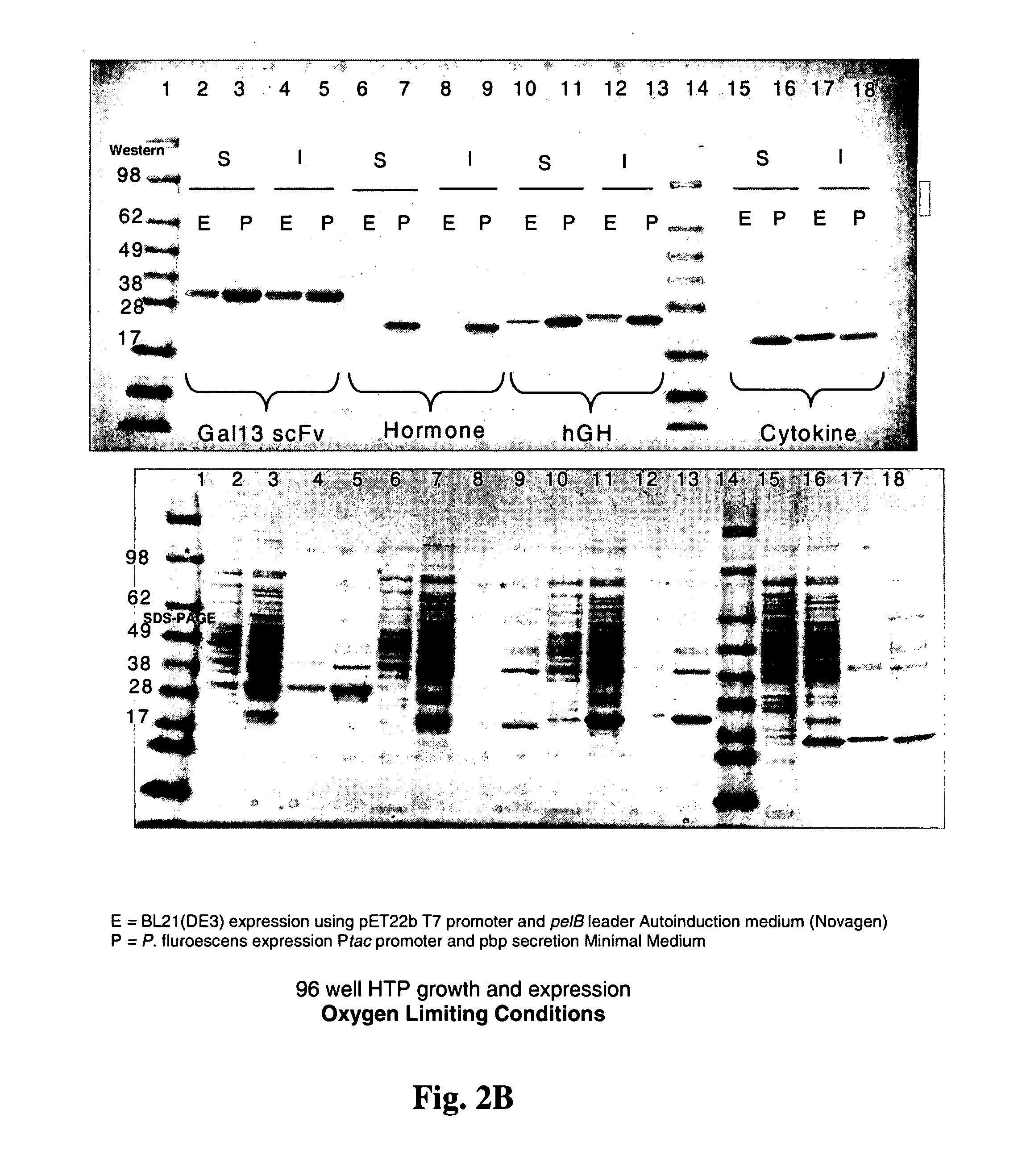
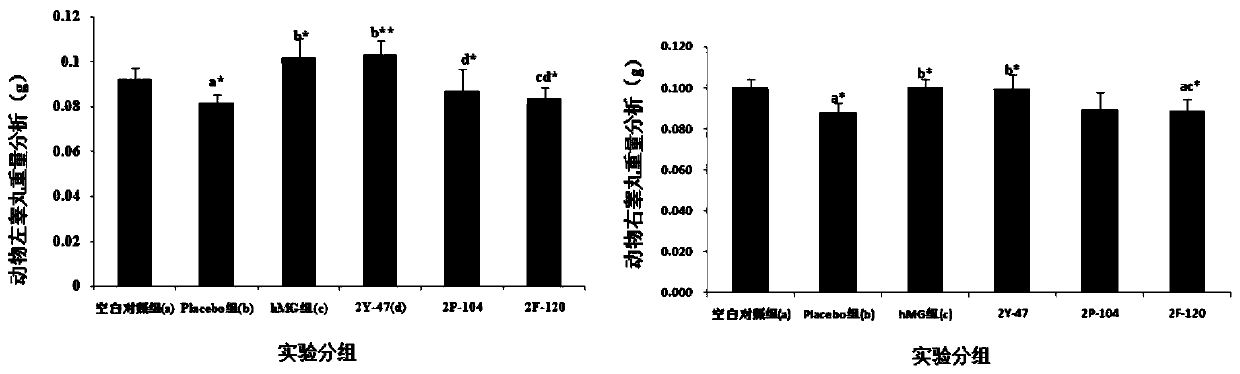
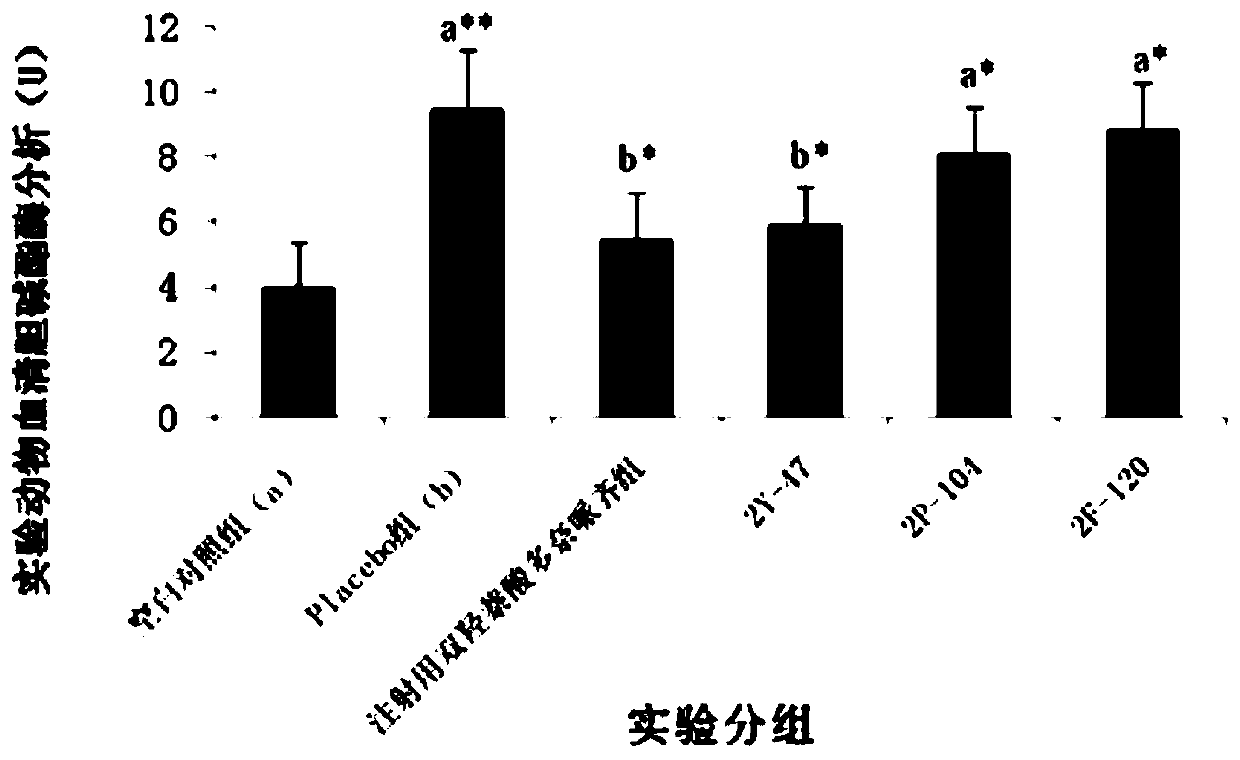
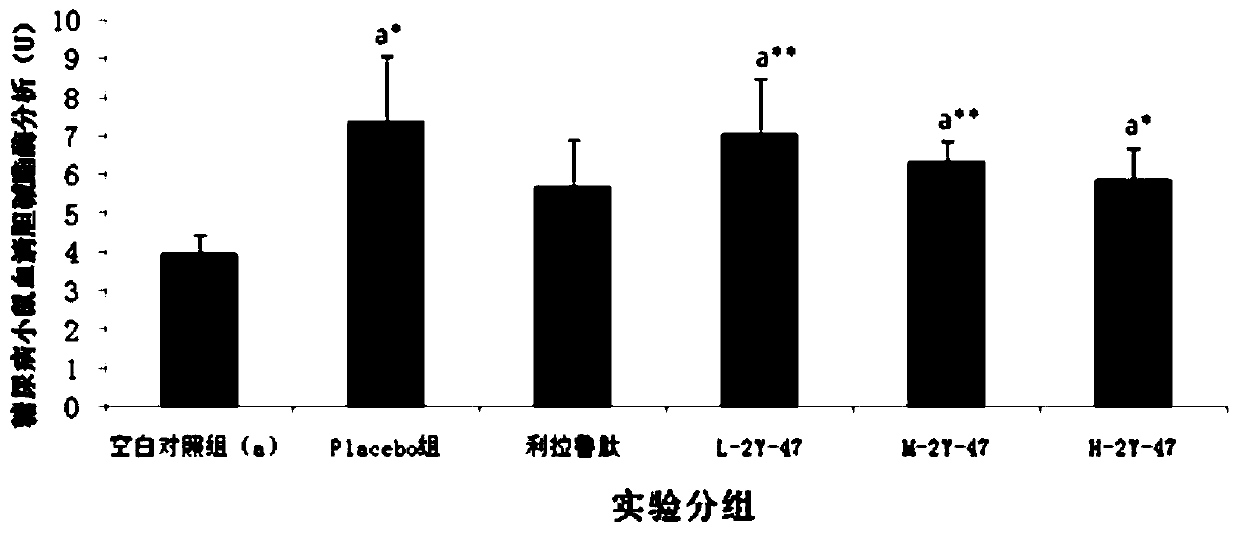
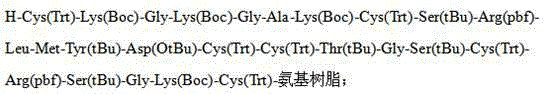Patents
Literature
34 results about "Disulphide bond formation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
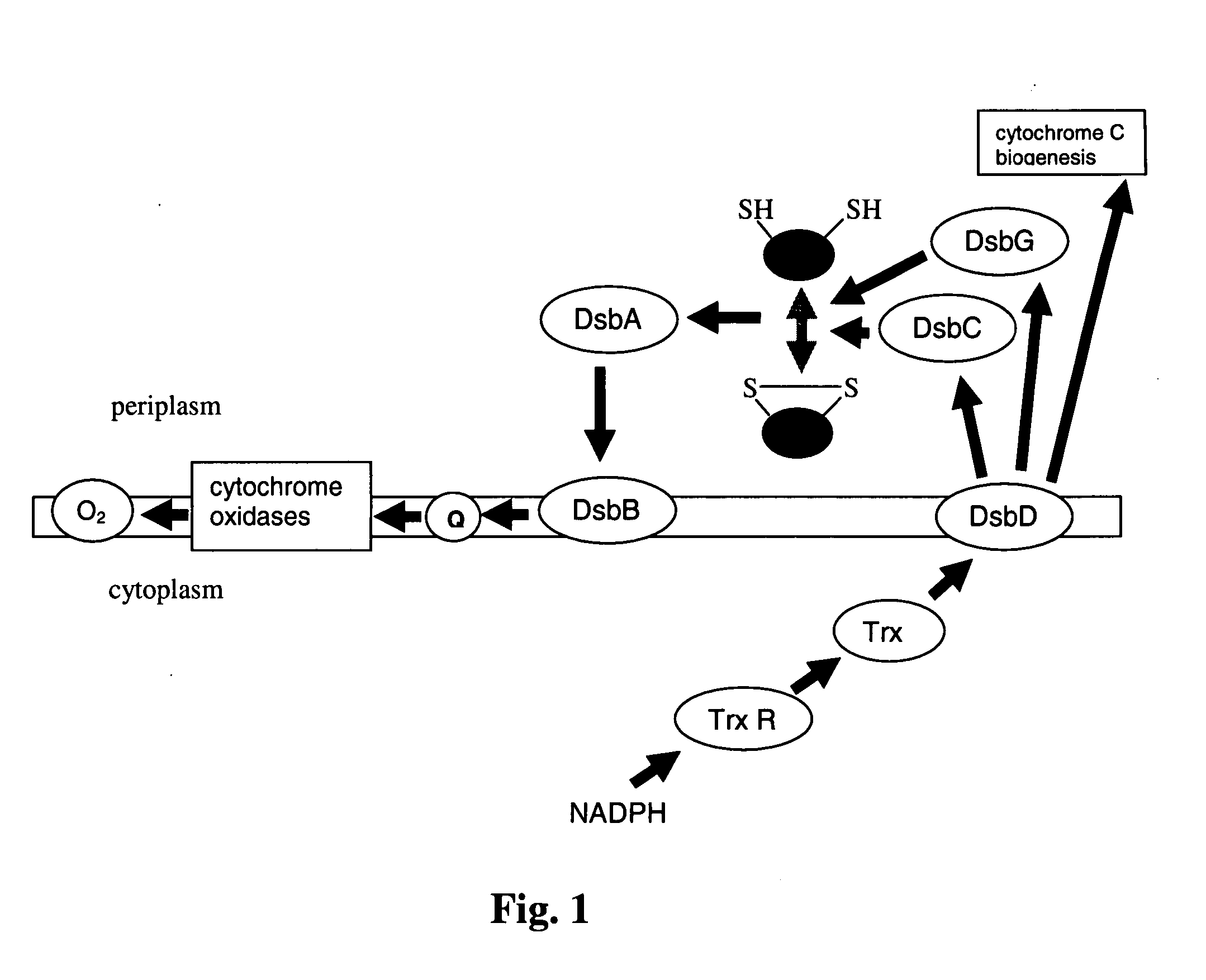
Disulfide bond formation protein B (DsbB) is a protein component of the pathway that leads to disulfide bond formation in periplasmic proteins of Escherichia coli and other bacteria.
