells on the surface that can be related to the target cell concentration of the original sample. The compact cytometer system provides a rugged, affordable and easy-to-use technique, which can be used in remote locations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TWENTE
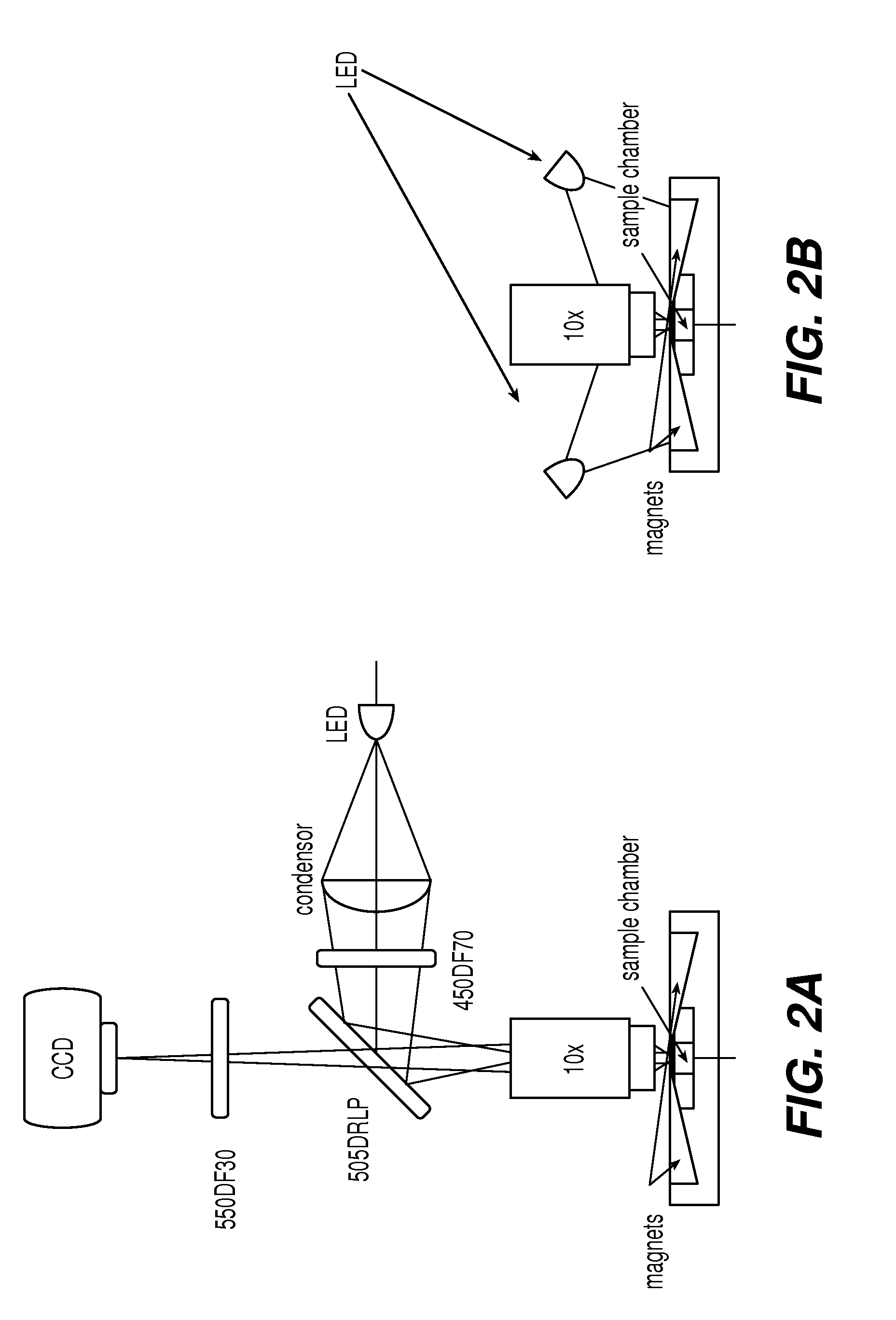
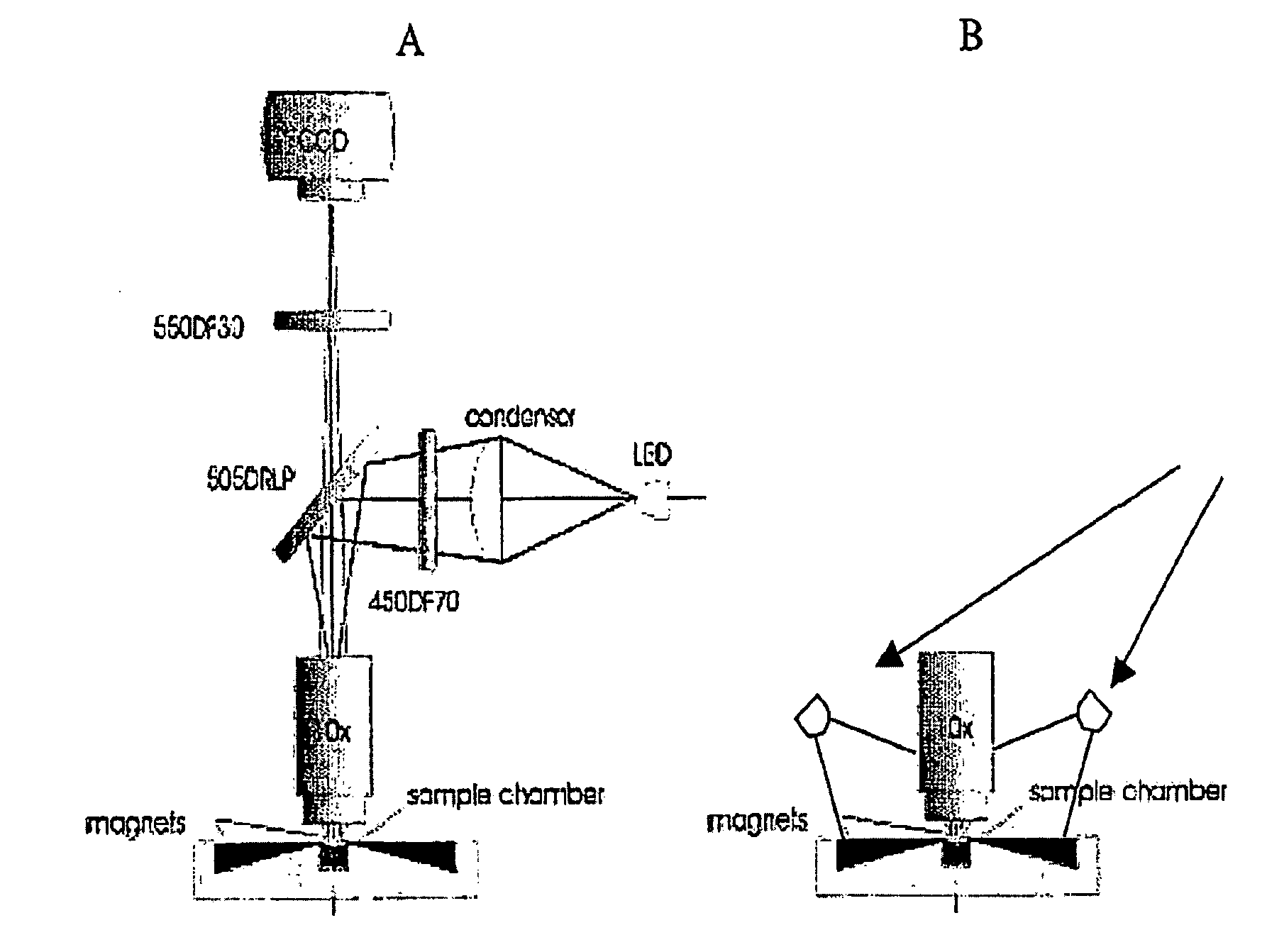
A simple and affordable method for immunophenotyping using a microfluidic chip sample preparation with image cytometry
ActiveUS20140038230A1Simple methodCheap componentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPoint of careFluorescence
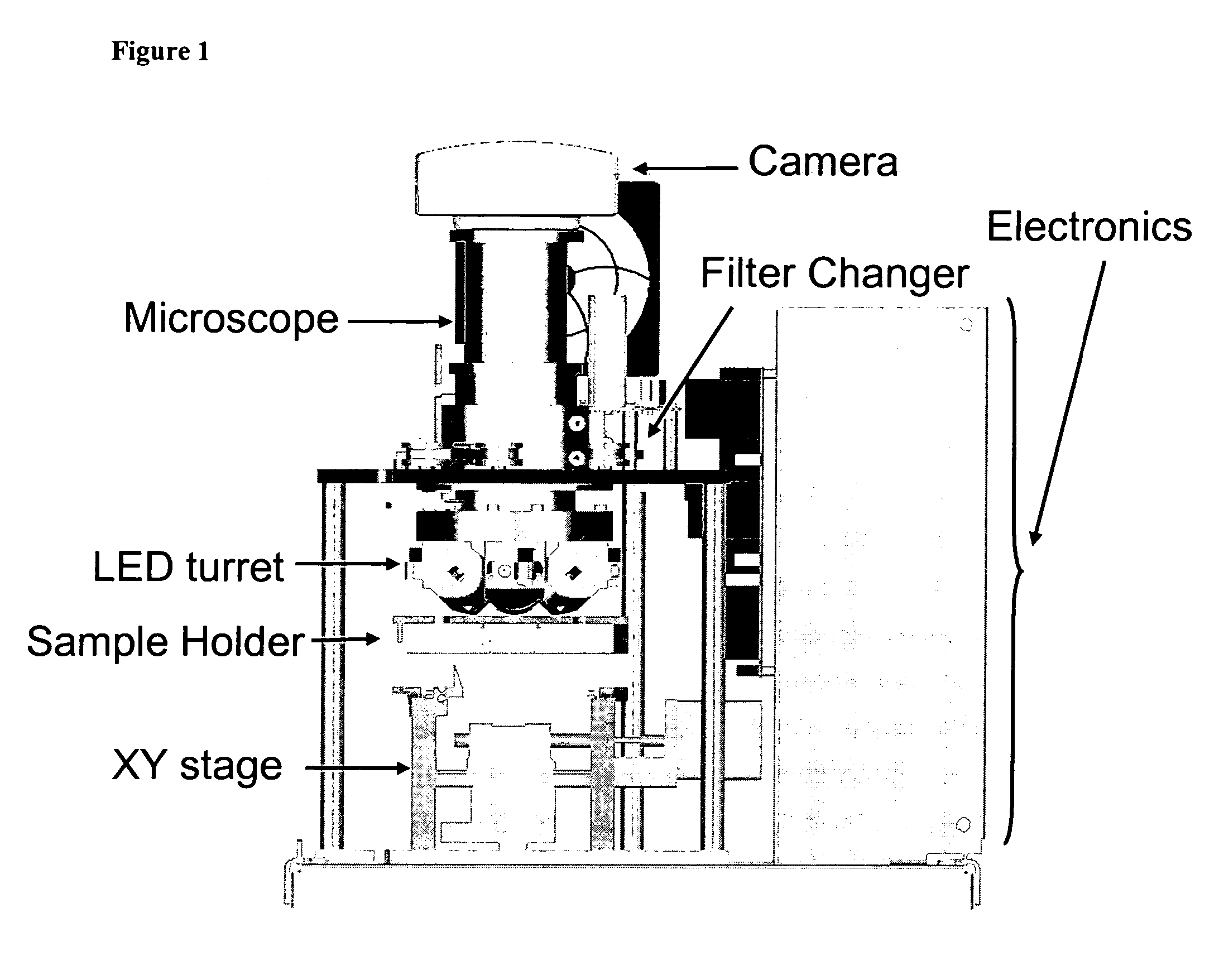
The enumeration of cells in fluids by flow cytometry is widely used across many disciplines such as assessment of leukocyte subsets in different bodily fluids or of bacterial contamination in environmental samples, food products and bodily fluids. For many applications the cost, size and complexity of the instruments prevents wider use, for example, CD4 analysis in HIV monitoring in resource-poor countries. The novel device, methods and system disclosed herein largely overcome these limitations. The system includes a simple system for CD4 and CD8 counting in point-of-care HIV staging within resource poor countries. Unlike previous approaches, no sample preparation is required with the sample added directly to a chip containing dried reagents by capillary flow. A large area image cytometer consisting of an LED module is used to excite the fluorochromes PerCP and APC labeled targets and a monochrome CCD camera with a combination of two macro lenses captures images of 40 mm2 of blood (approximately 1 microliter). CD4 and CD8-T-lymphocyte counts correlate well with those obtained by flow cytometry. The cytometer system described in the present invention provides an affordable and easy-to-use technique for use in remote locations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TWENTE
Methods and algorithms for cell enumeration in a low-cost cytometer
InactiveUS7764821B2Low costFunction increaseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWhite blood cellCcd camera
The enumeration of cells in fluids by flow cytometry is widely used across many disciplines such as assessment of leukocyte subsets in different bodily fluids or of bacterial contamination in environmental samples, food products and bodily fluids. For many applications the cost, size and complexity of the instruments prevents wider use, for example, CD4 analysis in HIV monitoring in resource-poor countries. The novel device, methods and algorithms disclosed herein largely overcome these limitations. Briefly, all cells in a biological sample are fluorescently labeled, but only the target cells are also magnetically labeled. In addition, non-magnetically labeled cells are imaged for viability in a modified slide configuration. The labeled sample, in a chamber or cuvet, is placed between two wedge-shaped magnets to selectively move the magnetically labeled cells to the observation surface of the cuvet. An LED illuminates the cells and a CCD camera captures the images of the fluorescent light emitted by the target cells. Image analysis performed with a novel algorithm provides a count of the cells on the surface that can be related to the target cell concentration of the original sample. The compact cytometer system provides a rugged, affordable and easy-to-use technique, which can be used in remote locations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TWENTE
Methods and Algorithms For Cell Enumeration in a Low-Cost Cytometer
InactiveUS20110052037A1Functional simplicity in designReduce operating costsCharacter and pattern recognitionMaterial analysisWhite blood cellFluorescence
The enumeration of cells in fluids by flow cytometry is widely used across many disciplines such as assessment of leukocyte subsets in different bodily fluids or of bacterial contamination in environmental samples, food products and bodily fluids. For many applications the cost, size and complexity of the instruments prevents wider use, for example, CD4 analysis in HIV monitoring in resource-poor countries. The novel device, methods and algorithms disclosed herein largely overcome these limitations. Briefly, all cells in a biological sample are fluorescently labeled, but only the target cells are also magnetically labeled. In addition, non-magnetically labeled cells are imaged for viability in a modified slide configuration. The labeled sample, in a chamber or cuvet, is placed between two wedge-shaped magnets to selectively move the magnetically labeled cells to the observation surface of the cuvet. An LED illuminates the cells and a CCD camera captures the images of the fluorescent light emitted by the target cells. Image analysis performed with a novel algorithm provides a count of the cells on the surface that can be related to the target cell concentration of the original sample. The compact cytometer system provides a rugged, affordable and easy-to-use technique, which can be used in remote locations.
