Helicobacter System And Uses Thereof
a technology of helicobacter and plasmid, applied in the field of helicobacter-based vectors, plasmid vectors and shuttle vector systems, can solve the problems of poor immunogenicity of antigens delivered, unable to find application in mucosal delivery systems, and hindering the development of mucosal vaccines
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Vectors and Transgenic H. pylori Organisms for Stable Expression of Foreign Proteins
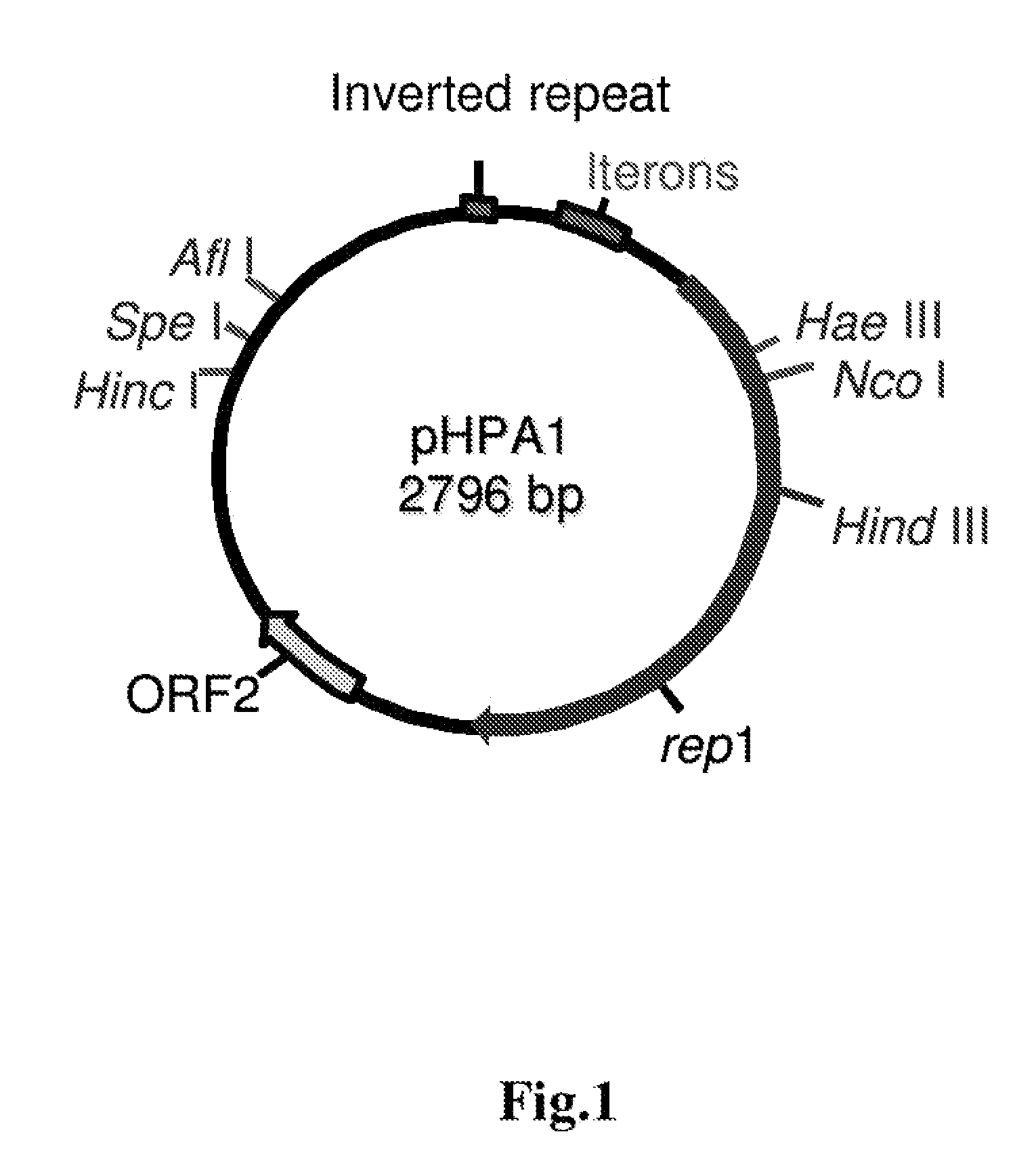
[0154] The genetic manipulation of H. pylori is uncommon. The present example demonstrates the utility of the invention for providing a genetically transformed Helicobacter, particularly transformed H. pylori. The transformed bacterium are prepared using plasmids and plasmid vectors derived from Helicobacter, which have had been subject to prior manipulation in a non-Helicobacter organism, such as E. coli.
