modified hepatitis C virus protein
A kind of technology of hepatitis C virus and composition, applied in the direction of virus, virus peptide, immunoglobulin, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0283] Example 1: Cysteine disulfide bond substitution mutations alone in the context of full-length E2 glycoprotein co-expression with E1
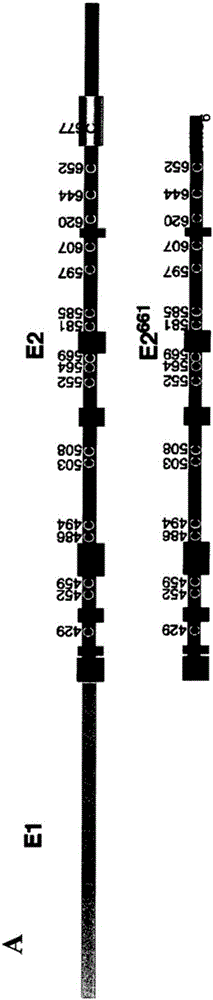
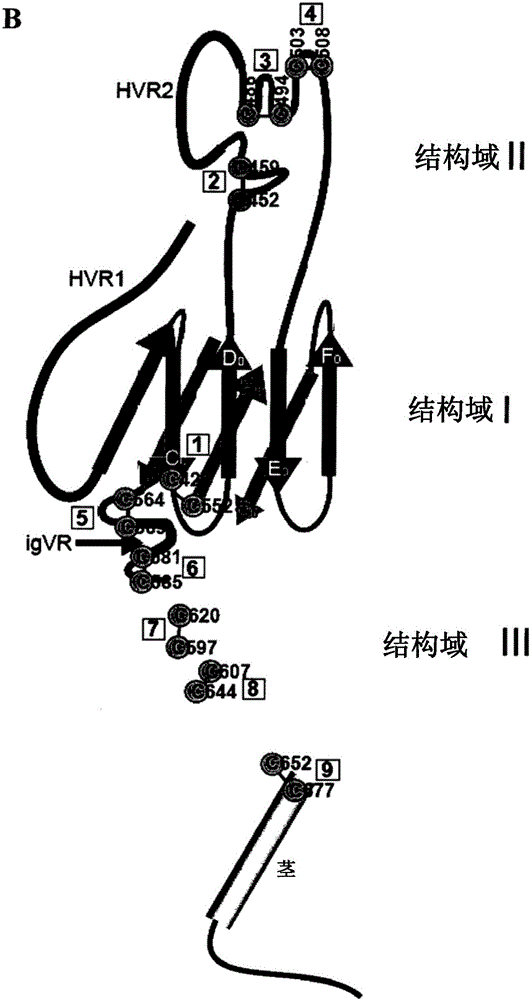
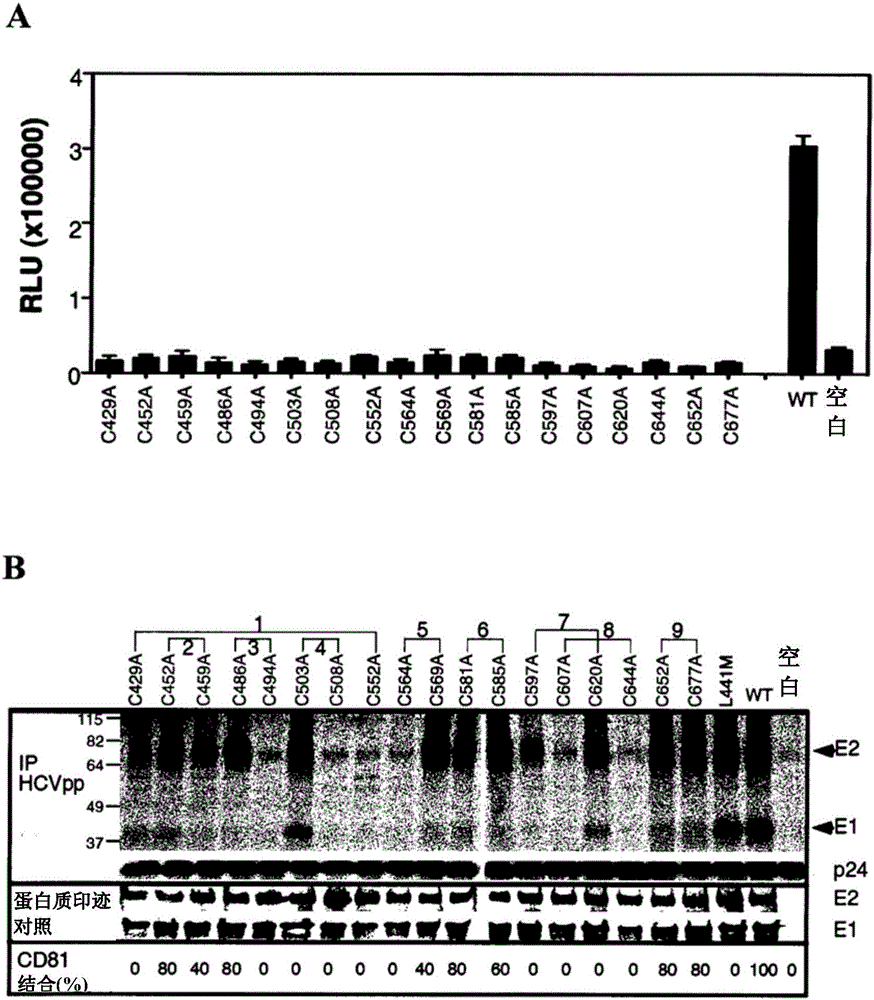
[0284] As proposed by Krey et al., 2010 (supra), the disulfide bond assignments for the domain structure of E2 are shown in Figure 1 and Table 2. In the context of E1E2 derived from the genotype 1a isolate H77c in HCVpp, the effect of replacing individual cysteines with alanines on E2 folding and function was assessed. Substitution of Cys to Ala abolished the ability of HCVpp to infect Huh7 hepatoma cells, suggesting that the nine disulfide bonds of E2 are critical for cell entry ability (Fig. 2A). Western blot analysis of transfected cell lysates with MAb H52 (for E2) and MAb A4 (for E1 ) showed that E1 and E2 were expressed at wild-type levels (Fig. 2B). However, the use of the conformation-dependent E2-specific MAb, H53, in immunoprecipitation of biosynthetically-tagged HCVpp indicated that the mutation had caused defects in the gly...
Embodiment 2
[0288] Example 2: Simultaneous mutagenesis of cysteine pairs involved in disulfide bond formation
[0289] Cys-to-Ala scanning of the HIV envelope glycoprotein gp120 / gp41 complex reveals that cysteine mutations alone do not favor functional protein folding, while simultaneous Ala substitutions are in 2 out of 10 disulfide bonds Both fold and function