Owner:VERIDEX LCC
Methods and Algorithms for Cell Enumeration in a Low-Cost Cytometer
InactiveUS20110044527A1Simple designLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWhite blood cellFluorescence
The enumeration of cells in fluids by flow cytometry is widely used across many disciplines such as assessment of leukocyte subsets in different bodily fluids or of bacterial contamination in environmental samples, food products and bodily fluids. For many applications the cost, size and complexity of the instruments prevents wider use, for example, CD4 analysis in HIV monitoring in resource-poor countries. The novel device, methods and algorithms disclosed herein largely overcome these limitations. Briefly, all cells in a biological sample are fluorescently labeled, but only the target cells are also magnetically labeled. The labeled sample, in a chamber or cuvet, is placed between two wedge-shaped magnets to selectively move the magnetically labeled cells to the observation surface of the cuvet. An LED illuminates the cells and a CCD camera captures the images of the fluorescent light emitted by the target cells. Image analysis performed with a novel algorithm provides a count of the cells on the surface that can be related to the target cell concentration of the original sample. The compact cytometer system provides a rugged, affordable and easy-to-use technique, which can be used in remote locations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TWENTE
Microchip-based system for hiv diagnostics
InactiveUS20060234209A1Efficient captureEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesDiseaseCD4 Lymphocyte
The invention relates to microchip-based assays to measure HIV-associated analytes of interest (e.g., CD4 lymphocytes, HIV RNA and liver enzymes) in a sample from a subject infected with the HIV virus. Methods of the present invention are optimal for use in monitoring HIV disease in resource-poor settings.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
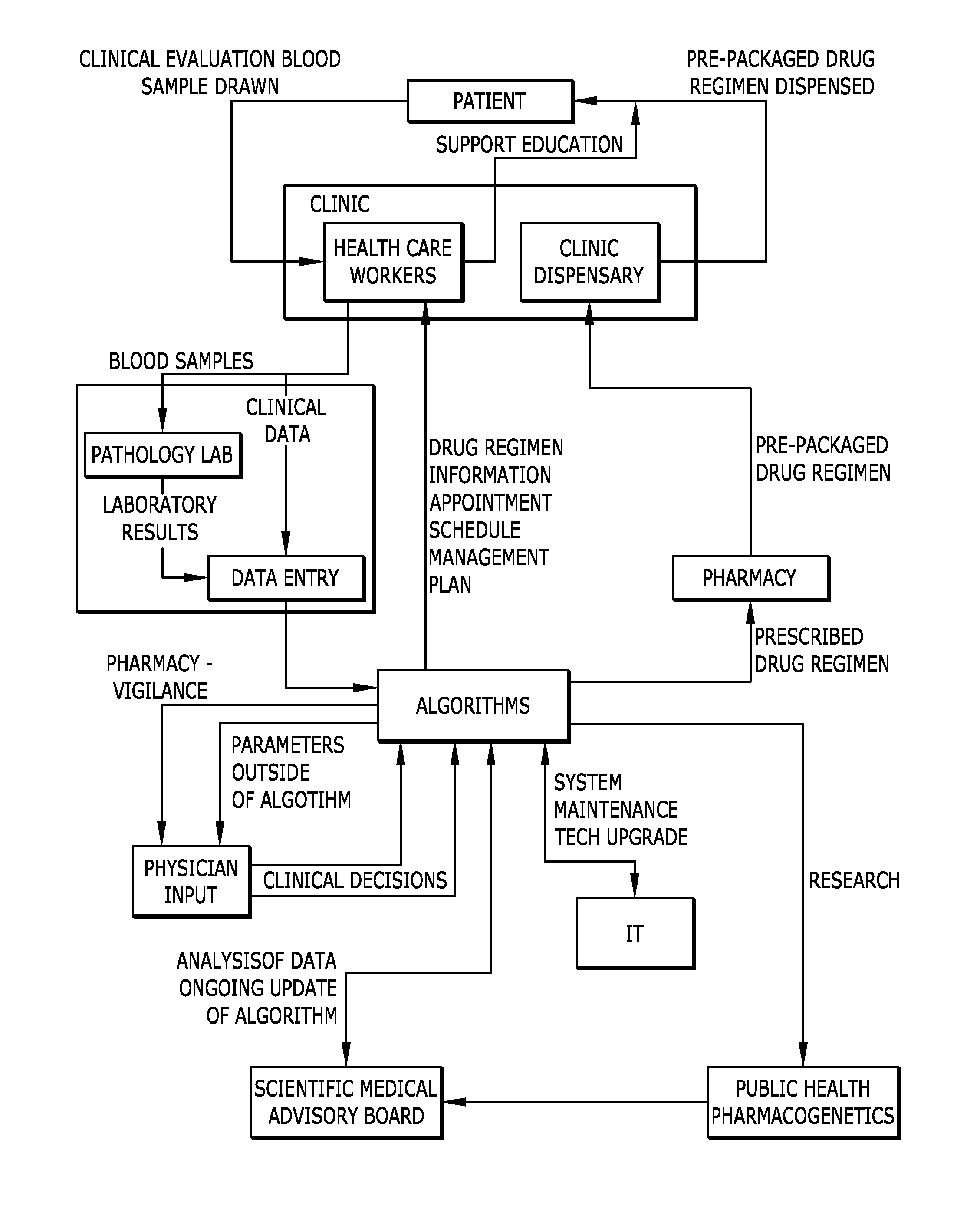
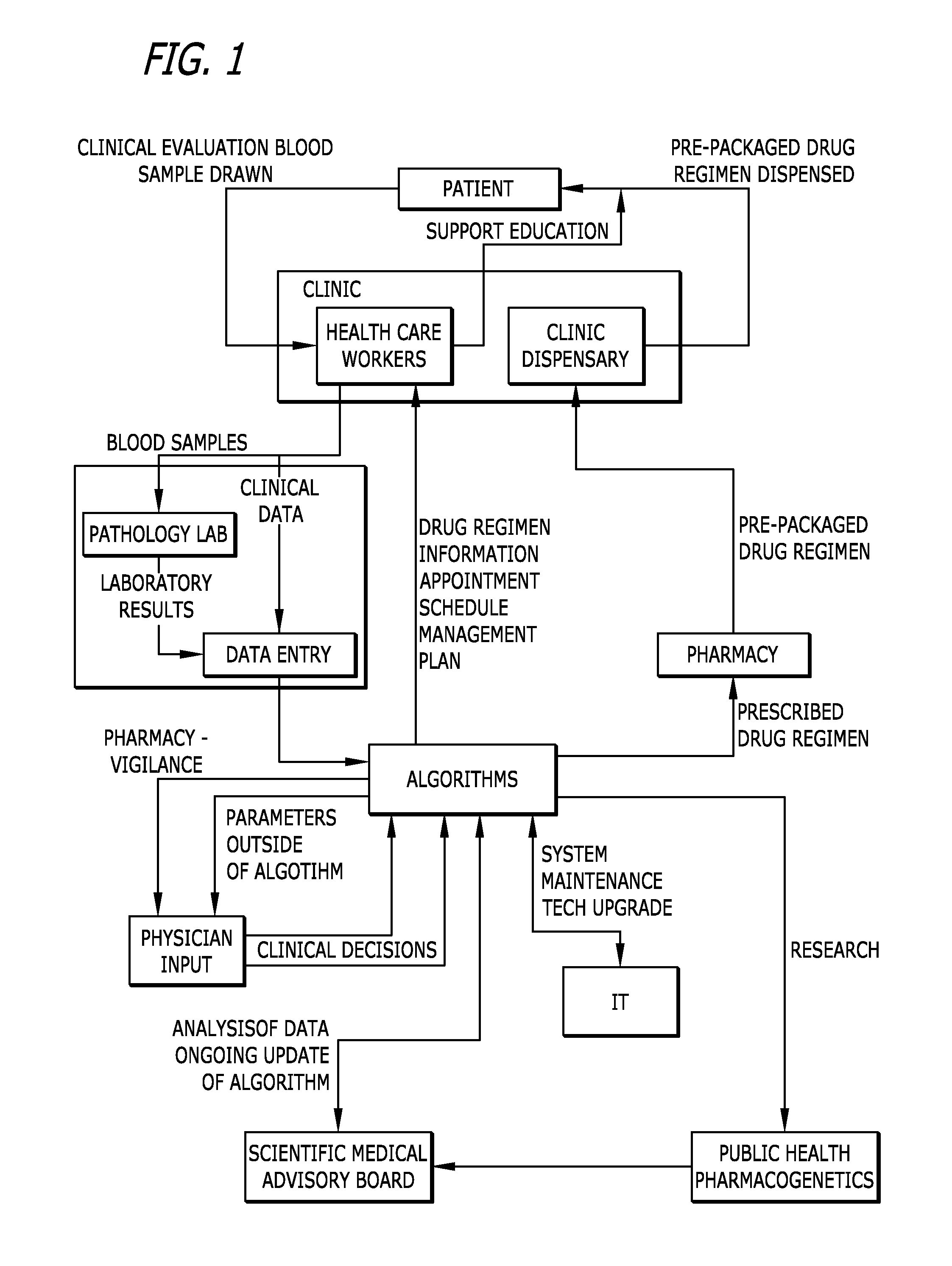
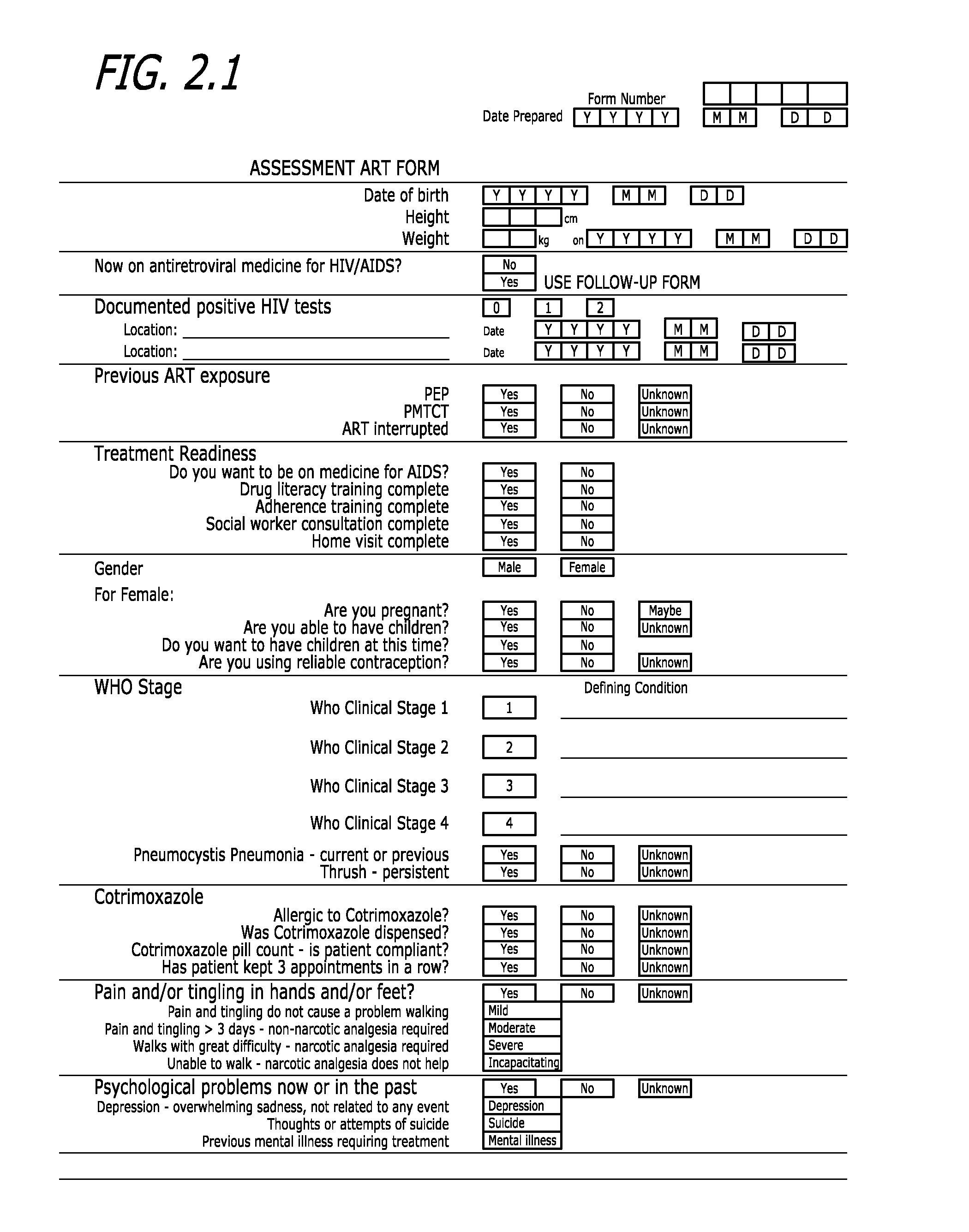
Disease management system
InactiveUS20070156344A1Drug and medicationsComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionData interpretationData harvesting
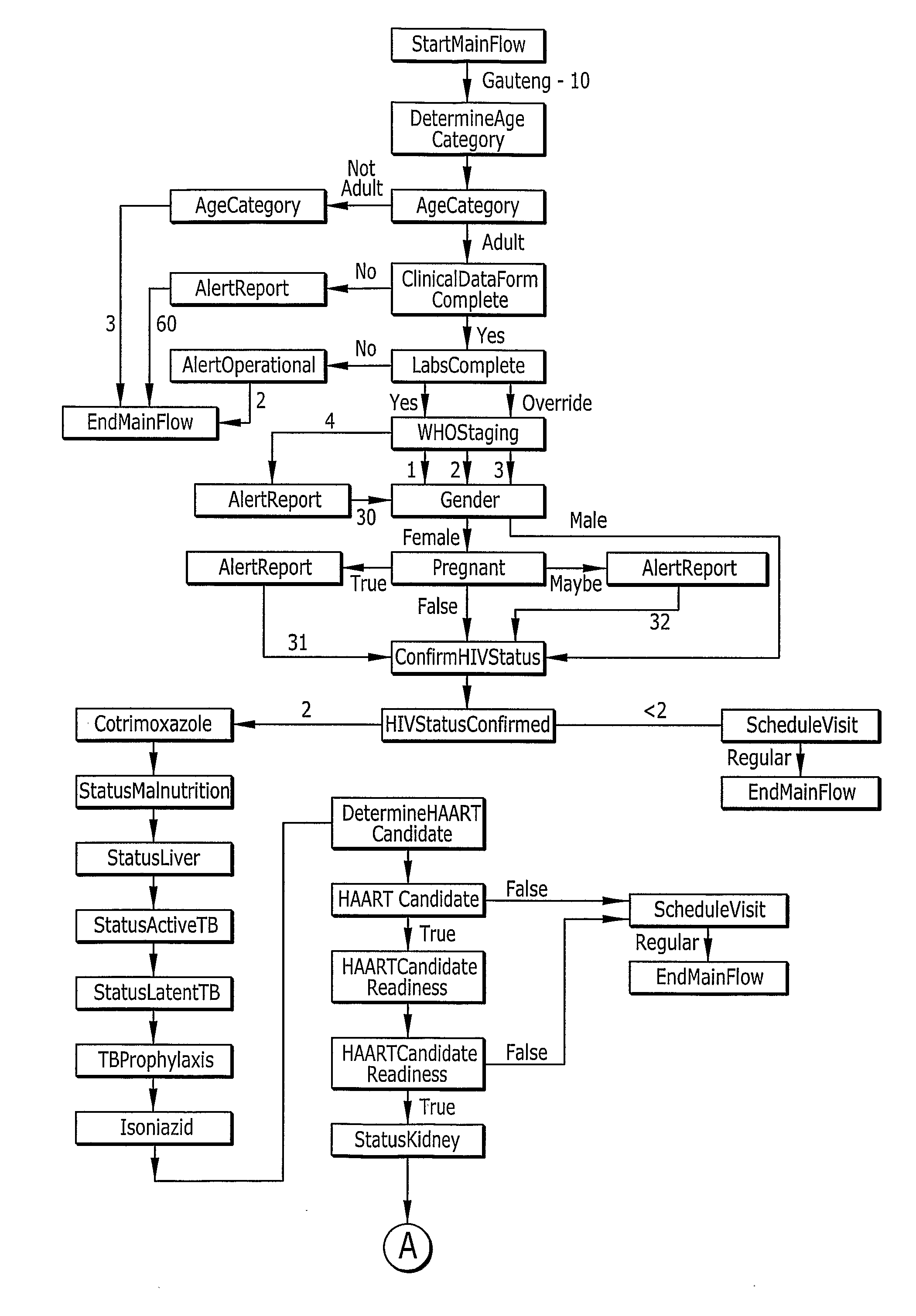
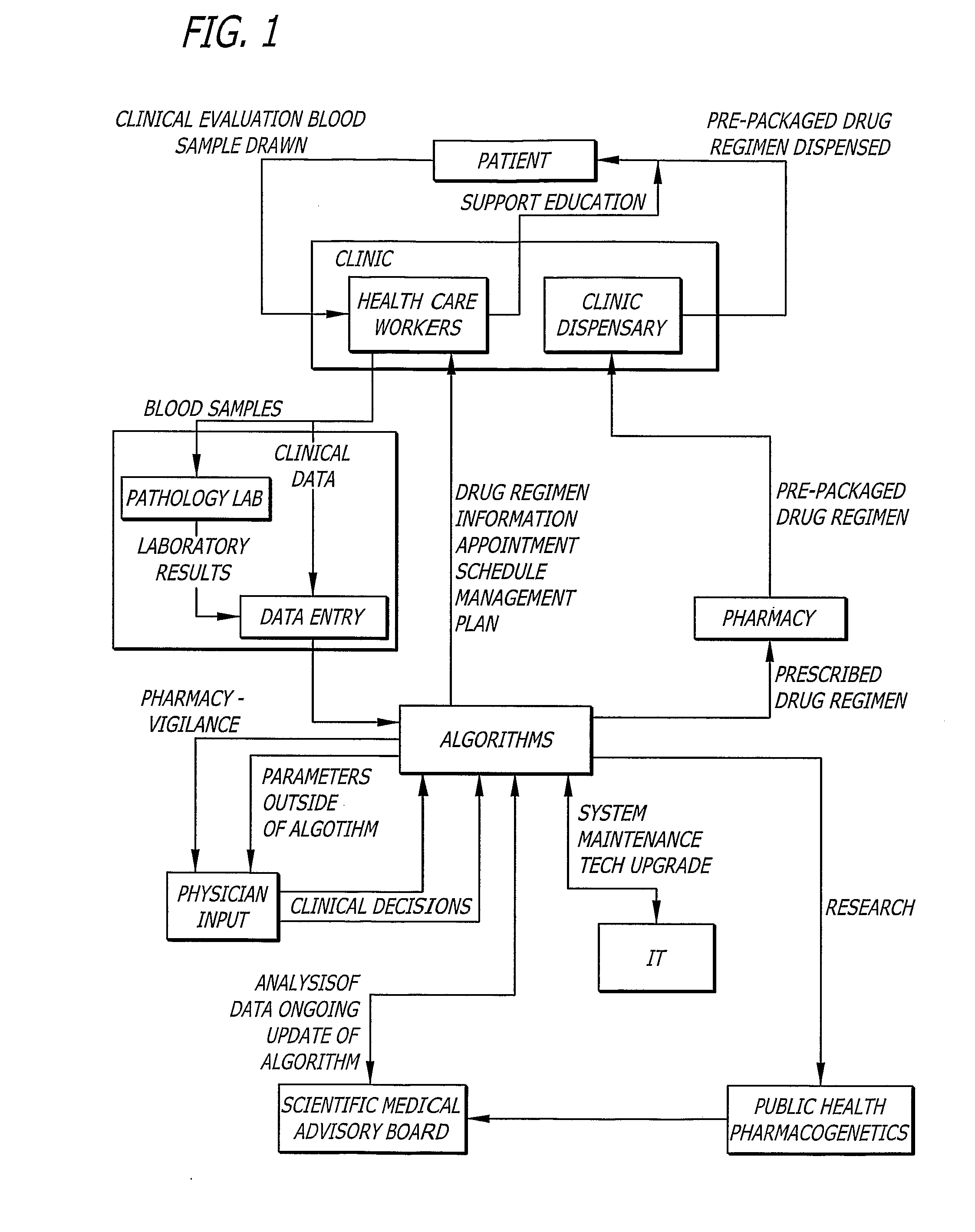
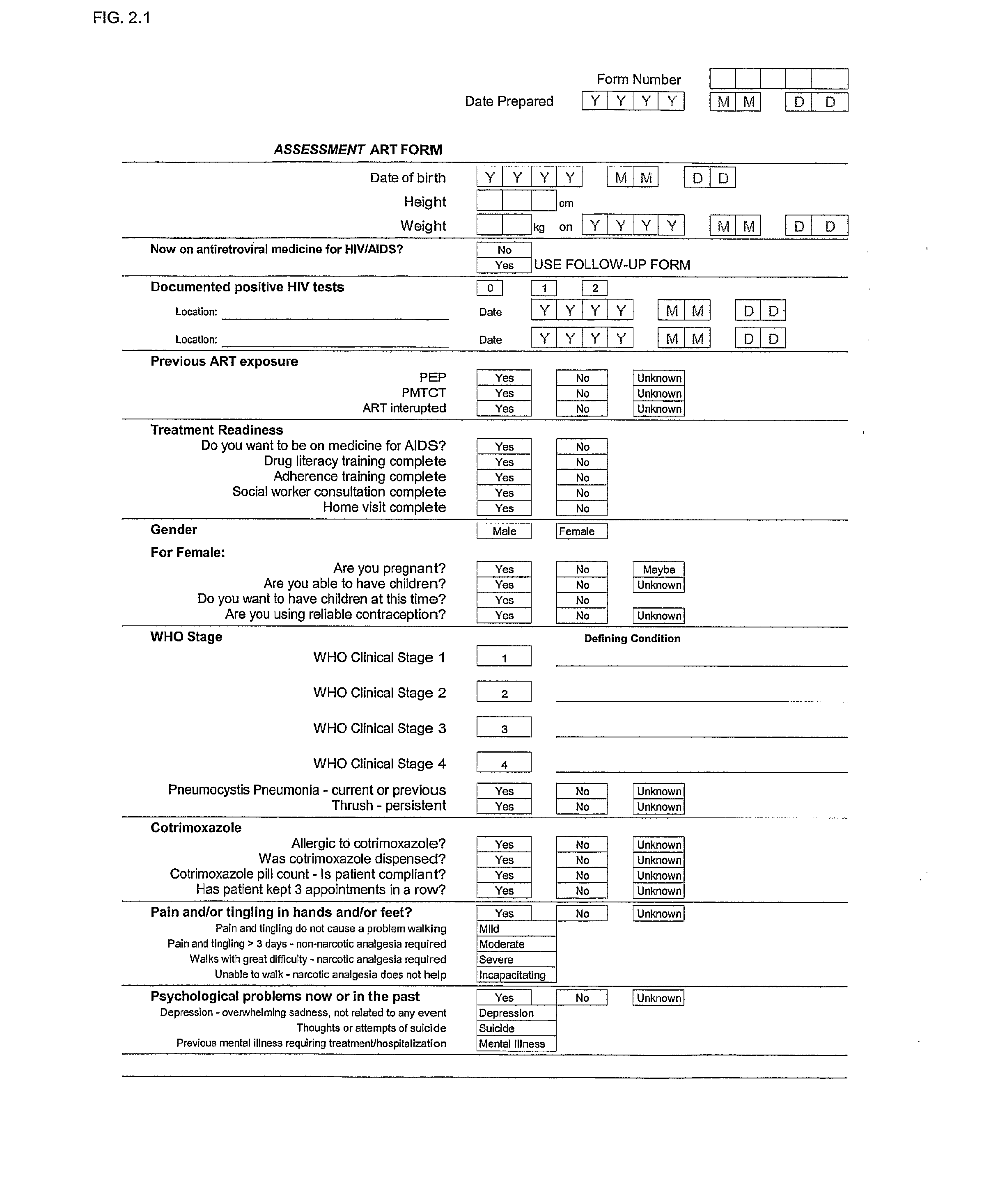
A comprehensive disease management system providing advanced diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic capabilities to healthcare workers located in remote, rural and resource-poor urban centers is disclosed. Additionally, a method of managing disease in a patient located remotely relative to interpretation and therapeutic dispensing services is provided including methods of data collection, data interpretation and therapeutic dispensing. An algorithm is disclosed to provide non-physician healthcare workers in remote, rural and resource-poor urban centers to manage disease in patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease.