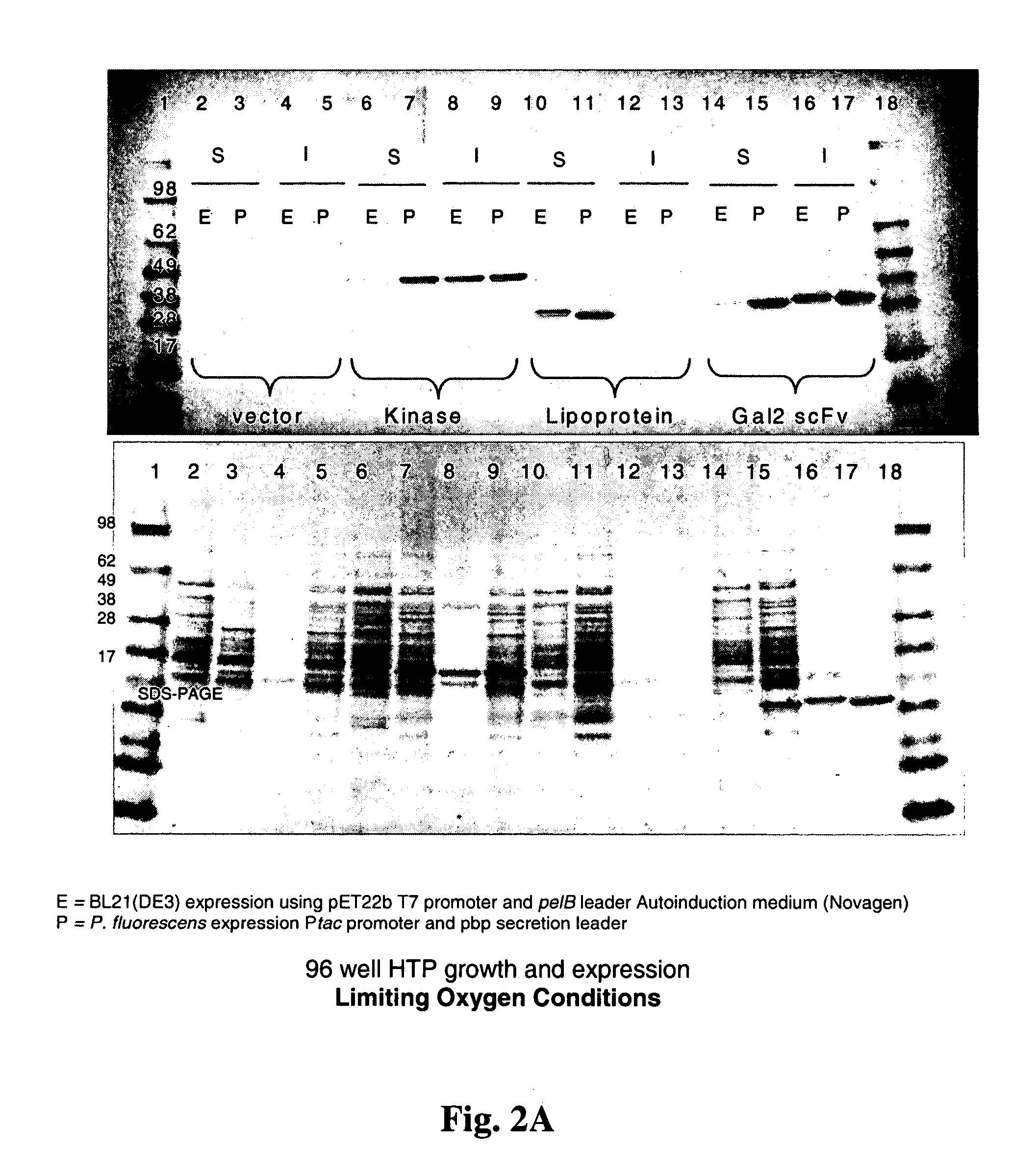
Expression of heterologous proteins
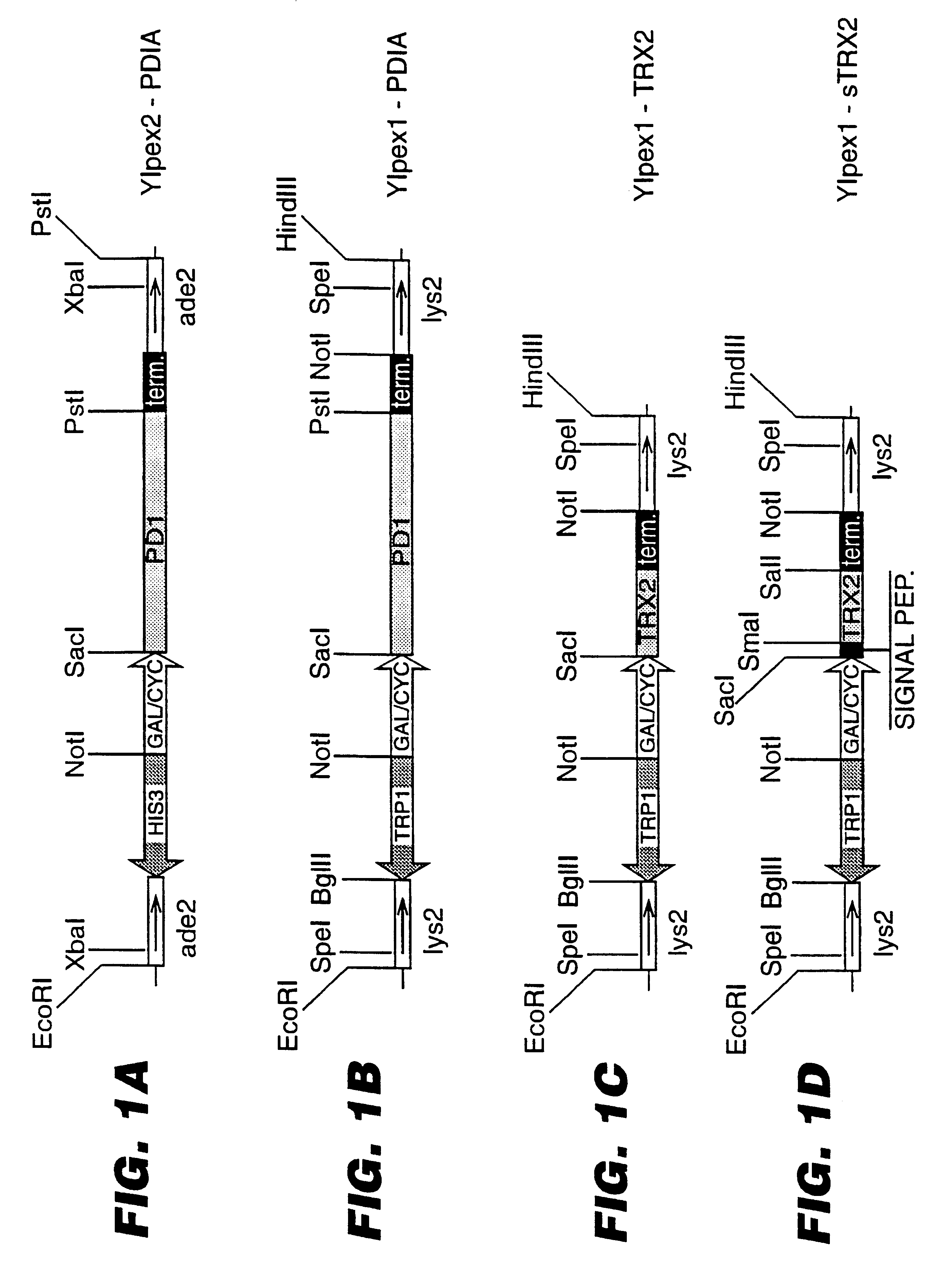
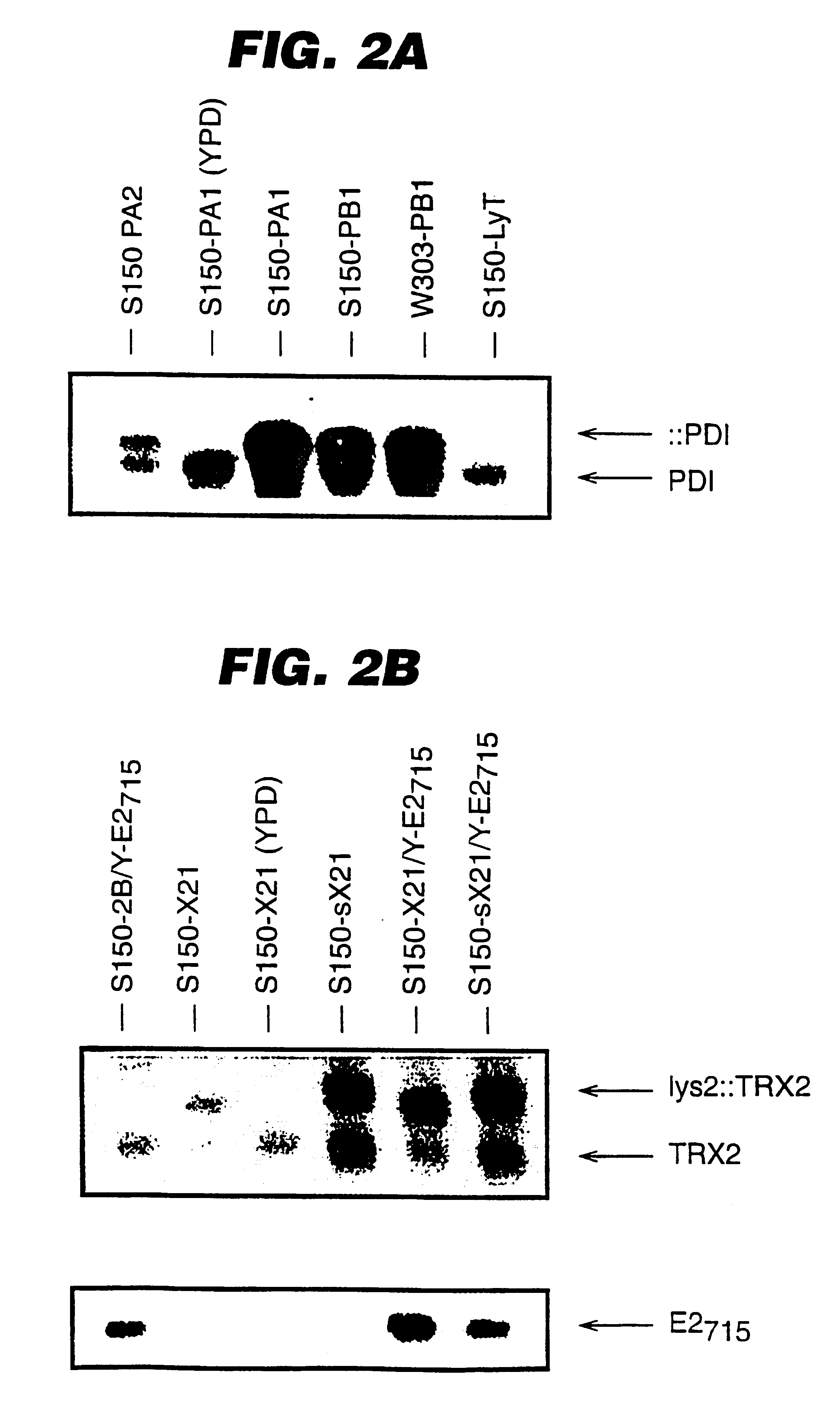
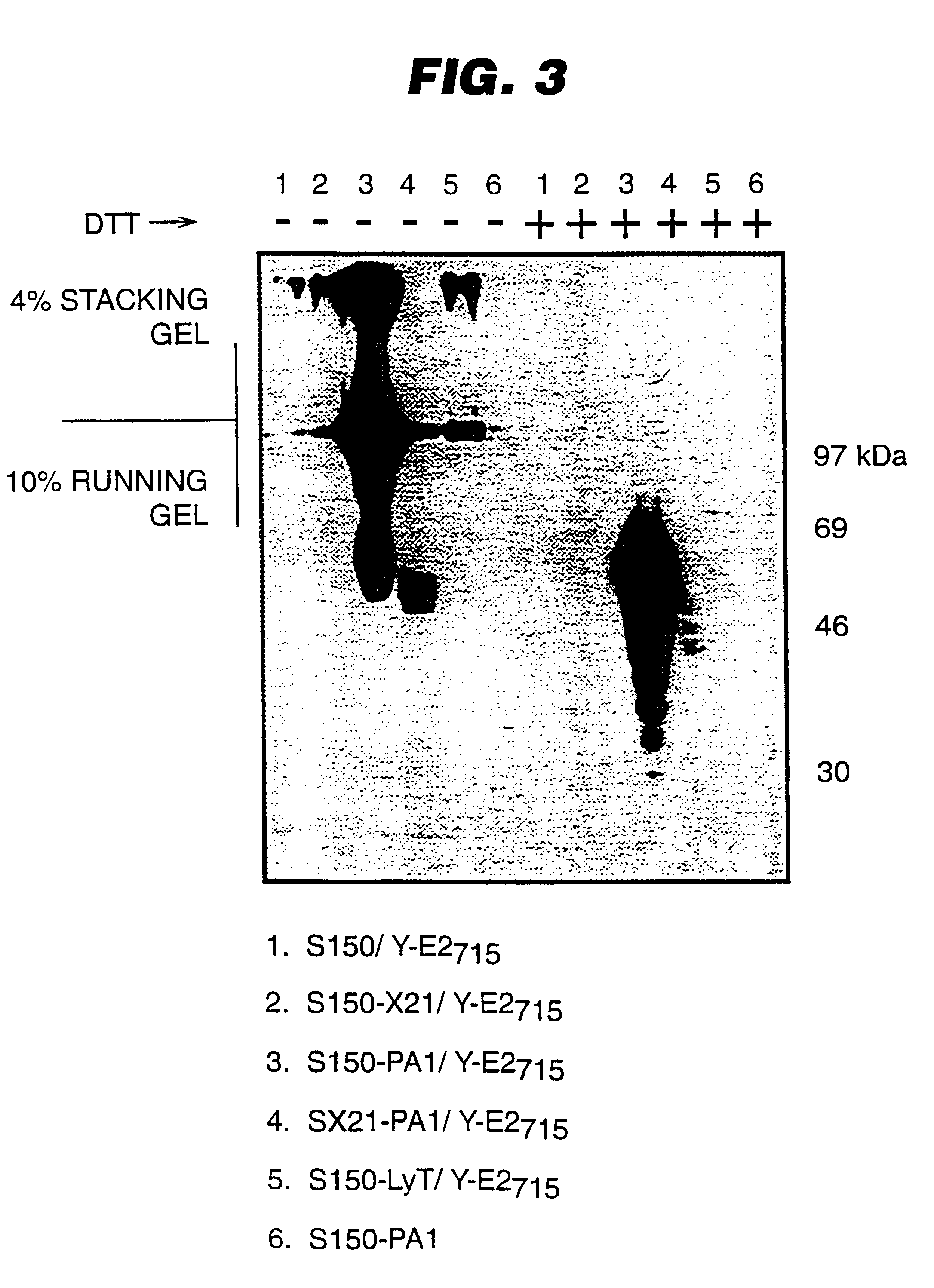
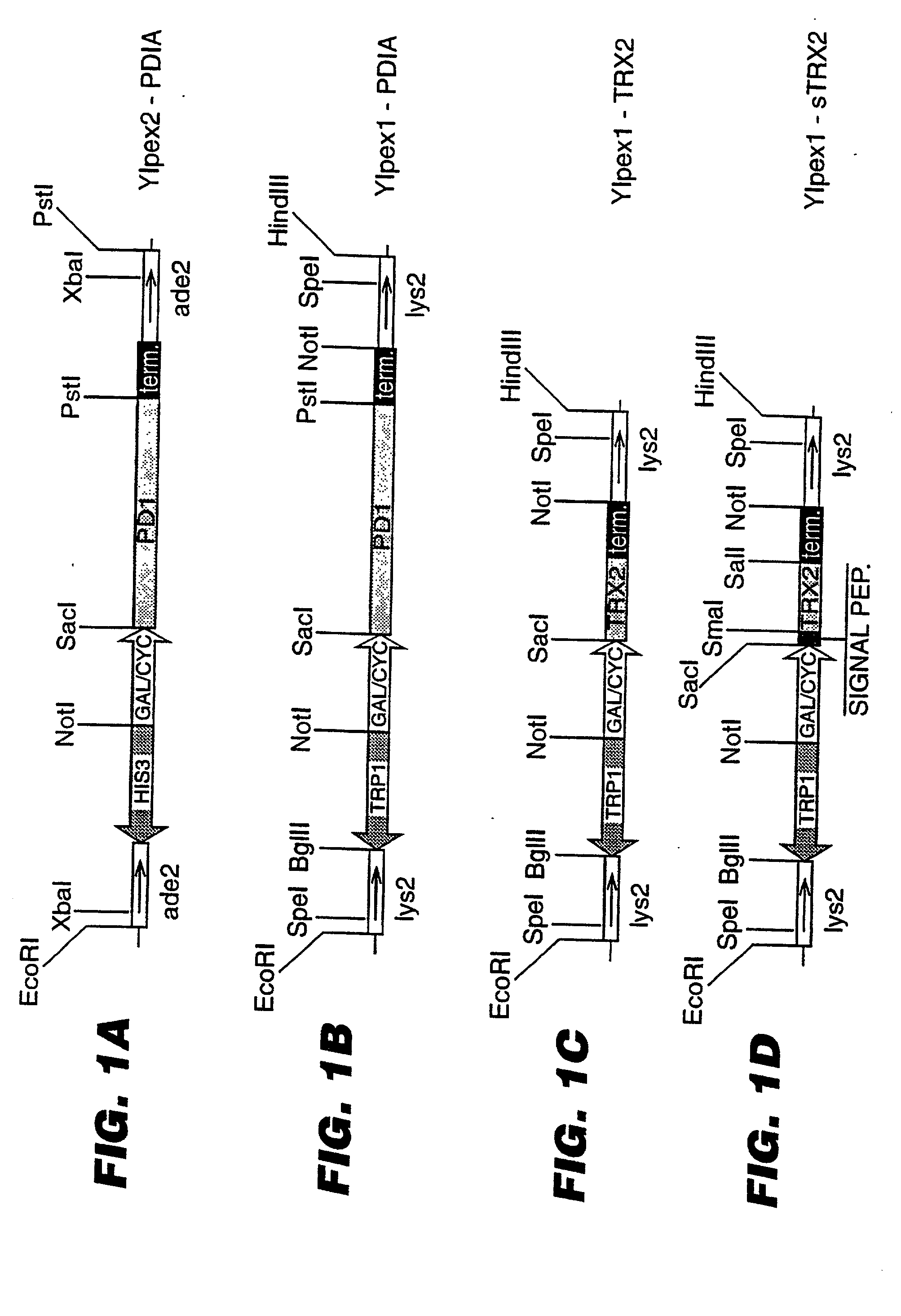
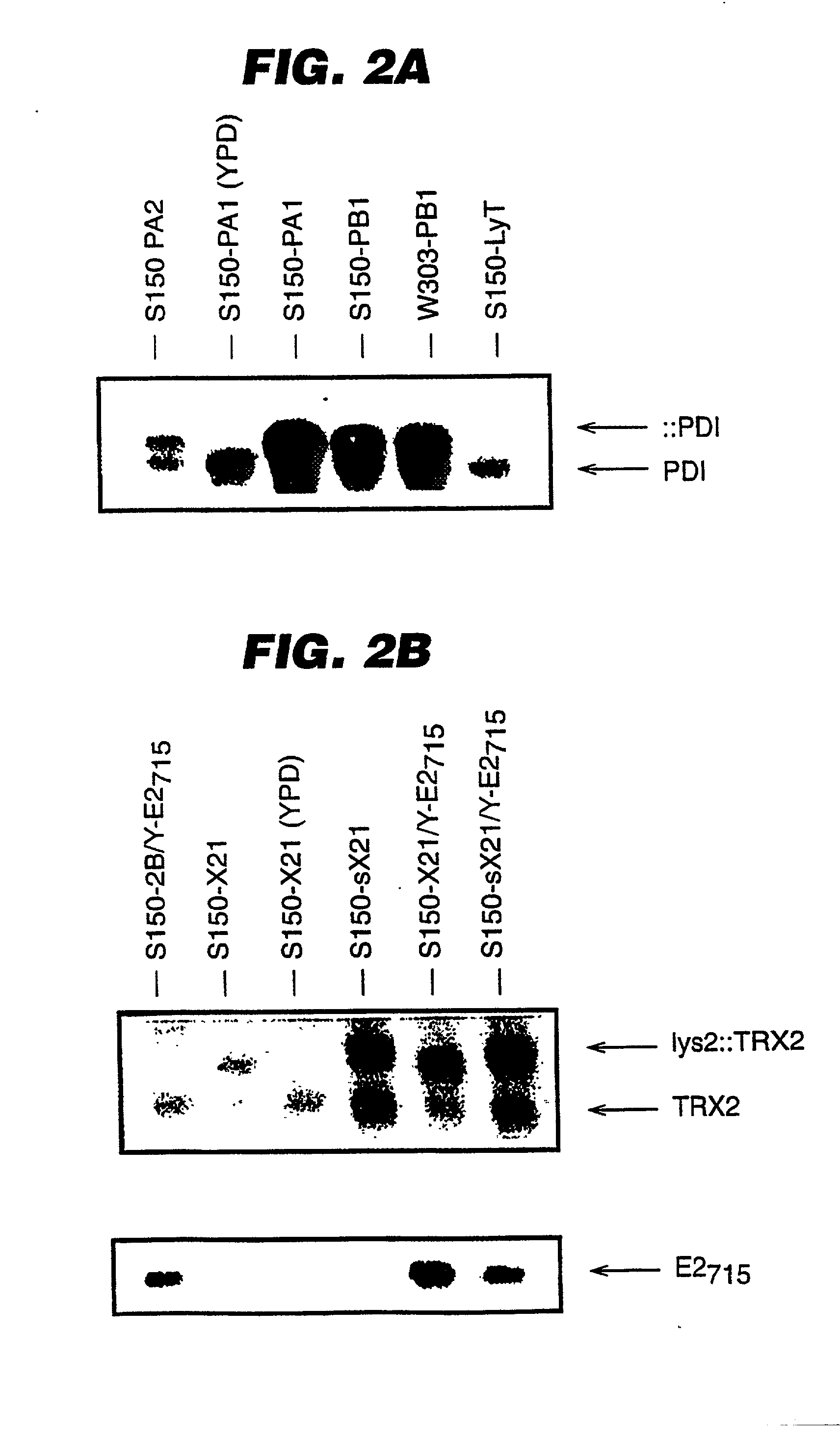
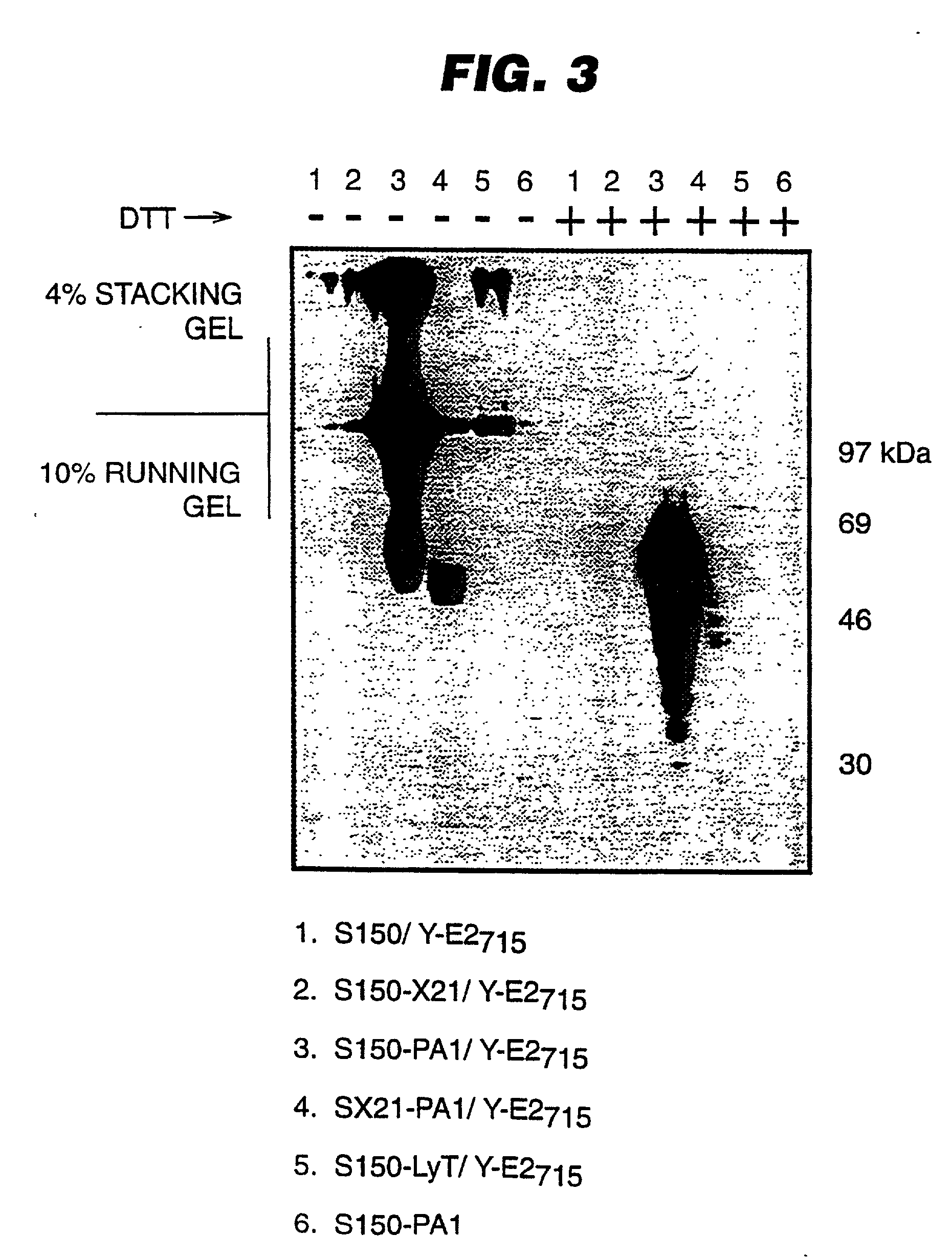
An expression system which provides heterologous proteins expressed by a non-native host organism but which have native-protein-like biological activity and / or structure. Disclosed are vectors, expression hosts and methods for expressing the heterologous proteins. The expression system involves co-expression of protein factor(s) which is / are capable of catalyzing disulphide bond formation and desired heterologous protein(s). The expression system is presented using yeast cells as the preferred host, protein disulphide isomerase (PDI) and thioredoxin (TRX) as the preferred examples of the protein factors and HCV-E2715 envelope glycoprotein and human FIGF as the preferred examples of the heterologous proteins.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
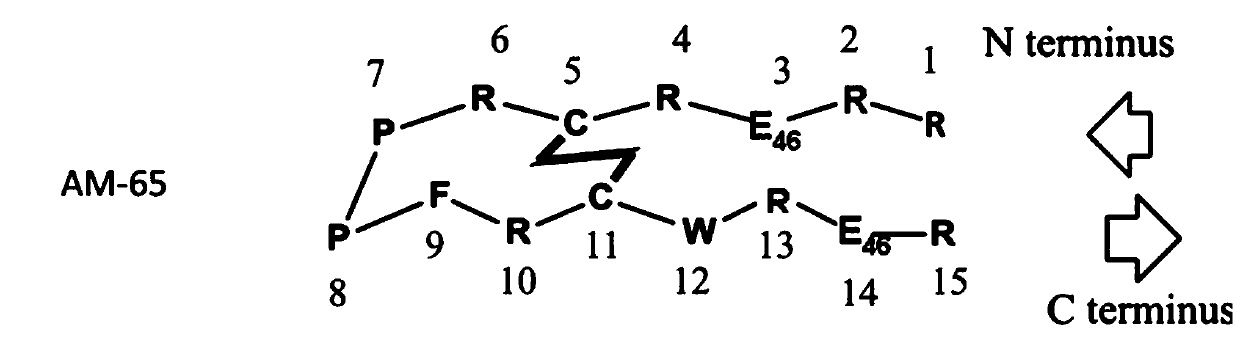
Solid-phase synthesis method of ziconotide by segment process
InactiveCN104974237AHigh yieldShort synthesis cyclePeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesDisulfide bondingDisulphide bond formation
The invention belongs to the field of polypeptide synthesis, and relates to a solid-phase synthesis method of ziconotide by a segment process. The method aims to solve the technical problems of long synthesis period and low crude peptide purity in the existing preparation method, and the technical problems of complex operation, low total yield and the like in the disulfide-bond formation process. The technical scheme is as follows: the method comprises the following steps: synthesizing four segment peptides [19-25]A, [12-18]B, [6-11]C and [1-5]D of ziconotide by a solid-phase process; sequentially connecting the all-protected peptide fragments B, C and D to the peptide resin A, and cracking to obtain a ziconotide linear peptide; and finally, carrying out liquid-phase one-step oxidization, which has the advantages of mild conditions, simplified operation, easy after-treatment and environment friendliness, to obtain the ziconotide. The technical scheme can greatly shorten the synthesis period, lower the synthesis and purification difficulty and the production cost, and enhance the purity of the linear peptide and the total yield of the product. The method is beneficial to industrial large-scale production.
Owner:JINAN KANGHE MEDICAL TECH
Pharmaceutical proteins, human therapeutics, human serum albumin insulin, native cholera toxic B submitted on transgenic plastids
InactiveUS20060117412A1Eliminate needLarge biomassSerum albuminDepsipeptidesInsulin-like growth factorEscherichia coli
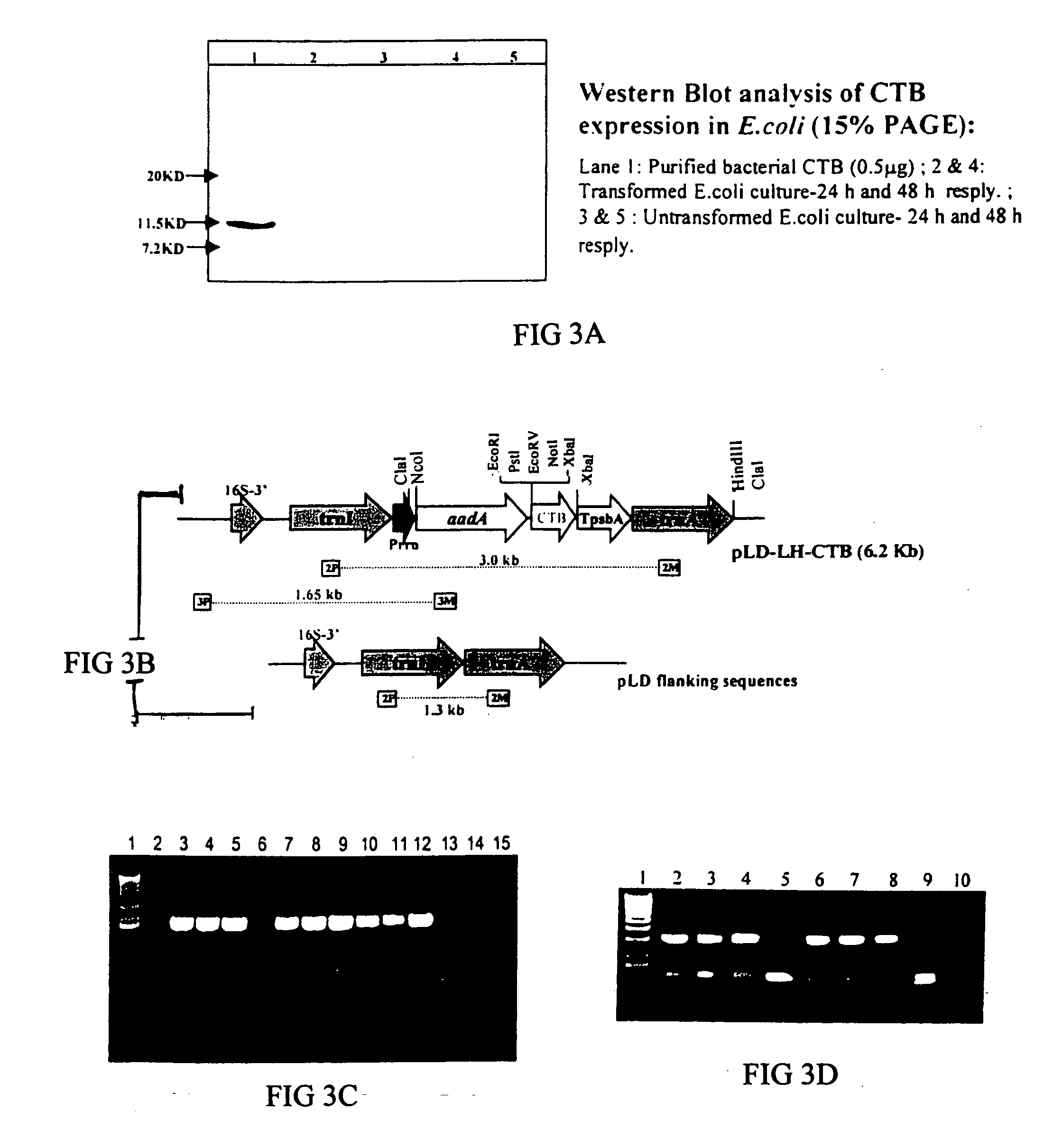
