Method for extracting edible rice starch and rice protein from broken rice with excessive pesticide residues
A technology of rice starch and rice protein, applied in the field of food processing, can solve the problems of wasting energy, damage product quality, reduce product yield, etc., and achieve the effects of good safety, increased yield, and reduced residual protein
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] (1) Raw material crushing: the ratio of rice to water to liquid is 1:6 (g / L), soaked in 0.1% alkali solution, and use a colloid mill to crush the raw materials, and after crushing, the rice milk is then ultrafinely crushed by an ultrafine pulverizer;
[0037] (2) rice milk reaction: stirring the rice milk obtained in step (1) for 6 hours;
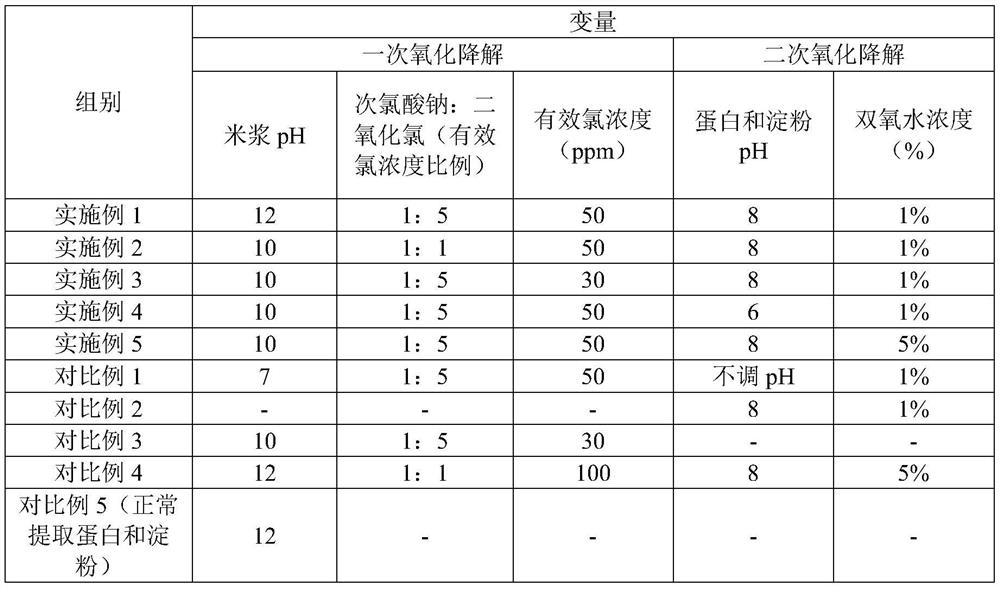
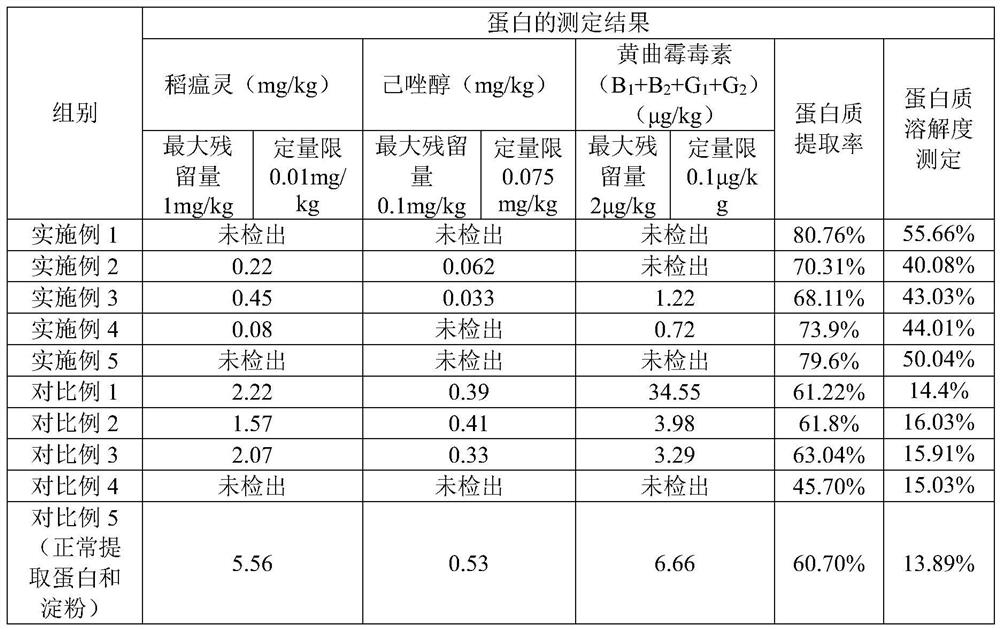
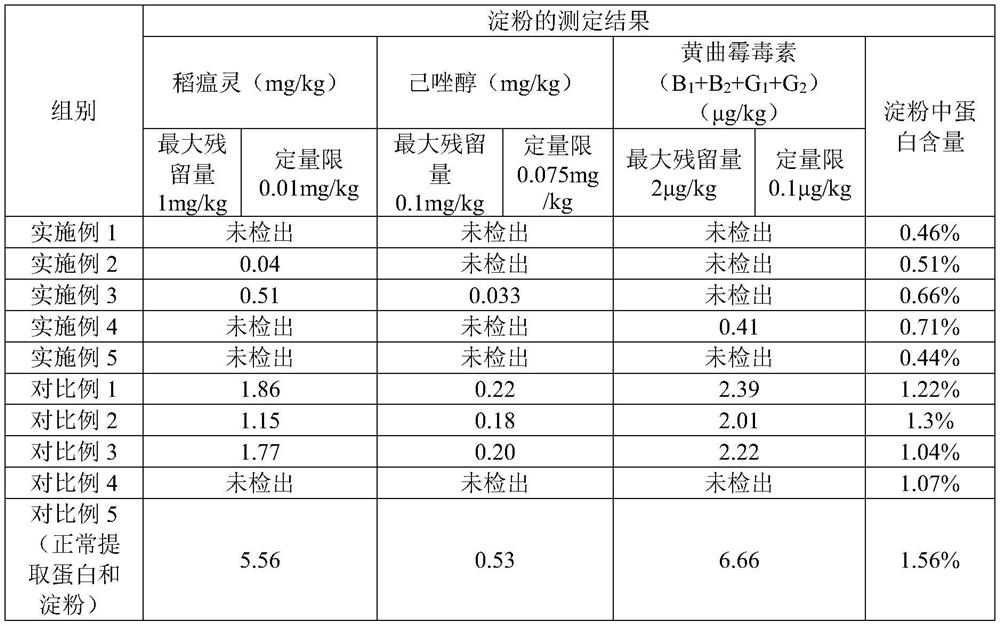
[0038] (3) The first oxidative degradation of pesticide residues and toxins: adjust the pH of the rice milk obtained in step (2) to 12, add sodium hypochlorite and chlorine dioxide, the molar ratio of the two is (1:5), and make the available chlorine concentration 50ppm , and stirred for 30min;
[0039] (4) centrifugation: the rice milk obtained in step (3) is centrifuged in a centrifuge, and the light phase obtained is protein liquid, and the heavy phase is starch;
[0040] (5) Oxidative degradation of pesticide residue toxins for the second time: adjust the pH of the protein solution obtained in step (4) to 8, add hydrogen peroxid...
Embodiment 2
[0050] (1) Raw material pulverization: the ratio of rice to water to liquid is 1:6 (g / L), soaked in 0.1% alkali solution, and use a colloid mill to pulverize the raw materials.
[0051] (2) rice milk reaction: stirring the rice milk obtained in step (1) for 6 hours;