[0155] Several H. pylori plasmids described in the literature can be successfully converted to H. pylori / E. coli shuttle vectors. Many strains of E. coli have been reported to be naturally competent for DNA uptake. Resistance markers for streptomycin, rifampin and metronidazole have also been successfully transformed into most strains of H. pylori. However, while plasmid DNA from E. coli and other organisms can be introduced into H. pylori, these plasmids cannot be stably maintained. Moreover, H. ...
example 2
Expression Vectors and Selection of Antigens for Stable Expression
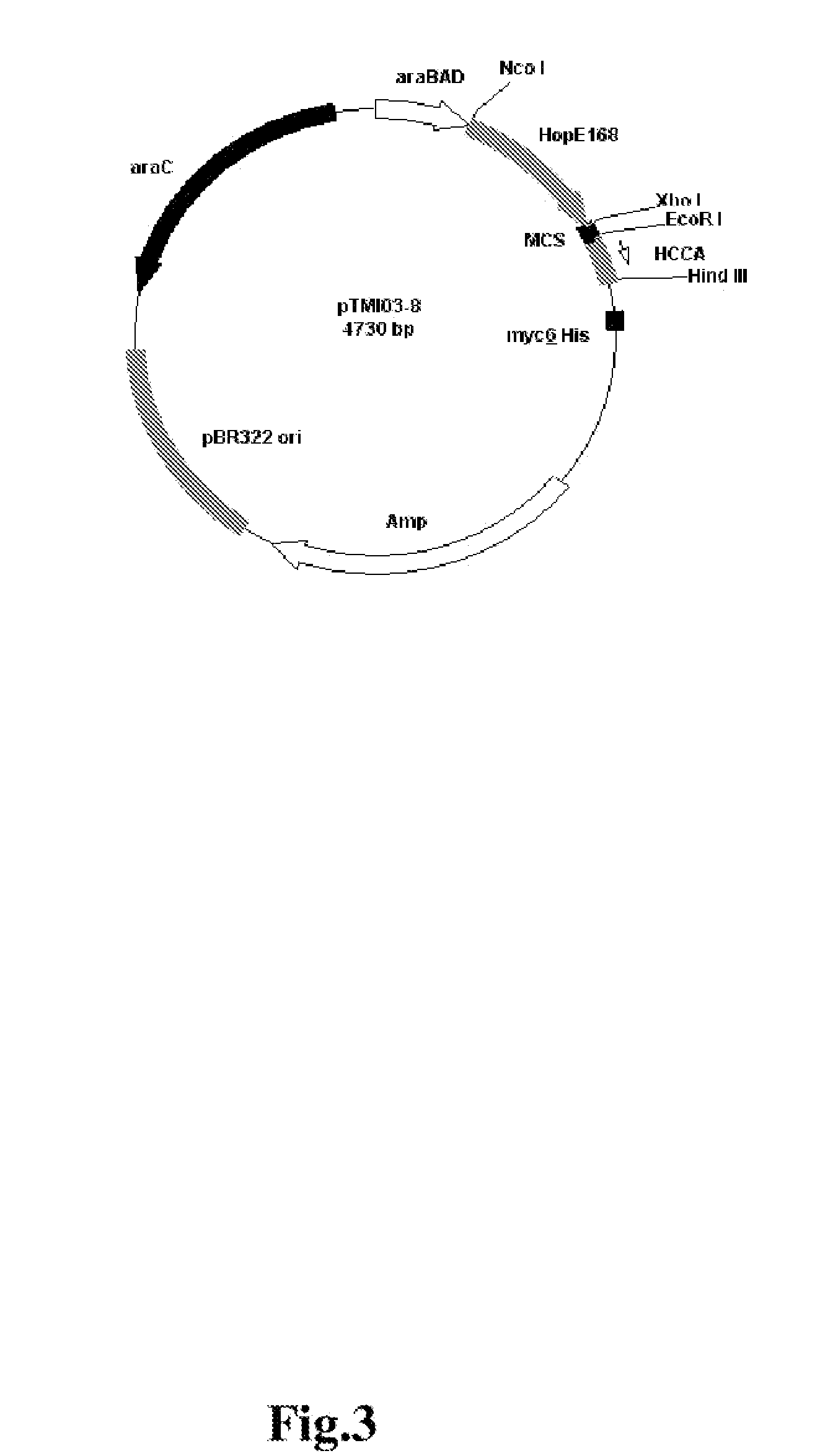
[0167] Because HopE is a native protein of H. pylori, it is tolerated by this organism and can thus form a construct useful for expressing foreign antigens or other heterologous gene products in H. pylori. Other H. pylori / E. coli shuttle vectors that can be readily developed as described above include, for example, vectors comprising two plasmid ori sites and markers which are suitable for each host. Markers might include genes for chloramphenicol / kanamycin resistance as well as promoters that can be recognized by both the E. coli and H. pylori transcriptional systems.
[0168] The requirements for replication E. coli can be achieved by using any of a number of known E. coli plasmids (e.g., pBR322).
[0169] Constructed shuttle vectors can be tested for replication in both E. coli and H. pylori in vitro and compared to existing shuttle plasmids described in the literature.