Transgenic chloroplast technology could provide a viable solution to the production of Insulin-like Growth Factor I (IGF-I), Human Serum Albumin (HSA), or interferons (IFN) because of hyper-expression capabilities, ability to fold and process eukaryotic proteins with disulfide bridges (thereby eliminating the need for expensive post-purification processing). Tobacco is an ideal choice because of its large biomass, ease of scale-up (million seeds per plant), genetic manipulation and impending need to explore alternate uses for this hazardous crop. Therefore, all three human proteins will be expressed as follows: a) Develop recombinant DNA vectors for enhanced expression via tobacco chloroplast genomes b) generate transgenic plants c) characterize transgenic expression of proteins or fusion proteins using molecular and biochemical methods d) large scale purification of therapeutic proteins from transgenic tobacco and comparison of current purification / processing methods in E. coli or yeast e) Characterization and comparison of therapeutic proteins (yield, purity, functionality) produced in yeast or E. coli with transgenic tobacco f) animal testing and pre-clinical trials for effectiveness of the therapeutic proteins. Mass production of affordable vaccines can be achieved by genetically engineering plants to produce recombinant proteins that are candidate vaccine antigens. The B subunits of Enteroxigenic E. coli (LTB) and cholera toxin of Vibrio cholerae (CTB) are examples of such antigens. When the native LTB gene was expressed via the tobacco nuclear genome, LTB accumulated at levels less than 0.01% of the total soluble leaf protein. Production of effective levels of LTB in plants, required extensive codon modification. Amplification of an unmodified CTB coding sequence in chloroplasts, up to 10,000 copies per cell, resulted in the accumulation of up to 4.1% of total soluble tobacco leaf protein as oligomers (about 410 fold higher expression levels than that of the unmodified LTB gene). PCR and Southern blot analyses confirmed stable integration of the CTB gene into the chloroplast genome. Western blot analysis showed that chloroplast synthesized CTB assembled into oligomers and was antigenically identical to purified native CTB. Also, GM1-ganglioside binding assays confirmed that chloroplast synthesized CTB binds to the intestinal membrane receptor of cholera toxin, indicating correct folding and disulfide bond formation within the chloroplast. In contrast to stunted nuclear transgenic plants, chloroplast transgenic plants were morphologically indistinguishable from untransformed plants, when CTB was constitutively expressed. The introduced gene was stably inherited in the subsequent generation as confirmed by PCR and Southern blot analyses. Incrased production of an efficient transmucosal carrier molecule and delivery system, like CTB, in transgenic chloroplasts makes plant based oral vaccines and fusion proteins with CTB needing oral administration a much more practical approach.