Owner:DISEASE MANAGEMENT SERVICES
Sensor Technology for Diagnosing Tuberculosis
ActiveUS20150301021A1Enhanced sensitivity and selectivityFast and reliable diagnosisVibration measurement in solidsImmobilised enzymesMedicineNanoparticle
A sensor technology comprising a single nano-material (gold nanoparticles and / or carbon nanotube) based sensor or a plurality of sensors in conjunction with a pattern recognition algorithm for non-invasive and accurate diagnosis of tuberculosis caused by M. tuberculosis bacteria in a subject. The sensor technology is suitable for population screening of tuberculosis, particularly in resource-poor and developing countries.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
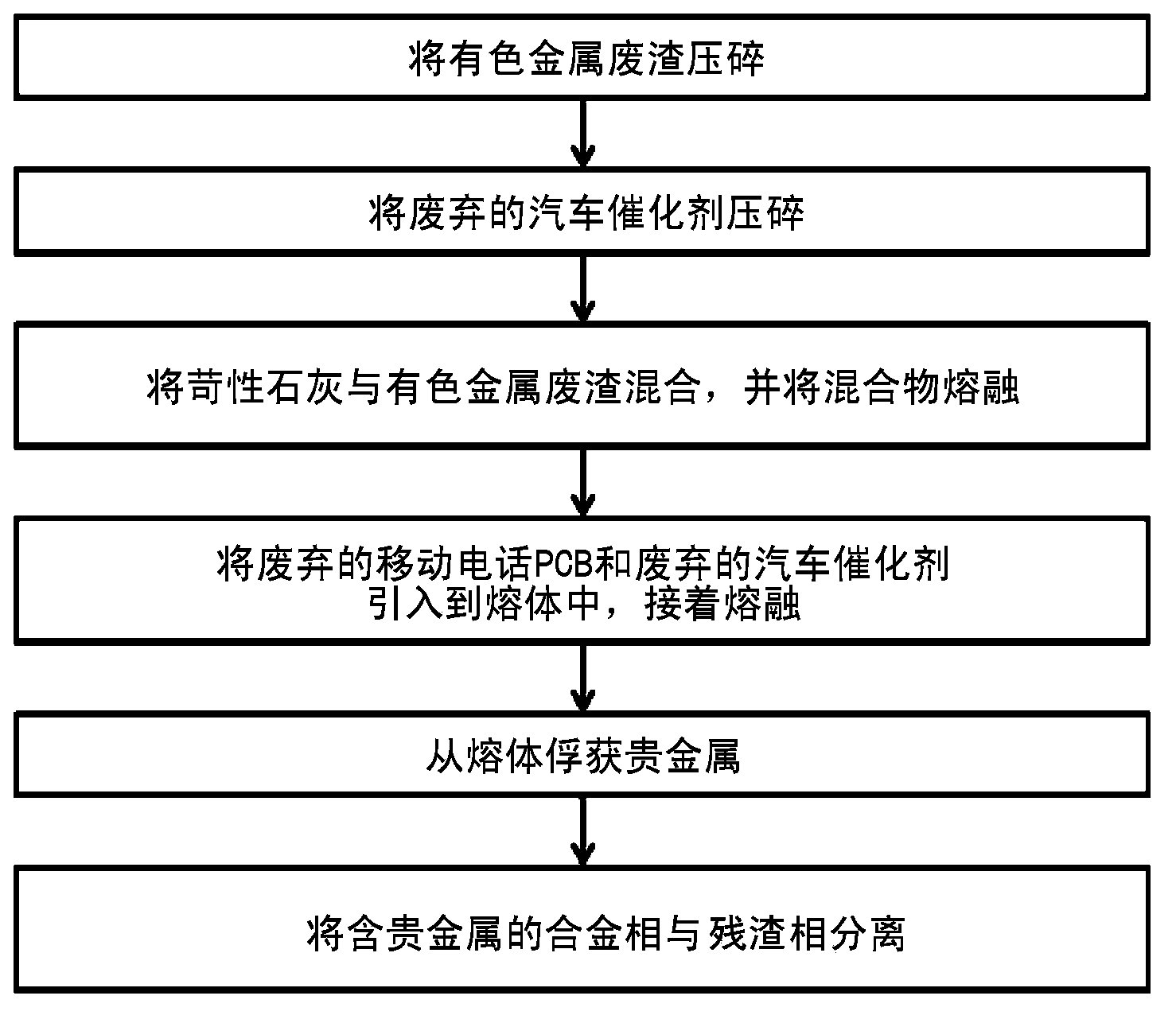
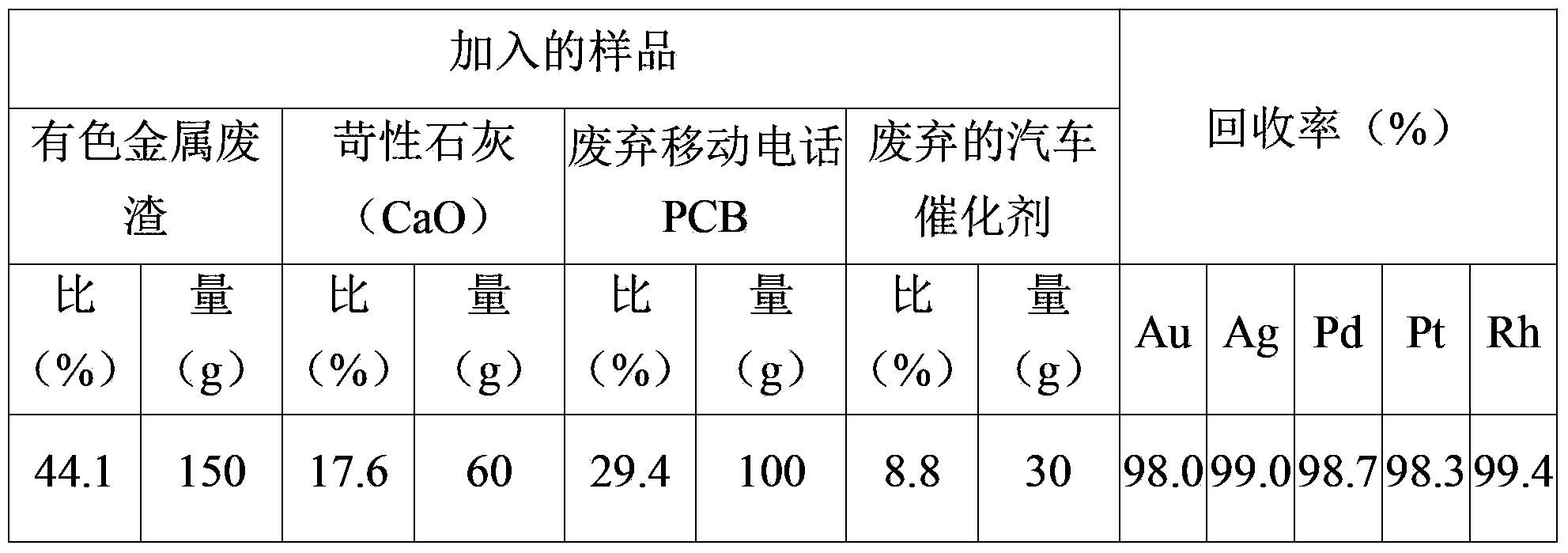
Method for concentrating and recovering noble metals from printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phones and catalysts of discarded cars using discarded nonferrous slag
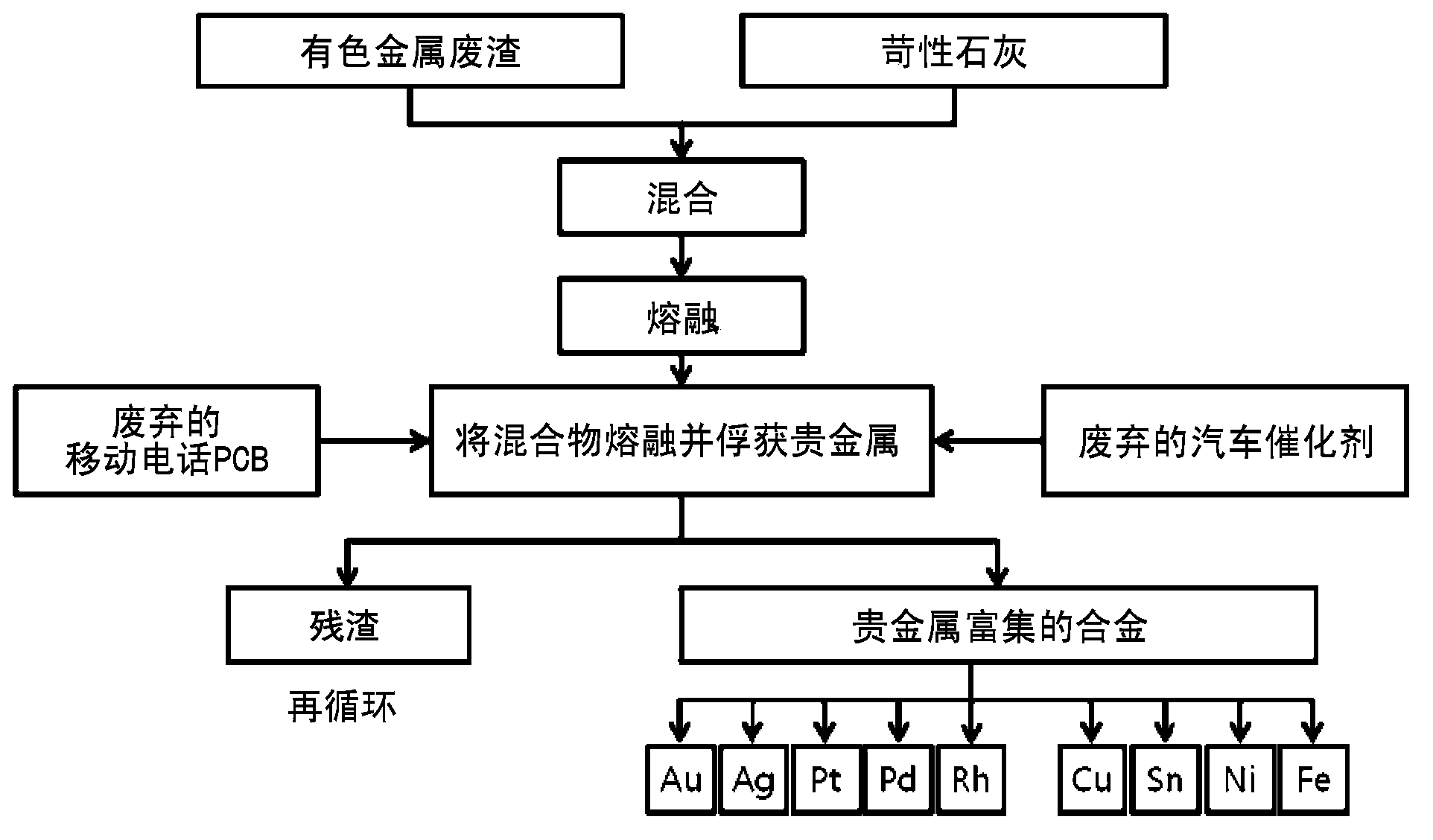
The present invention relates to a method for concentrating and recovering noble metals from printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phones and catalysts of discarded cars using discarded nonferrous slag, which is industrial waste discharged from a process for refining nonferrous metals such as copper, lead, zinc and the like, and more specifically, to a method for concentrating and recovering gold, silver, platinum, palladium, rhodium and the like contained in printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phones and catalysts of discarded cars by melting discarded nonferrous slag, printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phones and catalysts of discarded cars at a high temperature through a single process to reduce and separate iron oxide contained in the discarded nonferrous slag and simultaneously melting and separating copper, iron, tin, and nickel contained in the printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phones to use the generated iron, copper, tin, and nickel alloy as a collector metal for noble metals. The method for concentrating and recovering noble metals from printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phones and catalysts of discarded cars using discarded nonferrous slag of the present invention comprises the steps of: mixing and melting discarded nonferrous slag and a solvent, which is a slag composition controller; inserting printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phones and catalysts of discarded cars to the obtained molten metal to melt the same; and maintaining the same for a predetermined amount of time to separate the same into a noble metal-collected alloy phase and a slag phase containing no noble metals. In addition, the present invention relates to a method for recovering valuable metals such as iron, copper, tin, nickel and the like in addition to noble metals such as gold, silver, platinum, palladium, and rhodium from printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phones and catalysts of discarded cars, and recycling the generated slag without environmental problems. According to the present invention, the amount of the generated alloy phase is increased without using a collector metal for noble metals such as copper, iron, lead, and nickel and carbon as a reducing agent which increase processing costs by using discarded nonferrous slag, which is industrial waste discharged from a process for refining nonferrous metals such as copper, lead, zinc, and the like, as a solvent, which is a slag composition controller, and a noble metal collector simultaneously, and using a plastic component contained in printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phones as a reducing agent, and thus an alloy phase and a slag phase can be readily separated, thereby simultaneously reducing processing time and minimizing the amount of a solvent such as alumina (Al2O3), quicklime (CaO), magnesia (MgO), iron oxide (FeO) and silica (SiO2). Accordingly, noble metals such as gold, silver, platinum, palladium, rhodium and the like can be concentrated and recovered through a single process by simultaneously treating different industrial waste such as printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phones and catalysts of discarded cars, and waste material can be recycled to be used as a material for the high-technology industry, and thus it is possible to maximize the coefficient of utilization of noble metal resources in resource-poor Korea, which depends on imports for all of noble metal resources.
Owner:KOREA INST OF GEOSCI & MINERAL RESOURCES
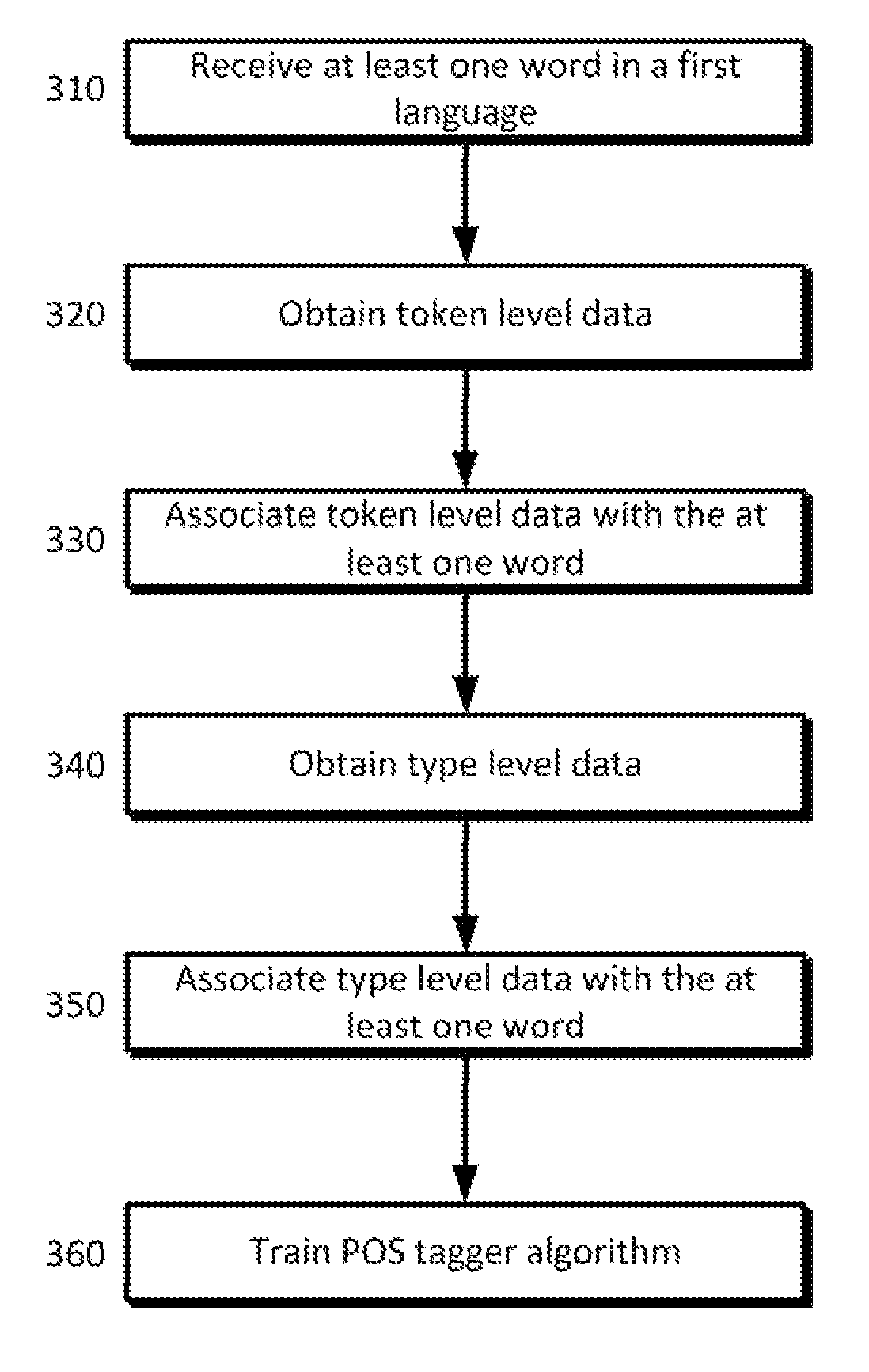
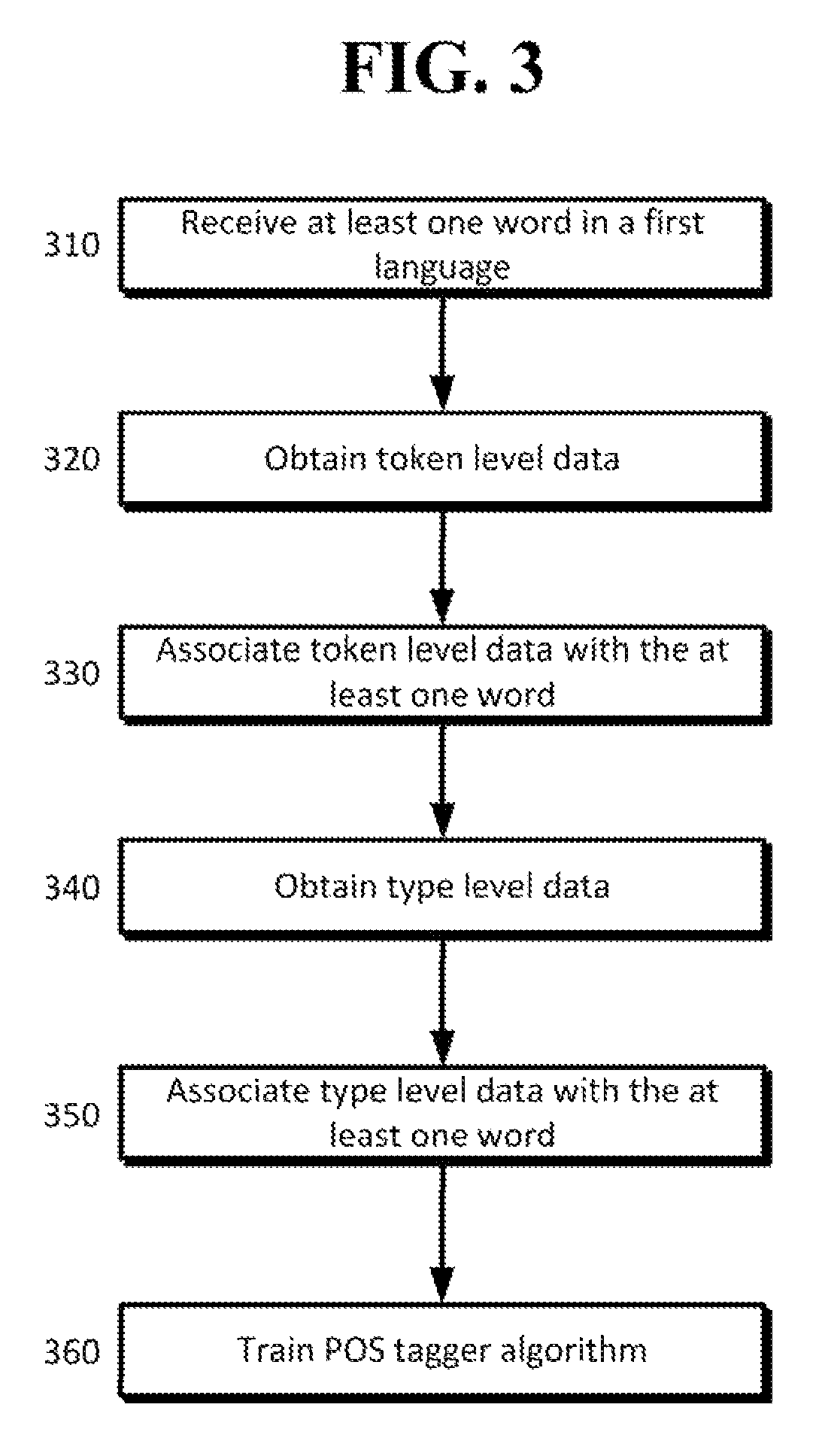
Weakly supervised part-of-speech tagging with coupled token and type constraints
ActiveUS9311299B1Natural language translationSemantic analysisConditional random fieldPart of speech
A method and system are provided for a part-of-speech tagger that may be particularly useful for resource-poor languages. Use of manually constructed tag dictionaries from dictionaries via bitext can be used as type constraints to overcome the scarcity of annotated data in some instances. Additional token constraints can be projected from a resource-rich source language via word-aligned bitext. Several example models are provided to demonstrate this such as a partially observed conditional random field model, where coupled token and type constraints may provide a partial signal for training. The disclosed method achieves a significant relative error reduction over the prior state of the art.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method for preparing sulfuric acid by roasting power plant desuifurized cinder with fluidized bed roaster
InactiveCN101249955AImprove protectionSolve processing problemsSulfur compoundsEnergy inputAfter treatmentSulfur
Owner:李德安
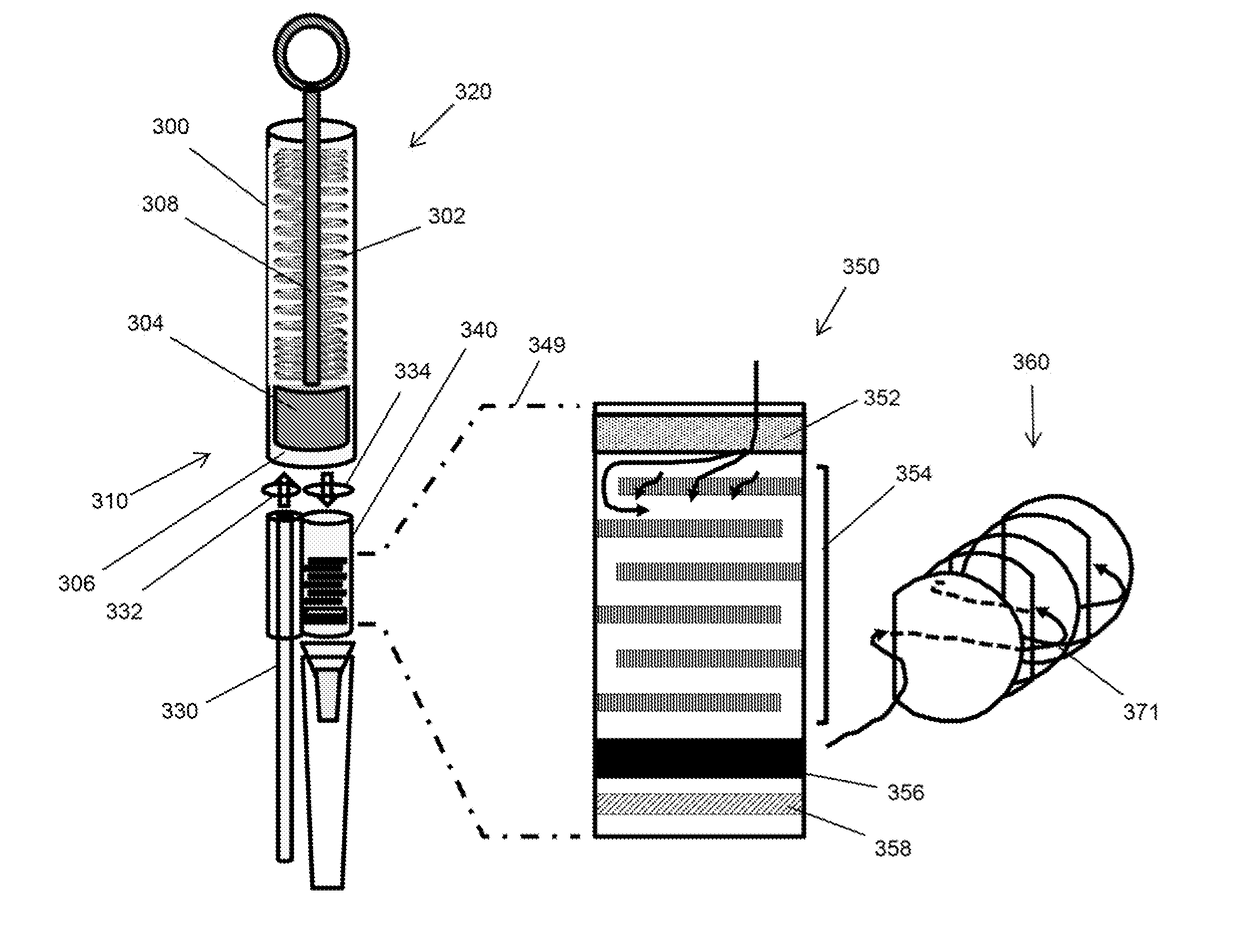
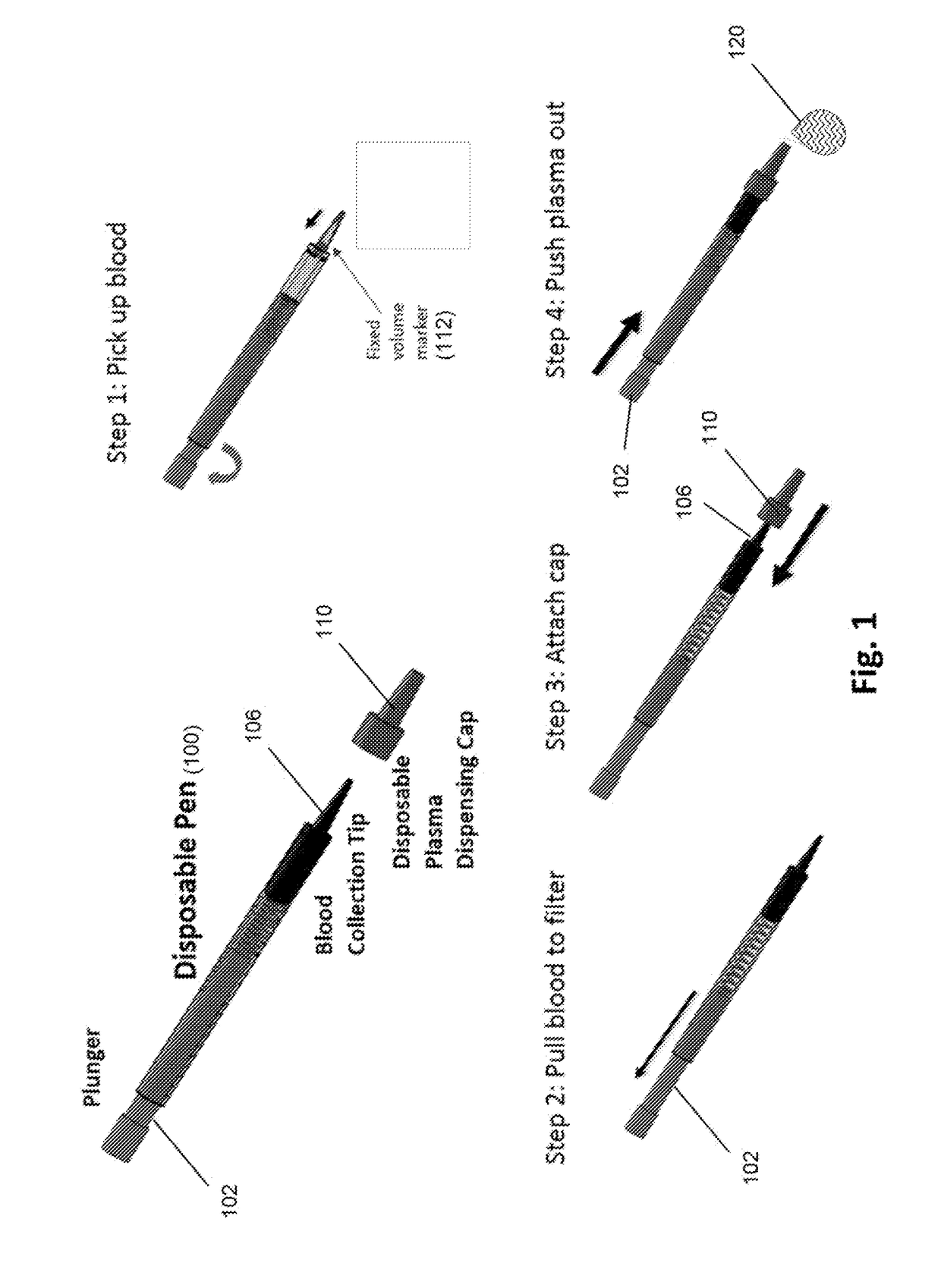
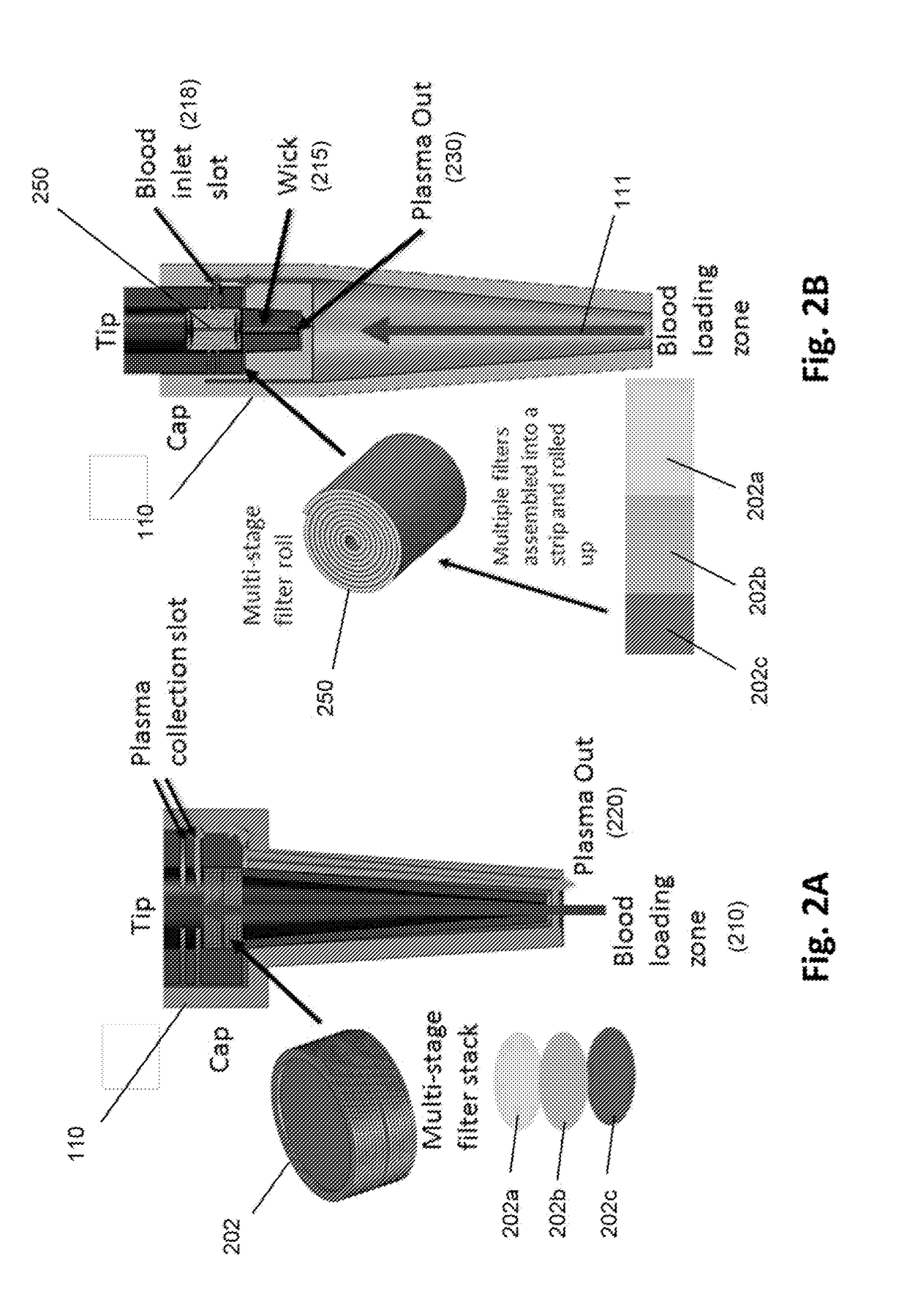
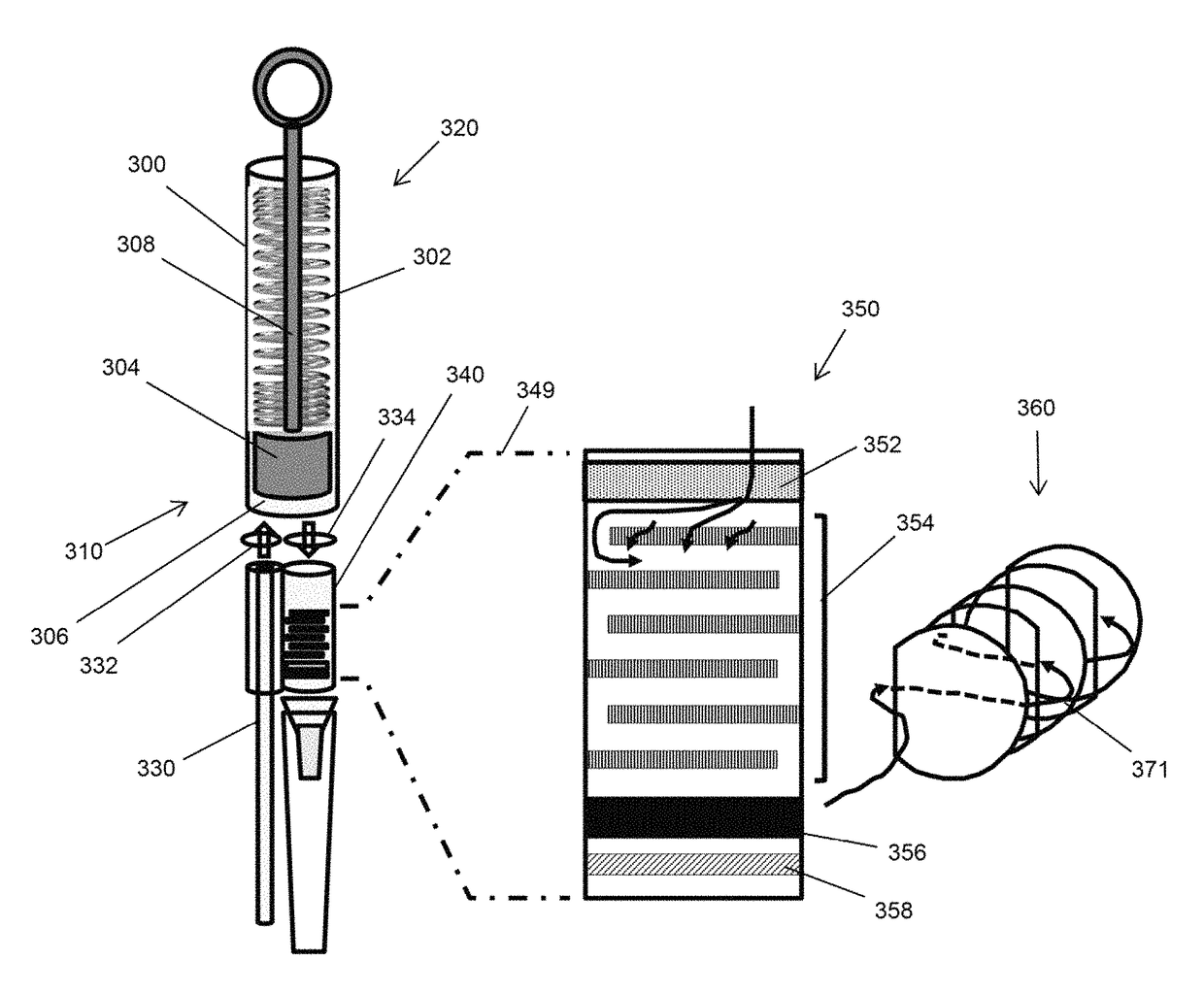
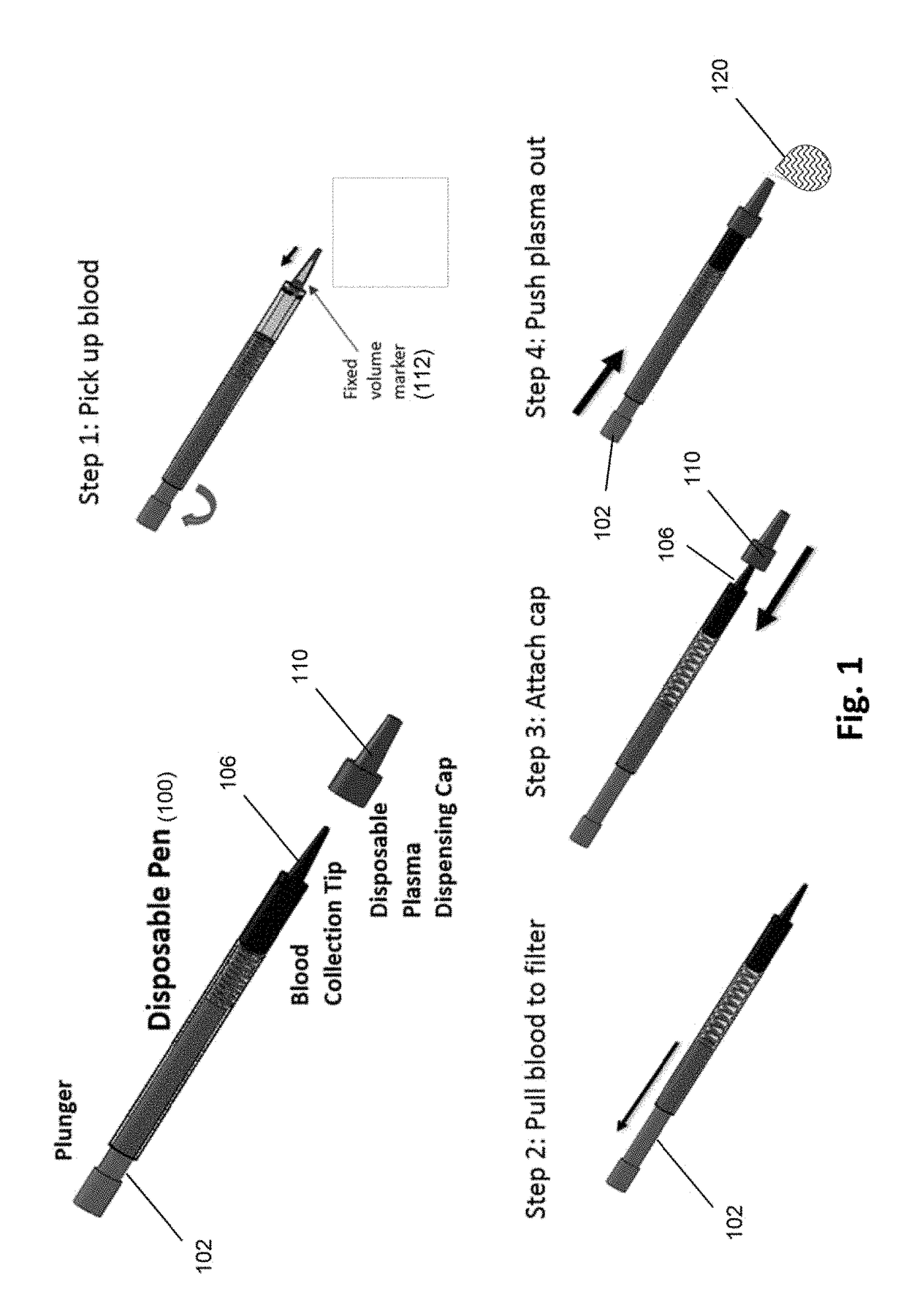
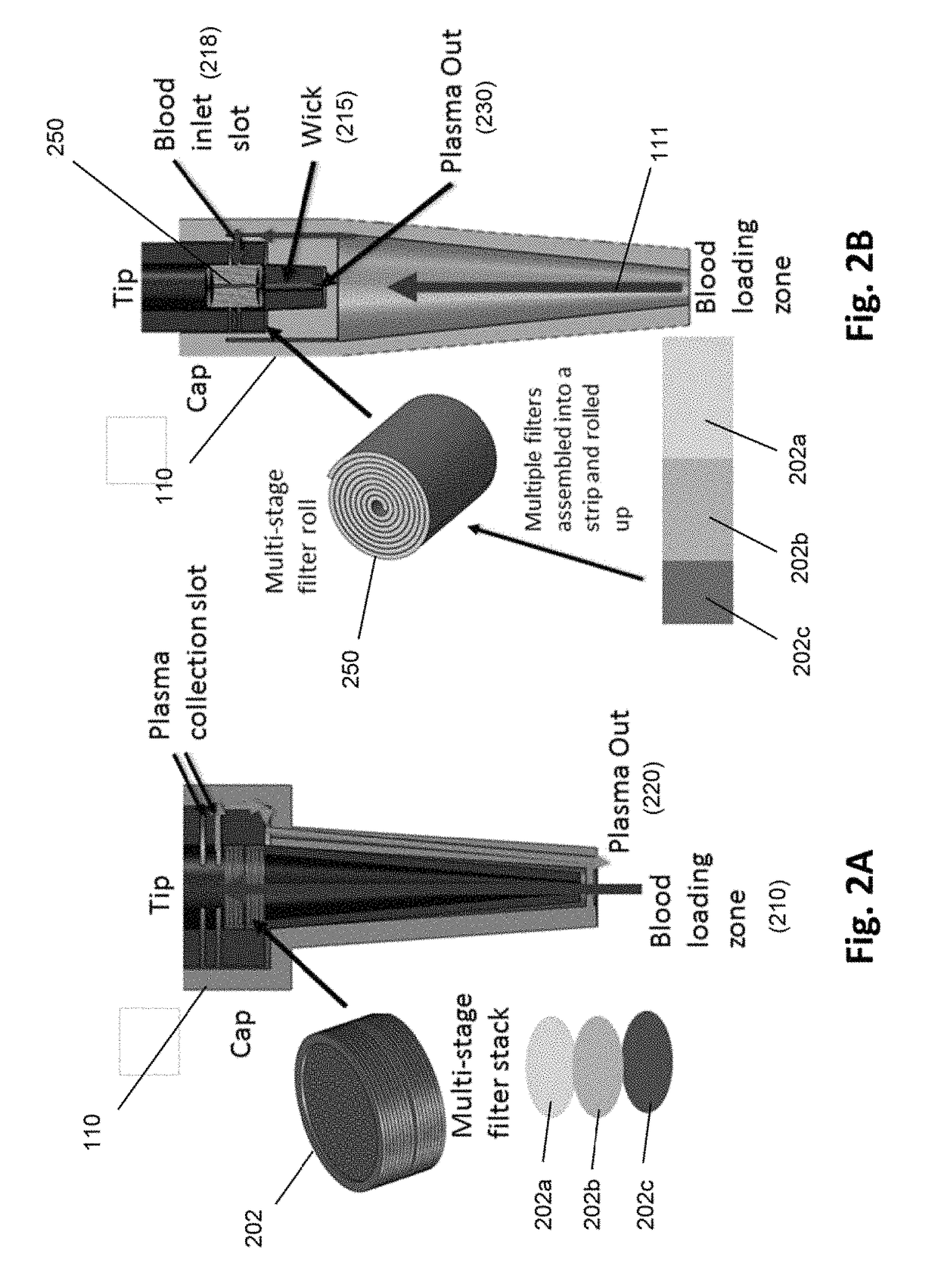
Microscale plasma separator
ActiveUS20170354361A1The solution result is accurateLow costHaemofiltrationPharmaceutical containersPoint of carePlasma iron
The invention is directed to methods and devices for efficient separation of plasma irons whole blood which are suitable for point of care use in resource poor environments, in some embodiments, elements of such devices comprise (a) a sample collection receptacle (SCR) with at least one port, the sample collection receptacle capable of holding a predetermined volume of a sample of undiluted whole blood drawn through a port; (b) a filter chamber having an inlet and an outlet, and containing at least one filter capable of separating plasma from blood cells as sample passes from an inlet side to an outlet side of the at least one filter whenever the filter chamber is placed in Quid communication with a port of the sample collection receptacle; and (c) a manually driven pump operationally associated with the SCR and filter chamber for (i) drawing a predetermined volume of sample into ore SCR by a first user action and (ii) driving the predetermined volume at a substantially constant linear flow under a pressure not exceeding 2 psi from the SCR through the filter chamber and the outlet of the filter chamber by a second user action.