[0170] The choice of antigen or other heterologo...
example 3
Virulence, LD50
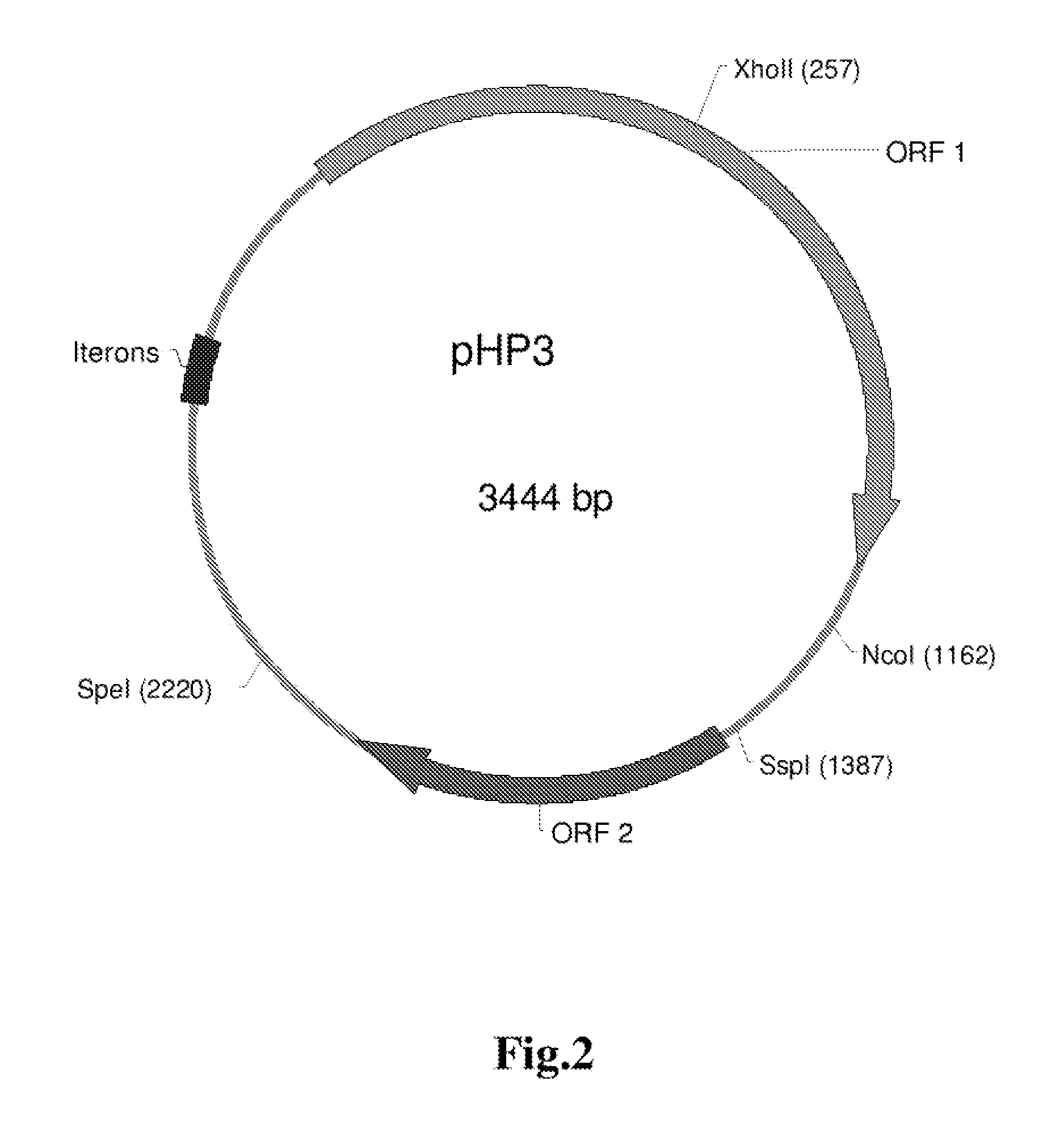
[0179] As described in Examples 1 and 2, Helicobacter-based vectors such as pHP3 and pHP623 are capable of providing protection against infection in a mammal, such as a mouse or human. In the present example, a murine model is used to demonstrate the utility of using the Helicobacter-based systems to provide delivery of a pharmacologically active molecule of interest to a mammal, including a human. The murine model is employed to demonstrate the activity of a transgenic strain of H. pylori to elicit a serological response to an expressed surface antigen in vivo.
[0180] Mice are infected with wild-type H. pylori, while other mice are inoculated by gavage with temperature-sensitive H. pylori as described in Example 2. Sera from both control and test animals are assayed for antibody and gastric histology are performed on sacrificed animals in accordance with the schedule shown in Table 1. A mouse urea breath test can also be used.
[0181] A 50% decrease in virulence (fro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com