Owner:DANIELL HENRY
Stabilised proteins for immunising against staphylococcus aureus
ActiveUS20150203542A1High antigen stabilityHigh selectivityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigenDisulphide bond formation
Elimination of disulphide bond formation of cysteine-containing S. aureus antigens enhances antigen stability. The invention provides variant forms of cysteine-containing S. aureus antigen with a point mutation that replaces, deletes or modifies the cysteine residue.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Plasmid for efficiently expressing polypeptide toxin as well as preparation method and application of plasmid
PendingCN114107353AIncreased expression of solubleAchieve high-yield expressionNucleic acid vectorPeptide preparation methodsDisulfide bondingDisulphide bond formation
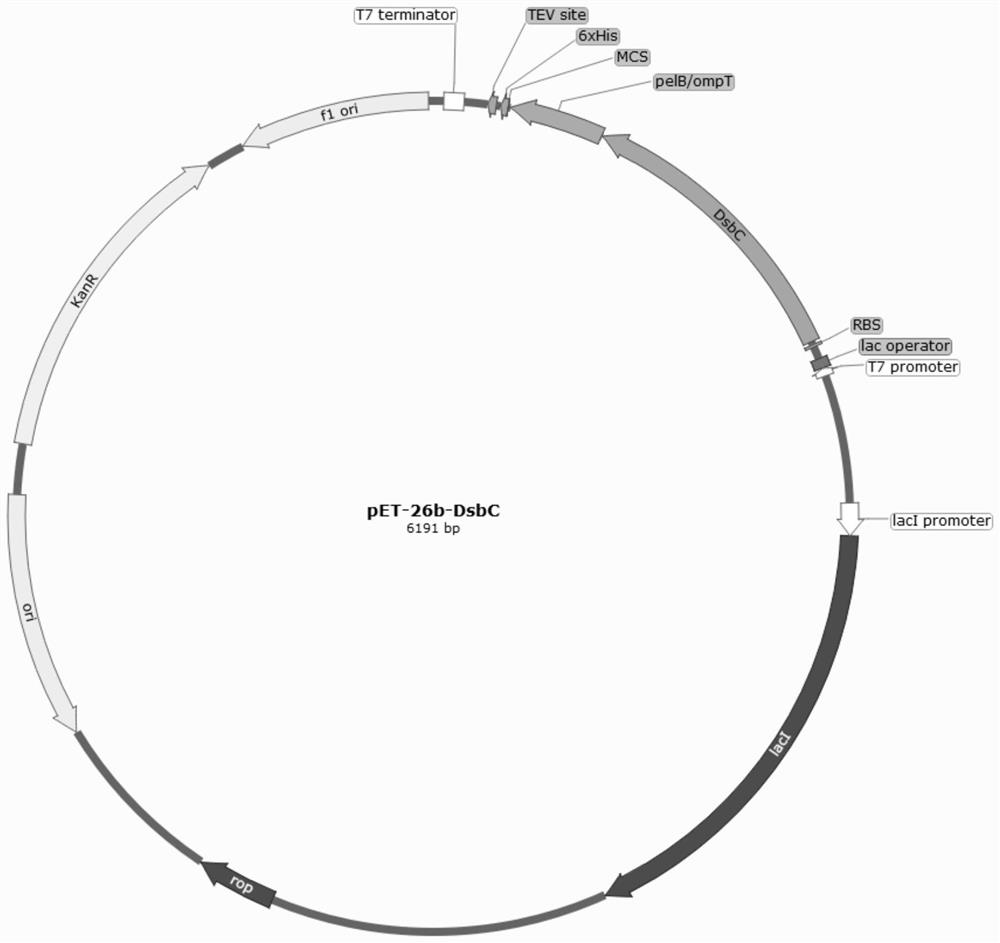
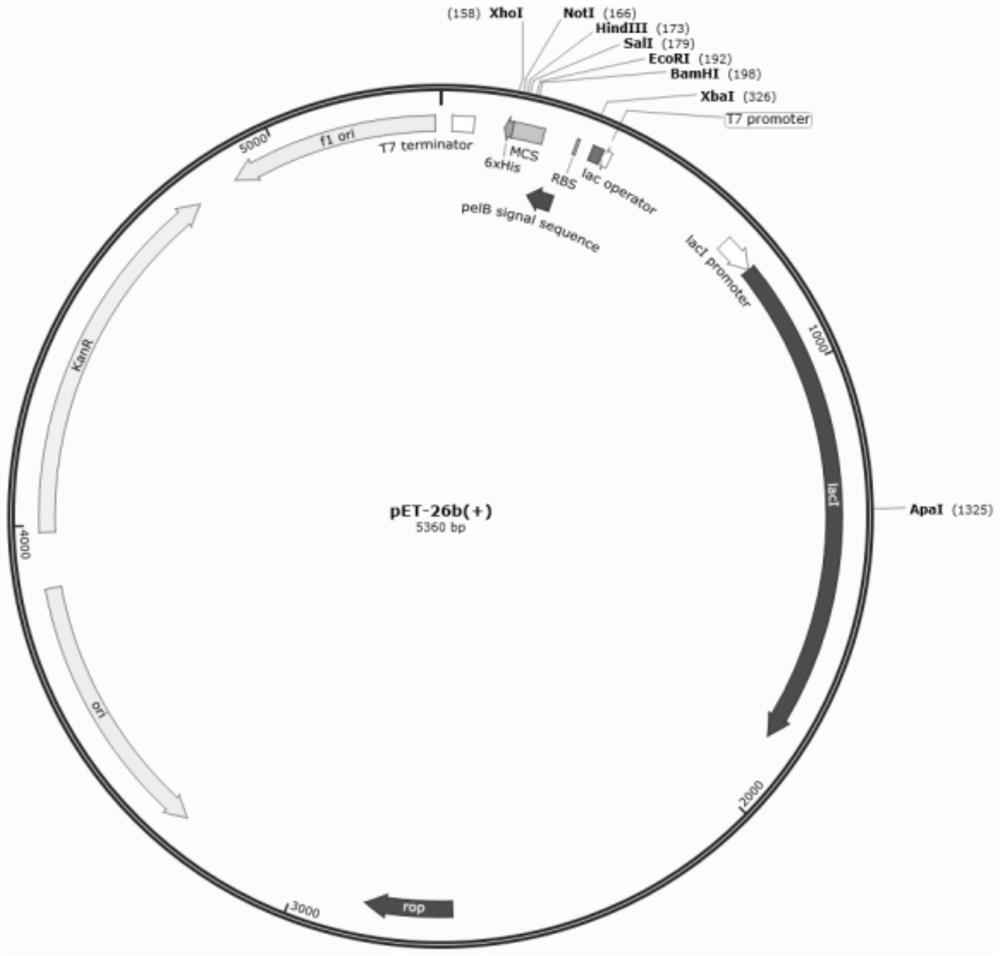
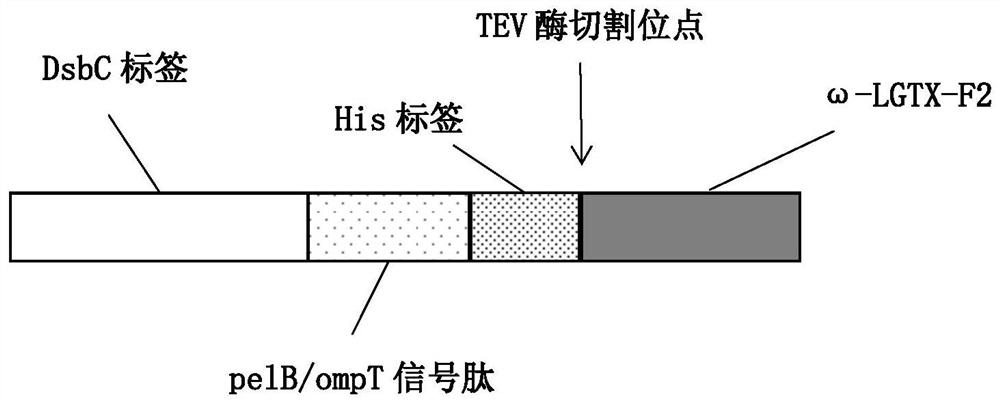
The plasmid for efficiently expressing the polypeptide toxin provided by the invention is obtained by cloning a coding gene of the polypeptide toxin into a plasmid vector pET-26b-DsbC, the plasmid vector pET-26b-DsbC carries His, pelB / ompT and a DsbC tag, the DsbC tag and a pelB / ompT signal peptide jointly act, polypeptide to be expressed is transferred into periplasm which is more beneficial to protein folding and disulfide bond formation, and the expression efficiency of the polypeptide toxin is improved. The soluble expression of the polypeptide toxin is improved, the problem of no expression or low expression quantity of the polypeptide toxin is solved, and the high-yield expression of the polypeptide toxin is realized. The invention further provides a preparation method of the plasmid, the plasmid for expressing the spider toxin is prepared, then the gene engineering bacteria are used for culturing and expressing the spider toxin, the prepared spider toxin is high in yield and low in production cost, and the preparation method has huge application prospects in the field of polypeptide toxin production.
Owner:成都佩德生物医药有限公司
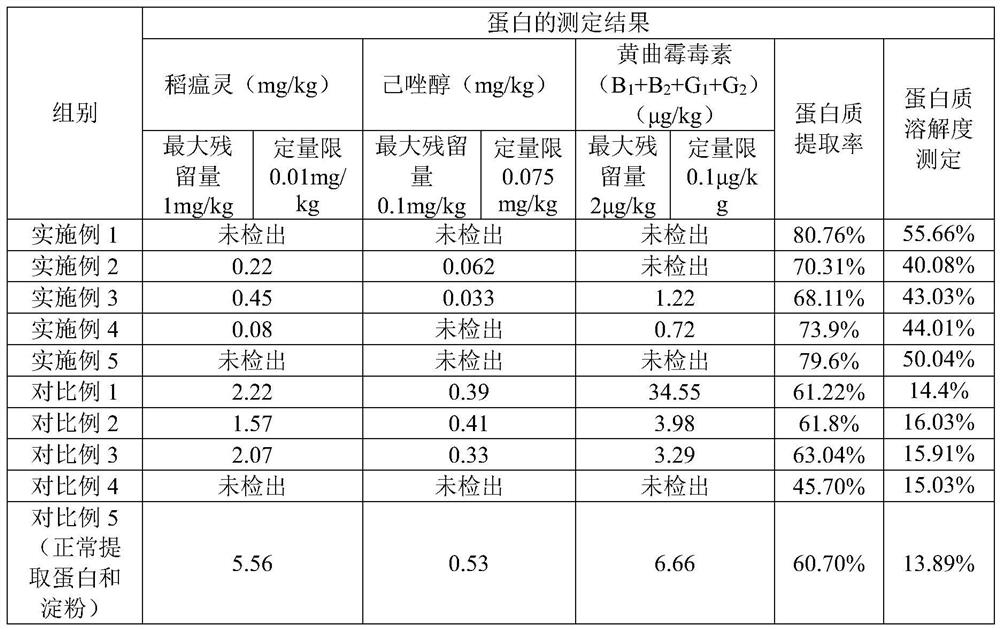
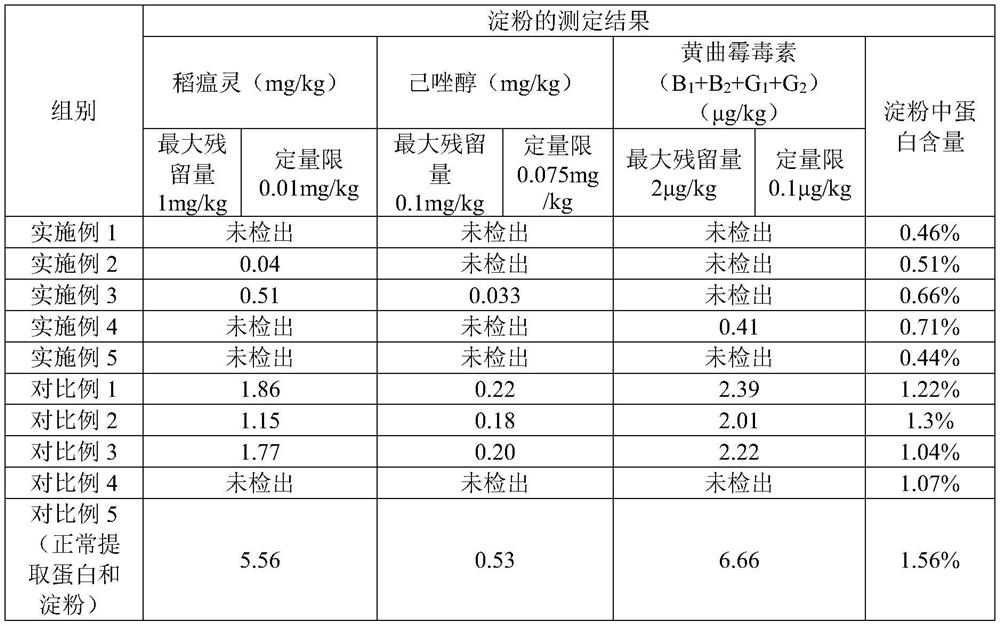
Method for extracting edible rice starch and rice protein from broken rice with excessive pesticide residues
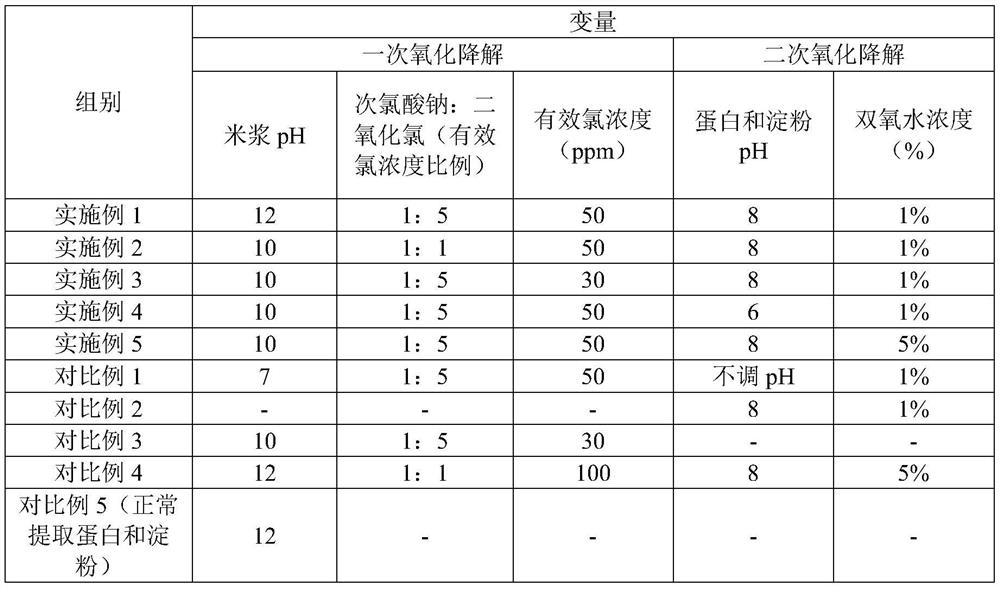
The invention discloses a method for extracting edible rice starch and rice protein from broken rice with excessive pesticide residues. According to the method, pesticide residues such as isoprothiolane and hexaconazole and mycotoxins such as aflatoxin are oxidized and degraded into non-toxic substances through oxidizing agents such as sodium hypochlorite, chlorine dioxide and hydrogen peroxide, disulfide bonds of protein are opened at the same time, stable sulfonic acid groups with high solubility are formed, protein dissolution is increased, the yield is increased, residual protein in starch is reduced, and protein and starch products with better safety are obtained.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Processes for improved disulfide bond formation in recombinant systems
InactiveUS20070238153A1Increase productionIncrease contentBacteriaSugar derivativesDisulphide bond formationOxidation-Reduction Agent
Methods and prokaryotic expression systems for producing recombinant disulfide bond-containing proteins are described including increasing the level of at least one redox cofactor in the cell to enhance disulfide bond formation are disclosed. Processes of increasing levels of redox cofactors include media supplementation and genetic modification of the host cell. The process can yield increased levels of soluble or active protein, or can assist the proper processing of recombinant proteins in expression systems.