Owner:WAINAMICS INC
Sensor technology for diagnosing tuberculosis
ActiveUS10168315B2Enhanced sensitivity and selectivityFast and reliable diagnosisDisease diagnosisRespiratory organ evaluationMedicineNanoparticle
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
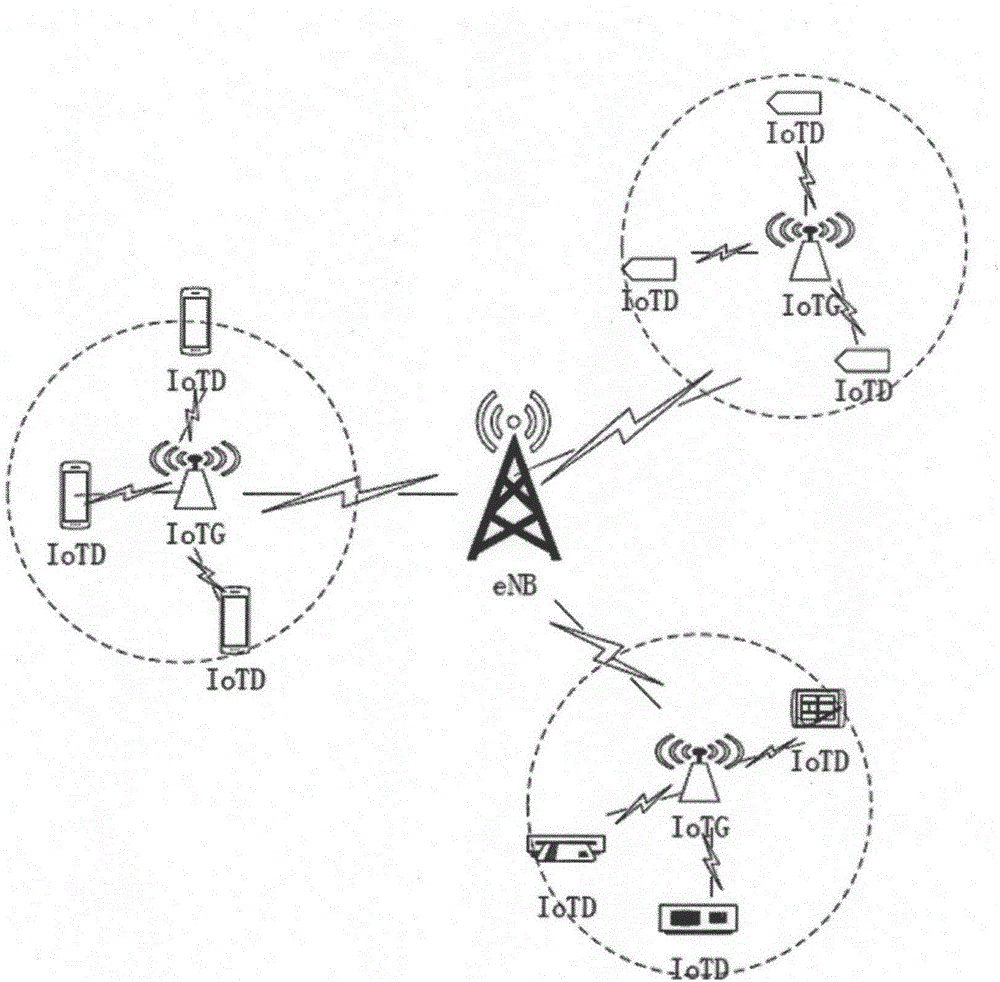
LTE technology-based resource allocation method for uplink of internet of things
The invention relates to an LTE technology-based resource allocation method for the uplink of an internet of things. The invention provides a solution for realizing the internet of things based on the LTE technology and also provides an allocation method for uplink resources based on QoS. In the resource-poor condition, resources are allocated to delay-sensitive users preferentially, so that the bandwidth requirements of the above users are met. In the resource-rich condition, resources are allocated to users as required according to the actual requirements of the users. On the basis that the QoS is met, the resource utilization rate of the system is maximized.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
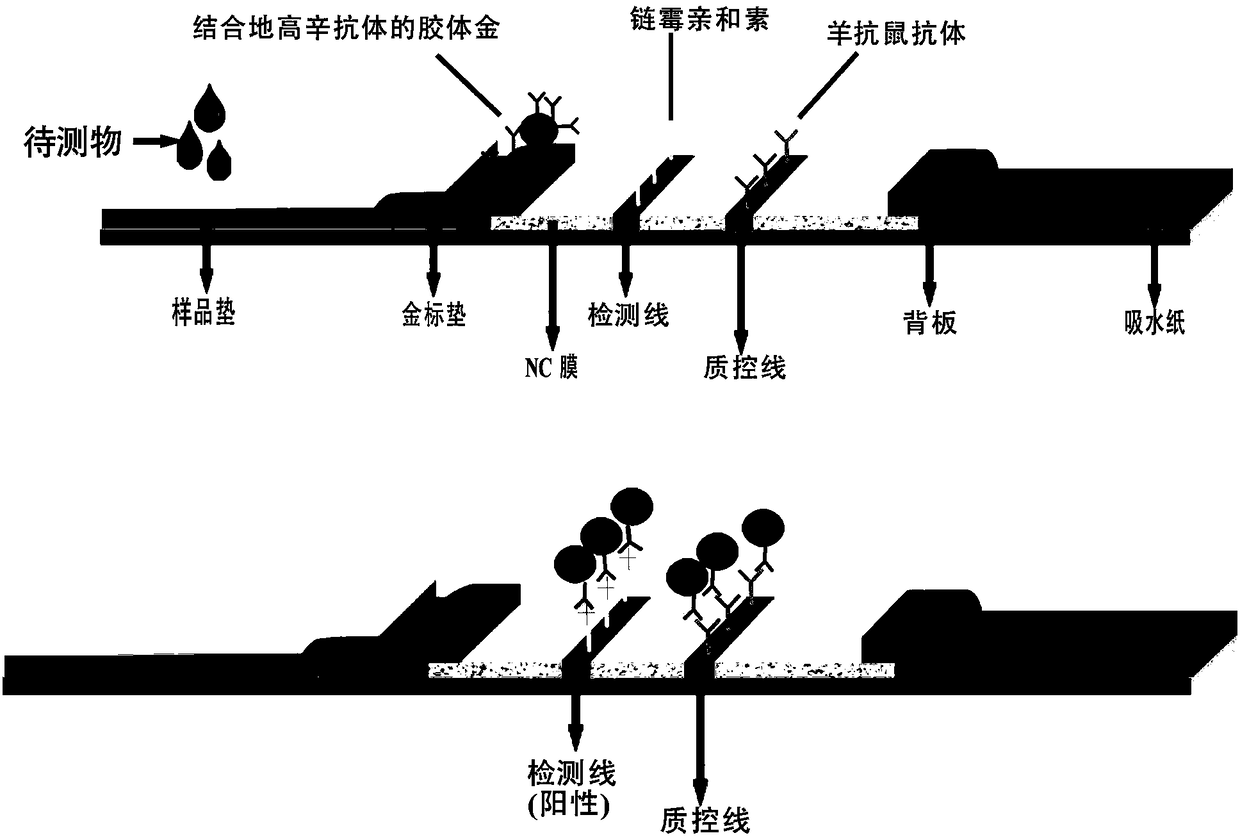
Method and application for detecting listeria monocytogene by combining isothermal amplification of recombinase polymerase and test strip
InactiveCN108148894AEnsure safetyStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisPolymerase LColloid
The invention discloses a method for detecting listeria monocytogene by combining isothermal amplification of recombinase polymerase and a test strip. The method comprises the following steps: selecting an hlyA gene as a detection target gene, designing a primer pair having specificity for the listeria monocytogene, adopting the listeria monocytogene genome DNA as a template, performing the specific isothermal amplification, and obtaining a detection result by utilizing a colloid gold test strip. The method is rapid, simple, high in specificity, high in sensitivity and high in repetition; by adopting the method, the isothermal amplification only needs 10 minutes at 39 DEG C; the detection result of the colloid gold test strip can be made within 5 minutes, the detection result can be observed by eyes, the entire reaction process does not need the expensive experiment instrument and only needs on isothermal instrument, and the method can be applied to the remote regions, the resource-poor regions and the on-site detection. The method is expected to become a simple conventional detection means and has important significance for ensuring the food security.
Owner:中科智测(天津)科技有限公司
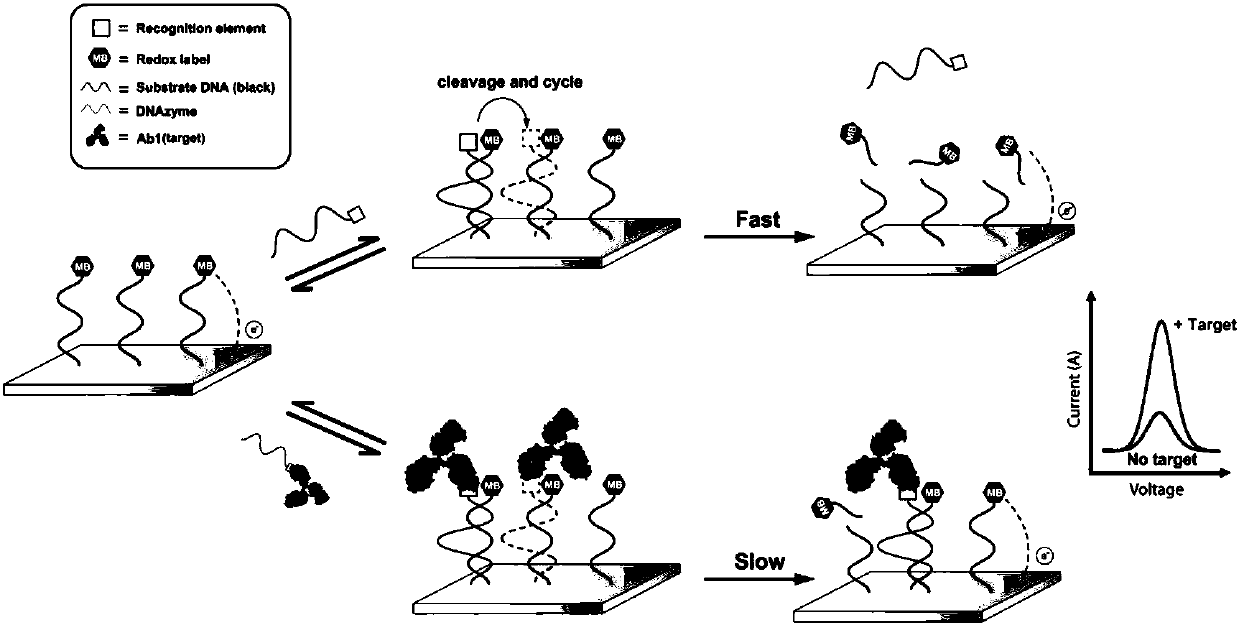
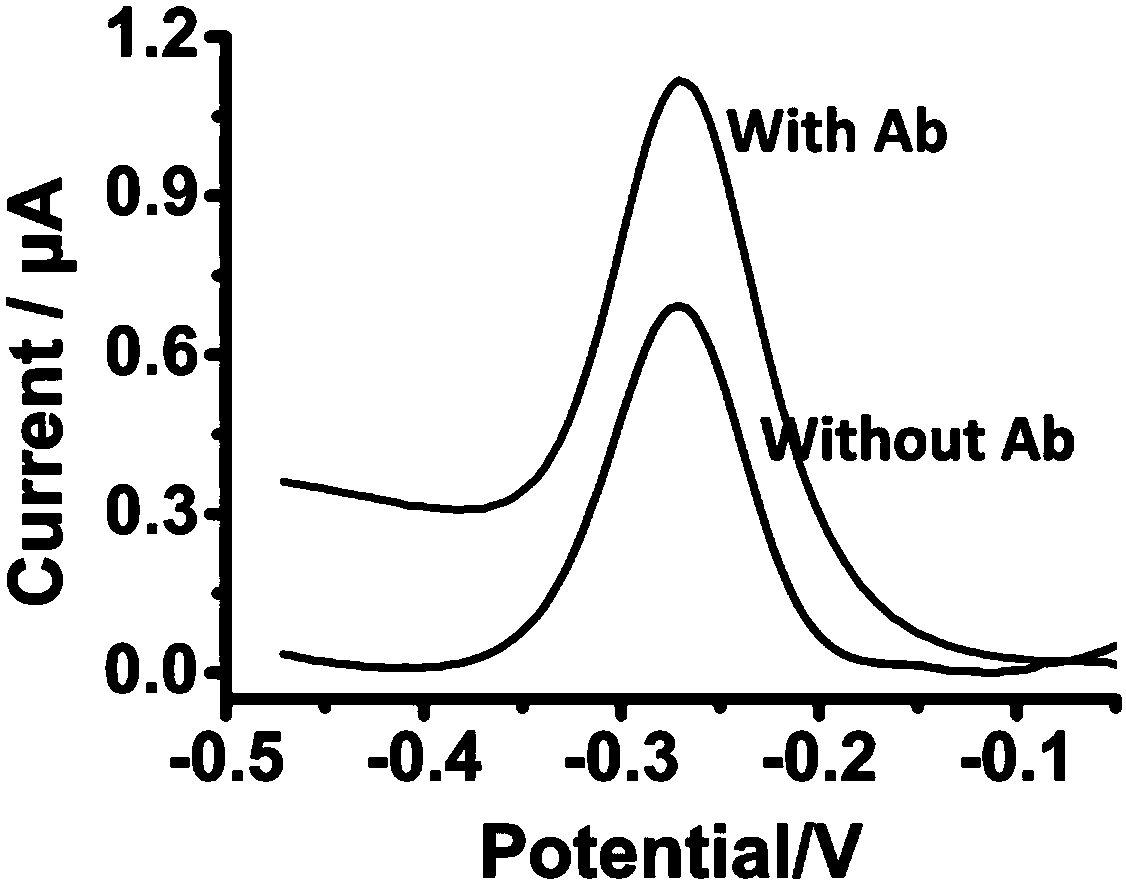
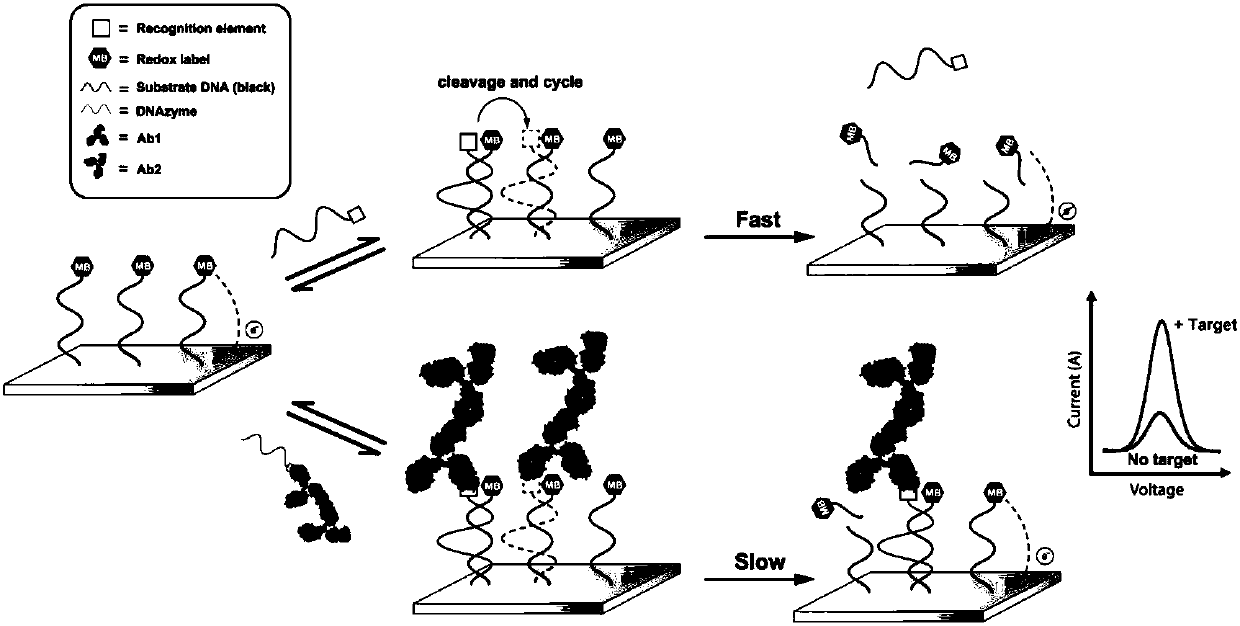
Dynamic sandwich structure-based electrochemical sensor, and making method and application thereof
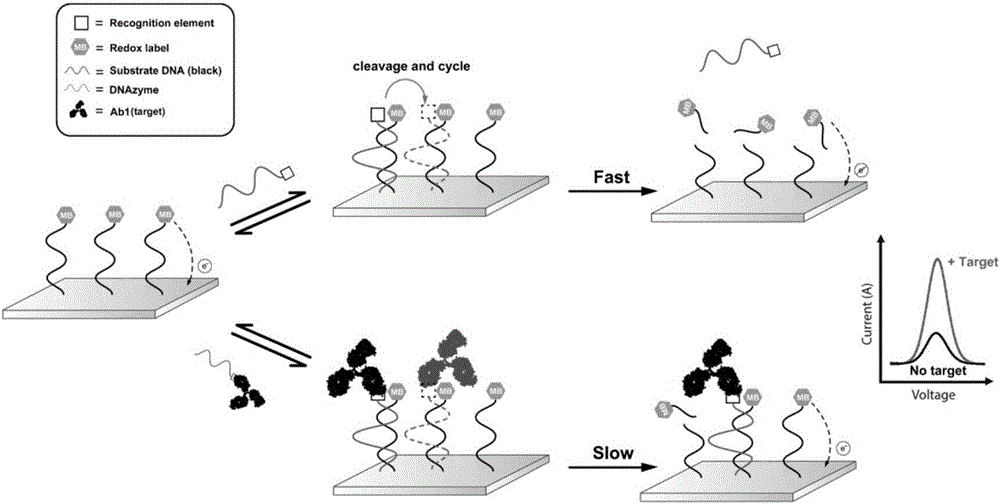
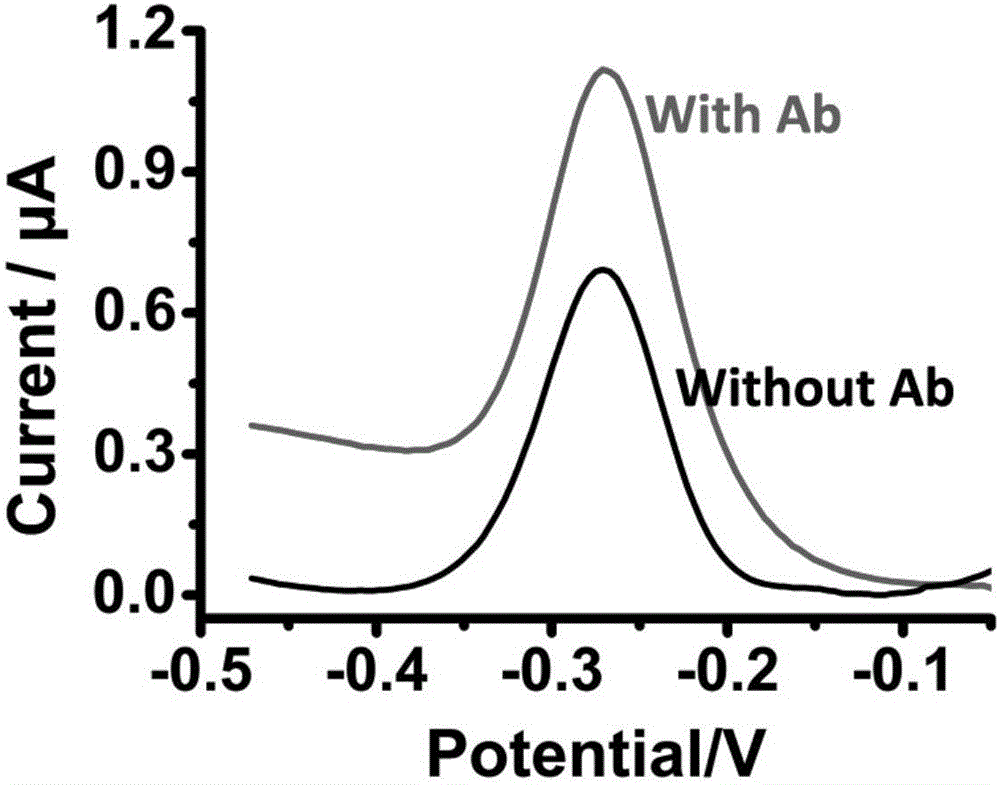
ActiveCN105911289AAchieve buffHigh selectivityBiological testingMaterial electrochemical variablesProtein targetElectrochemical biosensor
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioelectrochemistry, and concretely relates to a dynamic sandwich structure-based electrochemical sensor, and a making method and an application thereof. The electrochemical sensor is composed of an electrode, a signal chain and a reaction system, the electrode adopts a gold electrode, the signal chain is a segment of single-stranded DNA, the 5' end of the DNA chain is modified with a mercapto group, the 3' end of the DNA chain is modified with methylene blue, the mercapto group and the surface of the gold electrode are self-assembled to form a gold-mercapto bond standing on the surface of the gold electrode, the reaction system contains DNAzyme and a necessary reaction buffer system, the DNAzyme can be complemented and paired to the signal chain and cuts the signal chain into two segments of DNA short strands, and the DNAzyme is marked with a target protein identification element, and can be used for quantitatively detecting proteins and interaction among the proteins. The electrochemical sensor is simple to operate, can be operated by operators without special training, and is suitable for being used in remote regions and resource-poor regions.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Methods and algorithms for cell enumeration in a low-cost cytometer
InactiveUS8189899B2Low costFunction increaseCharacter and pattern recognitionMaterial analysisWhite blood cellCcd camera
The enumeration of cells in fluids by flow cytometry is widely used across many disciplines such as assessment of leukocyte subsets in different bodily fluids or of bacterial contamination in environmental samples, food products and bodily fluids. For many applications the cost, size and complexity of the instruments prevents wider use, for example, CD4 analysis in HIV monitoring in resource-poor countries. The novel device, methods and algorithms disclosed herein largely overcome these limitations. Briefly, all cells in a biological sample are fluorescently labeled, but only the target cells are also magnetically labeled. In addition, non-magnetically labeled cells are imaged for viability in a modified slide configuration. The labeled sample, in a chamber or cuvet, is placed between two wedge-shaped magnets to selectively move the magnetically labeled cells to the observation surface of the cuvet. An LED illuminates the cells and a CCD camera captures the images of the fluorescent light emitted by the target cells. Image analysis performed with a novel algorithm provides a count of the cells on the surface that can be related to the target cell concentration of the original sample. The compact cytometer system provides a rugged, affordable and easy-to-use technique, which can be used in remote locations.
Owner:VERIDEX LCC
Simple and affordable method for immunophenotyping using a microfluidic chip sample preparation with image cytometry
ActiveUS9442106B2Simpler and cheap and robustIntuitive imagePreparing sample for investigationBiological particle analysisPoint of careFluorescence
The system includes a simple system for CD4 and CD8 counting in point-of-care HIV staging within resource poor countries. Unlike previous approaches, no sample preparation is required with the sample added directly to a chip containing dried reagents by capillary flow. A large area image cytometer consisting of an LED module is used to excite the fluorochromes PerCP and APC labeled targets and a monochrome CCD camera with a combination of two macro lenses captures images of 40 mm2 of blood (approximately 1 micro liter). CD4 and CD8-T-lymphocyte counts correlate well with those obtained by flow cytometry. The cytometer system described in the present invention provides an affordable and easy-to-use technique for use in remote locations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TWENTE
