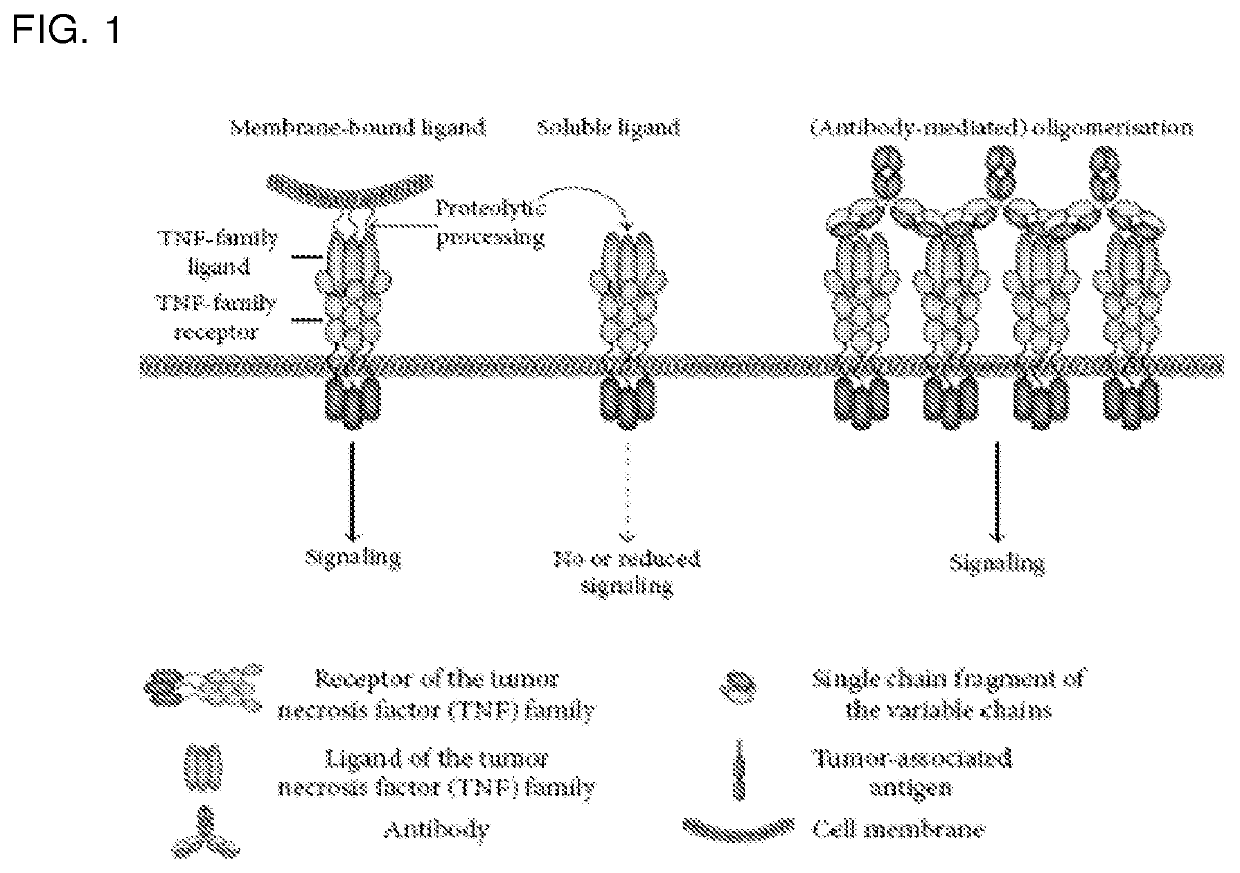
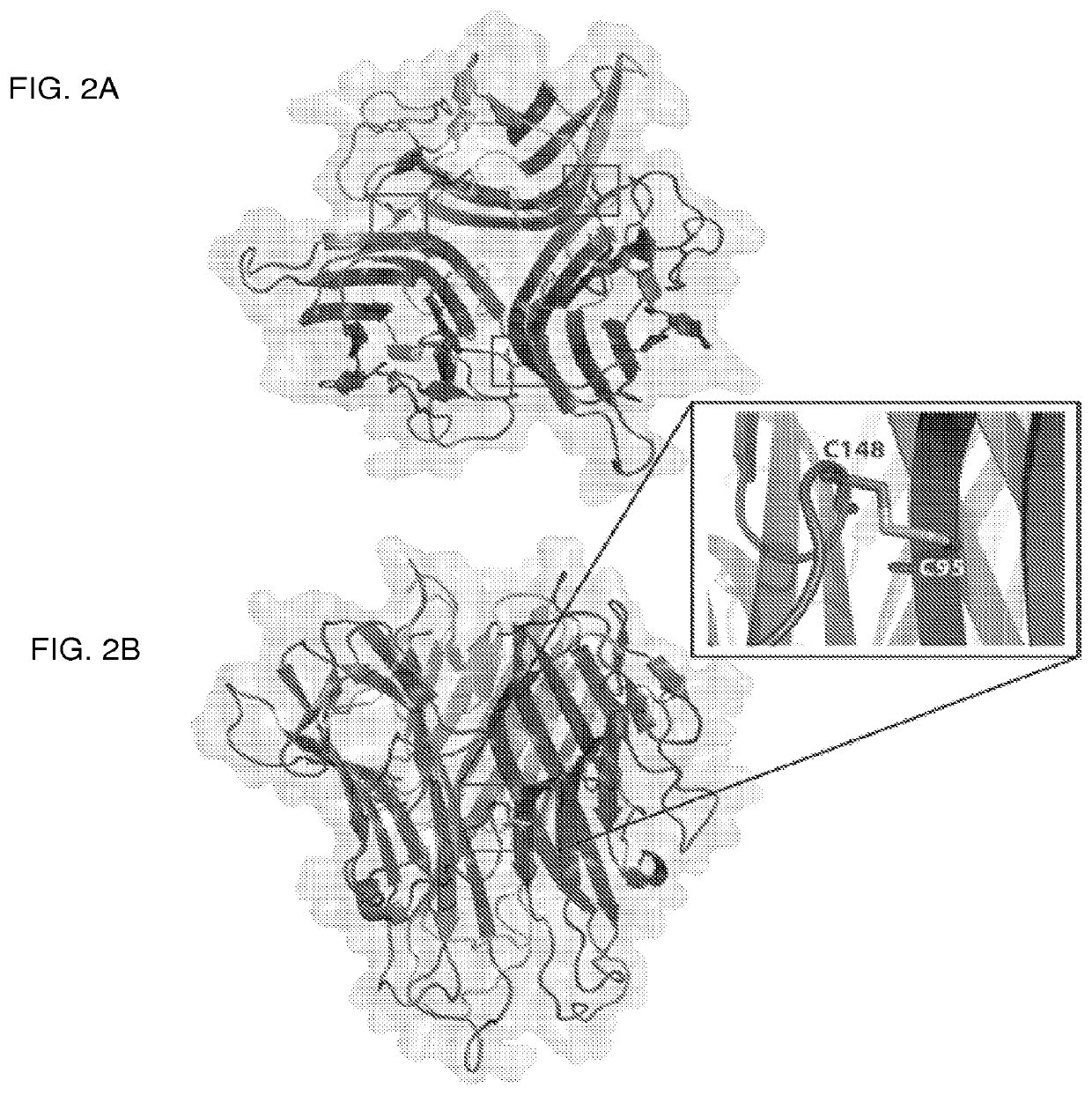
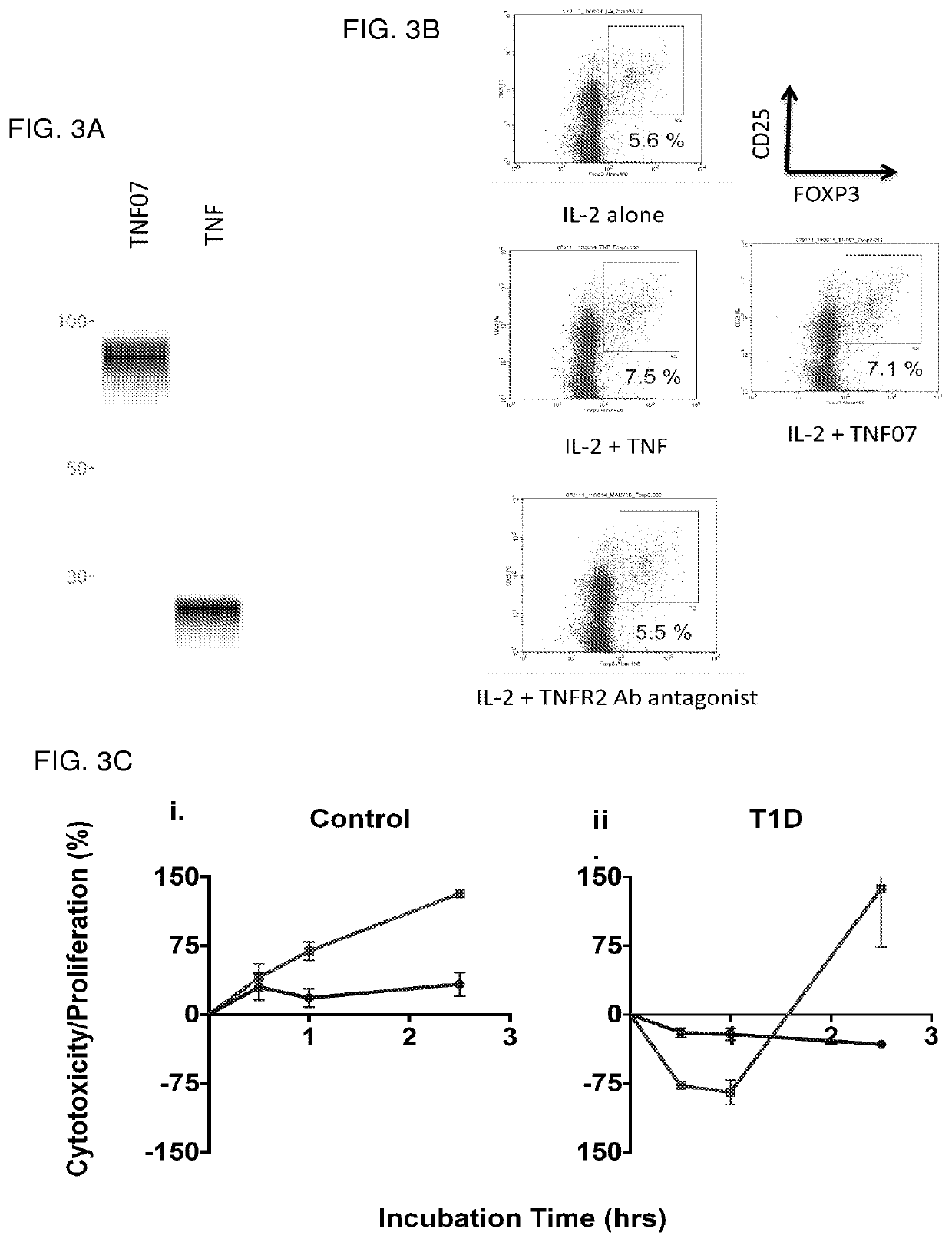
Tumor necrosis factor superfamily and tnf-like ligand muteins and methods of preparing and using the same
a tumor necrosis factor and superfamily technology, applied in tumor necrosis factor, metabolism disorder, immunological disorders, etc., can solve the problems of degrading and removal of soluble tnfsf ligands from the body, and achieve the effect of avoiding adverse side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
and Methods
[0323]Reagents
[0324]Recombinant human and mouse TNF-α was purchased from Leinco Technologies (St. Louis, Mo.), and recombinant human IL-2 was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, Mo.). Human monoclonal antibodies against TNFR2 were from internal sources and external commercial vendors. Intracellular staining of FOXP3 and CD25 were performed using either FOXP3 Fix / Perm Buffer set (Biolegend) or Human FOXP3 Buffer set (BD Biosciences).
[0325]Human Subjects
[0326]Subjects used in this study were either Type-1 diabetic subjects or non-affected control subjects. They were recruited from Massachusetts General Hospital with full institutional approval