Owner:PFENEX
Modification and dimerization preparation and application of novel growth hormone releasing hormone similar peptide
ActiveCN111533800AEnhance release activityHigh activityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDisulfide bondingDimer
The invention provides application of a molecular allosteric body and dimer of a human growth hormone releasing hormone (hGHRH) similar peptide in treating GH deficiency, infertility, senile dementiaand diabetes and enhancing immunity. The dimer is formed by connecting two identical hGHRH similar peptide monomers containing a single cysteine molecule allosteric structure through a disulfide bondformed by cysteine, and an H-shaped structure (intramolecular single Ser-to-Cys substitution) is formed. A side chain epsilon-amino of one lysine of the GHRH similar peptide is also subjected to fattyacid chain modification. Through fatty acid modification, the GH sustained release time of the GHRH similar peptide monomer or dimer is prolonged in vivo, and the longest release time reaches 17 days. The invention finds that the GHRH dimer with long-acting activity has an Aib-to-2Ala substitution structure, an 18C-to-18C disulfide bond formation structure, a C20 fatty acid chain modification structure and a C-terminal amidation structure.
Owner:深圳纳福生物医药有限公司
Stabilised proteins for immunising against staphylococcus aureus
Elimination of disulphide bond formation of cysteine-containing S.aureus antigens enhances antigen stability. The invention provides variant forms of cysteine-containing S.aureus antigen with a point mutation that replaces, deletes or modifies the cysteine residue.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Stabilised proteins for immunising against staphylococcus aureus
InactiveUS20150202277A1High antigen stabilityHigh selectivityBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsAntigenCysteine thiolate
Elimination of disulphide bond formation of cysteine-containing S.aureus antigens enhances antigen stability. The invention provides a composition comprising variant forms of cysteine-containing S.aureus antigen with a point mutation that replaces, deletes or modifies the cysteine residue.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
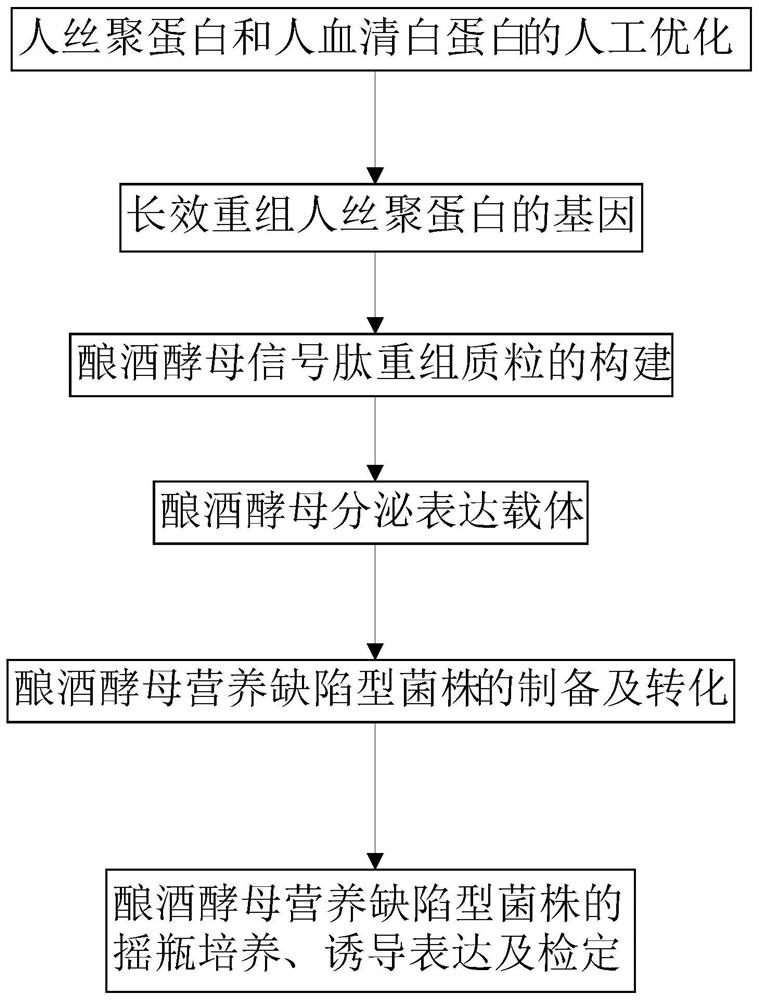
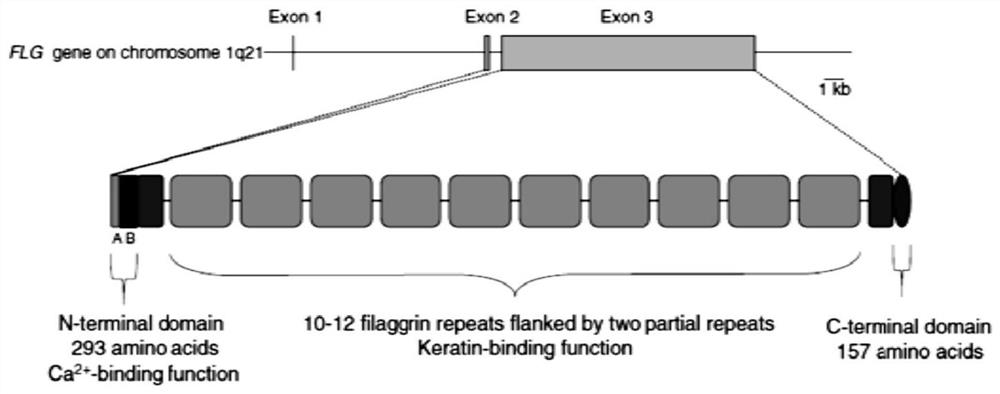
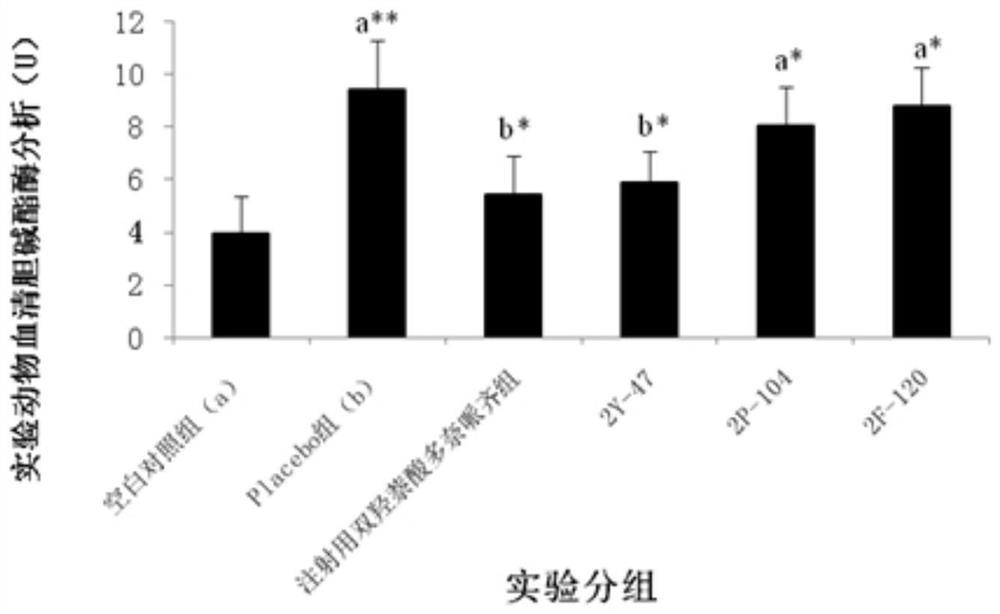
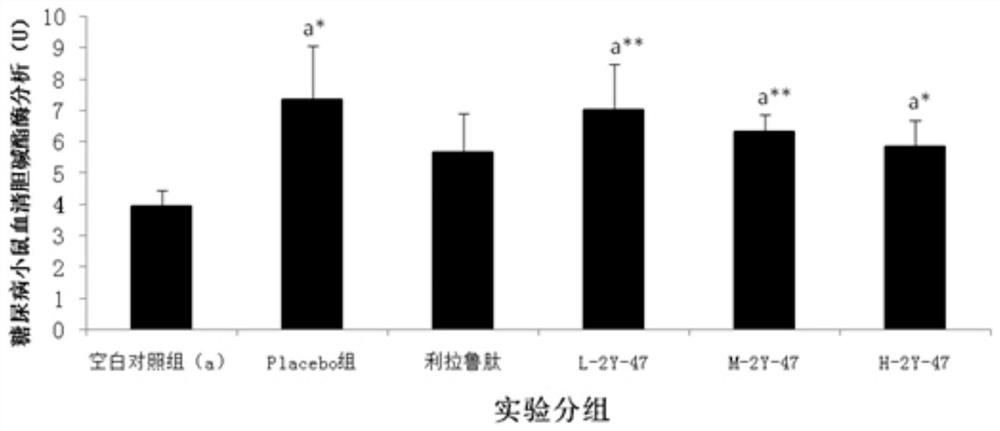
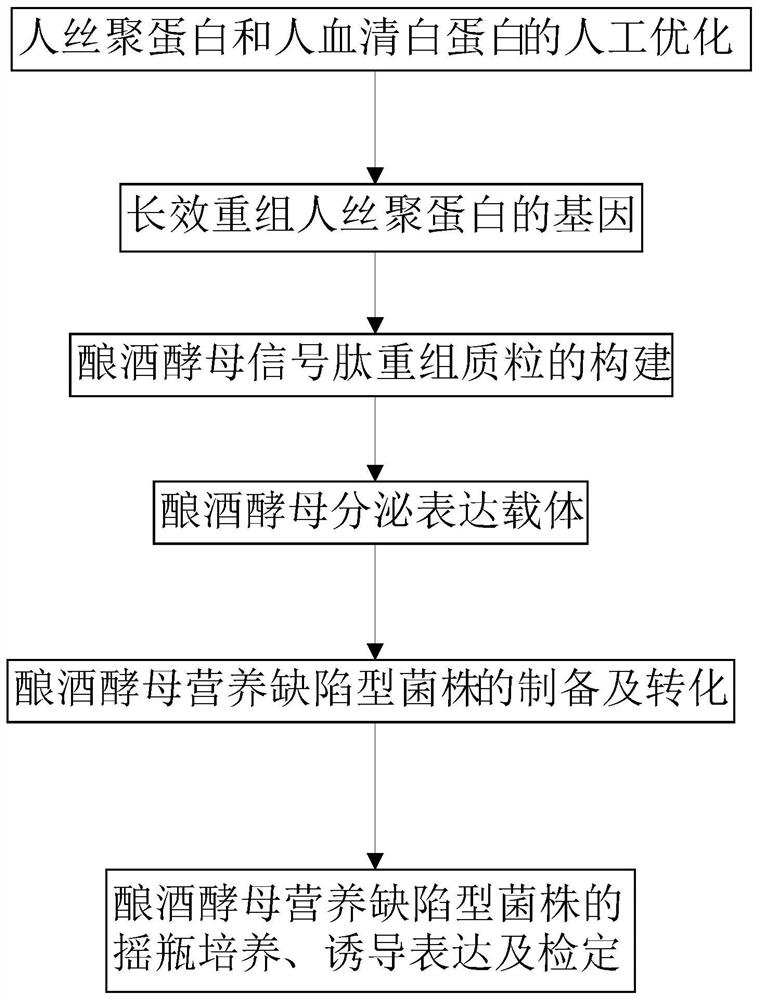
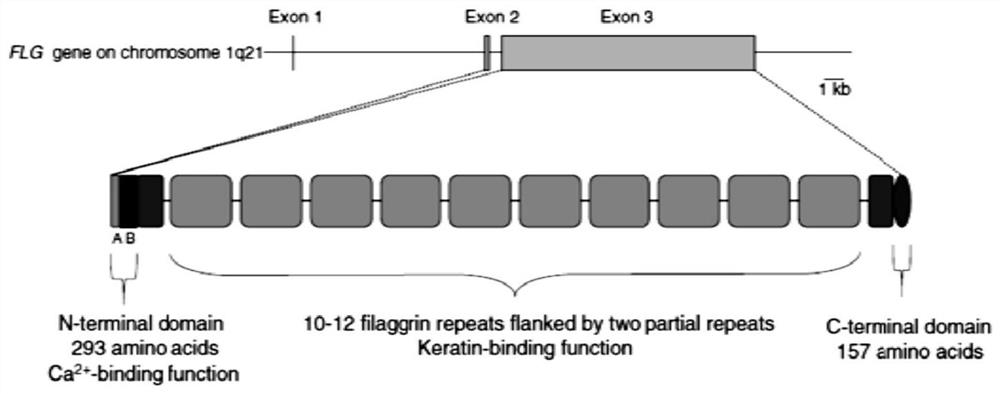
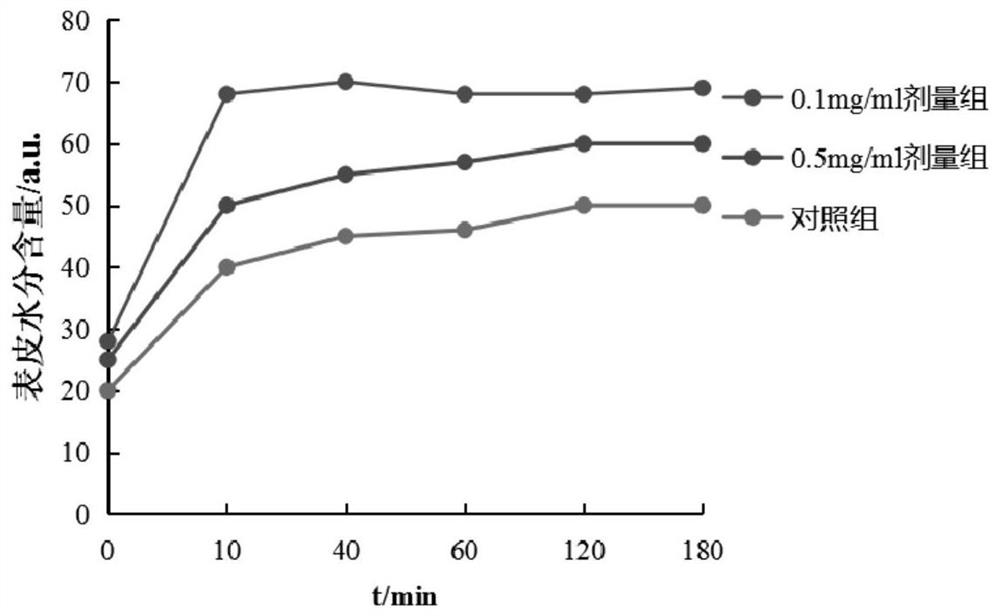
Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressed long-acting recombinant human filaggrin and application thereof
ActiveCN113045638AImprove stabilityPromote aggregationCosmetic preparationsFungiDisulfide bondingDisulphide bond formation
The invention discloses a saccharomyces cerevisiae expressed long-acting recombinant human filaggrin and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the long-acting recombinant human filaggrin is as shown in Seq ID NO.1, and the amino acid sequence corresponding to the nucleotide sequence of the long-acting recombinant human filaggrin is as shown in Seq ID NO.2. The amino acid sequence of the long-acting recombinant human filaggrin comprises an amino acid sequence of filaggrin and an amino acid sequence of human serum albumin, and the amino acid sequence of the filaggrin comprises an amino acid sequence corresponding to a monomer structure at the C end of a filaggrin nucleotide sequence repetitive unit. The long-acting recombinant human filaggrin provided by the invention can promote aggregation of keratin intermediate silk and formation of disulfide bonds between the intermediate silk, prevent loss of epidermal moisture and invasion of external allergic substances, and reduce sensitivity of ultraviolet-induced epidermal apoptosis. The fusion with HAS(Human serum albumin) effectively improves the stability of the recombinant protein.