are rescued (van Anken et al., Mol Biol Cell 19:4298-309, 2008). To reduce the tendency of proteins to mispair due to the presence of unpaired cysteines, Ala-substitutions of each disulfide bond pair were performed simultaneously. For the double Cys-to-Ala mutant, intracellular expression and polyprotein processing of E1 and E2 were confirmed by Western blot ( Figure 3A ), however, lacked HCVpp entry activity (data not shown). Incorporation of H53-reactive E2 into HCVpp was observed for C452A / C459A (domain II), C581A / C585A and C652A / C677A (domain III), which did not form heterodimers with E1 ( Figure 3A ). In these 3 cas...
Embodiment 3
[0290] Embodiment 3: in the truncated E2 glycoprotein (E2 661 Single cysteine and pairwise disulfide bond substitution mutations in -his)
[0291] Next, in the receptor binding domain of E2 (residues 384-661, E2 661 -His) to assess the effect of the Cys-to-Ala mutation, E2 folds independently of E1, retains the 3-domain structure described by Krey et al., 2010 (supra), and retains CD81 and SRB1 binding function. All mutants were secreted from transfected 293T cells at wild-type levels, as shown by immunoprecipitation of metabolically tagged proteins with anti-His antibody via the C-terminal 6-His tag ( Figure 4A , upper tile). E2 661 All but one of the MAb H53-reactivity profiles of the -His mutants largely mirrored those observed for the corresponding E1E2 mutants ( Figure 4A , 2nd and 3rd tiles, see Fig. 2B). Thus, Cys residues essential for H53 reactivity include C494, C508 (DII), C552, C564 (DI), C607 and C644 (DIII), while C452, C459, C486, C503 (DII), C569, C581...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com