Microsatellite marker applied to growth trait analysis of Macrobrachium nipponense and application thereof
A technology for microsatellite markers and growth traits, which is applied in the field of biological genetics and breeding of Macrobrachium prawns, can solve the problems of habitat disturbance, damage to the structure of population growth traits, and achieves the effect of stable PCR amplification results and assisted breeding.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1 Measurement and Recording of Macrobrachium japonicus Population Growth Character Phenotype Values
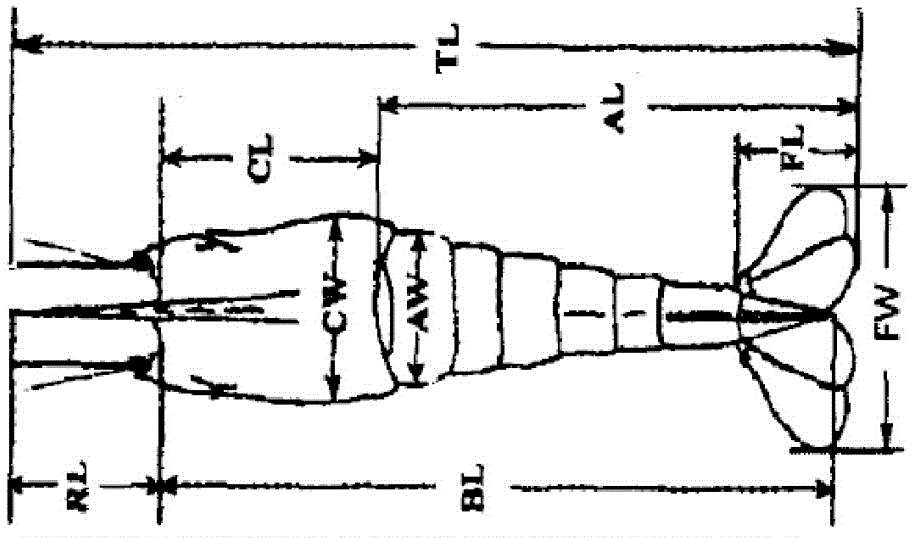
[0032] 24 live samples of Macrobrachium japonicus were selected from Baiyangdian Lake (BYD) in Hebei, Hengshui Lake in Hebei (HSH), Weishan Lake in Shandong (WSH) and Hongze Lake in Jiangsu (HZH). Macrobrachium japonicus was weighed and measured, and the measurement indicators included weight, total length, body length, carapace length, carapace width, carapace height, abdomen length, abdomen width, abdomen height, tail fan length, There are 14 measurable traits including the width of the tail fan, the length of the forehead sword, the length of the second leg, and the length of the second leg. Schematic diagram of the measurement site for the morphological parameters of Macrobrachium japonicus figure 1 shown. The measurement is accurate to 0.02mm. in:
[0033] Body weight (BW): the wet weight of the whole body, use filter paper to absorb the water on the bo...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Example 2 Extraction of Total DNA from Macrobrachium japonicus Wild Population Muscle
[0048] The total muscle DNA was extracted using a marine animal genome extraction kit, and the specific steps were as follows:
[0049] (1) Cut no more than 30 mg of tissue material, put it into a centrifuge tube filled with 200 μL GA buffer, and vortex for 15 seconds.
[0050] (2) Add 20 μL of Proteinase K (20mg / ml) solution, vortex to mix, and briefly centrifuge to remove water droplets on the inner wall of the tube cap. Place at 56°C until the tissue is completely dissolved, centrifuge briefly to remove water droplets on the inner wall of the tube cap, and proceed to the next step.
[0051] (3) Add 200 μL buffer GB, mix thoroughly by inversion, place at 70°C for 10 minutes, the solution should become clear, and briefly centrifuge to remove water droplets on the inner wall of the tube cap.
[0052](4) Add 200 μL of absolute ethanol and mix thoroughly by inversion. At this time, f...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Example 3 Development of Microsatellite Marker Primers
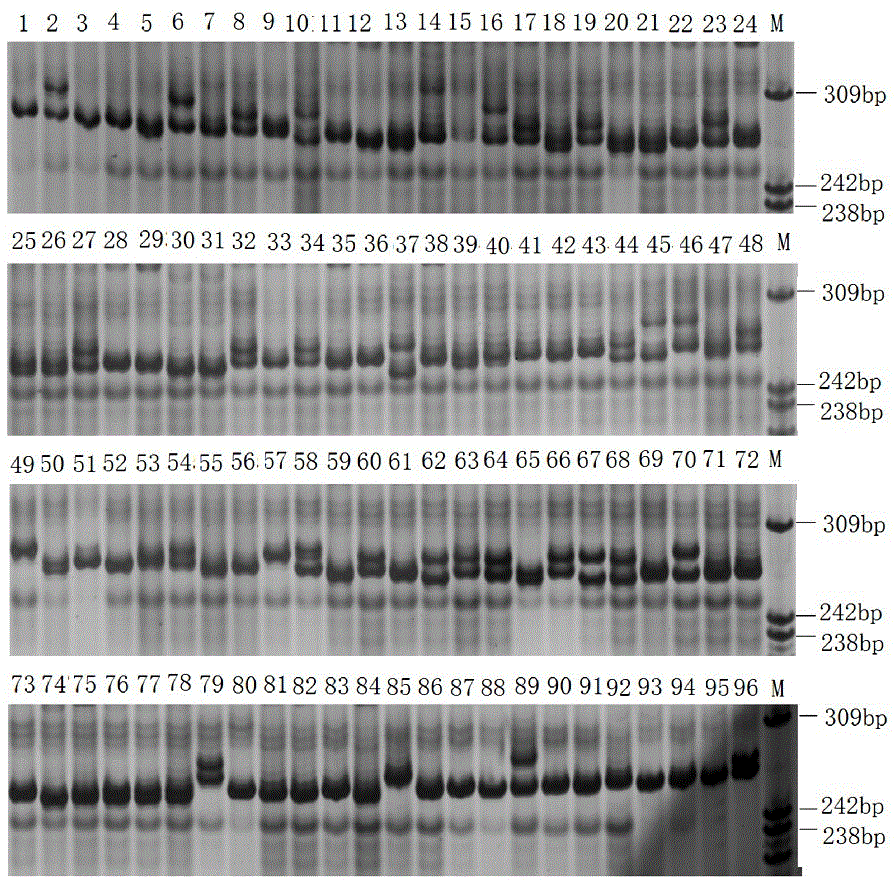
[0061] (1) Macrobrachium japonicus was purchased from the Baiyangdian aquatic product market. The muscle tissue was taken under sterile conditions, and the total RNA of the muscle tissue was extracted, and sent to a biological company for transcriptome sequencing to obtain transcriptome data; the assembled length was obtained using MISA software. The unigenes over 1kb are identified for SSR. The identification criteria are: the minimum repeats of precise SSR markers containing two, three, four, five and six nucleotide types are 9, 6, 5, and 4 times respectively, using SSRHunter1.3 Perform SSR marker screening to ensure that the front and rear flanks of the sequence are of sufficient length for primer design. Use Primer Permier 6 to design primers based on the screened SSRs; the main parameters of the design are: the optimal length of the primer is 18-25 bp, the length of the PCR product fragment is 100-350 bp, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com