Microscale plasma separator
ActiveUS10105083B1Efficient removalSimplifying and accelerating useHaemofiltrationPharmaceutical containersPoint of careEngineering
The invention is directed to methods and devices for efficient separation of plasma from whole blood which are suitable for point of care use in resource poor environments. In some embodiments, elements of such devices comprise (a) a sample collection receptacle (SCR) with at least one port, the sample collection receptacle capable of holding a predetermined volume of a sample of undiluted whole blood drawn through a port; (b) a filter chamber having an inlet and an outlet, and containing at least one filter capable of separating plasma from blood cells as sample passes from an inlet side to an outlet side of the at least one filter whenever the filter chamber is placed in fluid communication with a port of the sample collection receptacle; and (c) a manually driven pump operationally associated with the SCR and filter chamber for (i) drawing a predetermined volume of sample into the SCR by a first user action and (ii) driving the predetermined volume at a substantially constant linear flow under a pressure not exceeding 2 psi from the SCR through the filter chamber and the outlet of the filter chamber by a second user action.
Owner:WAINAMICS INC
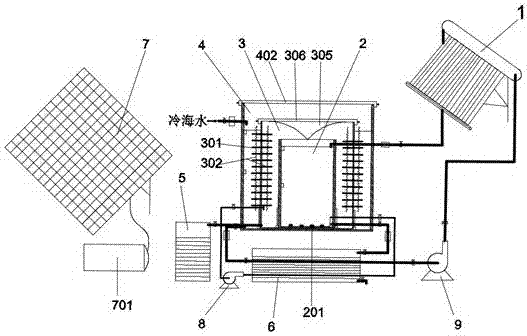
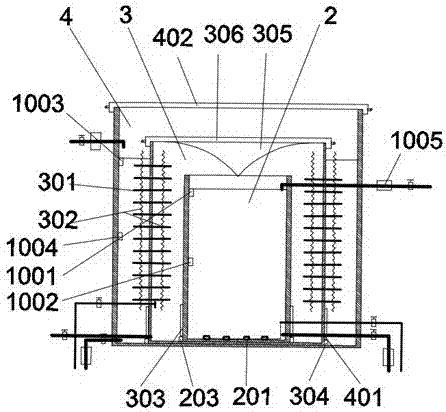
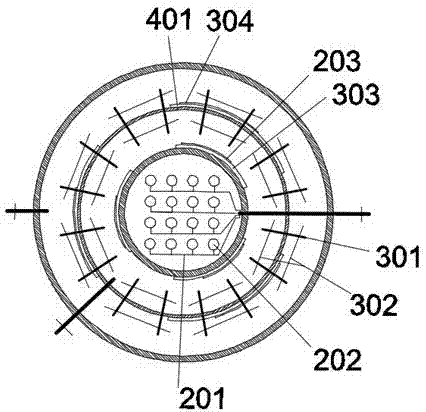
Sleeve type bubbling-humidifying seawater desalinating device
PendingCN107344739AEasy to disassembleEasy to installGeneral water supply conservationSeawater treatmentSeawaterResource poor
The invention discloses a sleeve type bubbling-humidifying seawater desalinating device. The device comprises a solar heat collector, a bubbling evaporation cylinder, bubblers, a condensing cylinder, hot pipes, corrugated heat conducting plates, a seawater cooling cylinder, a fresh-water tank, a concentrated seawater heat exchange slot, a solar photovoltaic panel, a storage battery, an air pump, a water pump and an automatic water changing system, wherein the bubbling evaporation cylinder, the condensing cylinder and the seawater cooling cylinder form a sleeve structure from inside to outside; the solar heat collector is connected to the bubbling evaporation cylinder through a pipeline; the hot pipes and the corrugated heat conducting plates are arranged on the wall of the condensing cylinder; and the bubblers are mounted at the bottom of the bubbling evaporation cylinder. According to the sleeve type bubbling-humidifying seawater desalinating device, solar energy is utilized for supplying heat and power, and bubbling humidification and dehumidification principles are adopted, so that the device is compact in structure, high in energy utilization rate, can be used for acquiring fresh water from seawater and has very important significance to the fresh water production for fresh water resource poor regions such as islands.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for making fuels by utilizing fermentation of waste cotton clothes
The invention discloses a method for making fuels by utilizing fermentation of waste cotton clothes, and belongs to the technical field of resource regeneration. The method comprises six steps of pretreatment, acidification, hydrolysis and saccharification, filtration, neutralization and fermentation. The used raw materials are waste cotton clothes, so that the handling problem of the waste cotton clothes is solved, and the produced alcohol serving as a cleaning fuel has an extremely high application value and an economic benefit in the resource-poor and energy-scarcity modern society.
Owner:民勤县家兴节能服务有限公司
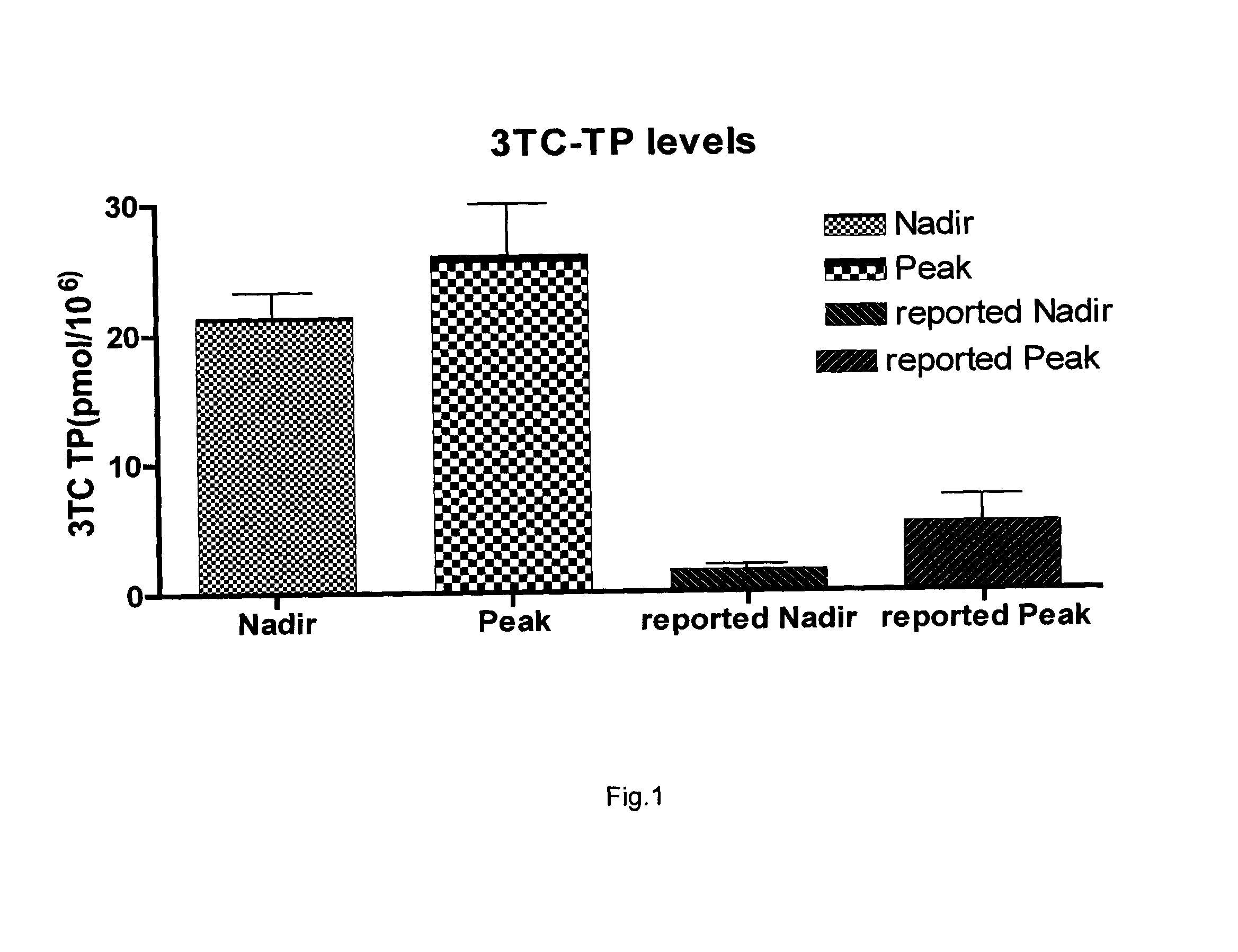
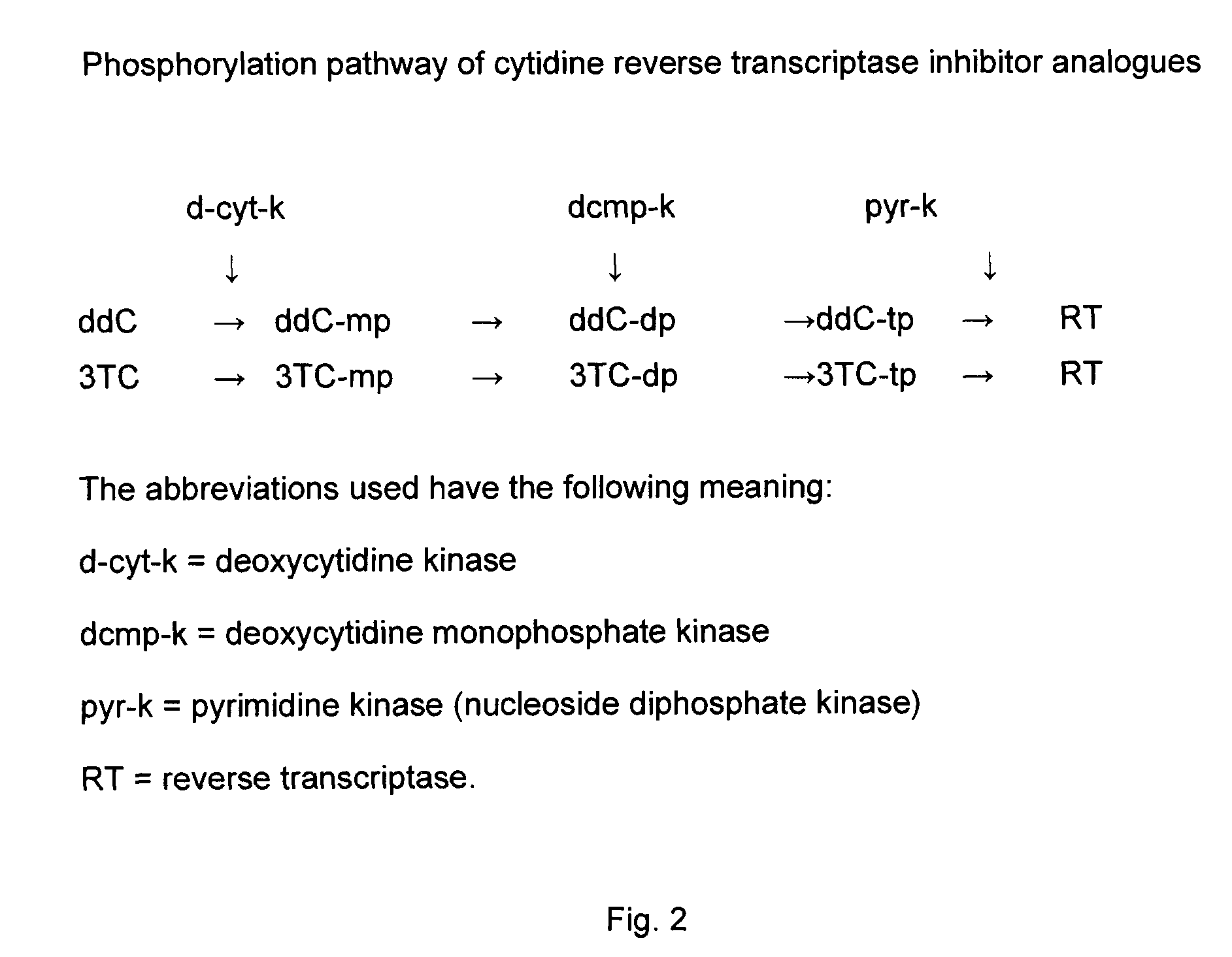
Zalcitabine (Ddc) Boosted Lamivudine (3Tc) Compositions for Antiretroviral Therapy
ActiveUS20080214590A1High activityImprovement of TC antiretroviral activityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideTolerabilitySide effect
Boosted cytidine analogue reverse transcriptase inhibitor antiretroviral compound is a new therapeutic anti HIV option, in combination with another drug such as a NRTI or a protease inhibitor. It's heightened and sustained antiretroviral potency is due to the increased intracellular level of 3TC triphosphate, the active form of 3TC. This effect is obtained by combining 3TC, in usual doses, with a reduced dose of ddC, in the same pharmaceutical formulation. The product could be administered twice or even once daily, which is convenient, and does not increase the pill burden for the patient. The reduced ddC dosage prevents the occurrence of ddC related side effects. Other cytidine derivatives (racemic or negative enantiomers) could have the same effects as ddC and could probably be combined with 3TC, and have the same effect. On the other hand, low dose ddC may also increase the intracellular levels of other cytidine derivatives as it does for 3TC. Boosted cytidine analogue reverse transcriptase inhibitor antiretroviral compound could also be formulated in combination with another drug such as another NRTI (e.g. abacavir) or any protease inhibitor in the same capsule or tablet. This approach offers a dual anti-HIV therapy that is as efficacious as the routine triple therapy. In this way the HIV treatment cost could be significantly reduced which is imperative for resource-poor settings. This new formulation is convenient and well tolerated with no additional toxicity than that of the combining drug (NRTI or protease inhibitor) and 3TC. Moreover, this will enable a larger number of patients to benefit from the already known 3TC effects. It will also increase the 3TC effects in those organs or HIV sanctuaries with usually reduced 3TC concentrations or activity. It could be indicated in both the initial as well as in salvage HIV therapy. It could also be used for therapy optimization or simplification. Moreover, in combination with another NRTI such as abacavir, or even alone, it could be beneficial for reducing the HIV harm in resource-poor settings.