[0052] (3) The first oxidative degradation of pesticide residues and toxins: adjust the pH of the rice milk obtained in step (2) to 10, add sodium hypochlorite and chlorine dioxide, the molar ratio of the two is (1:1), and the available chlorine concentration is 50ppm , and stirred for 30min;
[0053] (4) centrifugation: the rice milk obtained in step (3) is centrifuged in a centrifuge, and the light phase obtained is protein liquid, and the heavy phase is starch;
[0054] (5) Oxidative degradation of pesticide residue toxins for the second time: adjust the pH of the protein solution obtained in step (4) to 8, add hydrogen peroxide to make its mass concentration 1%, and stir for 30 minutes; add water to the star...
Embodiment 3
[0064] (1) Raw material crushing: the ratio of rice to water to liquid is 1:6 (g / L), soaked in 0.1% alkali solution, and use a colloid mill to crush the raw materials, and after crushing, the rice milk is then ultrafinely crushed by an ultrafine pulverizer;
[0065] (2) rice milk reaction: stirring the rice milk obtained in step (1) for 6 hours;
[0066] (3) The first oxidative degradation of pesticide residues and toxins: adjust the pH of the rice milk obtained in step (2) to 10, add sodium hypochlorite and chlorine dioxide, the molar ratio of the two is (1:5), and make the available chlorine concentration 30ppm , and stirred for 30min;
[0067] (4) centrifugation: the rice milk obtained in step (3) is centrifuged in a centrifuge, and the light phase obtained is protein liquid, and the heavy phase is starch;
[0068] (5) Oxidative degradation of pesticide residue toxins for the second time: adjust the pH of the protein solution obtained in step (4) to 8, add hydrogen peroxid...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com