Owner:WUHU YINGTE FEIER BIOLOGICAL PROD IND RES INST CO LTD +1
Stabilised proteins for immunising against staphylococcus aureus
InactiveUS20150191513A1High antigen stabilityHigh selectivityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigenStaphylococcus cohnii
Elimination of disulphide bond formation of cysteine-containing S. aureus antigens enhances antigen stability. The invention provides variant forms of cysteine-containing S. aureus antigen with a point mutation that replaces, deletes or modifies the cysteine residue.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Expression of heterologous proteins
An expression system which provides heterologous proteins expressed by a non-native host organism but which have native-protein-like biological activity and / or structure. Disclosed are vectors, expression hosts and methods for expressing the heterologous proteins. The expression system involves co-expression of protein factor(s) which is / are capable of catalyzing disulphide bond formation and desired heterologous protein(s). The expression system is presented using yeast cells as the preferred host, protein disulphide isomerase (PDI) and thioredoxin (TRX) as the preferred examples of the protein factors and HCV-E2715 envelope glycoprotein and human FIGF as the preferred examples of the heterologous proteins.
Owner:CHIRON A CORP
Stabilised proteins for immunising against staphylococcus aureus
InactiveUS20150203543A1High selectivityPreventing oligomerizationBacterial antigen ingredientsSugar derivativesAntigenDisulphide bond formation
Elimination of disulphide bond formation of cysteine-containing S. aureus antigens enhances antigen stability. The invention provides variant forms of cysteine-containing S. aureus antigen with a point mutation that replaces, deletes or modifies the cysteine residue.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Method of treatment
PendingCN111417401APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsDisulfide bondingDisease
The present invention relates generally to the field of immunomodulation. Taught herein is an agent for inhibiting immunostimulation mediated by a Toll-like receptor useful in the treatment of viral and microbial pathogenesis, diseases involving elements of autoimmunity and inflammation as well as cancer. The agent antagonizes disulfide bond formation between C98 and C475 of Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) thereby preventing TLR7 activation.Pharmaceutical compositions are also enabled herein.
Owner:ROYAL MELBOURNE INST OF TECH +3
Stabilised proteins for immunising against Staphylococcus aureus
Elimination of disulphide bond formation ofcysteine-containing S.aureus antigens enhances antigen stability. The invention provides a composition comprising variant forms of cysteine-containing S.aureus antigen with a point mutation that replaces, deletes or modifies the cysteine residue.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
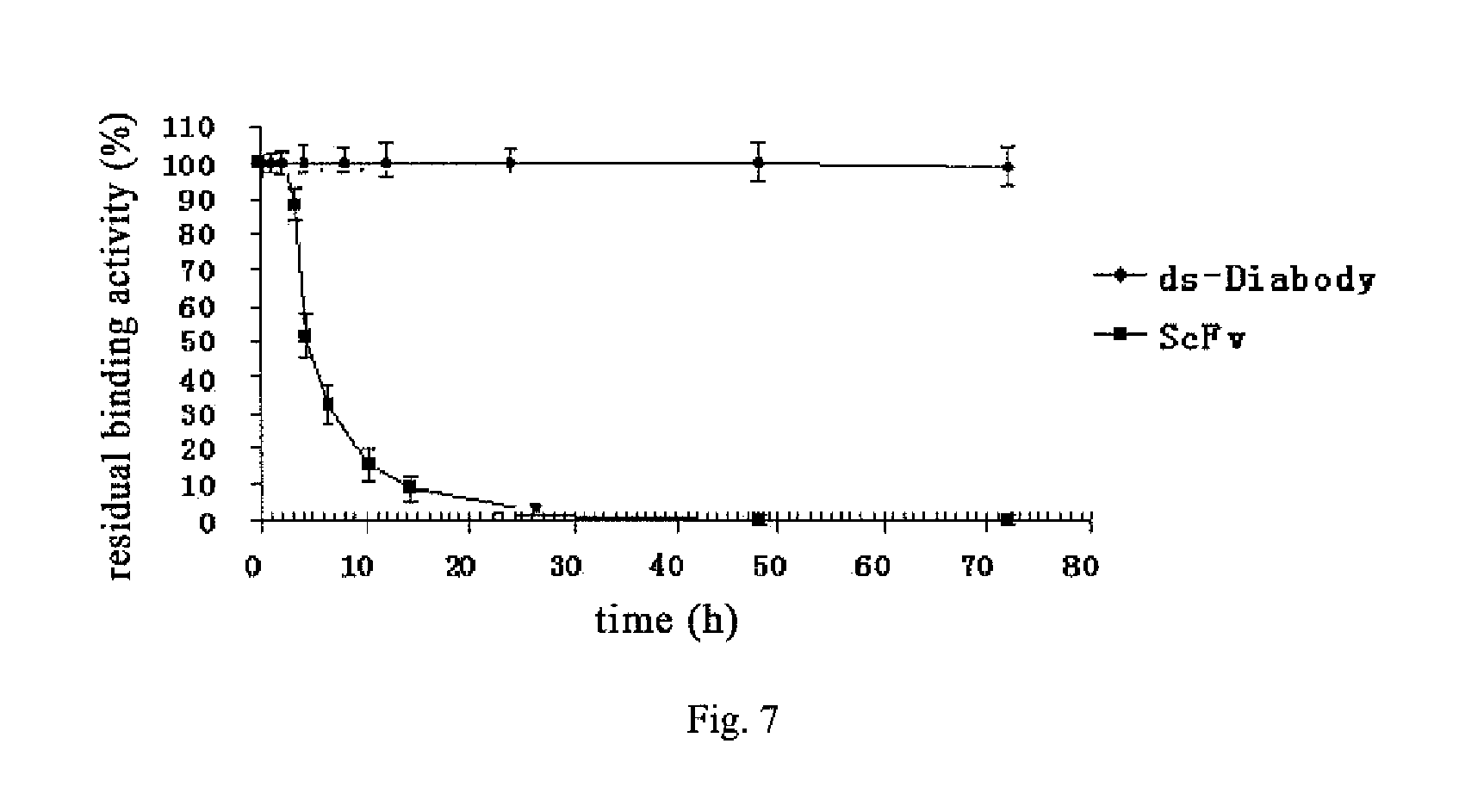
Anti-bfgf humanized double-stranded antibody with stable disulfide bond, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveUS20140350225A1High affinityImprove stabilityImmunoglobulins against growth factorsAntibody ingredientsAntigenTumor target
Disclosed are an anti-bFGF humanized double-stranded antibody with stable disulfide bond, the preparation method and the applications thereof. The amino acid sequence of the anti-bFGF humanized ds-Diabody is shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The nucleotide sequence of gene encoding the anti-bFGF humanized ds-Diabody is shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. By site-directed mutation, two cysteine residues are introduced into each single-stranded antibody, thus introducing the disulfide bond and form ds-Diabody. It is shown by experiments that the obtained ds-Diabody has the following advantages: enhanced stability; better affinity when binding to the specific antigen bFGF; moderate relative molecular weight, good tumor targeting, more powerful in tumor tissue penetration, and higher blood clearance rate, showing a broad application prospects in the clinic diagnosis and tumor therapy.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Preparation and application of novel ghrelin-like peptide modification and dimerization
ActiveCN111533800BEnhance release activityHigh activityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDisulfide bondingDimer
The invention provides the molecular degeneration of human growth hormone release hormone (HGHRH) peptides and its di clustering in the treatment of GH deficiency, infertility, dementia, diabetes, and enhanced immunity.The di agent of the present invention is two similar HGHRH -like peptide monomers that contain a single beurine molecular degeneration are connected by a sulfur (sulfurine formed by cysteine, and form an H -shaped structure (internal single ser → CYS inside the molecule → CYSreplace).The present invention also modifies the fatty acid chain of one of the lysine ε‑ amino groups of one of the lysine in the GHRH -like peptide.Extend the GHRH -like peptide monomer or di -polycatus in the body through fatty acid decoration, up to 17 days in the GH in the body.The present invention found that GHRH diodes with long -term activity have AIB → 2 ALA replacement, 18 C‑ 18 C formal sulfur formation, C20 fatty acid chain modification, and C -side amineization structure.
Owner:深圳纳福生物医药有限公司
A long-acting recombinant human filaggrin expressed by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its application
ActiveCN113045638BImprove stabilityPromote aggregationCosmetic preparationsFungiDisulfide bondingDisulphide bond formation
The invention discloses a long-acting recombinant human filaggrin expressed by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its application. The nucleotide sequence of the long-acting recombinant human filaggrin is shown in Seq ID NO.1. The long-acting recombinant human filaggrin The amino acid sequence corresponding to the nucleotide sequence is shown in Seq ID NO.2. The amino acid sequence of long-acting recombinant human filaggrin includes the amino acid sequence of filaggrin and the amino acid sequence of human serum albumin. The amino acid sequence of filaggrin includes a monomer structure corresponding to the C-terminus of the filaggrin nucleotide sequence repeat amino acid sequence. The long-acting recombinant human filaggrin provided by the invention can promote the aggregation of keratin intermediate filaments and the formation of disulfide bonds between intermediate filaments, prevent the loss of epidermal water and the invasion of external allergic substances, and reduce the apoptosis of epidermal cells induced by ultraviolet rays sensitivity. The fusion of HAS effectively improves the stability of the recombinant protein.
Owner:WUHU YINGTE FEIER BIOLOGICAL PROD IND RES INST CO LTD +1
Preparation method of beta-defensin 2 antibacterial peptide
PendingCN114044817AReduce generationHigh purityPeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesDisulfide bondingDipeptide
The invention discloses a preparation method of a beta-defensin 2 antibacterial peptide. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, selecting Fmoc-Pro-2-Chloro-Resin resin, carrying out swelling, and then removing an Fmoc protecting group; and S2, according to the sequence of the beta-defensin 2 antibacterial peptide, sequentially carrying out coupling from the C terminal to the N terminal until the last amino acid Fmoc-Gly-OH, and removing the Fmoc protecting group to obtain the beta-defensin 2 antibacterial peptide resin peptide. According to the preparation method, an Fmoc solid phase method is used, short dipeptide and short tripeptide are selected as reaction raw materials for coupling, generation of impurities is reduced, the idea that a pair of disulfide bonds is formed through oxidation to form a relatively stable structure, and then the remaining two pairs of disulfide bonds are formed through natural oxidation is adopted, so that the purposes of high purity and high yield of a crude product are achieved; the method has the advantages of high operability and reduction of emission of three wastes, can be used for large-scale production, has high theoretical guidance value and considerable economic and practical value, and is wide in application prospect.