and informed consent (MGH-2001P001379). Each subject donated 4 tubes of blood and the blood was used fresh in the morning for the preparation of either CD8 T cells for the WST-1 proliferation / death assay or CD4 T cells for the T regulatory assays. For the WST-1 assays of cell proliferation or death, each autoimmune subject was si...
example 2
ion of Wild-Type Soluble TNF-α and the TNF-α Mutein
[0329]In this example, the wild-type soluble TNF-α is a TNF-α monomer and the TNF-α mutein is a disulfide-bonded homo-trimer of TNF-α muteins in which each monomer contains S171C and G224C cysteine substitutions. Construction of wild-type soluble TNF-α and the TNF-α mutein involved original gene synthesis of the DNA fragments into the His6-thrombin-site-TNF-α gene-fusion and these were subcloned into pDEST42 expression vector. Positive clones were confirmed by restriction enzyme digestion and sequence validation. Wild-type soluble TNF-α and the TNF-α mutein were expressed in E. coli strain BL21 DE3 pLys S using the following conditions: a seed culture was incubated at 37° C. for 16 hours and was used to inoculate 4 liter of tissue culture media, which was incubated at 37° C. until A600=0.8. Protein expression was induced with IPTG (0.1 mM) for 16 hours at 18° C. Cells were harvested by centrifugation and stored at −80° C.
[0330]Cell ...
example 3
lot Analysis of the TNF-α Mutein
[0333]In this example, the wild-type soluble TNF-α is a TNF-α monomer and the TNF mutein is a disulfide-bonded homo-trimer of TNF-α muteins in which each monomer contains S171C and G224C cysteine substitutions. Wild-type soluble TNF-α and TNF-α mutein were analyzed on a Peggy Automated Western Assay Platform in size separation mode (ProteinSimple, Santa Clara, Calif.). Samples (0.5 μg / ul) were mixed at a ratio of 3:1 with a 4× Mastermix containing fluorescent molecular weight standards and sample buffer, but without DTT (Dithiothreitol) reducing agent. To further prevent reduction, the samples were not subjected to high (95° C.) temperature as is customary, but rather were kept on ice until use. All running parameters were left at their defaults, except for loading time (12 seconds instead of default of 8 seconds) and for first antibody incubation time (240 min instead of default of 120 min). Detection of wild-type soluble TNF-α and the TNF-α mutein w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Solubility (mass) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com