Owner:TOMA EMIL
Simple and affordable method for immuophenotyping using a microfluidic chip sample preparation with image cytometry
ActiveUS20180031554A1Simple methodCheap componentBiological material analysisPoint of careFluorescence
The system includes a simple system for CD4 and CD8 counting in point-of-care HIV staging within resource poor countries. Unlike previous approaches, no sample preparation is required with the sample added directly to a chip containing dried reagents by capillary flow. A large area image cytometer consisting of an LED module is used to excite the fluorochromes PerCP and APC labeled targets and a monochrome CCD camera with a combination of two macro lenses captures images of 40 mm2 of blood (approximately 1 microliter). CD4 and CD8-T-lymphocyte counts correlate well with those obtained by flow cytometry. The cytometer system described in the present invention provides an affordable and easy-to-use technique for use in remote locations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TWENTE
Disease Management System
InactiveUS20110213623A1Drug and medicationsComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionDiseaseData interpretation
A comprehensive disease management system providing advanced diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic capabilities to healthcare workers located in remote, rural and resource-poor urban centers is disclosed. Additionally, a method of managing disease in a patient located remotely relative to interpretation and therapeutic dispensing services is provided including methods of data collection, data interpretation and therapeutic dispensing. An algorithm is disclosed to provide non-physician healthcare workers in remote, rural and resource-poor urban centers to manage disease in patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease.
Owner:DISEASE MANAGEMENT SERVICES
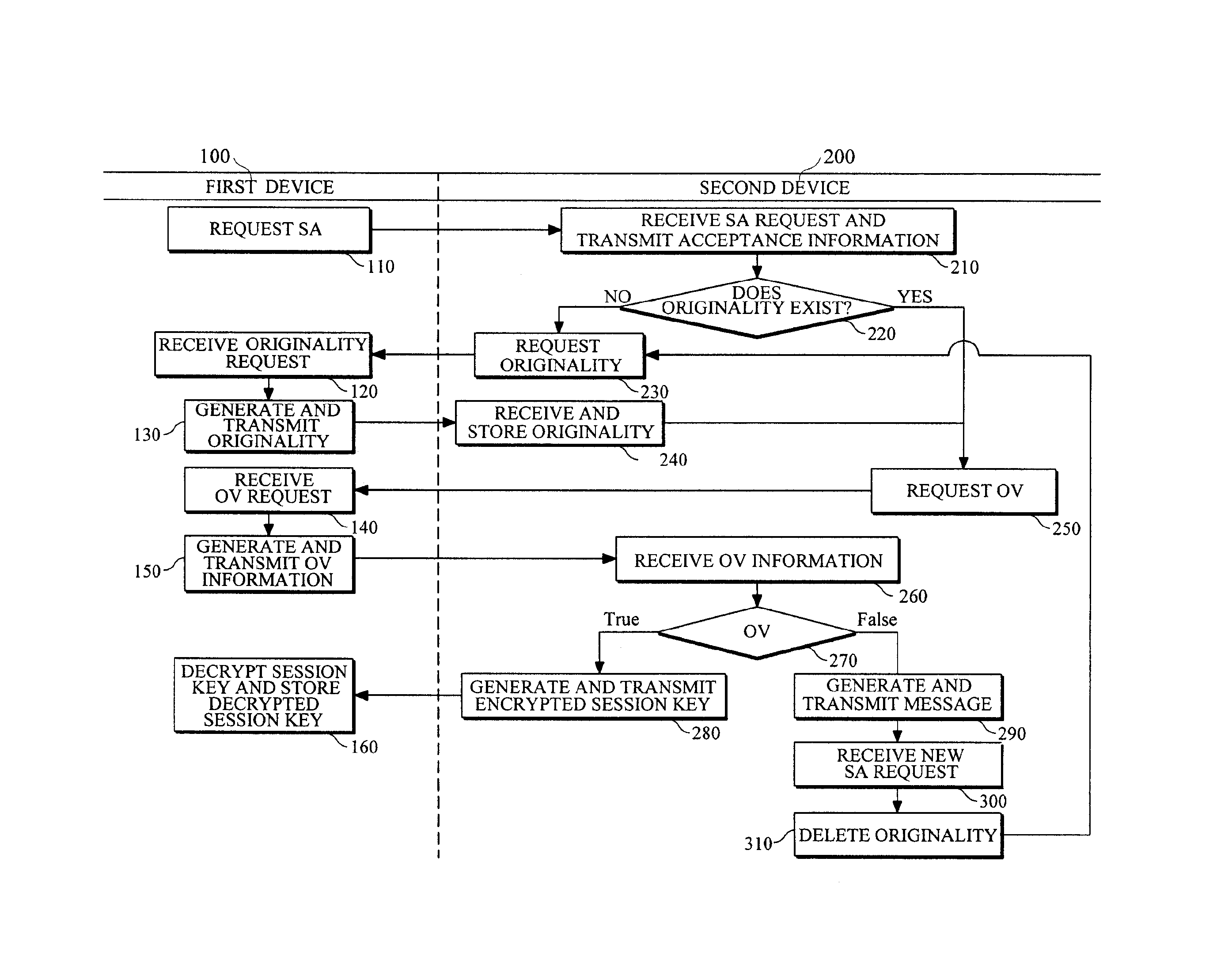
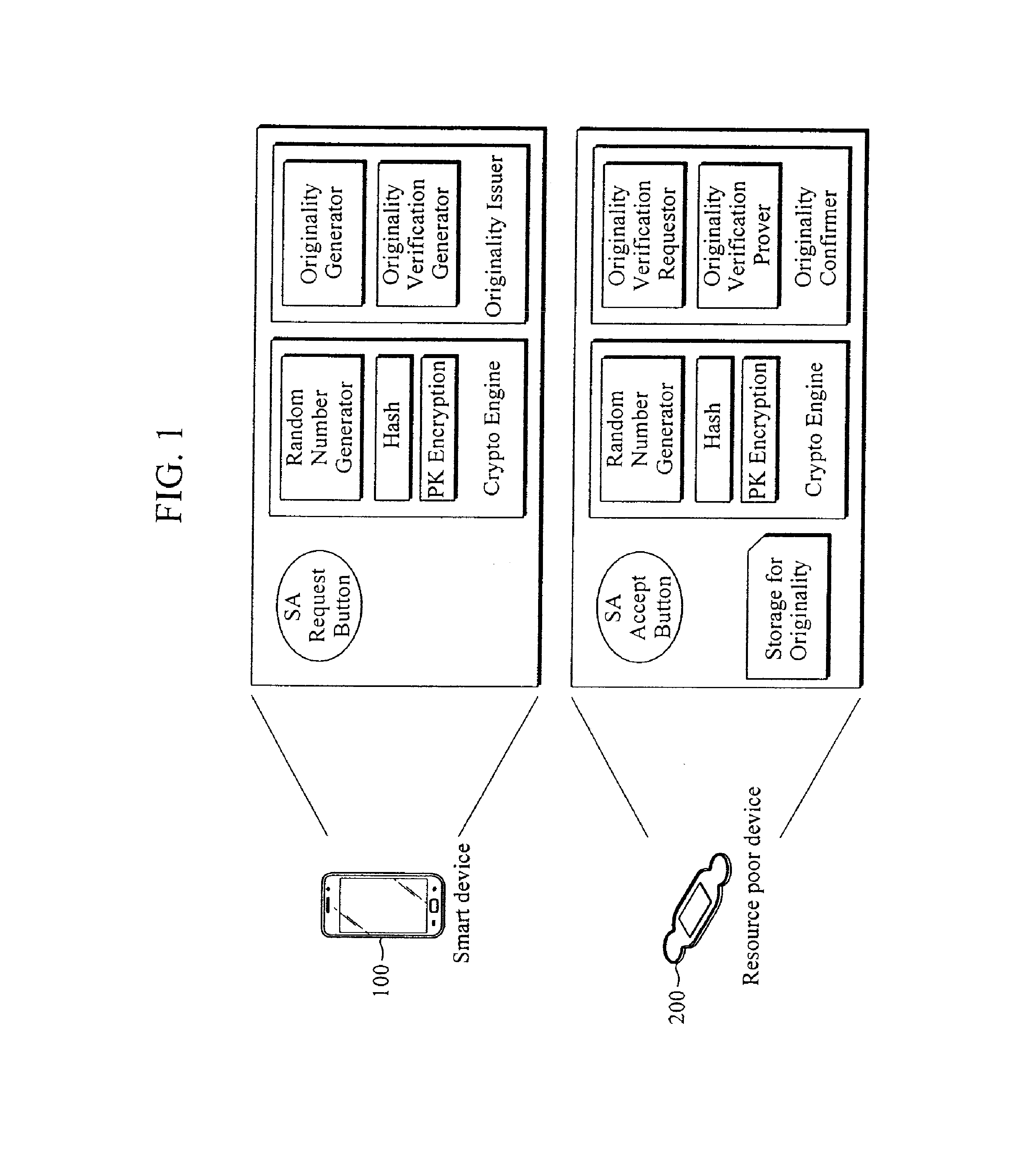
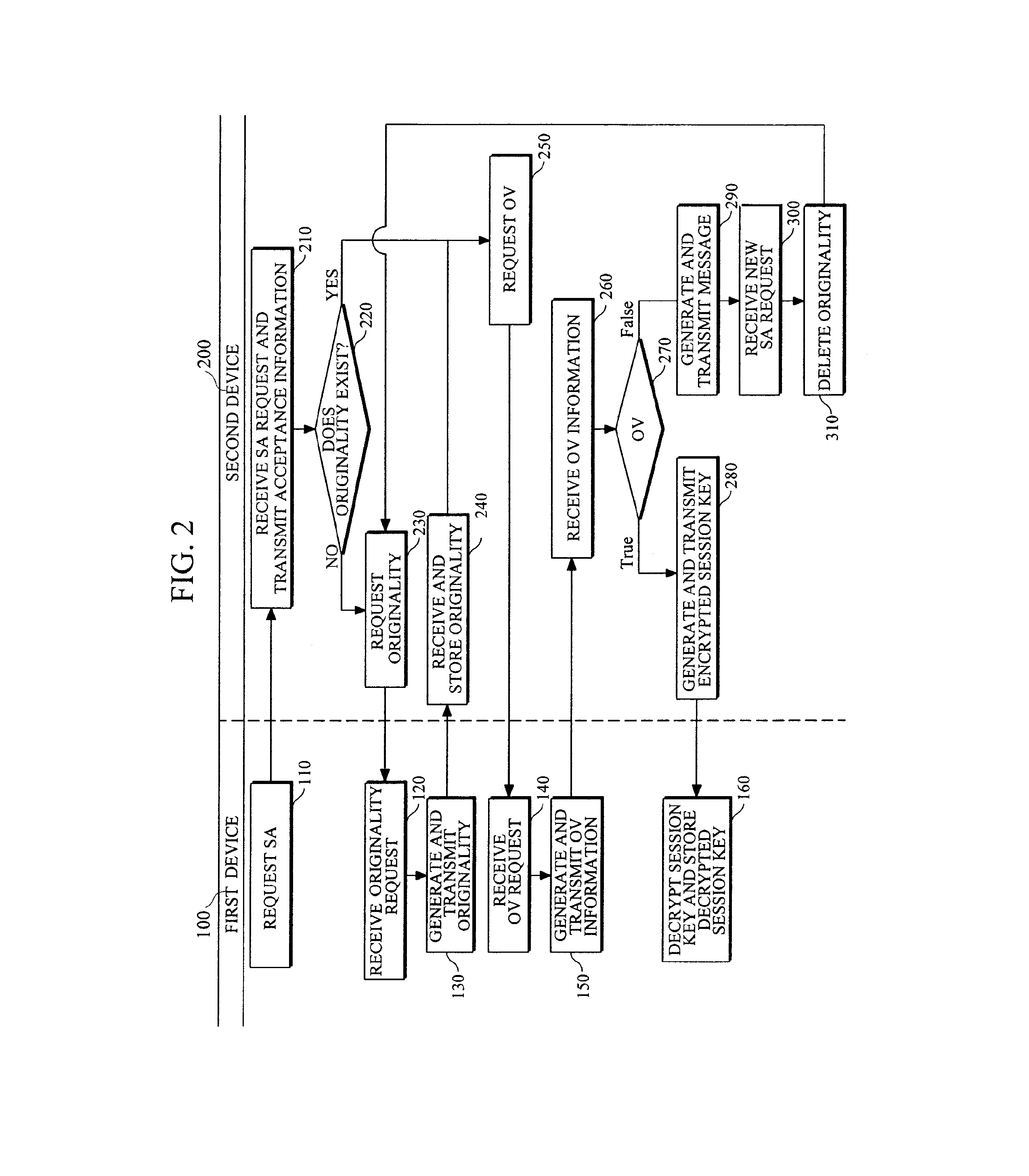
Method and devices for security association (SA) between devices
InactiveUS20130074152A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsPrivate networkSecurity association
In one aspect, there is provided a method and apparatus for security association (SA) upon communication between devices. When a mobile device is connected to another mobile device without subscribing to a specific service or a private network, SA may be established. For example, the SA may be used for resource saving and secure connections of resource poor devices (for example, a medical patch) having a relatively poor resource, such as insufficient battery power or computing power.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
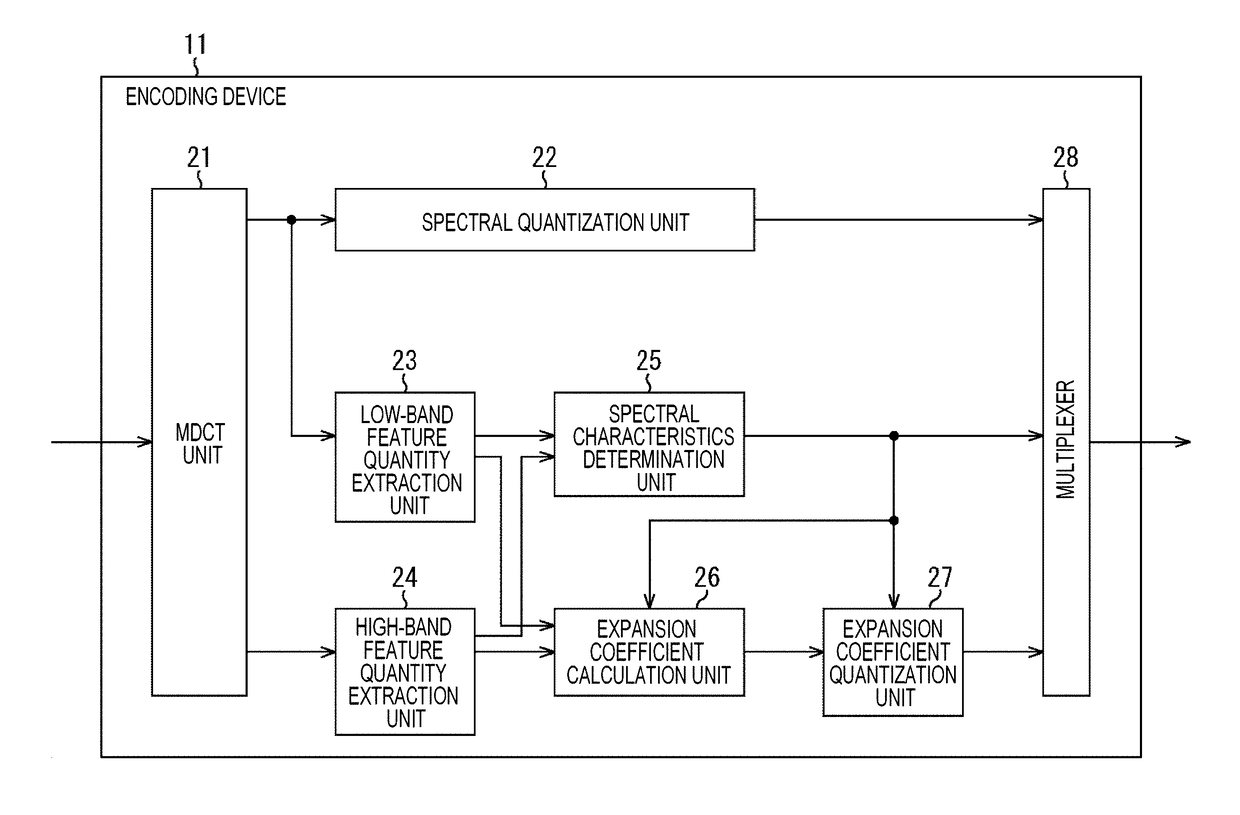
Encoding device and method, decoding device and method, and program
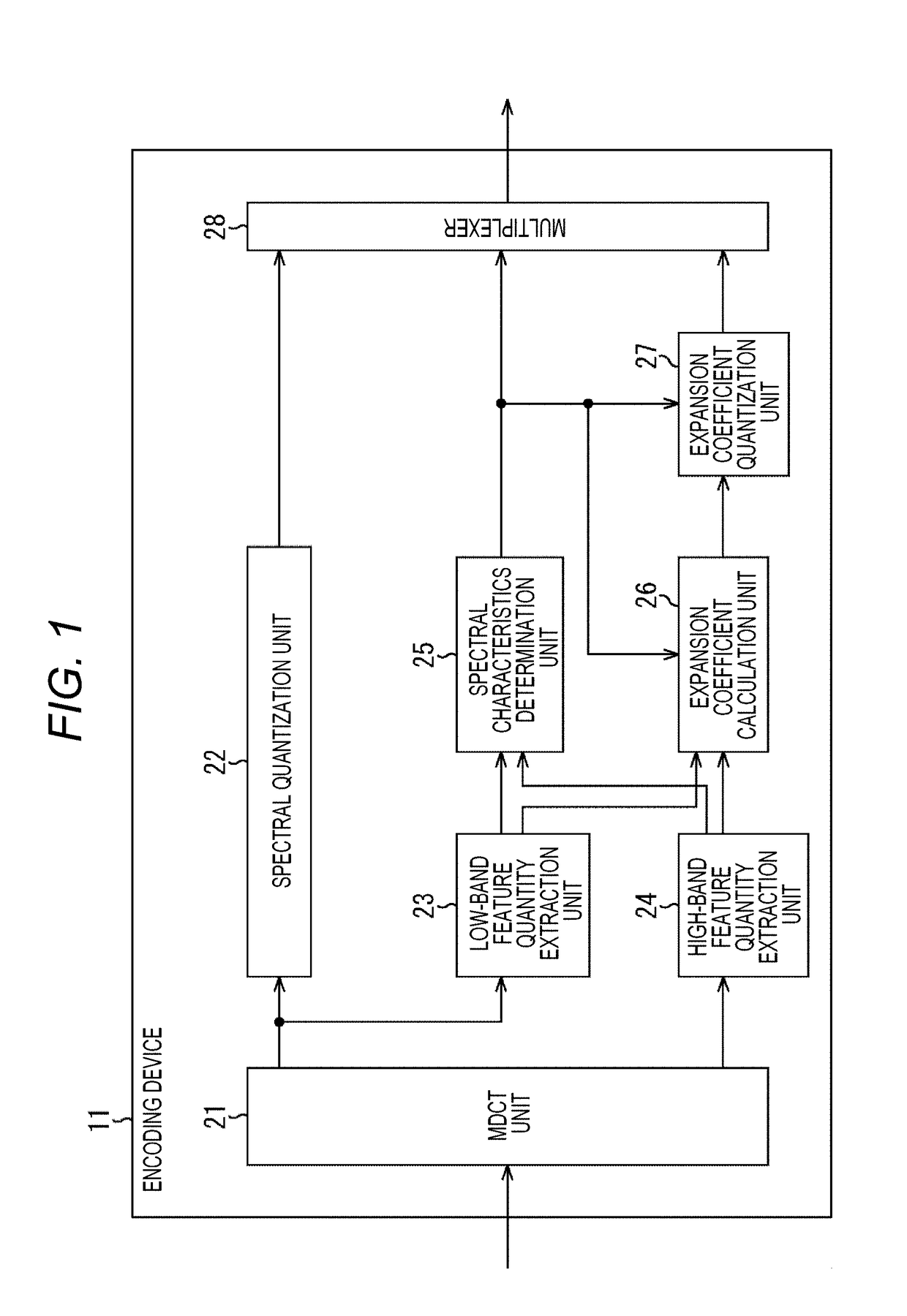
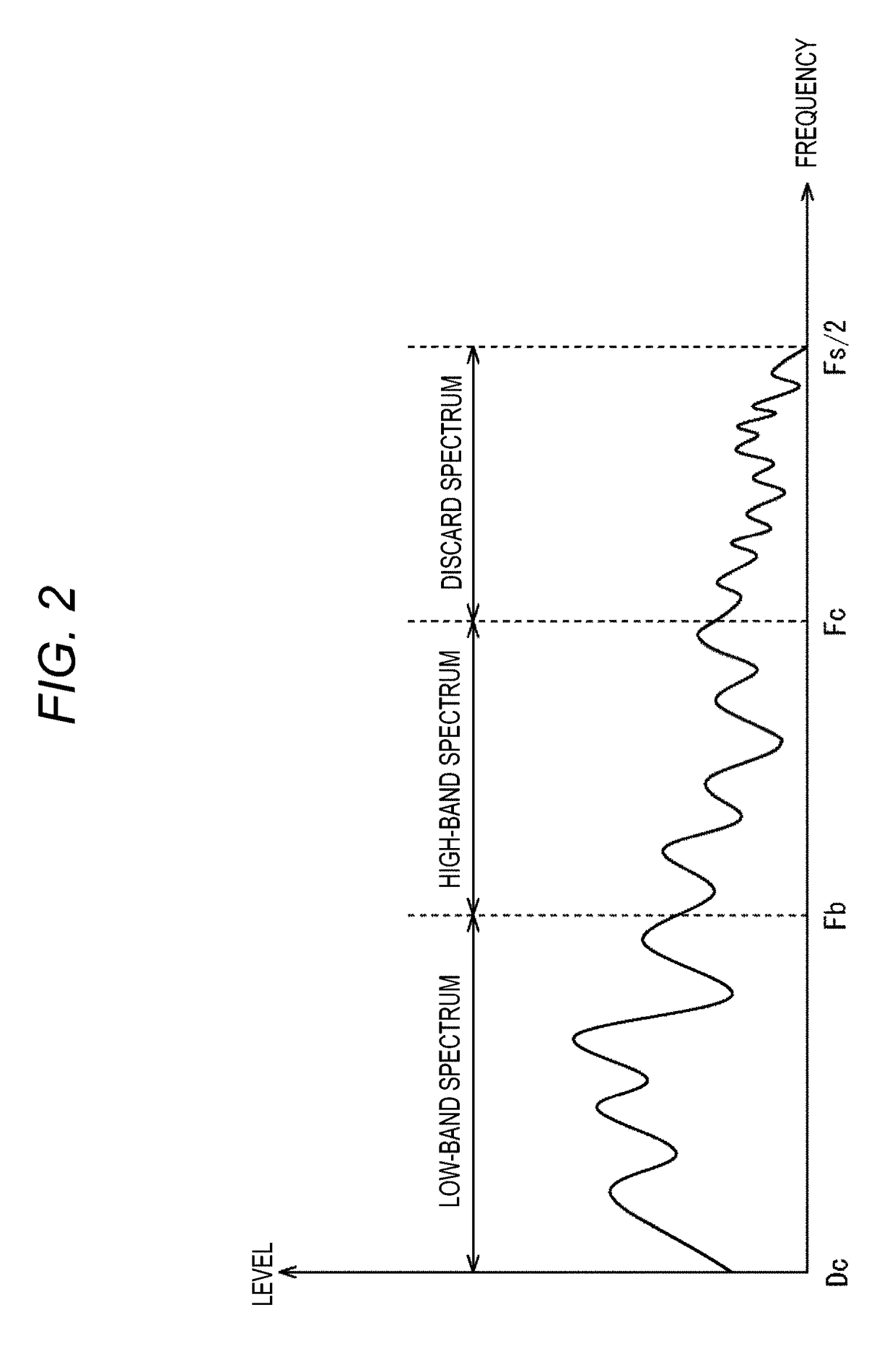
ActiveUS20170270940A1High-quality soundSpeech analysisCode conversionBand spectrumFrequency spectrum
The present technology relates to an encoding device and a method, a decoding device and a method, and a program that enables acquisitions of high-quality sound even in a resource-poor setting.A demultiplexer demultiplexes a supplied code string, to obtain the quantized low-band spectrum, the spectral characteristic code, and the quantized expansion coefficient(s). At this point, the code string includes a single quantized expansion coefficient or quantized expansion coefficients of the respective bands in the high band depending on the spectral characteristic code. A spectral inverse quantization unit obtains the low-band spectrum by inversely quantizing the quantized low-band spectrum. An expansion coefficient inverse quantization unit obtains the expansion coefficient(s) by inversely quantizing the quantized expansion coefficient(s). An expanded spectrum generation unit generates an expanded spectrum, in accordance with the low-band spectrum and the expansion coefficient(s) depending on the spectral characteristic code. An IMDCT unit generates a band-expanded time-series signal from the low-band spectrum and the expanded spectrum. The present technology can be applied to decoding devices.