Owner:HANGZHOU GOTOP BIOTECH
Tumor necrosis factor superfamily and tnf-like ligand muteins and methods of preparing and using the same
PendingUS20220098263A1Prevent adverse side effectsAvoid undesired formationAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDisulfide bondingDisease
The invention features homo-multimers, e.g., homo-trimers, of TNFSF or TNF-like ligand muteins in which each TNFSF ligand or TNF-like ligand mutein monomer contains at least one cysteine residue substitution or insertion that promotes the formation of a disulfide bond with a cysteine residue on a neighboring TNFSF or TNF-like ligand mutein monomer. The invention features methods of producing such TNFSF and TNF-like ligand muteins, pharmaceutical compositions containing such muteins, and methods of using such muteins in cancer immunotherapy, in treating autoimmune and neurological diseases, and in reducing or eliminating the complications and risks of rejection in organ transplantation or tissue or organ repair or regeneration.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
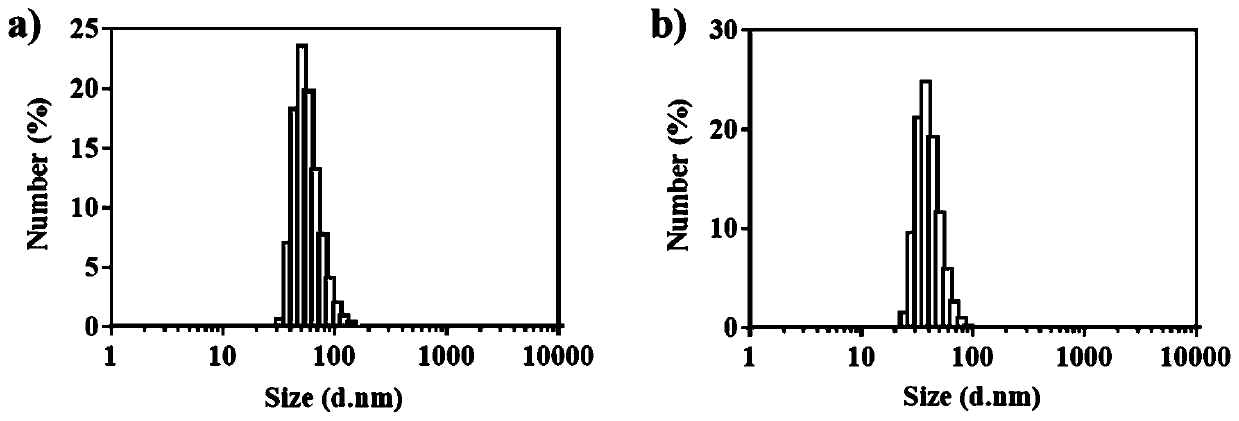
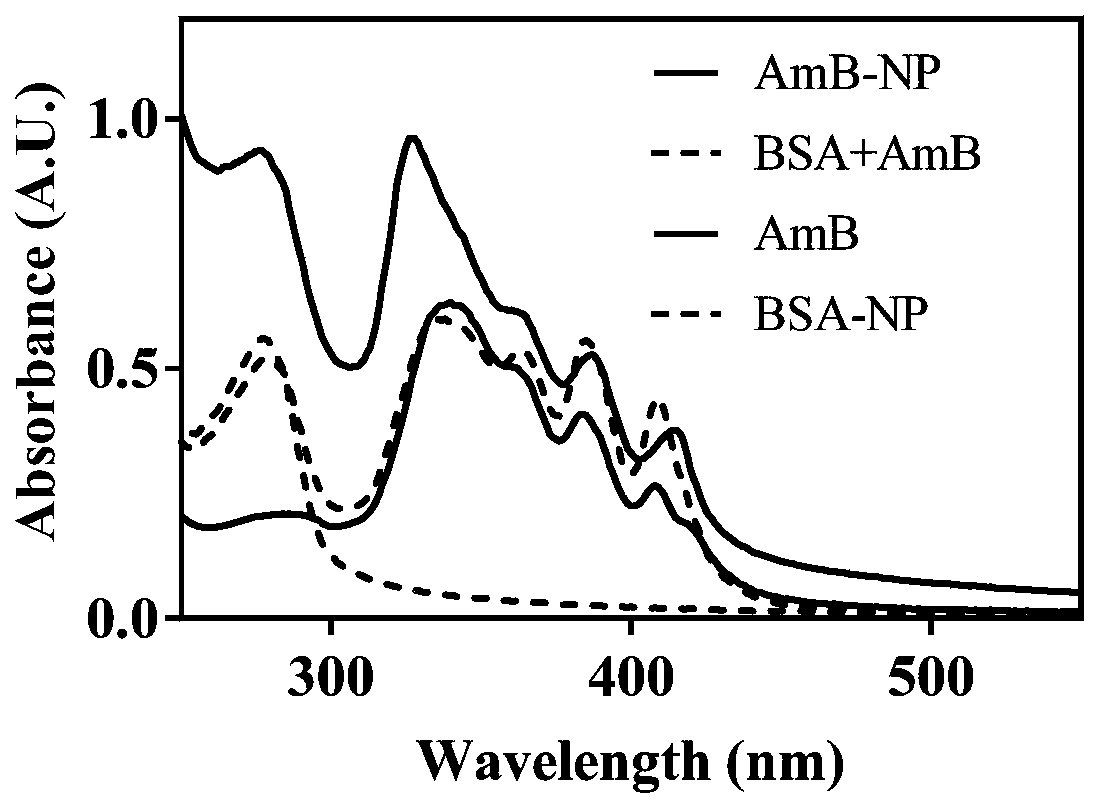
A kind of amphotericin b albumin nano-preparation and its preparation method and application
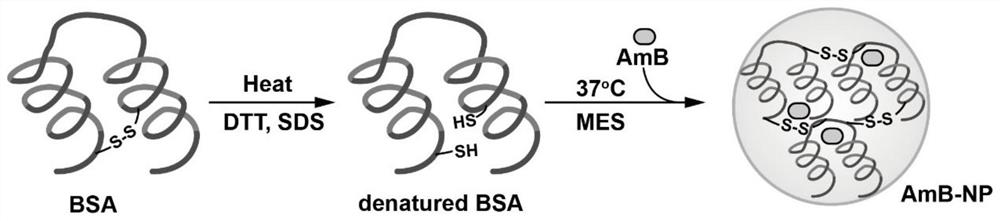
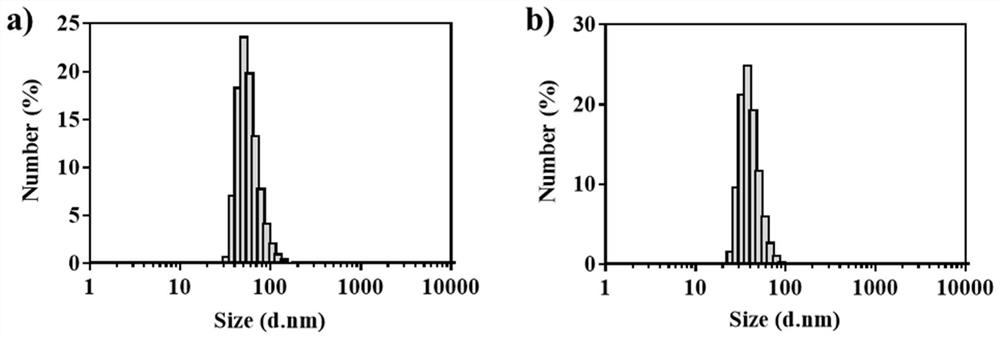
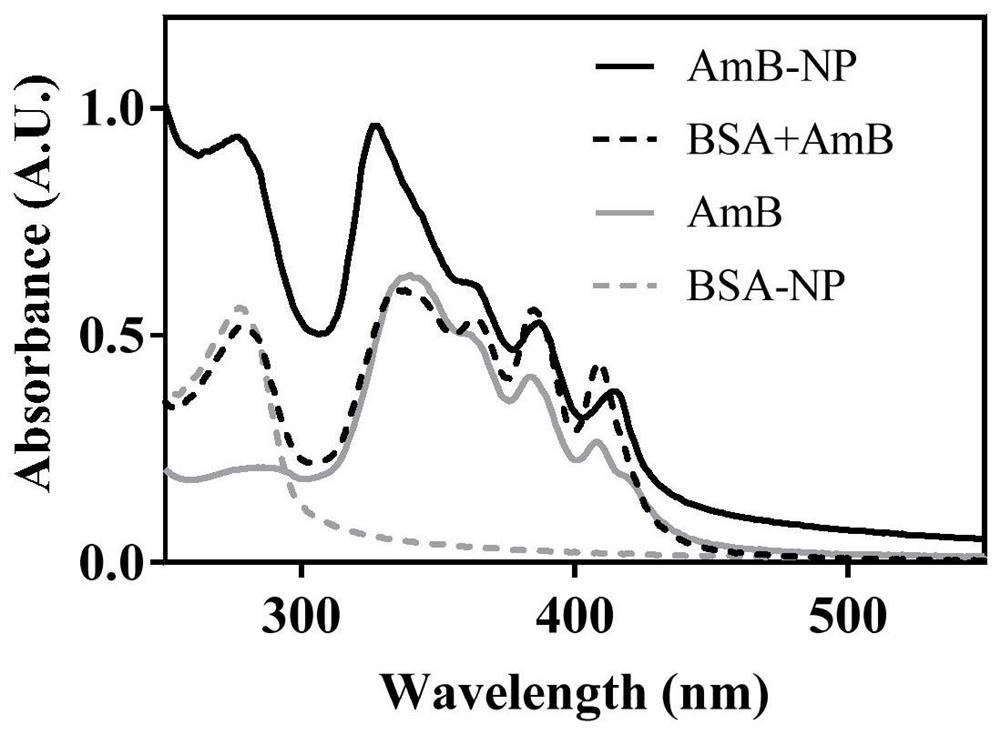
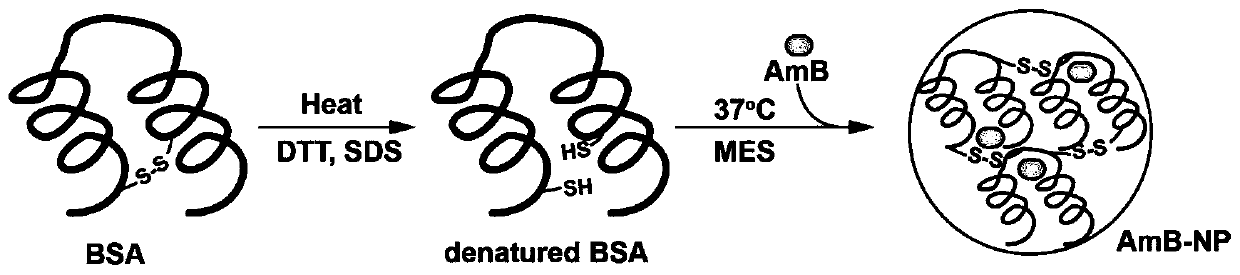
ActiveCN111529506BGuaranteed stabilityAvoid side effectsOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsDisulfide bondingDisulphide bond formation
The present invention relates to a kind of amphotericin B albumin nano-preparation and its preparation method and application, wherein through the effect of heating, reducing agent and surfactant, destroy the hydrophobic area of protein and intramolecular disulfide bond, form free thiol-rich Albumin molecules form albumin nanoparticles through the intermolecular disulfide bond network and hydrophobic interaction. In the process of forming the intermolecular disulfide bond network, the small molecule antibacterial drug amphotericin B is introduced to form Protein Nanoformulations. Compared with the prior art, the present invention makes full use of the high binding force between amphotericin B and albumin, transforms its existing deficiencies into advantages, and is expected to exert great application potential in anti-infection therapy, through in vitro and In vivo experiments showed that the nanosystem altered the biodistribution of amphotericin B and reduced drug accumulation in the kidney.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Amphotericin B albumin nanometer preparation and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111529506AImprove solubilityEffective infectionOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsDisulfide bondingDisulphide bond formation
The invention relates to an amphotericin B albumin nanometer preparation and a preparation method and application thereof. Under the action of heating, a reducing agent and a surfactant, a hydrophobicregion and intramolecular disulfide bonds of proteins are destroyed, albumin molecules rich in free sulfhydryl are formed; through an intermolecular disulfide bond network and hydrophobic interaction, albumin nanometer particles are formed; in the process of forming the intermolecular disulfide bond network, micromolecule antibacterials amphotericin B is introduced, and the amphotericin B albuminnanometer preparation can be formed. Compared with the prior art, high binding force between amphotericin B and albumin is sufficiently used, defects existing in the prior art are converted into advantages, and the amphotericin B albumin nanometer preparation hopefully exerts great application potentials in anti-infective therapy. In vitro and in vivo experiments indicate that the nanometer system changes biological distribution of the amphotericin B, and accumulation of medicines in kidneys is reduced.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
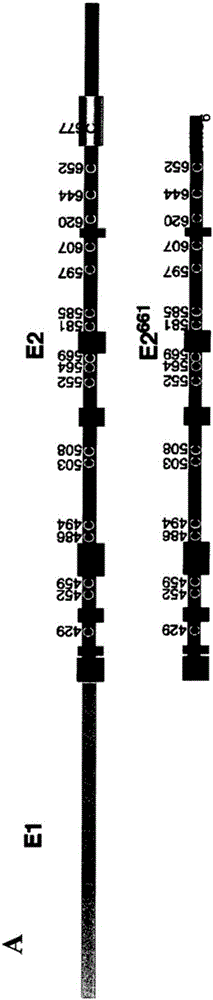
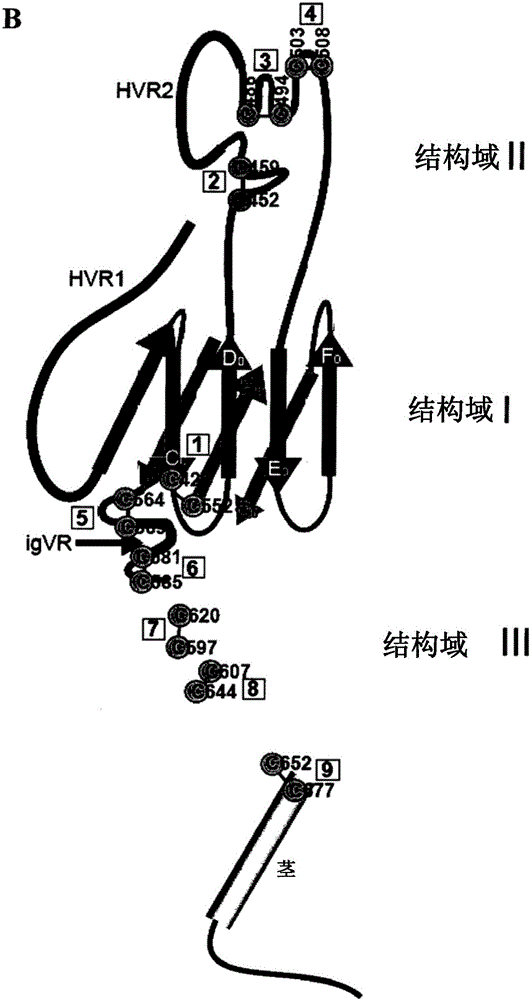
modified hepatitis C virus protein
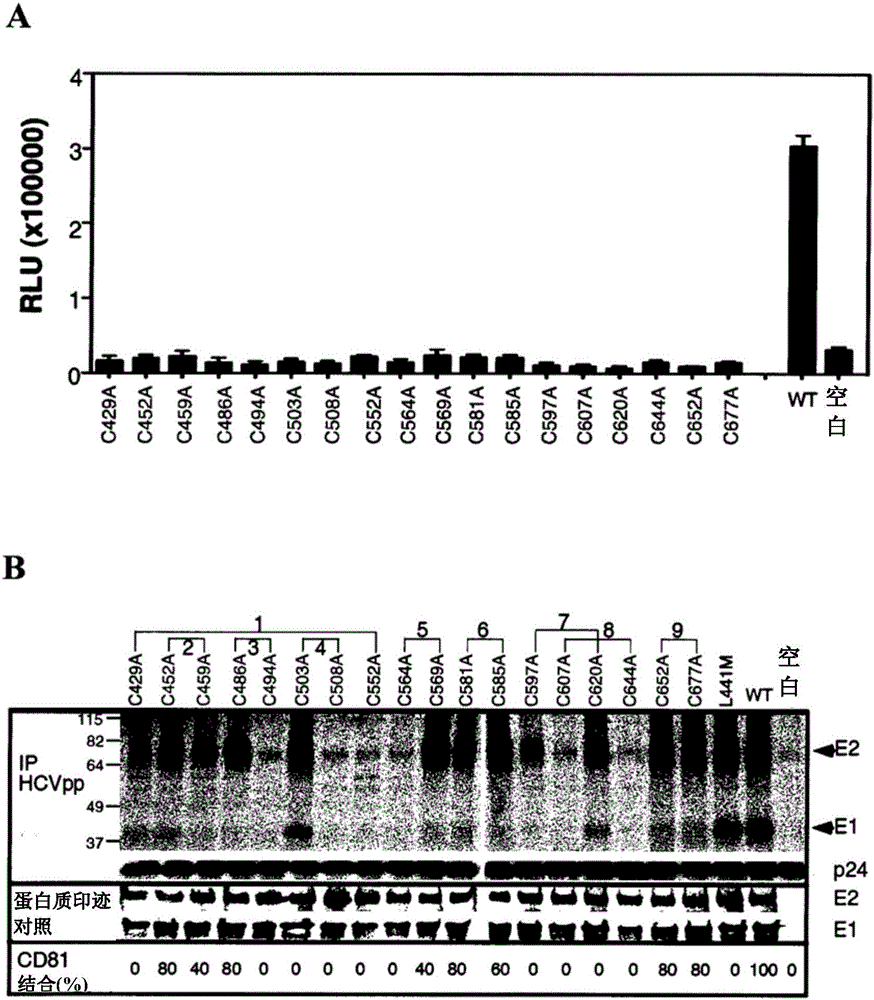
ActiveCN103354748BSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsDisulfide bondingDisulphide bond formation
The present invention provides compositions comprising hepatitis C virus (HCV) envelope 2 (E2) polypeptides, including receptor-binding variants, and various uses thereof, wherein the polypeptides are modified to comprise: (i) A cysteine mutated or interrupted at 2, 3 or 4 cysteines from C452, C486, C569, and C597; and, wherein, relative to an HCV E2 polypeptide without cysteine modification, the polypeptide passes Intermolecular disulfide bonds form substantially few multimers and CD81 binding is substantially retained. The present invention provides methods for preparing a composition comprising at least 40%, or at least 45%, or at least 50%, or at least 55%, or at least 60%, or at least 65%, or at least 70% monomeric HCV E2 polypeptide, so The method comprises expressing a polypeptide in a host cell and isolating the expressed product, wherein the polypeptide is an HCV E2 polypeptide including receptor binding variants, and wherein the polypeptide is modified to comprise: (i) a protein selected from the group consisting of C452 Cysteines mutated or interrupted at 2, 3 or 4 cysteines of C486, C569 and C597.
