Method for analyzing aeromonas hydrophila infected macrobrachium nipponense blood cell differential expression protein based on proteomics quantitative technology
A technology of Aeromonas hydrophila and proteomics, applied in the field of freshwater aquaculture, can solve the problems of high cost, large demand and inability to label animal models.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
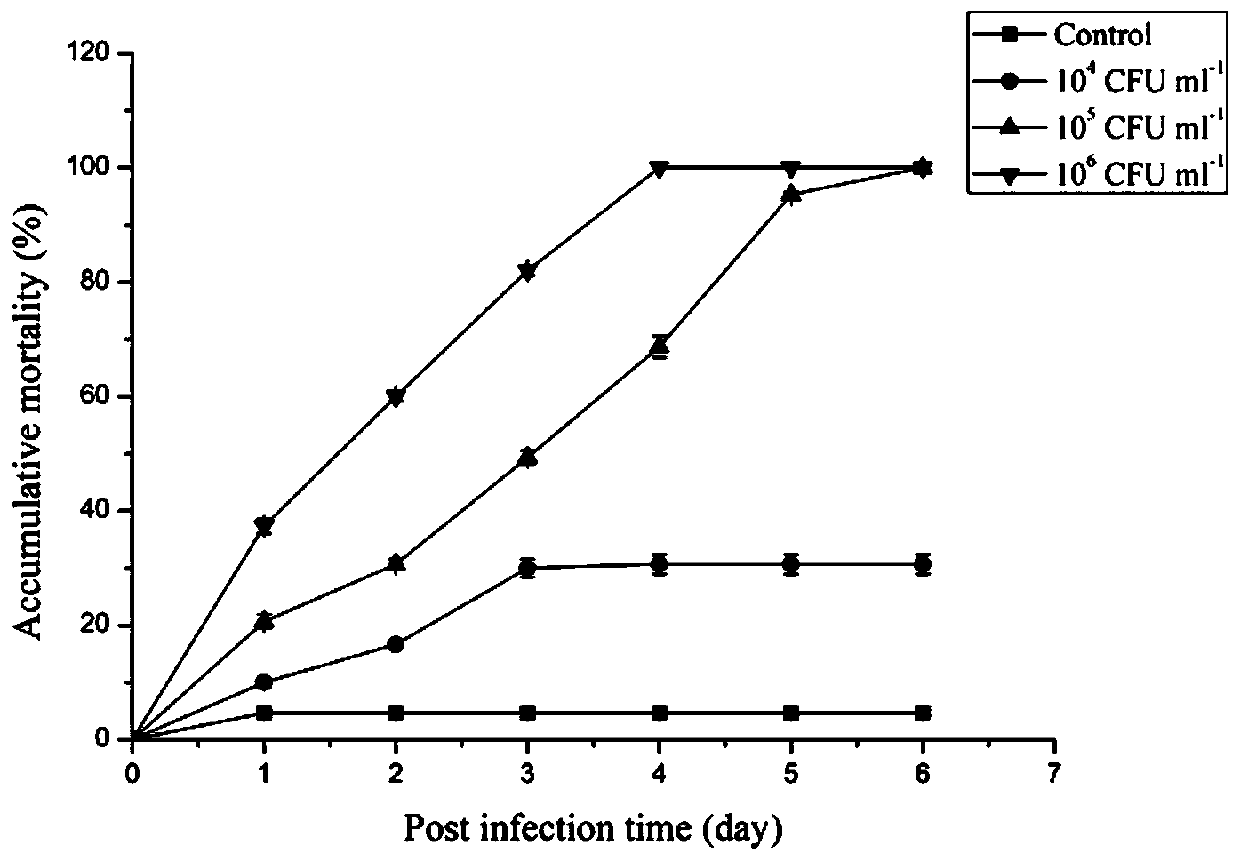
[0051] 1. Determination of bacterial infection concentration: Macrobrachium japonica is from Weishan Lake in Jining, with a body length of 6-8cm. Healthy Macrobrachium japonica is kept in the laboratory for a week. Prepare Aeromonas hydrophila suspension and set three concentration gradients (1×10 4 CFU / ml, 1×10 5 CFU / ml, 1×10 6 CFU / ml) is used for intramuscular injection of Macrobrachium japonicus, 50 μl / tail, and the negative control group is injected with the same amount of 0.85% (w / v) NaCl solution (pH=7.0), 50 shrimps in each group, three parallels, and the cumulative Mortality curve to determine the optimal infection concentration.
[0052] After Macrobrachium japonicus was infected with Aeromonas hydrophila, the death of Macrobrachium prawn was counted every day, and the cumulative mortality curve was drawn (see figure 1 ). in 1×10 4 In the CFU / ml infection group, the cumulative mortality rate reached 10%±0.82 on day 1, 16.67%±0.47 and 30%±1.63 on day 2 and day 3 r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com