Owner:SONY CORP
An electrochemical sensor based on a dynamic sandwich structure and its preparation and application
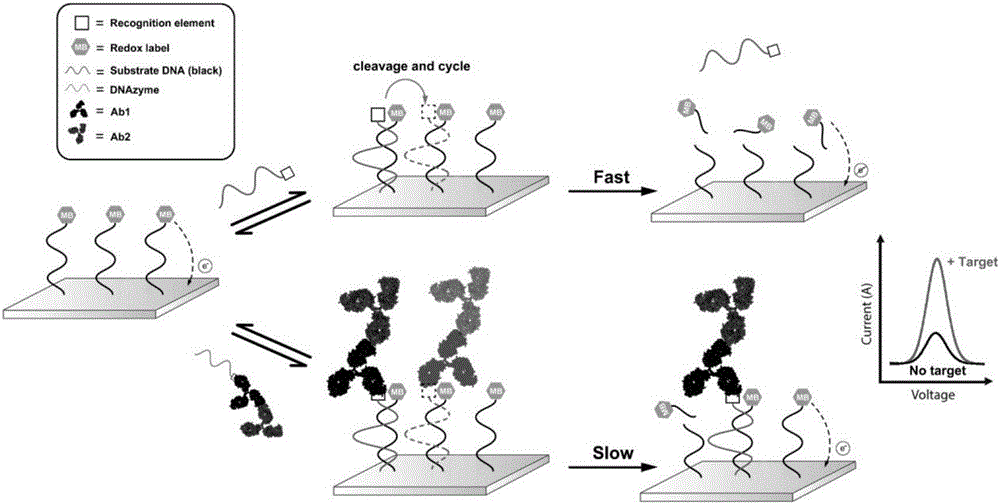
ActiveCN105911289BHigh selectivityEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProtein targetElectrochemical gas sensor
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioelectrochemistry, and concretely relates to a dynamic sandwich structure-based electrochemical sensor, and a making method and an application thereof. The electrochemical sensor is composed of an electrode, a signal chain and a reaction system, the electrode adopts a gold electrode, the signal chain is a segment of single-stranded DNA, the 5' end of the DNA chain is modified with a mercapto group, the 3' end of the DNA chain is modified with methylene blue, the mercapto group and the surface of the gold electrode are self-assembled to form a gold-mercapto bond standing on the surface of the gold electrode, the reaction system contains DNAzyme and a necessary reaction buffer system, the DNAzyme can be complemented and paired to the signal chain and cuts the signal chain into two segments of DNA short strands, and the DNAzyme is marked with a target protein identification element, and can be used for quantitatively detecting proteins and interaction among the proteins. The electrochemical sensor is simple to operate, can be operated by operators without special training, and is suitable for being used in remote regions and resource-poor regions.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for preparing sulfuric acid by roasting power plant desulfurized cinder with fluidized bed roaster
InactiveCN101249955BImprove protectionSolve processing problemsSulfur compoundsEnergy inputAfter treatmentFluidized bed
The invention discloses a process for calcining and preparing sulphuric acid by a fluidized bed furnace for desulfurizing waste residue of power plants. The process takes desulfurized waste residue of the power plants, sulfur and discarded coke dust as raw materials and employs the fluidized bed calcining furnace to initially prepare sulfur dioxide, wherein the obtained sulfur dioxide has the concentration of 8-13%, and then the obtained sulfur dioxide is taken as the raw material to prepare the sulphuric acid by employing the prior art, wherein the obtained sulphuric acid has the concentration of 93-98%. The process not only resolves the problem of after-treatment of the wastes and enables the wastes to be recycled, but also saves pyrite resources poor at home, and the generated economical benefits are quite considerable. And a calcium oxide waste residue is also generated in the process of production, which can be taken as desulfurizer of the power plants to be recycled after cooling treatment. Therefore, the process employed by the invention to prepare the sulphuric acid not only reduces cost for producing the sulphuric acid, but also reduces cost of thermal power plants.
Owner:李德安
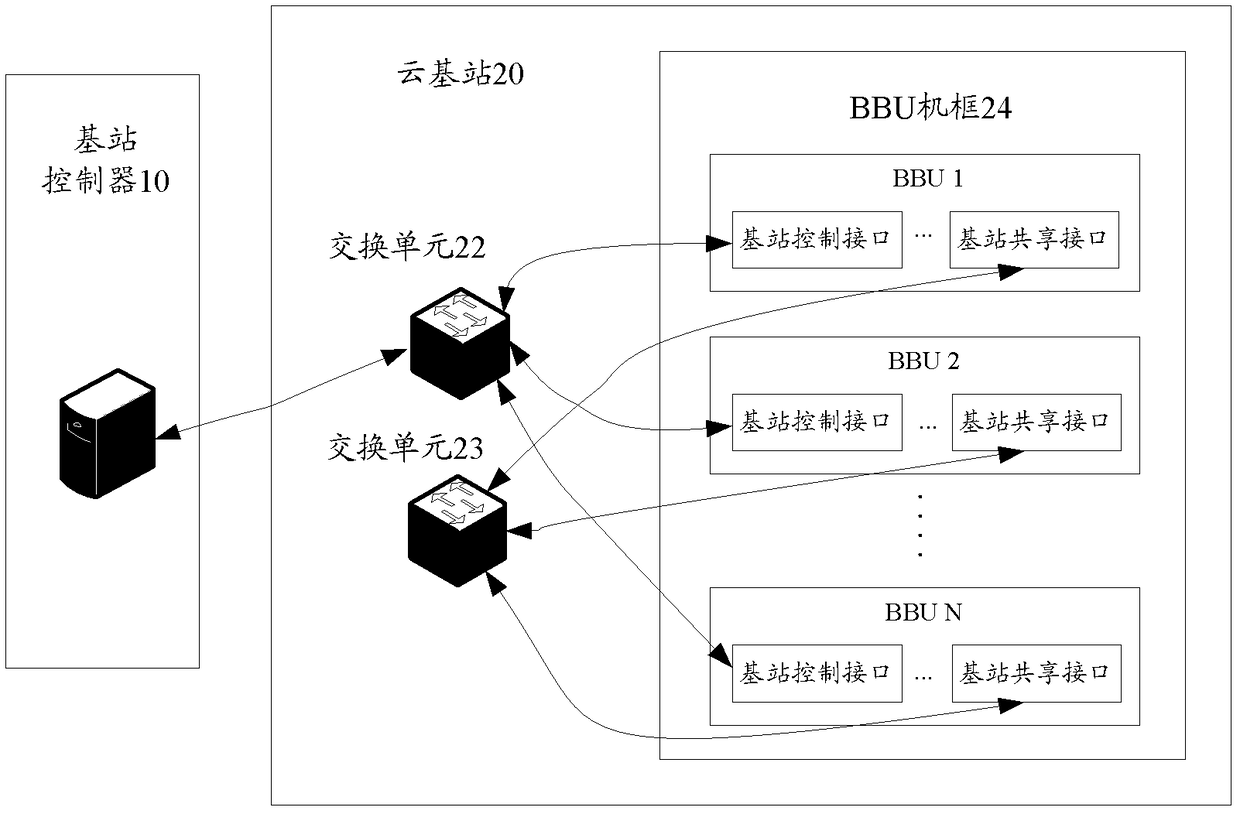
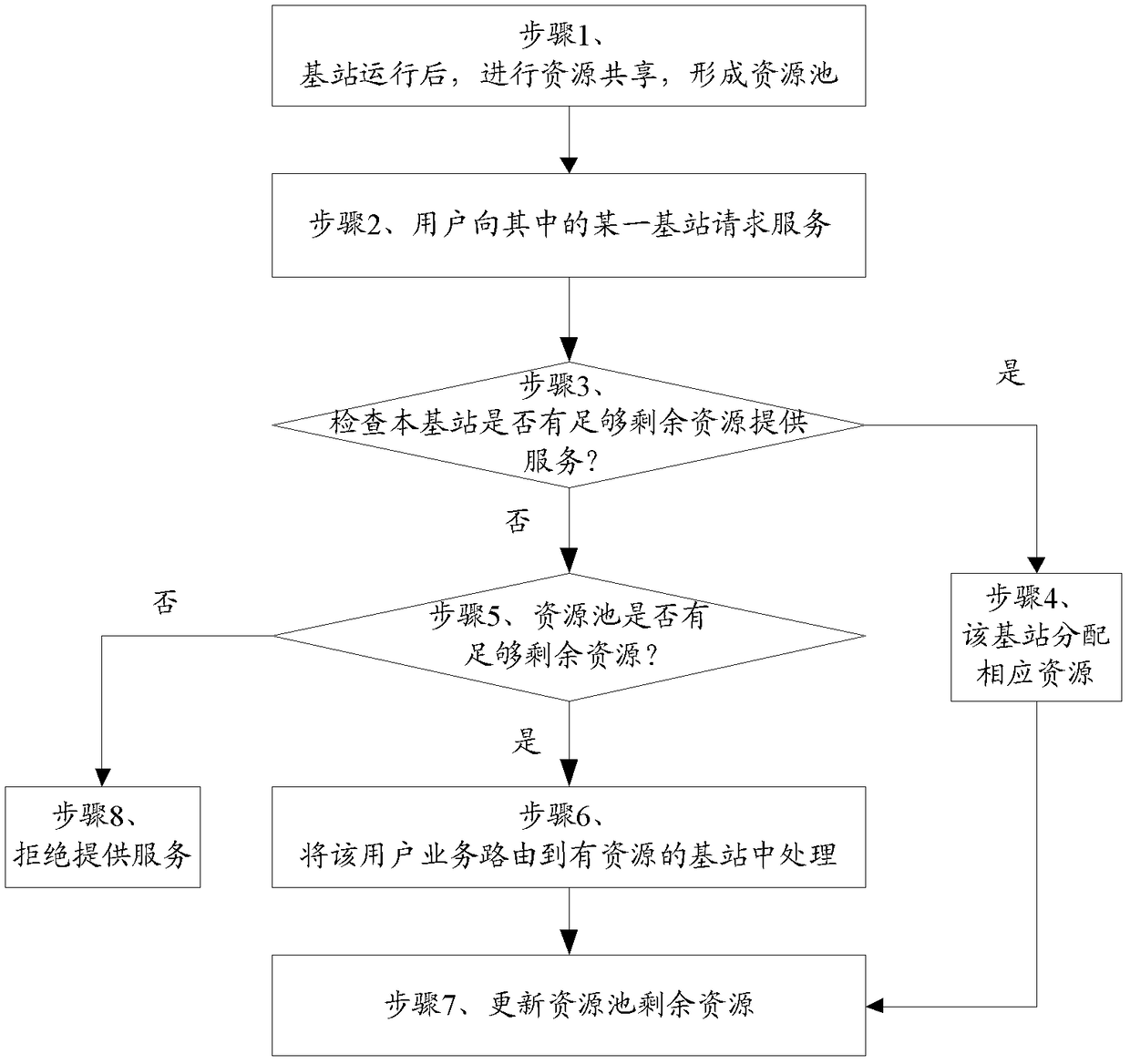
A base station resource sharing system and method
ActiveCN102378186BImprove utilization efficiencyReduce congestionNetwork planningAccess networkResource pool
The present invention provides a base station resource sharing system, including: a base station controller, a cloud base station, the cloud base station is composed of a plurality of base stations, and the resources of each base station are put into the same resource pool; the base station controller uses It is used to control the cloud base station and manage the wireless resources of the access network. The invention also provides a base station resource sharing method. Through a base station resource sharing system and method provided by the present invention, resources are dynamically allocated through resource pool sharing, network congestion is reduced, base station resource utilization efficiency is improved, base station user capacity is increased, and wireless network resources can be allocated according to service requirements Dynamic deployment to effectively deal with tidal effects.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com