Owner:THE MACFARLANE BURNET INST FOR MEDICAL RES & PUBLIC HEALTH LTD
A kind of cyclic polypeptide for resisting Candida albicans and its preparation method
ActiveCN109796523BImprove antibacterial propertiesLow MIC valueAntimycoticsPeptide/protein ingredientsDisulfide bondingDisulphide bond formation
The invention belongs to the technical field of antibacterial agents, and in particular relates to a cyclic polypeptide for resisting Candida albicans and a preparation method thereof. The amino acid sequence of the cyclic polypeptide is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, which is an intramolecular cyclic polypeptide, and an intramolecular disulfide bond is formed between two cysteine residues in its amino acid sequence to form a molecular Inner loop structure, in which the C-terminal end is composed of 8 arginines, the sequence contains two unnatural amino acids, and the proline at the β-turn angle of the polypeptide is replaced with D PRO‑ L PRO to increase stability in beta-turns. The cyclic polypeptide of the invention has simple amino acid sequence structure and convenient synthesis, is used for the prevention and treatment of diseases caused by Candida albicans, and has high antibacterial activity.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
A traditional Chinese medicine-magnetic nanocluster chemoimmunodrug delivery system and preparation method thereof
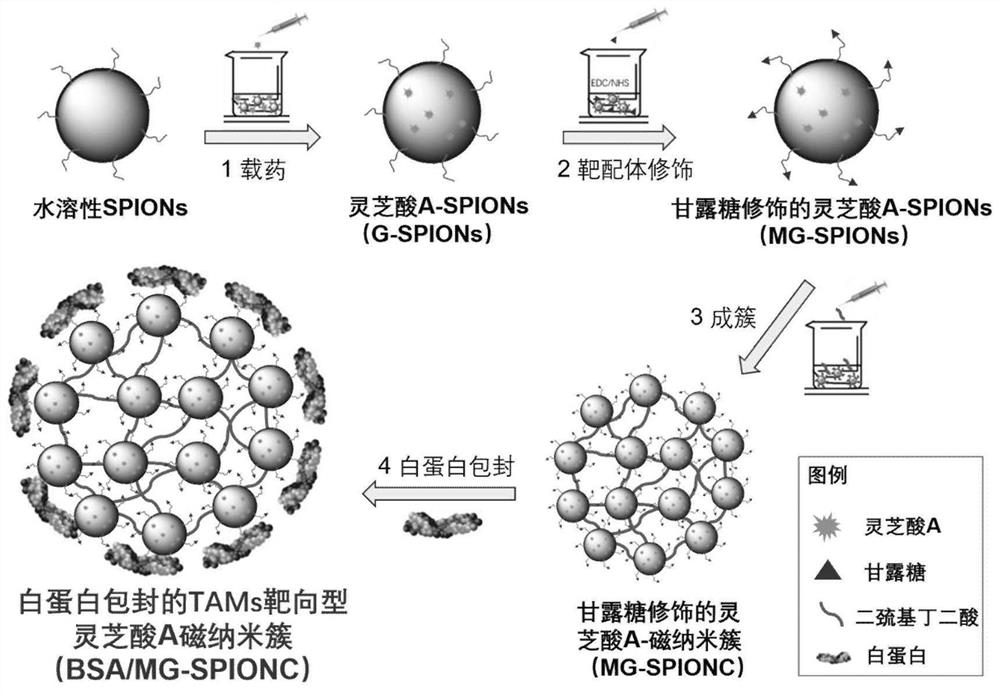
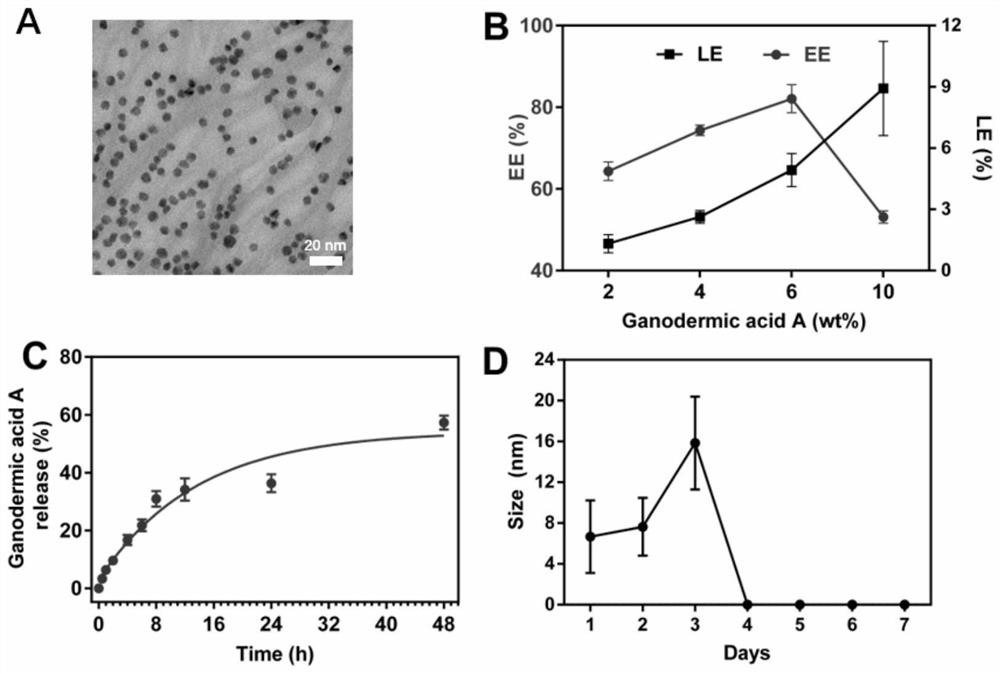
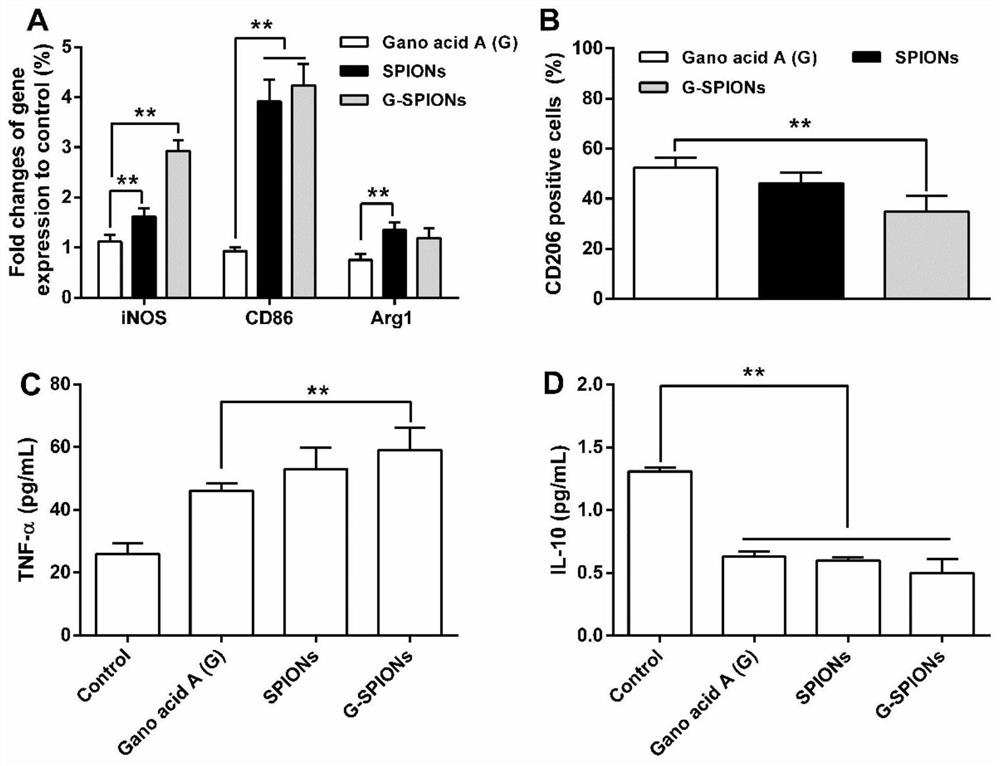
ActiveCN109045303BCirculatory stabilityAccurate targetPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDisulfide bondingDisulphide bond formation
The invention relates to a traditional Chinese medicine-magnetic nano-cluster chemoimmunomedicine delivery system and a preparation method thereof, comprising superparamagnetic oxide nanoparticles; the surface of the superparamagnetic oxide nanoparticles anchors drugs and targeting ligands of TAMs; The superparamagnetic oxide nanoparticles form a nano-cluster structure through a disulfide bond; the nano-cluster structure encapsulates proteins. The traditional Chinese medicine-magnetic nanocluster chemoimmunopharmaceutical delivery system of the present invention integrates the targeting advantages of magnetic tendency, ligand modification, and reduction sensitivity, and is a traditional Chinese medicine chemoimmunopharmaceutical delivery system with stable internal circulation, efficient tumor aggregation, and precise targeting of TAMs system.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE INST OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Stabilised proteins for immunising against Staphylococcus aureus
ActiveUS9926344B2High selectivityPreventing oligomerizationAntibacterial agentsDepsipeptidesAntigenDisulphide bond formation
Elimination of disulphide bond formation of cysteine-containing S. aureus antigens enhances antigen stability. The invention provides variant forms of cysteine-containing S. aureus antigen with a point mutation that replaces, deletes or modifies the cysteine residue.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Cyclic polypeptide for preventing candida albicans and preparation method of cyclic polypeptide
ActiveCN109796523AImprove antibacterial propertiesLow MIC valueAntimycoticsPeptide/protein ingredientsArginineCandida famata
The invention belongs to the technical field of antibacterial agents, and particularly relates to a cyclic polypeptide for preventing candida albicans and a preparation method of the cyclic polypeptide. The amino acid sequence of the cyclic polypeptide is represented by SEQ ID NO. 1, and the cyclic polypeptide is an intramolecular cyclic polypeptide; an intramolecular disulfide bond is formed between two cysteine residues in the amino acid sequence of the cyclic polypeptide, and accordingly, an intramolecular cyclic structure is formed; the tail of a terminal C is composed of eight arginines,the sequence has two unnatural amino acids, and proline located at the beta-turn of the polypeptide is replaced by DPRO-LPRO to improve the stability of the beta-turn. The cyclic polypeptide has a simple amino acid sequence structure, is convenient to synthesize, is used for preventing and treating diseases caused by the candida albicans, and has high antibacterial activity.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Multimeric hybrid fc proteins for replacement of ivig
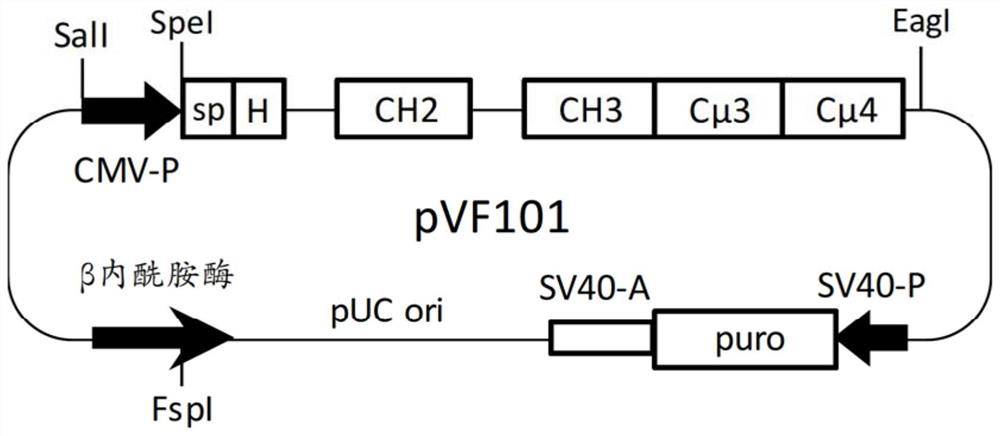
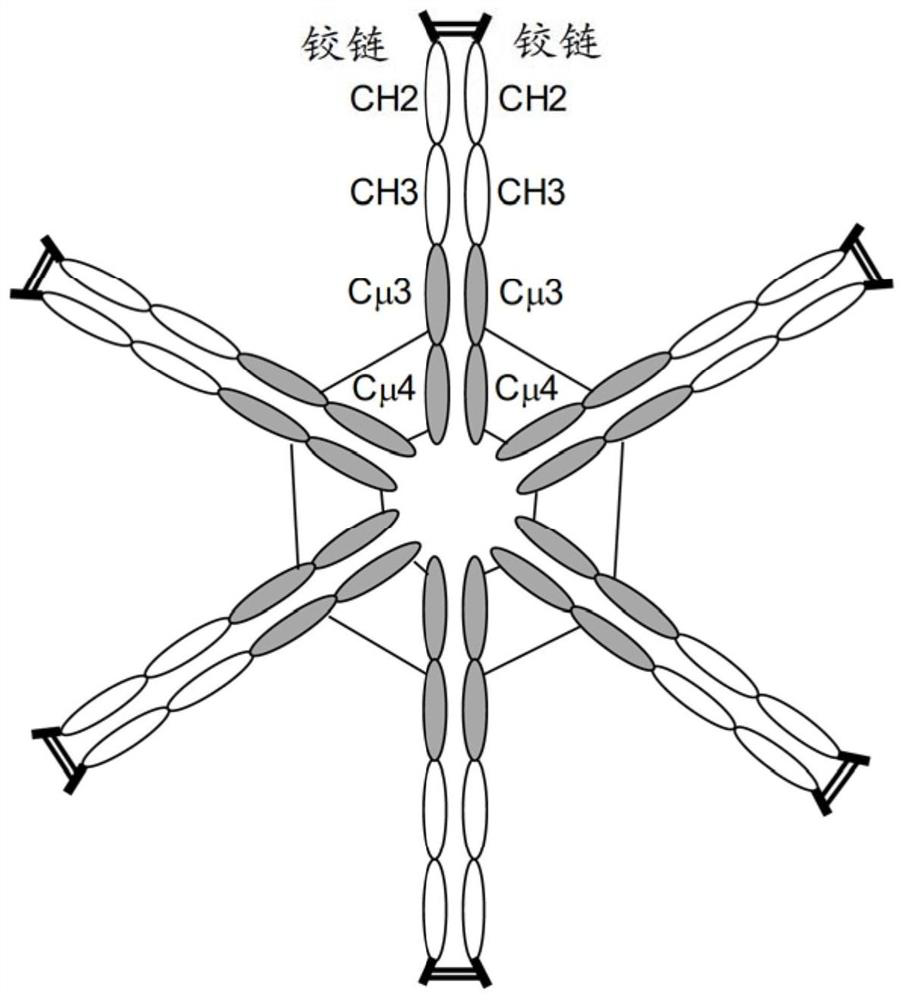
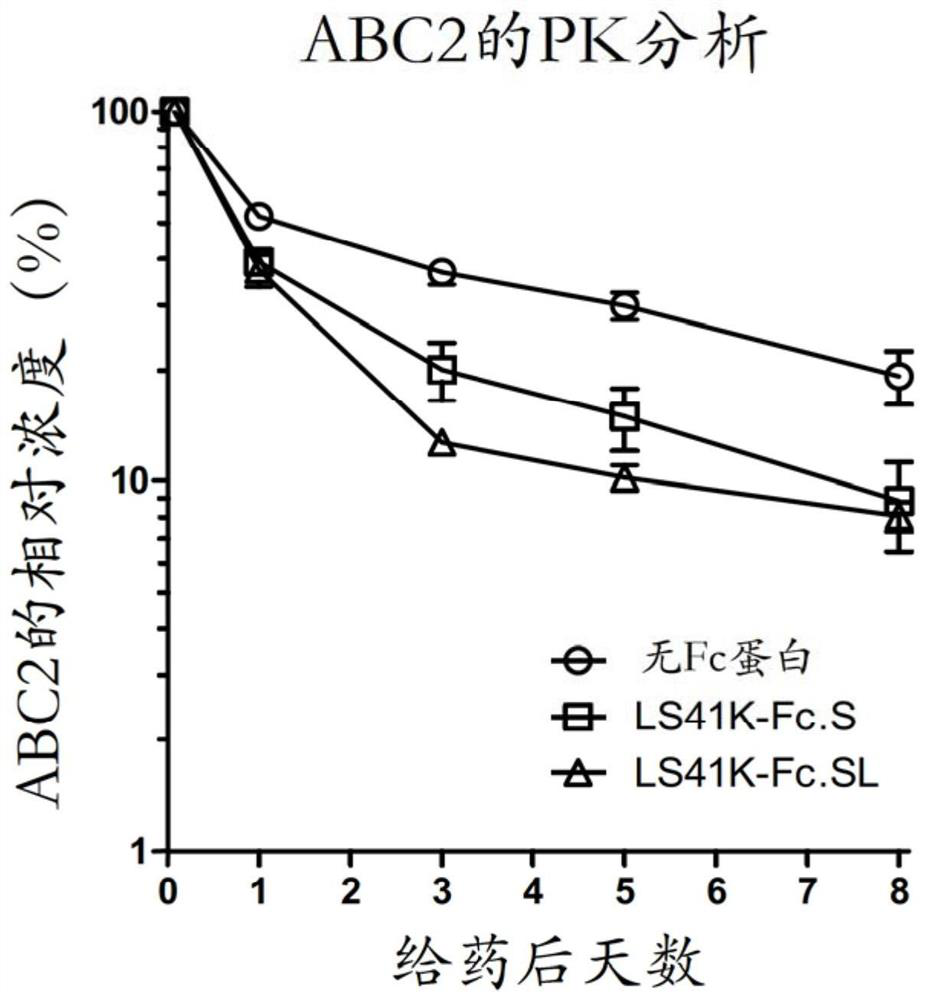
PendingCN113271972AHybrid immunoglobulinsPeptide/protein ingredientsDisulfide bondingDisulphide bond formation
The hybrid Fc proteins of this invention include IgG and IgM Fc components. The IgG Fc component includes at least a portion of a hinge region and CH2 and CHS regions. The IgM component includes C[mu]3 and C[mu]4 regions of a C[mu] constant region. The hybrid Fc proteins can form duplexes by interchain disulfide bonding between cysteines in their hinge regions. The hybrid Fc proteins can be used for treating immune disorders mediated by endogenous IgG, such as those previously treated with intravenous immunoglobulin.
Owner:JN BIOSCI
Helicomimetics and stabilized lxxll peptidomimetics
InactiveUS20050054770A1Enhance helical characterEasily be made selectivePeptidesPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCyclic peptideCysteine thiolate
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com